⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-24 更新
Why disentanglement-based speaker anonymization systems fail at preserving emotions?
Authors:Ünal Ege Gaznepoglu, Nils Peters
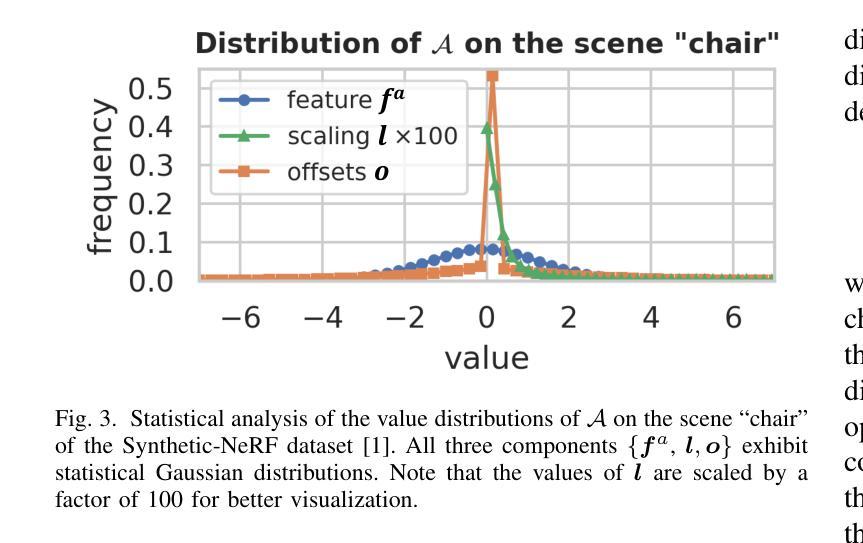
Disentanglement-based speaker anonymization involves decomposing speech into a semantically meaningful representation, altering the speaker embedding, and resynthesizing a waveform using a neural vocoder. State-of-the-art systems of this kind are known to remove emotion information. Possible reasons include mode collapse in GAN-based vocoders, unintended modeling and modification of emotions through speaker embeddings, or excessive sanitization of the intermediate representation. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of a state-of-the-art speaker anonymization system to understand the underlying causes. We conclude that the main reason is the lack of emotion-related information in the intermediate representation. The speaker embeddings also have a high impact, if they are learned in a generative context. The vocoder’s out-of-distribution performance has a smaller impact. Additionally, we discovered that synthesis artifacts increase spectral kurtosis, biasing emotion recognition evaluation towards classifying utterances as angry. Therefore, we conclude that reporting unweighted average recall alone for emotion recognition performance is suboptimal.
基于纠缠剥离的说话人匿名化技术涉及将语音分解成具有语义意义的表示,改变说话人的嵌入,并使用神经网络编解码器重新合成波形。目前最先进的这类系统已知会消除情绪信息。可能的原因包括基于GAN的编解码器中的模式崩溃、通过说话人嵌入进行情感和情感的意外建模和修改,或对中间表示的过度净化。在本文中,我们对最先进的说话人匿名化系统进行了全面评估,以了解潜在原因。我们得出结论,主要原因是中间表示中缺乏与情感相关的信息。如果说话人的嵌入是在生成环境中学习到的,那么它们也会产生重大影响。编解码器的超出分布性能的影响较小。此外,我们发现合成产生的伪迹会增加频谱峰度,导致情绪识别评估偏向于将话语分类为愤怒情绪。因此,我们得出结论,仅报告情绪识别的未加权平均召回率是不理想的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文研究了基于分离技术的说话人匿名化技术,该技术通过将语音分解为具有语义意义的表示,改变说话人嵌入,并使用神经网络vocoder重新合成波形来实现。当前先进技术主要面临的问题是消除情感信息。研究结果显示情感信息的缺失在生成过程的语言匿名化的重要原因中发挥了主要作用,尤其是,经过对现代语音识别技术的评估后发现主要是由于中间表达的情感信息缺失,且生成的说话人嵌入若生成于一个生成上下文背景下将带来重大影响。同时发现合成物的合成制品增加了谱峰偏度分布变化影响情感识别结果准确。最后总结当前单纯的报告平均未加权召回率来衡量情感识别性能是不够的。我们将持续评估新型的系统以便寻找更适合的评价方法以更准确测量出模型在处理真实复杂情境下的效果。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图


FlanEC: Exploring Flan-T5 for Post-ASR Error Correction
Authors:Moreno La Quatra, Valerio Mario Salerno, Yu Tsao, Sabato Marco Siniscalchi
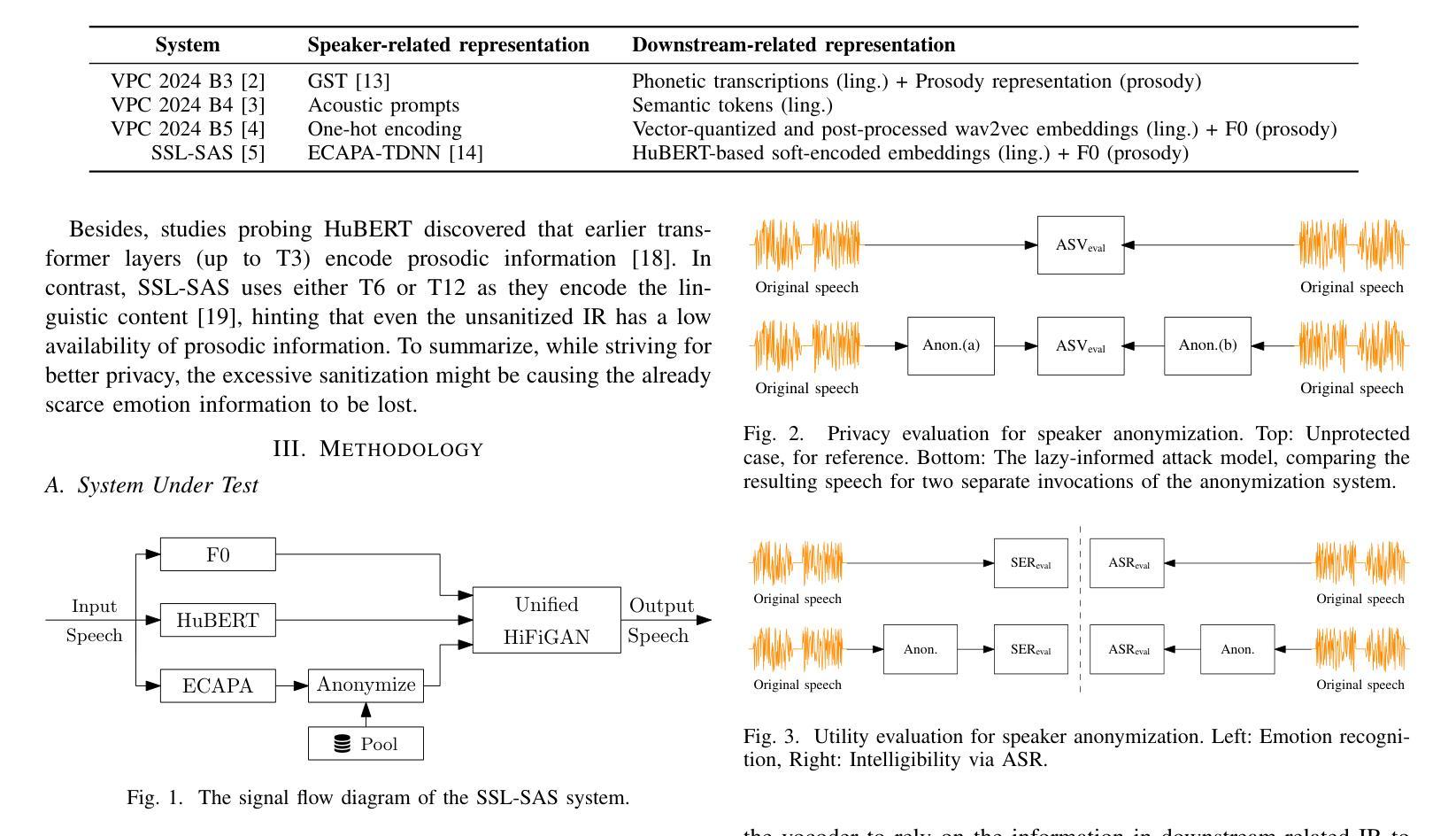
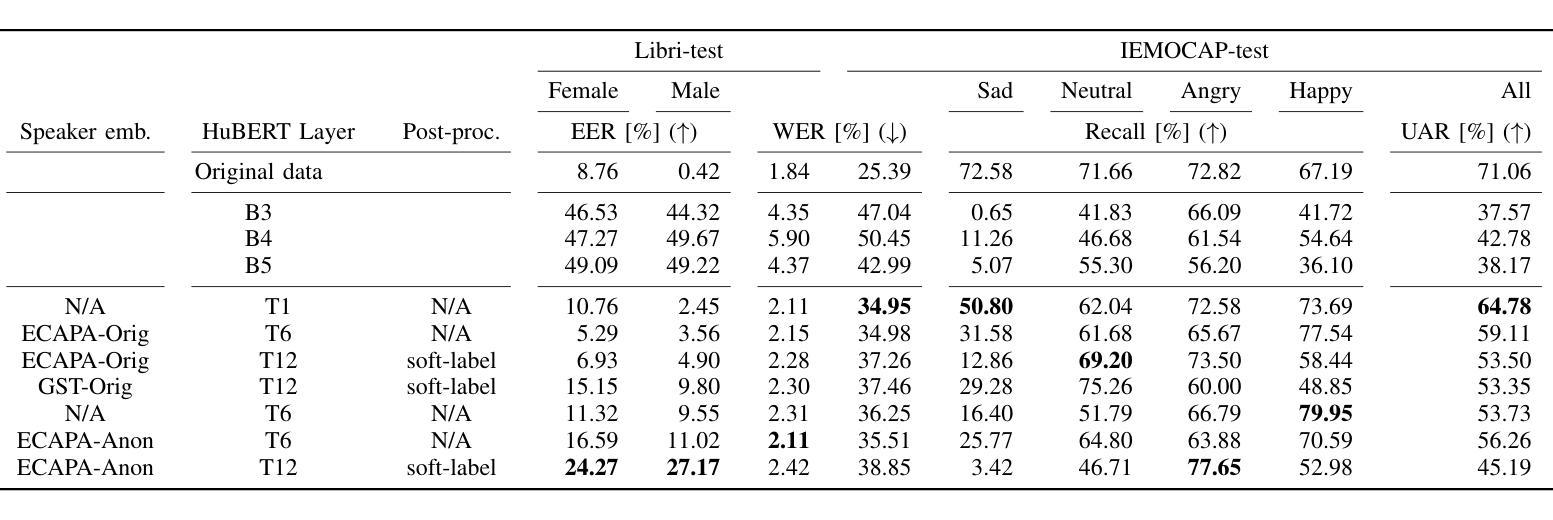
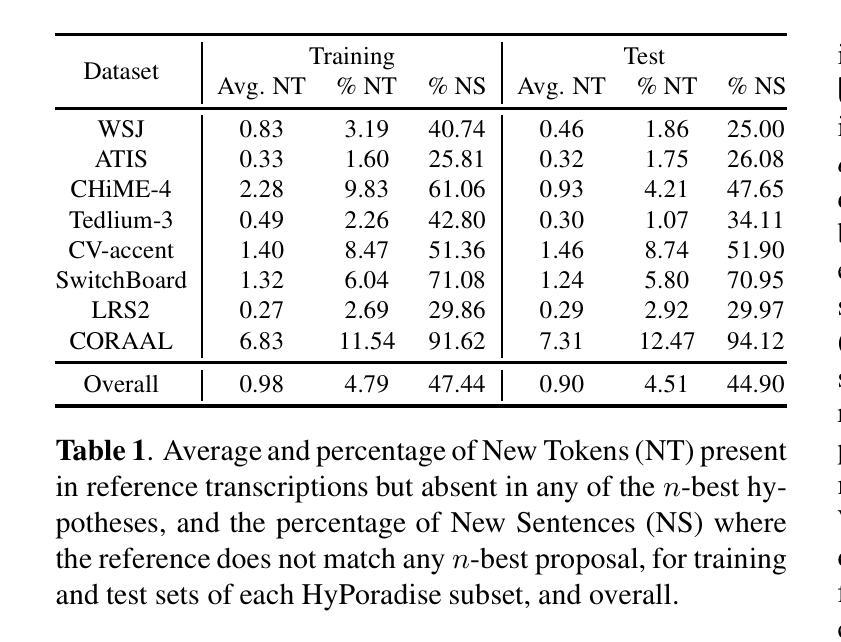
In this paper, we present an encoder-decoder model leveraging Flan-T5 for post-Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) Generative Speech Error Correction (GenSEC), and we refer to it as FlanEC. We explore its application within the GenSEC framework to enhance ASR outputs by mapping n-best hypotheses into a single output sentence. By utilizing n-best lists from ASR models, we aim to improve the linguistic correctness, accuracy, and grammaticality of final ASR transcriptions. Specifically, we investigate whether scaling the training data and incorporating diverse datasets can lead to significant improvements in post-ASR error correction. We evaluate FlanEC using the HyPoradise dataset, providing a comprehensive analysis of the model’s effectiveness in this domain. Furthermore, we assess the proposed approach under different settings to evaluate model scalability and efficiency, offering valuable insights into the potential of instruction-tuned encoder-decoder models for this task.
在这篇论文中,我们提出了一种利用Flan-T5进行自动语音识别(ASR)后的生成式语音错误校正(GenSEC)的编码器-解码器模型,我们将其称为FlanEC。我们探索了其在GenSEC框架内的应用,通过将n-best假设映射到单个输出句子来优化ASR的输出结果。我们利用ASR模型的n-best列表,旨在提高最终ASR转录的语言正确性、准确性和语法性。具体来说,我们研究了扩大训练数据并融入多种数据集是否能在ASR之后的错误校正方面带来显著改进。我们使用HyPoradise数据集对FlanEC进行了评估,全面分析了该模型在此领域的有效性。此外,我们在不同的设置下评估了所提出的方法,以评估模型的可扩展性和效率,为指令微调编码器-解码器模型在此任务上的潜力提供了有价值的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 2024 IEEE Workshop on Spoken Language Technology (SLT) - GenSEC Challenge
Summary
本文提出了一种利用Flan-T5的编码器-解码器模型进行自动语音识别(ASR)后的生成性语音错误校正(GenSEC),称为FlanEC。该研究旨在改进ASR输出结果的准确性、语法正确性,并探索通过映射n-best假设到单一输出句子的方法来增强ASR输出的质量。通过扩大训练数据并引入各种数据集来测试该模型的效果,并利用HyPoradise数据集对FlanEC进行了评估。研究还探讨了模型的可扩展性和效率,为指令微调编码器-解码器模型在该领域的潜力提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了利用Flan-T5的编码器-解码器模型进行语音错误校正的方法,旨在改进ASR输出的准确性、语法正确性。
- 通过映射n-best假设到单一输出句子来增强ASR输出的质量。
- 研究通过扩大训练数据和引入多种数据集来测试模型效果。
- 利用HyPoradise数据集对模型进行了评估。
- 研究探讨了模型在不同设置下的可扩展性和效率。
- 指令微调编码器-解码器模型在该领域的潜力得到了展示。
点此查看论文截图

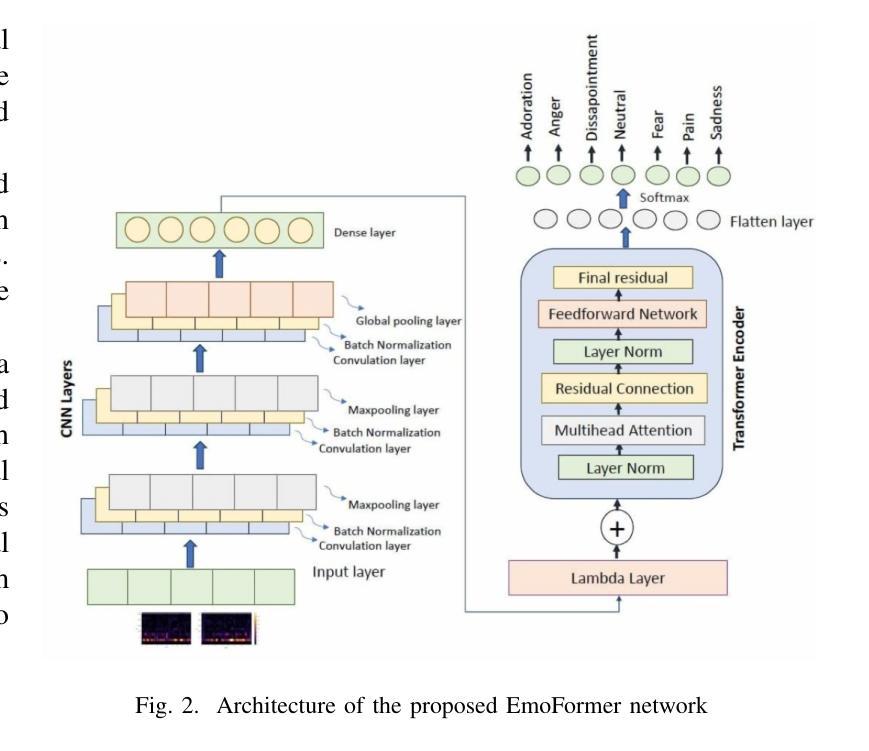
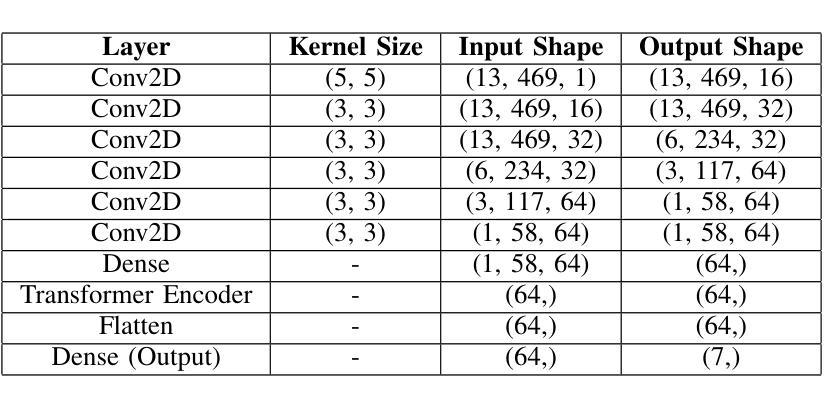
EmoFormer: A Text-Independent Speech Emotion Recognition using a Hybrid Transformer-CNN model
Authors:Rashedul Hasan, Meher Nigar, Nursadul Mamun, Sayan Paul
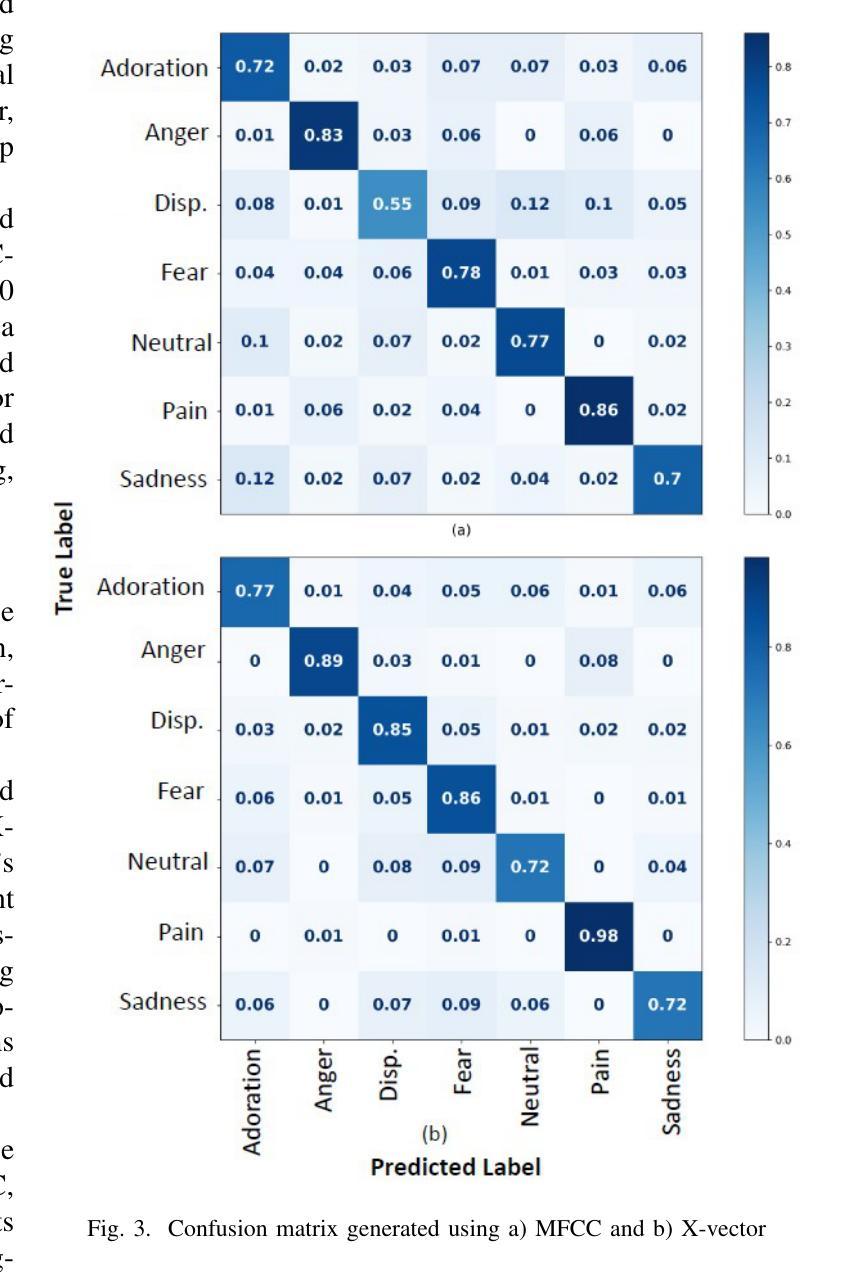
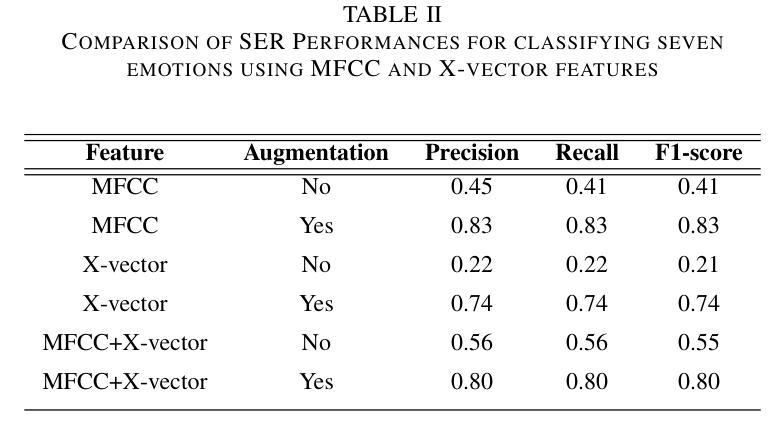
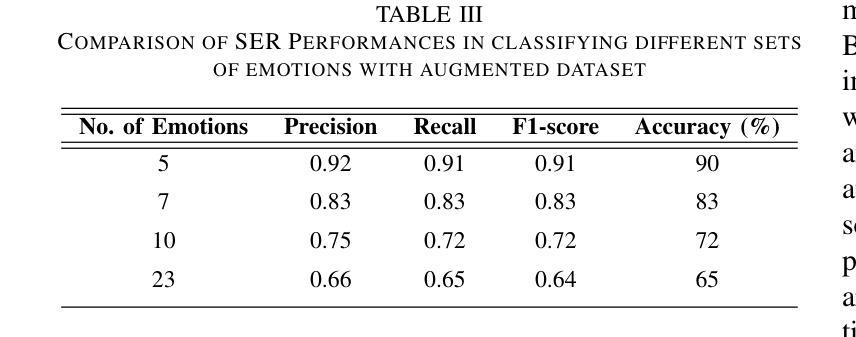
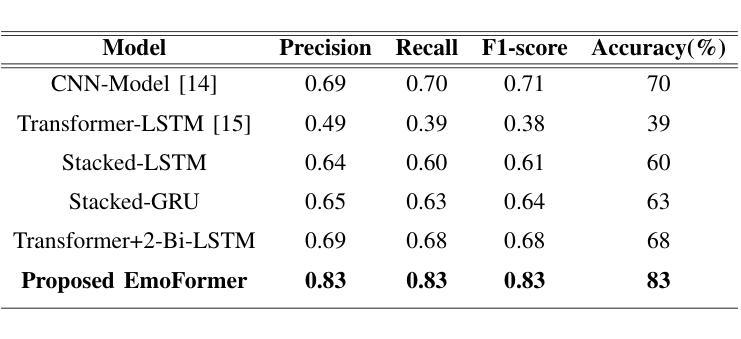
Speech Emotion Recognition is a crucial area of research in human-computer interaction. While significant work has been done in this field, many state-of-the-art networks struggle to accurately recognize emotions in speech when the data is both speech and speaker-independent. To address this limitation, this study proposes, EmoFormer, a hybrid model combining CNNs (CNNs) with Transformer encoders to capture emotion patterns in speech data for such independent datasets. The EmoFormer network was trained and tested using the Expressive Anechoic Recordings of Speech (EARS) dataset, recently released by META. We experimented with two feature extraction techniques: MFCCs and x-vectors. The model was evaluated on different emotion sets comprising 5, 7, 10, and 23 distinct categories. The results demonstrate that the model achieved its best performance with five emotions, attaining an accuracy of 90%, a precision of 0.92, a recall, and an F1-score of 0.91. However, performance decreased as the number of emotions increased, with an accuracy of 83% for seven emotions compared to 70% for the baseline network. This study highlights the effectiveness of combining CNNs and Transformer-based architectures for emotion recognition from speech, particularly when using MFCC features.
语音情感识别是计算机人机交互领域的一个重要研究方向。尽管该领域已经进行了大量工作,但在语音和说话人独立的数据集上,许多最先进的网络在准确识别情感方面仍面临困难。为了解决这一局限性,本研究提出了EmoFormer,这是一个混合模型,结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer编码器,以捕获此类独立数据集中的语音情感模式。EmoFormer网络使用META最近发布的表达无声语音记录(EARS)数据集进行训练和测试。我们实验了两种特征提取技术:MFCC和x-vectors。该模型在不同的情感集上进行了评估,包括包含5个、7个、10个和23个不同类别的情感集。结果表明,该模型在五种情感上表现最佳,准确率达到了90%,精确度达到了0.92,召回率和F1分数也均为0.91。然而,随着情感数量的增加,性能有所下降,在七种情感上的准确率为83%,而基线网络的准确率为70%。本研究强调了将CNN和基于Transformer的架构相结合,用于从语音中识别情感的有效性,特别是在使用MFCC特征时。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语音情感识别是计算机人机交互领域的一个重要研究课题。针对现有技术对网络在语音和说话人独立情感识别方面的局限,本研究提出了一种名为EmoFormer的混合模型,该模型结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)和Transformer编码器,以捕捉语音数据中的情感模式。使用META最近发布的表达无声录音语音(EARS)数据集进行训练和测试,实验采用了两种特征提取技术:MFCCs和x-vectors。在包含5、7、10和23个不同类别的情感集上评估该模型,结果显示,在五个情感类别上,模型表现最佳,准确率达到了90%,精确度、召回率和F1分数分别为0.92、0.91。但随着情感类别的增加,性能有所下降,七个情感的准确率为83%,而基准网络的准确率为70%。本研究强调了结合CNN和基于Transformer的架构进行语音情感识别的有效性,特别是使用MFCC特征时。
Key Takeaways
- 语音情感识别是计算机人机交互的重要研究领域。
- 当前研究提出了一种名为EmoFormer的混合模型,结合了CNN和Transformer编码器以识别语音中的情感。
- EmoFormer模型在包含不同数量情感类别的数据集上进行了评估,最佳表现是在五个情感类别上,准确率达到了90%。
- 随着情感类别的增加,模型的性能有所下降。
- 使用MFCC特征时,EmoFormer模型表现更优秀。
- 该研究强调了结合CNN和基于Transformer的架构进行语音情感识别的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

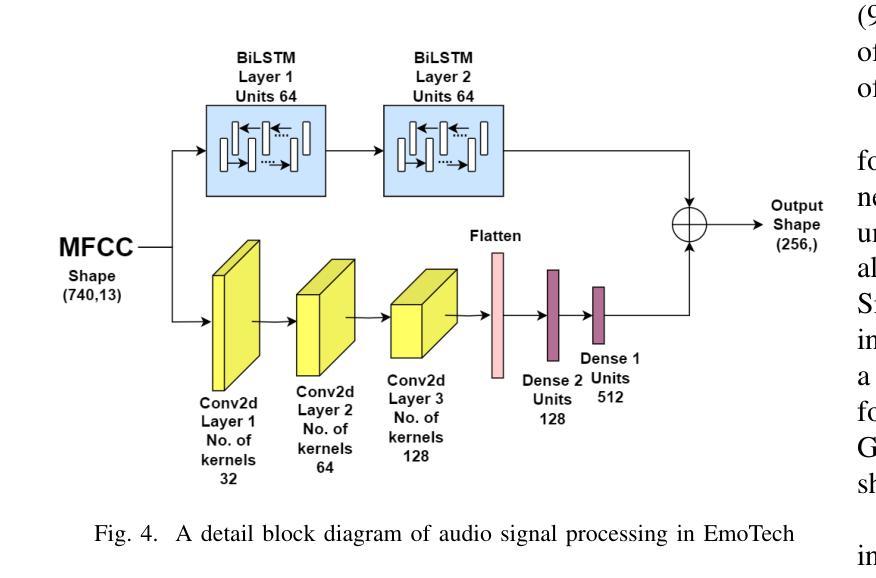
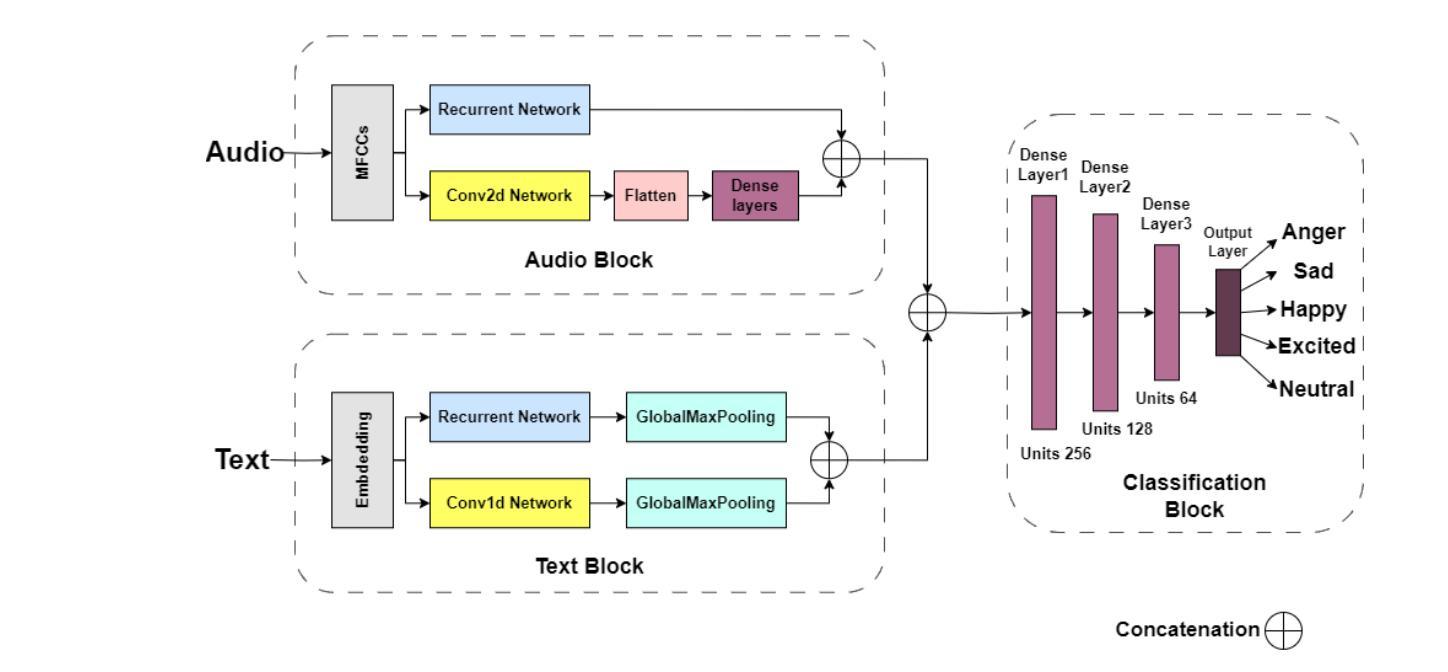
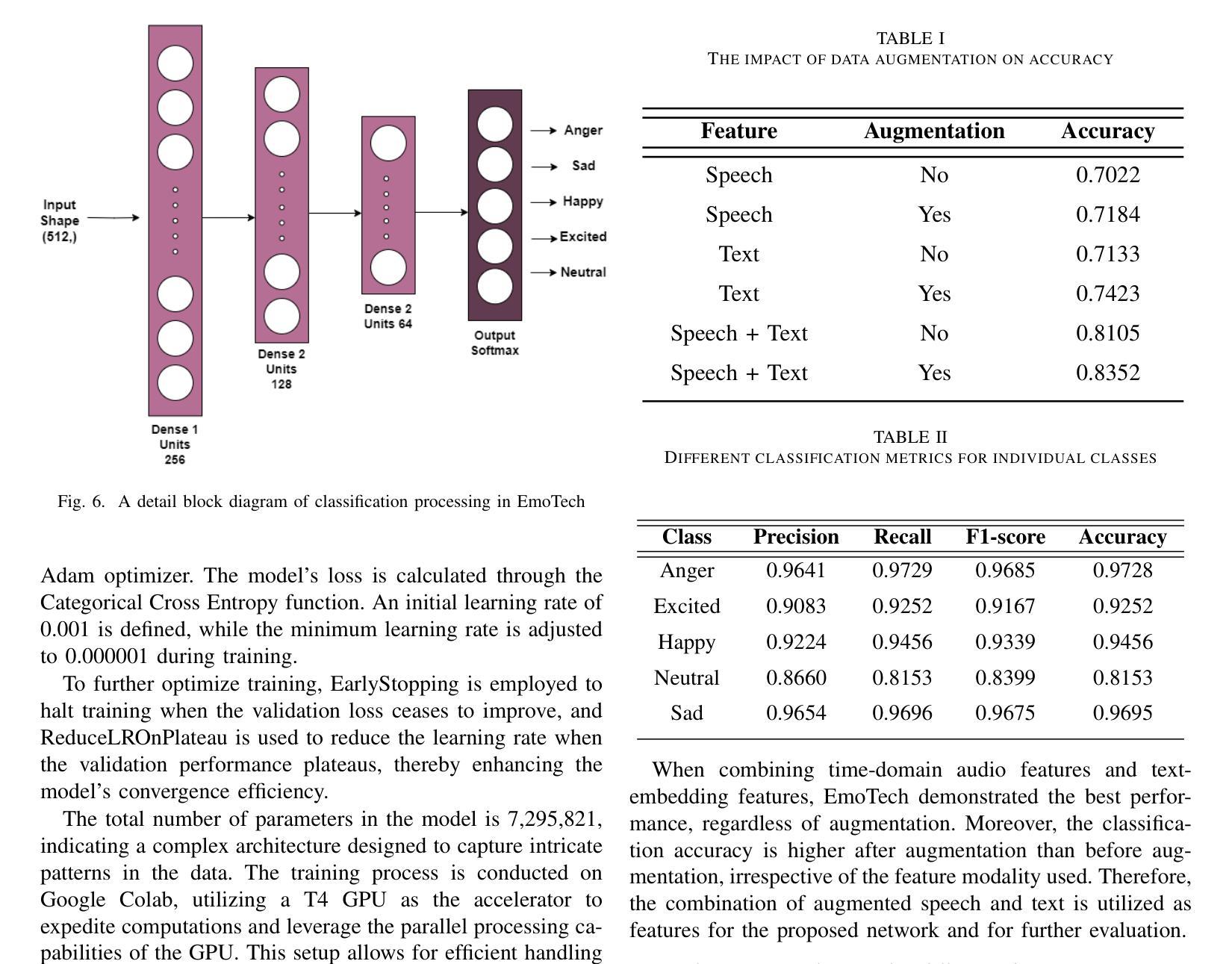
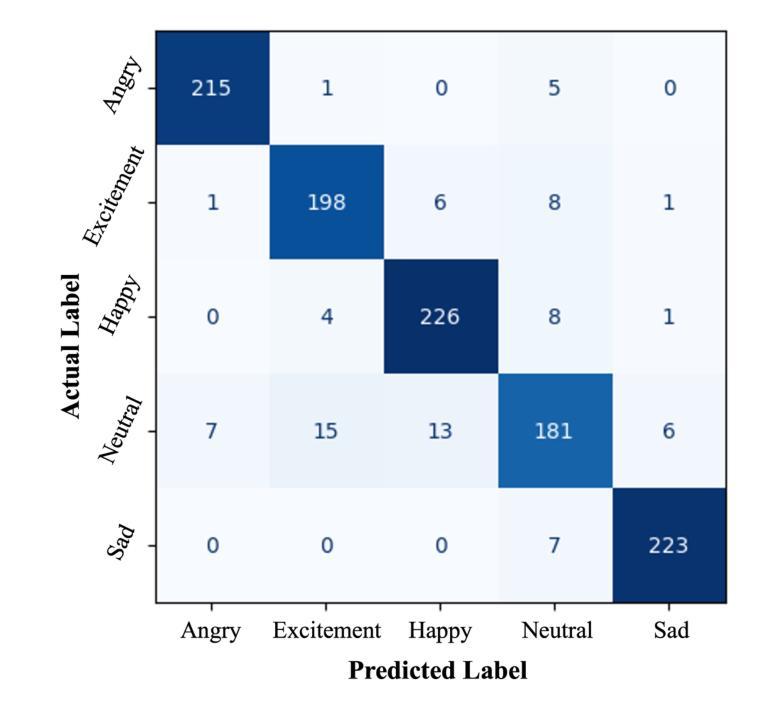
EmoTech: A Multi-modal Speech Emotion Recognition Using Multi-source Low-level Information with Hybrid Recurrent Network
Authors:Shamin Bin Habib Avro, Taieba Taher, Nursadul Mamun
Emotion recognition is a critical task in human-computer interaction, enabling more intuitive and responsive systems. This study presents a multimodal emotion recognition system that combines low-level information from audio and text, leveraging both Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Networks (BiLSTMs). The proposed system consists of two parallel networks: an Audio Block and a Text Block. Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) are extracted and processed by a BiLSTM network and a 2D convolutional network to capture low-level intrinsic and extrinsic features from speech. Simultaneously, a combined BiLSTM-CNN network extracts the low-level sequential nature of text from word embeddings corresponding to the available audio. This low-level information from speech and text is then concatenated and processed by several fully connected layers to classify the speech emotion. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed EmoTech accurately recognizes emotions from combined audio and text inputs, achieving an overall accuracy of 84%. This solution outperforms previously proposed approaches for the same dataset and modalities.
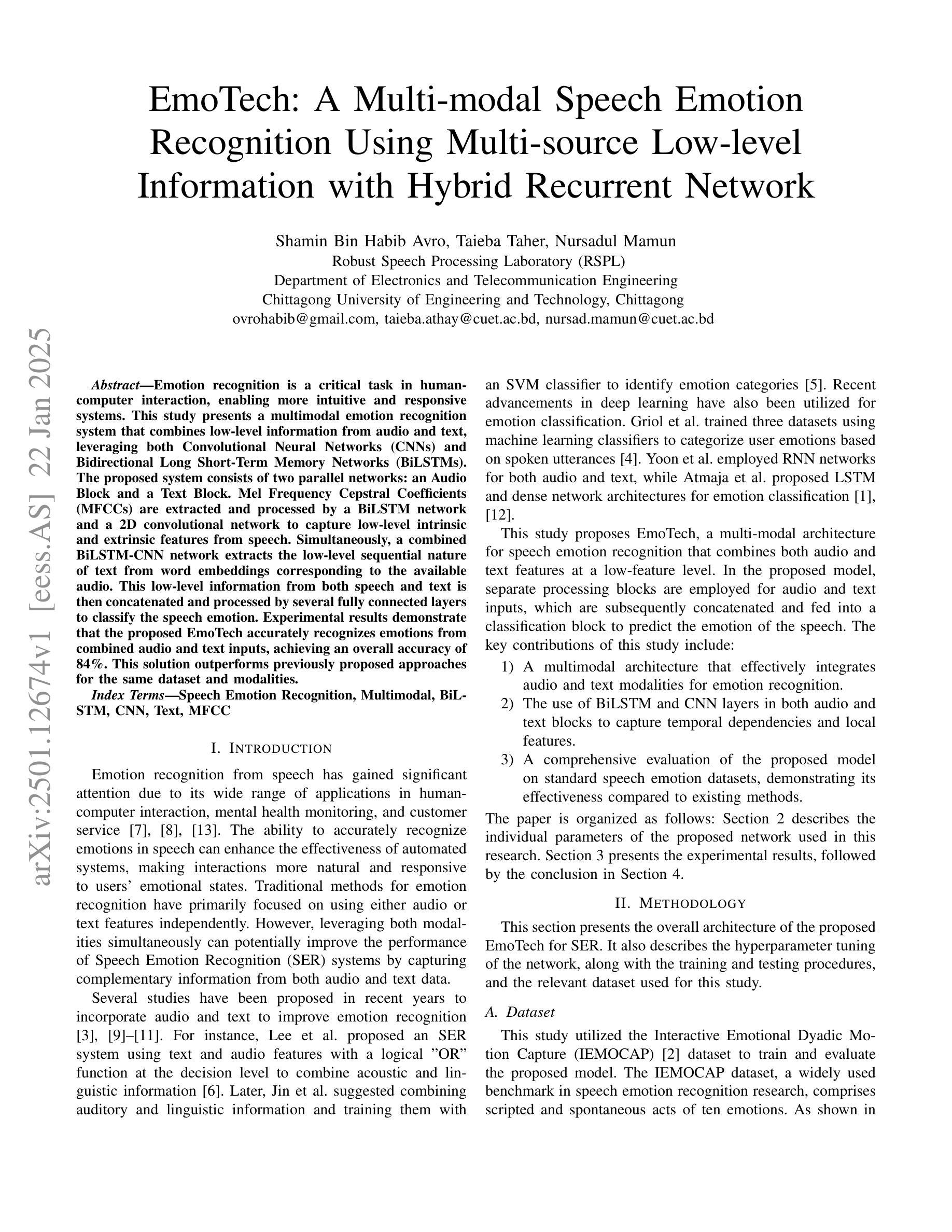
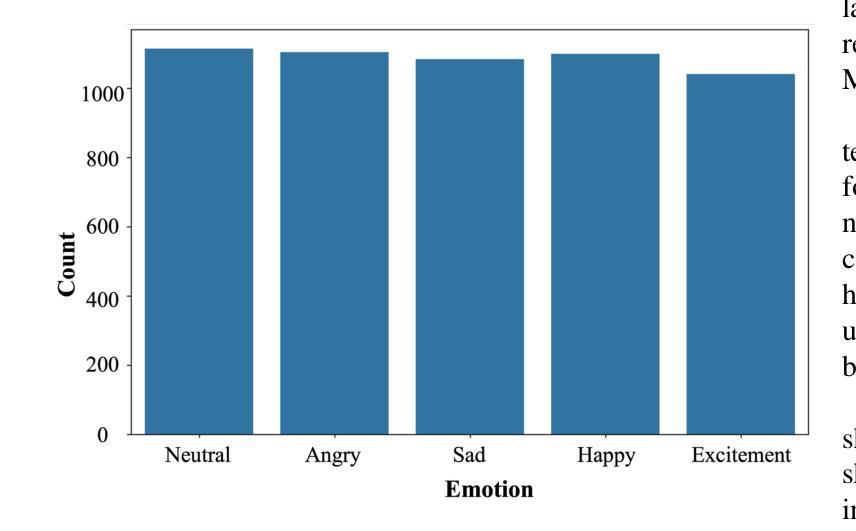
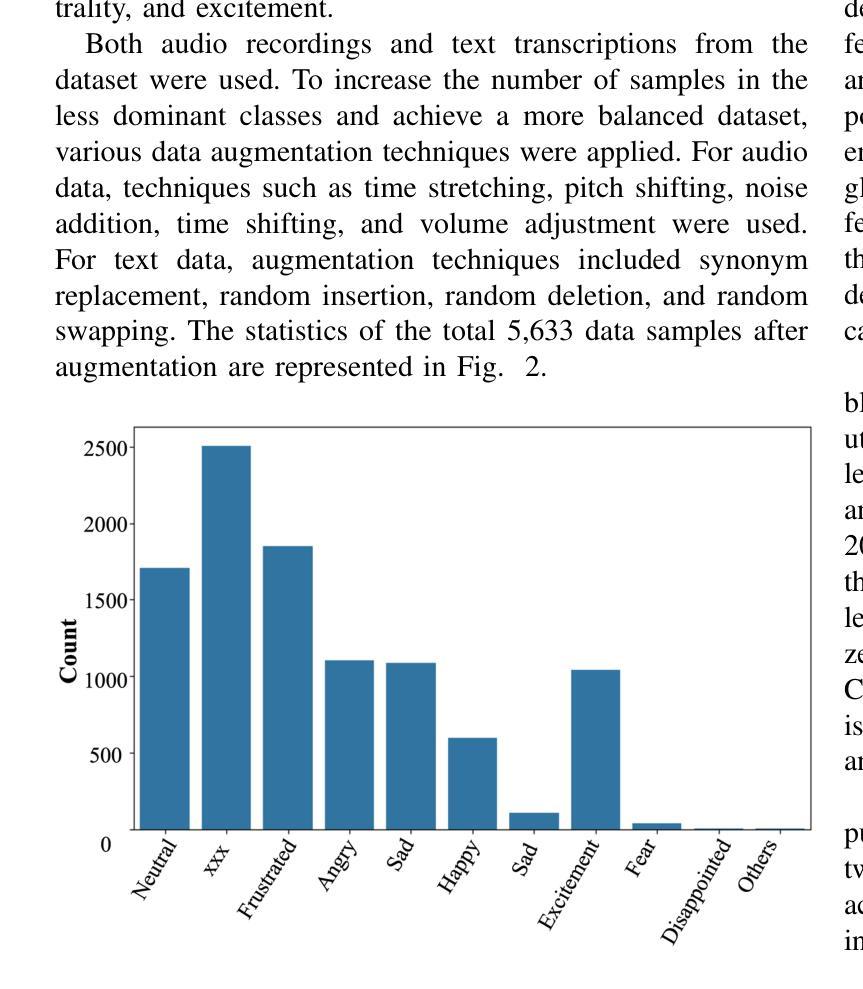
情感识别是人机交互中的一项关键任务,它使系统更加直观和响应迅速。本研究提出了一种多模态情感识别系统,该系统结合了音频和文本中的低级信息,并利用卷积神经网络(CNN)和双向长短时记忆网络(BiLSTM)。所提出的系统由两个并行网络组成:音频块和文本块。提取梅尔频率倒谱系数(MFCC),并通过双向LSTM网络和二维卷积网络进行处理,以捕获语音中的低级内在和外在特征。同时,结合双向LSTM-CNN网络从与可用音频对应的词嵌入中提取文本的低级序列特征。然后,将来自语音和文本的低级信息连接起来,并通过几个全连接层对语音情感进行分类。实验结果表明,所提出的技术能够从组合的音频和文本输入中准确识别情感,总体准确率达到了84%。对于同一数据集和模态而言,此解决方案的性能超过了先前提出的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本研究提出了一种多模态情感识别系统,该系统结合音频和文本的低级信息,利用卷积神经网络(CNN)和双向长短时记忆网络(BiLSTM)进行情感识别。该系统包括两个并行网络:音频块和文本块。通过双向LSTM网络和二维卷积网络处理梅尔频率倒谱系数(MFCCs),以捕获语音的内在和外在特征。同时,通过双向LSTM-CNN网络提取与音频相对应的文本词嵌入的低级序列特征。然后将语音和文本的低级信息结合起来,通过多个全连接层对语音情感进行分类。实验结果表明,所提出的EmoTech系统能够准确地识别来自音频和文本输入的情感,总体准确率为84%,并且优于先前针对同一数据集和模态提出的解决方案。
关键见解
- 多模态情感识别系统结合了音频和文本的低级信息。
- 利用卷积神经网络(CNN)和双向长短时记忆网络(BiLSTM)进行情感识别。
- 系统包括两个并行网络:音频块和文本块,分别处理语音和文本信息。
- MFCCs用于捕捉语音的内在和外在特征。
- 双向LSTM-CNN网络用于提取与音频相对应的文本词嵌入的低级序列特征。
- 系统通过将语音和文本的低级信息结合,实现情感分类,总体准确率为84%。
点此查看论文截图
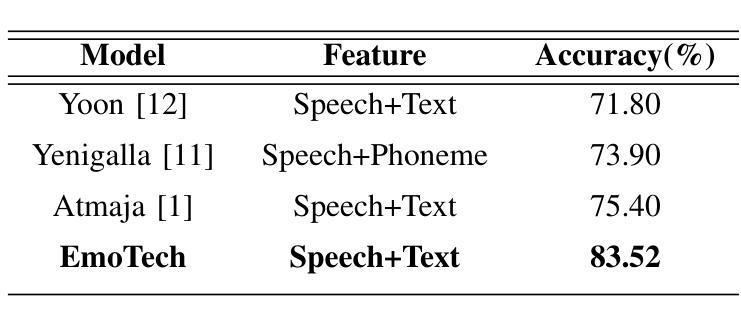
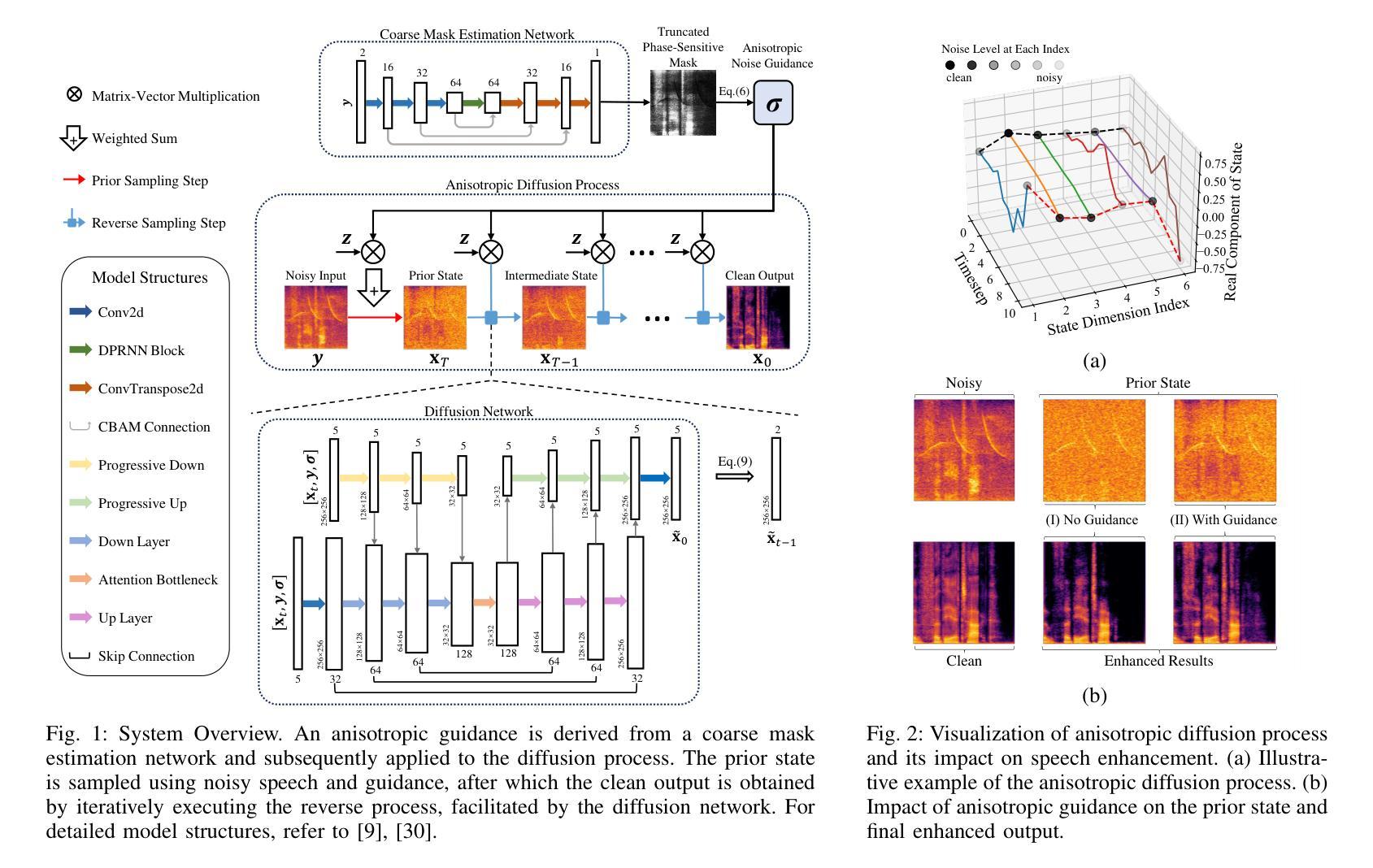
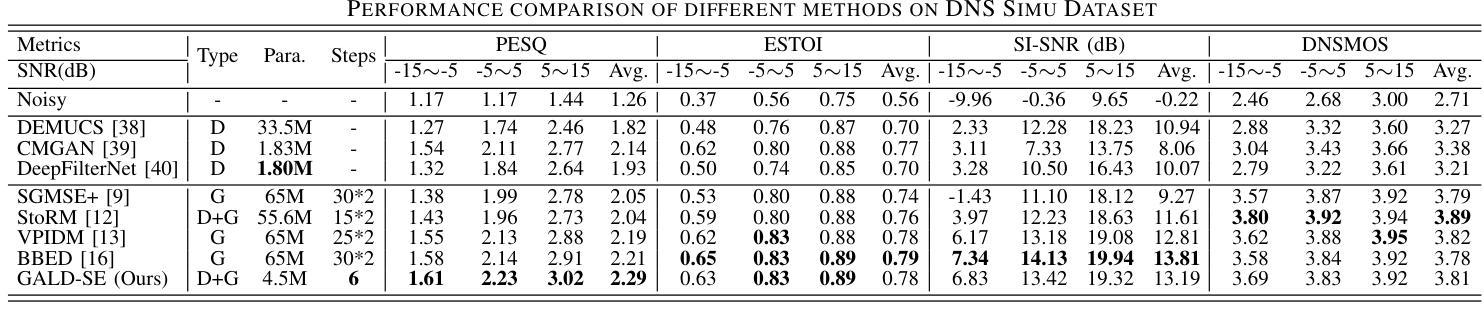
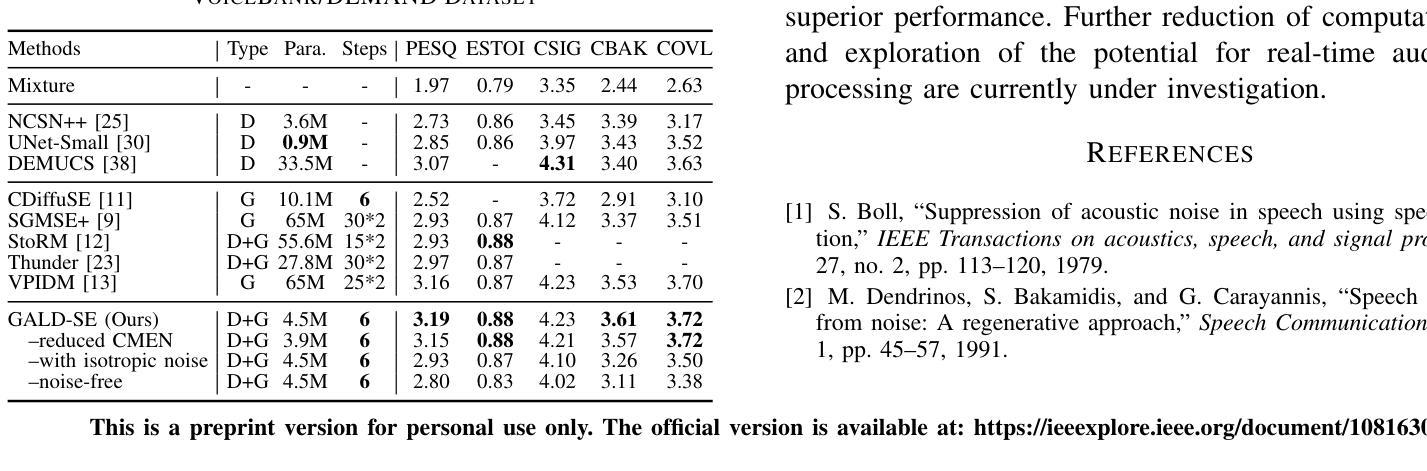
GALD-SE: Guided Anisotropic Lightweight Diffusion for Efficient Speech Enhancement
Authors:Chengzhong Wang, Jianjun Gu, Dingding Yao, Junfeng Li, Yonghong Yan
Speech enhancement is designed to enhance the intelligibility and quality of speech across diverse noise conditions. Recently, diffusion model has gained lots of attention in speech enhancement area, achieving competitive results. Current diffusion-based methods blur the signal with isotropic Gaussian noise and recover clean speech from the prior. However, these methods often suffer from a substantial computational burden. We argue that the computational inefficiency partially stems from the oversight that speech enhancement is not purely a generative task; it primarily involves noise reduction and completion of missing information, while the clean clues in the original mixture do not need to be regenerated. In this paper, we propose a method that introduces noise with anisotropic guidance during the diffusion process, allowing the neural network to preserve clean clues within noisy recordings. This approach substantially reduces computational complexity while exhibiting robustness against various forms of noise and speech distortion. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results with only approximately 4.5 million parameters, a number significantly lower than that required by other diffusion methods. This effectively narrows the model size disparity between diffusion-based and predictive speech enhancement approaches. Additionally, the proposed method performs well in very noisy scenarios, demonstrating its potential for applications in highly challenging environments.
语音增强旨在提高语音在不同噪声条件下的清晰度和质量。最近,扩散模型在语音增强领域引起了广泛关注,并取得了具有竞争力的结果。当前基于扩散的方法通过等向高斯噪声模糊信号,并从先前状态恢复干净语音。然而,这些方法通常面临巨大的计算负担。我们认为,计算效率低下部分源于对语音增强的误解,它不仅仅是一个生成任务;它主要涉及噪声减少和缺失信息的补充,而原始混合中的干净线索不需要重新生成。在本文中,我们提出了一种在扩散过程中引入各向异性引导噪声的方法,允许神经网络在嘈杂的录音中保留干净线索。这种方法在降低计算复杂性的同时,对各种形式的噪声和语音失真表现出稳健性。实验表明,该方法仅使用大约450万个参数就达到了最新技术水平,这个数字远低于其他扩散方法所需的参数。这有效地缩小了基于扩散的语音增强方法和预测性语音增强方法之间的模型规模差距。此外,该方法在噪声很大的场景中表现良好,显示出其在极具挑战性的环境中的应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在语音增强领域受到广泛关注,但计算效率较低。本文提出了一种新的方法,通过引入具有定向指导的噪声扩散过程,减少计算复杂度并提高对不同噪声和语音失真的鲁棒性。实验表明,该方法实现了卓越的性能,缩小了扩散方法和预测语音增强方法之间的模型规模差距。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在语音增强领域备受瞩目,具有竞争性的结果。
- 当前扩散模型存在计算效率问题。
- 语音增强不仅是生成任务,更主要是噪声减少和缺失信息的补充。
- 本文提出了一种新的方法,通过引入具有定向指导的噪声扩散过程,提高计算效率和鲁棒性。
- 实验证明该方法实现了卓越性能,模型参数数量大幅降低。
- 与其他扩散方法相比,本文方法缩小了模型规模差距。
点此查看论文截图

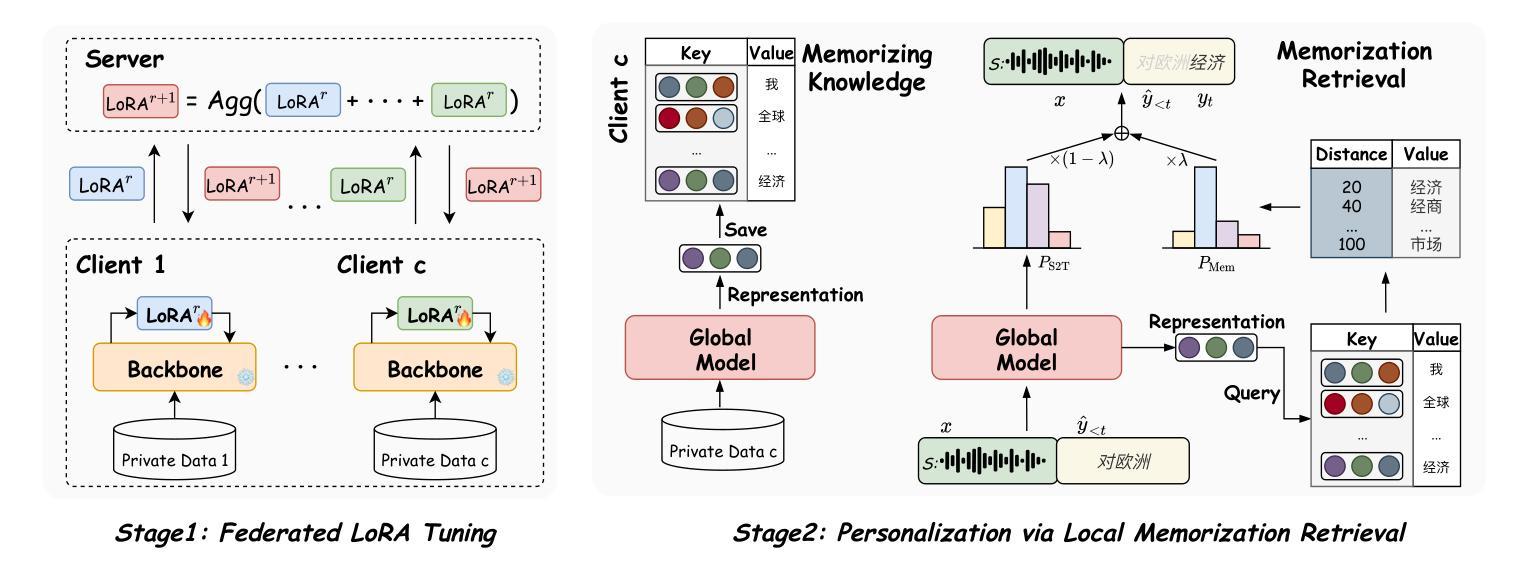
Communication-Efficient Personalized Federated Learning for Speech-to-Text Tasks
Authors:Yichao Du, Zhirui Zhang, Linan Yue, Xu Huang, Yuqing Zhang, Tong Xu, Linli Xu, Enhong Chen
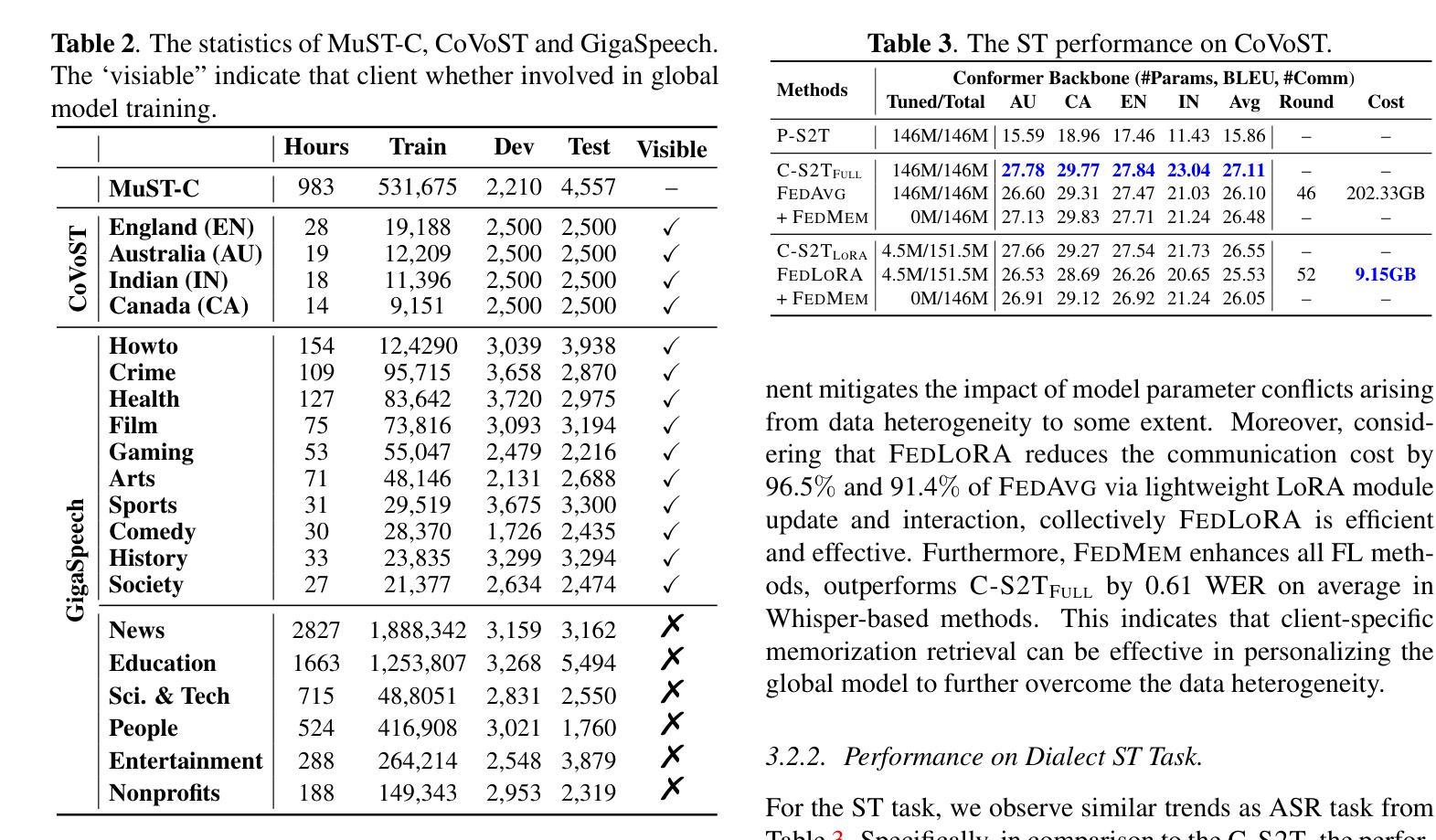
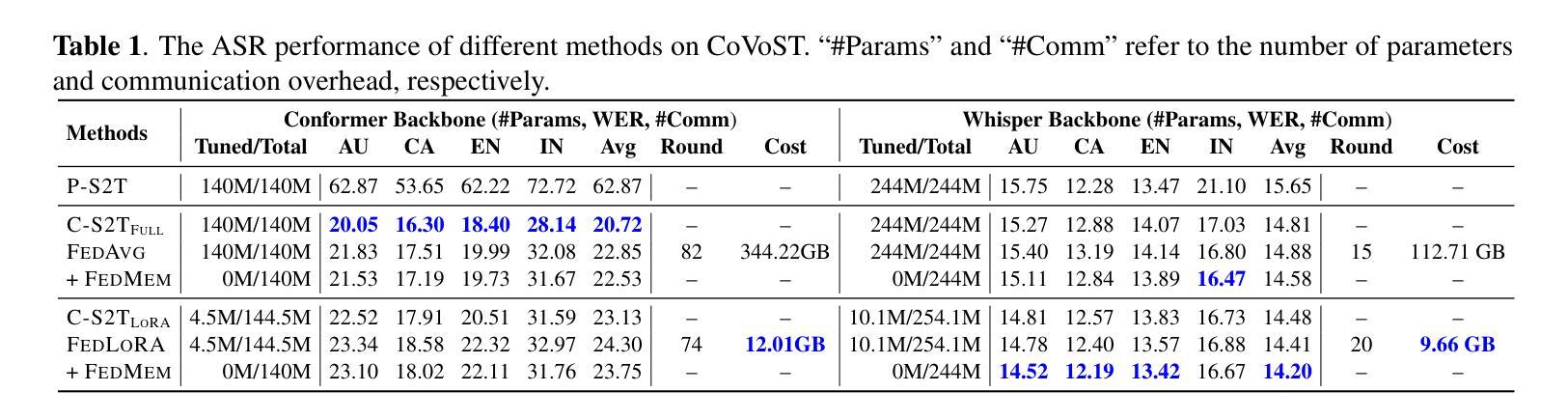
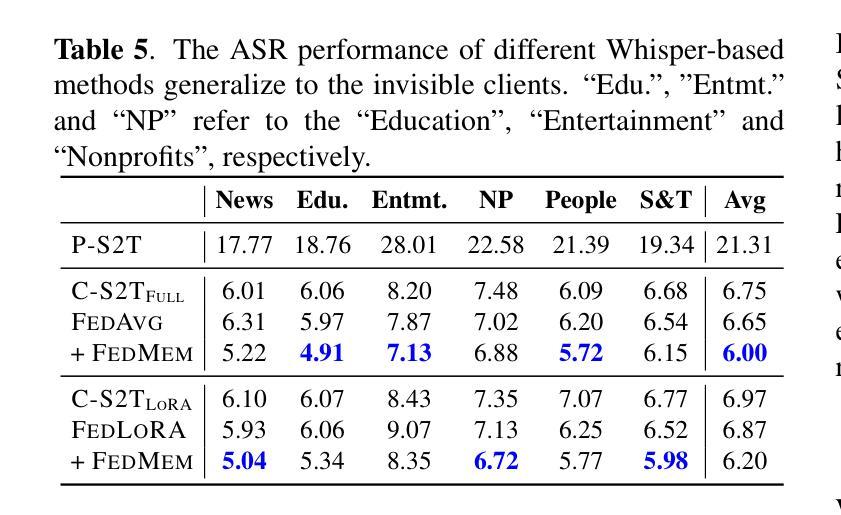
To protect privacy and meet legal regulations, federated learning (FL) has gained significant attention for training speech-to-text (S2T) systems, including automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speech translation (ST). However, the commonly used FL approach (i.e., \textsc{FedAvg}) in S2T tasks typically suffers from extensive communication overhead due to multi-round interactions based on the whole model and performance degradation caused by data heterogeneity among clients.To address these issues, we propose a personalized federated S2T framework that introduces \textsc{FedLoRA}, a lightweight LoRA module for client-side tuning and interaction with the server to minimize communication overhead, and \textsc{FedMem}, a global model equipped with a $k$-nearest-neighbor ($k$NN) classifier that captures client-specific distributional shifts to achieve personalization and overcome data heterogeneity. Extensive experiments based on Conformer and Whisper backbone models on CoVoST and GigaSpeech benchmarks show that our approach significantly reduces the communication overhead on all S2T tasks and effectively personalizes the global model to overcome data heterogeneity.
为了保护隐私并满足法规要求,联邦学习(FL)在训练语音到文本(S2T)系统方面引起了广泛关注,这些系统包括自动语音识别(ASR)和语音翻译(ST)。然而,S2T任务中常用的联邦学习(即\text{FedAvg})方法通常面临由于基于整个模型的多次交互导致的通信开销过大,以及因客户端之间的数据异质性导致的性能下降问题。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种个性化的联邦S2T框架,引入\text{FedLoRA},这是一个轻量级的LoRA模块,用于客户端调优和与服务器交互,以最小化通信开销;以及\text{FedMem},这是一个配备k近邻(kNN)分类器的全局模型,能够捕捉客户端特定的分布变化,以实现个性化和克服数据异质性。基于Conformer和Whisper骨干模型在CoVoST和GigaSpeech基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法显著减少了所有S2T任务的通信开销,并有效地将全局个性化以克服数据异质性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2024
Summary
本文关注于联邦学习(FL)在训练语音到文本(S2T)系统中的应用,特别是针对自动语音识别(ASR)和语音翻译(ST)。针对现有联邦学习方法(如FedAvg)在S2T任务中面临的通信开销大和数据异构性导致的性能下降问题,提出一种个性化联邦S2T框架。该框架引入FedLoRA模块进行客户端调优和与服务器交互,以减小通信开销,并采用FedMem全局模型配备k-最近邻(k-NN)分类器,以捕捉客户端特定的分布变化,实现个性化并克服数据异构性。实验表明,该方法在减少通信开销和个性化全局模型方面效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习(FL)在训练语音到文本(S2T)系统,包括自动语音识别(ASR)和语音翻译(ST)中受到关注。
- 现有联邦学习方法在S2T任务中面临通信开销大和数据异构性问题。
- 提出的个性化联邦S2T框架通过引入FedLoRA模块和FedMem全局模型,解决上述问题。
- FedLoRA模块用于客户端调优和与服务器交互,减小通信开销。
- FedMem全局模型配备k-最近邻(k-NN)分类器,捕捉客户端特定分布变化,实现个性化并克服数据异构性。
- 实验表明,该方法在减少通信开销和个性化全局模型方面效果显著。
- 该框架的应用有助于提升S2T任务的效率和性能。
点此查看论文截图


DurFlex-EVC: Duration-Flexible Emotional Voice Conversion Leveraging Discrete Representations without Text Alignment
Authors:Hyung-Seok Oh, Sang-Hoon Lee, Deok-Hyeon Cho, Seong-Whan Lee
Emotional voice conversion (EVC) involves modifying various acoustic characteristics, such as pitch and spectral envelope, to match a desired emotional state while preserving the speaker’s identity. Existing EVC methods often rely on text transcriptions or time-alignment information and struggle to handle varying speech durations effectively. In this paper, we propose DurFlex-EVC, a duration-flexible EVC framework that operates without the need for text or alignment information. We introduce a unit aligner that models contextual information by aligning speech with discrete units representing content, eliminating the need for text or speech-text alignment. Additionally, we design a style autoencoder that effectively disentangles content and emotional style, allowing precise manipulation of the emotional characteristics of the speech. We further enhance emotional expressiveness through a hierarchical stylize encoder that applies the target emotional style at multiple hierarchical levels, refining the stylization process to improve the naturalness and expressiveness of the converted speech. Experimental results from subjective and objective evaluations demonstrate that our approach outperforms baseline models, effectively handling duration variability and enhancing emotional expressiveness in the converted speech.
情感语音转换(EVC)涉及修改各种声学特征,如音高和频谱包络,以匹配所需的情感状态,同时保留说话者的身份。现有的EVC方法通常依赖于文本转录或时间对齐信息,并且在有效处理不同语音时长方面存在困难。在本文中,我们提出了无需文本或对齐信息的时长灵活EVC框架DurFlex-EVC。我们引入了一个单元对齐器,通过将对齐语音与代表内容的离散单元来建模上下文信息,从而消除了对文本或语音文本对齐的需求。此外,我们设计了一个风格自编码器,它能有效地分离内容和情感风格,允许精确操纵语音的情感特征。我们还通过分层风格化编码器进一步增强了情感表现力,该编码器在多个层次上应用目标情感风格,改进了风格化过程,提高了转换语音的自然度和表现力。主观和客观评估的实验结果表明,我们的方法优于基线模型,能够有效处理时长变化,增强转换语音的情感表现力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 11 figures, 12 tables
Summary
情感语音转换(EVC)通过修改音高和频谱包络等声学特征,以达到匹配特定情感状态的同时保留说话者身份。现有的EVC方法常依赖于文本转录或时间对齐信息,并难以有效处理不同语长的语音。本文提出无需文本或对齐信息的时长灵活EVC框架DurFlex-EVC。我们引入了一个单位对齐器,通过将对齐语音与代表内容的离散单元建模,消除了对文本或语音文本对齐的需求。此外,我们设计了一个风格自编码器,有效地分离内容和情感风格,允许精确操控语音的情感特征。我们还通过分层风格编码器增强情感表现力,该编码器在多个层次上应用目标情感风格,细化风格化过程,以提高转换语音的自然度和表现力。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于基准模型,能够有效处理时长变化,增强转换语音的情感表现力。
Key Takeaways
- 情感语音转换(EVC)是通过改变声学特征来匹配情感状态,同时保持说话者身份。
- 现有EVC方法依赖文本转录或时间对齐信息,处理不同语长时存在困难。
- DurFlex-EVC框架无需文本或对齐信息,通过单位对齐器与风格自编码器有效进行语音转换。
- 单位对齐器利用离散单元代表内容,消除了对文本和语音文本对齐的需求。
- 风格自编码器能够分离内容和情感风格,允许精确操控语音的情感特征。
- 提出的分层风格编码器能增强情感表现力,通过实验验证其优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图