⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-24 更新
TeD-Loc: Text Distillation for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Authors:Shakeeb Murtaza, Soufiane Belharbi, Marco Pedersoli, Eric Granger
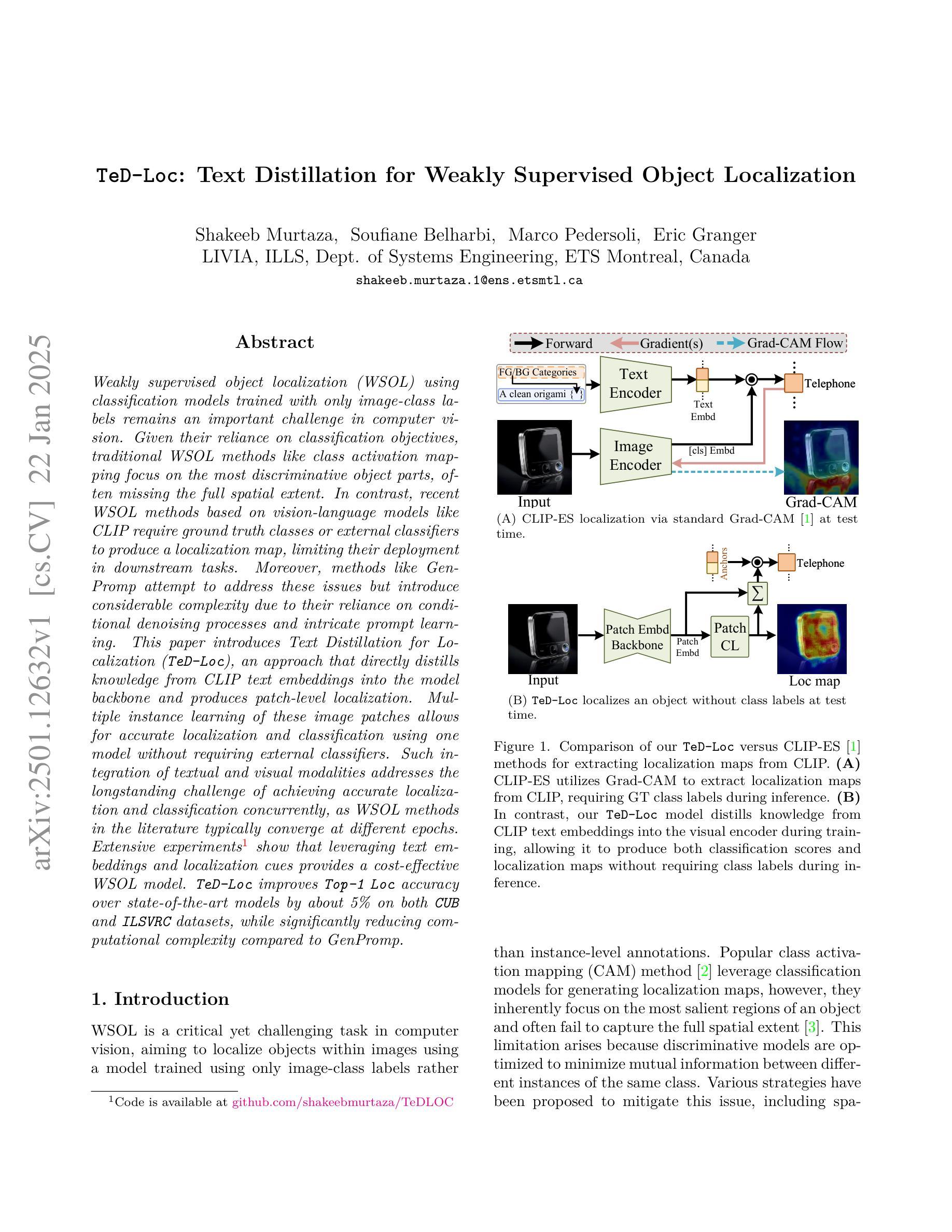
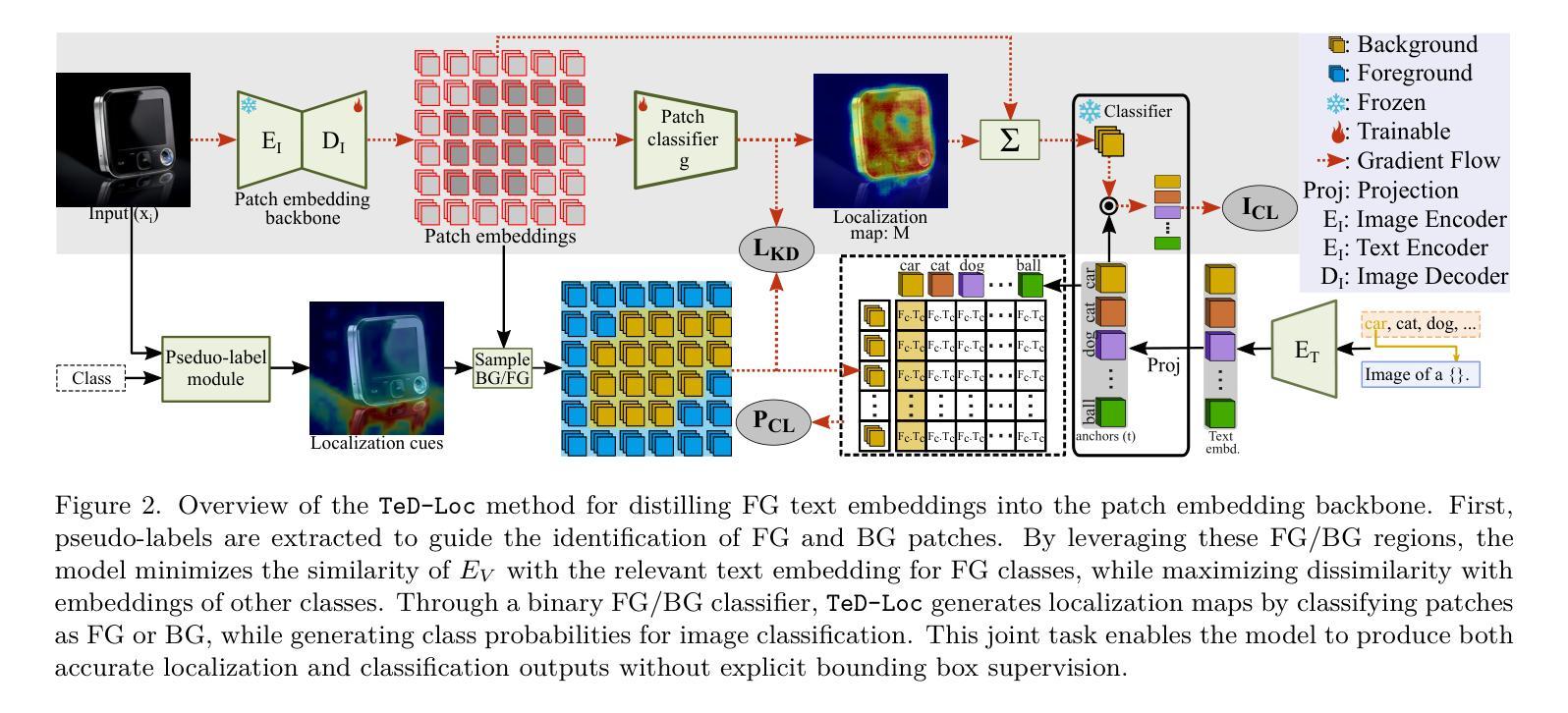
Weakly supervised object localization (WSOL) using classification models trained with only image-class labels remains an important challenge in computer vision. Given their reliance on classification objectives, traditional WSOL methods like class activation mapping focus on the most discriminative object parts, often missing the full spatial extent. In contrast, recent WSOL methods based on vision-language models like CLIP require ground truth classes or external classifiers to produce a localization map, limiting their deployment in downstream tasks. Moreover, methods like GenPromp attempt to address these issues but introduce considerable complexity due to their reliance on conditional denoising processes and intricate prompt learning. This paper introduces Text Distillation for Localization (TeD-Loc), an approach that directly distills knowledge from CLIP text embeddings into the model backbone and produces patch-level localization. Multiple instance learning of these image patches allows for accurate localization and classification using one model without requiring external classifiers. Such integration of textual and visual modalities addresses the longstanding challenge of achieving accurate localization and classification concurrently, as WSOL methods in the literature typically converge at different epochs. Extensive experiments show that leveraging text embeddings and localization cues provides a cost-effective WSOL model. TeD-Loc improves Top-1 LOC accuracy over state-of-the-art models by about 5% on both CUB and ILSVRC datasets, while significantly reducing computational complexity compared to GenPromp.
使用仅带有图像类别标签进行分类模型训练的弱监督目标定位(WSOL)仍然是计算机视觉领域的一项重要挑战。传统的WSOL方法如类激活映射依赖于分类目标,关注的是最具判别力的目标部分,通常会忽略目标的整体空间范围。相比之下,最近的基于视觉语言模型的WSOL方法(如CLIP)需要真实类别标签或外部分类器来生成定位图,这限制了它们在下游任务中的应用。此外,像GenPromp这样的方法试图解决这些问题,但由于它们依赖于条件去噪过程和复杂提示学习,因此引入了相当大的复杂性。本文介绍了用于定位的文本蒸馏(TeD-Loc)方法,该方法直接从CLIP文本嵌入中蒸馏知识并注入模型主干中,从而实现了补丁级别的定位。对这些图像补丁进行多次实例学习,允许使用一个模型进行准确的目标定位和分类,无需外部分类器。文本和视觉模态的这种集成解决了长期以来准确同时实现定位和分类的挑战,因为文献中的WSOL方法通常在不同的周期收敛。大量实验表明,利用文本嵌入和定位线索提供了具有成本效益的WSOL模型。TeD-Loc在CUB和ILSVRC数据集上的Top-1 LOC准确率提高了约5%,与GenPromp相比,计算复杂度大大降低。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Text Distillation for Localization(TeD-Loc)的方法,它通过蒸馏CLIP文本嵌入知识直接对模型进行训练,实现图像补丁级别的定位。利用多实例学习对这些图像补丁进行训练,使得模型无需外部分类器就能实现准确定位和分类。该方法有效结合了文本和视觉模态,解决了弱监督目标定位中长期存在的准确定位和分类同步实现的挑战。实验表明,利用文本嵌入和定位线索的TeD-Loc模型在成本和性能上均优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- TeD-Loc方法利用CLIP文本嵌入知识直接训练模型,实现图像补丁级别的定位。
- 多实例学习用于训练图像补丁,使模型无需外部分类器就能实现准确定位和分类。
- 结合文本和视觉模态,解决了弱监督目标定位中长期存在的挑战。
- TeD-Loc在CUB和ILSVRC数据集上的定位准确度优于现有模型。
- TeD-Loc模型相比GenPromp,计算复杂度更低。
- 利用文本嵌入和定位线索的TeD-Loc模型在成本效益上具有优势。
点此查看论文截图
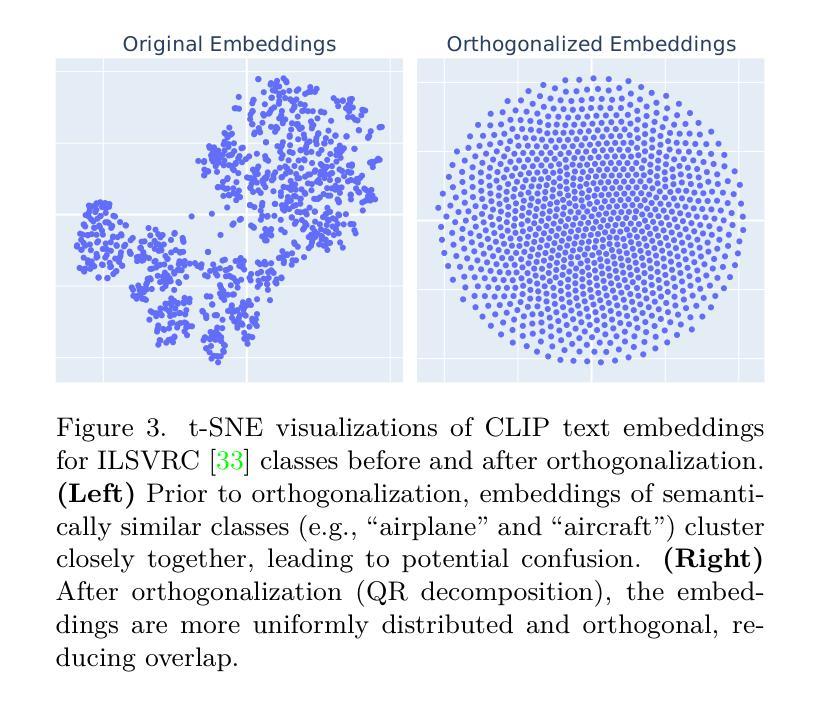
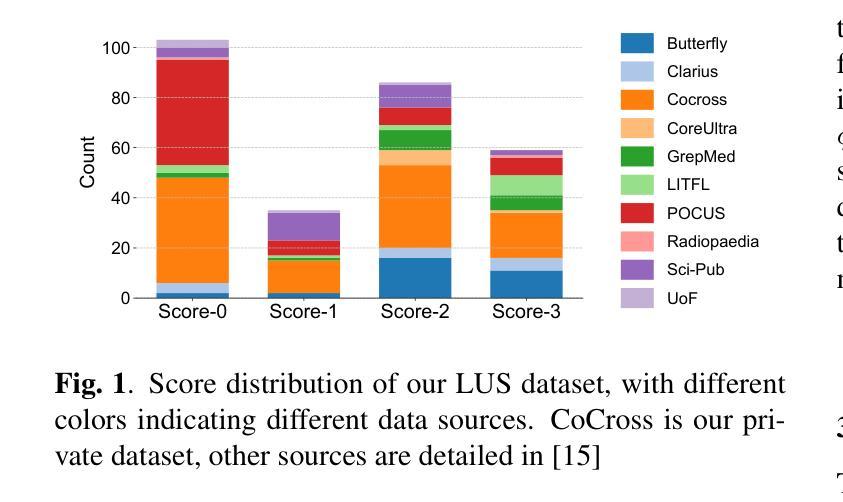
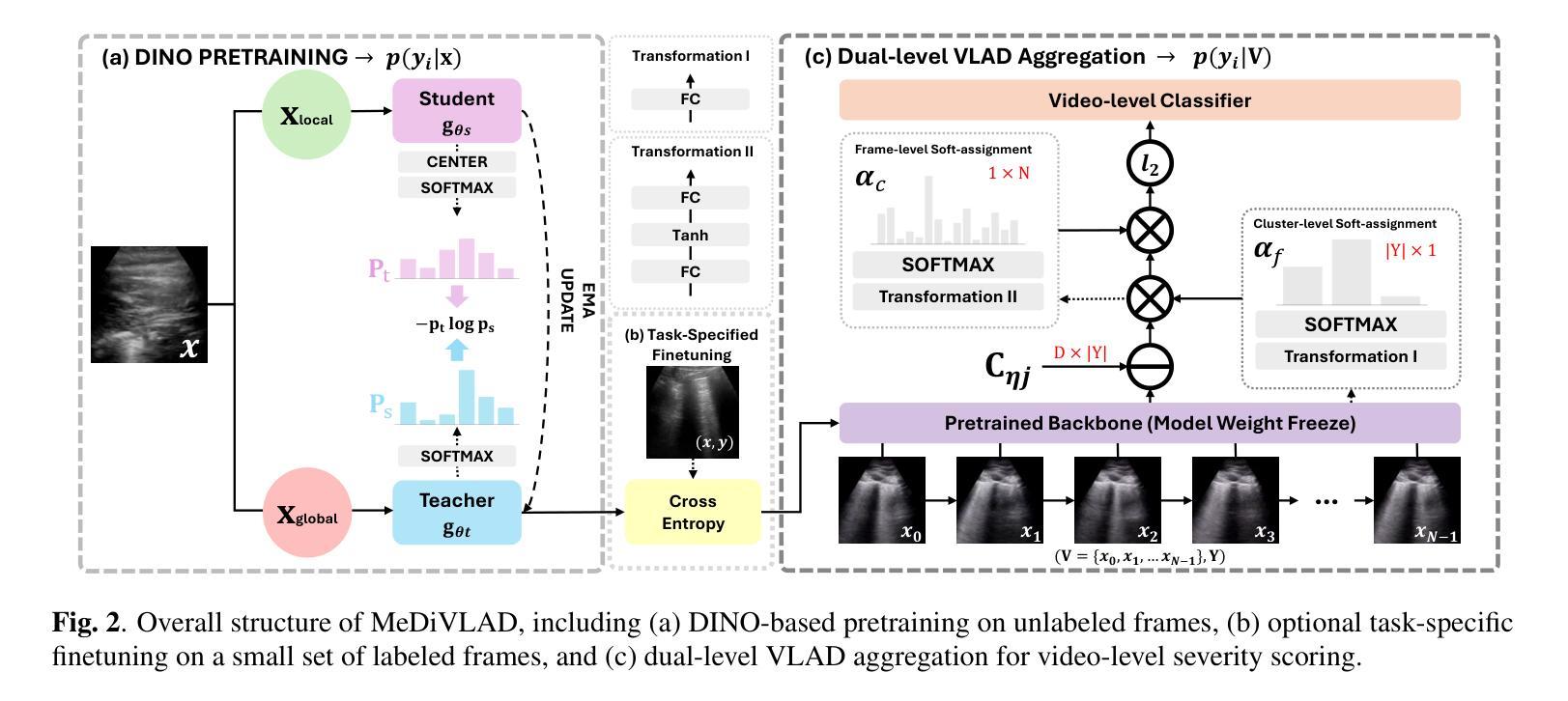
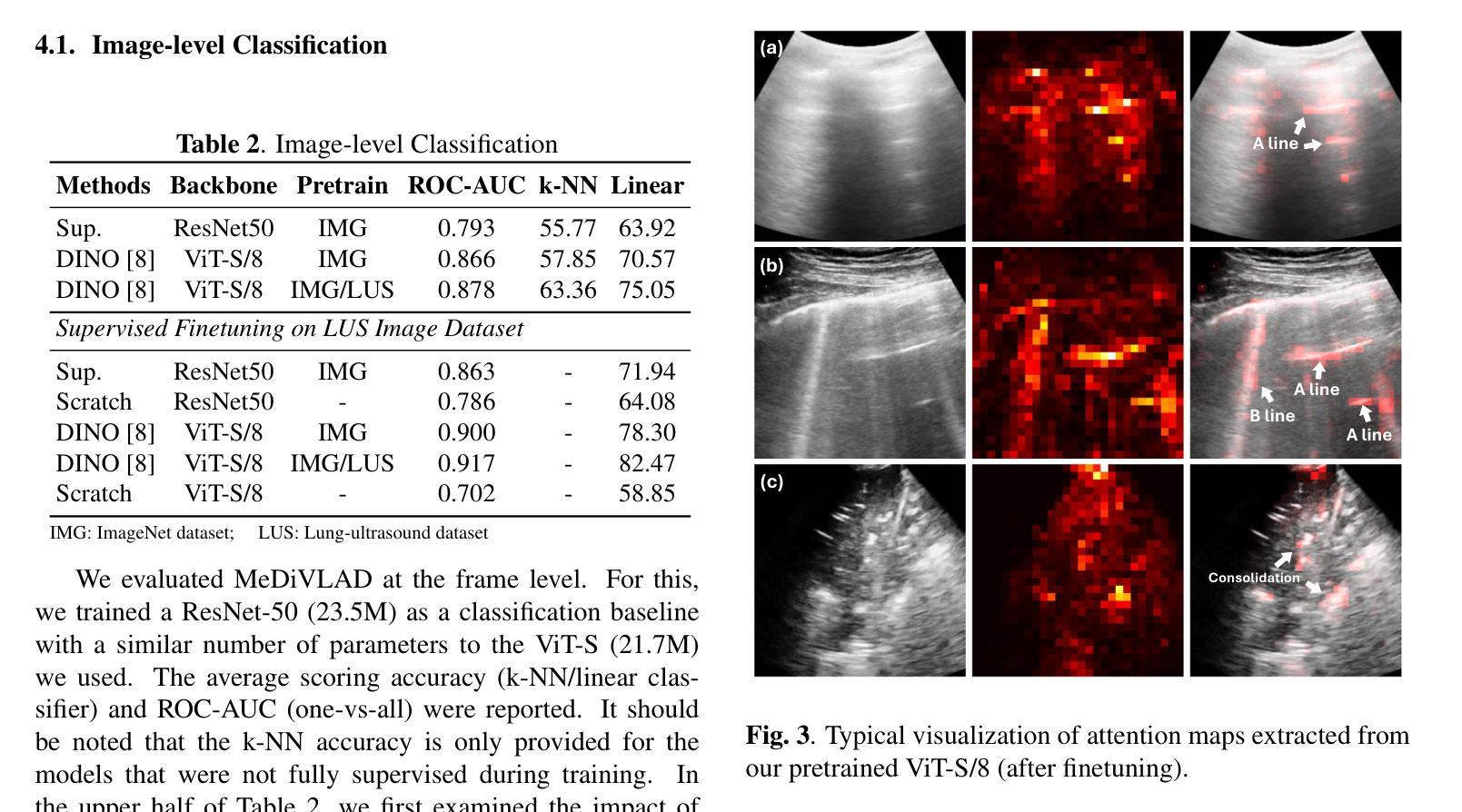
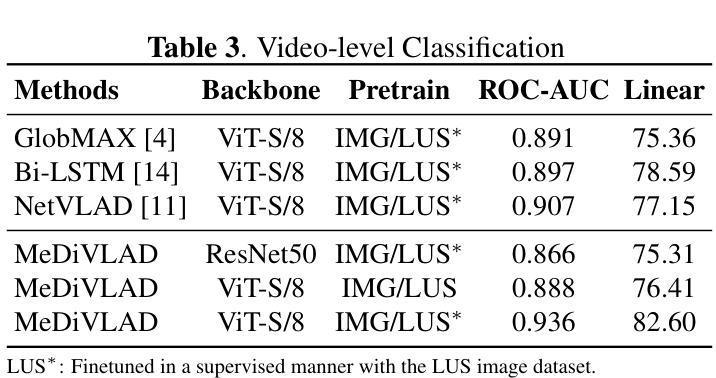
Efficient Lung Ultrasound Severity Scoring Using Dedicated Feature Extractor
Authors:Jiaqi Guo, Yunnan Wu, Evangelos Kaimakamis, Georgios Petmezas, Vasileios E. Papageorgiou, Nicos Maglaveras, Aggelos K. Katsaggelos
With the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, ultrasound imaging has emerged as a promising technique for COVID-19 detection, due to its non-invasive nature, affordability, and portability. In response, researchers have focused on developing AI-based scoring systems to provide real-time diagnostic support. However, the limited size and lack of proper annotation in publicly available ultrasound datasets pose significant challenges for training a robust AI model. This paper proposes MeDiVLAD, a novel pipeline to address the above issue for multi-level lung-ultrasound (LUS) severity scoring. In particular, we leverage self-knowledge distillation to pretrain a vision transformer (ViT) without label and aggregate frame-level features via dual-level VLAD aggregation. We show that with minimal finetuning, MeDiVLAD outperforms conventional fully-supervised methods in both frame- and video-level scoring, while offering classification reasoning with exceptional quality. This superior performance enables key applications such as the automatic identification of critical lung pathology areas and provides a robust solution for broader medical video classification tasks.
随着COVID-19大流行的到来,由于其无创、经济且便携的特性,超声成像已成为COVID-19检测的一种有前途的技术。为此,研究人员致力于开发基于人工智能的评分系统,以提供实时诊断支持。然而,公开可用的超声数据集的大小有限且缺乏适当的注释,这给训练稳健的人工智能模型带来了重大挑战。本文针对上述问题提出了MeDiVLAD这一全新的流程方案,用于多级肺超声(LUS)严重性评分。具体来说,我们利用自我知识蒸馏来预训练一个无标签的视觉转换器(ViT),并通过双级VLAD聚合技术聚合帧级特征。我们表明,通过最小的微调,MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分方面都优于传统的全监督方法,同时提供出色的分类推理质量。这种卓越的性能能够支持关键应用,如自动识别关键的肺部病理区域,并为更广泛的医学视频分类任务提供稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE ISBI 2025
Summary
随着COVID-19的爆发,超声成像因其无创性、经济性和便携性而在新冠肺炎检测中展现出巨大潜力。研究者们致力于开发基于人工智能的评分系统以提供实时诊断支持。然而,公开可用的超声数据集的大小有限且缺乏适当的标注,给训练稳健的人工智能模型带来了挑战。本文提出了MeDiVLAD,一个针对多层次肺部超声(LUS)严重程度评分问题的新型管道。我们利用自我知识蒸馏来预训练一个无需标签的视界变压器(ViT),并通过两级VLAD聚合来汇集帧级特征。研究表明,MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分上均优于传统的全监督方法,同时分类推理质量优异。其卓越的性能使关键应用如自动识别关键肺部病理区域得以实现,并为更广泛的医疗视频分类任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 超声成像在COVID-19检测中表现出巨大的潜力,尤其是其无创性、经济性和便携性特点受到重视。
- 公开可用的超声数据集存在局限性,如尺寸有限和缺乏适当标注,对训练人工智能模型构成挑战。
- 研究提出了MeDiVLAD管道来解决多层次肺部超声(LUS)严重程度评分问题。
- MeDiVLAD利用自我知识蒸馏预训练一个无需标签的视界变压器(ViT)。
- 通过帧级特征的双重级别VLAD聚合,MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分上表现优异。
- MeDiVLAD分类推理质量高,可应用于自动鉴别关键肺部病理区域等关键应用。
点此查看论文截图

Make VLM Recognize Visual Hallucination on Cartoon Character Image with Pose Information
Authors:Bumsoo Kim, Wonseop Shin, Kyuchul Lee, Yonghoon Jung, Sanghyun Seo
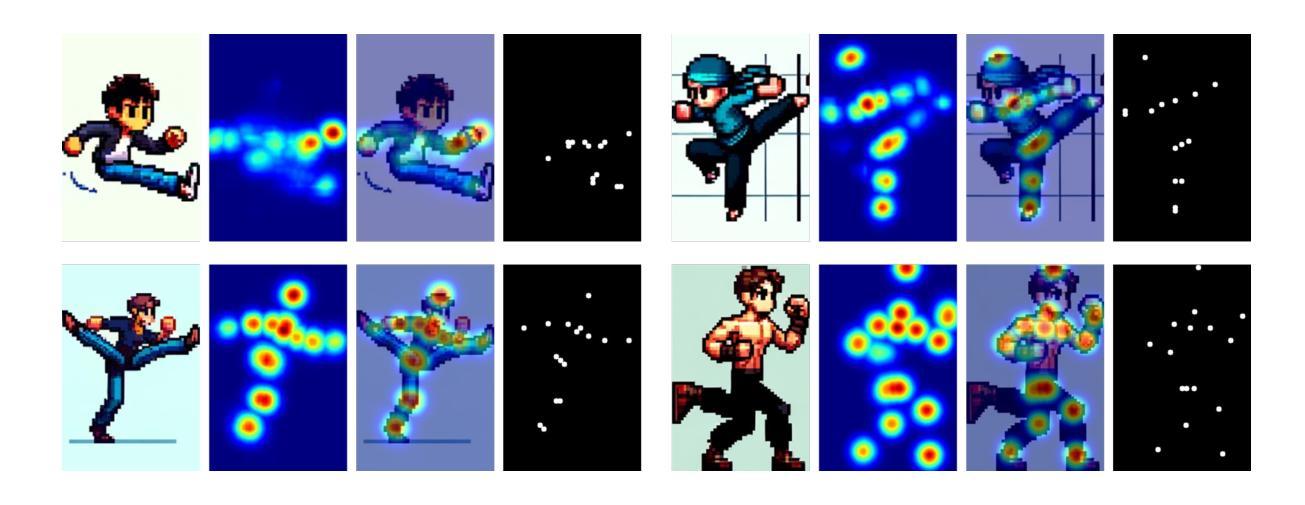
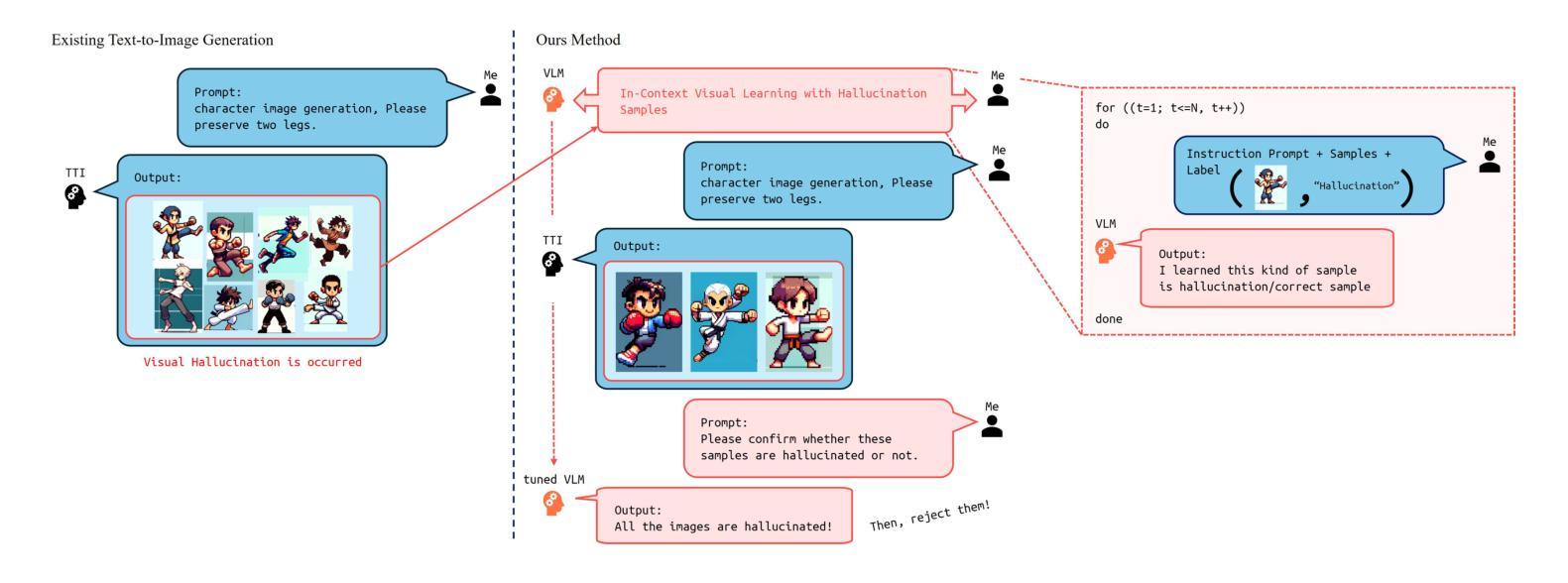
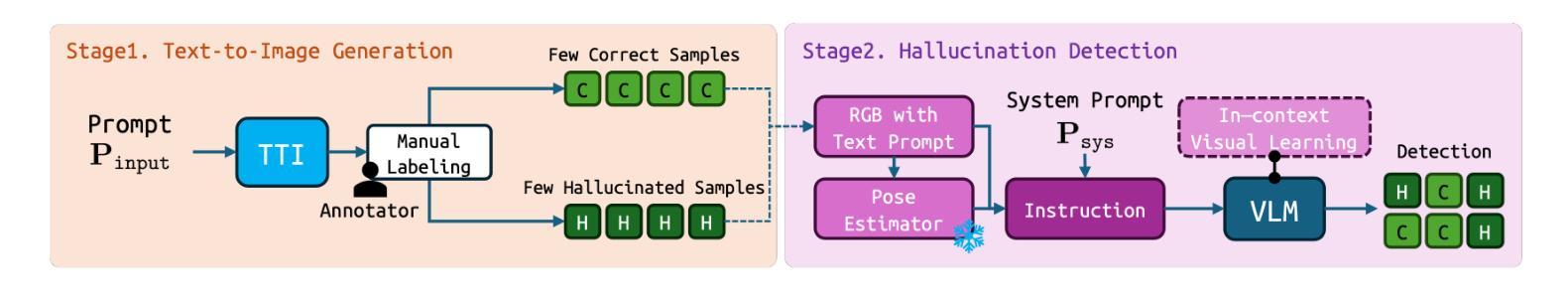
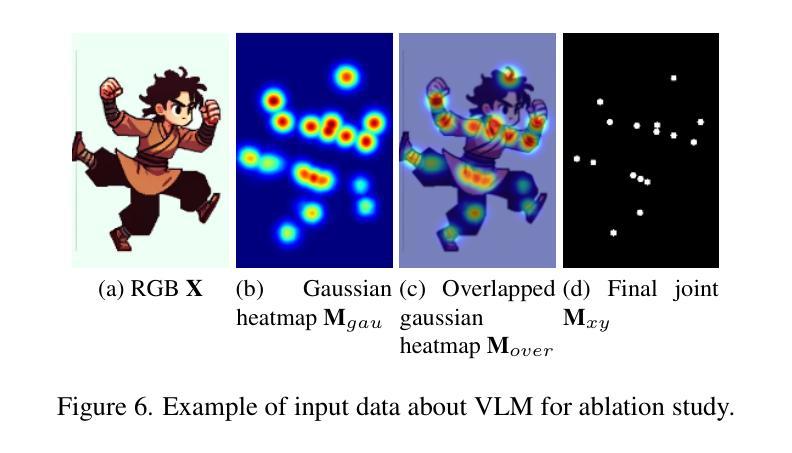
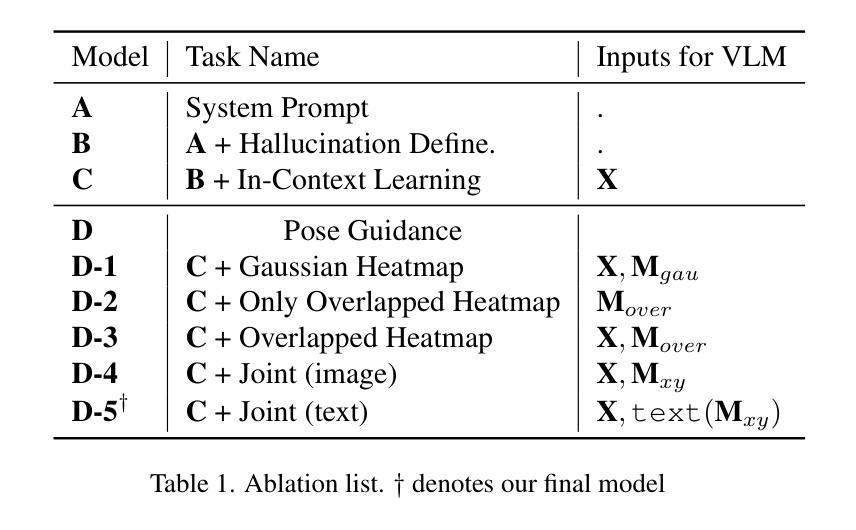
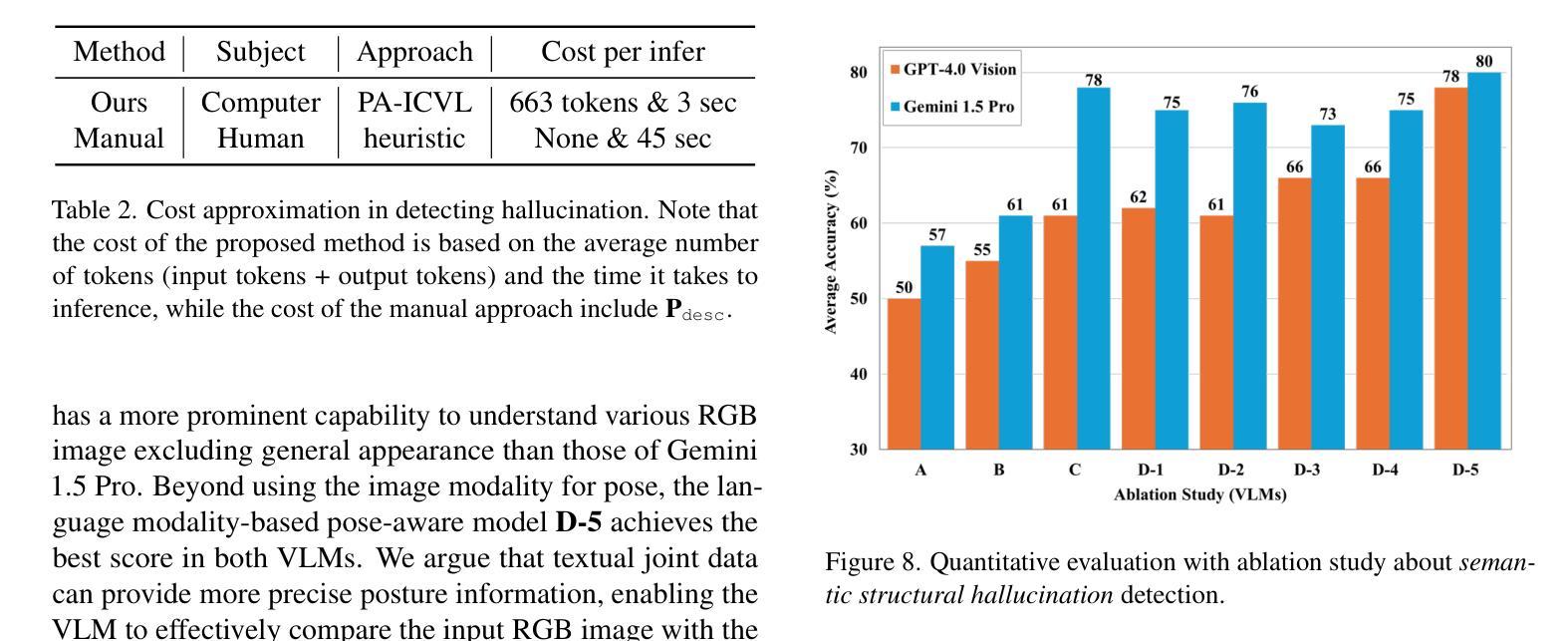
Leveraging large-scale Text-to-Image (TTI) models have become a common technique for generating exemplar or training dataset in the fields of image synthesis, video editing, 3D reconstruction. However, semantic structural visual hallucinations involving perceptually severe defects remain a concern, especially in the domain of non-photorealistic rendering (NPR) such as cartoons and pixelization-style character. To detect these hallucinations in NPR, We propose a novel semantic structural hallucination detection system using Vision-Language Model (VLM). Our approach is to leverage the emerging capability of large language model, in-context learning which denotes that VLM has seen some examples by user for specific downstream task, here hallucination detection. Based on in-context learning, we introduce pose-aware in-context visual learning (PA-ICVL) which improve the overall performance of VLM by further inputting visual data beyond prompts, RGB images and pose information. By incorporating pose guidance, we enable VLMs to make more accurate decisions. Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in identifying visual hallucinations compared to baseline methods relying solely on RGB images. Within selected two VLMs, GPT-4v, Gemini pro vision, our proposed PA-ICVL improves the hallucination detection with 50% to 78%, 57% to 80%, respectively. This research advances a capability of TTI models toward real-world applications by mitigating visual hallucinations via in-context visual learning, expanding their potential in non-photorealistic domains. In addition, it showcase how users can boost the downstream-specialized capability of open VLM by harnessing additional conditions. We collect synthetic cartoon-hallucination dataset with TTI models, this dataset and final tuned VLM will be publicly available.
利用大规模文本到图像(TTI)模型已成为图像合成、视频编辑、三维重建等领域生成范例或训练数据集的一种常见技术。然而,语义结构视觉幻觉涉及感知上的严重缺陷仍然是一个令人关注的问题,特别是在非光栅渲染(NPR)领域,如卡通和像素化风格的角色。为了在非光栅渲染中检测这些幻觉,我们提出了一种使用视觉语言模型(VLM)的新型语义结构幻觉检测系统。我们的方法是利用大型语言模型的上下文学习能力,这意味着VLM已经看到一些用户为特定下游任务提供的示例,这里是幻觉检测。基于上下文学习,我们引入了姿态感知上下文视觉学习(PA-ICVL),通过输入超出提示的视觉数据、RGB图像和姿态信息,提高了VLM的整体性能。通过融入姿态指导,我们使VLM能够做出更准确的决策。实验结果表明,与仅依赖RGB图像的基线方法相比,在识别视觉幻觉方面取得了显著改进。在选定的两个VLM中,GPT-4v和Gemini pro vision,我们提出的PA-ICVL将幻觉检测提高了50%至78%、57%至80%。这项研究通过上下文视觉学习减轻视觉幻觉,推进了TTI模型在现实世界应用的能力,扩大了其在非光栅渲染领域的潜力。此外,它展示了用户如何通过利用附加条件来提升开放VLM的下游专用能力。我们使用TTI模型收集了合成卡通幻觉数据集,该数据集和最终调整过的VLM将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV 2025, Project page: https://gh-bumsookim.github.io/Cartoon-Hallucinations-Detection/
Summary
大规模文本到图像(TTI)模型在图像合成、视频编辑、3D重建等领域生成范例或训练数据集已成为常见技术。然而,语义结构视觉幻觉仍是一个令人担忧的问题,特别是在非光栅渲染(NPR)领域,如卡通和像素化风格的角色。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的语义结构幻觉检测新系统。借助大型语言模型的上下文学习能力,我们引入了姿势感知上下文视觉学习(PA-ICVL),通过输入视觉数据、提示、RGB图像和姿势信息,提高了VLM的整体性能。实验结果表明,与仅依赖RGB图像的基准方法相比,PA-ICVL在识别视觉幻觉方面取得了显著改进。此研究通过上下文视觉学习减轻视觉幻觉,扩展了TTI模型在非光栅渲染领域的潜力,并展示了用户如何通过利用额外条件增强开放VLM的下游专业能力。我们还将公开收集的合成卡通幻觉数据集和最终调整后的VLM。
Key Takeaways
- 大型文本到图像(TTI)模型广泛用于图像合成、视频编辑和3D重建领域的数据集生成。
- 语义结构视觉幻觉问题仍然显著,特别是在非光栅渲染领域如卡通和像素化角色中。
- 提出了一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的语义结构幻觉检测新系统。
- 利用大型语言模型的上下文学习能力进行姿势感知上下文视觉学习(PA-ICVL)。
- PA-ICVL显著提高了幻觉检测性能,与基准方法相比有所改善。
- 此研究扩展了TTI模型在非光栅渲染领域的潜力,并展示了如何利用额外条件增强VLM的下游专业能力。
点此查看论文截图