⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-25 更新
Exploring Finetuned Audio-LLM on Heart Murmur Features
Authors:Adrian Florea, Xilin Jiang, Nima Mesgarani, Xiaofan Jiang
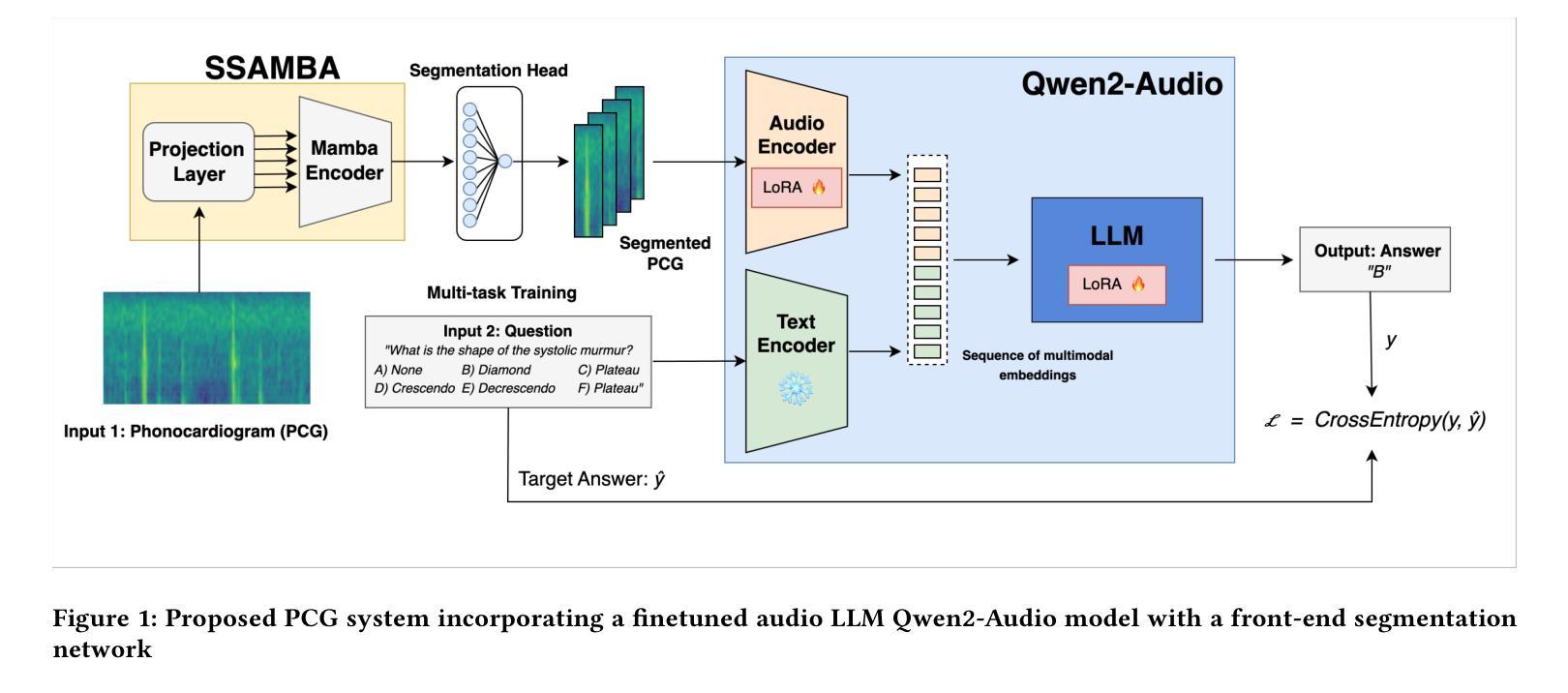
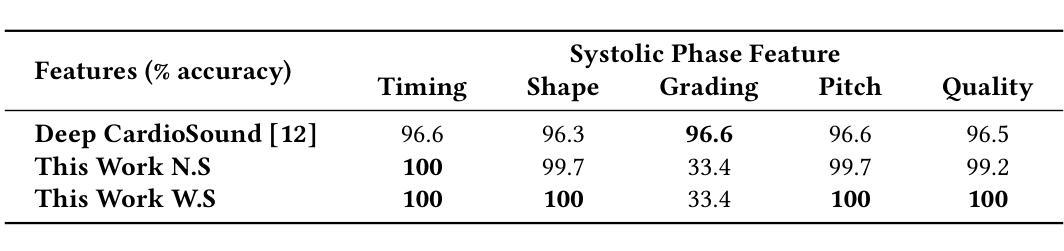
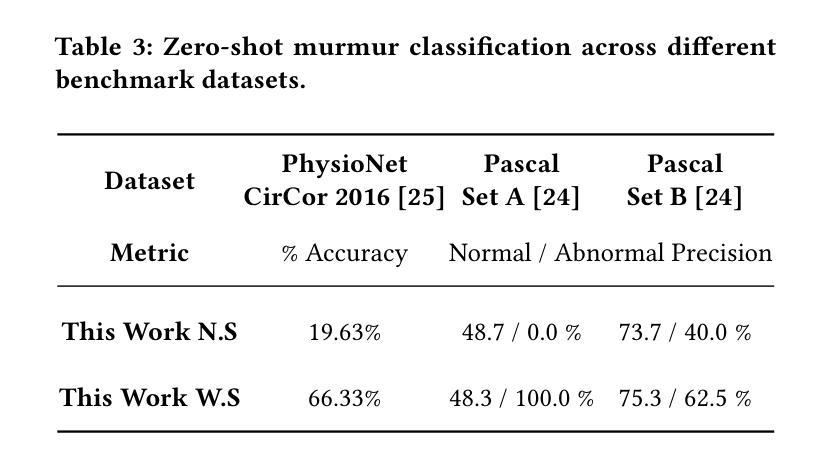
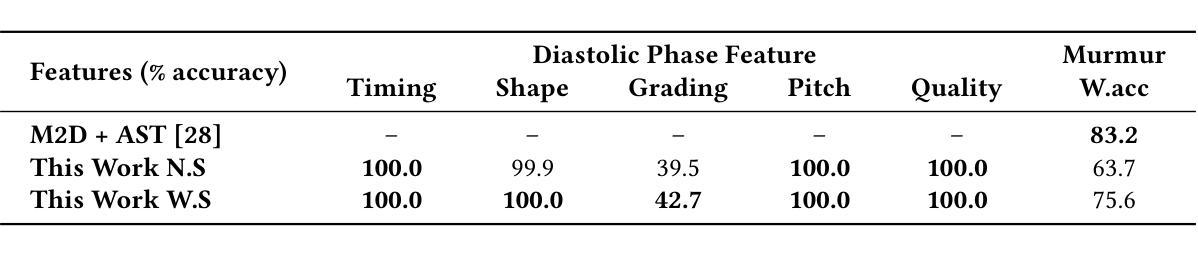
Large language models (LLMs) for audio have excelled in recognizing and analyzing human speech, music, and environmental sounds. However, their potential for understanding other types of sounds, particularly biomedical sounds, remains largely underexplored despite significant scientific interest. In this study, we focus on diagnosing cardiovascular diseases using phonocardiograms, i.e., heart sounds. Most existing deep neural network (DNN) paradigms are restricted to heart murmur classification (healthy vs unhealthy) and do not predict other acoustic features of the murmur such as timing, grading, harshness, pitch, and quality, which are important in helping physicians diagnose the underlying heart conditions. We propose to finetune an audio LLM, Qwen2-Audio, on the PhysioNet CirCor DigiScope phonocardiogram (PCG) dataset and evaluate its performance in classifying 11 expert-labeled murmur features. Additionally, we aim to achieve more noise-robust and generalizable system by exploring a preprocessing segmentation algorithm using an audio representation model, SSAMBA. Our results indicate that the LLM-based model outperforms state-of-the-art methods in 8 of the 11 features and performs comparably in the remaining 3. Moreover, the LLM successfully classifies long-tail murmur features with limited training data, a task that all previous methods have failed to classify. These findings underscore the potential of audio LLMs as assistants to human cardiologists in enhancing heart disease diagnosis.
对于音频的大型语言模型(LLMs)已经在识别和分析人类语音、音乐和环境声音方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,尽管科学界对其充满兴趣,但它们对于理解其他类型的声音,尤其是生物医学声音,还有很大的潜力尚未挖掘。在这项研究中,我们关注于心音图(即心脏声音)的心血管疾病诊断。现有的大多数深度神经网络(DNN)模式仅限于心脏杂音分类(健康与否),并不能预测杂音的其他声学特征,如时间、等级、严厉程度、音高和音质等,这些特征在帮助医生诊断潜在的心脏状况时十分重要。我们提议微调音频LLM Qwen2-Audio在PhysioNet CirCor DigiScope心音图数据集上,并评估其在分类专家标注的11个杂音特征方面的性能。此外,我们还希望通过使用音频表示模型的预处理分割算法SSAMBA,实现更稳健且通用的系统。我们的结果表明,基于LLM的模型在11个特征中有8个优于当前先进技术方法,其余3个表现相当。此外,LLM成功分类了长尾杂音特征,而之前在有限训练数据的情况下,所有方法均未能进行分类。这些发现突显了音频LLM在辅助人类心脏病学家提高心脏病诊断方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figure, and 3 tables. Submitted to IEEE/ACM Conference on Connected Health: Applications, Systems , and Engineering Technologies
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的音频技术在识别和分析人类语音、音乐和环境声音方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,它们在理解其他类型的声音,特别是生物医学声音方面的潜力,尽管有大量的科学兴趣,但仍被大大低估。本研究专注于使用心音图(心脏声音)诊断心血管疾病。大多数现有的深度神经网络(DNN)模式仅限于心脏杂音分类(健康与否),并不能预测杂音的其他声学特征,如时间、分级、粗糙度、音高等,这些特征在帮助医生诊断潜在的心脏疾病中非常重要。本研究提出对音频LLM Qwen2-Audio进行微调,在PhysioNet CirCor DigiScope心音图数据集上评估其在分类11种专家标记的杂音特征方面的性能。此外,本研究还旨在通过探索使用音频表示模型的预处理分割算法SSAMBA,实现更抗噪声和更具通用性的系统。结果表明,基于LLM的模型在11个特征中的8个上优于最新方法,并在其余3个上表现相当。此外,LLM成功地对长尾杂音特征进行了分类,而以前的所有方法都无法完成此任务。这些发现强调了音频LLM作为人类心脏病诊断的辅助工具的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在音频领域具有出色的识别和分析能力,但在生物医学声音方面的应用仍被低估。
- 本研究关注于心音图(心音)在心血管疾病诊断中的应用。
- 现有深度神经网络(DNN)主要局限于心脏杂音分类,无法预测杂音的其他声学特征。
- 研究提出对音频LLM Qwen2-Audio进行微调以分类心音图中的杂音特征。
- 基于LLM的模型在多数杂音特征分类上表现优越,尤其是长尾杂音特征的分类。
- 预处理分割算法SSAMBA有助于提高系统的噪声鲁棒性和通用性。
点此查看论文截图

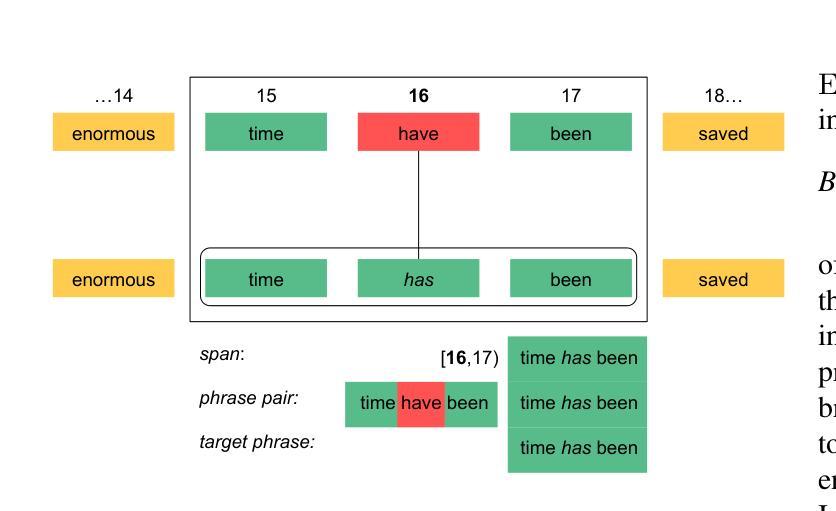
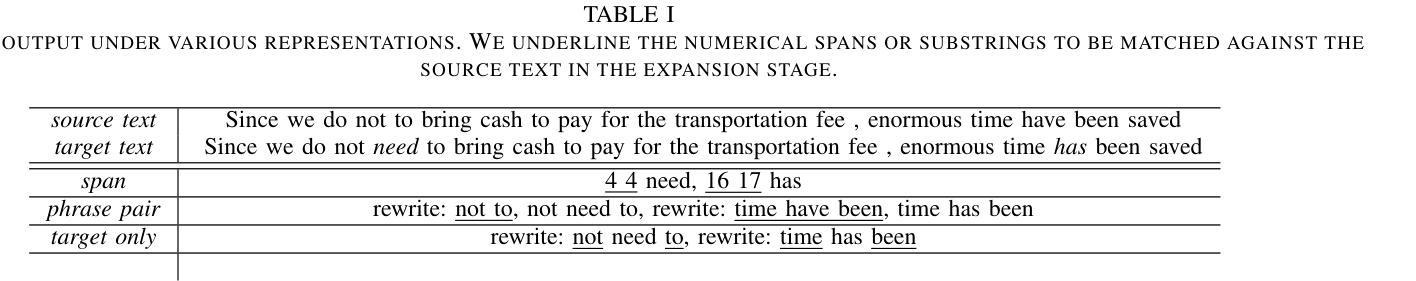
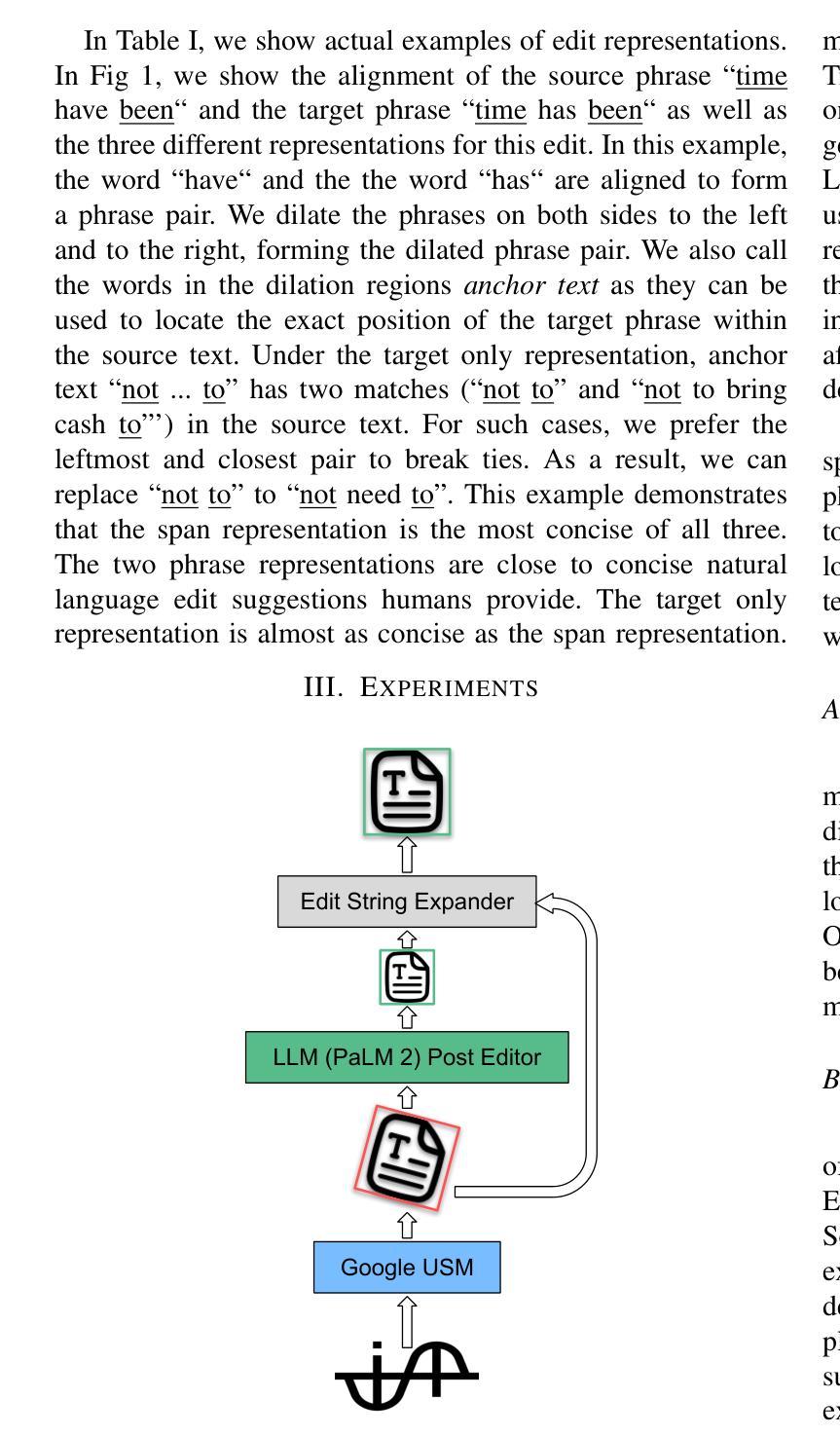
Predicting Compact Phrasal Rewrites with Large Language Models for ASR Post Editing
Authors:Hao Zhang, Felix Stahlberg, Shankar Kumar
Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at rewriting tasks such as text style transfer and grammatical error correction. While there is considerable overlap between the inputs and outputs in these tasks, the decoding cost still increases with output length, regardless of the amount of overlap. By leveraging the overlap between the input and the output, Kaneko and Okazaki (2023) proposed model-agnostic edit span representations to compress the rewrites to save computation. They reported an output length reduction rate of nearly 80% with minimal accuracy impact in four rewriting tasks. In this paper, we propose alternative edit phrase representations inspired by phrase-based statistical machine translation. We systematically compare our phrasal representations with their span representations. We apply the LLM rewriting model to the task of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) post editing and show that our target-phrase-only edit representation has the best efficiency-accuracy trade-off. On the LibriSpeech test set, our method closes 50-60% of the WER gap between the edit span model and the full rewrite model while losing only 10-20% of the length reduction rate of the edit span model.
大型语言模型(LLM)擅长文本改写任务,如文本风格转换和语法错误修正。虽然这些任务的输入和输出之间存在大量重叠,但随着输出长度的增加,解码成本仍然会增加,无论重叠程度如何。Kaneko和Okazaki(2023年)利用输入和输出之间的重叠,提出了与模型无关的编辑跨度表示法,以压缩重写内容,从而节省计算量。他们报告称,在四项重写任务中,输出长度缩减率接近80%,且对精度的影响微乎其微。在本文中,我们受到基于短语的统计机器翻译的启发,提出了替代的编辑短语表示法。我们系统地比较了我们的短语表示法与他们的跨度表示法。我们将LLM重写模型应用于语音识别(ASR)的后期编辑任务,并发现我们的目标短语仅编辑表示法具有最佳的效率-准确性权衡。在LibriSpeech测试集上,我们的方法缩小了编辑跨度模型和全重写模型之间词错误率(WER)的差距的50-60%,同时只失去了编辑跨度模型长度缩减率的10-20%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在文本风格转换和语法错误纠正等改写任务中表现优异。利用输入和输出之间的重叠性,Kaneko和Okazaki提出了模型无关的编辑跨度表示法来压缩重写内容以节省计算。受短语统计机器翻译的启发,我们提出新的短语编辑表示方法,系统性地对比了短语表示与跨度表示法。我们将LLM重写模型应用于语音识别(ASR)后编辑任务,发现目标短语编辑表示法具有最佳的效率与准确性权衡。在LibriSpeech测试集上,我们的方法缩小了编辑跨度模型和全重写模型之间的词错误率(WER)差距的50-60%,同时仅损失了编辑跨度模型的长度缩减率的10-20%。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLM)擅长文本改写任务,如文本风格转换和语法错误纠正。
- Kaneko和Okazaki利用输入和输出间的重叠性,提出模型无关的编辑跨度表示法来压缩重写内容以节省计算成本。
- 编辑跨度表示法能够实现近80%的输出长度缩减率,且对准确性影响极小。
- 提出的短语编辑表示法受到短语统计机器翻译的启发,并与跨度表示法进行了系统性对比。
- 将LLM重写模型应用于语音识别(ASR)后编辑任务时,目标短语编辑表示法展现出最佳的效率与准确性权衡。
- 在LibriSpeech测试集上,新方法缩小了词错误率(WER)差距的50-60%,相较于编辑跨度模型。
点此查看论文截图

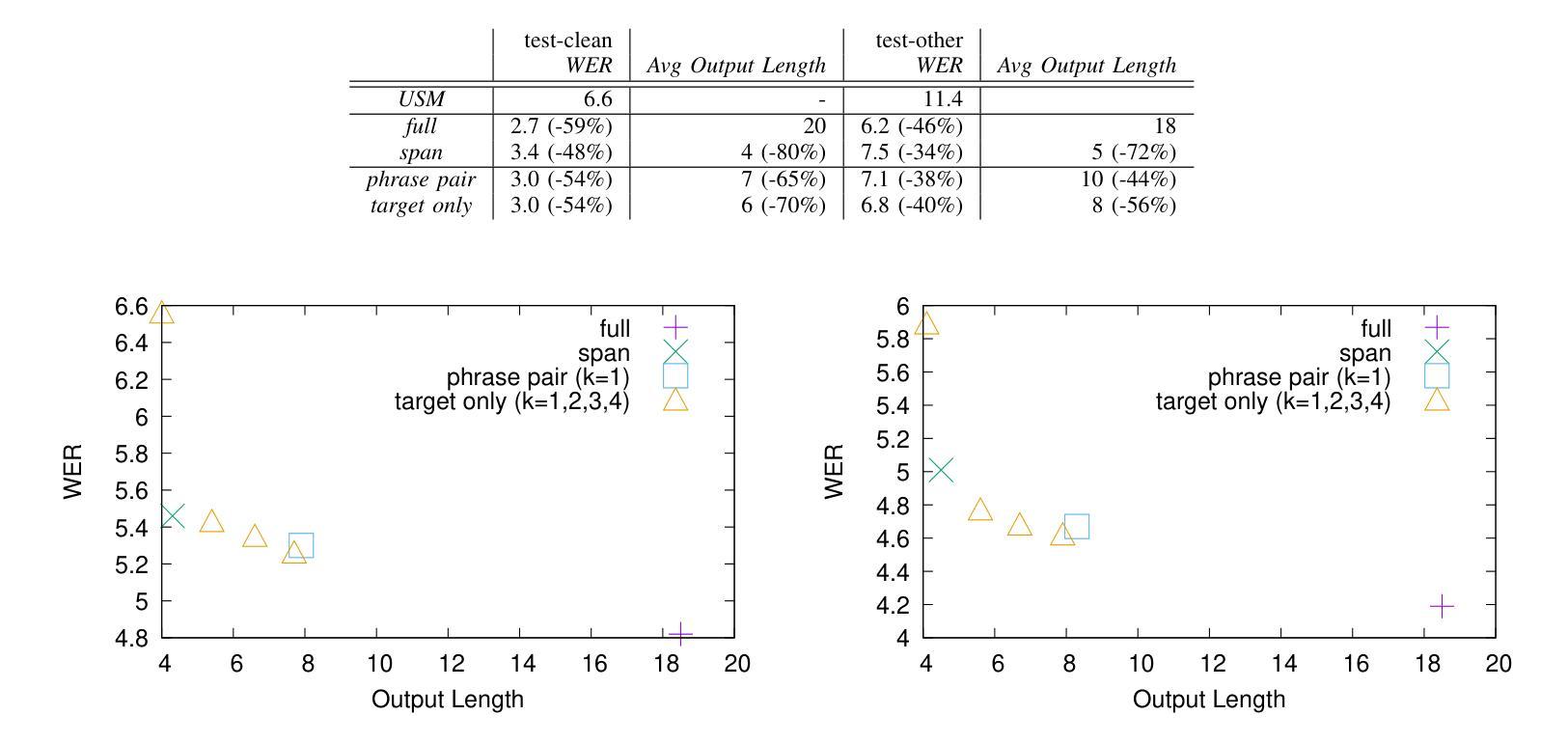
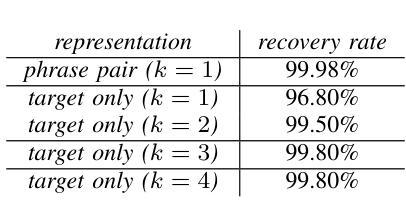
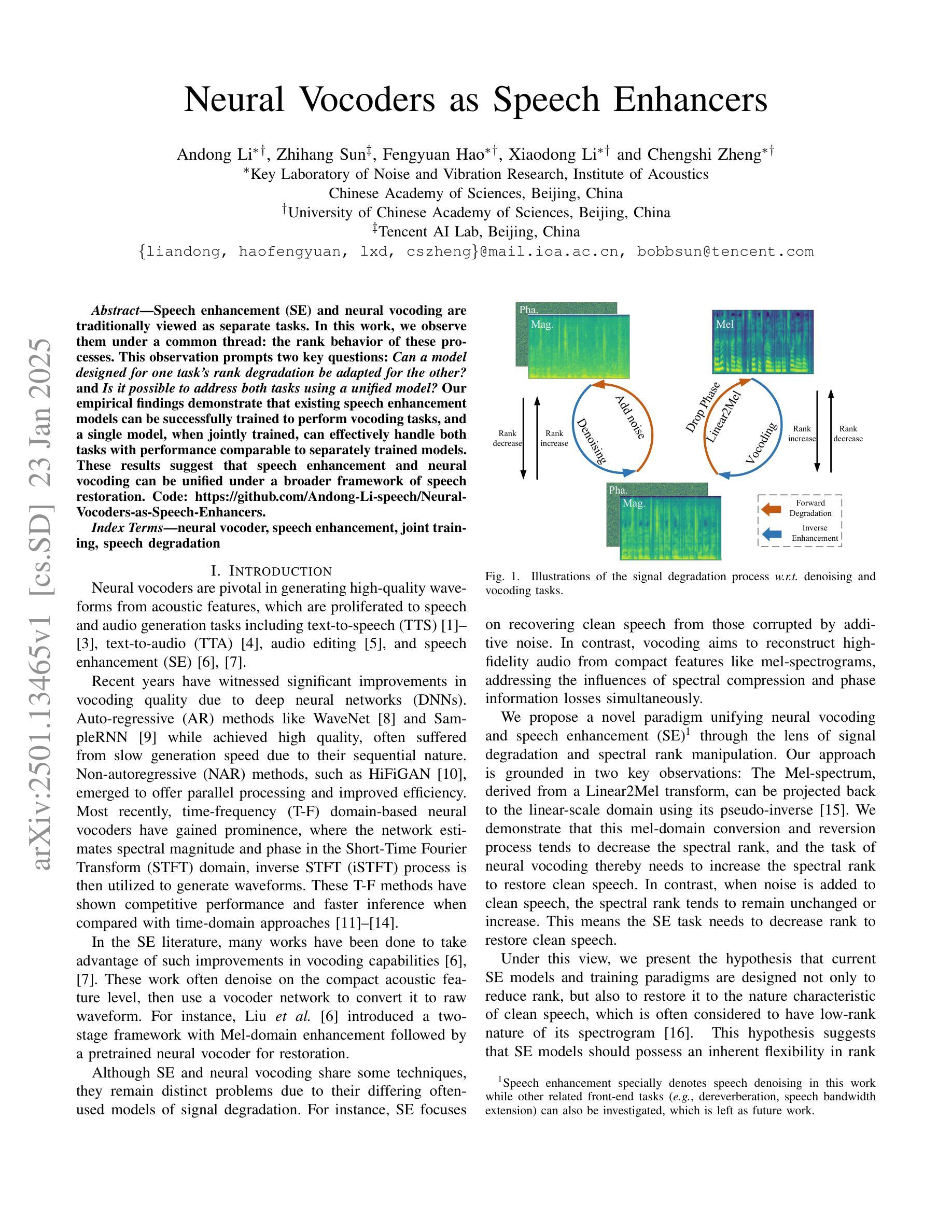
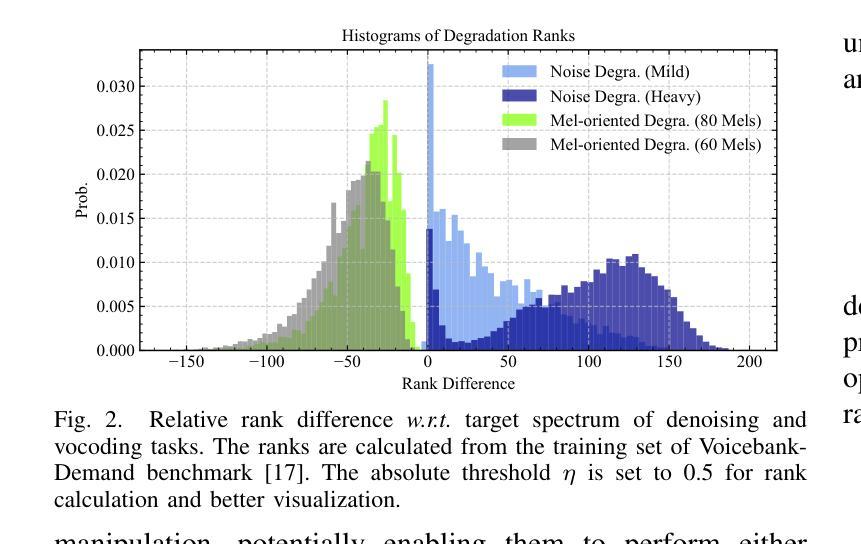
Neural Vocoders as Speech Enhancers
Authors:Andong Li, Zhihang Sun, Fengyuan Hao, Xiaodong Li, Chengshi Zheng
Speech enhancement (SE) and neural vocoding are traditionally viewed as separate tasks. In this work, we observe them under a common thread: the rank behavior of these processes. This observation prompts two key questions: \textit{Can a model designed for one task’s rank degradation be adapted for the other?} and \textit{Is it possible to address both tasks using a unified model?} Our empirical findings demonstrate that existing speech enhancement models can be successfully trained to perform vocoding tasks, and a single model, when jointly trained, can effectively handle both tasks with performance comparable to separately trained models. These results suggest that speech enhancement and neural vocoding can be unified under a broader framework of speech restoration. Code: https://github.com/Andong-Li-speech/Neural-Vocoders-as-Speech-Enhancers.
语音增强(SE)和神经声码(Neural Vocoding)传统上被视为两个独立的任务。在这项工作中,我们从这些过程等级行为的共同点进行观察。这一观察结果引发了两个关键问题:一是“为某一任务的等级退化设计的模型是否可以适应另一任务?”二是“是否可以使用统一模型来解决这两个任务?”我们的经验发现表明,现有的语音增强模型可以成功训练以执行声码任务,并且当单一模型进行联合训练时,可以有效地处理这两个任务,其性能可与单独训练的模型相媲美。这些结果表明,语音增强和神经声码可以在更广泛的语音恢复框架下统一起来。代码:https://github.com/Andong-Li-speech/Neural-Vocoders-as-Speech-Enhancers。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文探讨了语音增强和神经声码器两个传统上被视为独立的任务之间的联系。通过观察它们的等级行为,发现这两个任务具有共同的特点。实证研究结果表明,现有的语音增强模型可以成功训练用于声码器任务,并且一个联合训练模型可以同时处理这两个任务,性能与单独训练的模型相当。这暗示着语音增强和神经声码器可以在更广泛的语音恢复框架下统一起来。
Key Takeaways
- 语音增强和神经声码器是两个传统独立任务,但本文通过观察它们的等级行为发现了它们的共同特点。
- 现有语音增强模型可以成功训练用于声码器任务。
- 一个联合训练模型可以同时处理语音增强和神经声码器任务。
- 联合训练模型的性能与单独训练的模型相当。
- 实证研究证明了统一框架下处理这两个任务的可行性。
- 语音增强和神经声码器都属于语音恢复的范畴,可以在更广泛的框架下进行统一。
点此查看论文截图

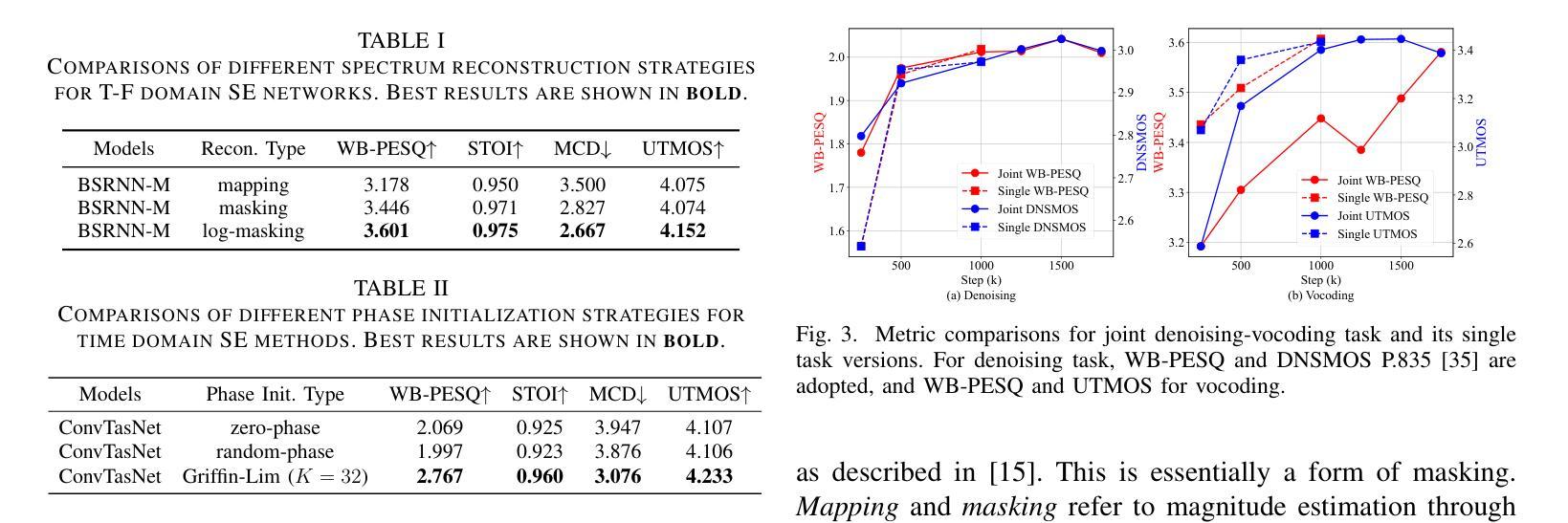
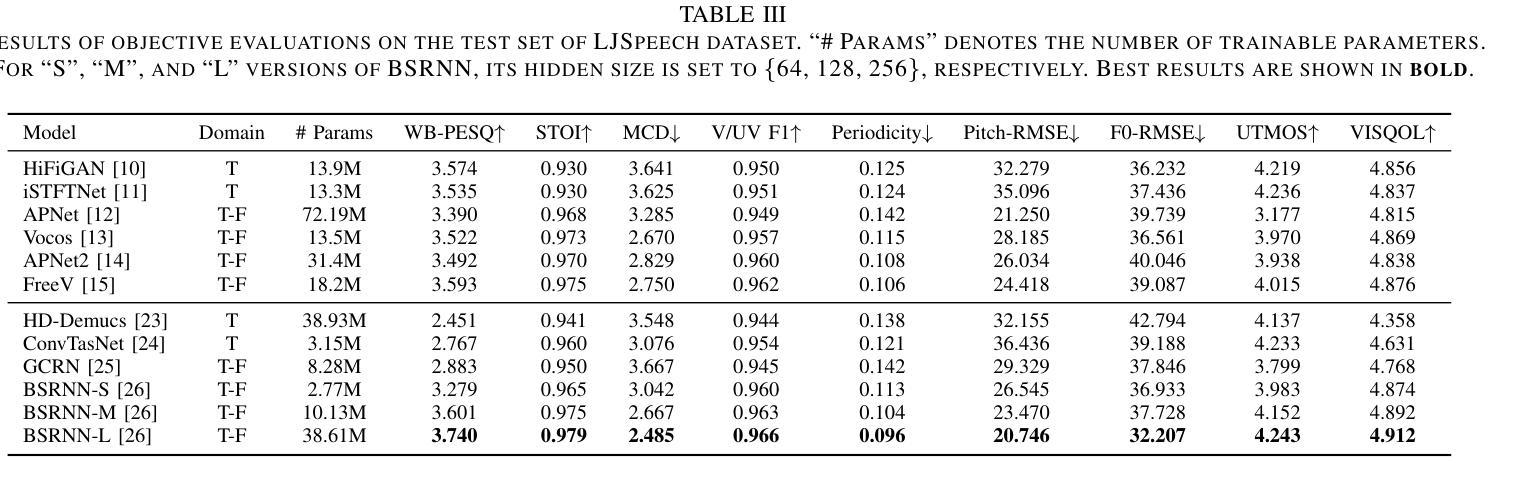
Bridging The Multi-Modality Gaps of Audio, Visual and Linguistic for Speech Enhancement
Authors:Meng-Ping Lin, Jen-Cheng Hou, Chia-Wei Chen, Shao-Yi Chien, Jun-Cheng Chen, Xugang Lu, Yu Tsao
Speech Enhancement (SE) aims to improve the quality of noisy speech. It has been shown that additional visual cues can further improve performance. Given that speech communication involves audio, visual, and linguistic modalities, it is natural to expect another performance boost by incorporating linguistic information. However, bridging the modality gaps to efficiently incorporate linguistic information, along with audio and visual modalities during knowledge transfer, is a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-modality learning framework for SE. In the model framework, a state-of-the-art diffusion Model backbone is utilized for Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement (AVSE) modeling where both audio and visual information are directly captured by microphones and video cameras. Based on this AVSE, the linguistic modality employs a PLM to transfer linguistic knowledge to the visual acoustic modality through a process termed Cross-Modal Knowledge Transfer (CMKT) during AVSE model training. After the model is trained, it is supposed that linguistic knowledge is encoded in the feature processing of the AVSE model by the CMKT, and the PLM will not be involved during inference stage. We carry out SE experiments to evaluate the proposed model framework. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed AVSE system significantly enhances speech quality and reduces generative artifacts, such as phonetic confusion compared to the state-of-the-art. Moreover, our visualization results demonstrate that our Cross-Modal Knowledge Transfer method further improves the generated speech quality of our AVSE system. These findings not only suggest that Diffusion Model-based techniques hold promise for advancing the state-of-the-art in AVSE but also justify the effectiveness of incorporating linguistic information to improve the performance of Diffusion-based AVSE systems.
语音增强(SE)旨在提高带噪声语音的质量。研究表明,额外的视觉线索可以进一步提高性能。鉴于语音通信涉及音频、视觉和语言学模式,融入语言学信息来提高性能是自然而然的想法。然而,在知识转移过程中,弥合模式间的差距以有效地融入语言学信息,同时结合音频和视觉模式是一项具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们为SE提出了一种新型多模式学习框架。在该模型框架中,我们采用最先进的扩散模型主干进行视听语音增强(AVSE)建模,其中音频和视觉信息由麦克风和摄像机直接捕获。基于AVSE,语言学模式采用PLM(预训练语言模型),通过跨模态知识转移(CMKT)过程在AVSE模型训练阶段将语言知识转移到视觉声学模式。模型训练完成后,假设语言知识通过CMKT编码在AVSE模型的特性处理中,且PLM不会参与推理阶段。我们进行了SE实验来评估所提出的模型框架。实验结果表明,与最先进的水平相比,我们提出的AVSE系统显著提高了语音质量,减少了生成物中的伪影,如语音混淆。此外,我们的可视化结果证明,我们的跨模态知识转移方法进一步提高了AVSE系统的生成语音质量。这些发现不仅表明基于扩散模型的技术在推进AVSE方面前景广阔,而且验证了融入语言学信息以提高基于扩散的AVSE系统性能的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本文主要探讨多模态学习框架在语音增强(SE)中的应用。研究提出一种基于扩散模型的音频视觉语音增强(AVSE)模型框架,该框架结合了音频、视觉和语言三种模态的信息。在模型训练中,通过跨模态知识转移(CMKT)将语言模态的知识转移到视觉声学模态。实验结果表明,该模型能显著提高语音质量和降低生成过程中的失真和音素混淆等副作用。本研究表明扩散模型技术在AVSE方面具有发展潜力,并且结合语言信息能提高扩散模型的AVSE系统性能。
关键见解
- 多模态学习框架结合了音频、视觉和语言三种模态的信息,以提高语音增强(SE)的性能。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的音频视觉语音增强(AVSE)模型框架,利用麦克风和视频摄像头直接捕获音频和视觉信息。
- 通过跨模态知识转移(CMKT)在AVSE模型训练中转移语言模态的知识。
- 实验结果表明,该模型能显著提高语音质量和降低生成过程中的失真和音素混淆。
- 扩散模型技术在AVSE方面展现出发展潜力。
- 结合语言信息能提高扩散模型的AVSE系统性能。
点此查看论文截图

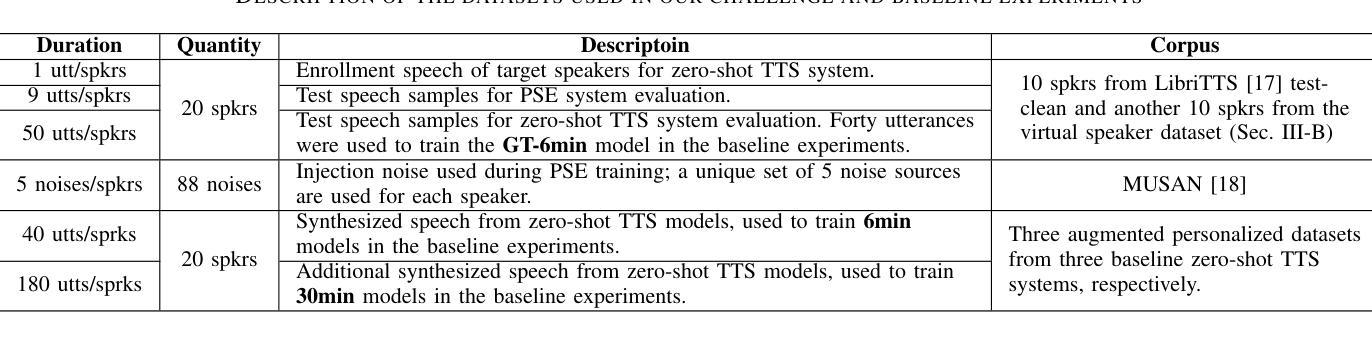
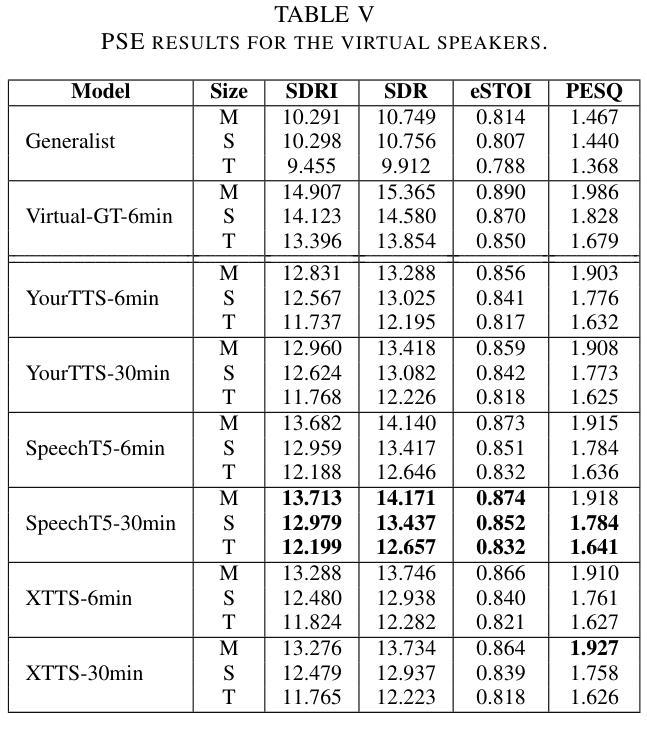
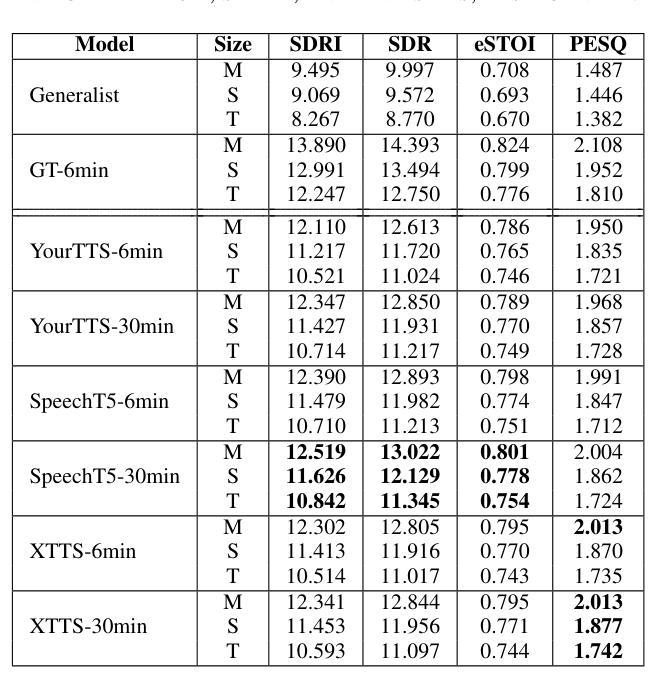
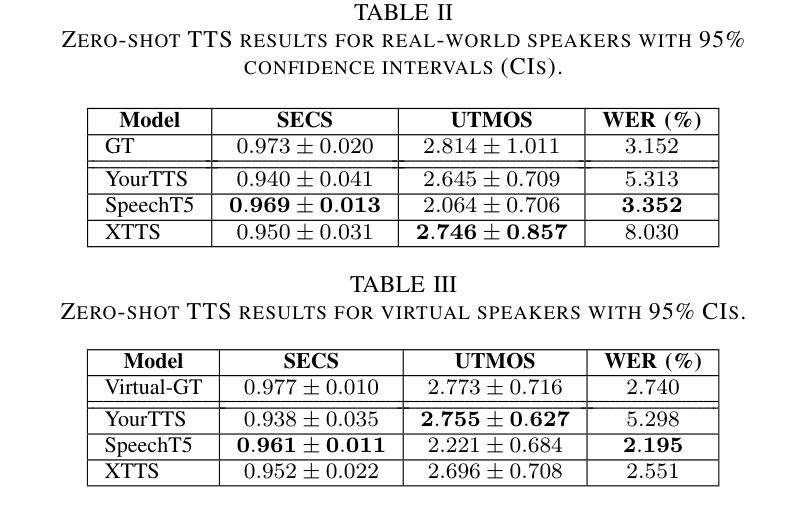
Generative Data Augmentation Challenge: Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis for Personalized Speech Enhancement
Authors:Jae-Sung Bae, Anastasia Kuznetsova, Dinesh Manocha, John Hershey, Trausti Kristjansson, Minje Kim
This paper presents a new challenge that calls for zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems to augment speech data for the downstream task, personalized speech enhancement (PSE), as part of the Generative Data Augmentation workshop at ICASSP 2025. Collecting high-quality personalized data is challenging due to privacy concerns and technical difficulties in recording audio from the test scene. To address these issues, synthetic data generation using generative models has gained significant attention. In this challenge, participants are tasked first with building zero-shot TTS systems to augment personalized data. Subsequently, PSE systems are asked to be trained with this augmented personalized dataset. Through this challenge, we aim to investigate how the quality of augmented data generated by zero-shot TTS models affects PSE model performance. We also provide baseline experiments using open-source zero-shot TTS models to encourage participation and benchmark advancements. Our baseline code implementation and checkpoints are available online.
本文提出了一个新的挑战,旨在利用零样本文本到语音(TTS)系统为下游任务增强语音数据,作为ICASSP 2025生成数据增强研讨会的一部分。由于隐私担忧和从测试场景中录制音频的技术困难,收集高质量个性化数据具有挑战性。为了解决这些问题,使用生成模型进行合成数据生成已经引起了广泛关注。在此挑战中,首先要求参与者构建零样本TTS系统以增强个性化数据。随后,要求使用此增强的个性化数据集训练PSE系统。通过这一挑战,我们旨在研究零样本TTS模型生成的增强数据质量如何影响PSE模型性能。我们还使用开源零样本TTS模型提供基线实验,以鼓励参与并评估进展。我们的基线代码实现和检查点已在线提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025 Satellite Workshop: Generative Data Augmentation for Real-World Signal Processing Applications
Summary
本文介绍了在ICASSP 2025生成数据增强研讨会上提出的新挑战,即利用零样本文本到语音(TTS)系统增强语音数据,用于下游任务个性化语音增强(PSE)。由于隐私问题和现场录音的技术困难,收集高质量个性化数据具有挑战性。因此,利用生成模型生成合成数据已成为关注的焦点。该挑战要求参与者首先建立零样本TTS系统以增强个性化数据,然后训练使用此增强个性化数据集的PSE系统。此挑战旨在研究零样本TTS模型生成的增强数据质量对PSE模型性能的影响,并提供使用开源零样本TTS模型的基线实验以鼓励参与并评估进展。
Key Takeaways
- 本文介绍了一个新挑战,旨在利用零样本文本到语音(TTS)系统增强语音数据,以改进个性化语音增强(PSE)系统的性能。
- 收集高质量个性化数据存在挑战,由于隐私问题和现场录音的技术困难,合成数据生成成为解决方案。
- 挑战要求参与者建立零样本TTS系统以增强个性化数据,并用此增强数据集训练PSE系统。
- 该挑战旨在研究零样本TTS模型生成的增强数据质量对PSE模型性能的影响。
- 提供基线实验,使用开源零样本TTS模型,以鼓励参与并评估进展。
- 线上提供基线代码实现和检查点。
- 通过此挑战,期望推动个性化语音增强技术的发展,并深入了解数据质量在其中的作用。
点此查看论文截图

Let SSMs be ConvNets: State-space Modeling with Optimal Tensor Contractions
Authors:Yan Ru Pei
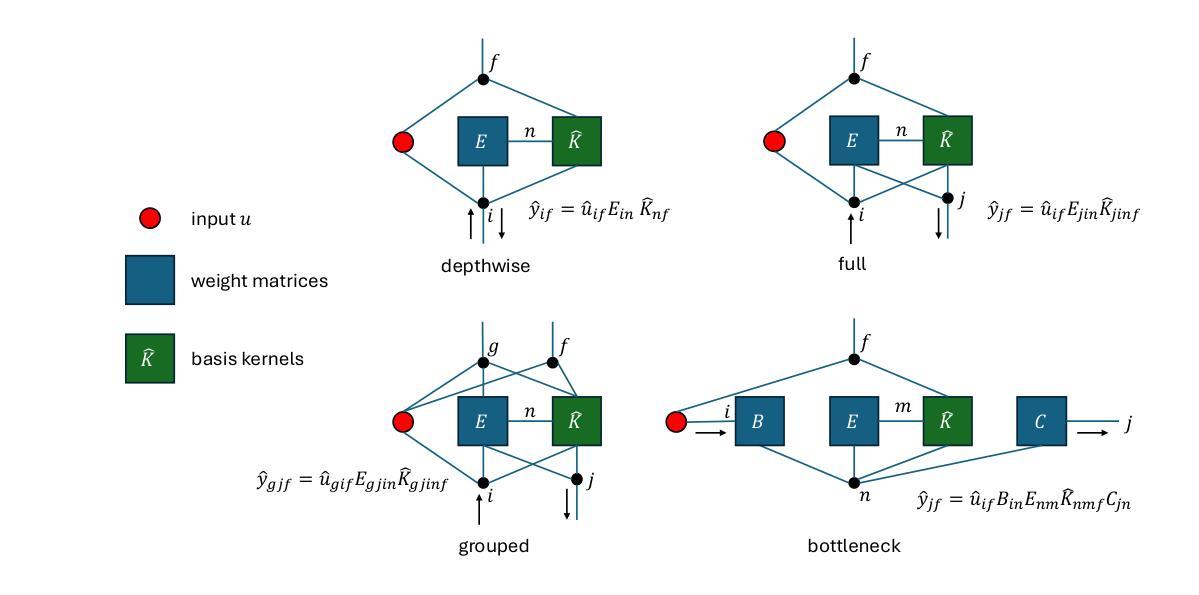
We introduce Centaurus, a class of networks composed of generalized state-space model (SSM) blocks, where the SSM operations can be treated as tensor contractions during training. The optimal order of tensor contractions can then be systematically determined for every SSM block to maximize training efficiency. This allows more flexibility in designing SSM blocks beyond the depthwise-separable configuration commonly implemented. The new design choices will take inspiration from classical convolutional blocks including group convolutions, full convolutions, and bottleneck blocks. We architect the Centaurus network with a mixture of these blocks, to balance between network size and performance, as well as memory and computational efficiency during both training and inference. We show that this heterogeneous network design outperforms its homogeneous counterparts in raw audio processing tasks including keyword spotting, speech denoising, and automatic speech recognition (ASR). For ASR, Centaurus is the first network with competitive performance that can be made fully state-space based, without using any nonlinear recurrence (LSTMs), explicit convolutions (CNNs), or (surrogate) attention mechanism. Source code is available at github.com/Brainchip-Inc/Centaurus
我们介绍了Centaurus网络,它是一类由广义状态空间模型(SSM)块组成的网络。在训练过程中,SSM操作可以被视为张量收缩。然后可以为每个SSM块系统地确定张量收缩的最佳顺序,以最大化训练效率。这允许在设计SSM块时具有更大的灵活性,超越了通常实现的深度可分离配置。新的设计选择将从经典的卷积块中获得灵感,包括分组卷积、全卷积和瓶颈块。我们使用这些块的混合来构建Centaurus网络,以在网络规模和性能之间取得平衡,同时在训练和推理期间的内存和计算效率之间取得平衡。我们证明了这种异构网络设计在原始音频处理任务上的表现优于其同构的对应物,包括关键词识别、语音降噪和自动语音识别(ASR)。对于ASR,Centaurus是第一个具有竞争力的完全基于状态空间的网络,无需使用任何非线性递归(LSTM)、显式卷积(CNN)或(替代)注意力机制。源代码可在github.com/Brainchip-Inc/Centaurus上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 7 figures
Summary
Centaurus网络结合了广义状态空间模型(SSM)块,通过系统确定SSM块的最优张量收缩顺序以优化训练效率。新设计允许更多灵活性,并超越了深度可分离配置的局限。通过混合不同的SSM块和经典卷积块,实现了网络大小与性能、内存与计算效率的平衡。在原始音频处理任务中,包括关键词识别、语音降噪和自动语音识别(ASR),Centaurus网络表现出优于同类网络的性能。特别是在ASR领域,Centaurus网络成为首个完全基于状态空间模型、无需非线性递归(LSTM)、显式卷积(CNN)或替代注意力机制的网络,表现出强大的竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- Centaurus网络结合广义状态空间模型(SSM)块,通过系统优化张量收缩顺序提升训练效率。
- SSM块设计更具灵活性,超越深度可分离配置的局限。
- 结合不同的SSM块和经典卷积块,实现网络大小、性能、内存和计算效率的平衡。
- Centaurus网络在原始音频处理任务中表现优越,包括关键词识别、语音降噪和自动语音识别(ASR)。
- Centaurus网络在ASR领域的表现尤为突出,成为首个无需非线性递归(LSTM)、显式卷积(CNN)或替代注意力机制的网络。
- 该网络的源代码可在github.com/Brainchip-Inc/Centaurus找到。
点此查看论文截图

Interactive Cycle Model: The Linkage Combination among Automatic Speech Recognition, Large Language Models and Smart Glasses
Authors:Libo Wang
This research proposes the interaction loop model “ASR-LLMs-Smart Glasses”, which model combines automatic speech recognition, large language model and smart glasses to facilitate seamless human-computer interaction. And the methodology of this research involves decomposing the interaction process into different stages and elements. Speech is captured and processed by ASR, then analyzed and interpreted by LLMs. The results are then transmitted to smart glasses for display. The feedback loop is complete when the user interacts with the displayed data. Mathematical formulas are used to quantify the performance of the model that revolves around core evaluation points: accuracy, coherence, and latency during ASR speech-to-text conversion. The research results are provided theoretically to test and evaluate the feasibility and performance of the model. Detailed architectural details and experimental process have been uploaded to Github, the link is:https://github.com/brucewang123456789/GeniusTrail.git.
本研究提出了“ASR-LLMs-智能眼镜”交互循环模型,该模型结合了自动语音识别、大型语言模型和智能眼镜,促进了无缝的人机交互。研究方法涉及将交互过程分解成不同的阶段和元素。语音被ASR捕获并处理,然后通过LLMs进行分析和解释。结果随后传输到智能眼镜进行显示。当用户与显示的数据进行交互时,反馈循环完成。研究使用数学公式来量化模型性能,围绕核心评估点:ASR语音到文本转换过程中的准确性、连贯性和延迟。研究结果从理论上提供了测试和评估模型可行性和性能的依据。详细的架构细节和实验过程已经上传到Github,链接为:https://github.com/brucewang123456789/GeniusTrail.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF OpenReview submitted. 10 pages of text and 2 figures
Summary:该研究提出了一个名为“ASR-LLMs-智能眼镜”的互动循环模型,该模型结合了自动语音识别、大型语言模型和智能眼镜,以促进无缝人机交互。研究方法涉及将互动过程分解成不同的阶段和元素。通过ASR捕捉和处理语音,然后由LLMs进行分析和解释。结果将传输到智能眼镜进行显示。在用户与显示的数据进行交互时,反馈循环完成。围绕核心评估点(准确性、连贯性和延迟性),使用数学公式对模型性能进行量化。研究结果在理论上进行了测试和评估模型的可行性及性能。详细的架构和实验过程已上传至GitHub,链接为:[链接地址]。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出了一种新型的互动循环模型——“ASR-LLMs-智能眼镜”,整合了自动语音识别、大型语言模型和智能眼镜技术。
- 模型的工作流程包括:通过ASR捕捉和处理语音,LLMs进行结果分析和解释,然后将结果传输至智能眼镜进行显示。
- 用户与智能眼镜展示的数据互动完成反馈循环。
- 模型性能评估主要通过三个核心点:准确性、连贯性和延迟性。
- 研究结果在理论上进行了测试,证明了模型的可行性及性能。
- 详细的模型架构和实验过程已公开在GitHub上,供公众查阅和参考。
点此查看论文截图