⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-28 更新
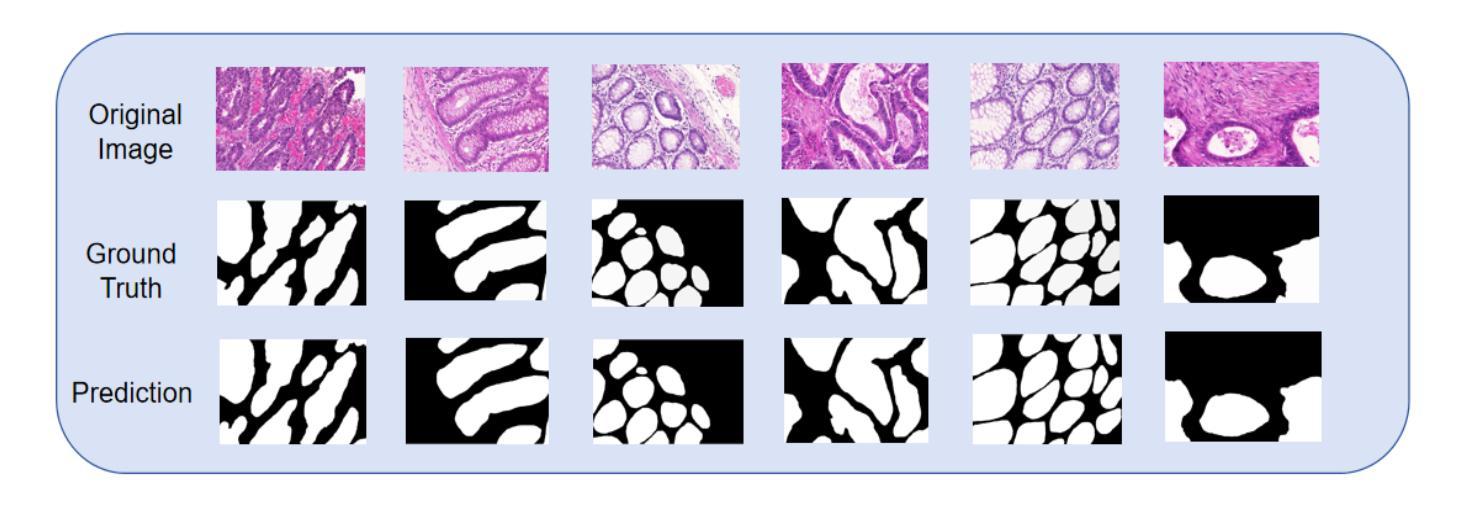
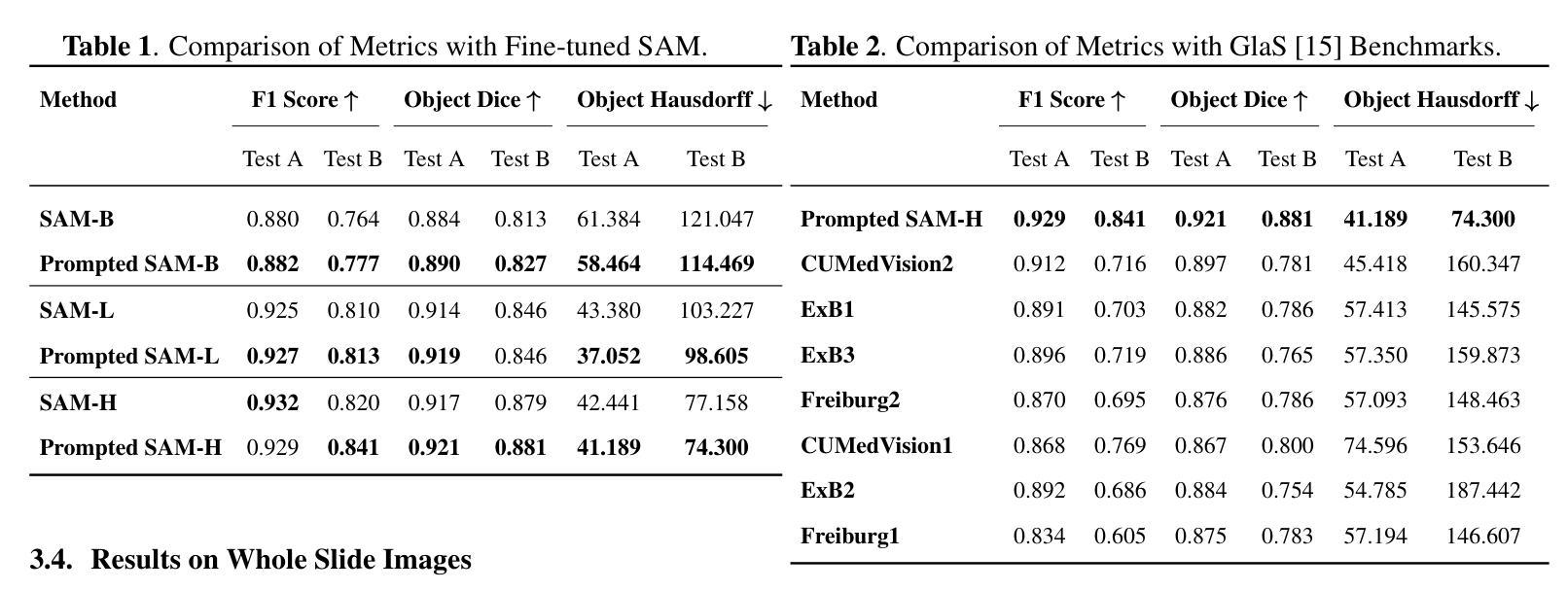
Gland Segmentation Using SAM With Cancer Grade as a Prompt
Authors:Yijie Zhu, Shan E Ahmed Raza
Cancer grade is a critical clinical criterion that can be used to determine the degree of cancer malignancy. Revealing the condition of the glands, a precise gland segmentation can assist in a more effective cancer grade classification. In machine learning, binary classification information about glands (i.e., benign and malignant) can be utilized as a prompt for gland segmentation and cancer grade classification. By incorporating prior knowledge of the benign or malignant classification of the gland, the model can anticipate the likely appearance of the target, leading to better segmentation performance. We utilize Segment Anything Model to solve the segmentation task, by taking advantage of its prompt function and applying appropriate modifications to the model structure and training strategies. We improve the results from fine-tuned Segment Anything Model and produce SOTA results using this approach.
癌症分级是一个重要的临床标准,可以用来确定癌症的恶性程度。精确的腺体分割可以揭示腺体的状况,从而有助于更有效地进行癌症分级分类。在机器学习中,关于腺体(即良性和恶性)的二元分类信息可以作为腺体分割和癌症分级分类的提示。通过结合腺体良性或恶性分类的先验知识,模型可以预测目标的可能外观,从而提高分割性能。我们利用Segment Anything Model来解决分割任务,通过利用其提示功能并对模型结构和训练策略进行适当的修改。我们通过对Segment Anything Model进行微调,改进了结果,并使用这种方法取得了最新结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISBI 2025
Summary
癌症分级是评估癌症恶性程度的重要临床标准。精确的腺体分割可以揭示腺体状况,进而更精准地进行癌症分级。在机器学习中,利用腺体(良性或恶性)的二元分类信息,可作为腺体分割和癌症分级分类的提示。结合腺体良性或恶性的先验知识,模型可以预测目标的可能出现情况,从而提高分割性能。我们利用Segment Anything Model完成分割任务,通过调整模型结构和训练策略,改进了fine-tuned Segment Anything Model的结果,并获得了先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症分级是评估癌症恶性程度的关键临床标准。
- 精确的腺体分割有助于更准确的癌症分级。
- 机器学习中可利用腺体的二元分类信息进行癌症分级。
- 结合腺体的良性或恶性先验知识可提高模型预测的准确性。
- 使用Segment Anything Model进行腺体分割,改进了fine-tuned模型的结果。
- 适当调整模型结构和训练策略可提高分割性能。
点此查看论文截图

Ambient pressure growth of bilayer nickelate single crystals with superconductivity over 90 K under high pressure
Authors:Feiyu Li, Di Peng, Jie Dou, Ning Guo, Liang Ma, Chao Liu, Lingzhen Wang, Yulin Zhang, Jun Luo, Jie Yang, Jian Zhang, Weizhao Cai, Jinguang Cheng, Qiang Zheng, Rui Zhou, Qiaoshi Zeng, Xutang Tao, Junjie Zhang
Recently, the Ruddlesden-Popper bilayer nickelate La3Ni2O7 has been discovered as a high temperature superconductor with Tc near 80 K above 14 GPa.[1-3] The search for nickelate superconductors with higher Tc, the preparation of high-quality single crystals, and the removal of high-pressure conditions including single crystal growth under high gas pressure and achievement of high Tc superconductivity under high pressure, are the most challenging tasks. Here, we present ambient pressure flux growth of high-quality bilayer nickelate single crystals with superconductivity up to 91 K under high pressure. Single crystals of bilayer La3-xRxNi2O7-y with dimensions up to 220 um on the edge were successfully grown using flux method at atmosphere conditions. Single crystal X-ray diffraction, nuclear quadrupole resonance, energy dispersion spectroscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy measurements evidenced high quality of bilayer La2SmNi2O7-y single crystals in average structure and local structure. Superconductivity has been observed in high pressure resistivity measurements of annealed La2SmNi2O7-y single crystals with Tc onset up to 91 K, which is the highest among the known superconducting nickelates. Our results not only demonstrate a new and easy-to-access method for synthesizing high-quality bilayer nickelate single crystals, but also providing a direction for discovering superconducting nickelates with higher Tc.
最近,Ruddlesden-Popper双层镍酸盐La3Ni2O7被发现是一种高温超导体,在高于14 GPa的条件下,其居里温度(Tc)接近80 K^[1-3]^。寻找具有更高居里温度的镍酸盐超导体、制备高质量单晶以及消除高压条件(包括高压气体环境下的单晶生长以及高压下实现高居里温度超导性)是最具挑战性的任务。在这里,我们展示了在环境压力下通过助熔剂法生长高质量双层镍酸盐单晶的方法,这些单晶在高压下表现出高达91 K的超导性。在常压条件下,我们成功使用助熔剂法生长了边缘尺寸高达220微米双层La3-xRxNi2O7-y单晶。通过单晶X射线衍射、核四极共振、能量色散光谱和扫描透射电子显微镜测量,证明了La2SmNi2O7-y双层单晶的平均结构和局部结构的高品质。我们对退火后的La2SmNi2O7-y单晶进行了高压电阻率测量,观察到其超导性,起始居里温度高达91 K,这是已知超导镍酸盐中最高的一种。我们的结果不仅展示了一种合成高质量双层镍酸盐单晶的新方法,也为发现具有更高居里温度的镍酸盐超导体提供了方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 figures and 1 table
Summary
本文报道了采用大气压流体生长法成功合成高质量双层镍酸盐单晶La3-xRxNi2O7-y,并在高压电阻率测量中观察到高达91K的超导性。这不仅展示了合成高质量双层镍酸盐单晶的新方法,而且为发现具有更高临界温度的超导镍酸盐提供了方向。
Key Takeaways
- La3Ni2O7被发现是一种高温超导体,临界温度(Tc)在高压下接近80K。
- 研究人员成功地在常压下使用流体生长法合成高质量的双层镍酸盐单晶La3-xRxNi2O7-y,尺寸可达220微米。
- 通过X射线衍射、核磁共振、能量色散光谱和扫描透射电子显微镜等技术证实了这些单晶的高品质。
- 在退火后的La2SmNi2O7-y单晶中观察到高达91K的超导性,这是已知超导镍酸盐中的最高值。
- 该方法不仅易于访问,而且为合成高质量双层镍酸盐单晶提供了新的途径。
- 此项研究为发现具有更高临界温度的超导镍酸盐提供了方向。
点此查看论文截图

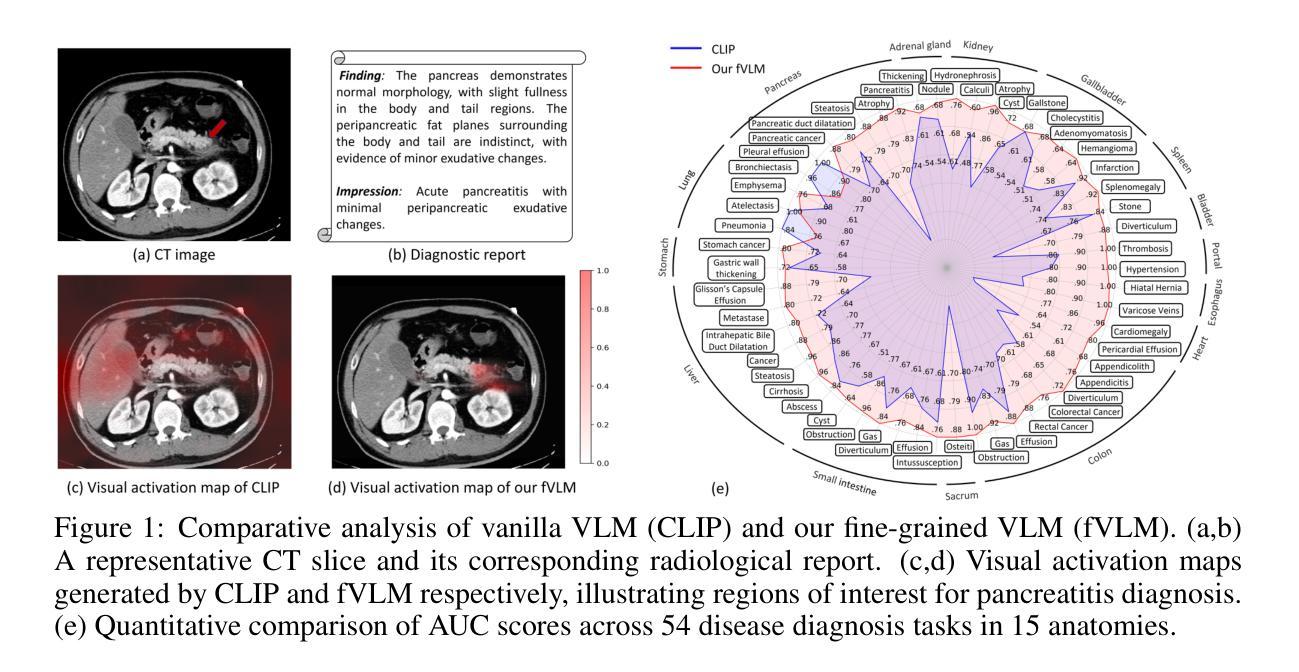
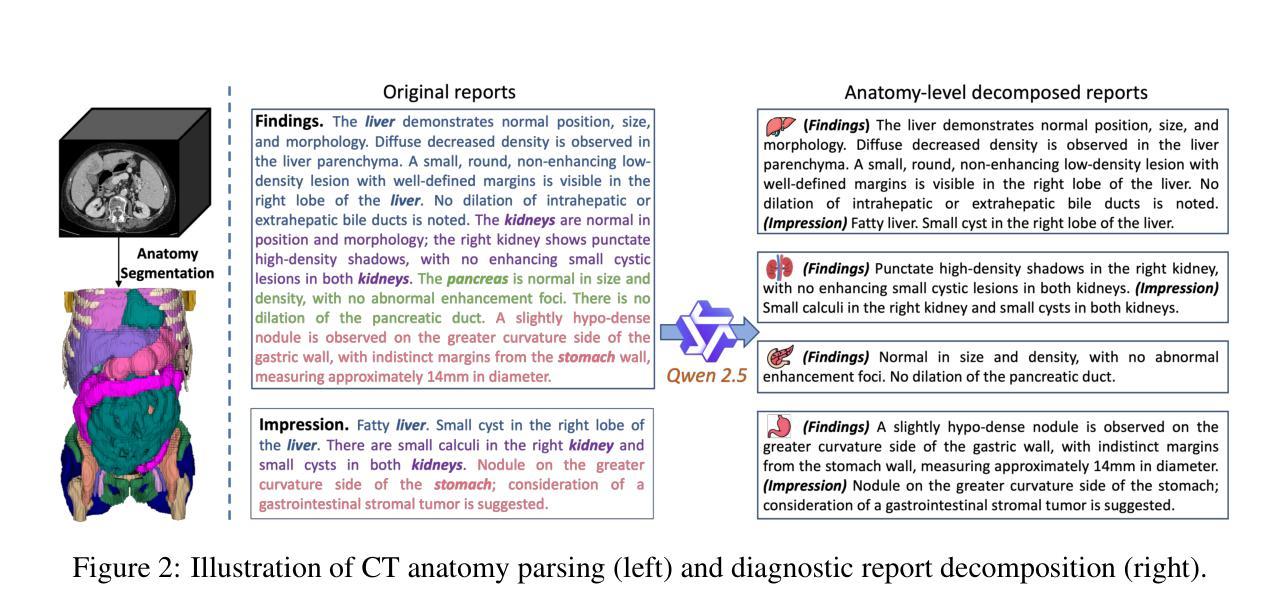
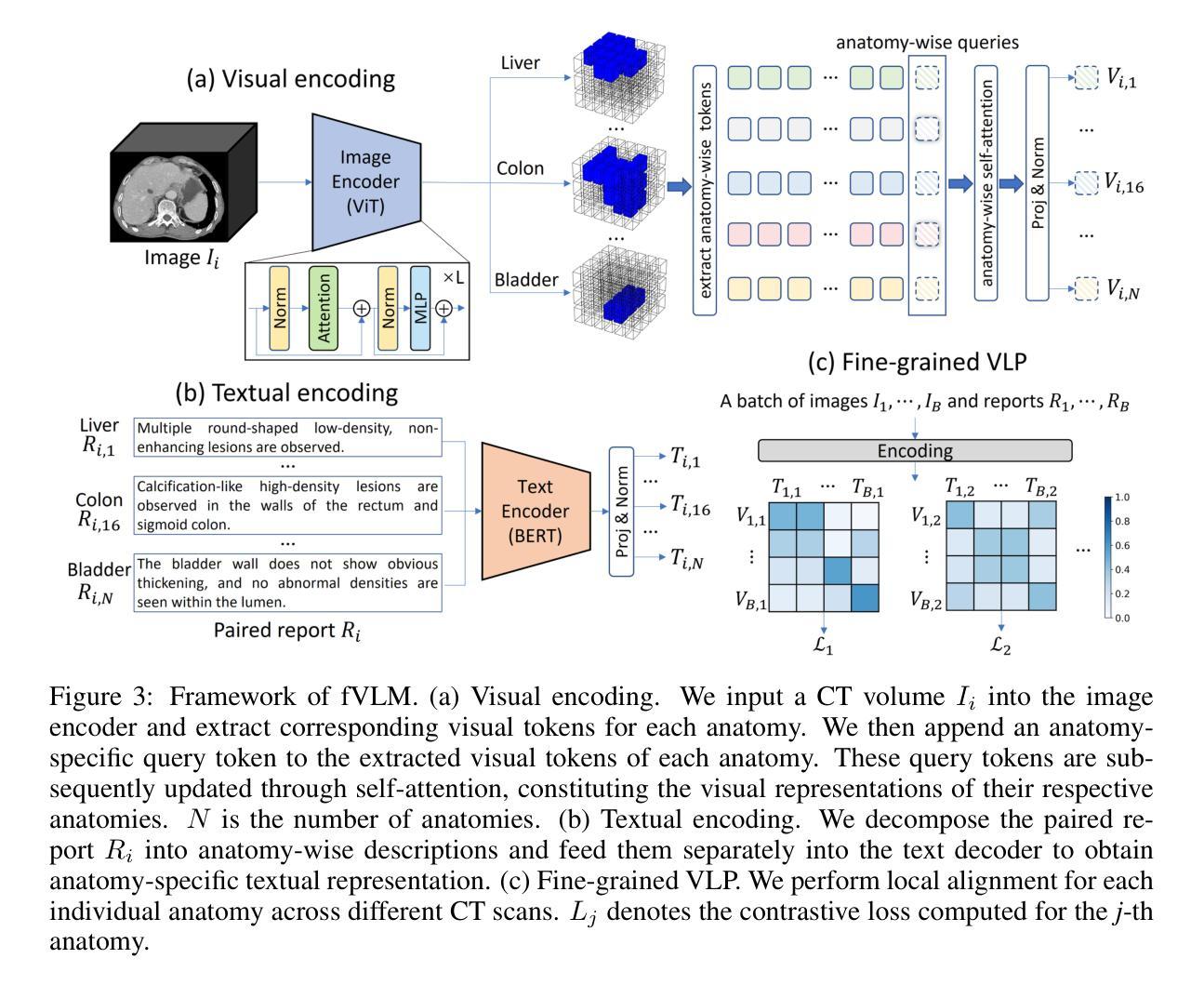
Large-scale and Fine-grained Vision-language Pre-training for Enhanced CT Image Understanding
Authors:Zhongyi Shui, Jianpeng Zhang, Weiwei Cao, Sinuo Wang, Ruizhe Guo, Le Lu, Lin Yang, Xianghua Ye, Tingbo Liang, Qi Zhang, Ling Zhang
Artificial intelligence (AI) shows great potential in assisting radiologists to improve the efficiency and accuracy of medical image interpretation and diagnosis. However, a versatile AI model requires large-scale data and comprehensive annotations, which are often impractical in medical settings. Recent studies leverage radiology reports as a naturally high-quality supervision for medical images, using contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) to develop language-informed models for radiological image interpretation. Nonetheless, these approaches typically contrast entire images with reports, neglecting the local associations between imaging regions and report sentences, which may undermine model performance and interoperability. In this paper, we propose a fine-grained vision-language model (fVLM) for anatomy-level CT image interpretation. Specifically, we explicitly match anatomical regions of CT images with corresponding descriptions in radiology reports and perform contrastive pre-training for each anatomy individually. Fine-grained alignment, however, faces considerable false-negative challenges, mainly from the abundance of anatomy-level healthy samples and similarly diseased abnormalities. To tackle this issue, we propose identifying false negatives of both normal and abnormal samples and calibrating contrastive learning from patient-level to disease-aware pairing. We curated the largest CT dataset to date, comprising imaging and report data from 69,086 patients, and conducted a comprehensive evaluation of 54 major and important disease diagnosis tasks across 15 main anatomies. Experimental results demonstrate the substantial potential of fVLM in versatile medical image interpretation. In the zero-shot classification task, we achieved an average AUC of 81.3% on 54 diagnosis tasks, surpassing CLIP and supervised methods by 12.9% and 8.0%, respectively.
人工智能(AI)在协助放射科医生提高医学图像解读和诊断的效率与准确性方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,一个多才多艺的AI模型需要大规模的数据和全面的注释,这在医疗环境中往往不切实际。最近的研究利用放射学报告作为医学图像的自然高质量监督,使用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)开发用于放射学图像解读的语言信息模型。然而,这些方法通常将整个图像与报告进行对比,忽略了成像区域与报告句子之间的局部关联,这可能会损害模型的性能和可互操作性。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于解剖学层面CT图像解读的精细视觉语言模型(fVLM)。具体来说,我们显式地将CT图像的解剖区域与放射学报告中的相应描述相匹配,并对每个解剖结构进行对比预训练。然而,精细对齐面临着相当大的假阴性挑战,主要来自解剖层面健康样本的丰富以及类似的疾病异常。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了识别正常和异常样本的假阴性,并从患者层面校准对比学习以识别疾病感知配对。我们整理了迄今为止最大的CT数据集,包含来自69,086名患者的成像和报告数据,并对涉及15个主要解剖结构的54个主要和重要疾病诊断任务进行了全面评估。实验结果表明fVLM在多种医学图像解读中具有巨大潜力。在零样本分类任务中,我们在54项诊断任务上实现了平均AUC为81.3%,比CLIP和监督方法分别高出12.9%和8.0%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
本文探讨了人工智能在医学图像解读和诊断中的辅助潜力。针对当前方法在医疗环境中大规模数据和全面注释的需求,研究利用放射学报告作为高质量医学图像监督的自然来源,并采用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)来开发用于放射学图像解读的语言辅助模型。文章提出了一种精细的视觉语言模型(fVLM),用于解剖级别的CT图像解读。通过明确匹配CT图像的解剖区域与放射学报告中的相应描述,并对每个解剖部位进行个别对比预训练。为解决精细对齐中的假阴性挑战,该研究提出识别正常和异常样本的假阴性,并从患者级别校准对比学习至疾病感知配对。研究使用了迄今为止最大的CT数据集,涵盖了来自69,086名患者的成像和报告数据,并对涉及五大解剖学领域的五大重要疾病诊断任务进行了全面评估。实验结果显示fVLM在多样医学图像解读中具有巨大潜力,零样本分类任务平均AUC达81.3%,较CLIP和监督方法分别高出12.9%和8.0%。
Key Takeaways
- AI在医学图像解读和诊断中具有辅助潜力,可提高效率和准确性。
- 当前方法需要大量数据和注释,这在医疗环境中不实际。
- 研究利用放射学报告作为高质量医学图像监督的自然来源。
- 采用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)开发语言辅助模型用于医学图像解读。
- 提出精细的视觉语言模型(fVLM)用于解剖级别的CT图像解读。
- fVLM通过明确匹配CT图像的解剖区域与报告描述进行对正训练。
点此查看论文截图

ECTIL: Label-efficient Computational Tumour Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) assessment in breast cancer: Multicentre validation in 2,340 patients with breast cancer
Authors:Yoni Schirris, Rosie Voorthuis, Mark Opdam, Marte Liefaard, Gabe S Sonke, Gwen Dackus, Vincent de Jong, Yuwei Wang, Annelot Van Rossum, Tessa G Steenbruggen, Lars C Steggink, Liesbeth G. E. de Vries, Marc van de Vijver, Roberto Salgado, Efstratios Gavves, Paul J van Diest, Sabine C Linn, Jonas Teuwen, Renee Menezes, Marleen Kok, Hugo Horlings
The level of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) is a prognostic factor for patients with (triple-negative) breast cancer (BC). Computational TIL assessment (CTA) has the potential to assist pathologists in this labour-intensive task, but current CTA models rely heavily on many detailed annotations. We propose and validate a fundamentally simpler deep learning based CTA that can be trained in only ten minutes on hundredfold fewer pathologist annotations. We collected whole slide images (WSIs) with TILs scores and clinical data of 2,340 patients with BC from six cohorts including three randomised clinical trials. Morphological features were extracted from whole slide images (WSIs) using a pathology foundation model. Our label-efficient Computational stromal TIL assessment model (ECTIL) directly regresses the TILs score from these features. ECTIL trained on only a few hundred samples (ECTIL-TCGA) showed concordance with the pathologist over five heterogeneous external cohorts (r=0.54-0.74, AUROC=0.80-0.94). Training on all slides of five cohorts (ECTIL-combined) improved results on a held-out test set (r=0.69, AUROC=0.85). Multivariable Cox regression analyses indicated that every 10% increase of ECTIL scores was associated with improved overall survival independent of clinicopathological variables (HR 0.86, p<0.01), similar to the pathologist score (HR 0.87, p<0.001). We demonstrate that ECTIL is highly concordant with an expert pathologist and obtains a similar hazard ratio. ECTIL has a fundamentally simpler design than existing methods and can be trained on orders of magnitude fewer annotations. Such a CTA may be used to pre-screen patients for, e.g., immunotherapy clinical trial inclusion, or as a tool to assist clinicians in the diagnostic work-up of patients with BC. Our model is available under an open source licence (https://github.com/nki-ai/ectil).
肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(TILs)的水平是(三阴性)乳腺癌(BC)患者的预后因素。计算TIL评估(CTA)有潜力帮助病理学家完成这项劳动密集型任务,但当前的CTA模型严重依赖于许多详细的注释。我们提出并验证了一种基于深度学习的根本更简单的CTA,在数百倍更少的病理学家注释上只需十分钟即可完成训练。我们收集了来自六个队列的2340名乳腺癌患者的全片图像(WSIs)和TILs评分及临床数据,其中包括三项随机临床试验。形态学特征是从全片图像(WSIs)中提取出来的,使用的是病理基础模型。我们的标签效率计算性间质TIL评估模型(ECTIL)直接从这些特征中回归TILs评分。ECTIL仅在数百个样本上进行训练(ECTIL-TCGA)就能与病理学家在五组不同外部队列中的结果一致(r=0.54-0.74,AUROC=0.80-0.94)。在五个队列的所有幻灯片上进行训练(ECTIL-combined)提高了在保留测试集上的结果(r=0.69,AUROC=0.85)。多元Cox回归分析显示,ECTIL评分每增加10%,总体生存率就会提高,这与病理学家评分相似,且独立于临床病理变量(HR 0.86,p<0.01)。我们证明ECTIL与专家病理学家高度一致,并且获得类似的危险比率。ECTIL的根本设计比现有方法更简单,可以在数量级更少的注释上进行训练。这种CTA可用于对例如免疫疗法临床试验的入选患者进行预筛选,或作为协助临床医生对乳腺癌患者进行诊断工作的工具。我们的模型可在开源许可证下使用(https://github.com/nki-ai/ectil)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review. 54 pages including supplementary materials, 2 main tables, 3 main figures, 14 supplementary figures, 4 supplementary tables
Summary
该文探讨了肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(TILs)水平在预测三阴性乳腺癌患者预后中的作用。提出并验证了一种基于深度学习的计算肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞评估(CTA)方法,该方法更为简单,仅需十分之一的病理学家标注即可训练完成。研究使用包含三阴性乳腺癌患者的2,340张全切片图像(WSIs)和临床数据,建立了一种标签效率高的计算性间质肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞评估模型(ECTIL)。该模型直接从形态特征回归TILs评分,仅对数百个样本进行训练即可与病理学家达到一致。此外,该研究还表明,ECTIL评分每增加10%,患者的总体生存率就会提高,与临床病理变量无关。总体而言,ECTIL与病理学家评估结果高度一致,且模型设计更简单,所需标注数据更少。这种CTA可用于筛选适合免疫治疗临床试验的患者,或作为诊断乳腺癌患者的工具。模型可在开放源代码许可证下获取。
Key Takeaways
- 肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(TILs)水平是三阴性乳腺癌的重要预后因素。
- 提出了一种基于深度学习的简化计算肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞评估(CTA)模型(ECTIL)。
- ECTIL模型可在仅使用少数病理学家标注的情况下进行训练,大大提高了标签效率。
- ECTIL模型的预测结果与病理学家高度一致,并在多个外部队列中进行了验证。
- ECTIL评分与患者的总体生存率呈正相关。
- ECTIL模型可用于筛选适合免疫治疗临床试验的患者或辅助临床医生诊断乳腺癌。
点此查看论文截图

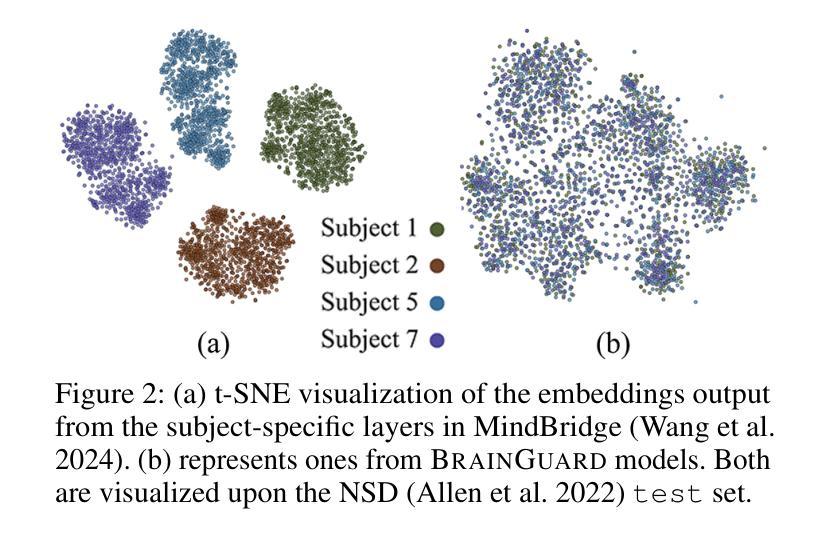
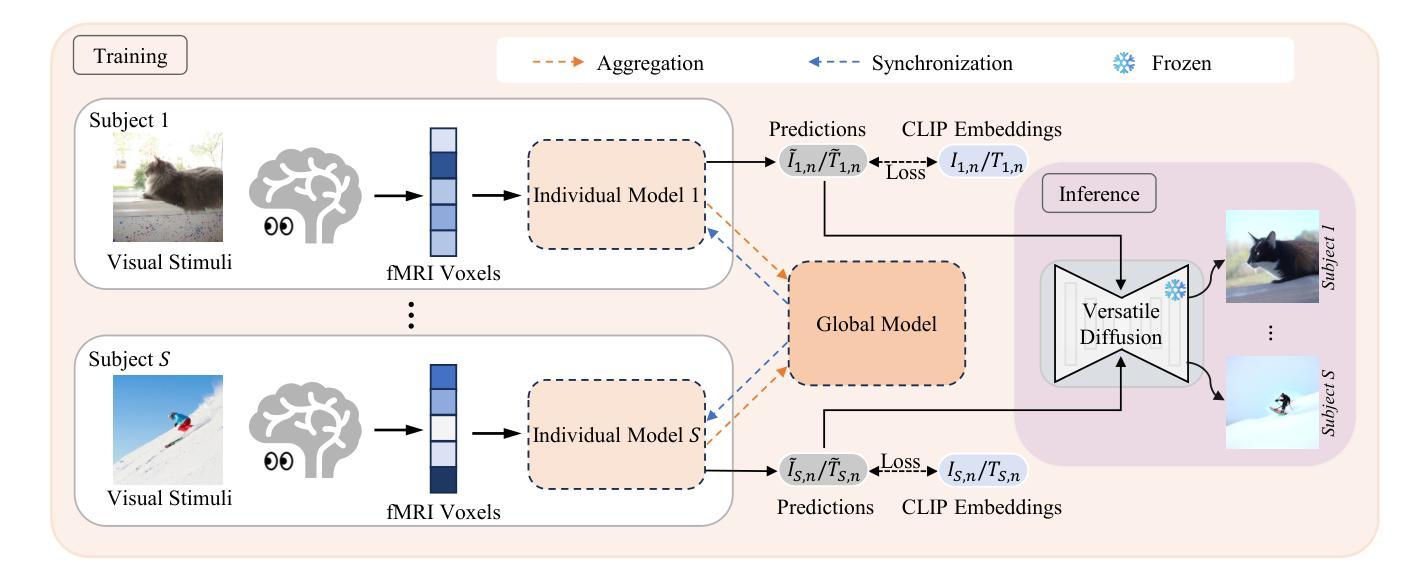
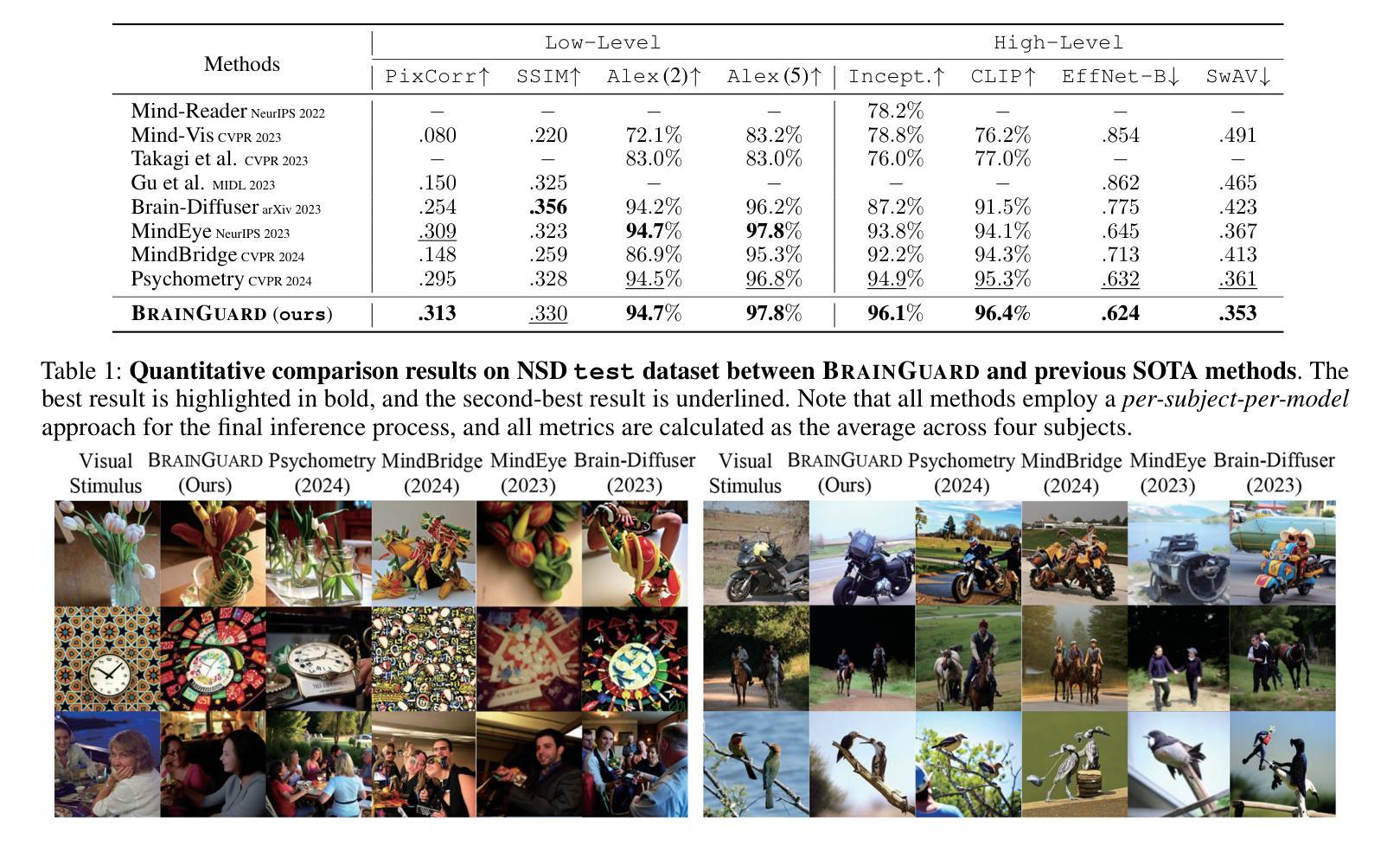
BrainGuard: Privacy-Preserving Multisubject Image Reconstructions from Brain Activities
Authors:Zhibo Tian, Ruijie Quan, Fan Ma, Kun Zhan, Yi Yang
Reconstructing perceived images from human brain activity forms a crucial link between human and machine learning through Brain-Computer Interfaces. Early methods primarily focused on training separate models for each individual to account for individual variability in brain activity, overlooking valuable cross-subject commonalities. Recent advancements have explored multisubject methods, but these approaches face significant challenges, particularly in data privacy and effectively managing individual variability. To overcome these challenges, we introduce BrainGuard, a privacy-preserving collaborative training framework designed to enhance image reconstruction from multisubject fMRI data while safeguarding individual privacy. BrainGuard employs a collaborative global-local architecture where individual models are trained on each subject’s local data and operate in conjunction with a shared global model that captures and leverages cross-subject patterns. This architecture eliminates the need to aggregate fMRI data across subjects, thereby ensuring privacy preservation. To tackle the complexity of fMRI data, BrainGuard integrates a hybrid synchronization strategy, enabling individual models to dynamically incorporate parameters from the global model. By establishing a secure and collaborative training environment, BrainGuard not only protects sensitive brain data but also improves the image reconstructions accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BrainGuard sets a new benchmark in both high-level and low-level metrics, advancing the state-of-the-art in brain decoding through its innovative design.
从人类大脑活动重建感知图像,是脑机接口实现人类与机器学习之间联系的关键环节。早期的方法主要关注于针对每个个体进行单独模型的训练,以解释个体在大脑活动上的差异,忽略了跨主体的共性价值。尽管近期的研究已经探索了跨主体的方法,但这些方法面临重大挑战,尤其是在数据隐私和有效管理个体差异方面。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了BrainGuard,这是一个保护隐私的协作训练框架,旨在提高从多主体fMRI数据中重建图像的能力,同时保护个人隐私。BrainGuard采用协作的全局-局部架构,其中个体模型在每个主体的局部数据上进行训练,并与共享的全局模型协同工作,捕获并利用跨主体的模式。这种架构消除了汇总多个主体fMRI数据的需要,从而确保了隐私保护。为了应对fMRI数据的复杂性,BrainGuard集成了一种混合同步策略,使个体模型能够动态地融入全局模型的参数。通过建立安全、协作的训练环境,BrainGuard不仅保护了敏感的脑数据,而且提高了图像重建的准确性。大量实验表明,BrainGuard在高级和低级指标上均设定了新的基准,通过其创新设计,在脑解码方面达到了最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025 oral
Summary
本文介绍了BrainGuard框架在保护隐私的同时提高多主题fMRI数据图像重建的准确性。该框架采用协作全局-局部架构,训练个体模型处理本地数据,并通过共享全局模型捕捉和利用跨主题模式,无需聚合跨主题的fMRI数据,从而确保隐私保护。BrainGuard通过混合同步策略提高fMRI数据的处理效率,提高图像重建的准确性,并保护敏感的脑数据。实验表明,BrainGuard在设计创新方面达到了高水平指标和低水平指标的最新基准。
Key Takeaways
- Brain-Computer Interfaces重建人脑感知图像在机器学习领域的重要性。
- 早期方法主要关注为每个人训练单独的模型以应对大脑活动的个体差异,但忽略了跨主题的共性。
- BrainGuard框架是一个隐私保护的合作训练框架,旨在提高多主题fMRI数据的图像重建精度。
- BrainGuard采用协作全局-局部架构,通过个体模型和全局模型的结合来处理数据隐私和个体差异挑战。
- BrainGuard框架集成了混合同步策略,能够提高fMRI数据处理效率并改进图像重建准确性。
- BrainGuard通过创建安全合作训练环境,既保护敏感的大脑数据又提高图像重建的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

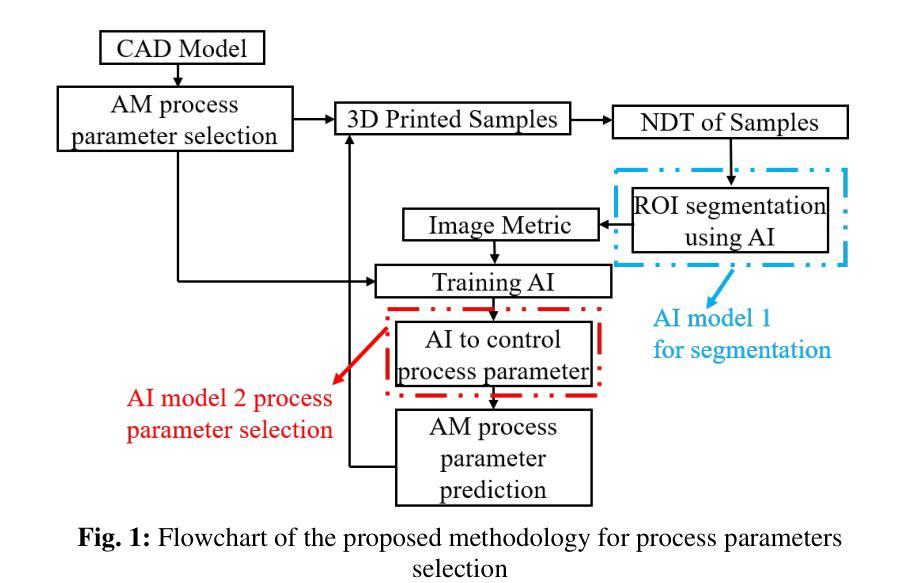
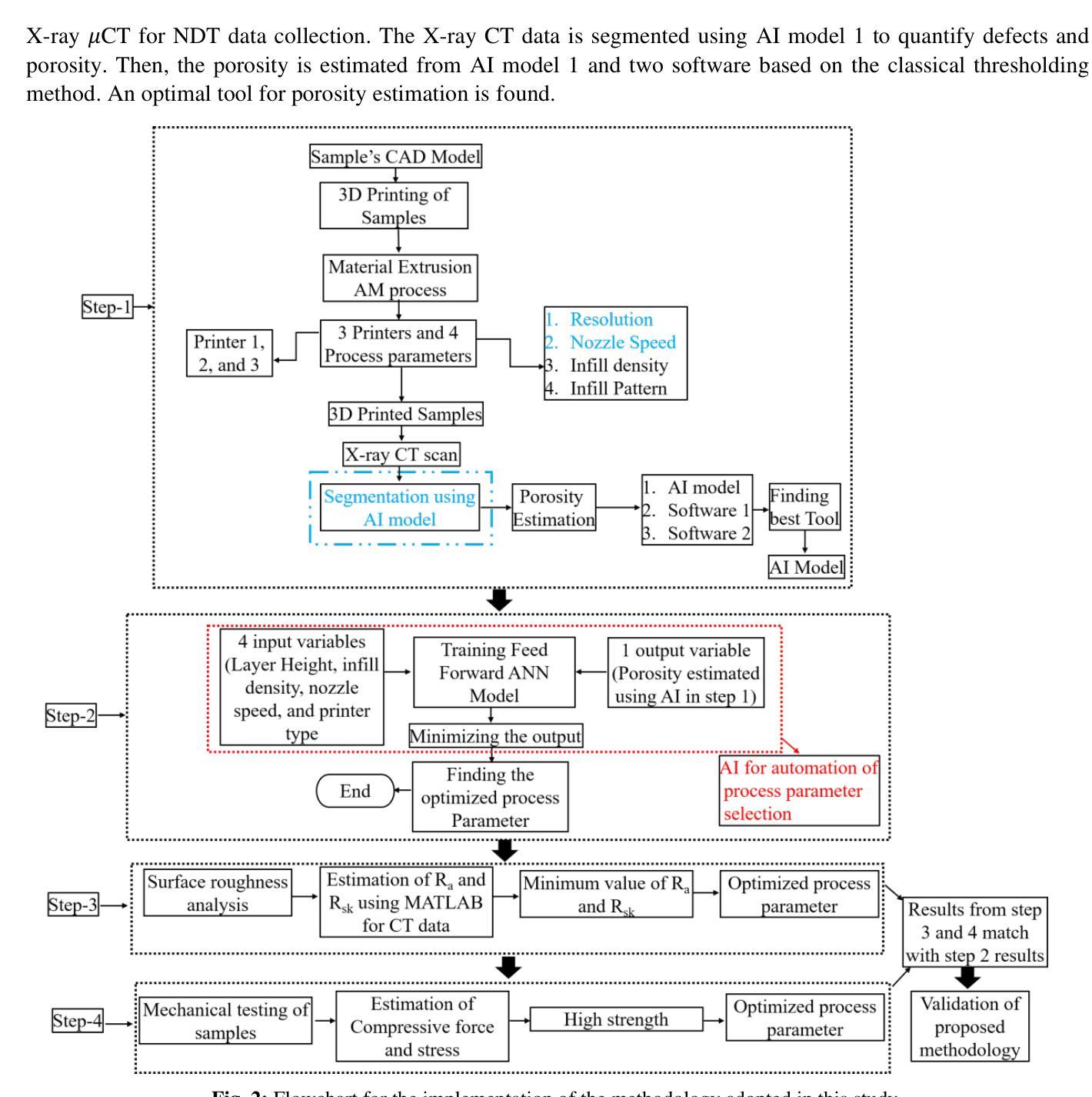
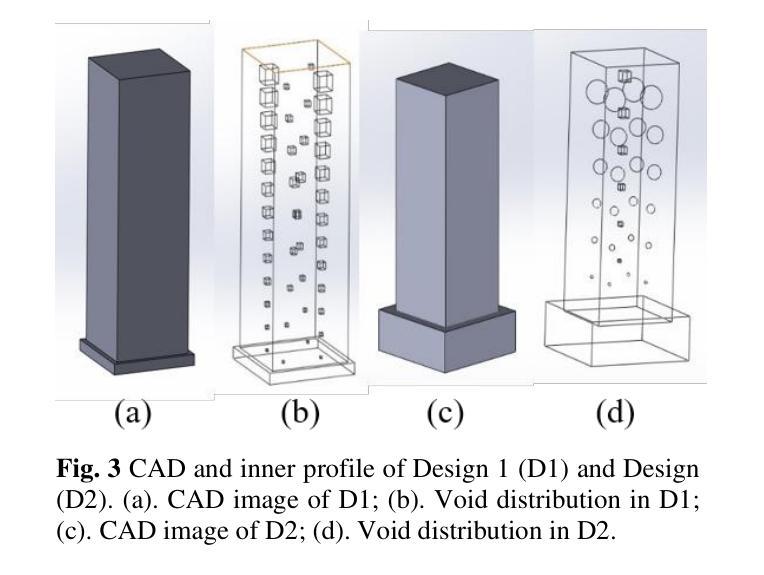
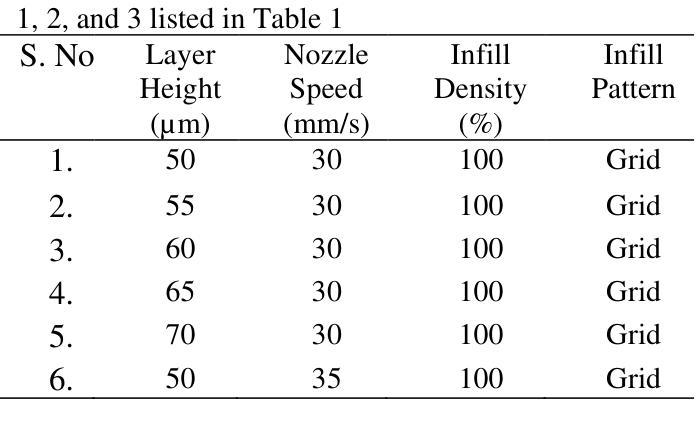
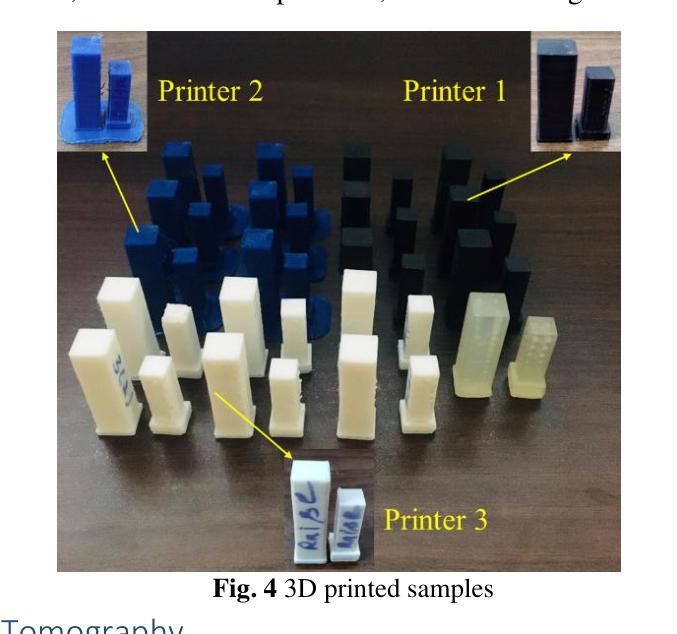
Additive Manufacturing Processes Protocol Prediction by Artificial Intelligence using X-ray Computed Tomography data
Authors:Sunita Khod, Akshay Dvivedi, Mayank Goswami
The quality of the part fabricated from the Additive Manufacturing (AM) process depends upon the process parameters used, and therefore, optimization is required for apt quality. A methodology is proposed to set these parameters non-iteratively without human intervention. It utilizes Artificial Intelligence (AI) to fully automate the process, with the capability to self-train any apt AI model by further assimilating the training data.This study includes three commercially available 3D printers for soft material printing based on the Material Extrusion (MEX) AM process. The samples are 3D printed for six different AM process parameters obtained by varying layer height and nozzle speed. The novelty part of the methodology is incorporating an AI-based image segmentation step in the decision-making stage that uses quality inspected training data from the Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) method. The performance of the trained AI model is compared with the two software tools based on the classical thresholding method. The AI-based Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model is trained from NDT-assessed and AI-segmented data to automate the selection of optimized process parameters. The AI-based model is 99.3 % accurate, while the best available commercial classical image method is 83.44 % accurate. The best value of overall R for training ANN is 0.82. The MEX process gives a 22.06 % porosity error relative to the design. The NDT-data trained two AI models integrated into a series pipeline for optimal process parameters are proposed and verified by classical optimization and mechanical testing methods.
通过增材制造(AM)工艺制作的零件质量取决于所使用的工艺参数,因此需要进行优化以达到所需的质量。提出了一种非迭代地设置这些参数的方法,无需人工干预。该方法利用人工智能(AI)来完全自动化流程,并且能够通过进一步同化训练数据来自我训练任何适合的人工智能模型。该研究包括三种基于材料挤出(MEX)AM工艺的商用3D打印软件,用于打印软材料。样本是通过改变层高和喷嘴速度而获得的六个不同的AM工艺参数进行3D打印的。该方法的创新之处在于决策阶段融入了基于人工智能的图像分割步骤,该步骤使用来自无损检测(NDT)方法的质检训练数据。将训练好的AI模型性能与基于经典阈值方法的两个软件工具进行比较。基于AI的人工神经网络(ANN)模型通过NDT评估和AI分割数据进行训练,以自动选择优化的工艺参数。基于AI的模型的准确度为99.3%,而现有最佳商业经典图像方法的准确度为83.44%。训练ANN的最佳整体R值为0.82。MEX工艺在设计基础上存在22.06%的孔隙率误差。通过经典优化方法和机械测试方法对经过NDT数据训练的两个人工智能模型进行集成,用于优化工艺参数的建议和验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 21 figures, 5 tables
摘要
增材制造(AM)过程中制造的零件质量取决于所使用的工艺参数,因此需要进行优化以达到适当的质量。提出了一种非迭代设置这些参数的方法,无需人工干预。它利用人工智能(AI)来完全自动化流程,并具有通过进一步同化训练数据来自我训练任何适当的人工智能模型的能力。该研究包括三种商业可用的基于材料挤出(MEX)AM工艺的软材料3D打印机。为六个不同的AM工艺参数打印样品,通过改变层高和喷嘴速度获得这些参数。该方法的创新之处在于决策阶段融入了基于AI的图像分割步骤,使用来自无损检测(NDT)方法的质量检验训练数据。将训练有素的人工智能模型的性能与基于经典阈值方法的两个软件工具进行比较。基于NDT评估和AI分割数据训练的神经网络(ANN)模型被训练用来自动选择优化的工艺参数。AI模型的准确度为99.3%,而现有的最佳商业经典图像方法的准确度为83.44%。训练ANN的整体最佳R值为0.82。MEX工艺在设计上产生22.06%的孔隙率误差。通过经典优化和机械测试方法,提出了由NDT数据训练的两个人工智能模型集成到系列管道中以获得最佳工艺参数的建议,并进行了验证。
关键见解
- 增材制造过程中零件的质量取决于工艺参数的优化。
- 提出了一种非迭代设置工艺参数的方法,使用人工智能完全自动化流程。
- 方法结合了基于AI的图像分割步骤,使用无损检测(NDT)的质量检验数据。
- AI模型在自动化选择优化工艺参数方面表现出高准确性(99.3%)。
- 与现有商业经典图像方法相比,AI模型具有更高的性能。
- MEX工艺在设计上存在一定的孔隙率误差。
点此查看论文截图



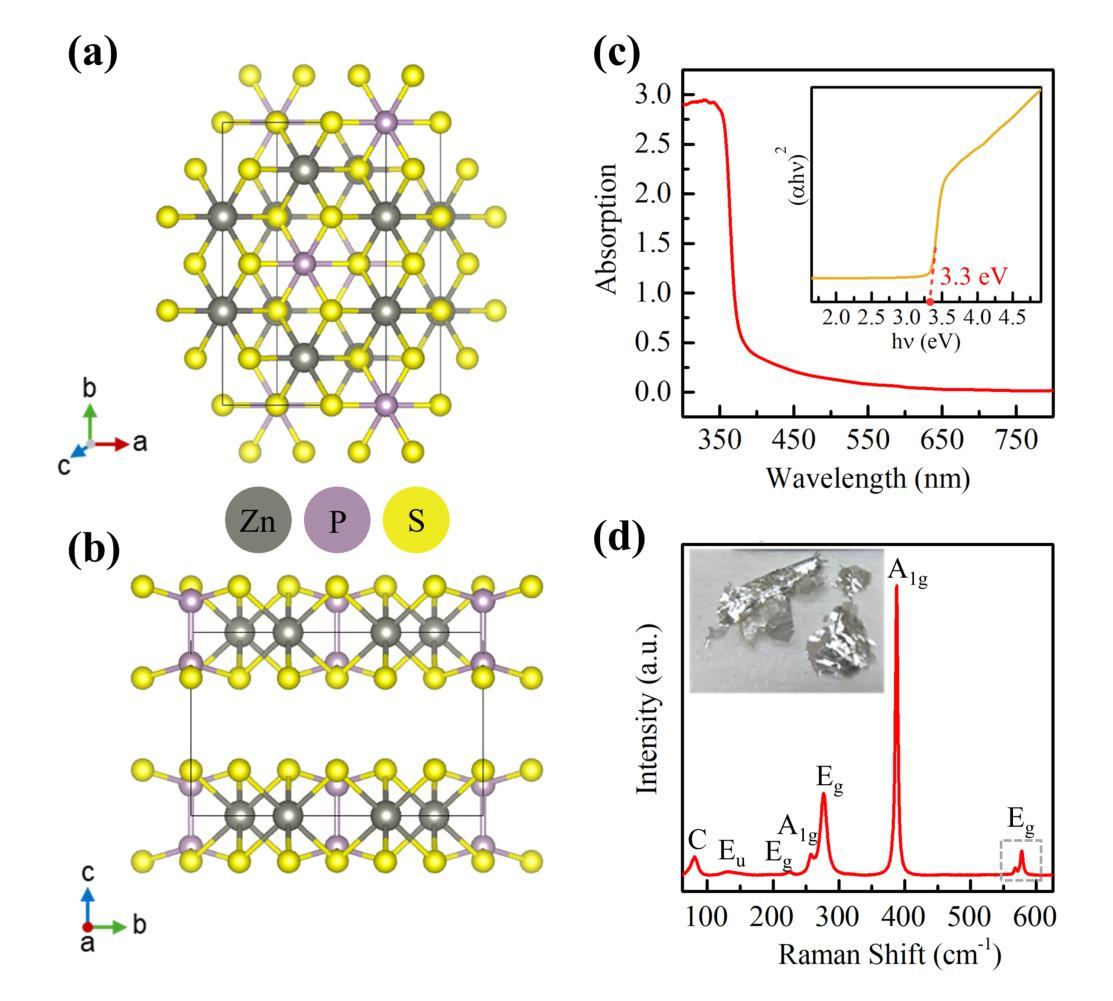
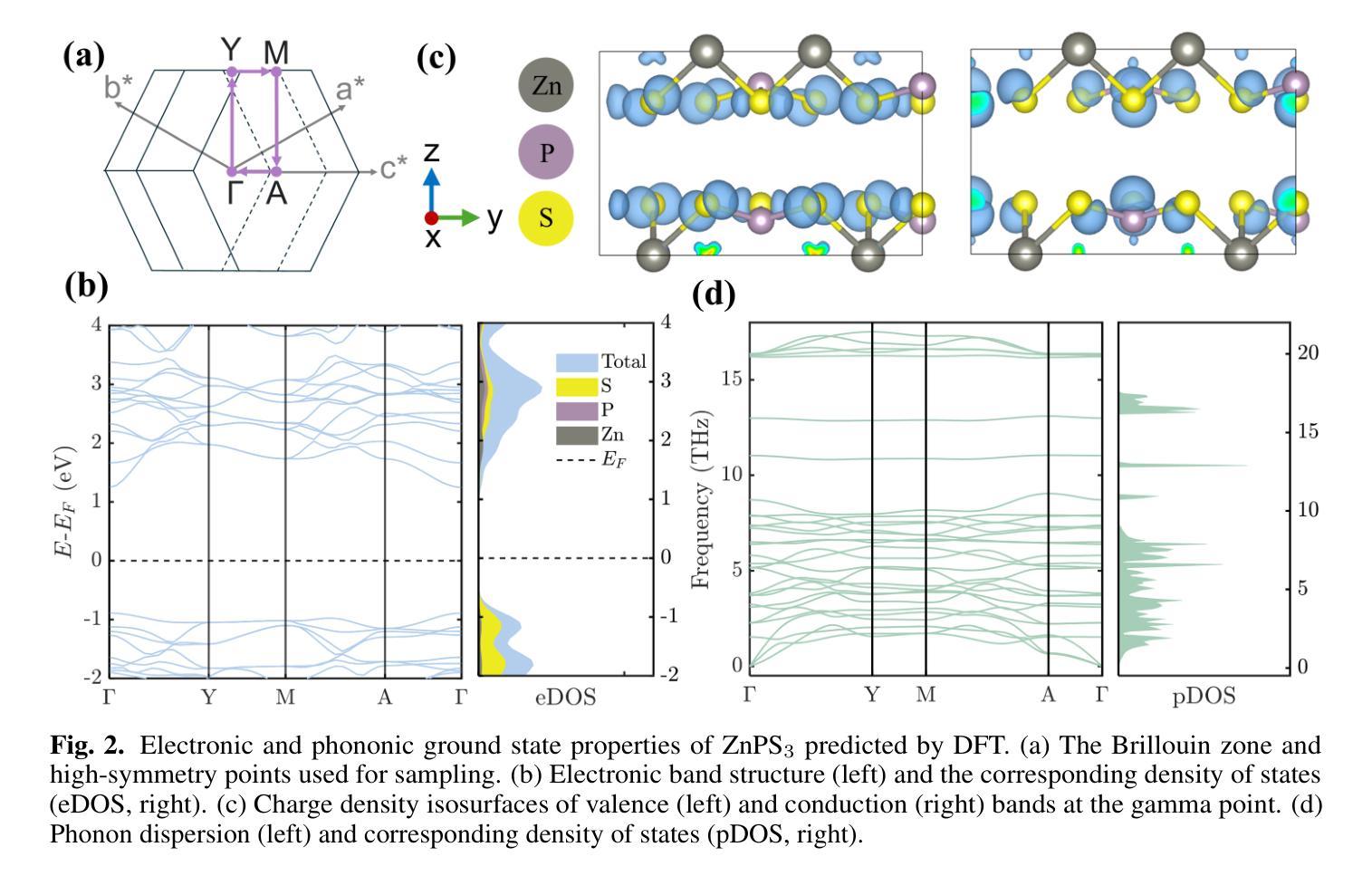
Thermal and dimensional stability of photocatalytic material ZnPS$_3$ under extreme environmental conditions
Authors:Abhishek Mukherjee, Vivian J. Santamaría-García, Damian Wlodarczyk, Ajeesh K. Somakumar, Piotr Sybilski, Ryan Siebenaller, Emmanuel Rowe, Saranya Narayanan, Michael A. Susner, L. Marcelo Lozano-Sanchez, Andrzej Suchocki, Julio L. Palma, Svetlana V. Boriskina
Zinc phosphorus trisulfide (ZnPS$_3$), a promising material for photocatalysis and energy storage, is shown in this study to exhibit remarkable stability under extreme conditions. We explore its optical and structural properties under high pressure and cryogenic temperatures using photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, Raman scattering, and density functional theory (DFT). Our results identify a pressure-induced phase transition starting at 6.75 GPa and stabilizing by 12.5 GPa, after which ZnPS$_3$ demonstrates robust stability across a broad pressure range of 15 to 100 GPa. DFT calculations predict a semiconductor-to-semimetal transition at 100 GPa, while PL measurements reveal defect-assisted emissions that quench under pressure due to enhanced non-radiative recombination. At cryogenic temperatures, PL quenching intensifies as non-radiative processes dominate, driven by a rising Gr"uneisen parameter and reduced phonon population. Cryogenic X-ray diffraction (XRD) also reveals a high mean thermal expansion coefficient (TEC) of (4.369 $\pm$ 0.393) $\times$ 10$^{-5}$ K$^{-1}$, among the highest reported for 2D materials. This unique combination of tunable electronic properties under low pressure and high thermal sensitivity makes ZnPS$_3$ a strong candidate for sensing applications in extreme environments.
本研究显示,三硫化锌磷(ZnPS$_3$)作为光催化与能量储存的有前景材料,在极端条件下表现出显著的稳定性。我们利用光致发光(PL)光谱、拉曼散射和密度泛函理论(DFT)等方法,探究其高压和低温条件下的光学和结构特性。结果表明,从6.75 GPa开始发生压力诱导的相变,并在达到12.5 GPa时稳定下来。此后,ZnPS$_3$在较宽的压强范围内表现出较强的稳定性(最高至常温时的水压的数千倍)。DFT计算预测在高压下会发生半导体到半金属的过渡,而PL测量显示缺陷辅助发射,随着压力的增加因非辐射复合增强而猝灭。在低温下,由于格里涅森参数上升和振动数减少,非辐射过程占据主导地位,导致PL猝灭加剧。低温X射线衍射还揭示其平均热膨胀系数(TEC)较高,为(4.369 $\pm$ 0.393)× 10$^{-5}$ K$^{-1}$,在二维材料中是最高的报道值之一。在压力较小的环境中可调节其电子特性和高热敏感性,这使得ZnPS$_3$成为在极端环境中用于感应应用的强大候选材料。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究发现锌磷硫化物(ZnPS$_3$)在极端条件下表现出卓越稳定性,并探索了其高压和低温下的光学和结构特性。通过光致发光(PL)光谱学、拉曼散射、密度泛函理论(DFT)等研究表明,ZnPS$_3$在高压下发生相变,并在特定压力下展现出稳定的半导体至半金属转变。此外,其缺陷辅助发射在高压和低温下发生非辐射复合而猝灭。其高热膨胀系数使其成为极端环境感应应用的优秀候选材料。
Key Takeaways
- ZnPS$_3$在极端条件下展现出卓越稳定性。
- 通过PL光谱学、拉曼散射和DFT研究了ZnPS$_3$的光学和结构特性。
- ZnPS$_3$在高压下发生相变,并在100 GPa时表现出半导体至半金属的转变。
- PL测量揭示了缺陷辅助发射,这些发射在高压和低温下由于非辐射复合而猝灭。
- ZnPS$_3$的高热膨胀系数使其成为极端环境感应应用的优秀候选材料。
- DFT计算预测了ZnPS$_3$在高压下的电子性质变化。
点此查看论文截图

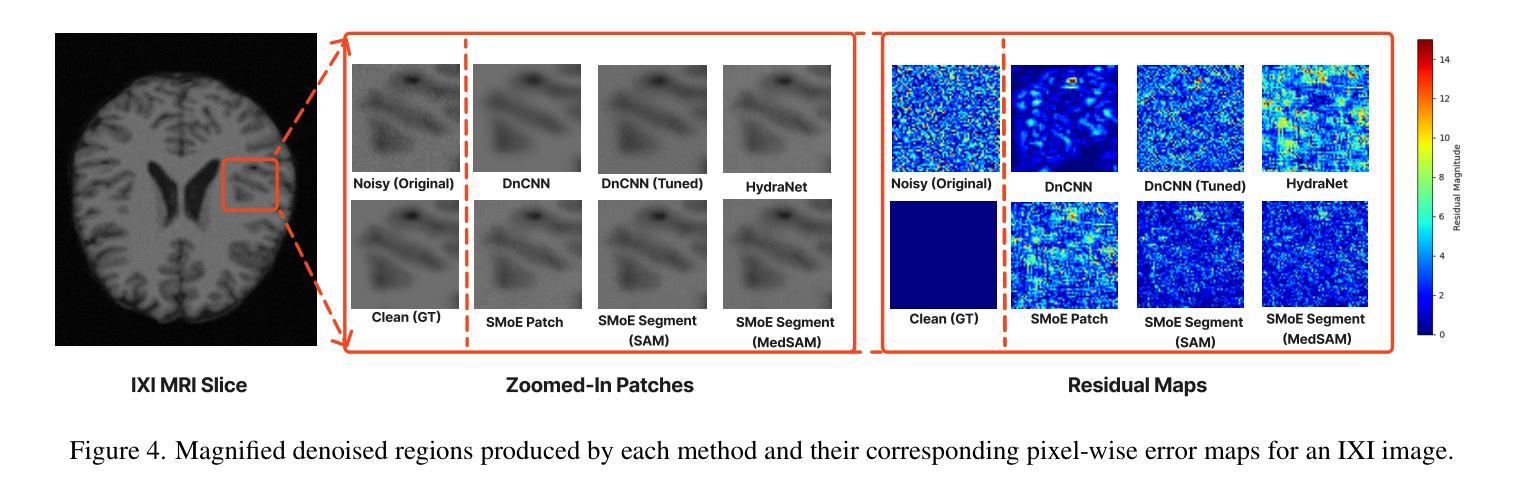
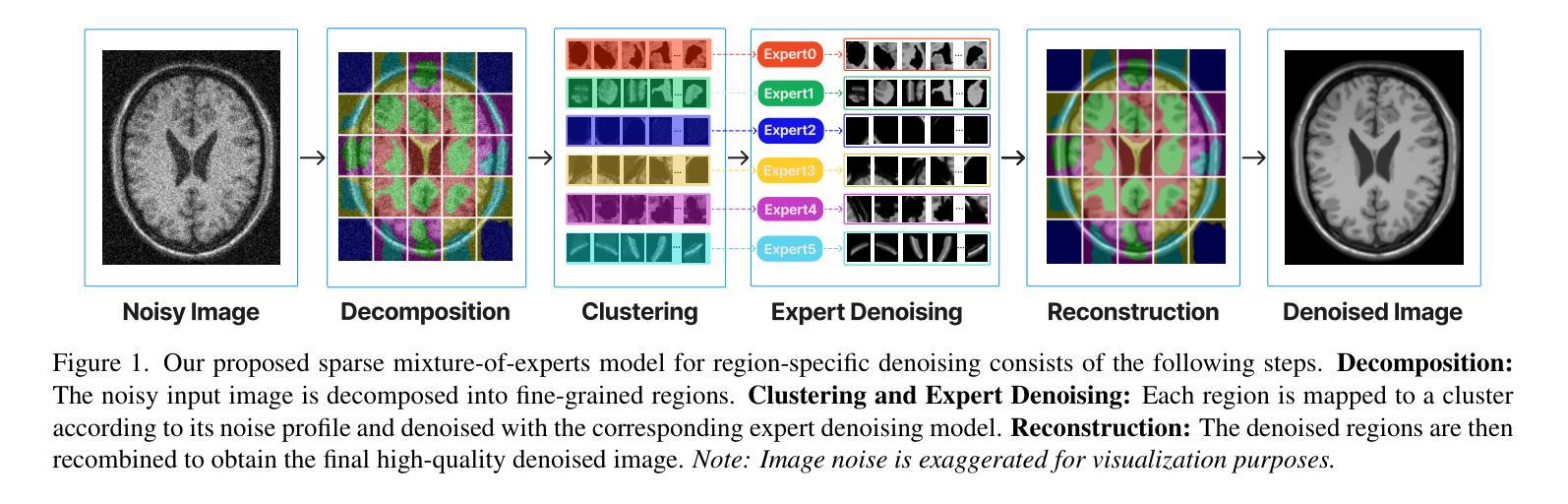
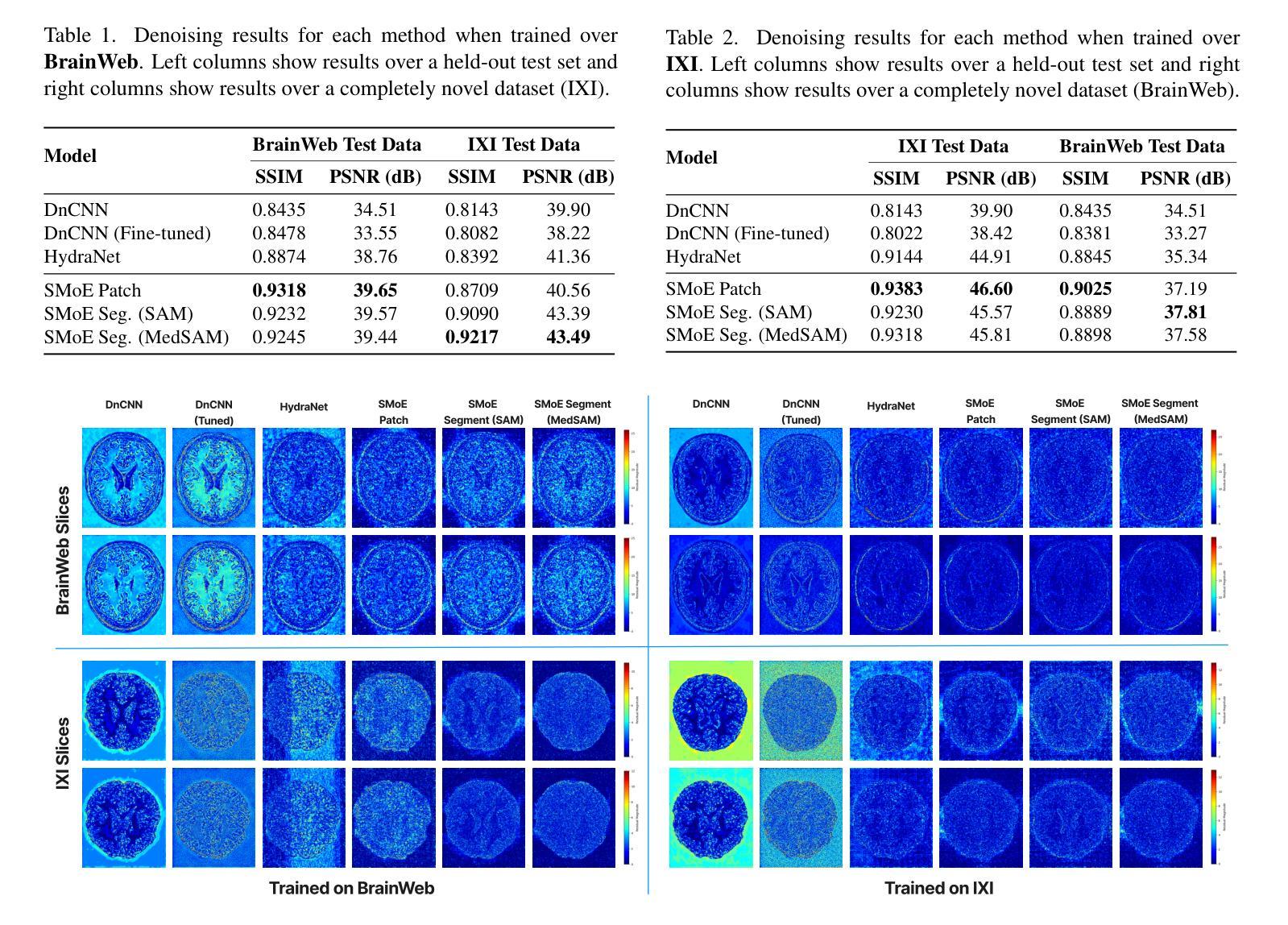
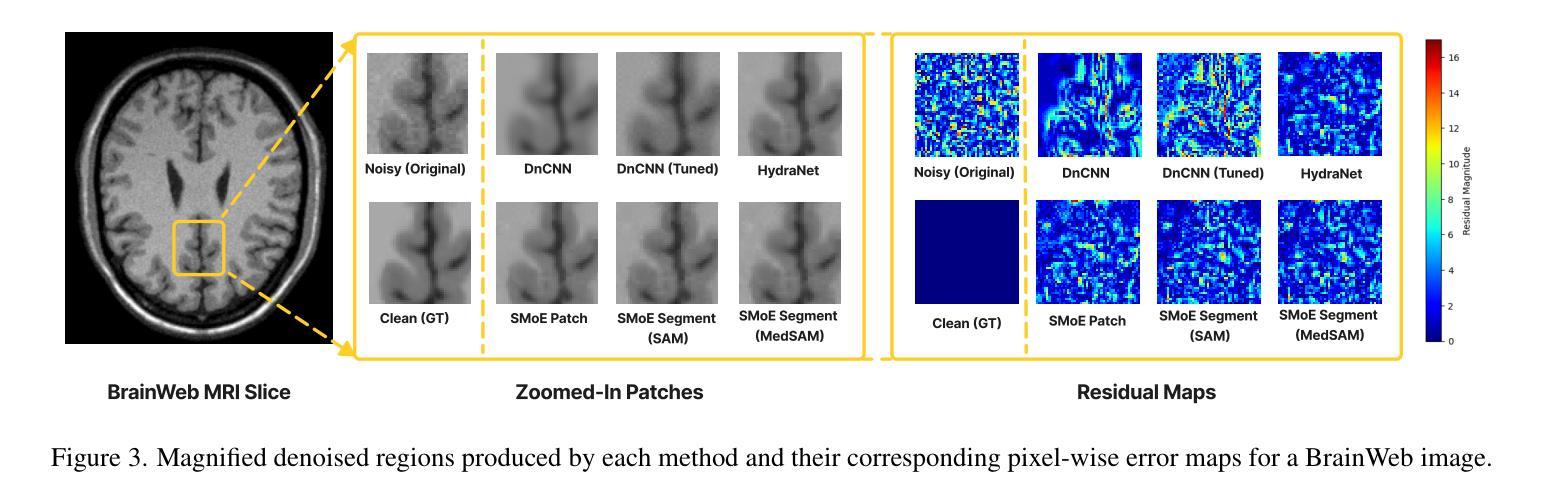
Sparse Mixture-of-Experts for Non-Uniform Noise Reduction in MRI Images
Authors:Zeyun Deng, Joseph Campbell
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an essential diagnostic tool in clinical settings, but its utility is often hindered by noise artifacts introduced during the imaging process.Effective denoising is critical for enhancing image quality while preserving anatomical structures. However, traditional denoising methods, which often assume uniform noise distributions, struggle to handle the non-uniform noise commonly present in MRI images. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach leveraging a sparse mixture-of-experts framework for MRI image denoising. Each expert is a specialized denoising convolutional neural network fine-tuned to target specific noise characteristics associated with different image regions. Our method demonstrates superior performance over state-of-the-art denoising techniques on both synthetic and real-world brain MRI datasets. Furthermore, we show that it generalizes effectively to unseen datasets, highlighting its robustness and adaptability.
磁共振成像(MRI)是临床环境中重要的诊断工具,但在成像过程中引入的噪声伪影经常阻碍其应用。有效去噪对于提高图像质量同时保留解剖结构至关重要。然而,传统的去噪方法通常假设噪声分布均匀,难以处理MRI图像中常见的非均匀噪声。在本文中,我们介绍了一种利用稀疏混合专家框架进行MRI图像去噪的新方法。每个专家都是一个针对特定噪声特性进行微调的去噪卷积神经网络,这些特性与不同图像区域相关。我们的方法在合成和真实世界的大脑MRI数据集上的表现均优于最先进的去噪技术。此外,我们还表明,它对未见数据集具有有效的泛化能力,突显了其稳健性和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the WACV Workshop on Image Quality
摘要
该论文提出了一种基于稀疏混合专家框架的MRI图像去噪新方法。每个专家都是一个针对特定图像区域噪声特性精细调整的专门去噪卷积神经网络。该方法在合成和真实世界的大脑MRI数据集上表现出优于最新去噪技术的性能,并可有效推广至未见数据集,凸显其稳健性和适应性。
关键见解
- MRI在临床诊断中扮演重要角色,但其成像过程中的噪声伪影影响了其效用。
- 有效去噪对于提高图像质量并保留解剖结构至关重要。
- 传统去噪方法在处理MRI图像中常见的非均匀噪声时遇到困难。
- 该论文引入了一种新的基于稀疏混合专家框架的MRI图像去噪方法。
- 该方法利用多个卷积神经网络专家,每个专家针对特定图像区域的特定噪声特性进行微调。
- 在合成和真实世界的大脑MRI数据集上,该方法表现出卓越的去噪性能。
- 该方法能够有效地推广至未见数据集,显示出其稳健性和适应性。
点此查看论文截图


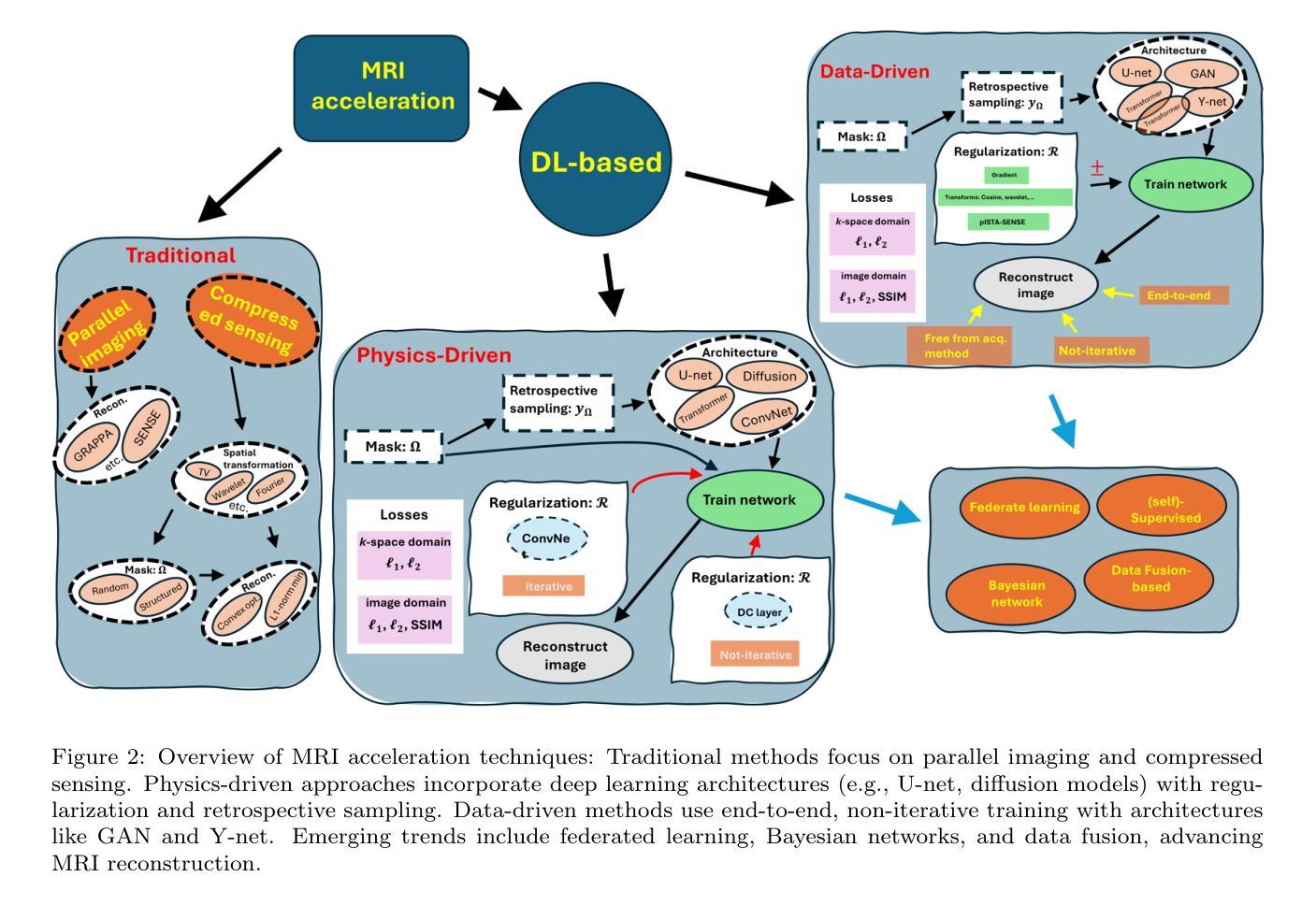
Advancing MRI Reconstruction: A Systematic Review of Deep Learning and Compressed Sensing Integration
Authors:Mojtaba Safari, Zach Eidex, Chih-Wei Chang, Richard L. J. Qiu, Xiaofeng Yang
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging modality and provides comprehensive anatomical and functional insights into the human body. However, its long acquisition times can lead to patient discomfort, motion artifacts, and limiting real-time applications. To address these challenges, strategies such as parallel imaging have been applied, which utilize multiple receiver coils to speed up the data acquisition process. Additionally, compressed sensing (CS) is a method that facilitates image reconstruction from sparse data, significantly reducing image acquisition time by minimizing the amount of data collection needed. Recently, deep learning (DL) has emerged as a powerful tool for improving MRI reconstruction. It has been integrated with parallel imaging and CS principles to achieve faster and more accurate MRI reconstructions. This review comprehensively examines DL-based techniques for MRI reconstruction. We categorize and discuss various DL-based methods, including end-to-end approaches, unrolled optimization, and federated learning, highlighting their potential benefits. Our systematic review highlights significant contributions and underscores the potential of DL in MRI reconstruction. Additionally, we summarize key results and trends in DL-based MRI reconstruction, including quantitative metrics, the dataset, acceleration factors, and the progress of and research interest in DL techniques over time. Finally, we discuss potential future directions and the importance of DL-based MRI reconstruction in advancing medical imaging. To facilitate further research in this area, we provide a GitHub repository that includes up-to-date DL-based MRI reconstruction publications and public datasets-https://github.com/mosaf/Awesome-DL-based-CS-MRI.
磁共振成像(MRI)是一种非侵入性的成像技术,能够全面提供人体解剖和功能性洞察。然而,其较长的采集时间可能导致患者不适、运动伪影,并限制实时应用。为了应对这些挑战,已经应用了并行成像等策略,利用多个接收器线圈来加速数据采集过程。此外,压缩感知(CS)是一种方法,可以从稀疏数据中促进图像重建,通过最小化所需的数据收集量来显著减少图像采集时间。最近,深度学习(DL)已经崭露头角,成为提高MRI重建的强大工具。它已经与并行成像和CS原理相结合,实现了更快、更准确的MRI重建。本文全面回顾了基于深度学习的MRI重建技术。我们对各种基于深度学习方法进行分类和讨论,包括端到端方法、滚动优化和联邦学习,并重点介绍它们的潜在优势。我们的系统评价突出了重要贡献,并强调了深度学习在MRI重建中的潜力。此外,我们总结了基于深度学习的MRI重建的关键结果和趋势,包括定量指标、数据集、加速因子以及深度学习技术的进展和研究兴趣随时间的变化。最后,我们讨论了潜在的未来方向和基于深度学习的MRI重建在推动医学成像方面的重要性。为了促进该领域的研究,我们提供了一个GitHub仓库,其中包含最新的基于深度学习的MRI重建出版物和公共数据集:[https://github.com/mosaf/Awesome-DL-based-CS-MRI。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文综述了基于深度学习的MRI重建技术,讨论了各类方法如并行成像和压缩感知的优缺点,并重点介绍了深度学习方法在MRI重建中的应用及其潜力。文章还总结了基于深度学习的MRI重建的关键结果和趋势,提供了GitHub仓库以推动相关研究。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像(MRI)是一种非侵入性的成像方式,能够提供全面的解剖和功能性人体信息。
- MRI的长采集时间可能导致患者不适、运动伪影,并限制实时应用。
- 并行成像和压缩感知是两种解决MRI采集时间问题的策略。并行成像利用多接收器线圈加速数据采集过程,而压缩感知则从稀疏数据中重建图像,显著减少图像采集时间。
- 深度学习在MRI重建中展现出巨大潜力,已结合并行成像和压缩感知原理实现更快、更准确的MRI重建。
- 文章综述了基于深度学习的MRI重建的各种方法,包括端到端方法、未滚动优化和联邦学习等。
- 文章总结了基于深度学习的MRI重建的关键结果和趋势,包括定量指标、数据集、加速因子以及深度学习技术的进步和研究兴趣的变化。
点此查看论文截图

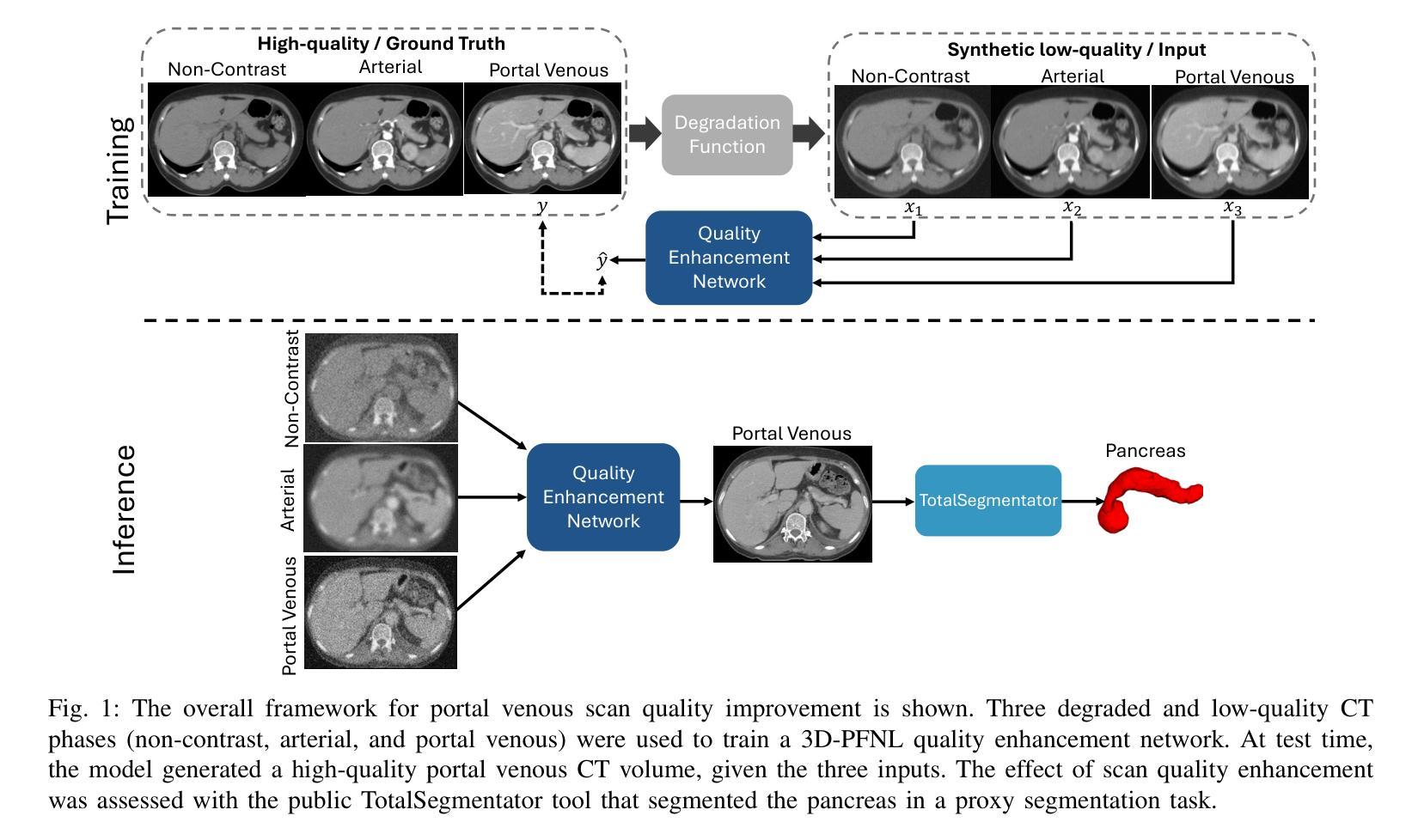
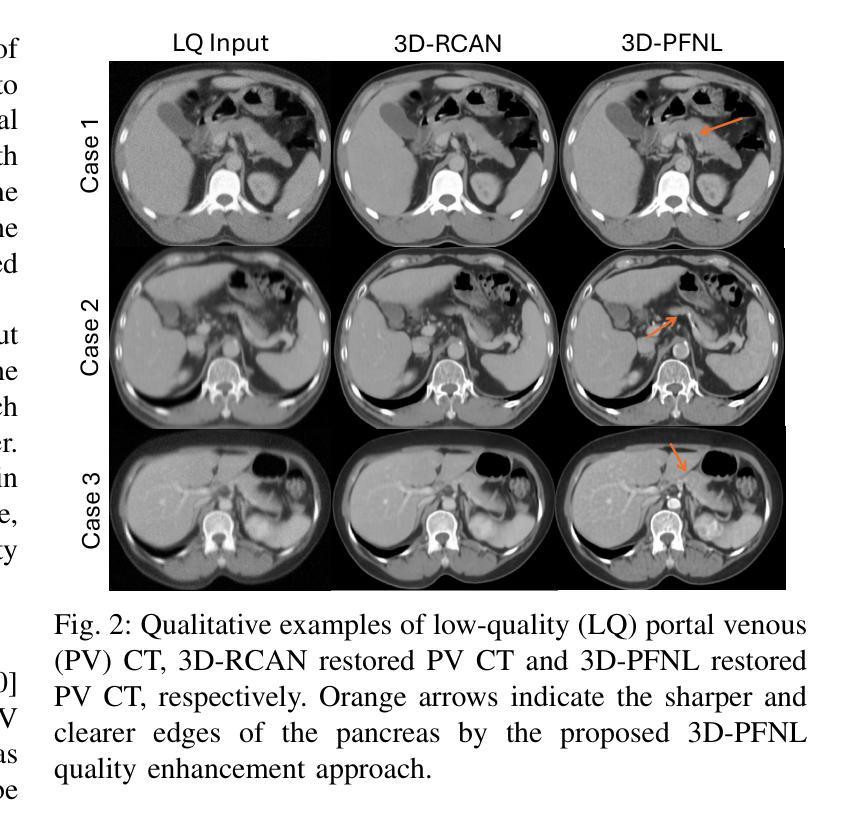
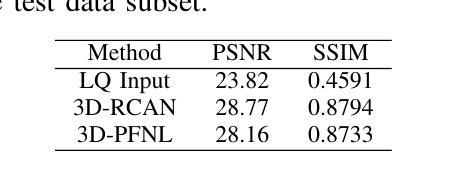
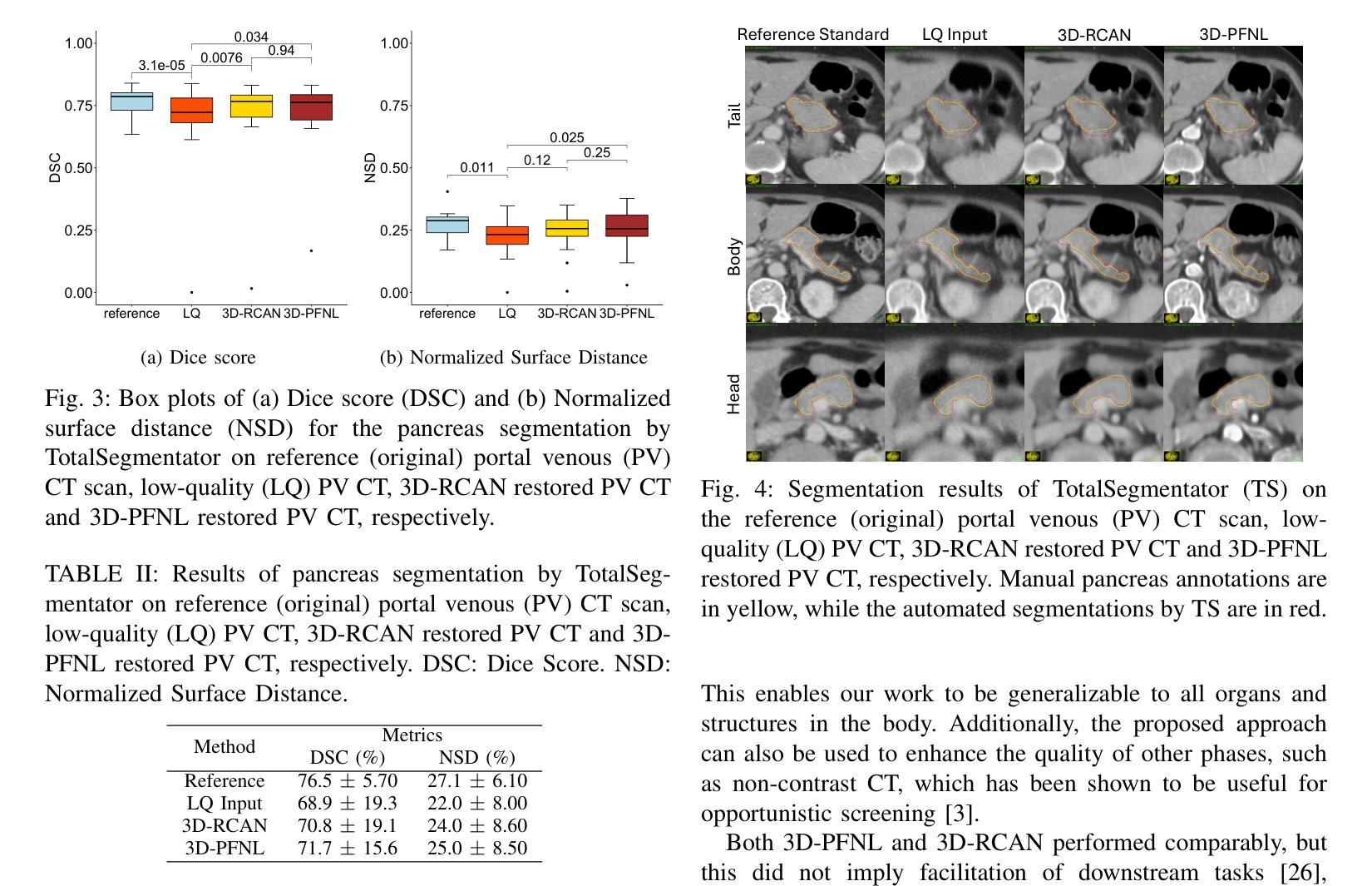
Leveraging Multiphase CT for Quality Enhancement of Portal Venous CT: Utility for Pancreas Segmentation
Authors:Xinya Wang, Tejas Sudharshan Mathai, Boah Kim, Ronald M. Summers
Multiphase CT studies are routinely obtained in clinical practice for diagnosis and management of various diseases, such as cancer. However, the CT studies can be acquired with low radiation doses, different scanners, and are frequently affected by motion and metal artifacts. Prior approaches have targeted the quality improvement of one specific CT phase (e.g., non-contrast CT). In this work, we hypothesized that leveraging multiple CT phases for the quality enhancement of one phase may prove advantageous for downstream tasks, such as segmentation. A 3D progressive fusion and non-local (PFNL) network was developed. It was trained with three degraded (low-quality) phases (non-contrast, arterial, and portal venous) to enhance the quality of the portal venous phase. Then, the effect of scan quality enhancement was evaluated using a proxy task of pancreas segmentation, which is useful for tracking pancreatic cancer. The proposed approach improved the pancreas segmentation by 3% over the corresponding low-quality CT scan. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to harness multiphase CT for scan quality enhancement and improved pancreas segmentation.
在临床实践中,多阶段CT检查常被用于各种疾病的诊断和治疗,如癌症。然而,CT检查可以以较低的辐射剂量获取,使用不同的扫描仪,并经常受到运动和金属伪影的影响。之前的方法主要着眼于提高某一特定CT阶段的质量(例如,非对比CT)。在此工作中,我们假设利用多个CT阶段来提高某一阶段的质量可能对下游任务(如分割)具有优势。我们开发了一个3D渐进融合和非局部(PFNL)网络。它采用三种退化(低质量)阶段(非对比、动脉和门静脉)进行训练,以提高门静脉阶段的质量。然后,通过胰腺分割的代理任务评估扫描质量提高的效果,这对追踪胰腺癌非常有用。所提出的方法在相应的低质量CT扫描上提高了胰腺分割的准确度为百分之三。据我们所知,我们是首次利用多阶段CT进行扫描质量提高和改进胰腺分割。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ISBI 2025
Summary
利用多期CT数据进行质量控制改进可提高胰腺癌跟踪检测中的胰腺分段精度。通过研发3D渐进融合与非局部网络(PFNL),以三个降质(低质量)阶段(非对比剂、动脉期和门静脉期)的训练提升门静脉期图像质量。此方法在提高胰腺分段质量方面优于对应的低质量CT扫描。本研究首创利用多期CT技术提升扫描质量和改进胰腺分段。
Key Takeaways
- 多期CT研究在临床实践中被广泛应用于各种疾病的诊断和管理,如癌症。
- CT研究可采用低剂量辐射、不同扫描仪进行,但可能受到运动和金属伪影的影响。
- 现有方法主要关注某一特定CT阶段的质效提升,例如非对比剂CT。
- 利用多期CT数据进行质量控制改进可提高下游任务(如分割)的性能。
- 研发了3D渐进融合与非局部(PFNL)网络,以低质量CT阶段训练来提升门静脉期图像质量。
- 通过使用胰腺分割作为代理任务,评估了扫描质量提升的效果,这对胰腺癌的跟踪检测具有实用价值。
点此查看论文截图

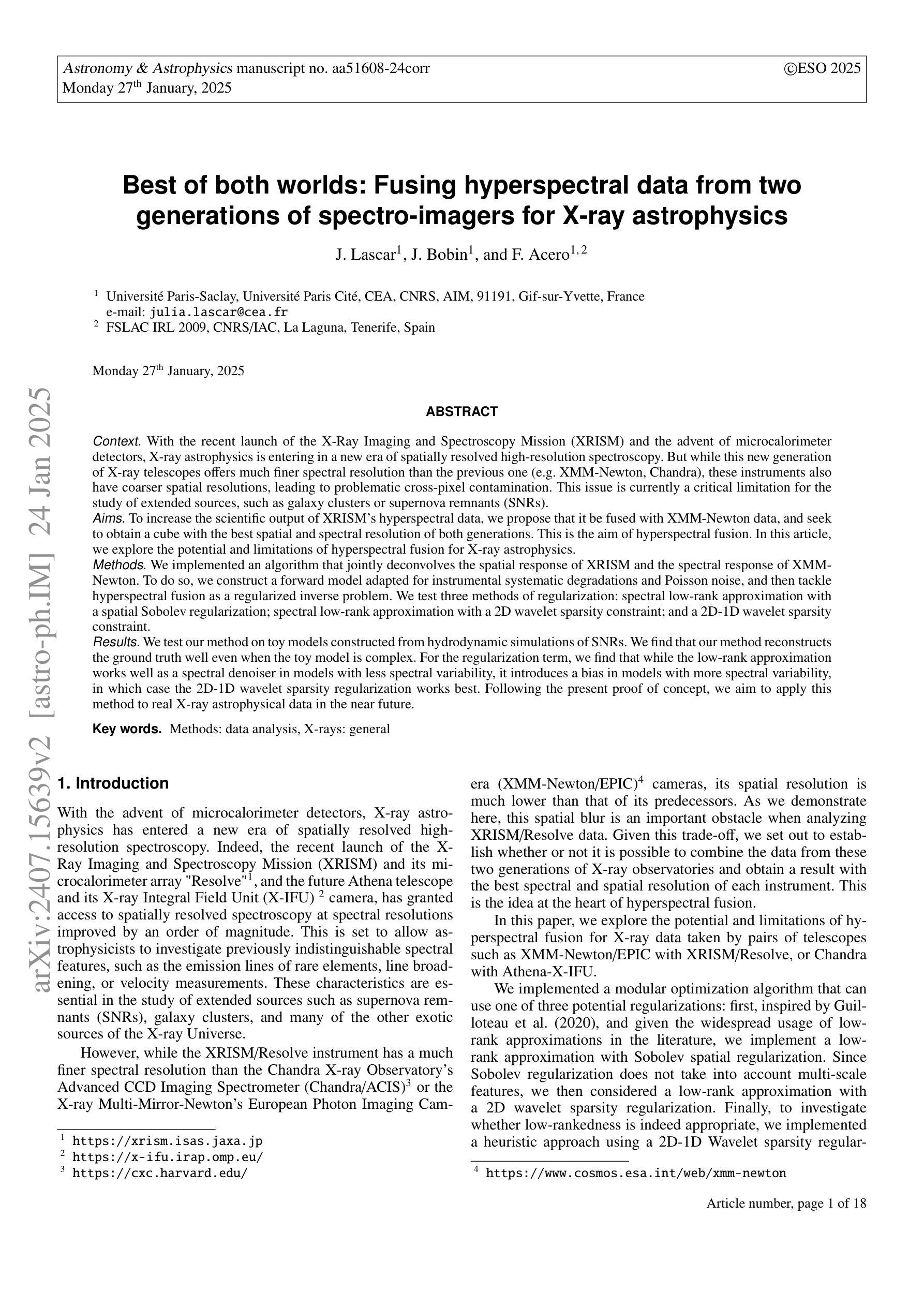
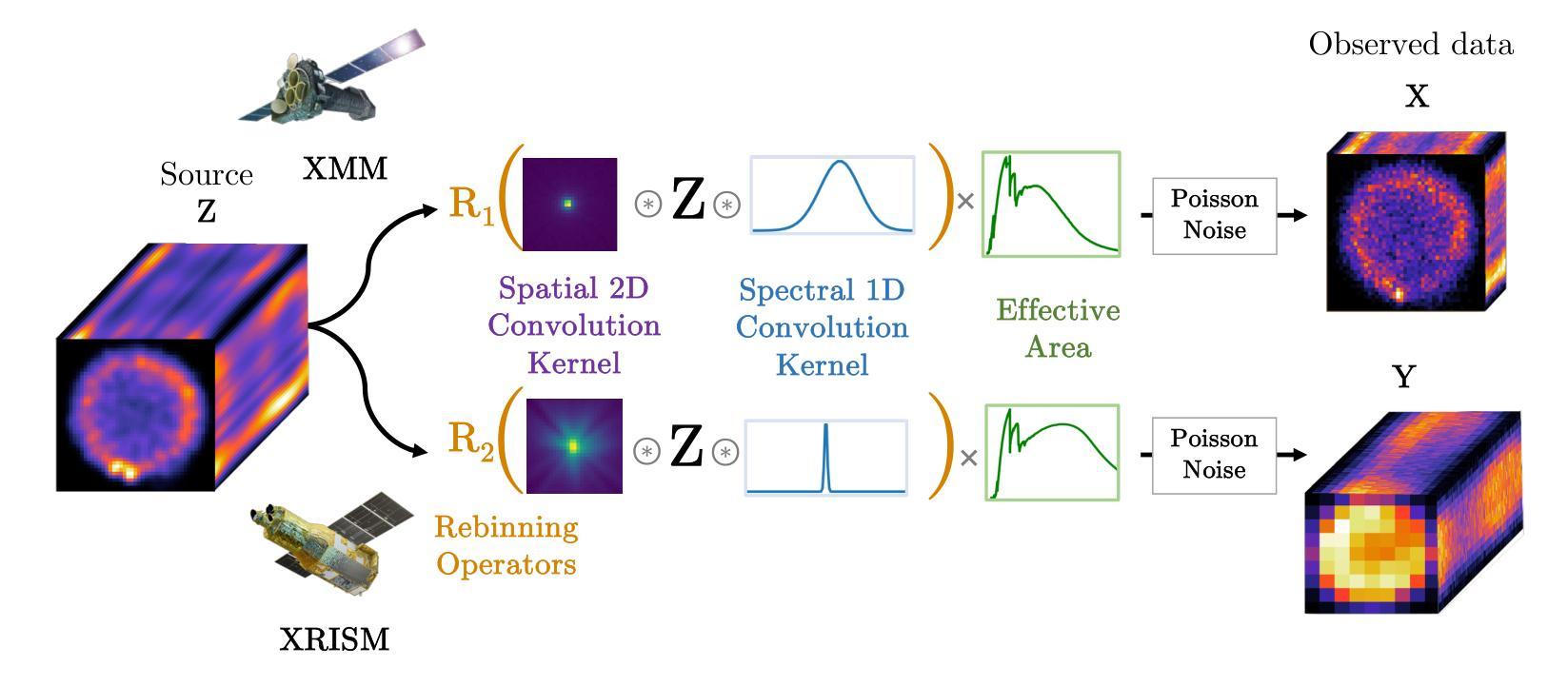
Best of both worlds: Fusing hyperspectral data from two generations of spectro-imagers for X-ray astrophysics
Authors:Julia Lascar, Jérôme Bobin, Fabio Acero
With the launch of the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) and the advent of microcalorimeter detectors, X-ray astrophysics is entering in a new era of spatially resolved high resolution spectroscopy. But while this new generation of X-ray telescopes have much finer spectral resolutions than their predecessors (e.g. XMM-Newton, Chandra), they also have coarser spatial resolutions, leading to problematic cross-pixel contamination. This issue is currently a critical limitation for the study of extended sources such as galaxy clusters or supernova remnants. To increase the scientific output of XRISM’s hyperspectral data, we propose to fuse it with XMM-Newton data, and seek to obtain a cube with the best spatial and spectral resolution of both generations. This is the aim of hyperspectral fusion. In this article, we have implemented an algorithm that jointly deconvolves the spatial response of XRISM and the spectral response of XMM-Newton. To do so, we construct a forward model adapted for instrumental systematic degradations and Poisson noise, then tackle hyperspectral fusion as a regularized inverse problem. We test three methods of regularization: low rank approximation with Sobolev regularization; low rank approximation with 2D wavelet sparsity ; and 2D-1D wavelet sparsity. We test our method on toy models constructed from hydrodynamic simulations of supernova remnants. We find that our method reconstructs the ground truth well even when the toy model is complex. For the regularization term, we find that while the low rank approximation worked well as a spectral denoiser in models with less spectral variability, it introduced a bias in models with more spectral variability, in which case the 2D-1D wavelet sparsity regularization worked best. After demonstrating a proof of concept in this article, we aim to apply this method to real X-ray astrophysical data in the near future.
随着X射线成像与光谱任务(XRISM)的发射和微热量计的诞生,X射线天体物理学正进入空间高分辨率光谱学的新时代。虽然这一代X射线望远镜的光谱分辨率比其前辈(如XMM-牛顿和钱德拉)更为精细,但它们的空间分辨率相对较差,导致了跨像素污染的问题。目前这一问题对于扩展源(如星系团或超新星遗迹)的研究是一个关键的限制。为了提高XRISM高光谱数据的科学产出,我们提议将其与XMM-牛顿数据进行融合,并寻求获得具有两者最佳空间和时间分辨率的立方体。这是高光谱融合的目标。在本文中,我们实现了一种算法,该算法联合反卷积XRISM的空间响应和XMM-牛顿的光谱响应。为此,我们构建了一个适应仪器系统退化和泊松噪声的前向模型,然后将高光谱融合视为正则化逆问题。我们测试了三种正则化方法:基于索博列夫正则化的低秩逼近、基于二维小波稀疏性的低秩逼近和二维到一维小波稀疏性。我们用超新星遗迹的水动力模拟构建的玩具模型来测试我们的方法。我们发现即使在玩具模型复杂的情况下,我们的方法也能很好地重建真实值。对于正则化项,我们发现低秩逼近在光谱变化较少的模型中作为光谱去噪器效果较好,但在光谱变化较大的模型中引入了偏差,在这种情况下,二维到一维小波稀疏性正则化表现最好。在本文中验证了这一理念后,我们计划在不久的将来将此方法应用于真实的X射线天文数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This article was accepted by Astronomy and Astophysics. The code described in this article is available at: https://github.com/JMLascar/HIFReD_fusion
摘要
新一代X射线望远镜进入空间分辨高光谱时代,面临跨像素污染问题。为提升XRISM高光谱数据科学产出,提出融合XRISM与XMM-Newton数据的方法,旨在获得兼具两者最佳空间与光谱分辨率的数据立方体。本研究实现了一种联合解卷算法,针对XRISM的空间响应和XMM-Newton的光谱响应进行解卷。建立正向模型以应对仪器系统退化和泊松噪声问题,将高光谱融合视为正则化反问题进行处理。测试三种正则化方法,发现对于具有复杂光谱变化的模型,二维一维小波稀疏正则化表现最佳。本研究为将该方法应用于真实X射线天文数据奠定了基础。
关键见解
- X射线天体物理学进入高光谱时代,面临跨像素污染问题。
- XRISM与XMM-Newton数据融合旨在提高科学产出,获得最佳空间与光谱分辨率的数据立方体。
- 实施联合解卷算法,针对XRISM和XMM-Newton的数据特性进行解卷。
- 建立正向模型以应对仪器退化和噪声问题。
- 测试三种正则化方法,包括低秩近似与Sobolev正则化、低秩近似与二维小波稀疏性以及二维一维小波稀疏性。
- 对于具有复杂或变化丰富的光谱模型,二维一维小波稀疏正则化表现最佳。
- 本研究为将算法应用于真实X射线天文数据奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图
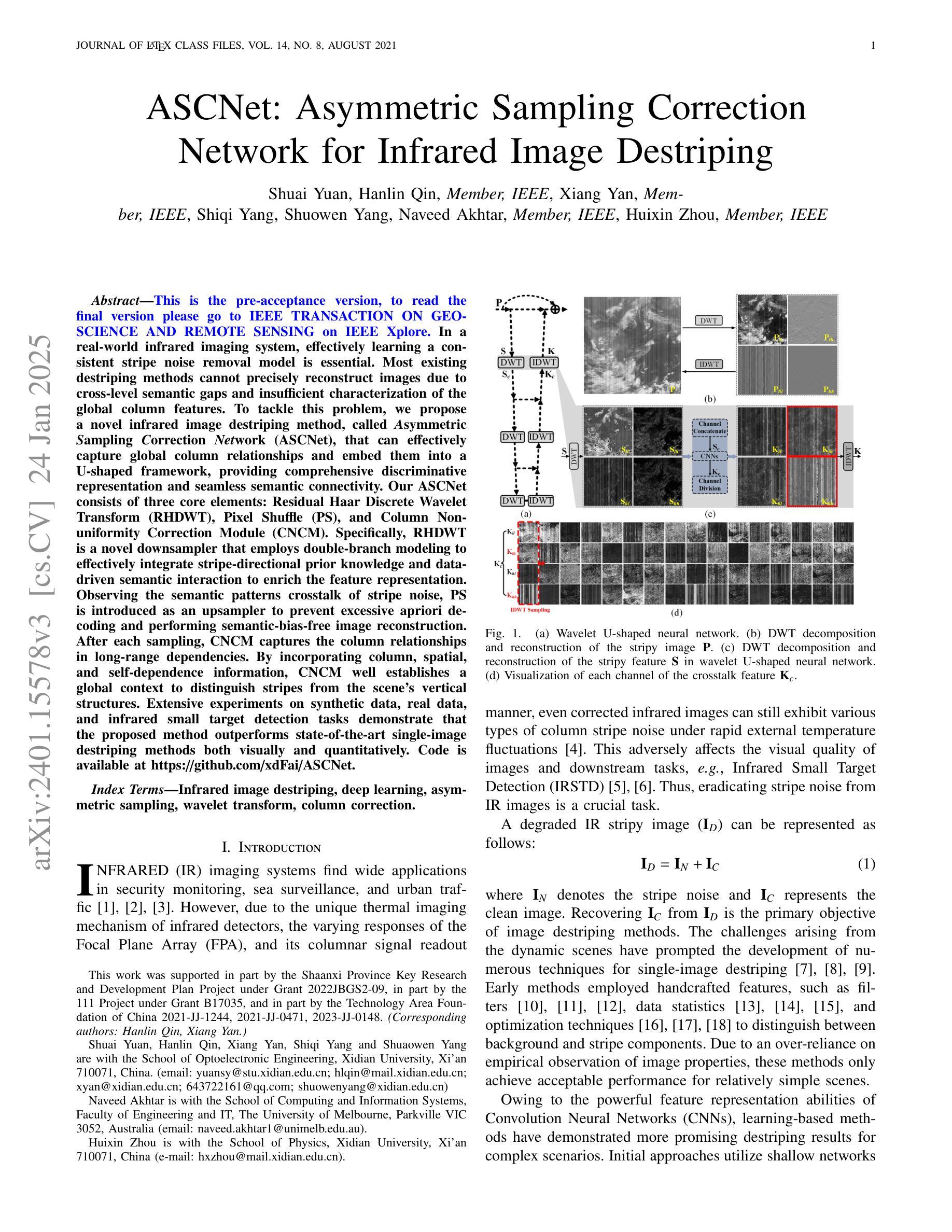
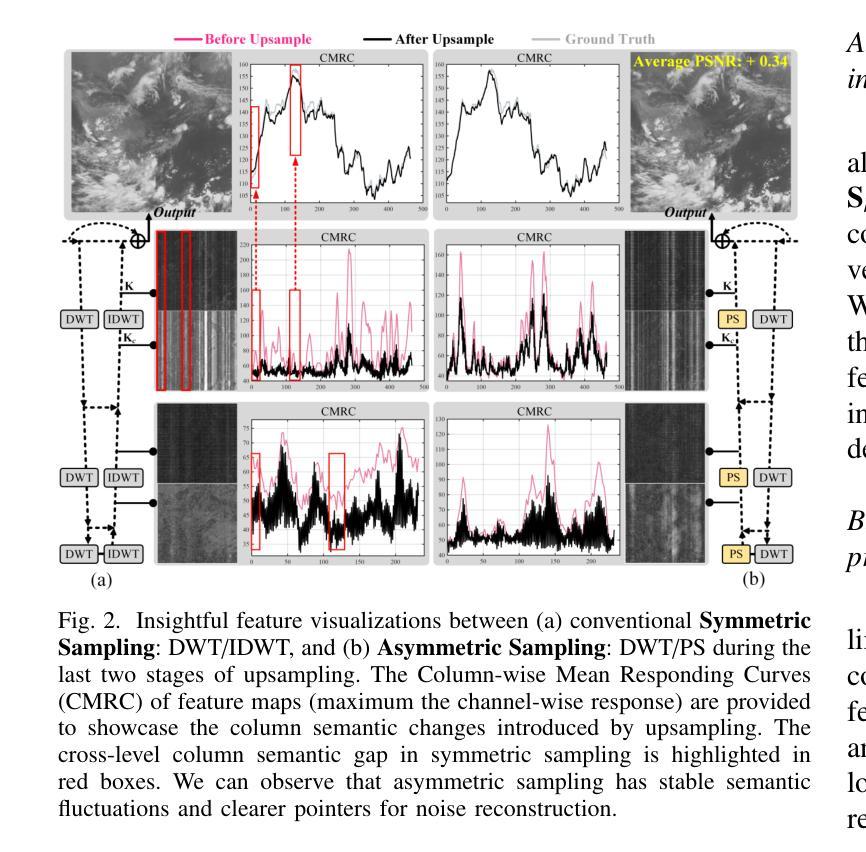
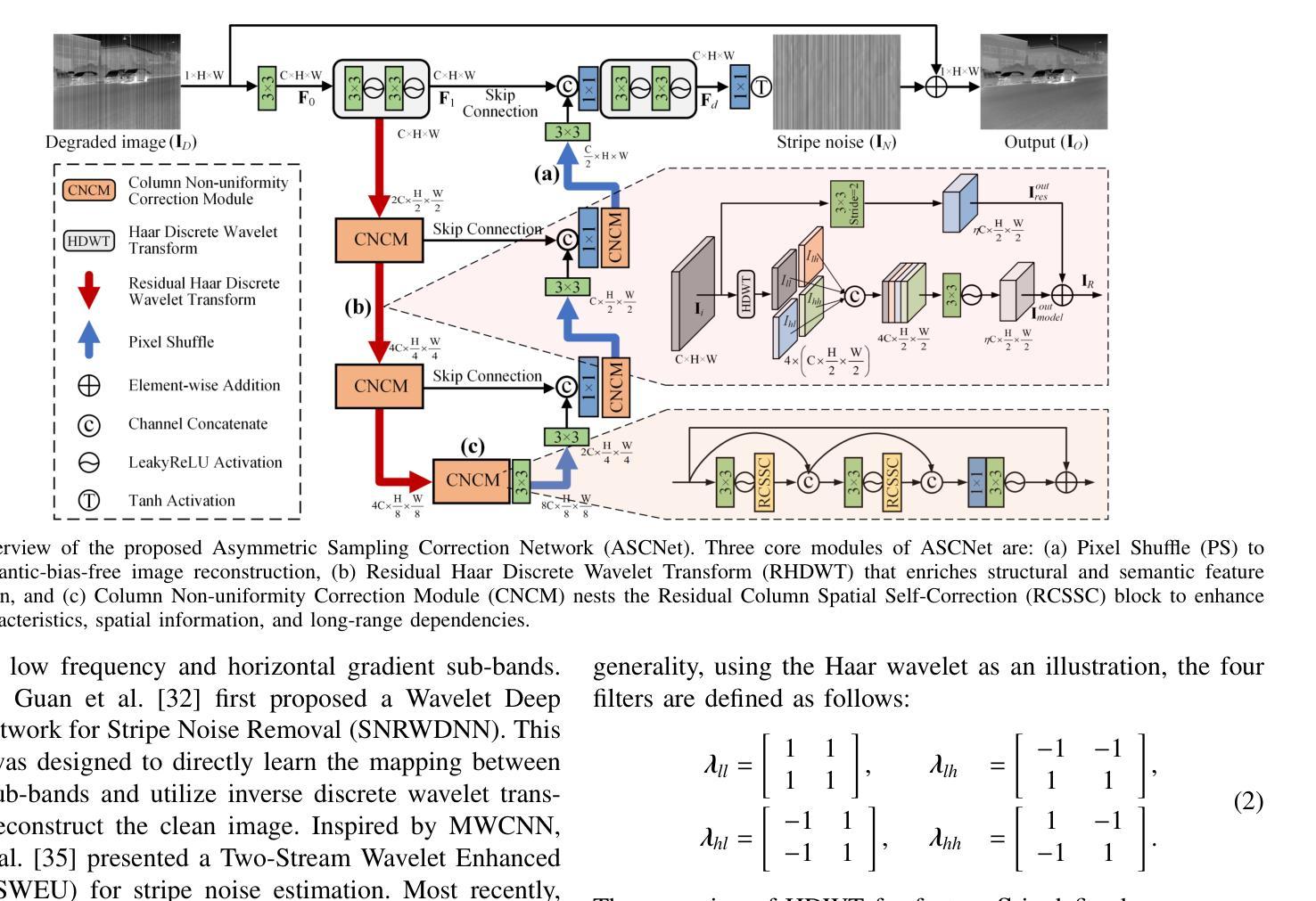
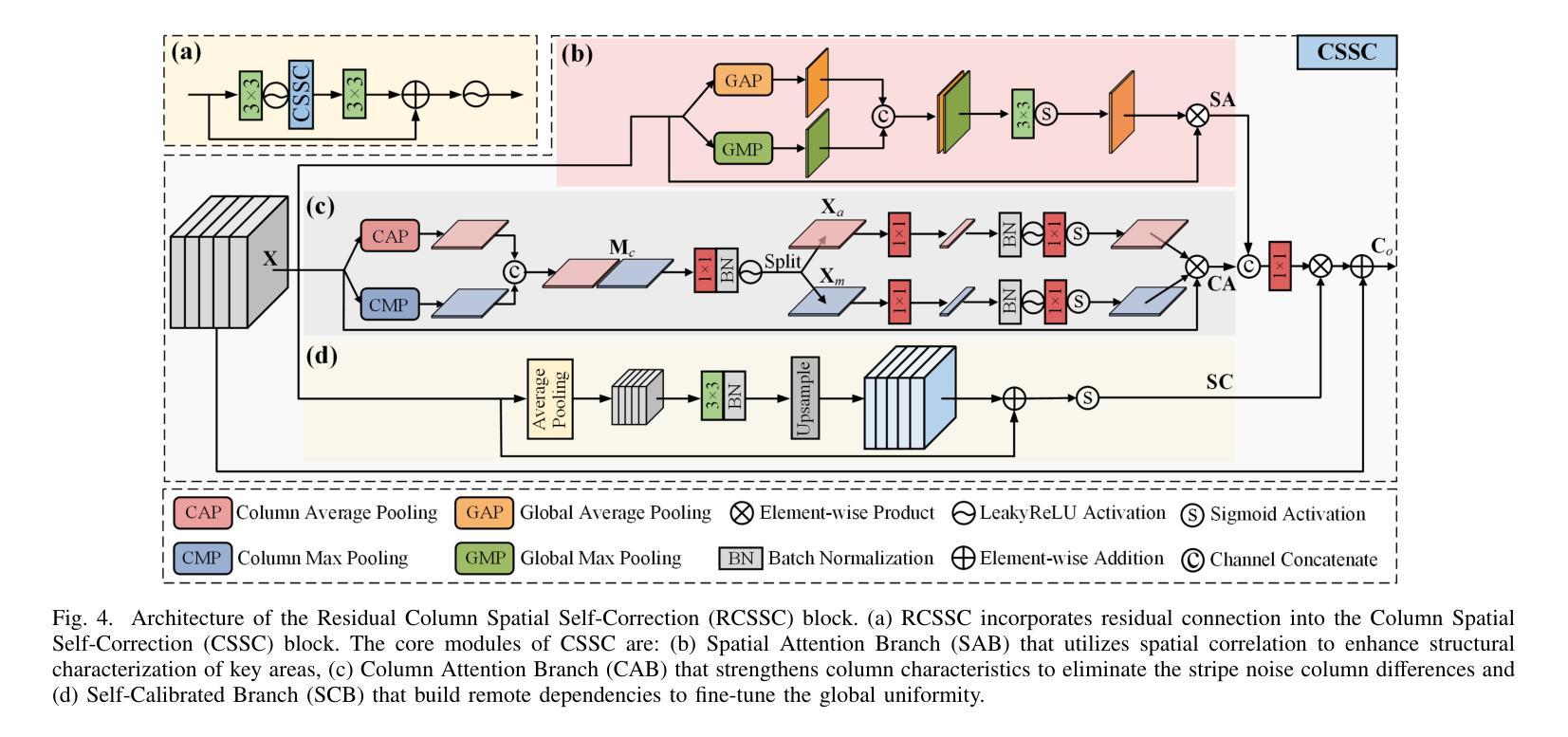
ASCNet: Asymmetric Sampling Correction Network for Infrared Image Destriping
Authors:Shuai Yuan, Hanlin Qin, Xiang Yan, Shiqi Yang, Shuowen Yang, Naveed Akhtar, Huixin Zhou
In a real-world infrared imaging system, effectively learning a consistent stripe noise removal model is essential. Most existing destriping methods cannot precisely reconstruct images due to cross-level semantic gaps and insufficient characterization of the global column features. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel infrared image destriping method, called Asymmetric Sampling Correction Network (ASCNet), that can effectively capture global column relationships and embed them into a U-shaped framework, providing comprehensive discriminative representation and seamless semantic connectivity. Our ASCNet consists of three core elements: Residual Haar Discrete Wavelet Transform (RHDWT), Pixel Shuffle (PS), and Column Non-uniformity Correction Module (CNCM). Specifically, RHDWT is a novel downsampler that employs double-branch modeling to effectively integrate stripe-directional prior knowledge and data-driven semantic interaction to enrich the feature representation. Observing the semantic patterns crosstalk of stripe noise, PS is introduced as an upsampler to prevent excessive apriori decoding and performing semantic-bias-free image reconstruction. After each sampling, CNCM captures the column relationships in long-range dependencies. By incorporating column, spatial, and self-dependence information, CNCM well establishes a global context to distinguish stripes from the scene’s vertical structures. Extensive experiments on synthetic data, real data, and infrared small target detection tasks demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art single-image destriping methods both visually and quantitatively. Our code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/xdFai/ASCNet.
在真实世界的红外成像系统中,有效地学习一致的条纹噪声去除模型至关重要。大多数现有的去条纹方法由于跨级别语义鸿沟和对全局列特征描述不足,无法精确重建图像。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的红外图像去条纹方法,称为不对称采样校正网络(ASCNet),可以有效地捕获全局列关系并将其嵌入U形框架中,提供全面的判别表示和无缝语义连接。我们的ASCNet由三个核心组件组成:残差哈尔离散小波变换(RHDWT)、像素洗牌(PS)和列非均匀性校正模块(CNCM)。具体来说,RHDWT是一种新型的下采样器,采用双分支建模,有效地结合了条纹方向先验知识和数据驱动的语义交互,以丰富特征表示。观察到条纹噪声的语义模式串扰,引入PS作为上采样器,以防止过度先验解码并进行语义无偏图像重建。每次采样后,CNCM捕获长范围依赖关系中的列关系。通过结合列、空间和自依赖信息,CNCM很好地建立了全局上下文,以区分条纹和场景的垂直结构。在合成数据、真实数据和红外小目标检测任务上的大量实验表明,该方法在视觉和定量上均优于最先进的单图像去条纹方法。我们的代码将在https://github.com/xdFai/ASCNet上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的红外图像去条纹噪声方法,名为不对称采样校正网络(ASCNet)。该方法能有效捕捉全局列关系,并将其嵌入U型框架中,提供全面的判别表示和无缝语义连接。核心元素包括残差哈尔离散小波变换(RHDWT)、像素洗牌(PS)和列非均匀校正模块(CNCM)。实验表明,该方法在合成数据、真实数据和红外小目标检测任务上,无论在视觉上还是数量上都优于最新的单图像去条纹方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了新型红外图像去条纹噪声方法ASCNet。
- ASCNet能有效捕捉全局列关系并嵌入U型框架。
- 方法包括RHDWT、PS和CNCM三个核心元素。
- RHDWT是新型下采样器,能整合条纹方向先验知识和数据驱动语义交互。
- PS作为上采样器,能防止过度先验解码,实现语义偏差自由图像重建。
- CNCM能捕捉长距离依赖中的列关系,并建立全局上下文以区分条纹和场景垂直结构。
- 在合成数据、真实数据和红外小目标检测任务上,ASCNet表现优越。
点此查看论文截图