⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
Lightweight Weighted Average Ensemble Model for Pneumonia Detection in Chest X-Ray Images
Authors:Suresh Babu Nettur, Shanthi Karpurapu, Unnati Nettur, Likhit Sagar Gajja, Sravanthy Myneni, Akhil Dusi, Lalithya Posham
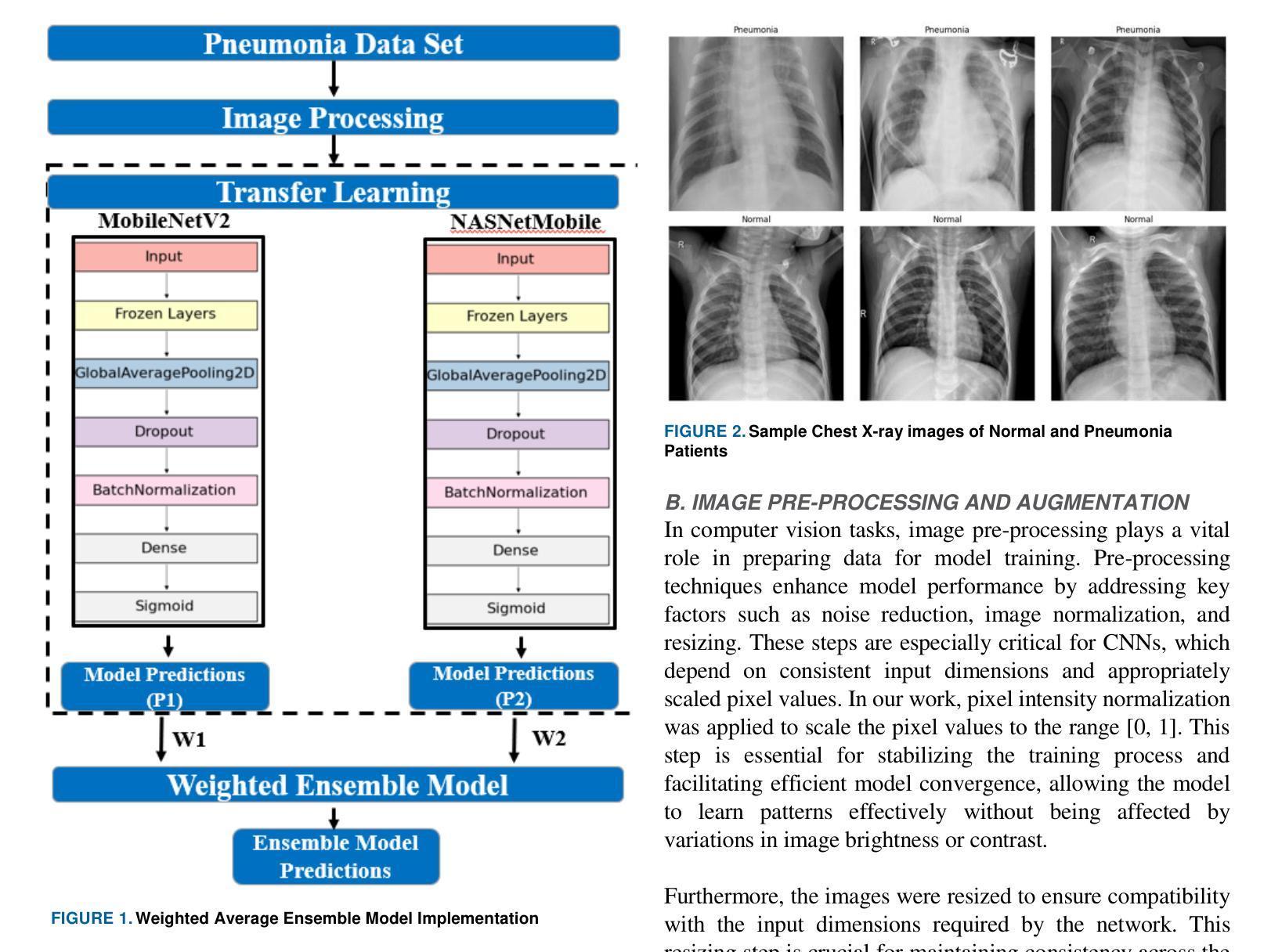
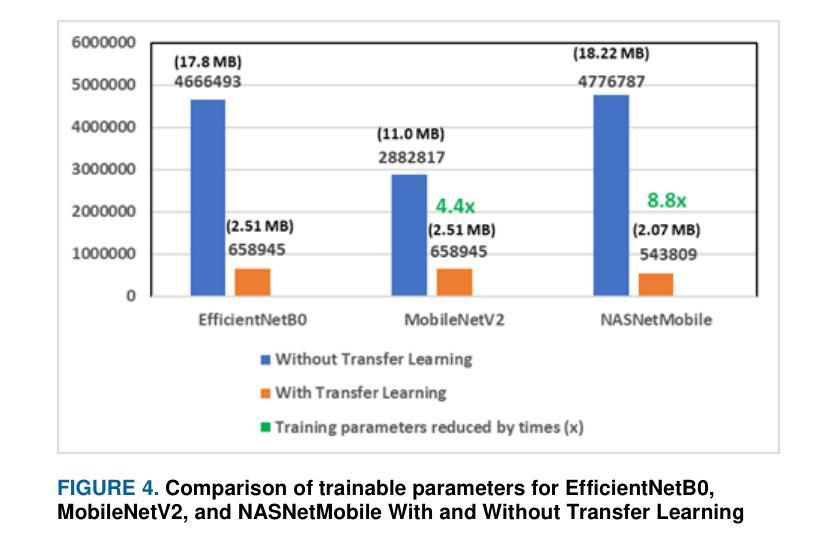
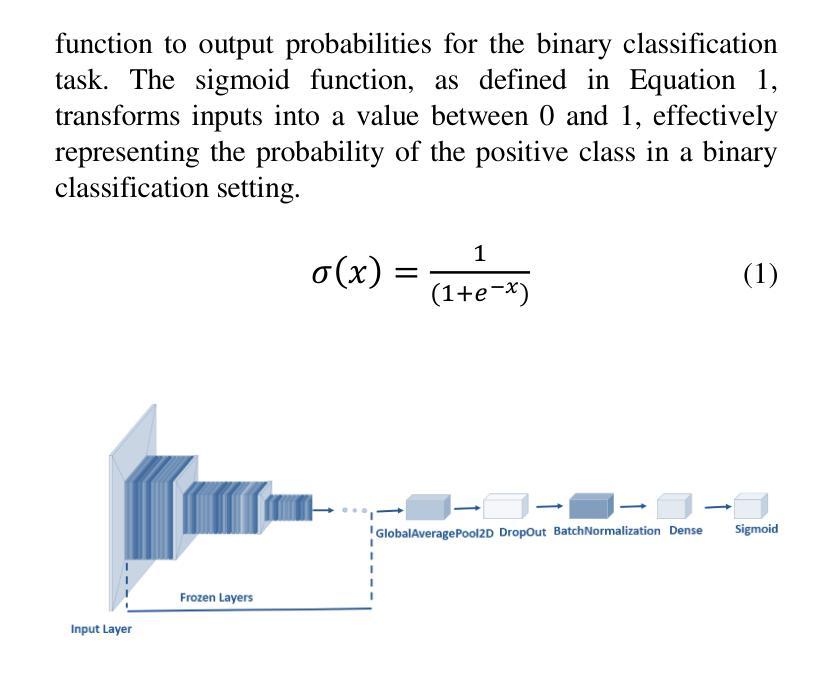
Pneumonia is a leading cause of illness and death in children, underscoring the need for early and accurate detection. In this study, we propose a novel lightweight ensemble model for detecting pneumonia in children using chest X-ray images. This ensemble model integrates two pre-trained convolutional neural networks (CNNs), MobileNetV2 and NASNetMobile, selected for their balance of computational efficiency and accuracy. These models were fine-tuned on a pediatric chest X-ray dataset and combined to enhance classification performance. Our proposed ensemble model achieved a classification accuracy of 98.63%, significantly outperforming individual models such as MobileNetV2 (97.10%) and NASNetMobile(96.25%) in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. Moreover, the ensemble model outperformed state-of-the-art architectures, including ResNet50, InceptionV3, and DenseNet201, while maintaining computational efficiency. The proposed lightweight ensemble model presents a highly effective and resource-efficient solution for pneumonia detection, making it particularly suitable for deployment in resource-constrained settings.
肺炎是儿童疾病和死亡的主要原因之一,强调了对早期和准确检测的需求。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种新型的轻量级集成模型,用于利用胸部X射线图像检测儿童肺炎。该集成模型集成了两个经过预训练的卷积神经网络(CNN),即MobileNetV2和NASNetMobile,它们被选中是因为在计算效率和准确性之间达到了平衡。这些模型在一个儿童胸部X射线数据集上进行微调,并结合使用以提高分类性能。我们提出的集成模型达到了98.63%的分类准确率,在准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数方面显著优于MobileNetV2(97.10%)和NASNetMobile(96.25%)等单个模型。此外,该集成模型在保持计算效率的同时,还优于最新的架构,包括ResNet50、InceptionV3和DenseNet201。所提出的轻量级集成模型为肺炎检测提供了一种高效且资源利用合理的解决方案,特别适用于资源受限的环境中的部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Corresponding authors: Shanthi Karpurapu (shanthi.karpurapu@gmail.com), Suresh Babu Nettur (nettursuresh@gmail.com)
Summary
本研究提出一种用于儿童肺炎检测的轻量级集成模型,该模型结合了MobileNetV2和NASNetMobile两个预训练卷积神经网络,实现了高效率和准确性的平衡。在儿科胸部X光图像数据集上微调后,集成模型在分类性能上有所提升,达到了98.63%的分类准确率,显著优于单个模型以及一些最先进架构的模型。该模型在保持计算效率的同时,展现了高效且资源利用优化的肺炎检测解决方案,尤其适用于资源受限的环境。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种轻量级集成模型,用于儿童肺炎的胸部X光图像检测。
- 集成模型结合了MobileNetV2和NASNetMobile两个预训练卷积神经网络。
- 集成模型在儿科胸部X光图像数据集上进行了微调,提高了分类性能。
- 模型达到了98.63%的分类准确率,优于单个模型和其他先进架构的模型。
- 模型在保持高准确率的同时,具有良好的计算效率。
- 该模型特别适用于资源受限的环境中的肺炎检测。
点此查看论文截图

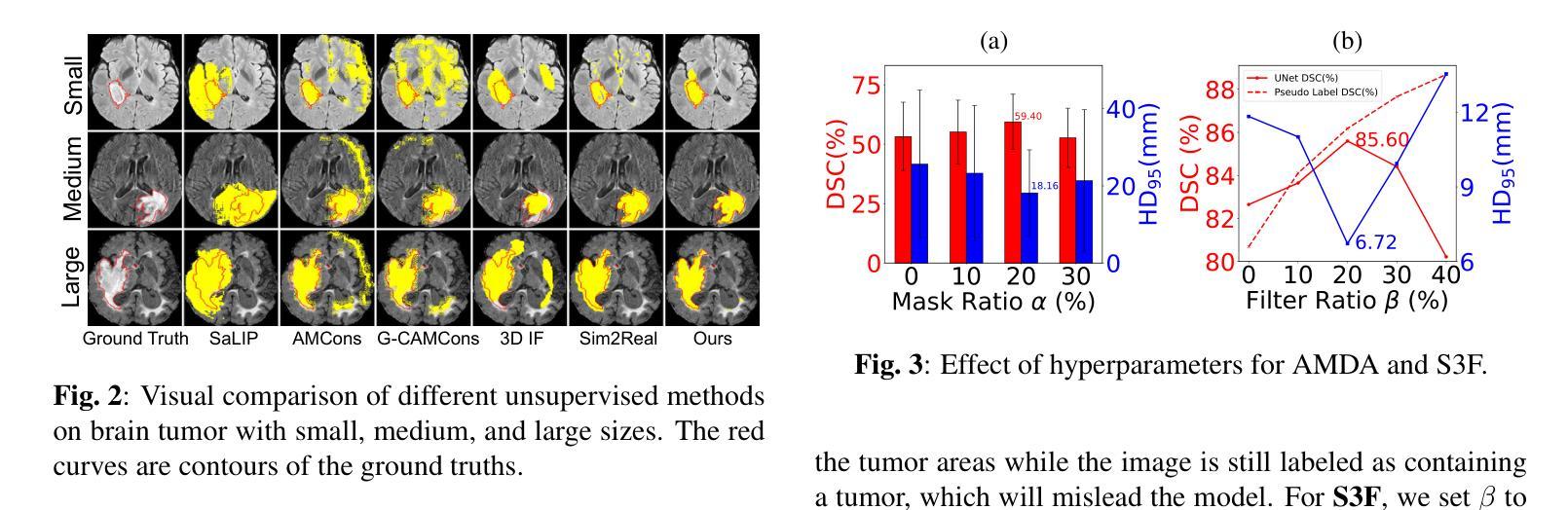
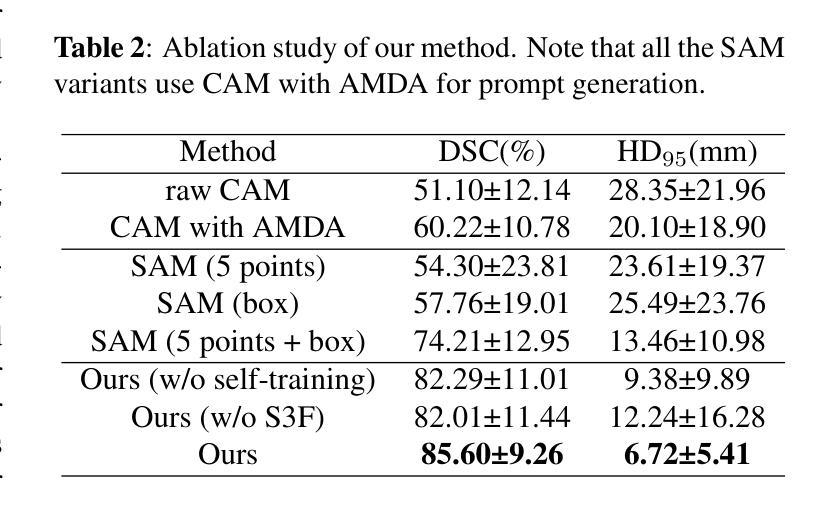
CLISC: Bridging clip and sam by enhanced cam for unsupervised brain tumor segmentation
Authors:Xiaochuan Ma, Jia Fu, Wenjun Liao, Shichuan Zhang, Guotai Wang
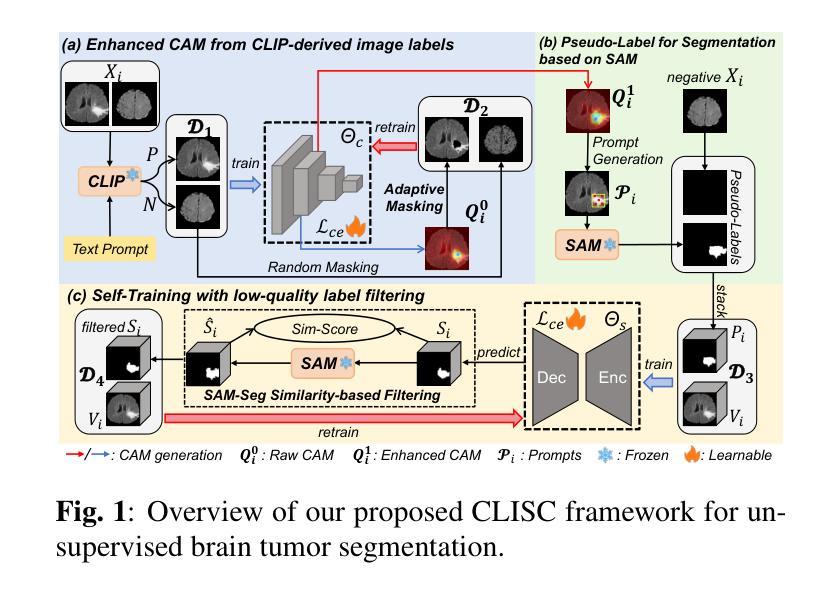
Brain tumor segmentation is important for diagnosis of the tumor, and current deep-learning methods rely on a large set of annotated images for training, with high annotation costs. Unsupervised segmentation is promising to avoid human annotations while the performance is often limited. In this study, we present a novel unsupervised segmentation approach that leverages the capabilities of foundation models, and it consists of three main steps: (1) A vision-language model (i.e., CLIP) is employed to obtain image-level pseudo-labels for training a classification network. Class Activation Mapping (CAM) is then employed to extract Regions of Interest (ROIs), where an adaptive masking-based data augmentation is used to enhance ROI identification.(2) The ROIs are used to generate bounding box and point prompts for the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to obtain segmentation pseudo-labels. (3) A 3D segmentation network is trained with the SAM-derived pseudo-labels, where low-quality pseudo-labels are filtered out in a self-learning process based on the similarity between the SAM’s output and the network’s prediction. Evaluation on the BraTS2020 dataset demonstrates that our approach obtained an average Dice Similarity Score (DSC) of 85.60%, outperforming five state-of-the-art unsupervised segmentation methods by more than 10 percentage points. Besides, our approach outperforms directly using SAM for zero-shot inference, and its performance is close to fully supervised learning.
脑肿瘤分割对于肿瘤诊断具有重要意义,目前深度学习方法依赖于大量标注图像进行训练,标注成本高昂。无监督分割方法有望在避免人工标注的同时实现性能提升。本研究提出了一种新型无监督分割方法,该方法利用基础模型的能力,主要包括三个步骤:(1)采用视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)获取图像级别的伪标签,用于训练分类网络。然后采用类激活映射(CAM)提取感兴趣区域(ROI),并使用基于自适应掩模的数据增强来提高ROI识别。(2)使用ROI生成边界框和点提示,以供Segment Anything Model(SAM)获得分割伪标签。(3)使用SAM生成的伪标签训练3D分割网络,在自我学习过程中过滤掉低质量的伪标签,该过程基于SAM输出与网络预测之间的相似性。在BraTS2020数据集上的评估表明,我们的方法获得了平均Dice相似度得分(DSC)为85.60%,比五种最先进的无监督分割方法的性能高出10个百分点以上。此外,我们的方法优于直接使用SAM进行零样本推理,其性能接近全监督学习。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22st IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2025)
Summary
本研究提出了一种基于基础模型的无监督分割方法,用于脑肿瘤分割。该方法包括三个主要步骤:利用视觉语言模型获得图像级别的伪标签以训练分类网络;使用区域激活映射提取感兴趣区域,并进行自适应掩膜增强;利用感兴趣区域生成边界框和点提示,训练三维分割网络。在BraTS2020数据集上的评估显示,该方法平均Dice相似度得分为85.6%,比五种最先进的无监督分割方法高出超过10个百分点。同时,与直接应用SAM进行零样本推断相比,该方法性能优越,并接近全监督学习的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种新的无监督分割方法用于脑肿瘤分割,基于基础模型。
- 方法包括三个主要步骤:获取图像级伪标签、提取感兴趣区域,以及生成边界框和点提示进行网络训练。
- 使用区域激活映射和自适应掩膜增强提高感兴趣区域的识别能力。
- 在BraTS2020数据集上的评估显示,该方法性能优越,平均Dice相似度得分为85.6%,远超其他无监督方法。
点此查看论文截图

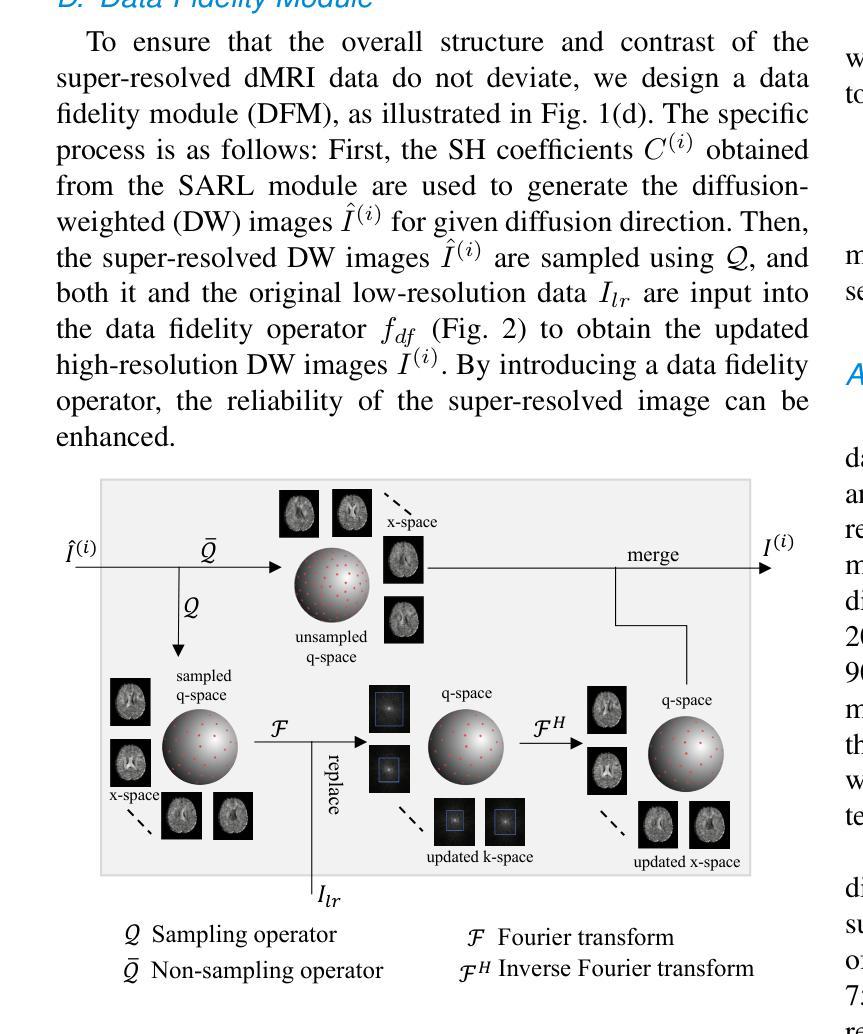
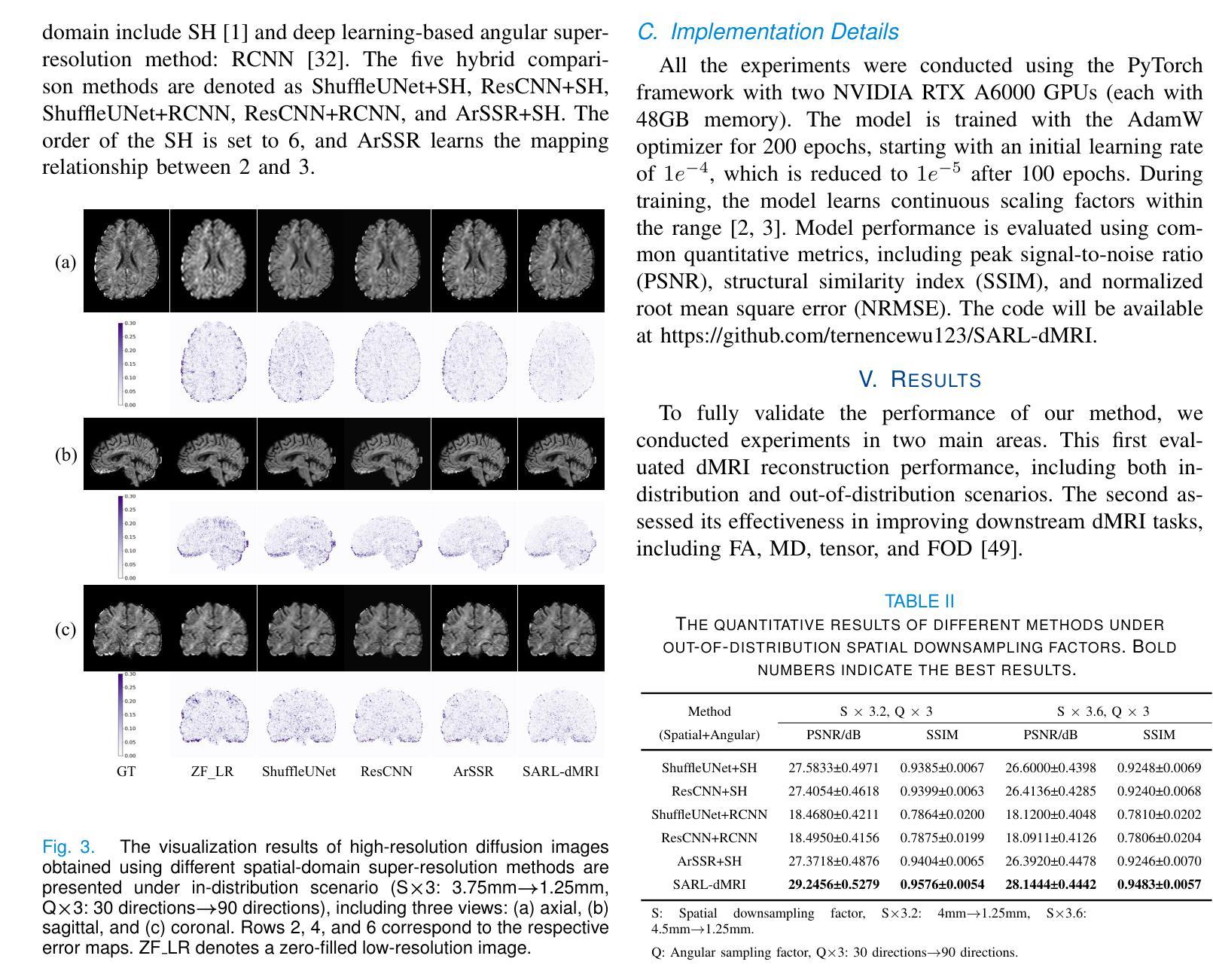
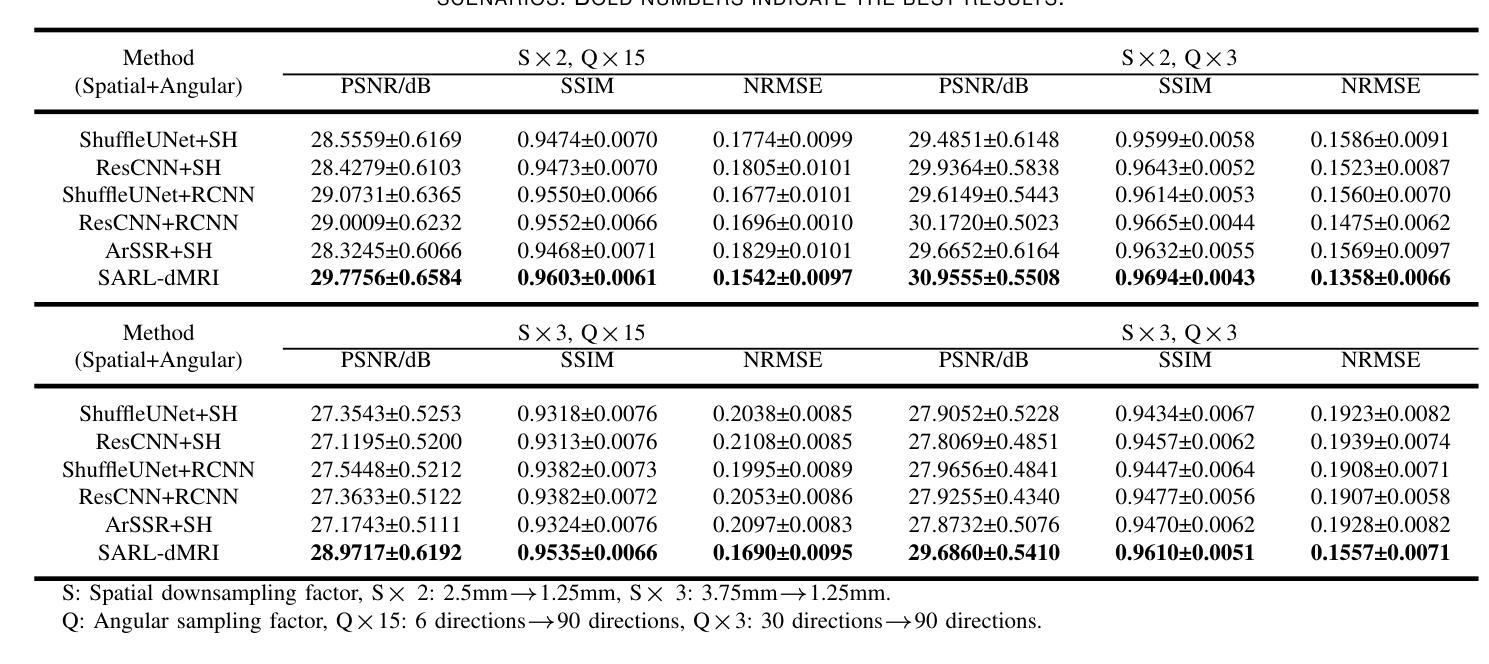
Spatial-Angular Representation Learning for High-Fidelity Continuous Super-Resolution in Diffusion MRI
Authors:Ruoyou Wu, Jian Cheng, Cheng Li, Juan Zou, Wenxin Fan, Hua Guo, Yong Liang, Shanshan Wang
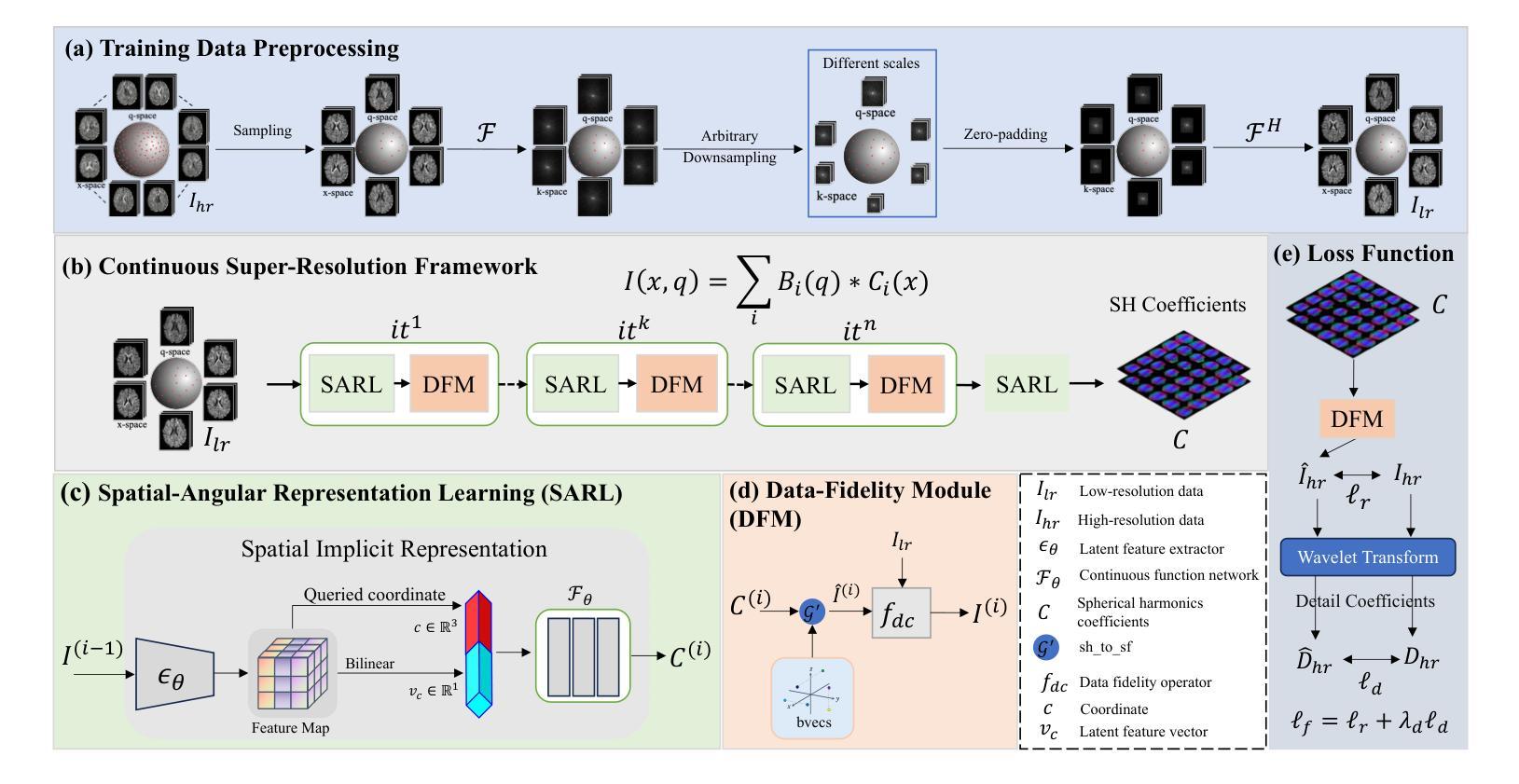
Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) often suffers from low spatial and angular resolution due to inherent limitations in imaging hardware and system noise, adversely affecting the accurate estimation of microstructural parameters with fine anatomical details. Deep learning-based super-resolution techniques have shown promise in enhancing dMRI resolution without increasing acquisition time. However, most existing methods are confined to either spatial or angular super-resolution, limiting their effectiveness in capturing detailed microstructural features. Furthermore, traditional pixel-wise loss functions struggle to recover intricate image details essential for high-resolution reconstruction. To address these challenges, we propose SARL-dMRI, a novel Spatial-Angular Representation Learning framework for high-fidelity, continuous super-resolution in dMRI. SARL-dMRI explores implicit neural representations and spherical harmonics to model continuous spatial and angular representations, simultaneously enhancing both spatial and angular resolution while improving microstructural parameter estimation accuracy. To further preserve image fidelity, a data-fidelity module and wavelet-based frequency loss are introduced, ensuring the super-resolved images remain consistent with the original input and retain fine details. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, compared to five other state-of-the-art methods, our method significantly enhances dMRI data resolution, improves the accuracy of microstructural parameter estimation, and provides better generalization capabilities. It maintains stable performance even under a 45$\times$ downsampling factor.
扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)由于成像硬件和系统噪声的固有局限性,常常存在空间分辨率和角度分辨率低的问题,这不利于对具有精细解剖结构的微观结构参数进行准确估计。基于深度学习技术的超分辨率技术显示出提高dMRI分辨率的潜力,而无需增加采集时间。然而,大多数现有方法仅限于空间或角度超分辨率,在捕捉详细的微观结构特征方面的效果有限。此外,传统的逐像素损失函数难以恢复对于高分辨率重建至关重要的复杂图像细节。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了SARL-dMRI,这是一种用于dMRI中高质量连续超分辨率的新型空间-角度表示学习框架。SARL-dMRI探索隐式神经表示和球面谐波来对连续的空间和角度表示进行建模,同时提高空间和角度分辨率,并改善微观结构参数估计的准确性。为了进一步保持图像保真度,引入了数据保真度模块和小波频损失技术,确保超分辨率图像与原始输入保持一致并保留细节。大量实验表明,与其他五种先进方法相比,我们的方法在增强dMRI数据分辨率、提高微观结构参数估计准确性以及提供更好泛化能力方面表现出显著优势。即使在45倍的降采样系数下,它也能保持稳定的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
Summary
基于深度学习技术的超分辨率技术可以提高扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)的分辨率,而不增加采集时间。然而,大多数现有方法仅限于空间或角超分辨率,难以捕捉详细的微观结构特征。为此,本文提出了SARL-dMRI,一种用于dMRI高保真连续超分辨率的新型空间角表示学习框架。SARL-dMRI采用隐式神经表示和球面谐波建模连续的空间和角表示,可同时提高空间和角分辨率,提高微观结构参数估计的准确性。引入数据保真模块和小波基频损失以保留图像的细节和保真度。实验表明,与其他五种先进方法相比,该方法显著提高dMRI数据分辨率、提高微观结构参数估计的准确性,并具有较好的泛化能力,在45倍降采样下仍能保持稳定的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)受到硬件和系统噪声的限制,存在空间和角分辨率低的问题。
- 深度学习超分辨率技术可提高dMRI分辨率,无需增加采集时间。
- 现有方法主要限于空间或角超分辨率,难以全面捕捉微观结构特征。
- SARL-dMRI是一个新型框架,采用隐式神经表示和球面谐波进行空间角表示学习,提高空间和角分辨率。
- SARL-dMRI引入数据保真模块和小波基频损失,确保图像细节和保真度的保留。
- 实验表明,SARL-dMRI在dMRI数据分辨率、微观结构参数估计准确性方面显著优于其他方法,并具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
Real-Time Brain Tumor Detection in Intraoperative Ultrasound Using YOLO11: From Model Training to Deployment in the Operating Room
Authors:Santiago Cepeda, Olga Esteban-Sinovas, Roberto Romero, Vikas Singh, Prakash Shetty, Aliasgar Moiyadi, Ilyess Zemmoura, Giuseppe Roberto Giammalva, Massimiliano Del Bene, Arianna Barbotti, Francesco DiMeco, Timothy R. West, Brian V. Nahed, Ignacio Arrese, Roberto Hornero, Rosario Sarabia
Intraoperative ultrasound (ioUS) is a valuable tool in brain tumor surgery due to its versatility, affordability, and seamless integration into the surgical workflow. However, its adoption remains limited, primarily because of the challenges associated with image interpretation and the steep learning curve required for effective use. This study aimed to enhance the interpretability of ioUS images by developing a real-time brain tumor detection system deployable in the operating room. We collected 2D ioUS images from the Brain Tumor Intraoperative Database (BraTioUS) and the public ReMIND dataset, annotated with expert-refined tumor labels. Using the YOLO11 architecture and its variants, we trained object detection models to identify brain tumors. The dataset included 1,732 images from 192 patients, divided into training, validation, and test sets. Data augmentation expanded the training set to 11,570 images. In the test dataset, YOLO11s achieved the best balance of precision and computational efficiency, with a mAP@50 of 0.95, mAP@50-95 of 0.65, and a processing speed of 34.16 frames per second. The proposed solution was prospectively validated in a cohort of 15 consecutively operated patients diagnosed with brain tumors. Neurosurgeons confirmed its seamless integration into the surgical workflow, with real-time predictions accurately delineating tumor regions. These findings highlight the potential of real-time object detection algorithms to enhance ioUS-guided brain tumor surgery, addressing key challenges in interpretation and providing a foundation for future development of computer vision-based tools for neuro-oncological surgery.
术中超声(ioUS)在脑肿瘤手术中是一个很有价值的工具,因为它具有通用性、性价比,并能无缝融入手术流程。然而,它的应用仍然有限,主要是因为与图像解读相关的挑战以及有效使用所需的高难度学习曲线。本研究旨在通过开发一种可在手术室部署的实时脑肿瘤检测系统,提高ioUS图像的解读性。我们从脑肿瘤术中数据库(BraTioUS)和公共ReMIND数据集收集了二维ioUS图像,这些图像都经过专家修正的肿瘤标签进行标注。我们使用YOLO11架构及其变体训练目标检测模型,以识别脑肿瘤。数据集包含来自192名患者的1732张图像,分为训练集、验证集和测试集。通过数据增强,训练集扩充至11570张图像。在测试数据集中,YOLO11s在精度和计算效率方面达到了最佳平衡,mAP@50为0.95,mAP@50-95为0.65,处理速度为每秒34.16帧。所提出的解决方案在连续接受手术的15名脑肿瘤患者队列中进行了前瞻性验证。神经外科医生证实,它能无缝融入手术流程,实时预测准确勾画出肿瘤区域。这些发现突显了实时目标检测算法在增强ioUS引导的脑肿瘤手术中的潜力,解决了解读方面的关键挑战,并为基于计算机视觉的神经肿瘤手术工具的未来开发奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究旨在开发实时脑肿瘤检测体系以增强术中超声(ioUS)图像的可解释性,以提高脑肿瘤手术中使用ioUS的价值。研究使用YOLO11架构及其变体训练目标检测模型,对来自Brain Tumor Intraoperative Database(BraTioUS)和公共ReMIND数据集的二维ioUS图像进行训练。数据集包含来自192名患者的1732张图像,分为训练集、验证集和测试集。数据增强将训练集扩展到11570张图像。在测试数据集中,YOLO11s实现了最佳的精度和计算效率平衡,mAP@50为0.95,mAP@50-95为0.65,处理速度为每秒34.16帧。在连续接受手术的15名脑肿瘤患者队列中进行的试验验证了该解决方案的有效性,神经外科医生确认其无缝集成到手术工作流程中,可实时准确预测肿瘤区域。该研究强调了实时目标检测算法在增强ioUS引导的脑肿瘤手术中的潜力,解决了解释上的关键挑战,并为基于计算机视觉的神经肿瘤外科手术的未来发展奠定了基础。
关键发现
- 开发了一个实时脑肿瘤检测体系,用于增强术中超声(ioUS)图像的可解释性。
- 采用YOLO11架构及其变体进行目标检测模型的训练。
- 数据集包括来自BraTioUS和ReMIND的二维ioUS图像数据。
- 数据增强技术有效扩展了训练集规模。
- YOLO11s模型在测试中表现优异,达到了较高的精度和处理速度。
- 解决方案在实际手术中得到验证,能无缝融入手术流程,并准确预测肿瘤区域。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Video Vision Transformer for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis from 3D Brain MRI
Authors:Taymaz Akan, Sait Alp, Md. Shenuarin Bhuiyan, Elizabeth A. Disbrow, Steven A. Conrad, John A. Vanchiere, Christopher G. Kevil, Mohammad A. N. Bhuiyan
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder affecting millions worldwide, necessitating early and accurate diagnosis for optimal patient management. In recent years, advancements in deep learning have shown remarkable potential in medical image analysis. Methods In this study, we present “ViTranZheimer,” an AD diagnosis approach which leverages video vision transformers to analyze 3D brain MRI data. By treating the 3D MRI volumes as videos, we exploit the temporal dependencies between slices to capture intricate structural relationships. The video vision transformer’s self-attention mechanisms enable the model to learn long-range dependencies and identify subtle patterns that may indicate AD progression. Our proposed deep learning framework seeks to enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of AD diagnosis, empowering clinicians with a tool for early detection and intervention. We validate the performance of the video vision transformer using the ADNI dataset and conduct comparative analyses with other relevant models. Results The proposed ViTranZheimer model is compared with two hybrid models, CNN-BiLSTM and ViT-BiLSTM. CNN-BiLSTM is the combination of a convolutional neural network (CNN) and a bidirectional long-short-term memory network (BiLSTM), while ViT-BiLSTM is the combination of a vision transformer (ViT) with BiLSTM. The accuracy levels achieved in the ViTranZheimer, CNN-BiLSTM, and ViT-BiLSTM models are 98.6%, 96.479%, and 97.465%, respectively. ViTranZheimer demonstrated the highest accuracy at 98.6%, outperforming other models in this evaluation metric, indicating its superior performance in this specific evaluation metric. Conclusion This research advances the understanding of applying deep learning techniques in neuroimaging and Alzheimer’s disease research, paving the way for earlier and less invasive clinical diagnosis.
阿尔茨海默症(AD)是一种影响全球数百万人的神经退行性疾病,需要早期和准确的诊断以实现最佳的患者管理。近年来,深度学习在医学图像分析方面已显示出显著潜力。在本研究中,我们提出了一种名为“ViTranZheimer”的AD诊断方法,该方法利用视频视觉变压器(Video Vision Transformer)分析3D脑部MRI数据。通过将3D MRI体积视为视频,我们利用切片之间的时间依赖性来捕捉复杂结构关系。视频视觉变压器的自注意力机制使模型能够学习长期依赖性并识别可能指示AD进展的微妙模式。我们提出的深度学习框架旨在提高AD诊断的准确性和敏感性,为临床医生提供一种早期检测和干预的工具。我们使用ADNI数据集验证了视频视觉变压器的性能,并与其他相关模型进行了比较分析。结果提出的ViTranZheimer模型与两种混合模型(CNN-BiLSTM和ViT-BiLSTM)进行了比较。CNN-BiLSTM是卷积神经网络(CNN)和双向长短期记忆网络(BiLSTM)的组合,而ViT-BiLSTM则是视觉变压器(ViT)与BiLSTM的组合。ViTranZheimer、CNN-BiLSTM和ViT-BiLSTM模型中实现的准确度分别为98.6%、96.479%和97.465%。ViTranZheimer在准确性方面达到了最高的98.6%,在评估指标上优于其他模型,表明其在该特定评估指标上的卓越性能。结论本研究深化了对深度学习技术在神经影像学和阿尔茨海默症研究中的应用理解,为更早和侵入性较小的临床诊断铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出一种利用视频视觉转换器(ViTranZheimer)分析3D脑MRI数据,以诊断阿尔茨海默病(AD)的方法。通过处理3D MRI体积数据作为视频,捕捉切片间的时序依赖性,并学习长期依赖关系和识别微妙的模式以指示AD进展。与现有模型相比,ViTranZheimer模型的诊断准确率和灵敏度更高,为临床医生提供早期检测和干预的工具。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究利用视频视觉转换器(ViTranZheimer)进行阿尔茨海默病(AD)的诊断,这是一种新型的深度学习框架。
- 该模型采用3D脑MRI数据作为输入,并将其视为视频进行处理。
- 通过捕捉切片间的时序依赖性,ViTranZheimer能够学习长期依赖关系并识别微妙的模式以指示AD的进展。
- 研究验证了ViTranZheimer模型的性能,并通过与其他相关模型的比较分析,显示出其较高的诊断准确率。
- ViTranZheimer模型与CNN-BiLSTM和ViT-BiLSTM两种混合模型进行了比较,准确率分别为98.6%、96.479%和97.465%,显示出ViTranZheimer在诊断AD方面的优越性。
- 本研究推动了深度学习在神经影像学和阿尔茨海默病研究中的应用,为早期和微创的临床诊断铺平了道路。
点此查看论文截图

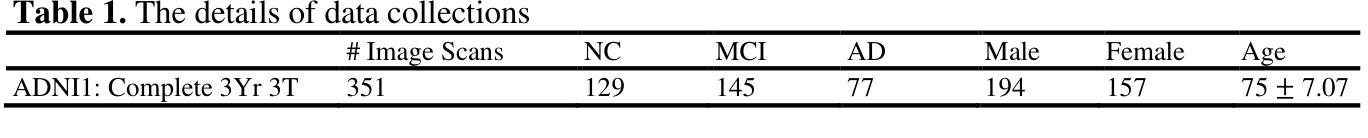
Compensator-based small animal IMRT enables conformal preclinical dose painting: application to tumor hypoxia
Authors:Jordan M. Slagowski, Erik Pearson, Rajit Tummala, Gage Redler, Daniela Olivera Velarde, Boris Epel, Howard J. Halpern, Bulent Aydogan
Techniques for preclinical intensity modulated radiation therapy are being developed to improve translation by replicating the clinical paradigm. This study presents the first treatment planning comparison between small animal IMRT (SA-IMRT) and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (CRT) in a model application, oxygen-guided dose painting of tumor hypoxia, using actual mouse data. A novel compensator-based platform was employed to generate SA-IMRT and CRT plans with 2-15 beam angles for seventeen mice with fibrosarcoma tumors. The whole tumor received a dose of 22.5 Gy, with a simultaneous integrated boost of 13 Gy to hypoxic voxels identified via electron paramagnetic resonance imaging. Plan quality was assessed using the Paddick conformity index (CI), uniformity, and dose volume histograms. For 3-angles, SA-IMRT yielded significantly improved dose conformity (median hypoxic CI =0.45 versus 0.17), tumor dose uniformity (11.0% versus 14.3%), and dosimetric spread between boost and non-boost targets (D50% difference = 13.0 Gy [ideal], 13.1 Gy [SA-IMRT], 7. 3 Gy [CRT]). No significant improvement in CI was associated with >3 beam angles (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p < 0.05). This study demonstrates that SA-IMRT provides significant improvements in radiation plan quality and yields dose distributions that more closely mimic the clinical setting relative to current CRT approaches.
目前正开发用于临床前强度调节放射治疗的技术,以复制临床范例来改善翻译。本研究旨在呈现小动物IMRT(SA-IMRT)与三维适形放射治疗(CRT)之间的首次治疗计划比较。在一项模型应用中,我们使用实际的鼠数据,借助氧导向的剂量绘制肿瘤缺氧图谱。采用新型补偿器平台生成SA-IMRT和CRT计划,为17只患有纤维肉瘤肿瘤的鼠标设置了2-15个光束角度。整个肿瘤接受22.5 Gy的剂量,同时对通过电子顺磁共振成像识别出的缺氧体素给予13 Gy的同时集成提升剂量。计划质量使用Paddick一致性指数(CI)、均匀性和剂量体积直方图进行评估。对于3个角度,SA-IMRT的剂量一致性、肿瘤剂量均匀性和提升与非提升目标之间的剂量学扩散均有显著改善(缺氧CI中位数= 0.45比0.17;11.0%比14.3%;D50%差异= 13.0 Gy [理想],13.1 Gy [SA-IMRT],7.3 Gy [CRT])。而对于大于3个光束角度的情况,并未出现CI的显著改善(Wilcoxon符号秩检验,p < 0.05)。本研究表明,相对于当前的CRT方法,SA-IMRT在放射治疗计划质量方面提供了显著改善,并产生了更接近于临床环境的剂量分布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究比较了小动物IMRT(SA-IMRT)与传统三维适形放疗(CRT)在治疗肿瘤缺氧中的计划差异。采用新型补偿器平台,对17只携带纤维肉瘤肿瘤的鼠标进行2-15个光束角度的计划制定。结果显示,对于3个角度,SA-IMRT在剂量符合度、肿瘤剂量均匀性和剂量体积直方图等方面显著优于CRT。随着光束角度的增加,改善并不显著。总体而言,SA-IMRT在计划质量和剂量分布方面提供更优越的模拟临床环境效果。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究对比了小动物IMRT(SA-IMRT)与三维适形放疗(CRT)在治疗肿瘤缺氧方面的计划差异。
- 采用新型补偿器平台进行治疗计划。
- 对于3个光束角度,SA-IMRT在剂量符合度、肿瘤剂量均匀性和剂量体积直方图等方面显著优于CRT。
- SA-IMRT提供的计划质量改善显著,剂量分布更贴近临床环境。
- 随着光束角度增加,改善并不显著。
- 研究使用的模型应用是氧导向的剂量描绘肿瘤缺氧,使用实际的老鼠数据。
点此查看论文截图

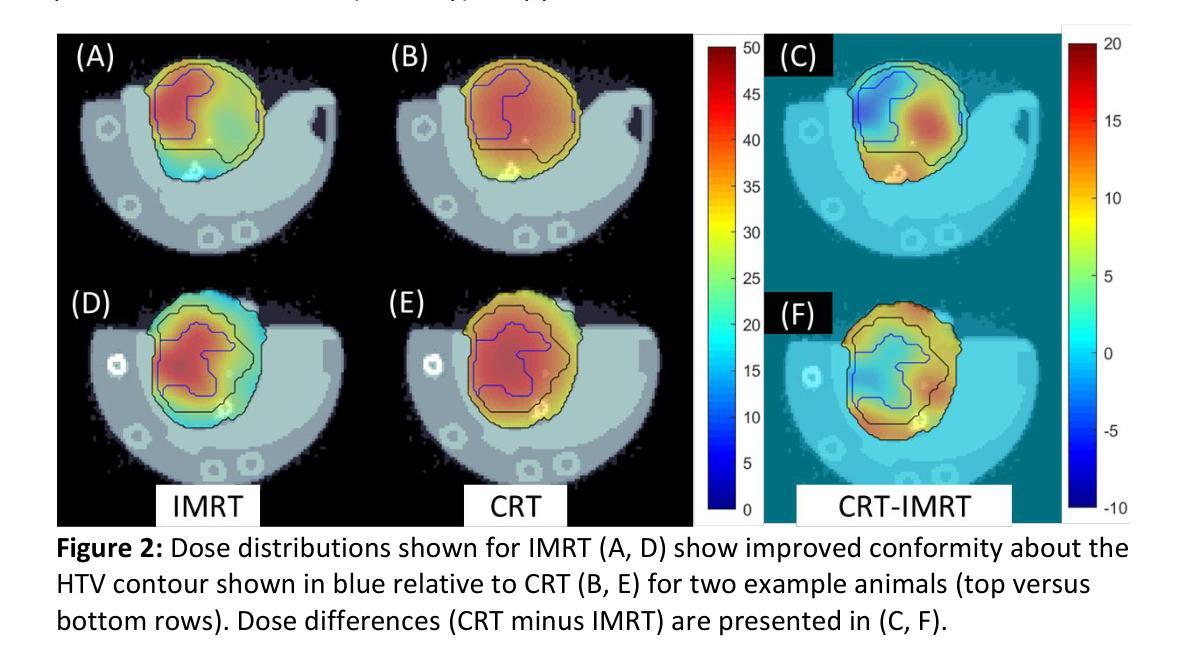
Marker Track: Accurate Fiducial Marker Tracking for Evaluation of Residual Motions During Breath-Hold Radiotherapy
Authors:Aimee Guo, Weihua Mao
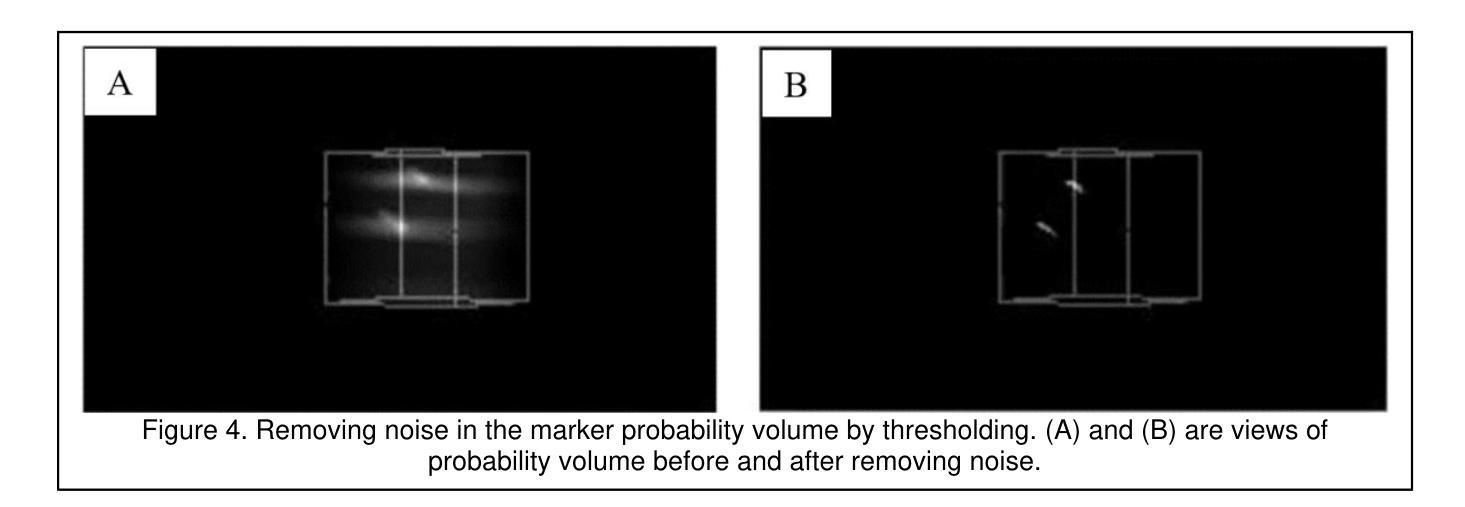
Fiducial marker positions in projection image of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans have been studied to evaluate daily residual motion during breath-hold radiation therapy. Fiducial marker migration posed challenges in accurately locating markers, prompting the development of a novel algorithm that reconstructs volumetric probability maps of marker locations from filtered gradient maps of projections. This guides the development of a Python-based algorithm to detect fiducial markers in projection images using Meta AI’s Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2). Retrospective data from a pancreatic cancer patient with two fiducial markers were analyzed. The three-dimensional (3D) marker positions from simulation computed tomography (CT) were compared to those reconstructed from CBCT images, revealing a decrease in relative distances between markers over time. Fiducial markers were successfully detected in 2777 out of 2786 projection frames. The average standard deviation of superior-inferior (SI) marker positions was 0.56 mm per breath-hold, with differences in average SI positions between two breath-holds in the same scan reaching up to 5.2 mm, and a gap of up to 7.3 mm between the end of the first and beginning of the second breath-hold. 3D marker positions were calculated using projection positions and confirmed marker migration. This method effectively calculates marker probability volume and enables accurate fiducial marker tracking during treatment without requiring any specialized equipment, additional radiation doses, or manual initialization and labeling. It has significant potential for automatically assessing daily residual motion to adjust planning margins, functioning as an adaptive radiation therapy tool.
在研究锥束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)投影图像中的标记点位置时,旨在评估呼吸控制放射治疗期间的每日残留运动。标记点的迁移在准确定位标记点方面带来了挑战,促使开发了一种新型算法,该算法通过投影的梯度图过滤来重建标记点位置的体积概率图。这为基于Python的算法开发提供了指导,该算法使用Meta AI的Segment Anything Model 2(SAM 2)来检测投影图像中的标记点。分析了一位胰腺癌患者的回顾性数据,该患者有两个标记点。模拟计算机断层扫描(CT)中的三维(3D)标记点位置与从CBCT图像重建的位置进行了比较,结果显示标记点之间的相对距离随时间减少。在2786个投影帧中,标记点成功检测了2777个。同一扫描中两次呼吸之间上位-下位(SI)标记点位置的平均标准偏差为每次呼吸保持0.56毫米,两次呼吸之间的平均SI位置差异可达5.2毫米,第一次呼吸保持结束与第二次开始之间的间隔可达7.3毫米。使用投影位置和确认的标记迁移计算了3D标记点位置。该方法有效地计算了标记概率体积,并能够在治疗过程中实现准确的标记点跟踪,无需任何专用设备、额外的辐射剂量或手动初始化和标记。对于自动评估每日残留运动以调整计划余量并作为自适应放射治疗工具,该方法具有巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 9 figures, Regeneron STS 2025 project. Project page: https://sites.google.com/view/markertrack?usp=sharing
摘要
基于锥形束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)投影图像的标记点位置研究,用于评估呼吸控制放射治疗期间的每日残余运动。由于标记点迁移带来的挑战,研究者开发出一种基于投影梯度图过滤重建标记点位置概率图的算法。这引导了基于Python的算法开发,利用Meta AI的SAM 2模型检测投影图像中的标记点。回顾分析胰腺癌患者的数据,对比模拟计算机断层扫描(CT)的3D标记点位置与从CBCT图像重建的位置,发现随时间推移标记点间的相对距离缩短。在2786个投影帧中成功检测到2777个标记点。呼吸控制期间上-下(SI)标记点位置的平均标准偏差为每呼吸控制期0.56毫米,同一扫描中两个呼吸控制期之间的平均SI位置差异最大可达5.2毫米,首个呼吸控制期结束与第二个呼吸控制期开始之间的间隔最大可达7.3毫米。该方法有效计算标记点概率体积,可在不增加特殊设备、辐射剂量或手动初始化和标记的情况下,准确跟踪治疗过程中的标记点位置。这对于自动评估每日残余运动以调整计划余量、作为自适应放射治疗工具具有显著潜力。
关键见解
- 研究利用CBCT投影图像的标记点位置评估呼吸控制放射治疗期间的每日残余运动。
- 标记点迁移带来定位挑战,推动开发新型算法以重建标记点位置概率图。
- 使用Python和Meta AI的SAM 2模型检测投影图像中的标记点。
- 对比模拟CT与CBCT图像的3D标记点位置,发现随时间推移标记点间的相对距离缩短。
- 在大部分投影帧中成功检测到标记点,部分位置差异在毫米级别。
- 该方法有效计算标记点概率体积,可准确跟踪治疗过程中的标记点位置。
点此查看论文截图


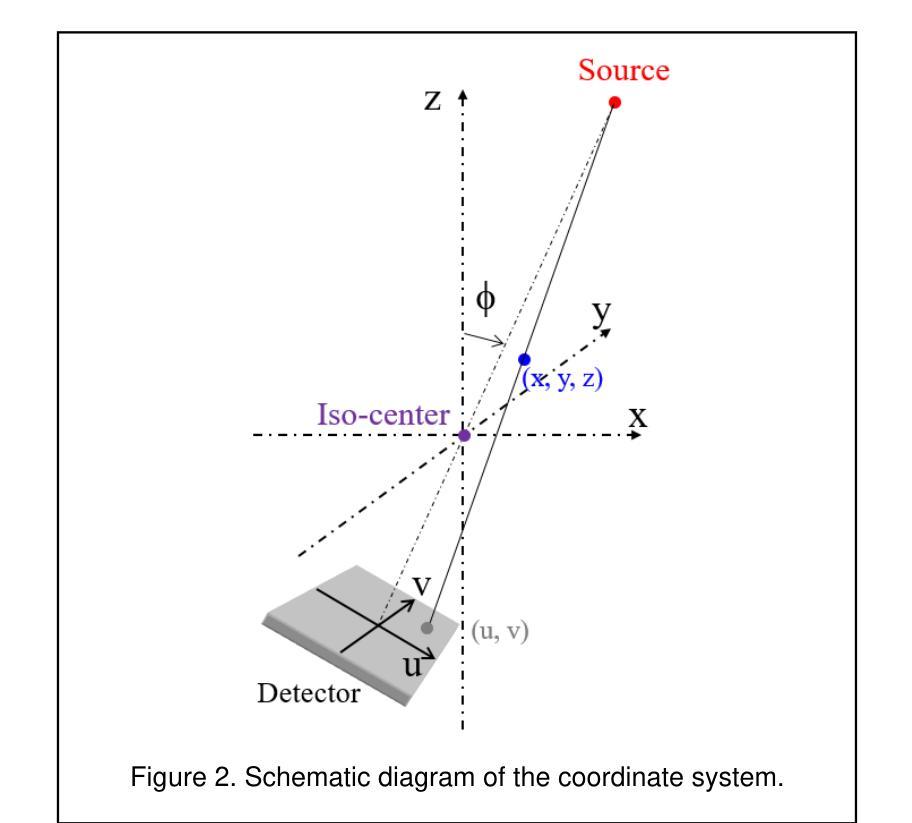

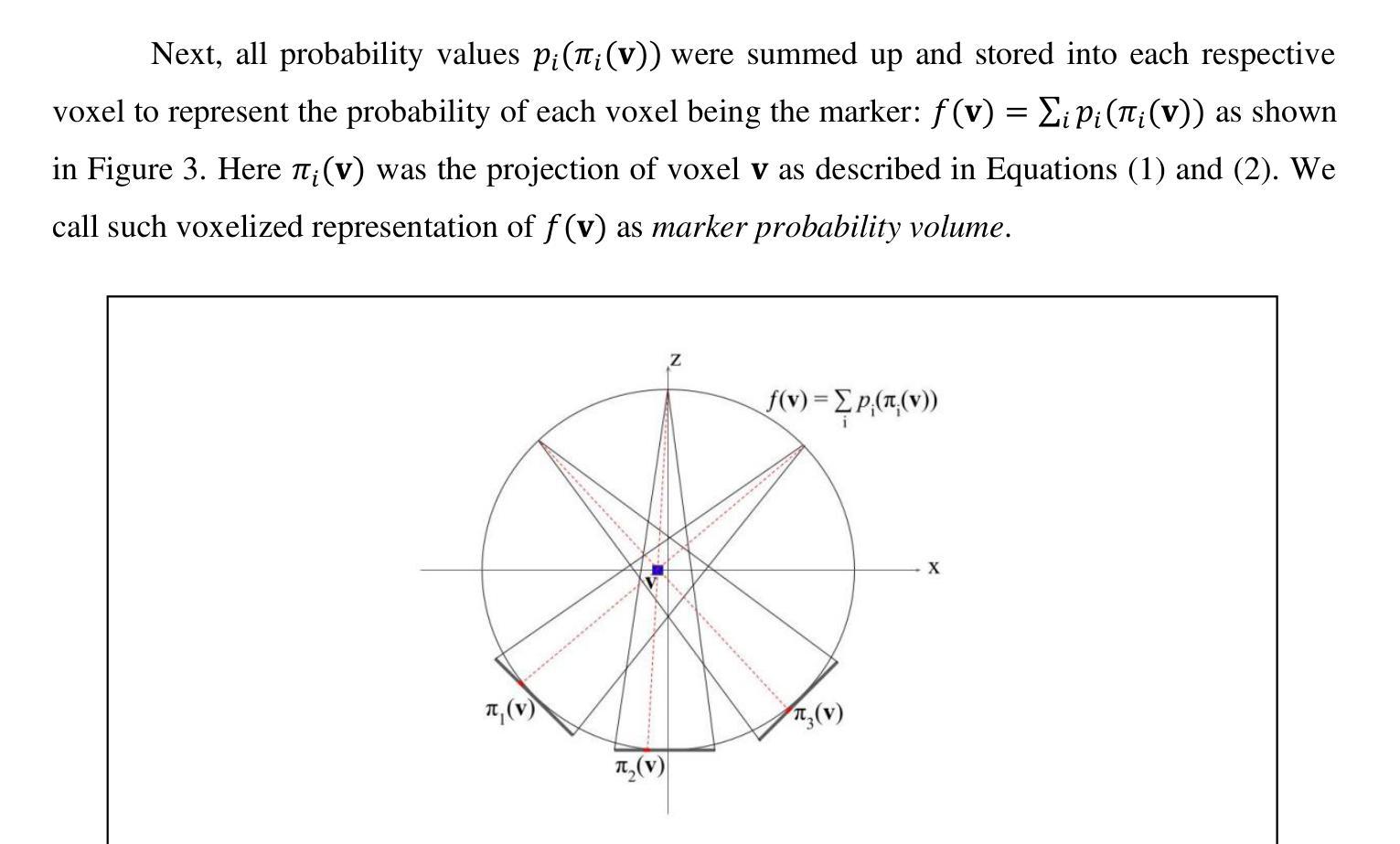
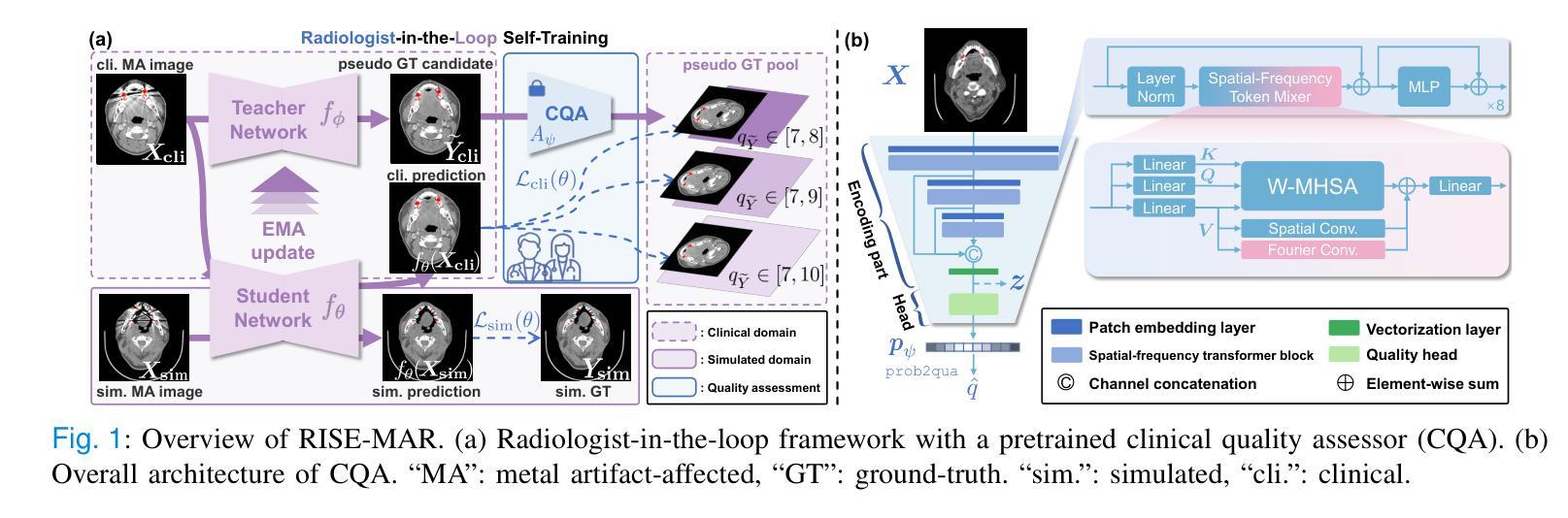
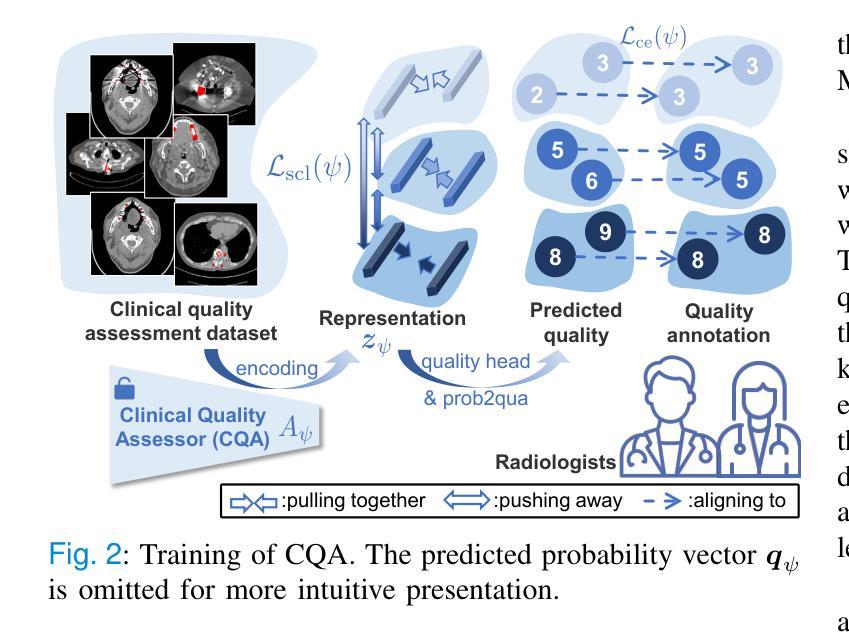
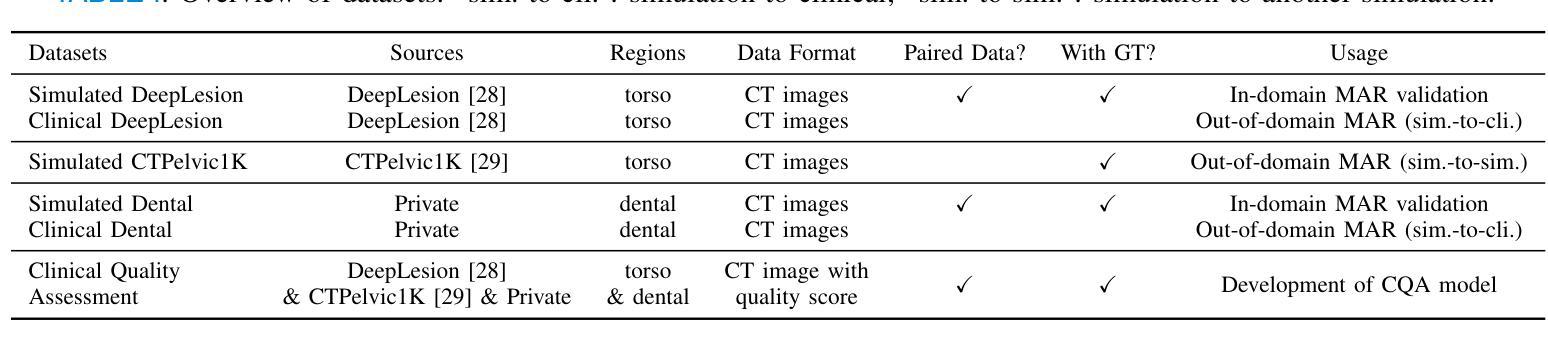
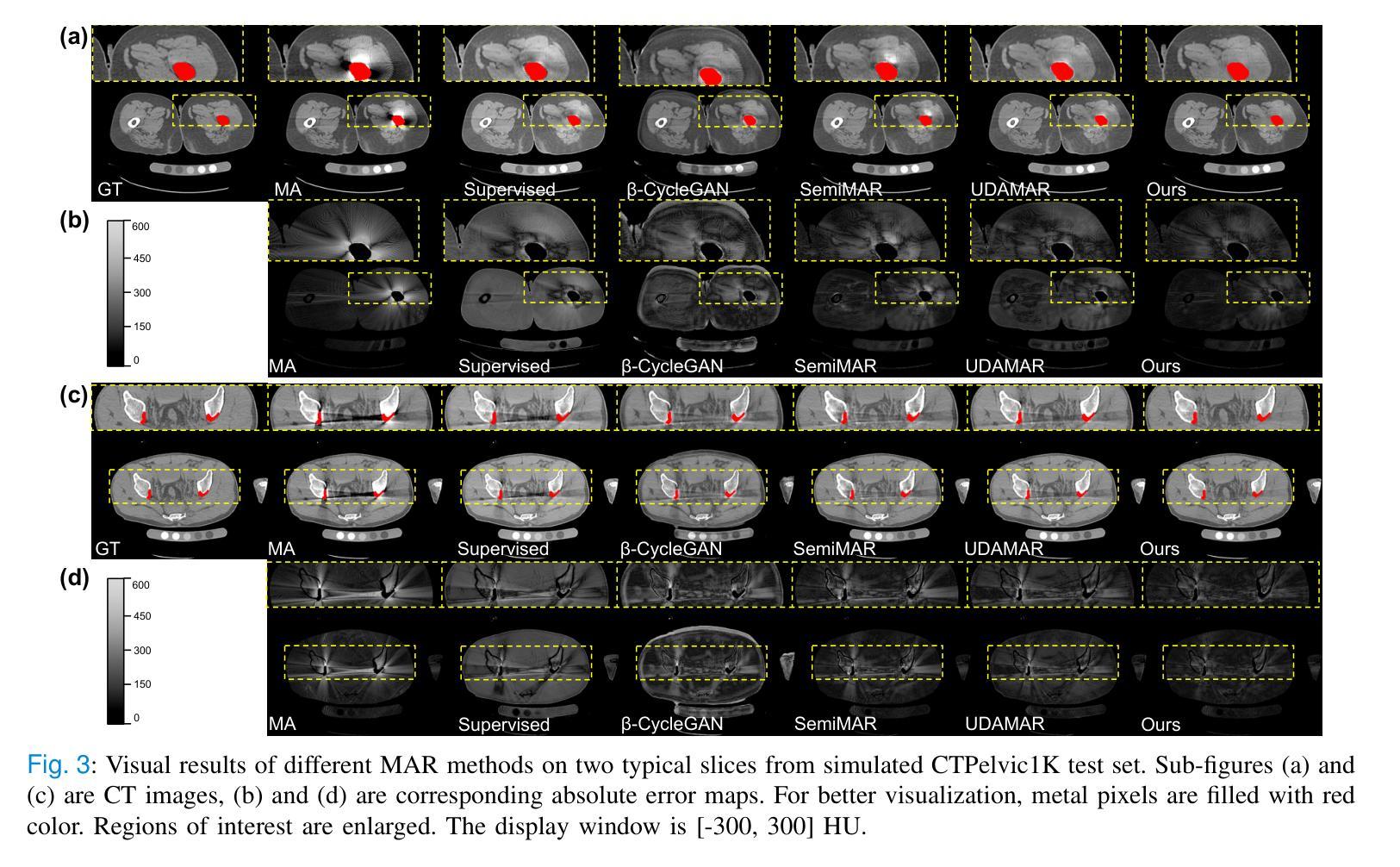
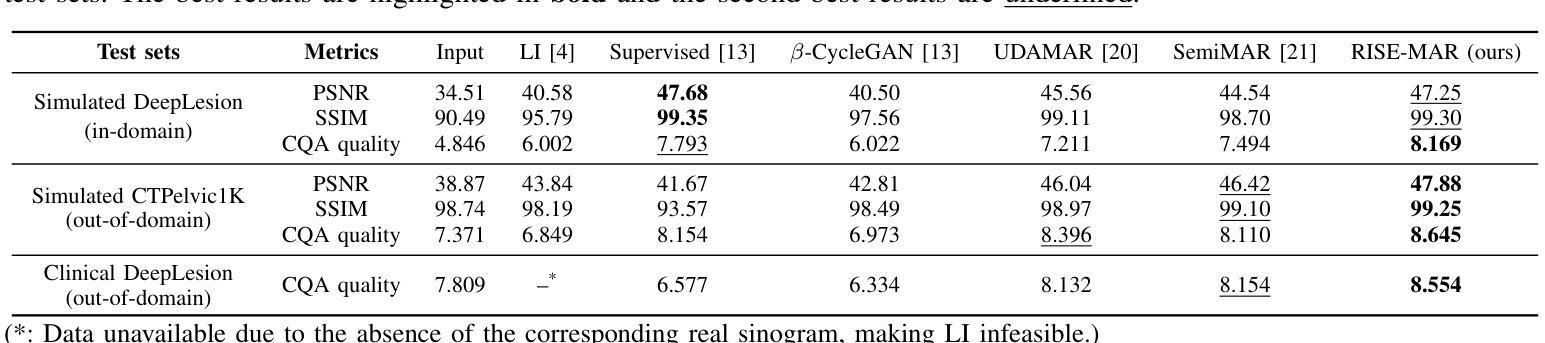
Radiologist-in-the-Loop Self-Training for Generalizable CT Metal Artifact Reduction
Authors:Chenglong Ma, Zilong Li, Yuanlin Li, Jing Han, Junping Zhang, Yi Zhang, Jiannan Liu, Hongming Shan
Metal artifacts in computed tomography (CT) images can significantly degrade image quality and impede accurate diagnosis. Supervised metal artifact reduction (MAR) methods, trained using simulated datasets, often struggle to perform well on real clinical CT images due to a substantial domain gap. Although state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods use pseudo ground-truths generated by a prior network to mitigate this issue, their reliance on a fixed prior limits both the quality and quantity of these pseudo ground-truths, introducing confirmation bias and reducing clinical applicability. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Radiologist-In-the-loop SElf-training framework for MAR, termed RISE-MAR, which can integrate radiologists’ feedback into the semi-supervised learning process, progressively improving the quality and quantity of pseudo ground-truths for enhanced generalization on real clinical CT images. For quality assurance, we introduce a clinical quality assessor model that emulates radiologist evaluations, effectively selecting high-quality pseudo ground-truths for semi-supervised training. For quantity assurance, our self-training framework iteratively generates additional high-quality pseudo ground-truths, expanding the clinical dataset and further improving model generalization. Extensive experimental results on multiple clinical datasets demonstrate the superior generalization performance of our RISE-MAR over state-of-the-art methods, advancing the development of MAR models for practical application. Code is available at https://github.com/Masaaki-75/rise-mar.
计算机断层扫描(CT)图像中的金属伪影会显著降低图像质量并阻碍准确诊断。使用模拟数据集训练的监督型金属伪影减少(MAR)方法通常在实际的临床CT图像上表现不佳,这主要是因为存在较大的领域差距。尽管最先进的半监督方法使用由先前网络生成的伪真实标签来缓解这个问题,但它们对固定先验的依赖限制了这些伪真实标签的质量和数量,引入了确认偏见并降低了临床适用性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的金属伪影减少的半监督自训练框架,名为RISE-MAR。该框架能够将放射科医生的反馈整合到半监督学习过程中,逐步改善伪真实标签的质量和数量,以提高在实际临床CT图像上的泛化能力。为保证质量,我们引入了临床质量评估模型,模拟放射科医生评估,有效地选择高质量的伪真实标签用于半监督训练。为保证数量,我们的自训练框架通过迭代生成额外的高质量伪真实标签,扩大临床数据集,进一步改善模型的泛化能力。在多个临床数据集上的广泛实验结果证明,我们的RISE-MAR的泛化性能优于最先进的方法,推动了MAR模型在实际应用中的发展。相关代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/Masaaki-75/rise-mar。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE TMI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种融合放射科医生反馈的半监督学习方法RISE-MAR,用于减少计算机断层扫描(CT)图像中的金属伪影。该方法通过逐步改进伪真实标签的质量和数量,提高了模型在真实临床CT图像上的泛化能力。引入临床质量评估模型模拟放射科医生评估,选择高质量的伪真实标签进行半监督训练,同时迭代生成更多高质量的伪真实标签,扩大临床数据集,进一步提高模型的泛化性能。实验结果表明,RISE-MAR方法相较于现有方法在金属伪影去除方面表现出更优越的泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- 金属伪影在CT图像中会导致图像质量下降,影响准确诊断。
- 现有监督型金属伪影减少(MAR)方法在实际临床CT图像上的表现存在局限性。
- 提出的RISE-MAR方法结合放射科医生反馈,逐步改进伪真实标签的质量和数量。
- 引入临床质量评估模型模拟放射科医生评估,选择高质量的伪真实标签进行半监督训练。
- RISE-MAR方法通过迭代生成更多高质量的伪真实标签,扩大临床数据集,提高模型的泛化性能。
- 实验结果表明RISE-MAR方法相较于现有方法在金属伪影去除方面表现优越。
点此查看论文截图
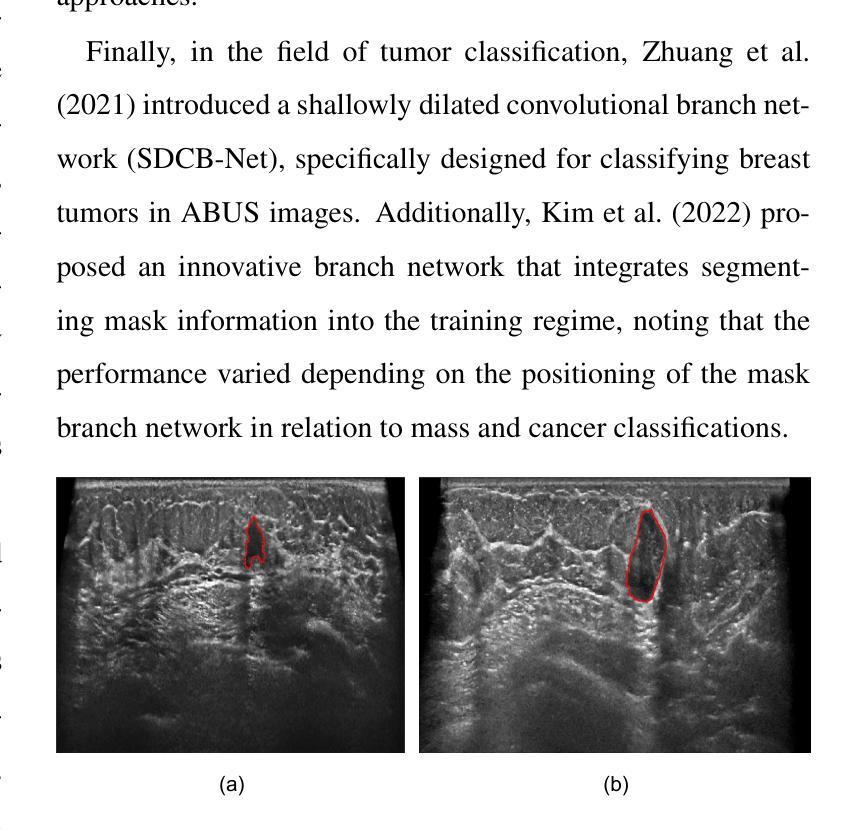
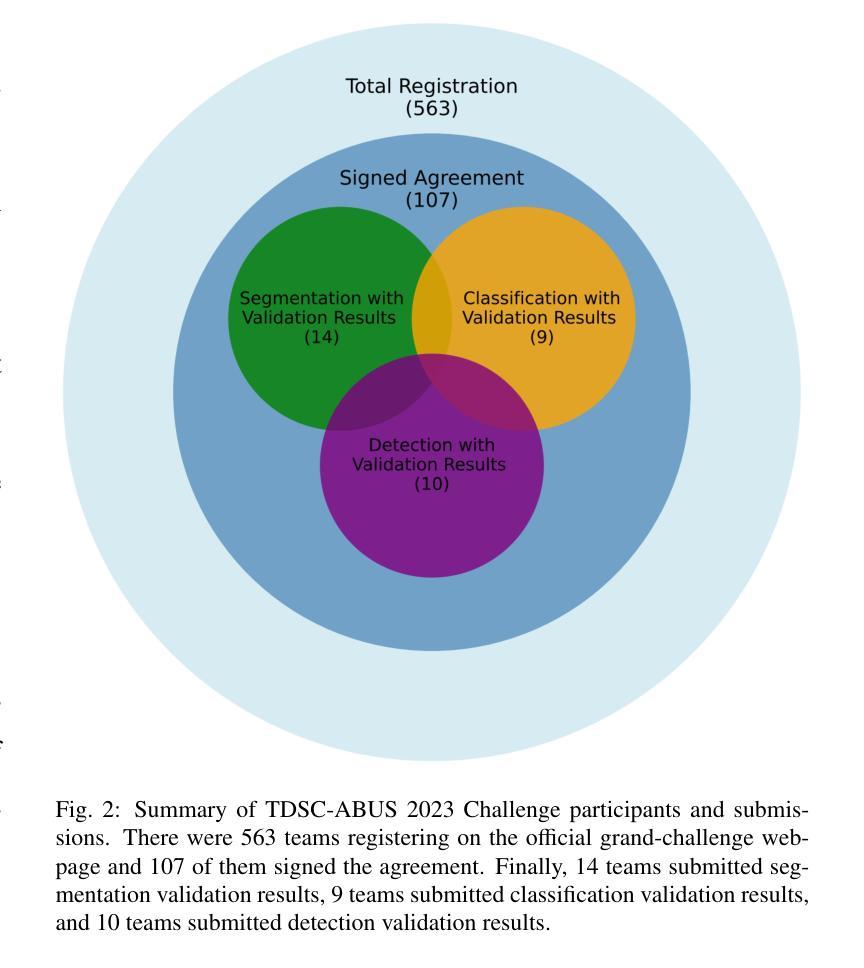
Tumor Detection, Segmentation and Classification Challenge on Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound: The TDSC-ABUS Challenge
Authors:Gongning Luo, Mingwang Xu, Hongyu Chen, Xinjie Liang, Xing Tao, Dong Ni, Hyunsu Jeong, Chulhong Kim, Raphael Stock, Michael Baumgartner, Yannick Kirchhoff, Maximilian Rokuss, Klaus Maier-Hein, Zhikai Yang, Tianyu Fan, Nicolas Boutry, Dmitry Tereshchenko, Arthur Moine, Maximilien Charmetant, Jan Sauer, Hao Du, Xiang-Hui Bai, Vipul Pai Raikar, Ricardo Montoya-del-Angel, Robert Marti, Miguel Luna, Dongmin Lee, Abdul Qayyum, Moona Mazher, Qihui Guo, Changyan Wang, Navchetan Awasthi, Qiaochu Zhao, Wei Wang, Kuanquan Wang, Qiucheng Wang, Suyu Dong
Breast cancer is one of the most common causes of death among women worldwide. Early detection helps in reducing the number of deaths. Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound (ABUS) is a newer approach for breast screening, which has many advantages over handheld mammography such as safety, speed, and higher detection rate of breast cancer. Tumor detection, segmentation, and classification are key components in the analysis of medical images, especially challenging in the context of 3D ABUS due to the significant variability in tumor size and shape, unclear tumor boundaries, and a low signal-to-noise ratio. The lack of publicly accessible, well-labeled ABUS datasets further hinders the advancement of systems for breast tumor analysis. Addressing this gap, we have organized the inaugural Tumor Detection, Segmentation, and Classification Challenge on Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound 2023 (TDSC-ABUS2023). This initiative aims to spearhead research in this field and create a definitive benchmark for tasks associated with 3D ABUS image analysis. In this paper, we summarize the top-performing algorithms from the challenge and provide critical analysis for ABUS image examination. We offer the TDSC-ABUS challenge as an open-access platform at https://tdsc-abus2023.grand-challenge.org/ to benchmark and inspire future developments in algorithmic research.
乳腺癌是全球女性死亡的主要原因之一。早期发现有助于减少死亡人数。自动三维乳腺超声(ABUS)是一种新型的乳腺筛查方法,相对于手持式乳腺X线摄影,它具有安全、快速和更高的乳腺癌检测率等优点。肿瘤检测、分割和分类是医学图像分析的关键组成部分,在3D ABUS的上下文中尤其具有挑战性,这是由于肿瘤大小、形状存在重大差异,肿瘤边界不清,以及信噪比低。缺乏可公开访问、标注良好的ABUS数据集进一步阻碍了乳腺肿瘤分析系统的进步。为解决这一空白,我们组织了首届自动三维乳腺超声肿瘤检测、分割和分类挑战赛(TDSC-ABUS2023)。这一倡议旨在引领该领域的研究,并为与3D ABUS图像分析相关的任务建立明确的基准。本文总结了挑战赛中表现最佳的算法,并对ABUS图像检查进行了关键分析。我们在https://tdsc-abus2023.grand-challenge.org/上提供TDSC-ABUS挑战作为开放访问平台,以评估和激励算法研究的未来发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了乳腺癌的普遍性和早期检测的重要性,重点介绍了自动化3D乳腺超声(ABUS)这一新兴乳腺筛查方法相较于手持式乳腺摄影术的优势。文章指出,肿瘤检测、分割和分类在医学图像分析中的关键作用,特别是在3D ABUS中的挑战。为解决缺乏公开、标注良好的ABUS数据集的问题,举办了首届肿瘤检测、分割和分类挑战赛——自动化3D乳腺超声2023(TDSC-ABUS2023)。该挑战旨在推动该领域的研究,并为3D ABUS图像分析任务建立基准标准。本文总结了挑战中表现最佳的算法,并对ABUS图像检查进行了关键分析。同时提供了TDSC-ABUS挑战的开放访问平台。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌是世界范围内导致女性死亡的主要原因之一,早期发现对减少死亡人数至关重要。
- 自动化3D乳腺超声(ABUS)是一种新兴的乳腺筛查方法,相对于手持式乳腺摄影术具有安全、快速和更高的癌症检测率等优点。
- 肿瘤检测、分割和分类是医学图像分析的关键部分,尤其在3D ABUS中面临挑战,包括肿瘤大小、形状的巨大差异、肿瘤边界不清晰和信噪比低等。
- 缺乏公开、标注良好的ABUS数据集阻碍了乳腺肿瘤分析系统的进展。
- TDSC-ABUS2023挑战赛旨在推动3D ABUS图像分析领域的研究,并建立基准标准。
- 挑战赛中表现最佳的算法被总结在本论文中,并对ABUS图像检查进行了关键分析。
点此查看论文截图

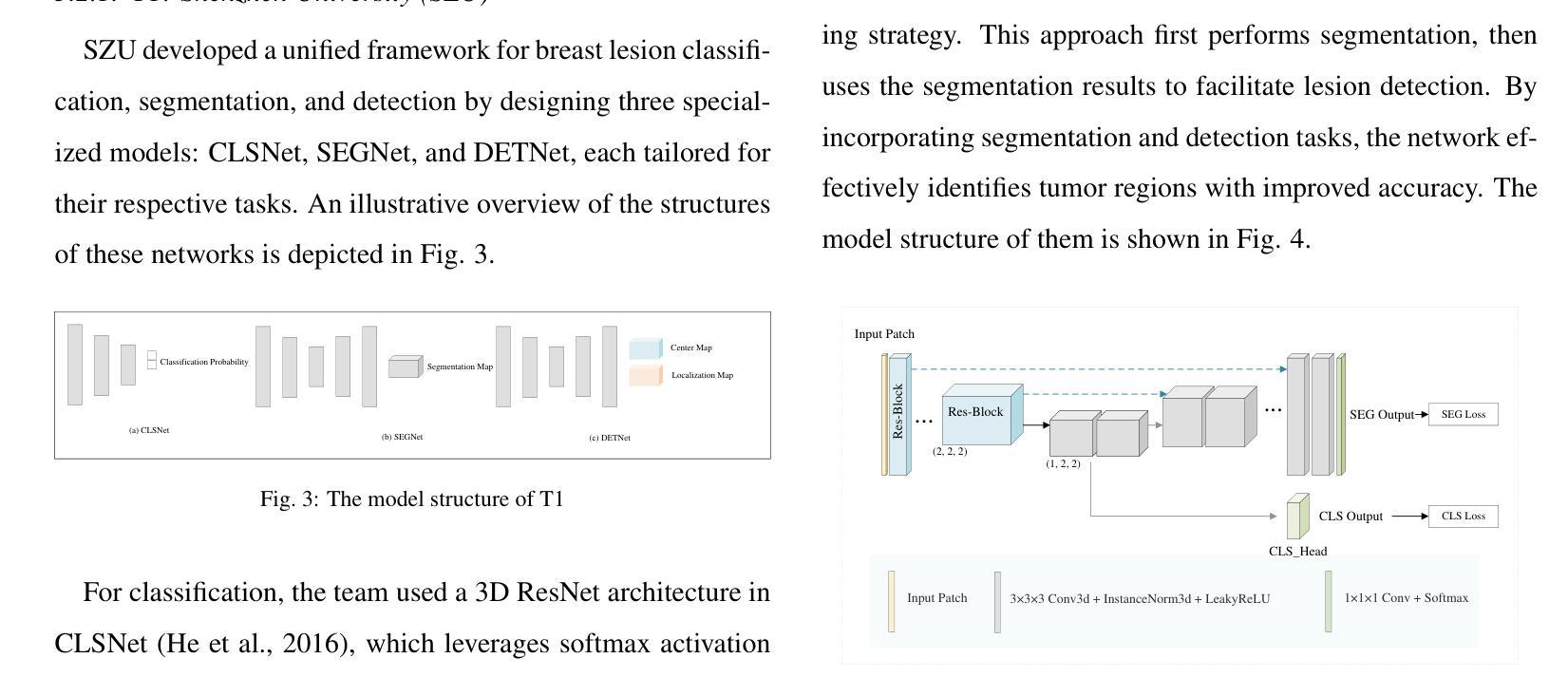
Comparative clinical evaluation of “memory-efficient” synthetic 3d generative adversarial networks (gan) head-to-head to state of art: results on computed tomography of the chest
Authors:Mahshid shiri, Chandra Bortolotto, Alessandro Bruno, Alessio Consonni, Daniela Maria Grasso, Leonardo Brizzi, Daniele Loiacono, Lorenzo Preda
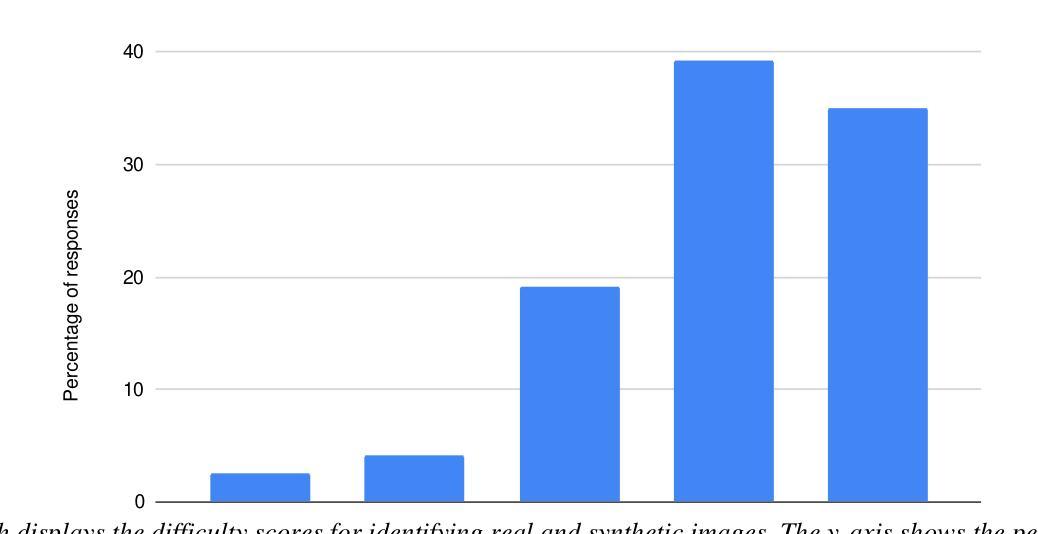
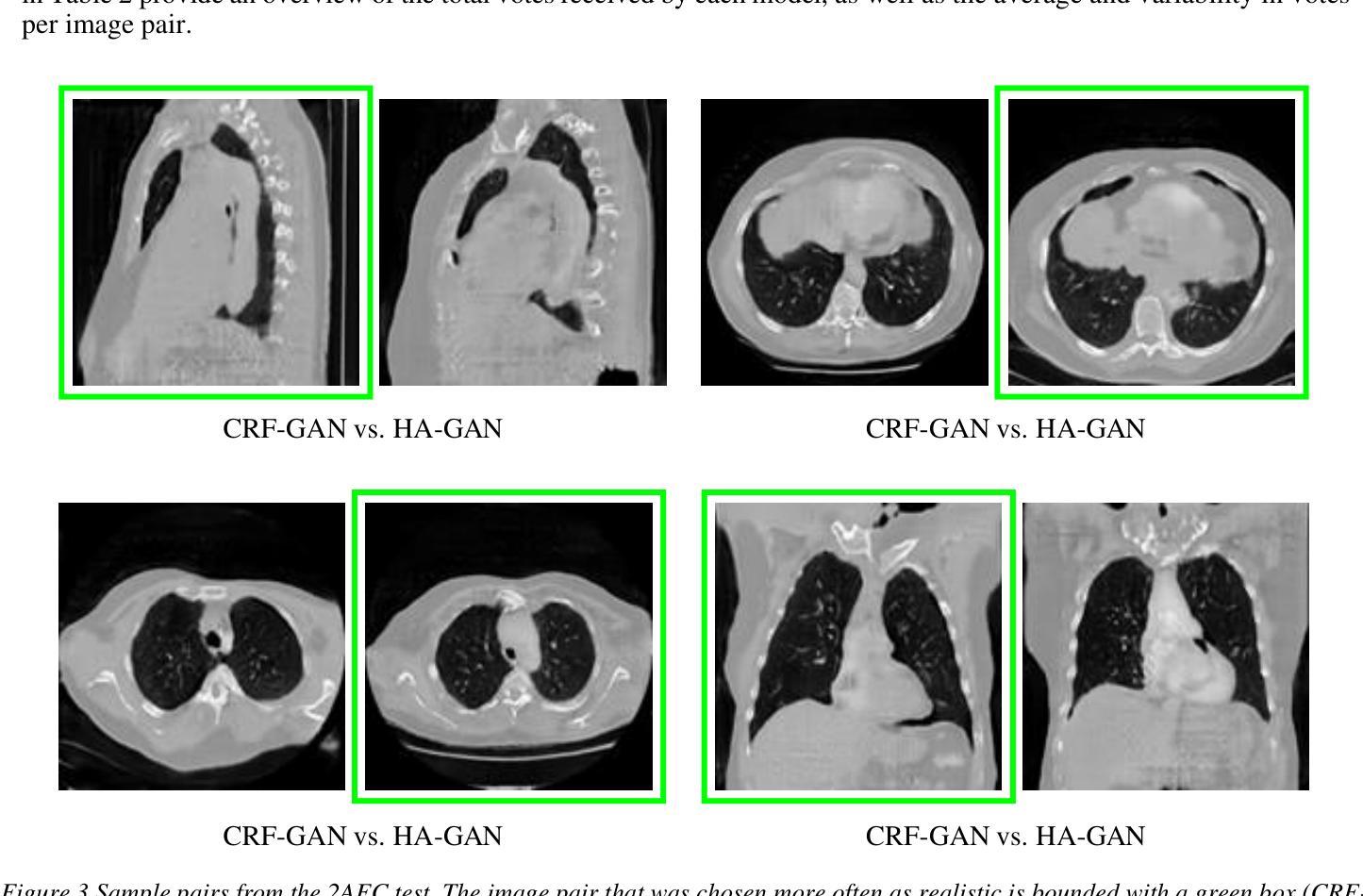
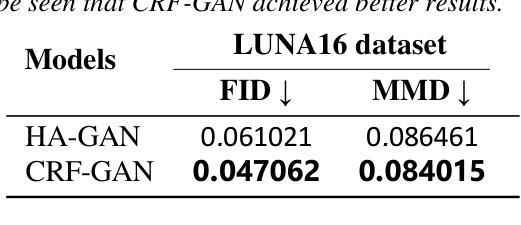
Introduction: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are increasingly used to generate synthetic medical images, addressing the critical shortage of annotated data for training Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems. This study introduces a novel memory-efficient GAN architecture, incorporating Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) to generate high-resolution 3D medical images and evaluates its performance against the state-of-the-art hierarchical (HA)-GAN model. Materials and Methods: The CRF-GAN was trained using the open-source lung CT LUNA16 dataset. The architecture was compared to HA-GAN through a quantitative evaluation, using Frechet Inception Distance (FID) and Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) metrics, and a qualitative evaluation, through a two-alternative forced choice (2AFC) test completed by a pool of 12 resident radiologists, in order to assess the realism of the generated images. Results: CRF-GAN outperformed HA-GAN with lower FID (0.047 vs. 0.061) and MMD (0.084 vs. 0.086) scores, indicating better image fidelity. The 2AFC test showed a significant preference for images generated by CRF-Gan over those generated by HA-GAN with a p-value of 1.93e-05. Additionally, CRF-GAN demonstrated 9.34% lower memory usage at 256 resolution and achieved up to 14.6% faster training speeds, offering substantial computational savings. Discussion: CRF-GAN model successfully generates high-resolution 3D medical images with non-inferior quality to conventional models, while being more memory-efficient and faster. Computational power and time saved can be used to improve the spatial resolution and anatomical accuracy of generated images, which is still a critical factor limiting their direct clinical applicability.
引言:生成对抗网络(GANs)越来越多地被用于生成合成医学图像,以解决训练人工智能(AI)系统时注释数据的严重短缺问题。本研究介绍了一种新的内存高效的GAN架构,它结合了条件随机场(CRFs)来生成高分辨率的3D医学图像,并与最先进的分层(HA)-GAN模型评估其性能。材料与方法:CRF-GAN使用开源的肺部CT LUNA16数据集进行训练。通过与HA-GAN进行定量评估,使用Frechet Inception Distance(FID)和Maximum Mean Discrepancy(MMD)指标,以及定性评估,通过由12名住院医师完成的两种替代强制选择(2AFC)测试,以评估生成图像的真实性。结果:CRF-GAN在FID(0.047 vs 0.061)和MMD(0.084 vs 0.086)得分上优于HA-GAN,表明图像保真度更高。2AFC测试显示,CRF-Gan生成的图像比HA-GAN生成的图像更受欢迎,p值为1.93e-05。此外,CRF-GAN在256分辨率下内存使用率低9.34%,训练速度提高了高达14.6%,从而实现了大量的计算节省。讨论:CRF-GAN模型能够成功生成高分辨率的3D医学图像,其质量与传统模型相当或更好,同时更节省内存、速度更快。所节省的计算能力和时间可用于提高生成图像的空间分辨率和解剖准确性,这仍然是限制其直接临床应用的关键因素。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的优异性能,它已被广泛用于生成合成医学图像以解决训练人工智能系统所需的标注数据短缺的问题。本研究介绍了一种新型的、内存效率高的GAN架构——CRF-GAN,它能生成高分辨率的3D医学图像,并且相较于现有的分层(HA)-GAN模型表现出了更好的性能。CRF-GAN通过定量评估和定性评估两种方法进行了验证,结果证明了其在图像真实感、内存使用和训练速度上的优势。
Key Takeaways
- CRF-GAN结合了条件随机场(CRFs)以生成高分辨率的3D医学图像,该架构为解决医学图像数据短缺的问题提供了新的思路。
- CRF-GAN使用公开的肺部CT LUNA数据集进行训练,显示出出色的图像保真度。
- 与先进的HA-GAN模型相比,CRF-GAN在Frechet Inception Distance (FID)和Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD)两个评估指标上表现更优,显示出更高的图像质量。
- CRF-GAN生成的图像在由放射科医生进行的真实感测试中获得了显著偏好。
- CRF-GAN具有更低的内存使用率和更快的训练速度,具备更大的实用价值。
- 计算能力的节省可用于提升生成图像的空间分辨率和解剖精度,这在直接应用于临床时尤为重要。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Self-Supervised Grading of Prostate Cancer Pathology
Authors:Riddhasree Bhattacharyya, Surochita Pal Das, Sushmita Mitra
Prostate cancer grading using the ISUP system (International Society of Urological Pathology) for treatment decisions is highly subjective and requires considerable expertise. Despite advances in computer-aided diagnosis systems, few have handled efficient ISUP grading on Whole Slide Images (WSIs) of prostate biopsies based only on slide-level labels. Some of the general challenges include managing gigapixel WSIs, obtaining patch-level annotations, and dealing with stain variability across centers. One of the main task-specific challenges faced by deep learning in ISUP grading, is the learning of patch-level features of Gleason patterns (GPs) based only on their slide labels. In this scenario, an efficient framework for ISUP grading is developed. The proposed TSOR is based on a novel Task-specific Self-supervised learning (SSL) model, which is fine-tuned using Ordinal Regression. Since the diversity of training samples plays a crucial role in SSL, a patch-level dataset is created to be relatively balanced w.r.t. the Gleason grades (GGs). This balanced dataset is used for pre-training, so that the model can effectively learn stain-agnostic features of the GP for better generalization. In medical image grading, it is desirable that misclassifications be as close as possible to the actual grade. From this perspective, the model is then fine-tuned for the task of ISUP grading using an ordinal regression-based approach. Experimental results on the most extensive multicenter prostate biopsies dataset (PANDA challenge), as well as the SICAP dataset, demonstrate the effectiveness of this novel framework compared to state-of-the-art methods.
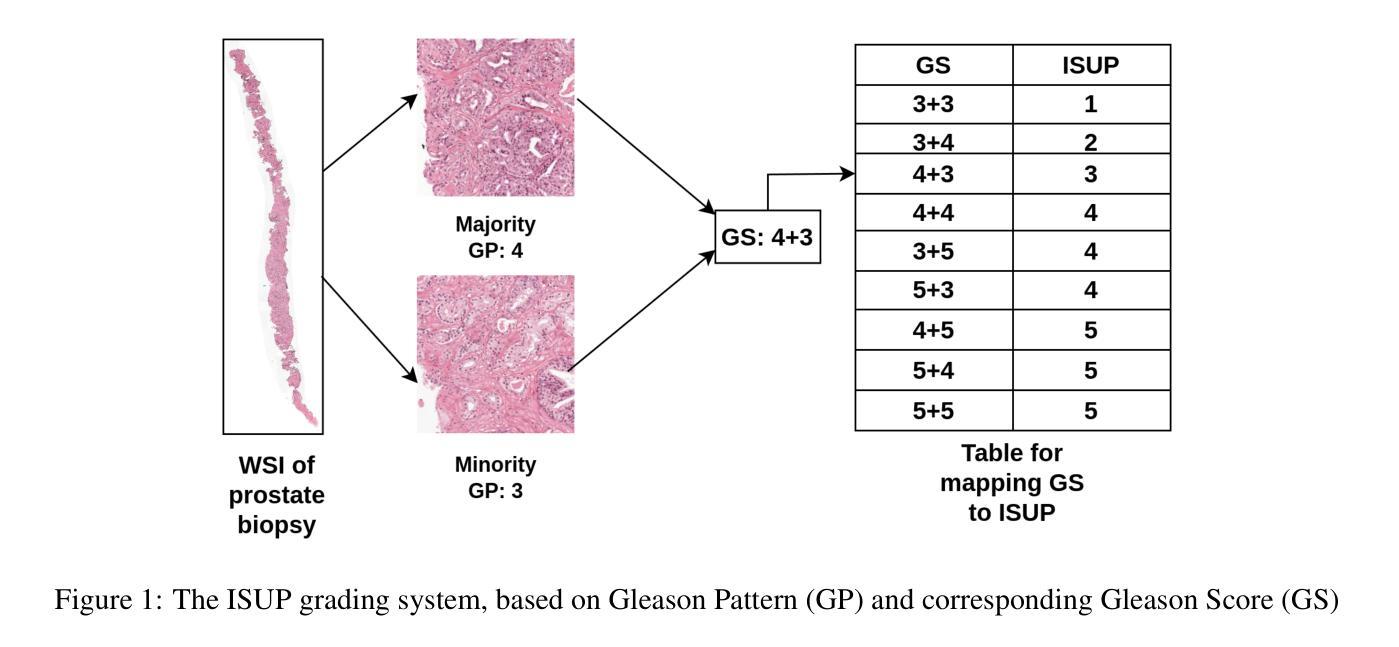
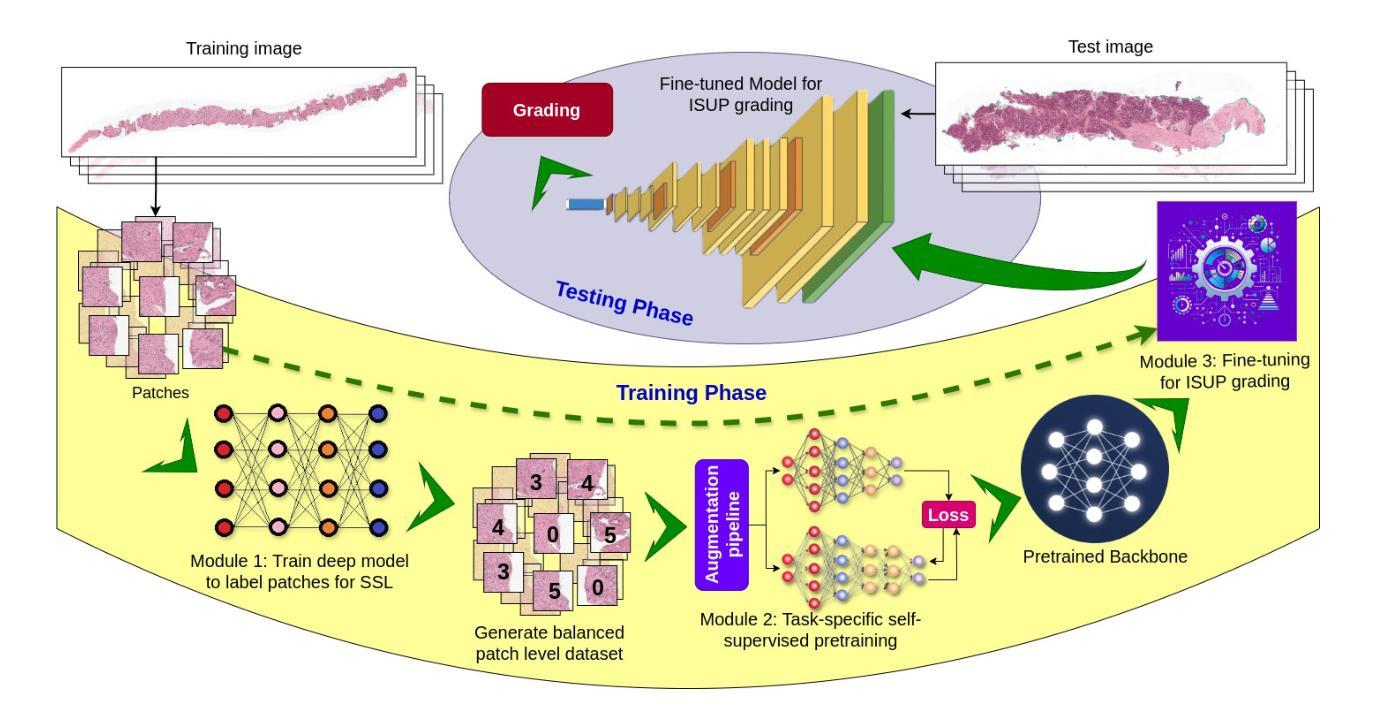
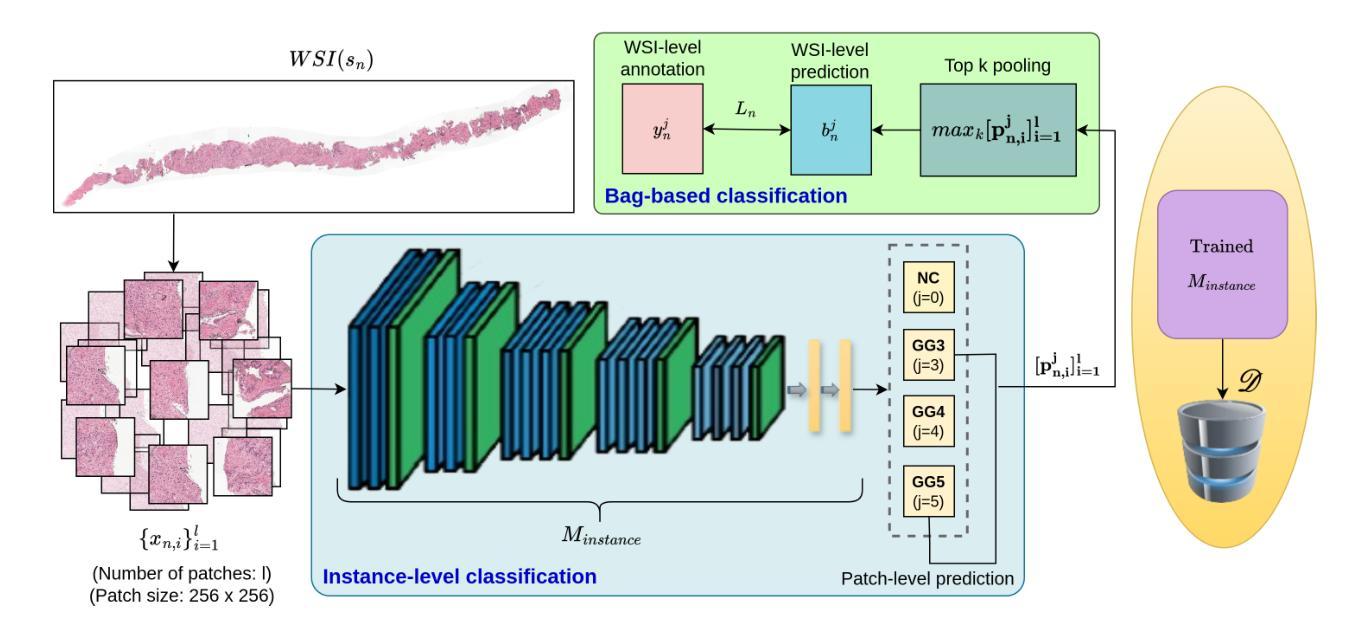
使用国际泌尿病理学学会(ISUP)系统对前列腺癌进行分级以做出治疗决策是非常主观的,并且需要相当的专业知识。尽管计算机辅助诊断系统有所进步,但很少有人能有效地处理基于前列腺活检全切片图像(WSI)的ISUP分级,仅仅基于切片级别的标签。一些通用挑战包括处理千兆像素的WSI、获取补丁级别的注释以及处理跨中心的染色变量。深度学习在ISUP分级中面临的主要任务特定挑战之一是,仅基于其切片标签学习Gleason模式(GP)的补丁级别特征。针对这种情况,开发了一个有效的ISUP分级框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于任务特定自监督学习(SSL)模型的全新框架,用于前列腺癌分级。该框架通过序数回归进行微调,并创建了一个相对平衡的补丁级别数据集,以提高模型的泛化能力。在医学图像分级中,该模型能够将误分类尽可能接近实际等级。在多中心前列腺活检数据集(PANDA挑战数据集)以及SICAP数据集上的实验结果表明,该框架相较于现有先进技术更为有效。
Key Takeaways
- 前列腺癌分级采用国际泌尿病理学会(ISUP)系统对于治疗决策至关重要,但存在主观性和挑战。
- 计算机辅助诊断系统在处理全幻灯片图像(WSIs)的ISUP分级方面有所进展,但仍面临处理gigapixel WSIs、获取补丁级别注释和应对不同中心染色变异的挑战。
- 深度学习在ISUP分级中的主要挑战是学习基于幻灯片标签的补丁级别的格莱森模式(GP)的特征。
- 提出了一种基于任务特定自监督学习(SSL)模型的框架,通过序数回归微调进行前列腺癌的ISUP分级。
- 创建了一个相对平衡的补丁级别数据集,以提高模型的泛化能力,并关注染色无关的特征学习。
- 模型在多中心前列腺活检数据集(如PANDA挑战数据集)和SICAP数据集上的实验结果表明其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

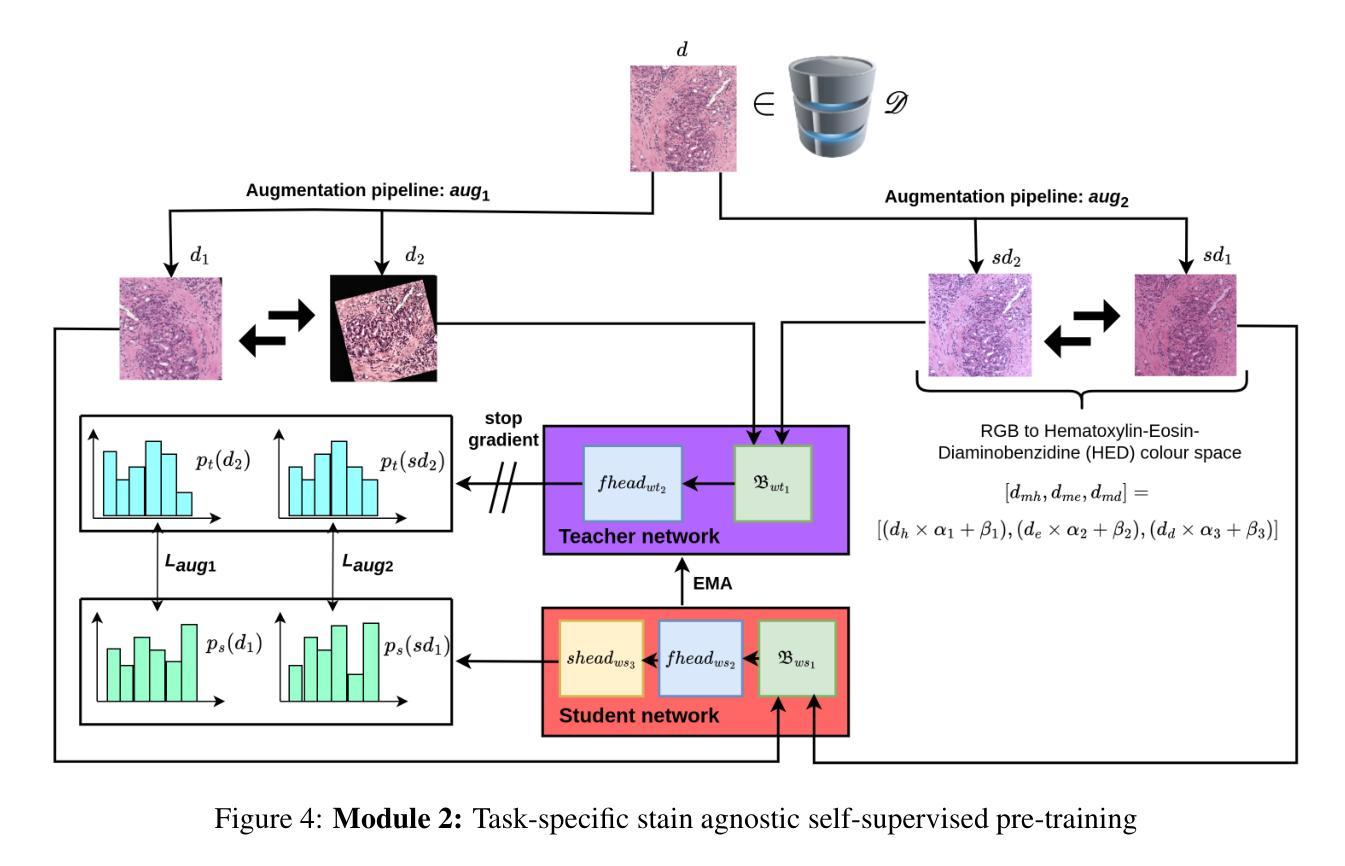
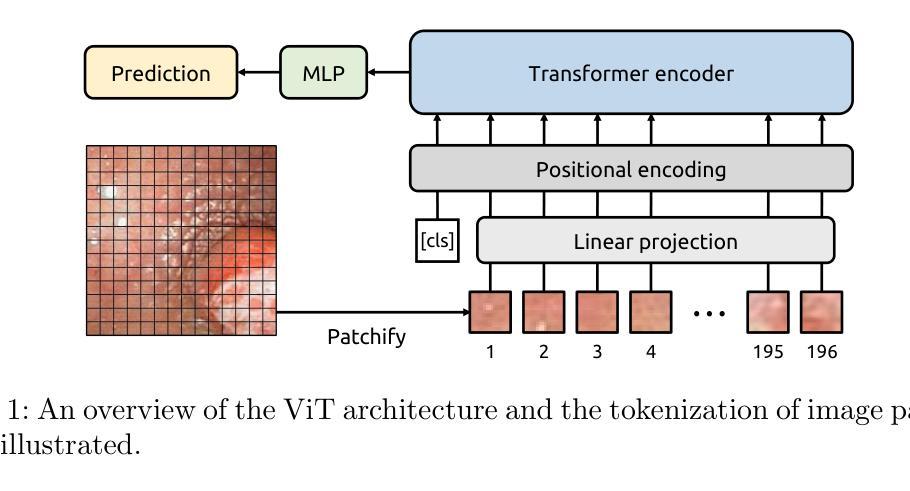
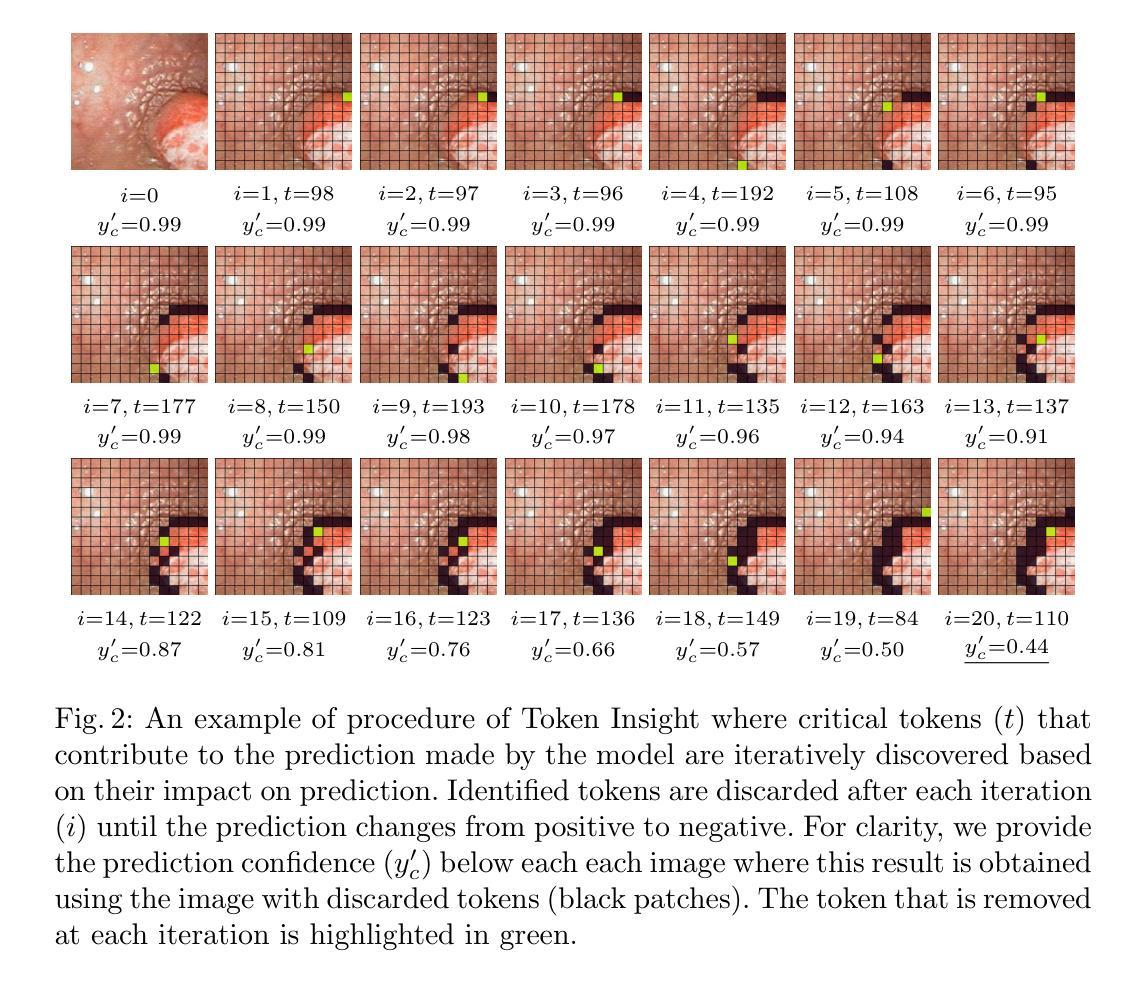
Identifying Critical Tokens for Accurate Predictions in Transformer-based Medical Imaging Models
Authors:Solha Kang, Joris Vankerschaver, Utku Ozbulak
With the advancements in self-supervised learning (SSL), transformer-based computer vision models have recently demonstrated superior results compared to convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and are poised to dominate the field of artificial intelligence (AI)-based medical imaging in the upcoming years. Nevertheless, similar to CNNs, unveiling the decision-making process of transformer-based models remains a challenge. In this work, we take a step towards demystifying the decision-making process of transformer-based medical imaging models and propose Token Insight, a novel method that identifies the critical tokens that contribute to the prediction made by the model. Our method relies on the principled approach of token discarding native to transformer-based models, requires no additional module, and can be applied to any transformer model. Using the proposed approach, we quantify the importance of each token based on its contribution to the prediction and enable a more nuanced understanding of the model’s decisions. Our experimental results which are showcased on the problem of colonic polyp identification using both supervised and self-supervised pretrained vision transformers indicate that Token Insight contributes to a more transparent and interpretable transformer-based medical imaging model, fostering trust and facilitating broader adoption in clinical settings.
随着自监督学习(SSL)的进步,基于转换器的计算机视觉模型最近展现出比卷积神经网络(CNNs)更优越的结果,并有望在接下来的几年内在基于人工智能(AI)的医疗成像领域占据主导地位。然而,与CNN类似,揭示基于转换器模型的决策过程仍然是一个挑战。在这项工作中,我们朝着揭示基于转换器医疗成像模型的决策过程迈出了一步,并提出了一种名为“Token Insight”的新方法,该方法可以识别对模型预测做出贡献的关键令牌。我们的方法依赖于基于转换器模型的固有令牌丢弃原则性方法,无需额外的模块,并且可以应用于任何转换器模型。通过使用所提出的方法,我们根据每个令牌对预测的贡献来量化其重要性,并实现对模型决策的更微妙理解。我们在结肠息肉识别问题上展示的实验结果,使用监督学习和自监督预训练的视觉转换器都表明,Token Insight有助于创建更透明、可解释的基于转换器的医疗成像模型,增强信任,促进在临床环境中的更广泛应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in MICCAI 2024 Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging (MLMI)
Summary
随着自监督学习(SSL)的发展,基于转换器的计算机视觉模型在医疗图像领域展现出优于卷积神经网络(CNNs)的结果,并有望在接下来的几年内在人工智能医疗成像领域占据主导地位。然而,揭开基于转换器模型的决策过程仍然是一个挑战。本研究朝着解密基于转换器的医疗成像模型的决策过程迈出了一步,提出了一种名为Token Insight的新方法,可识别对模型预测至关重要的关键令牌。我们的方法依赖于转换器模型特有的令牌丢弃原则,无需额外的模块,可应用于任何转换器模型。通过所提出的方法,我们根据每个令牌对预测的贡献来量化其重要性,使我们对模型的决策有更细致的理解。我们在结肠息肉识别问题上展示了使用监督学习和自监督预训练视觉转换器的方法,结果表明Token Insight有助于建立更透明、可解释的基于转换器的医疗成像模型,增强信任,便于在临床环境中更广泛的应用。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督学习在医疗图像领域推动了基于转换器模型的进步,使其有望在未来几年内主导人工智能医疗成像领域。
- 基于转换器的模型决策过程仍然是一个挑战,需要更深入的理解和解释。
- 提出了一种名为Token Insight的新方法,用于识别对模型预测至关重要的关键令牌。
- Token Insight方法基于转换器模型的令牌丢弃原则,无需额外的模块,具有广泛的应用性。
- Token Insight能够量化每个令牌对预测的贡献,提供更深入的模型决策理解。
- 在结肠息肉识别问题上的实验结果表明,Token Insight有助于提高模型的透明度和可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

Gland Segmentation Using SAM With Cancer Grade as a Prompt
Authors:Yijie Zhu, Shan E Ahmed Raza
Cancer grade is a critical clinical criterion that can be used to determine the degree of cancer malignancy. Revealing the condition of the glands, a precise gland segmentation can assist in a more effective cancer grade classification. In machine learning, binary classification information about glands (i.e., benign and malignant) can be utilized as a prompt for gland segmentation and cancer grade classification. By incorporating prior knowledge of the benign or malignant classification of the gland, the model can anticipate the likely appearance of the target, leading to better segmentation performance. We utilize Segment Anything Model to solve the segmentation task, by taking advantage of its prompt function and applying appropriate modifications to the model structure and training strategies. We improve the results from fine-tuned Segment Anything Model and produce SOTA results using this approach.
癌症分级是一个重要的临床标准,可以用来确定癌症的恶性程度。精确的腺体分割可以揭示腺体的状况,从而有助于更有效地进行癌症分级分类。在机器学习中,关于腺体(即良性和恶性)的二元分类信息可以作为腺体分割和癌症分级分类的提示。通过结合腺体良恶性分类的先验知识,模型可以预测目标的可能外观,从而提高分割性能。我们利用Segment Anything Model解决分割任务,通过发挥其提示功能并对模型结构和训练策略进行适当的修改。我们改进了微调后的Segment Anything Model的结果,并使用这种方法取得了最先进的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISBI 2025
Summary
癌症分级是判断癌症恶性程度的关键临床标准。精确的腺体分割有助于更精确地划分癌症等级。在机器学习中,可以利用腺体(良性或恶性)的二元分类信息,通过模型预测目标的可能外观,提高分割性能。我们利用Segment Anything Model解决分割任务,通过调整模型结构和训练策略,改进了fine-tuned Segment Anything Model的结果,取得目前最先进的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症分级是评估癌症恶性程度的重要临床标准。
- 精确的腺体分割有助于更准确地评估癌症等级。
- 在机器学习中,可以利用腺体的二元分类信息来进行腺体分割和癌症等级分类。
- 通过结合腺体的良性或恶性分类的先验知识,模型可以更好地预测目标的可能外观,从而提高分割性能。
- Segment Anything Model被用于解决分割任务。
- 我们通过调整模型结构和训练策略,改进了fine-tuned Segment Anything Model的结果。
点此查看论文截图

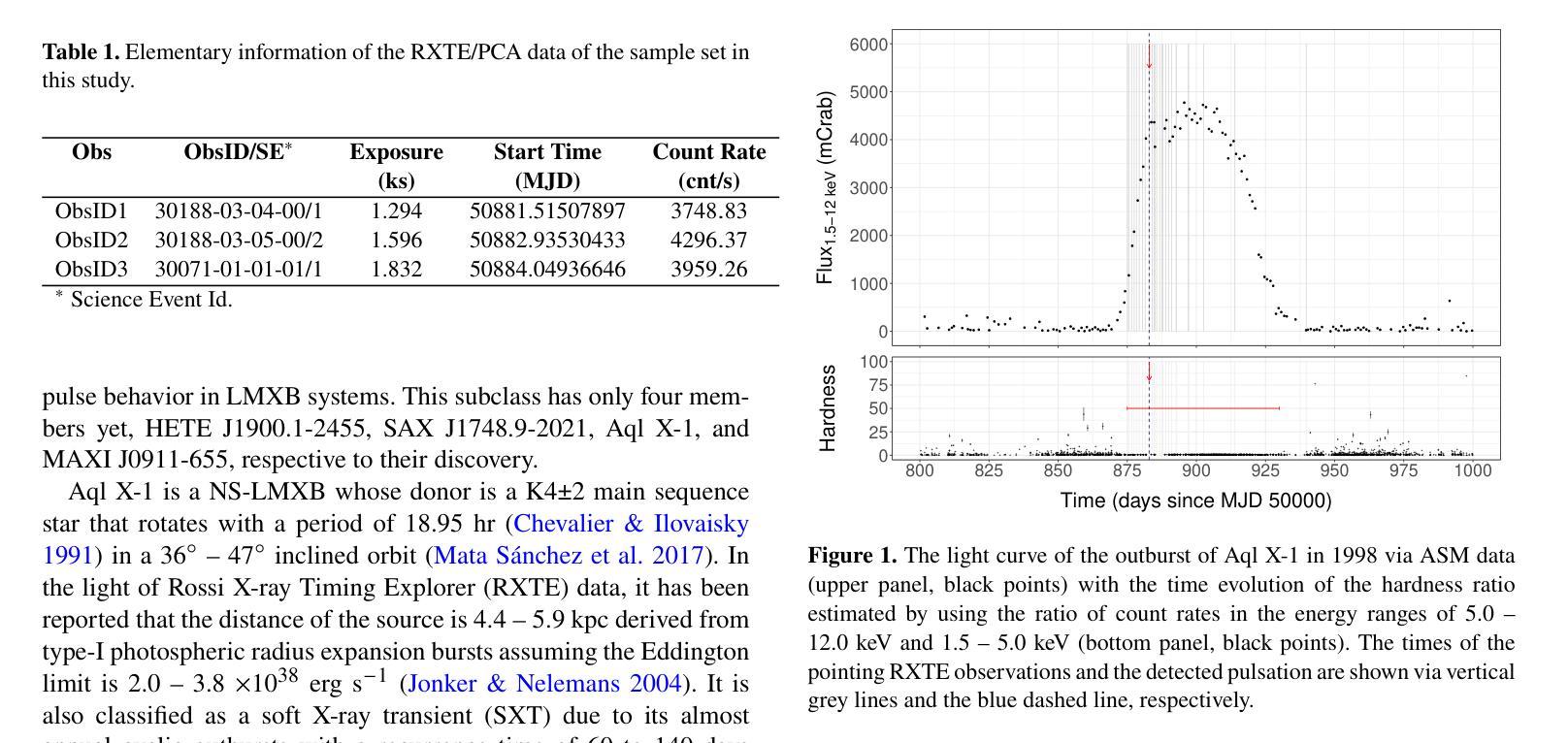
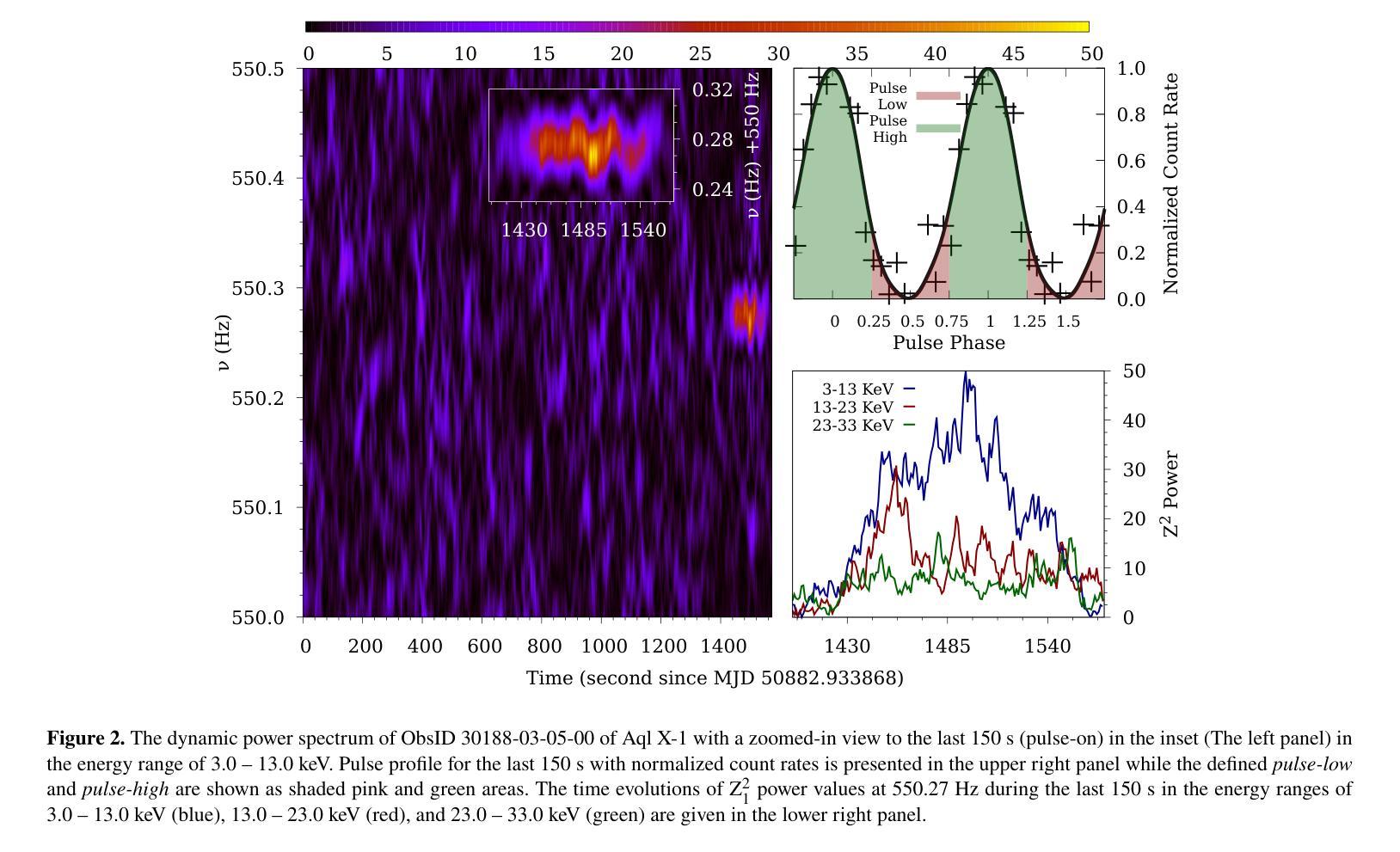
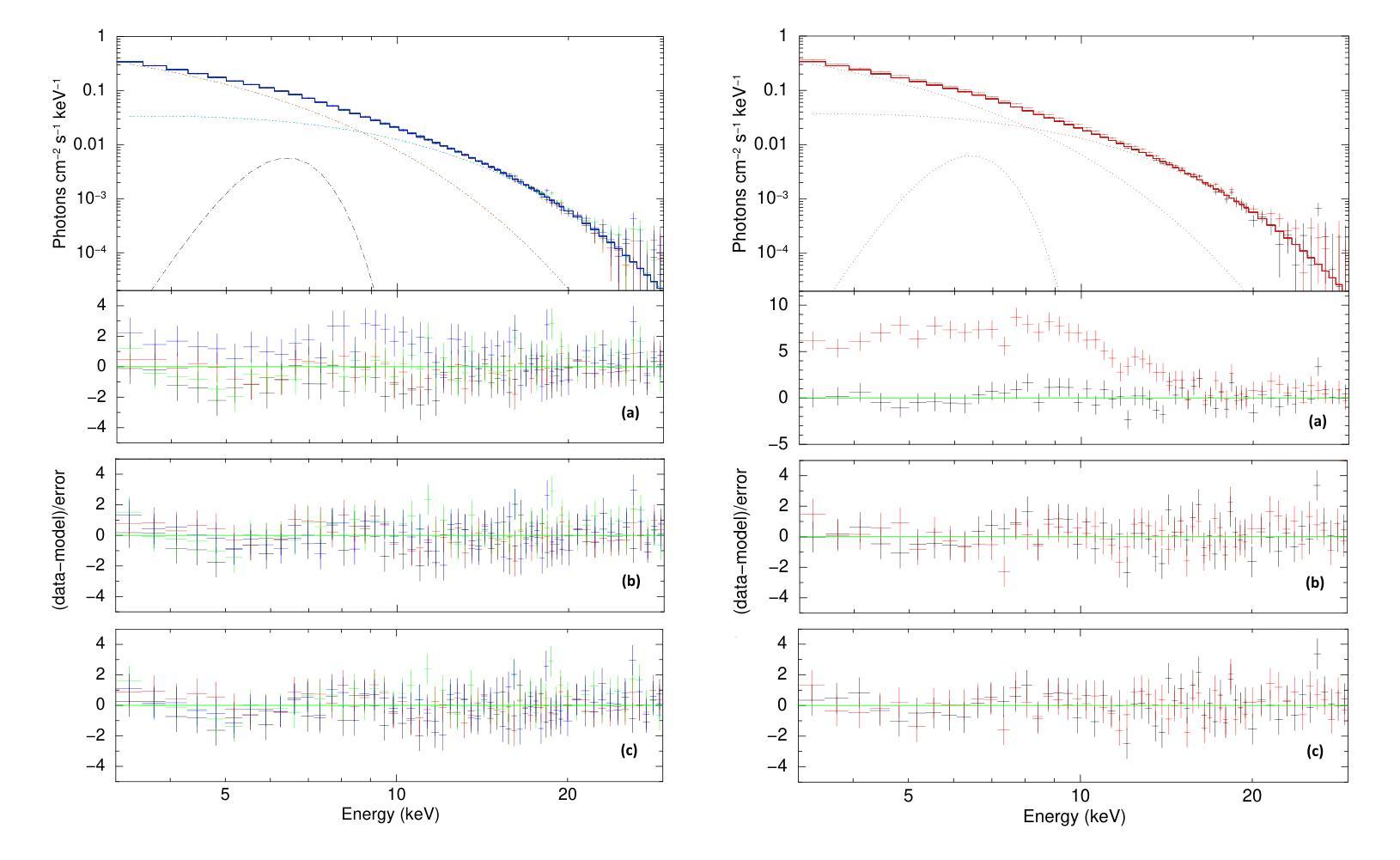
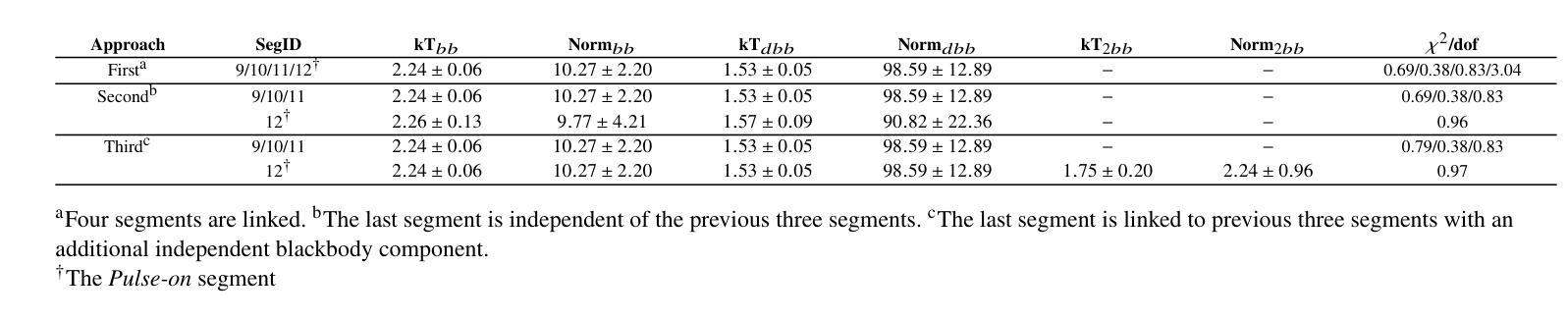
A Detailed Spectral Study of Intermittent-Accreting Millisecond X-ray Pulsar Aql X-1 during Pulse-on and Pulse-off Stages
Authors:T. Kocabıyık, C. Güngör, M. T. Sağlam, T. Güver, Z. F. Bostancı
We present a detailed spectral study of an intermittent-AMXP Aql X-1 during the pulse-on and pulse-off stages by using the archival RXTE data. We first perform temporal analysis by using Z$_n^2$ technique in three different energy bands, 3.0 – 13.0 keV, 13.0 – 23.0 keV and 23.0 – 33.0 keV, for the last 128 s time segment of the RXTE data including pulse-on region. We show that the pulse is the most significant in the softest band. We, then, show that the spectrum is represented the best via combination of absorbed blackbody, disk blackbody and a gaussian line. We modeled the last four segments of the data 30188-03-05-00 to better compare pulse-on and pulse-off stages. We found a vague residual in the spectral fit of the pulse-on segment between $\sim$3.0 – 13.0 keV which agrees with the result of temporal analysis. We show that the residual may be represented with an extra blackbody component with the temperature of 1.75 keV and the radius of 0.75$\pm$0.49 km. For deeper analysis, we performed phase-resolved spectroscopy to the last 128 s, pulse-on, segment. We obtain two separate spectra for the spin phase range of 0.75 – 0.25, pulse-high and 0.25 – 0.75, pulse-low and followed the same procedure. We display that the residual becomes more clear for pulse-high compared to the pulse-low. We report that the additional blackbody component, which models the residual, indicates a hotspot from the surface of the neutron star with the radius of 1.65$\pm$0.74 km whose temperature is 1.65 keV.
我们对间歇型AMXP水委一(Aql X-1)在脉冲开启和脉冲关闭阶段进行了详细的光谱研究,使用的是档案中的RXTE数据。我们首先使用$Z_n^2$技术,在三个不同的能段(3.0-13.0 keV、13.0-23.0 keV和23.0-33.0 keV)对包括脉冲开启区域在内的RXTE数据最后128秒的时间段进行时间分析。我们显示脉冲在最软的波段中最为显著。接着,我们展示光谱最好用吸收的黑体、盘黑体和一条高斯线组合表示。我们对数据最后四个片段(编号30188-03-05-00)进行建模,以便更好地比较脉冲开启和脉冲关闭阶段。我们在脉冲开启段约3.0-13.0 keV的光谱拟合中发现了模糊的残差,这与时间分析结果一致。我们表明,残差可以用额外的黑体成分来表示,其温度为1.75 keV,半径为0.75±0.49公里。为了进行更深入的分析,我们对最后128秒的脉冲开启段执行了相位解析光谱。我们为脉冲相位范围分别为0.75-0.25(脉冲高)和0.25-0.75(脉冲低)的两个阶段获得了两个独立光谱,并遵循了相同的程序。我们显示与脉冲低相比,脉冲高的残差变得更加清晰。我们报告说,额外的黑体成分模拟了残差,并指示来自中子星表面的热点,其半径为1.65±0.74公里,温度为1.65 keV。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in MNRAS. 7 Pages, 4 Figures
Summary
利用RXTE数据对间歇性AMXP Aql X-1的脉冲开启和脉冲关闭阶段进行了详细的谱研究。通过对不同能量段的时序分析,发现脉冲在较软波段最为显著。谱拟合采用吸收黑体、盘黑体和高斯线组合表示最佳。对比脉冲开启和脉冲关闭阶段,发现在特定能量段的谱拟合存在模糊残留,可通过额外的黑体组件进行建模,表示来自中子星表面的热点。
Key Takeaways
- 使用RXTE数据对Aql X-1的脉冲开启和脉冲关闭阶段进行了详细谱研究。
- 在不同能量段进行时序分析,发现最显著的脉冲位于较软波段。
- 谱可最佳表示为吸收黑体、盘黑体和高斯线组合。
- 对比脉冲开启和脉冲关闭阶段,发现特定能量段的谱拟合存在模糊残留。
- 模糊残留可通过额外的黑体组件进行建模,表示中子星表面的热点。
- 额外黑体组件的半径约为1.65±0.74公里,温度为1.65千电子伏特。
点此查看论文截图

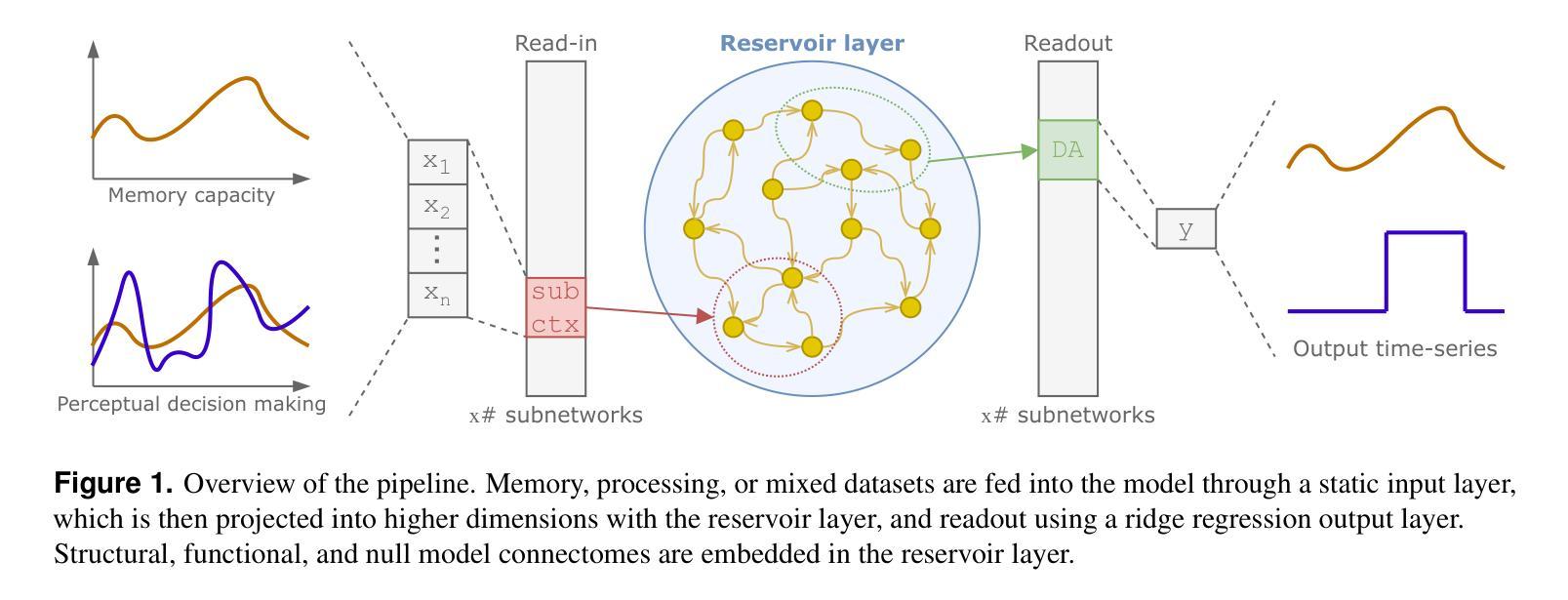
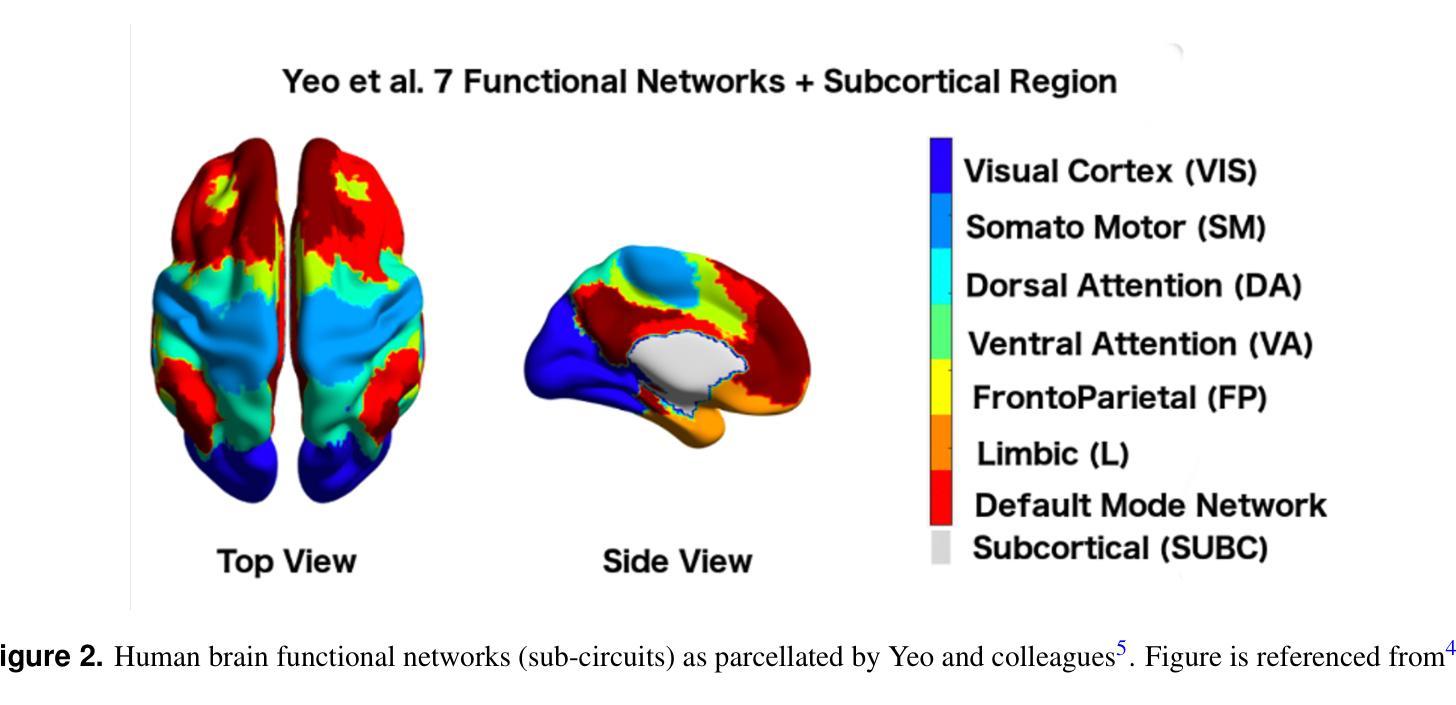
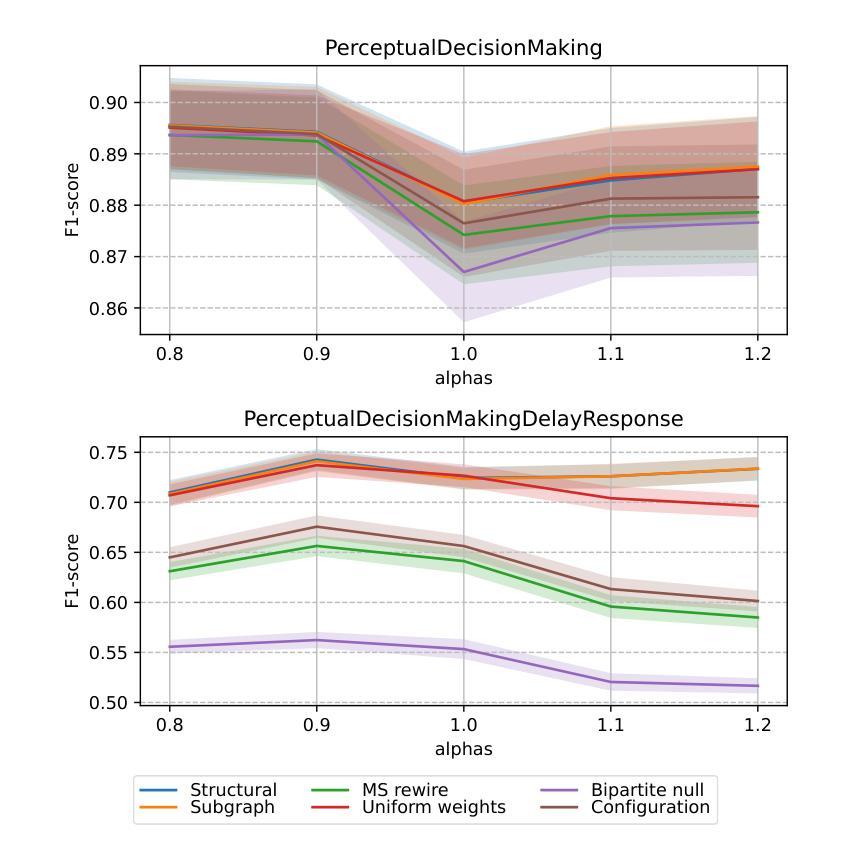
Accessing the topological properties of human brain functional sub-circuits in Echo State Networks
Authors:Bach Nguyen, Tianlong Chen, Shu Yang, Bojian Hou, Li Shen, Duy Duong-Tran
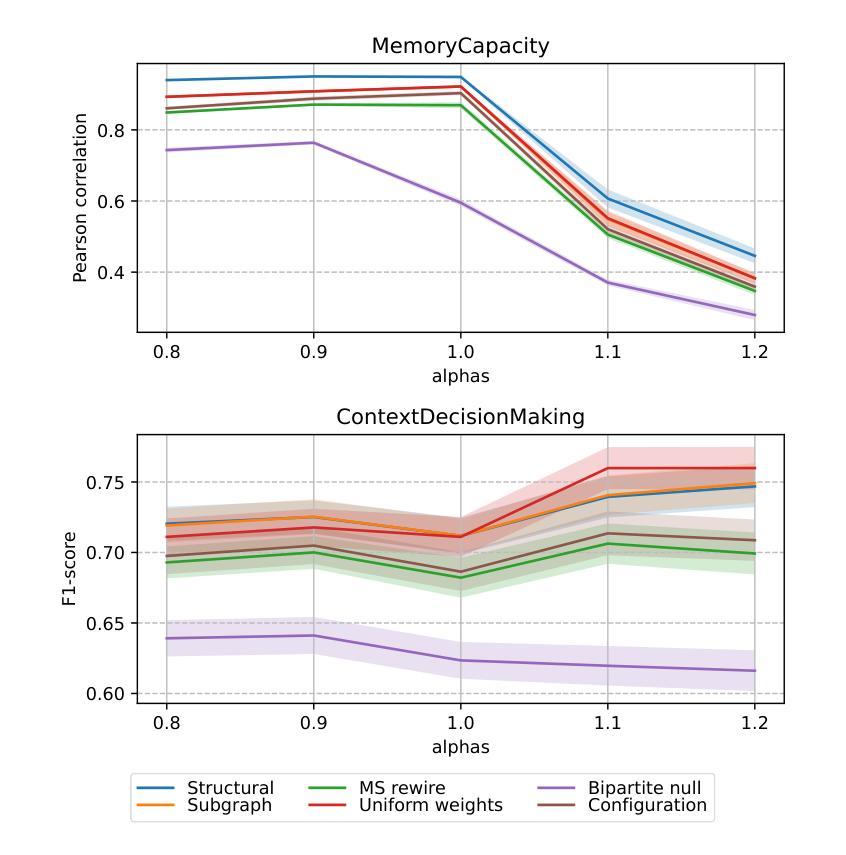
Recent years have witnessed an emerging trend in neuromorphic computing that centers around the use of brain connectomics as a blueprint for artificial neural networks. Connectomics-based neuromorphic computing has primarily focused on embedding human brain large-scale structural connectomes (SCs), as estimated from diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging (dMRI) modality, to echo-state networks (ESNs). A critical step in ESN embedding requires pre-determined read-in and read-out layers constructed by the induced subgraphs of the embedded reservoir. As \textit{a priori} set of functional sub-circuits are derived from functional MRI (fMRI) modality, it is unknown, till this point, whether the embedding of fMRI-induced sub-circuits/networks onto SCs is well justified from the neuro-physiological perspective and ESN performance across a variety of tasks. This paper proposes a pipeline to implement and evaluate ESNs with various embedded topologies and processing/memorization tasks. To this end, we showed that different performance optimums highly depend on the neuro-physiological characteristics of these pre-determined fMRI-induced sub-circuits. In general, fMRI-induced sub-circuit-embedded ESN outperforms simple bipartite and various null models with feed-forward properties commonly seen in MLP for different tasks and reservoir criticality conditions. We provided a thorough analysis of the topological properties of pre-determined fMRI-induced sub-circuits and highlighted their graph-theoretical properties that play significant roles in determining ESN performance.
近年来,神经形态计算领域出现了一种以脑连接组作为人工神经网络蓝图的新兴趋势。基于连接组的神经形态计算主要侧重于将基于扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)技术估计得到的大规模人类脑结构连接组(SCs)嵌入回声状态网络(ESNs)。在ESN嵌入过程中,一个关键步骤是构建由嵌入存储库中的诱导子图构成的预定义读入和读出层。由于先验的功能性子电路是从功能磁共振成像(fMRI)技术中派生出来的,到目前为止,尚不清楚从神经生理学角度将fMRI诱导的子电路/网络嵌入到结构连接组是否合理,以及在不同任务中ESN的性能表现如何。本文提出了一种实现和评估具有不同嵌入拓扑结构和处理/记忆任务的ESNs的管道。为此,我们表明不同的性能最优值在很大程度上取决于这些预先确定的fMRI诱导的子电路的神经生理学特征。总体而言,基于fMRI诱导的子电路嵌入的ESN在多种任务下优于常见于多层感知器的前馈特性的简单二分图和各种空模型,并且适应于存储库的关键条件。我们对预先确定的fMRI诱导的子电路进行了彻底的分析,并重点介绍了它们在确定ESN性能中发挥重要作用的图论属性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 12 figures
Summary
本文介绍了基于脑连接组(connectomics)的类脑计算趋势,重点研究将人类大脑的大规模结构连接体(SCs)嵌入回声状态网络(ESNs)的方法。文章提出了一个实施和评估具有不同嵌入拓扑结构和处理/记忆任务的ESNs的管道,并探讨了基于fMRI诱导的子电路嵌入对ESN性能的影响。研究发现,不同任务的最优性能高度依赖于这些预定义的fMRI诱导子电路的神经生理学特性。总体上,fMRI诱导的子电路嵌入的ESN在不同任务和储备池临界条件下,表现出优于简单的前馈多层感知机(MLP)模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前趋势:利用脑连接组作为人工神经网络蓝图,进行类脑计算研究。
- 研究重点:将人类大脑结构连接体嵌入回声状态网络(ESN)。
- ESN嵌入的关键步骤:需要预定义的读写层,由嵌入储备库诱导的子图构建。
- 研究空白:尚不清楚从神经生理学角度将fMRI诱导的子电路/网络嵌入SC是否合理。
- 研究方法:提出一个管道来实施和评估具有不同嵌入拓扑结构和处理任务的ESNs。
- 实验结果:fMRI诱导的子电路嵌入的ESN在不同任务中表现出更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

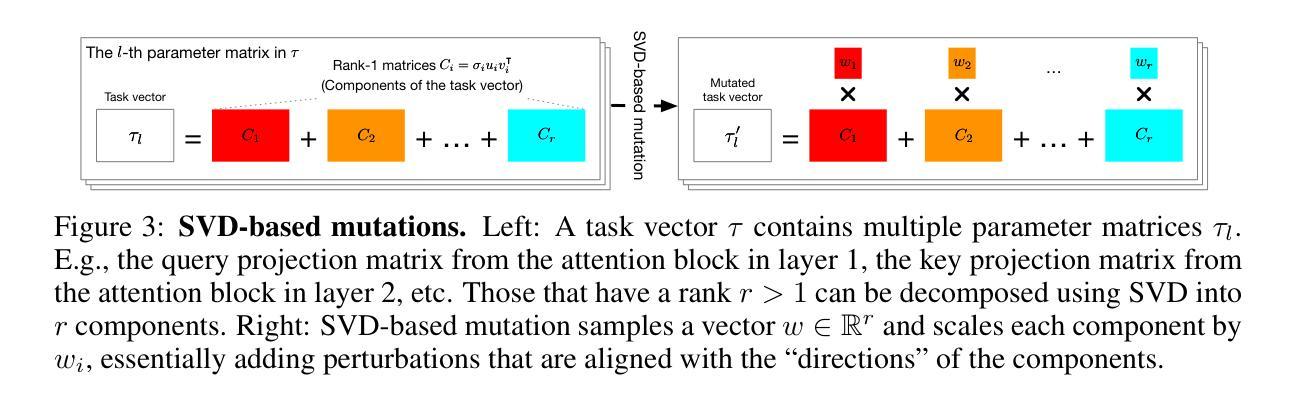
Agent Skill Acquisition for Large Language Models via CycleQD
Authors:So Kuroki, Taishi Nakamura, Takuya Akiba, Yujin Tang
Training large language models to acquire specific skills remains a challenging endeavor. Conventional training approaches often struggle with data distribution imbalances and inadequacies in objective functions that do not align well with task-specific performance. To address these challenges, we introduce CycleQD, a novel approach that leverages the Quality Diversity framework through a cyclic adaptation of the algorithm, along with a model merging based crossover and an SVD-based mutation. In CycleQD, each task’s performance metric is alternated as the quality measure while the others serve as the behavioral characteristics. This cyclic focus on individual tasks allows for concentrated effort on one task at a time, eliminating the need for data ratio tuning and simplifying the design of the objective function. Empirical results from AgentBench indicate that applying CycleQD to LLAMA3-8B-INSTRUCT based models not only enables them to surpass traditional fine-tuning methods in coding, operating systems, and database tasks, but also achieves performance on par with GPT-3.5-TURBO, which potentially contains much more parameters, across these domains. Crucially, this enhanced performance is achieved while retaining robust language capabilities, as evidenced by its performance on widely adopted language benchmark tasks. We highlight the key design choices in CycleQD, detailing how these contribute to its effectiveness. Furthermore, our method is general and can be applied to image segmentation models, highlighting its applicability across different domains.
训练大型语言模型以获取特定技能仍然是一项具有挑战性的工作。传统的训练方法常常面临数据分布不平衡和客观函数与目标特定性能不匹配的问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了CycleQD这一新方法,它利用质量多样性框架,通过算法的循环适应,结合基于模型合并的交叉和基于SVD的突变。在CycleQD中,每个任务的性能指标被交替用作质量度量,而其他任务则作为行为特征。这种对单个任务的循环关注允许每次集中精力完成一个任务,从而消除了对数据比率调整的需求,并简化了目标函数的设计。来自AgentBench的经验结果表明,将CycleQD应用于LLAMA3-8B-INSTRUCT基础模型,不仅能使它们在编码、操作系统和数据库任务上超越传统的微调方法,而且在这几个领域实现了与GPT-3.5-TURBO相当的性能,尽管GPT-3.5-TURBO可能包含更多的参数。关键的是,这种增强的性能是在保留稳健的语言能力的同时实现的,这在其广泛采用的语言基准任务上的表现得到了证明。我们强调了CycleQD中的关键设计选择,详细说明了这些是如何促成其有效性的。此外,我们的方法是通用的,可应用于图像分割模型,突出了其在不同领域的应用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)
Summary
CycleQD是一种针对大型语言模型的新型训练方法,旨在解决传统训练方式面临的挑战,如数据分布不均衡和目标函数与特定任务性能不匹配的问题。它通过质量多样性框架的循环适应算法、模型合并基础上的交叉以及SVD基础上的突变来实现。CycleQD能集中关注单一任务,简化目标函数设计,减少数据比率调整的需要。在AgentBench上的实验结果显示,对LLAMA3-8B-INSTRUCT基础模型应用CycleQD,在编码、操作系统和数据库任务上超越了传统微调方法,性能与GPT-3.5-TURBO相当。同时,该方法保留了强大的语言能力,并在广泛采用的语言基准任务上表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- CycleQD是一种针对大型语言模型的新型训练方法。
- CycleQD解决了传统训练方式中的数据分布不均衡和目标函数与任务性能不匹配的问题。
- CycleQD通过质量多样性框架的循环适应算法、模型合并基础上的交叉和SVD基础上的突变来实现。
- CycleQD能集中关注单一任务,简化目标函数设计,减少数据比率调整的需要。
- 在AgentBench的实验中,应用CycleQD的模型在编码、操作系统和数据库任务上超越了传统微调方法。
- CycleQD的性能与GPT-3.5-TURBO相当,同时保留了强大的语言能力。
- CycleQD方法在广泛采用的语言基准任务上表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

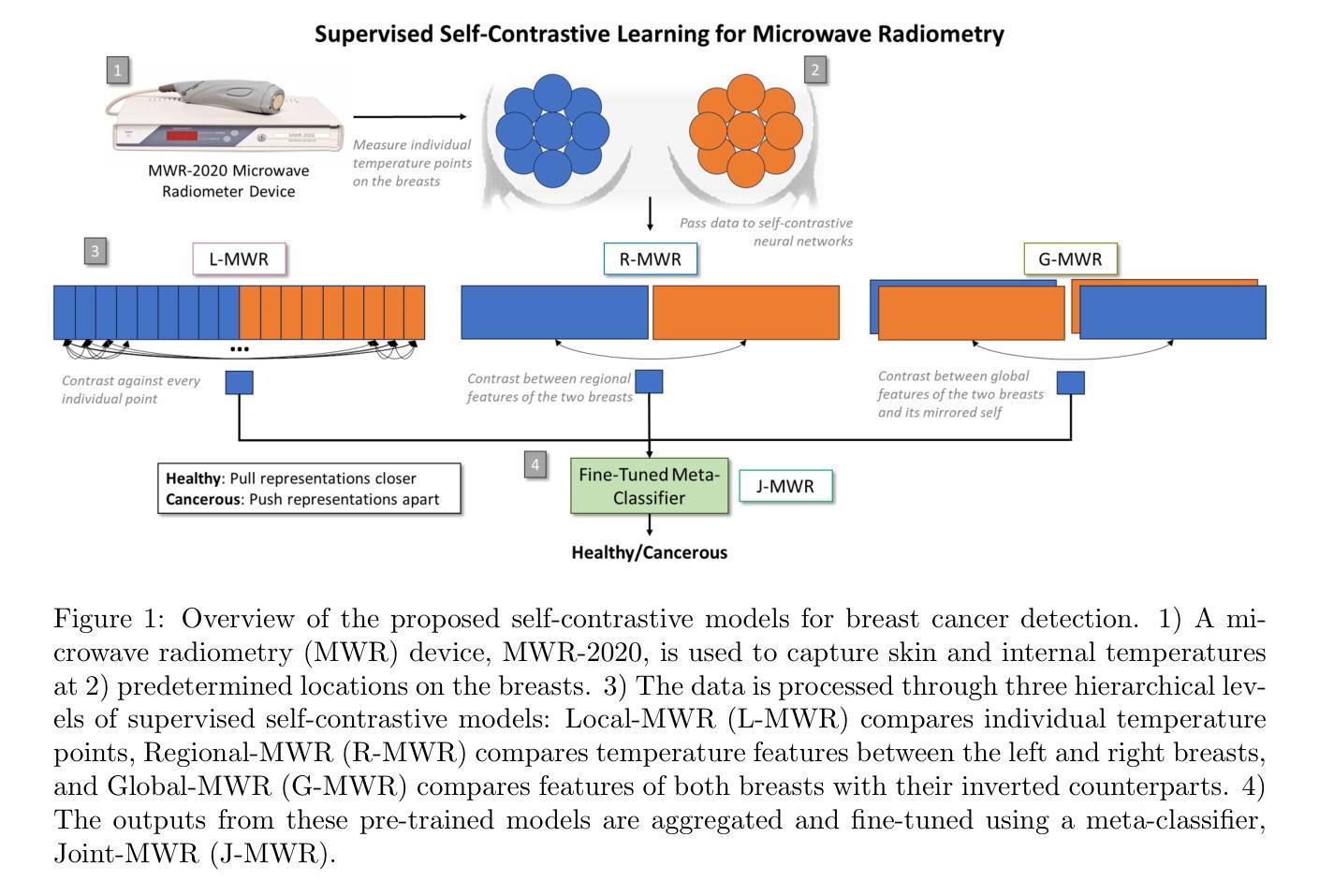
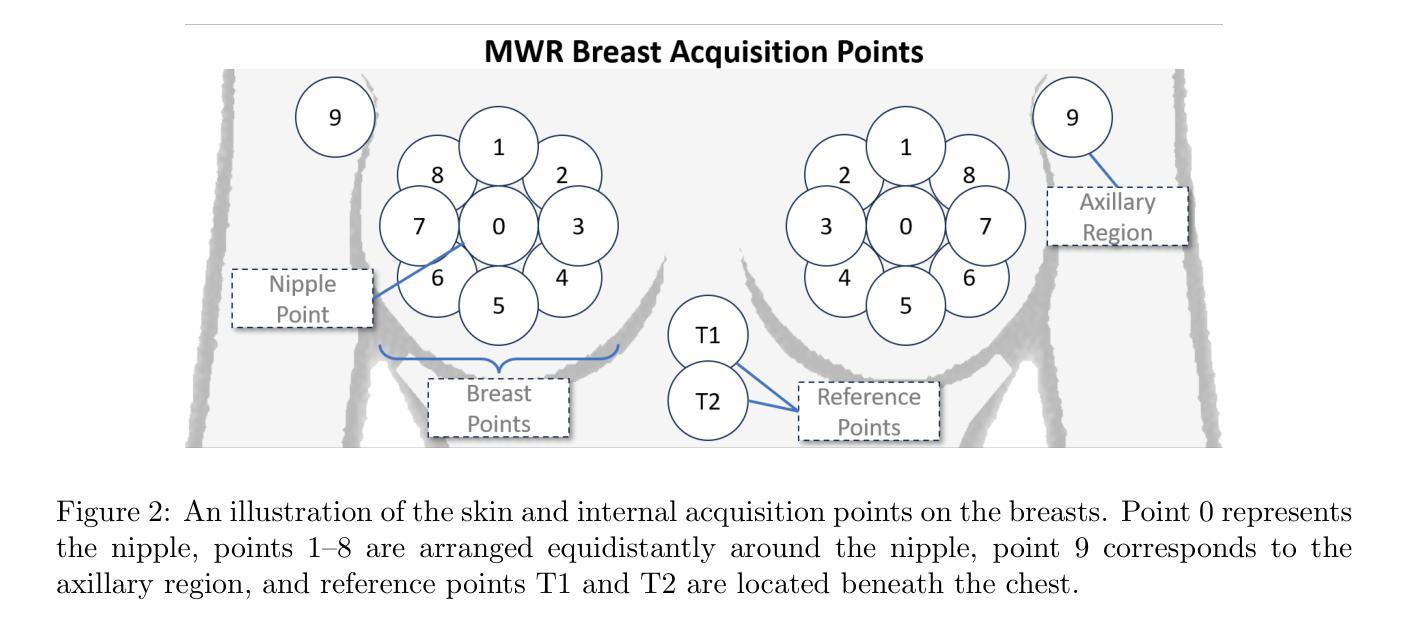
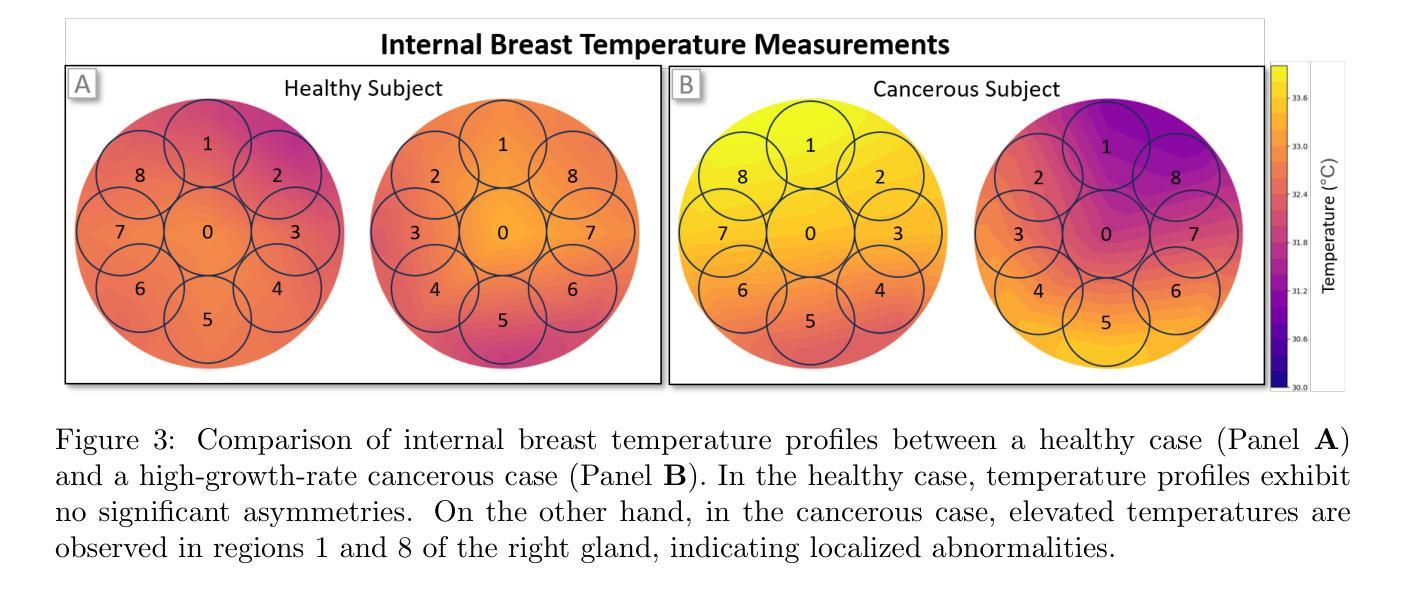
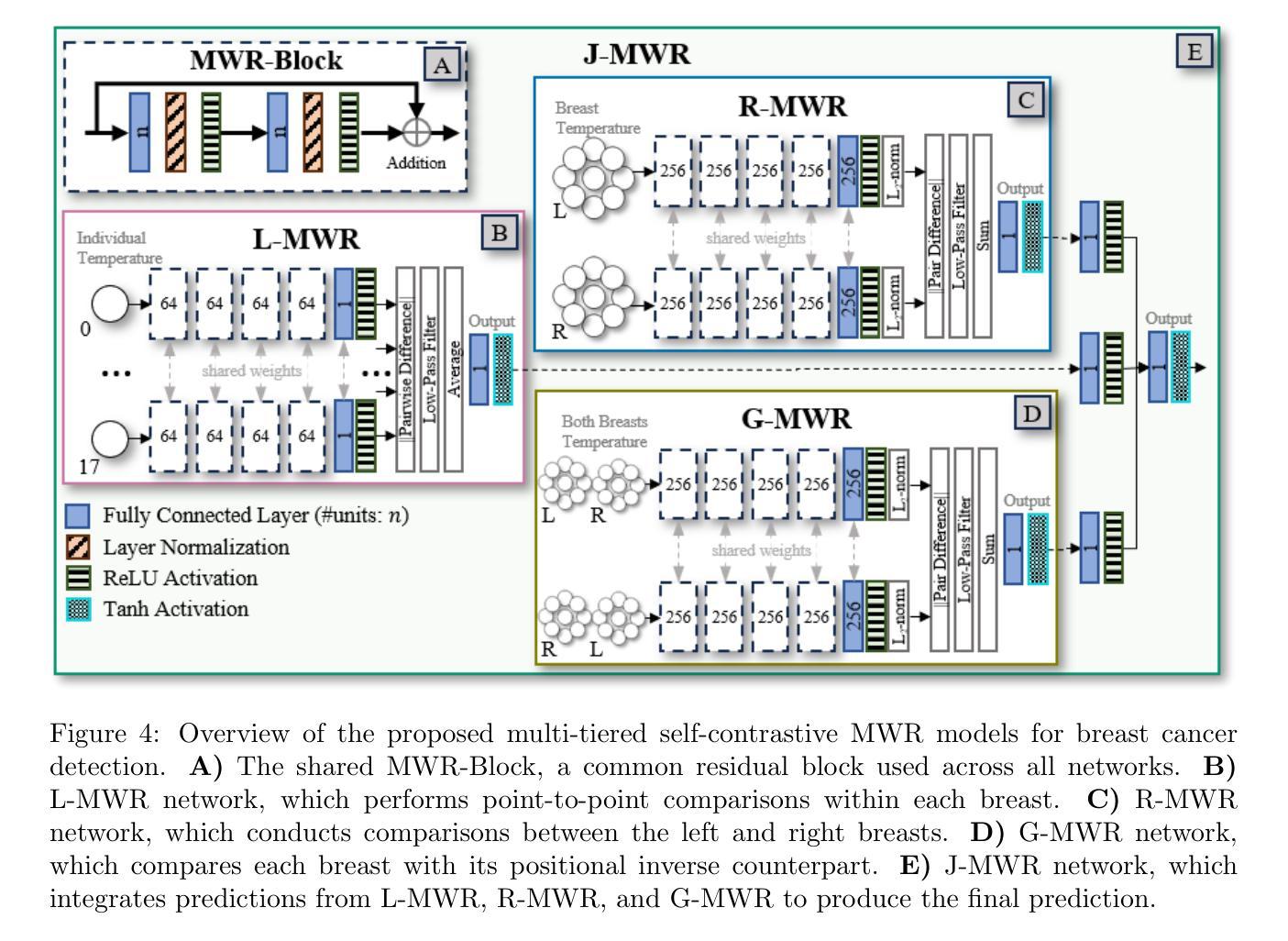
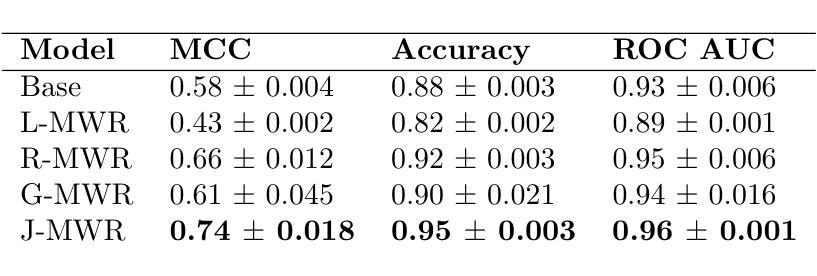
Multi-Tiered Self-Contrastive Learning for Medical Microwave Radiometry (MWR) Breast Cancer Detection
Authors:Christoforos Galazis, Huiyi Wu, Igor Goryanin
Improving breast cancer detection and monitoring techniques is a critical objective in healthcare, driving the need for innovative imaging technologies and diagnostic approaches. This study introduces a novel multi-tiered self-contrastive model tailored for microwave radiometry (MWR) in breast cancer detection. Our approach incorporates three distinct models: Local-MWR (L-MWR), Regional-MWR (R-MWR), and Global-MWR (G-MWR), designed to analyze varying sub-regional comparisons within the breasts. These models are integrated through the Joint-MWR (J-MWR) network, which leverages self-contrastive results at each analytical level to improve diagnostic accuracy. Utilizing a dataset of 4,932 female patients, our research demonstrates the efficacy of our proposed models. Notably, the J-MWR model achieves a Matthew’s correlation coefficient of 0.74 $\pm$ 0.018, surpassing existing MWR neural networks and contrastive methods. These findings highlight the potential of self-contrastive learning techniques in improving the diagnostic accuracy and generalizability for MWR-based breast cancer detection. This advancement holds considerable promise for future investigations into enabling point-of-care testing. The source code is available at: https://github.com/cgalaz01/self_contrastive_mwr.
提高乳腺癌检测和监测技术是医疗保健的重要目标,这推动了创新成像技术和诊断方法的需要。本研究引入了一种针对微波辐射仪(MWR)乳腺癌检测的新型分层自对比模型。我们的方法结合了三种不同的模型:Local-MWR(L-MWR)、Regional-MWR(R-MWR)和Global-MWR(G-MWR),旨在分析乳房内部不同亚区域的比较。这些模型通过Joint-MWR(J-MWR)网络进行集成,该网络利用每个分析级别的自对比结果来提高诊断准确性。利用4932名女性患者的数据集,我们的研究证明了所提出模型的有效性。值得注意的是,J-MWR模型的Matthew相关系数达到0.74±0.018,超越了现有的MWR神经网络和对比方法。这些发现突显了自对比学习技术在提高基于MWR的乳腺癌检测的诊断准确性和通用性方面的潜力。这一进展为未来的即时检测研究带来了巨大的希望。源代码可在https://github.com/cgalaz01/self_contrastive_mwr获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究采用新型多层自对比模型,结合微波辐射计技术,提高乳腺癌检测与监控技术。通过本地、区域和全局三个层次的微波辐射计模型分析,结合联合微波辐射计网络,提高诊断准确性。研究使用4932名女性患者数据集,结果显示联合微波辐射计模型马修相关系数达0.74±0.018,优于现有方法。这突显出自对比学习技术在微波辐射计乳腺癌检测中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究致力于提高乳腺癌检测和监控技术,引入新型多层自对比模型。
- 采用微波辐射计技术,结合三种不同层次的模型(Local-MWR、Regional-MWR、Global-MWR)进行分析。
- 通过联合微波辐射计网络(J-MWR)整合模型,利用各分析层次的自对比结果提高诊断准确性。
- 使用4932名女性患者数据集进行实证研究,结果显示J-MWR模型表现优异,马修相关系数达0.74±0.018。
- J-MWR模型优于现有的微波辐射计神经网络和对比方法,突显自对比学习技术在乳腺癌检测中的潜力。
- 源代码公开可用,为未来的研究和应用提供了基础。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient and Accurate Pneumonia Detection Using a Novel Multi-Scale Transformer Approach
Authors:Alireza Saber, Pouria Parhami, Alimohammad Siahkarzadeh, Mansoor Fateh, Amirreza Fateh
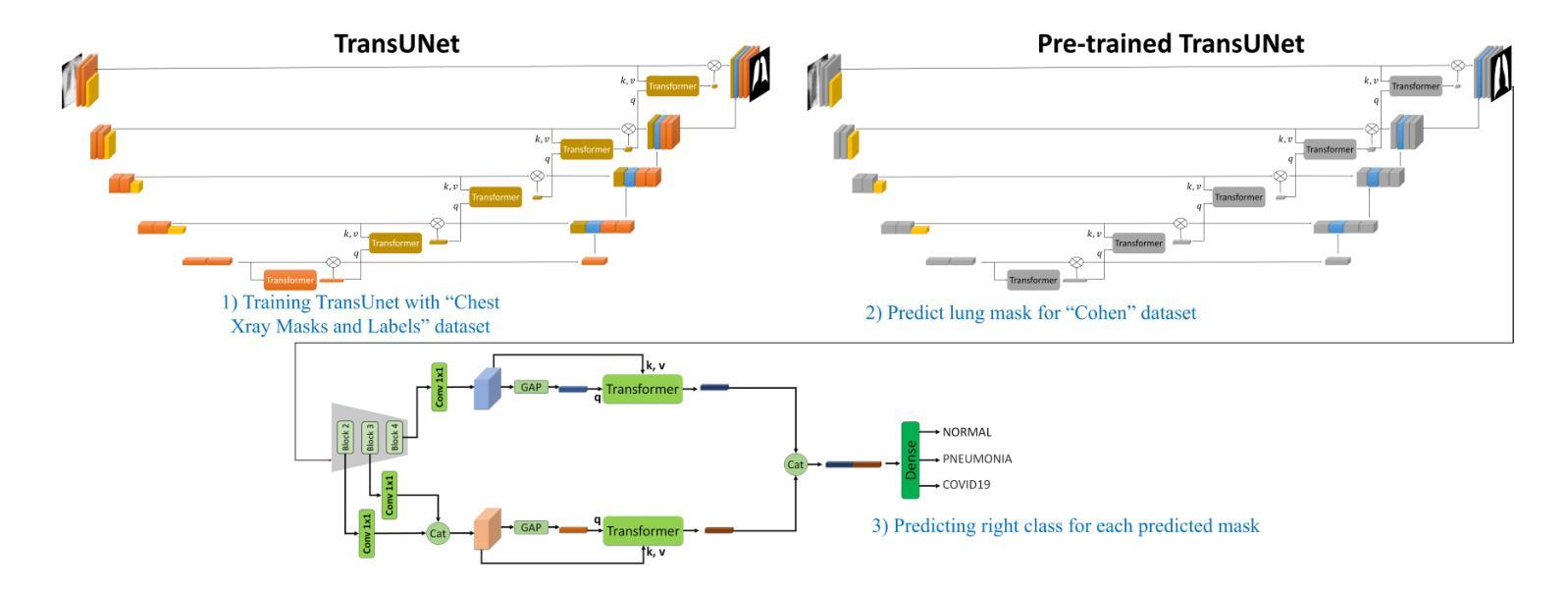
Pneumonia, a prevalent respiratory infection, remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, particularly among vulnerable populations. Chest X-rays serve as a primary tool for pneumonia detection; however, variations in imaging conditions and subtle visual indicators complicate consistent interpretation. Automated tools can enhance traditional methods by improving diagnostic reliability and supporting clinical decision-making. In this study, we propose a novel multi-scale transformer approach for pneumonia detection that integrates lung segmentation and classification into a unified framework. Our method introduces a lightweight transformer-enhanced TransUNet for precise lung segmentation, achieving a Dice score of 95.68% on the “Chest X-ray Masks and Labels” dataset with fewer parameters than traditional transformers. For classification, we employ pre-trained ResNet models (ResNet-50 and ResNet-101) to extract multi-scale feature maps, which are then processed through a modified transformer module to enhance pneumonia detection. This integration of multi-scale feature extraction and lightweight transformer modules ensures robust performance, making our method suitable for resource-constrained clinical environments. Our approach achieves 93.75% accuracy on the “Kermany” dataset and 96.04% accuracy on the “Cohen” dataset, outperforming existing methods while maintaining computational efficiency. This work demonstrates the potential of multi-scale transformer architectures to improve pneumonia diagnosis, offering a scalable and accurate solution to global healthcare challenges.”https://github.com/amirrezafateh/Multi-Scale-Transformer-Pneumonia“
肺炎是一种常见的呼吸道感染,仍然是全球发病率和死亡率的主要原因,特别是在脆弱人群中。胸部X射线是检测肺炎的主要工具;然而,成像条件的差异和微妙的视觉指标使一致的解读变得复杂。自动化工具可以通过提高诊断的可靠性和支持临床决策来增强传统方法。在研究中,我们提出了一种新的多尺度变换器方法,用于肺炎检测,该方法将肺部分割和分类整合到一个统一框架中。我们的方法引入了一种轻量级的变压器增强型TransUNet,用于精确的肺部分割,在“胸部X射线掩膜和标签”数据集上实现了95.68%的Dice得分,同时参数少于传统变压器。对于分类,我们采用预训练的ResNet模型(ResNet-50和ResNet-101)提取多尺度特征图,然后通过修改后的变压器模块进行处理,以提高肺炎检测的准确性。多尺度特征提取和轻量级变压器模块的集成确保了稳健的性能,使我们的方法适合资源受限的临床环境。我们的方法在“Kermany”数据集上实现了93.75%的准确率,在“Cohen”数据集上实现了96.04%的准确率,超越了现有方法的同时保持了计算效率。这项工作证明了多尺度变换器架构在肺炎诊断中的潜力,为全球医疗保健挑战提供了可伸缩和准确的解决方案。https://github.com/amirrezafateh/Multi-Scale-Transformer-Pneumonia
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用多尺度Transformer进行肺炎检测的新方法,将肺部分割和分类整合到统一框架中。采用轻量级Transformer增强的TransUNet进行精确肺分割,在“Chest X-ray Masks and Labels”数据集上达到95.68%的Dice得分。分类方面,采用预训练的ResNet模型提取多尺度特征图,通过修改后的Transformer模块进行处理,提高肺炎检测的准确性。该方法在“Kermany”和“Cohen”数据集上分别达到了93.75%和96.04%的准确率,展现出多尺度Transformer架构在肺炎诊断中的潜力,为全球医疗挑战提供可伸缩和准确的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 肺炎是一种全球性的常见病,仍然是发病率和死亡率的主要原因之一,特别是在脆弱人群中。
- 胸部X射线是检测肺炎的主要工具,但成像条件和细微的视觉指标会影响一致的解读。
- 自动化工具通过提高诊断可靠性和支持临床决策,能增强传统方法的效能。
- 提出了一种新的多尺度Transformer方法用于肺炎检测,整合肺部分割和分类到统一框架中。
- 采用轻量级Transformer进行精确肺分割,在特定数据集上取得了高Dice得分。
- 利用预训练的ResNet模型提取多尺度特征图,并通过修改后的Transformer模块提高肺炎检测的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

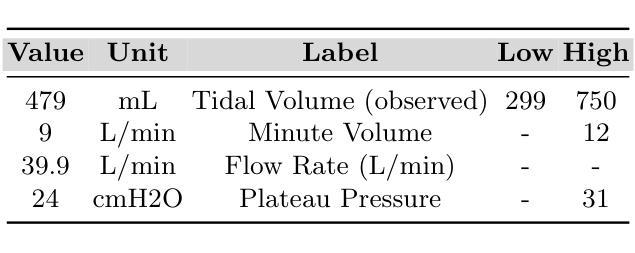
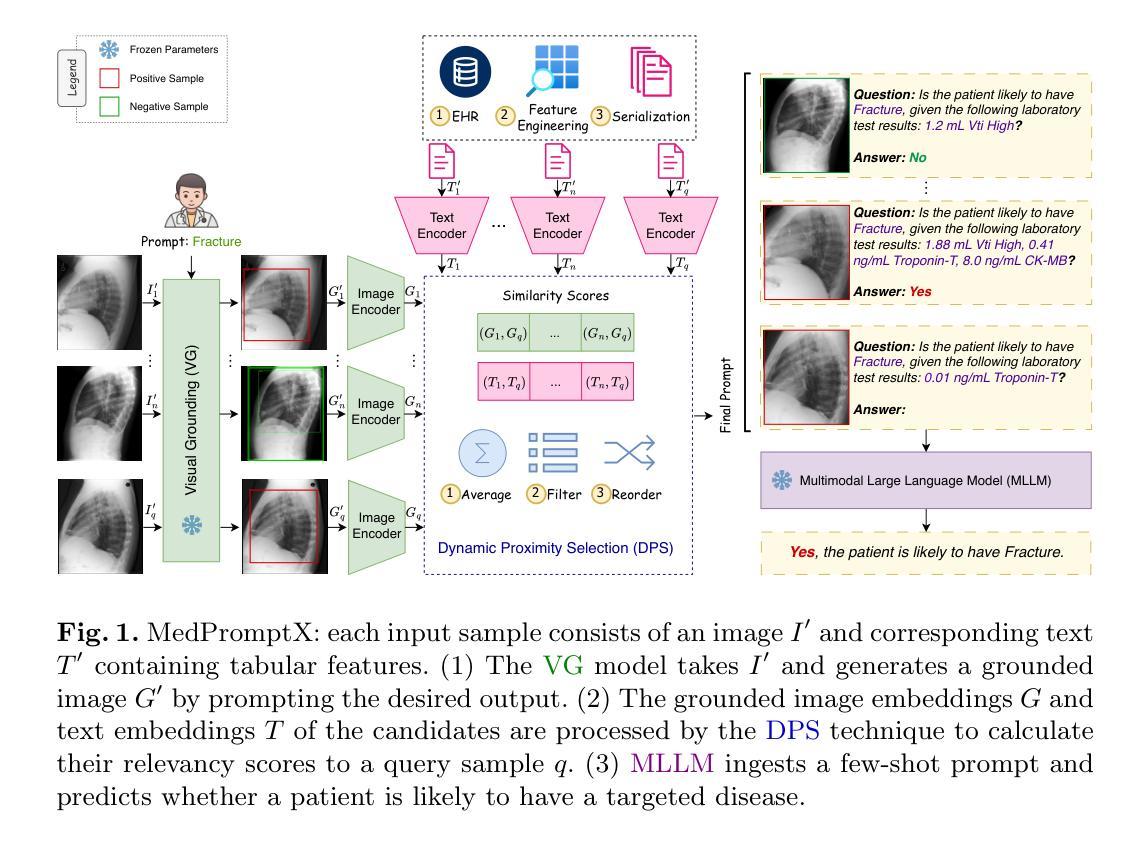
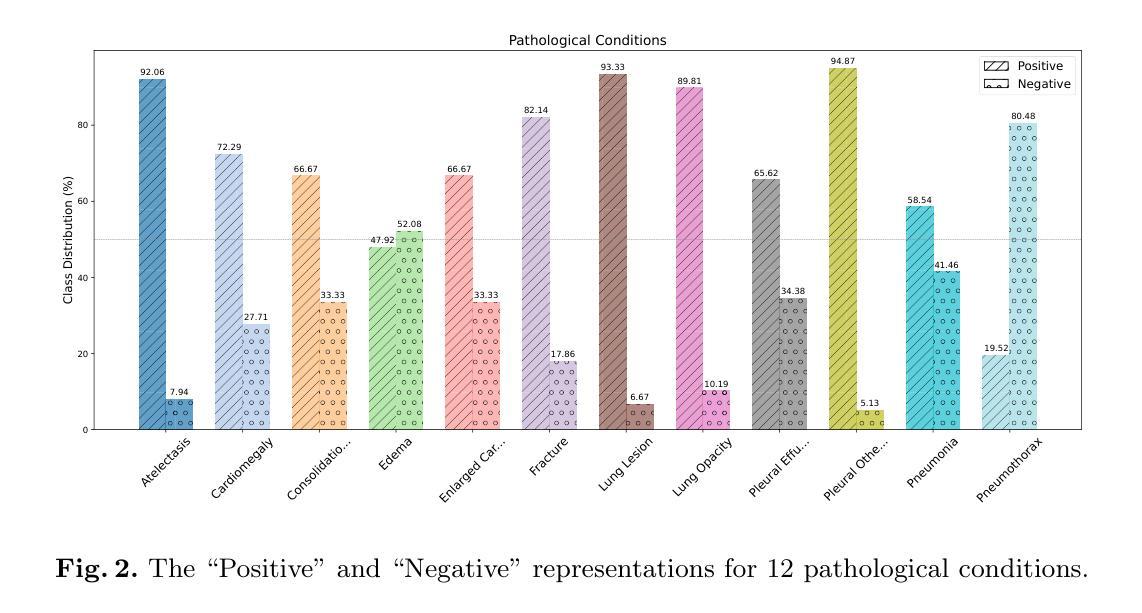
MedPromptX: Grounded Multimodal Prompting for Chest X-ray Diagnosis
Authors:Mai A. Shaaban, Adnan Khan, Mohammad Yaqub
Chest X-ray images are commonly used for predicting acute and chronic cardiopulmonary conditions, but efforts to integrate them with structured clinical data face challenges due to incomplete electronic health records (EHR). This paper introduces MedPromptX, the first clinical decision support system that integrates multimodal large language models (MLLMs), few-shot prompting (FP) and visual grounding (VG) to combine imagery with EHR data for chest X-ray diagnosis. A pre-trained MLLM is utilized to complement the missing EHR information, providing a comprehensive understanding of patients’ medical history. Additionally, FP reduces the necessity for extensive training of MLLMs while effectively tackling the issue of hallucination. Nevertheless, the process of determining the optimal number of few-shot examples and selecting high-quality candidates can be burdensome, yet it profoundly influences model performance. Hence, we propose a new technique that dynamically refines few-shot data for real-time adjustment to new patient scenarios. Moreover, VG narrows the search area in X-ray images, thereby enhancing the identification of abnormalities. We also release MedPromptX-VQA, a new in-context visual question answering dataset encompassing interleaved images and EHR data derived from MIMIC-IV and MIMIC-CXR-JPG databases. Results demonstrate the SOTA performance of MedPromptX, achieving an 11% improvement in F1-score compared to the baselines. Code and data are publicly available on https://github.com/BioMedIA-MBZUAI/MedPromptX.
胸部X光片图像常用于预测急性和慢性心肺疾病,但将其与结构化临床数据相结合的尝试面临由于电子健康记录(EHR)不完整而带来的挑战。本文介绍了MedPromptX,这是第一个结合多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)、少样本提示(FP)和视觉定位(VG)的临床决策支持系统,用于将图像与EHR数据相结合进行胸部X光诊断。预训练的MLLM用于补充缺失的EHR信息,为患者病史提供全面的理解。此外,FP降低了对MLLM进行大量培训的必要,同时有效地解决了虚构问题。然而,确定最佳数量的少数样本并选择高质量候选者的过程可能是一个繁重的任务,但它对模型性能产生深远影响。因此,我们提出了一种新技术,可以动态地完善少数样本数据,以实时适应新患者情况。此外,VG缩小了X光图像中的搜索区域,从而提高了异常检测的准确性。我们还发布了MedPromptX-VQA,这是一个新的上下文视觉问答数据集,涵盖了来自MIMIC-IV和MIMIC-CXR-JPG数据库交织的图像和EHR数据。结果表明,MedPromptX的性能处于领先水平,与基线相比,F1分数提高了11%。代码和数据已在https://github.com/BioMedIA-MBZUAI/MedPromptX上公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的临床决策支持系统——MedPromptX,它集成了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)、少样本提示(FP)和视觉定位(VG)技术,能够结合胸部X光图像与电子健康记录(EHR)数据进行诊断。通过使用预训练的大型语言模型来补充缺失的EHR信息,提高对病人医疗历史的全面理解。此外,少样本提示技术降低了模型训练的复杂性并解决了虚构问题,而视觉定位技术则提高了异常检测的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- MedPromptX是首个结合多模态大型语言模型、少样本提示和视觉定位技术的临床决策支持系统。
- 它能够整合胸部X光图像与电子健康记录(EHR)数据,进行更全面的诊断。
- 利用预训练的大型语言模型补充缺失的EHR信息,提高病人医疗历史的全面理解。
- 少样本提示技术降低了模型训练的需求并解决了虚构问题。
- 视觉定位技术提高了在X光图像中检测异常的准确性。
- MedPromptX-VQA数据集包含间断性图像和EHR数据,用于视觉问答任务。
点此查看论文截图