⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
HECLIP: Histology-Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Imputation of Transcriptomics Profiles
Authors:Qing Wang, Wen-jie Chen, Bo Li, Jing Su, Guangyu Wang, Qianqian Song
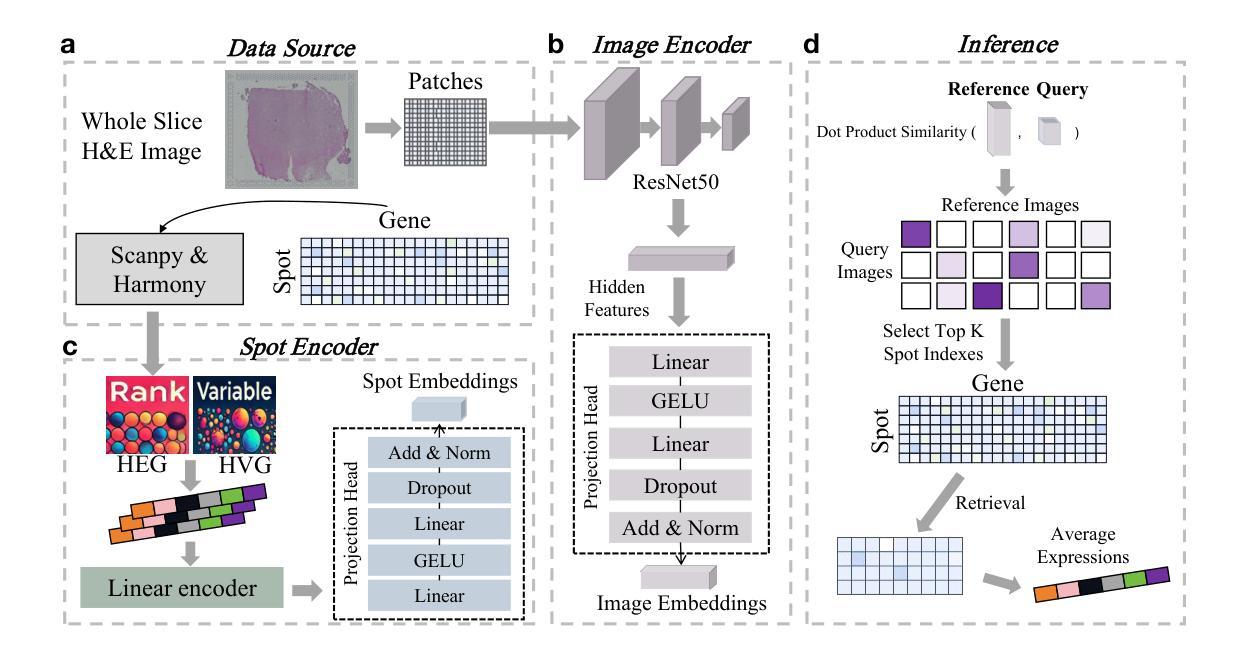
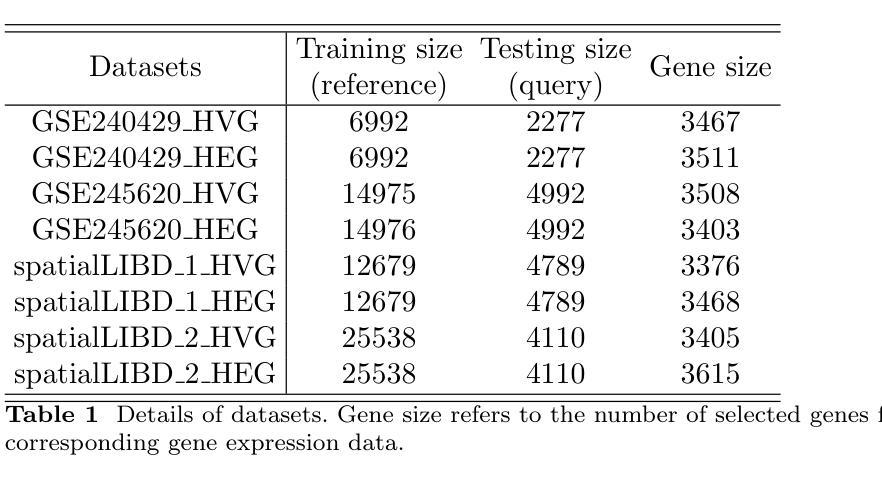
Histopathology, particularly hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, plays a critical role in diagnosing and characterizing pathological conditions by highlighting tissue morphology. However, H&E-stained images inherently lack molecular information, requiring costly and resource-intensive methods like spatial transcriptomics to map gene expression with spatial resolution. To address these challenges, we introduce HECLIP (Histology-Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Imputation of Profiles), an innovative deep learning framework that bridges the gap between histological imaging and molecular profiling. HECLIP is specifically designed to infer gene expression profiles directly from H&E-stained images, eliminating the need for expensive spatial transcriptomics assays. HECLIP leverages an advanced image-centric contrastive loss function to optimize image representation learning, ensuring that critical morphological patterns in histology images are effectively captured and translated into accurate gene expression profiles. This design enhances the predictive power of the image modality while minimizing reliance on gene expression data. Through extensive benchmarking on publicly available datasets, HECLIP demonstrates superior performance compared to existing approaches, delivering robust and biologically meaningful predictions. Detailed ablation studies further underscore its effectiveness in extracting molecular insights from histology images. Additionally, HECLIP’s scalable and cost-efficient approach positions it as a transformative tool for both research and clinical applications, driving advancements in precision medicine. The source code for HECLIP is openly available at https://github.com/QSong-github/HECLIP.
组织病理学,特别是苏木精和伊红(H\&E)染色,在通过突出组织形态来诊断和鉴定病理状况方面发挥着关键作用。然而,H&E染色图像本身缺乏分子信息,需要昂贵的空间转录组学等耗费资源的方法来绘制具有空间分辨率的基因表达图谱。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了HECLIP(用于推断轮廓的组织学增强对比学习,Histology-Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Imputation of Profiles),这是一种创新的深度学习框架,它弥补了组织成像和分子轮廓之间的空白。HECLIP特别设计用于直接从H&E染色图像推断基因表达轮廓,从而消除了昂贵的空间转录测定法的需求。HECLIP利用先进的以图像为中心的对比损失函数来优化图像表示学习,确保有效地捕获组织图像中的关键形态模式并将其翻译成准确的基因表达轮廓。这一设计提高了图像模态的预测能力,同时最大限度地减少对基因表达数据的依赖。在公开数据集上进行广泛的标准测试,HECLIP显示出优于现有方法的表现,能够做出稳健且具有生物学意义的预测。详细的消融研究进一步强调了它从组织图像中提取分子见解的有效性。此外,HECLIP的可扩展性和成本效益使其成为研究和临床应用中的变革性工具,推动精准医学的进步。HECLIP的源代码可公开访问:https://github.com/QSong-github/HECLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
HECLIP是一种基于深度学习的框架,能够从H&E染色图像中推断基因表达谱,无需依赖昂贵的空间转录组学检测。它通过图像对比损失函数优化图像表示学习,能够从组织学图像中捕捉关键形态模式并准确转化为基因表达谱。HECLIP在公开数据集上的表现优于现有方法,具有预测力强、对基因表达数据依赖低的特点。
Key Takeaways
- HECLIP是一种连接组织学成像和分子分型的深度学习方法。
- HECLIP能从H&E染色图像中直接推断基因表达谱,无需空间转录组学检测。
- 利用图像对比损失函数优化图像表示学习,有效捕捉组织学图像中的关键形态模式。
- HECLIP在公开数据集上的表现优异,预测力强,对基因表达数据的依赖较低。
- HECLIP通过简化流程,降低成本,为研究和临床应用提供了有力工具。
- 源码已公开可供使用。
点此查看论文截图

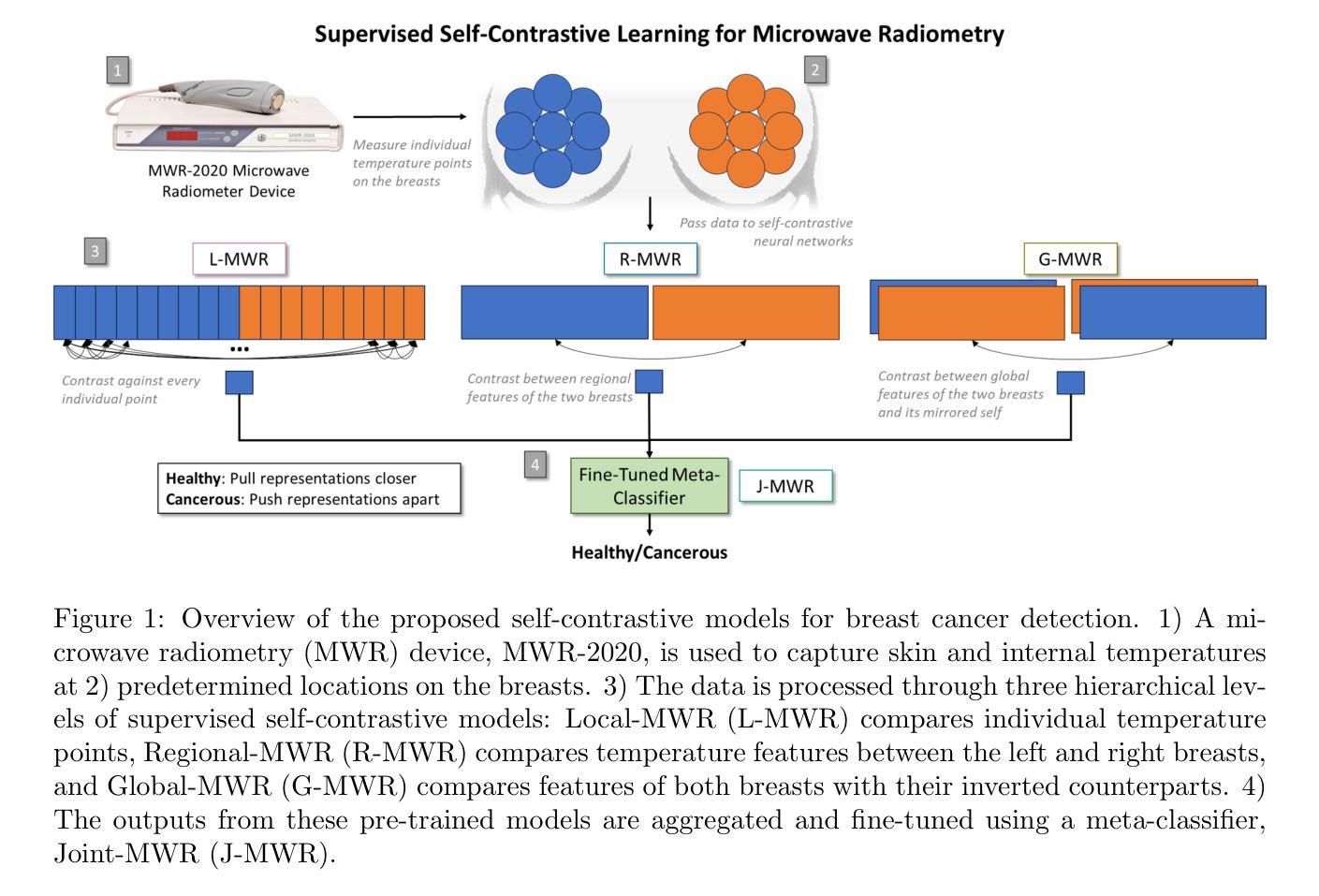
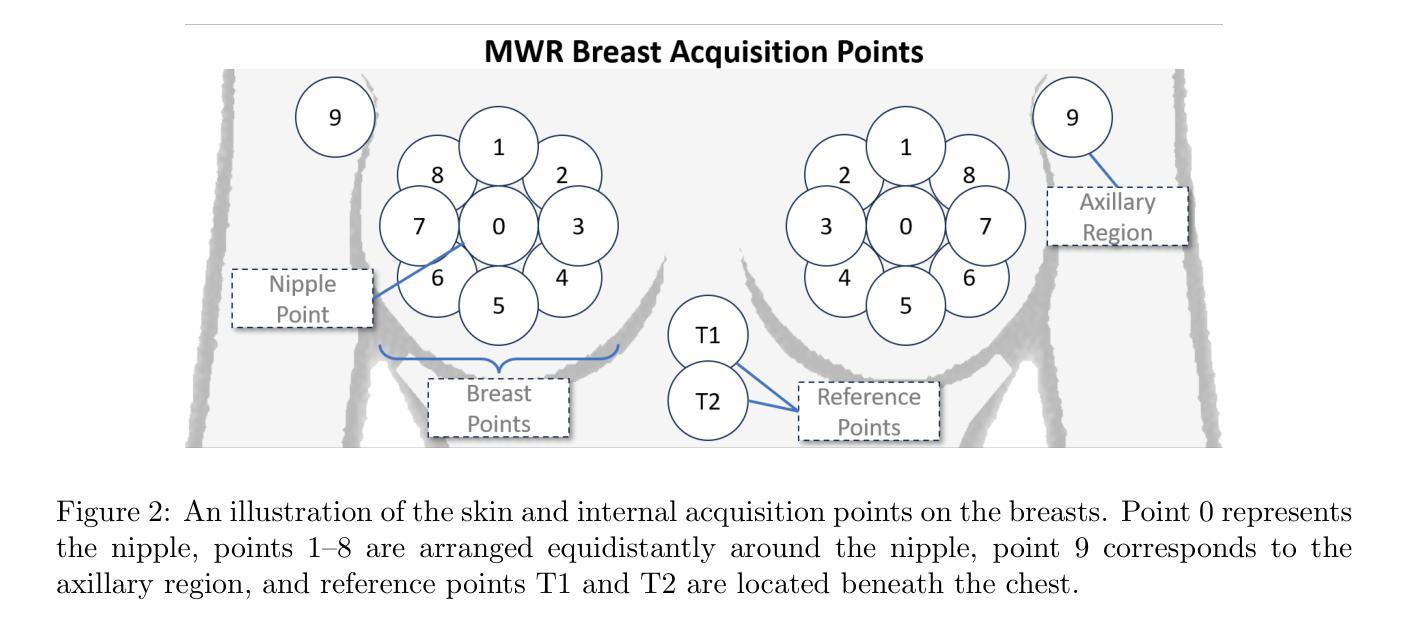
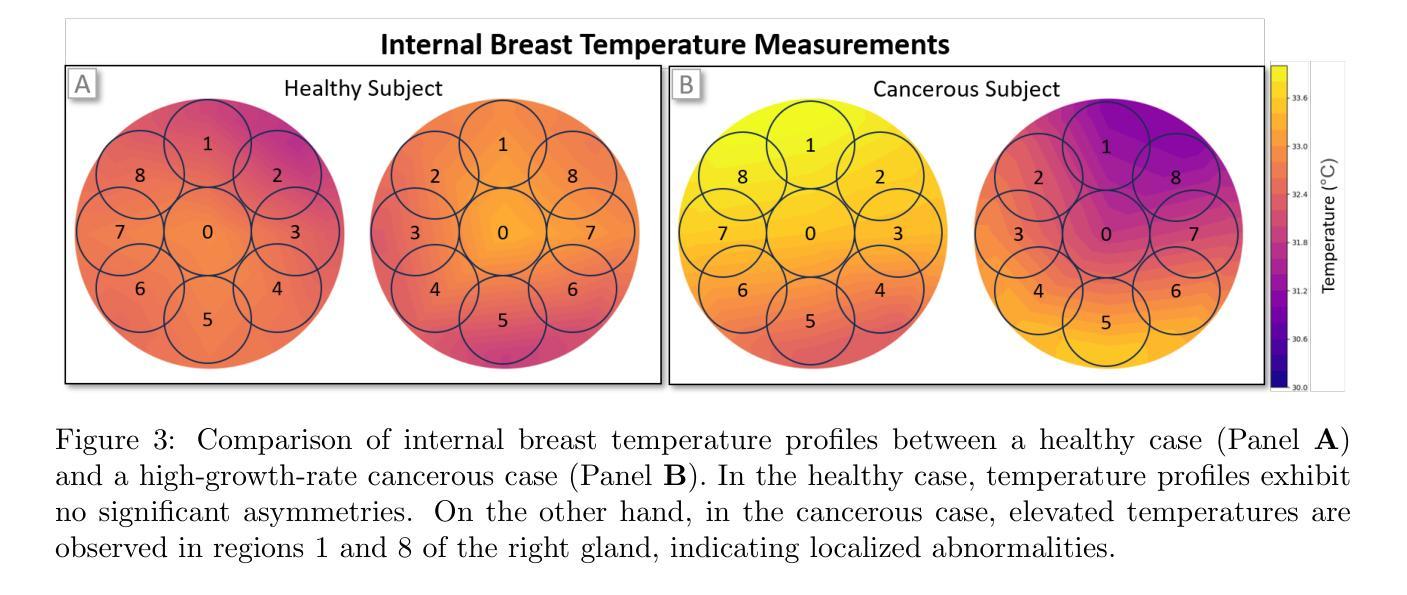
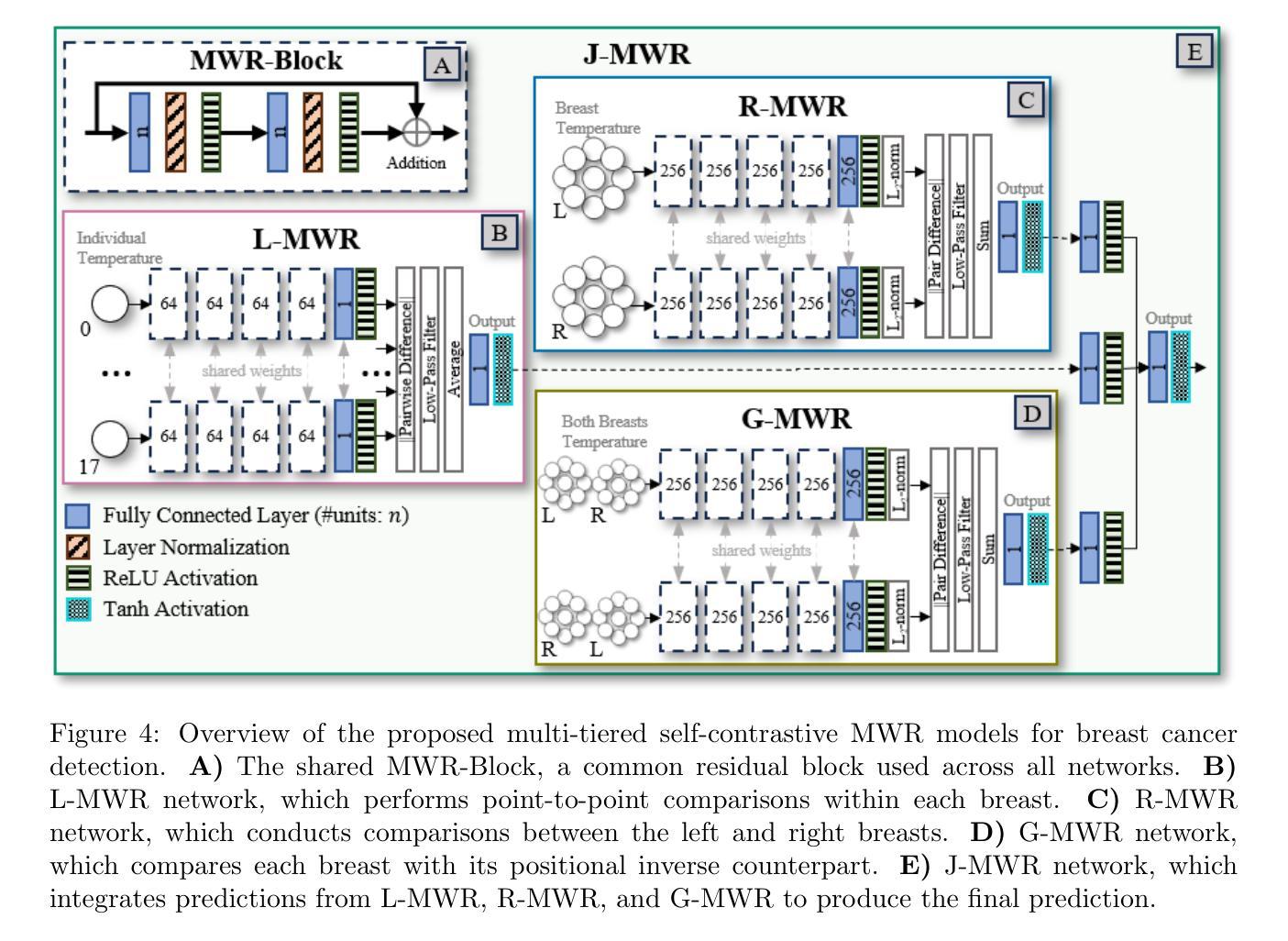
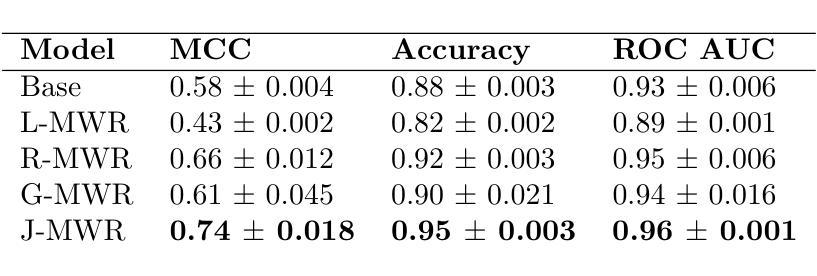
Multi-Tiered Self-Contrastive Learning for Medical Microwave Radiometry (MWR) Breast Cancer Detection
Authors:Christoforos Galazis, Huiyi Wu, Igor Goryanin
Improving breast cancer detection and monitoring techniques is a critical objective in healthcare, driving the need for innovative imaging technologies and diagnostic approaches. This study introduces a novel multi-tiered self-contrastive model tailored for microwave radiometry (MWR) in breast cancer detection. Our approach incorporates three distinct models: Local-MWR (L-MWR), Regional-MWR (R-MWR), and Global-MWR (G-MWR), designed to analyze varying sub-regional comparisons within the breasts. These models are integrated through the Joint-MWR (J-MWR) network, which leverages self-contrastive results at each analytical level to improve diagnostic accuracy. Utilizing a dataset of 4,932 female patients, our research demonstrates the efficacy of our proposed models. Notably, the J-MWR model achieves a Matthew’s correlation coefficient of 0.74 $\pm$ 0.018, surpassing existing MWR neural networks and contrastive methods. These findings highlight the potential of self-contrastive learning techniques in improving the diagnostic accuracy and generalizability for MWR-based breast cancer detection. This advancement holds considerable promise for future investigations into enabling point-of-care testing. The source code is available at: https://github.com/cgalaz01/self_contrastive_mwr.
提高乳腺癌检测和监测技术是医疗保健的重要目标,这推动了创新成像技术和诊断方法的需要。本研究引入了一种针对微波辐射计(MWR)乳腺癌检测的多层次自对比模型。我们的方法结合了三种不同的模型:局部MWR(L-MWR)、区域MWR(R-MWR)和全局MWR(G-MWR),旨在分析乳房内部不同亚区域的比较。这些模型通过联合MWR(J-MWR)网络进行集成,该网络利用各级的自我对比结果来提高诊断的准确性。利用4932名女性患者的数据集,我们的研究证明了所提出模型的有效性。值得注意的是,J-MWR模型达到了马修斯相关系数(Matthew’s correlation coefficient)0.74±0.018,超越了现有的MWR神经网络和对比方法。这些发现突出了自我对比学习技术在提高基于MWR的乳腺癌检测的诊断准确性和泛化潜力。这一进展为未来的现场检测研究带来了极大的希望。源代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/cgalaz01/self_contrastive_mwr。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对微波辐射计(MWR)乳腺癌检测的多层次自对比模型。该研究通过整合Local-MWR、Regional-MWR和Global-MWR三个模型,分析乳房不同亚区域的比较结果。通过Joint-MWR网络利用各级自对比结果,提高诊断准确性。研究使用4932名女性患者数据集验证模型效果,其中Joint-MWR模型达到较高的Matthew相关系数,表现出自我对比学习技术在提高MWR乳腺癌检测诊断准确性和通用性方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目标是提高乳腺癌检测和监测技术的准确性,引入了一种新型多层次自对比模型用于微波辐射计(MWR)技术。
- 整合了Local-MWR、Regional-MWR和Global-MWR三个模型,分别针对乳房不同亚区域进行分析。
- 通过Joint-MWR网络,结合各级自对比结果,旨在提高乳腺癌诊断的准确性。
- 使用4932名女性患者数据集验证了模型的有效性。
- Joint-MWR模型达到较高的Matthew相关系数,表现出优异的性能,超越了现有的MWR神经网络和对比方法。
- 研究强调了自对比学习技术在提高MWR乳腺癌检测方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图