⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
LinPrim: Linear Primitives for Differentiable Volumetric Rendering
Authors:Nicolas von Lützow, Matthias Nießner
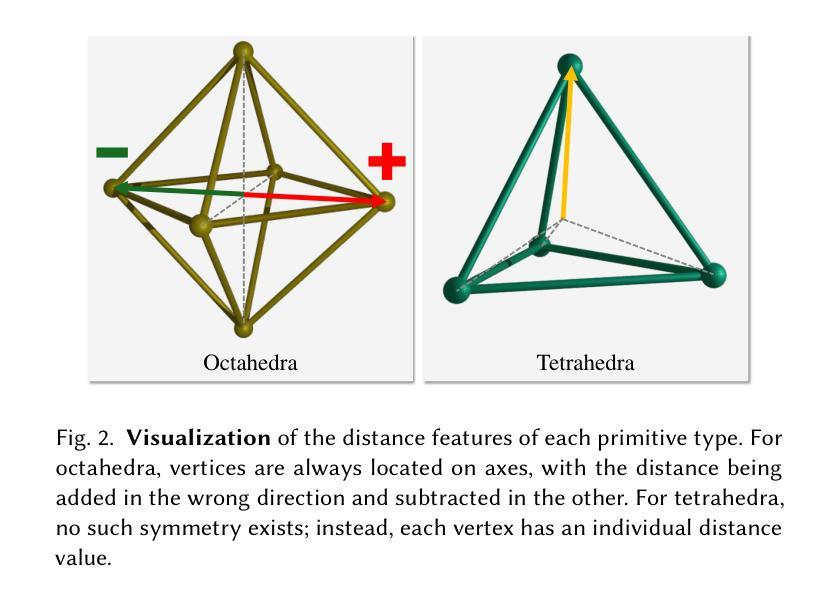
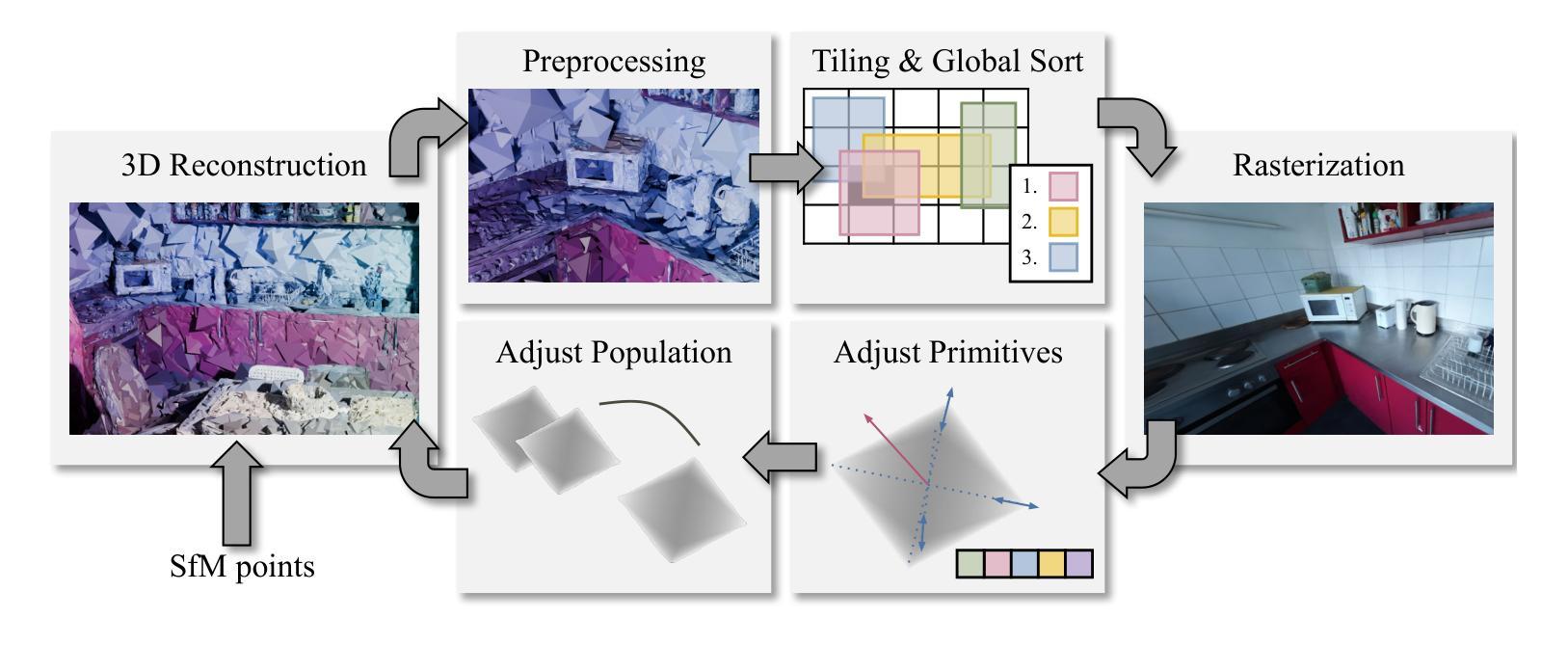
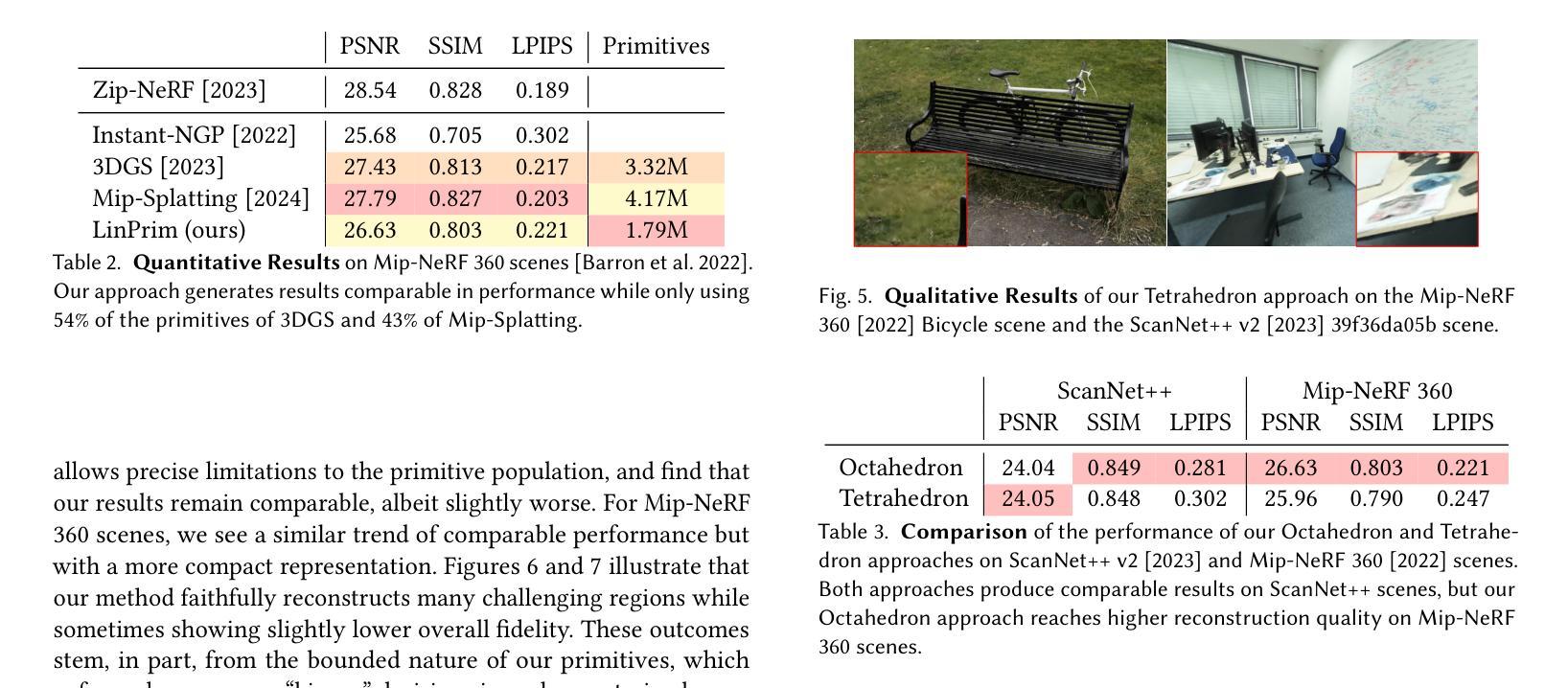
Volumetric rendering has become central to modern novel view synthesis methods, which use differentiable rendering to optimize 3D scene representations directly from observed views. While many recent works build on NeRF or 3D Gaussians, we explore an alternative volumetric scene representation. More specifically, we introduce two new scene representations based on linear primitives-octahedra and tetrahedra-both of which define homogeneous volumes bounded by triangular faces. This formulation aligns naturally with standard mesh-based tools, minimizing overhead for downstream applications. To optimize these primitives, we present a differentiable rasterizer that runs efficiently on GPUs, allowing end-to-end gradient-based optimization while maintaining realtime rendering capabilities. Through experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate comparable performance to state-of-the-art volumetric methods while requiring fewer primitives to achieve similar reconstruction fidelity. Our findings provide insights into the geometry of volumetric rendering and suggest that adopting explicit polyhedra can expand the design space of scene representations.
体积渲染已成为现代新型视图合成方法的中心,这些方法使用可微渲染来直接优化从观察到的视角表示的3D场景。虽然许多最新作品建立在NeRF或3D高斯模型之上,但我们探索了一种替代的体积场景表示。更具体地说,我们引入两种基于线性原始形状(八面体和四面体)的新场景表示,两者都定义了由三角形面界定的均匀体积。这种公式与标准网格化工具自然匹配,为下游应用减少了开销。为了优化这些原始形状,我们提出了一种可在GPU上高效运行的可微栅格化器,允许端到端的基于梯度的优化,同时保持实时渲染能力。通过在真实世界数据集上进行实验,我们展示了与最先进体积方法的可比性能,同时使用较少的原始形状实现了类似的重建保真度。我们的研究结果提供了关于体积渲染几何的见解,并表明采用明确的聚形可以扩大场景表示的设计空间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要介绍了在现代新颖视图合成方法中,体积渲染的核心地位及其应用场景。该方法采用可微分渲染来优化直接从观测视图得到的3D场景表示。虽然许多最新研究基于NeRF或3D高斯,但本文探索了另一种体积场景表示方法。具体来说,本文引入两种基于线性原始元素(八面体和四面体)的场景表示方法,这两种方法通过三角形面定义均匀体积。这种表述方式与标准网格工具相符,有助于下游应用的最小开销。为了优化这些原始元素,本文提出了一种高效GPU运行的微分光栅器,支持端到端的基于梯度的优化并保持实时渲染能力。通过实际数据集的实验验证,该方法性能与先进的体积渲染方法相当,以较少的原始元素达到相似的重建保真度。这为体积渲染的几何结构提供了洞察,并暗示采用明确的多面体可以扩展场景表示的设计空间。
Key Takeaways
- 现代新颖视图合成方法的核心是体积渲染技术。
- 可微分渲染技术被用于优化从观测视图的3D场景表示。
- 提出了一种基于线性原始元素(八面体和四面体)的体积场景表示新方法。
- 该方法与标准网格工具相符,有助于下游应用的最小开销。
- 提出了一种高效GPU运行的微分光栅器以优化原始元素。
- 实验证明,该方法性能与先进的体积渲染方法相当,需要的原始元素更少。
点此查看论文截图


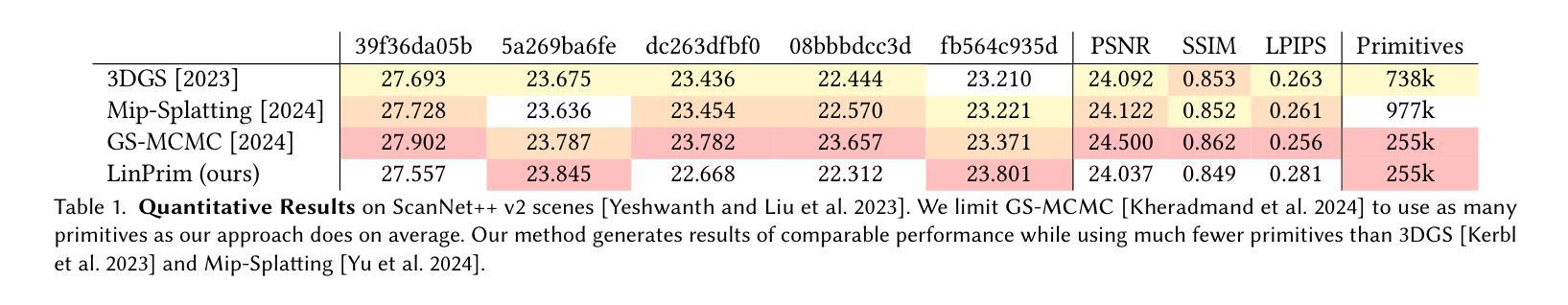
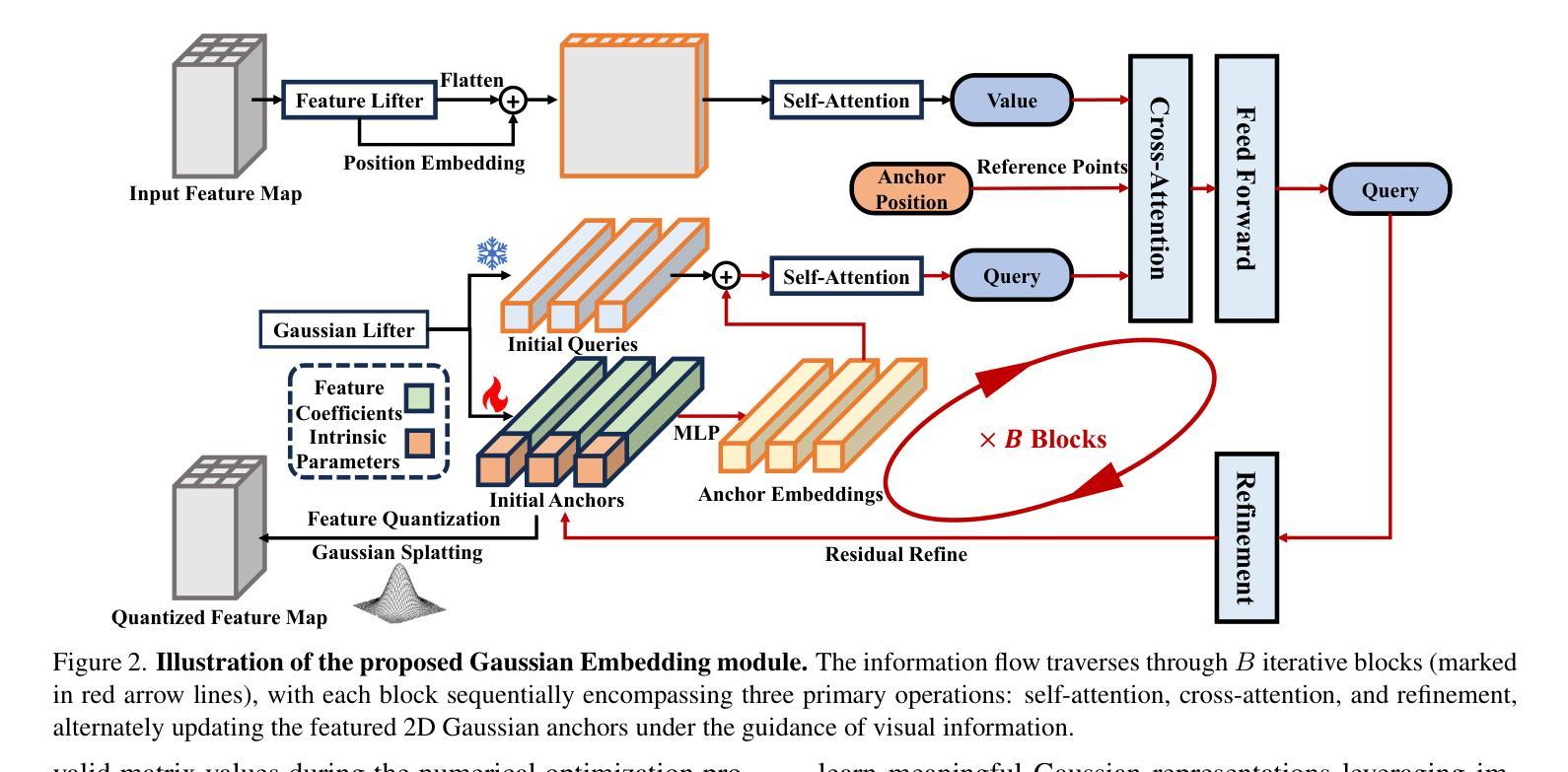
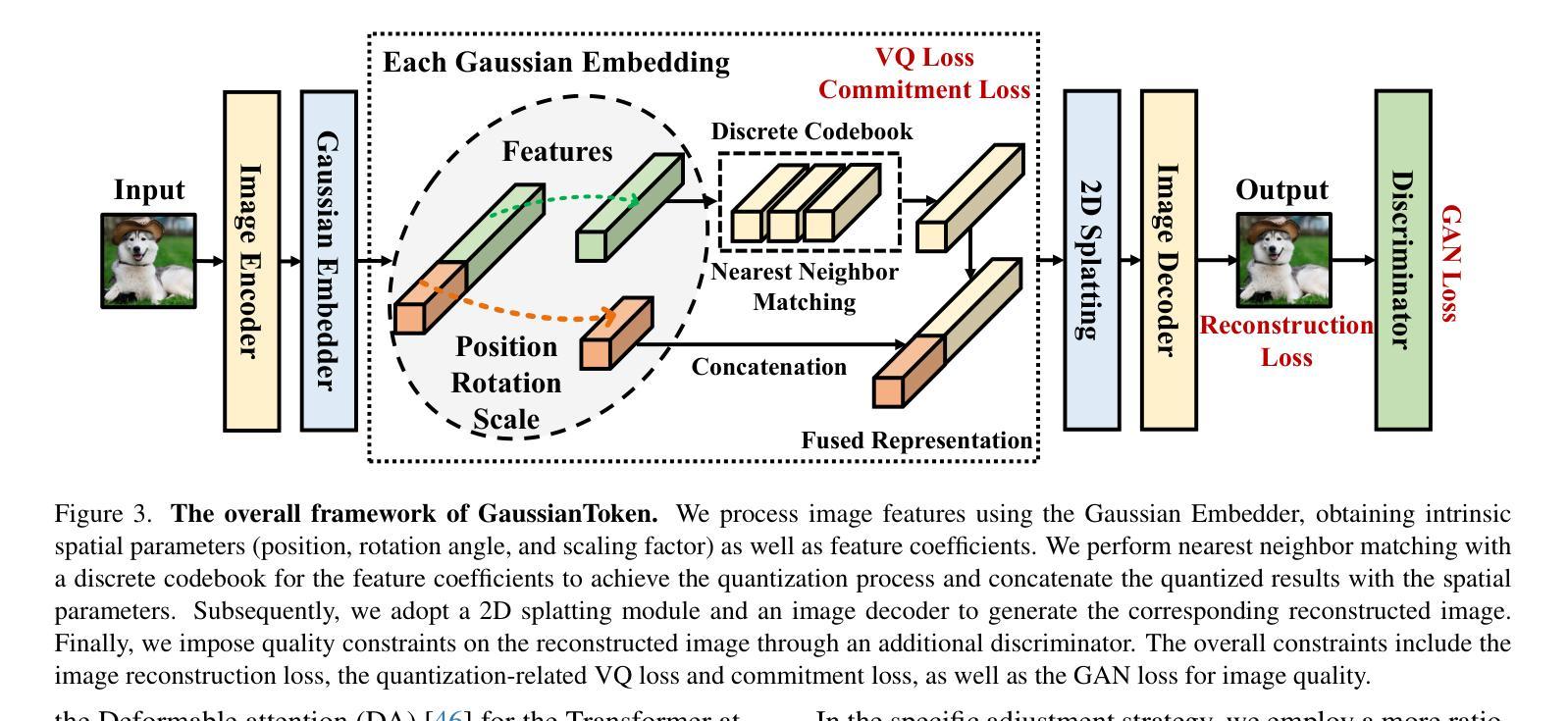
GaussianToken: An Effective Image Tokenizer with 2D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jiajun Dong, Chengkun Wang, Wenzhao Zheng, Lei Chen, Jiwen Lu, Yansong Tang
Effective image tokenization is crucial for both multi-modal understanding and generation tasks due to the necessity of the alignment with discrete text data. To this end, existing approaches utilize vector quantization (VQ) to project pixels onto a discrete codebook and reconstruct images from the discrete representation. However, compared with the continuous latent space, the limited discrete codebook space significantly restrict the representational ability of these image tokenizers. In this paper, we propose GaussianToken: An Effective Image Tokenizer with 2D Gaussian Splatting as a solution. We first represent the encoded samples as multiple flexible featured 2D Gaussians characterized by positions, rotation angles, scaling factors, and feature coefficients. We adopt the standard quantization for the Gaussian features and then concatenate the quantization results with the other intrinsic Gaussian parameters before the corresponding splatting operation and the subsequent decoding module. In general, GaussianToken integrates the local influence of 2D Gaussian distribution into the discrete space and thus enhances the representation capability of the image tokenizer. Competitive reconstruction performances on CIFAR, Mini-ImageNet, and ImageNet-1K demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework. Our code is available at: https://github.com/ChrisDong-THU/GaussianToken.
有效的图像令牌化对于多模态理解和生成任务都至关重要,因为需要与离散文本数据进行对齐。为此,现有方法使用向量量化(VQ)将像素投影到离散代码簿上,并从离散表示中重建图像。然而,与连续潜在空间相比,有限的离散代码簿空间显著限制了这些图像令牌化的表示能力。在本文中,我们提出GaussianToken:一种具有二维高斯涂抹技术的高效图像令牌化解决方案。我们首先将通过编码的样本表示为多个灵活的二维高斯特征,这些特征由位置、旋转角度、缩放因子和特征系数组成。我们对高斯特征采用标准量化方法,然后将量化结果与其他的固有高斯参数进行拼接,再执行相应的涂抹操作和随后的解码模块。总的来说,GaussianToken将二维高斯分布的局部影响集成到离散空间中,从而提高了图像令牌化的表示能力。在CIFAR、Mini-ImageNet和ImageNet-1K上的重建性能竞争结果证明了我们的框架的有效性。我们的代码位于:https://github.com/ChrisDong-THU/GaussianToken。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
论文提出了一种名为GaussianToken的有效图像标记器,采用二维高斯Splatting技术。通过将编码样本表示为多个灵活的二维高斯特征,并量化这些特征,再与固有高斯参数进行拼接后传入Splatting操作和后续解码模块,整合了二维高斯分布在离散空间中的局部影响,提高了图像标记器的表示能力。在CIFAR、Mini-ImageNet和ImageNet-1K上的重建性能表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 图像标记化对于多模态理解和生成任务至关重要,需要与离散文本数据进行对齐。
- 现有方法使用向量量化(VQ)将像素投影到离散代码本上,并从离散表示中重建图像。
- 离散代码本空间的局限性显著限制了图像标记器的表示能力。
- GaussianToken通过采用二维高斯Splatting技术解决这一问题。
- GaussianToken将编码样本表示为具有位置、旋转角度、缩放因子和特征系数的多个灵活特征二维高斯。
- GaussianToken通过量化高斯特征和与固有高斯参数的拼接,增强了图像标记器的表示能力。
点此查看论文截图

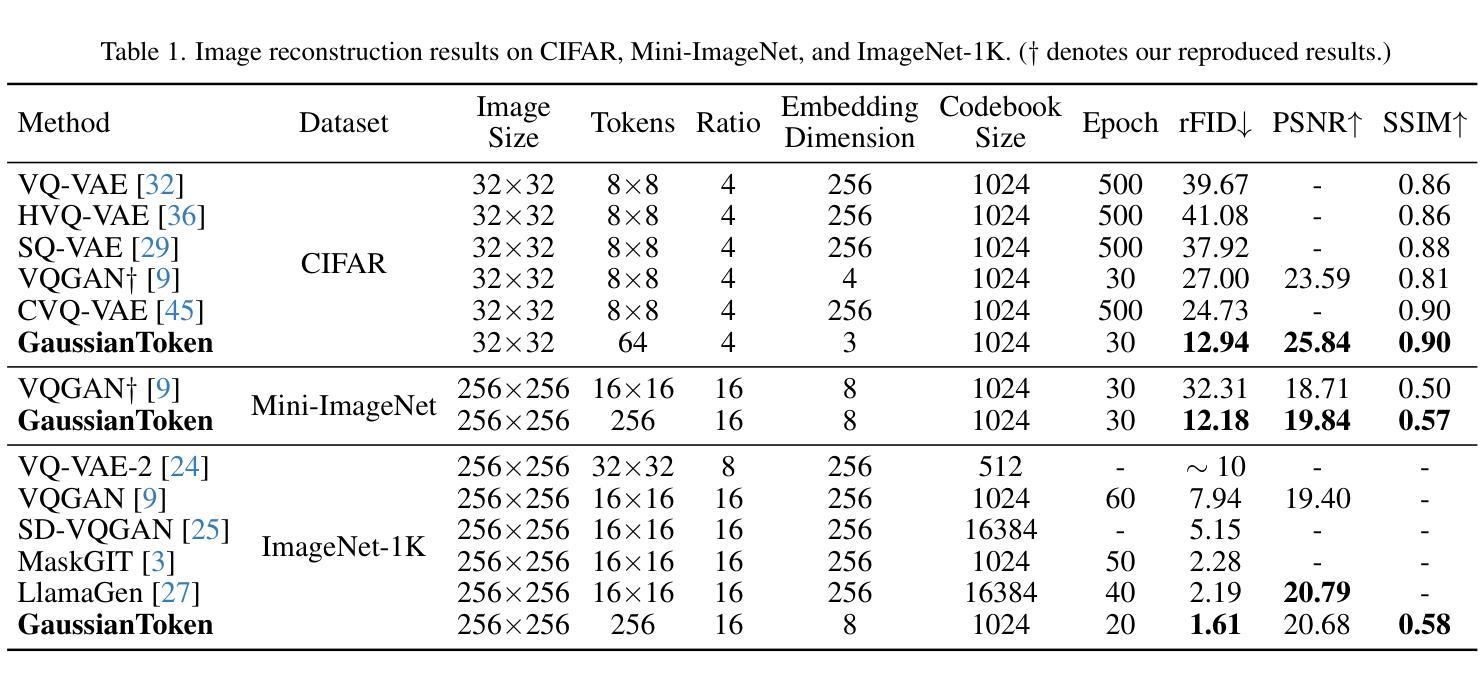
Towards Better Robustness: Progressively Joint Pose-3DGS Learning for Arbitrarily Long Videos
Authors:Zhen-Hui Dong, Sheng Ye, Yu-Hui Wen, Nannan Li, Yong-Jin Liu
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful representation due to its efficiency and high-fidelity rendering. However, 3DGS training requires a known camera pose for each input view, typically obtained by Structure-from-Motion (SfM) pipelines. Pioneering works have attempted to relax this restriction but still face difficulties when handling long sequences with complex camera trajectories. In this work, we propose Rob-GS, a robust framework to progressively estimate camera poses and optimize 3DGS for arbitrarily long video sequences. Leveraging the inherent continuity of videos, we design an adjacent pose tracking method to ensure stable pose estimation between consecutive frames. To handle arbitrarily long inputs, we adopt a “divide and conquer” scheme that adaptively splits the video sequence into several segments and optimizes them separately. Extensive experiments on the Tanks and Temples dataset and our collected real-world dataset show that our Rob-GS outperforms the state-of-the-arts.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)因其高效和高保真渲染而成为了一种强大的表示方法。然而,3DGS训练需要每个输入视图的已知相机姿态,通常通过结构从运动(SfM)管道获得。开创性的工作已经尝试放宽这一限制,但在处理具有复杂相机轨迹的长序列时仍面临困难。在这项工作中,我们提出了Rob-GS,这是一个稳健的框架,可以逐步估计相机姿态并对任意长的视频序列优化3DGS。我们利用视频的固有连续性,设计了一种相邻姿态跟踪方法,以确保连续帧之间的稳定姿态估计。为了处理任意长度的输入,我们采用了“分而治之”的方案,该方案自适应地将视频序列分割成几个片段并分别对其进行优化。在坦克和寺庙数据集以及我们收集的真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的Rob-GS优于最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了三维高斯混合技术(3DGS)在处理长视频序列时的应用难题,并推出了一种名为Rob-GS的稳健框架,能够逐步估计相机姿态并对任意长度的视频序列进行优化的三维高斯混合(3DGS)。借助视频的固有连续性设计了一种相邻姿态跟踪方法,实现了相邻帧之间的稳定姿态估计。通过“分而治之”的方案处理任意长度输入,自适应地将视频序列分割成多个片段分别优化。实验表明,Rob-GS在Tanks和Temples数据集以及真实世界数据集上的表现均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS具有高效和高保真渲染的优点,广泛应用于各种领域。
- 当前大多数训练要求已知输入视图的相机姿态,通常通过结构从运动(SfM)管道获得。但处理长序列时面临挑战。
- Rob-GS框架旨在解决这一问题,通过逐步估计相机姿态和优化任意长视频序列的3DGS。
- 利用视频的固有连续性设计相邻姿态跟踪方法,确保连续帧间稳定的姿态估计。
- Rob-GS采用“分而治之”策略来处理任意长度的输入视频序列,实现更准确的优化。在复杂的长序列处理上优势明显。自适应地将视频序列分割成多个片段进行优化处理,有助于实现更高的准确性和性能稳定性。对任意长度的视频序列均有效且表现出超越现有技术的性能优势。大量实验验证了其在多种数据集上的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

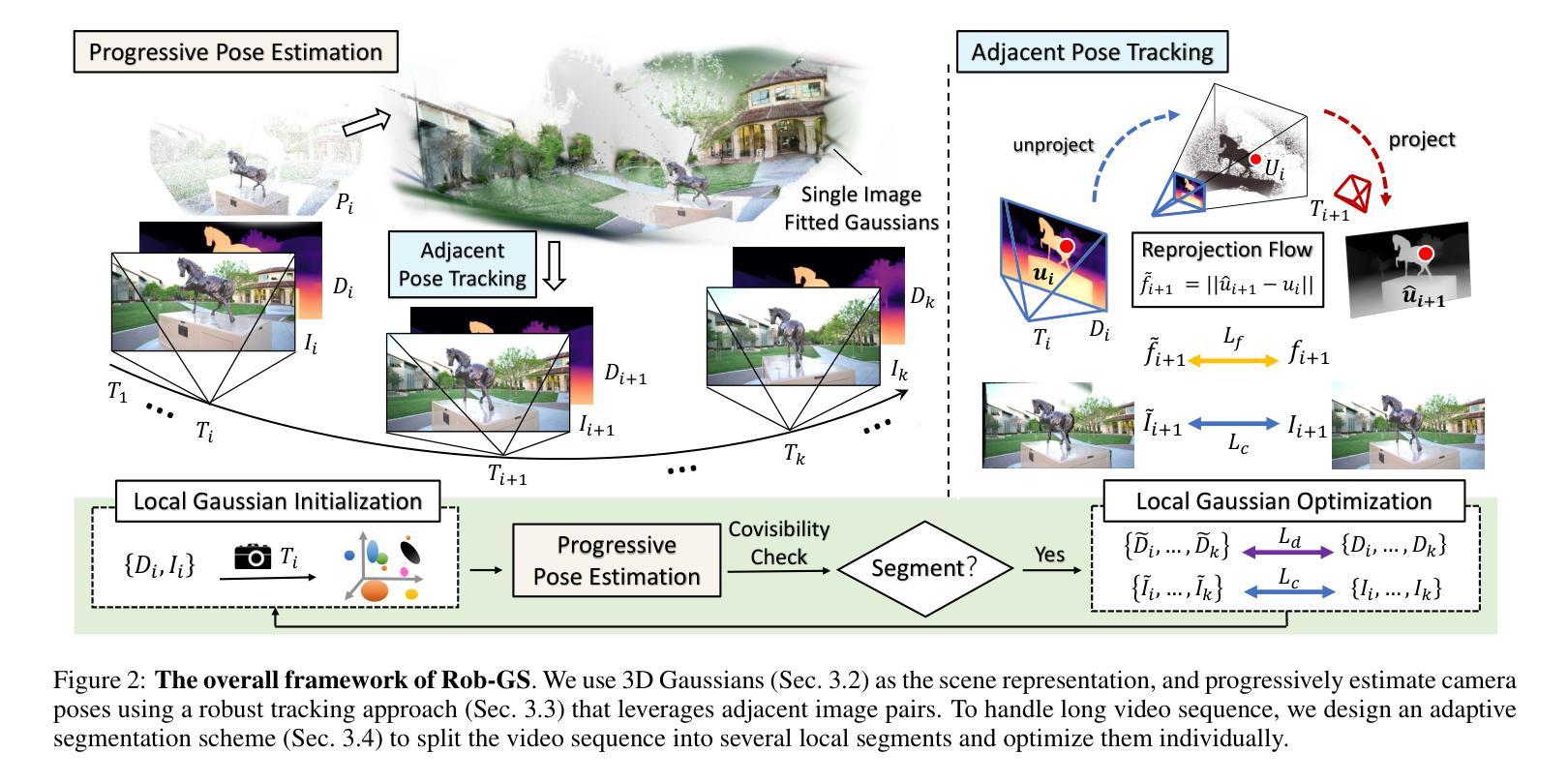
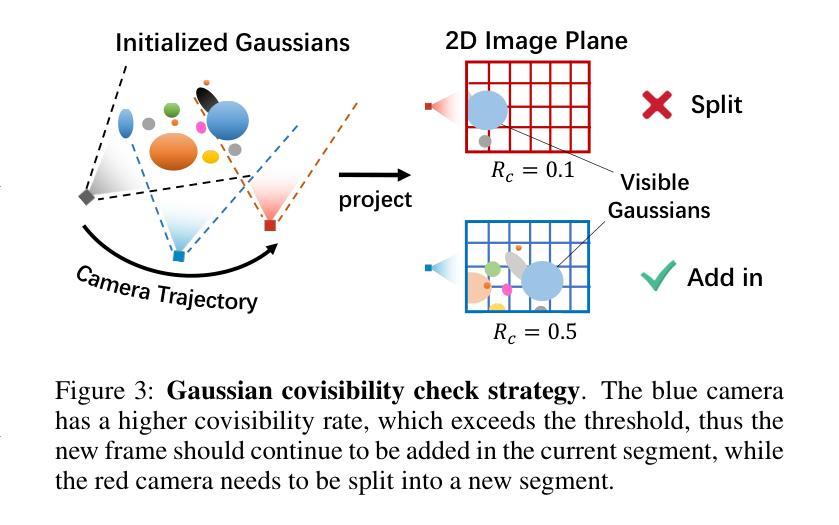
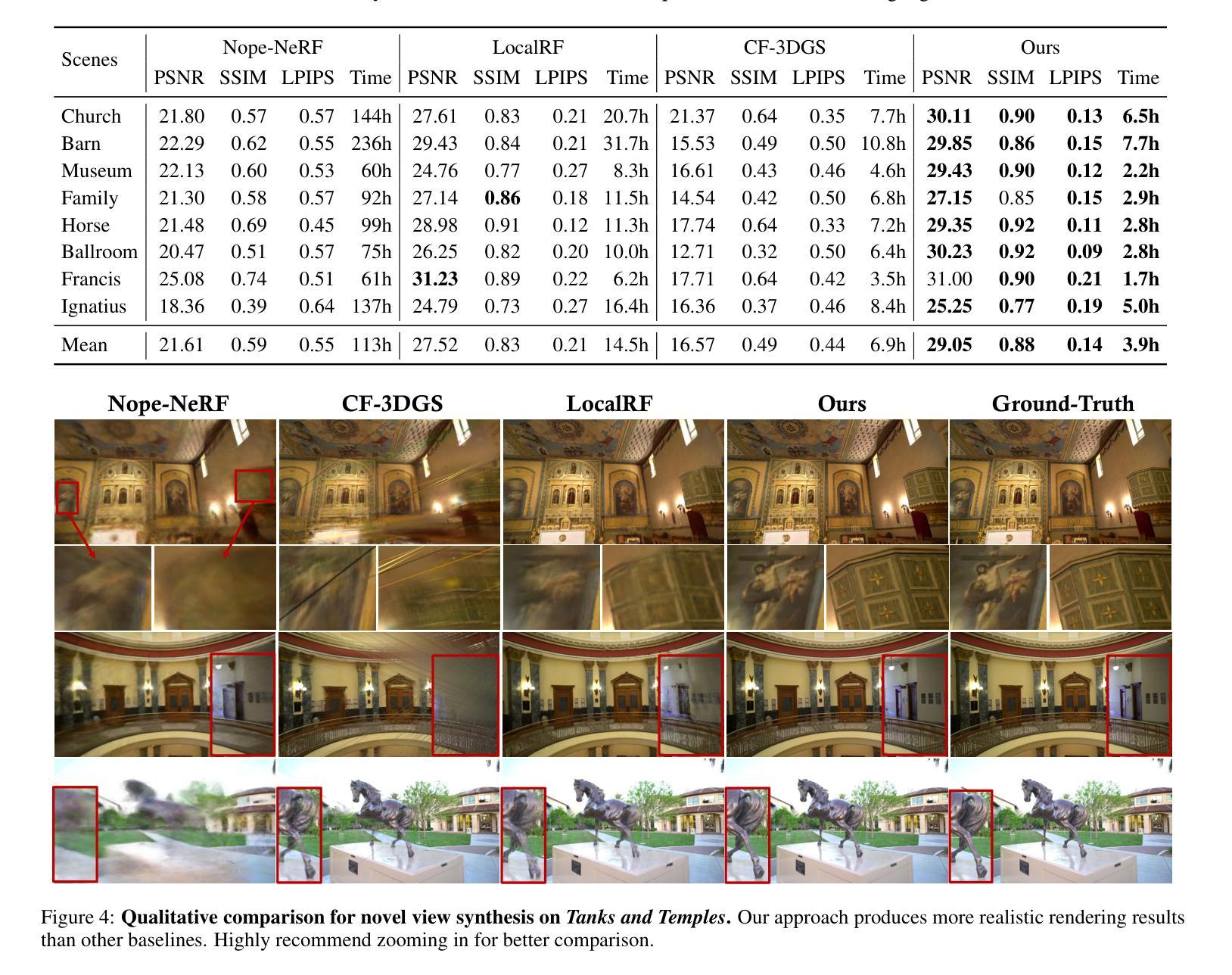
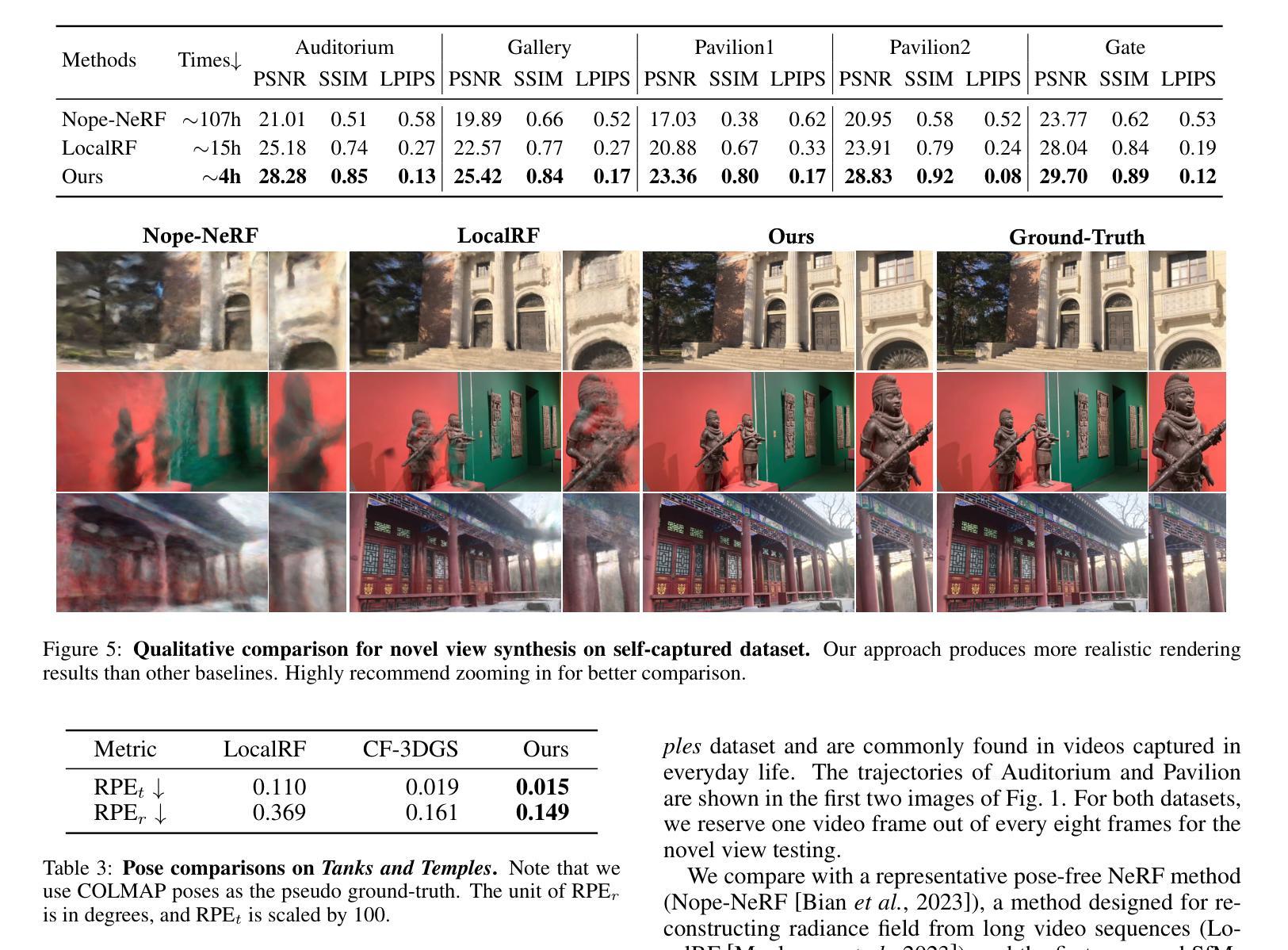
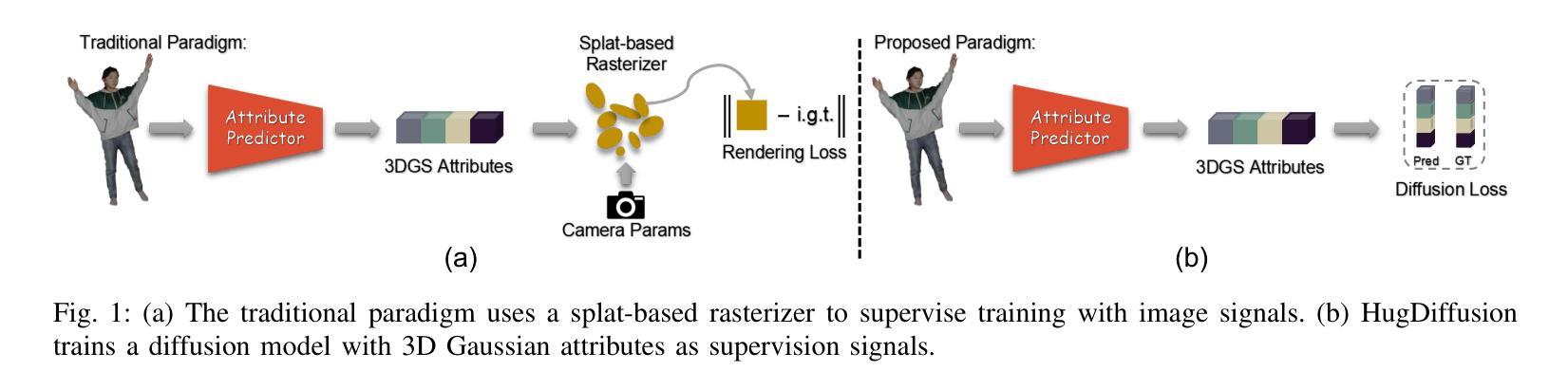
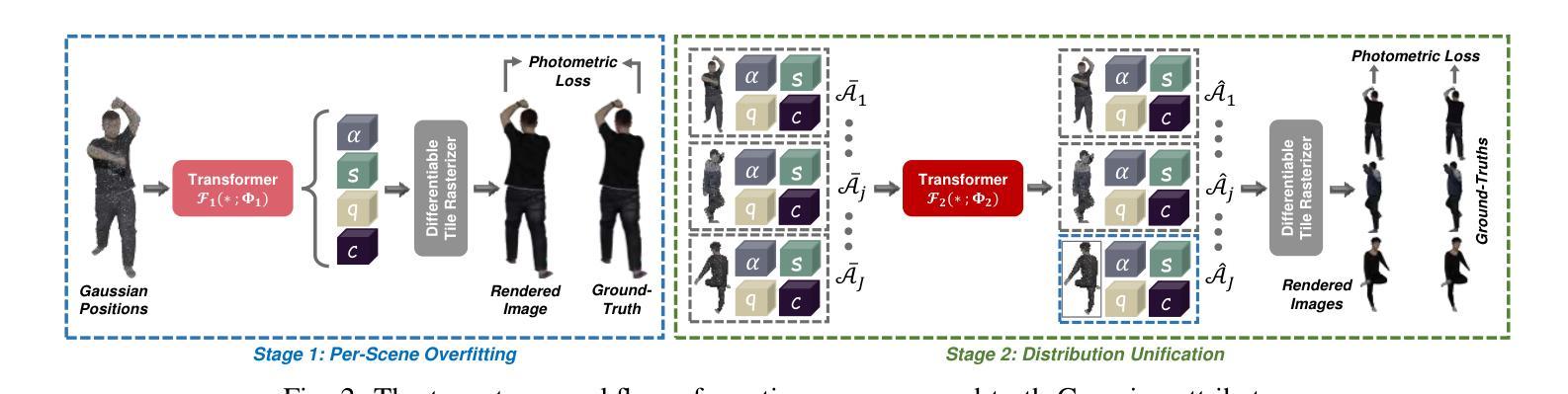
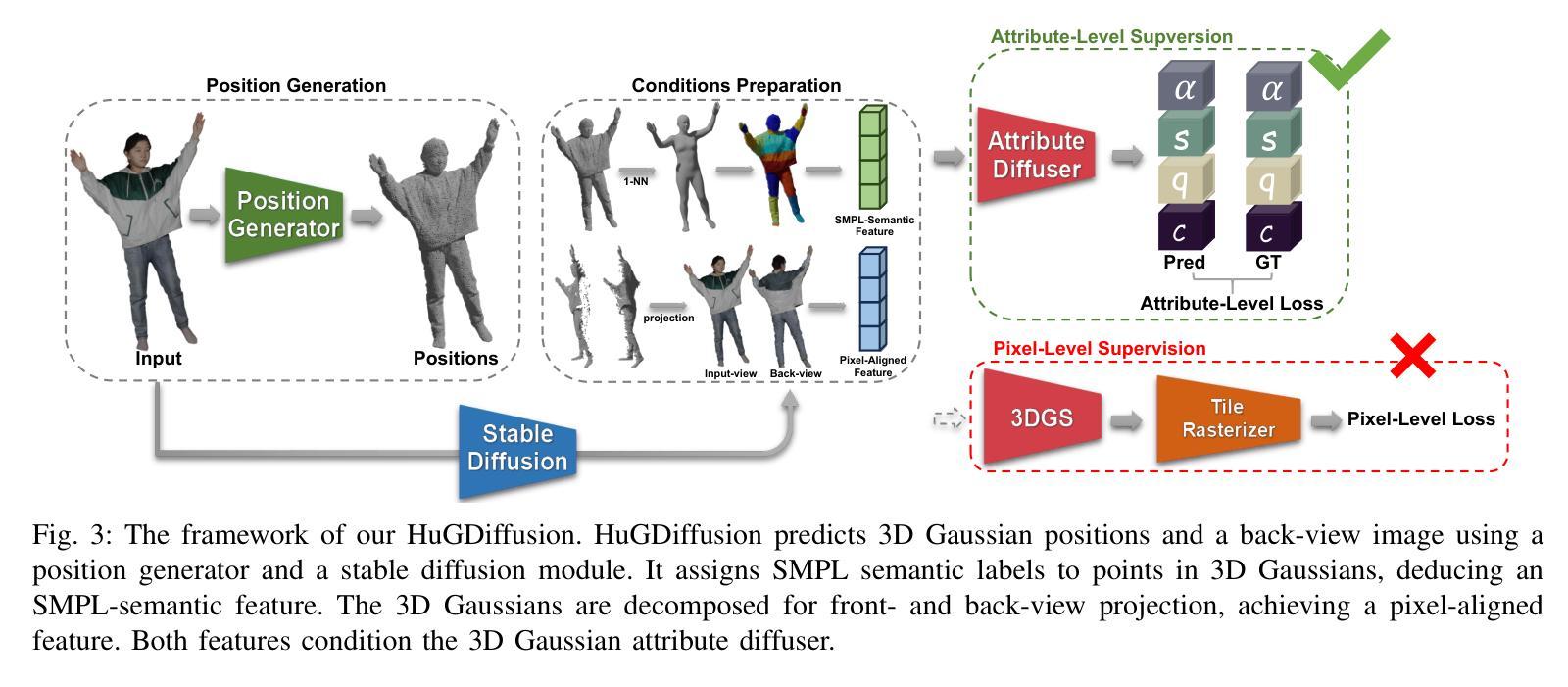
HuGDiffusion: Generalizable Single-Image Human Rendering via 3D Gaussian Diffusion
Authors:Yingzhi Tang, Qijian Zhang, Junhui Hou
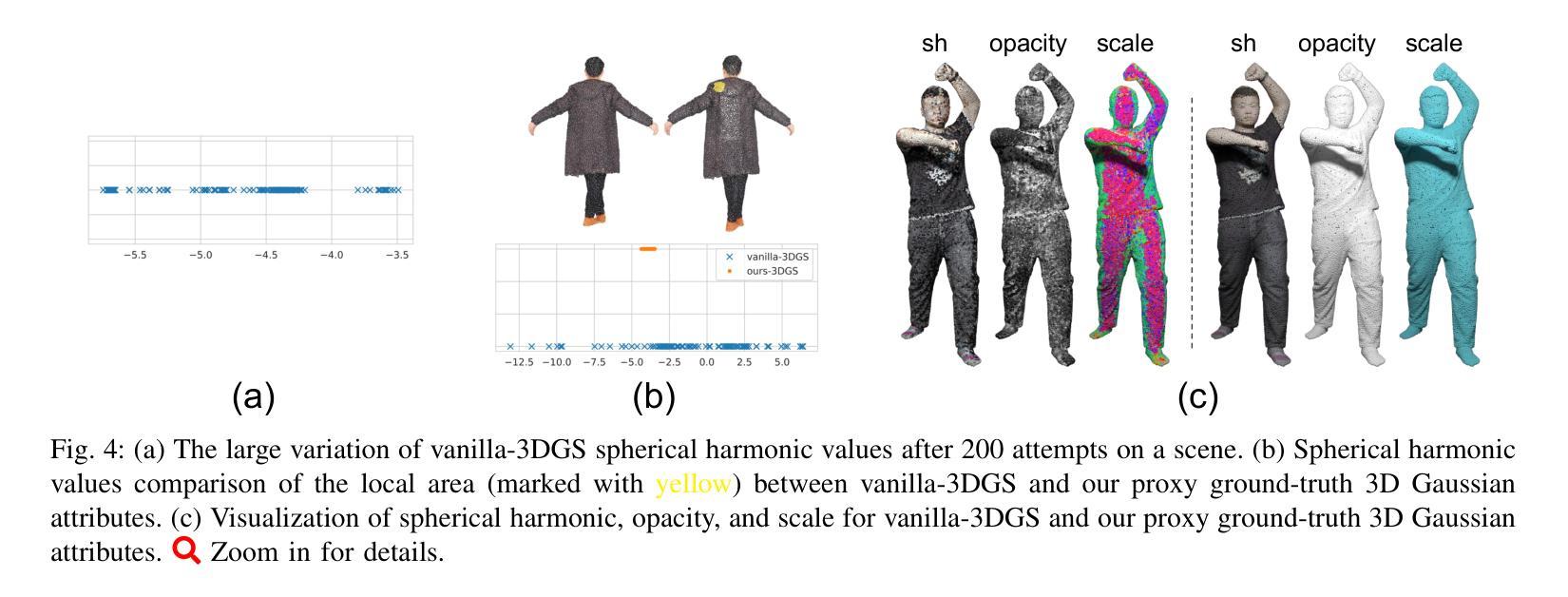
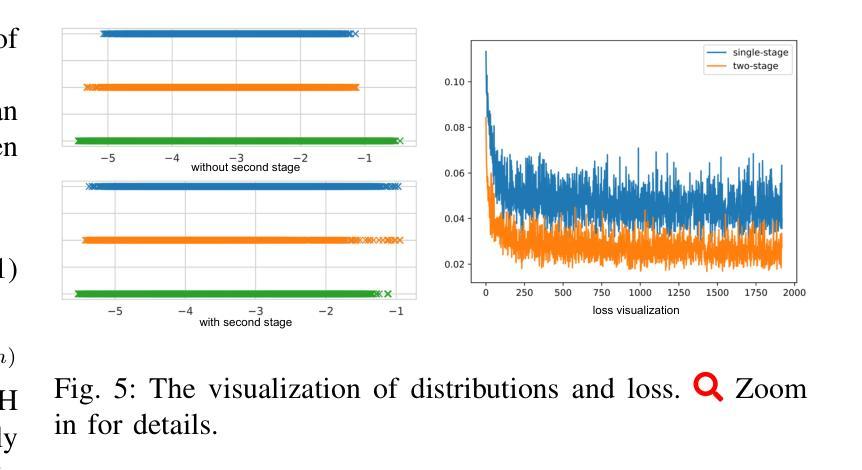
We present HuGDiffusion, a generalizable 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) learning pipeline to achieve novel view synthesis (NVS) of human characters from single-view input images. Existing approaches typically require monocular videos or calibrated multi-view images as inputs, whose applicability could be weakened in real-world scenarios with arbitrary and/or unknown camera poses. In this paper, we aim to generate the set of 3DGS attributes via a diffusion-based framework conditioned on human priors extracted from a single image. Specifically, we begin with carefully integrated human-centric feature extraction procedures to deduce informative conditioning signals. Based on our empirical observations that jointly learning the whole 3DGS attributes is challenging to optimize, we design a multi-stage generation strategy to obtain different types of 3DGS attributes. To facilitate the training process, we investigate constructing proxy ground-truth 3D Gaussian attributes as high-quality attribute-level supervision signals. Through extensive experiments, our HuGDiffusion shows significant performance improvements over the state-of-the-art methods. Our code will be made publicly available.
我们提出了HuGDiffusion,这是一个可通用的3D高斯展平(3DGS)学习管道,用于从单视图输入图像实现人物角色的新颖视图合成(NVS)。现有方法通常需要单目视频或校准的多视图图像作为输入,其在现实世界场景中,由于相机姿态的任意性和/或未知性,其适用性可能会减弱。在本文中,我们的目标是通过基于扩散的框架,根据从单幅图像中提取的人先验知识,生成一组3DGS属性。具体来说,我们从精心整合的人为中心的特征提取程序开始,以推断出信息丰富的条件信号。基于我们的经验观察,即联合学习整个3DGS属性是优化具有挑战性的,我们设计了一种多阶段生成策略,以获得不同类型3DGS属性。为了促进训练过程,我们研究构建了代理真实3D高斯属性作为高质量属性级别的监督信号。通过广泛的实验,我们的HuGDiffusion在最新方法的基础上表现出显著的性能改进。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种名为HuGDiffusion的通用3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)学习管道,用于从单视图输入图像实现人物角色的新颖视图合成(NVS)。现有方法通常需要单目视频或校准的多视图图像作为输入,其在现实世界场景中的适用性可能会因相机姿态的任意性和未知性而减弱。本文旨在通过基于扩散的框架,以从单幅图像中提取的人类先验为条件,生成3DGS属性集。具体来说,我们从精心整合的人为中心的特征提取程序开始,以推断信息丰富的条件信号。基于我们的经验观察,即联合学习整个3DGS属性集具有挑战性,我们设计了一种多阶段生成策略,以获得不同类型的3DGS属性。为了促进训练过程,我们研究构建代理真实3D高斯属性作为高质量属性级监督信号。通过广泛实验,HuGDiffusion相较于现有先进方法表现出显著性能提升。
要点
- 提出了HuGDiffusion学习管道,实现了从单视图输入图像进行人物角色的新颖视图合成。
- 针对现实世界场景中相机姿态的任意性和未知性,提升了方法的适用性。
- 通过人类先验为条件的扩散框架生成3DGS属性集。
- 精心设计人为中心的特征提取程序以推断信息丰富的条件信号。
- 采用多阶段生成策略,分阶段获得不同类型的3DGS属性。
- 通过构建代理真实3D高斯属性,提供高质量属性级监督信号,促进训练过程。
点此查看论文截图

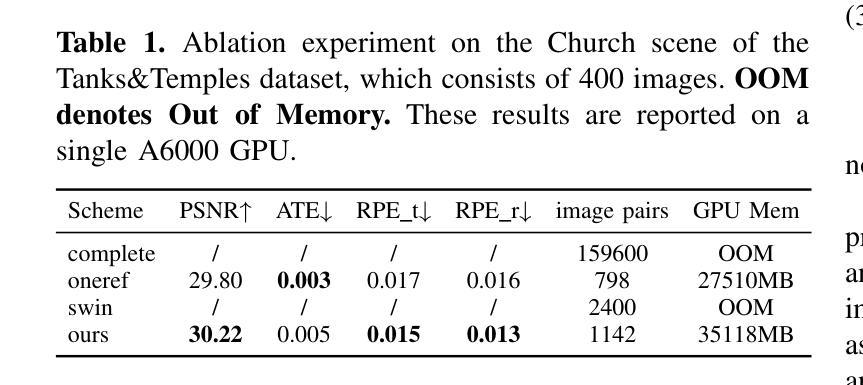
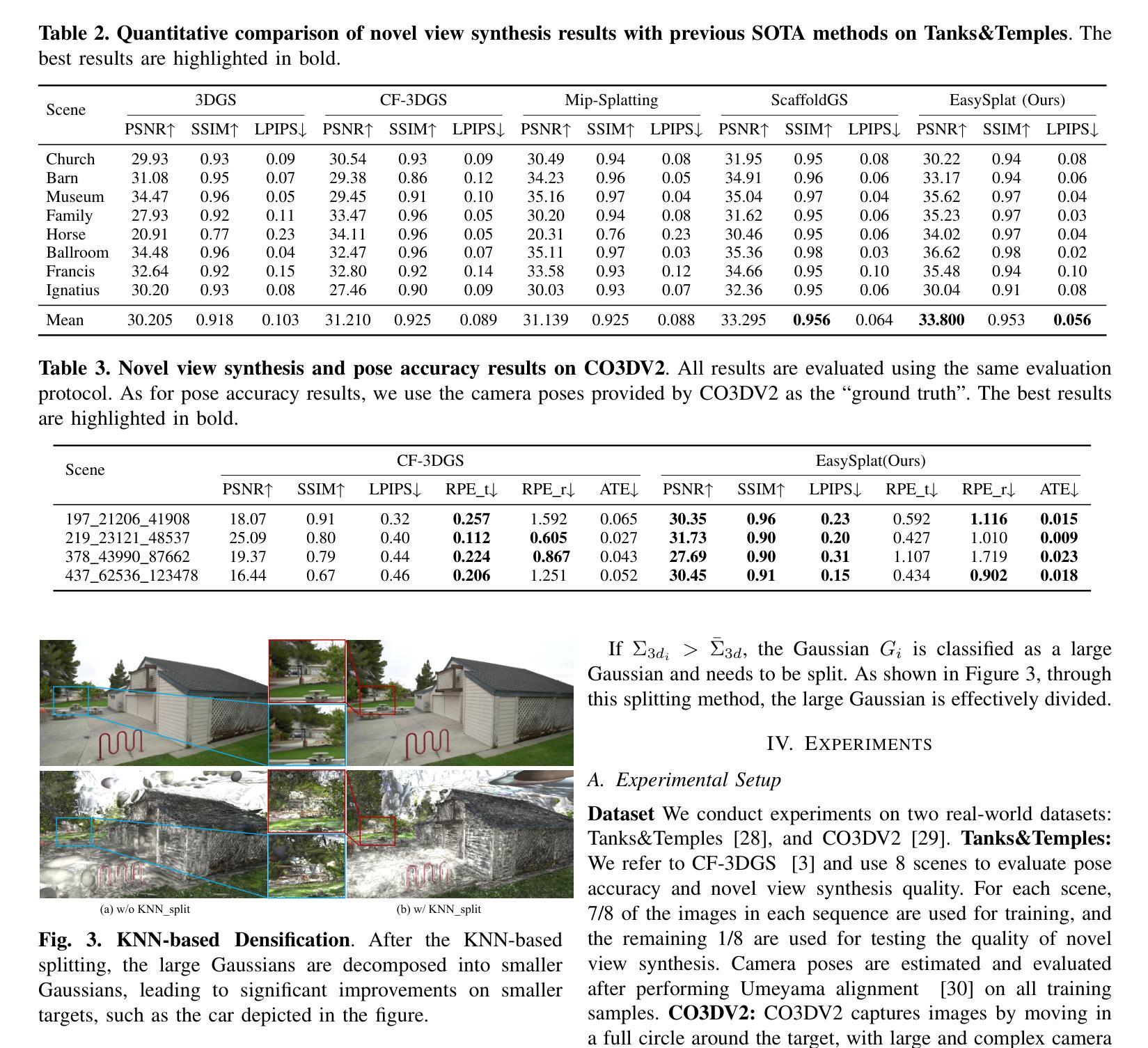
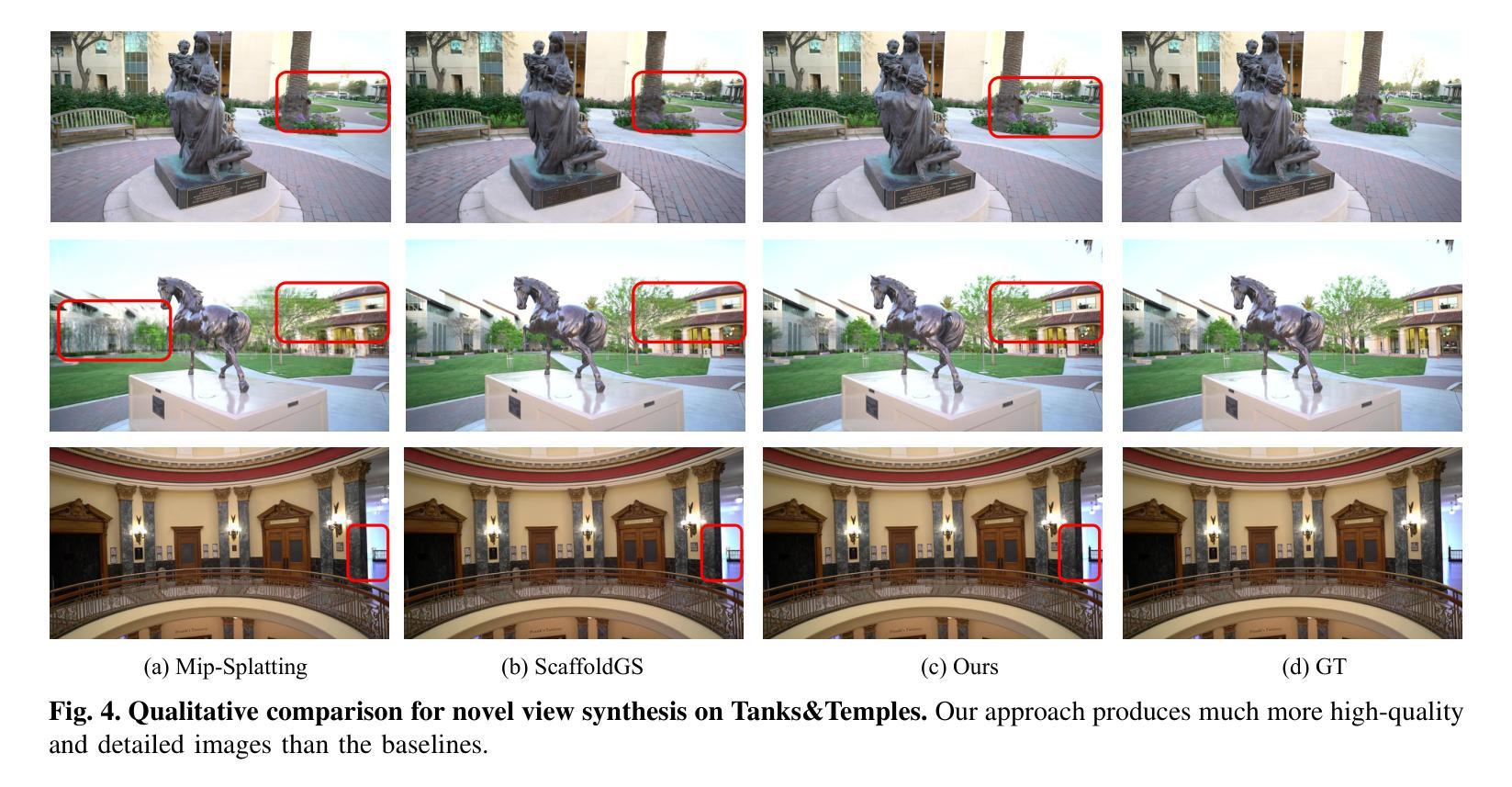
EasySplat: View-Adaptive Learning makes 3D Gaussian Splatting Easy
Authors:Ao Gao, Luosong Guo, Tao Chen, Zhao Wang, Ying Tai, Jian Yang, Zhenyu Zhang
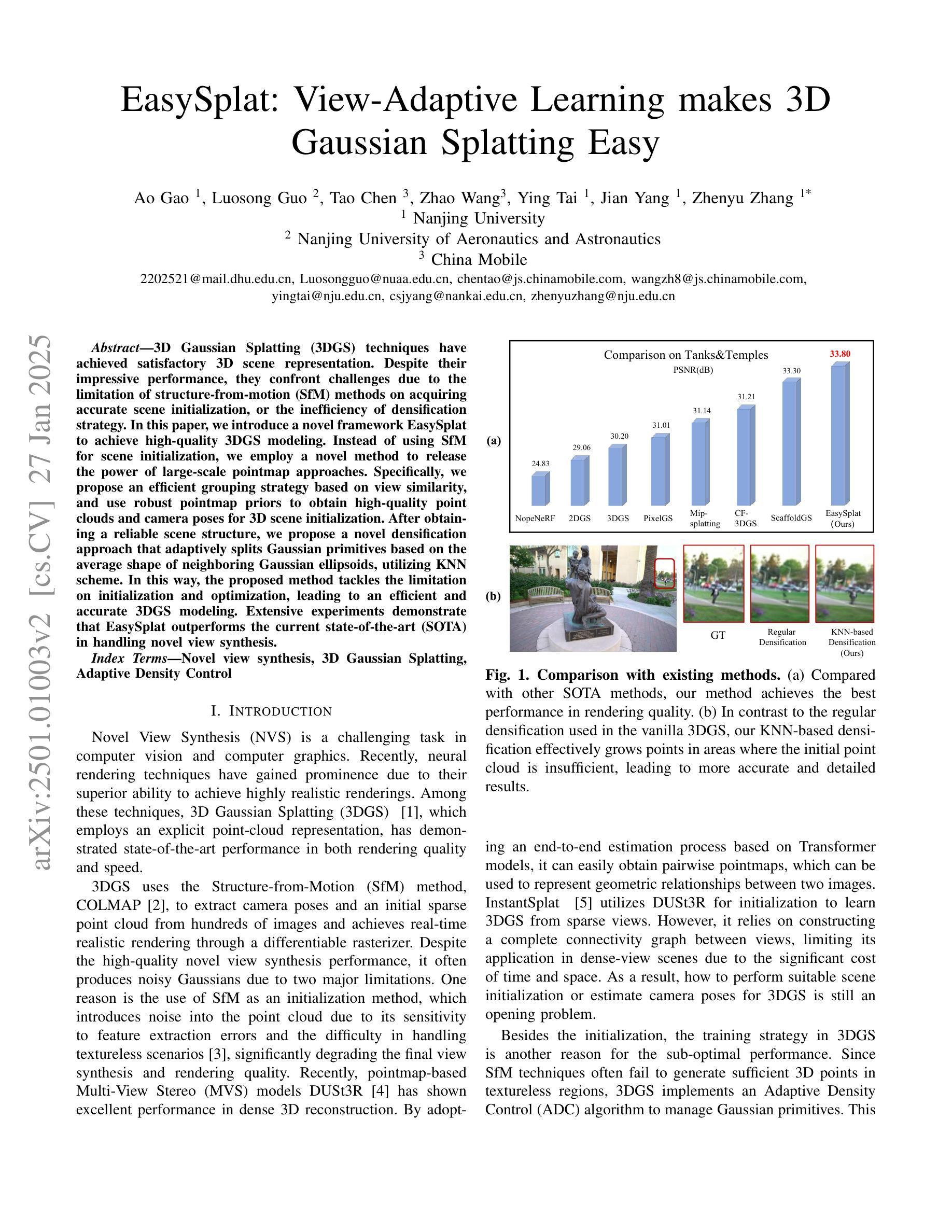
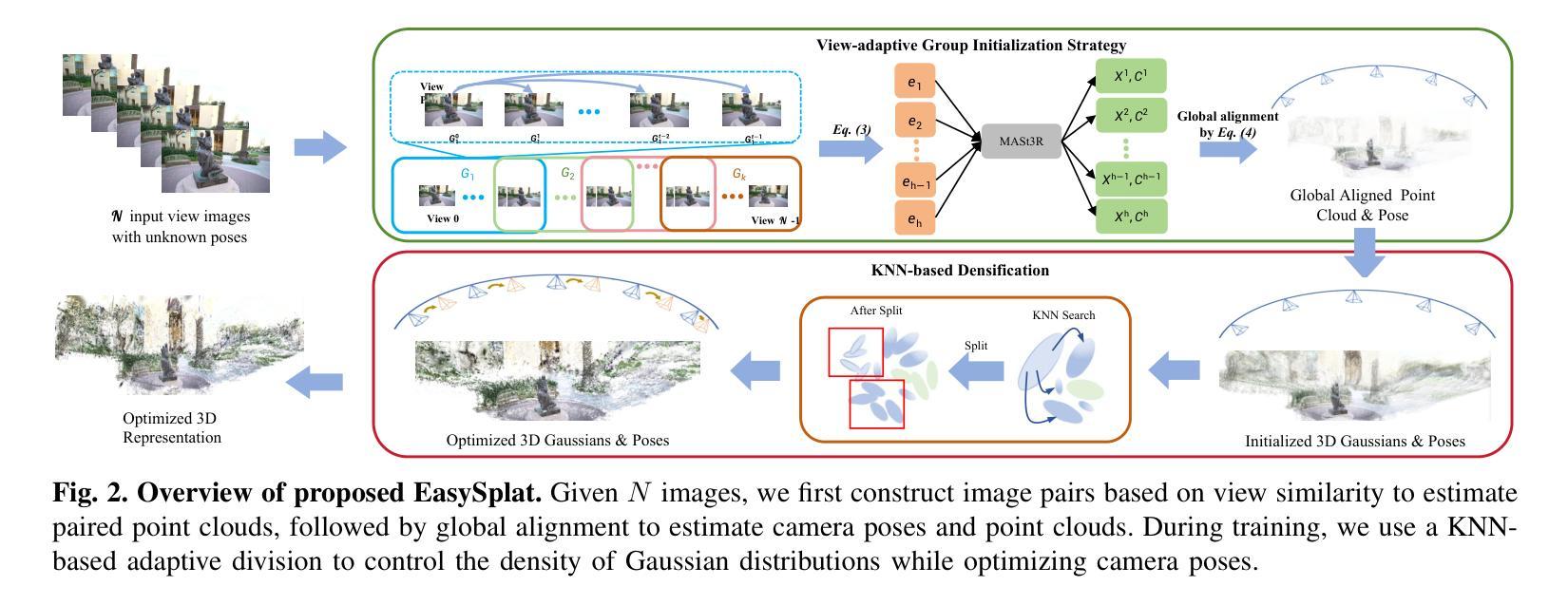
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) techniques have achieved satisfactory 3D scene representation. Despite their impressive performance, they confront challenges due to the limitation of structure-from-motion (SfM) methods on acquiring accurate scene initialization, or the inefficiency of densification strategy. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework EasySplat to achieve high-quality 3DGS modeling. Instead of using SfM for scene initialization, we employ a novel method to release the power of large-scale pointmap approaches. Specifically, we propose an efficient grouping strategy based on view similarity, and use robust pointmap priors to obtain high-quality point clouds and camera poses for 3D scene initialization. After obtaining a reliable scene structure, we propose a novel densification approach that adaptively splits Gaussian primitives based on the average shape of neighboring Gaussian ellipsoids, utilizing KNN scheme. In this way, the proposed method tackles the limitation on initialization and optimization, leading to an efficient and accurate 3DGS modeling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EasySplat outperforms the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) in handling novel view synthesis.
3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)技术在3D场景表示方面取得了令人满意的成果。尽管它们表现令人印象深刻,但它们仍面临挑战,主要由于结构从运动(SfM)方法的限制导致无法获取准确的场景初始化,或者密集化策略的效率低下。在本文中,我们介绍了一个新型框架EasySplat,以实现高质量3DGS建模。我们并非使用SfM进行场景初始化,而是采用了一种新方法释放大规模点云方法的潜力。具体来说,我们提出了一种基于视图相似性的高效分组策略,并利用稳健的点云先验知识来获得高质量的点云和相机姿态,用于3D场景初始化。在获得可靠的场景结构后,我们提出了一种新型的密集化方法,该方法根据相邻高斯椭圆体的平均形状自适应地拆分高斯原始数据,并利用KNN方案。通过这种方式,所提出的方法解决了初始化和优化方面的限制,实现了高效且准确的3DGS建模。大量实验表明,在处理新型视图合成方面,EasySplat的性能超过了当前最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 5figures
Summary
本文提出一种基于大规模点云方法的EasySplat框架,用于实现高质量的三维高斯展铺(3DGS)建模。它采用基于视图相似性的高效分组策略,并利用稳健的点云先验信息获取高质量点云和相机姿态,以实现3D场景初始化。此外,还提出了一种基于邻近高斯椭圆体平均形状的自适应分割的细化方法,从而解决了初始化和优化方面的限制,实现了高效且准确的三维场景建模。实验表明,EasySplat在新型视图合成方面优于当前最佳方法。
Key Takeaways
- EasySplat框架采用大规模点云方法实现高质量3DGS建模。
- 使用基于视图相似性的高效分组策略进行场景初始化。
- 稳健的点云先验信息用于获取高质量点云和相机姿态。
- 提出一种基于邻近高斯椭圆体平均形状的自适应分割细化方法。
- 该方法解决了初始化和优化方面的限制。
- EasySplat实现了高效且准确的三维场景建模。
点此查看论文截图

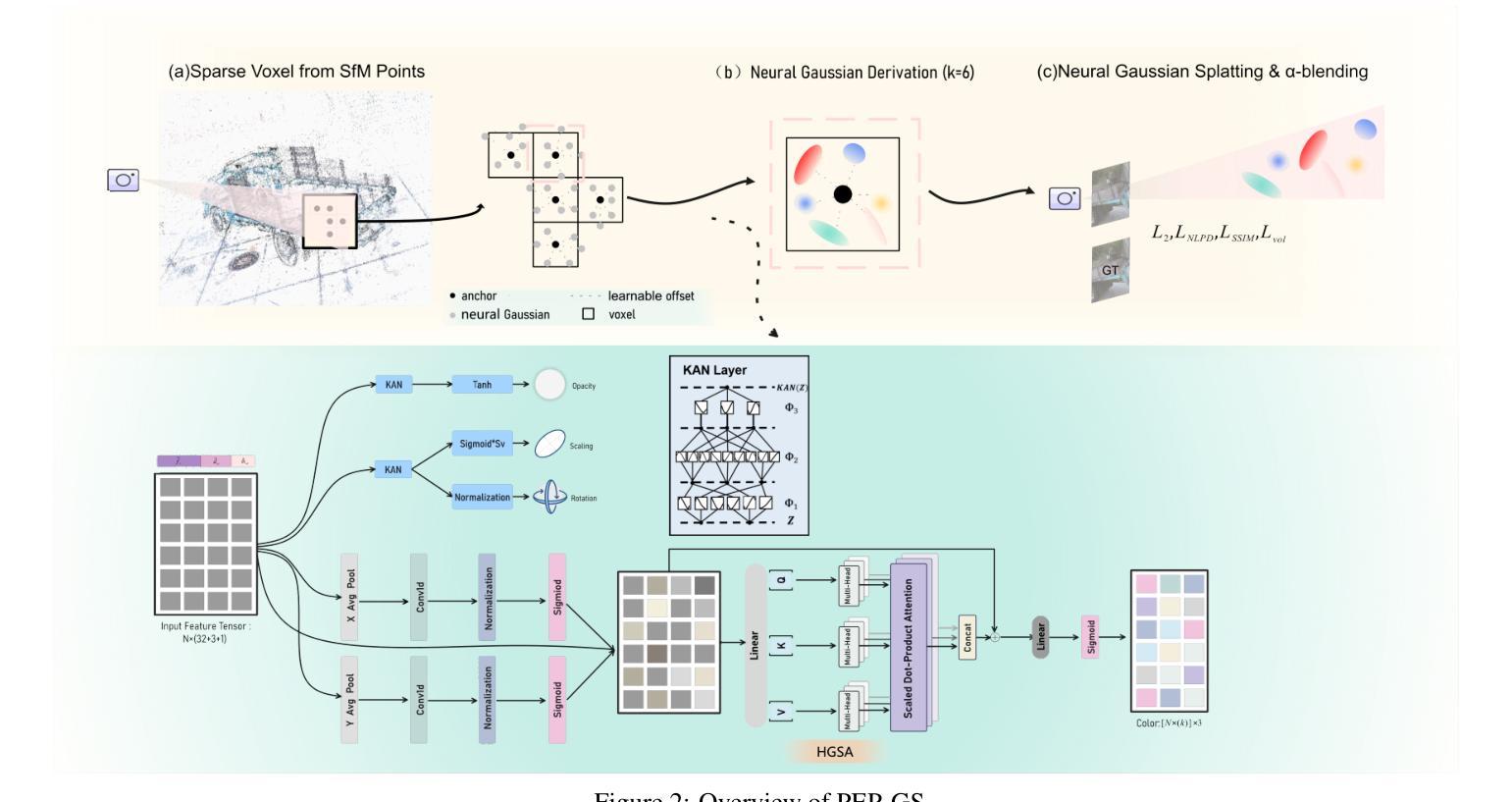
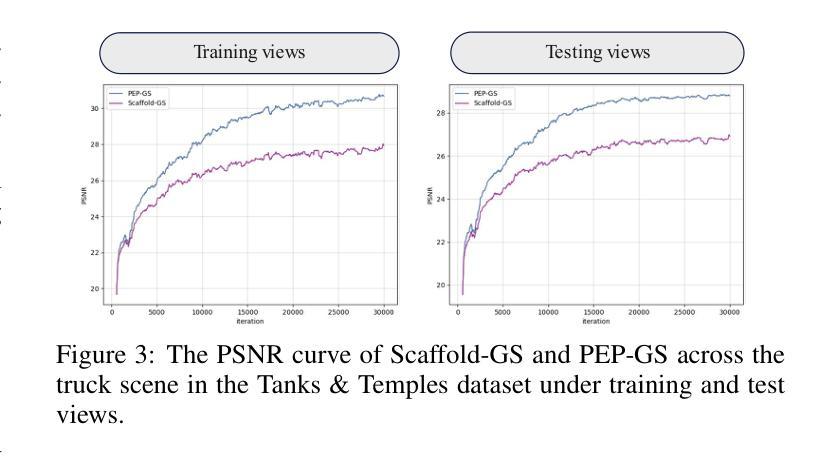
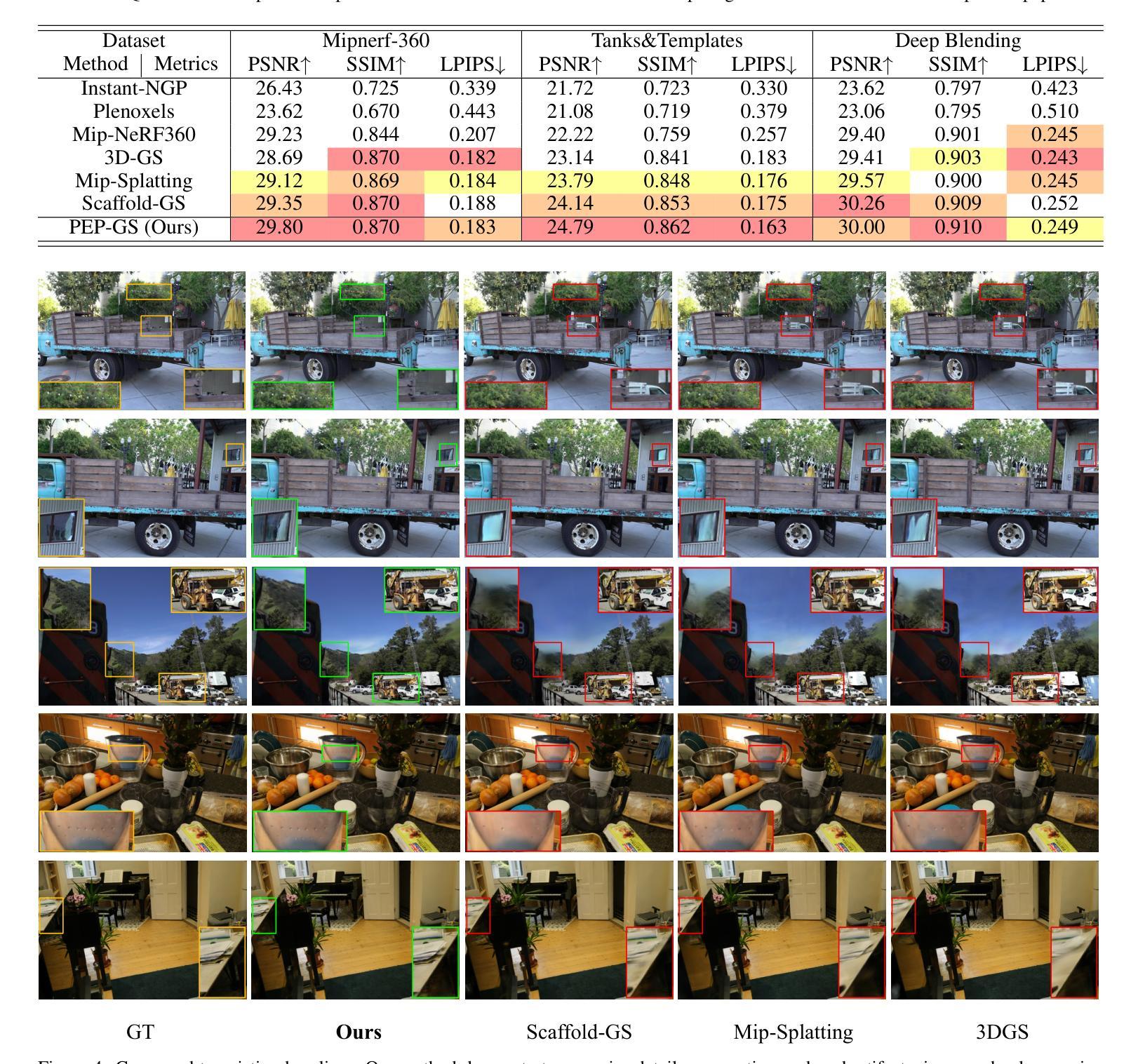
PEP-GS: Perceptually-Enhanced Precise Structured 3D Gaussians for View-Adaptive Rendering
Authors:Junxi Jin, Xiulai Li, Haiping Huang, Lianjun Liu, Yujie Sun, Boyi Liu
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has achieved significant success in real-time, high-quality 3D scene rendering. However, it faces several challenges, including Gaussian redundancy, limited ability to capture view-dependent effects, and difficulties in handling complex lighting and specular reflections. Additionally, methods that use spherical harmonics for color representation often struggle to effectively capture specular highlights and anisotropic components, especially when modeling view-dependent colors under complex lighting conditions, leading to insufficient contrast and unnatural color saturation. To address these limitations, we introduce PEP-GS, a perceptually-enhanced framework that dynamically predicts Gaussian attributes, including opacity, color, and covariance. We replace traditional spherical harmonics with a Hierarchical Granular-Structural Attention mechanism, which enables more accurate modeling of complex view-dependent color effects and specular highlights. By employing a stable and interpretable framework for opacity and covariance estimation, PEP-GS avoids the removal of essential Gaussians prematurely, ensuring a more accurate scene representation. Furthermore, perceptual optimization is applied to the final rendered images, enhancing perceptual consistency across different views and ensuring high-quality renderings with improved texture fidelity and fine-scale detail preservation. Experimental results demonstrate that PEP-GS outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in challenging scenarios involving view-dependent effects, specular reflections, and fine-scale details.
最近,3D高斯描画(3D-GS)在实时高质量3D场景渲染中取得了显著的成功。然而,它面临几个挑战,包括高斯冗余、捕捉视角相关效果的能力有限,以及处理复杂光线和镜面反射的困难。此外,使用球面谐波进行颜色表示的方法在捕捉镜面高光和偏振成分时经常遇到困难,特别是在复杂光照条件下对视角相关颜色进行建模时,这会导致对比度不足和颜色饱和度不自然。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了PEP-GS,这是一个感知增强框架,可以动态预测高斯属性,包括不透明度、颜色和协方差。我们用分层粒度结构注意机制取代了传统的球面谐波,这能够更准确地模拟复杂的视角相关颜色效果和镜面高光。通过采用稳定和可解释的不透明度和协方差估计框架,PEP-GS避免了过早删除重要的高斯值,确保了更准确的场景表示。此外,对最终渲染的图像应用了感知优化,增强了不同视图之间的感知一致性,确保高质量渲染,提高了纹理保真度和细节保留。实验结果表明,PEP-GS在涉及视角相关效果、镜面反射和细节精细的场景中表现优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代感知增强框架PEP-GS针对实时高质量渲染面临的挑战进行了改进。它通过动态预测高斯属性如透明度、颜色和协方差来克服高斯冗余问题,并且以层级化颗粒状结构注意机制取代了传统球谐进行色彩表达,提高了复杂环境下的渲染效果,更好地捕捉视差相关色彩效果和镜面高光。该框架保证渲染的稳定性与可解释性,避免了重要高斯的过早移除,确保更准确的场景表达。最终图像进行了感知优化,增强了不同视角下的感知一致性,保证了高质量渲染,提高了纹理保真度和精细细节保留。实验结果表明PEP-GS在视差效果、镜面反射和精细细节方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- PEP-GS针对实时高质量渲染中面临的挑战进行改进。它优化了场景建模、提高了图像渲染的精确度,在多种光照条件下都能有效捕捉视差相关色彩效果和镜面高光。
- PEP-GS通过动态预测高斯属性解决冗余问题,并利用层级化颗粒状结构注意机制进行色彩表达,提高复杂场景下的渲染效果。
- 该框架保证渲染的稳定性与可解释性,避免重要高斯属性的过早移除。通过感知优化,增强了不同视角下的感知一致性。相较于当前顶尖技术有更明显的优越性,尤其是在复杂的视图依赖性色彩模型与光照环境下进行建模的场景中表现得更为突出。
点此查看论文截图