⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
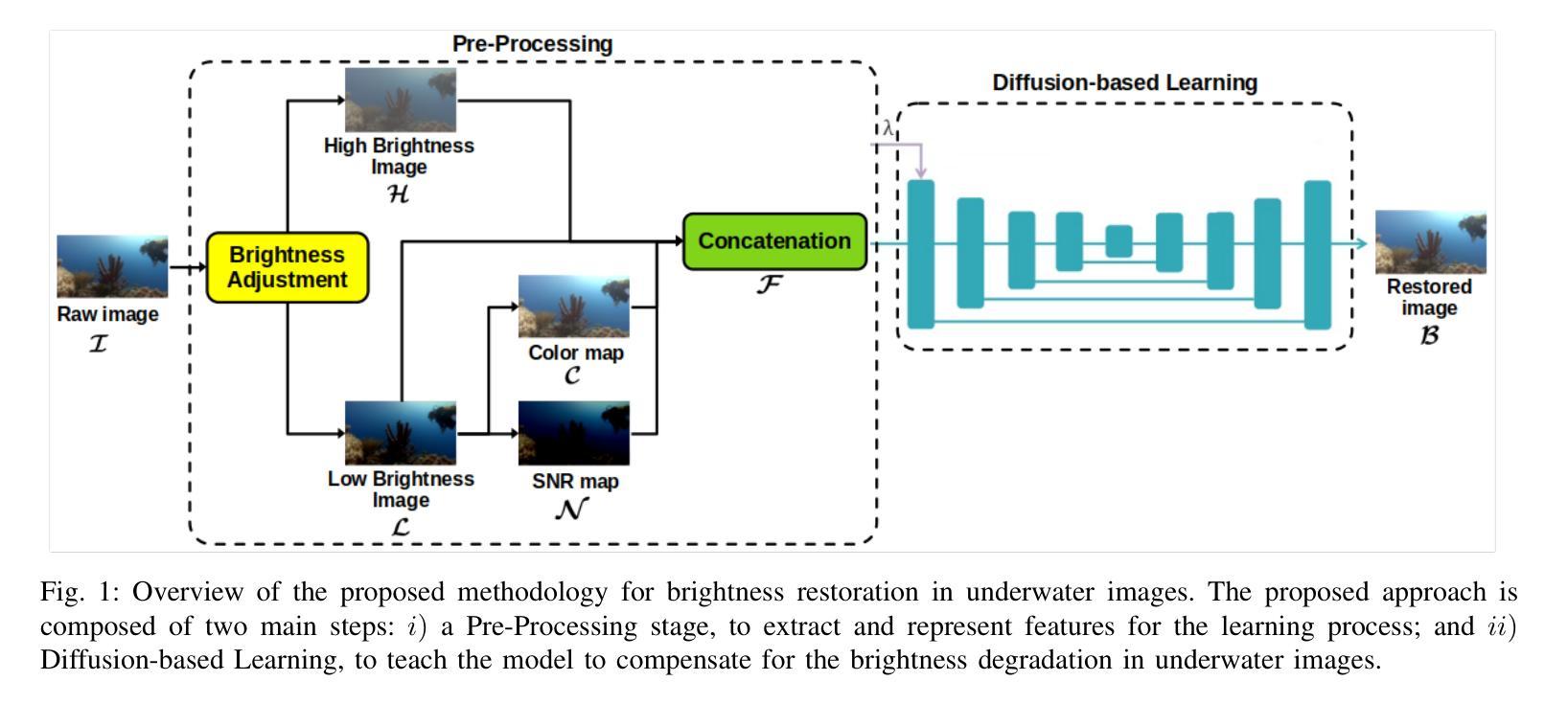
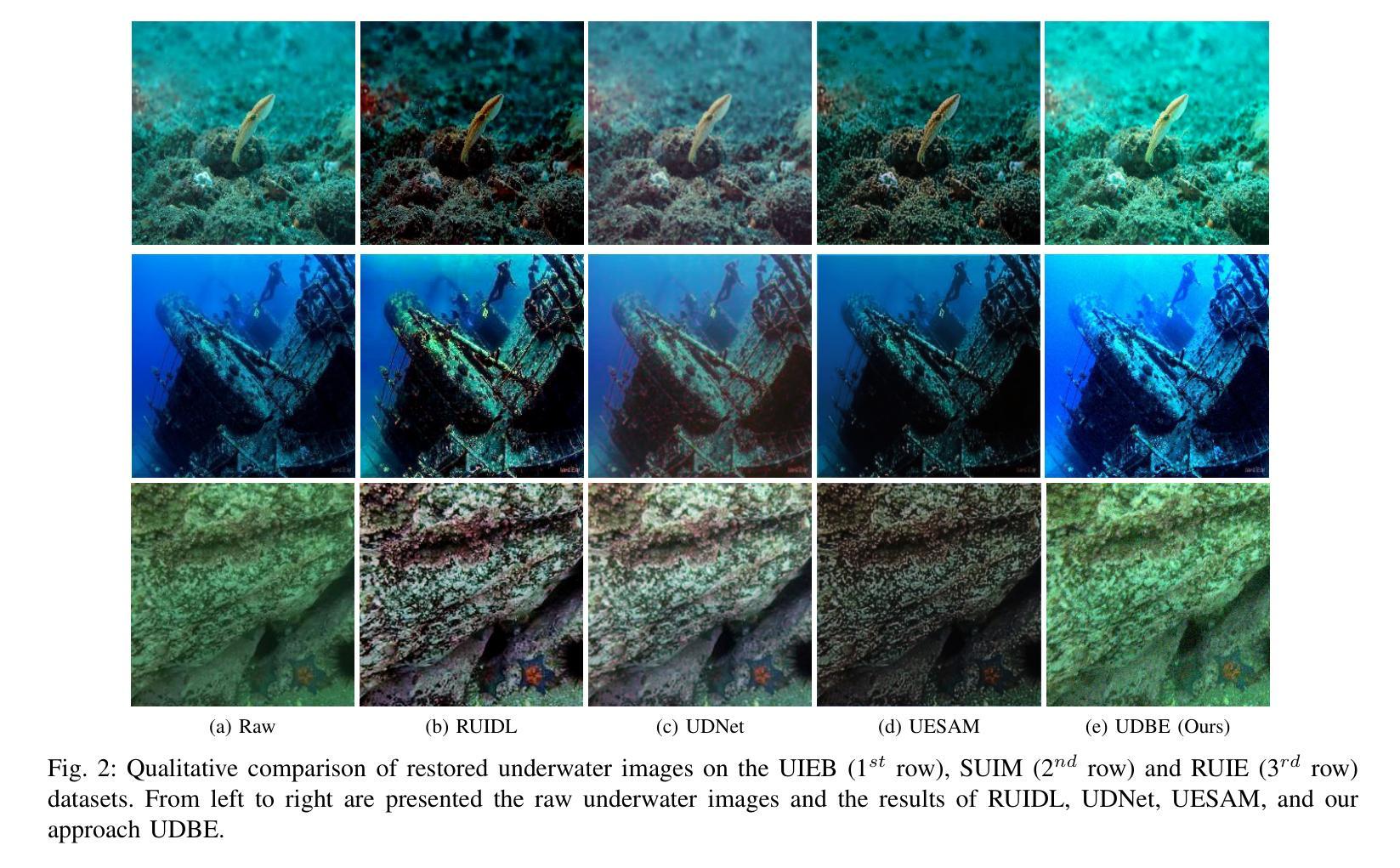
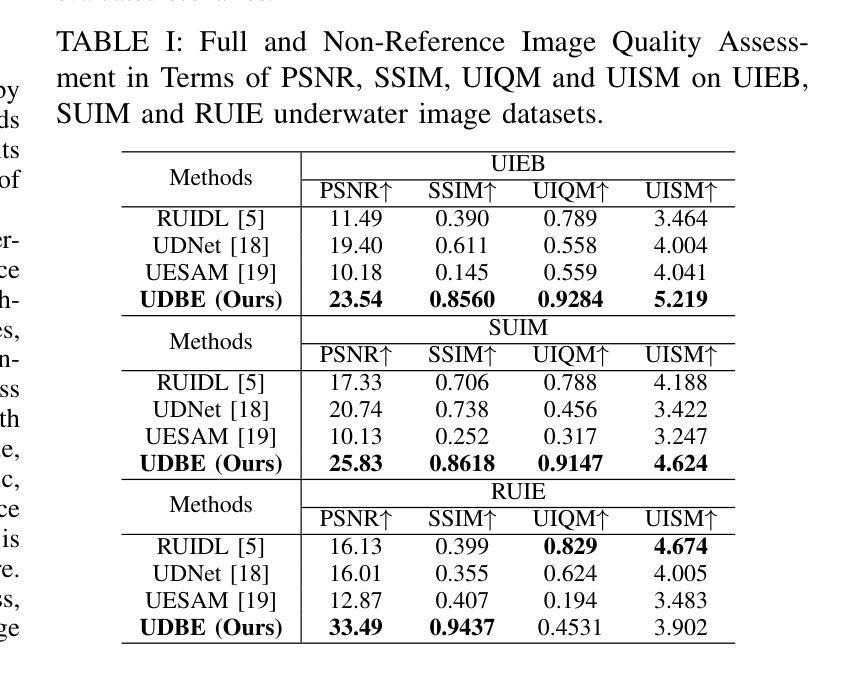
UDBE: Unsupervised Diffusion-based Brightness Enhancement in Underwater Images
Authors:Tatiana Taís Schein, Gustavo Pereira de Almeira, Stephanie Loi Brião, Rodrigo Andrade de Bem, Felipe Gomes de Oliveira, Paulo L. J. Drews-Jr
Activities in underwater environments are paramount in several scenarios, which drives the continuous development of underwater image enhancement techniques. A major challenge in this domain is the depth at which images are captured, with increasing depth resulting in a darker environment. Most existing methods for underwater image enhancement focus on noise removal and color adjustment, with few works dedicated to brightness enhancement. This work introduces a novel unsupervised learning approach to underwater image enhancement using a diffusion model. Our method, called UDBE, is based on conditional diffusion to maintain the brightness details of the unpaired input images. The input image is combined with a color map and a Signal-Noise Relation map (SNR) to ensure stable training and prevent color distortion in the output images. The results demonstrate that our approach achieves an impressive accuracy rate in the datasets UIEB, SUIM and RUIE, well-established underwater image benchmarks. Additionally, the experiments validate the robustness of our approach, regarding the image quality metrics PSNR, SSIM, UIQM, and UISM, indicating the good performance of the brightness enhancement process. The source code is available here: https://github.com/gusanagy/UDBE.
在水下环境中的应用在各种场景中至关重要,这推动了水下图像增强技术的不断发展。此领域的一个主要挑战是图像捕获的深度,随着深度的增加,环境会变暗。大多数现有的水下图像增强方法主要关注去噪和色彩调整,很少有工作专注于亮度增强。这项工作引入了一种使用扩散模型进行水下图像增强的新型无监督学习方法。我们的方法称为UDBE,它基于条件扩散来保持非配对输入图像的亮度细节。输入图像与色图和信号噪声关系图(SNR)相结合,以确保稳定的训练并防止输出图像中的颜色失真。结果表明,我们的方法在UIEB、SUIM和RUIE等水下图像基准测试集上取得了令人印象深刻的准确率。此外,实验验证了我们方法在图像质量指标PSNR、SSIM、UIQM和UISM方面的稳健性,表明亮度增强过程表现良好。源代码可在:https://github.com/gusanagy/UDBE处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper presented at ICMLA 2024
Summary
水下环境在多种场景中都极为重要,推动了水下图像增强技术的持续发展。在此领域的一大挑战是图像捕获的深度,随着深度的增加,环境会变暗。目前大多数水下图像增强方法主要关注去噪和色彩调整,很少有工作致力于亮度增强。本文引入了一种使用扩散模型进行水下图像增强的新型无监督学习方法。所提方法UDBE基于条件扩散,以保持未配对输入图像的亮度细节。输入图像与色彩图和信噪比关系图(SNR)相结合,以确保训练稳定并防止输出图像出现色彩失真。结果证明,该方法在UIEB、SUIM和RUIE等水下图像基准数据集上实现了较高的准确率。实验还验证了该方法在图像质量指标PSNR、SSIM、UIQM和UISM方面的稳健性,表明亮度增强过程表现良好。源代码可在https://github.com/gusanagy/UDBE获取。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像增强对于多种应用场景至关重要,尤其随着水下活动的不断增加。
- 当前技术挑战在于处理不同水深带来的环境变暗问题。
- 现有方法主要关注去噪和色彩调整,而亮度的增强则相对被忽视。
- 论文提出了一种新型的无监督学习方法UDBE,基于条件扩散模型进行水下图像增强。
- UDBE能够保持输入图像的亮度细节,结合色彩图和SNR来确保训练稳定性和图像质量。
- UDBE在多个水下图像基准数据集上实现了较高的准确率。
点此查看论文截图

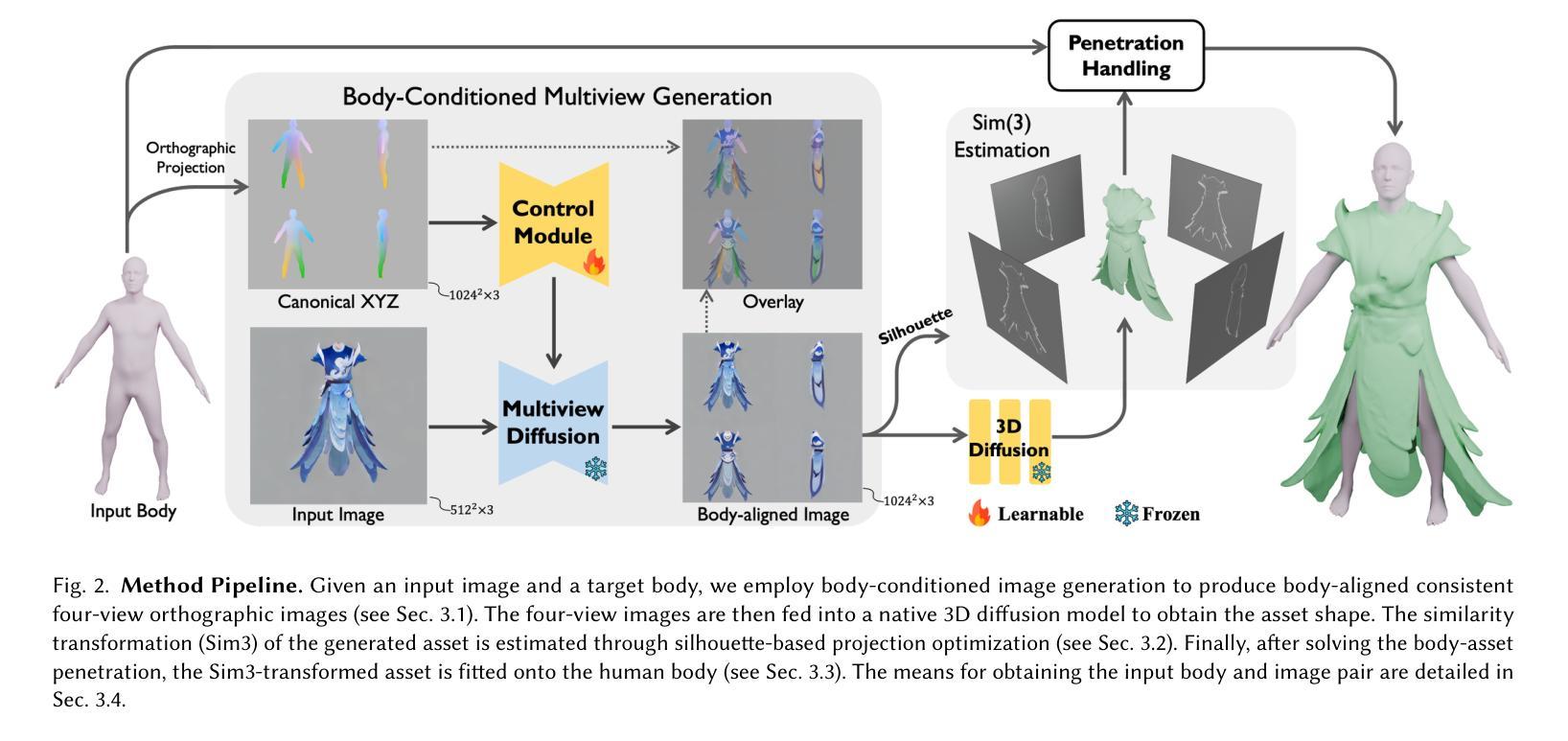
BAG: Body-Aligned 3D Wearable Asset Generation
Authors:Zhongjin Luo, Yang Li, Mingrui Zhang, Senbo Wang, Han Yan, Xibin Song, Taizhang Shang, Wei Mao, Hongdong Li, Xiaoguang Han, Pan Ji
While recent advancements have shown remarkable progress in general 3D shape generation models, the challenge of leveraging these approaches to automatically generate wearable 3D assets remains unexplored. To this end, we present BAG, a Body-aligned Asset Generation method to output 3D wearable asset that can be automatically dressed on given 3D human bodies. This is achived by controlling the 3D generation process using human body shape and pose information. Specifically, we first build a general single-image to consistent multiview image diffusion model, and train it on the large Objaverse dataset to achieve diversity and generalizability. Then we train a Controlnet to guide the multiview generator to produce body-aligned multiview images. The control signal utilizes the multiview 2D projections of the target human body, where pixel values represent the XYZ coordinates of the body surface in a canonical space. The body-conditioned multiview diffusion generates body-aligned multiview images, which are then fed into a native 3D diffusion model to produce the 3D shape of the asset. Finally, by recovering the similarity transformation using multiview silhouette supervision and addressing asset-body penetration with physics simulators, the 3D asset can be accurately fitted onto the target human body. Experimental results demonstrate significant advantages over existing methods in terms of image prompt-following capability, shape diversity, and shape quality. Our project page is available at https://bag-3d.github.io/.
尽管最近的进展在通用3D形状生成模型方面取得了显著的进步,但利用这些方法自动生成可穿戴3D资产的挑战仍然未被探索。为此,我们提出了BAG(Body-aligned Asset Generation)方法,它可输出能够在给定3D人体上自动穿戴的3D可穿戴资产。这是通过控制使用人体形状和姿势信息的3D生成过程来实现的。具体来说,我们首先构建了一个通用的单图像到一致的多视图图像扩散模型,并在大型Objaverse数据集上进行训练,以实现多样性和通用性。然后,我们训练了一个Controlnet来指导多视图生成器产生与身体对齐的多视图图像。控制信号利用目标人体的多视图2D投影,其中像素值代表标准空间中体表面的XYZ坐标。以身体为条件的多视图扩散产生与身体对齐的多视图图像,然后将其输入到本地3D扩散模型中,以产生资产的三维形状。最后,通过利用多视图轮廓监督恢复相似变换并借助物理模拟器解决资产与身体之间的穿透问题,可以准确地将3D资产匹配到目标人体上。实验结果表明,在图像提示遵循能力、形状多样性和形状质量方面,与现有方法相比具有显著优势。我们的项目页面可在https://bag-3d.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF video: https://youtu.be/XJtG82LjQKc
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为BAG的自动生成可穿戴3D资产的方法。该方法利用人体形态和姿态信息控制3D生成过程,实现自动将给定的3D人体穿上服装的效果。通过构建单图像到一致的多视角图像扩散模型,并在Objaverse数据集上进行训练,实现了多样性和泛化能力。训练控制网络Controlnet来指导多视角生成器生成与人体对齐的多视角图像,然后通过3D扩散模型生成资产的三维形状。最后,通过多视角轮廓监督恢复相似变换并解决资产与人体之间的穿透问题,使用物理模拟器准确地将3D资产适配到目标人体上。
Key Takeaways
- BAG方法实现了自动生成可穿戴3D资产的能力,解决了现有方法的挑战。
- 通过构建单图像到多视角图像扩散模型,实现了多样性和泛化能力。
- 控制网络Controlnet用于指导多视角生成器产生与人体对齐的图像。
- 利用人体形态和姿态信息的控制信号指导扩散过程,生成与人体对齐的多视角图像。
- 通过多视角轮廓监督恢复相似变换,解决了资产与人体之间的穿透问题。
- 使用物理模拟器将3D资产准确适配到目标人体上。
- 实验结果表明,BAG方法在图像提示遵循能力、形状多样性和形状质量方面均有显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

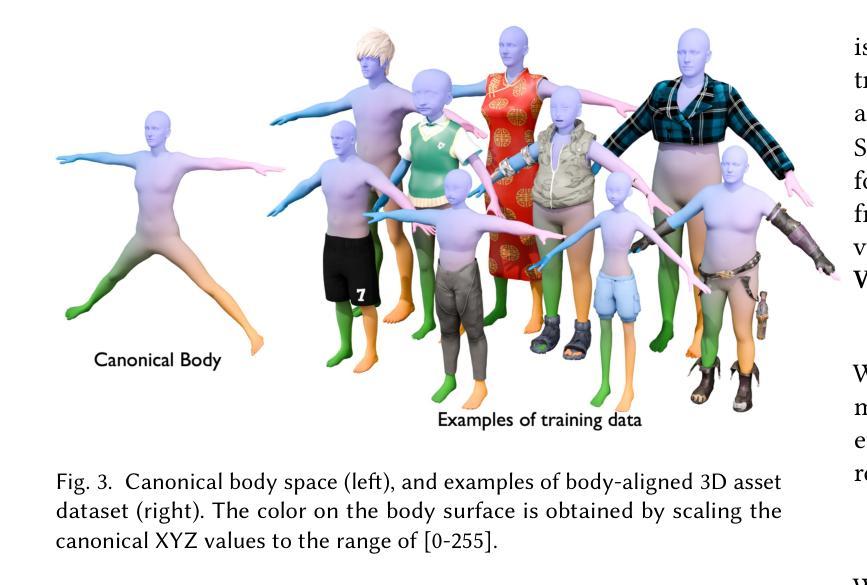
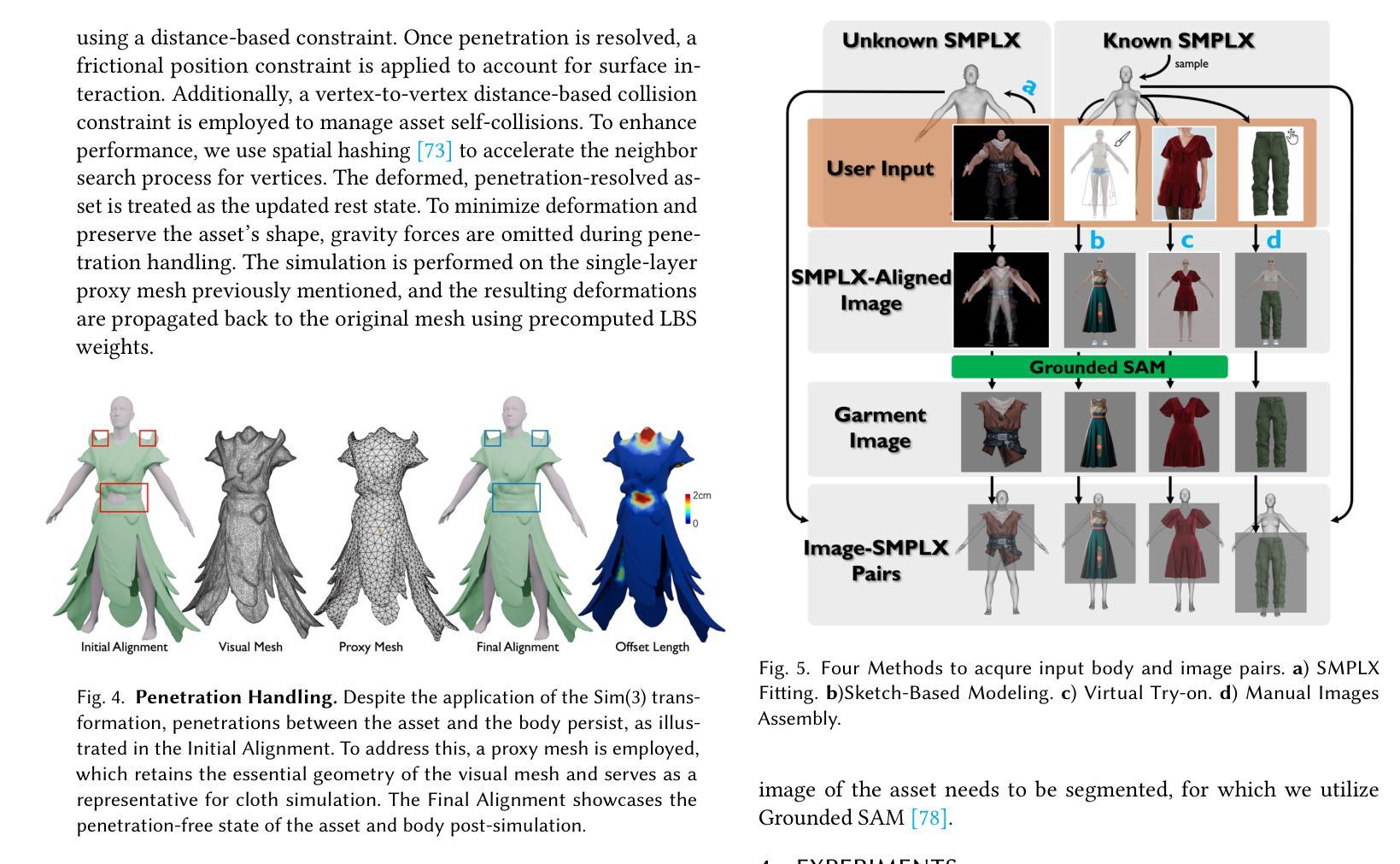
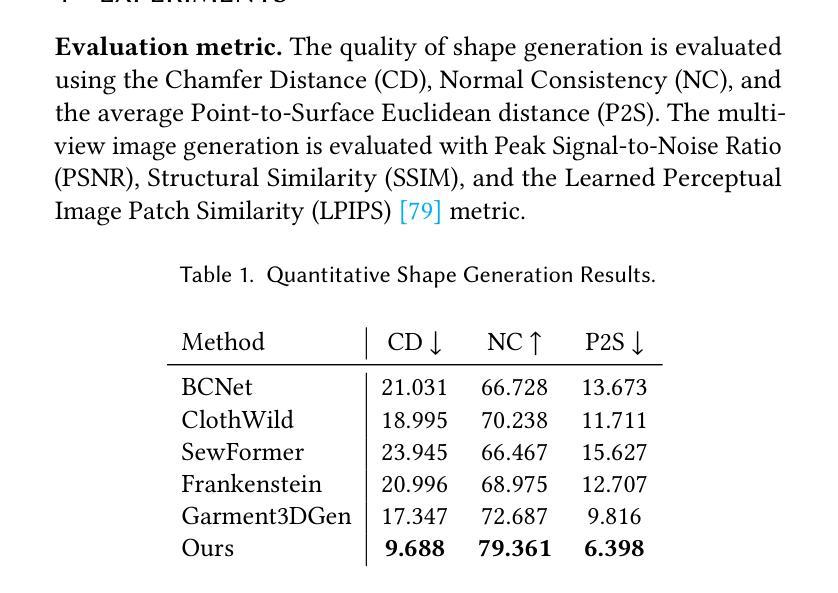
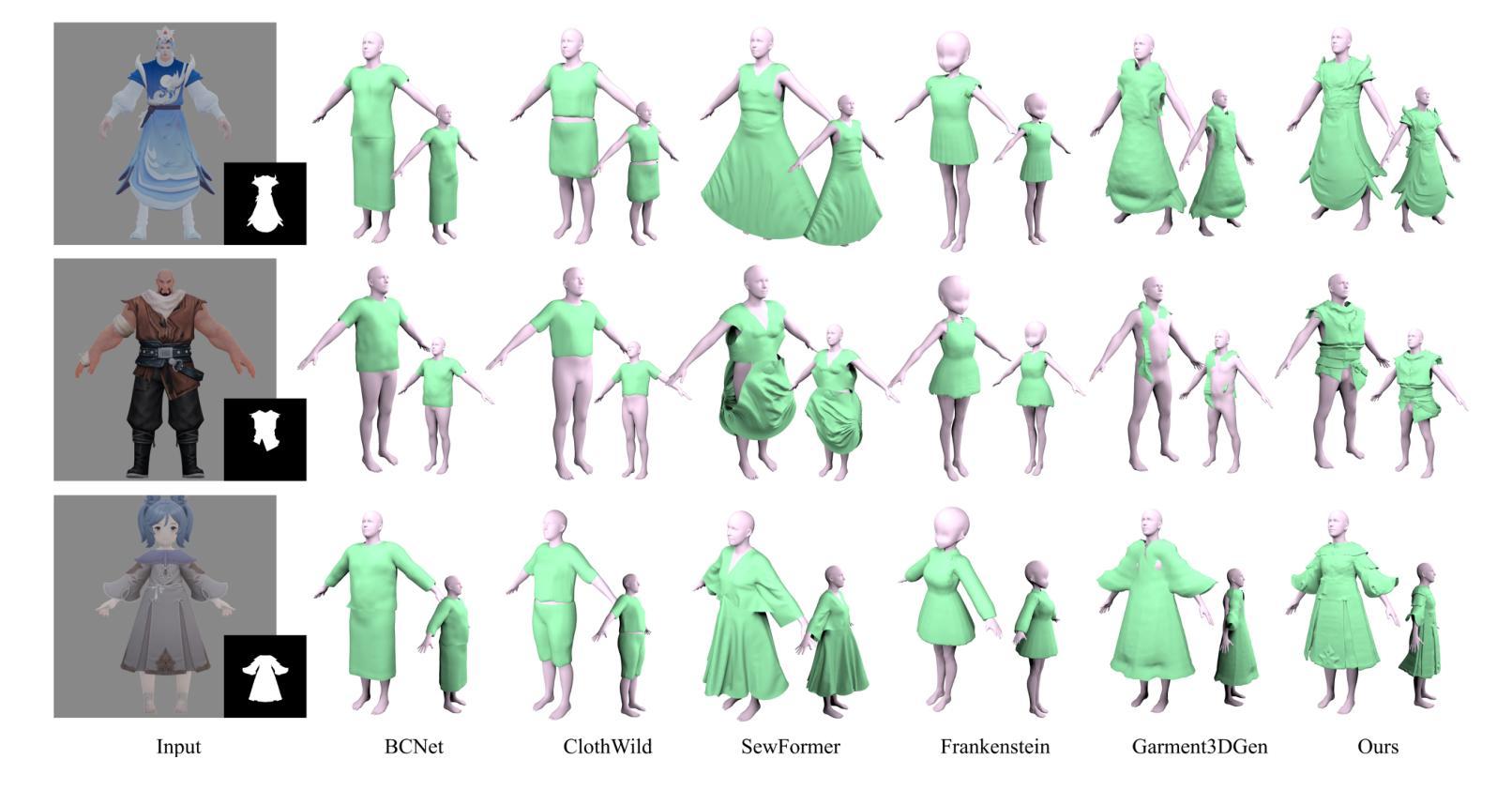
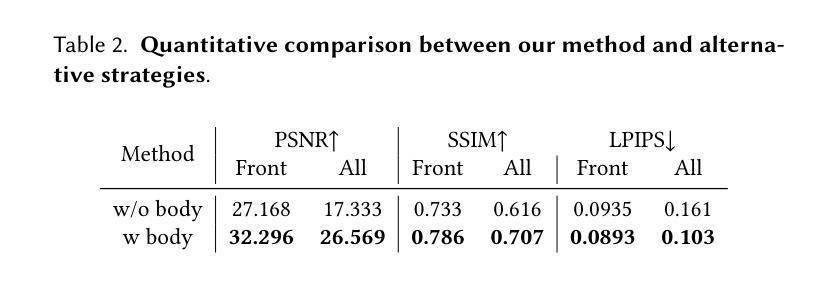
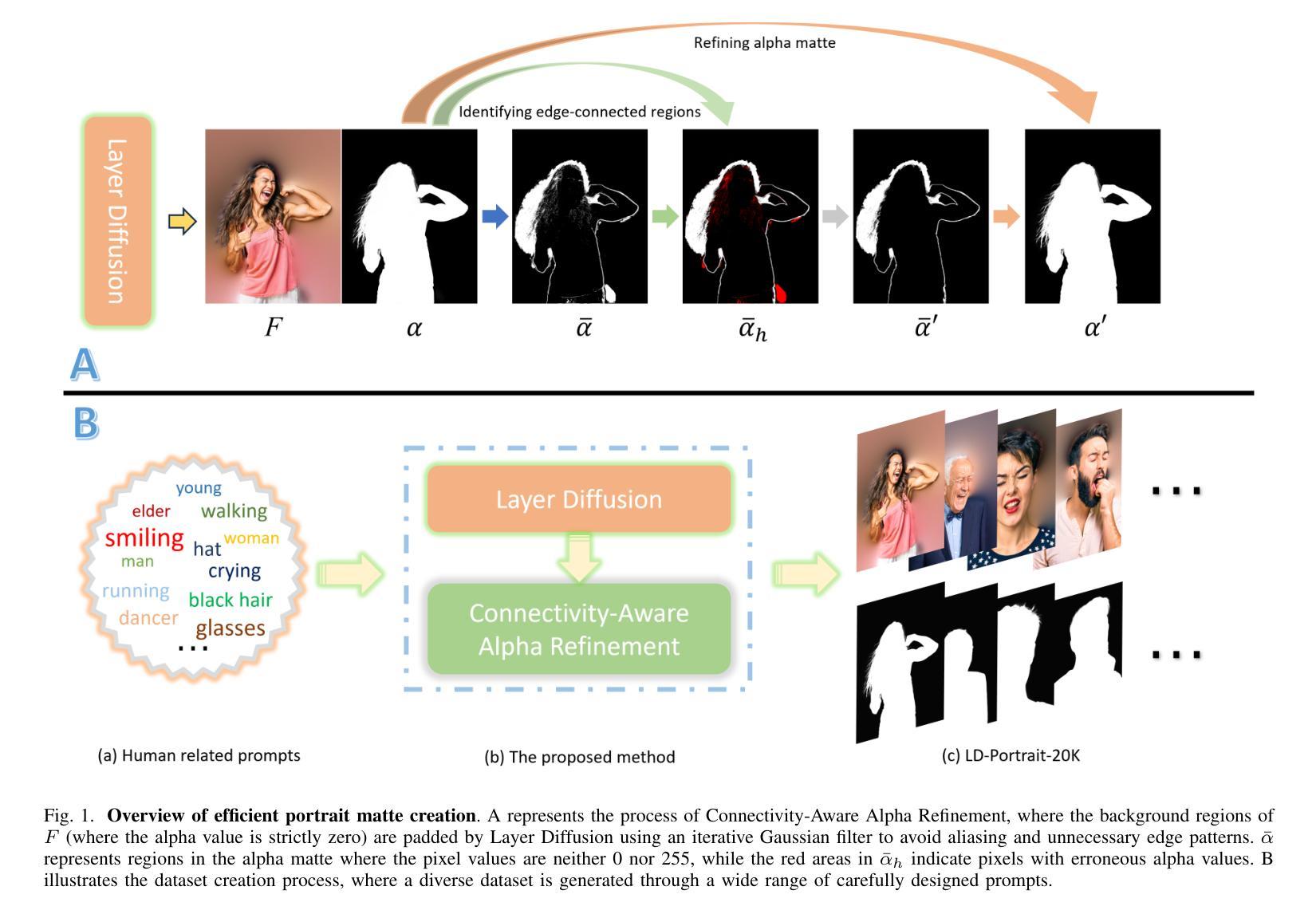
Efficient Portrait Matte Creation With Layer Diffusion and Connectivity Priors
Authors:Zhiyuan Lu, Hao Lu, Hua Huang
Learning effective deep portrait matting models requires training data of both high quality and large quantity. Neither quality nor quantity can be easily met for portrait matting, however. Since the most accurate ground-truth portrait mattes are acquired in front of the green screen, it is almost impossible to harvest a large-scale portrait matting dataset in reality. This work shows that one can leverage text prompts and the recent Layer Diffusion model to generate high-quality portrait foregrounds and extract latent portrait mattes. However, the portrait mattes cannot be readily in use due to significant generation artifacts. Inspired by the connectivity priors observed in portrait images, that is, the border of portrait foregrounds always appears connected, a connectivity-aware approach is introduced to refine portrait mattes. Building on this, a large-scale portrait matting dataset is created, termed LD-Portrait-20K, with $20,051$ portrait foregrounds and high-quality alpha mattes. Extensive experiments demonstrated the value of the LD-Portrait-20K dataset, with models trained on it significantly outperforming those trained on other datasets. In addition, comparisons with the chroma keying algorithm and an ablation study on dataset capacity further confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed matte creation approach. Further, the dataset also contributes to state-of-the-art video portrait matting, implemented by simple video segmentation and a trimap-based image matting model trained on this dataset.
学习有效的深度肖像抠图模型需要高质量且大量的训练数据。然而,肖像抠图很难同时满足质量和数量的要求。由于最准确的地面真实肖像抠图是是在绿幕前获取的,因此在现实中几乎不可能收集大规模的肖像抠图数据集。这项工作表明,可以利用文本提示和最新的层扩散模型生成高质量的肖像前景并提取潜在肖像抠图。然而,由于存在明显的生成瑕疵,这些肖像抠图不能直接使用。受肖像图像中观察到的连通性先验的启发,即肖像前景的边界总是相互连接的,引入了一种连通性感知方法来优化肖像抠图。在此基础上,创建了一个大规模的肖像抠图数据集,称为LD-Portrait-20K,包含20,051个肖像前景和高质量alpha抠图。大量实验证明了LD-Portrait-20K数据集的价值,在此数据集上训练的模型显著优于在其他数据集上训练的模型。此外,与色键算法的比较以及对数据集容量的消融研究进一步证实了所提出的抠图创建方法的有效性。此外,该数据集还为先进的视频肖像抠图做出了贡献,通过简单的视频分割和基于此数据集训练的基于修边图的图像抠图模型实现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了深度肖像抠图模型的学习需求及挑战。为解决高质量大规模训练数据的获取难题,研究利用文本提示和Layer Diffusion模型生成高质量肖像前景,并引入连接性感知方法优化生成的肖像抠图。为此创建了一个大规模肖像抠图数据集LD-Portrait-20K,实验证明该数据集的有效性,并在视频肖像抠图中得到应用。
Key Takeaways
- 深度肖像抠图模型需要高质量大规模的训练数据。
- 由于现实条件下获取准确地面真实肖像抠图数据的困难,研究利用文本提示和Layer Diffusion模型生成高质量肖像前景。
- 生成的肖像抠图存在生成瑕疵,引入连接性感知方法来优化。
- 创建了一个大规模的肖像抠图数据集LD-Portrait-20K,包含20,051个肖像前景和高质量alpha抠图。
- 实验证明LD-Portrait-20K数据集的有效性,训练在此数据集上的模型性能显著优于其他数据集。
- 与色键算法的比较及数据集容量的消融研究进一步证实了所提出的抠图创建方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

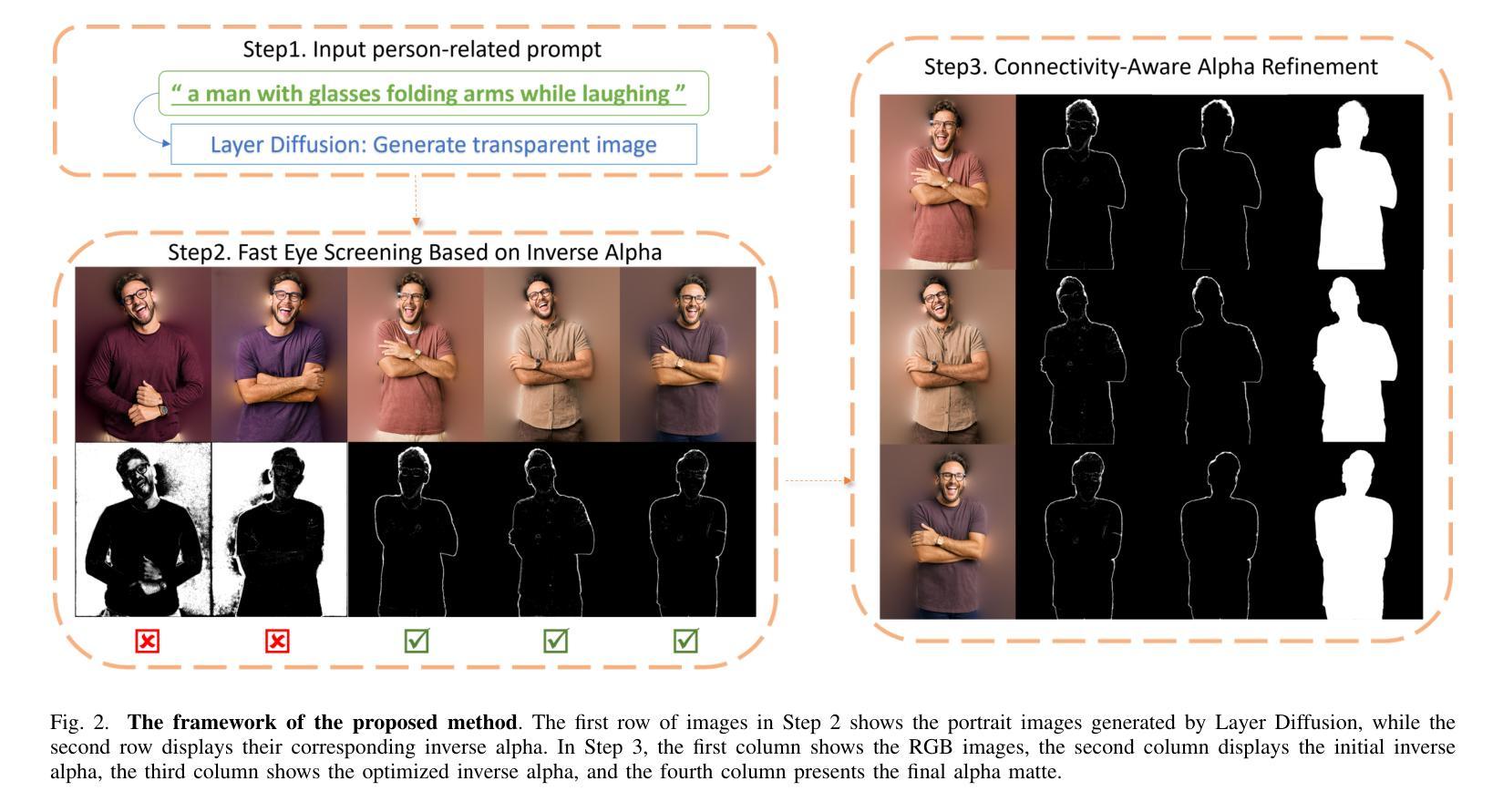

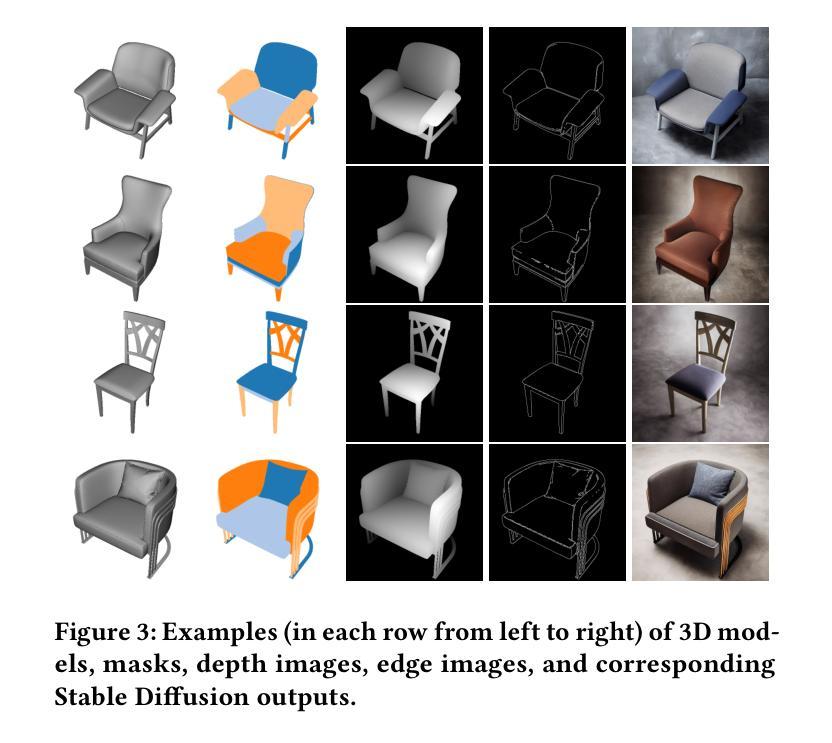
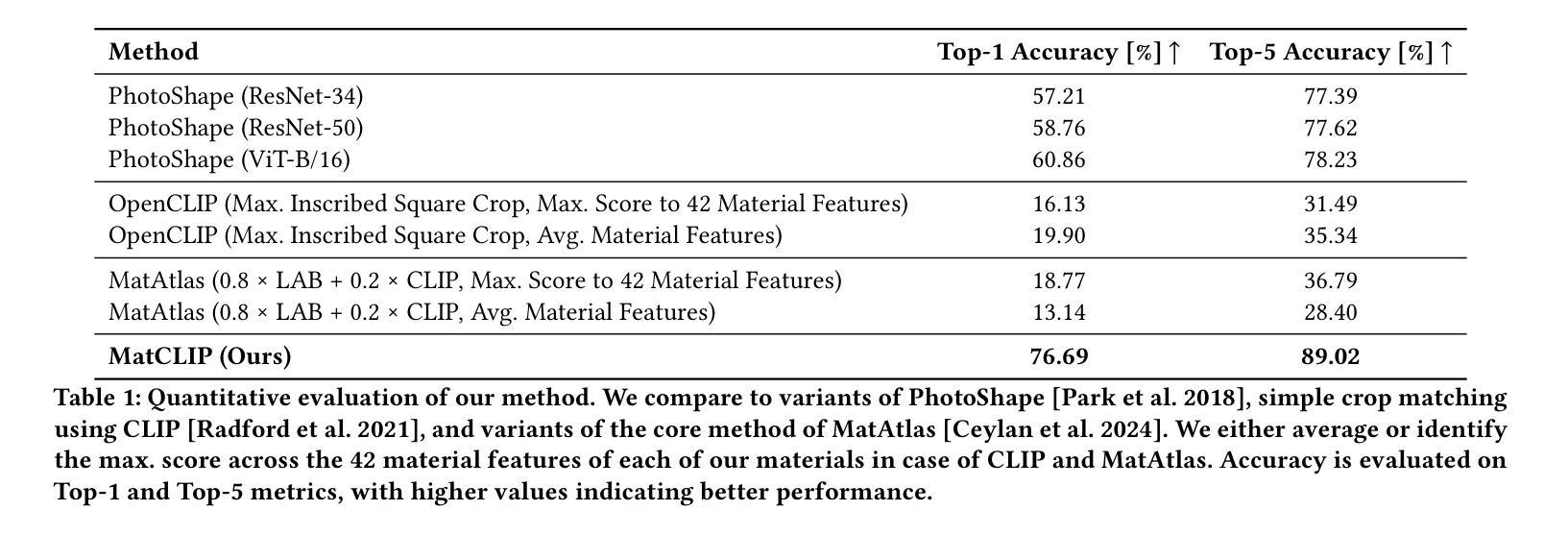
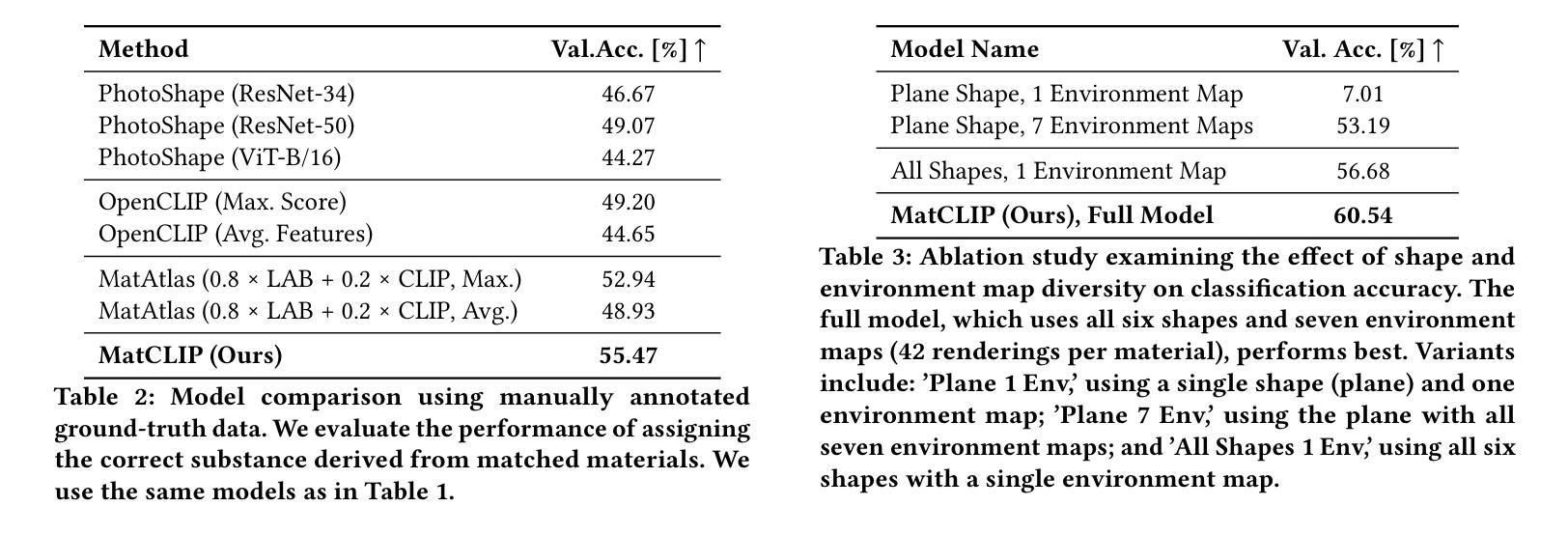
MatCLIP: Light- and Shape-Insensitive Assignment of PBR Material Models
Authors:Michael Birsak, John Femiani, Biao Zhang, Peter Wonka
Assigning realistic materials to 3D models remains a significant challenge in computer graphics. We propose MatCLIP, a novel method that extracts shape- and lighting-insensitive descriptors of Physically Based Rendering (PBR) materials to assign plausible textures to 3D objects based on images, such as the output of Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) or photographs. Matching PBR materials to static images is challenging because the PBR representation captures the dynamic appearance of materials under varying viewing angles, shapes, and lighting conditions. By extending an Alpha-CLIP-based model on material renderings across diverse shapes and lighting, and encoding multiple viewing conditions for PBR materials, our approach generates descriptors that bridge the domains of PBR representations with photographs or renderings, including LDM outputs. This enables consistent material assignments without requiring explicit knowledge of material relationships between different parts of an object. MatCLIP achieves a top-1 classification accuracy of 76.6%, outperforming state-of-the-art methods such as PhotoShape and MatAtlas by over 15 percentage points on publicly available datasets. Our method can be used to construct material assignments for 3D shape datasets such as ShapeNet, 3DCoMPaT++, and Objaverse. All code and data will be released.
为三维模型分配现实材料仍然是计算机图形学中的一项重大挑战。我们提出了一种名为MatCLIP的新方法,该方法提取基于物理渲染(PBR)材料的形状和光照不敏感描述符,根据图像(如潜在扩散模型(LDM)的输出或照片)为三维对象分配合理的纹理。将PBR材料与静态图像相匹配是具有挑战性的,因为PBR表示捕捉了在各种观看角度、形状和光照条件下材料的动态外观。我们通过扩展基于Alpha-CLIP的模型,在多种形状和光照下进行材料渲染,并对PBR材料进行多视角编码,产生描述符,架起PBR表示与照片或渲染图像(包括LDM输出)之间的桥梁。这实现了材料分配的一致性,无需明确对象不同部分之间的材料关系知识。MatCLIP在公开数据集上取得了76.6%的top-1分类准确率,相较于当前的主流方法PhotoShape和MatAtlas在公开数据集上的准确率有超过15个百分点的提升。我们的方法可用于构建如ShapeNet、3DCoMPaT++和Objaverse等三维形状数据集的材料分配。所有代码和数据都将发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, 10 pages
Summary
本文提出一种名为MatCLIP的新方法,用于为三维模型分配真实材料。该方法提取物理基础渲染(PBR)材料的形状和光照不敏感描述符,根据图像(如潜在扩散模型(LDM)的输出或照片)为3D对象分配合理的纹理。MatCLIP通过扩展Alpha-CLIP模型在材料渲染方面的应用,并编码PBR材料的多视角条件,生成了连接PBR表示与照片或渲染的图像描述符。这种方法可以在不需要明确了解对象各部分材料关系的情况下,实现一致的材料分配,准确率达到了76.6%,在公开数据集上较其他先进方法如PhotoShape和MatAtlas高出超过15个百分点。
Key Takeaways
- MatCLIP是一种新型方法,用于为三维模型分配真实材料,特别适用于物理基础渲染(PBR)材料。
- MatCLIP通过提取形状和光照不敏感描述符,根据图像为3D对象分配纹理。
- MatCLIP利用Alpha-CLIP模型处理材料渲染,并编码多种视角条件和光照条件下的PBR材料。
- MatCLIP生成图像描述符,可连接PBR表示与照片或渲染的图像。
- MatCLIP实现了在不了解对象各部分材料关系的情况下的一致材料分配。
- MatCLIP的准确率达到了76.6%,在公开数据集上的表现优于其他先进方法。
点此查看论文截图

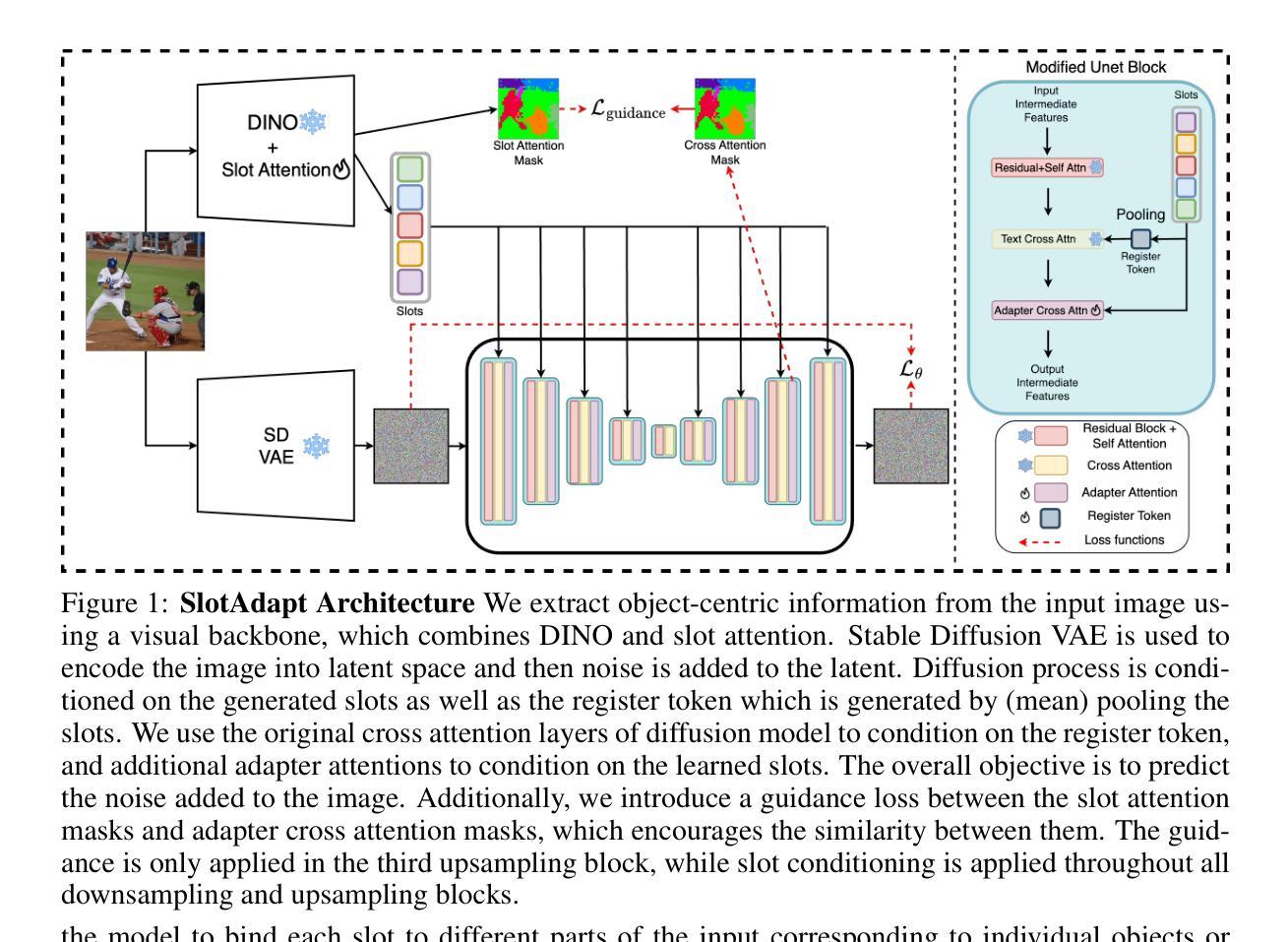
Slot-Guided Adaptation of Pre-trained Diffusion Models for Object-Centric Learning and Compositional Generation
Authors:Adil Kaan Akan, Yucel Yemez
We present SlotAdapt, an object-centric learning method that combines slot attention with pretrained diffusion models by introducing adapters for slot-based conditioning. Our method preserves the generative power of pretrained diffusion models, while avoiding their text-centric conditioning bias. We also incorporate an additional guidance loss into our architecture to align cross-attention from adapter layers with slot attention. This enhances the alignment of our model with the objects in the input image without using external supervision. Experimental results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques in object discovery and image generation tasks across multiple datasets, including those with real images. Furthermore, we demonstrate through experiments that our method performs remarkably well on complex real-world images for compositional generation, in contrast to other slot-based generative methods in the literature. The project page can be found at $\href{https://kaanakan.github.io/SlotAdapt/}{\text{this https url}}$.
我们提出了SlotAdapt,这是一种结合槽位注意力和预训练扩散模型的面向对象的学习方法,通过引入适配器来实现基于槽位的条件设置。我们的方法保留了预训练扩散模型的生成能力,同时避免了它们基于文本的条件设置的偏见。我们还在架构中加入了额外的指导损失,以调整适配器层的交叉注意力与槽位注意力的对齐。这增强了我们的模型与输入图像中的对象的对齐,而无需使用外部监督。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多个数据集上的对象发现和图像生成任务上优于最新技术,包括真实图像数据集。此外,通过实验证明,我们的方法在复杂的真实图像上的组合生成表现尤为出色,与文献中的其他基于槽位的生成方法形成鲜明对比。项目页面可在此处找到:[https://kaanakan.github.io/SlotAdapt/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR2025. $\href{https://kaanakan.github.io/SlotAdapt/}{\text{Project Page}}$
Summary
SlotAdapt是一种结合插槽注意力和预训练扩散模型的对象级学习方法,通过引入适配器实现插槽式条件。该方法保留了预训练扩散模型的生成能力,同时避免了其文本为中心的条件偏见。通过引入额外的指导损失,增强了模型与输入图像中对象的对齐度,无需外部监督。实验结果表明,该方法在多个数据集上的目标检测和图像生成任务上均优于现有技术,并且在复杂真实图像上的组合生成表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- SlotAdapt结合了插槽注意力和预训练的扩散模型,通过引入适配器实现基于插槽的条件学习。
- 该方法保留了预训练扩散模型的生成能力,并避免了文本为中心的条件偏见。
- 通过引入额外的指导损失,增强了模型与输入图像中对象的对齐精度。
- SlotAdapt在多个数据集上的目标检测和图像生成任务上表现出卓越性能。
- 该方法在复杂真实图像上的组合生成表现尤为出色。
- 此方法实现了在不使用外部监督的情况下提高模型与对象对齐的能力。
点此查看论文截图

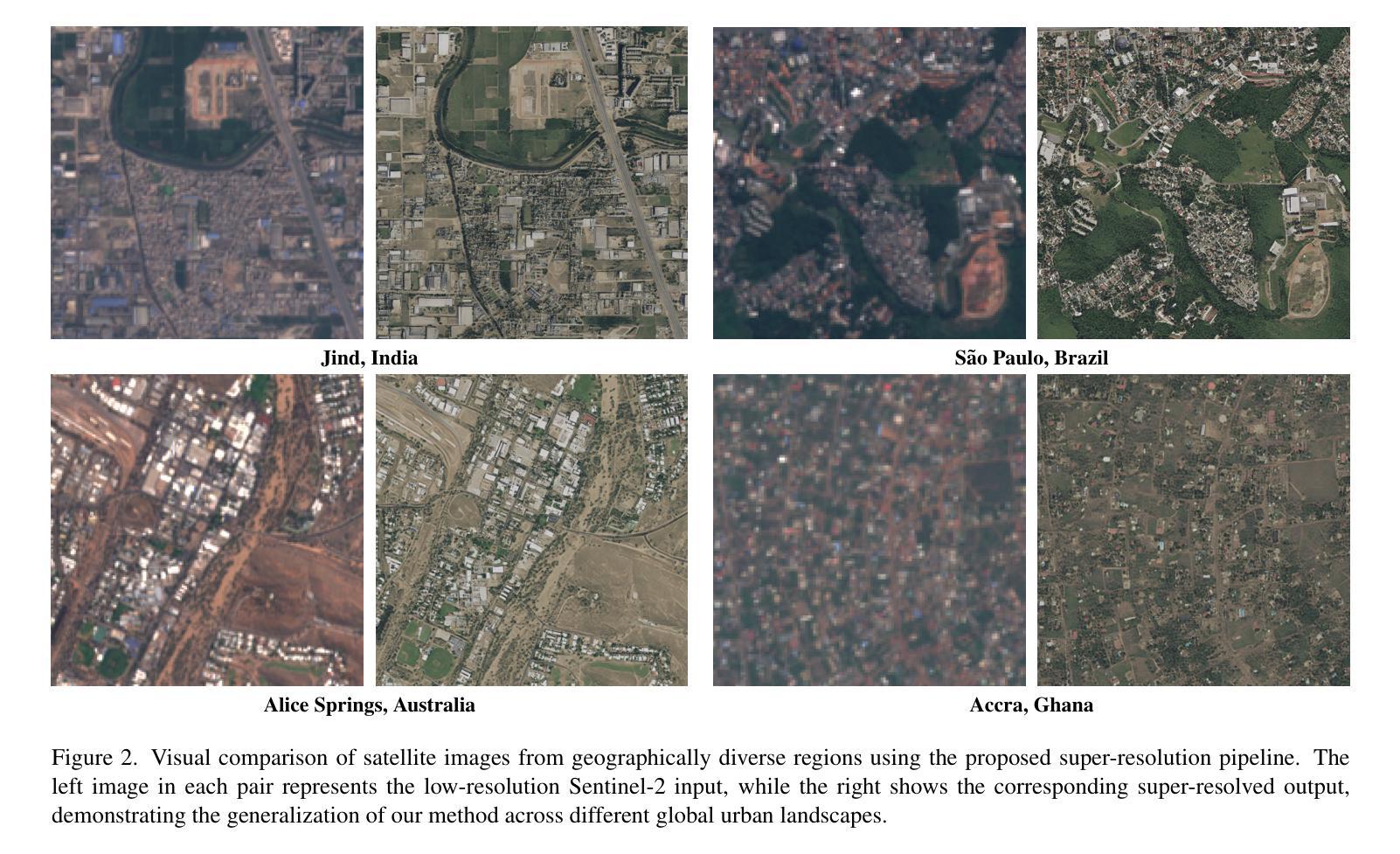
Can Location Embeddings Enhance Super-Resolution of Satellite Imagery?
Authors:Daniel Panangian, Ksenia Bittner
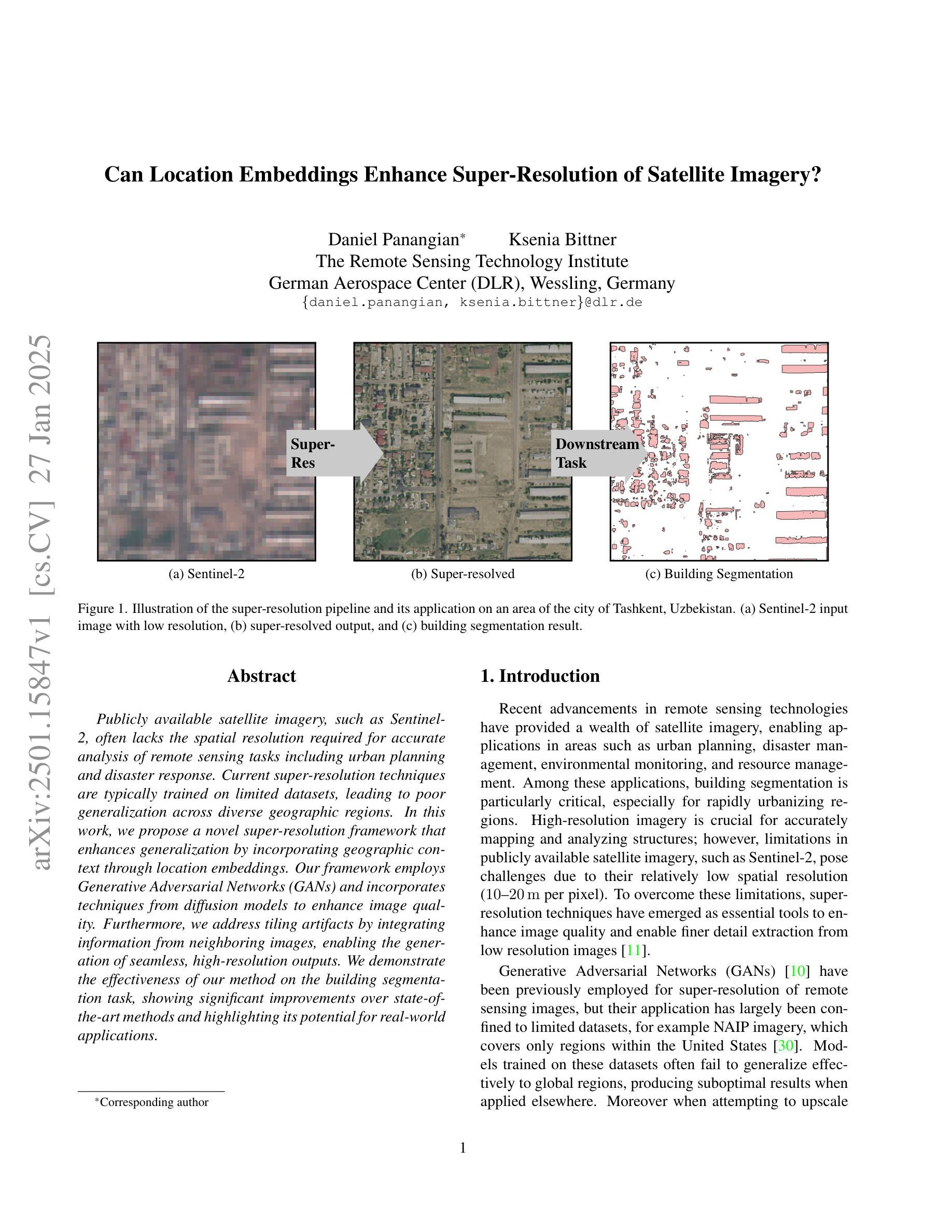
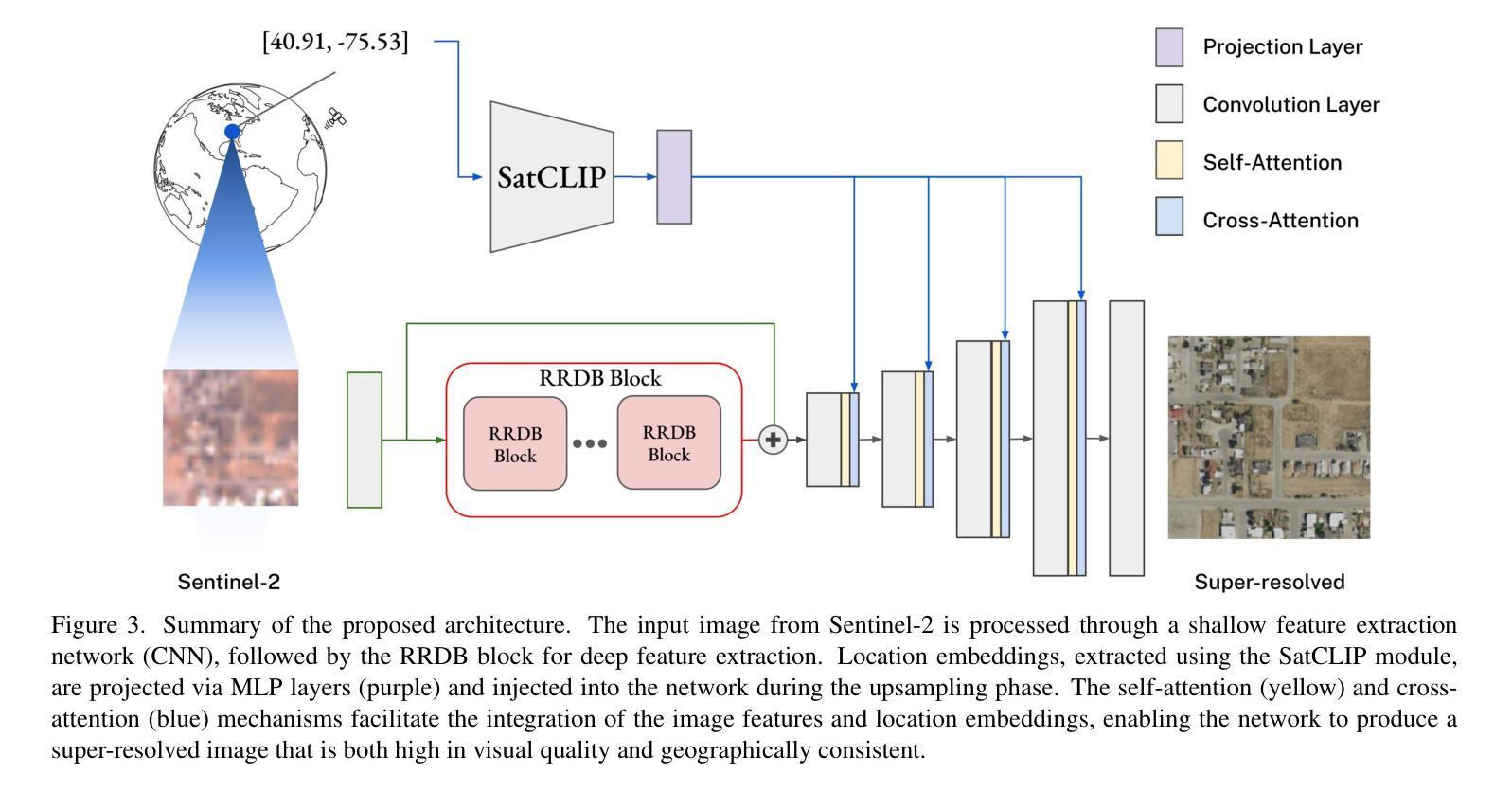
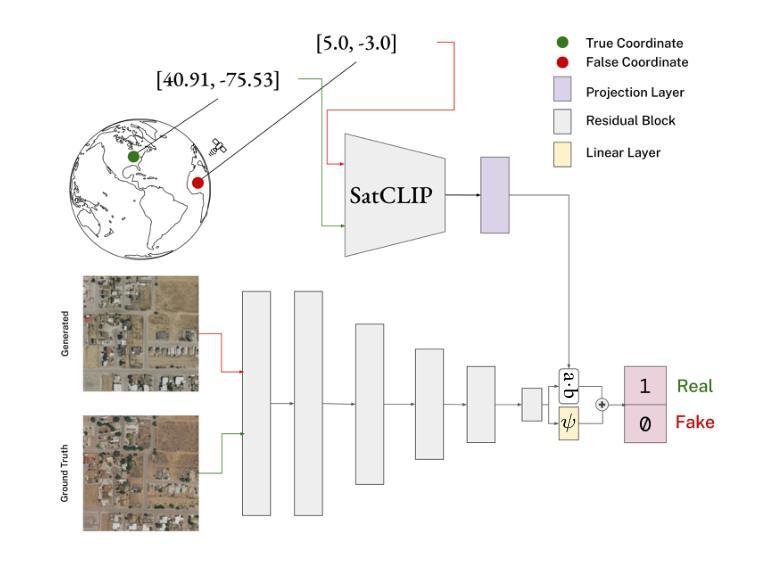
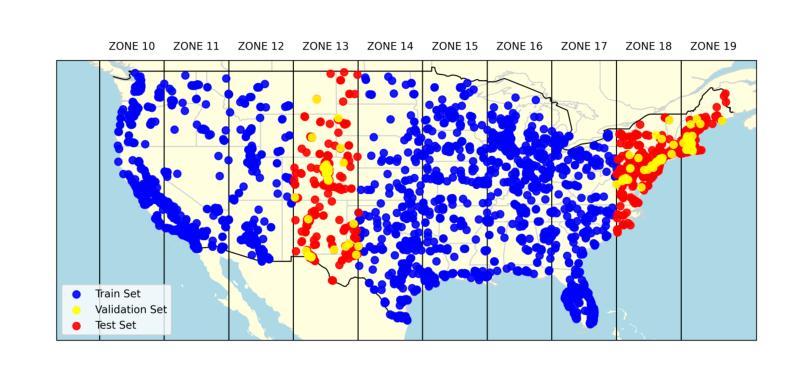
Publicly available satellite imagery, such as Sentinel- 2, often lacks the spatial resolution required for accurate analysis of remote sensing tasks including urban planning and disaster response. Current super-resolution techniques are typically trained on limited datasets, leading to poor generalization across diverse geographic regions. In this work, we propose a novel super-resolution framework that enhances generalization by incorporating geographic context through location embeddings. Our framework employs Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and incorporates techniques from diffusion models to enhance image quality. Furthermore, we address tiling artifacts by integrating information from neighboring images, enabling the generation of seamless, high-resolution outputs. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on the building segmentation task, showing significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods and highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
公开可用的卫星图像,如Sentinel-2,通常缺乏进行城市规划、灾害应对等遥感任务精确分析所需的空间分辨率。当前的超分辨率技术通常局限于有限的数据集进行训练,导致在不同地理区域的泛化能力较差。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新型超分辨率框架,该框架通过引入位置嵌入来提升对地理上下文的利用,从而增强泛化能力。我们的框架采用生成对抗网络(GANs),并结合扩散模型的技巧来提升图像质量。此外,我们通过对邻近图像的信息进行整合来解决拼贴痕迹问题,从而生成无缝、高分辨率的输出。我们在建筑分割任务上展示了该方法的有效性,证明了其相较于最先进的方法有着显著的提升,并强调了其在现实世界应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)
Summary
本文提出一种新型的超分辨率框架,该框架结合地理上下文通过位置嵌入增强图像质量,并采用生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型技术提高图像质量。此外,该框架解决了拼接产生的伪影问题,通过整合相邻图像的信息生成无缝、高分辨率的输出。在建筑分割任务上验证了该方法的有效性,显著优于现有方法,展现了其在真实世界应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出的新型超分辨率框架结合地理上下文通过位置嵌入增强图像质量。
- 利用生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型技术提高图像质量。
- 解决了拼接产生的伪影问题。
- 通过整合相邻图像信息生成无缝、高分辨率的输出。
- 在建筑分割任务上验证了方法的有效性。
- 与现有方法相比有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

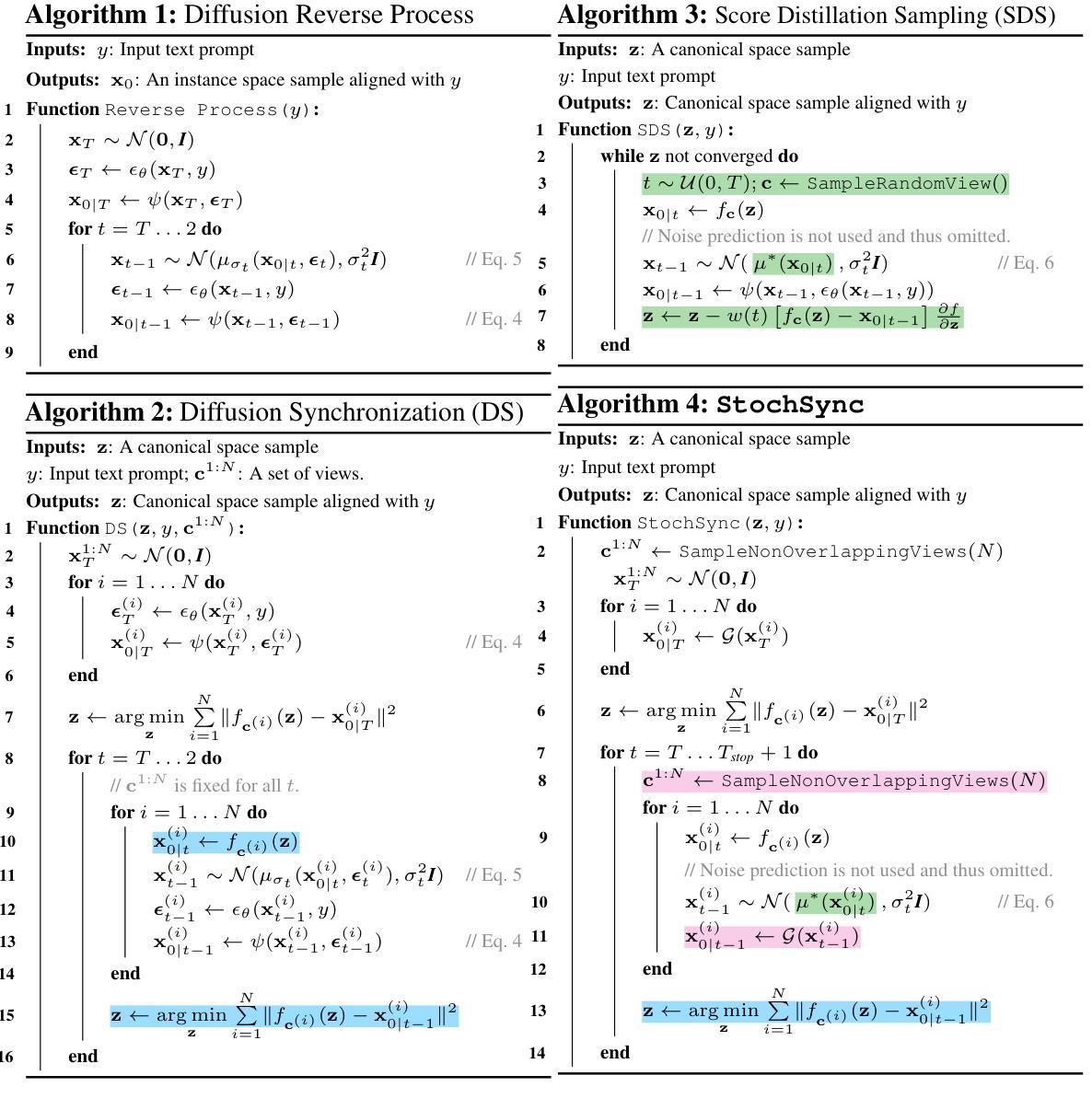
StochSync: Stochastic Diffusion Synchronization for Image Generation in Arbitrary Spaces
Authors:Kyeongmin Yeo, Jaihoon Kim, Minhyuk Sung
We propose a zero-shot method for generating images in arbitrary spaces (e.g., a sphere for 360{\deg} panoramas and a mesh surface for texture) using a pretrained image diffusion model. The zero-shot generation of various visual content using a pretrained image diffusion model has been explored mainly in two directions. First, Diffusion Synchronization-performing reverse diffusion processes jointly across different projected spaces while synchronizing them in the target space-generates high-quality outputs when enough conditioning is provided, but it struggles in its absence. Second, Score Distillation Sampling-gradually updating the target space data through gradient descent-results in better coherence but often lacks detail. In this paper, we reveal for the first time the interconnection between these two methods while highlighting their differences. To this end, we propose StochSync, a novel approach that combines the strengths of both, enabling effective performance with weak conditioning. Our experiments demonstrate that StochSync provides the best performance in 360{\deg} panorama generation (where image conditioning is not given), outperforming previous finetuning-based methods, and also delivers comparable results in 3D mesh texturing (where depth conditioning is provided) with previous methods.
我们提出了一种基于预训练图像扩散模型的零样本方法在任意空间(例如360°全景的球体或纹理的网格表面)生成图像。使用预训练的图像扩散模型进行各种视觉内容的零样本生成主要探索了两个方向。首先,扩散同步法是在不同的投影空间上联合执行反向扩散过程,同时在目标空间进行同步,当提供足够的条件时,可以生成高质量的结果,但在缺乏条件时,该方法会遇到困难。其次,分数蒸馏采样法是通过梯度下降逐步更新目标空间数据,这种方法虽然保证了更好的连贯性,但往往缺乏细节。在本文中,我们首次揭示了这两种方法之间的相互联系,同时强调了它们的差异。为此,我们提出了StochSync这一新方法,它结合了这两种方法的优点,能够在弱条件下实现有效性能。我们的实验表明,StochSync在无图像条件的全景图生成中取得了最佳性能,优于基于微调的方法,并且在提供深度条件的三维网格纹理生成中取得了与之前的方法相当的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://stochsync.github.io/ (ICLR 2025)
Summary
本文提出一种利用预训练图像扩散模型在任意空间(如球体生成360°全景图和网格表面生成纹理)进行零样本图像生成的方法。文章探讨了两种主要的零样本生成方式:Diffusion Synchronization和Score Distillation Sampling,并首次揭示了这两种方法之间的关联和差异。为此,本文提出了一种结合两者优点的新方法StochSync,能够在弱条件下实现有效性能。实验表明,StochSync在无需图像条件的情况下,性能最佳,且在需要深度条件的3D网格纹理生成方面也有较好的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种零样本方法在任意空间生成图像的新技术,使用预训练的图像扩散模型。
- 文章主要探讨了Diffusion Synchronization和Score Distillation Sampling两种零样本生成方式。
- 首次揭示了Diffusion Synchronization和Score Distillation Sampling两种方法的关联与差异。
- 提出了一种结合两者优点的新方法StochSync,能够在弱条件下实现有效性能。
- 实验表明,StochSync在无需图像条件的情况下,性能最佳,尤其在生成全景图方面。
- 在需要深度条件的3D网格纹理生成方面,StochSync也有较好的表现。
点此查看论文截图


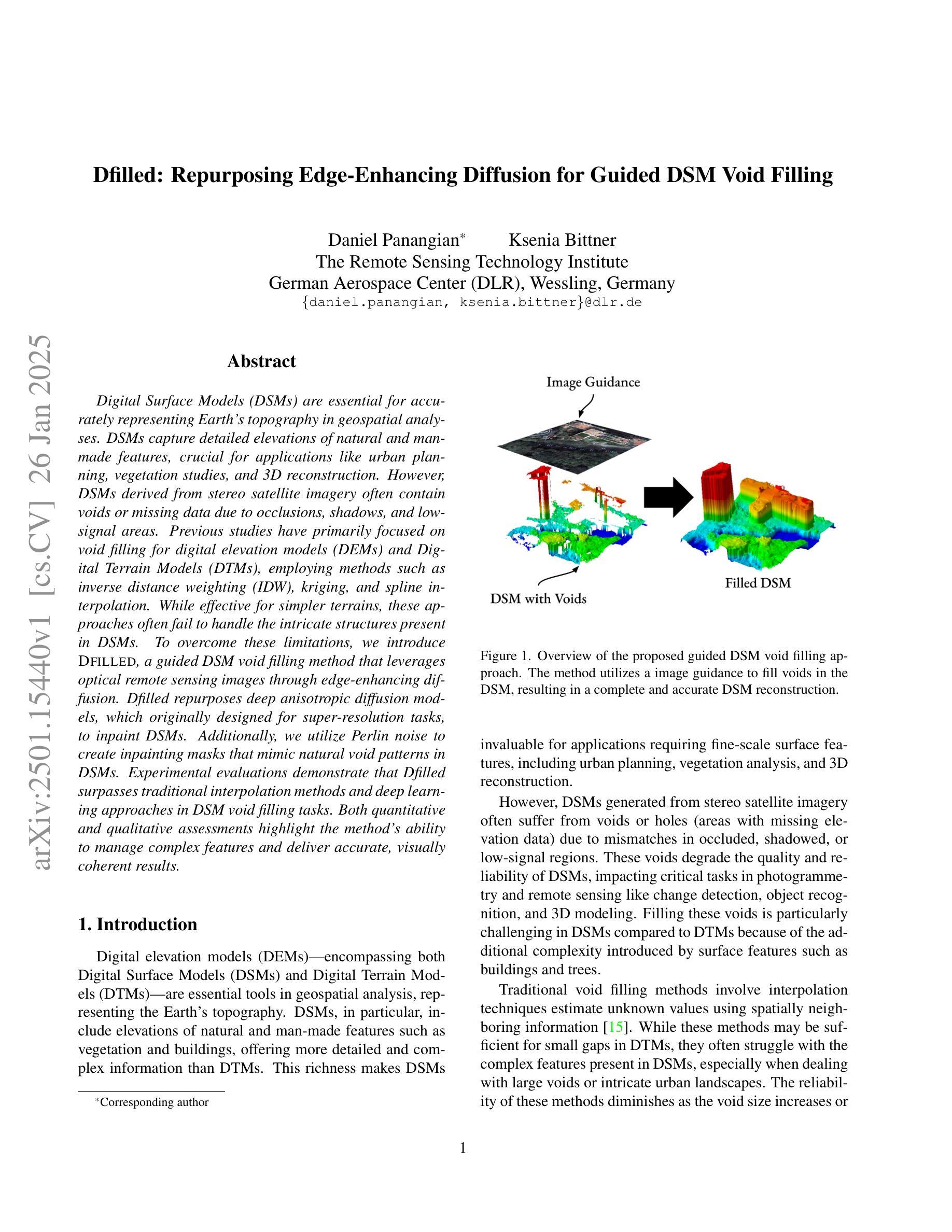
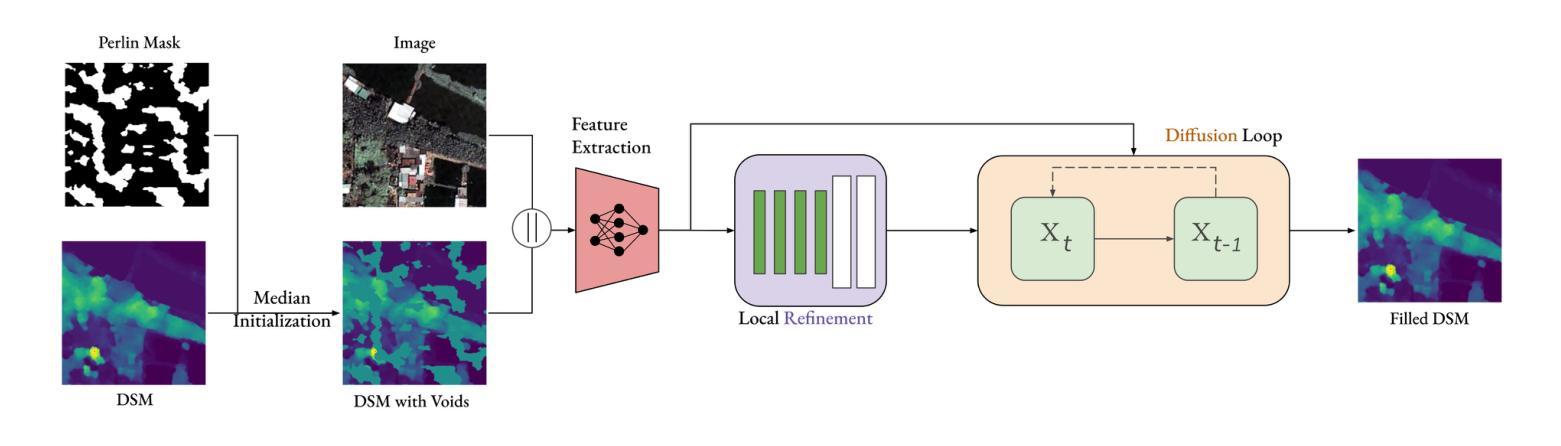
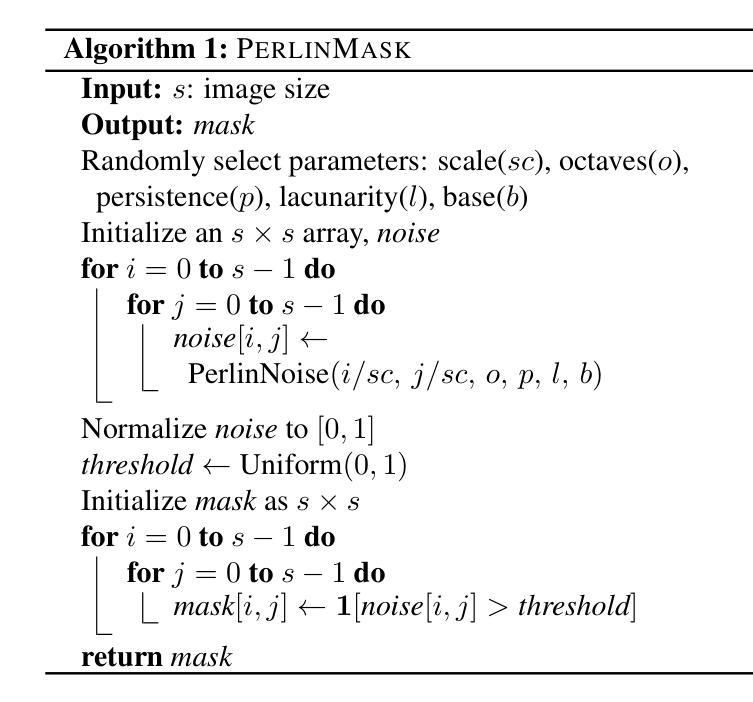
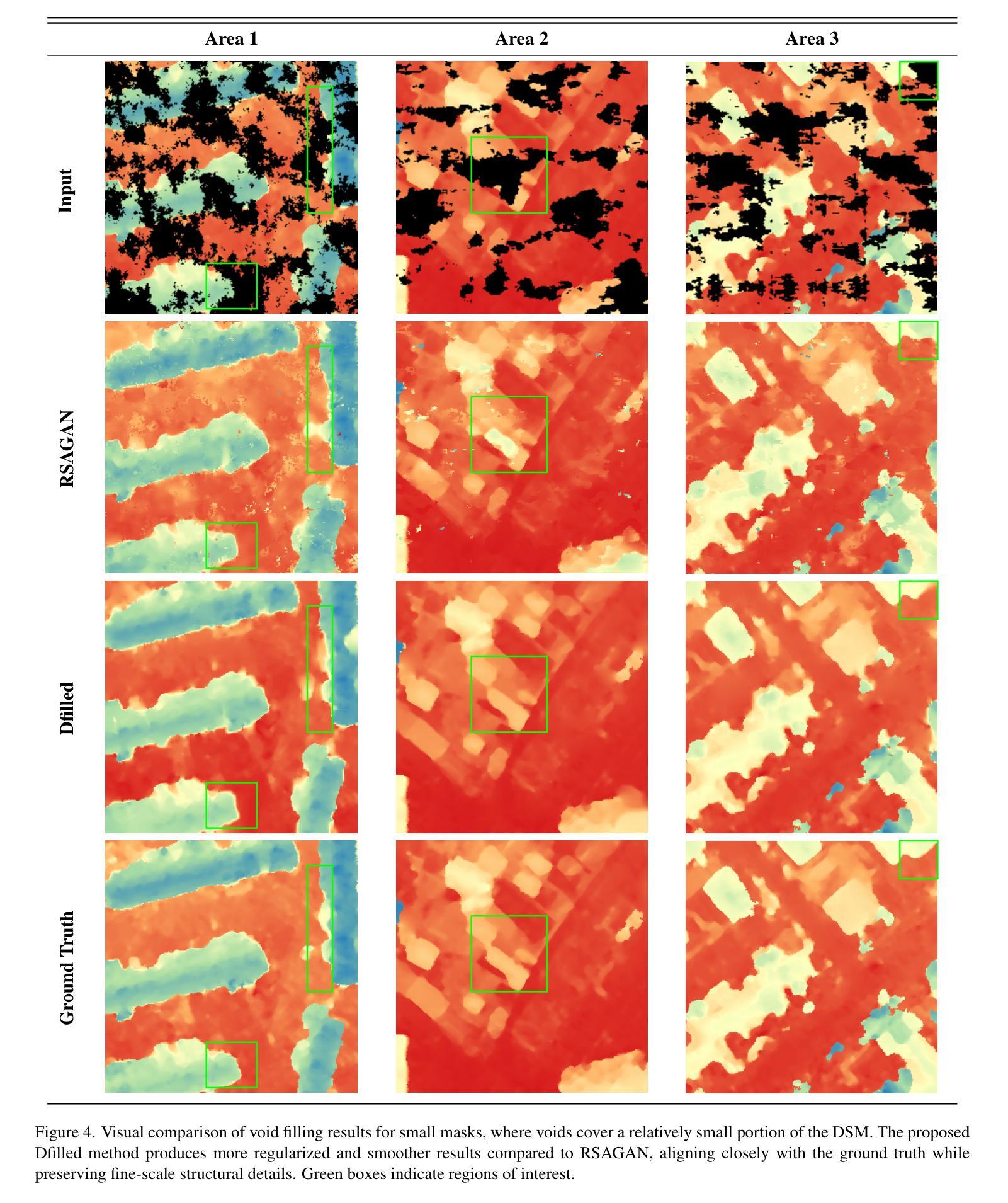
Dfilled: Repurposing Edge-Enhancing Diffusion for Guided DSM Void Filling
Authors:Daniel Panangian, Ksenia Bittner
Digital Surface Models (DSMs) are essential for accurately representing Earth’s topography in geospatial analyses. DSMs capture detailed elevations of natural and manmade features, crucial for applications like urban planning, vegetation studies, and 3D reconstruction. However, DSMs derived from stereo satellite imagery often contain voids or missing data due to occlusions, shadows, and lowsignal areas. Previous studies have primarily focused on void filling for digital elevation models (DEMs) and Digital Terrain Models (DTMs), employing methods such as inverse distance weighting (IDW), kriging, and spline interpolation. While effective for simpler terrains, these approaches often fail to handle the intricate structures present in DSMs. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Dfilled, a guided DSM void filling method that leverages optical remote sensing images through edge-enhancing diffusion. Dfilled repurposes deep anisotropic diffusion models, which originally designed for super-resolution tasks, to inpaint DSMs. Additionally, we utilize Perlin noise to create inpainting masks that mimic natural void patterns in DSMs. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that Dfilled surpasses traditional interpolation methods and deep learning approaches in DSM void filling tasks. Both quantitative and qualitative assessments highlight the method’s ability to manage complex features and deliver accurate, visually coherent results.
数字表面模型(DSMs)在地理空间分析中准确表示地球地形方面起着至关重要的作用。DSM捕获自然和人造特征的详细高程信息,对于城市规划、植被研究和3D重建等应用至关重要。然而,从立体卫星影像派生的DSMs通常由于遮挡、阴影和低信号区域而包含空隙或缺失数据。以往的研究主要集中在数字高程模型(DEMs)和数字地形模型(DTMs)的空隙填充上,采用的方法包括反距离加权(IDW)、克里金法和样条插值等。这些方法对于简单地形虽然有效,但往往难以处理DSM中存在的复杂结构。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了Dfilled,这是一种有指导的DSM空隙填充方法,它通过边缘增强扩散利用光学遥感图像。Dfilled将原本为超分辨率任务设计的深度各向异性扩散模型改用于填补DSM。此外,我们还利用Perlin噪声生成模仿DSM中自然空隙模式的填充掩膜。实验评估表明,在DSM空隙填充任务中,Dfilled超越了传统插值方法和深度学习方法。定量和定性评估都突出了该方法在处理复杂特征方面的能力,并能提供准确、视觉连贯的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW)
Summary:
数字表面模型(DSMs)在地理空间分析中准确表示地球地形至关重要。DSMs捕捉自然和人造特征的详细高程,对于城市规划、植被研究和3D重建等应用至关重要。然而,从立体卫星影像派生的DSMs常常由于遮挡、阴影和低信号区域而出现空白或缺失数据。尽管传统的插值方法如反距离权重(IDW)、克里格和样条插值对简单地形有效,但它们难以处理DSMs中的复杂结构。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了Dfilled方法,这是一种利用光学遥感图像进行边缘增强扩散的DSM空白填充方法。实验评估表明,Dfilled在DSM空白填充任务上超越了传统的插值方法和深度学习方法,无论是定量还是定性评估,都证明了该方法管理复杂特征并产生准确、视觉连贯结果的能力。
Key Takeaways:
- 数字表面模型(DSMs)在地理空间分析中扮演重要角色,用于准确表示地球的地形特征。
- DSMs通过捕捉自然和人造特征的详细高程,支持多种应用,如城市规划、植被研究和3D重建。
- 从立体卫星影像派生的DSMs可能会出现空白或缺失数据,这主要是由于遮挡、阴影和低信号区域导致的。
- 传统插值方法在处理DSMs中的复杂结构时存在局限性。
- Dfilled方法是一种新型的DSM空白填充技术,利用光学遥感图像进行边缘增强扩散。
- Dfilled方法通过利用深度各向异性扩散模型和Perlin噪声生成模仿DSM自然空白模式的填充掩膜来实现高效的空白填充。
- 实验评估表明,Dfilled在DSM空白填充任务上表现出色,优于传统的插值方法和深度学习方法。
点此查看论文截图

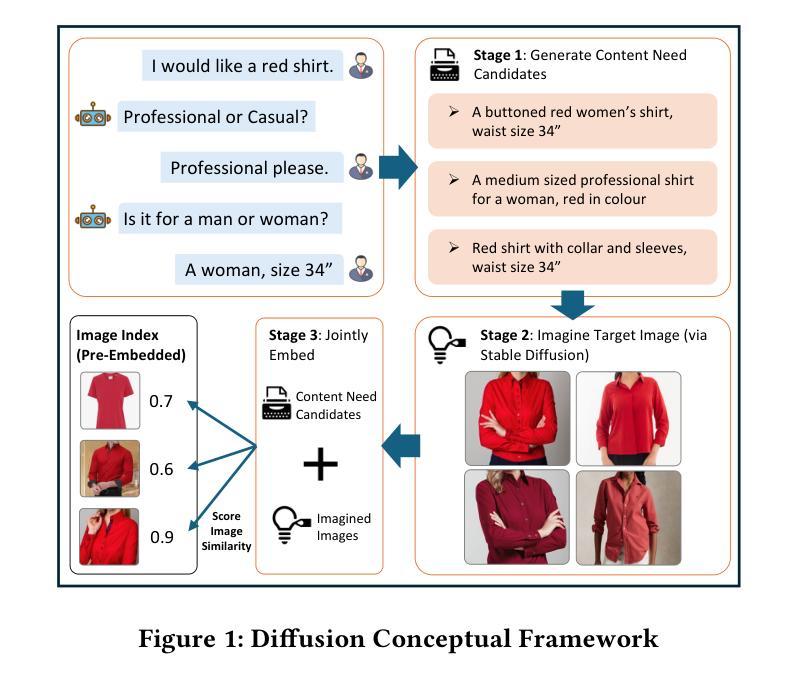
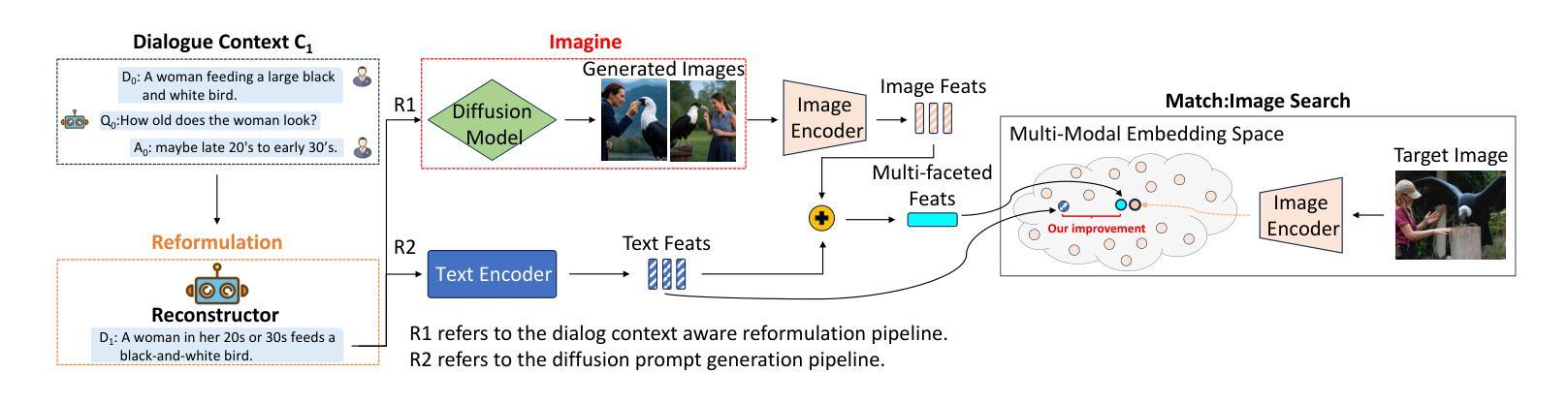
Zero-Shot Interactive Text-to-Image Retrieval via Diffusion-Augmented Representations
Authors:Zijun Long, Kangheng Liang, Gerardo Aragon-Camarasa, Richard Mccreadie, Paul Henderson
Interactive Text-to-Image Retrieval (I-TIR) has emerged as a transformative user-interactive tool for applications in domains such as e-commerce and education. Yet, current methodologies predominantly depend on finetuned Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), which face two critical limitations: (1) Finetuning imposes prohibitive computational overhead and long-term maintenance costs. (2) Finetuning narrows the pretrained knowledge distribution of MLLMs, reducing their adaptability to novel scenarios. These issues are exacerbated by the inherently dynamic nature of real-world I-TIR systems, where queries and image databases evolve in complexity and diversity, often deviating from static training distributions. To overcome these constraints, we propose Diffusion Augmented Retrieval (DAR), a paradigm-shifting framework that bypasses MLLM finetuning entirely. DAR synergizes Large Language Model (LLM)-guided query refinement with Diffusion Model (DM)-based visual synthesis to create contextually enriched intermediate representations. This dual-modality approach deciphers nuanced user intent more holistically, enabling precise alignment between textual queries and visually relevant images. Rigorous evaluations across four benchmarks reveal DAR’s dual strengths: (1) Matches state-of-the-art finetuned I-TIR models on straightforward queries without task-specific training. (2) Scalable Generalization: Surpasses finetuned baselines by 7.61% in Hits@10 (top-10 accuracy) under multi-turn conversational complexity, demonstrating robustness to intricate, distributionally shifted interactions. By eliminating finetuning dependencies and leveraging generative-augmented representations, DAR establishes a new trajectory for efficient, adaptive, and scalable cross-modal retrieval systems.
交互式文本到图像检索(I-TIR)已经成为电子商务和教育等领域应用的一种变革性的用户交互工具。然而,当前的方法主要依赖于微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),它们面临两个关键的局限性:(1)微调带来了巨大的计算开销和长期维护成本。(2)微调缩小了MLLMs的预训练知识分布,降低了它们对新场景的适应性。这些问题被真实世界中I-TIR系统的固有动态性质所加剧,其中查询和图像数据库的复杂性和多样性在不断发展变化,常常偏离静态训练分布。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了扩散增强检索(DAR),这是一个彻底绕过MLLM微调的模式转变框架。DAR将大型语言模型(LLM)引导查询细化与基于扩散模型(DM)的视觉合成相结合,以创建上下文丰富的中间表示。这种双模态方法更全面地解释了微妙的用户意图,实现了文本查询和视觉相关图像之间的精确对齐。在四个基准测试上的严格评估揭示了DAR的双重优势:(1)在直接查询上匹配最先进的微调I-TIR模型,无需特定任务训练。(2)可扩展的泛化能力:在多回合对话复杂性的情况下,在命中数@10(前10名的准确率)上超越微调基线7.61%,证明了对复杂、分布偏移交互的稳健性。通过消除微调依赖并利用生成增强表示,DAR为高效、自适应和可扩展的跨模态检索系统建立了新的轨迹。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
交互式文本到图像检索(I-TIR)已成为电子商务和教育等领域的重要工具。然而,当前的方法主要依赖于微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),存在两个关键问题:一是计算开销大且维护成本高;二是难以适应新场景。为解决这些问题,提出一种名为Diffusion Augmented Retrieval(DAR)的新框架,通过结合大型语言模型(LLM)引导查询优化和扩散模型(DM)的视觉合成,创建上下文丰富的中间表示。这一双模态方法更全面地解析用户意图,实现文本查询和视觉相关图像之间的精确对齐。评估表明,DAR在匹配现有技术的同时,具有出色的通用性和可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前I-TIR方法主要依赖微调的MLLMs,存在计算开销大和维护成本高的局限性。
- 扩散模型(DM)在视觉合成方面具有潜力,可以与LLM结合使用以提高检索精度。
- DAR框架通过结合LLM和DM创建上下文丰富的中间表示,实现文本查询和视觉图像的精确对齐。
- DAR在标准评估上实现了与现有技术相当的性能,同时具有出色的可扩展性和通用性。
- DAR通过消除对微调的需求并利用生成增强表示,为高效、自适应和可扩展的跨模态检索系统开辟了新途径。
- DAR框架适用于动态变化的查询和图像数据库,能够更好地适应现实世界的复杂性。
点此查看论文截图


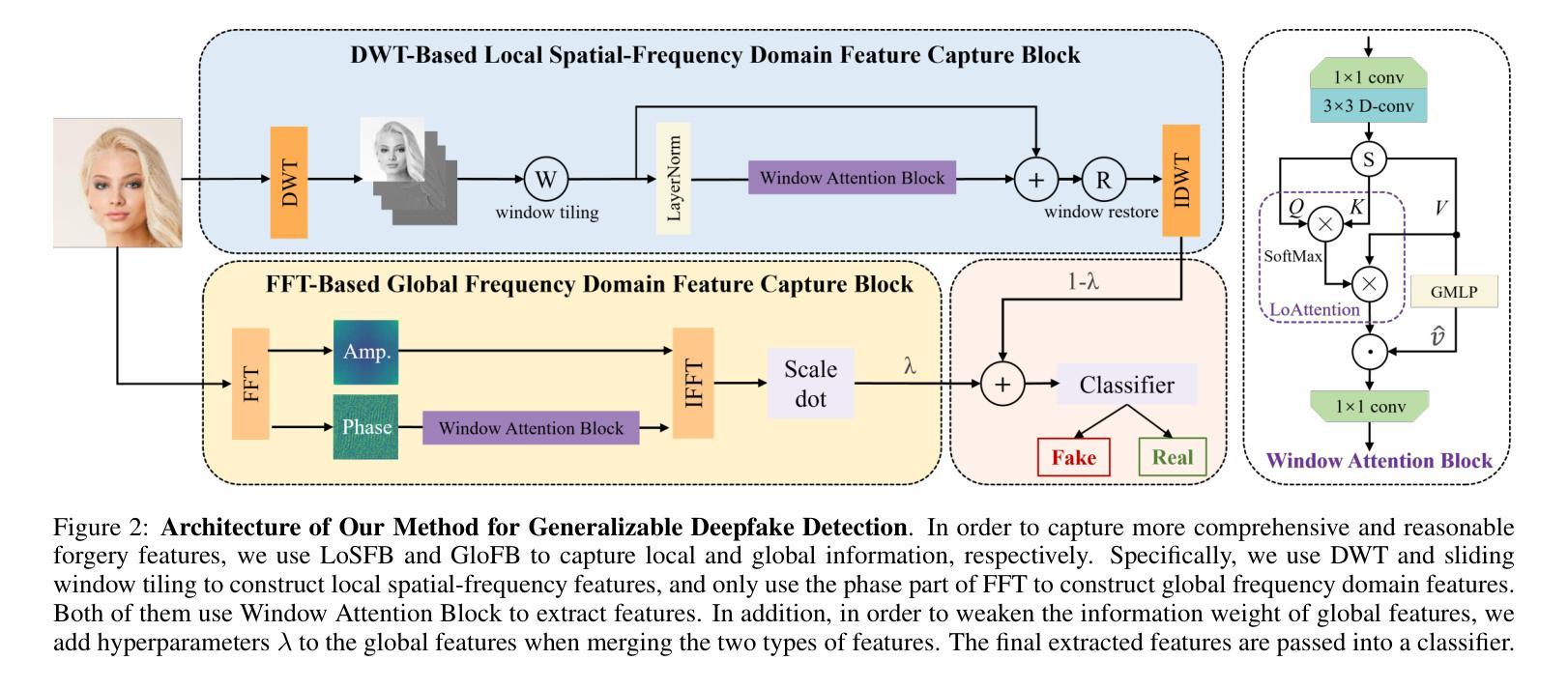
Generalizable Deepfake Detection via Effective Local-Global Feature Extraction
Authors:Jiazhen Yan, Ziqiang Li, Ziwen He, Zhangjie Fu
The rapid advancement of GANs and diffusion models has led to the generation of increasingly realistic fake images, posing significant hidden dangers and threats to society. Consequently, deepfake detection has become a pressing issue in today’s world. While some existing methods focus on forgery features from either a local or global perspective, they often overlook the complementary nature of these features. Other approaches attempt to incorporate both local and global features but rely on simplistic strategies, such as cropping, which fail to capture the intricate relationships between local features. To address these limitations, we propose a novel method that effectively combines local spatial-frequency domain features with global frequency domain information, capturing detailed and holistic forgery traces. Specifically, our method uses Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and sliding windows to tile forged features and leverages attention mechanisms to extract local spatial-frequency domain information. Simultaneously, the phase component of the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is integrated with attention mechanisms to extract global frequency domain information, complementing the local features and ensuring the integrity of forgery detection. Comprehensive evaluations on open-world datasets generated by 34 distinct generative models demonstrate a significant improvement of 2.9% over existing state-of-the-art methods.
生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的快速发展导致了越来越逼真的虚假图像生成,给社会带来了重大的潜在危险和威胁。因此,深度伪造检测已成为当今世界的紧迫问题。虽然一些现有的方法侧重于从局部或全局角度提取伪造特征,但它们往往忽视了这些特征的互补性。其他方法试图结合局部和全局特征,但依赖于简单的策略,如裁剪,这无法捕捉局部特征之间的复杂关系。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新的方法,该方法有效地结合了局部空间频域特征与全局频域信息,捕捉详细且整体的伪造痕迹。具体来说,我们的方法使用离散小波变换(DWT)和滑动窗口来划分伪造特征,并利用注意力机制提取局部空间频域信息。同时,我们将快速傅里叶变换(FFT)的相位成分与注意力机制相结合,提取全局频域信息,以补充局部特征并确保伪造检测的完整性。在由34种不同的生成模型生成的开放世界数据集上的综合评估表明,与现有的最先进的方法相比,我们的方法取得了2.9%的显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
本文介绍了生成对抗网络和扩散模型的快速发展带来的虚假图像生成问题,强调了深度伪造检测在现今社会的紧迫性。针对现有方法的局限性,提出了一种结合局部空间频率域特征和全局频率域信息的新方法,利用离散小波变换和滑动窗口进行伪造特征提取,并通过注意力机制融合局部和全局特征,提高了伪造检测的准确性和完整性。在公开数据集上的综合评估表明,该方法相较于现有最先进的方法有2.9%的显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- GANs和扩散模型的快速发展导致虚假图像越来越逼真,给社会带来潜在威胁,深度伪造检测成为重要议题。
- 现有方法主要关注局部或全局的伪造特征,但忽略了它们之间的互补性。
- 一些方法试图结合局部和全局特征,但采用简单策略如裁剪,无法捕捉复杂关系。
- 新方法结合局部空间频率域特征和全局频率域信息,使用离散小波变换和滑动窗口进行特征提取。
- 注意力机制用于融合局部和全局特征,确保检测准确性和完整性。
- 综合评估显示新方法在公开数据集上的性能相较于现有方法有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

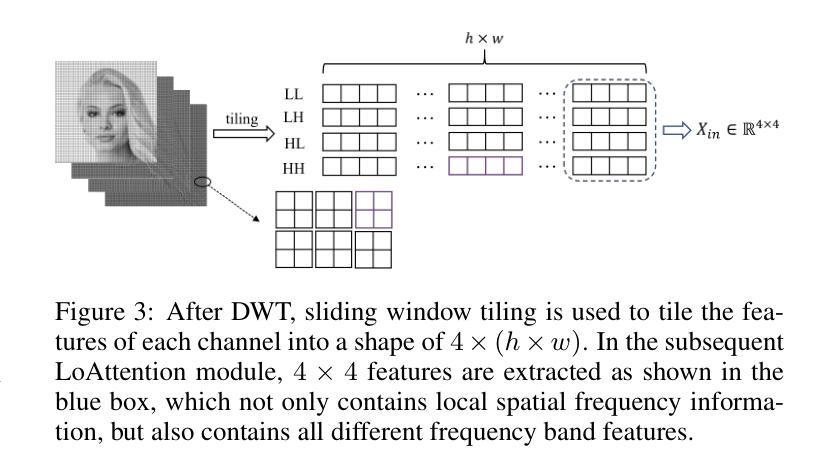
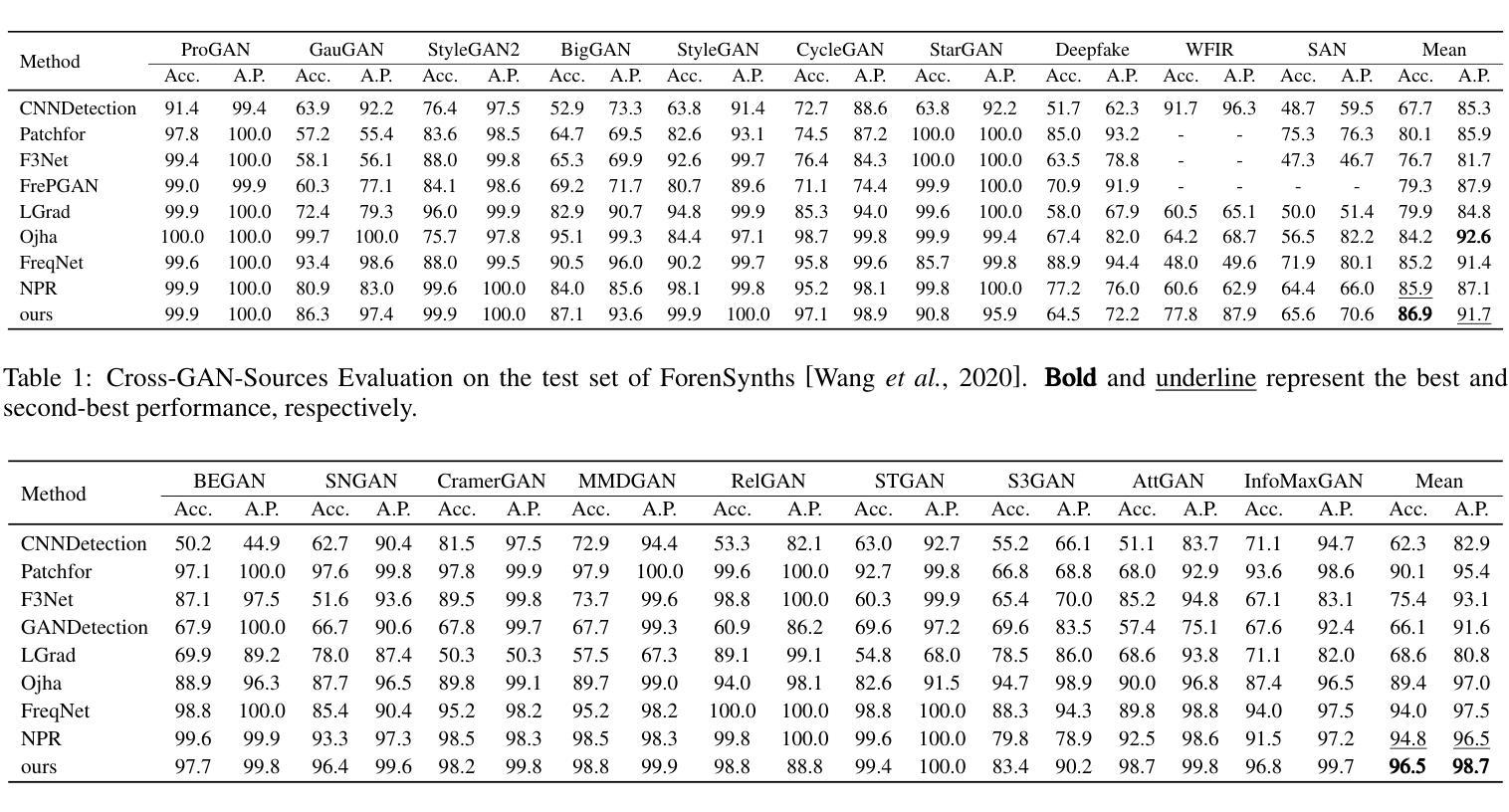
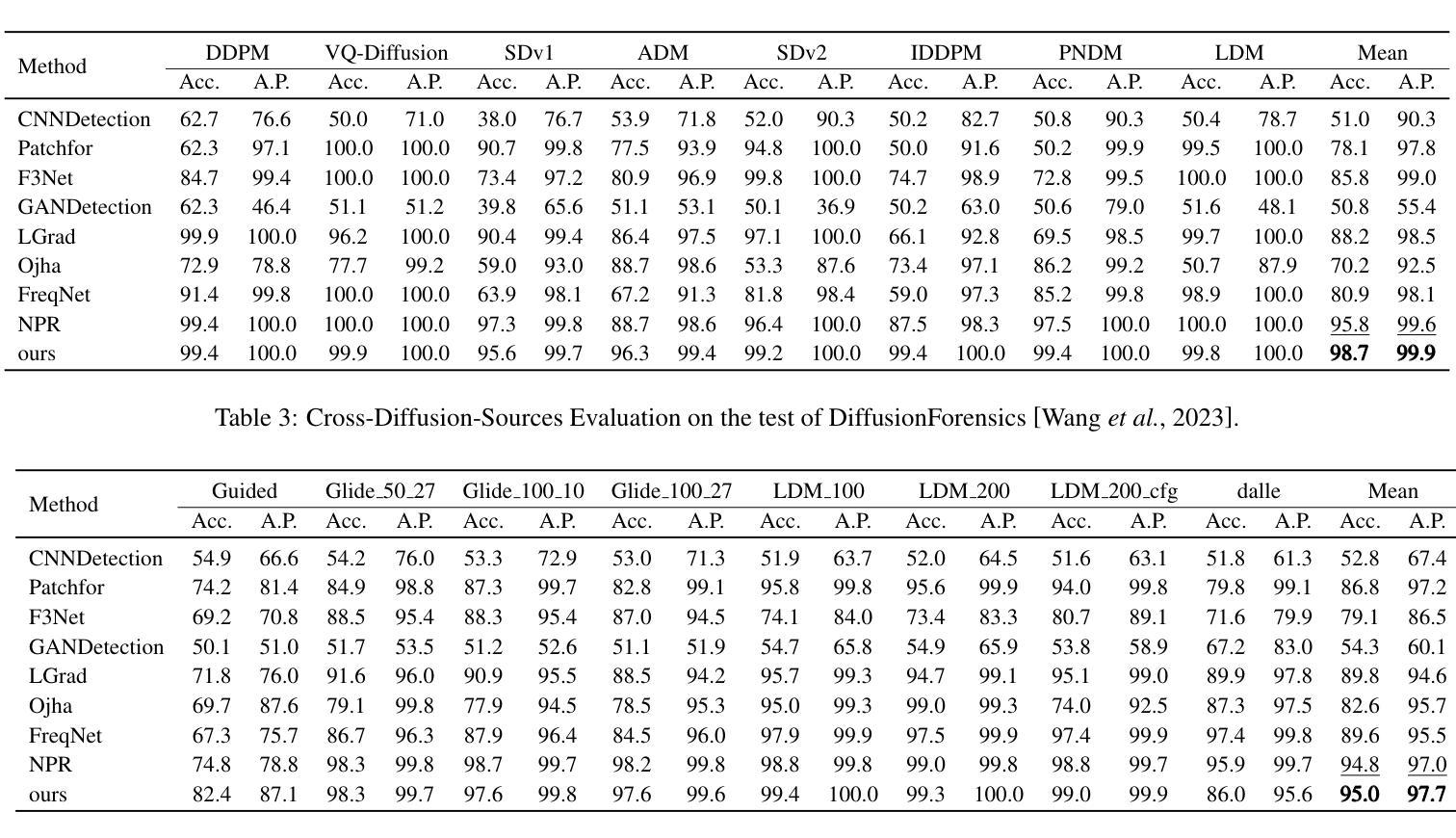
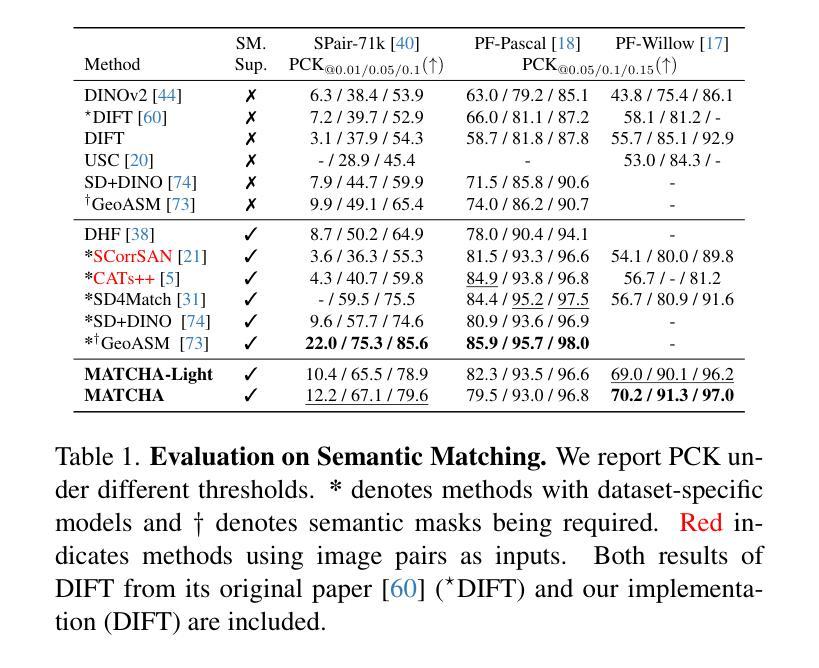
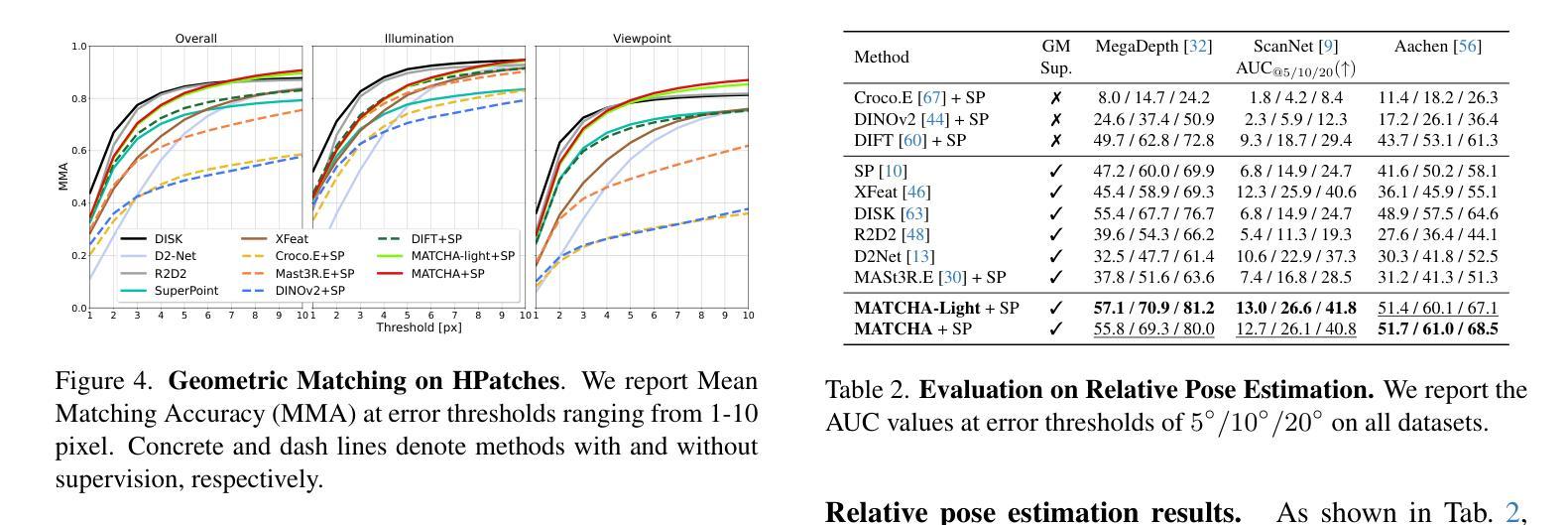
MATCHA:Towards Matching Anything
Authors:Fei Xue, Sven Elflein, Laura Leal-Taixé, Qunjie Zhou
Establishing correspondences across images is a fundamental challenge in computer vision, underpinning tasks like Structure-from-Motion, image editing, and point tracking. Traditional methods are often specialized for specific correspondence types, geometric, semantic, or temporal, whereas humans naturally identify alignments across these domains. Inspired by this flexibility, we propose MATCHA, a unified feature model designed to ``rule them all’’, establishing robust correspondences across diverse matching tasks. Building on insights that diffusion model features can encode multiple correspondence types, MATCHA augments this capacity by dynamically fusing high-level semantic and low-level geometric features through an attention-based module, creating expressive, versatile, and robust features. Additionally, MATCHA integrates object-level features from DINOv2 to further boost generalization, enabling a single feature capable of matching anything. Extensive experiments validate that MATCHA consistently surpasses state-of-the-art methods across geometric, semantic, and temporal matching tasks, setting a new foundation for a unified approach for the fundamental correspondence problem in computer vision. To the best of our knowledge, MATCHA is the first approach that is able to effectively tackle diverse matching tasks with a single unified feature.
建立图像之间的对应关系是计算机视觉领域的一个基本挑战,也是结构从运动、图像编辑和点跟踪等任务的基础。传统方法通常针对特定的对应关系类型(如几何、语义或时间)进行专业化处理,而人类自然地能够识别这些领域的对齐方式。受这种灵活性的启发,我们提出了MATCHA,这是一个统一的特征模型,旨在“一统天下”,在多种匹配任务中建立稳健的对应关系。基于扩散模型特征可以编码多种对应关系类型的见解,MATCHA通过基于注意力的模块动态融合高级语义和低级几何特征,增强这种能力,从而生成表达力强、通用性强、鲁棒性高的特征。此外,MATCHA还集成了DINOv2的对象级特征,进一步提高了泛化能力,使得单个特征就能够匹配任何内容。大量实验验证了MATCHA在几何、语义和时间匹配任务上均超越了最新方法,为计算机视觉中基本对应关系问题的统一方法设定了新的基础。据我们所知,MATCHA是第一个能够有效解决多种匹配任务的单统一特征方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个统一特征模型MATCHA,旨在通过融合扩散模型特征来建立跨不同匹配任务的稳健对应关系。MATCHA通过动态融合高级语义和低级几何特征,增强对应关系的表达能力、通用性和稳健性。此外,MATCHA集成了DINOv2的对象级特征,进一步提高泛化能力,使得单个特征能够匹配任何内容。实验证明,MATCHA在几何、语义和时序匹配任务上均超越了现有方法,为计算机视觉中的基本对应关系问题提供了新的统一解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- MATCHA是一个统一特征模型,旨在解决计算机视觉中跨图像对应关系的核心挑战。
- MATCHA融合扩散模型特征,具备处理多种对应关系类型的能力。
- 通过动态融合高级语义和低级几何特征,MATCHA增强了对应关系的表达能力、通用性和稳健性。
- MATCHA集成了DINOv2的对象级特征,提高了泛化能力,实现了单一特征对任何内容的匹配。
- 实验证明,MATCHA在几何、语义和时序匹配任务上的性能均超越了现有方法。
- MATCHA是首个能够有效处理多种匹配任务的单一统一特征方法。
点此查看论文截图


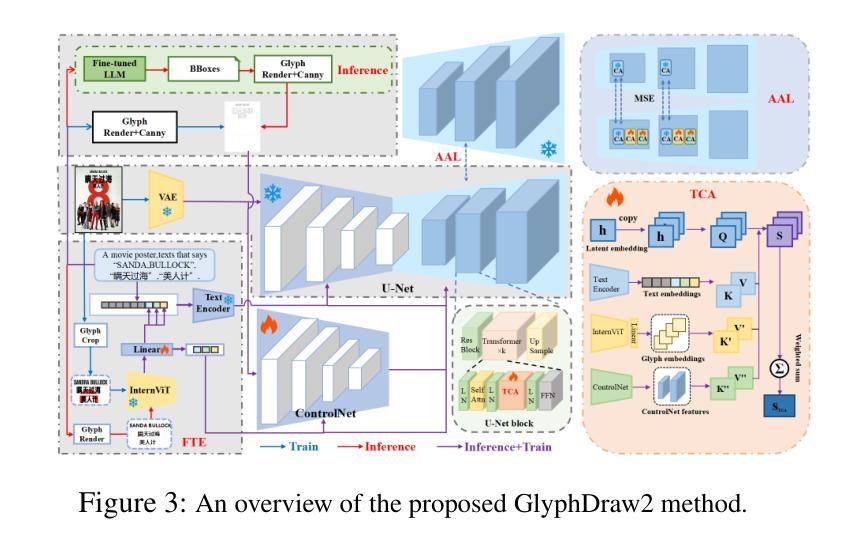
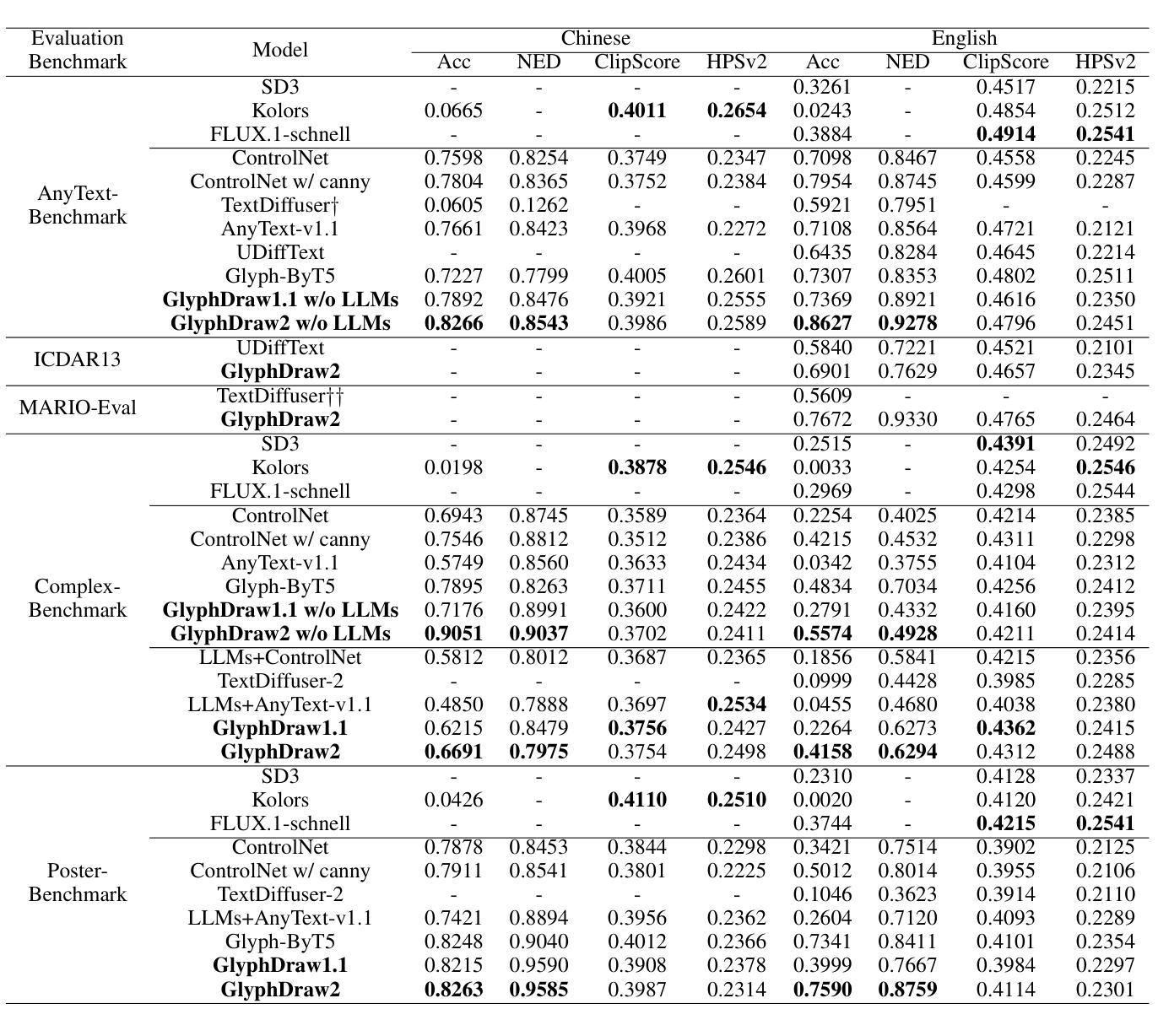
GlyphDraw2: Automatic Generation of Complex Glyph Posters with Diffusion Models and Large Language Models
Authors:Jian Ma, Yonglin Deng, Chen Chen, Haonan Lu, Zhenyu Yang
Posters play a crucial role in marketing and advertising by enhancing visual communication and brand visibility, making significant contributions to industrial design. With the latest advancements in controllable T2I diffusion models, increasing research has focused on rendering text within synthesized images. Despite improvements in text rendering accuracy, the field of automatic poster generation remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose an automatic poster generation framework with text rendering capabilities leveraging LLMs, utilizing a triple-cross attention mechanism based on alignment learning. This framework aims to create precise poster text within a detailed contextual background. Additionally, the framework supports controllable fonts, adjustable image resolution, and the rendering of posters with descriptions and text in both English and Chinese.Furthermore, we introduce a high-resolution font dataset and a poster dataset with resolutions exceeding 1024 pixels. Our approach leverages the SDXL architecture. Extensive experiments validate our method’s capability in generating poster images with complex and contextually rich backgrounds.Codes is available at https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/GlyphDraw2.
海报在营销和广告中扮演着至关重要的角色,通过增强视觉交流和品牌可见度,为工业设计做出了重大贡献。随着最新的可控T2I扩散模型的进步,越来越多的研究专注于在合成图像中进行文本渲染。尽管文本渲染的准确性有所提高,但自动海报生成领域仍然未被充分探索。在本文中,我们提出了一个具有文本渲染能力的自动海报生成框架,该框架利用基于对齐学习的大型语言模型(LLMs),采用三重交叉注意力机制。该框架旨在在一个详细的上下文背景中创建精确的海报文本。此外,该框架支持可控字体、可调整的图像分辨率以及中英文描述和文本的海报渲染。此外,我们还介绍了一个高分辨率字体数据集和一个分辨率超过1024像素的海报数据集。我们的方法利用SDXL架构。大量实验验证了我们方法在生成具有复杂和上下文丰富的背景的海报图像方面的能力。代码可在https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/GlyphDraw2中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
本文提出一种利用LLMs和基于对齐学习的三重交叉注意力机制的自动海报生成框架,可实现文本渲染。该框架旨在创建具有详细上下文背景的海报文本,并支持可控字体、可调图像分辨率以及中英文描述和文本的海报渲染。此外,引入高分辨率字体数据集和分辨率超过1024像素的海报数据集。实验证明该方法能够生成具有复杂和丰富上下文背景的海报图像。
Key Takeaways
- 海报在营销和广告中起到关键作用,提升视觉沟通和品牌可见度,对工业设计有重要贡献。
- 文本在合成图像中的渲染是近年来的研究热点,尤其是利用可控的T2I扩散模型。
- 当前研究尚未充分探索自动海报生成领域。
- 本文提出一种基于LLMs和基于对齐学习的三重交叉注意力机制的自动海报生成框架,具有文本渲染能力。
- 该框架旨在创建具有详细上下文背景的海报文本,支持多种字体、图像分辨率及中英文描述。
- 引入高分辨率字体数据集和海报数据集,分辨率超过1024像素。
点此查看论文截图



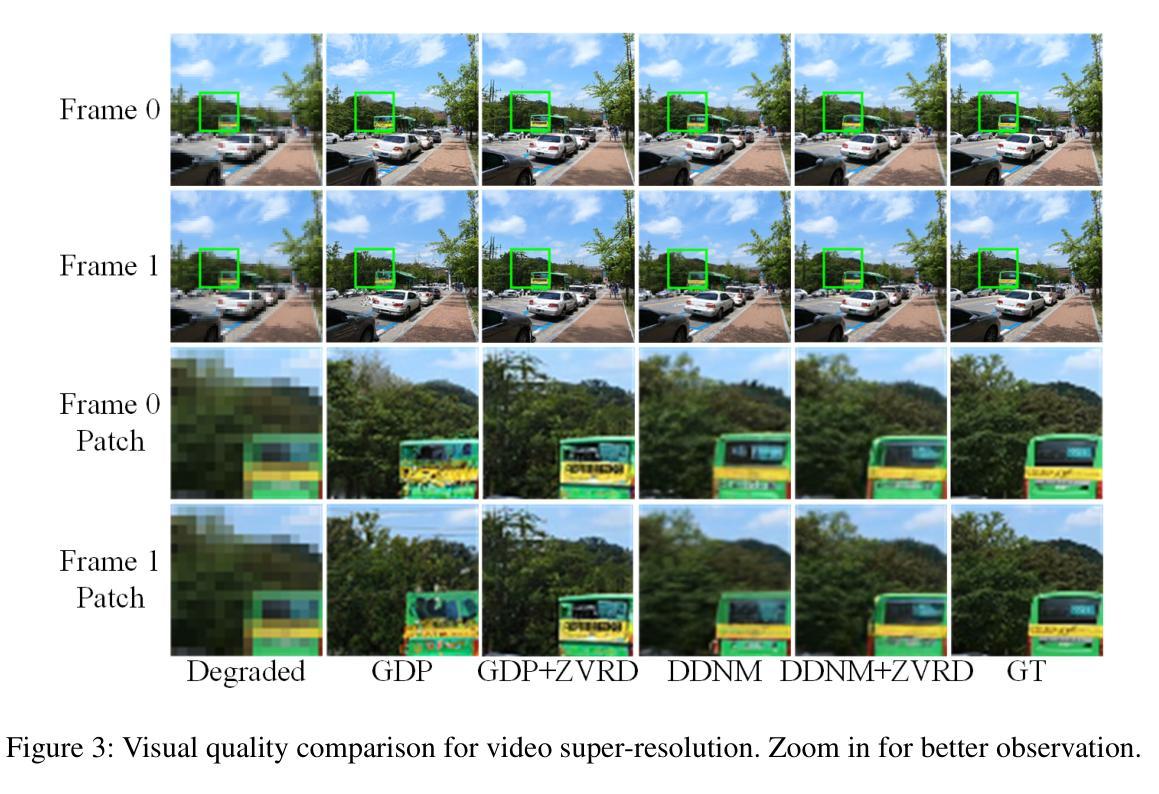
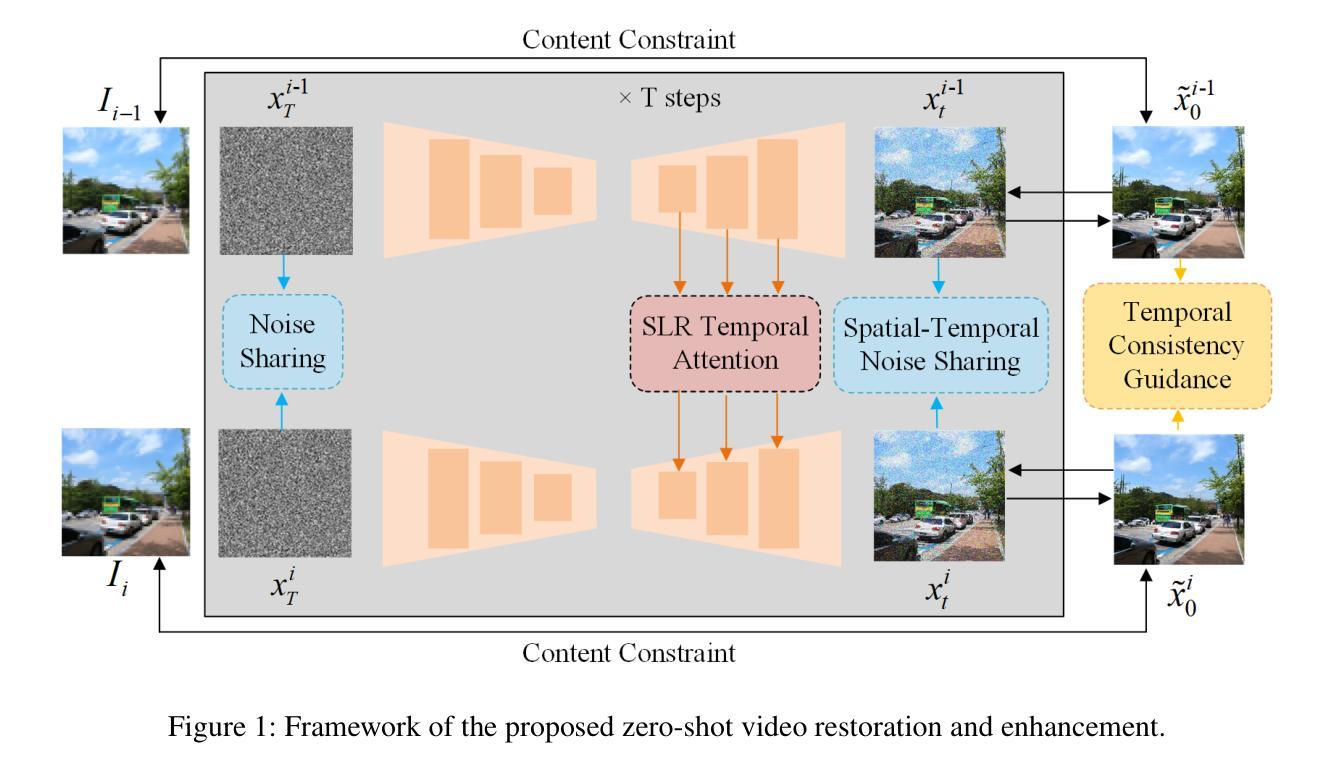
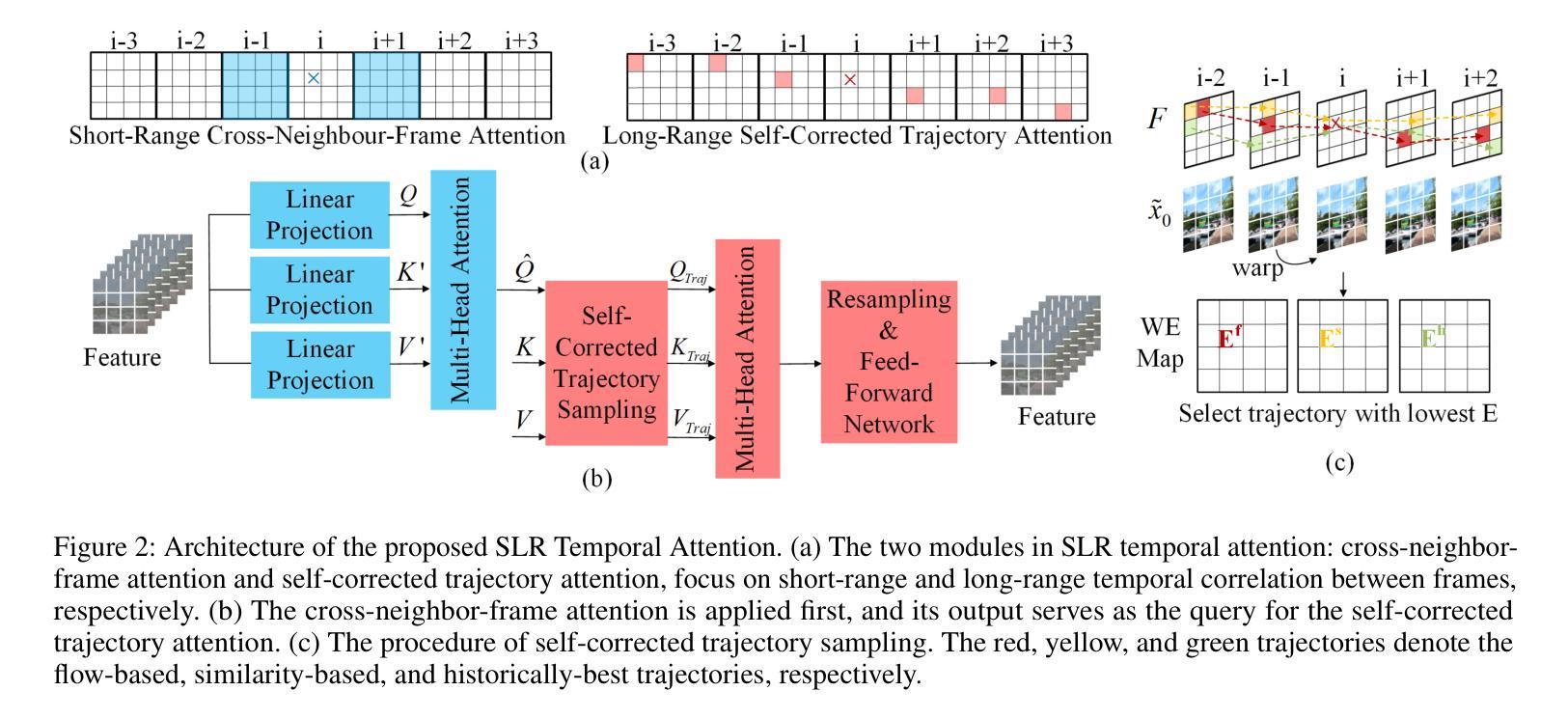
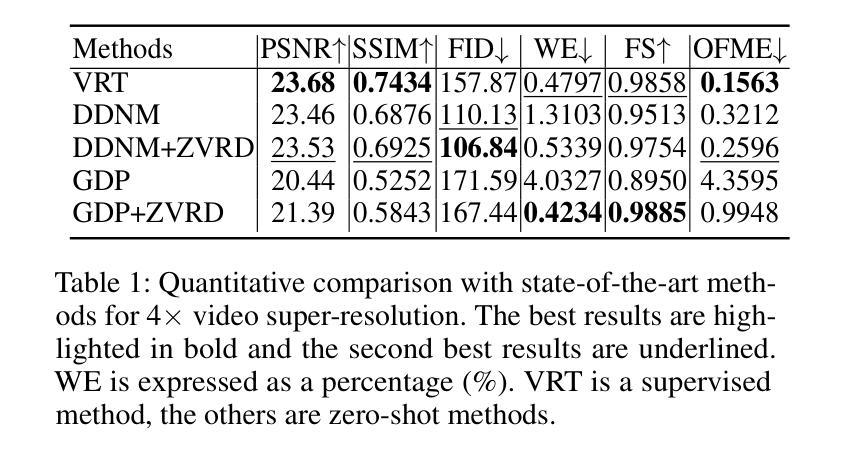
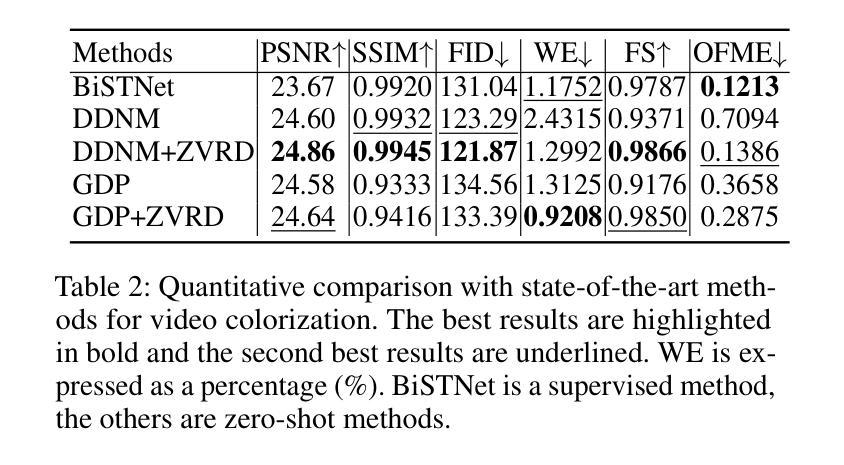
Zero-shot Video Restoration and Enhancement Using Pre-Trained Image Diffusion Model
Authors:Cong Cao, Huanjing Yue, Xin Liu, Jingyu Yang
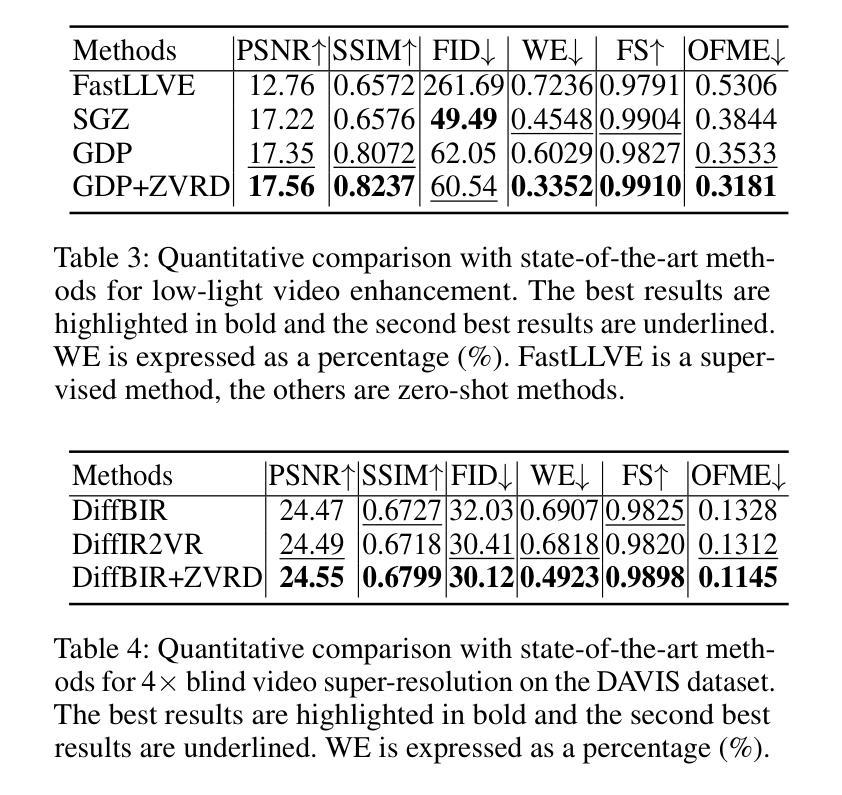
Diffusion-based zero-shot image restoration and enhancement models have achieved great success in various tasks of image restoration and enhancement. However, directly applying them to video restoration and enhancement results in severe temporal flickering artifacts. In this paper, we propose the first framework for zero-shot video restoration and enhancement based on the pre-trained image diffusion model. By replacing the spatial self-attention layer with the proposed short-long-range (SLR) temporal attention layer, the pre-trained image diffusion model can take advantage of the temporal correlation between frames. We further propose temporal consistency guidance, spatial-temporal noise sharing, and an early stopping sampling strategy to improve temporally consistent sampling. Our method is a plug-and-play module that can be inserted into any diffusion-based image restoration or enhancement methods to further improve their performance. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method. Our code is available at https://github.com/cao-cong/ZVRD.
基于扩散的零样本图像修复和增强模型在图像修复和增强的各种任务中取得了巨大的成功。然而,直接将其应用于视频修复和增强会导致严重的暂时闪烁伪影。在本文中,我们提出了基于预训练图像扩散模型的零样本视频修复和增强的第一个框架。通过用所提出的短长程(SLR)时间注意力层替换空间自注意力层,预训练的图像扩散模型可以利用帧之间的时间相关性。我们还提出了时间一致性指导、时空噪声共享和早期停止采样策略,以改善时间一致性的采样。我们的方法是一个即插即用的模块,可以插入到任何基于扩散的图像修复或增强方法中,以进一步提高其性能。实验结果证明了我们提出方法的优越性。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/cao-cong/ZVRD找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
扩散模型在零样本图像修复和增强任务中取得了巨大成功,但直接应用于视频修复和增强会导致严重的时序闪烁伪影。本文首次提出基于预训练图像扩散模型的零样本视频修复和增强框架。通过用所提出的长短程(SLR)时序注意力层替换空间自注意力层,预训练的图像扩散模型可以利用帧之间的时序相关性。本文还提出了时序一致性指导、时空噪声共享和早期停止采样策略,以改进时序一致采样。该方法是一个即插即用的模块,可以插入任何基于扩散的图像修复或增强方法中,以进一步提高其性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像修复和增强任务中表现优异,但直接应用于视频会导致时序伪影。
- 本文首次提出了基于预训练图像扩散模型的零样本视频修复和增强框架。
- 通过引入长短程(SLR)时序注意力层,模型能利用帧间的时序相关性。
- 提出了时序一致性指导、时空噪声共享和早期停止采样策略,以改善时序一致采样。
- 该方法是一个可插入任何扩散图像修复或增强方法的模块,能进一步提升性能。
- 实验结果证明该方法具有优越性。
点此查看论文截图


Information Theoretic Text-to-Image Alignment
Authors:Chao Wang, Giulio Franzese, Alessandro Finamore, Massimo Gallo, Pietro Michiardi
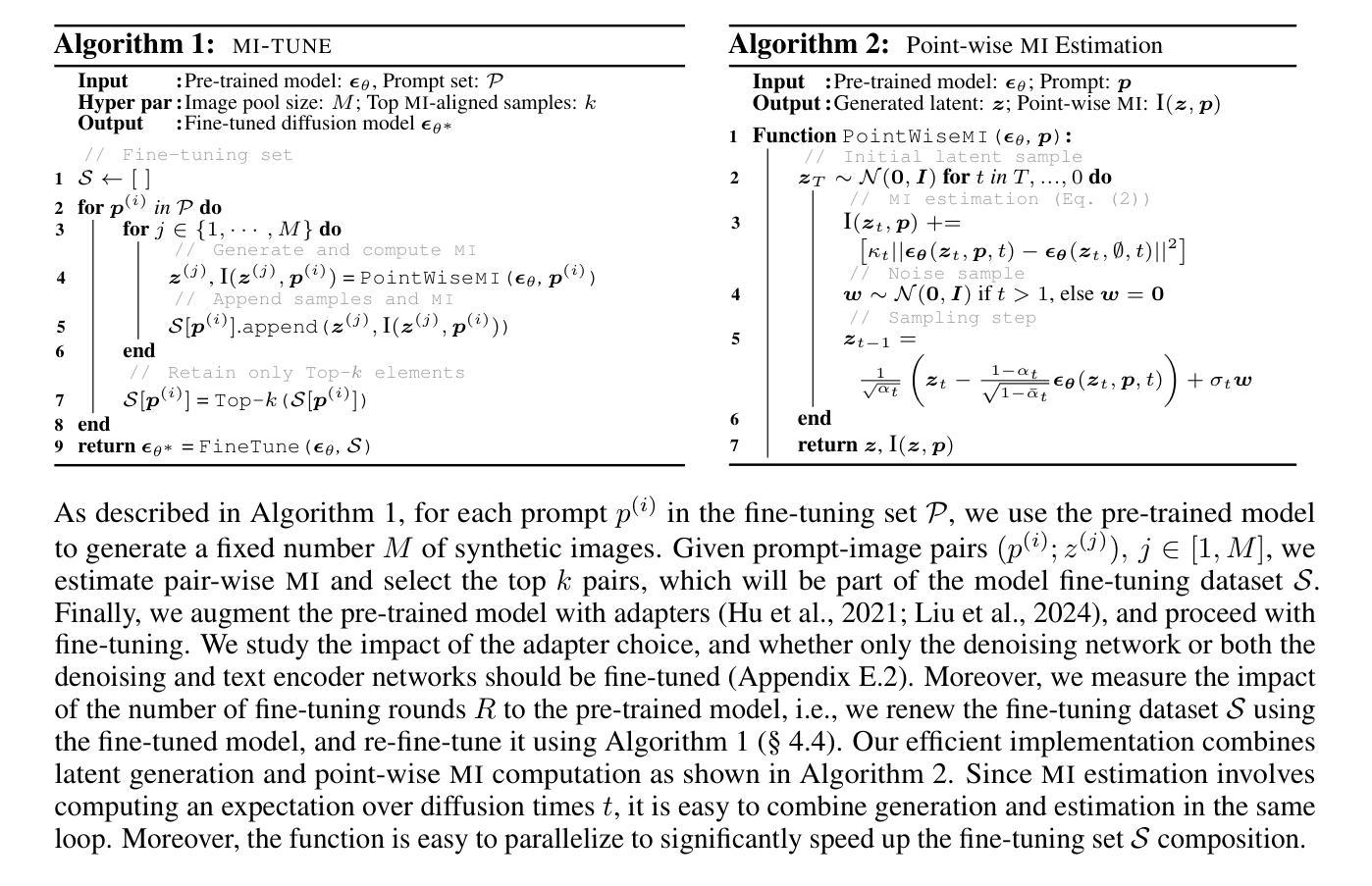
Diffusion models for Text-to-Image (T2I) conditional generation have recently achieved tremendous success. Yet, aligning these models with user’s intentions still involves a laborious trial-and-error process, and this challenging alignment problem has attracted considerable attention from the research community. In this work, instead of relying on fine-grained linguistic analyses of prompts, human annotation, or auxiliary vision-language models, we use Mutual Information (MI) to guide model alignment. In brief, our method uses self-supervised fine-tuning and relies on a point-wise (MI) estimation between prompts and images to create a synthetic fine-tuning set for improving model alignment. Our analysis indicates that our method is superior to the state-of-the-art, yet it only requires the pre-trained denoising network of the T2I model itself to estimate MI, and a simple fine-tuning strategy that improves alignment while maintaining image quality.
文本到图像(T2I)的条件生成扩散模型近期取得了巨大成功。然而,将这些模型与用户意图对齐仍然需要繁琐的试错过程,这个具有挑战性的对齐问题已引起了研究界的广泛关注。在这项工作中,我们没有依赖提示的精细语言分析、人工标注或辅助的视觉语言模型,而是使用互信息(MI)来引导模型对齐。简而言之,我们的方法采用自监督微调,并依赖于提示和图像之间的点(MI)估计来创建一个合成微调集,以提高模型对齐能力。我们的分析表明,我们的方法优于现有技术,但它只需要T2I模型本身的预训练去噪网络来估计MI,以及一种简单的微调策略,可以在保持图像质量的同时提高对齐精度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF to appear at ICLR25
Summary
基于文本的扩散模型(T2I)条件生成已取得了巨大成功,但在与用户意图对齐时仍面临繁琐的试错过程。本研究采用互信息(MI)引导模型对齐,无需依赖精细的语言分析提示、人工标注或辅助视觉语言模型。通过自监督微调并利用提示与图像之间的点级互信息估计,创建合成微调集以改善模型对齐。分析表明,该方法优于现有技术,仅依赖T2I模型的预训练去噪网络进行互信息估计,采用简单的微调策略提高对齐度同时保持图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的扩散模型已取得显著成功。
- 对齐模型与用户意图仍然是一个挑战,需要采用新的方法解决。
- 本研究使用互信息(MI)来引导模型对齐,无需依赖精细的语言分析或人工标注。
- 通过自监督微调改善模型对齐。
- 利用提示和图像之间的点级互信息估计来创建合成微调集。
- 该方法优于现有技术。
- 该方法仅依赖T2I模型的预训练去噪网络进行互信息估计,并采用简单的微调策略维持图像质量。
点此查看论文截图


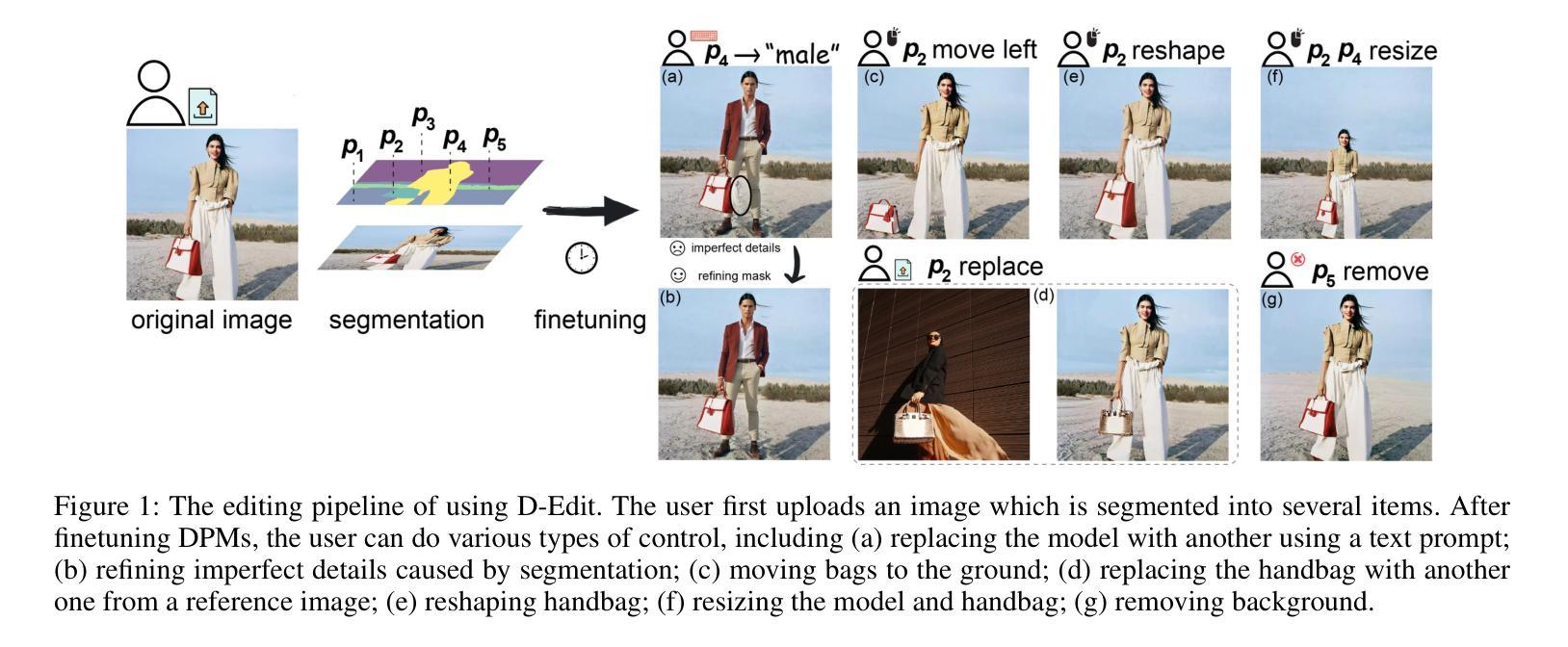
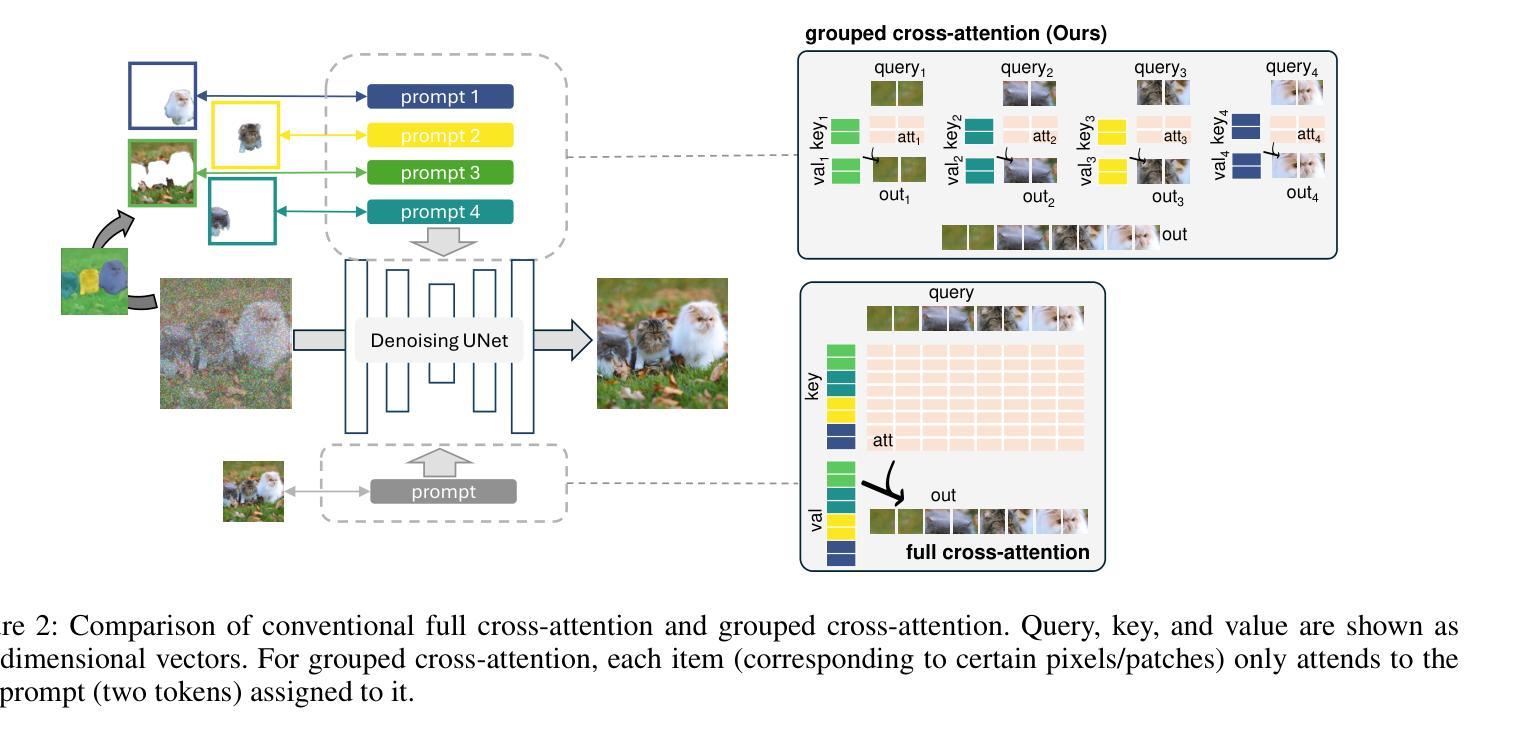
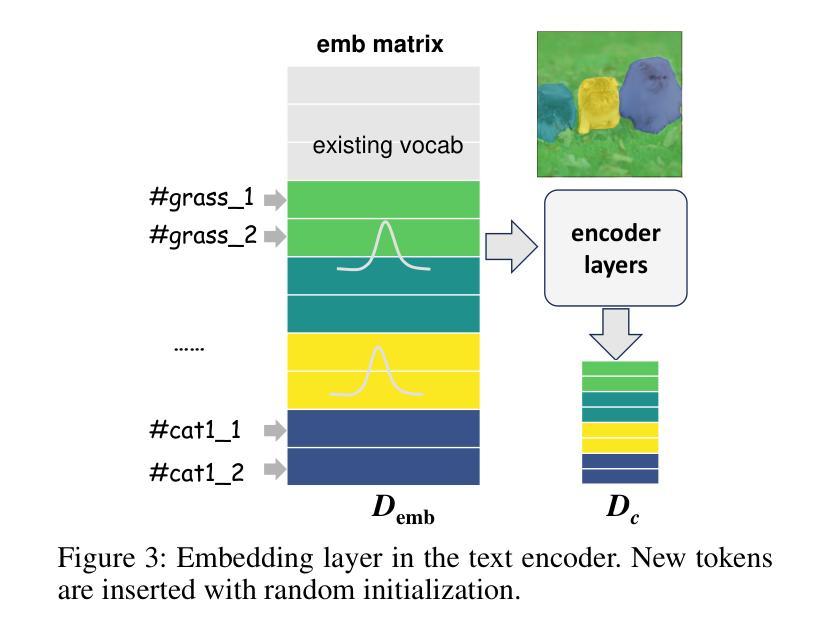
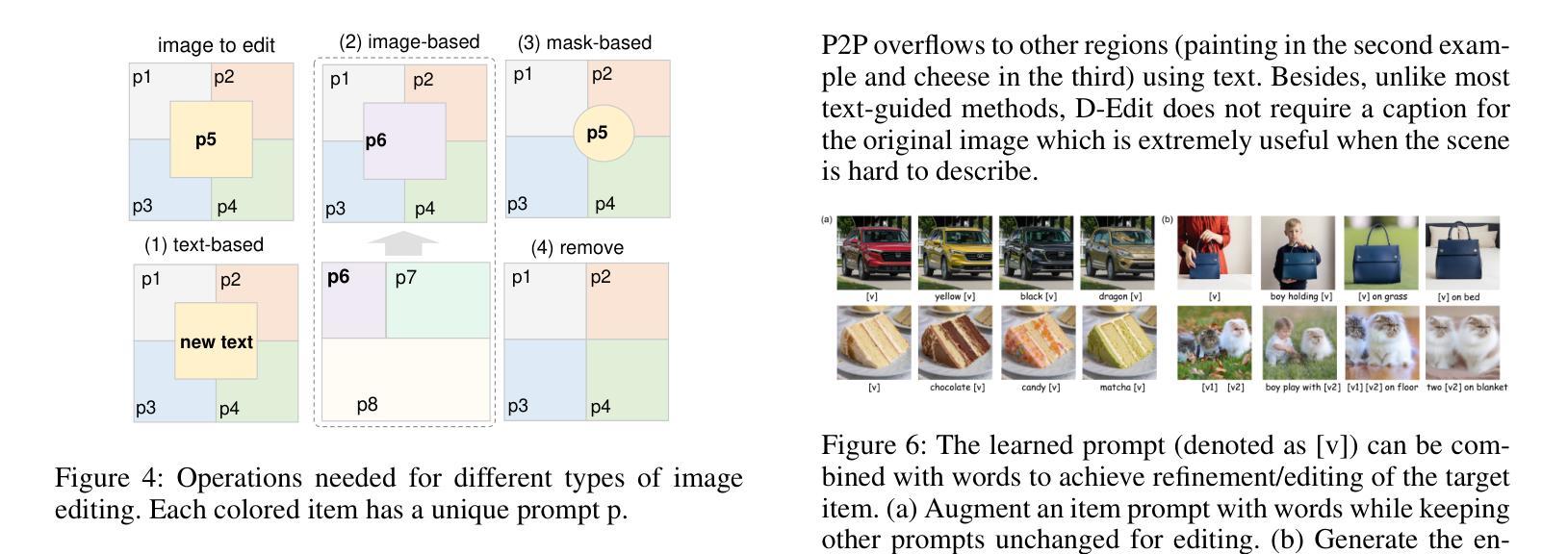
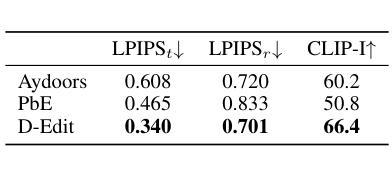
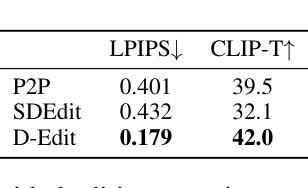
An Item is Worth a Prompt: Versatile Image Editing with Disentangled Control
Authors:Aosong Feng, Weikang Qiu, Jinbin Bai, Xiao Zhang, Zhen Dong, Kaicheng Zhou, Rex Ying, Leandros Tassiulas
Building on the success of text-to-image diffusion models (DPMs), image editing is an important application to enable human interaction with AI-generated content. Among various editing methods, editing within the prompt space gains more attention due to its capacity and simplicity of controlling semantics. However, since diffusion models are commonly pretrained on descriptive text captions, direct editing of words in text prompts usually leads to completely different generated images, violating the requirements for image editing. On the other hand, existing editing methods usually consider introducing spatial masks to preserve the identity of unedited regions, which are usually ignored by DPMs and therefore lead to inharmonic editing results. Targeting these two challenges, in this work, we propose to disentangle the comprehensive image-prompt interaction into several item-prompt interactions, with each item linked to a special learned prompt. The resulting framework, named D-Edit, is based on pretrained diffusion models with cross-attention layers disentangled and adopts a two-step optimization to build item-prompt associations. Versatile image editing can then be applied to specific items by manipulating the corresponding prompts. We demonstrate state-of-the-art results in four types of editing operations including image-based, text-based, mask-based editing, and item removal, covering most types of editing applications, all within a single unified framework. Notably, D-Edit is the first framework that can (1) achieve item editing through mask editing and (2) combine image and text-based editing. We demonstrate the quality and versatility of the editing results for a diverse collection of images through both qualitative and quantitative evaluations.
基于文本到图像扩散模型(DPMs)的成功,图像编辑是与AI生成内容进行交互的重要应用。在各种编辑方法中,提示空间内的编辑因其控制语义的能力和简洁性而受到更多关注。然而,由于扩散模型通常是在描述性文本标题上进行预训练的,直接在文本提示中进行编辑通常会导致生成的图像完全不同,这违反了图像编辑的要求。另一方面,现有的编辑方法通常考虑引入空间掩膜来保留未编辑区域的身份,而这些通常被DPMs忽略,从而导致不和谐的编辑结果。针对这两个挑战,在这项工作中,我们提出将全面的图像提示交互分解为多个项目提示交互,每个项目与特殊的预训练提示相关联。得到的框架被称为D-Edit,它基于预训练的扩散模型,通过解开交叉注意层来构建物品提示关联的两步优化。然后,可以通过操纵相应的提示来对特定项目进行灵活的图像编辑。我们在四种编辑操作中展示了最先进的成果,包括基于图像的编辑、基于文本的编辑、基于掩膜的编辑和项目移除,涵盖了大多数类型的编辑应用,都在一个统一的框架内完成。值得注意的是,D-Edit是第一个能够(1)通过掩膜编辑实现项目编辑并结合图像和文本基础的编辑框架。我们通过定性和定量评估,展示了编辑结果的质量和多样性,适用于各种图像集合。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本到图像扩散模型(DPMs)的成功,图像编辑是与AI生成内容进行交互的重要应用之一。本文关注扩散模型在图像编辑中的两个挑战:文本提示空间内的编辑和未编辑区域的身份保留。为此,本文提出了一个名为D-Edit的框架,基于预训练的扩散模型,通过分解图像与提示的交互为多个物品与提示的交互来解决这两个挑战。该框架采用两步优化来建立物品与提示的关联,可以通过操作相应的提示来对特定物品进行多样化的图像编辑。D-Edit在四种类型的编辑操作(基于图像、基于文本、基于掩码的编辑以及物品移除)中均展现出卓越的性能,且是唯一能够结合图像和文本进行编辑的框架。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像编辑中面临两个主要挑战:文本提示空间内的编辑和保留未编辑区域的身份。
- D-Edit框架解决了这两个挑战,通过将图像与提示的交互分解为多个物品与提示的交互。
- D-Edit基于预训练的扩散模型,采用两步优化建立物品与提示的关联。
- D-Edit支持多样化的图像编辑,通过操作相应的提示来对特定物品进行编辑。
- D-Edit在多种类型的编辑操作中展现出卓越性能,包括图像、文本、掩码编辑以及物品移除。
- D-Edit是首个能够结合图像和文本进行编辑的框架。
点此查看论文截图