⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
Controllable Forgetting Mechanism for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Kirill Paramonov, Mete Ozay, Eunju Yang, Jijoong Moon, Umberto Michieli
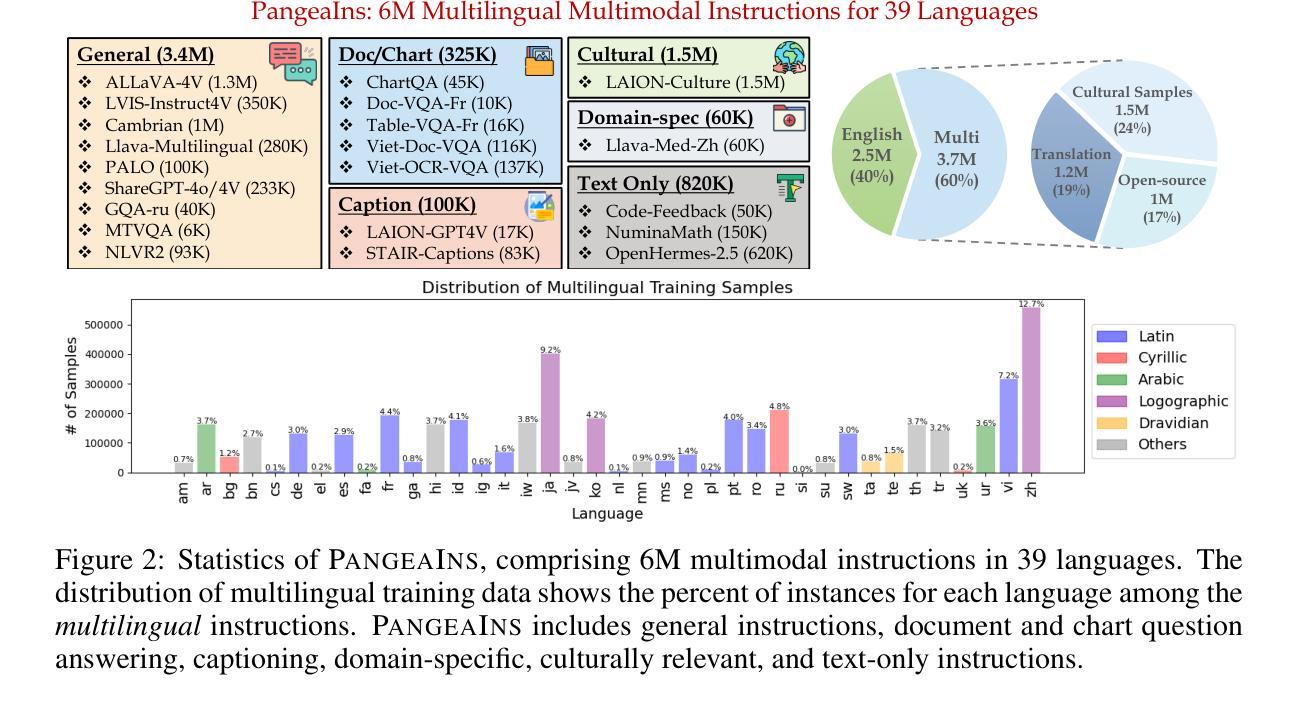
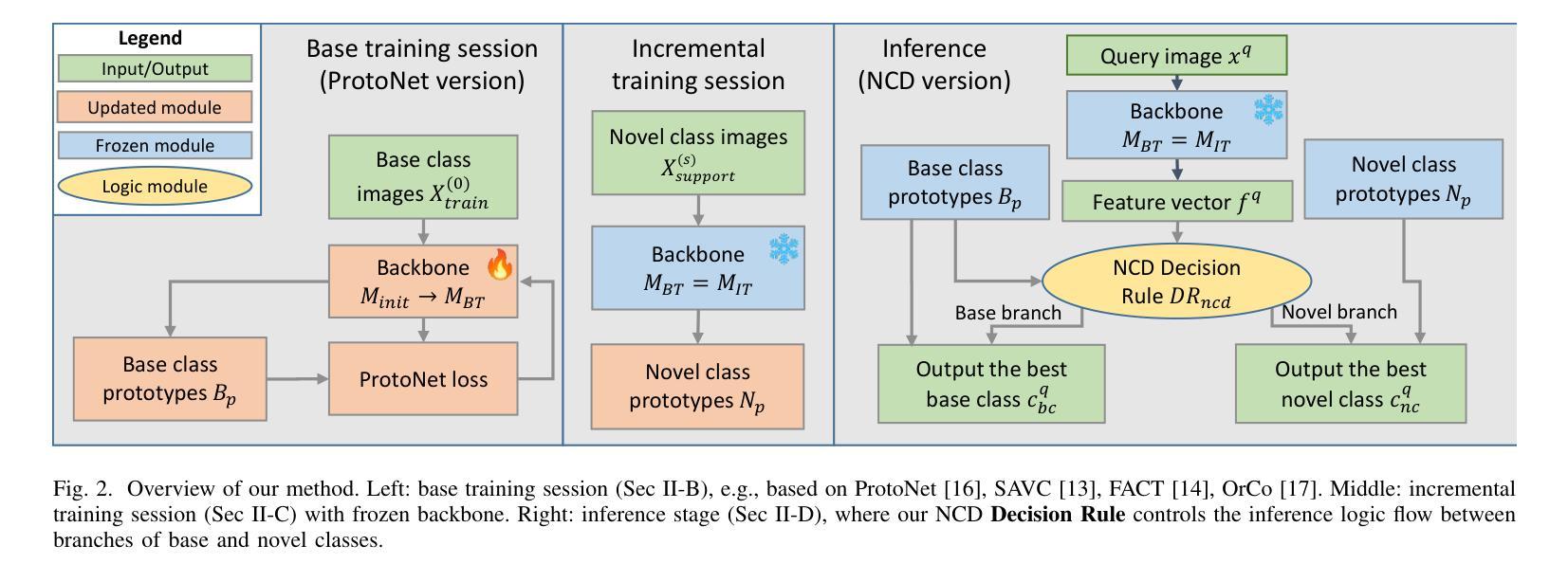
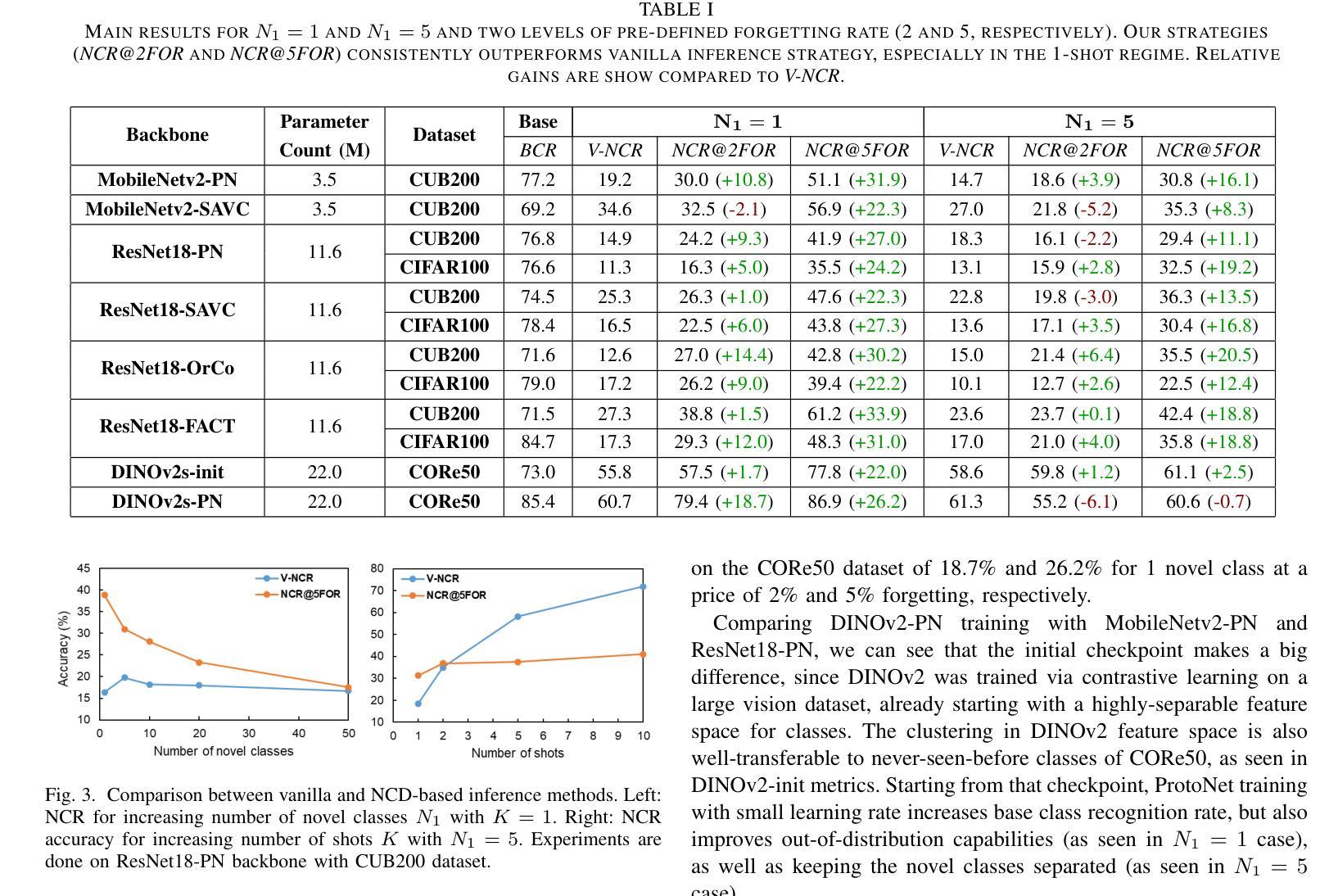
Class-incremental learning in the context of limited personal labeled samples (few-shot) is critical for numerous real-world applications, such as smart home devices. A key challenge in these scenarios is balancing the trade-off between adapting to new, personalized classes and maintaining the performance of the model on the original, base classes. Fine-tuning the model on novel classes often leads to the phenomenon of catastrophic forgetting, where the accuracy of base classes declines unpredictably and significantly. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective mechanism to address this challenge by controlling the trade-off between novel and base class accuracy. We specifically target the ultra-low-shot scenario, where only a single example is available per novel class. Our approach introduces a Novel Class Detection (NCD) rule, which adjusts the degree of forgetting a priori while simultaneously enhancing performance on novel classes. We demonstrate the versatility of our solution by applying it to state-of-the-art Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) methods, showing consistent improvements across different settings. To better quantify the trade-off between novel and base class performance, we introduce new metrics: NCR@2FOR and NCR@5FOR. Our approach achieves up to a 30% improvement in novel class accuracy on the CIFAR100 dataset (1-shot, 1 novel class) while maintaining a controlled base class forgetting rate of 2%.
在有限的个人标注样本(小样本)的背景下,类增量学习对于许多实际应用(如智能家居设备)至关重要。这些场景中的一个关键挑战是在适应新、个性化类别的同时保持模型对原始基础类别的性能。对新类别模型进行微调常常会导致灾难性遗忘现象,即基础类别的准确率不可预测且显著下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种简单有效的机制来解决这一挑战,通过控制新类别和基础类别准确率之间的权衡来实现。我们特别针对超低样本场景,每个新类别只有一个样本可用。我们的方法引入了新颖类别检测(NCD)规则,该规则可以预先调整遗忘程度,同时提高新类别的性能。我们将解决方案应用于最先进的少量类别增量学习(FSCIL)方法,并在不同设置中显示出持续的改进。为了更好地量化新类别和基础类别性能之间的权衡,我们引入了新的指标:NCR@2FOR和NCR@5FOR。我们的方法在CIFAR100数据集上实现了新类别准确率高达30%的改进(1个样本,1个新类别),同时保持基础类别遗忘率控制在2%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025
Summary
这篇论文针对有限个人标注样本下的类增量学习(few-shot)问题进行研究,特别是在超低样本场景(每个新类别只有一个样本)下。为解决适应新类别与保持基础类别性能之间的权衡问题,论文提出了一种简单有效的机制,并引入了一个新类检测规则(Novel Class Detection,NCD)。该机制有助于调整遗忘程度并提高新类别的性能。实验结果表明,该方法在不同的FSCIL方法中具有良好的适用性,在CIFAR100数据集上的新类别准确率提高了30%,同时保持基础类别遗忘率仅为2%。
Key Takeaways
- 论文聚焦于有限个人标注样本下的类增量学习问题,特别是在超低样本场景下的挑战。
- 论文提出了一个简单有效的机制来解决适应新类别与保持基础类别性能之间的权衡问题。
- 引入了一个名为Novel Class Detection(NCD)的新类检测规则,用于调整遗忘程度和提高新类别的性能。
- 论文引入了新的评估指标:NCR@2FOR和NCR@5FOR,以更好地量化新类别和基础类别性能之间的权衡。
- 论文方法在不同的FSCIL方法中具有良好适用性。
- 在CIFAR100数据集上,新类别准确率提高了30%,同时基础类别遗忘率仅为2%。
点此查看论文截图

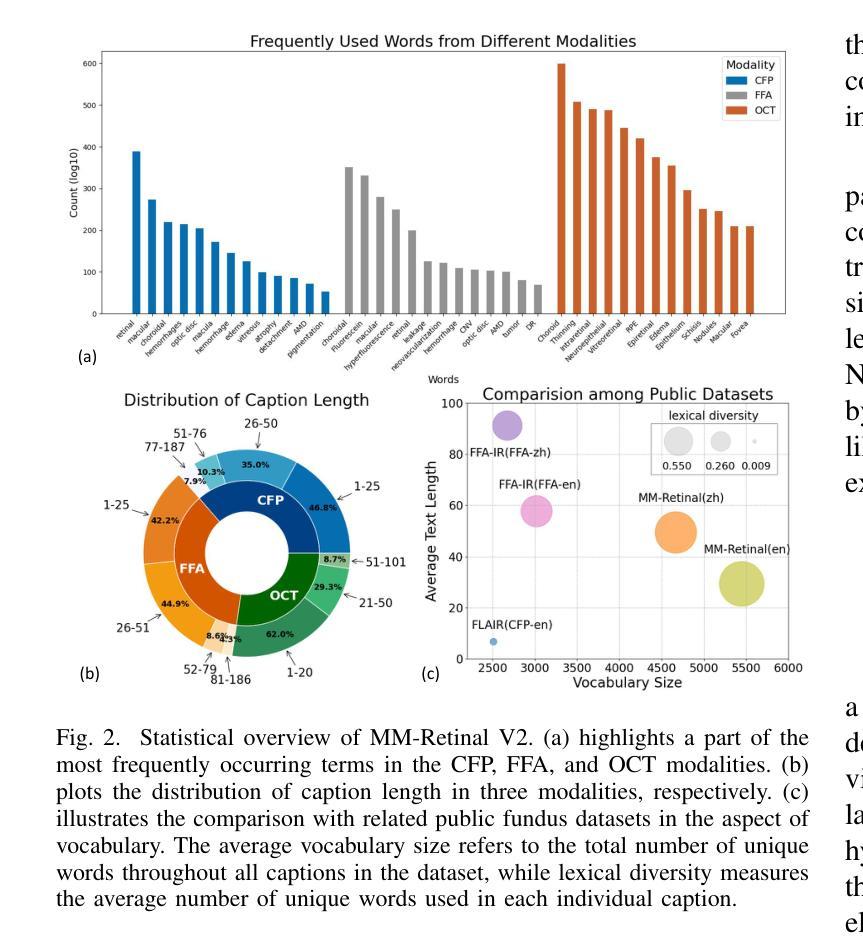
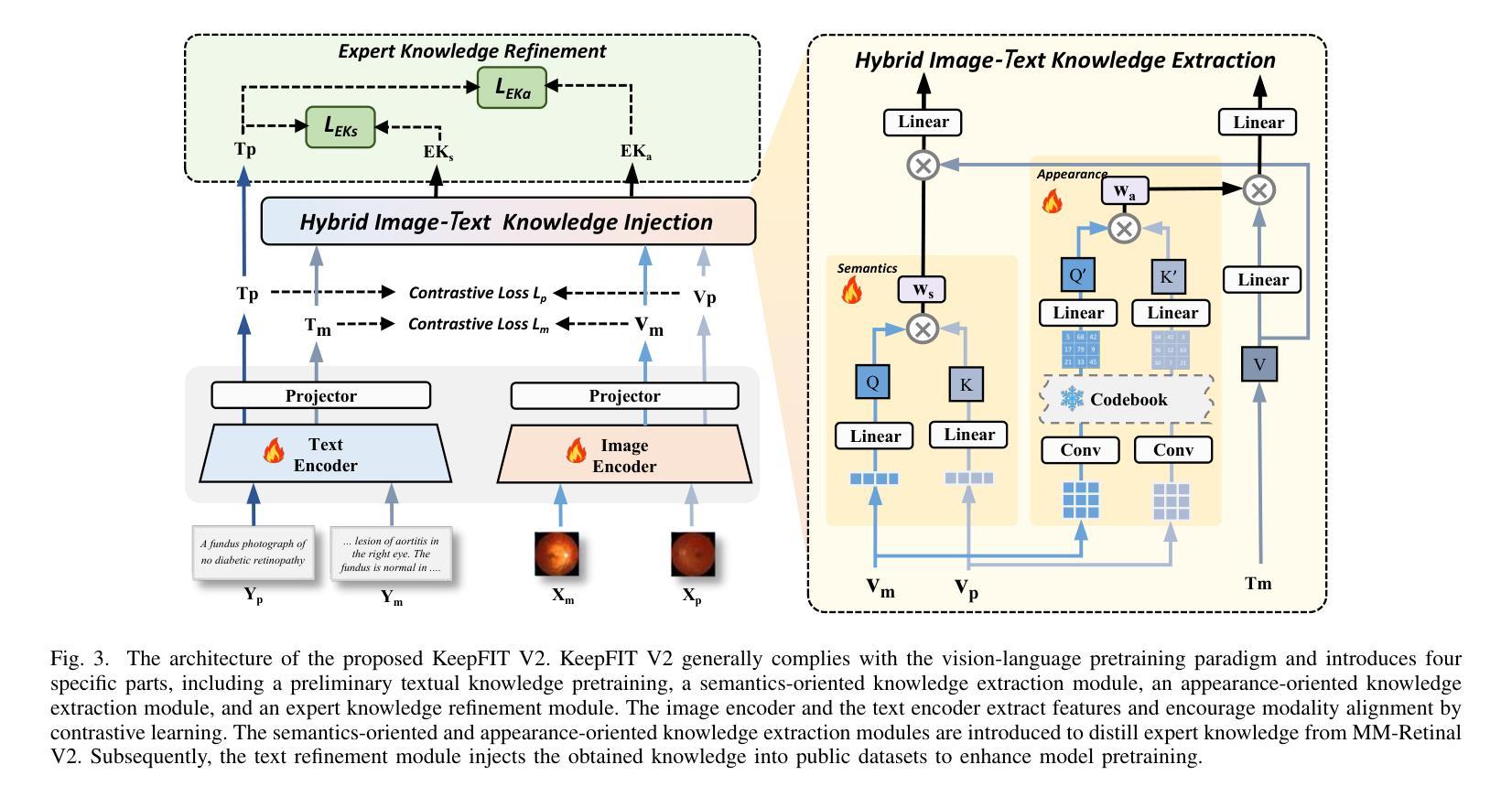
MM-Retinal V2: Transfer an Elite Knowledge Spark into Fundus Vision-Language Pretraining
Authors:Ruiqi Wu, Na Su, Chenran Zhang, Tengfei Ma, Tao Zhou, Zhiting Cui, Nianfeng Tang, Tianyu Mao, Yi Zhou, Wen Fan, Tianxing Wu, Shenqi Jing, Huazhu Fu
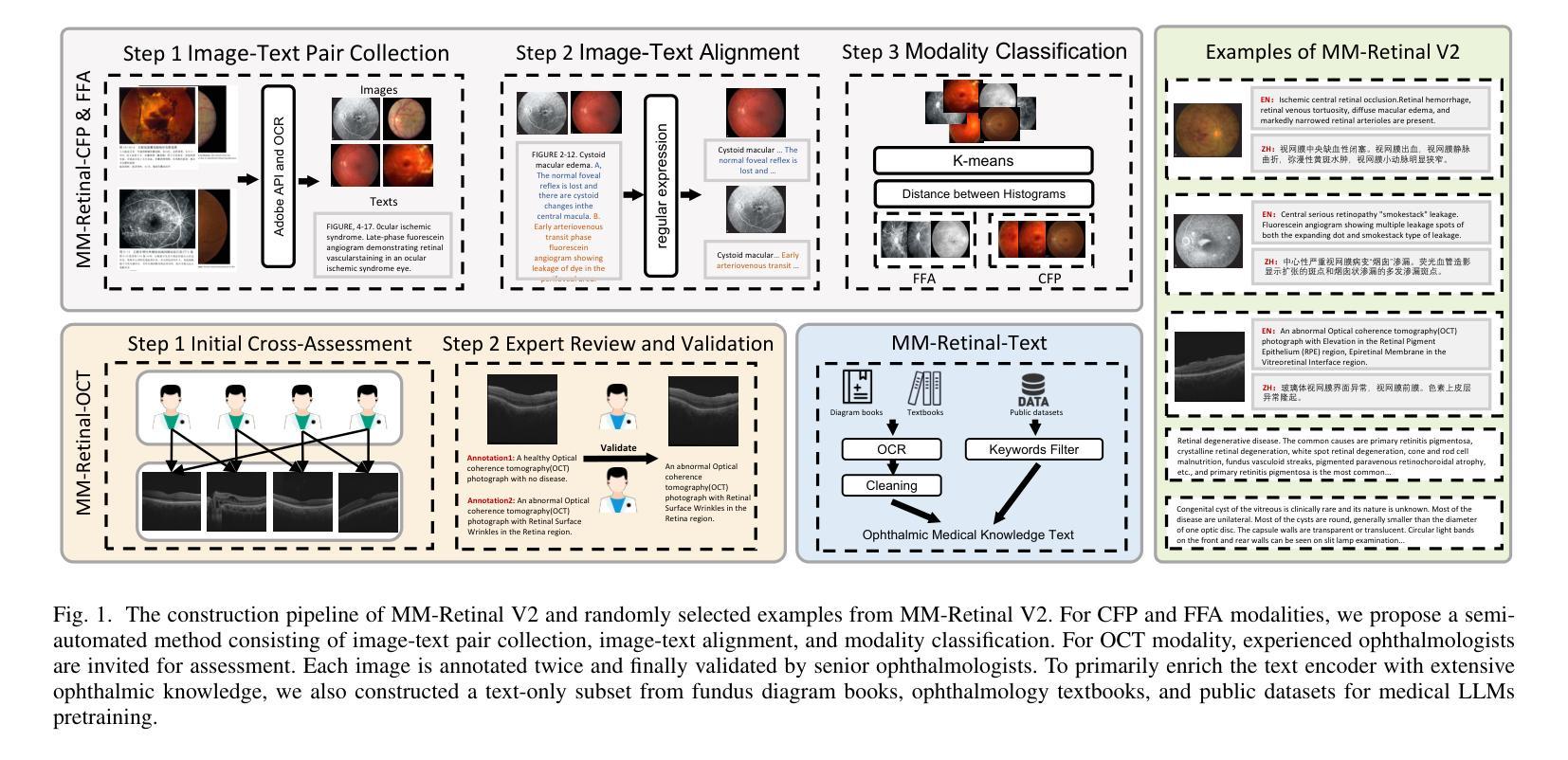
Vision-language pretraining (VLP) has been investigated to generalize across diverse downstream tasks for fundus image analysis. Although recent methods showcase promising achievements, they significantly rely on large-scale private image-text data but pay less attention to the pretraining manner, which limits their further advancements. In this work, we introduce MM-Retinal V2, a high-quality image-text paired dataset comprising CFP, FFA, and OCT image modalities. Then, we propose a novel fundus vision-language pretraining model, namely KeepFIT V2, which is pretrained by integrating knowledge from the elite data spark into categorical public datasets. Specifically, a preliminary textual pretraining is adopted to equip the text encoder with primarily ophthalmic textual knowledge. Moreover, a hybrid image-text knowledge injection module is designed for knowledge transfer, which is essentially based on a combination of global semantic concepts from contrastive learning and local appearance details from generative learning. Extensive experiments across zero-shot, few-shot, and linear probing settings highlight the generalization and transferability of KeepFIT V2, delivering performance competitive to state-of-the-art fundus VLP models trained on large-scale private image-text datasets. Our dataset and model are publicly available via https://github.com/lxirich/MM-Retinal.
视觉语言预训练(VLP)在眼底图像分析的多种下游任务中得到了广泛的应用。尽管最近的方法取得了令人瞩目的成果,但它们严重依赖于大规模的私有图像文本数据,却忽视了预训练的方式,这限制了其进一步的进展。在这项工作中,我们介绍了MM-Retinal V2,这是一个高质量的图文本配对数据集,包含CFP、FFA和OCT图像模式。然后,我们提出了一种新型的眼底视觉语言预训练模型,即KeepFIT V2。该模型通过精英数据的火花知识融入分类公共数据集进行预训练。具体来说,采用初步的文本预训练,为文本编码器配备主要的眼科文本知识。此外,设计了一个混合图像文本知识注入模块进行知识转移,这基本上是基于对比学习中全局语义概念和生成学习中局部外观细节的融合。在零样本、少样本和线性探测设置中的大量实验表明了KeepFIT V2的通用性和可迁移性,其性能与在大规模私有图像文本数据集上训练的最新眼底VLP模型相当。我们的数据集和模型可通过https://github.com/lxirich/MM-Retinal公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对眼底图像分析的跨任务通用化的视觉语言预训练(VLP)研究。针对现有方法过度依赖大规模私有图像文本数据而忽视预训练方式的问题,提出了新型的眼底视觉语言预训练模型KeepFIT V2。该模型通过整合精英数据和公共分类数据集的知识进行预训练。实验表明,KeepFIT V2具有良好的泛化性和迁移性,性能与在大规模私有图像文本数据集上训练的最新眼底VLP模型相当。
Key Takeaways
- 引入MM-Retinal V2数据集,包含多种眼底图像模态,如CFP、FFA和OCT。
- 提出新型眼底视觉语言预训练模型KeepFIT V2。
- KeepFIT V2整合精英数据和公共分类数据集的知识进行预训练。
- 采用初步文本预训练,为文本编码器提供眼科文本知识。
- 设计了混合图像-文本知识注入模块,实现知识迁移。
- 实验证明KeepFIT V2具有良好的泛化性和迁移性。
点此查看论文截图

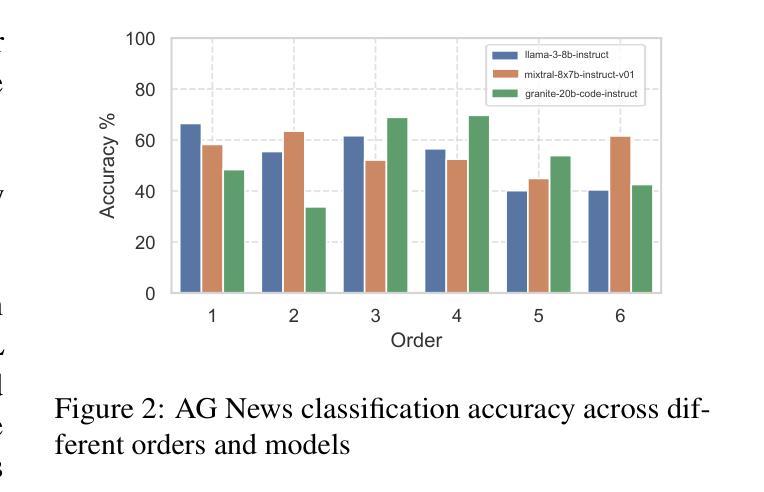
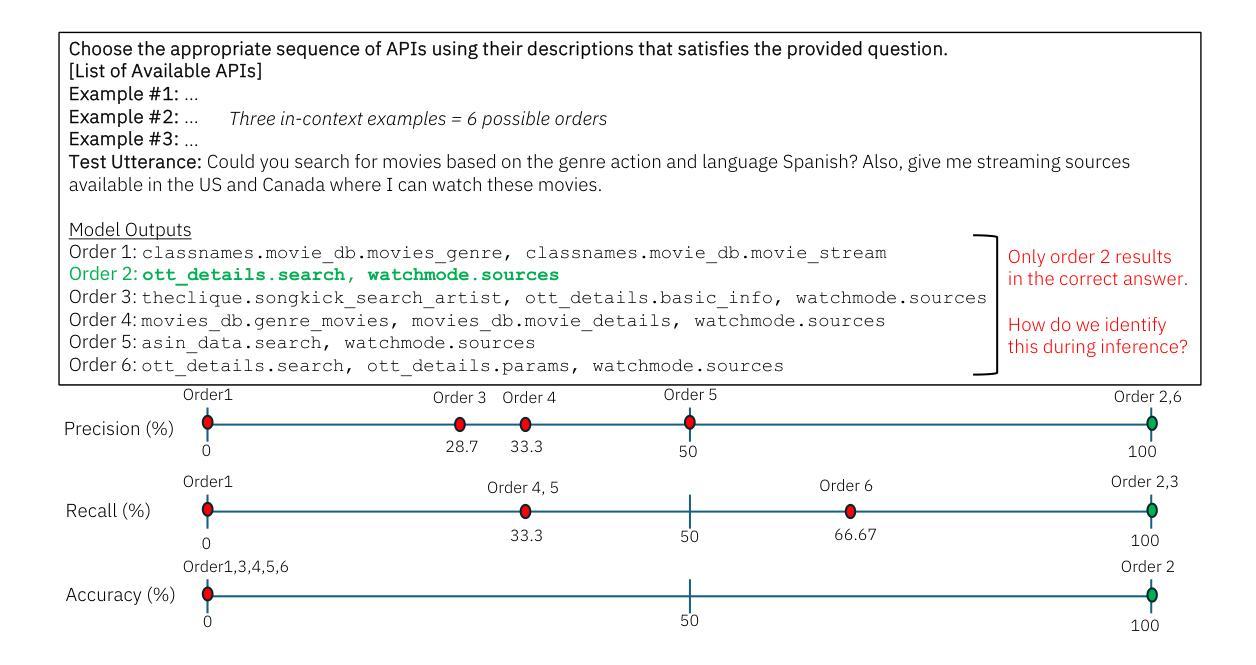
OptiSeq: Optimizing Example Ordering for In-Context Learning
Authors:Rahul Atul Bhope, Praveen Venkateswaran, K. R. Jayaram, Vatche Isahagian, Vinod Muthusamy, Nalini Venkatasubramanian
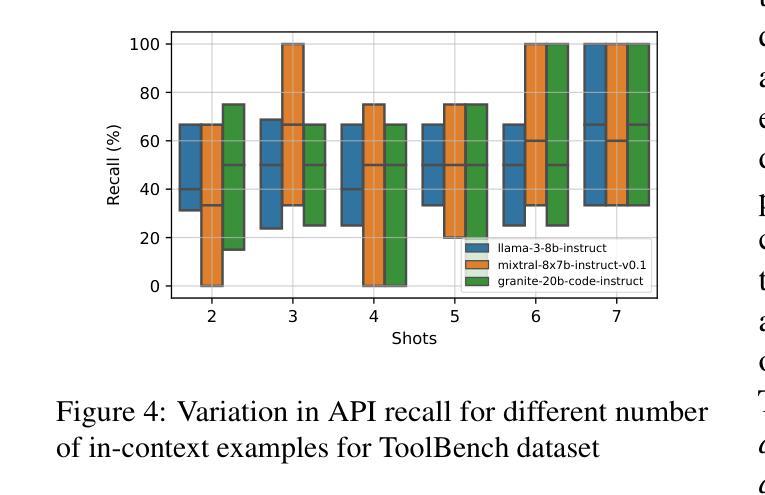
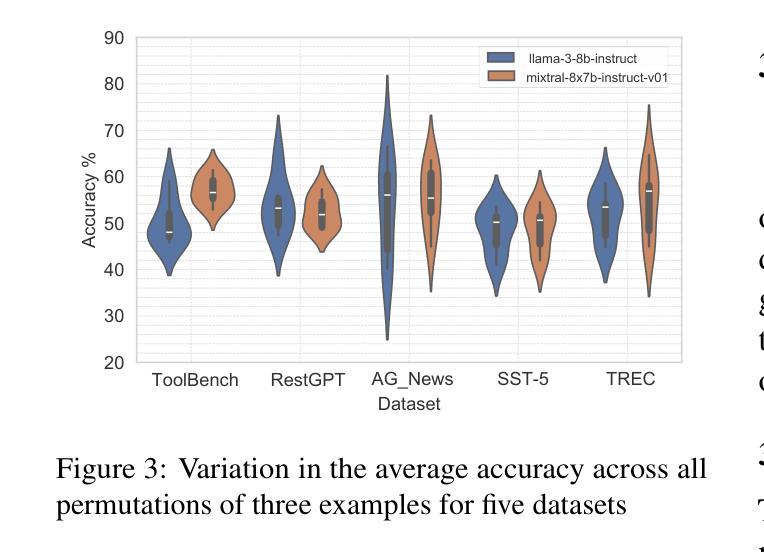
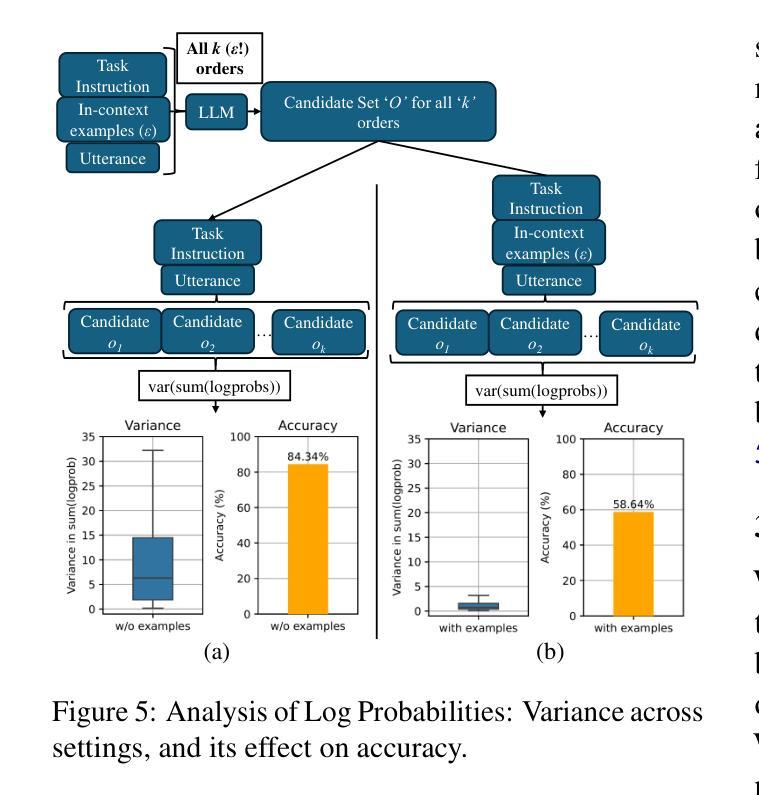
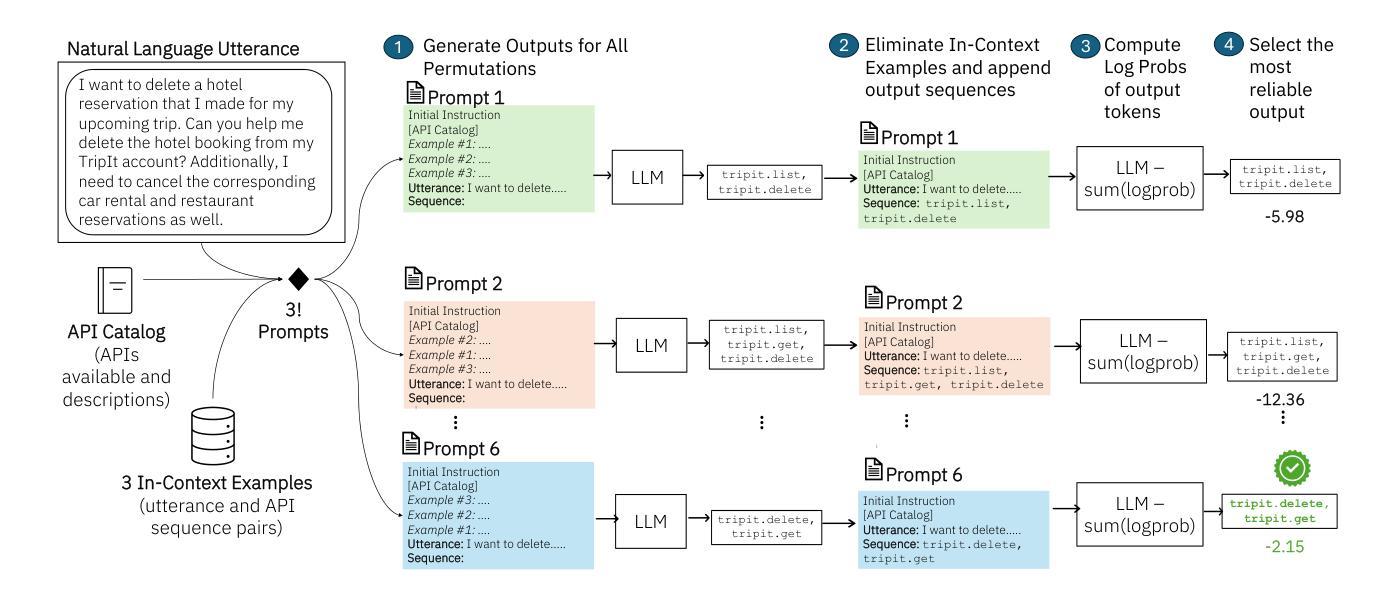
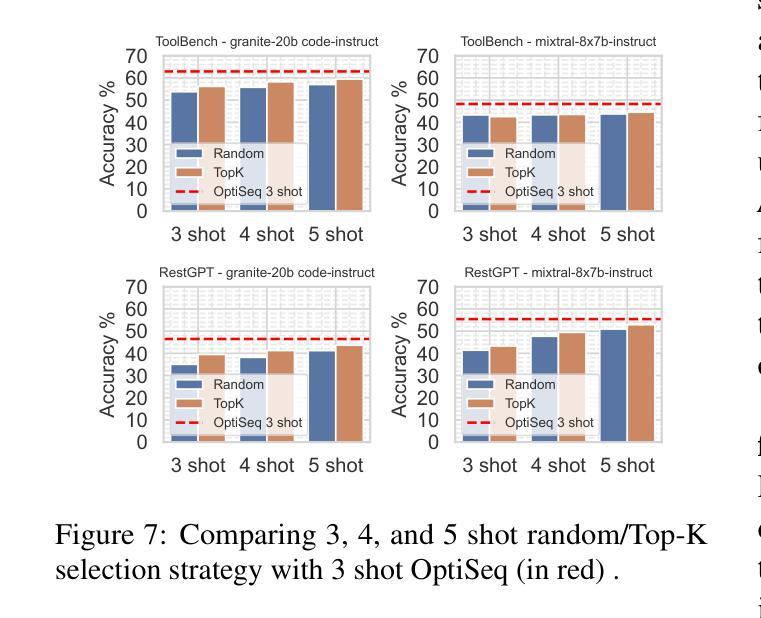
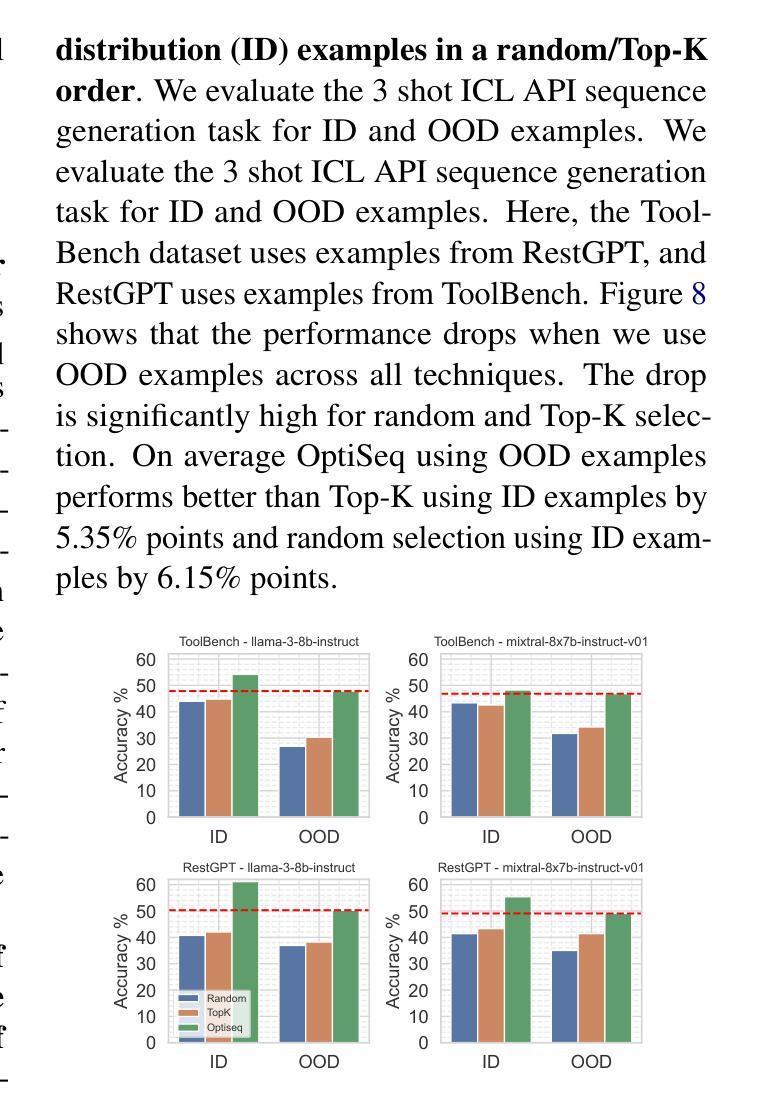
Developers using LLMs in their applications and agents have provided plenty of anecdotal evidence that in-context-learning (ICL) is fragile. In addition to the quantity and quality of examples, we show that the order in which the in-context examples are listed in the prompt affects the output of the LLM and, consequently, their performance. In this paper, we present OptiSeq, which introduces a score based on log probabilities of LLM outputs to prune the universe of possible example orderings in few-shot ICL and recommend the best order(s) by distinguishing between correct and incorrect outputs resulting from different order permutations. Through a detailed empirical evaluation on multiple LLMs, datasets and prompts, we demonstrate that OptiSeq improves accuracy by 6 - 10.5 percentage points across multiple tasks.
对于在其应用程序和代理中使用LLM的开发人员来说,他们提供了大量的经验证据表明上下文学习(ICL)是脆弱的。除了示例的数量和质量之外,我们还表明提示中上下文示例的列表顺序会影响LLM的输出以及他们的性能。在本文中,我们介绍了OptiSeq,它通过基于LLM输出的对数概率的评分来缩减少量上下文学习中的可能示例顺序宇宙,并通过区分不同顺序排列导致的正确和错误输出,推荐最佳顺序。通过对多个LLM、数据集和提示的详细经验评估,我们证明了OptiSeq在多个任务上的准确率提高了6-10.5个百分点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM应用中的上下文学习(ICL)存在脆弱性,除了示例的数量和质量外,示例在提示中的顺序也会影响LLM的输出和性能。本文提出OptiSeq方法,通过计算LLM输出的对数概率得分来评估不同示例顺序的可能性,并推荐最佳顺序组合。经验评估表明,OptiSeq能显著提高多个任务的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在应用中表现出上下文学习(ICL)的脆弱性。
- 示例在提示中的顺序对LLM的输出和性能有影响。
- OptiSeq方法通过计算LLM输出的对数概率得分来评估示例顺序。
- OptiSeq能提高多个任务的准确性,提高幅度达到6-10.5个百分点。
- 该方法能在不同LLM、数据集和提示中有效应用。
- OptiSeq能区分不同顺序组合产生的正确和错误输出。
点此查看论文截图

Training Dialogue Systems by AI Feedback for Improving Overall Dialogue Impression
Authors:Kai Yoshida, Masahiro Mizukami, Seiya Kawano, Canasai Kruengkrai, Hiroaki Sugiyama, Koichiro Yoshino
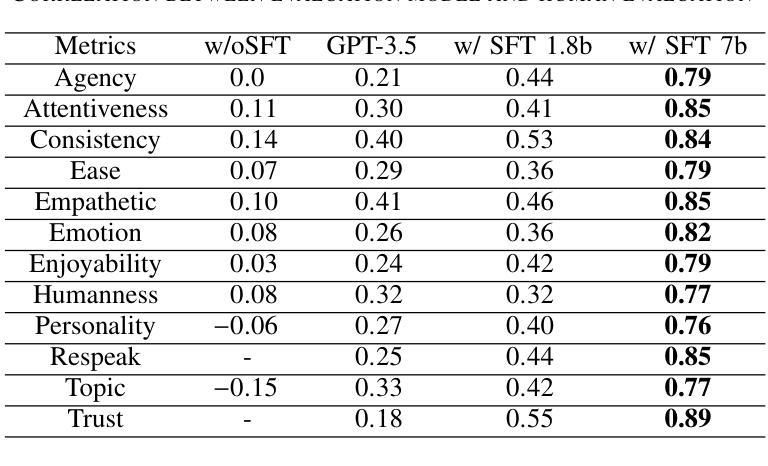
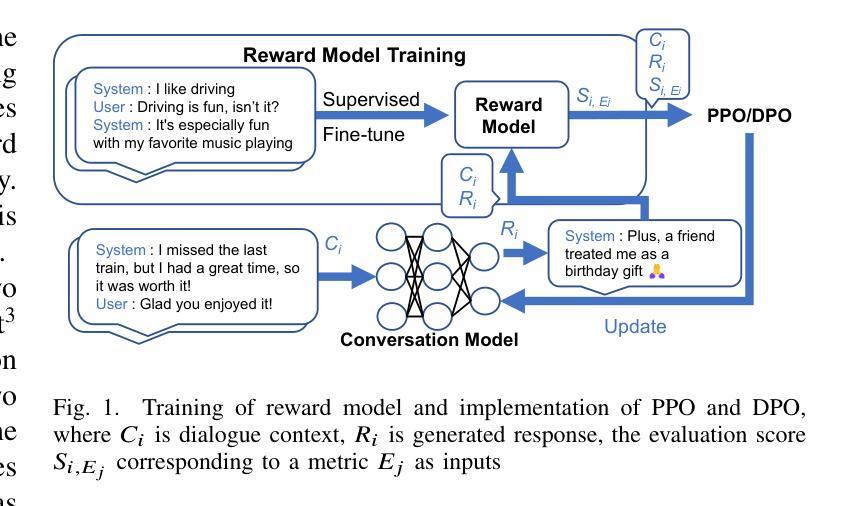
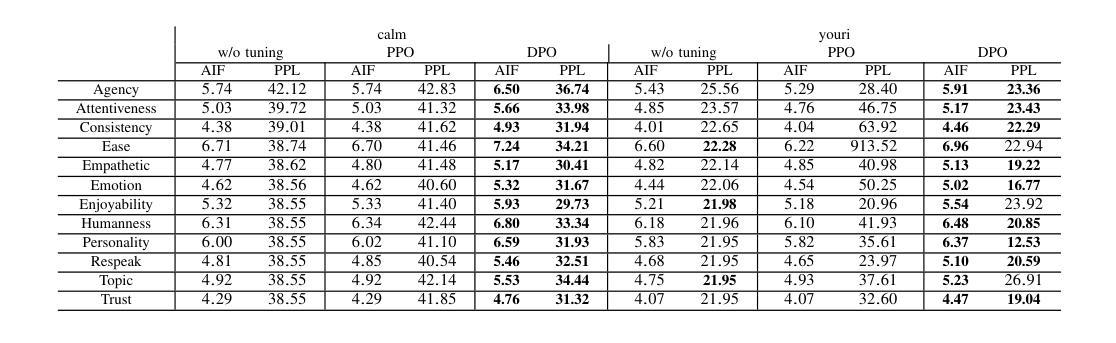
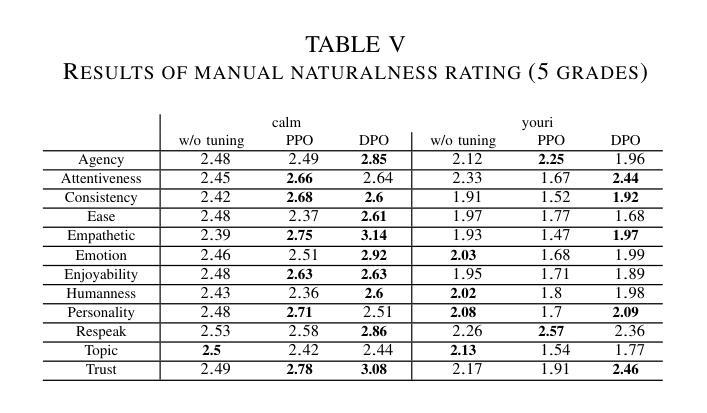
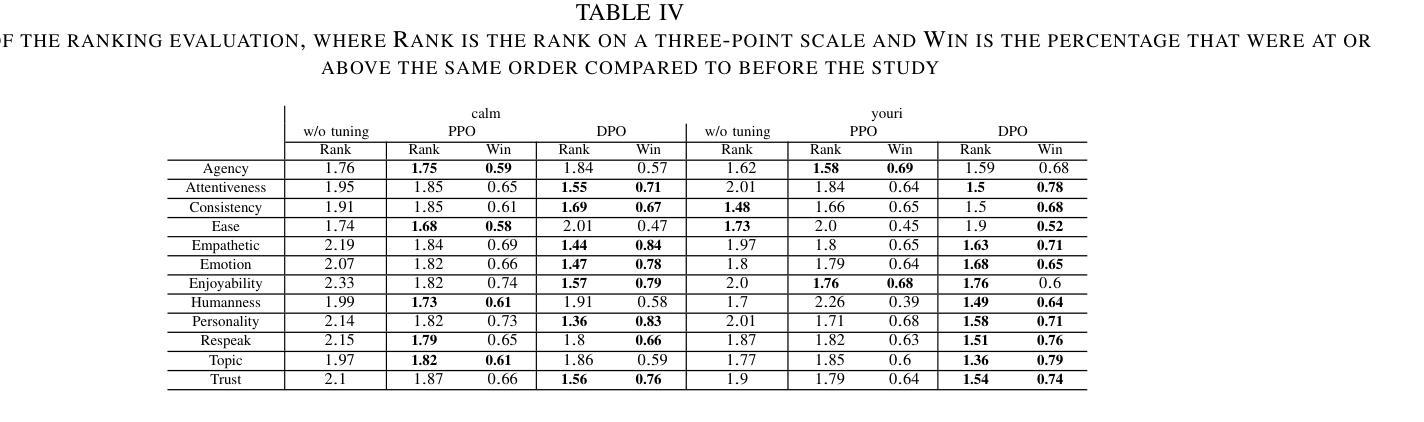
To improve user engagement during conversations with dialogue systems, we must improve individual dialogue responses and dialogue impressions such as consistency, personality, and empathy throughout the entire dialogue. While such dialogue systems have been developing rapidly with the help of large language models (LLMs), reinforcement learning from AI feedback (RLAIF) has attracted attention to align LLM-based dialogue models for such dialogue impressions. In RLAIF, a reward model based on another LLM is used to create a training signal for an LLM-based dialogue model using zero-shot/few-shot prompting techniques. However, evaluating an entire dialogue only by prompting LLMs is challenging. In this study, the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) of LLMs prepared reward models corresponding to 12 metrics related to the impression of the entire dialogue for evaluating dialogue responses. We tuned our dialogue models using the reward model signals as feedback to improve the impression of the system. The results of automatic and human evaluations showed that tuning the dialogue model using our reward model corresponding to dialogue impression improved the evaluation of individual metrics and the naturalness of the dialogue response.
为了提高用户与对话系统对话时的参与度,我们必须改善单独的对话回应和整个对话过程中的一致性、个性和同理心等对话印象。虽然借助大型语言模型(LLM),此类对话系统发展迅速,但通过人工智能反馈进行强化学习(RLAIF)已引起关注,以调整基于LLM的对话模型,使其具有此类对话印象。在RLAIF中,使用基于另一个LLM的奖励模型,通过零样本/小样本提示技术为基于LLM的对话模型创建训练信号。然而,仅通过提示LLM来评估整个对话是有挑战性的。在这项研究中,我们准备了对应于与整个对话印象相关的12个指标的奖励模型,对LLM进行有监督微调(SFT),以评估对话回应。我们使用奖励模型信号作为反馈来调整我们的对话模型,以提高系统印象。自动和人类评估的结果表明,使用对应于对话印象的我们的奖励模型调整对话模型,提高了单个指标的评价和对话回应的自然性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
该文探讨了如何通过改进对话系统的响应和印象来提升用户参与度。研究利用大型语言模型(LLM)和强化学习技术,通过构建奖励模型来调整对话模型,使其更具一致性、个性和同理心。为提高整个对话的印象评价,该研究对奖励模型进行了微调,对应12个与对话印象相关的指标。自动和人类评估结果均显示,使用对应对话印象的奖励模型调整对话模型,能提升个别指标的评价和对话的自然性。
Key Takeaways
- 对话系统的用户参与度可通过优化响应和印象提升。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)和强化学习技术用于调整对话模型。
- 奖励模型用于创建训练信号,以调整LLM的对话模型。
- 通过零样本或少样本提示技术实现训练信号的创建。
- 仅通过提示LLM来评估整个对话具有挑战性。
- 研究通过监督微调(SFT)LLM的奖励模型,对应12个与对话印象相关的指标以评估对话响应。
点此查看论文截图


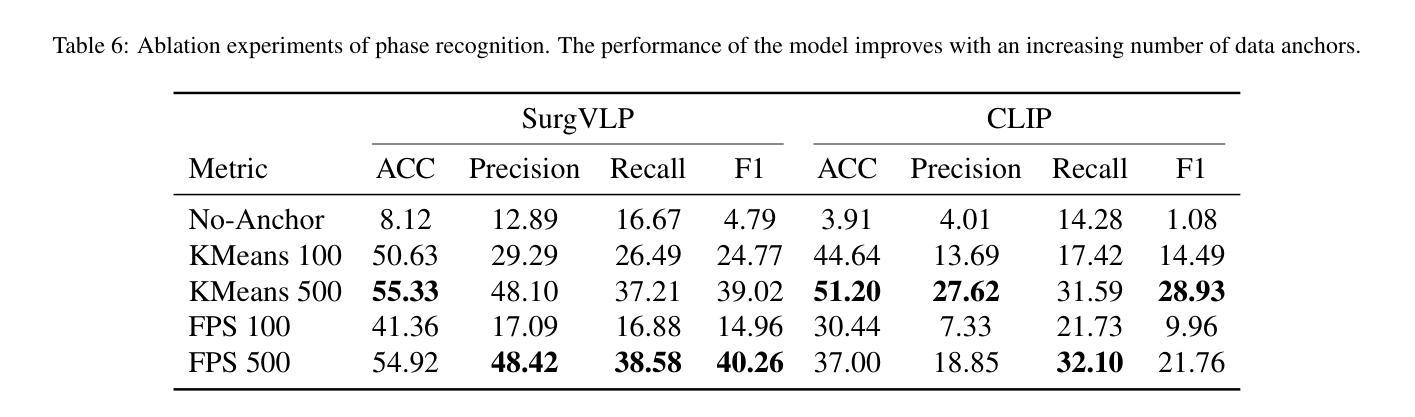
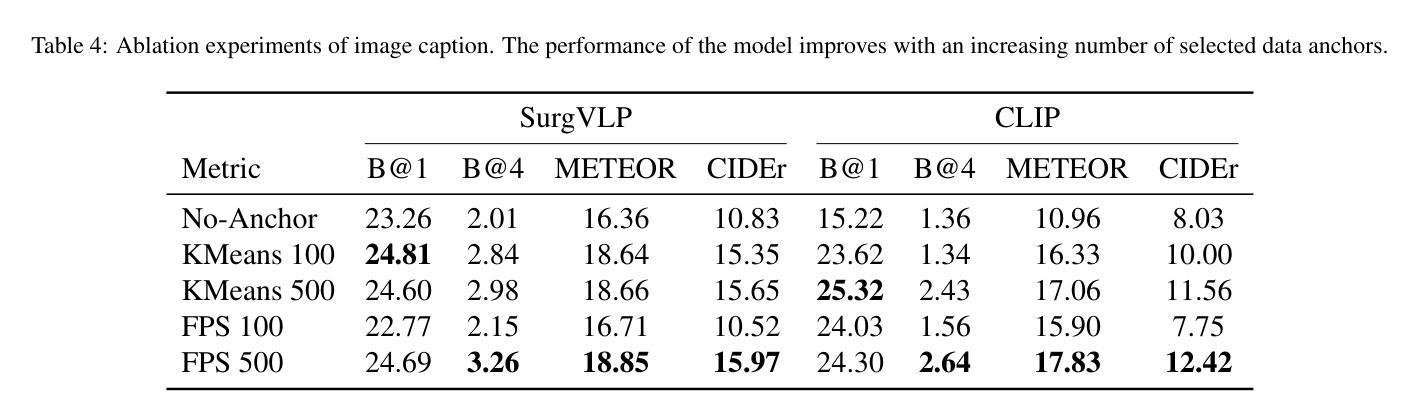
Text-driven Adaptation of Foundation Models for Few-shot Surgical Workflow Analysis
Authors:Tingxuan Chen, Kun Yuan, Vinkle Srivastav, Nassir Navab, Nicolas Padoy
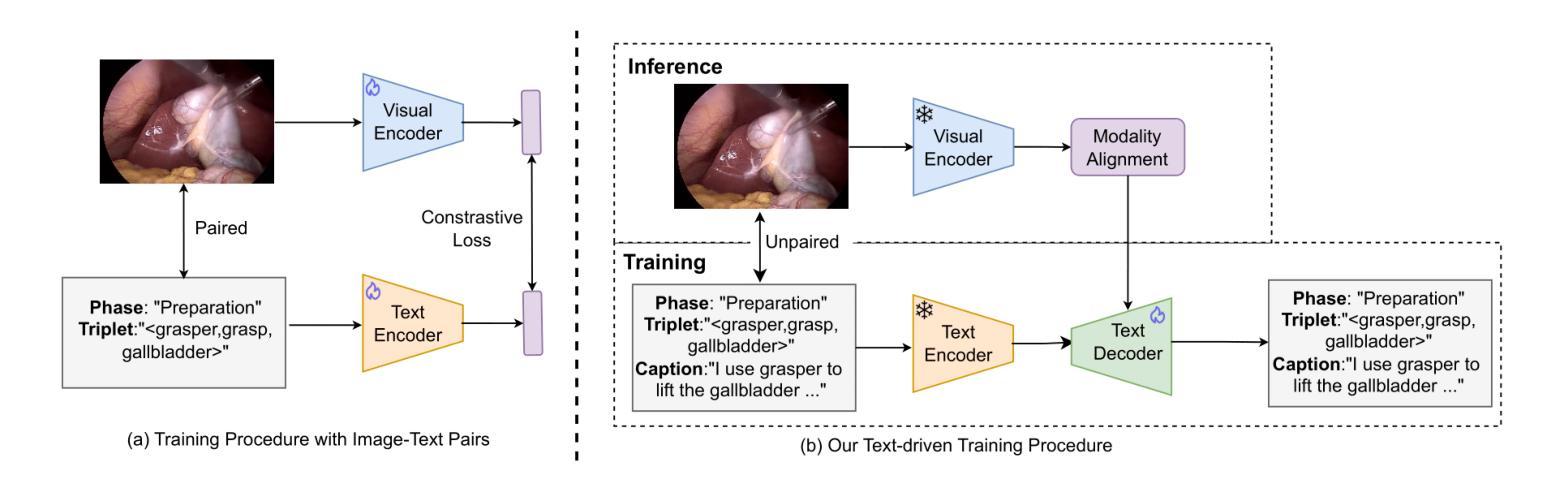
Purpose: Surgical workflow analysis is crucial for improving surgical efficiency and safety. However, previous studies rely heavily on large-scale annotated datasets, posing challenges in cost, scalability, and reliance on expert annotations. To address this, we propose Surg-FTDA (Few-shot Text-driven Adaptation), designed to handle various surgical workflow analysis tasks with minimal paired image-label data. Methods: Our approach has two key components. First, Few-shot selection-based modality alignment selects a small subset of images and aligns their embeddings with text embeddings from the downstream task, bridging the modality gap. Second, Text-driven adaptation leverages only text data to train a decoder, eliminating the need for paired image-text data. This decoder is then applied to aligned image embeddings, enabling image-related tasks without explicit image-text pairs. Results: We evaluate our approach to generative tasks (image captioning) and discriminative tasks (triplet recognition and phase recognition). Results show that Surg-FTDA outperforms baselines and generalizes well across downstream tasks. Conclusion: We propose a text-driven adaptation approach that mitigates the modality gap and handles multiple downstream tasks in surgical workflow analysis, with minimal reliance on large annotated datasets. The code and dataset will be released in https://github.com/CAMMA-public/Surg-FTDA
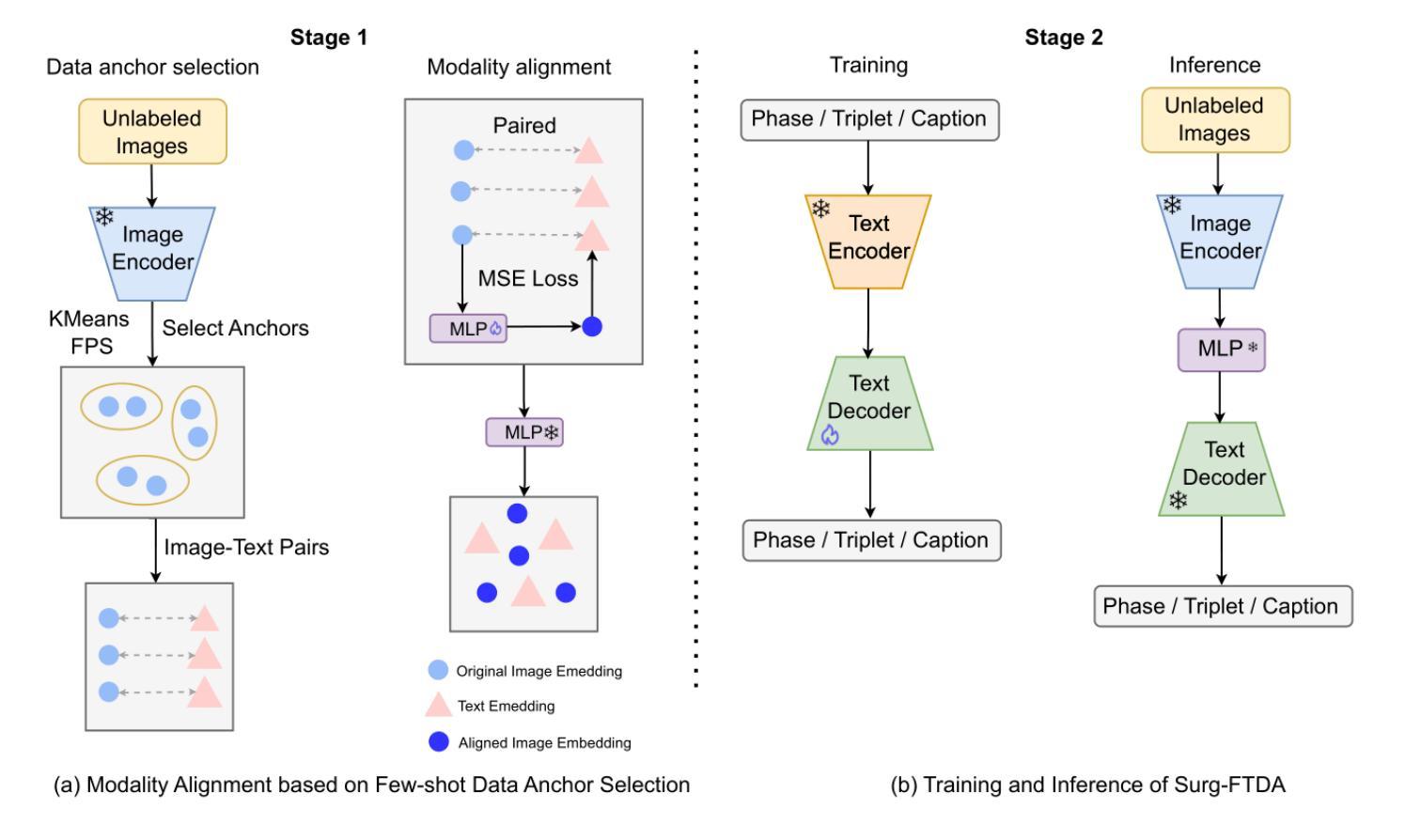
目的:手术流程分析对于提高手术效率和安全性至关重要。然而,先前的研究严重依赖于大规模标注数据集,这带来了成本、可扩展性和对专家标注的依赖等方面的挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Surg-FTDA(Few-shot文本驱动适应)方法,旨在使用最少的配对图像标签数据来处理各种手术流程分析任务。
方法:我们的方法有两个关键组成部分。首先,基于Few-shot选择的模态对齐会选择一小部分图像,并将它们的嵌入与下游任务的文本嵌入进行对齐,从而弥合了模态之间的差距。其次,文本驱动适应仅利用文本数据进行解码器训练,消除了对配对图像文本数据的需求。然后,该解码器应用于已对齐的图像嵌入,能够在没有明确的图像文本对的情况下执行图像相关任务。
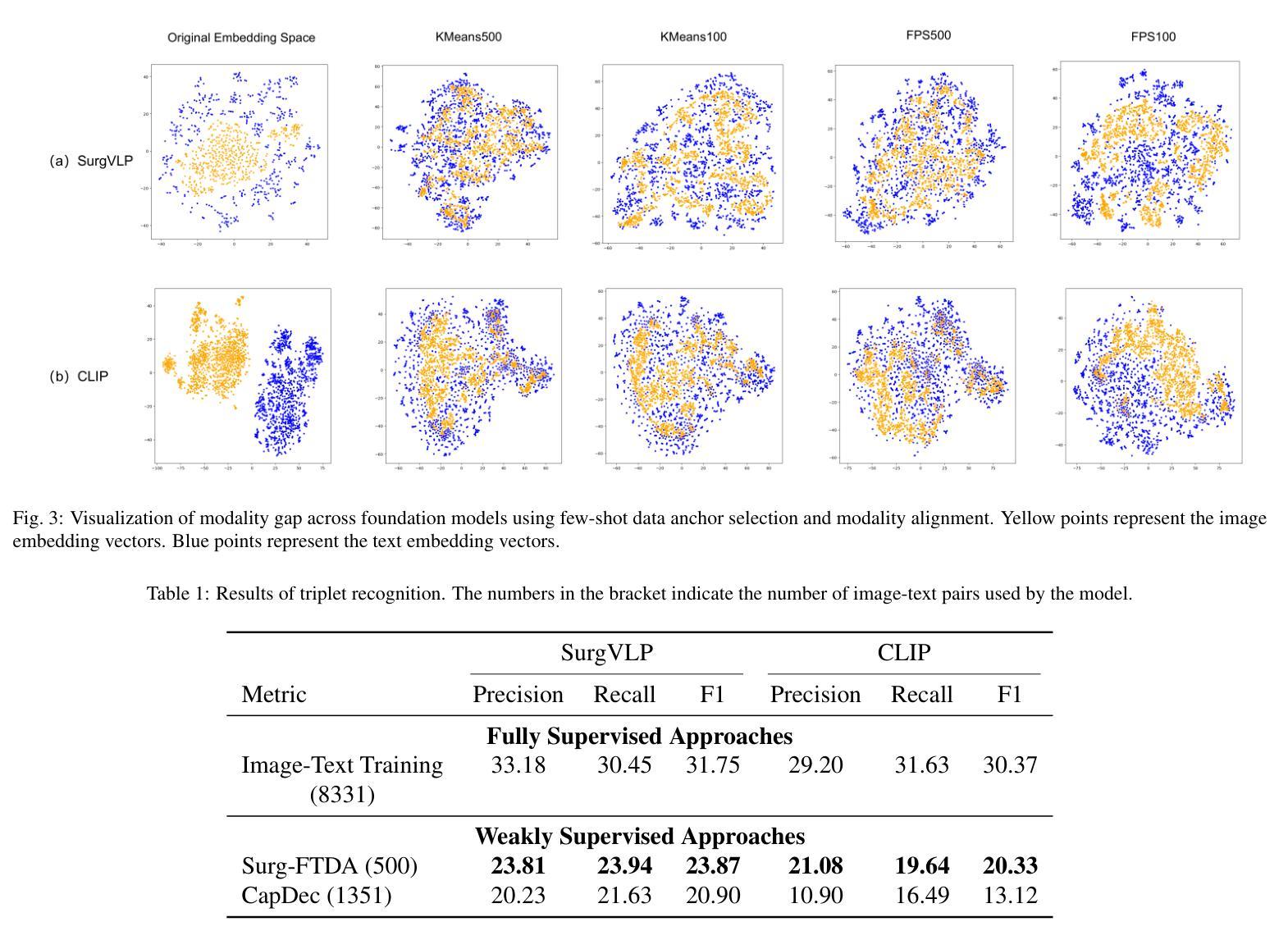
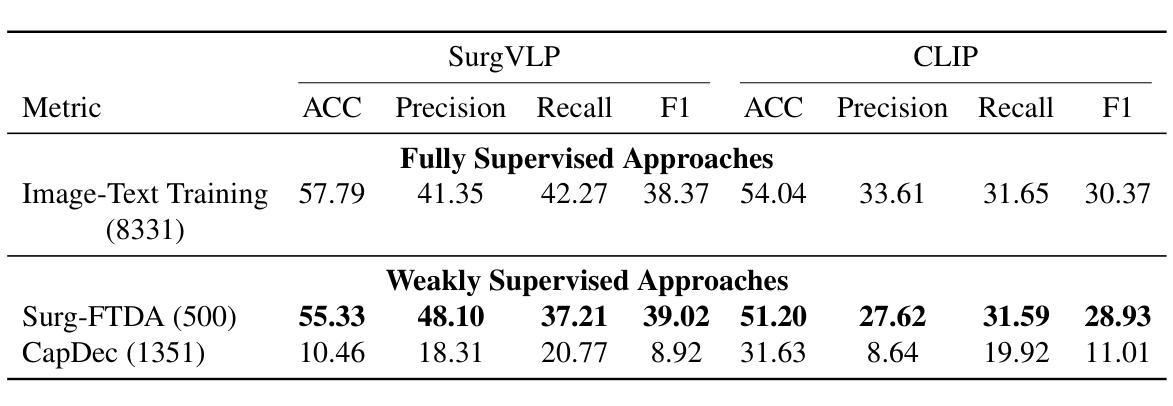
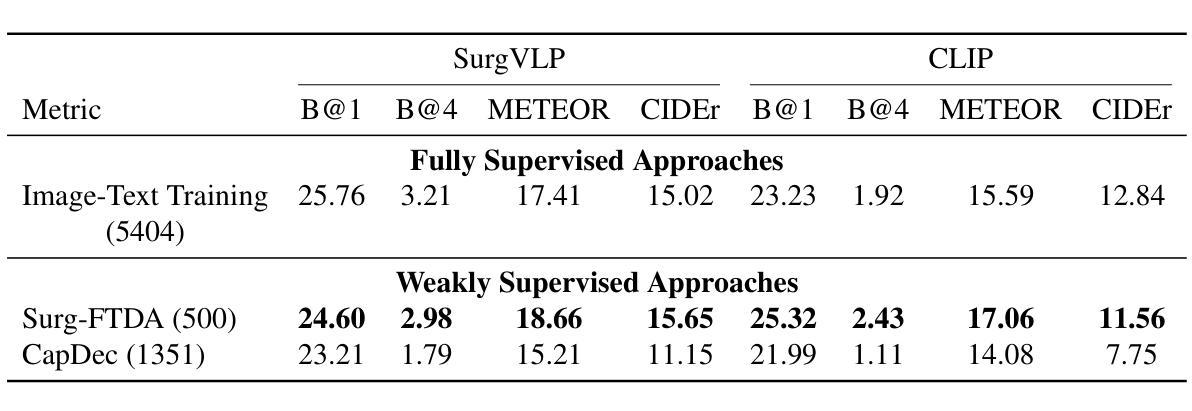
结果:我们对生成任务(图像字幕)和判别任务(三元组识别和阶段识别)进行了评估。结果表明,Surg-FTDA优于基线,并在下游任务中具有良好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Surg-FTDA(Few-shot文本驱动适应)的方法,用于改进手术效率和安全性的手术工作流程分析。该方法主要解决了大规模注释数据集带来的成本、可扩展性和依赖专家标注的问题。它通过选择少量图像与下游任务的文本嵌入进行对齐,并消除对配对图像文本数据的需求,从而处理各种手术工作流程分析任务。实验结果表明,该方法在生成任务(图像描述)和判别任务(三元组识别和阶段识别)中表现优异,具有良好的跨任务泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- Surg-FTDA方法旨在解决手术工作流程分析中大规模注释数据集带来的挑战。
- 方法包含两个关键组件:Few-shot选择式模态对齐和文本驱动适应。
- Few-shot选择式模态对齐通过选择少量图像并与下游任务的文本嵌入对齐,缩小了模态差距。
- 文本驱动适应仅利用文本数据进行解码器训练,消除了对配对图像文本数据的需求。
- Surg-FTDA在生成任务和判别任务中表现出色,包括图像描述、三元组识别和阶段识别。
- 该方法具有良好的跨任务泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


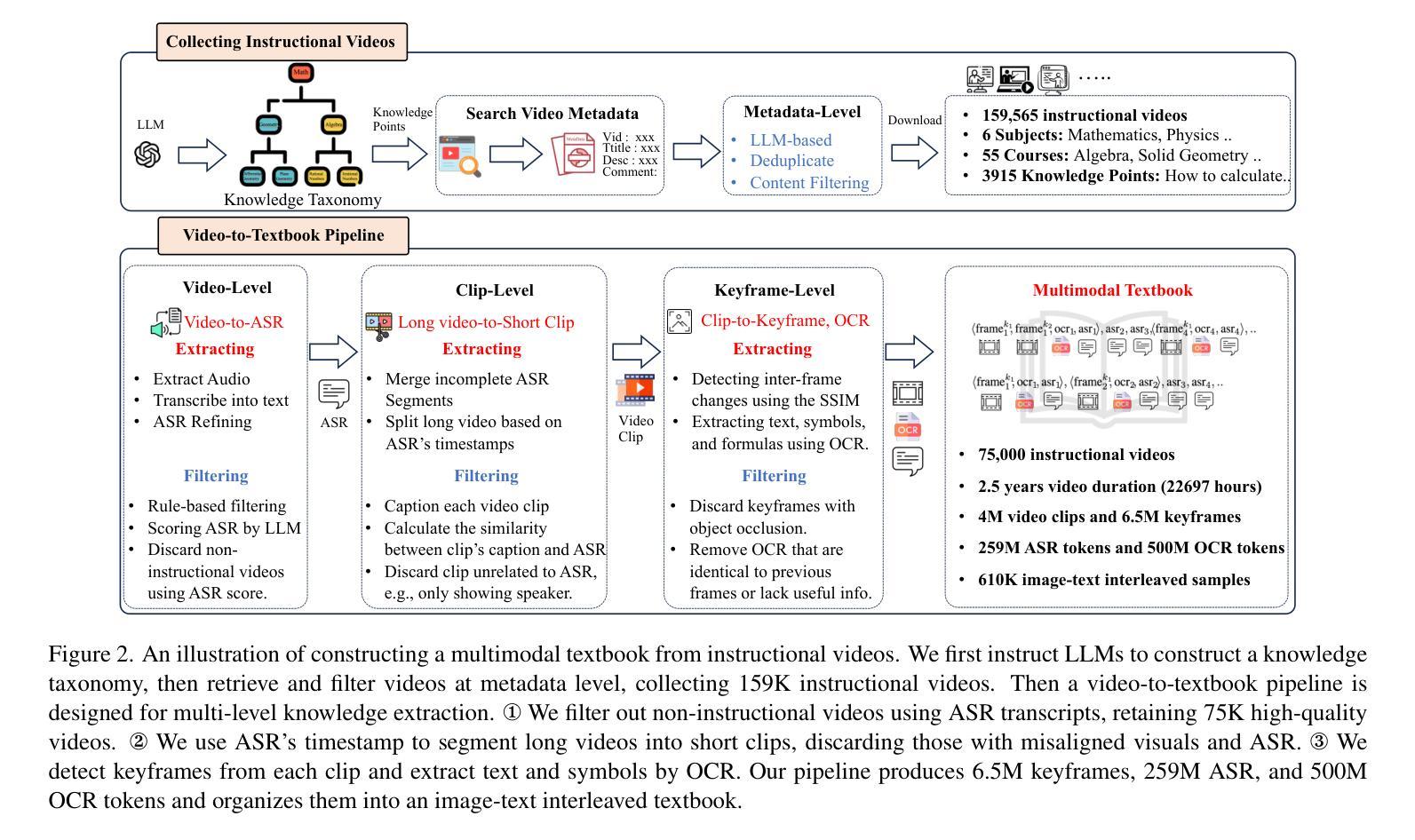
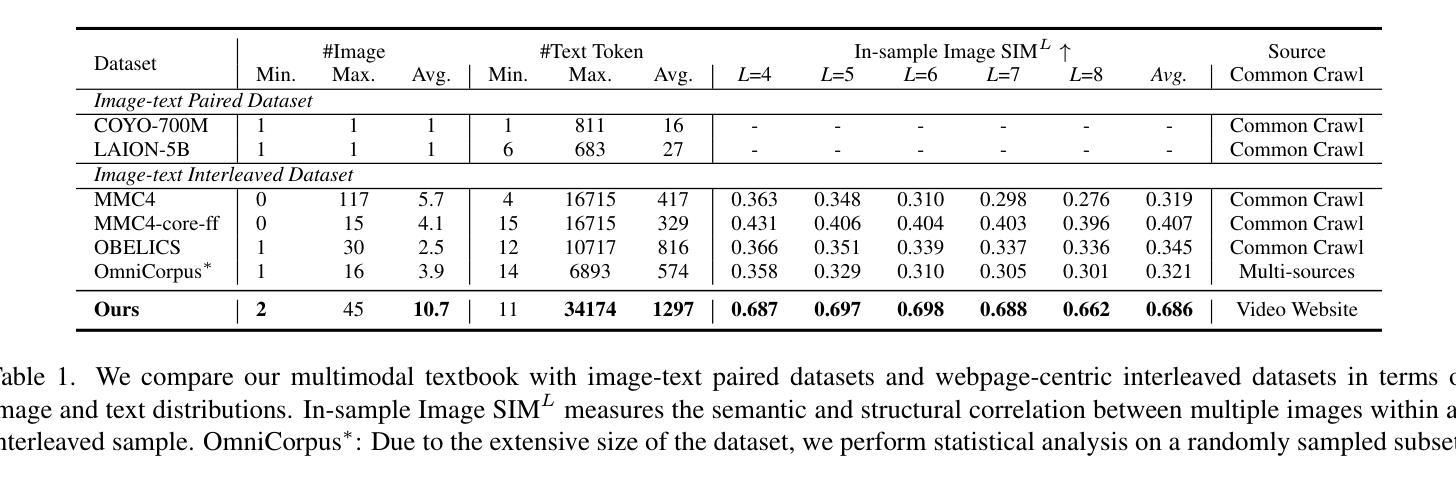
2.5 Years in Class: A Multimodal Textbook for Vision-Language Pretraining
Authors:Wenqi Zhang, Hang Zhang, Xin Li, Jiashuo Sun, Yongliang Shen, Weiming Lu, Deli Zhao, Yueting Zhuang, Lidong Bing
Compared to image-text pair data, interleaved corpora enable Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to understand the world more naturally like humans. However, such existing datasets are crawled from webpage, facing challenges like low knowledge density, loose image-text relations, and poor logical coherence between images. On the other hand, the internet hosts vast instructional videos (e.g., online geometry courses) that are widely used by humans to learn foundational subjects, yet these valuable resources remain underexplored in VLM training. In this paper, we introduce a high-quality \textbf{multimodal textbook} corpus with richer foundational knowledge for VLM pretraining. It collects over 2.5 years of instructional videos, totaling 22,000 class hours. We first use an LLM-proposed taxonomy to systematically gather instructional videos. Then we progressively extract and refine visual (keyframes), audio (ASR), and textual knowledge (OCR) from the videos, and organize as an image-text interleaved corpus based on temporal order. Compared to its counterparts, our video-centric textbook offers more coherent context, richer knowledge, and better image-text alignment. Experiments demonstrate its superb pretraining performance, particularly in knowledge- and reasoning-intensive tasks like ScienceQA and MathVista. Moreover, VLMs pre-trained on our textbook exhibit outstanding interleaved context awareness, leveraging visual and textual cues in their few-shot context for task solving. Our code are available at https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/multimodal_textbook.
与图像文本配对数据相比,交织语料库使视觉语言模型(VLMs)能够更自然地像人类一样理解世界。然而,这些现有的数据集都是从网页上爬取的,面临着知识密度低、图像文本关系松散、图像之间逻辑连贯性差等挑战。另一方面,互联网上有大量教学视频(如在线几何课程),人类广泛用来学习基础学科,但这些宝贵资源在VLM训练中尚未得到充分探索。在本文中,我们介绍了一个高质量的多模式教科书语料库,其中包含更丰富的基础知识,用于VLM预训练。它收集了超过2.5年的教学视频,总计22,000课时。我们首先使用大型语言模型(LLM)提出的分类法来系统地收集教学视频。然后,我们从视频中逐步提取和精炼视觉(关键帧)、音频(自动语音识别)和文本知识(光学字符识别),并按时间顺序组织成图像文本交织语料库。与其他资源相比,我们以学生为中心的视频教科书提供了更连贯的上下文、更丰富的知识和更好的图像文本对齐。实验证明其在预训练方面的卓越性能,特别是在知识和推理密集型任务(如ScienceQA和MathVista)中。此外,在我们教科书上进行预训练的VLM表现出出色交织上下文意识,利用视觉和文本线索解决少量上下文中的任务。我们的代码可通过https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/multimodal_textbook访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary:
本文介绍了一种用于视觉语言模型预训练的多模态教科书语料库。该语料库通过收集超过2.5年的教学视频,以时间顺序组织成图像文本交错语料库。与传统数据集相比,该视频为中心的教学书籍提供了更连贯的上下文、更丰富知识和更好的图像文本对齐。实验表明,在知识密集和推理密集型任务上,该语料库的预训练性能卓越。此外,在该教科书上进行预训练的视觉语言模型展现出出色的交错上下文意识,能够在解决任务时利用视觉和文本线索。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态教科书语料库结合了教学视频、图像和文本,为视觉语言模型预训练提供了更丰富、更连贯的知识。
- 与传统图像文本对数据相比,该语料库具有更好的图像文本对齐和逻辑连贯性。
- 通过收集大量教学视频,该语料库提供了一个视频为中心的学习资源平台。
- 在知识密集和推理密集型任务上,该语料库的预训练性能卓越。
- 预训练的视觉语言模型展现出出色的交错上下文意识,能利用视觉和文本线索解决任务。
- 该研究提供了一个公开可用的代码库,便于其他人使用和研究。
点此查看论文截图


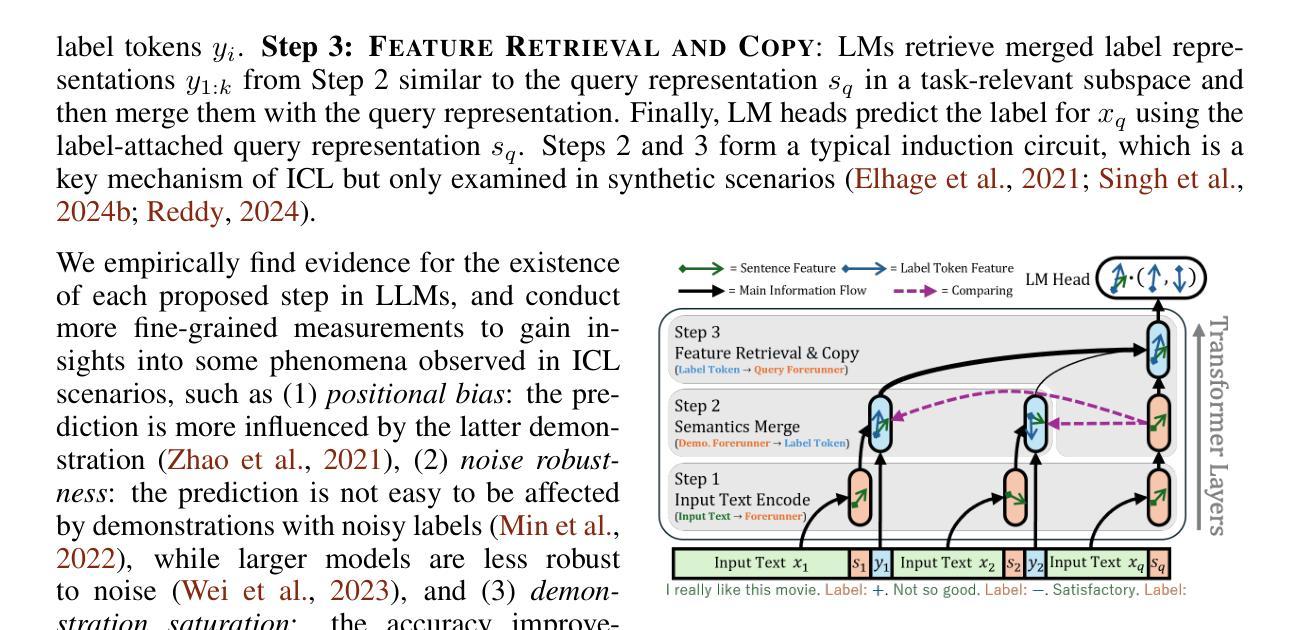
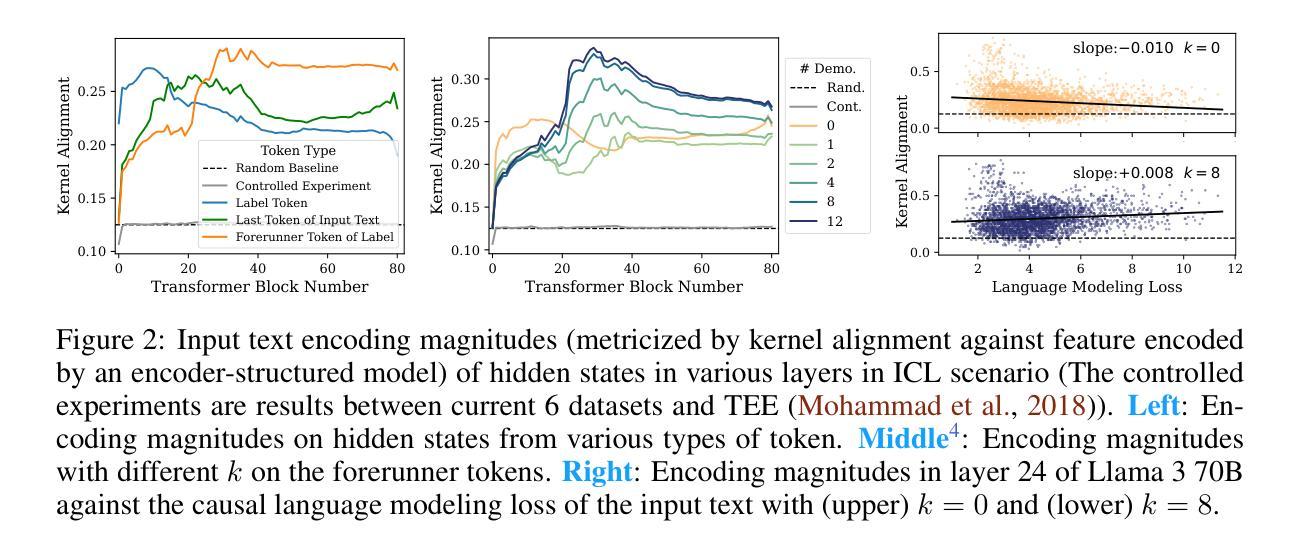
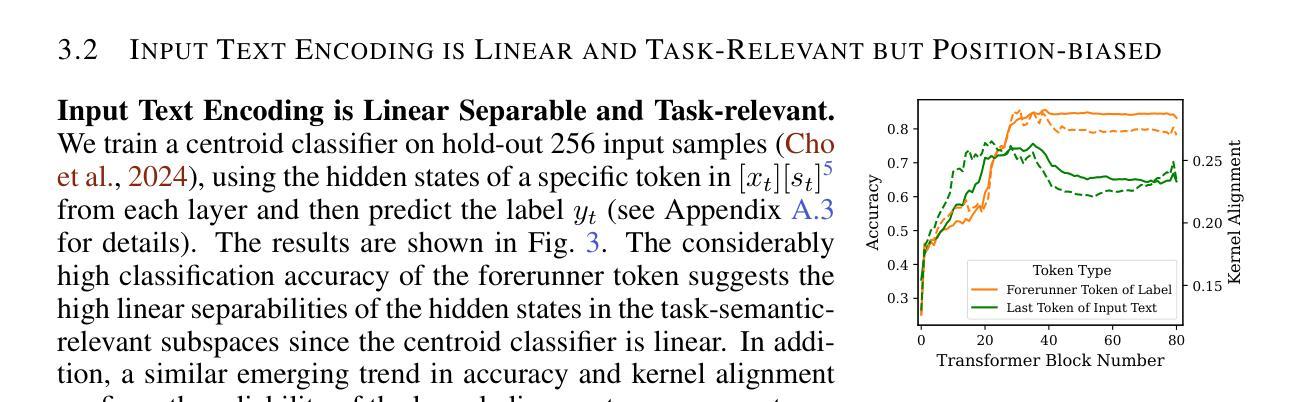
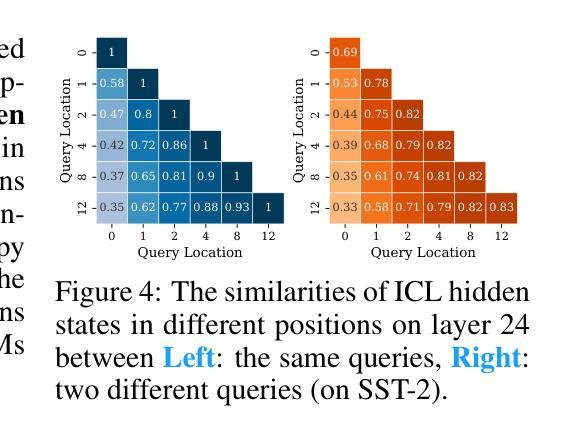
Revisiting In-context Learning Inference Circuit in Large Language Models
Authors:Hakaze Cho, Mariko Kato, Yoshihiro Sakai, Naoya Inoue
In-context Learning (ICL) is an emerging few-shot learning paradigm on Language Models (LMs) with inner mechanisms un-explored. There are already existing works describing the inner processing of ICL, while they struggle to capture all the inference phenomena in large language models. Therefore, this paper proposes a comprehensive circuit to model the inference dynamics and try to explain the observed phenomena of ICL. In detail, we divide ICL inference into 3 major operations: (1) Input Text Encode: LMs encode every input text (demonstrations and queries) into linear representation in the hidden states with sufficient information to solve ICL tasks. (2) Semantics Merge: LMs merge the encoded representations of demonstrations with their corresponding label tokens to produce joint representations of labels and demonstrations. (3) Feature Retrieval and Copy: LMs search the joint representations similar to the query representation on a task subspace, and copy the searched representations into the query. Then, language model heads capture these copied label representations to a certain extent and decode them into predicted labels. The proposed inference circuit successfully captured many phenomena observed during the ICL process, making it a comprehensive and practical explanation of the ICL inference process. Moreover, ablation analysis by disabling the proposed steps seriously damages the ICL performance, suggesting the proposed inference circuit is a dominating mechanism. Additionally, we confirm and list some bypass mechanisms that solve ICL tasks in parallel with the proposed circuit.
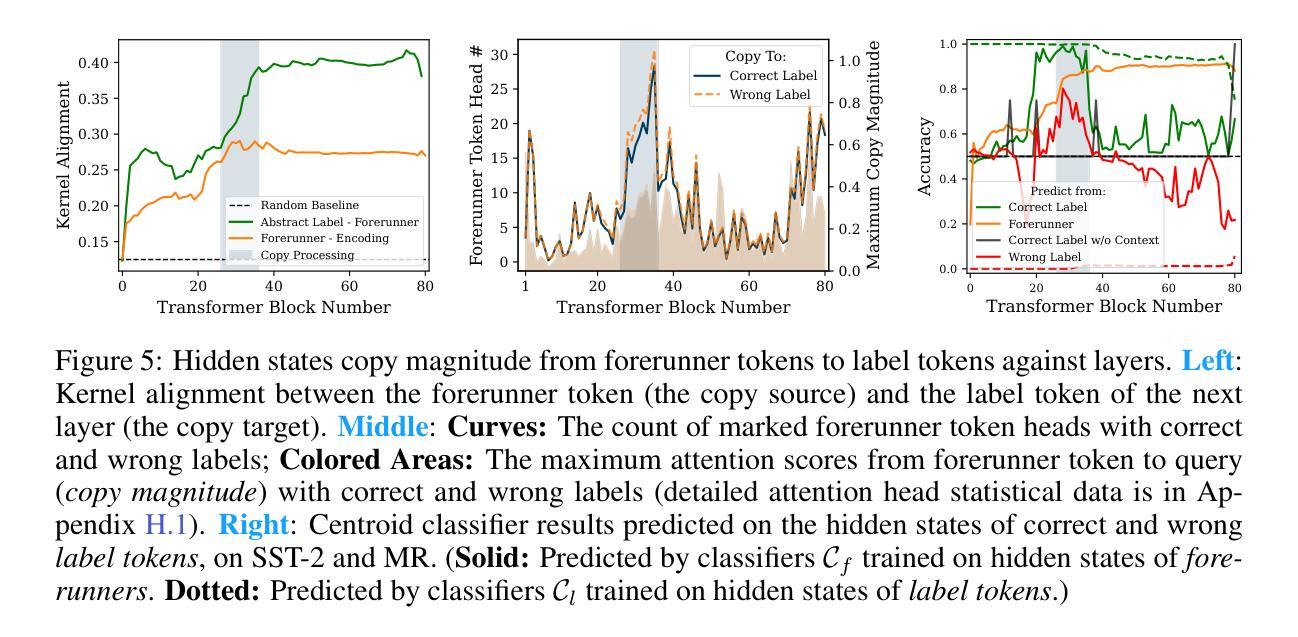
上下文学习(ICL)是一种新兴的语言模型(LM)小样本学习范式,其内部机制尚未被探索。虽然已有作品描述ICL的内部处理过程,但它们很难捕捉大型语言模型中的所有推理现象。因此,本文提出了一个全面的电路模型,以模拟推理动态,并试图解释观察到的ICL现象。具体来说,我们将ICL推理过程分为三大操作:
(1)输入文本编码:语言模型将每个输入文本(演示和查询)编码为隐藏状态的线性表示,其中包含足够的信息来解决ICL任务。
(2)语义合并:语言模型将演示的编码表示与其相应的标签标记合并,以产生标签和演示的联合表示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages, 41 figures, 8 tables. ICLR 2025 Accepted
Summary
ICL(In-context Learning)是一种新兴的语言模型(LMs)少样本学习范式,其内在机制尚未被完全探索。现有研究虽试图捕捉大型语言模型中的推理现象,但仍存在不足。本文提出了一个全面的推理电路来模拟ICL的推理过程,将ICL推理分为三大操作:输入文本编码、语义合并、特征检索与复制。此电路成功捕捉了ICL过程中的许多现象,为ICL的推理过程提供了全面而实用的解释。去除该电路步骤会导致ICL性能严重下降,验证了其主导机制的地位。同时,本文还确认并列出了一些与提议电路并行解决ICL任务的旁路机制。
Key Takeaways
- ICL是一种新兴的语言模型少样本学习范式,其内在机制尚未被完全探索。
- 现有研究在捕捉大型语言模型的推理现象时存在困难。
- 本文提出了一个全面的推理电路,将ICL推理分为输入文本编码、语义合并、特征检索与复制三大操作。
- 该电路成功捕捉了ICL过程中的许多现象,为ICL的推理过程提供了全面而实用的解释。
- 去除推理电路步骤会导致ICL性能严重下降,验证了该电路的主导机制地位。
- 除了主导机制外,还存在一些旁路机制并行解决ICL任务。
点此查看论文截图

Unleashing the Potential of Large Language Models for Predictive Tabular Tasks in Data Science
Authors:Yazheng Yang, Yuqi Wang, Yaxuan Li, Sankalok Sen, Lei Li, Qi Liu
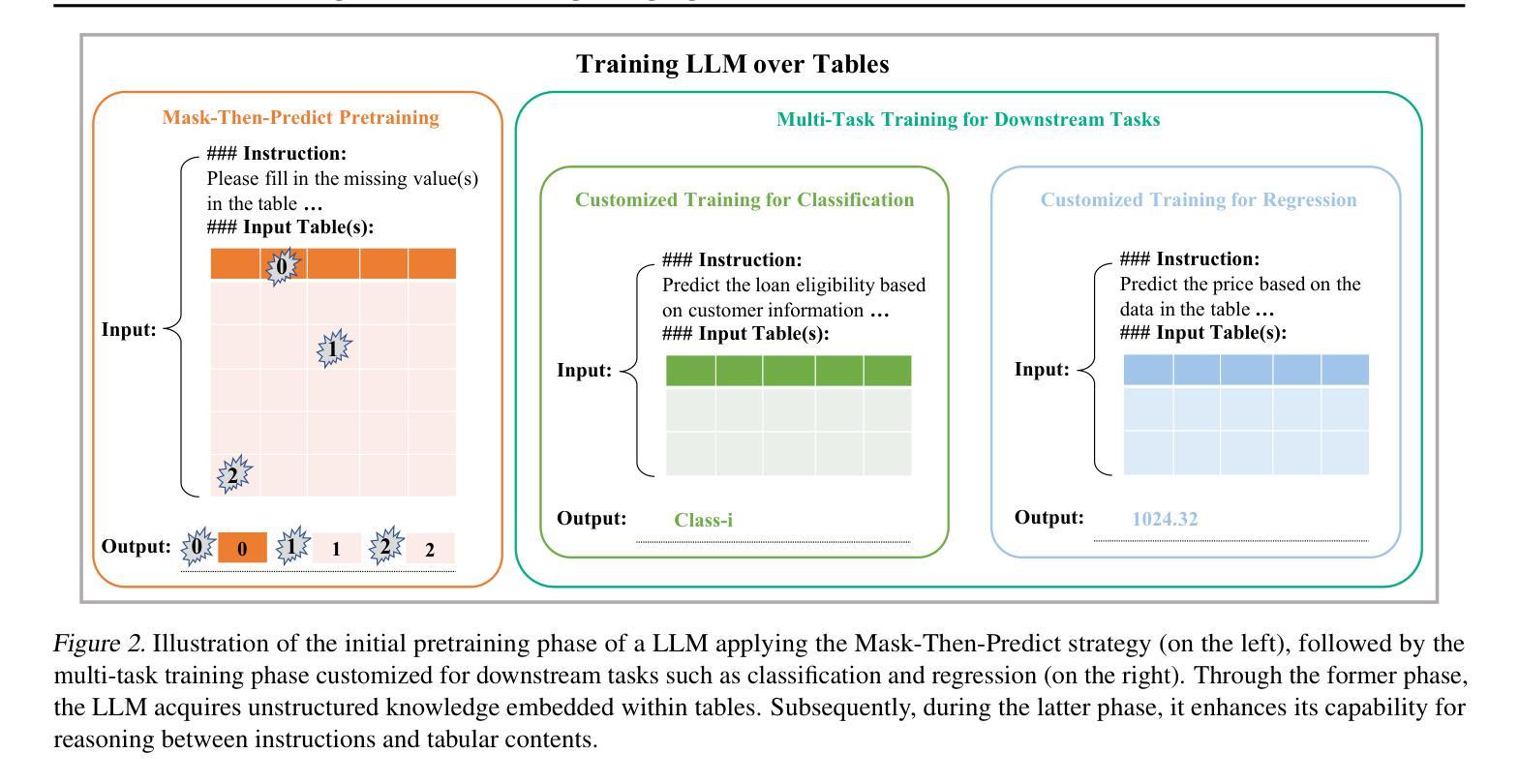
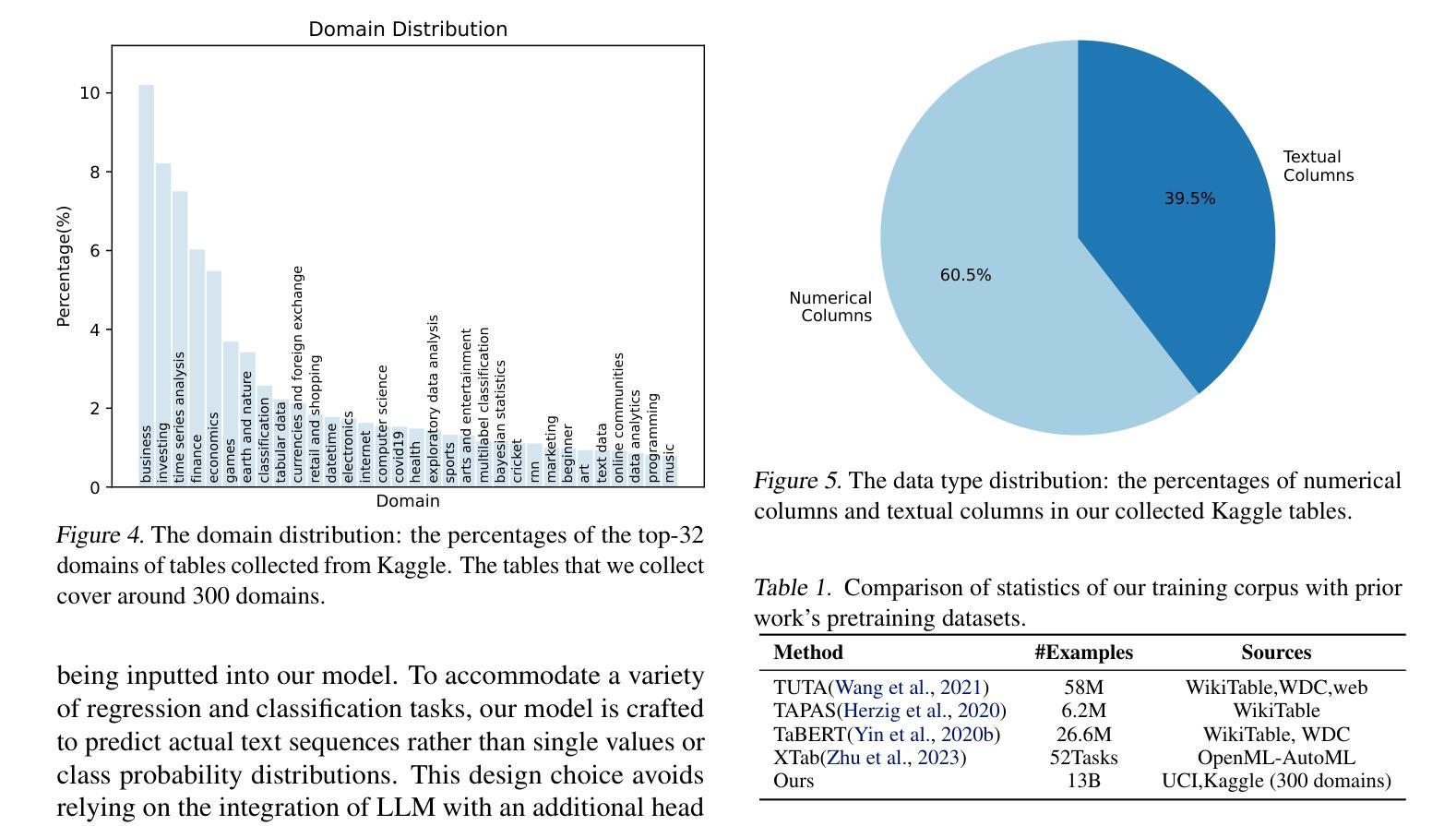
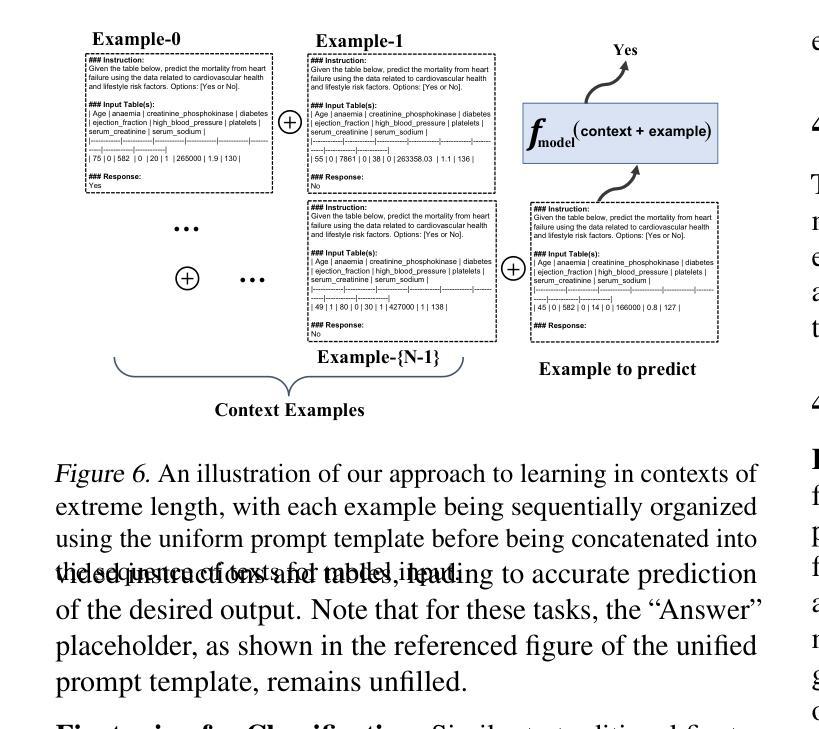
In the domain of data science, the predictive tasks of classification, regression, and imputation of missing values are commonly encountered challenges associated with tabular data. This research endeavors to apply Large Language Models (LLMs) towards addressing these predictive tasks. Despite their proficiency in comprehending natural language, LLMs fall short in dealing with structured tabular data. This limitation stems from their lacking exposure to the intricacies of tabular data during their foundational training. Our research aims to mitigate this gap by compiling a comprehensive corpus of tables annotated with instructions and executing large-scale training of Llama-2 on this enriched dataset. Furthermore, we investigate the practical application of applying the trained model to zero-shot prediction, few-shot prediction, and in-context learning scenarios. Through extensive experiments, our methodology has shown significant improvements over existing benchmarks. These advancements highlight the efficacy of tailoring LLM training to solve table-related problems in data science, thereby establishing a new benchmark in the utilization of LLMs for enhancing tabular intelligence.
在数据科学领域,分类、回归和缺失值填补的预测任务是处理表格数据时常见挑战。本研究旨在将大型语言模型(LLM)应用于解决这些预测任务。尽管LLM在自然语言理解方面表现出色,但在处理结构化表格数据时却显得不足。这种局限性源于其在基础训练过程中对表格数据复杂性缺乏接触。我们的研究旨在通过编译带有指令注释的表格综合语料库,并在丰富的数据集上执行大规模训练来缩小这一差距。此外,我们还将研究将训练有素的模型应用于零射击预测、少射击预测和上下文学习场景的实际应用。通过广泛的实验,我们的方法在现有基准测试中取得了显著改进。这些进步突显了针对数据科学中表格相关问题的LLM训练的重要性,从而为提高表格智能利用LLM建立了新的基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)对分类预测任务、回归预测任务和缺失值填补任务的研究表明,尽管LLM在自然语言理解方面表现出色,但在处理结构化表格数据时存在短板。本研究旨在通过编译带有指令注解的表格综合语料库,并对Llama-2模型进行大规模训练来弥补这一差距。同时,该研究还探讨了训练模型在实际应用中的零样本预测、小样本预测和上下文学习场景的应用效果。实验结果显示,该方法在现有基准测试上取得了显著改进,证明了针对表格相关问题的数据科学训练对提升大型语言模型的效能具有关键作用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理结构化表格数据时存在短板。
- 本研究旨在通过编译带有指令注解的表格综合语料库来弥补大型语言模型在处理表格数据时的不足。
- 对Llama-2模型进行大规模训练,提升其处理表格数据的能力。
- 研究探讨了训练模型在零样本预测、小样本预测和上下文学习场景的应用效果。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在现有基准测试上取得了显著改进。
- 针对表格相关问题的数据科学训练对提升大型语言模型的效能具有关键作用。
点此查看论文截图


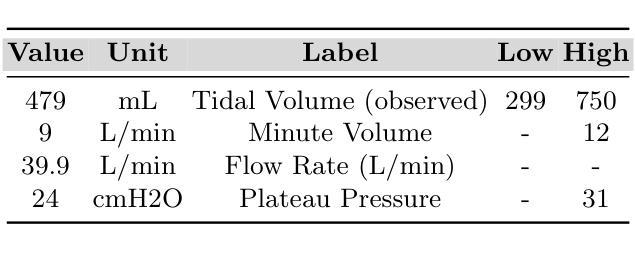
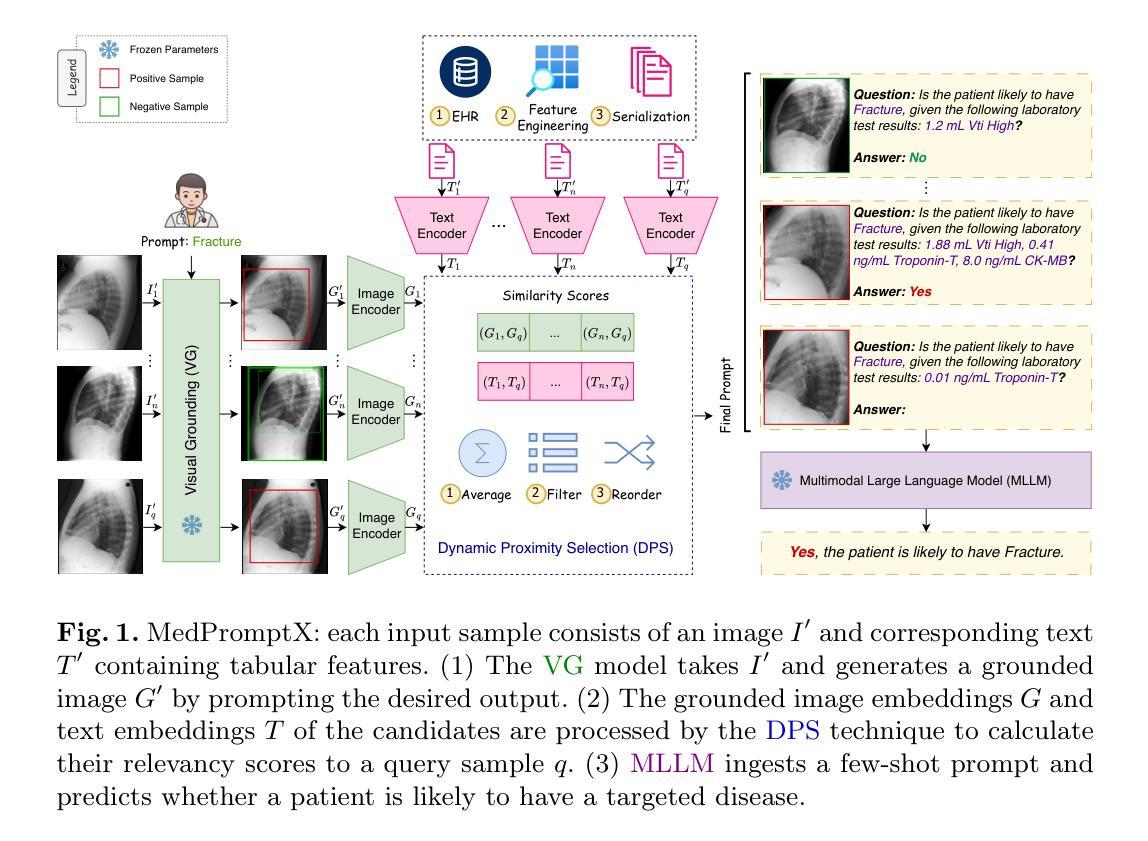
MedPromptX: Grounded Multimodal Prompting for Chest X-ray Diagnosis
Authors:Mai A. Shaaban, Adnan Khan, Mohammad Yaqub
Chest X-ray images are commonly used for predicting acute and chronic cardiopulmonary conditions, but efforts to integrate them with structured clinical data face challenges due to incomplete electronic health records (EHR). This paper introduces MedPromptX, the first clinical decision support system that integrates multimodal large language models (MLLMs), few-shot prompting (FP) and visual grounding (VG) to combine imagery with EHR data for chest X-ray diagnosis. A pre-trained MLLM is utilized to complement the missing EHR information, providing a comprehensive understanding of patients’ medical history. Additionally, FP reduces the necessity for extensive training of MLLMs while effectively tackling the issue of hallucination. Nevertheless, the process of determining the optimal number of few-shot examples and selecting high-quality candidates can be burdensome, yet it profoundly influences model performance. Hence, we propose a new technique that dynamically refines few-shot data for real-time adjustment to new patient scenarios. Moreover, VG narrows the search area in X-ray images, thereby enhancing the identification of abnormalities. We also release MedPromptX-VQA, a new in-context visual question answering dataset encompassing interleaved images and EHR data derived from MIMIC-IV and MIMIC-CXR-JPG databases. Results demonstrate the SOTA performance of MedPromptX, achieving an 11% improvement in F1-score compared to the baselines. Code and data are publicly available on https://github.com/BioMedIA-MBZUAI/MedPromptX.
胸部X光片图像通常用于预测急性和慢性心肺状况,但将其与结构化临床数据结合的努力面临着由于电子健康记录(EHR)不完整而带来的挑战。本文介绍了MedPromptX,这是第一个结合多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)、小样本提示(FP)和视觉定位(VG)的临床决策支持系统,用于将图像与EHR数据相结合进行胸部X光诊断。预训练的MLLM被用来补充缺失的EHR信息,为患者病史提供全面的理解。此外,FP降低了对MLLMs进行大量培训的必要,同时有效地解决了幻觉问题。然而,确定最佳的小样本数量并选择高质量候选对象的过程可能是一个繁重的任务,但它对模型性能产生深远影响。因此,我们提出了一种新技术,可以动态细化小样本数据,以适应用于新患者情境的实时调整。此外,VG缩小了X光片图像中的搜索区域,从而提高了异常识别的准确性。我们还发布了MedPromptX-VQA,这是一个新的上下文视觉问答数据集,涵盖了从MIMIC-IV和MIMIC-CXR-JPG数据库派生的交错图像和EHR数据。结果表明,MedPromptX的性能处于领先水平,与基线相比,F1分数提高了11%。代码和数据可在https://github.com/BioMedIA-MBZUAI/MedPromptX上公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了一个名为MedPromptX的临床决策支持系统,该系统结合了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)、少样本提示(FP)和视觉定位(VG)技术,将胸部X光图像与电子健康记录(EHR)数据相结合,用于胸部X光诊断。通过使用预训练的语言模型来补充缺失的EHR信息,提供全面的患者病史理解。此外,该系统采用少样本提示技术,减少了对MLLMs的广泛训练需求,并解决了虚构问题。文章还提出了一种新技术,可动态完善少样本数据,以适应新患者情景。视觉定位技术则缩小了X光图像的搜索范围,提高了异常识别的准确性。最后,文章发布了一个名为MedPromptX-VQA的新数据集,包含来自MIMIC-IV和MIMIC-CXR-JPG数据库的图片和EHR数据。MedPromptX系统的性能优于基线,F1分数提高了11%。
Key Takeaways:
- MedPromptX是首个结合多模态大型语言模型、少样本提示和视觉定位技术的临床决策支持系统。
- 系统通过预训练的语言模型补充缺失的EHR信息,提供全面的患者病史理解。
- 少样本提示技术减少了MLLMs的训练需求,并解决了虚构问题。
- 提出了一种动态完善少样本数据的新技术,以适应新患者情景。
- 视觉定位技术提高了X光图像中异常识别的准确性。
- 发布了MedPromptX-VQA数据集,包含图片和EHR数据,用于视觉问答任务。
- MedPromptX系统性能优越,与基线相比F1分数提高了11%。
点此查看论文截图

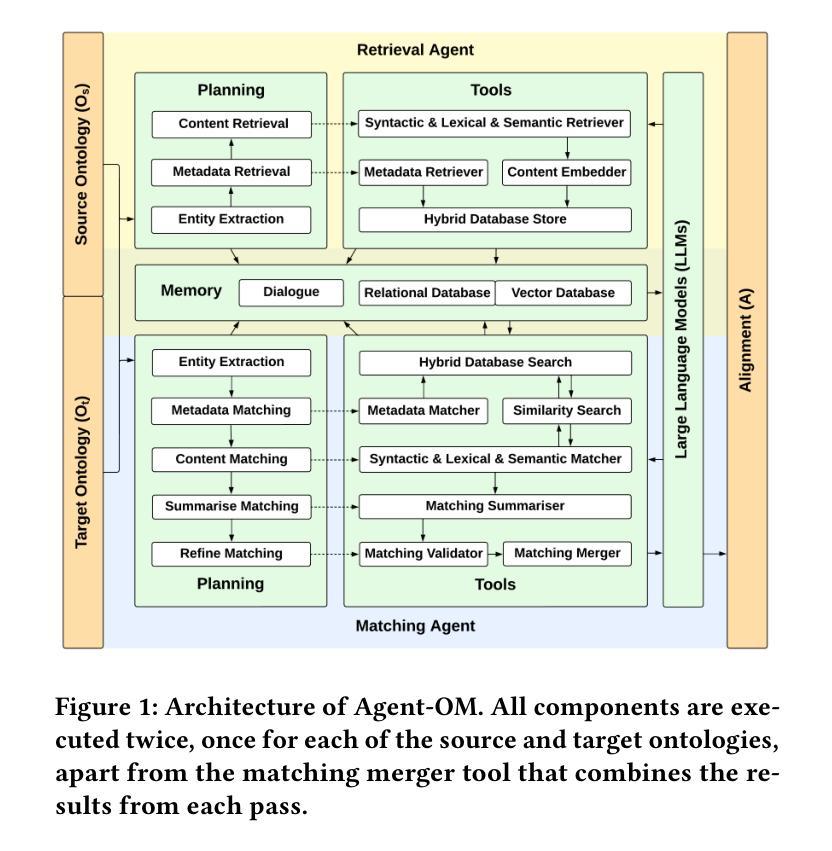
Agent-OM: Leveraging LLM Agents for Ontology Matching
Authors:Zhangcheng Qiang, Weiqing Wang, Kerry Taylor
Ontology matching (OM) enables semantic interoperability between different ontologies and resolves their conceptual heterogeneity by aligning related entities. OM systems currently have two prevailing design paradigms: conventional knowledge-based expert systems and newer machine learning-based predictive systems. While large language models (LLMs) and LLM agents have revolutionised data engineering and have been applied creatively in many domains, their potential for OM remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel agent-powered LLM-based design paradigm for OM systems. With consideration of several specific challenges in leveraging LLM agents for OM, we propose a generic framework, namely Agent-OM (Agent for Ontology Matching), consisting of two Siamese agents for retrieval and matching, with a set of OM tools. Our framework is implemented in a proof-of-concept system. Evaluations of three Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) tracks over state-of-the-art OM systems show that our system can achieve results very close to the long-standing best performance on simple OM tasks and can significantly improve the performance on complex and few-shot OM tasks.
本体匹配(OM)通过对齐相关实体,实现了不同本体之间的语义互操作,并解决了其概念上的异质性。目前,OM系统主要有两种流行的设计范式:传统的基于知识的专家系统和较新的基于机器学习的预测系统。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理已经彻底改变了数据工程,并已在许多领域得到创造性应用,但它们在OM中的潜力仍未得到充分探索。本研究引入了一种基于代理的LLM设计范式的新型OM系统。考虑到利用LLM代理进行OM面临的若干特定挑战,我们提出了一个通用框架,即Agent-OM(用于本体匹配的代理),该框架包含两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理以及一组OM工具。我们的框架在一个概念验证系统中实现。对三个本体对齐评估倡议(OAEI)赛道上的最新OM系统的评估表明,我们的系统在简单OM任务上的结果非常接近长期以来的最佳性能,并且在复杂和少镜头OM任务上可以显著提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 12 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本研究引入了一种新型基于LLM代理的OM系统设计范式,通过两个Siamese代理进行检索和匹配,并使用一套OM工具构建了一个通用的Agent-OM框架。该框架在证明概念系统中实现,并在三个OAEI轨道上对最新OM系统进行的评估表明,该系统在简单OM任务上表现接近最佳水平,并在复杂和少样本OM任务上显著提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- OM(本体匹配)有助于不同本体之间的语义互操作性,并通过对齐相关实体解决其概念上的异质性。
- 当前OM系统主要有两种设计范式:传统的知识型专家系统和新的基于机器学习的预测系统。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理在数据工程中具有革命性作用,但在OM方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。
- 本研究提出了一种新型的基于LLM代理的OM系统设计范式,解决了利用LLM代理进行OM时面临的一些特定挑战。
- 构建了一个通用的Agent-OM框架,包括用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理。
- 该框架在证明概念系统中实现,并在多个评估中表现优异,特别是在复杂和少样本OM任务上。
点此查看论文截图