⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
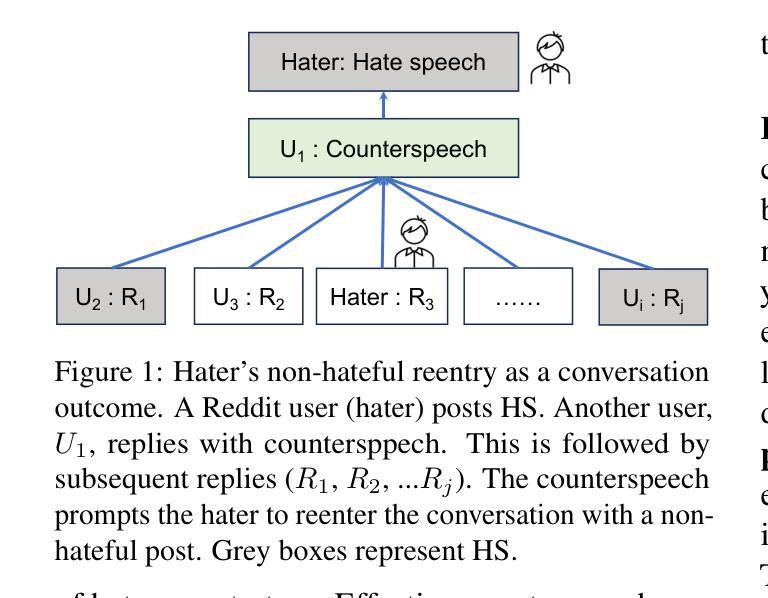
Echoes of Discord: Forecasting Hater Reactions to Counterspeech
Authors:Xiaoying Song, Sharon Lisseth Perez, Xinchen Yu, Eduardo Blanco, Lingzi Hong
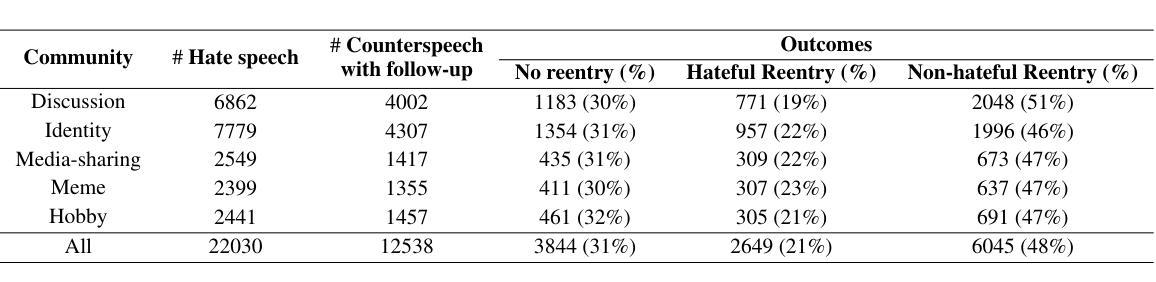
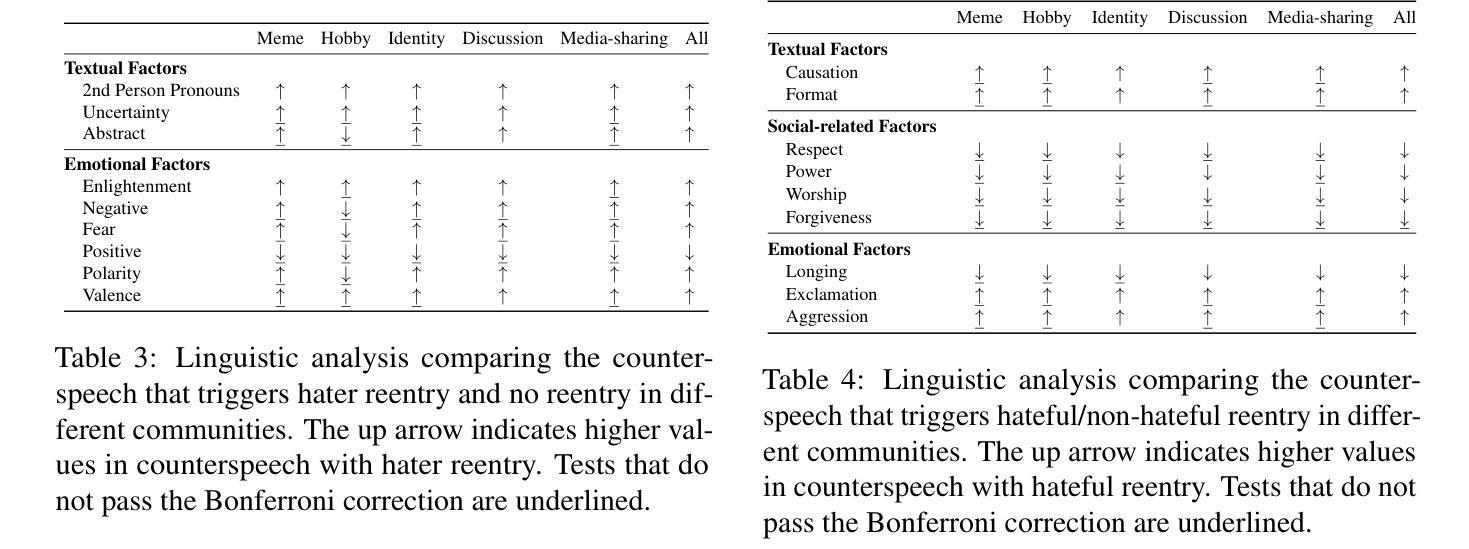
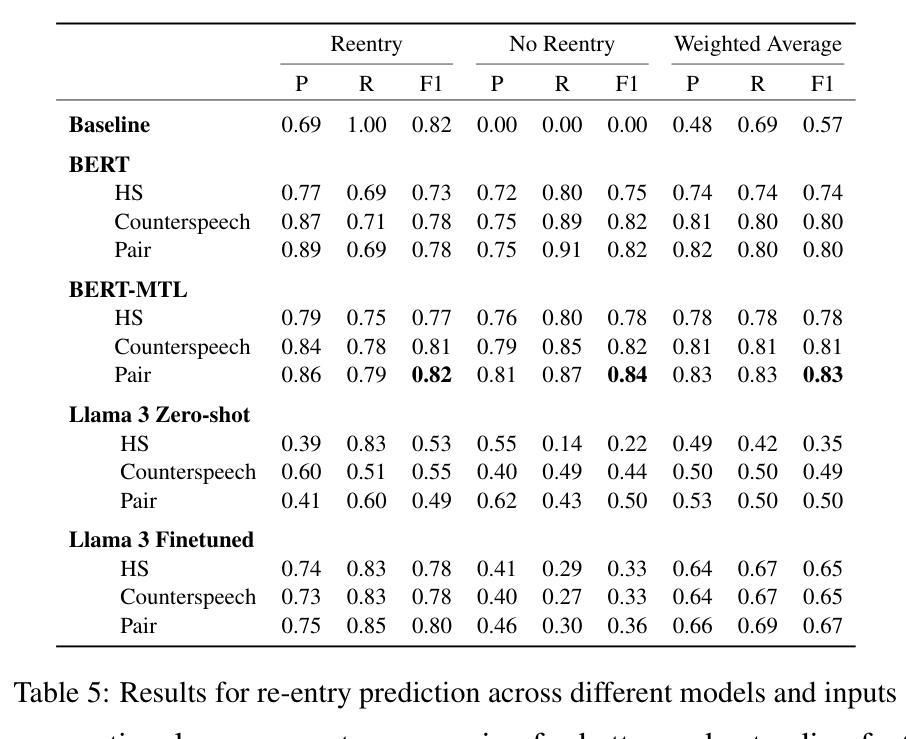
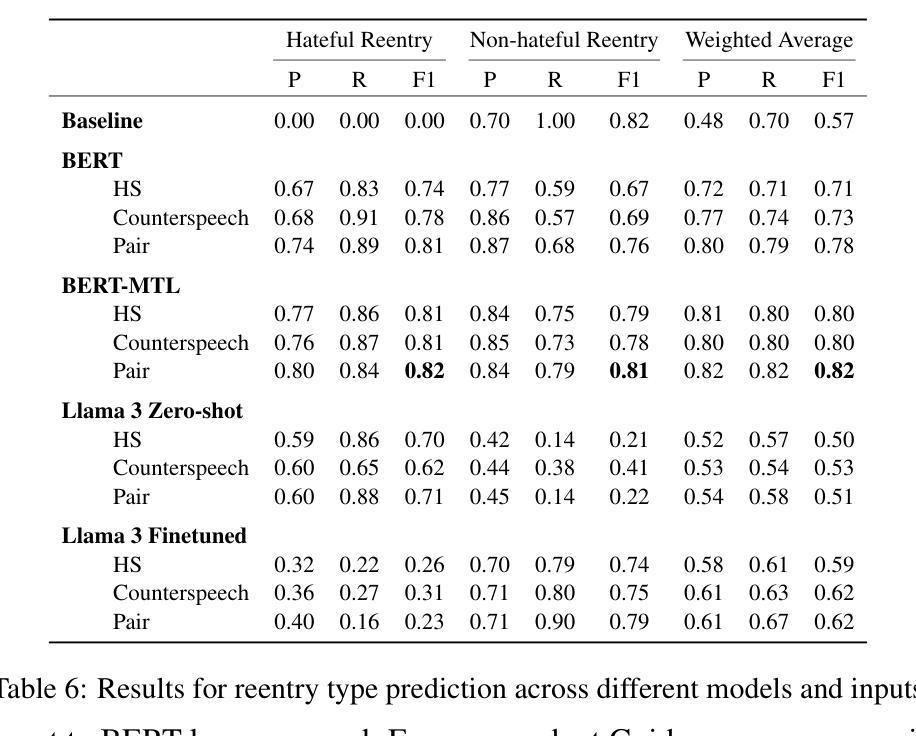
Hate speech (HS) erodes the inclusiveness of online users and propagates negativity and division. Counterspeech has been recognized as a way to mitigate the harmful consequences. While some research has investigated the impact of user-generated counterspeech on social media platforms, few have examined and modeled haters’ reactions toward counterspeech, despite the immediate alteration of haters’ attitudes being an important aspect of counterspeech. This study fills the gap by analyzing the impact of counterspeech from the hater’s perspective, focusing on whether the counterspeech leads the hater to reenter the conversation and if the reentry is hateful. We compile the Reddit Echoes of Hate dataset (ReEco), which consists of triple-turn conversations featuring haters’ reactions, to assess the impact of counterspeech. The linguistic analysis sheds insights on the language of counterspeech to hate eliciting different haters’ reactions. Experimental results demonstrate that the 3-way classification model outperforms the two-stage reaction predictor, which first predicts reentry and then determines the reentry type. We conclude the study with an assessment showing the most common errors identified by the best-performing model.
网络上的仇恨言论(HS)侵蚀了在线用户的包容性,传播了消极情绪和分裂。反仇恨言论已被认为是一种减轻其有害影响的方法。虽然一些研究已经调查了用户生成的反仇恨言论对社交媒体平台的影响,但很少有研究探讨和模拟仇恨者对反仇恨言论的反应,尽管仇恨者的态度立即改变是反仇恨言论的一个重要方面。本研究从仇恨者的角度分析了反仇恨言论的影响,重点关注反仇恨言论是否引导仇恨者重新参与对话,以及重新参与是否带有仇恨。为了评估反仇恨言论的影响,我们整理了Reddit仇恨回声数据集(ReEco),该数据集包含包含仇恨者反应的三轮对话。语言分析揭示了针对引发不同仇恨者反应的反仇恨言论的语言。实验结果表明,三方分类模型的表现优于两阶段反应预测器,该预测器首先预测重新参与,然后确定重新参与的类型。最后,我们对表现最好的模型所识别出的最常见错误进行了评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了在线平台上仇恨言论(HS)的问题,提出通过反言论来减轻仇恨言论的负面影响。文章着重分析了仇恨言论接收者对反仇恨言论的反馈,并从语言学的角度分析了不同反仇恨言论如何激发仇恨回应的不同反应。通过实验数据的分析,建立了一个三元分类模型,预测接收者的反应并判定反应是否包含仇恨元素。总结出研究评估结果和最佳模型的常见错误类型。
Key Takeaways
- 仇恨言论削弱在线用户包容性,加剧消极情绪和分裂氛围。
- 反仇恨言论被视作减轻仇恨言论负面影响的手段。
- 文章分析了从仇恨言论接收者视角,反仇恨言论的影响及其引发的反应。
- 研究通过Reddit Echoes of Hate数据集(ReEco)进行实证研究,关注接收者对反仇恨言论的反应和再次参与讨论的倾向性。
- 研究指出语言分析是理解反仇恨言论如何引发不同反应的关键。
- 三元分类模型在预测接收者反应方面表现优于两阶段反应预测模型。
点此查看论文截图

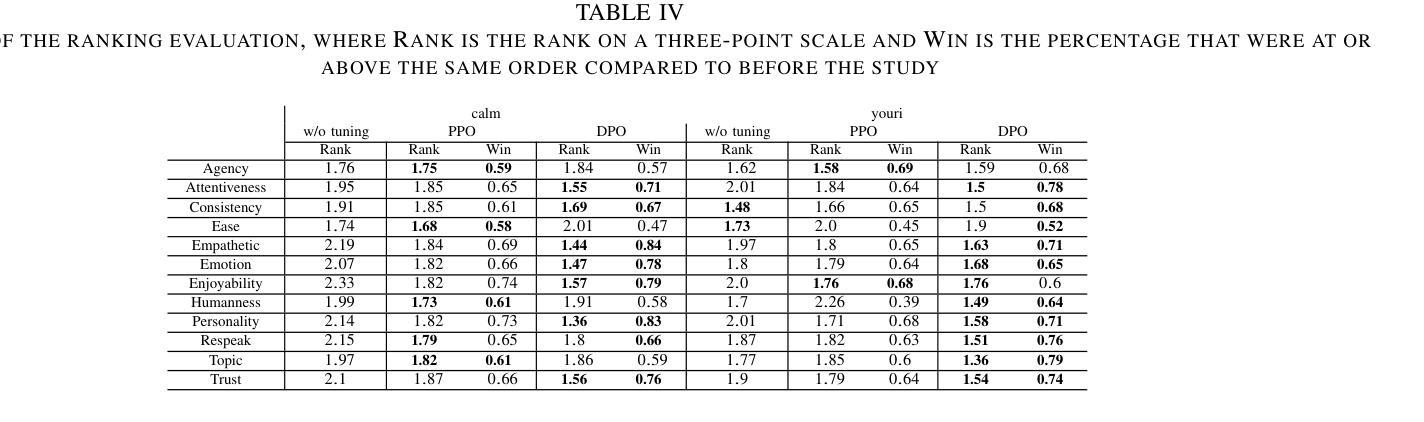
Training Dialogue Systems by AI Feedback for Improving Overall Dialogue Impression
Authors:Kai Yoshida, Masahiro Mizukami, Seiya Kawano, Canasai Kruengkrai, Hiroaki Sugiyama, Koichiro Yoshino
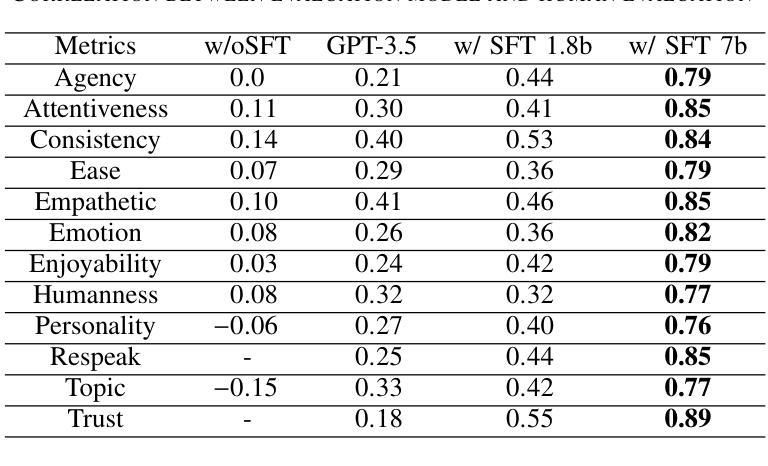
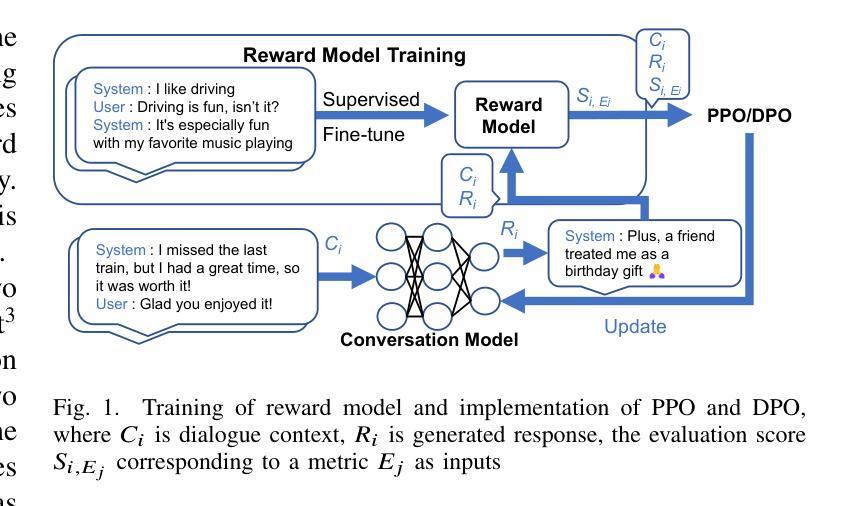
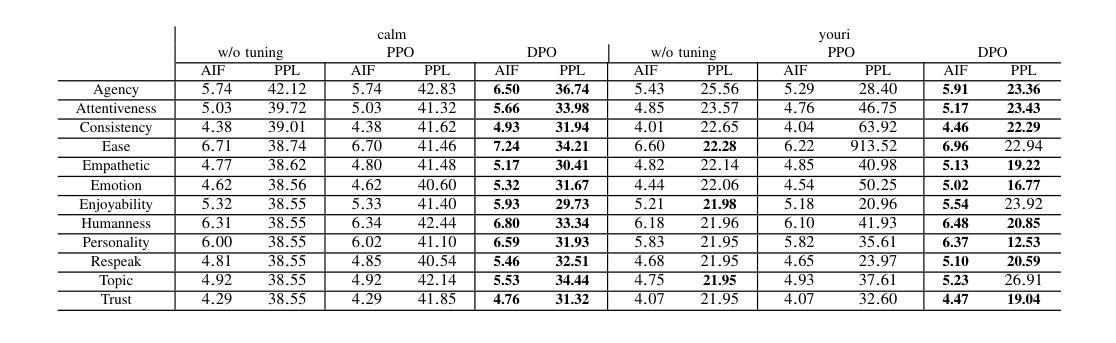
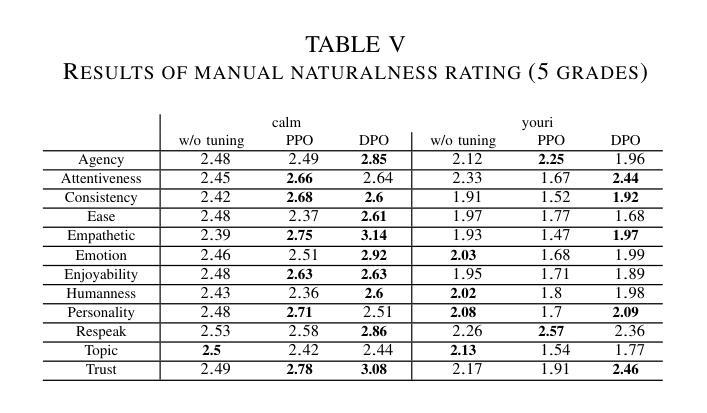
To improve user engagement during conversations with dialogue systems, we must improve individual dialogue responses and dialogue impressions such as consistency, personality, and empathy throughout the entire dialogue. While such dialogue systems have been developing rapidly with the help of large language models (LLMs), reinforcement learning from AI feedback (RLAIF) has attracted attention to align LLM-based dialogue models for such dialogue impressions. In RLAIF, a reward model based on another LLM is used to create a training signal for an LLM-based dialogue model using zero-shot/few-shot prompting techniques. However, evaluating an entire dialogue only by prompting LLMs is challenging. In this study, the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) of LLMs prepared reward models corresponding to 12 metrics related to the impression of the entire dialogue for evaluating dialogue responses. We tuned our dialogue models using the reward model signals as feedback to improve the impression of the system. The results of automatic and human evaluations showed that tuning the dialogue model using our reward model corresponding to dialogue impression improved the evaluation of individual metrics and the naturalness of the dialogue response.
为提高用户与对话系统对话时的参与度,我们必须改善单独的对话回应和整个对话过程中的一致性、个性和同理感等对话印象。虽然这类对话系统凭借大型语言模型(LLM)发展迅速,但利用人工智能反馈进行强化学习(RLAIF)已引起关注,以使基于LLM的对话模型与这类对话印象对齐。在RLAIF中,使用基于另一个LLM的奖励模型,通过零样本/少样本提示技术为基于LLM的对话模型创建训练信号。然而,仅通过提示LLM来评估整个对话是有挑战性的。本研究中,我们准备了与整个对话印象相关的12项指标的奖励模型,以评估对话回应,对LLM进行有监督微调(SFT)。我们使用奖励模型信号作为反馈来调整我们的对话模型,以提高系统印象。自动和人类评估的结果显示,使用与对话印象相对应的奖励模型调整对话模型,可以提高单个指标的评估结果和对话回应的自然性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary:
为提高对话系统的用户参与度,需提升整个对话过程中的对话响应和对话印象,如一致性、个性和同理心。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)助力对话系统快速发展,但利用强化学习从人工智能反馈(RLAIF)对齐LLM对话模型以达成对话印象的吸引力逐渐显现。本研究通过基于LLM的奖励模型,使用零样本/少样本提示技术为LLM对话模型创建训练信号。然而,仅通过提示LLM评估整个对话具有挑战性。因此,本研究通过监督微调(SFT)LLMs,准备对应于12个与整个对话印象相关的指标的奖励模型,以评估对话响应。使用奖励模型信号对对话框模型进行微调,以提高系统印象。自动和人类评估结果表明,使用对应于对话印象的奖励模型调整对话模型,提高了单个指标的评价和对话响应的自然性。
Key Takeaways:
- 为提高用户与对话系统的参与度,需增强对话响应和印象,如一致性、个性和同理心。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在对话系统发展中起到重要作用。
- 强化学习从人工智能反馈(RLAIF)有助于对齐LLM对话模型以达成对话印象。
- 利用LLM的奖励模型,通过零样本/少样本提示技术为LLM对话模型创建训练信号。
- 仅通过提示LLM评估整个对话存在挑战,因此需要监督微调LLMs,准备对应于整个对话印象的奖励模型。
- 通过使用奖励模型信号微调对话框模型,可以提高系统印象。
点此查看论文截图