⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
RAPID: Retrieval-Augmented Parallel Inference Drafting for Text-Based Video Event Retrieval
Authors:Long Nguyen, Huy Nguyen, Bao Khuu, Huy Luu, Huy Le, Tuan Nguyen, Tho Quan
Retrieving events from videos using text queries has become increasingly challenging due to the rapid growth of multimedia content. Existing methods for text-based video event retrieval often focus heavily on object-level descriptions, overlooking the crucial role of contextual information. This limitation is especially apparent when queries lack sufficient context, such as missing location details or ambiguous background elements. To address these challenges, we propose a novel system called RAPID (Retrieval-Augmented Parallel Inference Drafting), which leverages advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and prompt-based learning to semantically correct and enrich user queries with relevant contextual information. These enriched queries are then processed through parallel retrieval, followed by an evaluation step to select the most relevant results based on their alignment with the original query. Through extensive experiments on our custom-developed dataset, we demonstrate that RAPID significantly outperforms traditional retrieval methods, particularly for contextually incomplete queries. Our system was validated for both speed and accuracy through participation in the Ho Chi Minh City AI Challenge 2024, where it successfully retrieved events from over 300 hours of video. Further evaluation comparing RAPID with the baseline proposed by the competition organizers demonstrated its superior effectiveness, highlighting the strength and robustness of our approach.
从视频中检索事件并使用文本查询是一项因多媒体内容的快速增长而日益具有挑战性的任务。现有的基于文本的视频事件检索方法通常过于关注对象级别的描述,而忽略了上下文信息的关键作用。当查询缺乏足够的上下文时,这种局限性尤为明显,例如缺少地点细节或背景元素模糊。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种名为RAPID(基于检索增强的并行推理草稿)的新系统,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)和基于提示的学习来语义地修正和丰富用户查询的相关上下文信息。这些丰富的查询然后通过并行检索进行处理,接着是一个评估步骤,根据其与原始查询的匹配程度选择最相关的结果。在我们自定义开发的数据集上进行的大量实验表明,RAPID显著优于传统检索方法,特别是对于上下文不完整的查询。我们的系统通过参与2024年胡志明市人工智能挑战赛,在速度和准确性方面都得到了验证,成功地从超过300小时的视频中检索到了事件。与竞赛组织者提出的基线相比,对RAPID的进一步评估证明了其卓越的有效性,突出了我们方法的实力和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review at SoICT’24
Summary
多媒体内容的迅速增长使得基于文本查询从视频中检索事件变得越来越具有挑战性。现有方法往往侧重于对象级别的描述,忽略了上下文信息的重要作用。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种名为RAPID的新系统,利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和基于提示的学习,对用户的查询进行语义上的修正和丰富,并添加相关的上下文信息。通过我们自行开发的定制数据集上的大量实验,证明了RAPID系统在性能上显著优于传统检索方法,尤其是对于上下文缺失的查询。我们已在胡志明市人工智能挑战中验证其速度和准确性。对比主办方提出的基线模型,我们展示了自己的优势及稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 面对多媒体内容的迅速增长,从视频中基于文本查询检索事件变得更加具有挑战性。
- 传统方法主要关注对象级别的描述,忽略了上下文信息的重要性。
- RAPID系统通过利用大型语言模型和基于提示的学习,丰富用户查询的上下文信息。
- RAPID在处理和解决上下文缺失的查询方面表现出显著优势。
- RAPID系统已在定制的基准数据集上进行了广泛实验验证,证明其性能优于传统检索方法。
- RAPID在胡志明市人工智能挑战中成功验证了其速度和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

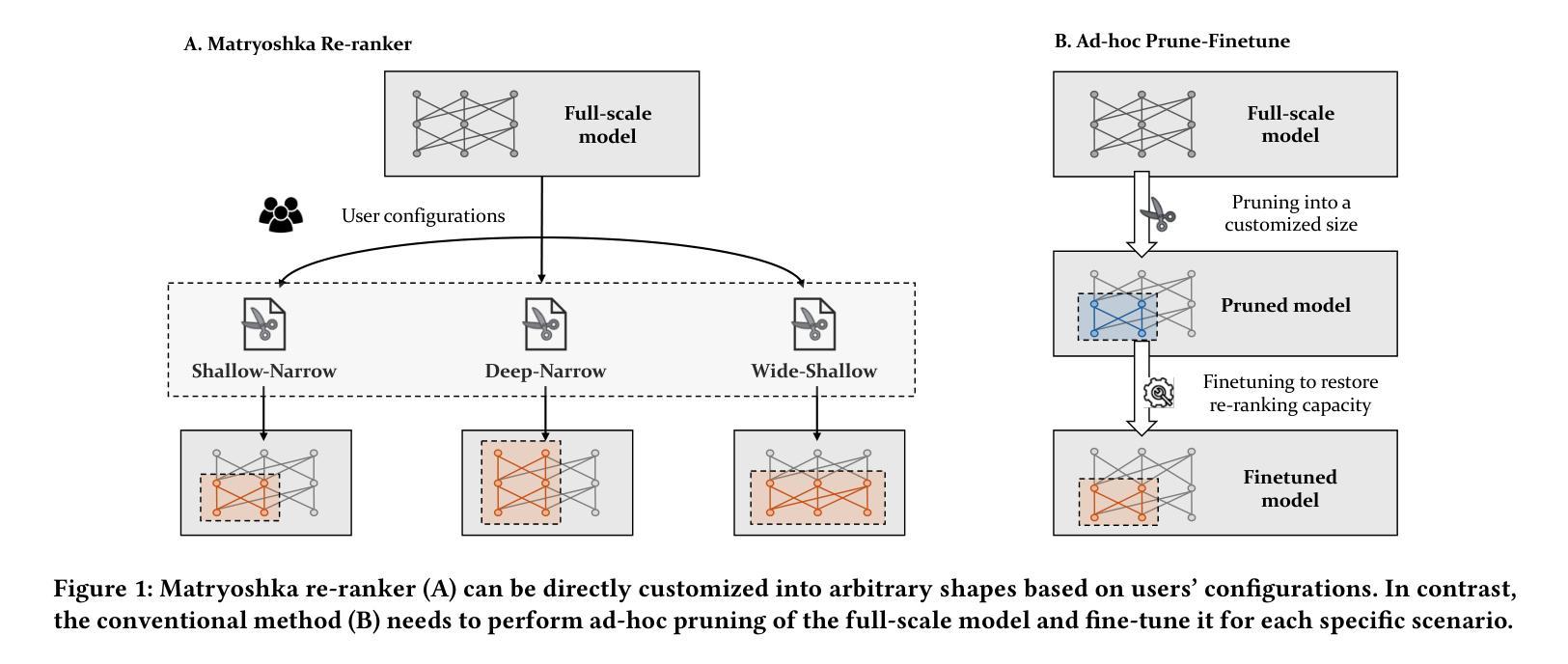
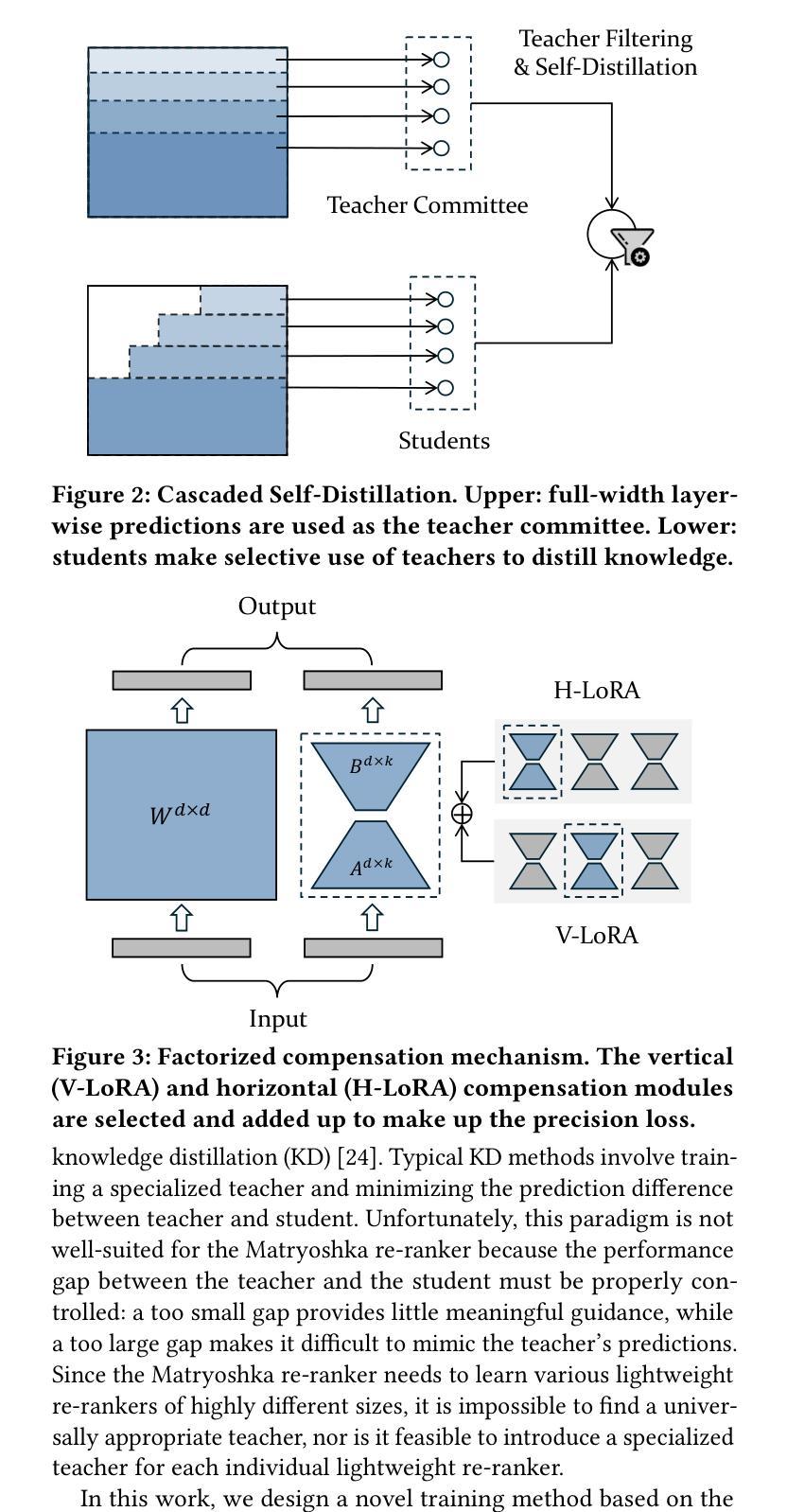
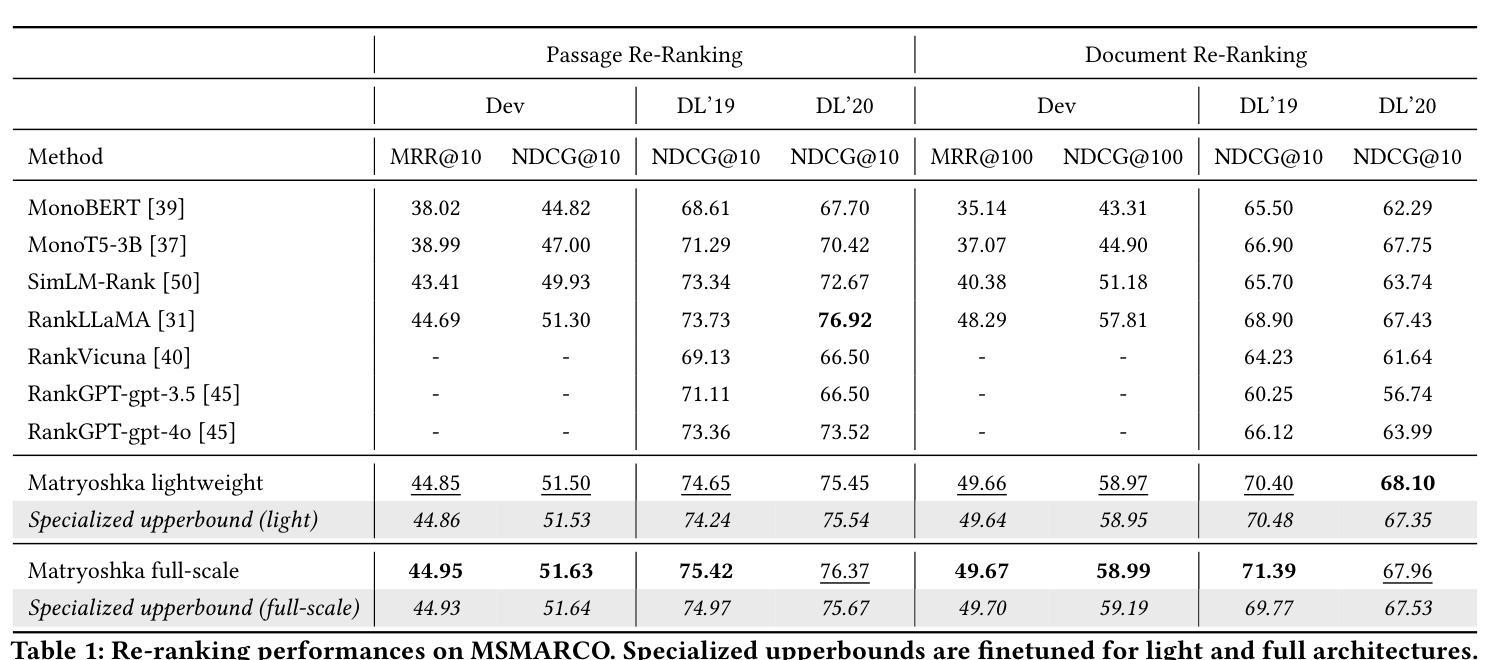
Matryoshka Re-Ranker: A Flexible Re-Ranking Architecture With Configurable Depth and Width
Authors:Zheng Liu, Chaofan Li, Shitao Xiao, Chaozhuo Li, Defu Lian, Yingxia Shao
Large language models (LLMs) provide powerful foundations to perform fine-grained text re-ranking. However, they are often prohibitive in reality due to constraints on computation bandwidth. In this work, we propose a \textbf{flexible} architecture called \textbf{Matroyshka Re-Ranker}, which is designed to facilitate \textbf{runtime customization} of model layers and sequence lengths at each layer based on users’ configurations. Consequently, the LLM-based re-rankers can be made applicable across various real-world situations. The increased flexibility may come at the cost of precision loss. To address this problem, we introduce a suite of techniques to optimize the performance. First, we propose \textbf{cascaded self-distillation}, where each sub-architecture learns to preserve a precise re-ranking performance from its super components, whose predictions can be exploited as smooth and informative teacher signals. Second, we design a \textbf{factorized compensation mechanism}, where two collaborative Low-Rank Adaptation modules, vertical and horizontal, are jointly employed to compensate for the precision loss resulted from arbitrary combinations of layer and sequence compression. We perform comprehensive experiments based on the passage and document retrieval datasets from MSMARCO, along with all public datasets from BEIR benchmark. In our experiments, Matryoshka Re-Ranker substantially outperforms the existing methods, while effectively preserving its superior performance across various forms of compression and different application scenarios.
大型语言模型(LLM)为进行精细文本重新排序提供了强大的基础。然而,由于计算带宽的限制,它们在现实中往往受到阻碍。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种名为“Matroyshka Re-Ranker”的灵活架构,旨在根据用户的配置,在运行时定制模型层和每层的序列长度。因此,基于LLM的重新排序器可应用于各种现实情况。灵活性的增加可能会以精度损失为代价。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一系列技术来优化性能。首先,我们提出了级联自蒸馏技术,其中每个子架构学习从其高级组件中保留精确的重新排序性能,这些预测结果可以被用作平滑且信息丰富的教师信号。其次,我们设计了一种分解补偿机制,其中两个协作的低秩适应模块(垂直和水平)被联合用于补偿由于任意组合的层和序列压缩而产生的精度损失。我们在MSMARCO的段落和文档检索数据集以及BEIR基准测试的所有公共数据集上进行了全面的实验。在我们的实验中,Matroyshka Re-Ranker显著优于现有方法,同时在各种形式的压缩和不同的应用场景中有效地保持了其卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The Web Conference 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个灵活的架构Matroyshka Re-Ranker,它能够在运行时根据用户需求定制模型层和序列长度,使得大型语言模型(LLM)更适用于各种实际情况。为解决灵活性可能带来的精度损失问题,文章引入了一系列优化技术,包括级联自蒸馏和因子化补偿机制。实验表明,Matryoshka Re-Ranker在压缩和各种应用场景下均保持了出色的性能,并显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- Matroyshka Re-Ranker架构提供了灵活的定制选项,允许根据用户需求调整模型层和序列长度。
- 灵活性可能会带来精度损失。
- 为优化性能,引入了级联自蒸馏技术,使子架构能够保持精确的重排性能。
- 因子化补偿机制通过两个协作的低秩适应模块(垂直和水平)来补偿因层和序列压缩而产生的精度损失。
- Matroyshka Re-Ranker在MSMARCO的passage和文档检索数据集以及BEIR基准测试的所有公共数据集上进行了实验。
- 实验结果表明,Matroyshka Re-Ranker在多种压缩形式和各种应用场景下均显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

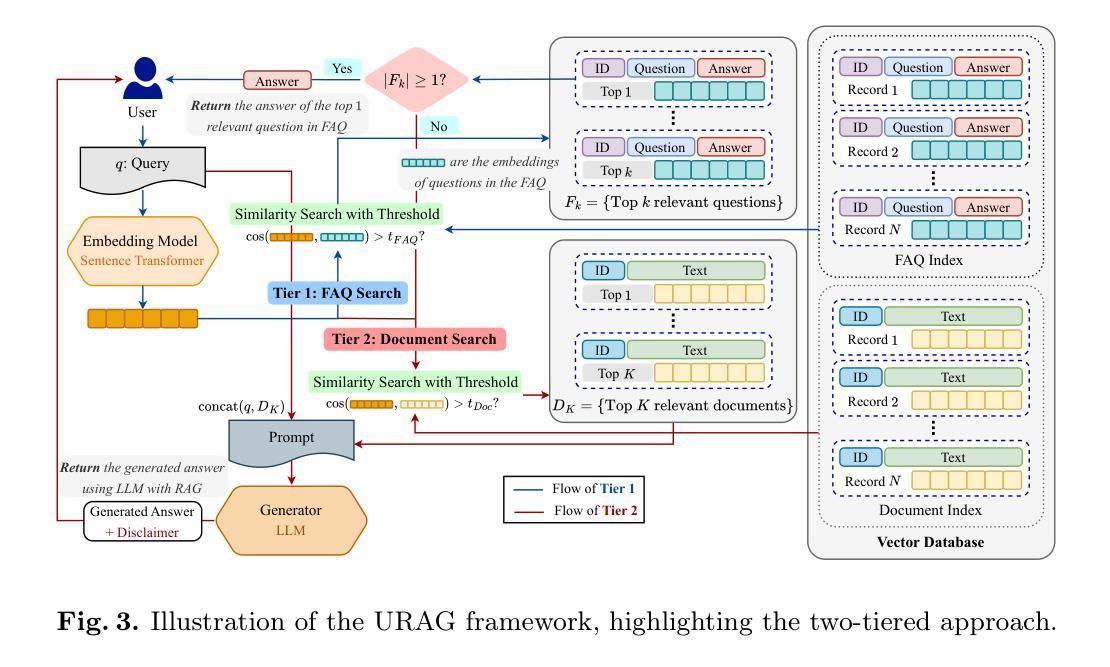
URAG: Implementing a Unified Hybrid RAG for Precise Answers in University Admission Chatbots – A Case Study at HCMUT
Authors:Long Nguyen, Tho Quan
With the rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence, particularly in Natural Language Processing, Large Language Models (LLMs) have become pivotal in educational question-answering systems, especially university admission chatbots. Concepts such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and other advanced techniques have been developed to enhance these systems by integrating specific university data, enabling LLMs to provide informed responses on admissions and academic counseling. However, these enhanced RAG techniques often involve high operational costs and require the training of complex, specialized modules, which poses challenges for practical deployment. Additionally, in the educational context, it is crucial to provide accurate answers to prevent misinformation, a task that LLM-based systems find challenging without appropriate strategies and methods. In this paper, we introduce the Unified RAG (URAG) Framework, a hybrid approach that significantly improves the accuracy of responses, particularly for critical queries. Experimental results demonstrate that URAG enhances our in-house, lightweight model to perform comparably to state-of-the-art commercial models. Moreover, to validate its practical applicability, we conducted a case study at our educational institution, which received positive feedback and acclaim. This study not only proves the effectiveness of URAG but also highlights its feasibility for real-world implementation in educational settings.
随着人工智能的快速进步,特别是在自然语言处理方面,大型语言模型(LLM)在教育问答系统,尤其是大学招生聊天机器人中,起到了至关重要的作用。诸如检索增强生成(RAG)等其他先进技术概念的发展,通过整合特定大学数据,增强了这些系统的功能,使LLM能够提供有关招生和学术咨询的信息回复。然而,这些增强的RAG技术通常涉及较高的操作成本,并且需要训练复杂的专业模块,这给实际部署带来了挑战。此外,在教育背景下,为了预防错信,提供准确答案至关重要,而LLM系统在没有适当的策略和方法的情况下,发现这是一个具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们介绍了统一RAG(URAG)框架,这是一种混合方法,可以显著提高响应的准确性,特别是对于关键查询。实验结果表明,URAG可以增强我们内部的轻量级模型,使其性能与最先进的商业模型相当。此外,为了验证其实用性,我们在教育机构进行了案例研究,并获得了积极的反馈和赞誉。这项研究不仅证明了URAG的有效性,而且强调了其在教育环境中实际应用的可行性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review at SoICT’24
Summary:随着人工智能的快速发展,特别是在自然语言处理领域,大型语言模型(LLM)在教育问答系统中扮演着至关重要的角色,如大学招生聊天机器人。为提高系统的性能,研究者开发了诸如检索增强生成(RAG)等先进技术,集成特定大学数据,使LLM能够提供有关招生和学术咨询的信息回复。然而,RAG技术的高运营成本和对复杂专业模块的迫切需求,为其实际应用带来了挑战。本研究介绍了一种混合方法——统一检索增强生成(URAG)框架,该方法显著提高了响应的准确性,尤其是对关键查询的响应。实验结果表明,URAG能够增强我们内部的轻量级模型,使其表现堪比最先进的商业模型。在教育机构进行的研究案例获得了积极的反馈和赞誉,证明了URAG的有效性和现实应用中的可行性。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在教育问答系统中扮演重要角色,如大学招生聊天机器人。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)技术为提高教育问答系统的性能起到了关键作用。
- RAG技术面临高运营成本和对复杂专业模块的迫切需求等挑战。
- 统一检索增强生成(URAG)框架是一种混合方法,旨在提高LLM在教育领域的响应准确性。
- 实验结果表明,URAG能够增强轻量级模型的表现,使其与最先进的商业模型相媲美。
- 在教育机构进行的研究案例证明了URAG的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

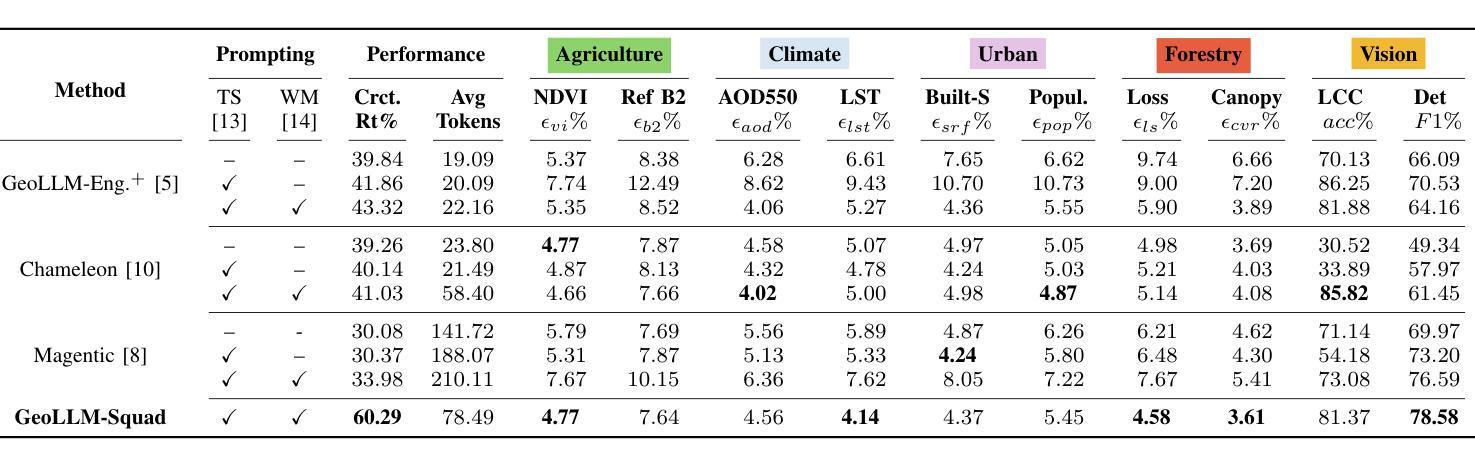
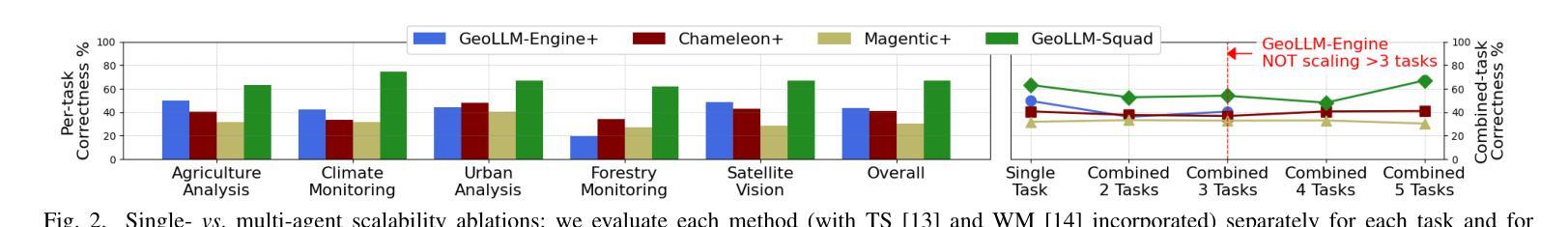
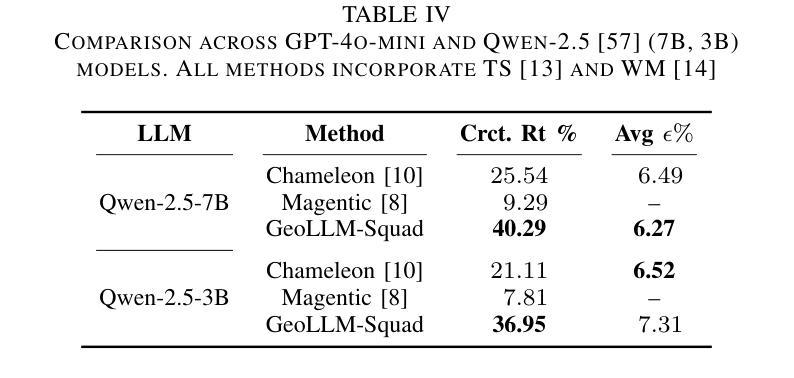
Multi-Agent Geospatial Copilots for Remote Sensing Workflows
Authors:Chaehong Lee, Varatheepan Paramanayakam, Andreas Karatzas, Yanan Jian, Michael Fore, Heming Liao, Fuxun Yu, Ruopu Li, Iraklis Anagnostopoulos, Dimitrios Stamoulis
We present GeoLLM-Squad, a geospatial Copilot that introduces the novel multi-agent paradigm to remote sensing (RS) workflows. Unlike existing single-agent approaches that rely on monolithic large language models (LLM), GeoLLM-Squad separates agentic orchestration from geospatial task-solving, by delegating RS tasks to specialized sub-agents. Built on the open-source AutoGen and GeoLLM-Engine frameworks, our work enables the modular integration of diverse applications, spanning urban monitoring, forestry protection, climate analysis, and agriculture studies. Our results demonstrate that while single-agent systems struggle to scale with increasing RS task complexity, GeoLLM-Squad maintains robust performance, achieving a 17% improvement in agentic correctness over state-of-the-art baselines. Our findings highlight the potential of multi-agent AI in advancing RS workflows.
我们推出了GeoLLM-Squad,这是一个地理空间Copilot,它为遥感(RS)工作流程引入了新型的多智能体范式。与依赖单一大型语言模型(LLM)的现有单智能体方法不同,GeoLLM-Squad通过将遥感任务委派给专业子智能体,实现了智能编排与地理空间任务解决的分离。我们的工作建立在开源的AutoGen和GeoLLM-Engine框架之上,能够实现模块化集成各种应用,涵盖城市监测、林业保护、气候分析和农业研究等领域。我们的结果表明,虽然单智能体系统在处理日益复杂的遥感任务时难以扩展,但GeoLLM-Squad能够保持稳健的性能,在智能正确性方面比最新基线提高了17%。我们的研究突出了多智能体人工智能在推动遥感工作流程方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于多智能体范式提出的GeoLLM-Squad系统,引入新型远程遥感工作流程。不同于依赖单一大型语言模型的传统方法,GeoLLM-Squad通过专业子智能体完成遥感任务,实现智能体编排与地理空间任务解决的分离。借助开源的AutoGen和GeoLLM-Engine框架,该系统支持模块化集成多种应用,如城市监测、林业保护、气候分析和农业研究等。在单智能体系统难以应对日益复杂的遥感任务时,GeoLLM-Squad展现了稳健性能,并在最新基准测试中提高了智能体正确性方面的表现。研究凸显了多智能体人工智能在推动遥感工作流程发展方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- GeoLLM-Squad是一个基于多智能体范式的地理空间Copilot系统,用于处理遥感任务。
- 与传统依赖单一大型语言模型的远程感应方法不同,GeoLLM-Squad采用专业子智能体来完成任务。
- GeoLLM-Squad实现了智能体编排与地理空间任务解决的分离。
- 该系统基于开源的AutoGen和GeoLLM-Engine框架构建,支持多种模块化集成应用。
- 与单智能体系统相比,GeoLLM-Squad在复杂的遥感任务中展现了稳健性能。
- GeoLLM-Squad在最新基准测试中提高了智能体的正确性表现。
点此查看论文截图


Enhancing Visual Inspection Capability of Multi-Modal Large Language Models on Medical Time Series with Supportive Conformalized and Interpretable Small Specialized Models
Authors:Huayu Li, Xiwen Chen, Ci Zhang, Stuart F. Quan, William D. S. Killgore, Shu-Fen Wung, Chen X. Chen, Geng Yuan, Jin Lu, Ao Li
Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in visual inspection of medical time-series data, achieving proficiency comparable to human clinicians. However, their broad scope limits domain-specific precision, and proprietary weights hinder fine-tuning for specialized datasets. In contrast, small specialized models (SSMs) excel in targeted tasks but lack the contextual reasoning required for complex clinical decision-making. To address these challenges, we propose ConMIL (Conformalized Multiple Instance Learning), a decision-support SSM that integrates seamlessly with LLMs. By using Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) to identify clinically significant signal segments and conformal prediction for calibrated set-valued outputs, ConMIL enhances LLMs’ interpretative capabilities for medical time-series analysis. Experimental results demonstrate that ConMIL significantly improves the performance of state-of-the-art LLMs, such as ChatGPT4.0 and Qwen2-VL-7B. Specifically, \ConMIL{}-supported Qwen2-VL-7B achieves 94.92% and 96.82% precision for confident samples in arrhythmia detection and sleep staging, compared to standalone LLM accuracy of 46.13% and 13.16%. These findings highlight the potential of ConMIL to bridge task-specific precision and broader contextual reasoning, enabling more reliable and interpretable AI-driven clinical decision support.
大型语言模型(LLM)在医疗时间序列数据的视觉检查方面表现出显著的能力,其熟练程度可与人类临床医生相媲美。然而,其广泛的范围限制了特定领域的精度,专有权重阻碍了针对特定数据集的微调。相比之下,小型专业化模型(SSMs)在目标任务上表现出色,但缺乏用于复杂临床决策所需的上下文推理能力。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了ConMIL(合规化多实例学习),这是一种决策支持SSM,可与LLM无缝集成。通过使用多实例学习(MIL)来识别临床上重要的信号段和合规预测来进行校准集值输出,ConMIL增强了LLM对医疗时间序列分析的解读能力。实验结果表明,ConMIL显著提高了最新LLM的性能,如ChatGPT4.0和Qwen2-VL-7B。具体来说,在心律失常检测和睡眠分期方面,由ConMIL支持的Qwen2-VL-7B对自信样本的精确度达到94.92%和96.82%,而单独的LLM准确度仅为46.13%和13.16%。这些发现突显了ConMil在任务特定精度和更广泛的上下文推理之间的桥梁作用,为实现更可靠和可解释的AI驱动的临床决策支持提供了潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在医疗时间序列数据的视觉检查中展现出令人瞩目的能力,其专业性堪比临床医生。然而,其广泛的应用范围限制了特定领域的精度,且专有权重阻碍了针对特定数据集的微调。相反,小型专业化模型(SSM)在目标任务上表现出色,但在复杂临床决策所需的上下文推理方面存在不足。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了ConMIL(Conformalized Multiple Instance Learning),这是一种决策支持SSM,可与LLMs无缝集成。通过多重实例学习(MIL)识别临床重要信号段和校准集合值输出的合规预测,ConMIL增强了LLM在医疗时间序列分析中的解释能力。实验结果表明,ConMIL显著提高了先进LLM的性能,如ChatGPT4.0和Qwen2-VL-7B。特别是ConMIL支持的Qwen2-VL-7B在心律失常检测和睡眠分期中的自信样本精度分别达到94.92%和96.82%,而单独的LLM精度仅为46.13%和13.16%。这些发现突显了ConMil在任务特定精度和更广泛的上下文推理之间的桥梁作用,为更可靠和可解释的AI驱动的临床决策支持提供了潜力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在医疗时间序列数据的视觉检查方面表现出强大的能力。
- LLM的广泛应用范围限制了其在特定领域的精度。
- SSM在目标任务一上的表现优秀,但在上下文推理方面存在不足。
- ConMIL通过结合MIL和合规预测增强了LLM的解释能力。
- ConMIL显著提高了先进LLM在医疗时间序列分析中的性能。
- ConMIL支持的Qwen2-VL-7B在心律失常检测和睡眠分期方面表现出高精确度。
点此查看论文截图

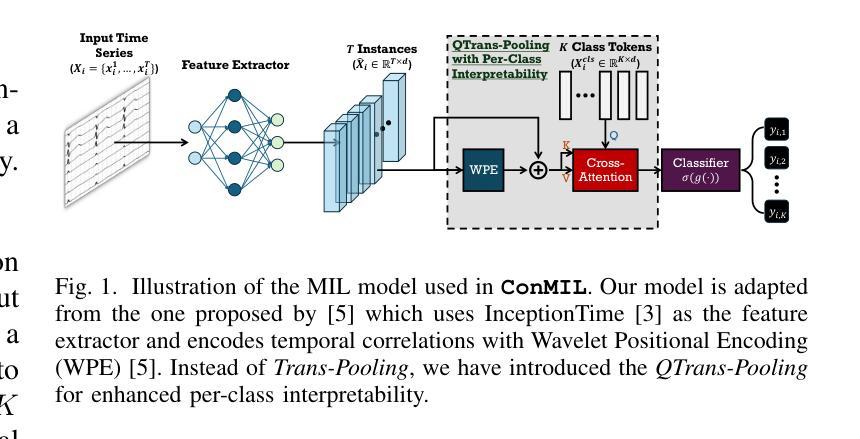
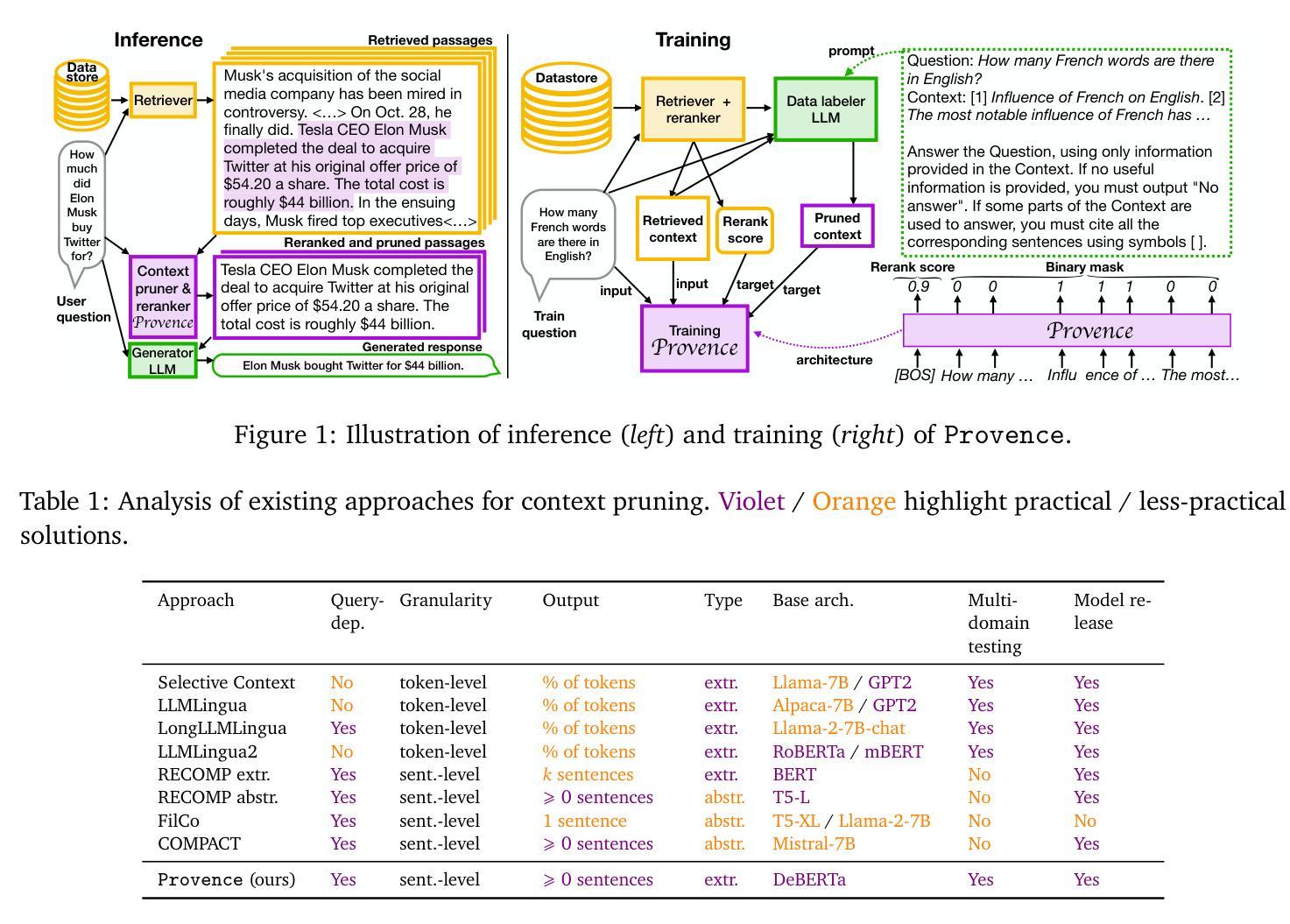
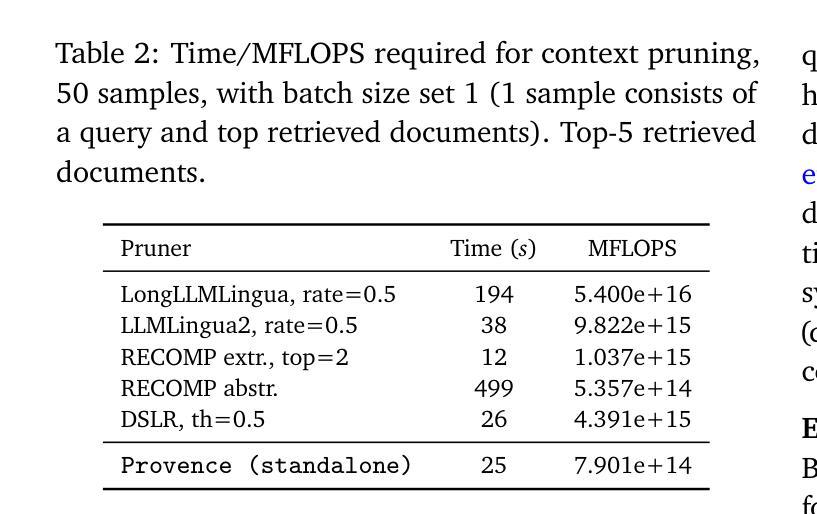
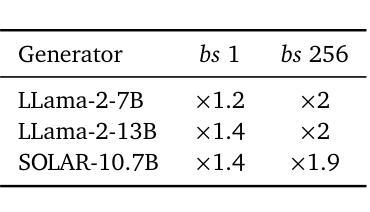
Provence: efficient and robust context pruning for retrieval-augmented generation
Authors:Nadezhda Chirkova, Thibault Formal, Vassilina Nikoulina, Stéphane Clinchant
Retrieval-augmented generation improves various aspects of large language models (LLMs) generation, but suffers from computational overhead caused by long contexts as well as the propagation of irrelevant retrieved information into generated responses. Context pruning deals with both aspects, by removing irrelevant parts of retrieved contexts before LLM generation. Existing context pruning approaches are however limited, and do not provide a universal model that would be both efficient and robust in a wide range of scenarios, e.g., when contexts contain a variable amount of relevant information or vary in length, or when evaluated on various domains. In this work, we close this gap and introduce Provence (Pruning and Reranking Of retrieVEd relevaNt ContExts), an efficient and robust context pruner for Question Answering, which dynamically detects the needed amount of pruning for a given context and can be used out-of-the-box for various domains. The three key ingredients of Provence are formulating the context pruning task as sequence labeling, unifying context pruning capabilities with context reranking, and training on diverse data. Our experimental results show that Provence enables context pruning with negligible to no drop in performance, in various domains and settings, at almost no cost in a standard RAG pipeline. We also conduct a deeper analysis alongside various ablations to provide insights into training context pruners for future work.
增强检索生成技术能够提升大型语言模型(LLM)的生成能力,但存在由于长文本语境导致的计算负担以及将不相关的检索信息传播到生成响应中的问题。语境修剪技术能够处理这两个问题,通过在LLM生成之前去除检索语境中的不相关部分。然而,现有的语境修剪方法存在局限性,并未提供一种通用模型,能够在多种场景下既高效又稳健,例如在语境包含可变量的相关信息或长度不同,或在各种领域进行评估时。在这项工作中,我们弥补了这一空白,并引入了名为“Provence”(检索相关语境的修剪与重新排序)的语境修剪器,这是一种用于问答的高效且稳健的语境修剪器,能够针对给定语境动态检测所需修剪的量,并可直接用于各种领域。Provence的三个关键要素是将语境修剪任务制定为序列标注,将语境修剪能力与语境重新排序相结合,并在多样化数据上进行训练。我们的实验结果表明,在各种领域和设置中,使用Provence进行语境修剪几乎不会对性能产生负面影响,并且在标准RAG管道中的成本几乎为零。我们还进行了更深入的分析,同时进行了各种切除研究,为未来训练语境修剪器提供见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025
Summary:基于摘要的技术论文。在大型语言模型生成过程中,引入检索增强技术的背景能够提高多种性能。但长远背景和无关检索信息可能被纳入生成响应,为解决这一问题,研究者提出了上下文修剪技术。然而,现有技术存在局限性,难以在多种场景下实现高效和稳健的上下文修剪。因此,本文引入了一种针对问答的上下文修剪技术——Provence(检索相关上下文修剪和重新排序)。它可动态检测给定上下文所需的修剪量,适用于各种领域。该技术的关键包括将上下文修剪任务转化为序列标注问题,统一上下文修剪和重新排序能力,以及进行多样化数据的训练。实验结果表明,在标准RAG管道中,使用Provence进行上下文修剪几乎不会降低性能。同时,本文还进行了深入的分析和消融研究,为未来的上下文修剪训练提供了见解。
Key Takeaways:
- 检索增强技术能提高大型语言模型的性能。
- 现有上下文修剪技术存在局限性,难以应对多种场景的挑战。
- 引入的“Provence”技术能动态检测所需修剪的上下文量,适用于各种领域。
- “Provence”技术的关键包括将上下文修剪任务转化为序列标注问题,统一上下文修剪和重新排序能力,以及进行多样化数据的训练。
- 实验结果显示,“Provence”技术在实现上下文修剪的同时几乎不影响性能。
- 通过深入分析和消融研究,为未来的上下文修剪训练提供了见解。
点此查看论文截图

Raiders of the Lost Dependency: Fixing Dependency Conflicts in Python using LLMs
Authors:Antony Bartlett, Cynthia Liem, Annibale Panichella
Fixing Python dependency issues is a tedious and error-prone task for developers, who must manually identify and resolve environment dependencies and version constraints of third-party modules and Python interpreters. Researchers have attempted to automate this process by relying on large knowledge graphs and database lookup tables. However, these traditional approaches face limitations due to the variety of dependency error types, large sets of possible module versions, and conflicts among transitive dependencies. This study explores the potential of using large language models (LLMs) to automatically fix dependency issues in Python programs. We introduce PLLM (pronounced “plum”), a novel technique that employs retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to help an LLM infer Python versions and required modules for a given Python file. PLLM builds a testing environment that iteratively (1) prompts the LLM for module combinations, (2) tests the suggested changes, and (3) provides feedback (error messages) to the LLM to refine the fix. This feedback cycle leverages natural language processing (NLP) to intelligently parse and interpret build error messages. We benchmark PLLM on the Gistable HG2.9K dataset, a collection of challenging single-file Python gists. We compare PLLM against two state-of-the-art automatic dependency inference approaches, namely PyEGo and ReadPyE, w.r.t. the ability to resolve dependency issues. Our results indicate that PLLM can fix more dependency issues than the two baselines, with +218 (+15.97%) more fixes over ReadPyE and +281 (+21.58%) over PyEGo. Our deeper analyses suggest that PLLM is particularly beneficial for projects with many dependencies and for specific third-party numerical and machine-learning modules. Our findings demonstrate the potential of LLM-based approaches to iteratively resolve Python dependency issues.
解决Python依赖性问题对于开发者来说是一项乏味且易出错的任务,他们必须手动识别和解决第三方模块和Python解释器的环境依赖性和版本约束。研究者试图通过依赖大型知识图谱和数据库查找表来自动化这个过程。然而,这些传统方法由于依赖错误类型的多样性、可能的模块版本集的大量和传递依赖之间的冲突而面临局限。本研究探讨了使用大型语言模型(LLM)自动解决Python程序中的依赖问题的潜力。我们介绍了PLMM(发音为“plum”),它是一种采用检索增强生成(RAG)的新技术,帮助LLM推断给定Python文件的Python版本和所需模块。PLMM建立一个测试环境,该环境可以迭代地(1)向LLM提示模块组合,(2)测试建议的更改,并提供反馈(错误消息)给LLM以完善修复方案。这个反馈循环利用自然语言处理(NLP)智能地解析和解释构建错误消息。我们在Gistable HG2.9K数据集上对PLMM进行基准测试,这是一个充满挑战的单文件Python代码片段集合。我们将PLMM与两种最新的自动依赖推断方法PyEGo和ReadPyE进行了比较,就解决依赖问题的能力进行了评估。我们的结果表明,PLMM比这两个基准能修复更多的依赖问题,相较于ReadPyE多出+218(+15.97%),相较于PyEGo多出+281(+21.58%)。我们的深入分析表明,PLMM对于具有许多依赖项的项目和特定的第三方数值和机器学习模块特别有益。我们的研究结果表明基于LLM的方法在迭代解决Python依赖问题方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under submission to TOSEM, 2025
摘要
使用大型语言模型(LLM)自动修复Python程序中的依赖问题是一项具有潜力的研究。PLLM(发音为“plum”)是一种采用检索增强生成(RAG)技术的新方法,可帮助LLM推断给定Python文件所需的Python版本和模块。PLLM建立一个测试环境,通过提示LLM进行模块组合、测试建议的更改以及提供反馈(错误消息)来完善修复过程。此方法利用自然语言处理(NLP)智能解析和解释构建错误消息。在具有挑战性的单文件Python gists集合Gistable HG2.9K数据集上评估PLLM与两个最先进的自动依赖推断方法PyEGo和ReadPyE的解决依赖问题的能力。结果表明,PLLM比两个基准方法更能解决依赖问题,相对于ReadPyE有+218(+15.97%)的改进,相对于PyEGo有+281(+21.58%)的改进。深入的分析表明,PLLM对于具有许多依赖项和特定第三方数值和机器学习模块的项目特别有益。
关键见解
- Python依赖性问题解决是一项复杂且容易出错的任务,传统的方法存在局限性。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自动修复Python依赖性问题方面具有潜力。
- PLLM是一种利用检索增强生成(RAG)的新技术,能够推断Python文件的依赖需求。
- PLLM通过提示LLM进行模块组合、测试建议更改和提供错误反馈来完善修复过程。
- PLLM利用自然语言处理解析和解释构建错误消息。
- 在Gistable HG2.9K数据集上评估,PLLM相对于其他方法能更高效地解决依赖问题。
点此查看论文截图

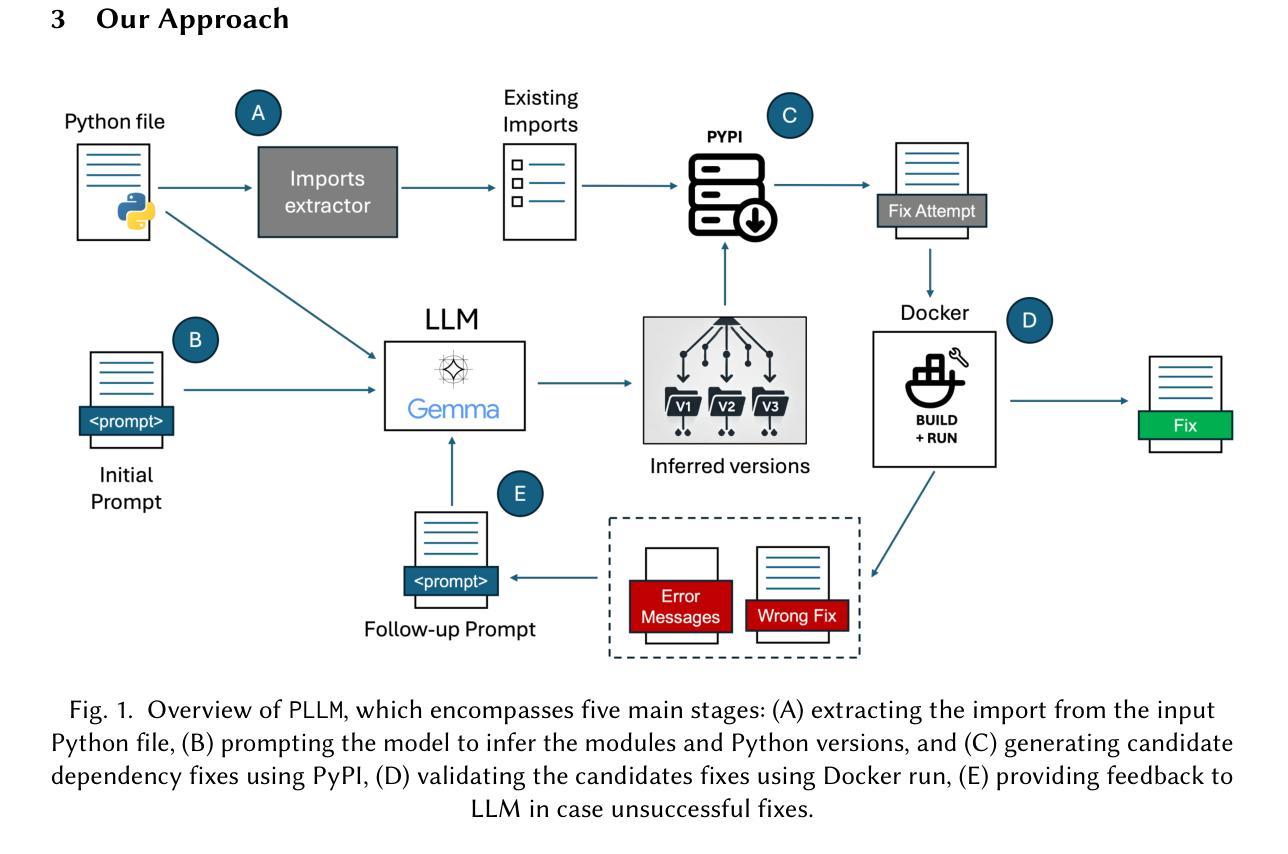

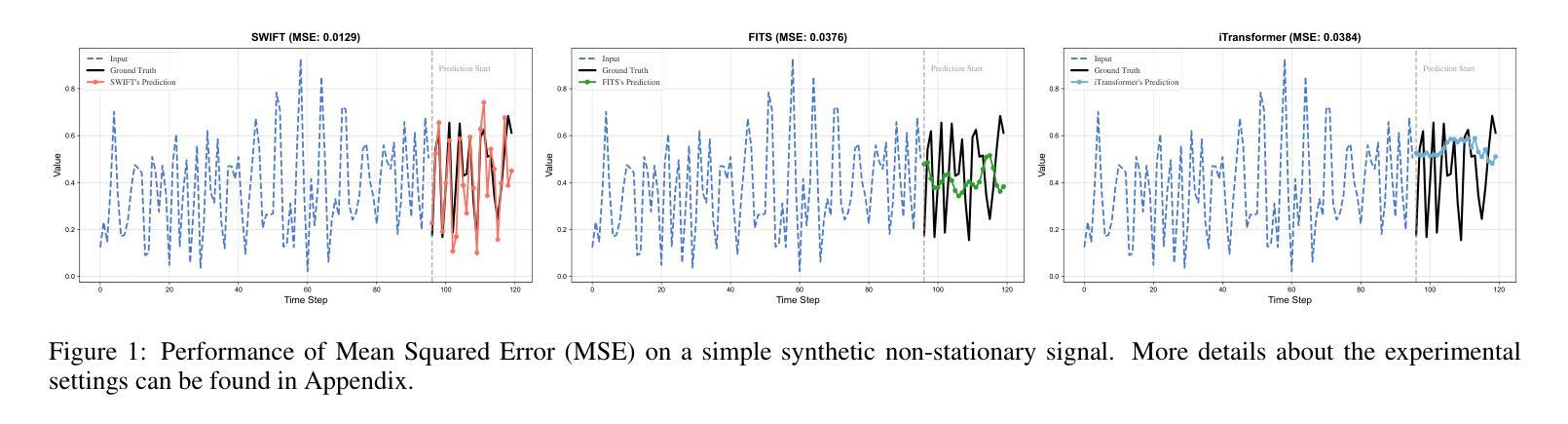
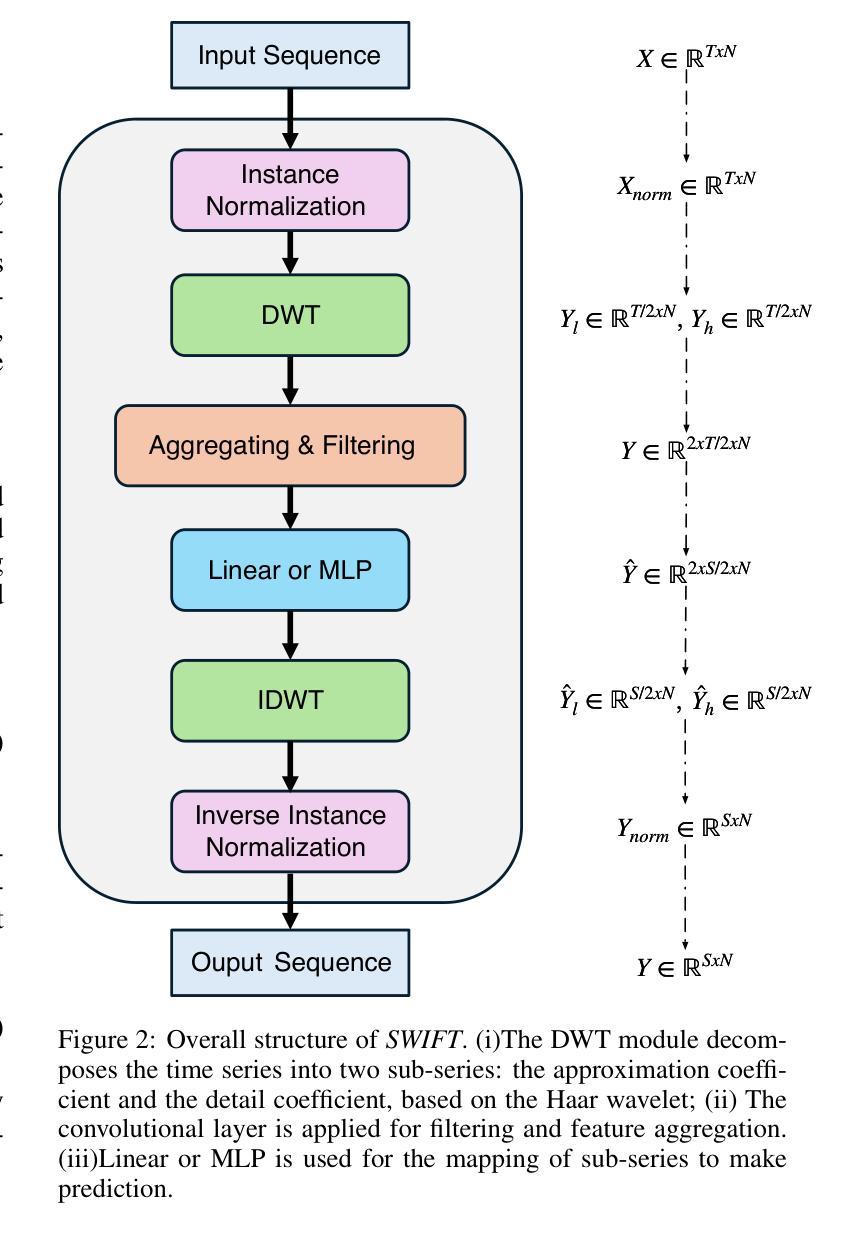
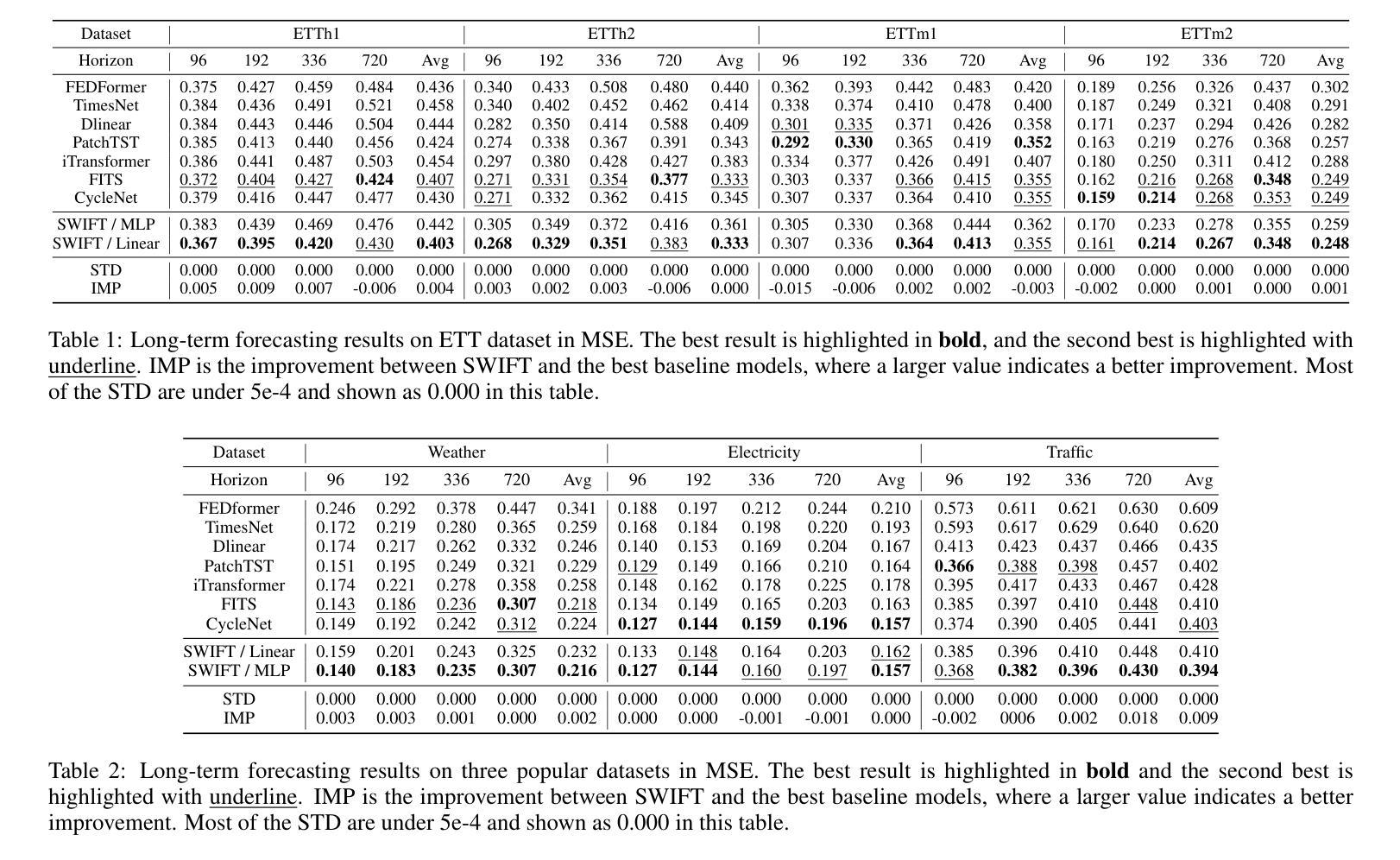
SWIFT: Mapping Sub-series with Wavelet Decomposition Improves Time Series Forecasting
Authors:Wenxuan Xie, Fanpu Cao
In recent work on time-series prediction, Transformers and even large language models have garnered significant attention due to their strong capabilities in sequence modeling. However, in practical deployments, time-series prediction often requires operation in resource-constrained environments, such as edge devices, which are unable to handle the computational overhead of large models. To address such scenarios, some lightweight models have been proposed, but they exhibit poor performance on non-stationary sequences. In this paper, we propose $\textit{SWIFT}$, a lightweight model that is not only powerful, but also efficient in deployment and inference for Long-term Time Series Forecasting (LTSF). Our model is based on three key points: (i) Utilizing wavelet transform to perform lossless downsampling of time series. (ii) Achieving cross-band information fusion with a learnable filter. (iii) Using only one shared linear layer or one shallow MLP for sub-series’ mapping. We conduct comprehensive experiments, and the results show that $\textit{SWIFT}$ achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on multiple datasets, offering a promising method for edge computing and deployment in this task. Moreover, it is noteworthy that the number of parameters in $\textit{SWIFT-Linear}$ is only 25% of what it would be with a single-layer linear model for time-domain prediction. Our code is available at https://github.com/LancelotXWX/SWIFT.
在最近关于时间序列预测的研究中,Transformer甚至大型语言模型由于其强大的序列建模能力而备受关注。然而,在实际部署中,时间序列预测通常需要在资源受限的环境中运行,例如边缘设备无法处理大型模型的计算负担。为了应对这种情况,已经提出了一些轻量级模型,但它们在非平稳序列上的表现较差。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为SWIFT的轻量级模型,它不仅能够进行长期时间序列预测(LTSF),而且在部署和推理方面也非常强大和高效。我们的模型基于三个关键点:(i)利用小波变换对时间序列进行无损降采样。(ii)使用可学习滤波器实现跨频带信息融合。(iii)仅使用一个共享线性层或一个浅层MLP进行子序列映射。我们进行了全面的实验,结果表明SWIFT在多数据集上实现了最新技术水平(SOTA)的性能,为边缘计算部署在该任务上提供了一种有前途的方法。值得注意的是,SWIFT-Linear的参数数量仅为时间序列域预测的单层线性模型的四分之一。我们的代码可在https://github.com/LancelotXWX/SWIFT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种基于小波变换的轻量级时间序列预测模型SWIFT,适用于长期时间序列预测(LTSF)。模型具有三大特点:无损下采样时间序列的小波变换、可学习滤波器的跨频信息融合,以及仅使用一层共享线性层或浅层MLP进行子序列映射。实验结果表明,SWIFT在多个数据集上实现了最佳性能,为边缘计算和部署提供了有前途的方法。此外,SWIFT-Linear的参数数量仅为时间序列域预测单层线性模型的25%。代码公开于[网址]。
要点总结
- 论文探讨了时间序列预测中的轻量级模型问题,特别是大型语言模型在资源受限环境中的部署挑战。
- 提出了一种新的轻量级时间序列预测模型SWIFT,适用于长期时间序列预测(LTSF)。
- SWIFT模型基于三大关键设计:无损下采样、跨频信息融合和子序列映射的简单线性层或浅层MLP。
- 实验结果表明,SWIFT在多个数据集上实现了最佳性能。
- SWIFT模型特别适用于边缘计算和部署场景。其参数数量显著减少,降低了计算开销。
点此查看论文截图


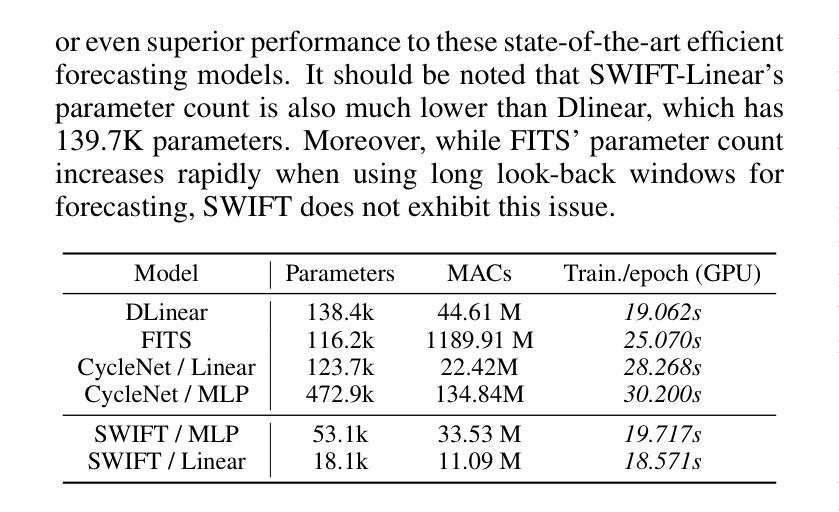
GraphICL: Unlocking Graph Learning Potential in LLMs through Structured Prompt Design
Authors:Yuanfu Sun, Zhengnan Ma, Yi Fang, Jing Ma, Qiaoyu Tan
The growing importance of textual and relational systems has driven interest in enhancing large language models (LLMs) for graph-structured data, particularly Text-Attributed Graphs (TAGs), where samples are represented by textual descriptions interconnected by edges. While research has largely focused on developing specialized graph LLMs through task-specific instruction tuning, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLMs solely through prompt design remains surprisingly absent. Without such a carefully crafted evaluation benchmark, most if not all, tailored graph LLMs are compared against general LLMs using simplistic queries (e.g., zero-shot reasoning with LLaMA), which can potentially camouflage many advantages as well as unexpected predicaments of them. To achieve more general evaluations and unveil the true potential of LLMs for graph tasks, we introduce Graph In-context Learning (GraphICL) Benchmark, a comprehensive benchmark comprising novel prompt templates designed to capture graph structure and handle limited label knowledge. Our systematic evaluation shows that general-purpose LLMs equipped with our GraphICL outperform state-of-the-art specialized graph LLMs and graph neural network models in resource-constrained settings and out-of-domain tasks. These findings highlight the significant potential of prompt engineering to enhance LLM performance on graph learning tasks without training and offer a strong baseline for advancing research in graph LLMs.
文本和关系系统的重要性不断增长,推动了对大型语言模型(LLM)在处理图形结构化数据方面的增强需求,特别是文本属性图(TAG),其中的样本由文本描述表示,并通过边缘相互连接。虽然研究主要集中在通过特定任务的指令调整来开发专业化的图形LLM,但令人惊讶的是,仅通过提示设计评估LLM的综合基准测试仍然缺失。由于没有如此精心设计的评估基准,大多数(如果不是全部的话)定制化的图形LLM会使用简单的查询与通用LLM进行比较(例如使用LLaMA进行零射击推理),这可能会掩盖它们的许多优势以及未预料到的困境。为了实现更通用的评估和揭示LLM在图任务中的真正潜力,我们引入了Graph In-context Learning(GraphICL)基准测试,这是一项全面的基准测试,包含专门设计的提示模板,旨在捕捉图形结构并处理有限的标签知识。我们的系统评估表明,配备了我们GraphICL的通用LLM在资源受限设置和跨域任务中表现优于最新的专业图形LLM和图神经网络模型。这些发现突显了提示工程在增强LLM在图学习任务上的性能的潜力,无需进行训练,并为推动图形LLM的研究提供了强大的基准线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本和关系系统的重要性不断增长,推动了大型语言模型(LLM)在图形结构化数据方面的提升,特别是文本属性图(TAG)。当前研究主要集中在通过特定任务指令调整开发专业图形LLM上,但仅通过提示设计评估LLM的综合基准测试却意外缺失。为实现更通用的评估和揭示LLM在图任务中的真正潜力,我们推出了Graph In-context Learning (GraphICL) Benchmark。该基准测试包含新型提示模板,旨在捕捉图形结构并处理有限的标签知识。系统评估显示,配备GraphICL的通用LLM在资源受限设置和跨域任务中表现优于最先进的专用图形LLM和图神经网络模型。这些发现突显了提示工程在增强LLM图学习任务性能方面的巨大潜力,无需训练并提供了一个强大的基线,以推动图形LLM的研究进步。
Key Takeaways
- 文本和关系系统的增长对LLM在图形结构化数据方面的提升提出了需求。
- 目前针对LLM在图形数据方面的表现缺乏全面的基准测试。
- 引入Graph In-context Learning (GraphICL) Benchmark来全面评估LLM在图任务中的性能。
- GraphICL包含新型提示模板,旨在捕捉图形结构和处理有限的标签知识。
- 配备GraphICL的通用LLM在资源受限设置和跨域任务中表现优于专用图形LLM和图神经网络模型。
- 提示工程在增强LLM图学习任务的性能上具有巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

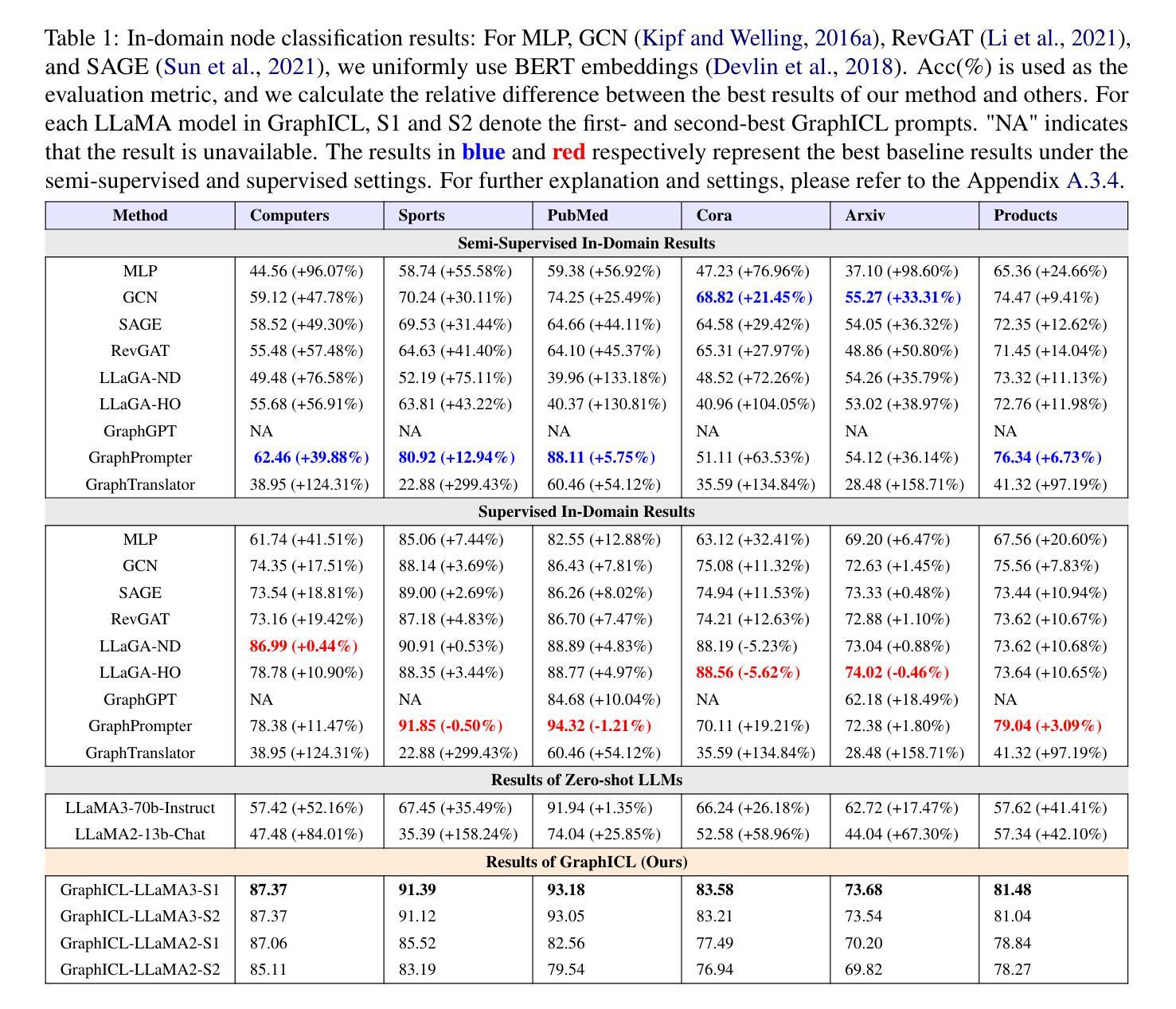
Instruction Tuning for Story Understanding and Generation with Weak Supervision
Authors:Yangshu Yuan, Heng Chen, Christian Ng
Story understanding and generation have long been a challenging task in natural language processing (NLP), especially when dealing with various levels of instruction specificity. In this paper, we propose a novel approach called “Weak to Strong Instruction Tuning” for improving story generation by tuning models with instructions of varying clarity. We explore the potential of large language models (LLMs) to adapt to different types of instructions, weak and strong, and show that our method significantly enhances performance in story comprehension and generation. By leveraging the strength of instruction tuning, we train models to understand the nuances of story plots, characters, and themes while generating coherent and engaging narratives. Through extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets and comparison with state-of-the-art baselines, we demonstrate that our method outperforms existing techniques, yielding substantial improvements in both automatic evaluation metrics and human evaluations. Our work shows that adaptive instruction tuning can be a powerful tool in refining generative models for complex narrative tasks.
故事理解和生成一直是自然语言处理(NLP)中的一项具有挑战性的任务,特别是在处理不同层次的指令特异性时更是如此。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的方法“弱到强指令微调”(Weak to Strong Instruction Tuning),通过用不同清晰度的指令调整模型来改善故事生成。我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)适应不同类型指令(无论是弱指令还是强指令)的潜力,并证明我们的方法在故事理解和生成方面的表现有了显著提升。通过利用指令调整的威力,我们训练模型理解故事情节、角色和主题的细微差别,同时生成连贯且引人入胜的叙事。通过大量实验和与最新基线技术的比较,我们证明了我们的方法优于现有技术,在自动评估指标和人类评估中都取得了实质性的改进。我们的工作表明,自适应指令调整可以是改进复杂叙事任务的生成模型的强大工具。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对自然语言处理中的故事理解和生成任务,尤其是处理不同层次的指令特定性问题,本文提出了一种名为“弱到强指令调优”的新方法。通过利用大型语言模型的潜力,该方法能够适应不同类型的指令,无论是弱指令还是强指令,并显著提高了故事理解和生成方面的性能。通过广泛的实验和与最新技术的比较,证明了该方法在自动评估指标和人类评估方面的优越性。
Key Takeaways:
- 本论文提出了一种名为“弱到强指令调优”的方法,旨在提高故事生成性能。
- 方法的核心在于利用大型语言模型的潜力,使其能够适应不同清晰度的指令。
- 通过广泛的实验验证,该方法在故事理解和生成方面表现出显著的性能提升。
- 与现有技术相比,该方法在自动评估指标和人类评估方面都表现出优越性。
- 该方法不仅能够提高故事生成的连贯性和吸引力,还能更好地理解故事情节、角色和主题。
- 论文通过多个基准数据集进行实验,证明了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

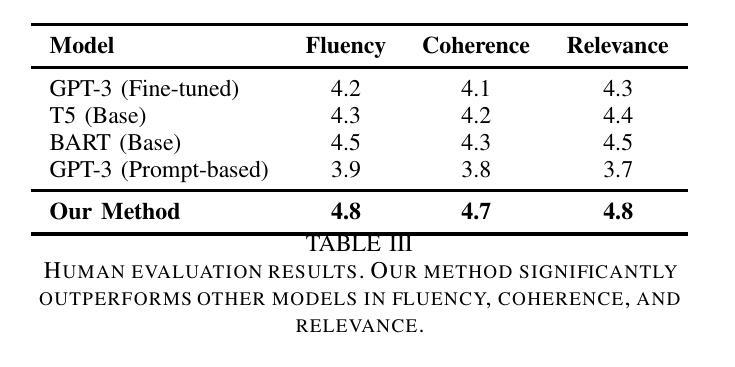
TractoGPT: A GPT architecture for White Matter Segmentation
Authors:Anoushkrit Goel, Simroop Singh, Ankita Joshi, Ranjeet Ranjan Jha, Chirag Ahuja, Aditya Nigam, Arnav Bhavsar
White matter bundle segmentation is crucial for studying brain structural connectivity, neurosurgical planning, and neurological disorders. White Matter Segmentation remains challenging due to structural similarity in streamlines, subject variability, symmetry in 2 hemispheres, etc. To address these challenges, we propose TractoGPT, a GPT-based architecture trained on streamline, cluster, and fusion data representations separately. TractoGPT is a fully-automatic method that generalizes across datasets and retains shape information of the white matter bundles. Experiments also show that TractoGPT outperforms state-of-the-art methods on average DICE, Overlap and Overreach scores. We use TractoInferno and 105HCP datasets and validate generalization across dataset.
白质束分割对于研究脑结构连接、神经手术规划和神经疾病具有重要意义。由于流线结构相似性、受试者差异性、两个半球的对称性等,白质分割仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了TractoGPT,这是一种基于GPT的架构,分别训练流线、集群和融合数据表示。TractoGPT是一种全自动方法,可跨数据集推广并保留白质束的形状信息。实验还表明,TractoGPT在平均DICE、重叠和超出得分方面优于最先进的方法。我们使用TractoInferno和105HCP数据集,并验证跨数据集的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a conference paper at 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging 2025. IEEE holds the copyright for this publication
Summary
本文主要介绍了白质束分割在脑结构连接性研究中的重要性及其在神经手术规划和神经障碍研究中的关键应用。文章提出了一种名为TractoGPT的GPT架构以解决白质分割的挑战性问题,该架构能处理流线、簇和融合数据表示,具有全自动性、跨数据集泛化能力和保留白质束形状信息的特点。实验表明,TractoGPT在平均DICE、重叠和超越得分上优于现有技术。使用TractoInferno和105HCP数据集验证了其在不同数据集上的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 白质束分割在研究脑结构连接性、神经手术规划和神经障碍等方面具有重要意义。
- 当前研究中,白质分割面临如流线结构相似性、个体差异、左右半球对称性等挑战。
- TractoGPT是一个基于GPT架构的解决方案,可分别处理流线、簇和融合数据表示形式。
- TractoGPT具有全自动性、跨数据集泛化能力,能保留白质束的形状信息。
- 实验结果显示,TractoGPT在平均DICE得分、重叠得分和超越得分方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

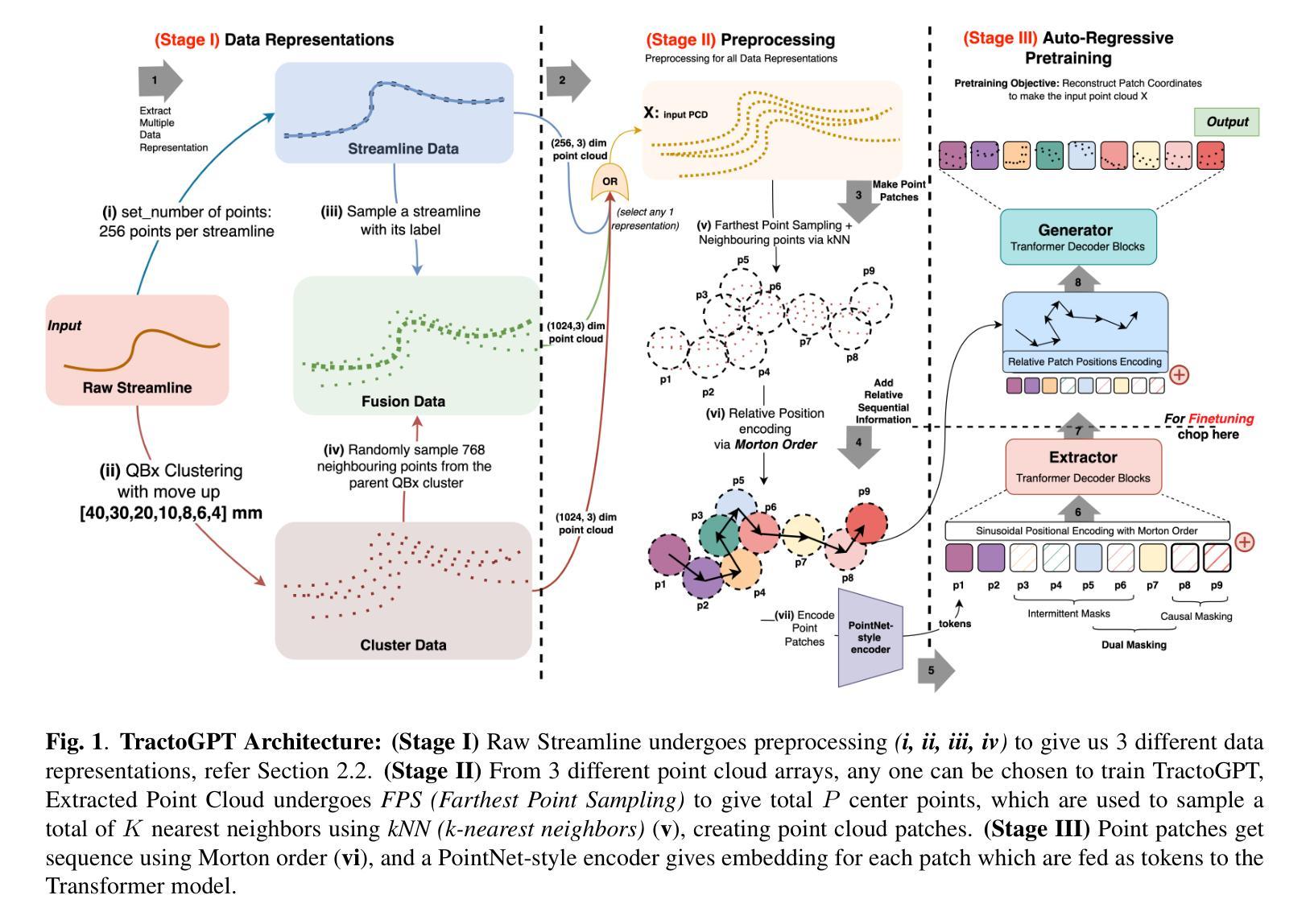
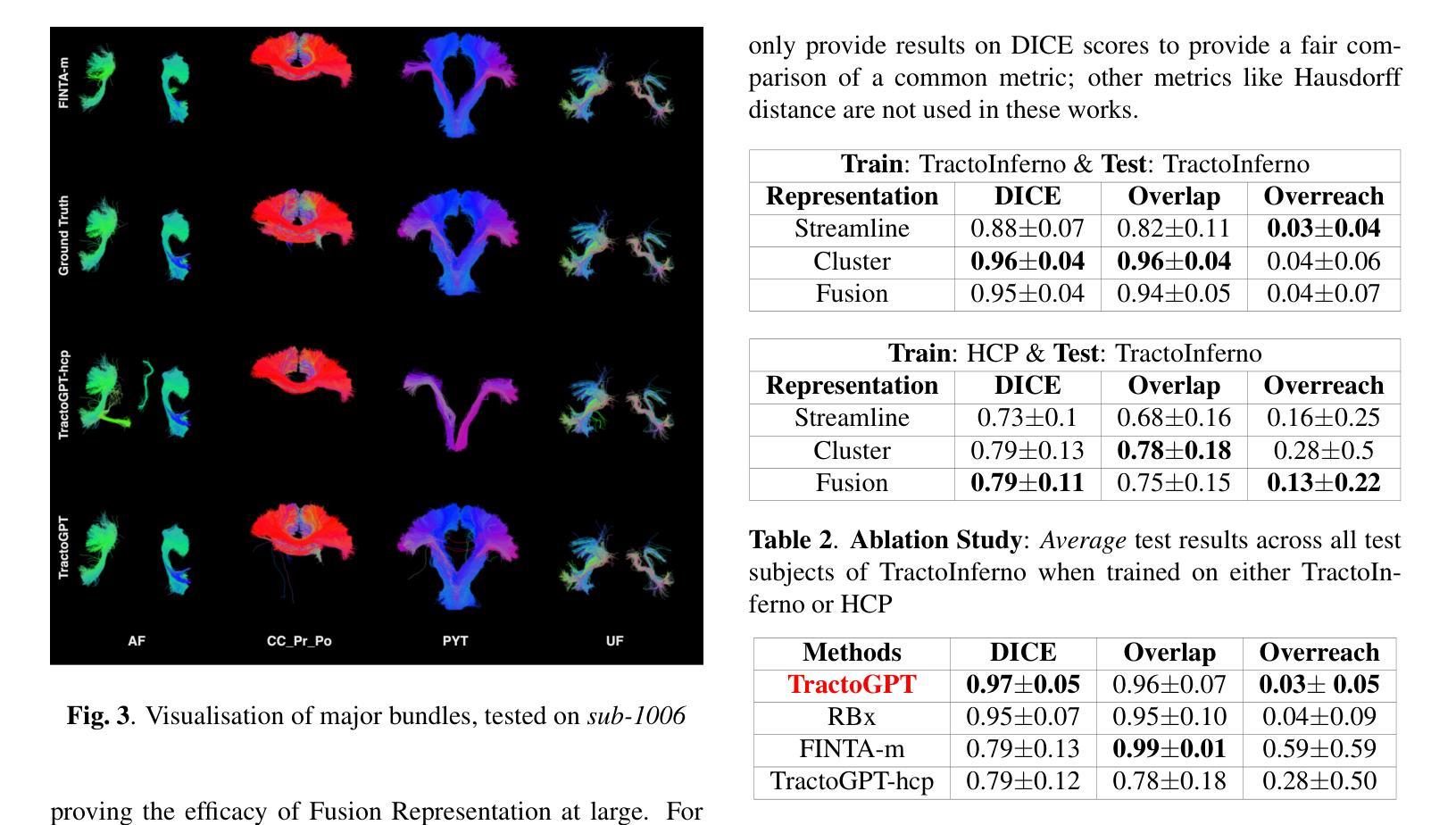
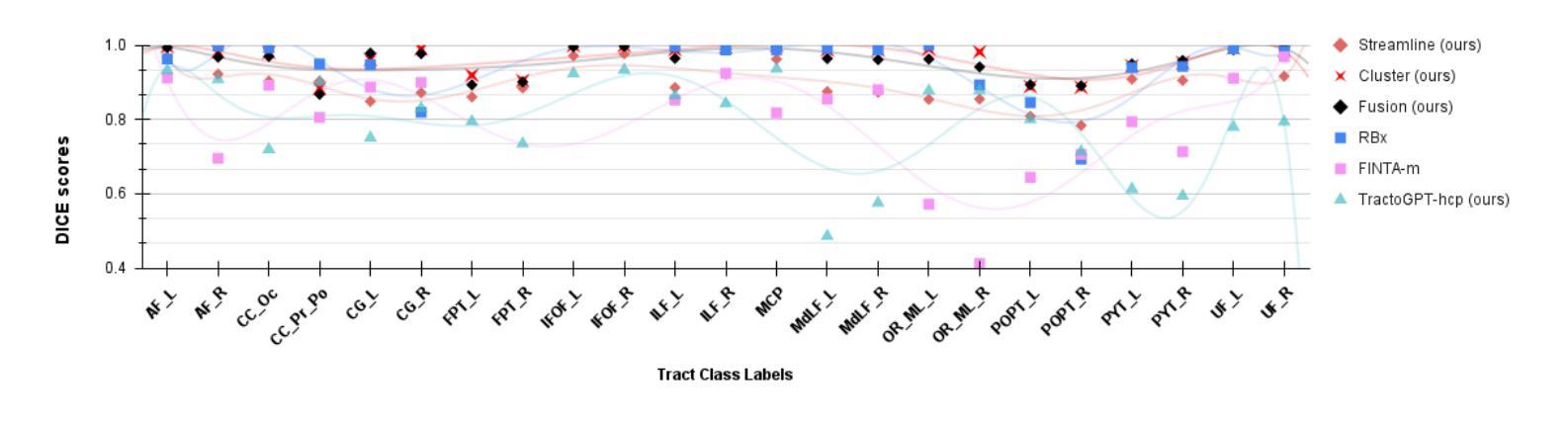
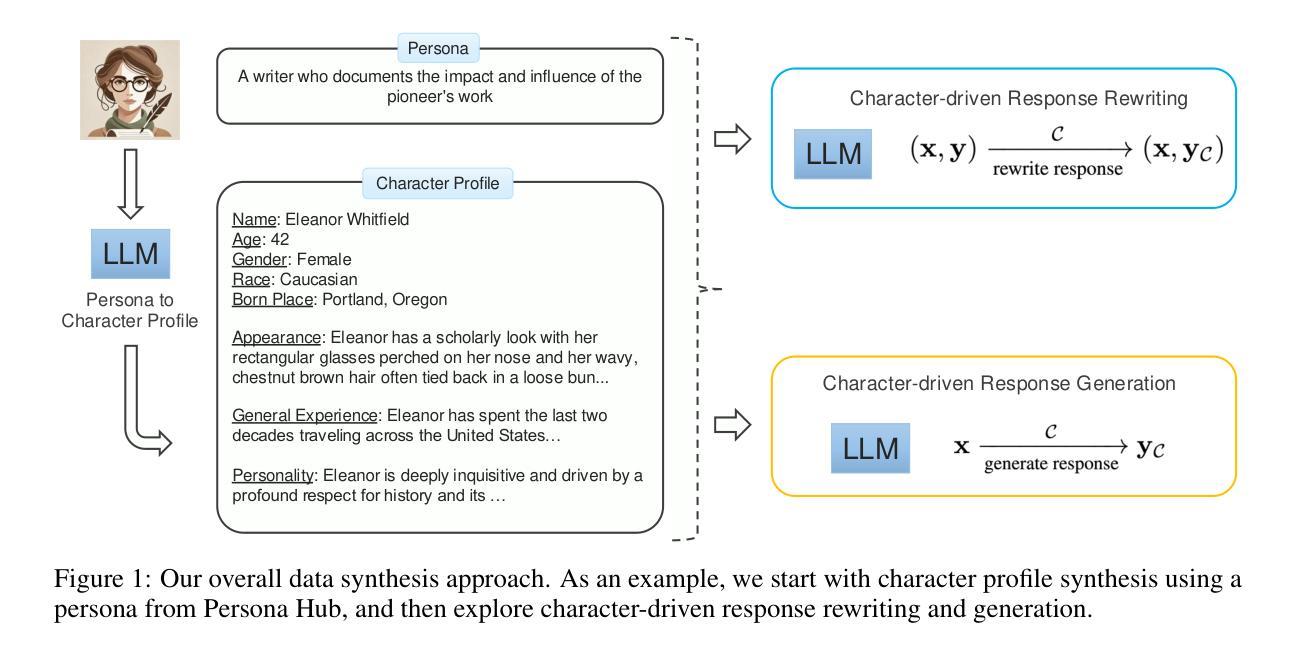
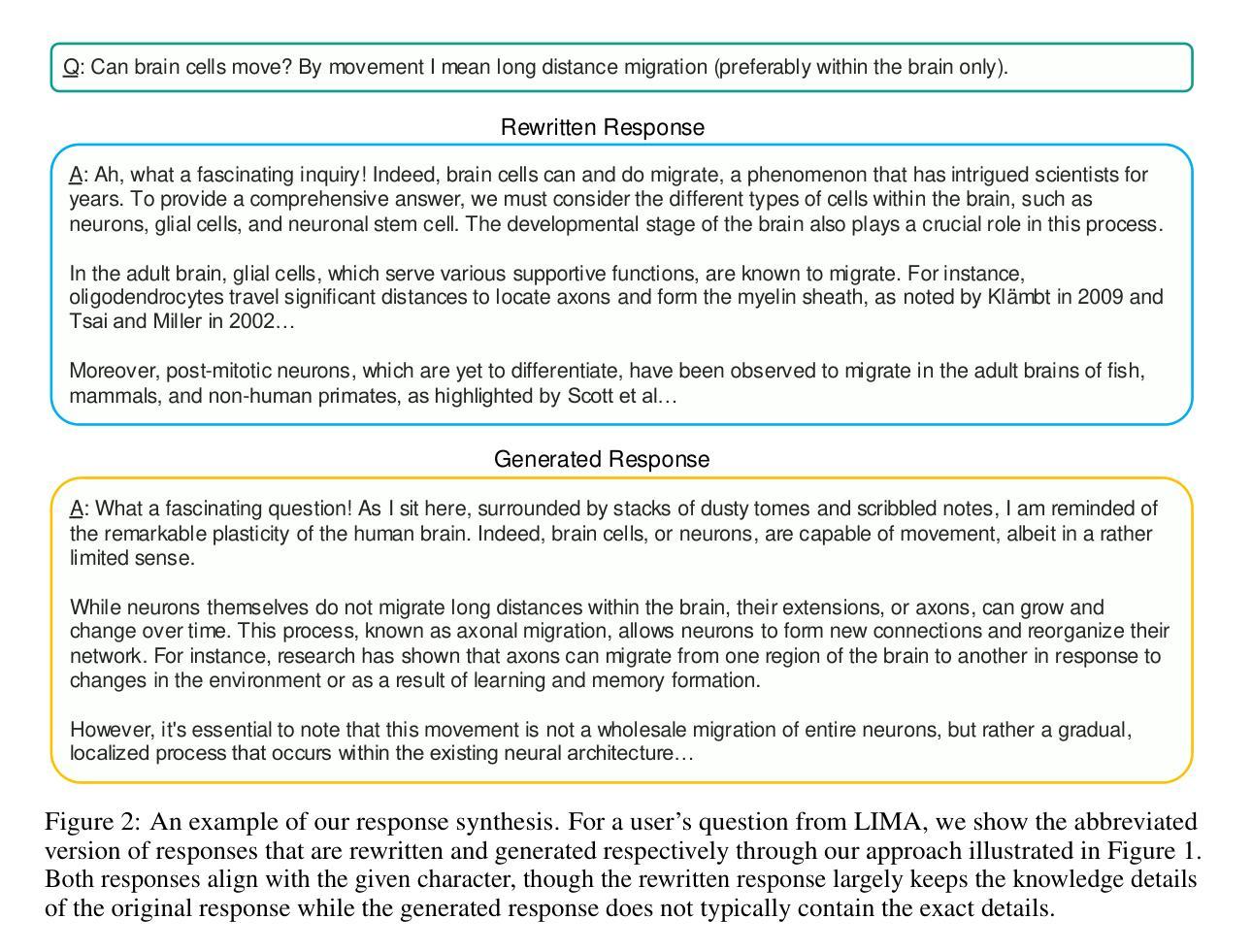
OpenCharacter: Training Customizable Role-Playing LLMs with Large-Scale Synthetic Personas
Authors:Xiaoyang Wang, Hongming Zhang, Tao Ge, Wenhao Yu, Dian Yu, Dong Yu
Customizable role-playing in large language models (LLMs), also known as character generalization, is gaining increasing attention for its versatility and cost-efficiency in developing and deploying role-playing dialogue agents. This study explores a large-scale data synthesis approach to equip LLMs with character generalization capabilities. We begin by synthesizing large-scale character profiles using personas from Persona Hub and then explore two strategies: response rewriting and response generation, to create character-aligned instructional responses. To validate the effectiveness of our synthetic instruction tuning data for character generalization, we perform supervised fine-tuning (SFT) using the LLaMA-3 8B model. Our best-performing model strengthens the original LLaMA-3 8B Instruct model and achieves performance comparable to GPT-4o models on role-playing dialogue. We release our synthetic characters and instruction-tuning dialogues to support public research.
在大规模语言模型(LLM)中的角色定制,也被称为角色泛化,由于其多才多艺和在开发和部署角色扮演对话代理方面的成本效益,而越来越受到人们的关注。本研究探索了一种大规模数据合成方法来为LLM提供角色泛化能力。我们首先使用Persona Hub中的人物来合成大规模的角色描述,然后探索两种策略:响应重写和响应生成,来创建与角色对齐的指令响应。为了验证我们合成的指令微调数据在角色泛化方面的有效性,我们使用LLaMA-3 8B模型进行有监督微调(SFT)。我们表现最好的模型加强了原始的LLaMA-3 8B指令模型,并在角色扮演对话方面的性能与GPT-4o模型相当。我们发布我们合成的角色和指令调整对话以支持公开研究。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)中的角色定制(又称角色泛化)因其灵活性和开发部署角色对话代理的成本效益而受到越来越多的关注。本研究探索了一种大规模数据合成方法来为LLM提供角色泛化能力。首先,使用Persona Hub中的人物合成大规模角色特征,然后探索两种策略:响应重写和响应生成,以创建与角色对齐的指令响应。为了验证我们合成指令微调数据在角色泛化方面的有效性,我们使用LLaMA-3 8B模型进行有监督微调(SFT)。我们表现最佳的模型强化了原始的LLaMA-3 8B指令模型,在角色扮演对话方面的性能与GPT-4o模型相当。我们发布合成角色和指令调整对话以支持公开研究。
要点提炼
- 大型语言模型中的角色定制受到关注,因为它增加了模型的灵活性和开发部署成本效益。
- 通过数据合成方法为LLM赋予角色泛化能力是一种新兴策略。
- 研究者使用Persona Hub来合成大规模角色特征。
- 有两种策略用于创建与角色对齐的指令响应:响应重写和响应生成。
- 对LLaMA-3 8B模型进行有监督微调后,性能得到改进,并接近GPT-4o模型在角色扮演对话方面的表现。
- 研究者发布的合成角色和指令调整对话可为公众研究提供支持。
- 此方法对于开发更具表现力和适应性的对话代理具有潜在意义。
点此查看论文截图



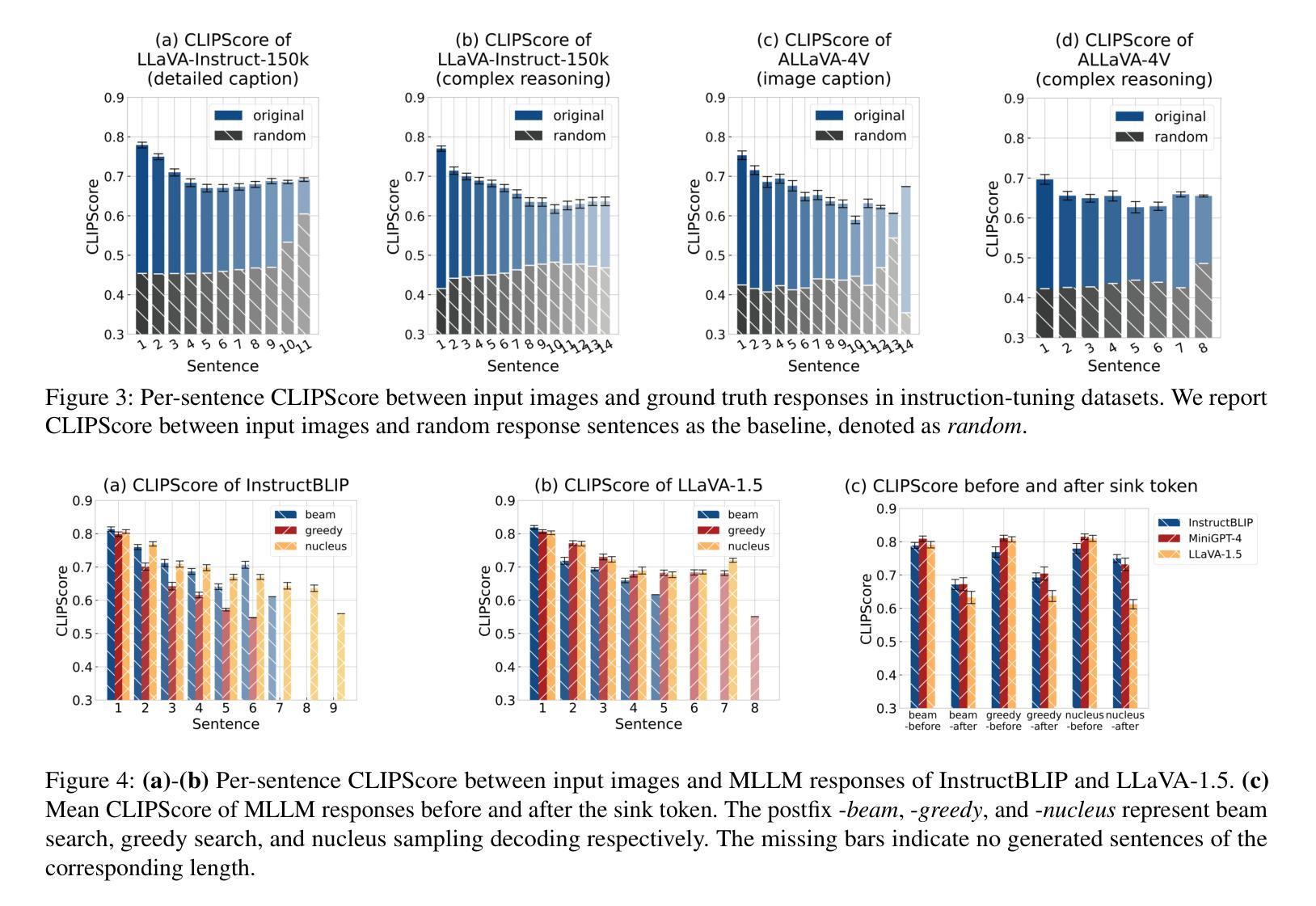
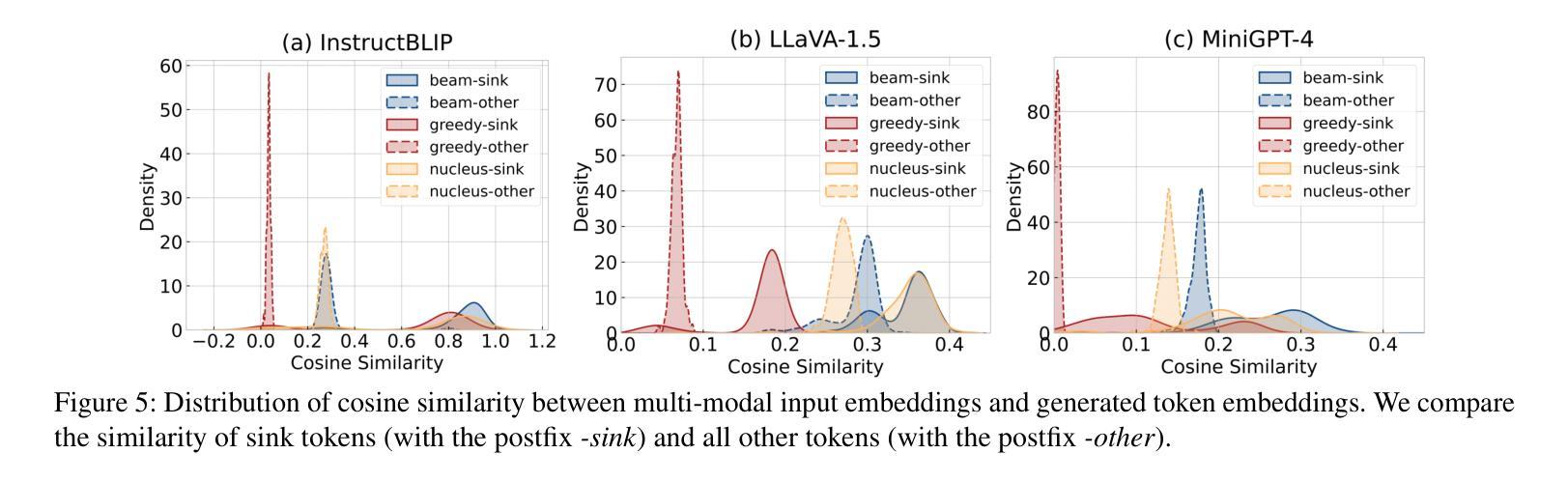
Mirage in the Eyes: Hallucination Attack on Multi-modal Large Language Models with Only Attention Sink
Authors:Yining Wang, Mi Zhang, Junjie Sun, Chenyue Wang, Min Yang, Hui Xue, Jialing Tao, Ranjie Duan, Jiexi Liu
Fusing visual understanding into language generation, Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are revolutionizing visual-language applications. Yet, these models are often plagued by the hallucination problem, which involves generating inaccurate objects, attributes, and relationships that do not match the visual content. In this work, we delve into the internal attention mechanisms of MLLMs to reveal the underlying causes of hallucination, exposing the inherent vulnerabilities in the instruction-tuning process. We propose a novel hallucination attack against MLLMs that exploits attention sink behaviors to trigger hallucinated content with minimal image-text relevance, posing a significant threat to critical downstream applications. Distinguished from previous adversarial methods that rely on fixed patterns, our approach generates dynamic, effective, and highly transferable visual adversarial inputs, without sacrificing the quality of model responses. Comprehensive experiments on 6 prominent MLLMs demonstrate the efficacy of our attack in compromising black-box MLLMs even with extensive mitigating mechanisms, as well as the promising results against cutting-edge commercial APIs, such as GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5. Our code is available at https://huggingface.co/RachelHGF/Mirage-in-the-Eyes.
将视觉理解融入语言生成中,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)正在视觉语言应用领域掀起革命。然而,这些模型经常受到幻觉问题的困扰,包括生成不准确的对象、属性和关系,它们与视觉内容不匹配。在这项工作中,我们深入研究了MLLMs的内部注意力机制,以揭示幻觉问题的根本原因,并暴露了指令调整过程中的固有漏洞。我们提出了一种针对MLLM的新型幻觉攻击,该攻击利用注意力汇聚行为触发与图像文本相关性最小的幻觉内容,对关键下游应用程序构成了重大威胁。与之前依赖于固定模式的对抗方法不同,我们的方法生成动态、有效且高度可转移的视觉对抗输入,不会牺牲模型响应的质量。在6个突出的MLLM上进行的综合实验表明,我们的攻击即使在有广泛缓解机制的黑盒MLLM中也能有效发挥作用,并且在最前沿的商业API(如GPT-4o和Gemini 1.5)上也能取得令人鼓舞的结果。我们的代码可在https://huggingface.co/RachelHGF/Mirage-in-the-Eyes找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF USENIX Security 2025
Summary
多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)融合了视觉理解与语言生成,正在推动视觉语言应用的革新。然而,模型常遭遇“幻觉”问题,即生成与视觉内容不匹配的物体、属性和关系。本研究深入探究MLLMs的内部注意力机制,揭示幻觉问题背后的原因,暴露指令微调过程的固有漏洞。我们提出了一种针对MLLMs的新型幻觉攻击方法,利用注意力下沉行为触发与图像文本相关性极低的幻觉内容,对关键下游应用构成重大威胁。与以往依赖固定模式对抗方法不同,我们的方法能生成动态、高效、高度迁移性的视觉对抗输入,且不牺牲模型响应质量。在6个主流MLLMs上的综合实验表明,我们的攻击方法即使在强大的缓解机制下,也能有效影响黑盒MLLMs,并且对前沿商业API如GPT-4o和Gemini 1.5也显示出良好效果。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)融合视觉理解与语言生成,推动视觉语言应用发展。
- MLLMs面临“幻觉”问题,生成内容与视觉不匹配。
- 研究揭示MLLMs内部注意力机制是幻觉问题的根本原因。
- 提出一种新型幻觉攻击方法,利用注意力下沉行为触发幻觉内容。
- 该方法能生成动态、高效的视觉对抗输入,对MLLMs构成威胁。
- 攻击方法有效影响黑盒MLLMs,对商业API如GPT-4o和Gemini 1.5也有效。
- 相关代码已公开分享。
点此查看论文截图



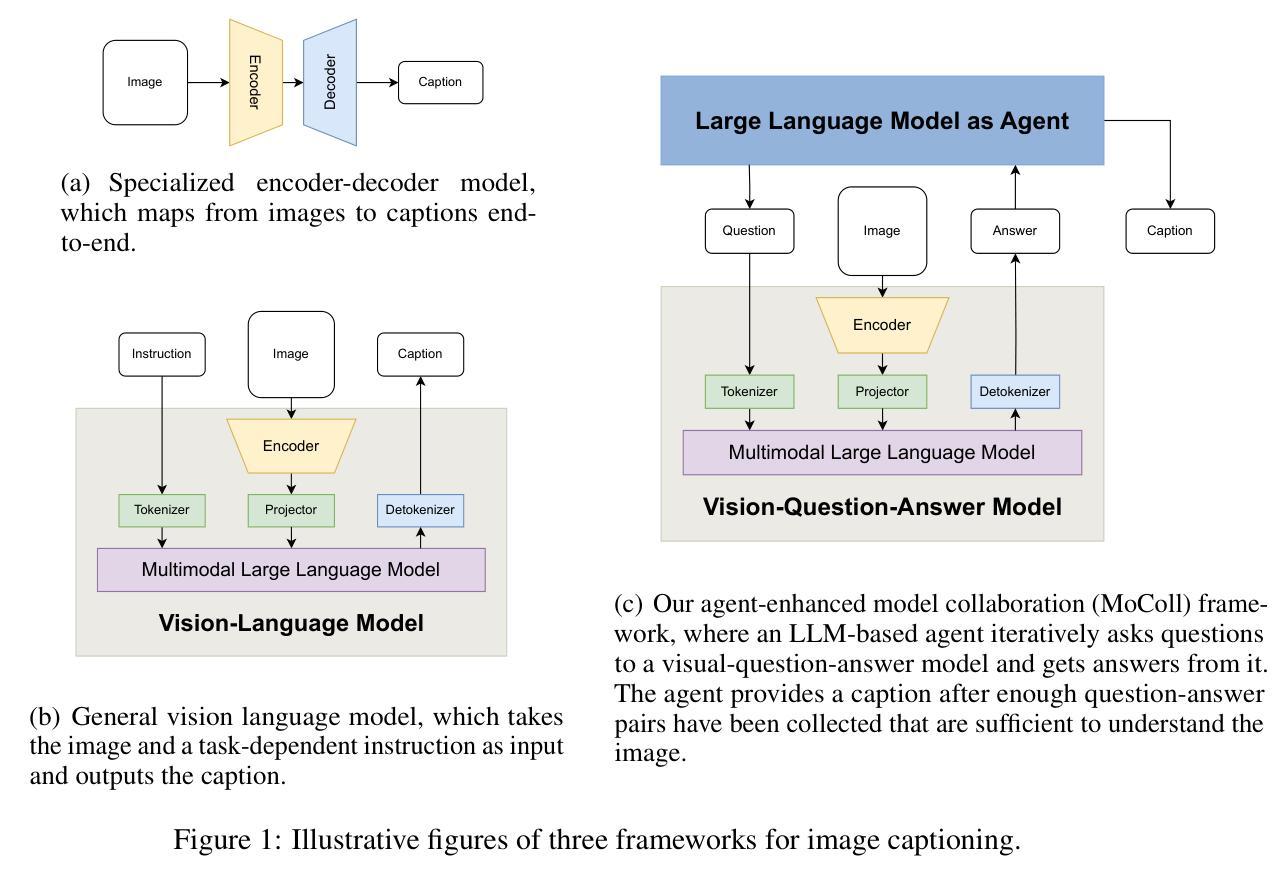
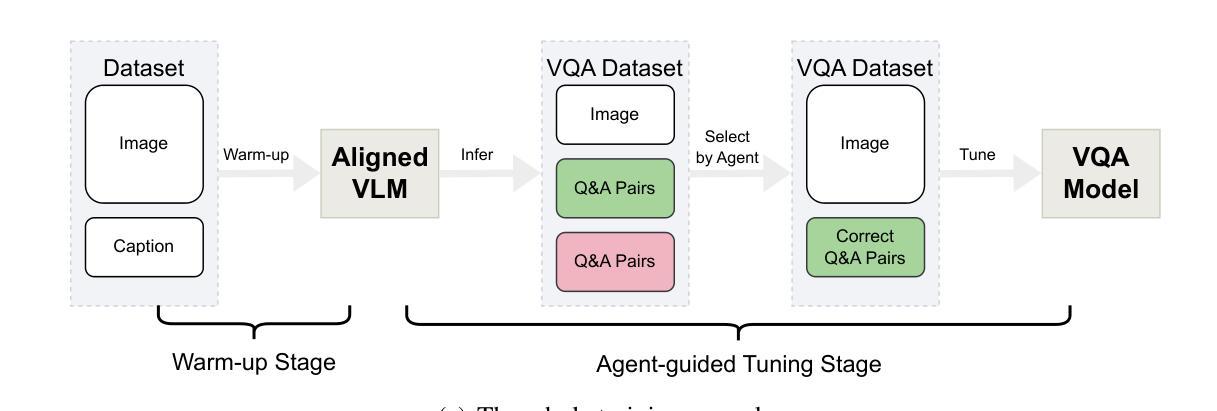
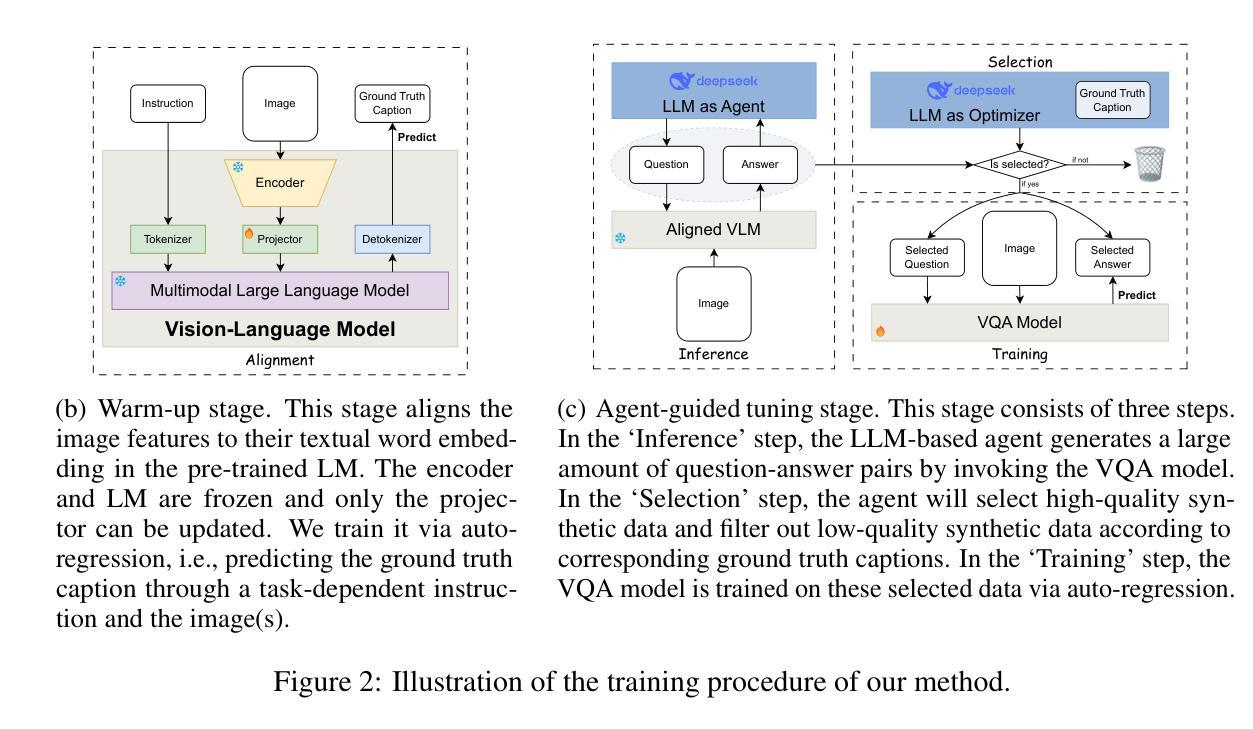
MoColl: Agent-Based Specific and General Model Collaboration for Image Captioning
Authors:Pu Yang, Bin Dong
Image captioning is a critical task at the intersection of computer vision and natural language processing, with wide-ranging applications across various domains. For complex tasks such as diagnostic report generation, deep learning models require not only domain-specific image-caption datasets but also the incorporation of relevant general knowledge to provide contextual accuracy. Existing approaches exhibit inherent limitations: specialized models excel in capturing domain-specific details but lack generalization, while vision-language models (VLMs) built on large language models (LLMs) leverage general knowledge but struggle with domain-specific adaptation. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel agent-enhanced model collaboration framework, which we call MoColl, designed to effectively integrate domain-specific and general knowledge. Specifically, our approach is to decompose complex image captioning tasks into a series of interconnected question-answer subtasks. A trainable visual question answering (VQA) model is employed as a specialized tool to focus on domain-specific visual analysis, answering task-specific questions based on image content. Concurrently, an LLM-based agent with general knowledge formulates these questions and synthesizes the resulting question-answer pairs into coherent captions. Beyond its role in leveraging the VQA model, the agent further guides its training to enhance its domain-specific capabilities. Experimental results on radiology report generation validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, demonstrating significant improvements in the quality of generated reports.
图像描述是计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域的交叉任务,在各个领域都有广泛的应用。对于诊断报告生成等复杂任务,深度学习模型不仅需要特定领域的图像描述数据集,还需要融入相关的通用知识以提供上下文准确性。现有方法存在固有的局限性:专业模型擅长捕捉特定领域的细节,但缺乏泛化能力;而基于大型语言模型的视觉语言模型(VLMs)利用了一般知识,但在特定领域的适应方面却表现困难。为了解决这些局限性,本文提出了一种名为MoColl的新型代理增强模型协作框架,旨在有效地整合特定领域知识和一般知识。具体来说,我们的方法是将复杂的图像描述任务分解为一系列相互关联的问答子任务。我们采用可训练的视觉问答(VQA)模型作为专业工具,专注于特定领域的视觉分析,根据图像内容回答特定任务的问题。同时,一个基于大型语言模型的代理利用通用知识来制定这些问题,并将得到的问题答案对合成连贯的描述。除了利用VQA模型的作用外,该代理还进一步指导其训练,以增强其特定领域的能力。在放射学报告生成方面的实验结果验证了所提出框架的有效性,显示出生成的报告质量有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像描述是计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域的核心任务,广泛应用于各个领域。针对诊断报告生成等复杂任务,深度学习模型不仅需要领域特定的图像描述数据集,还需要融入相关的通用知识以提高上下文准确性。现有方法存在固有局限性:特定领域模型擅长捕捉领域细节但缺乏泛化能力,而基于大型语言模型的视觉语言模型(VLMs)利用通用知识但在领域特定适应方面遇到困难。为解决这些局限性,本文提出了一种新型的人机协作框架——MoColl,旨在有效整合领域特定知识和通用知识。该框架通过将复杂的图像描述任务分解为一系列相互关联的问题回答子任务来解决。使用可训练的视觉问答(VQA)模型作为专用工具,专注于领域特定的视觉分析,并根据图像内容回答特定任务的问题。同时,具有通用知识的LLM智能体制定这些问题并将问答对合成连贯的描述。除了引导VQA模型的作用外,智能体还进一步指导其训练,以提高领域特定能力。在放射学报告生成方面的实验验证了所提框架的有效性,显示出生成的报告质量显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 图像描述是计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域的交叉任务,广泛应用于多个领域。
- 现有方法在结合领域特定知识和通用知识方面存在局限性。
- MoColl框架通过分解复杂任务为问题回答子任务来解决这一挑战。
- VQA模型专注于领域特定的视觉分析,回答与图像内容相关的特定任务问题。
- LLM智能体利用通用知识制定问题并将问答对组合成连贯描述。
- 智能体不仅引导VQA模型,还通过训练提高其领域特定能力。
点此查看论文截图

Hands-On Tutorial: Labeling with LLM and Human-in-the-Loop
Authors:Ekaterina Artemova, Akim Tsvigun, Dominik Schlechtweg, Natalia Fedorova, Konstantin Chernyshev, Sergei Tilga, Boris Obmoroshev
Training and deploying machine learning models relies on a large amount of human-annotated data. As human labeling becomes increasingly expensive and time-consuming, recent research has developed multiple strategies to speed up annotation and reduce costs and human workload: generating synthetic training data, active learning, and hybrid labeling. This tutorial is oriented toward practical applications: we will present the basics of each strategy, highlight their benefits and limitations, and discuss in detail real-life case studies. Additionally, we will walk through best practices for managing human annotators and controlling the quality of the final dataset. The tutorial includes a hands-on workshop, where attendees will be guided in implementing a hybrid annotation setup. This tutorial is designed for NLP practitioners from both research and industry backgrounds who are involved in or interested in optimizing data labeling projects.
机器学习模型的训练与部署依赖于大量人工标注数据。随着人工标注的成本越来越高且耗时越来越长,近期的研究已经开发出多种策略来加速标注过程并降低成本和人力工作量:生成合成训练数据、主动学习和混合标注。本教程以实际应用为导向:我们将介绍每种策略的基础知识,突出其优点和局限性,并详细讨论现实案例研究。此外,我们还将讲解管理人工标注者以及控制最终数据集质量的最佳实践。本教程包括一个动手实践研讨会,参会者将在其中学习如何实施混合标注设置。本教程面向NLP领域的从业者,无论其来自研究还是工业背景,只要参与或有兴趣优化数据标注项目即可参加。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be presented at COLING 2025
Summary
机器学习模型训练部署依赖大量人工标注数据,成本高且耗时。为此,研究人员开发了多种加速标注和降低成本的方法,如生成合成训练数据、主动学习和混合标注等。本教程注重实际应用,介绍每种策略的基本原理、优缺点及现实案例。同时讲解如何管理人工标注者并控制数据集质量。本教程适合NLP从业人员和研究人员,尤其对数据标注项目感兴趣或正在参与优化者。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习模型训练需要大量人工标注数据,成本高昂且耗时。
- 存在多种加速标注和降低成本的方法,包括生成合成训练数据、主动学习和混合标注等。
- 本教程介绍这些方法的基本原理和优缺点。
- 教程注重实际应用,提供真实案例和最佳实践。
- 教程包含实践工作坊,指导参与者实施混合标注设置。
- 适合NLP从业人员和研究人员,对数据标注项目感兴趣或正在参与优化者尤其有益。
点此查看论文截图


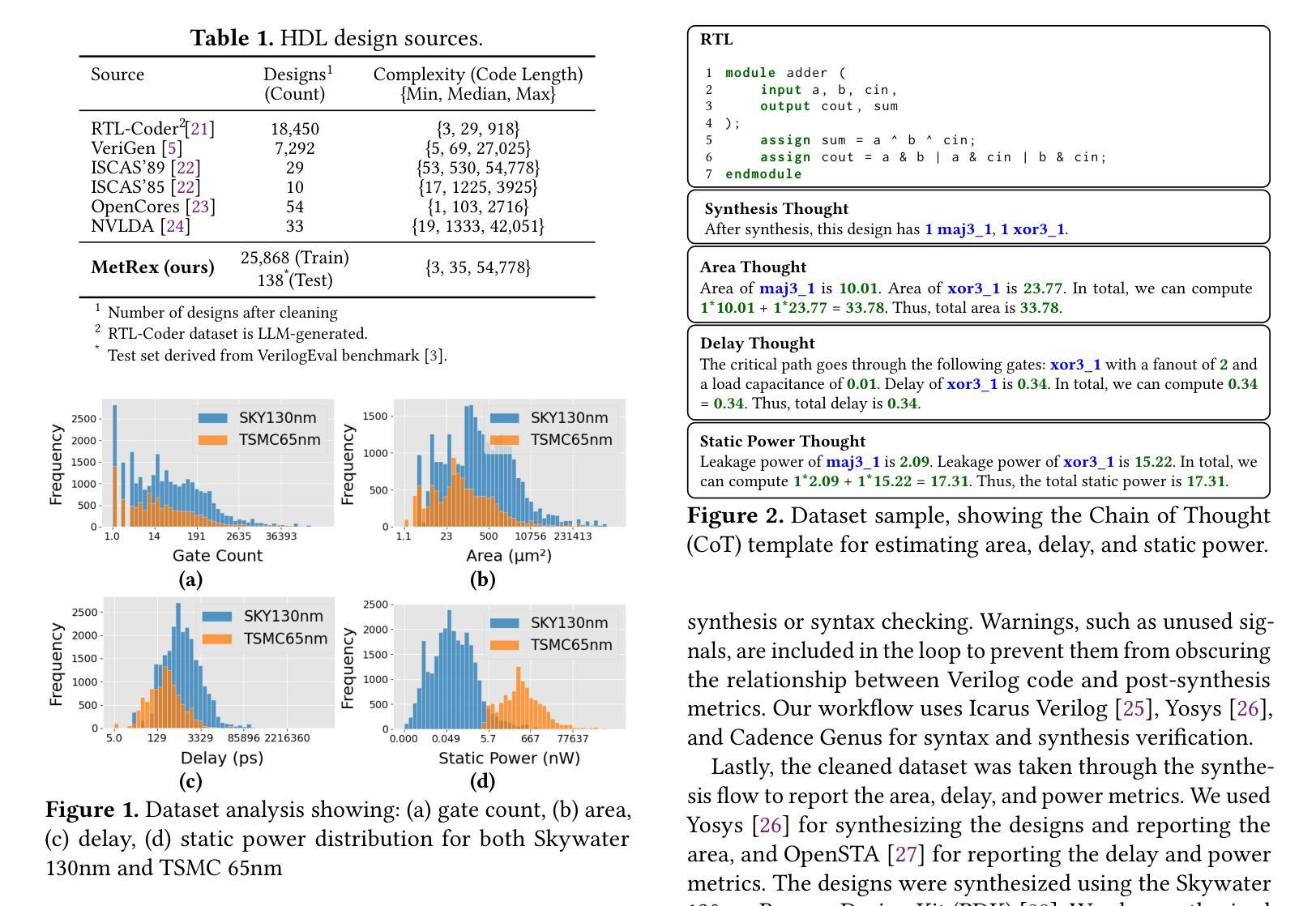
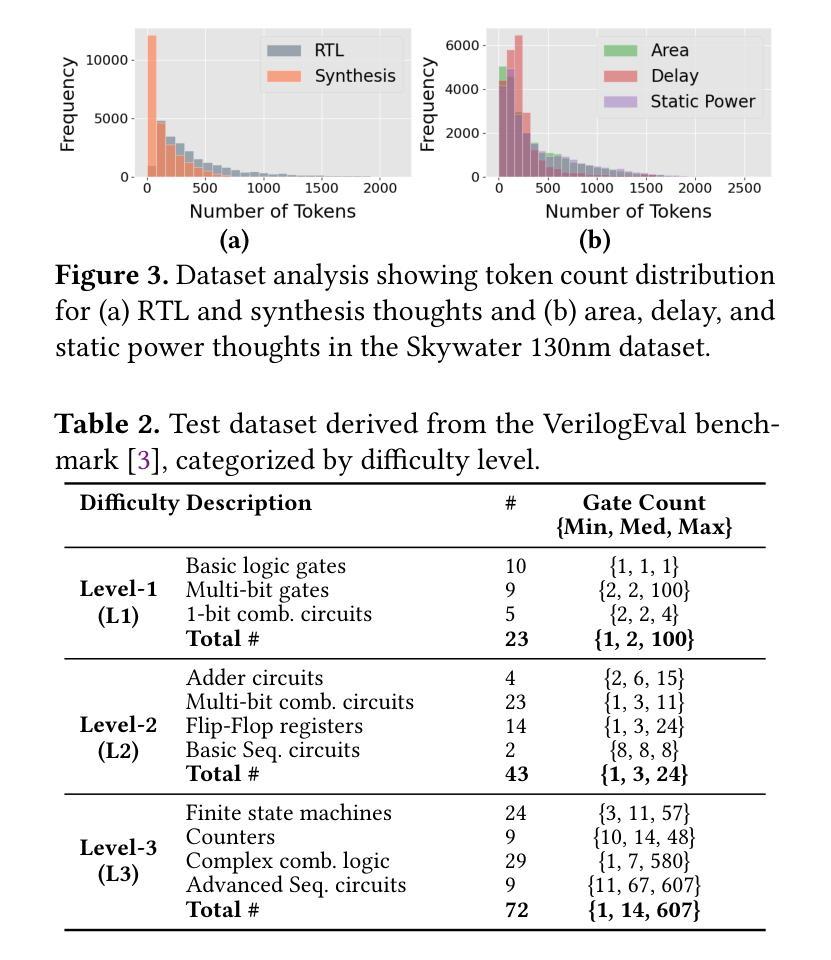
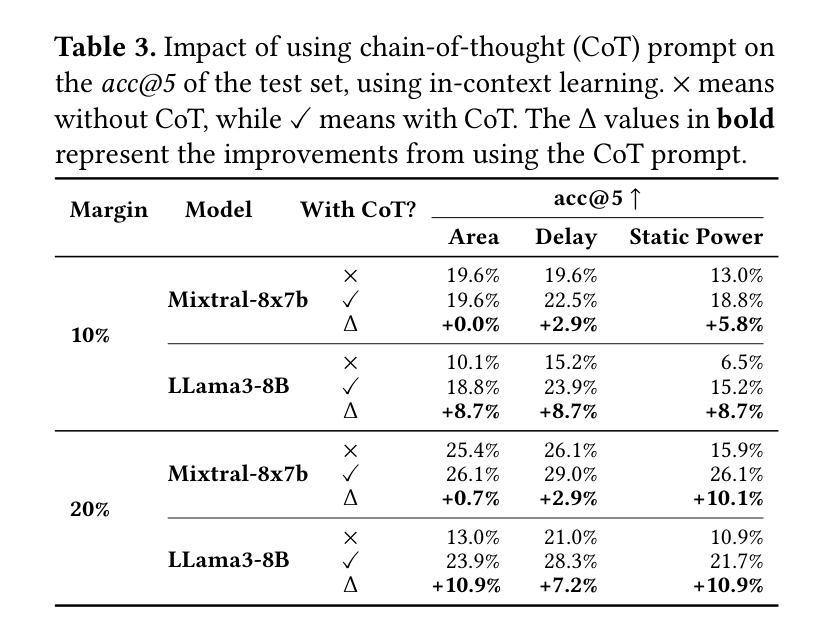
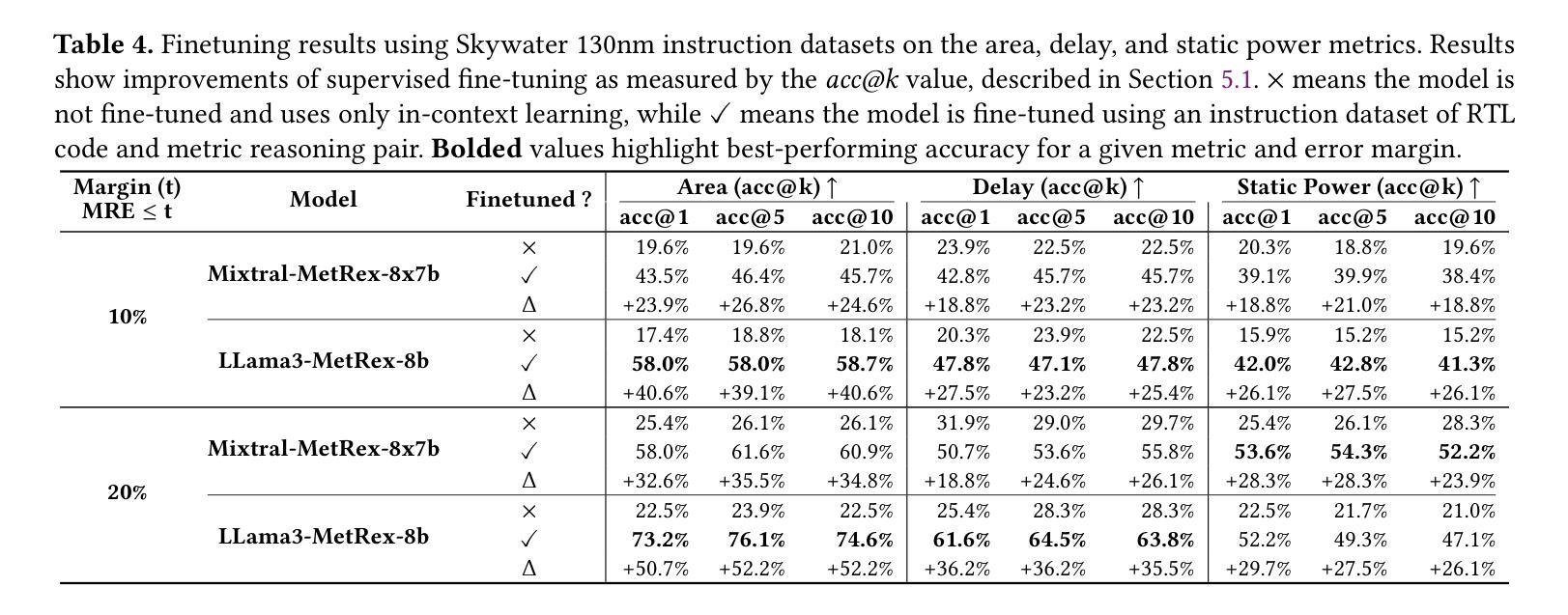
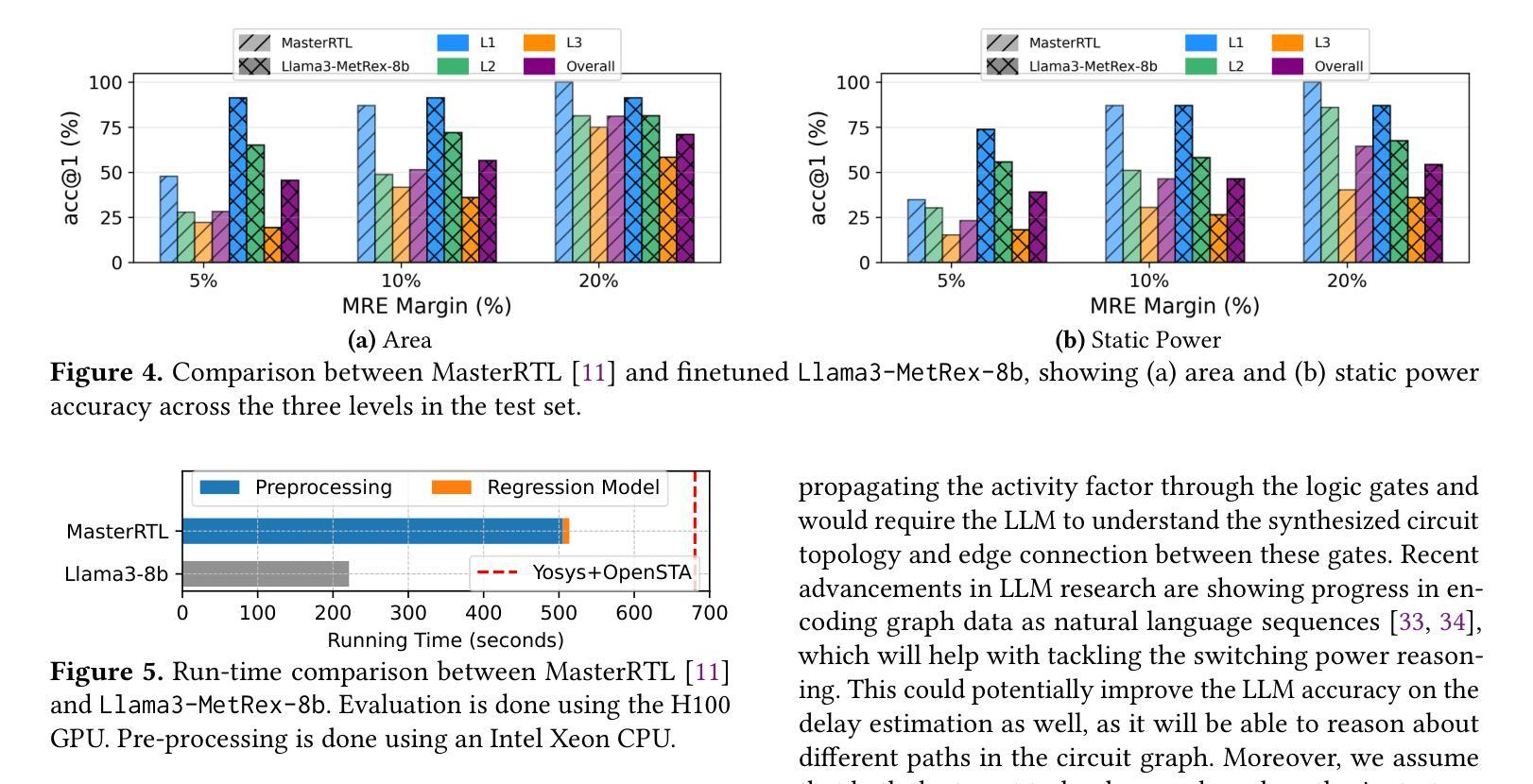
MetRex: A Benchmark for Verilog Code Metric Reasoning Using LLMs
Authors:Manar Abdelatty, Jingxiao Ma, Sherief Reda
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been applied to various hardware design tasks, including Verilog code generation, EDA tool scripting, and RTL bug fixing. Despite this extensive exploration, LLMs are yet to be used for the task of post-synthesis metric reasoning and estimation of HDL designs. In this paper, we assess the ability of LLMs to reason about post-synthesis metrics of Verilog designs. We introduce MetRex, a large-scale dataset comprising 25,868 Verilog HDL designs and their corresponding post-synthesis metrics, namely area, delay, and static power. MetRex incorporates a Chain of Thought (CoT) template to enhance LLMs’ reasoning about these metrics. Extensive experiments show that Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) boosts the LLM’s reasoning capabilities on average by 37.0%, 25.3%, and 25.7% on the area, delay, and static power, respectively. While SFT improves performance on our benchmark, it remains far from achieving optimal results, especially on complex problems. Comparing to state-of-the-art regression models, our approach delivers accurate post-synthesis predictions for 17.4% more designs (within a 5% error margin), in addition to offering a 1.7x speedup by eliminating the need for pre-processing. This work lays the groundwork for advancing LLM-based Verilog code metric reasoning.
大型语言模型(LLM)已被应用于各种硬件设计任务,包括Verilog代码生成、EDA工具脚本编写和RTL错误修复。尽管进行了广泛的探索,但LLM尚未用于HDL设计的后综合度量推理和估算任务。在本文中,我们评估了LLM对Verilog设计后综合指标进行推理的能力。我们引入了MetRex,这是一个大规模数据集,包含25,868个Verilog HDL设计及其相应的后综合度量,即面积、延迟和静态功耗。MetRex采用“思维链”(Chain of Thought,CoT)模板,以增强LLM对这些指标的推理能力。大量实验表明,监督微调(SFT)平均提高了LLM在面积、延迟和静态功率方面的推理能力,分别提高了37.0%、25.3%和25.7%。虽然SFT在我们的基准测试中提高了性能,但距离达到最佳结果还有很大差距,尤其是在复杂问题上。与最先进的回归模型相比,我们的方法在5%误差范围内为更多设计提供了准确的后综合预测(增加了17.4%),并且由于不需要预处理,提供了1.7倍的加速。这项工作为推进基于LLM的Verilog代码度量推理奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)首次被应用于Verilog设计后综合度量推理任务,并成功生成相应的数据集MetRex。通过监督微调(SFT)增强LLM的推理能力,显著提高区域、延迟和静态功率的预测精度。与现有回归模型相比,该方法的预测准确性更高,处理速度更快。这为LLM在Verilog代码度量推理中的应用奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)首次应用于Verilog设计后综合度量推理任务。
- 引入了MetRex数据集,包含25,868个Verilog HDL设计及对应的后综合度量。
- 采用监督微调(SFT)增强LLM的推理能力。
- SFT显著提高区域、延迟和静态功率的预测精度。
- 与现有回归模型相比,LLM方法预测更准确,处理速度更快。
- MetRex数据集通过Chain of Thought(CoT)模板增强LLM的推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

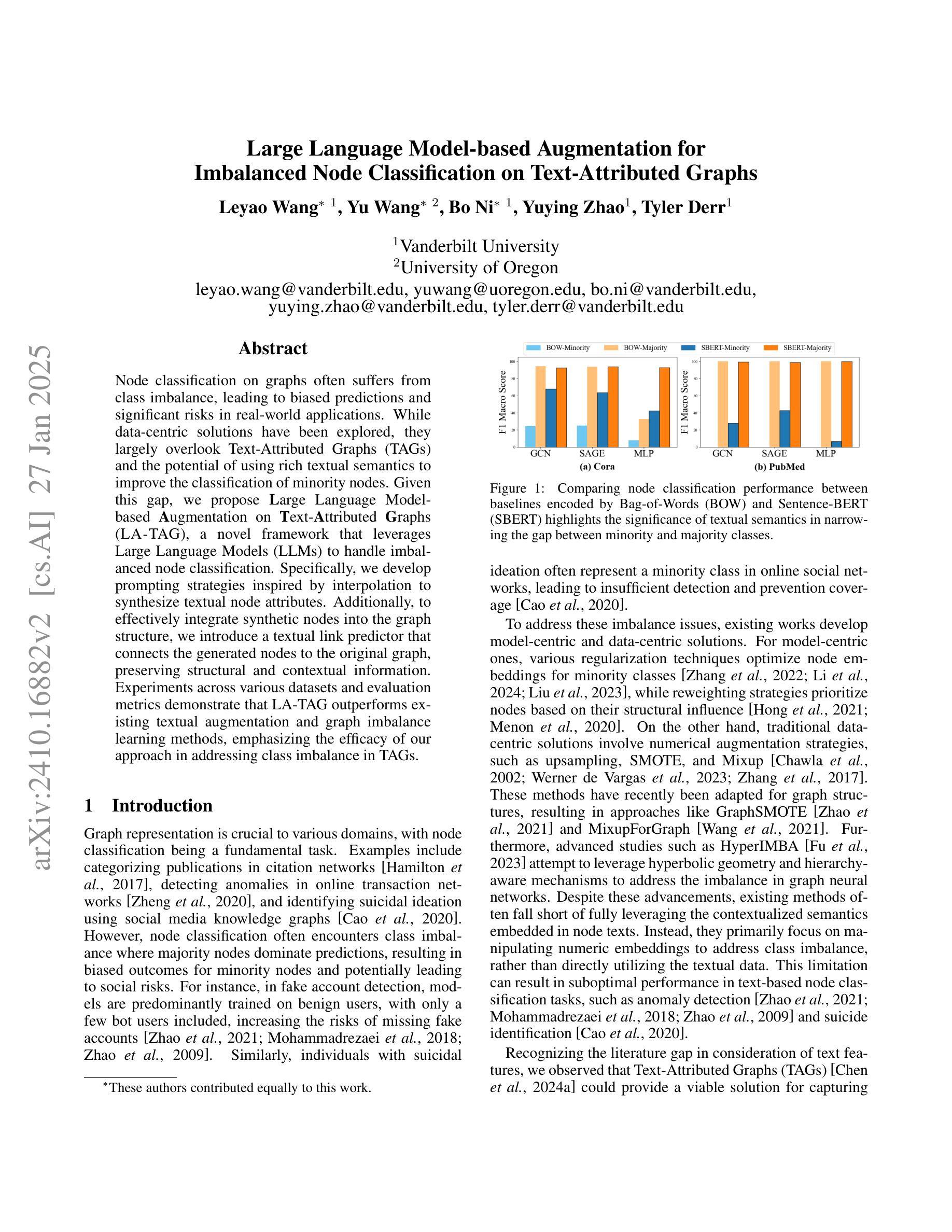
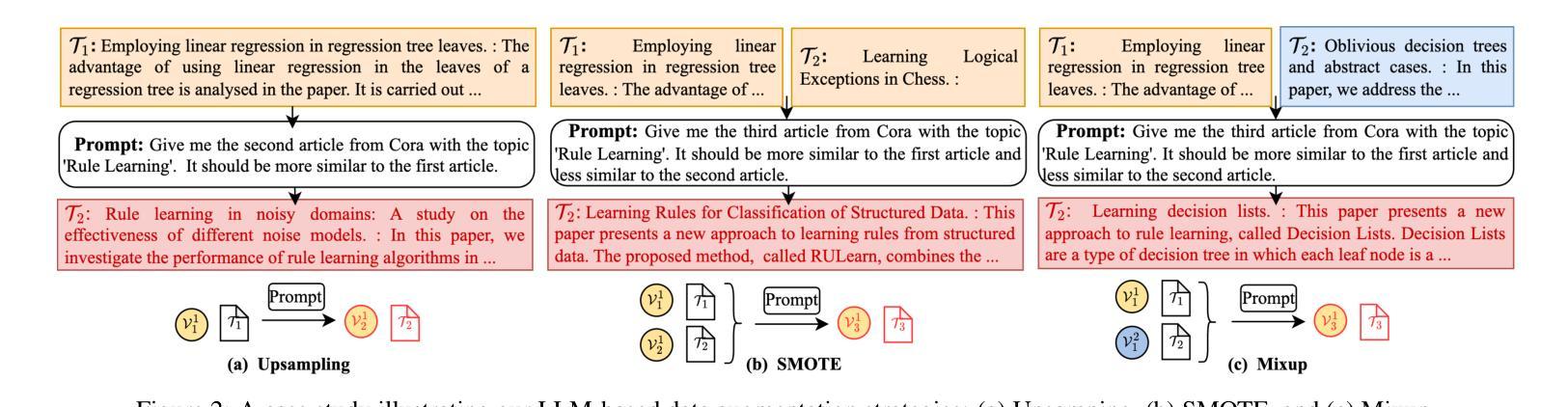
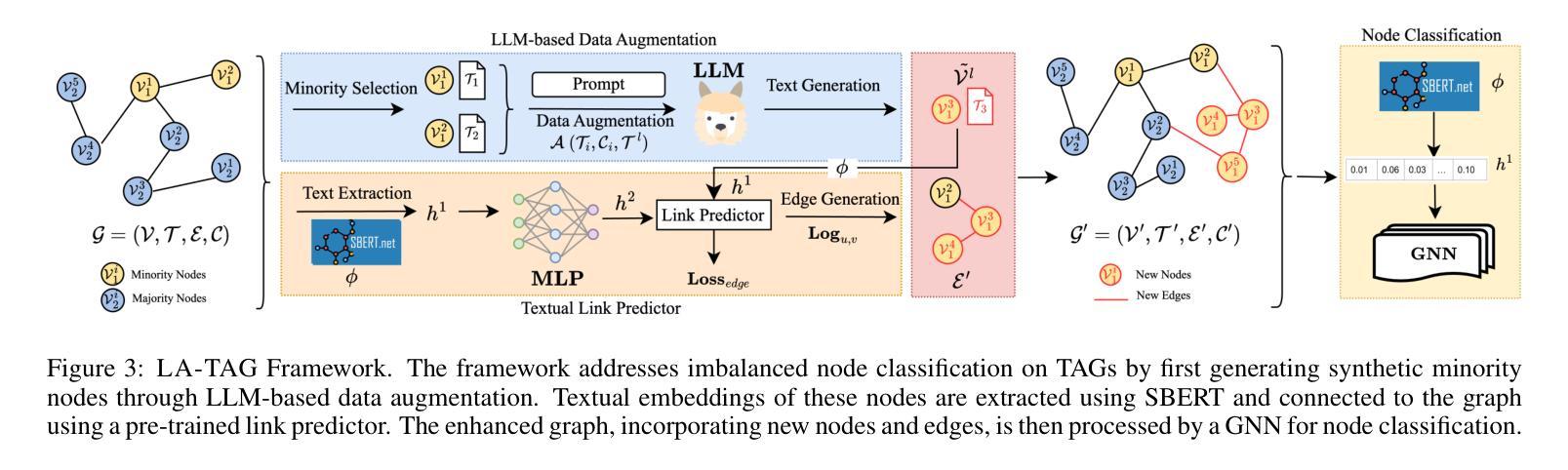
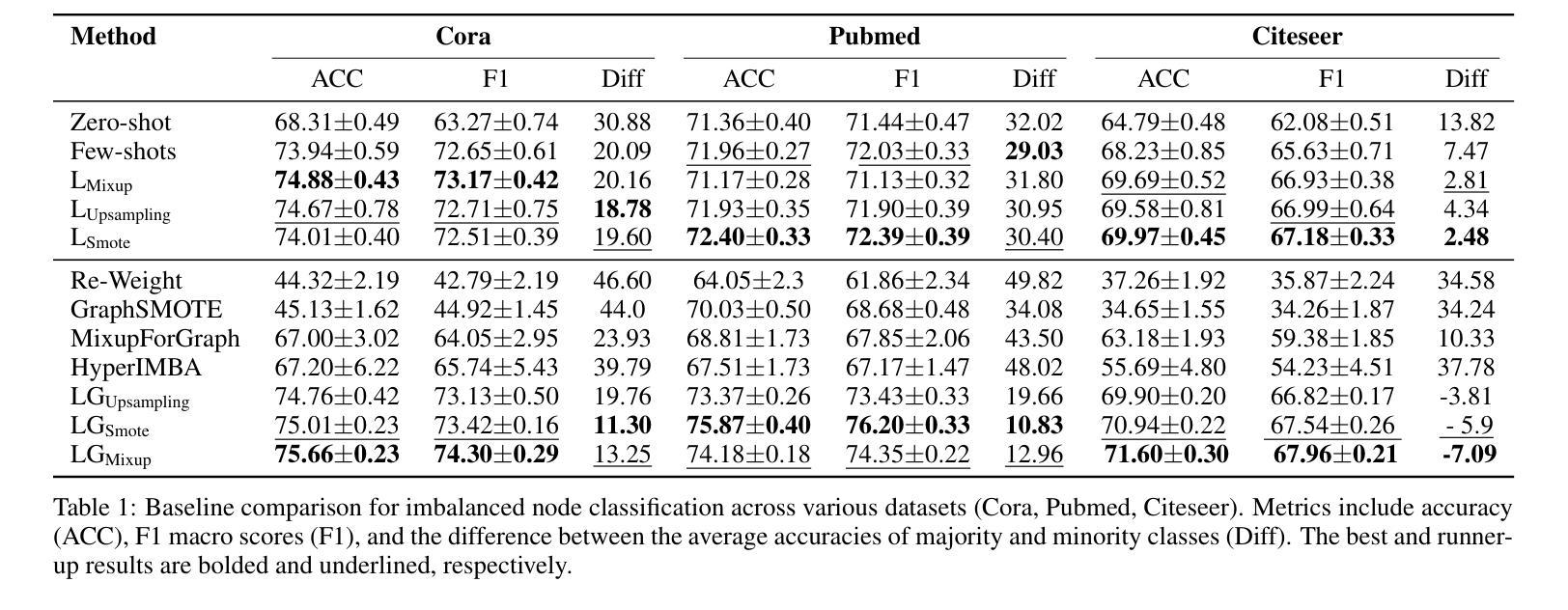
Large Language Model-based Augmentation for Imbalanced Node Classification on Text-Attributed Graphs
Authors:Leyao Wang, Yu Wang, Bo Ni, Yuying Zhao, Tyler Derr
Node classification on graphs often suffers from class imbalance, leading to biased predictions and significant risks in real-world applications. While data-centric solutions have been explored, they largely overlook Text-Attributed Graphs (TAGs) and the potential of using rich textual semantics to improve the classification of minority nodes. Given this gap, we propose Large Language Model-based Augmentation on Text-Attributed Graphs (LA-TAG), a novel framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to handle imbalanced node classification. Specifically, we develop prompting strategies inspired by interpolation to synthesize textual node attributes. Additionally, to effectively integrate synthetic nodes into the graph structure, we introduce a textual link predictor that connects the generated nodes to the original graph, preserving structural and contextual information. Experiments across various datasets and evaluation metrics demonstrate that LA-TAG outperforms existing textual augmentation and graph imbalance learning methods, emphasizing the efficacy of our approach in addressing class imbalance in TAGs.
图上的节点分类常常受到类别不平衡的影响,从而导致预测结果有偏向性,并且在现实应用中存在较大的风险。虽然数据驱动解决方案已被探索,但它们在很大程度上忽略了文本属性图(TAGs)和利用丰富的文本语义来改善少数节点分类的潜力。针对这一空白领域,我们提出了基于大型语言模型的文本属性图增强(LA-TAG)这一新型框架,利用大型语言模型(LLM)来处理不平衡节点分类问题。具体来说,我们开发了一种基于插值的提示策略来合成文本节点属性。此外,为了有效地将合成节点集成到图结构中,我们引入了一种文本链接预测器,将生成的节点与原始图连接起来,保留结构和上下文信息。在不同数据集和评价指标上进行的实验表明,LA-TAG在文本增强和图不平衡学习方面优于现有方法,突显了我们的方法在解决TAG中的类别不平衡问题的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages
Summary
文本针对图结构中的节点分类问题进行了探讨,特别是面临类别不均衡导致的预测偏差和实际应用风险。针对文本属性图(TAGs)中的少数节点分类问题,提出了基于大语言模型(LLMs)的增强方法LA-TAG。该方法利用大语言模型开发插值启发式的提示策略,合成文本节点属性,并通过文本链接预测器将合成节点有效地融入图结构,保留结构和上下文信息。实验表明,LA-TAG在多种数据集和评价指标上优于现有的文本增强和图不平衡学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- 节点分类在图结构中面临类别不均衡问题,导致预测偏差和实际应用风险。
- 现有数据中心的解决方案大多忽略了文本属性图(TAGs)和丰富文本语义在改进少数节点分类中的潜力。
- LA-TAG利用大语言模型(LLMs)处理不平衡节点分类问题,通过合成文本节点属性提升分类效果。
- LA-TAG采用插值启发式的提示策略来开发提示方法。
- 为将合成节点有效地融入图结构,LA-TAG引入了文本链接预测器。
- 文本链接预测器能够保留结构和上下文信息。
- 实验表明,LA-TAG在多个数据集和评价指标上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
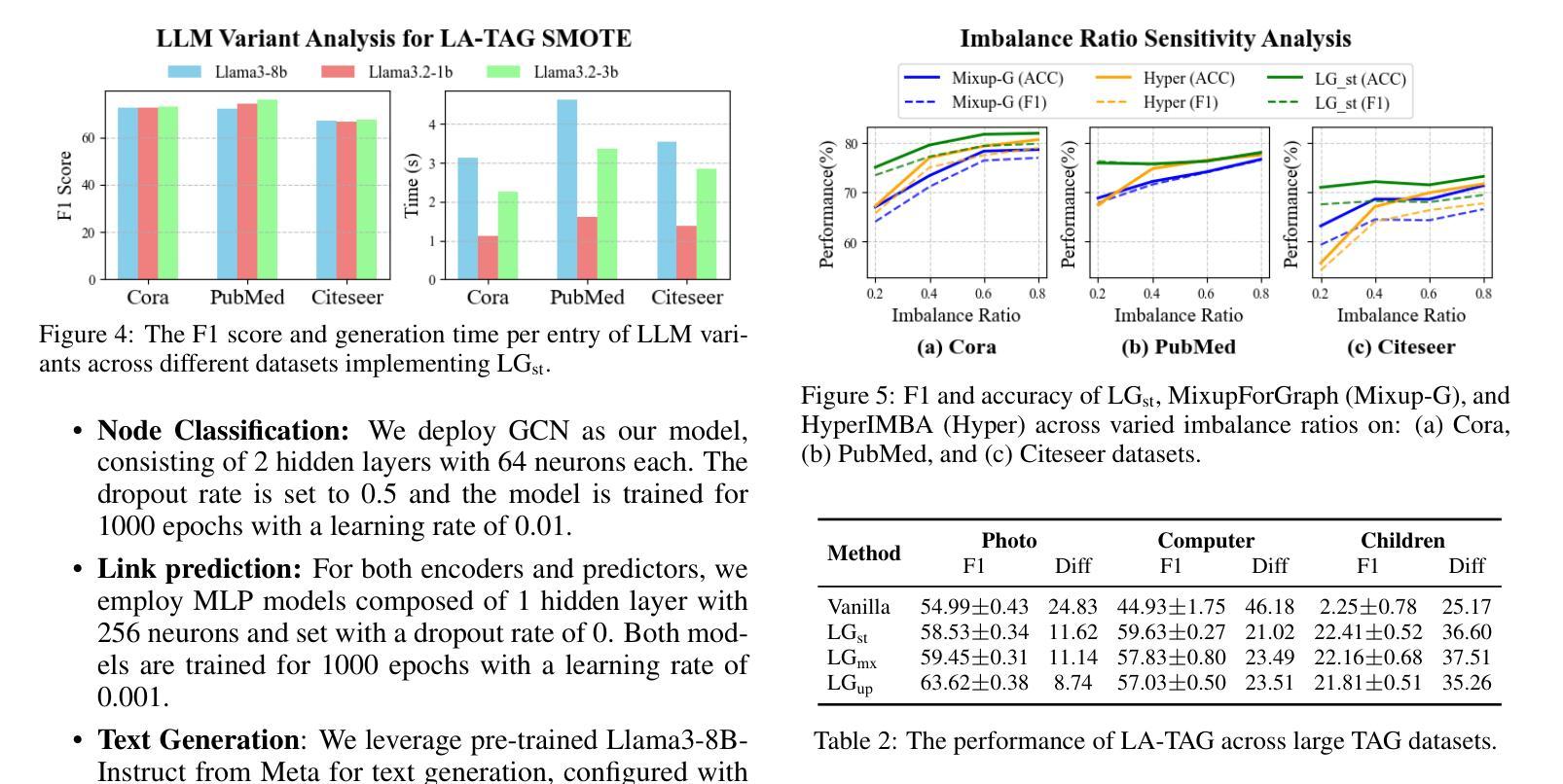
DeSTA2: Developing Instruction-Following Speech Language Model Without Speech Instruction-Tuning Data
Authors:Ke-Han Lu, Zhehuai Chen, Szu-Wei Fu, Chao-Han Huck Yang, Jagadeesh Balam, Boris Ginsburg, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang, Hung-yi Lee
Recent end-to-end speech language models (SLMs) have expanded upon the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by incorporating pre-trained speech models. However, these SLMs often undergo extensive speech instruction-tuning to bridge the gap between speech and text modalities. This requires significant annotation efforts and risks catastrophic forgetting of the original language capabilities. In this work, we present a simple yet effective automatic process for creating speech-text pair data that carefully injects speech paralinguistic understanding abilities into SLMs while preserving the inherent language capabilities of the text-based LLM. Our model demonstrates general capabilities for speech-related tasks without the need for speech instruction-tuning data, achieving impressive performance on Dynamic-SUPERB and AIR-Bench-Chat benchmarks. Furthermore, our model exhibits the ability to follow complex instructions derived from LLMs, such as specific output formatting and chain-of-thought reasoning. Our approach not only enhances the versatility and effectiveness of SLMs but also reduces reliance on extensive annotated datasets, paving the way for more efficient and capable speech understanding systems.
最近的端到端语音语言模型(SLM)通过融入预训练的语音模型,扩大了大型语言模型(LLM)的功能。然而,这些SLM通常需要经过大量的语音指令调整,以弥补语音和文本模态之间的差距。这需要大量的标注工作,并存在遗忘原始语言能力的风险。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单有效的自动创建语音文本配对数据的过程,该方法能够精心地将语音副语言理解的能力注入SLM中,同时保留基于文本的LLM的固有语言能力。我们的模型展示了在不需要语音指令调整数据的情况下,进行语音相关任务的通用能力,在Dynamic-SUPERB和AIR-Bench-Chat基准测试中取得了令人印象深刻的表现。此外,我们的模型还展示了遵循LLM衍生的复杂指令的能力,如特定的输出格式和链式思维推理。我们的方法不仅提高了SLM的通用性和有效性,而且减少了对于大量标注数据集的依赖,为更高效、更强大的语音理解系统铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
近期,端对端语音语言模型(SLM)通过融入预训练语音模型,扩大了大型语言模型(LLM)的能力。然而,这些SLM需要经过大量的语音指令调整来弥合语音与文本模式之间的差距,这需要大量的标注工作并存在遗忘原有语言能力的风险。本研究提出了一种简单有效的自动创建语音文本配对数据的方法,该方法能够谨慎地将语音副语言理解力注入SLM中,同时保留基于文本的LLM的固有语言能力。我们的模型在动态SUPERB和AIR-Bench-Chat基准测试中表现出色,无需语音指令调整数据即可进行语音相关任务。此外,我们的模型展现出遵循LLM派生的复杂指令的能力,如特定输出格式和链式思维推理。我们的方法不仅提高了SLM的通用性和效率,还降低了对大量标注数据集的依赖,为更有效率、能力更强的语音理解系统铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 端对端语音语言模型(SLM)结合了预训练语音模型和大型语言模型(LLM),增强了语言处理能力。
- SLM需要通过大量的语音指令调整来适应语音和文本模式之间的差距,这增加了标注工作的负担并可能导致原有语言能力的遗忘。
- 提出了一种自动创建语音文本配对数据的方法,能巧妙地将语音副语言理解力注入SLM,同时保持LLM的固有语言能力。
- 模型在多个基准测试中表现出色,无需额外的语音指令调整即可处理语音相关任务。
- 模型能够遵循复杂的指令,包括特定的输出格式和链式思维推理,展现了其广泛的应用潜力。
- 该方法提高了SLM的通用性和效率,为更高效的语音理解系统提供了可能。
点此查看论文截图

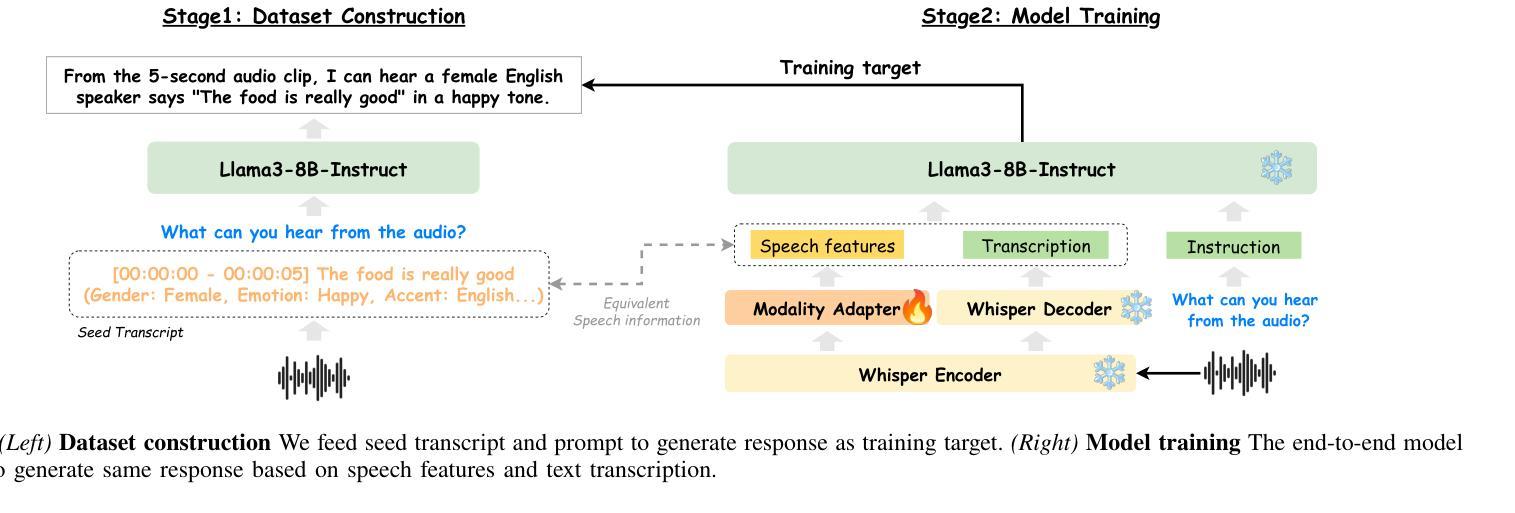
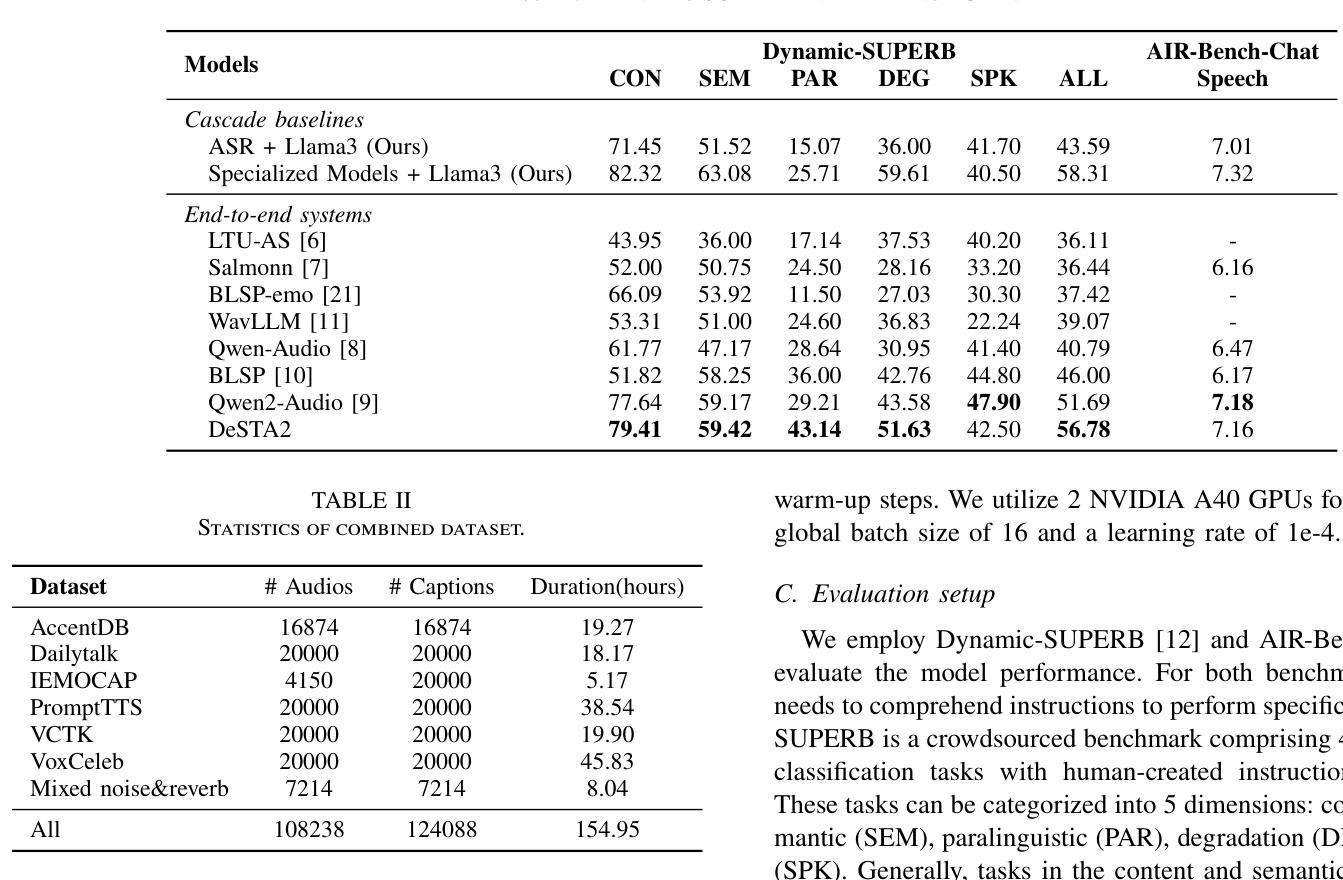
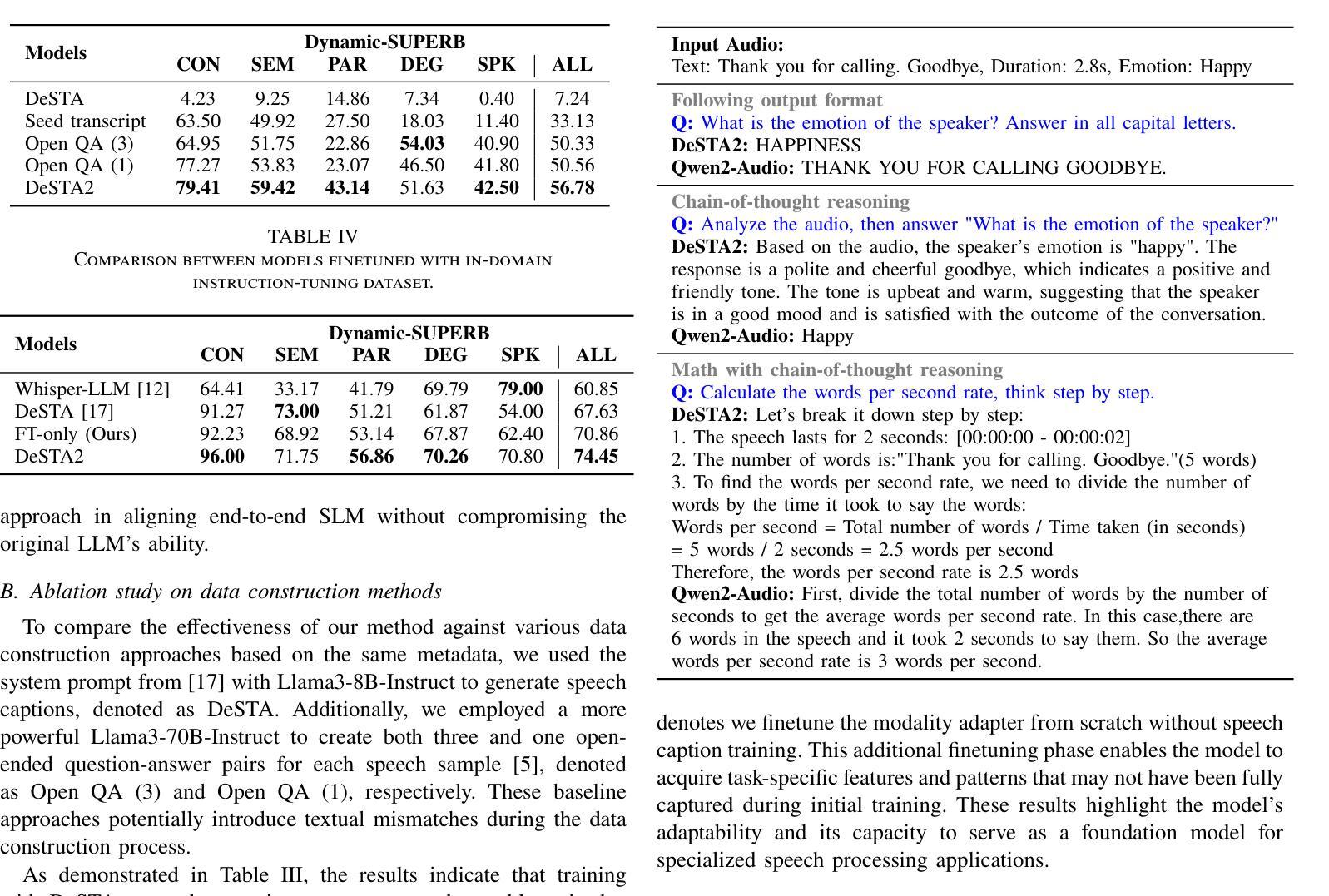
MOSAIC: Multiple Observers Spotting AI Content, a Robust Approach to Machine-Generated Text Detection
Authors:Matthieu Dubois, François Yvon, Pablo Piantanida
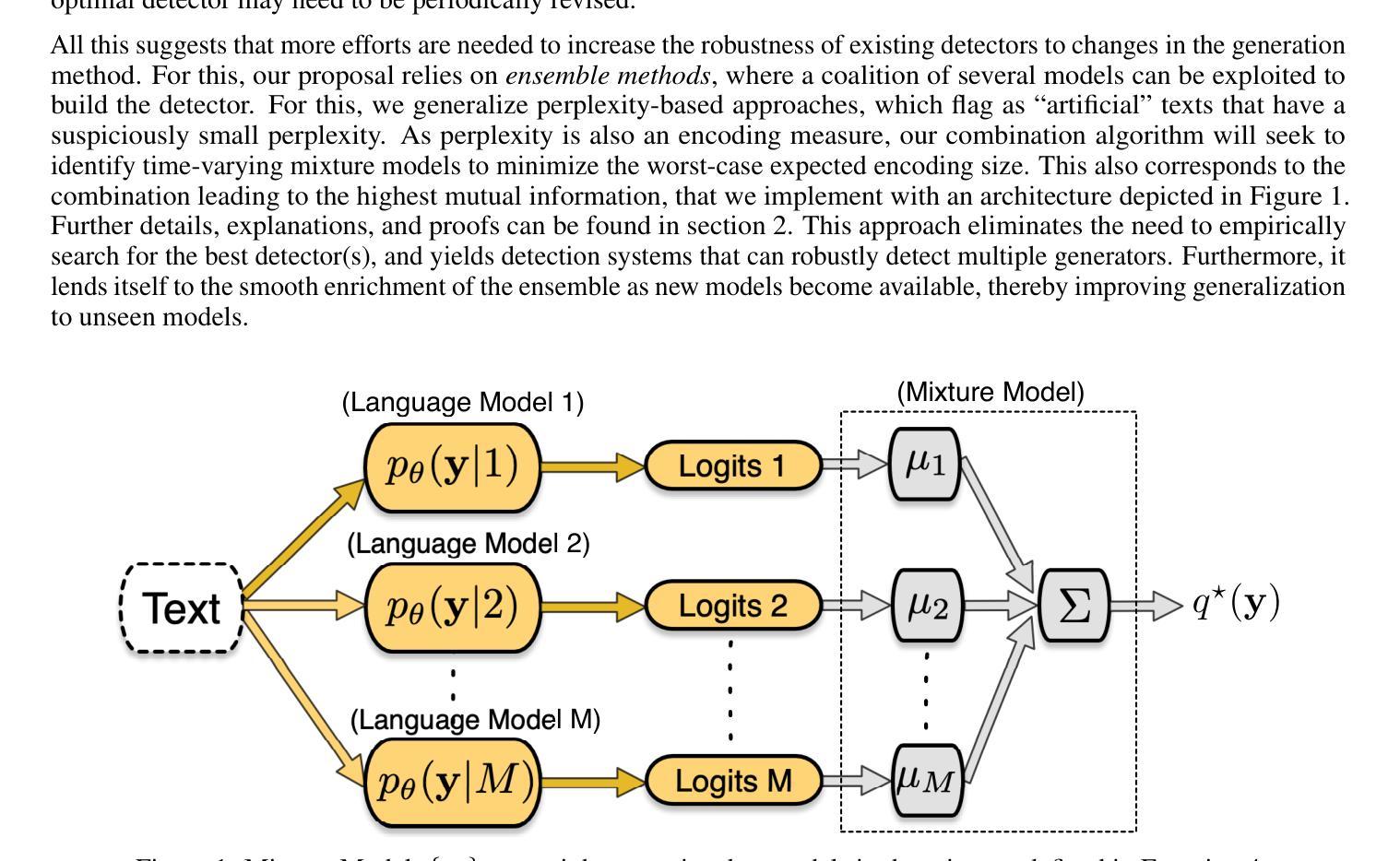
The dissemination of Large Language Models (LLMs), trained at scale, and endowed with powerful text-generating abilities has vastly increased the threats posed by generative AI technologies by reducing the cost of producing harmful, toxic, faked or forged content. In response, various proposals have been made to automatically discriminate artificially generated from human-written texts, typically framing the problem as a classification problem. Most approaches evaluate an input document by a well-chosen detector LLM, assuming that low-perplexity scores reliably signal machine-made content. As using one single detector can induce brittleness of performance, we instead consider several and derive a new, theoretically grounded approach to combine their respective strengths. Our experiments, using a variety of generator LLMs, suggest that our method effectively leads to robust detection performances. An early version of the code is available at https://github.com/BaggerOfWords/MOSAIC.
大规模训练的大型语言模型(LLM)具有强大的文本生成能力,其传播大大降低了生成人工智能技术的威胁,减少了制造有害、有毒、伪造或伪造内容的成本。为了应对这一问题,已经提出了多种自动区分人工生成文本和人类编写文本的方法,通常将这一问题构建为分类问题。大多数方法通过精心选择的检测器LLM来评估输入文档,假设低困惑度分数可靠地表示机器生成的内容。由于使用单个检测器可能会导致性能脆弱,因此我们考虑多个因素,并推导出一种结合各自优势的新方法,该方法在理论上有所依据。我们的实验使用了各种生成式LLM,结果表明我们的方法可以有效地实现稳健的检测性能。该代码的初步版本可在https://github.com/BaggerOfWords/MOSAIC上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Still a work in progress, early version of the code can be found here :https://github.com/BaggerOfWords/MOSAIC
Summary
大规模训练的语言模型(LLM)具备强大的文本生成能力,降低了产生有害、有毒、虚假或伪造内容的成本,从而极大地增加了生成式人工智能技术的威胁。为应对这一问题,已提出多种自动区分人工生成文本和人类撰写文本的方法,通常将问题视为分类问题。我们的实验表明,结合多个检测器的方法可以有效地提高检测性能。相关代码的早期版本可在https://github.com/BaggerOfWords/MOSAIC获取。
Key Takeaways
- LLM的普及降低了产生有害、有毒、虚假或伪造内容的成本,增加了生成式AI技术的威胁。
- 自动区分人工生成文本和人类撰写文本的方法通常将问题视为分类问题。
- 大多数方法通过选择适当的检测LLM来评估输入文档,低困惑度分数可靠地表示机器生成的内容。
- 使用单个检测器可能导致性能上的脆弱性。
- 结合多个检测器的方法可以提高检测性能。
- 实验表明,该方法在多种生成LLM上的检测性能表现稳健。
点此查看论文截图


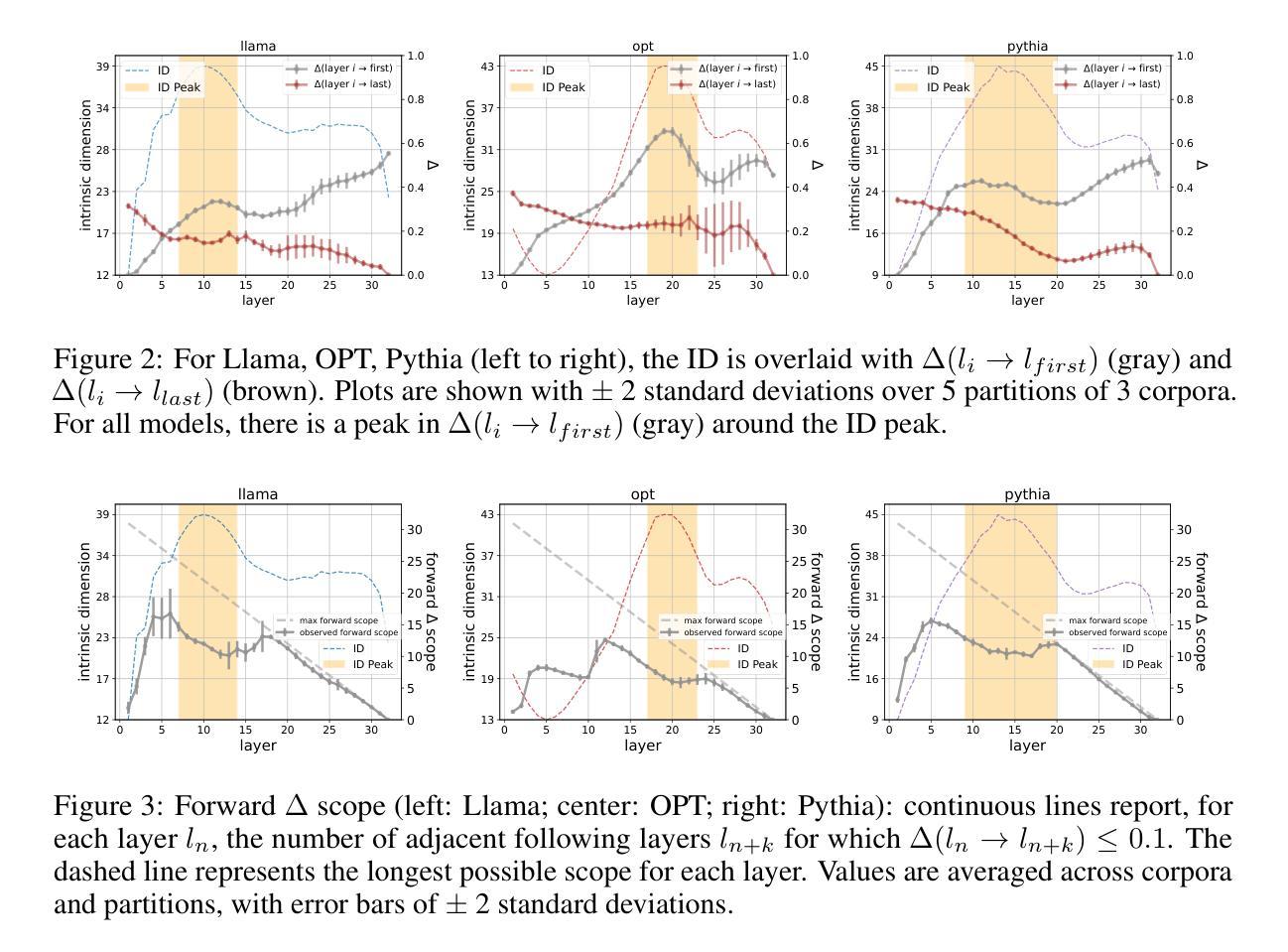
Emergence of a High-Dimensional Abstraction Phase in Language Transformers
Authors:Emily Cheng, Diego Doimo, Corentin Kervadec, Iuri Macocco, Jade Yu, Alessandro Laio, Marco Baroni
A language model (LM) is a mapping from a linguistic context to an output token. However, much remains to be known about this mapping, including how its geometric properties relate to its function. We take a high-level geometric approach to its analysis, observing, across five pre-trained transformer-based LMs and three input datasets, a distinct phase characterized by high intrinsic dimensionality. During this phase, representations (1) correspond to the first full linguistic abstraction of the input; (2) are the first to viably transfer to downstream tasks; (3) predict each other across different LMs. Moreover, we find that an earlier onset of the phase strongly predicts better language modelling performance. In short, our results suggest that a central high-dimensionality phase underlies core linguistic processing in many common LM architectures.
语言模型(LM)是一种将语言上下文映射到输出标记的模型。然而,关于这种映射还有很多未知,包括其几何属性如何与其功能相关联。我们采用高级几何方法对其进行分析,观察了五个基于预训练转换器的语言模型和三个输入数据集,发现了一个以高内在维度为特征的独特阶段。在此阶段,表示(1)对应于输入的第一个完整语言抽象;(2)是第一个切实转移到下游任务的表示;(3)在不同语言模型中相互预测。此外,我们发现该阶段的早期发生强烈预示着更好的语言建模性能。简而言之,我们的结果表明,许多常见的语言模型架构中的核心语言处理都以一个高维度的中心阶段为基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as conference paper at ICLR 2025
Summary:语言模型(LM)将语言上下文映射到输出标记上,但其映射的几何特性与其功能之间的关系尚不清楚。研究采用高级几何分析方法,观察到五个预训练基于转换器的LM和三个输入数据集之间存在一个高内在维度特征明显的阶段。在这个阶段,语言模型的表示对应于输入的第一个完整语言抽象,能够切实转移到下游任务,并在不同的LM之间互相预测。此外,阶段开始的早晚强烈预示着语言建模性能的好坏。总之,结果表明核心语言处理在许多常见LM架构中都有一个高维度的中心阶段。
Key Takeaways:
- 语言模型将语言上下文映射到输出标记上,但其映射的几何特性与功能关系尚不清楚。
- 存在一个高内在维度特征明显的阶段,这是许多预训练基于转换器的LM和输入数据集之间的共同特征。
- 在这个阶段,语言模型的表示对应于输入的第一个完整语言抽象。
- 这一阶段的表示能够切实转移到下游任务。
- 不同LM之间的表示在这一阶段互相预测。
- 阶段开始的早晚强烈预示语言建模性能的好坏。
点此查看论文截图