⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
Mixture-of-Mamba: Enhancing Multi-Modal State-Space Models with Modality-Aware Sparsity
Authors:Weixin Liang, Junhong Shen, Genghan Zhang, Ning Dong, Luke Zettlemoyer, Lili Yu
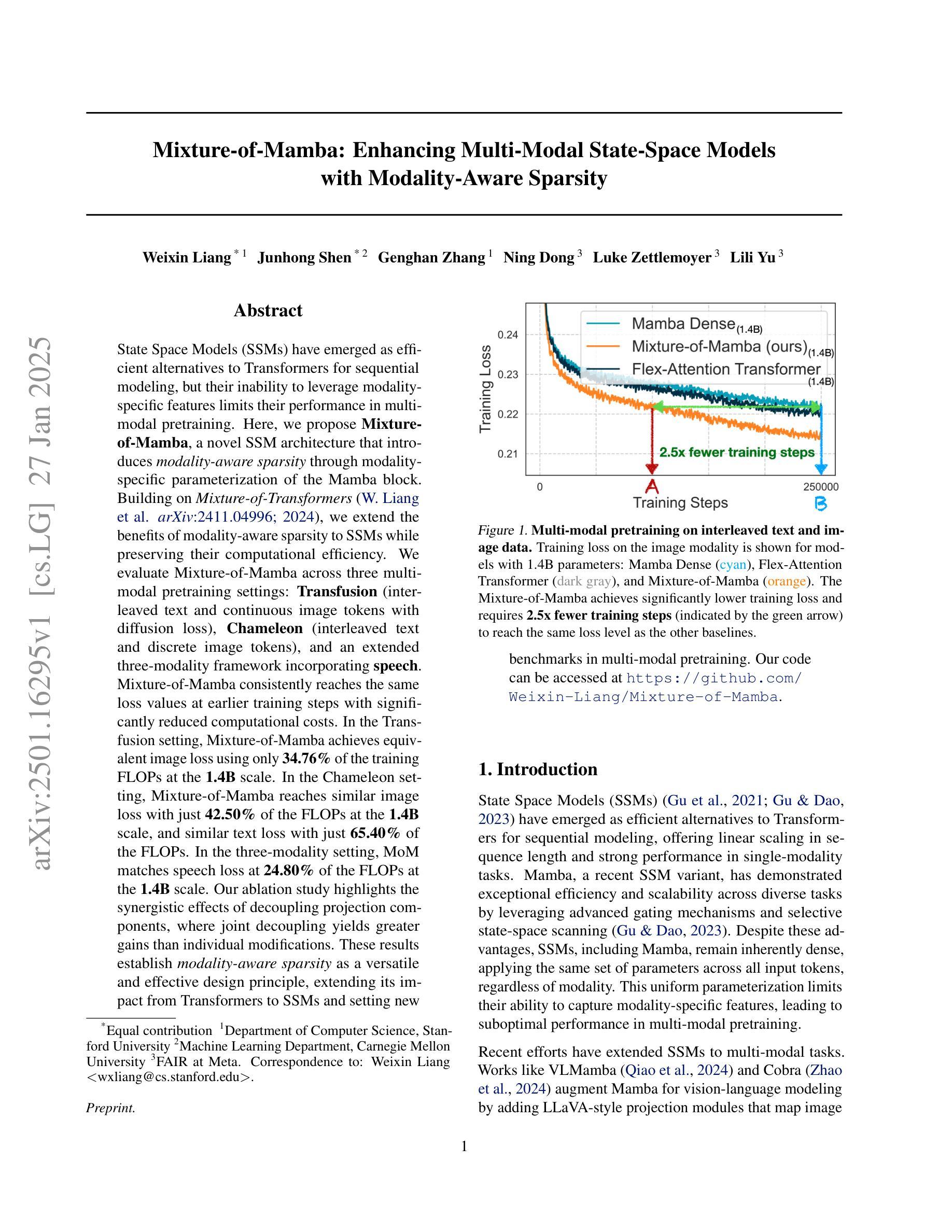
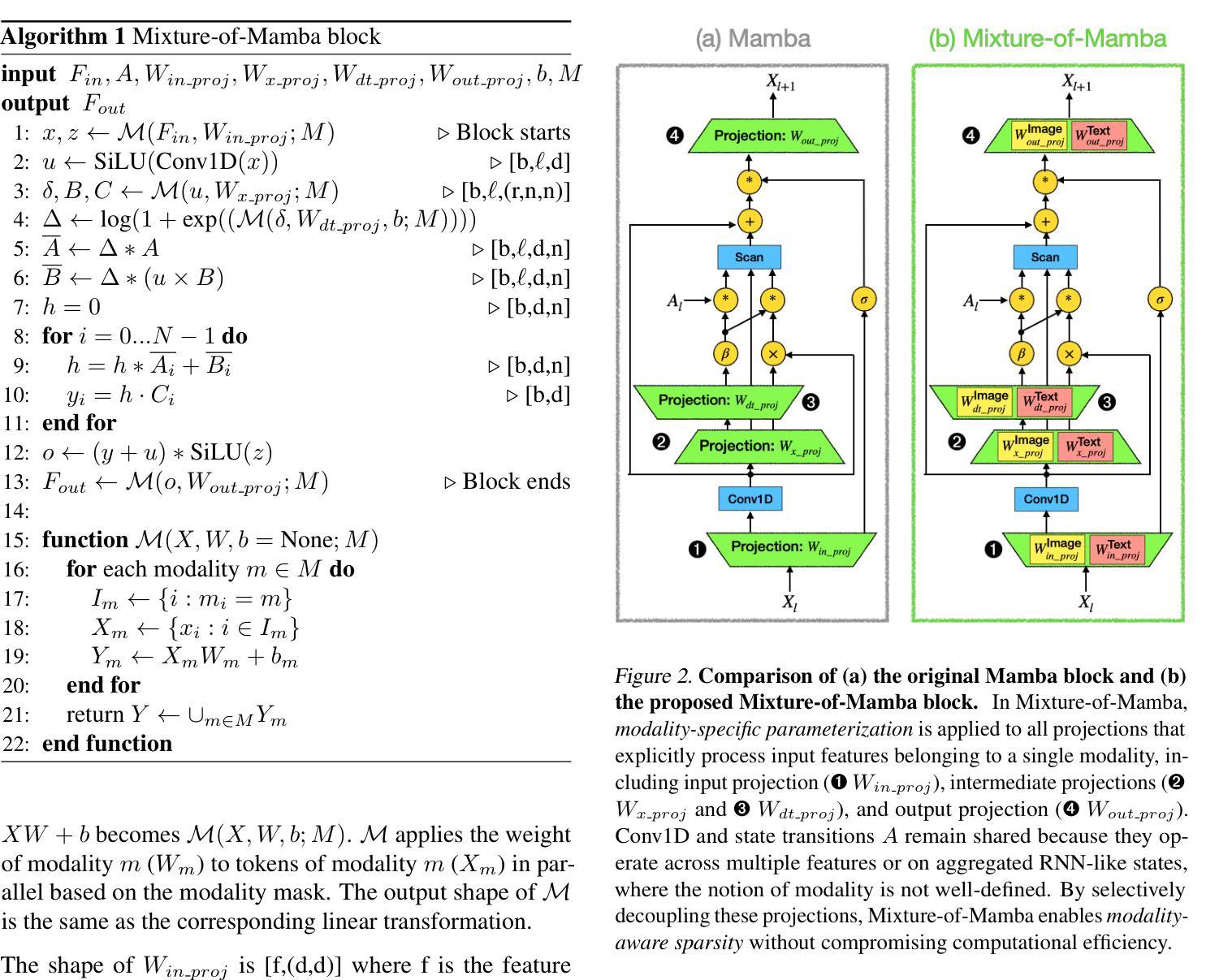
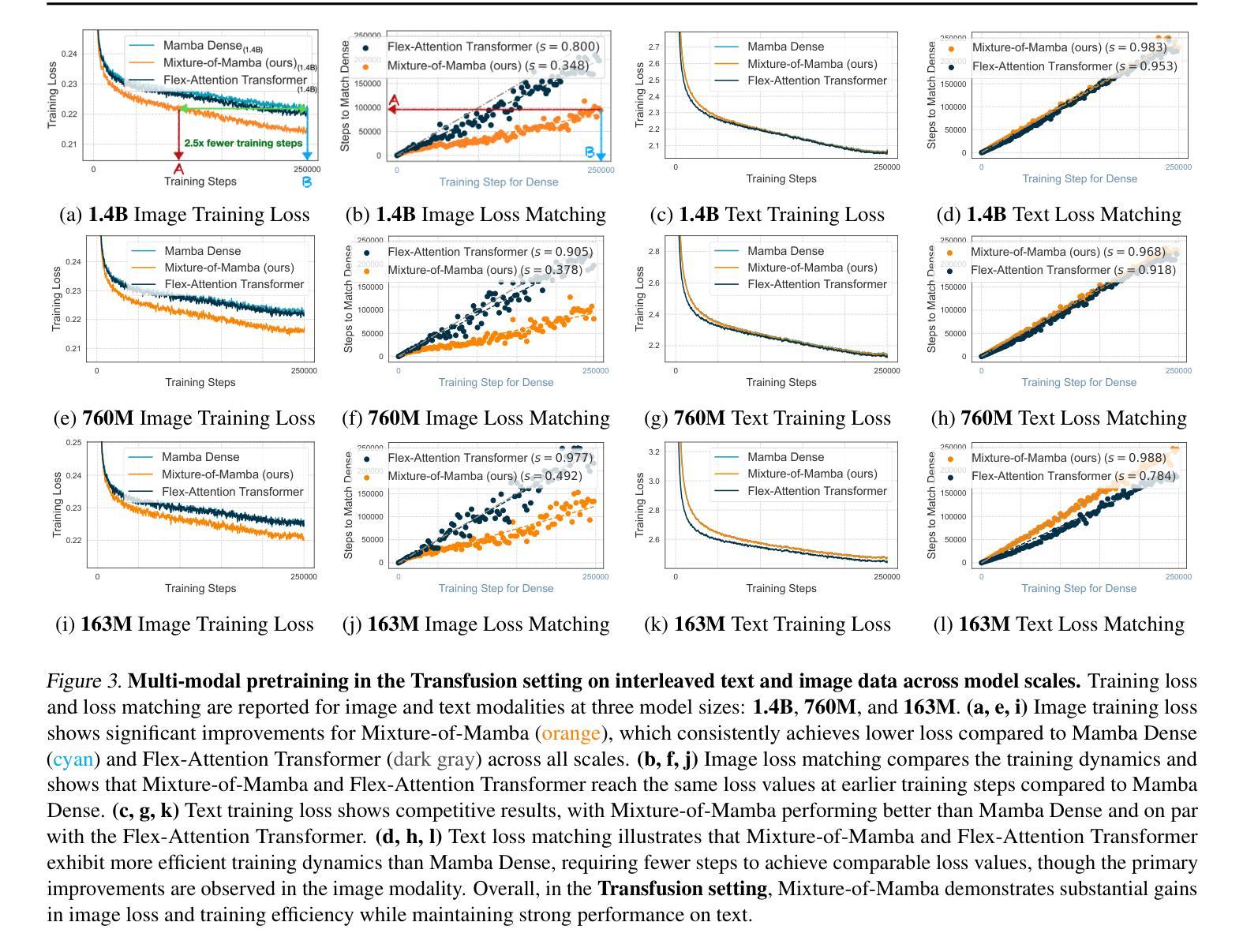
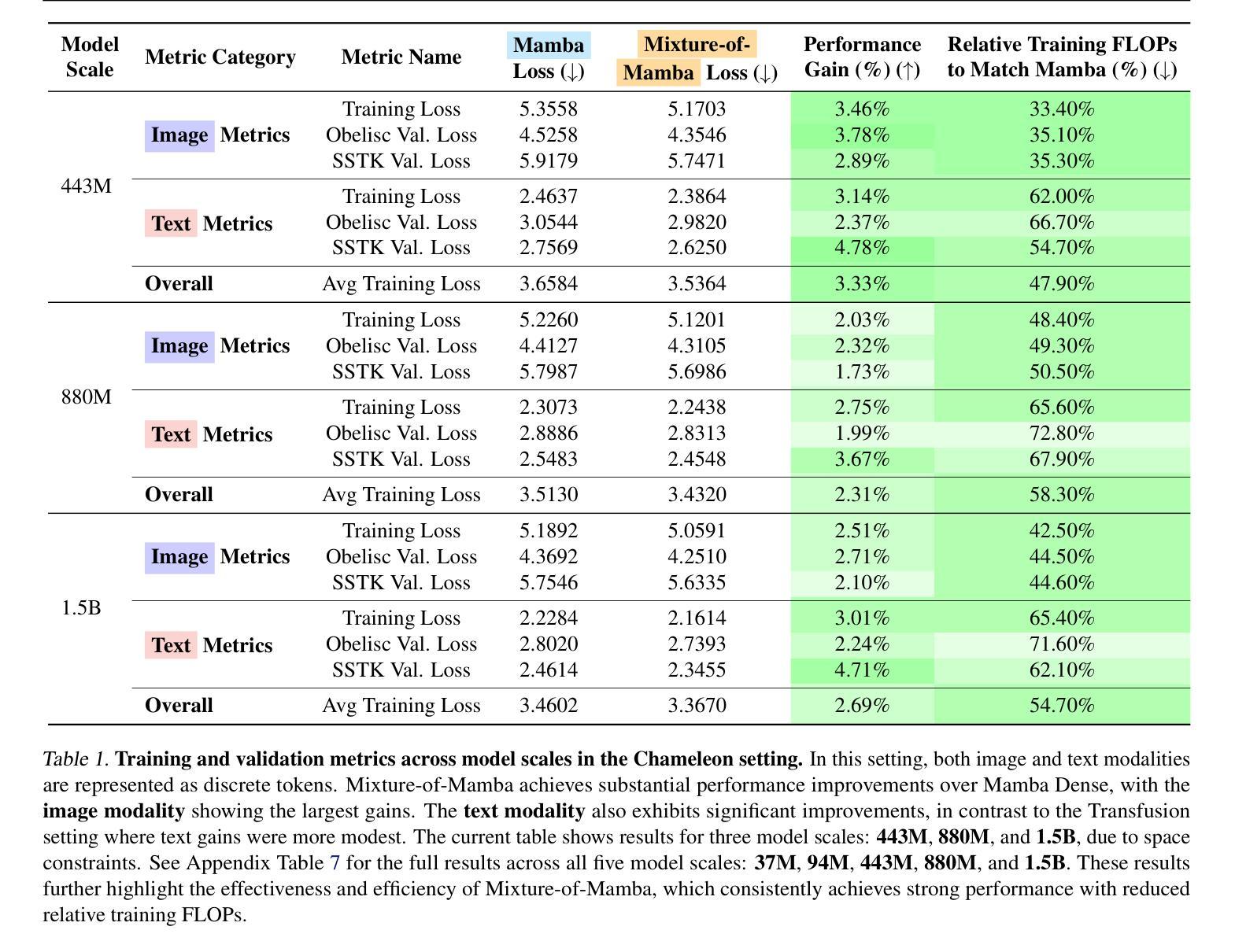
State Space Models (SSMs) have emerged as efficient alternatives to Transformers for sequential modeling, but their inability to leverage modality-specific features limits their performance in multi-modal pretraining. Here, we propose Mixture-of-Mamba, a novel SSM architecture that introduces modality-aware sparsity through modality-specific parameterization of the Mamba block. Building on Mixture-of-Transformers (W. Liang et al. arXiv:2411.04996; 2024), we extend the benefits of modality-aware sparsity to SSMs while preserving their computational efficiency. We evaluate Mixture-of-Mamba across three multi-modal pretraining settings: Transfusion (interleaved text and continuous image tokens with diffusion loss), Chameleon (interleaved text and discrete image tokens), and an extended three-modality framework incorporating speech. Mixture-of-Mamba consistently reaches the same loss values at earlier training steps with significantly reduced computational costs. In the Transfusion setting, Mixture-of-Mamba achieves equivalent image loss using only 34.76% of the training FLOPs at the 1.4B scale. In the Chameleon setting, Mixture-of-Mamba reaches similar image loss with just 42.50% of the FLOPs at the 1.4B scale, and similar text loss with just 65.40% of the FLOPs. In the three-modality setting, MoM matches speech loss at 24.80% of the FLOPs at the 1.4B scale. Our ablation study highlights the synergistic effects of decoupling projection components, where joint decoupling yields greater gains than individual modifications. These results establish modality-aware sparsity as a versatile and effective design principle, extending its impact from Transformers to SSMs and setting new benchmarks in multi-modal pretraining. Our code can be accessed at https://github.com/Weixin-Liang/Mixture-of-Mamba
状态空间模型(SSMs)作为序列建模的有效替代方案,已经崭露头角。然而,它们无法利用特定模态的特征,这在多模态预训练中限制了性能。在这里,我们提出了名为Mixture-of-Mamba的新型SSM架构,它通过Mamba块的特定模态参数化引入了模态感知稀疏性。基于Mixture-of-Transformers(W. Liang等人,arXiv:2411.04996;2024),我们将模态感知稀疏性的好处扩展到SSM,同时保持其计算效率。我们在三种多模态预训练环境中评估了Mixture-of-Mamba的效果:Transfusion(交替文本和连续图像令牌与扩散损失)、Chameleon(交替文本和离散图像令牌),以及一个包含语音的扩展三模态框架。Mixture-of-Mamba在较早的训练步骤中始终达到相同的损失值,并大大降低了计算成本。在Transfusion设置中,Mixture-of-Mamba仅使用34.76%的训练浮点运算量就达到了相当的图像损失值在规模为1.4B时。在Chameleon设置中,Mixture-of-Mamba在规模为1.4B时仅以42.5%的浮点运算量达到相似的图像损失值,并以仅65.4%的浮点运算量达到相似的文本损失值。在三模态设置中,MoM在规模为1.4B时仅以24.8%的浮点运算量达到语音损失匹配水平。我们的消融研究突出了分离投影组件的协同作用,联合分离比单独修改能获得更大的收益。这些结果确立了模态感知稀疏性作为一种通用且有效的设计原则的地位,将其影响从Transformer扩展到SSM,并为多模态预训练设定了新的基准。我们的代码可访问于 https://github.com/Weixin-Liang/Mixture-of-Mamba
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
状态空间模型(SSMs)作为序列建模的有效替代方案,展现出其高效性,但在多模态预训练中的性能受限于无法利用模态特定特征。为此,我们提出了Mixture-of-Mamba这一新型SSM架构,它通过模态特定参数化Mamba块引入模态感知稀疏性。在Mixture-of-Transformers的基础上,我们拓展了模态感知稀疏性的优势至SSM,同时保持了其计算效率。Mixture-of-Mamba在多模态预训练的三种设置中进行了评估:融合(文本和连续图像标记交替出现并使用扩散损失)、变色龙(交替使用文本和离散图像标记),以及一个包含语音的三模态扩展框架。Mixture-of-Mamba在减少计算成本的同时,能够在早期训练步骤达到相同的损失值。在融合设置中,Mixture-of-Mamba仅使用34.76%的训练浮点运算(FLOPs)便达到相同的图像损失值。在变色龙设置中,它在1.4B规模下以42.5%的FLOPs达到相似的图像损失,并以65.4%的FLOPs达到相似的文本损失。在三模态设置中,MoM在1.4B规模下以24.8%的FLOPs匹配语音损失。我们的消融研究突出了分离投影组件的协同作用,联合分离比单独修改产生更大的收益。这些结果证明了模态感知稀疏性是一种通用且有效的设计原则,它从Transformer扩展至SSM,并为多模态预训练设定了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 状态空间模型(SSMs)在计算效率上展现出优势,但多模态预训练性能受限。
- Mixture-of-Mamba架构通过引入模态感知稀疏性,提升了SSM在多模态预训练中的性能。
- Mixture-of-Mamba在多种多模态预训练设置中进行评估,包括Transfusion、Chameleon和三模态扩展框架。
- Mixture-of-Mamba能在早期训练步骤达到相同损失值,同时显著降低计算成本。
- 在特定的多模态预训练设置中,Mixture-of-Mamba使用较少的计算资源即可达到相似的性能。
- 消融研究强调了分离投影组件的协同作用,联合分离效果更佳。
点此查看论文截图
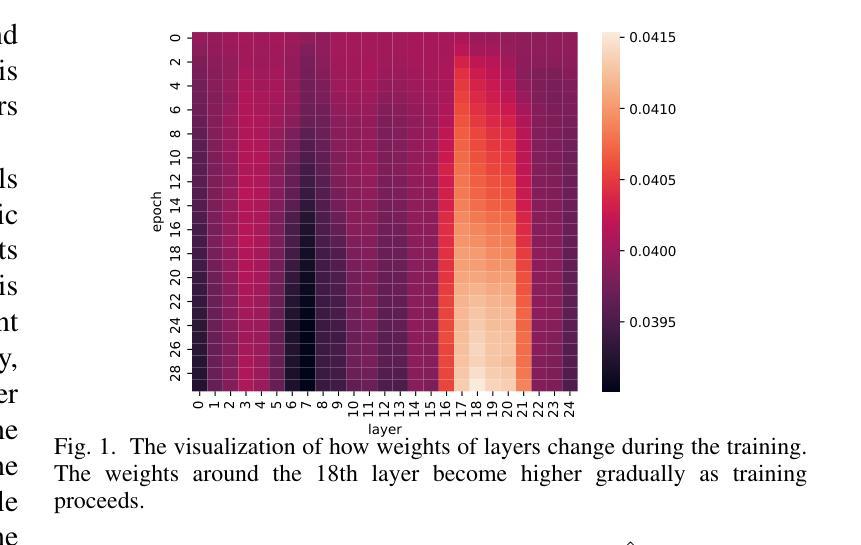
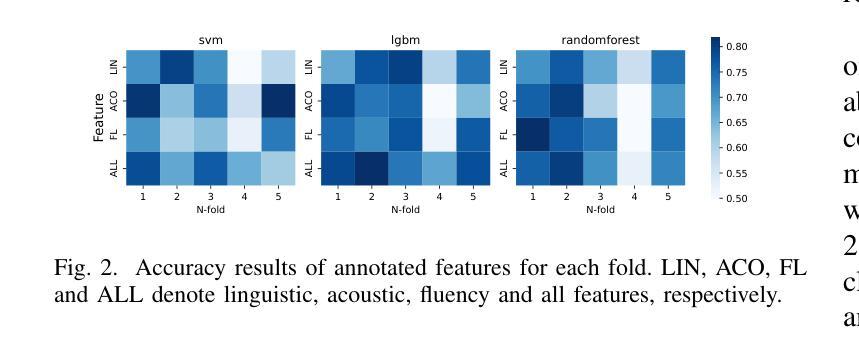
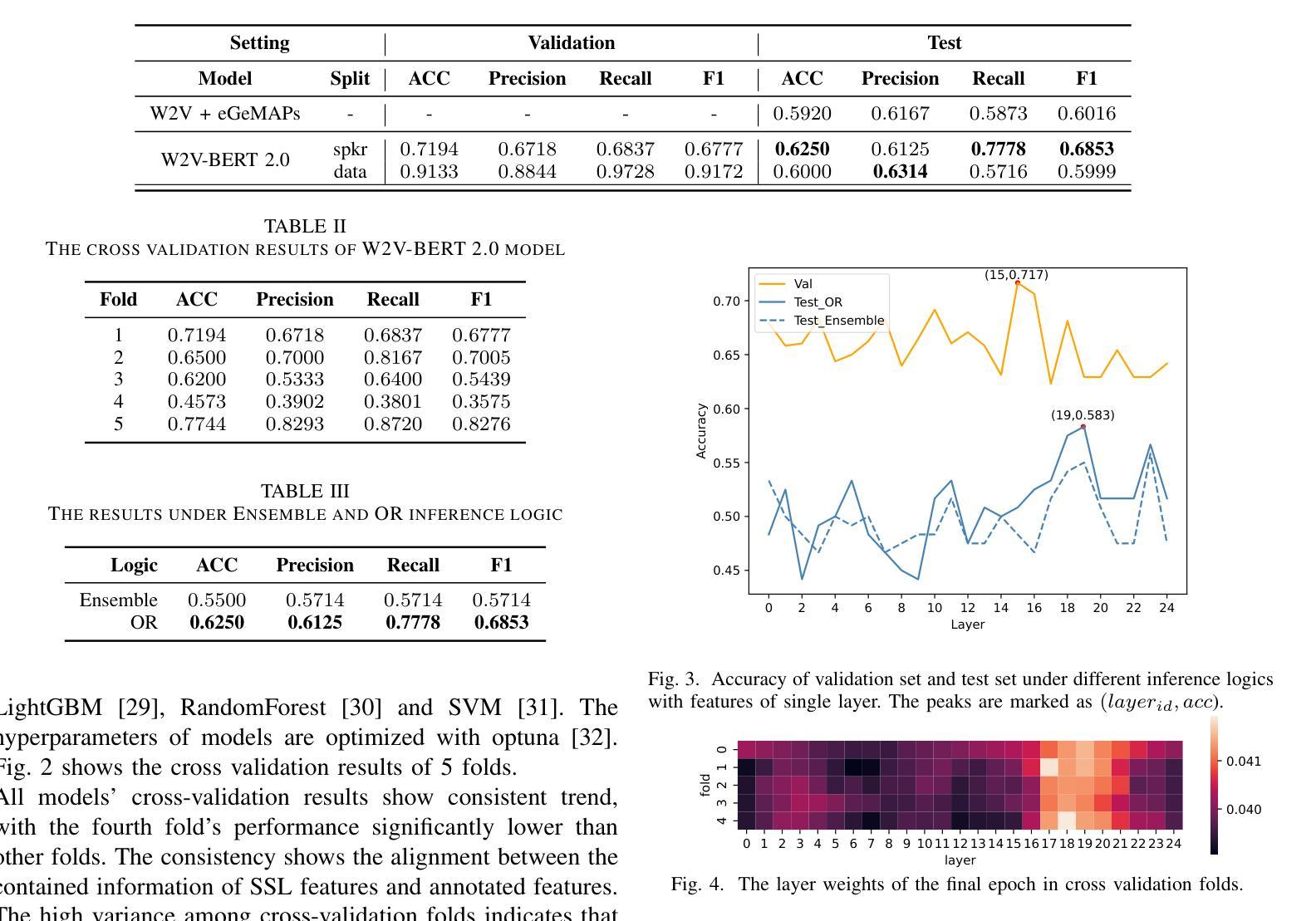
Enhancing and Exploring Mild Cognitive Impairment Detection with W2V-BERT-2.0
Authors:Yueguan Wang, Tatsunari Matsushima, Soichiro Matsushima, Toshimitsu Sakai
This study explores a multi-lingual audio self-supervised learning model for detecting mild cognitive impairment (MCI) using the TAUKADIAL cross-lingual dataset. While speech transcription-based detection with BERT models is effective, limitations exist due to a lack of transcriptions and temporal information. To address these issues, the study utilizes features directly from speech utterances with W2V-BERT-2.0. We propose a visualization method to detect essential layers of the model for MCI classification and design a specific inference logic considering the characteristics of MCI. The experiment shows competitive results, and the proposed inference logic significantly contributes to the improvements from the baseline. We also conduct detailed analysis which reveals the challenges related to speaker bias in the features and the sensitivity of MCI classification accuracy to the data split, providing valuable insights for future research.
本研究探索了一种多语言音频自监督学习模型,该模型使用TAUKADIAL跨语言数据集检测轻度认知障碍(MCI)。虽然基于BERT模型的语音转录检测是有效的,但由于缺乏转录和时序信息,仍存在局限性。为了解决这些问题,研究直接从语音片段中提取特征,使用W2V-BERT-2.0。我们提出了一种可视化方法来检测用于MCI分类的关键模型层,并设计了一种考虑MCI特征的特定推理逻辑。实验显示结果具有竞争力,所提出的推理逻辑对基线改进做出了重大贡献。我们还进行了详细分析,揭示了与说话者偏见相关的挑战以及MCI分类精度对数据分割的敏感性,为未来研究提供了宝贵见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ICASSP-SPADE workshop 2025
Summary
本研究利用多语言音频自监督学习模型,结合TAUKADIAL跨语言数据集,对轻度认知障碍(MCI)进行检测。研究采用基于语音特征的W2V-BERT-2.0模型,克服了依赖转录的BERT模型因缺乏转录和时序信息而存在的局限性。此外,研究还提出了一种可视化方法,用于检测用于MCI分类的关键模型层,并设计了针对MCI特性的推理逻辑。实验表明,该方法具有竞争力,提出的推理逻辑对改进基线有显著贡献。同时,研究还详细分析了与说话者相关的特征挑战和数据分割对MCI分类精度的影响,为未来的研究提供了宝贵见解。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用多语言音频自监督学习模型,利用TAUKADIAL跨语言数据集进行轻度认知障碍(MCI)检测。
- 针对现有基于语音转录的BERT模型的局限性,引入基于语音特征的W2V-BERT-2.0模型。
- 首次提出可视化方法以检测用于MCI分类的关键模型层。
- 设计针对MCI特性的推理逻辑,显著提高了检测准确率。
- 实验结果显示所提出的方法具有竞争力。
- 研究发现说话者相关的特征挑战对MCI分类的影响。
点此查看论文截图

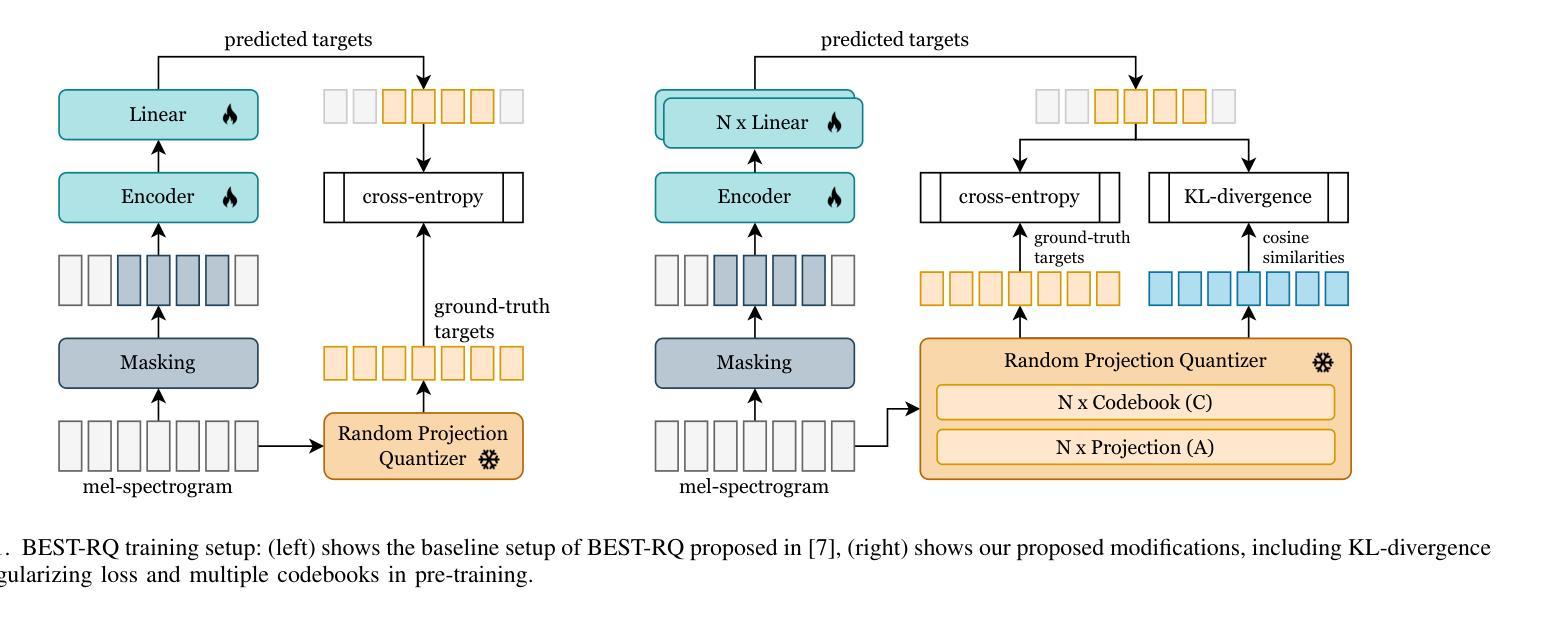
Optimized Self-supervised Training with BEST-RQ for Speech Recognition
Authors:Ilja Baumann, Dominik Wagner, Korbinian Riedhammer, Tobias Bocklet
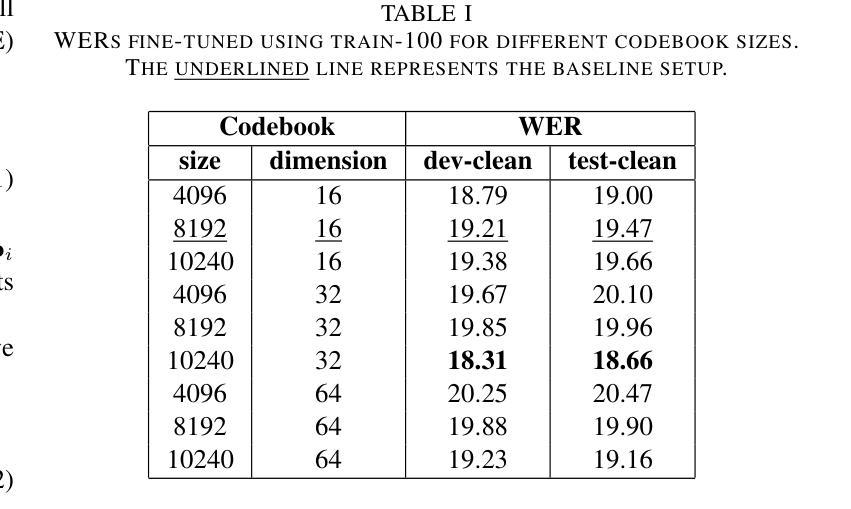
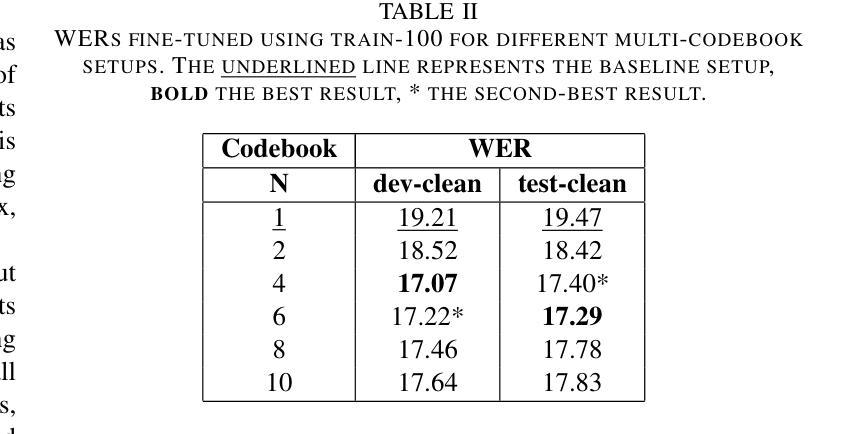
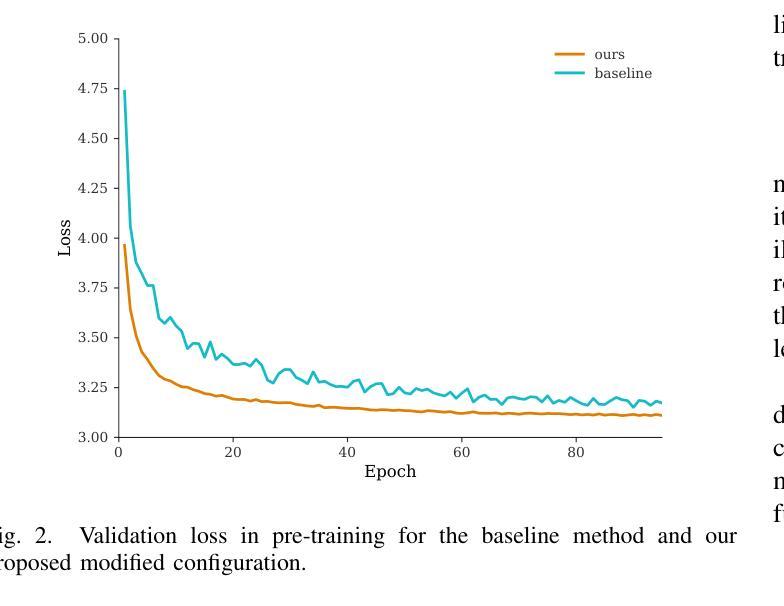
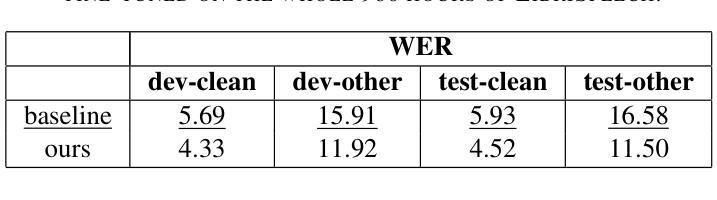
Self-supervised learning has been successfully used for various speech related tasks, including automatic speech recognition. BERT-based Speech pre-Training with Random-projection Quantizer (BEST-RQ) has achieved state-of-the-art results in speech recognition. In this work, we further optimize the BEST-RQ approach using Kullback-Leibler divergence as an additional regularizing loss and multi-codebook extension per cluster derived from low-level feature clustering. Preliminary experiments on train-100 split of LibriSpeech result in a relative improvement of 11.2% on test-clean by using multiple codebooks, utilizing a combination of cross-entropy and Kullback-Leibler divergence further reduces the word error rate by 4.5%. The proposed optimizations on full LibriSpeech pre-training and fine-tuning result in relative word error rate improvements of up to 23.8% on test-clean and 30.6% on test-other using 6 codebooks. Furthermore, the proposed setup leads to faster convergence in pre-training and fine-tuning and additionally stabilizes the pre-training.
自监督学习已成功应用于各种语音相关任务,包括自动语音识别。基于BERT的随机投影量化器(BEST-RQ)的语音预训练在语音识别方面取得了最先进的成果。在这项工作中,我们进一步使用Kullback-Leibler散度作为额外的正则化损失,并利用基于低级别特征聚类的每个集群的多代码本扩展来优化BEST-RQ方法。在LibriSpeech的train-100分割上进行初步实验,通过使用多个代码本,测试clean上的相对改进了11.2%。结合交叉熵和Kullback-Leibler散度,进一步降低了单词错误率4.5%。对LibriSpeech的完全预训练和微调提出的优化,在测试clean上相对单词错误率提高了23.8%,在测试其他上提高了30.6%,使用6个代码本。此外,该设置还导致了预训练和微调中的更快收敛,并额外稳定了预训练。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于BERT的语音预训练方法BEST-RQ的优化研究。通过使用Kullback-Leibler散度作为额外的正则化损失和多代码本扩展,对LibriSpeech数据集进行初步实验,取得了显著的词错误率改进。优化后的方法在测试集clean上相对改进了高达23.8%,在其他测试集上相对改进了30.6%,同时使用多种代码本还能加速预训练和微调过程的收敛,并增强其稳定性。
Key Takeaways
- BERT-based Speech pre-Training with Random-projection Quantizer (BEST-RQ)已用于语音识别任务,并获得了业界最佳结果。
- 研究者对BEST-RQ方法进行了优化,采用Kullback-Leibler散度作为正则化损失和多代码本扩展方法。
- 在LibriSpeech数据集上进行的初步实验显示,使用多个代码本相较于未优化模型降低了词错误率(WER)。在测试集clean上的相对改进达到了高达23.8%,在其他测试集上的相对改进达到了高达30.6%。
- 结合交叉熵和Kullback-Leibler散度的优化方法进一步降低了词错误率。
点此查看论文截图

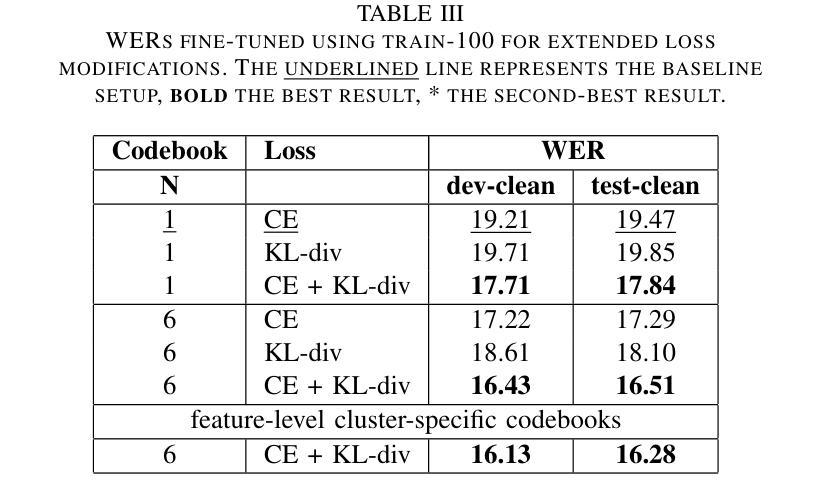
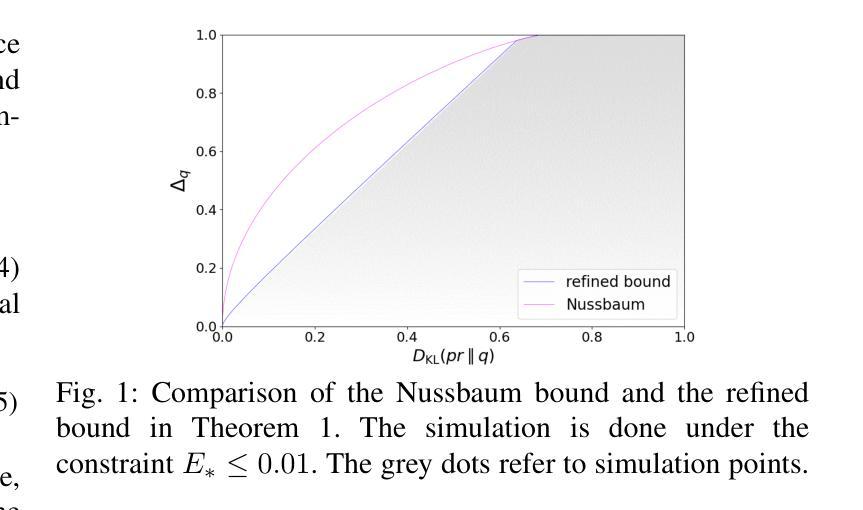
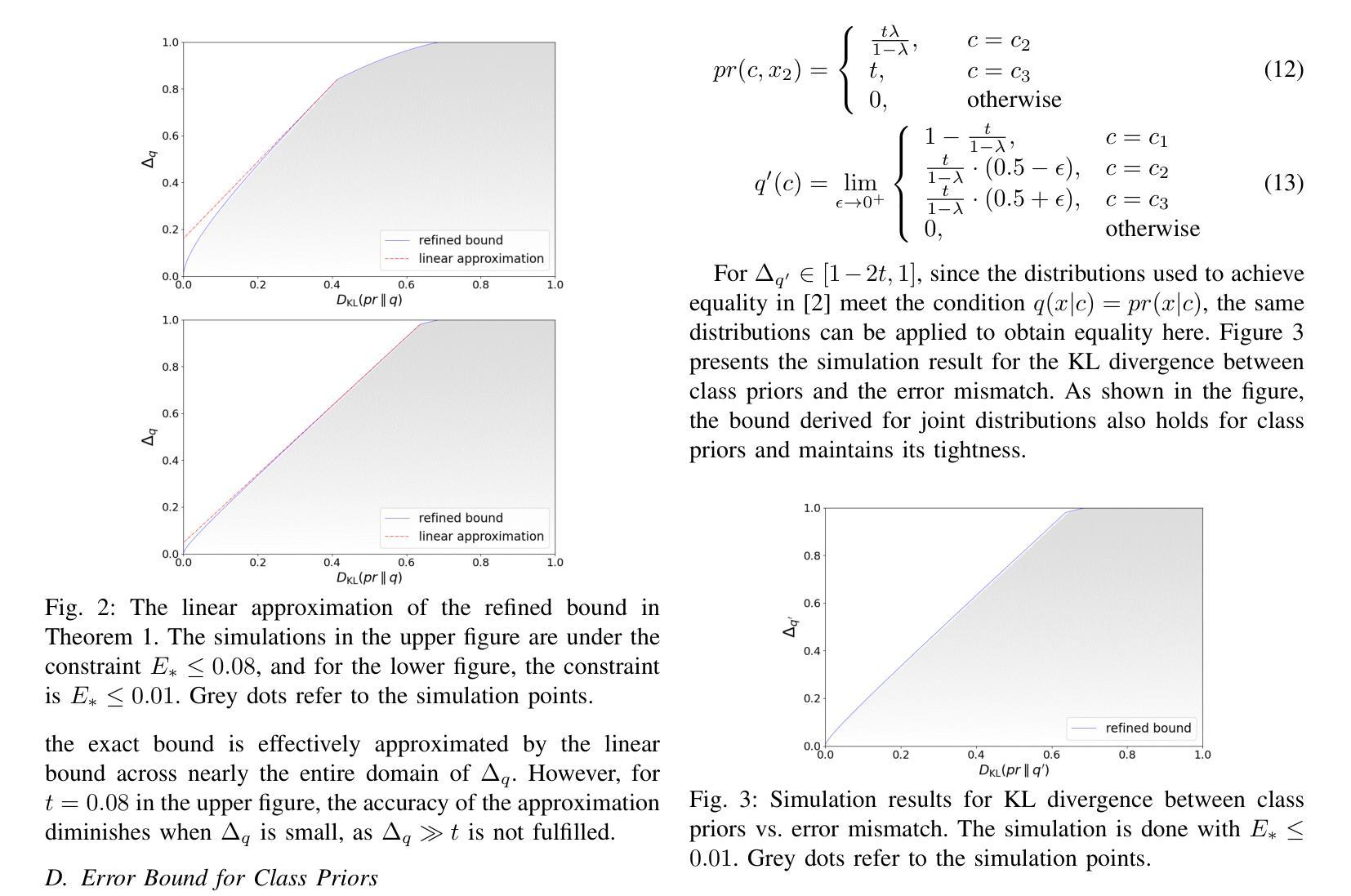
Classification Error Bound for Low Bayes Error Conditions in Machine Learning
Authors:Zijian Yang, Vahe Eminyan, Ralf Schlüter, Hermann Ney
In statistical classification and machine learning, classification error is an important performance measure, which is minimized by the Bayes decision rule. In practice, the unknown true distribution is usually replaced with a model distribution estimated from the training data in the Bayes decision rule. This substitution introduces a mismatch between the Bayes error and the model-based classification error. In this work, we apply classification error bounds to study the relationship between the error mismatch and the Kullback-Leibler divergence in machine learning. Motivated by recent observations of low model-based classification errors in many machine learning tasks, bounding the Bayes error to be lower, we propose a linear approximation of the classification error bound for low Bayes error conditions. Then, the bound for class priors are discussed. Moreover, we extend the classification error bound for sequences. Using automatic speech recognition as a representative example of machine learning applications, this work analytically discusses the correlations among different performance measures with extended bounds, including cross-entropy loss, language model perplexity, and word error rate.
在统计分类和机器学习领域,分类误差是一项重要的性能度量,通过贝叶斯决策规则来最小化。在实践中,贝叶斯决策规则中的未知真实分布通常会用基于训练数据估计的模型分布来替代。这种替代引入了贝叶斯误差和基于模型的分类误差之间的不匹配。在这项工作中,我们应用分类误差界限来研究机器学习中的误差不匹配与Kullback-Leibler散度之间的关系。受近期许多机器学习任务中观察到的低模型分类误差的启发,为了将贝叶斯误差限定在较低范围,我们提出了低贝叶斯误差条件下的分类误差界限的线性近似。然后,讨论了类别先验的界限。此外,我们扩展了序列的分类误差界限。以自动语音识别作为机器学习的代表性应用,这项工作通过扩展的界限分析讨论了不同的性能度量之间的相关性,包括交叉熵损失、语言模型困惑度和词错误率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文探讨了统计分类和机器学习中的分类错误衡量标准,介绍了贝叶斯决策规则中的误差与模型分布之间的不匹配问题。文章通过分类误差界限研究了误差不匹配与Kullback-Leibler散度的关系,提出了低贝叶斯误差条件下的分类误差界限的线性近似方法,并讨论了类别先验的界限。此外,文章还将分类误差界限扩展到序列,以自动语音识别为例,讨论了不同性能衡量标准(包括交叉熵损失、语言模型困惑度和词错误率)的关联。
Key Takeaways
- 分类错误是衡量机器学习模型性能的重要标准,贝叶斯决策规则旨在最小化此误差。
- 在实践中,模型的未知真实分布通常使用从训练数据中估计出的模型分布来替代,这引入了贝叶斯误差和模型基于的分类误差之间的不匹配。
- 文章通过分类误差界限研究了误差不匹配与Kullback-Leibler散度的关系。
- 对于低贝叶斯误差条件,文章提出了分类误差界限的线性近似方法。
- 文章讨论了类别先验的界限。
- 文章将分类误差界限扩展到序列,并探讨了自动语音识别等机器学习应用中不同性能衡量标准之间的关联。
点此查看论文截图

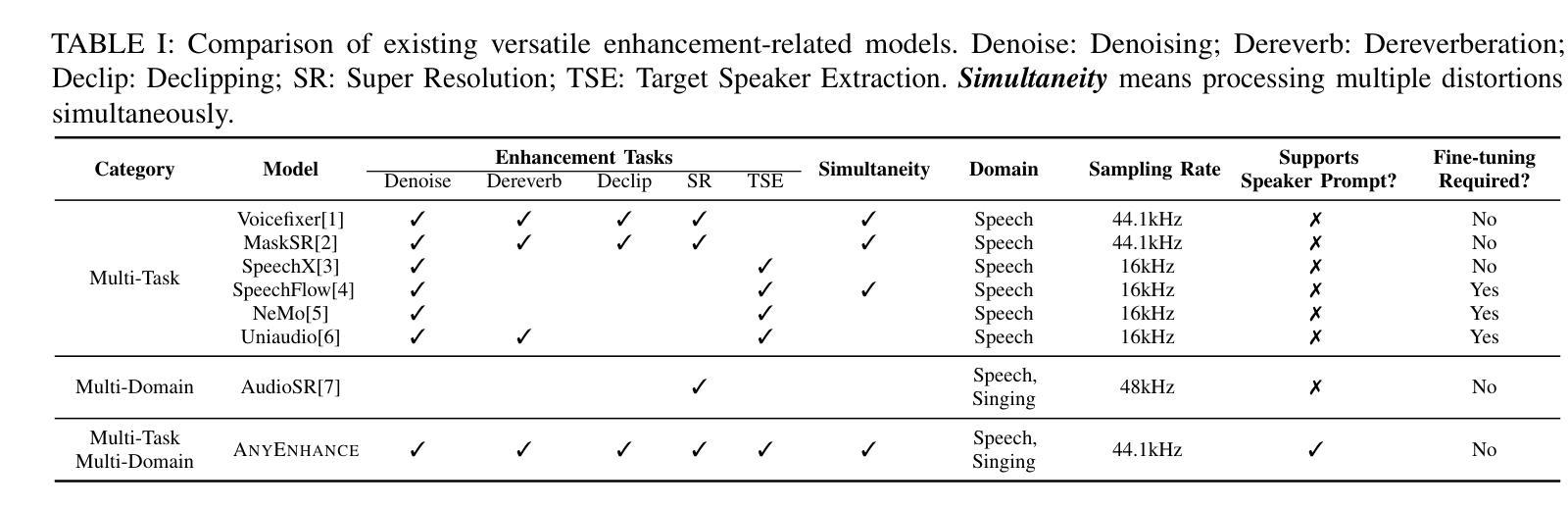
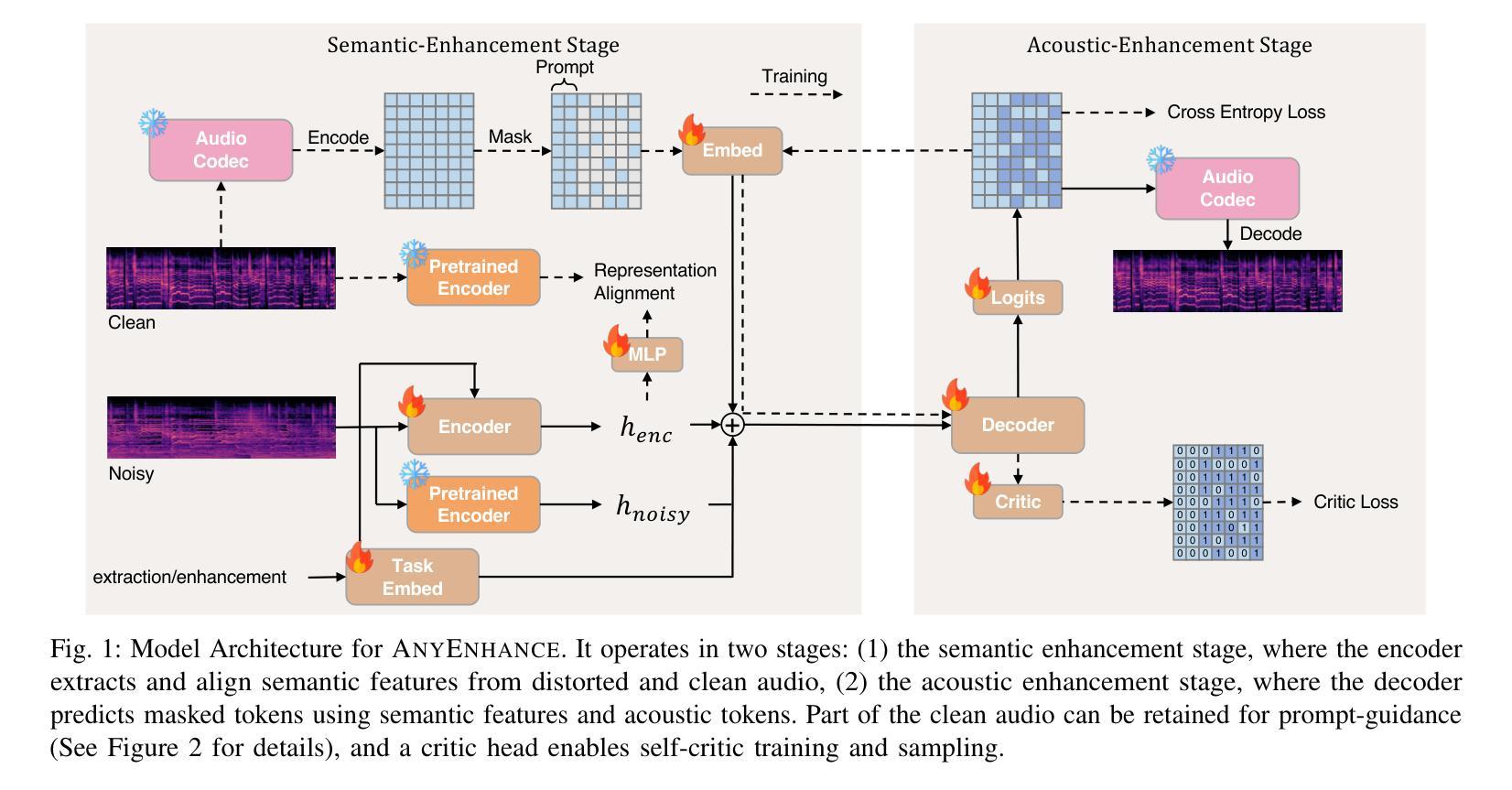
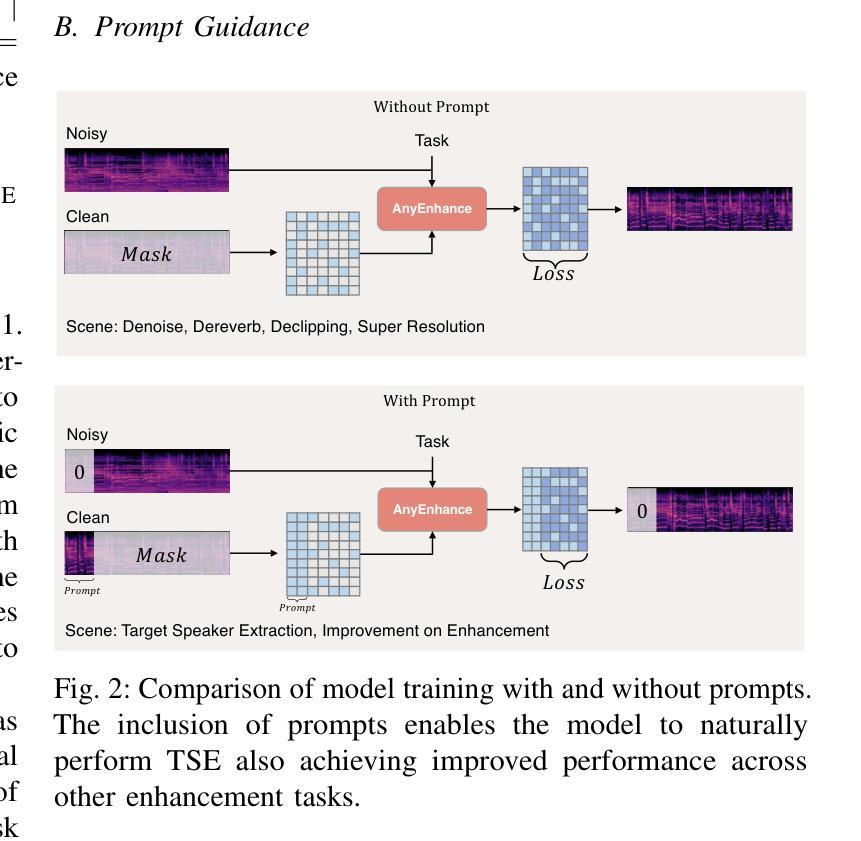
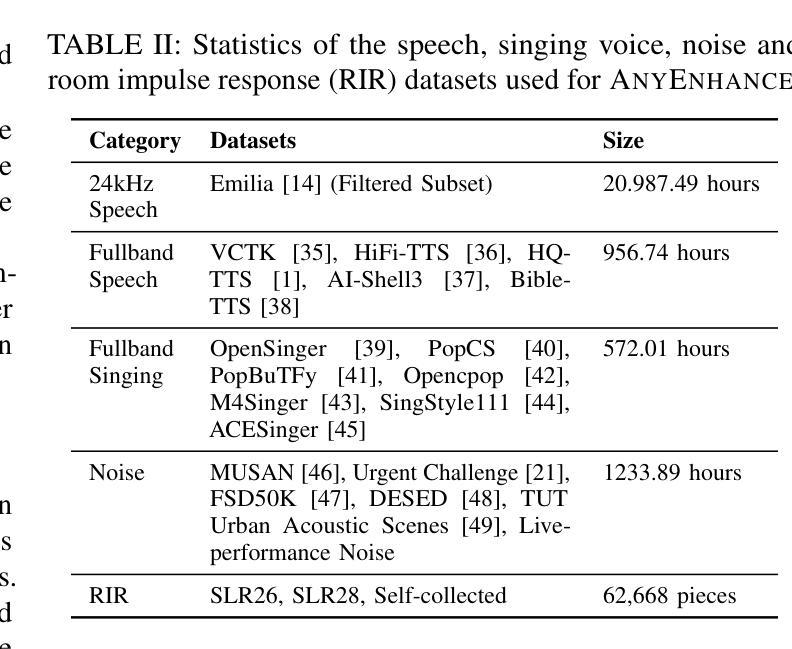
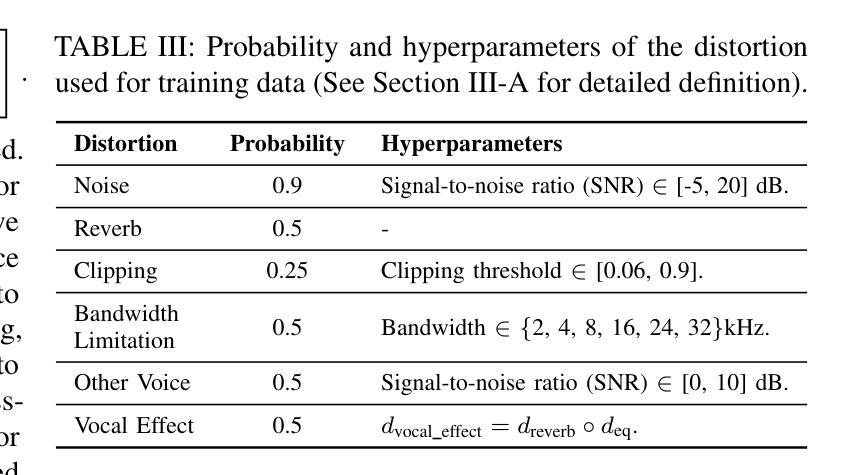
AnyEnhance: A Unified Generative Model with Prompt-Guidance and Self-Critic for Voice Enhancement
Authors:Junan Zhang, Jing Yang, Zihao Fang, Yuancheng Wang, Zehua Zhang, Zhuo Wang, Fan Fan, Zhizheng Wu
We introduce AnyEnhance, a unified generative model for voice enhancement that processes both speech and singing voices. Based on a masked generative model, AnyEnhance is capable of handling both speech and singing voices, supporting a wide range of enhancement tasks including denoising, dereverberation, declipping, super-resolution, and target speaker extraction, all simultaneously and without fine-tuning. AnyEnhance introduces a prompt-guidance mechanism for in-context learning, which allows the model to natively accept a reference speaker’s timbre. In this way, it could boost enhancement performance when a reference audio is available and enable the target speaker extraction task without altering the underlying architecture. Moreover, we also introduce a self-critic mechanism into the generative process for masked generative models, yielding higher-quality outputs through iterative self-assessment and refinement. Extensive experiments on various enhancement tasks demonstrate AnyEnhance outperforms existing methods in terms of both objective metrics and subjective listening tests. Demo audios are publicly available at https://amphionspace.github.io/anyenhance/.
我们介绍了AnyEnhance,这是一个统一的生成模型,用于处理语音和歌声的增强。基于掩模生成模型,AnyEnhance能够同时处理语音和歌声,支持广泛的增强任务,包括去噪、去混响、去剪辑、超分辨率和目标说话人提取,而且无需微调。AnyEnhance引入了一种上下文学习中的提示引导机制,允许模型原生接受参考说话人的音色。这样,当参考音频可用时,它可以提高增强性能,并在不改变底层架构的情况下实现目标说话人提取任务。此外,我们还将在生成过程中为掩模生成模型引入自我批判机制,通过迭代自我评估和细化产生更高质量的输出。对各种增强任务的广泛实验表明,AnyEnhance在客观指标和主观听觉测试方面均优于现有方法。演示音频可在https://amphionspace.github.io/anyenhance/公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures
Summary
AnyEnhance是一个统一的生成模型,用于处理语音和歌唱声音的增强。它基于掩模生成模型,支持多种增强任务,如去噪、去混响、去剪辑、超分辨率和目标说话人提取。AnyEnhance引入提示指导机制,可在有参考音频的情况下提高增强性能,并启用目标说话人提取任务。此外,它还引入了自我批判机制,通过迭代自我评估和细化产生更高质量的输出。实验表明,AnyEnhance在客观指标和主观听觉测试方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- AnyEnhance是一个统一的生成模型,用于语音和歌唱声音增强。
- 支持多种增强任务,包括去噪、去混响、去剪辑、超分辨率和目标说话人提取。
- AnyEnhance通过引入提示指导机制,在有参考音频的情况下提高增强性能。
- 引入自我批判机制,通过迭代自我评估和细化提高输出质量。
- 该模型可以同时处理多种任务,无需微调。
- AnyEnhance在客观指标和主观听觉测试方面的性能优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Robust Cross-Etiology and Speaker-Independent Dysarthric Speech Recognition
Authors:Satwinder Singh, Qianli Wang, Zihan Zhong, Clarion Mendes, Mark Hasegawa-Johnson, Waleed Abdulla, Seyed Reza Shahamiri
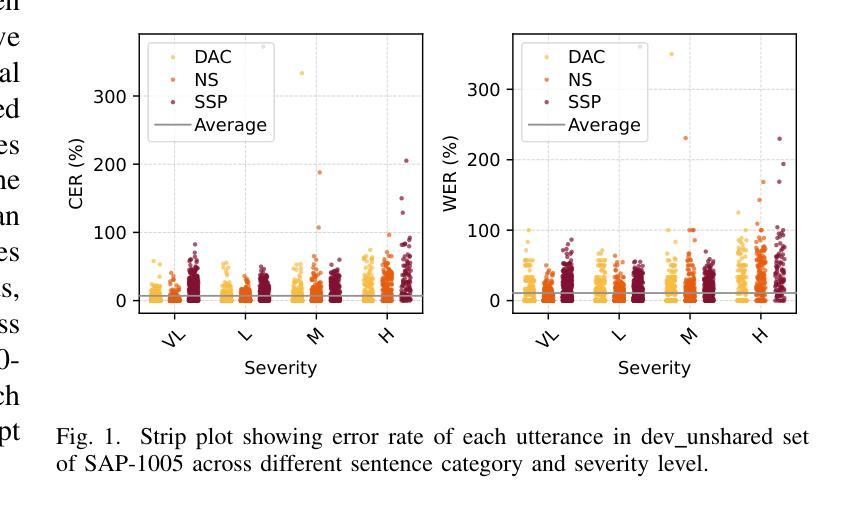
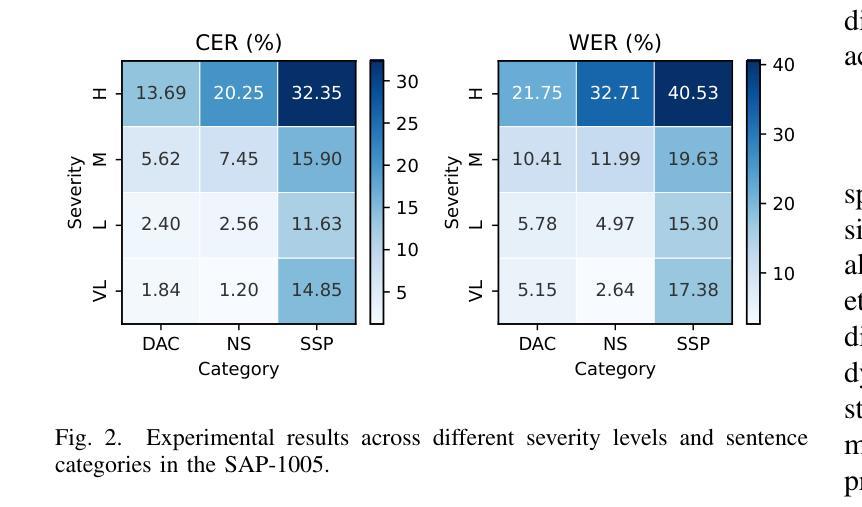
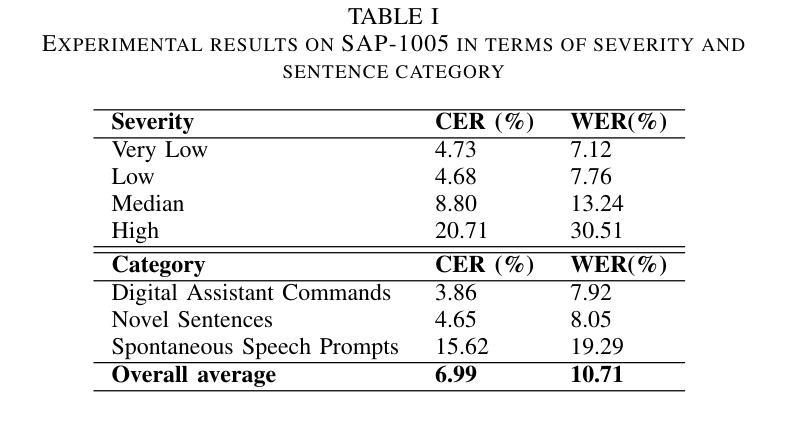
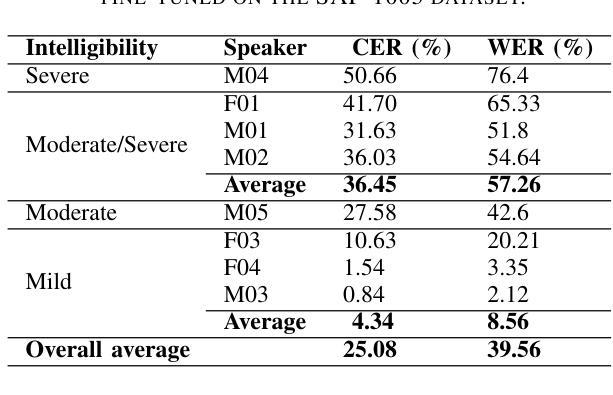
In this paper, we present a speaker-independent dysarthric speech recognition system, with a focus on evaluating the recently released Speech Accessibility Project (SAP-1005) dataset, which includes speech data from individuals with Parkinson’s disease (PD). Despite the growing body of research in dysarthric speech recognition, many existing systems are speaker-dependent and adaptive, limiting their generalizability across different speakers and etiologies. Our primary objective is to develop a robust speaker-independent model capable of accurately recognizing dysarthric speech, irrespective of the speaker. Additionally, as a secondary objective, we aim to test the cross-etiology performance of our model by evaluating it on the TORGO dataset, which contains speech samples from individuals with cerebral palsy (CP) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). By leveraging the Whisper model, our speaker-independent system achieved a CER of 6.99% and a WER of 10.71% on the SAP-1005 dataset. Further, in cross-etiology settings, we achieved a CER of 25.08% and a WER of 39.56% on the TORGO dataset. These results highlight the potential of our approach to generalize across unseen speakers and different etiologies of dysarthria.
本文介绍了一个独立于说话者的言语障碍语音识别系统。我们重点关注于评估最近发布的语音无障碍项目(SAP-1005)数据集,该数据集包含帕金森病患者(PD)的语音数据。尽管言语障碍语音识别的研究日益增多,但许多现有系统都是依赖于说话者和自适应的,限制了它们在不同说话者和病因中的通用性。我们的主要目标是开发一个稳健的独立于说话者的模型,能够准确识别言语障碍语音,而无论说话者如何。此外,我们的次要目标是通过在TORGO数据集上评估模型来测试模型的跨病因性能。TORGO数据集包含来自脑瘫(CP)和肌萎缩性侧索硬化症(ALS)患者的语音样本。通过利用Whisper模型,我们的独立于说话者的系统实现了SAP-1005数据集上的字符错误率(CER)为6.99%,单词错误率(WER)为10.71%。此外,在跨病因设置下,我们在TORGO数据集上实现了CER为25.08%,WER为39.56%。这些结果突显了我们的方法在不同未见过的说话者和不同的言语障碍病因中的通用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary:
本研究提出一个不依赖于特定说话者的语言障碍语音识别系统,重点在于评估最新发布的语音可访问性项目(SAP-1005)数据集,其中包含帕金森病患者(PD)的语音数据。系统旨在开发一个稳健的跨说话者模型,能够准确识别语言障碍语音,无论说话者如何。使用whisper模型,该模型在SAP-1005数据集上取得了字符错误率(CER)为6.99%,词错误率(WER)为10.71%的成绩。此外,在跨疾病设置下,模型在TORGO数据集上取得了CER为25.08%,WER为39.56%的成绩。这些结果表明,该方法具有跨未见说话者和不同语言障碍类型的推广潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究提出了一个不依赖于特定说话者的语言障碍语音识别系统。
- 系统评估了SAP-1005数据集,包含帕金森病患者(PD)的语音数据。
- 利用whisper模型,系统在SAP-1005数据集上实现了较好的识别效果。
- 系统尝试在TORGO数据集上进行跨疾病测试,取得了一定成绩。
- 该系统具有跨未见说话者和不同语言障碍类型的推广潜力。
- 该研究填补了关于语言障碍语音识别的现有系统的不足,如依赖特定说话者或缺乏跨不同说话者和病因的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

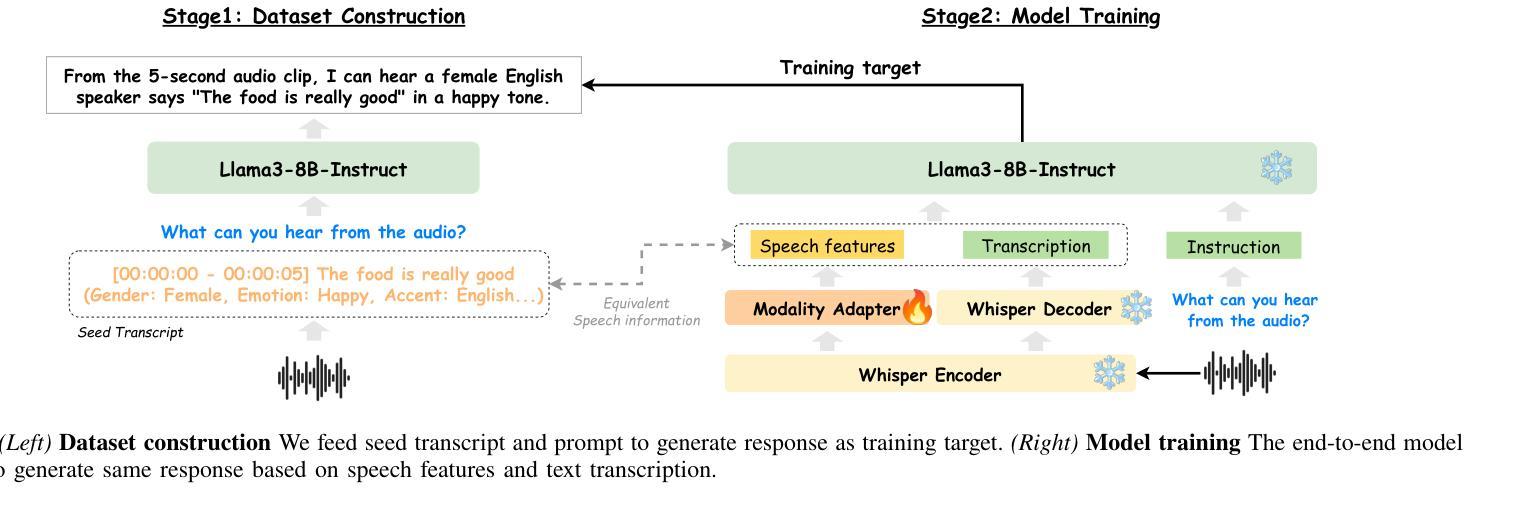
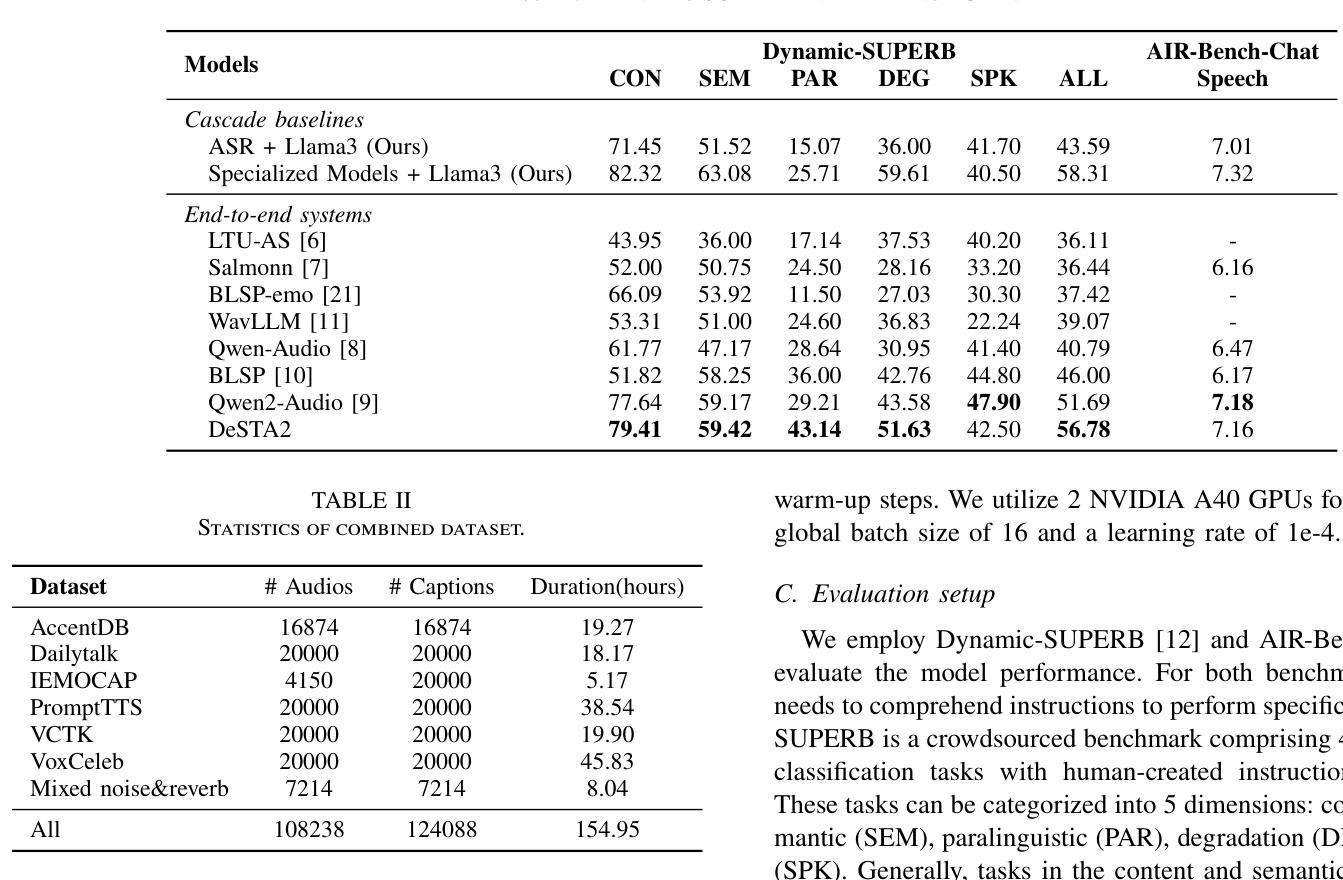
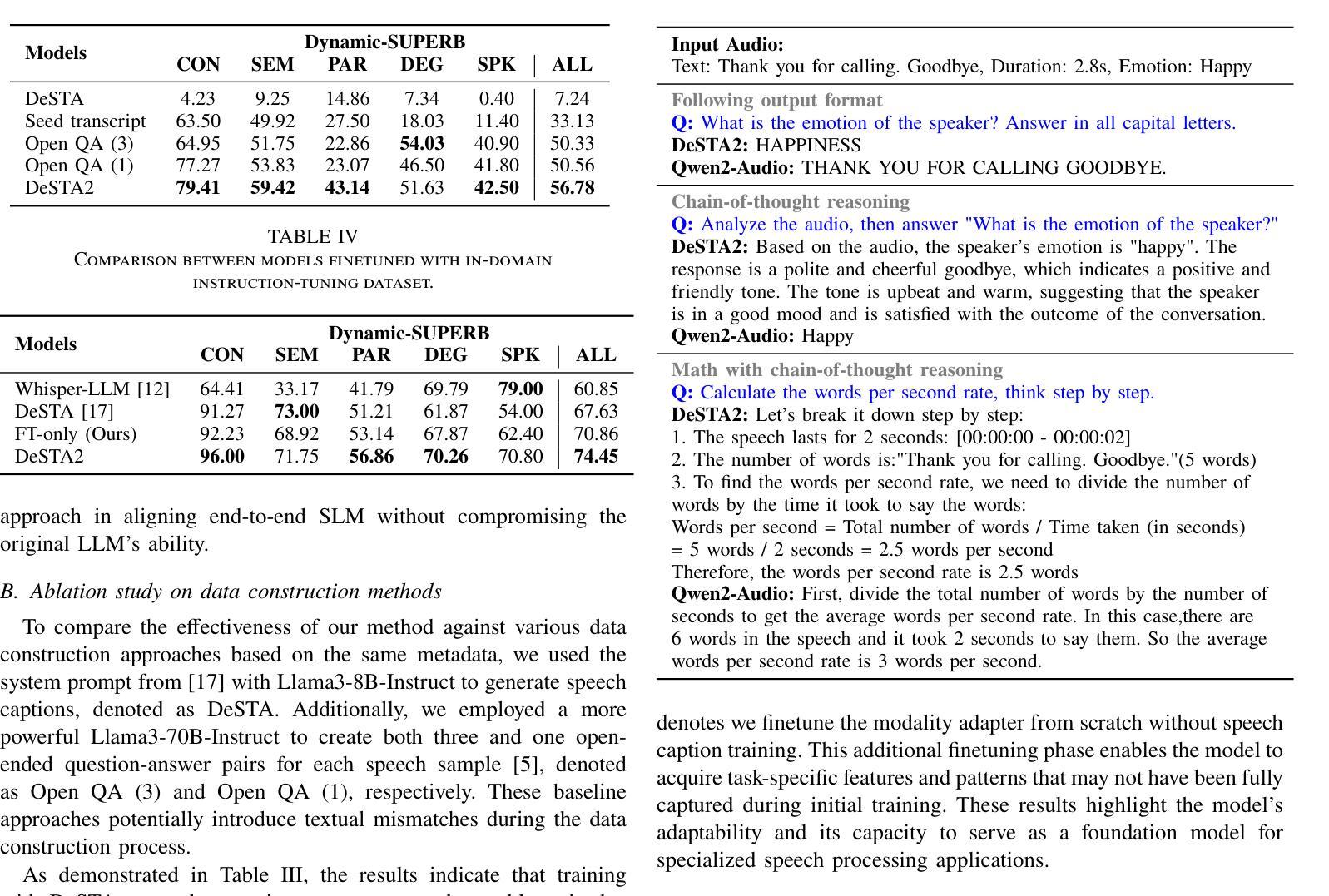
DeSTA2: Developing Instruction-Following Speech Language Model Without Speech Instruction-Tuning Data
Authors:Ke-Han Lu, Zhehuai Chen, Szu-Wei Fu, Chao-Han Huck Yang, Jagadeesh Balam, Boris Ginsburg, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang, Hung-yi Lee
Recent end-to-end speech language models (SLMs) have expanded upon the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by incorporating pre-trained speech models. However, these SLMs often undergo extensive speech instruction-tuning to bridge the gap between speech and text modalities. This requires significant annotation efforts and risks catastrophic forgetting of the original language capabilities. In this work, we present a simple yet effective automatic process for creating speech-text pair data that carefully injects speech paralinguistic understanding abilities into SLMs while preserving the inherent language capabilities of the text-based LLM. Our model demonstrates general capabilities for speech-related tasks without the need for speech instruction-tuning data, achieving impressive performance on Dynamic-SUPERB and AIR-Bench-Chat benchmarks. Furthermore, our model exhibits the ability to follow complex instructions derived from LLMs, such as specific output formatting and chain-of-thought reasoning. Our approach not only enhances the versatility and effectiveness of SLMs but also reduces reliance on extensive annotated datasets, paving the way for more efficient and capable speech understanding systems.
最近的端到端语音语言模型(SLM)通过融入预训练的语音模型,扩大了大型语言模型(LLM)的能力。然而,这些SLM通常需要进行大量的语音指令调整,以弥合语音和文本模态之间的差距。这需要大量的标注工作,并存在原有语言能力灾难性遗忘的风险。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
近期端对端语音语言模型(SLM)结合预训练语音模型,提升了大型语言模型(LLM)的功能。然而,这些SLM需要经过大量的语音指令调整来弥合语音与文本模态之间的差距,这需要大量的标注工作并存在遗忘原始语言能力的风险。本研究提出了一种简单有效的自动创建语音文本对数据的过程,该方法能够谨慎地将语音副语言理解力注入SLM中,同时保留文本基础LLM的固有语言能力。我们的模型在动态SUPERB和AIR-Bench-Chat基准测试中表现出色,无需语音指令调整数据即可进行语音相关任务。此外,我们的模型展现出遵循LLM派生的复杂指令的能力,如特定的输出格式和链式思维推理。我们的方法不仅提高了SLM的通用性和效率,还减少了对面大量标注数据集的依赖,为构建更高效、更强大的语音理解系统铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 端对端语音语言模型(SLM)结合了预训练语音模型以提升大型语言模型(LLM)的功能。
- SLMs需要通过语音指令调整来桥接语音和文本模态之间的差距,这需要大量标注数据并存在遗忘原始语言能力的风险。
- 提出了一种自动创建语音文本对数据的方法,以注入语音副语言理解力并保留LLM的固有语言能力。
- 模型在多个基准测试中表现出色,无需额外的语音指令调整即可执行语音相关任务。
- 模型能够遵循复杂的指令,包括特定的输出格式和链式思维推理。
- 方法提高了SLM的通用性和效率。
点此查看论文截图