⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-29 更新
CLISC: Bridging clip and sam by enhanced cam for unsupervised brain tumor segmentation
Authors:Xiaochuan Ma, Jia Fu, Wenjun Liao, Shichuan Zhang, Guotai Wang
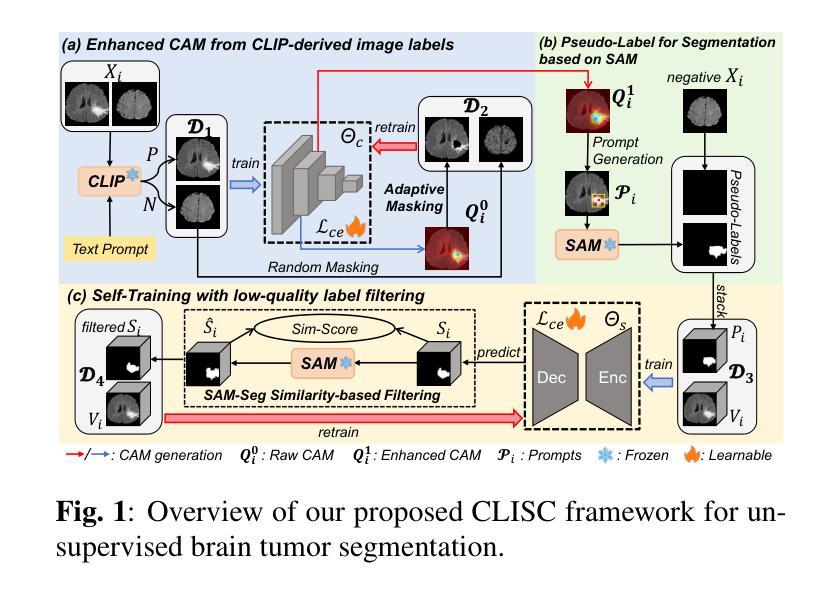
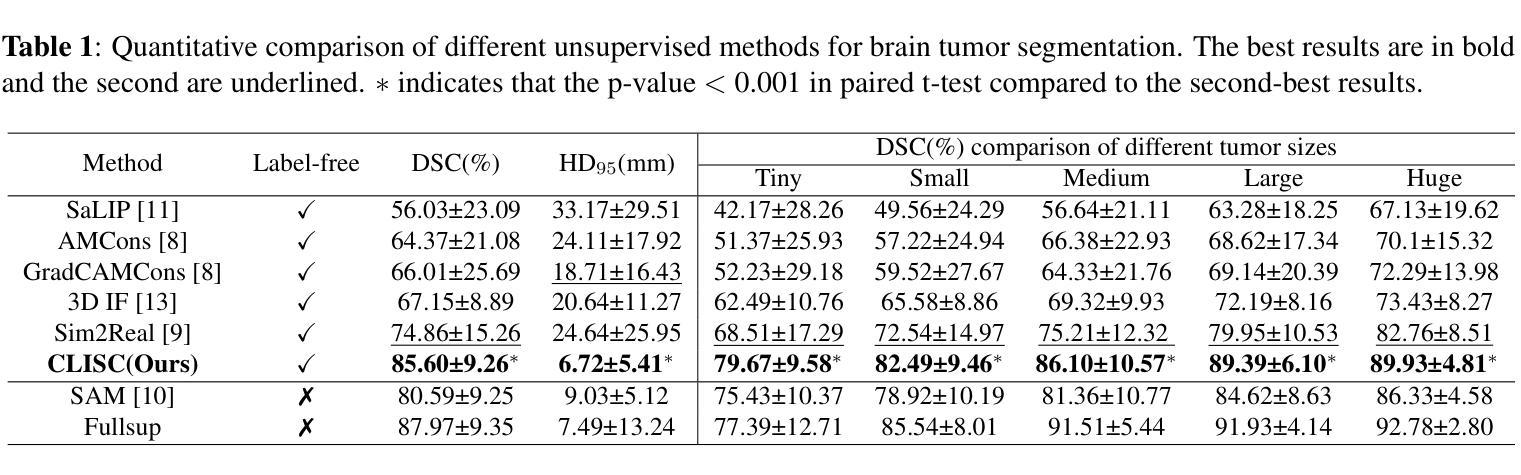
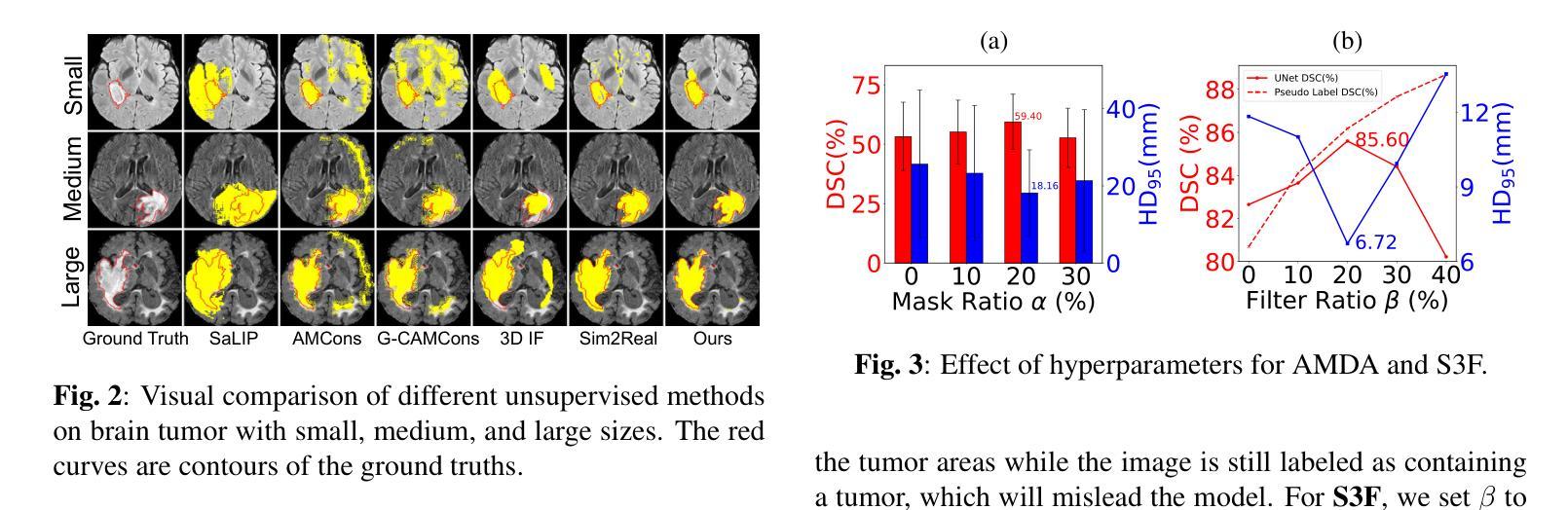
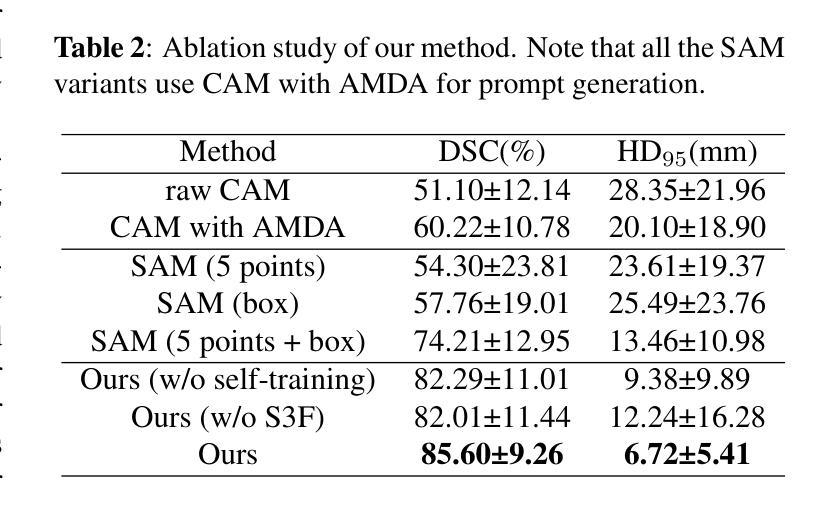
Brain tumor segmentation is important for diagnosis of the tumor, and current deep-learning methods rely on a large set of annotated images for training, with high annotation costs. Unsupervised segmentation is promising to avoid human annotations while the performance is often limited. In this study, we present a novel unsupervised segmentation approach that leverages the capabilities of foundation models, and it consists of three main steps: (1) A vision-language model (i.e., CLIP) is employed to obtain image-level pseudo-labels for training a classification network. Class Activation Mapping (CAM) is then employed to extract Regions of Interest (ROIs), where an adaptive masking-based data augmentation is used to enhance ROI identification.(2) The ROIs are used to generate bounding box and point prompts for the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to obtain segmentation pseudo-labels. (3) A 3D segmentation network is trained with the SAM-derived pseudo-labels, where low-quality pseudo-labels are filtered out in a self-learning process based on the similarity between the SAM’s output and the network’s prediction. Evaluation on the BraTS2020 dataset demonstrates that our approach obtained an average Dice Similarity Score (DSC) of 85.60%, outperforming five state-of-the-art unsupervised segmentation methods by more than 10 percentage points. Besides, our approach outperforms directly using SAM for zero-shot inference, and its performance is close to fully supervised learning.
脑肿瘤分割对于肿瘤诊断具有重要意义,当前深度学习方法依赖于大量标注图像进行训练,标注成本高昂。无监督分割方法具有避免人工标注的潜力,但性能往往受到限制。本研究提出了一种新型无监督分割方法,该方法利用基础模型的能力,主要包含三个步骤:(1)采用视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)获取用于训练分类网络的图像级伪标签。然后采用类激活映射(CAM)提取感兴趣区域(ROI),并使用自适应掩膜式数据增强来提高ROI识别。(2)使用ROI生成边界框和点提示,以供分段任何模型(SAM)获得分割伪标签。(3)使用SAM衍生的伪标签训练3D分割网络,在自我学习过程中过滤掉低质量的伪标签,该过程基于SAM输出与网络预测之间的相似性。在BraTS2020数据集上的评估表明,我们的方法获得了平均Dice相似度分数(DSC)为85.60%,比五种最先进的无监督分割方法的性能高出超过10个百分点。此外,我们的方法优于直接使用SAM进行零样本推理,其性能接近完全监督学习。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22st IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2025)
Summary
基于计算机视觉模型的无监督脑肿瘤分割方法取得了突破性进展。通过CLIP模型获取图像级别的伪标签训练分类网络,利用CAM提取感兴趣区域并进行自适应掩膜增强;再结合SAM模型生成边界框和点提示获得分割伪标签,最后通过自学习过程筛选出高质量伪标签用于训练三维分割网络。该技术在BraTS2020数据集上的平均Dice相似度达到85.6%,超越其他五种前沿无监督分割技术并接近全监督学习的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种新型无监督脑肿瘤分割方法,结合计算机视觉模型和自适应数据增强技术。
- 利用CLIP模型获取图像级别的伪标签进行训练分类网络,并通过CAM提取感兴趣区域。
- 利用SAM模型生成边界框和点提示以获取分割伪标签。
- 通过自学习过程筛选出高质量伪标签用于训练三维分割网络。
- 该方法在BraTS2020数据集上的性能卓越,平均Dice相似度达到85.6%。
- 此方法超越了五种最新的无监督分割技术,并接近全监督学习的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

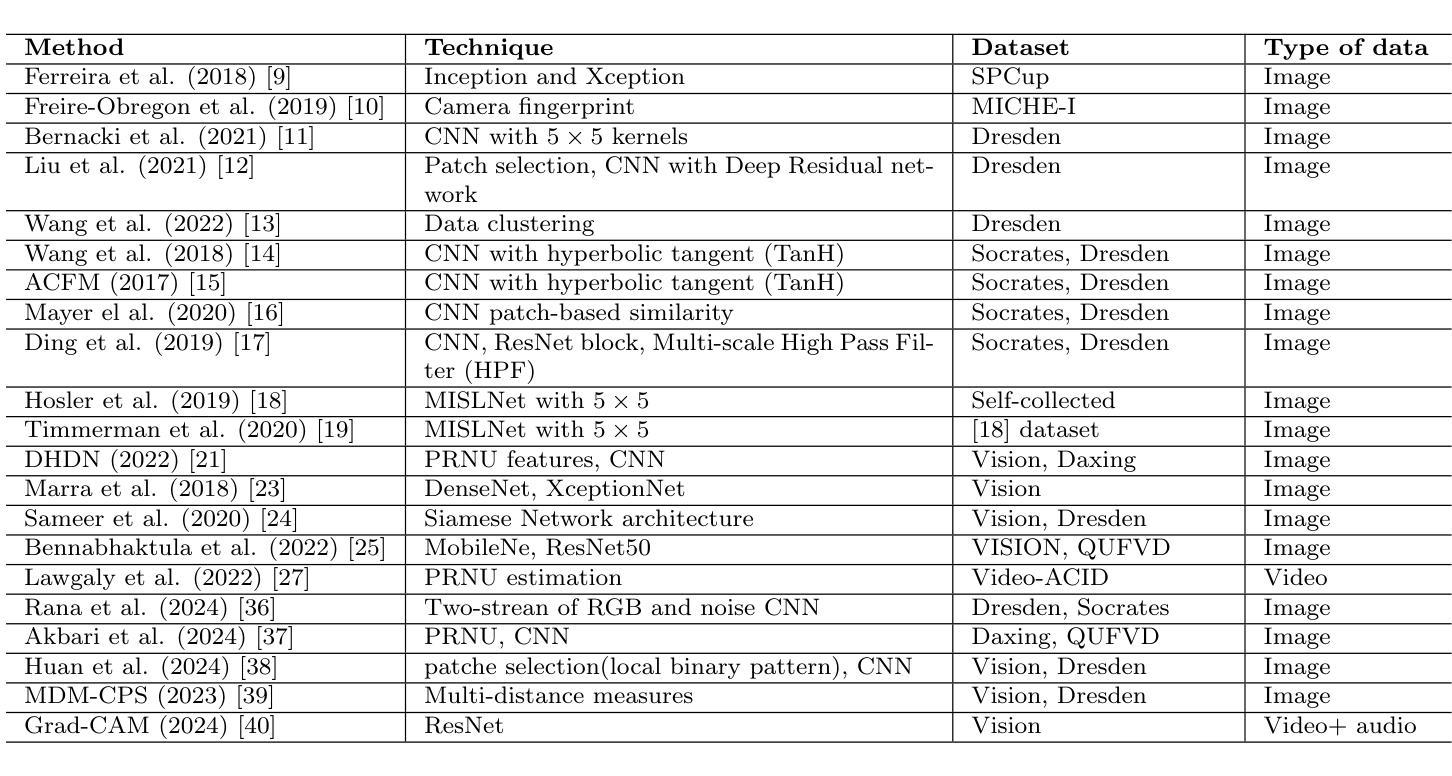
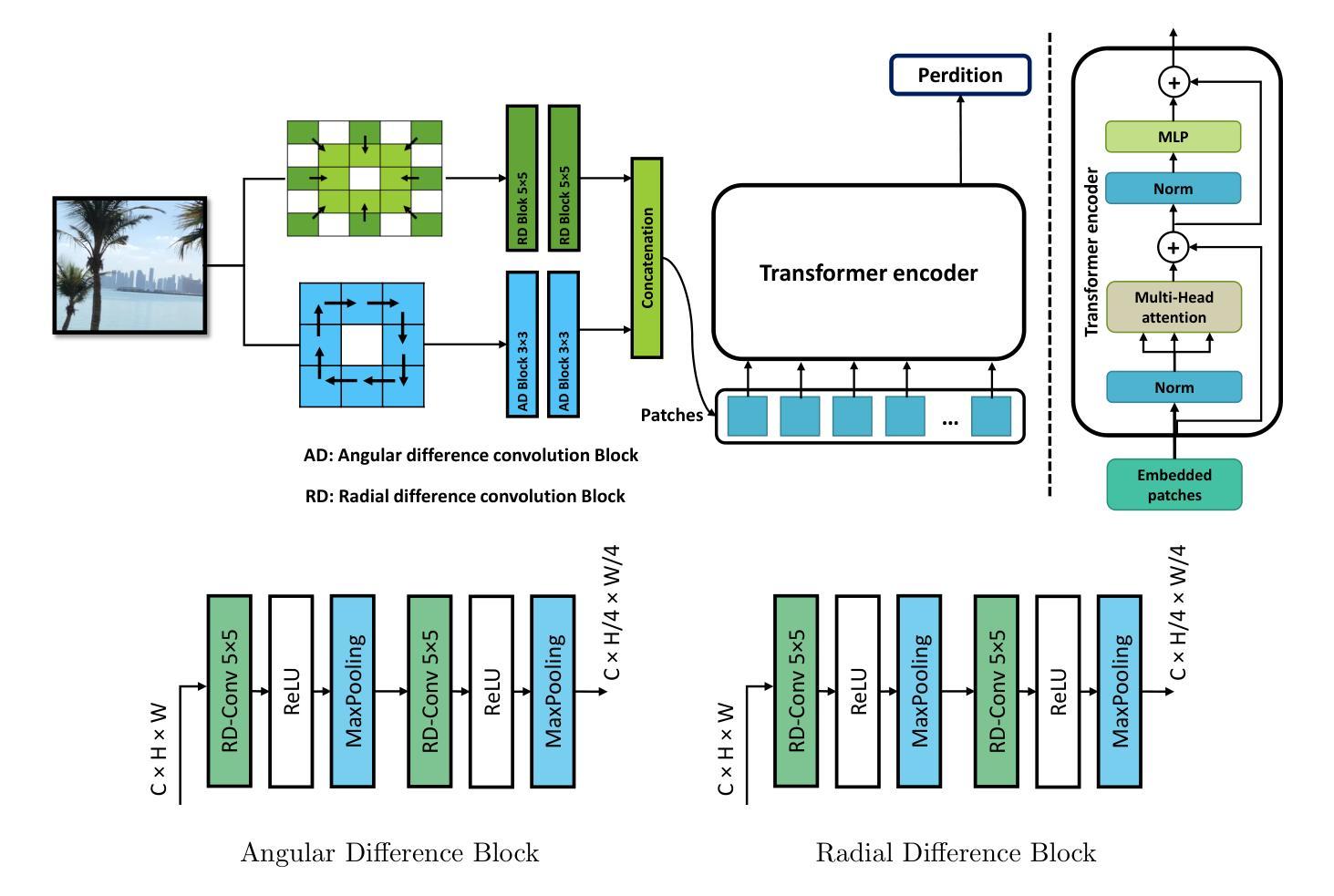
PDC-ViT : Source Camera Identification using Pixel Difference Convolution and Vision Transformer
Authors:Omar Elharrouss, Younes Akbari, Noor Almaadeed, Somaya Al-Maadeed, Fouad Khelifi, Ahmed Bouridane
Source camera identification has emerged as a vital solution to unlock incidents involving critical cases like terrorism, violence, and other criminal activities. The ability to trace the origin of an image/video can aid law enforcement agencies in gathering evidence and constructing the timeline of events. Moreover, identifying the owner of a certain device narrows down the area of search in a criminal investigation where smartphone devices are involved. This paper proposes a new pixel-based method for source camera identification, integrating Pixel Difference Convolution (PDC) with a Vision Transformer network (ViT), and named PDC-ViT. While the PDC acts as the backbone for feature extraction by exploiting Angular PDC (APDC) and Radial PDC (RPDC). These techniques enhance the capability to capture subtle variations in pixel information, which are crucial for distinguishing between different source cameras. The second part of the methodology focuses on classification, which is based on a Vision Transformer network. Unlike traditional methods that utilize image patches directly for training the classification network, the proposed approach uniquely inputs PDC features into the Vision Transformer network. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the PDC-ViT approach, it has been assessed on five different datasets, which include various image contents and video scenes. The method has also been compared with state-of-the-art source camera identification methods. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed system in terms of accuracy and robustness when compared to its competitors. For example, our proposed PDC-ViT has achieved an accuracy of 94.30%, 84%, 94.22% and 92.29% using the Vision dataset, Daxing dataset, Socrates dataset and QUFVD dataset, respectively.
源相机识别已作为一种关键解决方案,用于解决涉及恐怖主义、暴力和其他犯罪活动的关键案件。追踪图像/视频的来源可以帮助执法机构收集证据和构建事件的时间线。此外,确定某一设备的所有者可以缩小涉及智能手机的刑事调查的搜索范围。本文提出了一种基于像素的源相机识别新方法,将像素差异卷积(PDC)与视觉转换器网络(ViT)相结合,名为PDC-ViT。其中,PDC作为特征提取的主干,利用角度PDC(APDC)和径向PDC(RPDC)。这些技术提高了捕捉像素信息中细微变化的能力,这对于区分不同源相机至关重要。该方法的第二部分侧重于分类,基于视觉转换器网络。与传统方法不同,传统方法直接使用图像补丁来训练分类网络,所提出的方法独特地将PDC特征输入到视觉转换器网络中。为了证明PDC-ViT方法的有效性,它已在五个不同的数据集上进行了评估,这些数据集包括各种图像内容和视频场景。该方法还与国家先进的源相机识别方法进行了比较。实验结果表明,与竞争对手相比,该系统在准确性和稳健性方面表现出有效性和优越性。例如,我们提出的PDC-ViT在Vision数据集、大兴数据集、苏格拉底数据集和QUFVD数据集上分别实现了94.30%、84%、94.22%和92.29%的准确率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本提出了一种新的基于像素的源相机识别方法,该方法结合像素差异卷积(PDC)和视觉转换器网络(ViT),被称为PDC-ViT。该方法通过利用角PDC(APDC)和径向PDC(RPDC)作为特征提取的后备,并创新地将PDC特征输入到视觉转换器网络中进行分类。实验结果表明,与现有源相机识别方法相比,该系统的准确性和鲁棒性更高。
Key Takeaways
- 源相机识别在解决涉及恐怖主义、暴力和其他犯罪活动的关键案件中至关重要。
- 新的像素差异卷积(PDC)与视觉转换器网络(ViT)结合的PDC-ViT方法被提出用于源相机识别。
- PDC特征提取技术通过利用角PDC(APDC)和径向PDC(RPDC)增强捕捉像素细微变化的能力,这对于区分不同源相机至关重要。
- PDC-ViT的独特之处在于将PDC特征输入到视觉转换器网络中进行分类,不同于传统方法直接使用图像块进行训练。
- PDC-ViT方法已在五个不同的数据集上进行了评估,包括各种图像内容和视频场景。
- 实验结果表明,与现有方法相比,PDC-ViT系统在准确性和鲁棒性方面表现出卓越的性能。
- PDC-ViT在Vision数据集、大兴数据集、苏格拉底数据集和QUFVD数据集上的准确率分别为94.30%、84%、94.22%和92.29%。
点此查看论文截图

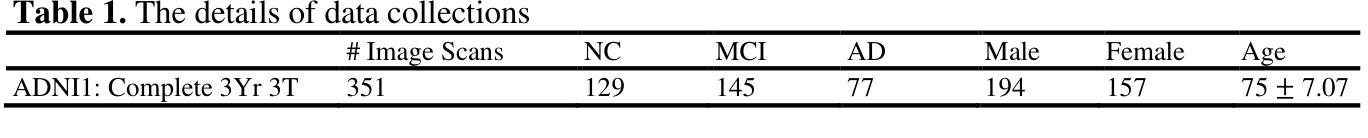
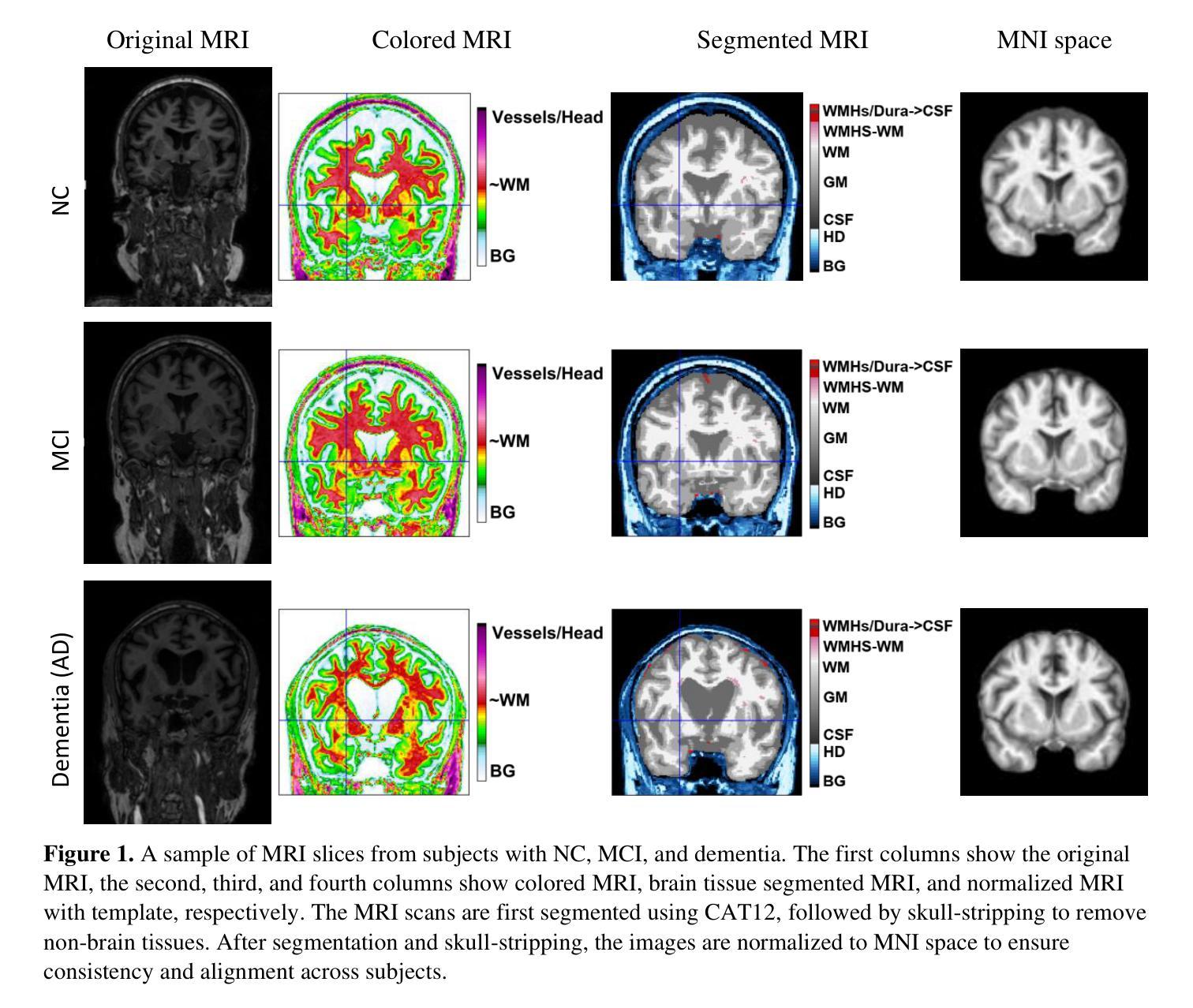
Leveraging Video Vision Transformer for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis from 3D Brain MRI
Authors:Taymaz Akan, Sait Alp, Md. Shenuarin Bhuiyan, Elizabeth A. Disbrow, Steven A. Conrad, John A. Vanchiere, Christopher G. Kevil, Mohammad A. N. Bhuiyan
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder affecting millions worldwide, necessitating early and accurate diagnosis for optimal patient management. In recent years, advancements in deep learning have shown remarkable potential in medical image analysis. Methods In this study, we present “ViTranZheimer,” an AD diagnosis approach which leverages video vision transformers to analyze 3D brain MRI data. By treating the 3D MRI volumes as videos, we exploit the temporal dependencies between slices to capture intricate structural relationships. The video vision transformer’s self-attention mechanisms enable the model to learn long-range dependencies and identify subtle patterns that may indicate AD progression. Our proposed deep learning framework seeks to enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of AD diagnosis, empowering clinicians with a tool for early detection and intervention. We validate the performance of the video vision transformer using the ADNI dataset and conduct comparative analyses with other relevant models. Results The proposed ViTranZheimer model is compared with two hybrid models, CNN-BiLSTM and ViT-BiLSTM. CNN-BiLSTM is the combination of a convolutional neural network (CNN) and a bidirectional long-short-term memory network (BiLSTM), while ViT-BiLSTM is the combination of a vision transformer (ViT) with BiLSTM. The accuracy levels achieved in the ViTranZheimer, CNN-BiLSTM, and ViT-BiLSTM models are 98.6%, 96.479%, and 97.465%, respectively. ViTranZheimer demonstrated the highest accuracy at 98.6%, outperforming other models in this evaluation metric, indicating its superior performance in this specific evaluation metric. Conclusion This research advances the understanding of applying deep learning techniques in neuroimaging and Alzheimer’s disease research, paving the way for earlier and less invasive clinical diagnosis.
阿尔茨海默症(AD)是一种影响全球数百万人的神经退行性疾病,需要进行早期和准确的诊断以进行最佳的患者管理。近年来,深度学习在医学图像分析方面的进展显示出巨大的潜力。在此研究中,我们提出了“ViTranZheimer”的AD诊断方法,该方法利用视频视觉转换器(Video Vision Transformer)分析3D大脑MRI数据。通过将3D MRI体积视为视频,我们利用切片之间的时间依赖性来捕捉复杂结构关系。视频视觉转换器的自注意力机制使模型能够学习长期依赖性并识别可能指示AD进展的微妙模式。我们提出的深度学习框架旨在提高AD诊断的准确性和敏感性,为临床医生提供一种早期检测和干预的工具。我们使用ADNI数据集验证了视频视觉转换器的性能,并与其他相关模型进行了比较分析。结果:所提出的ViTranZheimer模型与两种混合模型(CNN-BiLSTM和ViT-BiLSTM)进行了比较。CNN-BiLSTM是卷积神经网络(CNN)和双向长短期记忆网络(BiLSTM)的组合,而ViT-BiLSTM是视觉转换器(ViT)与BiLSTM的组合。ViTranZheimer、CNN-BiLSTM和ViT-BiLSTM模型中实现的准确度分别为98.6%、96.479%和97.465%。ViTranZheimer在准确度方面表现出最高水平,达到98.6%,在此评估指标上优于其他模型,表明其在这一特定评估指标上的性能卓越。结论:该研究深化了深度学习技术在神经影像学和阿尔茨海默症研究中的应用,为更早且侵入性较小的临床诊断铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出了一种名为“ViTranZheimer”的深度学习框架,用于利用视频视觉转换器分析三维脑MRI数据,以诊断阿尔茨海默病(AD)。该框架通过利用视频视觉转换器的自注意力机制,学习长期依赖关系并识别可能指示AD进展的微妙模式。该研究使用ADNI数据集验证了视频视觉转换器的性能,并与其它相关模型进行了比较分析。结果显示,ViTranZheimer模型的准确率为98.6%,优于CNN-BiLSTM和ViT-BiLSTM模型。此研究为早期诊断阿尔茨海默病提供了新的工具。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了“ViTranZheimer”深度学习框架,用于阿尔茨海默病的诊断。
- 利用视频视觉转换器分析三维脑MRI数据。
- 视频视觉转换器的自注意力机制能学习长期依赖关系并识别AD进展的微妙模式。
- 使用ADNI数据集验证了视频视觉转换器的性能。
- ViTranZheimer模型的诊断准确率达到了98.6%。
- ViTranZheimer模型的性能优于CNN-BiLSTM和ViT-BiLSTM模型。
点此查看论文截图

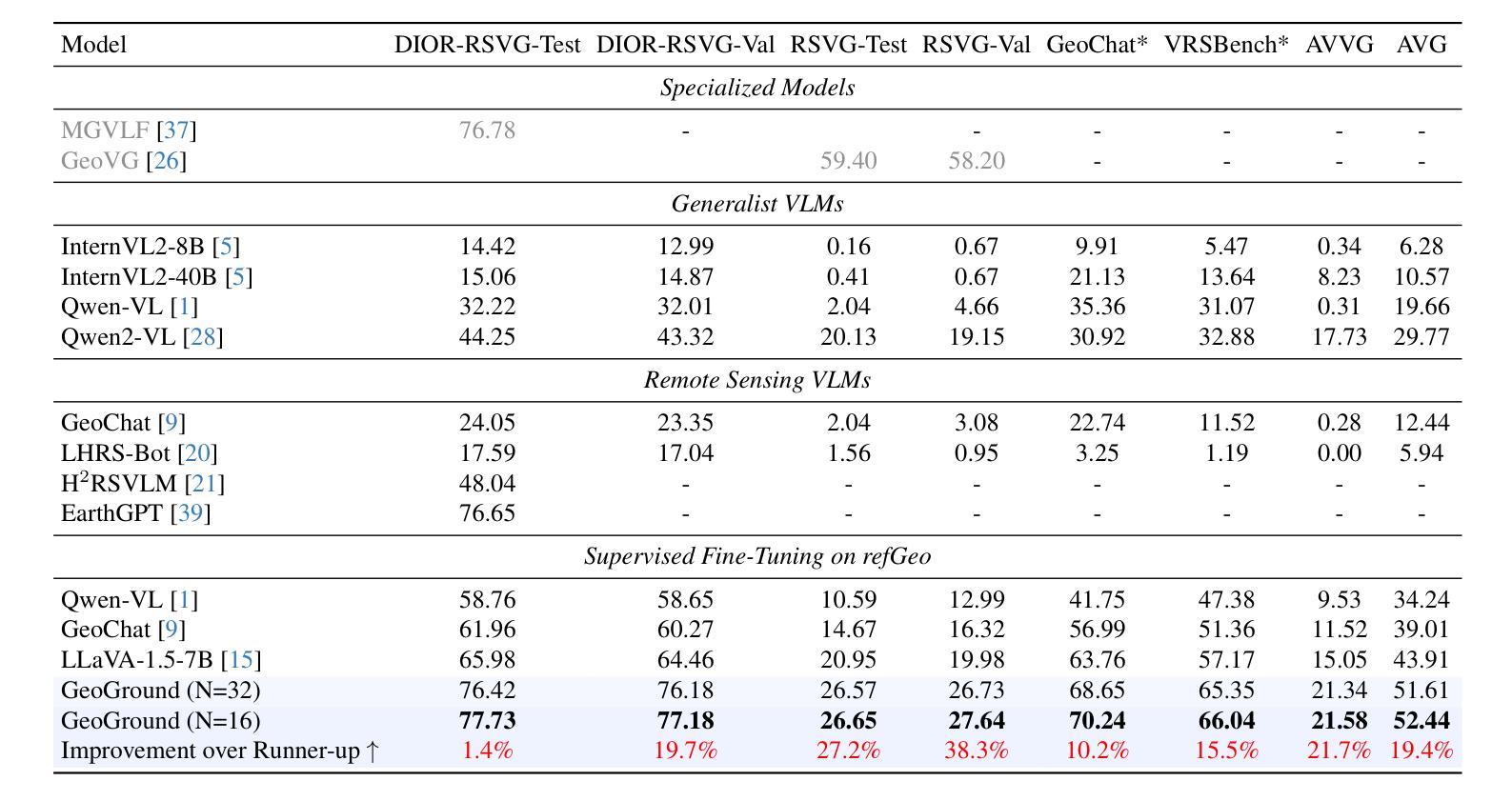
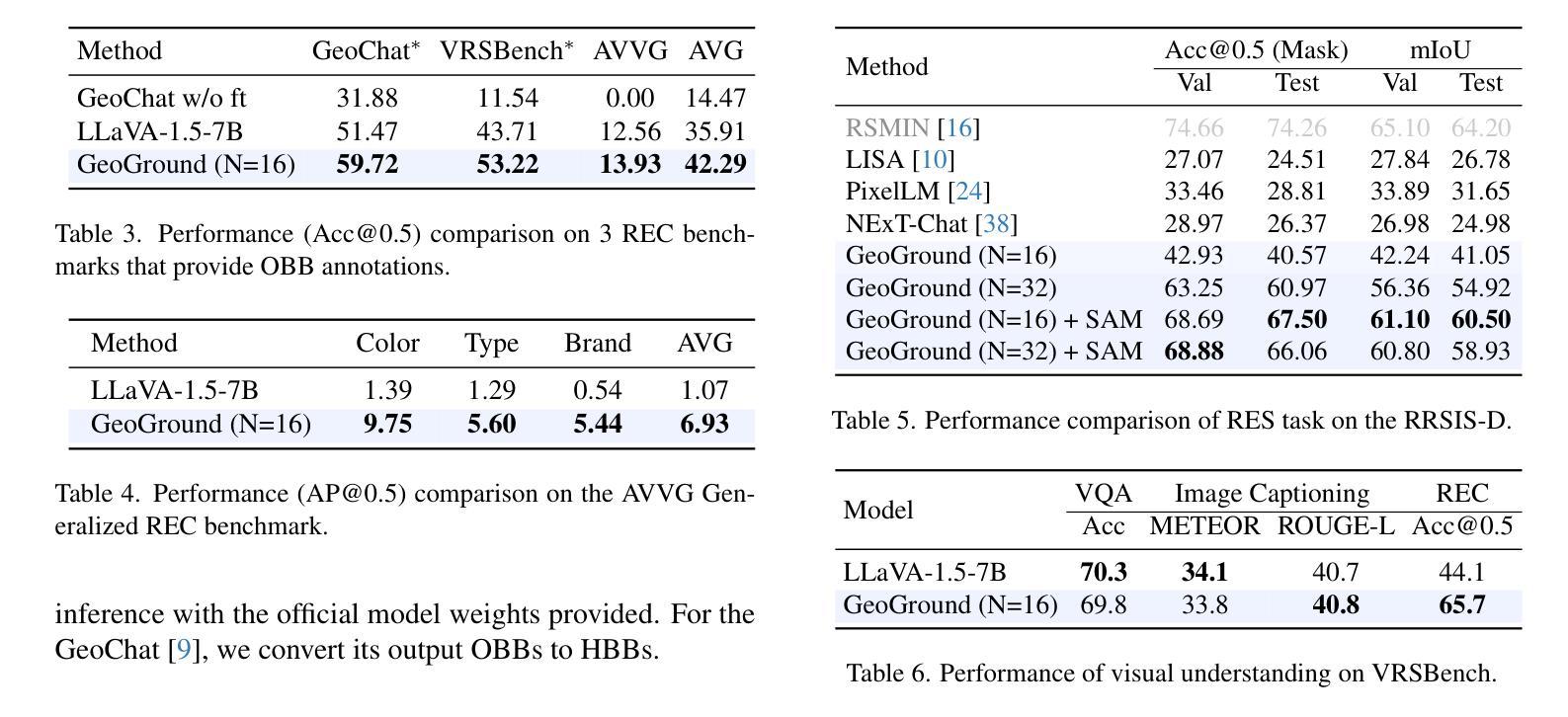
GeoGround: A Unified Large Vision-Language Model for Remote Sensing Visual Grounding
Authors:Yue Zhou, Mengcheng Lan, Xiang Li, Yiping Ke, Xue Jiang, Litong Feng, Wayne Zhang
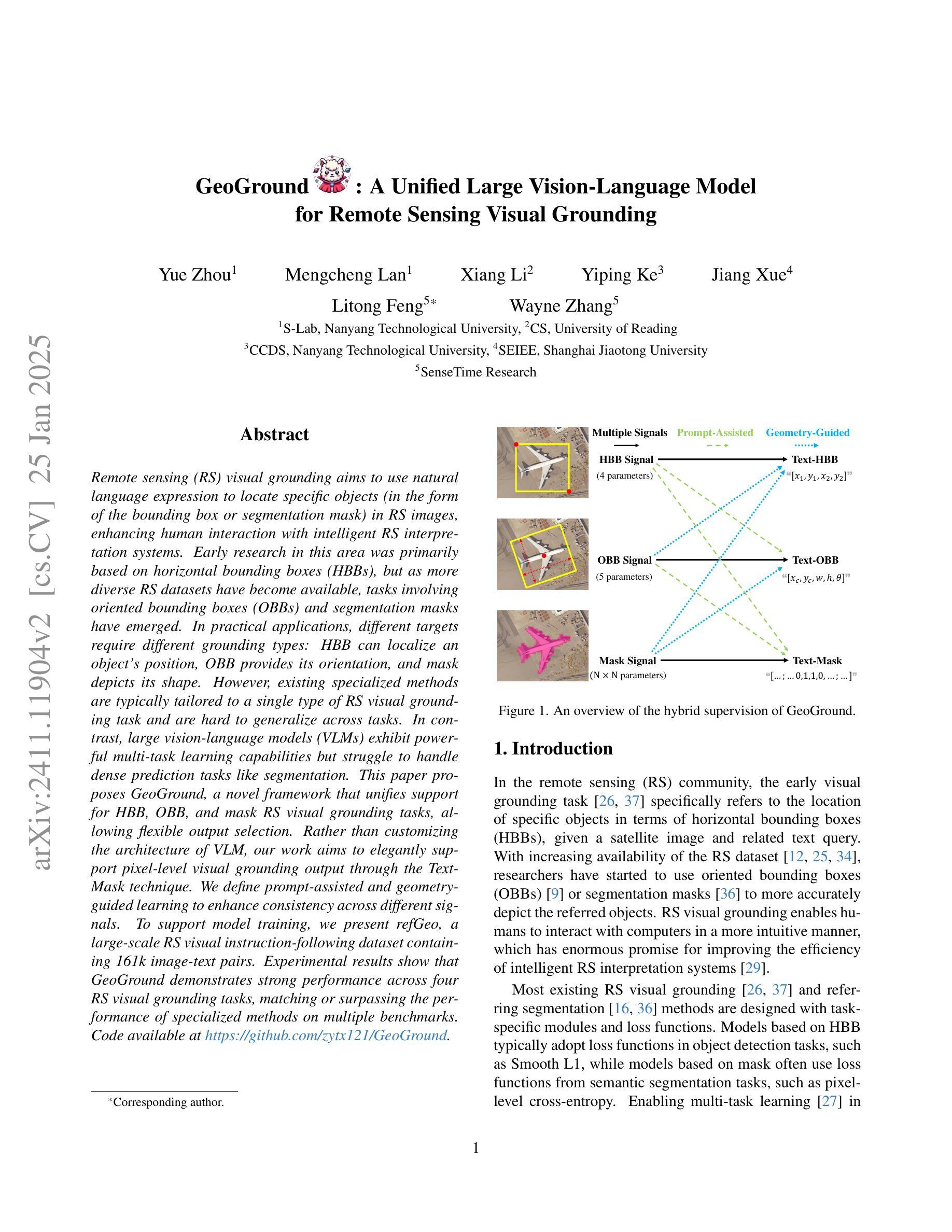
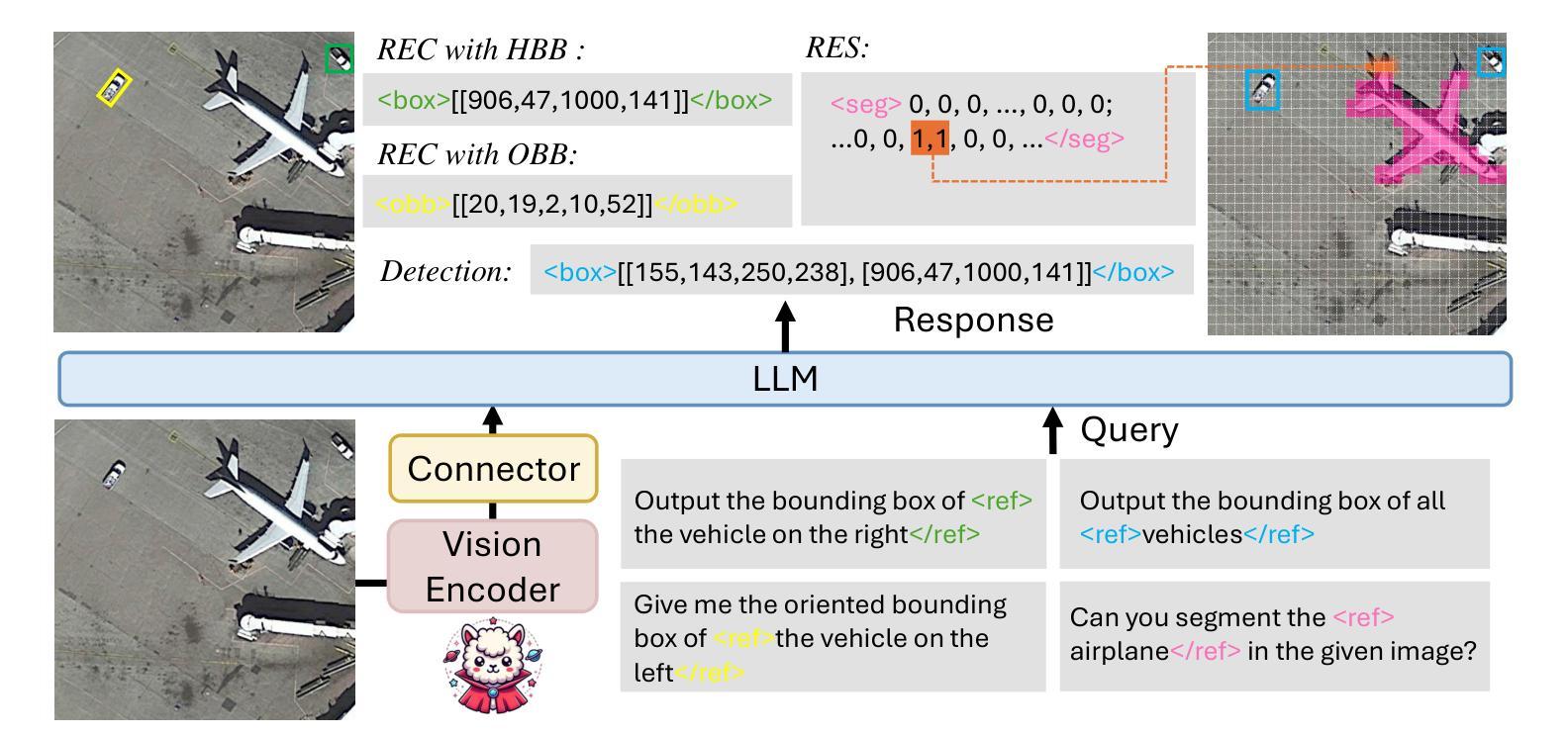
Remote sensing (RS) visual grounding aims to use natural language expression to locate specific objects (in the form of the bounding box or segmentation mask) in RS images, enhancing human interaction with intelligent RS interpretation systems. Early research in this area was primarily based on horizontal bounding boxes (HBBs), but as more diverse RS datasets have become available, tasks involving oriented bounding boxes (OBBs) and segmentation masks have emerged. In practical applications, different targets require different grounding types: HBB can localize an object’s position, OBB provides its orientation, and mask depicts its shape. However, existing specialized methods are typically tailored to a single type of RS visual grounding task and are hard to generalize across tasks. In contrast, large vision-language models (VLMs) exhibit powerful multi-task learning capabilities but struggle to handle dense prediction tasks like segmentation. This paper proposes GeoGround, a novel framework that unifies support for HBB, OBB, and mask RS visual grounding tasks, allowing flexible output selection. Rather than customizing the architecture of VLM, our work aims to elegantly support pixel-level visual grounding output through the Text-Mask technique. We define prompt-assisted and geometry-guided learning to enhance consistency across different signals. To support model training, we present refGeo, a large-scale RS visual instruction-following dataset containing 161k image-text pairs. Experimental results show that GeoGround demonstrates strong performance across four RS visual grounding tasks, matching or surpassing the performance of specialized methods on multiple benchmarks. Code available at https://github.com/zytx121/GeoGround
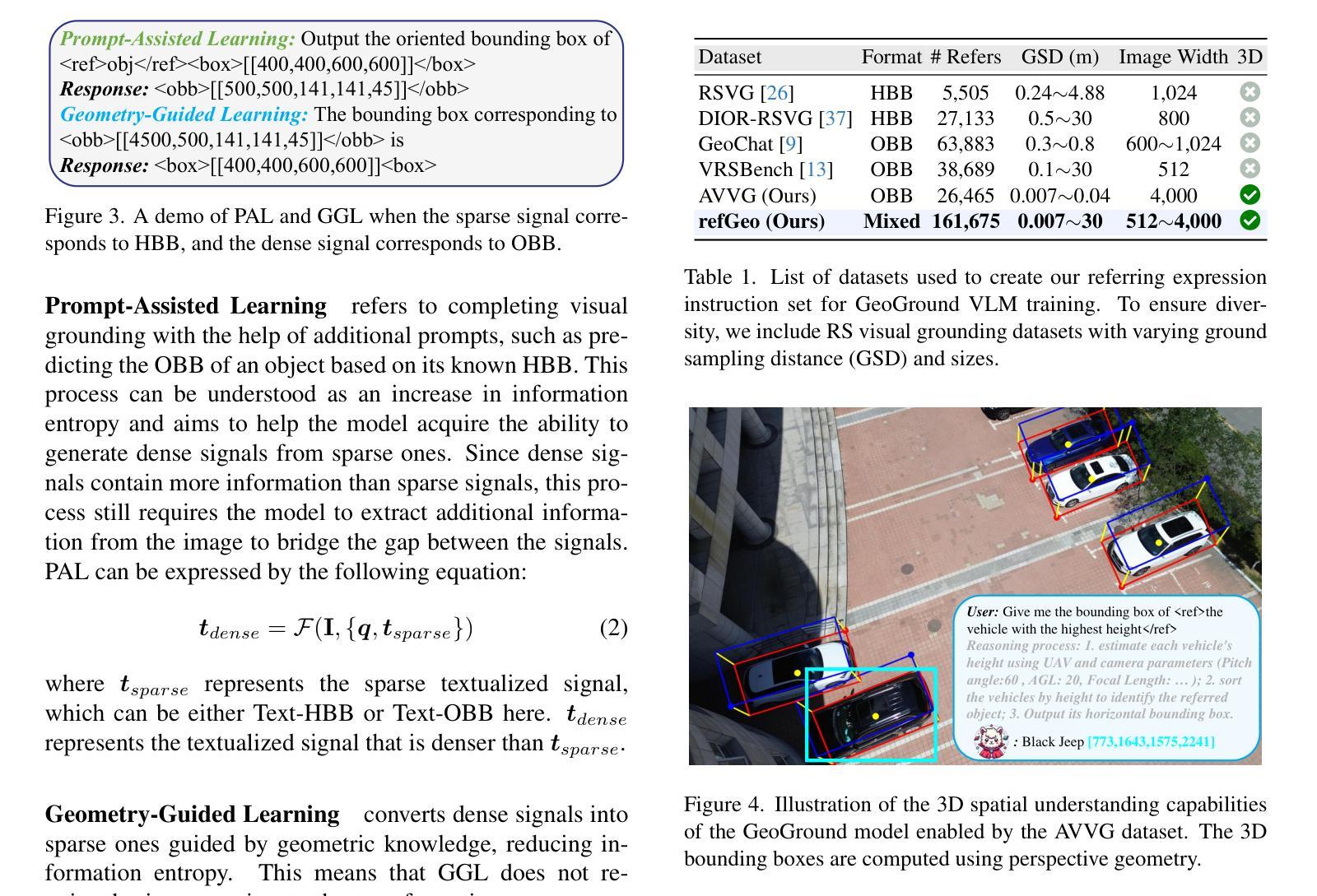
遥感(RS)视觉定位旨在利用自然语言表达式在遥感图像中定位特定对象(以边界框或分割掩码的形式),增强人类与智能遥感解释系统的交互。早期的研究主要基于水平边界框(HBB),但随着更多遥感数据集的可用,出现了涉及定向边界框(OBB)和分割掩码的任务。在实际应用中,不同的目标需要不同类型的定位:HBB可以定位对象的位置,OBB提供其方向,而掩码描绘其形状。然而,现有的专用方法通常针对单一的遥感视觉定位任务,难以跨任务推广。相比之下,大型视觉语言模型(VLM)表现出强大的多任务学习能力,但在处理如分割之类的密集预测任务时却表现挣扎。本文提出了GeoGround,这是一个新颖的统一框架,支持HBB、OBB和掩码遥感视觉定位任务,允许灵活输出选择。我们的工作旨在通过文本掩码技术巧妙地支持像素级视觉定位输出,而不是定制VLM的架构。我们定义了提示辅助和几何引导学习以增强不同信号之间的一致性。为了支持模型训练,我们提供了refGeo,这是一个大规模的遥感视觉指令跟随数据集,包含16.1万张图像文本对。实验结果表明,GeoGround在四个遥感视觉定位任务上表现出强劲的性能,在多个基准测试中达到或超越了专用方法的表现。代码可访问 https://github.com/zytx121/GeoGround
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 19 figures
Summary
本文介绍了遥感视觉定位技术中的一项新研究,名为GeoGround。该技术旨在统一支持水平边界框(HBB)、定向边界框(OBB)和掩膜三种遥感视觉定位任务,允许灵活输出选择。该研究通过Text-Mask技术实现像素级视觉定位输出,并提出prompt辅助和几何引导学习以增强不同信号之间的一致性。为支持模型训练,研究团队还推出了大规模的遥感视觉指令数据集refGeo,包含16.1万张图像文本对。GeoGround在四个遥感视觉定位任务中表现出强大的性能,在多个基准测试中匹配或超越了专用方法的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感视觉定位技术(RS visual grounding)利用自然语言表达式在遥感图像中定位特定对象,增强人与智能遥感解释系统的交互。
- 早期研究主要基于水平边界框(HBB),但现在随着更丰富的遥感数据集的出现,涉及定向边界框(OBB)和掩膜的任务已兴起。
- 不同目标需要不同类型的定位方式:HBB可定位对象位置,OBB提供方向信息,掩膜描绘对象形状。
- 现有方法通常专为单一类型的遥感视觉定位任务设计,难以跨任务推广。
- GeoGround框架统一支持HBB、OBB和掩膜遥感视觉定位任务,允许灵活输出选择。
- 通过Text-Mask技术实现像素级视觉定位输出。
- GeoGround在多个基准测试中表现优异,匹配或超越专用方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图
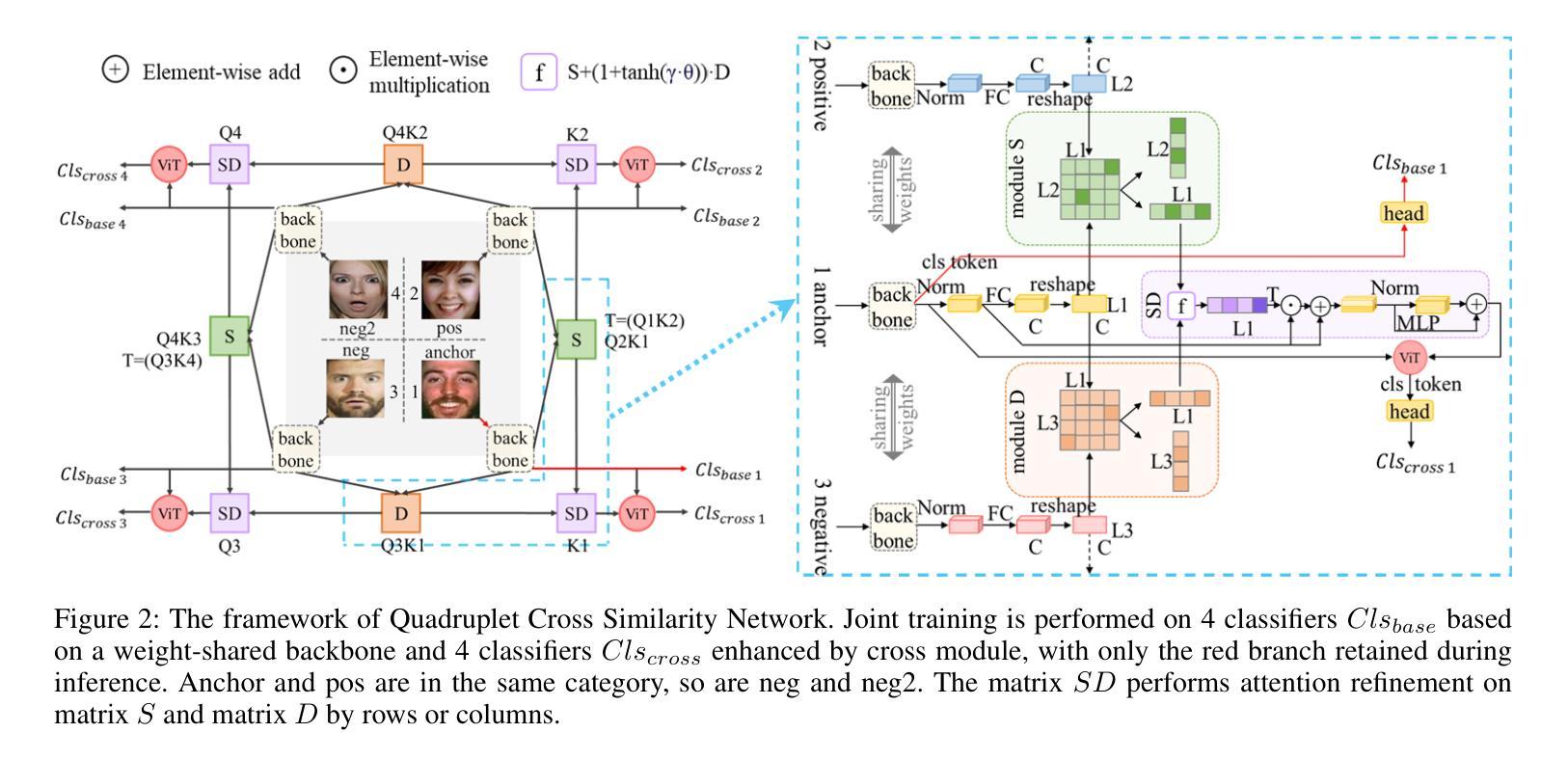
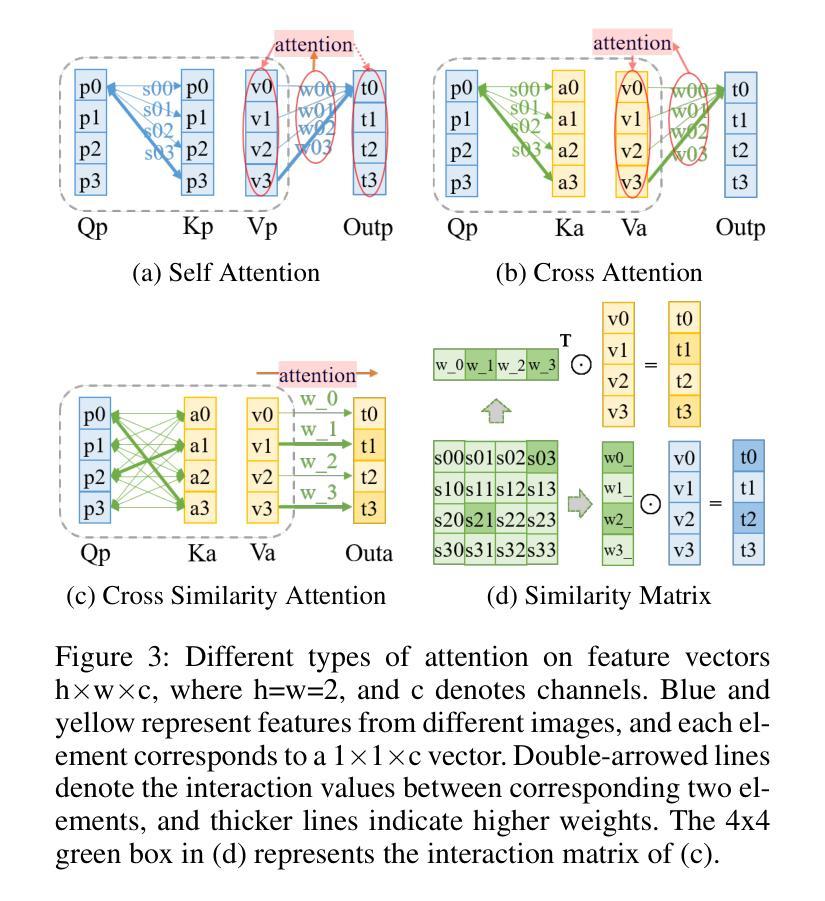
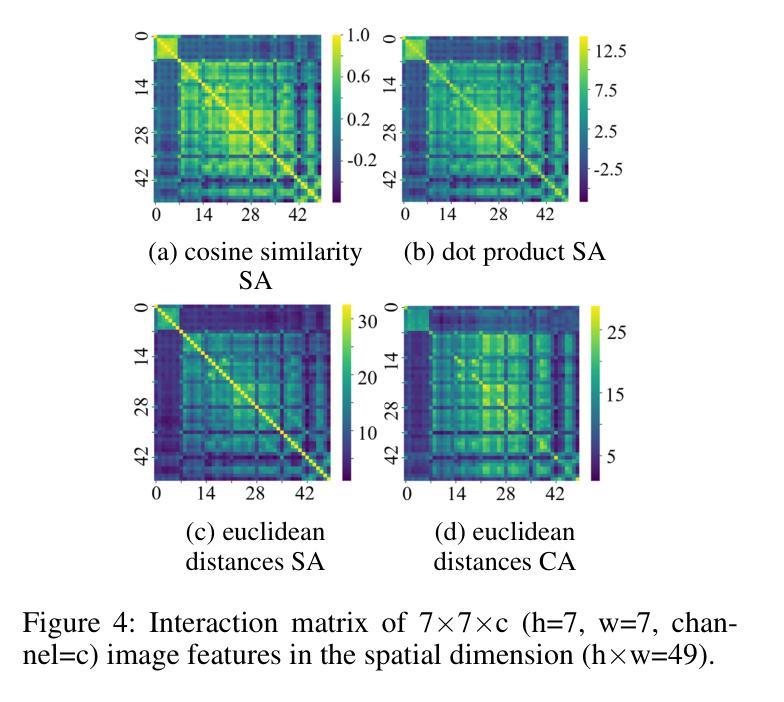
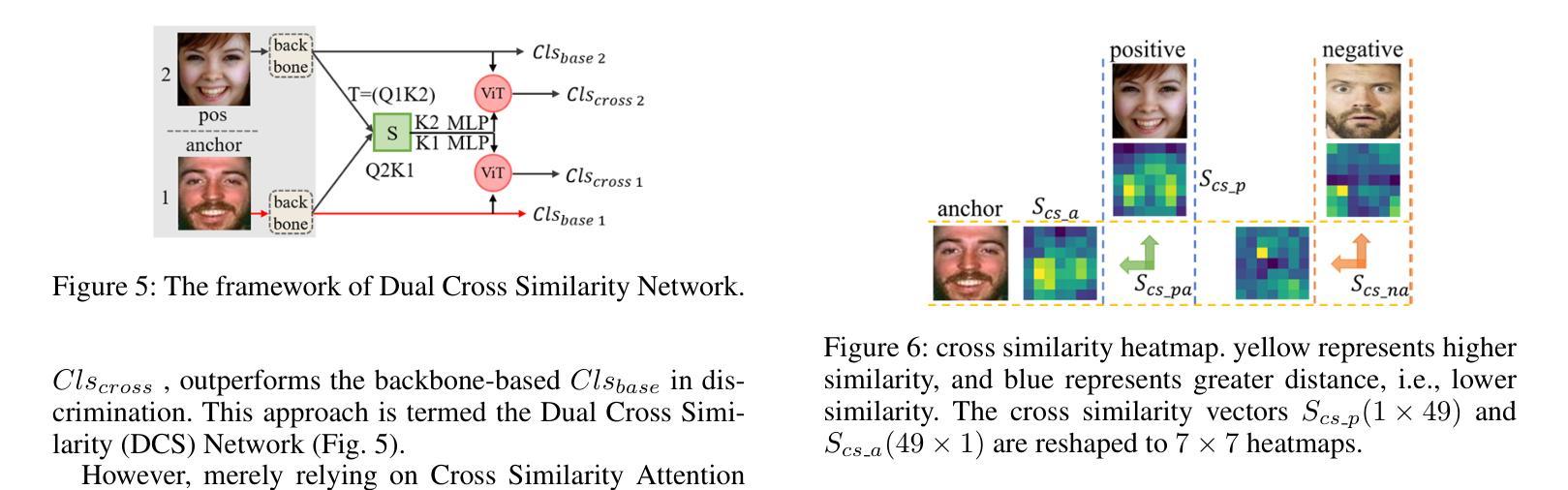
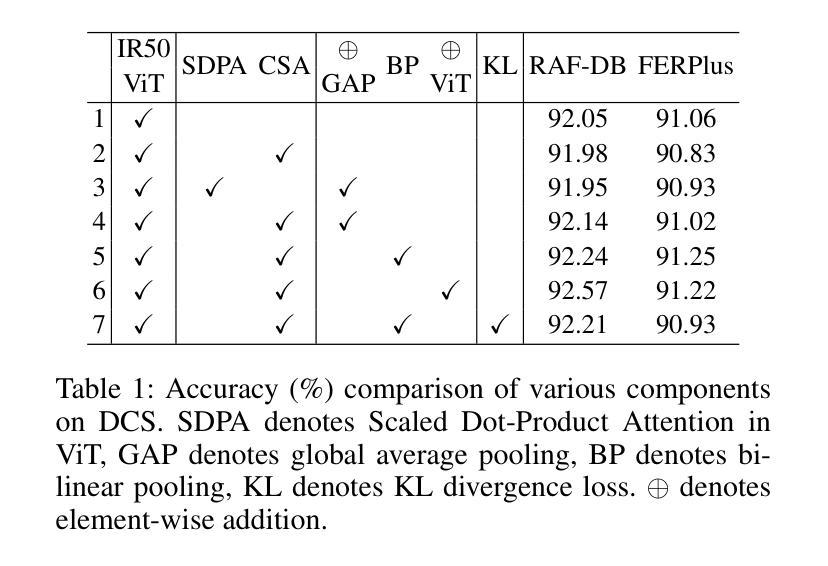
QCS: Feature Refining from Quadruplet Cross Similarity for Facial Expression Recognition
Authors:Chengpeng Wang, Li Chen, Lili Wang, Zhaofan Li, Xuebin Lv
Facial expression recognition faces challenges where labeled significant features in datasets are mixed with unlabeled redundant ones. In this paper, we introduce Cross Similarity Attention (CSA) to mine richer intrinsic information from image pairs, overcoming a limitation when the Scaled Dot-Product Attention of ViT is directly applied to calculate the similarity between two different images. Based on CSA, we simultaneously minimize intra-class differences and maximize inter-class differences at the fine-grained feature level through interactions among multiple branches. Contrastive residual distillation is utilized to transfer the information learned in the cross module back to the base network. We ingeniously design a four-branch centrally symmetric network, named Quadruplet Cross Similarity (QCS), which alleviates gradient conflicts arising from the cross module and achieves balanced and stable training. It can adaptively extract discriminative features while isolating redundant ones. The cross-attention modules exist during training, and only one base branch is retained during inference, resulting in no increase in inference time. Extensive experiments show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on several FER datasets.
面部表情识别面临着数据集中的标记重要特征与未标记冗余特征混合的挑战。在本文中,我们引入交叉相似性注意力(CSA)来从图像对中提取更丰富的内在信息,克服了当直接使用ViT的缩放点积注意力计算两个不同图像之间的相似性时存在的局限性。基于CSA,我们通过多个分支之间的交互,在细粒度特征级别同时减小类内差异并最大化类间差异。利用对比残差蒸馏将跨模块中学习到的信息转回基础网络。我们巧妙地设计了一个四分支中心对称网络,命名为四元组交叉相似性(QCS),该网络缓解了跨模块产生的梯度冲突,实现了平衡稳定的训练。它可以自适应地提取判别特征,同时隔离冗余特征。在训练过程中存在交叉注意力模块,而在推理期间仅保留一个基础分支,因此不会增加推理时间。大量实验表明,我们提出的方法在多个面部表情识别数据集上达到了最新性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文引入了一种名为Cross Similarity Attention(CSA)的技术,用于从图像对中挖掘更丰富的内在信息,解决了在面部表情识别中,数据集中标签重要的特征与未标签的冗余特征混合的问题。通过CSA,本文在细粒度特征层面同时减小了类内差异并放大了类间差异。此外,还巧妙地设计了名为Quadruplet Cross Similarity(QCS)的四分支中心对称网络,缓解了跨模块引起的梯度冲突,实现了平衡稳定的训练。该方法可在训练过程中自适应提取判别特征并隔离冗余特征,且推理时间并未增加。实验表明,该方法在多个面部表情识别数据集上达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 引入Cross Similarity Attention(CSA)技术,从图像对中挖掘更丰富内在信息。
- 解决数据集中标签重要特征与未标签冗余特征混合的问题。
- 通过CSA技术,同时减小类内差异并放大类间差异。
- 采用对比残差蒸馏技术将跨模块学到的信息回馈到基础网络。
- 设计了四分支中心对称网络Quadruplet Cross Similarity(QCS)。
- QCS网络缓解了跨模块引起的梯度冲突,实现了平衡稳定的训练。
点此查看论文截图

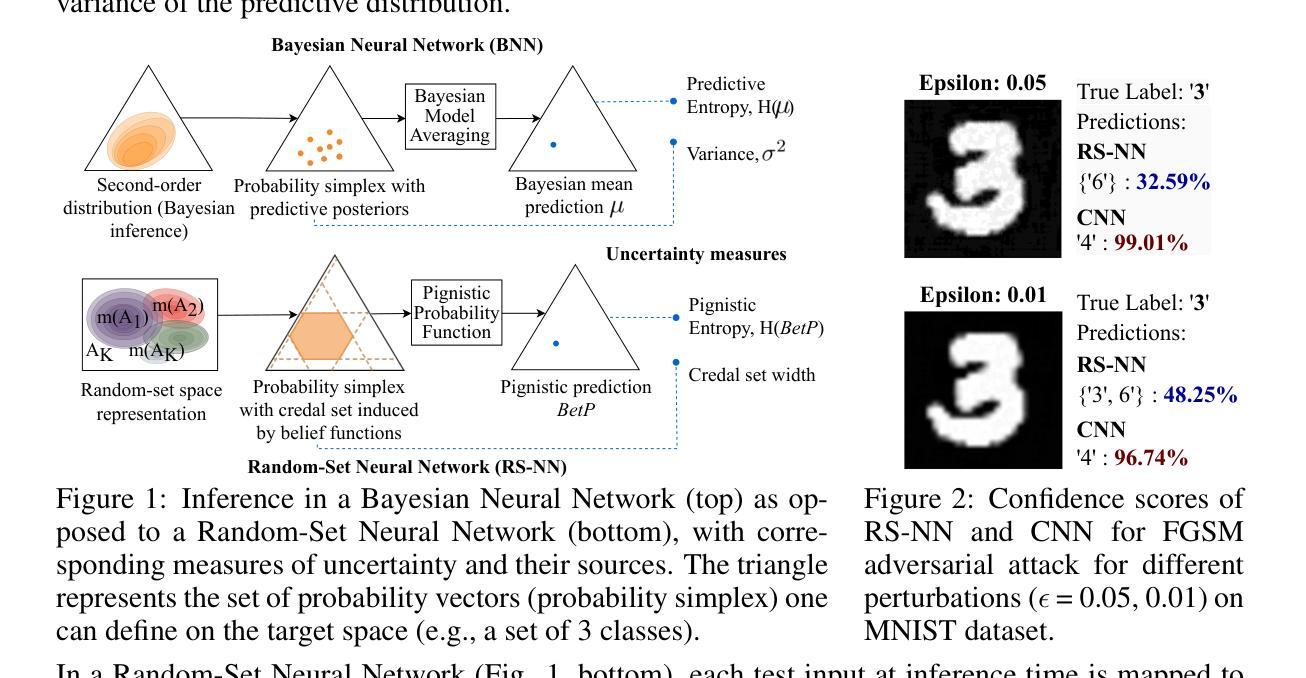
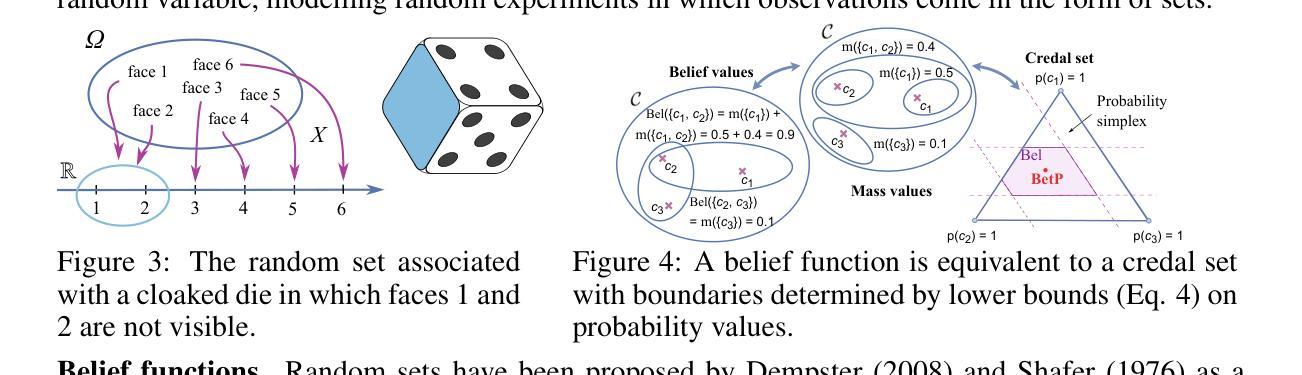
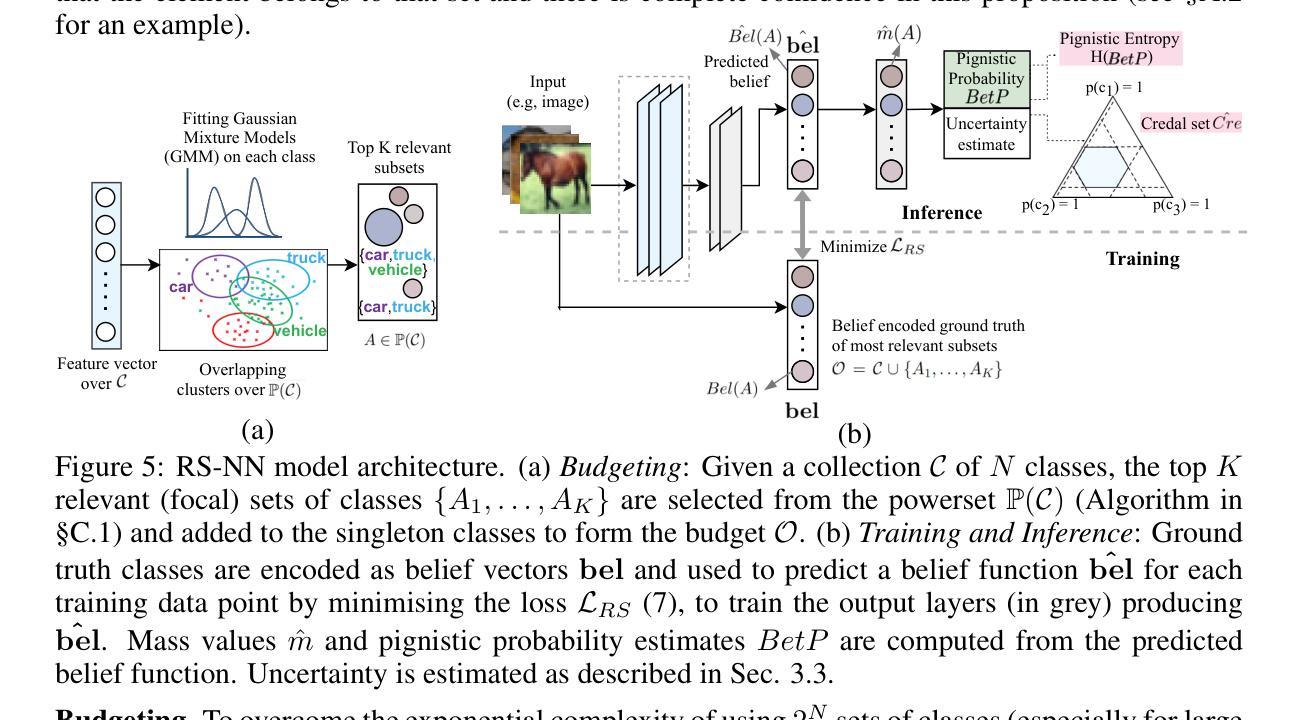
Random-Set Neural Networks (RS-NN)
Authors:Shireen Kudukkil Manchingal, Muhammad Mubashar, Kaizheng Wang, Keivan Shariatmadar, Fabio Cuzzolin
Machine learning is increasingly deployed in safety-critical domains where erroneous predictions may lead to potentially catastrophic consequences, highlighting the need for learning systems to be aware of how confident they are in their own predictions: in other words, ‘to know when they do not know’. In this paper, we propose a novel Random-Set Neural Network (RS-NN) approach to classification which predicts belief functions (rather than classical probability vectors) over the class list using the mathematics of random sets, i.e., distributions over the collection of sets of classes. RS-NN encodes the ‘epistemic’ uncertainty induced by training sets that are insufficiently representative or limited in size via the size of the convex set of probability vectors associated with a predicted belief function. Our approach outperforms state-of-the-art Bayesian and Ensemble methods in terms of accuracy, uncertainty estimation and out-of-distribution (OoD) detection on multiple benchmarks (CIFAR-10 vs SVHN/Intel-Image, MNIST vs FMNIST/KMNIST, ImageNet vs ImageNet-O). RS-NN also scales up effectively to large-scale architectures (e.g. WideResNet-28-10, VGG16, Inception V3, EfficientNetB2 and ViT-Base-16), exhibits remarkable robustness to adversarial attacks and can provide statistical guarantees in a conformal learning setting.
机器学习在安全性至关重要的领域得到了越来越广泛的应用,错误的预测可能导致灾难性的后果,这凸显了学习系统需要了解自己对预测的信心程度的重要性,换句话说,就是“要知道自己不知道”。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的随机集神经网络(RS-NN)分类方法,该方法使用随机集的数学原理预测类列表上的信念函数(而不是传统的概率向量)。RS-NN通过预测的信念函数关联的凸概率向量集的大小,对由训练集引起的不充分代表性或有限大小的“主观”不确定性进行编码。我们的方法在多个基准测试(CIFAR-10与SVHN/Intel-Image、MNIST与FMNIST/KMNIST、ImageNet与ImageNet-O)上的准确性、不确定性估计和超出分布(OoD)检测方面均优于最先进的贝叶斯和集成方法。RS-NN还能有效地扩展到大规模架构(如WideResNet-28-10、VGG16、Inception V3、EfficientNetB2和ViT-Base-16),对对抗性攻击表现出惊人的稳健性,并在符合学习环境中提供统计保证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025
Summary
本论文提出了一种基于随机集神经网络(RS-NN)的分类方法,通过随机集数学理论预测类别信念函数而非传统概率向量。该方法通过训练集相关的不确定性和集合凸概率向量大小编码“知识不确定性”,并在多个基准测试中展现出优异的准确性、不确定性估计和超出分布检测性能。此外,RS-NN可有效扩展到大型架构,对抗攻击具有出色稳健性,并在合规学习环境中提供统计保障。
Key Takeaways
- 本论文关注机器学习在关键安全领域中的预测置信度问题,提出了基于随机集神经网络(RS-NN)的分类方法。
- RS-NN通过预测信念函数而非传统概率向量来评估模型预测的不确定性。
- RS-NN通过编码训练集相关的不确定性,展现出色的性能,尤其在数据集不足或规模有限的情况下。
- 在多个基准测试中,RS-NN在准确性、不确定性估计和超出分布检测方面优于现有先进贝叶斯和集成方法。
- RS-NN能有效扩展到大型架构,并且对抗攻击具有稳健性。
- RS-NN可在合规学习环境中提供统计保障,为机器学习模型的可靠性和安全性提供保障。
点此查看论文截图