⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-30 更新
Sensitivity of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping in Clinical Brain Research
Authors:Fahad Salman, Abhisri Ramesh, Thomas Jochmann, Mirjam Prayer, Ademola Adegbemigun, Jack A. Reeves, Gregory E. Wilding, Junghun Cho, Dejan Jakimovski, Niels Bergsland, Michael G. Dwyer, Robert Zivadinov, Ferdinand Schweser
Background: Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) of the brain is an advanced MRI technique for assessing tissue characteristics based on magnetic susceptibility, which varies with the composition of the tissue, such as iron, calcium, and myelin levels. QSM consists of multiple processing steps, with various choices for each step. Despite its increasing application in detecting and monitoring neurodegenerative diseases, the impact of algorithmic choices in QSM’s workflow on clinical outcomes has not been thoroughly quantified. Objective: This study aimed to evaluate how choices in background field removal (BFR), dipole inversion algorithms, and anatomical referencing impact the sensitivity and reproducibility error of QSM in detecting group-level and longitudinal changes in deep gray matter susceptibility in a clinical setting. Methods: We compared 378 different QSM pipelines using a 10-year follow-up dataset of healthy adults. We analyzed the sensitivity of pipelines to detect known aging-related susceptibility changes in the DGM over time. Results: We found high variability in the sensitivity of QSM pipelines to detect susceptibility changes. The study highlighted that while most pipelines could detect changes reliably, the choice of BFR algorithm and the referencing strategy substantially influenced the outcome reproducibility error and sensitivity. Notably, pipelines using RESHARP with AMP-PE, HEIDI or LSQR inversion showed the highest overall sensitivity. Conclusions: The findings underscore the critical influence of algorithmic choices in QSM processing on the accuracy and reliability of detecting physiological changes in the brain. This has profound implications for clinical research and trials where QSM is used as a biomarker for disease progression, highlighting that careful consideration should be given to pipeline configuration to optimize clinical outcomes.
背景:脑定量敏感性映射(QSM)是一种基于磁化率的组织特性评估的高级MRI技术。这种技术会随着组织的成分(如铁、钙和髓磷脂水平)而变化。QSM包含多个处理步骤,每个步骤都有多种选择。尽管其在检测神经退行性疾病方面的应用日益广泛,但QSM工作流中算法选择对临床结果的影响尚未得到充分的量化评估。
目的:本研究旨在评估背景场移除(BFR)、偶极反转算法和解剖参照的选择对QSM检测临床环境中深层灰质群体水平和纵向变化的敏感性以及重现性误差的影响。
方法:我们使用健康成年人的10年随访数据集,对比了378种不同的QSM管道。我们分析了管道对检测已知与衰老相关的DGM易感性变化的敏感性。
结果:我们发现QSM管道检测易感性变化的敏感性存在很大差异。研究表明,虽然大多数管道都能可靠地检测到变化,但BFR算法和参照策略的选择对结果的重现性误差和敏感性有着显著影响。值得注意的是,使用RESHARP与AMP-PE、HEIDI或LSQR反转的管道表现出最高的总体敏感性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了定量磁化率成像(QSM)中背景场移除(BFR)、偶极反转算法和解剖参照的选择对检测深层灰质磁化率变化的敏感性及重现性误差的影响。研究指出,不同算法的选择对QSM检测生理变化结果的准确性和可靠性具有重要影响,特定算法组合展现较高灵敏度。这对使用QSM作为疾病进展生物标志物的临床研究与试验具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- QSM是一种基于磁化率评估脑组织特性的高级MRI技术,该技术通过不同组织成分(如铁、钙和髓磷脂)的磁化率变化进行成像。
- QSM工作流程中的算法选择会对临床结果产生影响,但这一影响尚未被全面量化。
- 研究通过对健康成年人进行长达十年的随访数据集比较了378种不同的QSM管道。
- 在检测已知与衰老相关的磁化率变化方面,QSM管道的敏感性存在很大差异。
- BFR算法和参照策略的选择对结果的可靠性和敏感性有显著影响。
- 使用特定算法组合(如RESHARP与AMP-PE、HEIDI或LSQR反转)的管道展现出最高的总体灵敏度。
点此查看论文截图

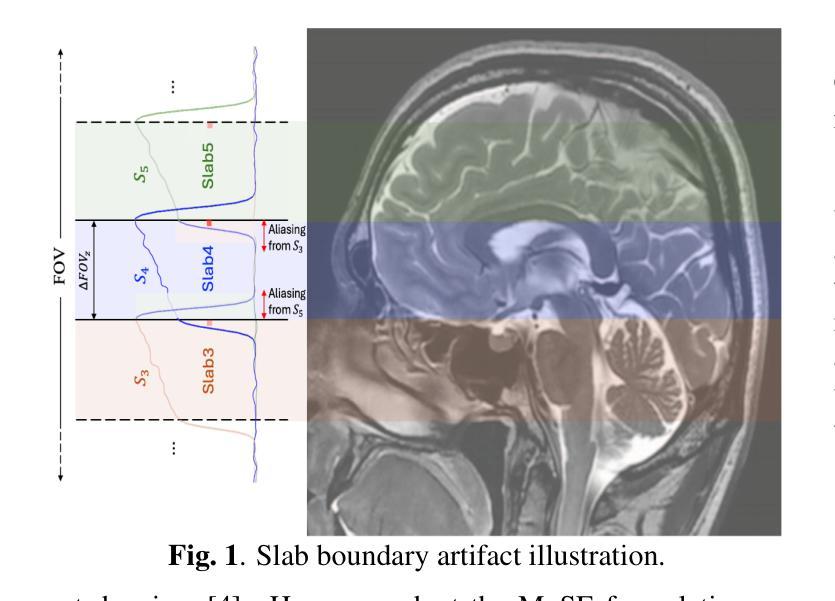
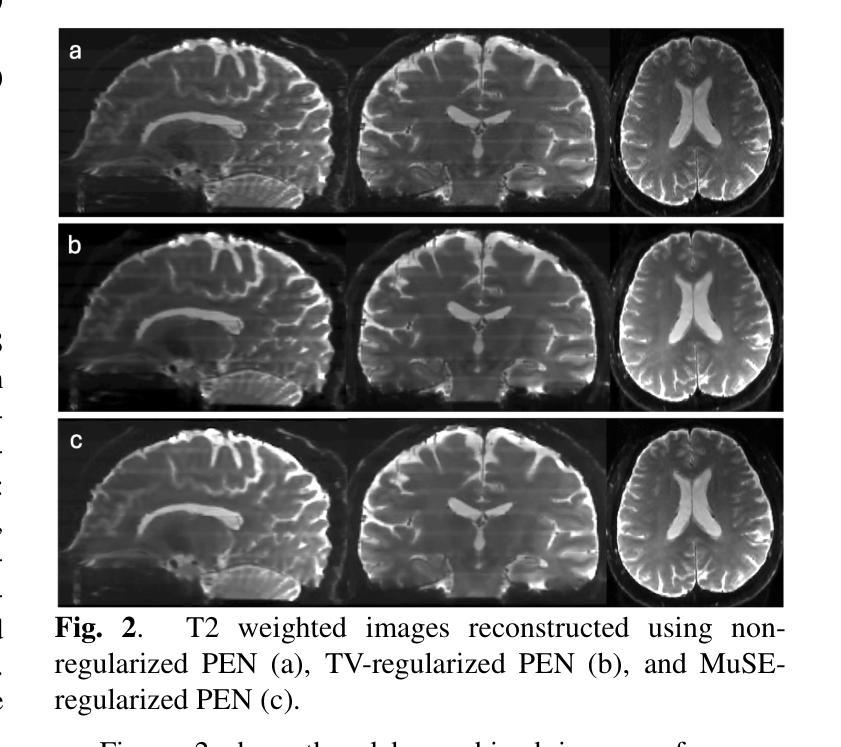
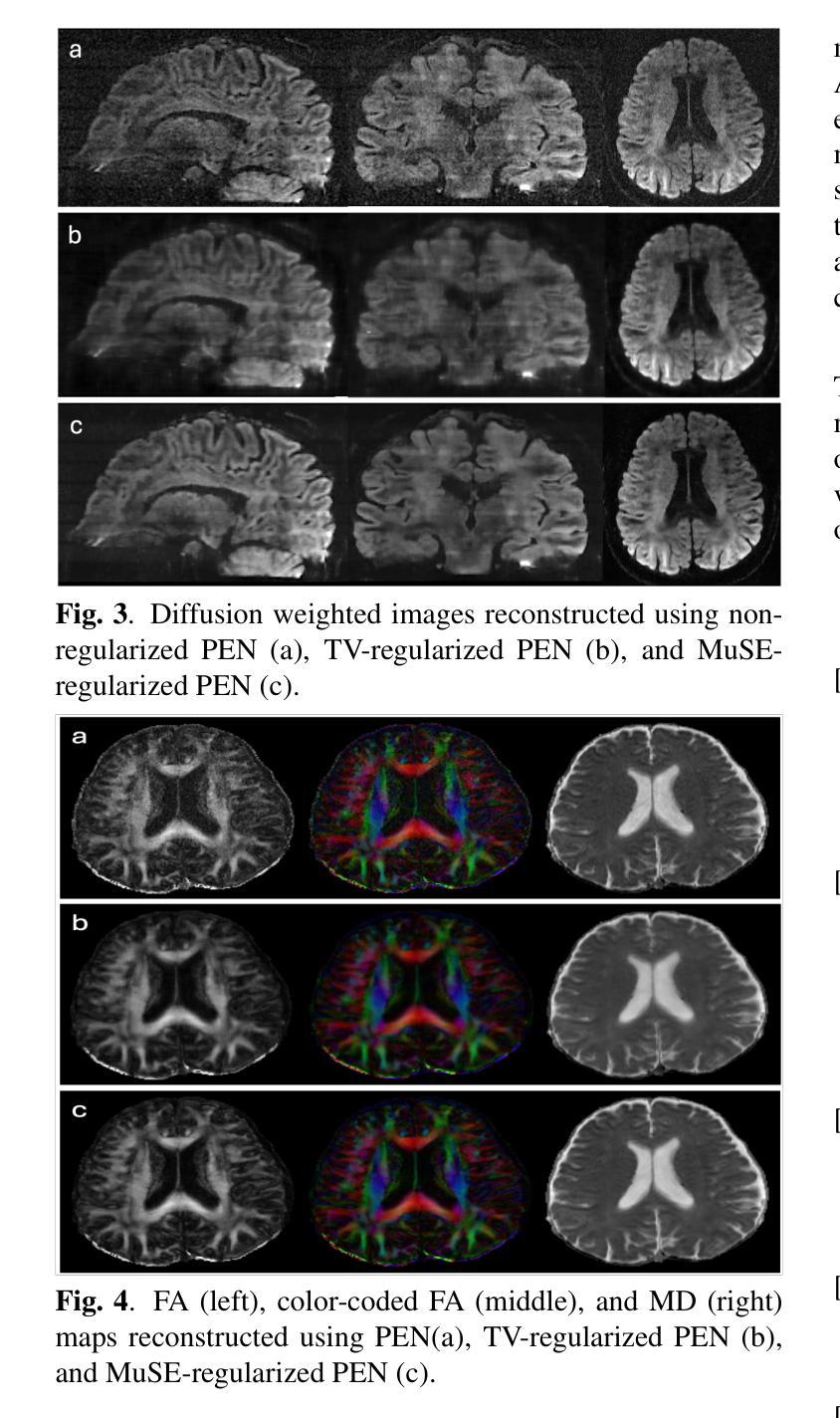
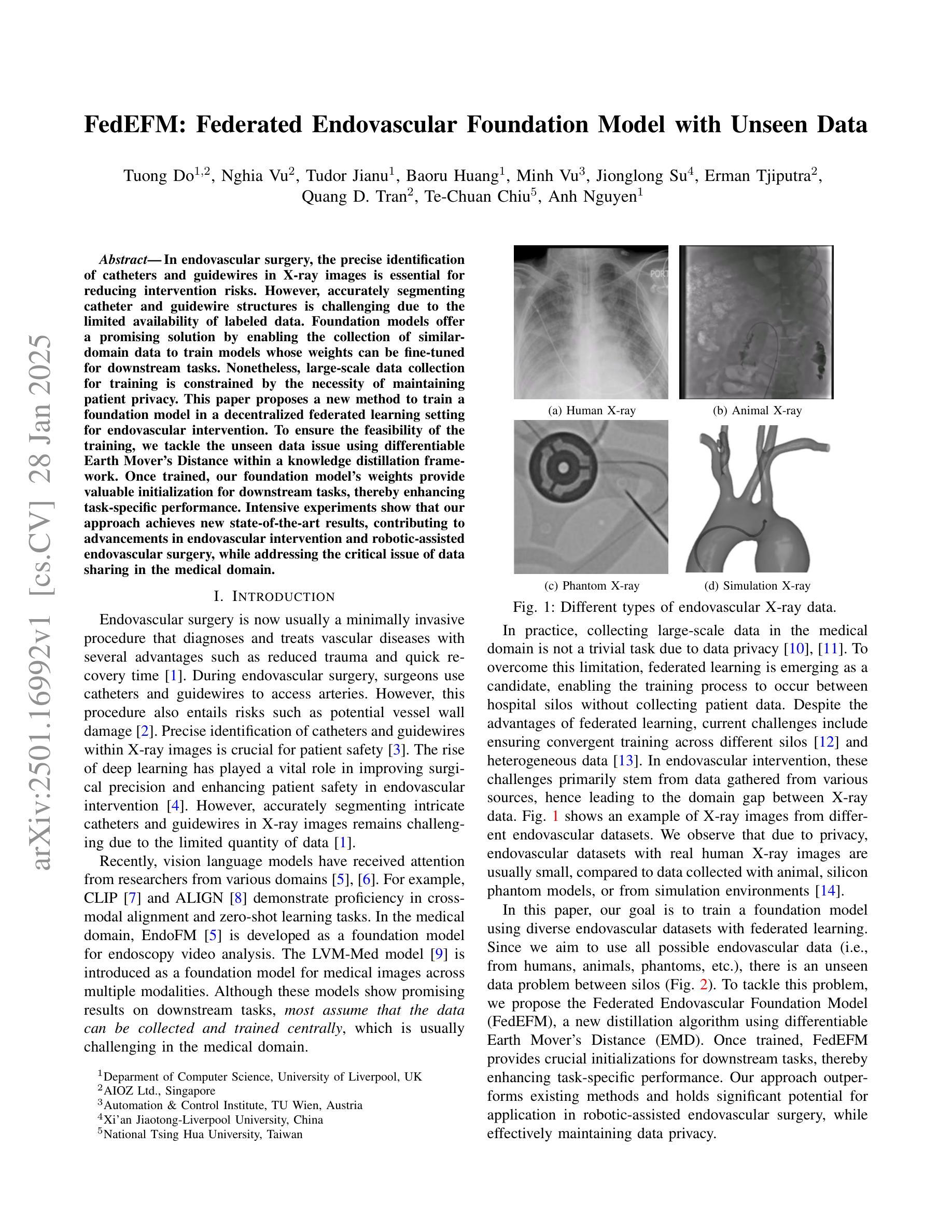
Three-Dimensional Diffusion-Weighted Multi-Slab MRI With Slice Profile Compensation Using Deep Energy Model
Authors:Reza Ghorbani, Jyothi Rikhab Chand, Chu-Yu Lee, Mathews Jacob, Merry Mani
Three-dimensional (3D) multi-slab acquisition is a technique frequently employed in high-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI in order to achieve the best signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) efficiency. However, this technique is limited by slab boundary artifacts that cause intensity fluctuations and aliasing between slabs which reduces the accuracy of anatomical imaging. Addressing this issue is crucial for advancing diffusion MRI quality and making high-resolution imaging more feasible for clinical and research applications. In this work, we propose a regularized slab profile encoding (PEN) method within a Plug-and-Play ADMM framework, incorporating multi-scale energy (MuSE) regularization to effectively improve the slab combined reconstruction. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves image quality compared to non-regularized and TV-regularized PEN approaches. The regularized PEN framework provides a more robust and efficient solution for high-resolution 3D diffusion MRI, potentially enabling clearer, more reliable anatomical imaging across various applications.
三维(3D)多薄层采集技术是高分辨率扩散加权MRI中经常采用的一种技术,以实现最佳信噪比(SNR)效率。然而,该技术受限于薄层边界伪影,导致薄层之间的强度波动和混叠,从而降低了结构成像的准确性。解决这一问题对于提高扩散MRI质量以及使高分辨率成像在临床和研究应用中更加可行至关重要。在这项工作中,我们在Plug-and-Play ADMM框架内提出了一种正则化薄层轮廓编码(PEN)方法,采用多尺度能量(MuSE)正则化,以有效提高薄层组合重建的效果。实验结果表明,与未正则化和TV正则化的PEN方法相比,所提出的方法显著提高了图像质量。正则化的PEN框架为高分屛的三维扩散MRI提供了更稳健和高效的解决方案,有望在各种应用中实现更清晰、更可靠的结构成像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 4 figures, ISBI2025 Conference paper
Summary
三维多层面采集在高分辨率扩散加权MRI中常用来实现最佳的信噪比效率,但受限于层面边界伪影,导致层面间强度波动和混叠,降低了成像准确性。本研究提出一种基于Plug-and-Play ADMM框架的正则化层面轮廓编码(PEN)方法,采用多尺度能量(MuSE)正则化有效提高层面组合重建效果。实验结果表明,该方法相较于非正则化和TV正则化的PEN方法能显著提高图像质量,为各种应用提供更清晰、更可靠的解剖图像。
Key Takeaways
- 三维多层面采集在扩散加权MRI中重要,但受层面边界伪影限制。
- 层面边界伪影导致强度波动和混叠,降低成像准确性。
- 提出一种基于Plug-and-Play ADMM框架的正则化PEN方法。
- 采用多尺度能量(MuSE)正则化提高层面组合重建效果。
- 实验结果表明,该方法能显著提高图像质量。
- 正则化PEN方法为高分辨率3D扩散MRI提供更稳健、高效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

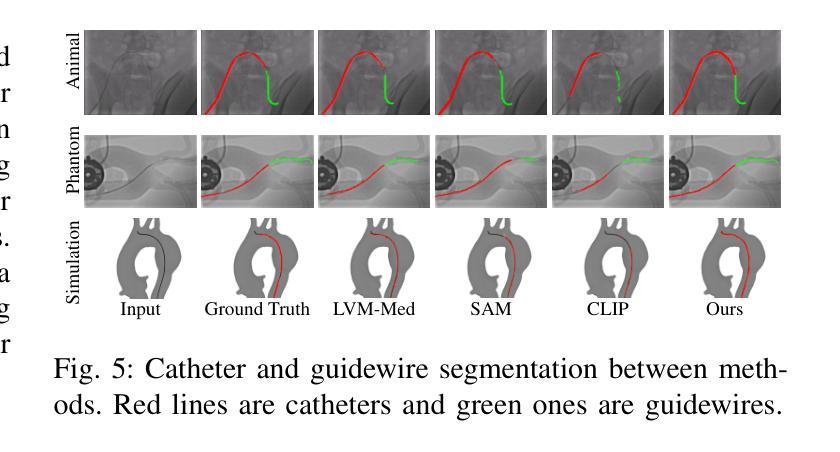
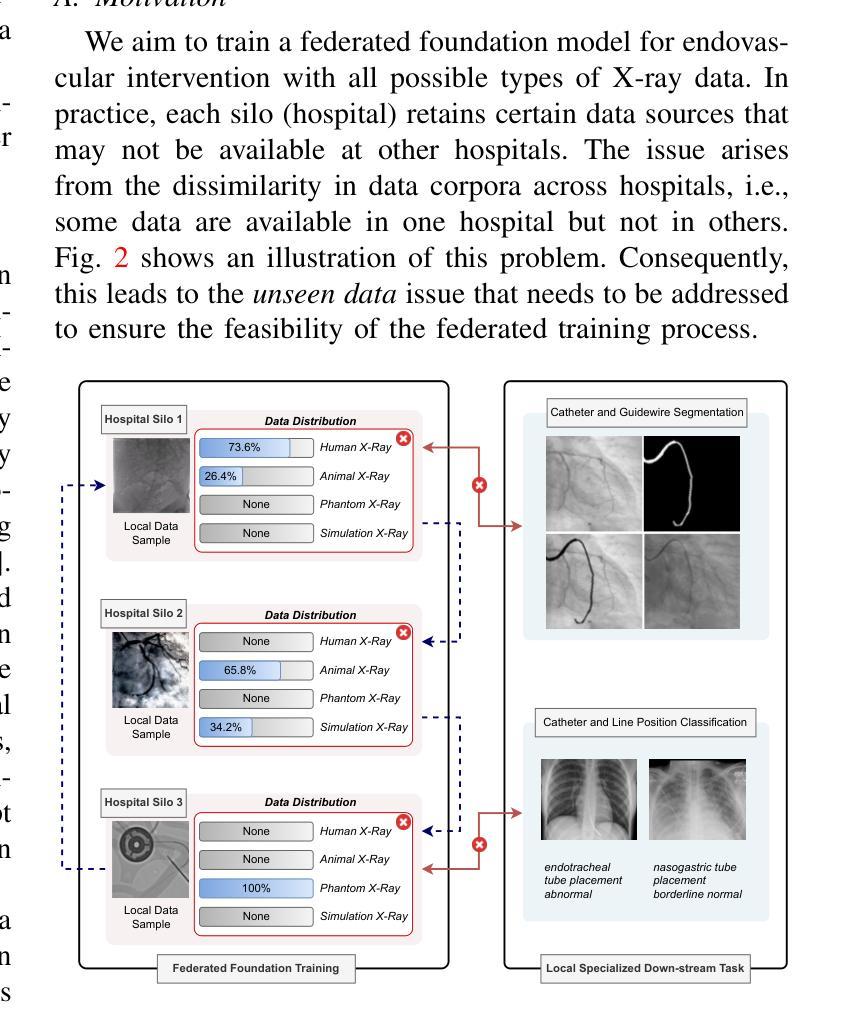
FedEFM: Federated Endovascular Foundation Model with Unseen Data
Authors:Tuong Do, Nghia Vu, Tudor Jianu, Baoru Huang, Minh Vu, Jionglong Su, Erman Tjiputra, Quang D. Tran, Te-Chuan Chiu, Anh Nguyen
In endovascular surgery, the precise identification of catheters and guidewires in X-ray images is essential for reducing intervention risks. However, accurately segmenting catheter and guidewire structures is challenging due to the limited availability of labeled data. Foundation models offer a promising solution by enabling the collection of similar domain data to train models whose weights can be fine-tuned for downstream tasks. Nonetheless, large-scale data collection for training is constrained by the necessity of maintaining patient privacy. This paper proposes a new method to train a foundation model in a decentralized federated learning setting for endovascular intervention. To ensure the feasibility of the training, we tackle the unseen data issue using differentiable Earth Mover’s Distance within a knowledge distillation framework. Once trained, our foundation model’s weights provide valuable initialization for downstream tasks, thereby enhancing task-specific performance. Intensive experiments show that our approach achieves new state-of-the-art results, contributing to advancements in endovascular intervention and robotic-assisted endovascular surgery, while addressing the critical issue of data sharing in the medical domain.
在血管内手术中,X光图像中对导管和导丝的精确识别对于降低干预风险至关重要。然而,由于标记数据的有限可用性,准确分割导管和导丝结构具有挑战性。基础模型通过收集类似领域的数据来训练模型,其权重可以进行微调以适应下游任务,因此提供了一种有前途的解决方案。然而,大规模的数据收集用于训练受到保持患者隐私的制约。本文提出了一种在分散的联邦学习环境中训练基础模型的新方法,用于血管内干预。为了确保训练的可行性,我们采用知识蒸馏框架内的可微分的地球移动者距离来解决未见数据的问题。一旦训练完成,我们的基础模型的权重为下游任务提供了有价值的初始化,从而提高了任务特定性能。密集的实验表明,我们的方法取得了最新的最先进的成果,为血管内干预和机器人辅助血管内手术的发展做出了贡献,同时解决了医疗领域数据共享的关键问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages. Accepted to ICRA 2025
Summary
本文提出在分布式联邦学习环境中训练基础模型的新方法,用于血管内介入手术。为解决训练过程中未见数据的问题,采用可微分的Earth Mover’s Distance在知识蒸馏框架内进行处理。训练后的基础模型权重为下游任务提供有价值的初始化,从而提高任务特定性能。实验证明,该方法达到最新水平,促进血管内介入和机器人辅助血管内手术的发展,同时解决医疗领域数据共享的关键问题。
Key Takeaways
- 在血管内手术中,X光影像中精确识别导管和导丝对降低干预风险至关重要。
- 准确分割导管和导丝结构具有挑战性,因为缺乏标记数据。
- 基础模型通过收集类似领域的数据来训练模型,其权重可以进行微调以适应下游任务,为解决上述问题提供了有前景的解决方案。
- 论文提出在分布式联邦学习环境中训练基础模型的新方法,适用于血管内介入治疗。
- 为确保训练的可行性,采用可微分的Earth Mover’s Distance在知识蒸馏框架内解决未见数据的问题。
- 训练后的基础模型权重为下游任务提供有价值的初始化,从而提高任务性能。
点此查看论文截图

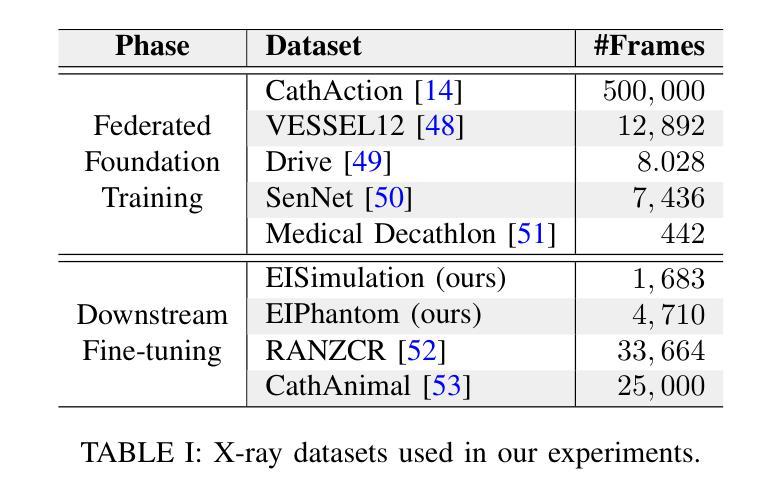
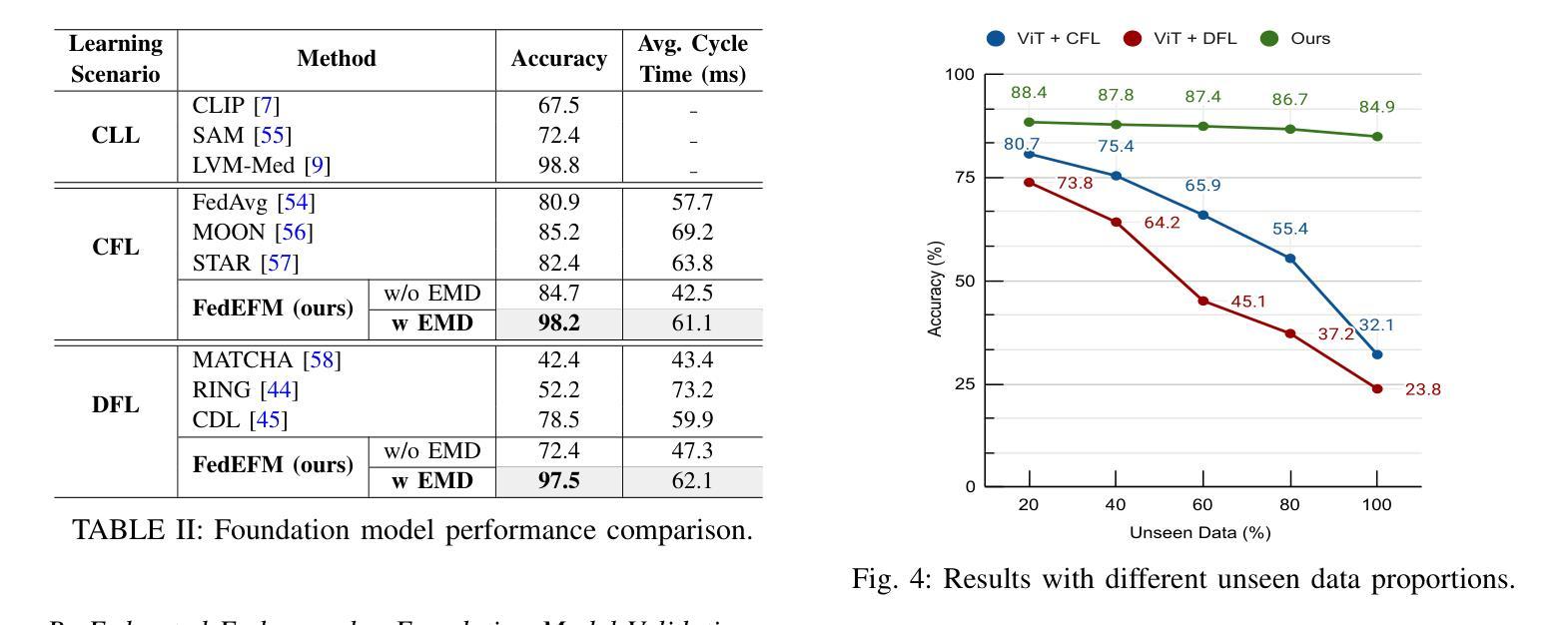

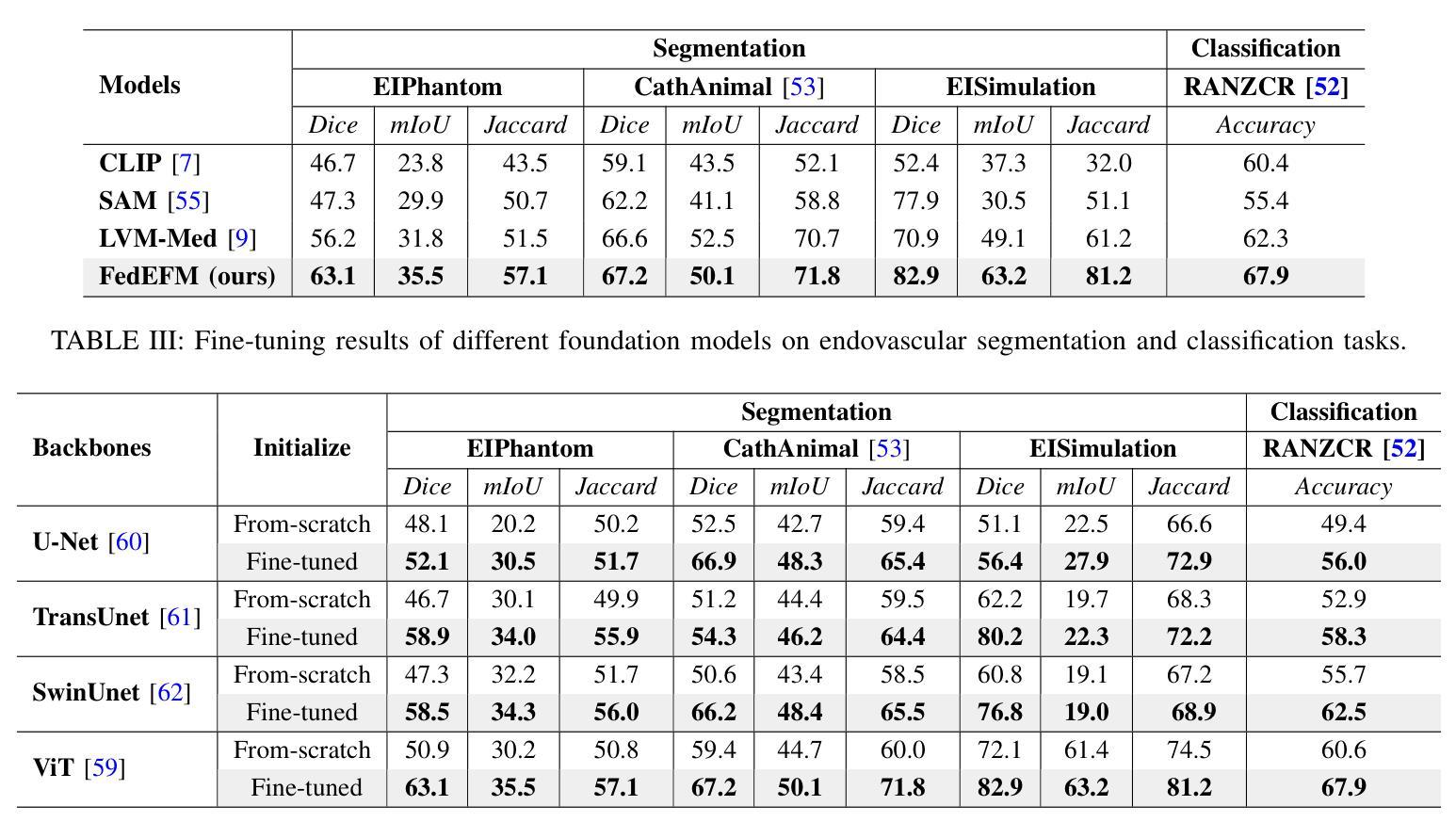
Dynamic Hypergraph Representation for Bone Metastasis Cancer Analysis
Authors:Yuxuan Chen, Jiawen Li, Huijuan Shi, Yang Xu, Tian Guan, Lianghui Zhu, Yonghong He, Anjia Han
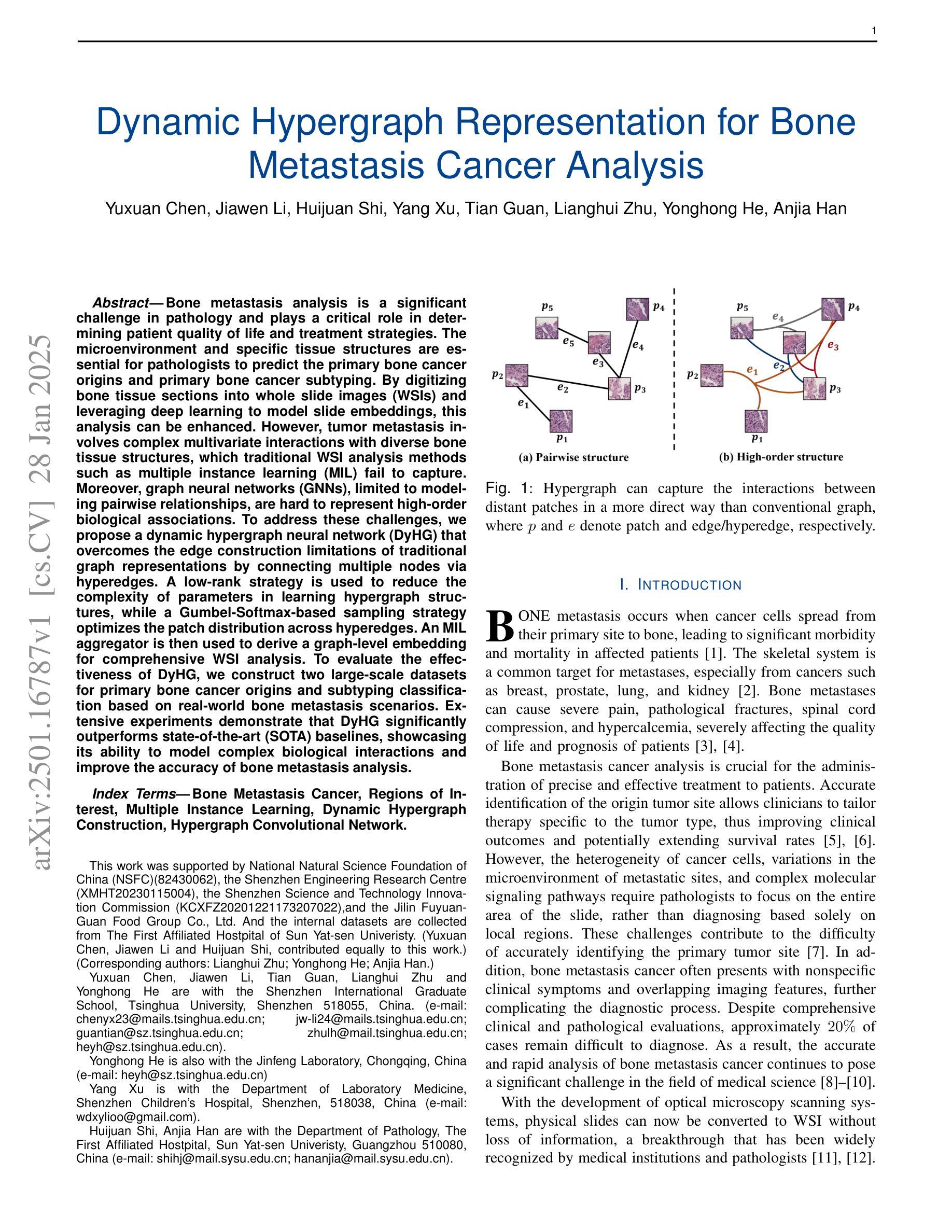
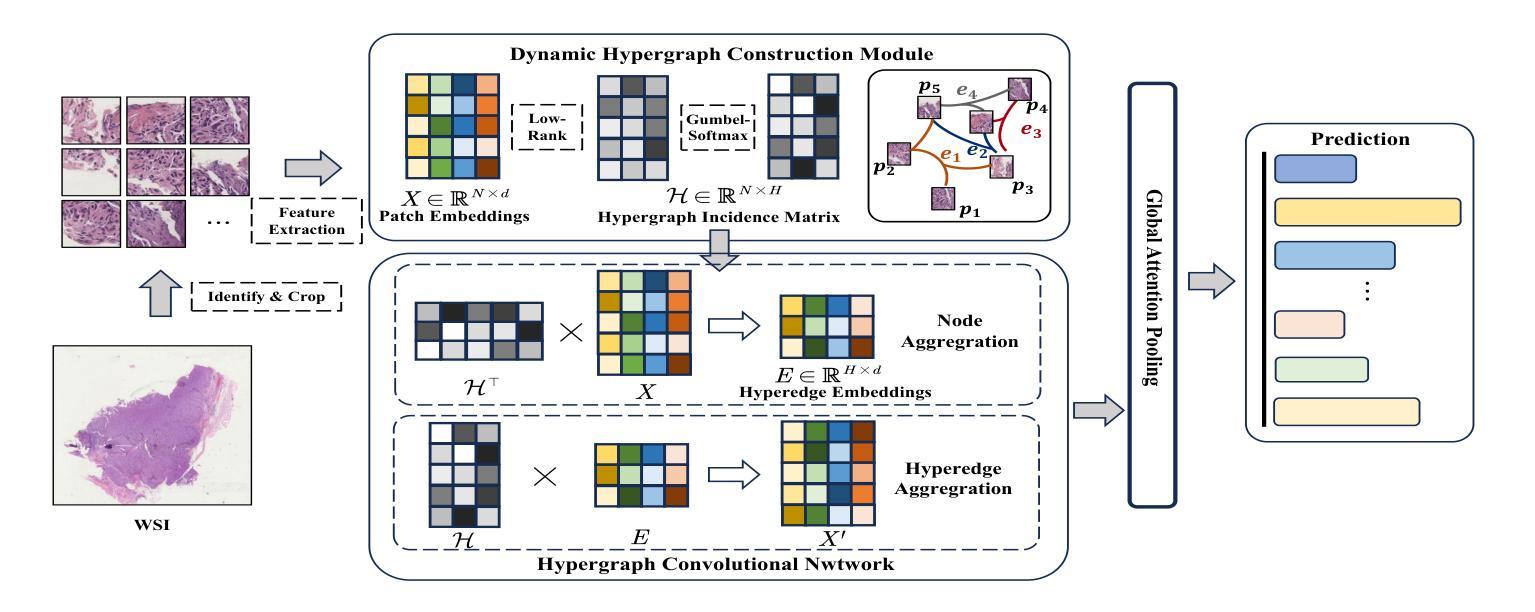
Bone metastasis analysis is a significant challenge in pathology and plays a critical role in determining patient quality of life and treatment strategies. The microenvironment and specific tissue structures are essential for pathologists to predict the primary bone cancer origins and primary bone cancer subtyping. By digitizing bone tissue sections into whole slide images (WSIs) and leveraging deep learning to model slide embeddings, this analysis can be enhanced. However, tumor metastasis involves complex multivariate interactions with diverse bone tissue structures, which traditional WSI analysis methods such as multiple instance learning (MIL) fail to capture. Moreover, graph neural networks (GNNs), limited to modeling pairwise relationships, are hard to represent high-order biological associations. To address these challenges, we propose a dynamic hypergraph neural network (DyHG) that overcomes the edge construction limitations of traditional graph representations by connecting multiple nodes via hyperedges. A low-rank strategy is used to reduce the complexity of parameters in learning hypergraph structures, while a Gumbel-Softmax-based sampling strategy optimizes the patch distribution across hyperedges. An MIL aggregator is then used to derive a graph-level embedding for comprehensive WSI analysis. To evaluate the effectiveness of DyHG, we construct two large-scale datasets for primary bone cancer origins and subtyping classification based on real-world bone metastasis scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DyHG significantly outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines, showcasing its ability to model complex biological interactions and improve the accuracy of bone metastasis analysis.
骨转移分析是病理学领域的一个重大挑战,对于确定患者的生活质量和治疗策略起着至关重要的作用。病理学家预测原发性骨癌的起源和原发性骨癌亚型时,微环境和特定的组织结构都是至关重要的。通过将骨组织切片数字化为全切片图像(WSIs)并利用深度学习来构建幻灯片嵌入,可以增强这种分析。然而,肿瘤转移涉及与多种骨组织结构的复杂多元交互,传统的WSI分析方法(如多实例学习(MIL))无法捕捉到这一点。此外,图神经网络(GNNs)受限于建模二元关系,难以表示高阶生物关联。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种动态超图神经网络(DyHG),它通过超边连接多个节点,克服了传统图表示在构建边缘上的局限性。利用低秩策略降低学习超图结构参数的复杂性,而基于Gumbel-Softmax的采样策略优化了超边之间的斑块分布。然后,使用MIL聚合器推导图级嵌入,用于全面的WSI分析。为了评估DyHG的有效性,我们构建了两个大规模数据集,用于基于现实世界的骨转移情景进行原发性骨癌起源和分型分类。大量实验表明,DyHG显著优于最新技术水平的基线方法,展示了其建模复杂生物交互和提高骨转移分析准确性的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages,11 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个动态超图神经网络(DyHG)模型,用于解决病理学中骨转移分析面临的挑战。该模型通过构建超图来克服传统图表示的边缘构建限制,并采用了低阶策略来降低学习超图结构的参数复杂性。此外,使用基于Gumbel-Softmax的采样策略优化超边中的补丁分布,并结合多实例聚合器进行全幻灯片级别的分析。实验证明,DyHG在原发性骨癌起源和分型分类方面显著优于现有方法,展现了其处理复杂生物学交互和改进骨转移分析准确性的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 骨转移分析在病理学中是一项重要挑战,涉及预测骨癌起源和分型。
- 传统WSI分析方法(如多实例学习)无法捕捉复杂的骨转移多元交互。
- 图神经网络受限于建模二元关系,难以表示高阶生物关联。
- 提出的动态超图神经网络(DyHG)通过构建超图克服这些限制。
- DyHG使用低阶策略学习超图结构,优化补丁分布并使用多实例聚合进行WSI分析。
- DyHG在基于真实世界骨转移场景的骨癌起源和分型分类方面表现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图
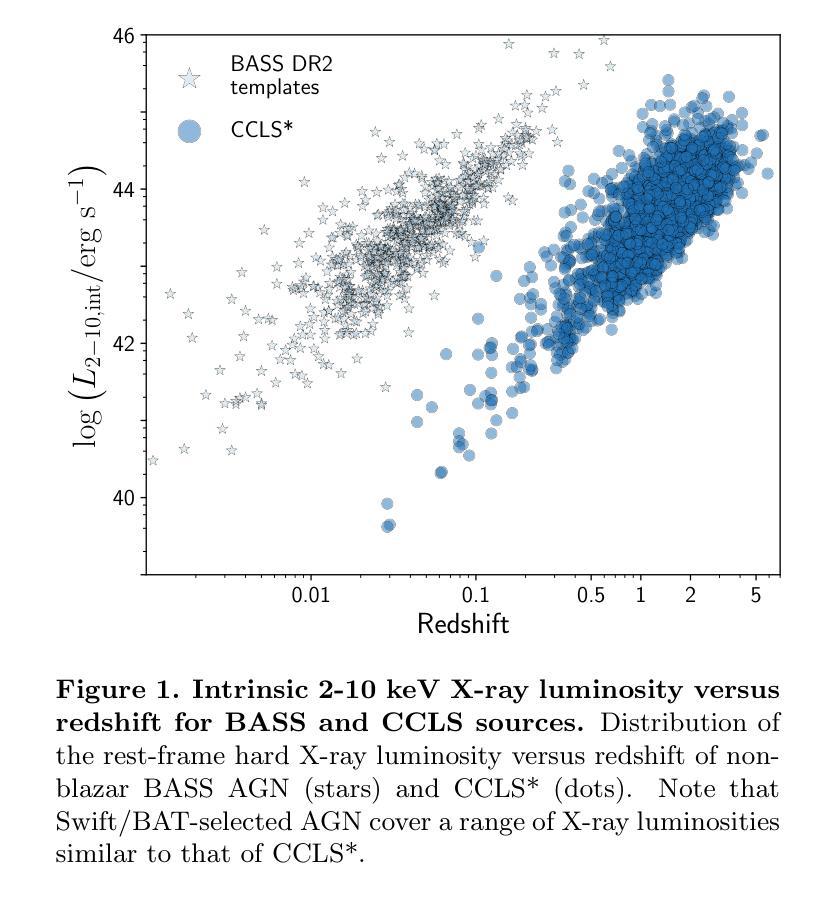
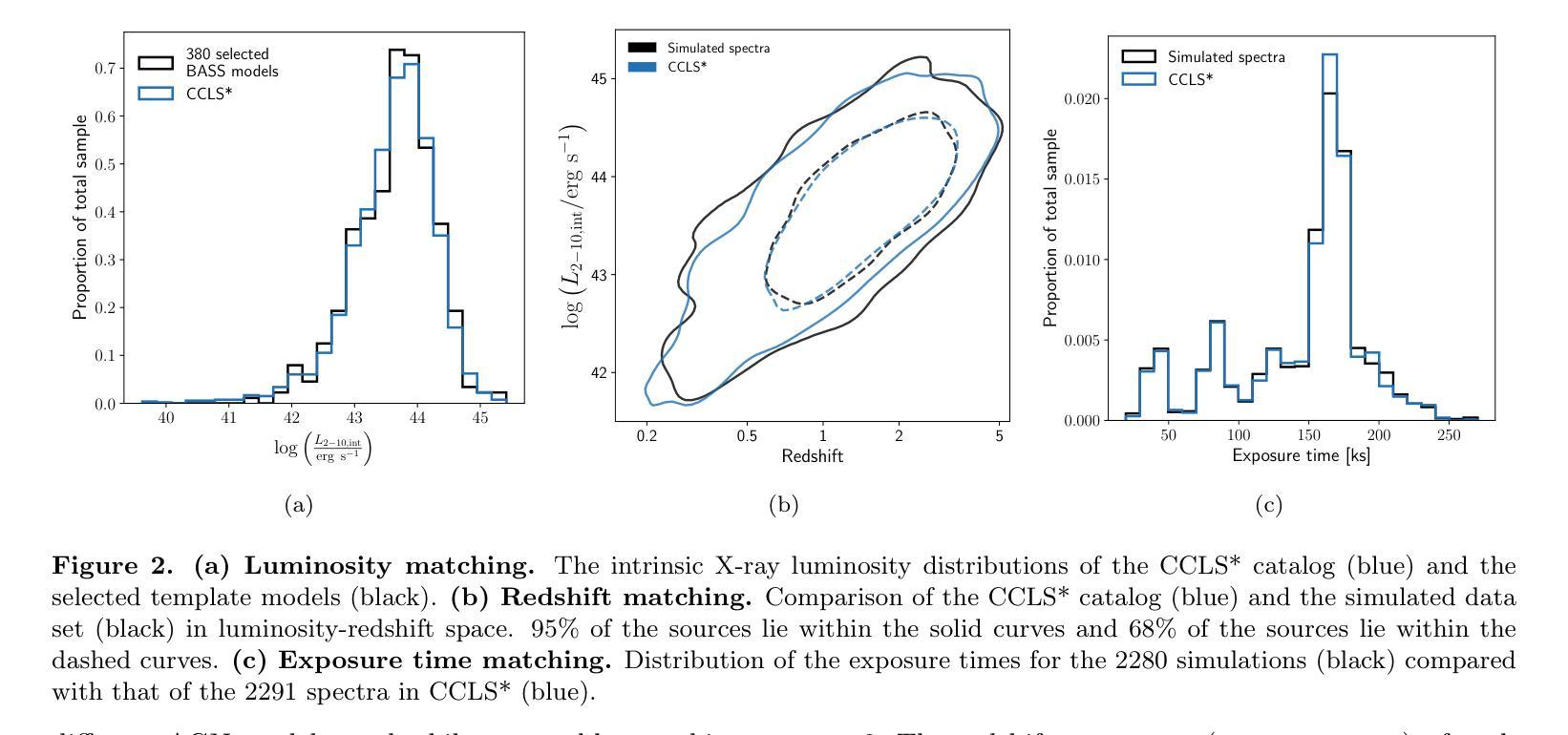
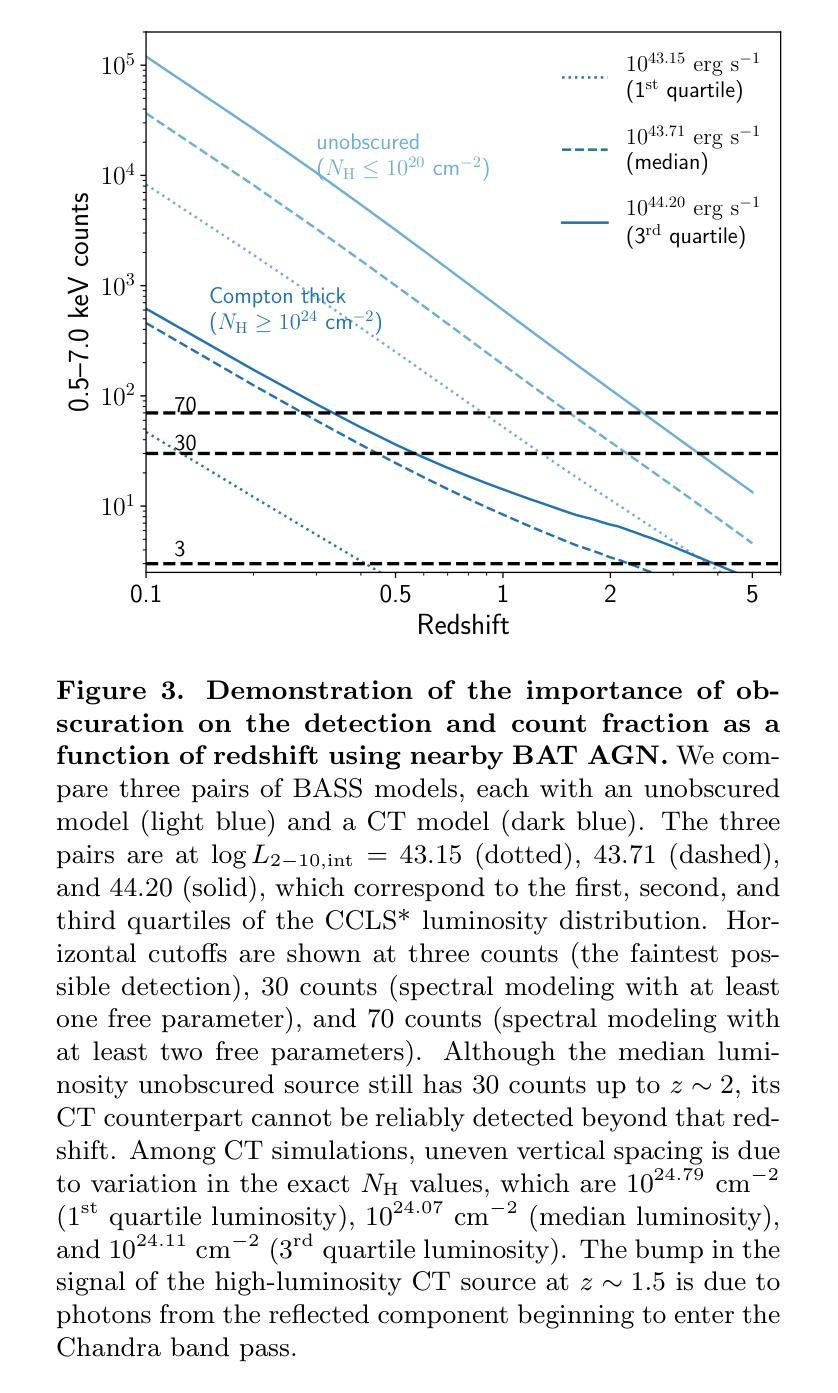
BASS XLV: Quantifying AGN Selection Effects in the Chandra COSMOS-Legacy Survey with BASS
Authors:Yarone M. Tokayer, Michael J. Koss, C. Megan Urry, Priyamvada Natarajan, Richard Mushotzky, Mislav Balokovic, Franz E. Bauer, Peter Boorman, Alessandro Peca, Claudio Ricci, Federica Ricci, Daniel Stern, Ezequiel Treister, Benny Trakhtenbrot
Deep extragalactic X-ray surveys, such as the Chandra COSMOS-Legacy field (CCLS), are prone to be biased against active galactic nuclei (AGN) with high column densities due to their lower count rates at a given luminosity. To quantify this selection effect, we forward model nearby ($z\sim0.05$) AGN from the BAT AGN Spectroscopic Survey (BASS) with well-characterized ($\gtrsim$1000 cts) broadband X-ray spectra (0.5-195 keV) to simulate the CCLS absorption distribution. We utilize the BASS low-redshift analogs with similar luminosities to the CCLS ($L_\mathrm{2-10\ keV}^\mathrm{int}\sim10^{42-45}\ \mathrm{erg}\ \mathrm{s}^{-1}$), which are much less affected by obscuration and low-count statistics, as the seed for our simulations, and follow the spectral fitting of the CCLS. Our simulations reveal that Chandra would fail to detect the majority (53.3%; 563/1056) of obscured ($N_\mathrm{H}>10^{22}\ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$) simulated BASS AGN given the observed redshift and luminosity distribution of the CCLS. Even for detected sources with sufficient counts ($\geq30$) for spectral modeling, the level of obscuration is significantly overestimated. This bias is most extreme for objects whose best fit indicates a high-column density AGN ($N_\mathrm{H}\geq10^{24}\ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$), since the majority (66.7%; 18/27) of these are actually unobscured sources ($N_\mathrm{H}<10^{22}\ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$). This implies that previous studies may have significantly overestimated the increase in the obscured fraction with redshift and the fraction of luminous obscured AGN. Our findings highlight the importance of directly considering obscuration biases and forward modeling in X-ray surveys, as well as the need for higher-sensitivity X-ray missions such as the Advanced X-ray Imaging Satellite (AXIS), and the importance of multi-wavelength indicators to estimate obscuration in distant supermassive black holes.
深度星系外X射线调查,如钱德拉宇宙学大尺度结构(CCLS)调查,由于给定光度下的计数率较低,容易对高柱密度活动星系核(AGN)产生偏见。为了量化这种选择效应,我们利用BAT AGN光谱调查(BASS)附近的(z~0.05)且特征明显的(≥1000个计数)宽频X射线光谱(0.5-195 keV)来模拟CCLS吸收分布。我们利用BASS的低红移类似物作为模拟的种子,这些类似物的光度与CCLS相似(L_int_2-10\ keV~~介于10^42至10^45之间),受遮蔽和低计数统计的影响较小,然后跟随CCLS的光谱拟合。我们的模拟表明,鉴于CCLS观测到的红移和光度分布,钱德拉将无法检测到大多数(53.3%;563/1056)遮蔽的(NH> 10^22 cm^-2)模拟BASS AGN。即使对于具有足够计数(≥30)进行光谱建模的已检测源,遮蔽程度也被大大高估了。对于最佳拟合指示高柱密度(NH≥ 10^24 cm^-2)的天体,这种偏见最为极端,因为大多数(占66.7%;有半数以上的星系属于未被遮蔽的情况。这暗示之前的许多研究可能已经显著高估了遮蔽比例随红移的增加以及高光度遮蔽星系的比例。我们的研究强调了直接考虑遮蔽偏见和正向建模的重要性。因此需要根据具体情况,设立适应性较强的太空调查机构来改善对未来深远高灵空间星座事件的正确统计、调研估算甚至推举等方法具有理论支持和评估提升价值的宝贵思路也渐受瞩目。,而更为敏感的X射线任务例如先进X射线成像卫星(AXIS)的必要性则变得更为迫切凸显其必要性以及应用多重波长指标在估算遥远超大质量黑洞遮蔽中的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages, 20 figures. Accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal
摘要
针对深远的银河系外X射线巡天观测如CCLS存在高柱密度活动星系核(AGNs)的选择偏见问题,我们通过模拟研究评估了这一选择效应。利用BASS低红移类似天体的宽带X射线光谱进行模拟,模拟样本与CCLS类似光度范围内的天体相似,受遮蔽影响较小且低计数统计更少。模拟显示,对于给定CCLS观测到的红移和光度分布的遮蔽模拟BASS AGN(柱密度大于$ 10^{22}\ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$ ),Chandra将遗漏多数(约半数以上)。即使在具有足够计数(大于或等于30)进行光谱建模的检测源中,遮蔽程度的估计也偏高。对于最佳拟合显示高柱密度AGNs(柱密度大于或等于$ 10^{24}\ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$ )的对象,这种偏见尤为极端,其中大多数(约三分之二)实际上为未遮蔽源(柱密度小于$ 10^{22}\ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$)。这意味着之前的研究可能显著高估了随红移变化的遮蔽部分增加情况和遮蔽型高光度AGNs的比例。我们的研究结果强调了直接考虑遮蔽偏见和前向建模对X射线调查的重要性,强调了更灵敏的X射线任务(如AXIS卫星)的重要性以及通过多波长指标来估计遥远超大质量黑洞遮蔽的必要性。
关键见解
- 深远的银河系外X射线巡天观测如CCLS存在对高柱密度活动星系核(AGNs)的选择偏见问题。
- 模拟研究表明,给定CCLS观测到的红移和光度分布,多数遮蔽型BASS AGN将被遗漏。
- 即使考虑到足够的计数用于光谱建模的遮蔽型源中,估计的遮蔽程度也可能偏高。
- 存在严重的对高柱密度AGNs的偏见:大多数被认为是高柱密度的源实际上并非如此。
- 之前的研究可能高估了随红移变化的遮蔽部分增加情况和遮蔽型高光度AGNs的比例。
- 在X射线调查中需要直接考虑遮蔽偏见并进行前向建模。
点此查看论文截图

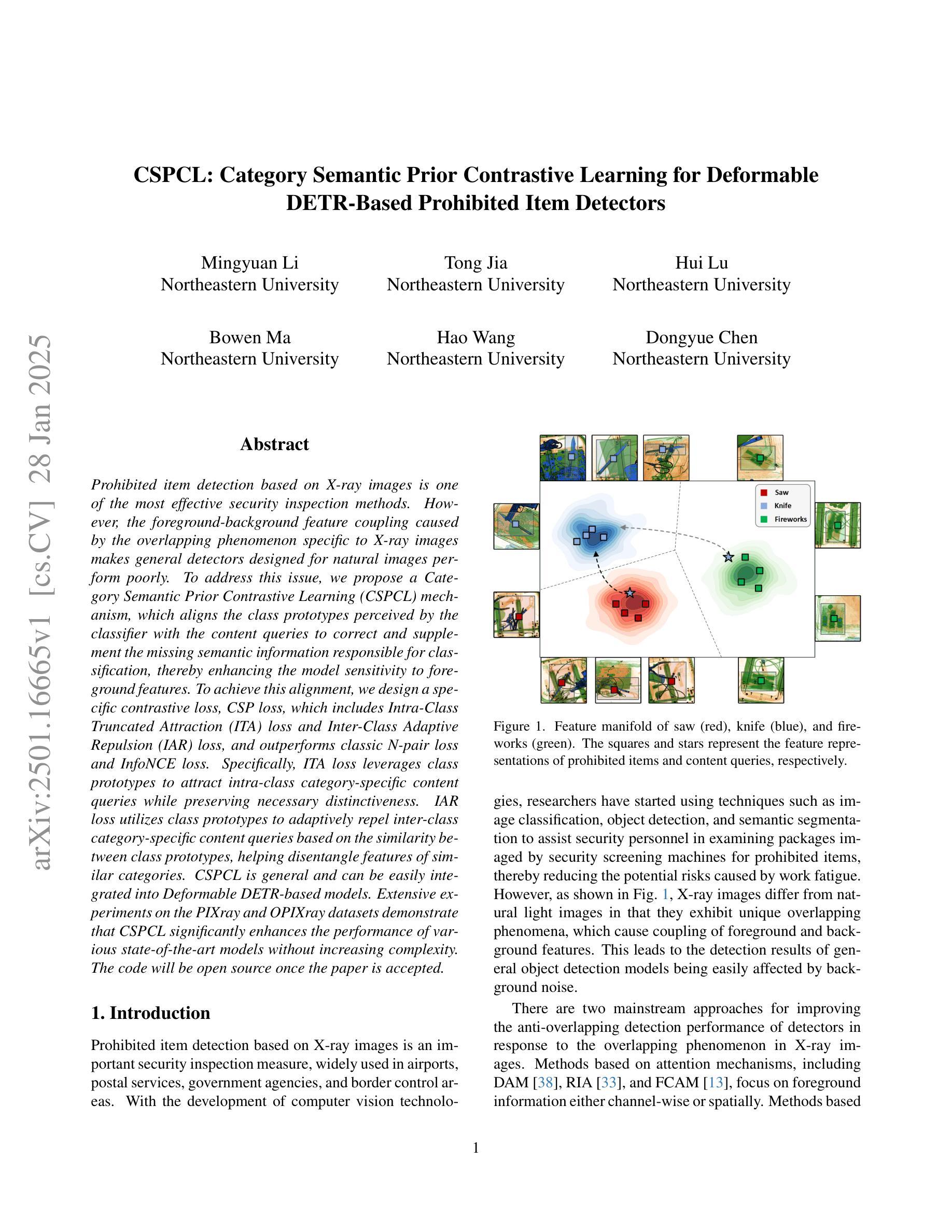
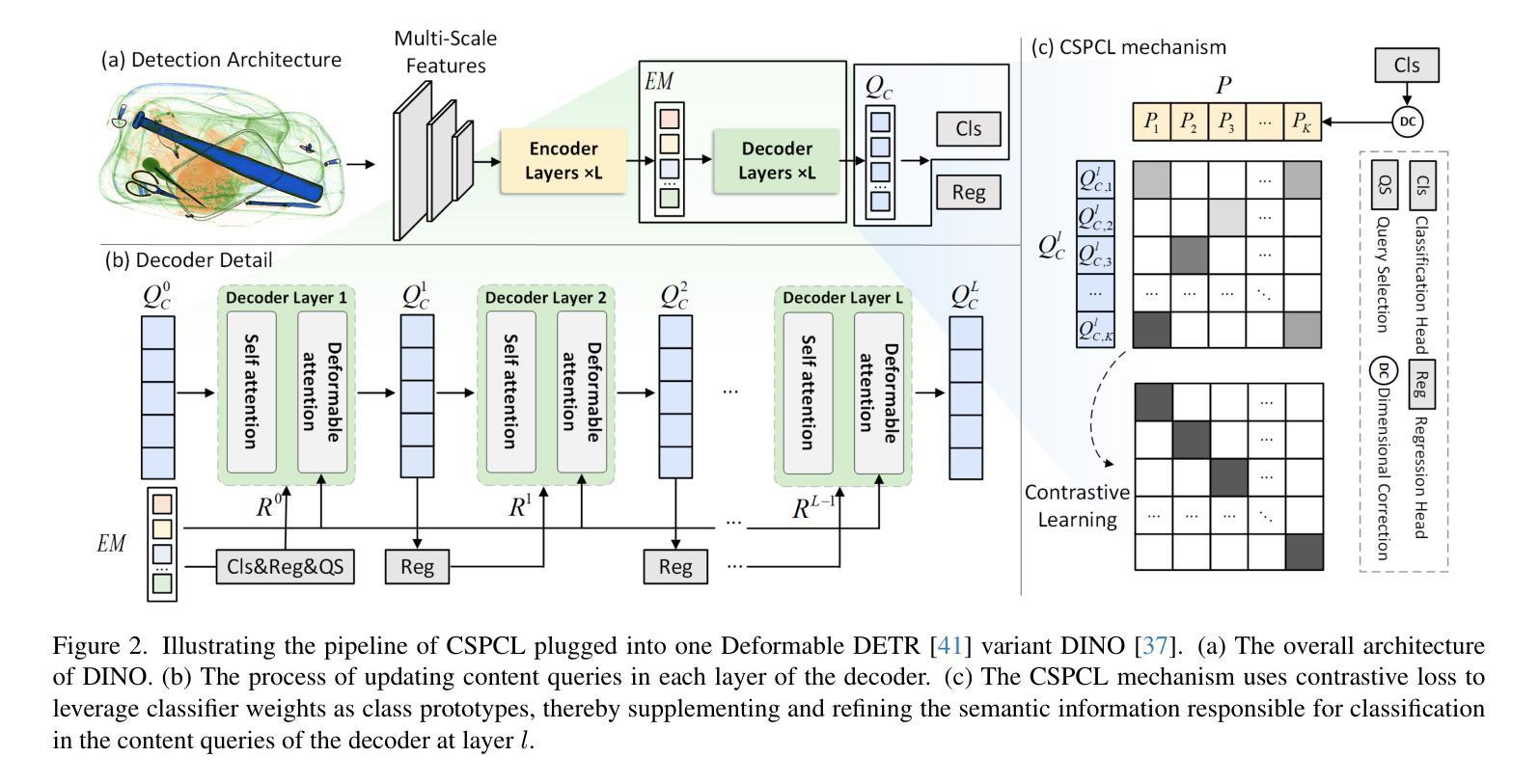
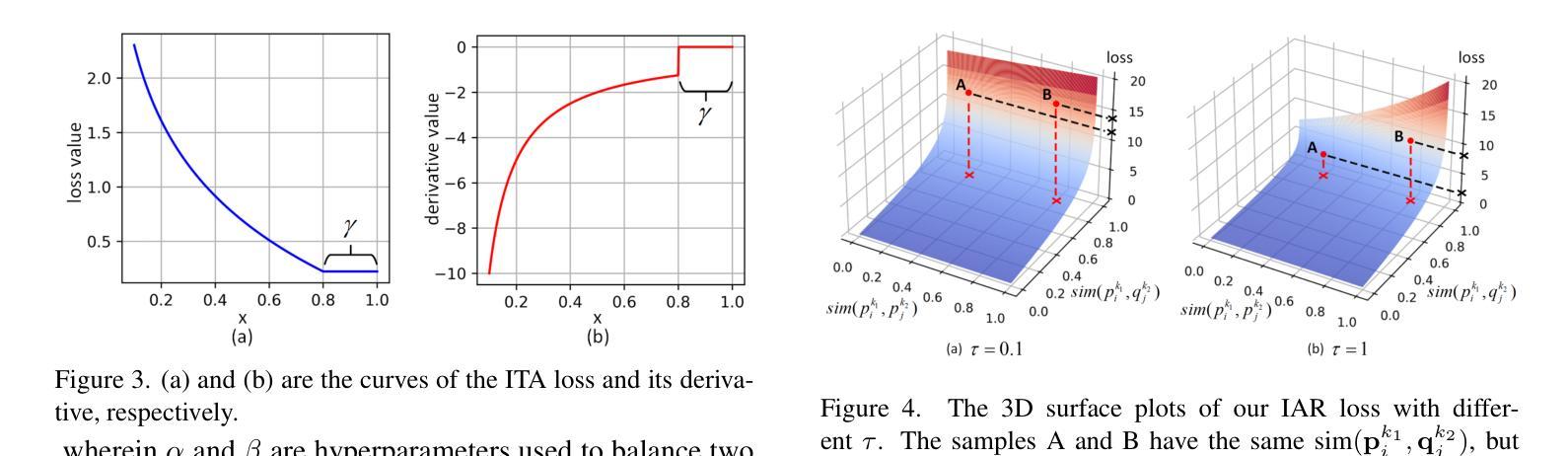
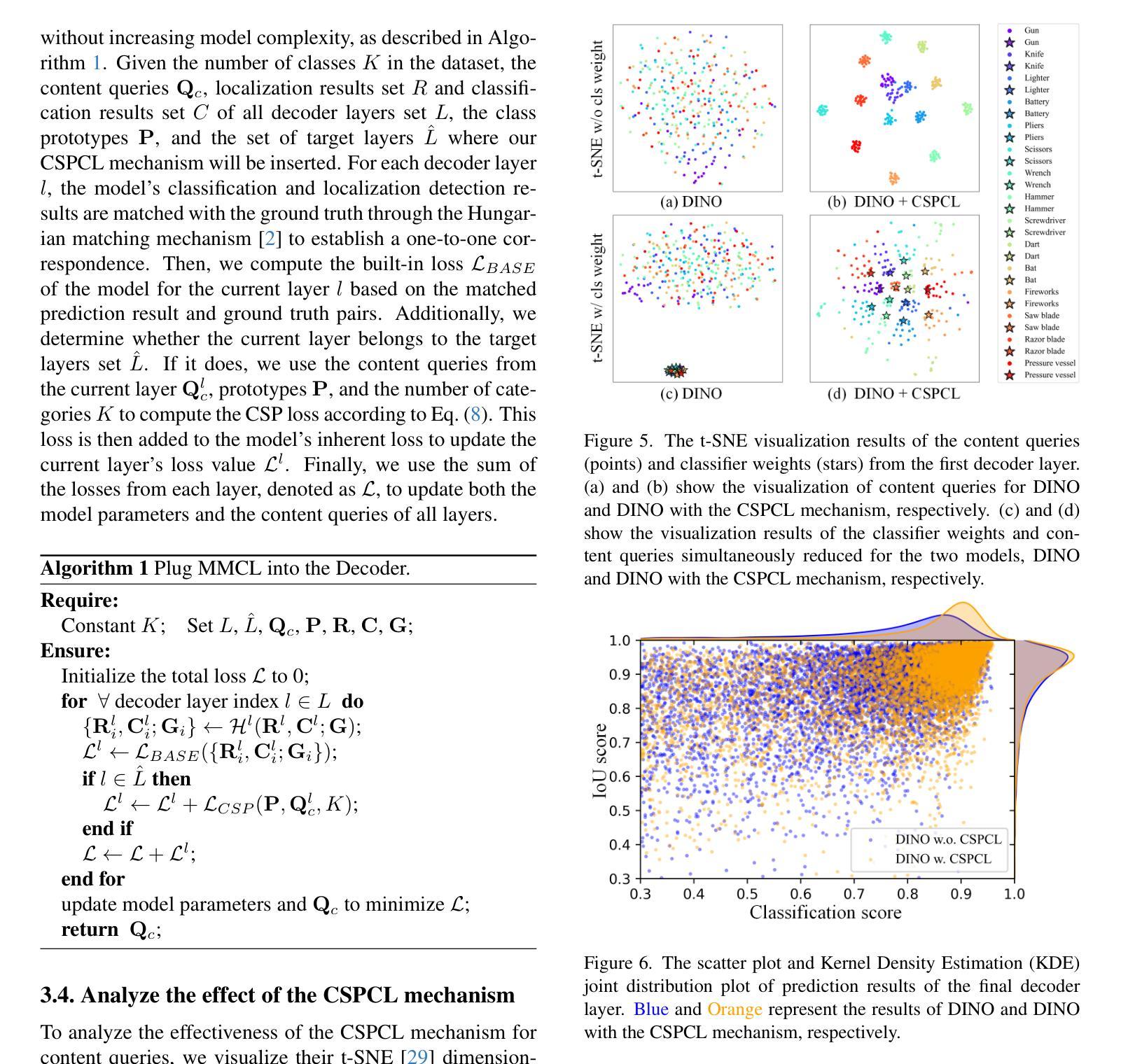
CSPCL: Category Semantic Prior Contrastive Learning for Deformable DETR-Based Prohibited Item Detectors
Authors:Mingyuan Li, Tong Jia, Hui Lu, Bowen Ma, Hao Wang, Dongyue Chen
Prohibited item detection based on X-ray images is one of the most effective security inspection methods. However, the foreground-background feature coupling caused by the overlapping phenomenon specific to X-ray images makes general detectors designed for natural images perform poorly. To address this issue, we propose a Category Semantic Prior Contrastive Learning (CSPCL) mechanism, which aligns the class prototypes perceived by the classifier with the content queries to correct and supplement the missing semantic information responsible for classification, thereby enhancing the model sensitivity to foreground features.To achieve this alignment, we design a specific contrastive loss, CSP loss, which includes Intra-Class Truncated Attraction (ITA) loss and Inter-Class Adaptive Repulsion (IAR) loss, and outperforms classic N-pair loss and InfoNCE loss. Specifically, ITA loss leverages class prototypes to attract intra-class category-specific content queries while preserving necessary distinctiveness. IAR loss utilizes class prototypes to adaptively repel inter-class category-specific content queries based on the similarity between class prototypes, helping disentangle features of similar categories.CSPCL is general and can be easily integrated into Deformable DETR-based models. Extensive experiments on the PIXray and OPIXray datasets demonstrate that CSPCL significantly enhances the performance of various state-of-the-art models without increasing complexity.The code will be open source once the paper is accepted.
基于X射线图像的违禁品检测是最有效的安全检查方法之一。然而,X射线图像特有的重叠现象导致的前景背景特征耦合,使得为自然图像设计的通用检测器表现不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种类别语义先验对比学习(CSPCL)机制,该机制将分类器感知的类别原型与内容查询对齐,以修正和补充负责分类的缺失语义信息,从而提高模型对前景特征的敏感性。为了实现这种对齐,我们设计了一种特定的对比损失,即CSP损失,它包括类内截断吸引(ITA)损失和类间自适应排斥(IAR)损失,并优于经典的N-pair损失和InfoNCE损失。具体而言,ITA损失利用类别原型来吸引类内特定的内容查询,同时保持必要的区分性。IAR损失则利用类别原型,根据类别原型之间的相似性,自适应地排斥类间特定的内容查询,有助于解开相似类别的特征。CSPCL是通用的,可以轻松地集成到基于可变形DETR的模型中。在PIXray和OPIXray数据集上的大量实验表明,CSPCL能显著提高各种最新模型的性能,且不会增加复杂性。论文被接受后,代码将开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
基于X光图像的违禁品检测是安全检测中最有效的方法之一。针对X光图像特有的重叠现象导致的前景背景特征耦合问题,通用自然图像检测器表现不佳。为此,我们提出了类别语义先验对比学习(CSPCL)机制,通过使分类器感知的类别原型与内容查询对齐,修正并补充缺失的语义信息,提高模型对前景特征的敏感性。为实现这一对齐,我们设计了特定的对比损失CSP损失,包括类内截断吸引(ITA)损失和类间自适应排斥(IAR)损失,且表现优于经典的N-pair损失和InfoNCE损失。CSPCL机制通用性强,可轻松融入基于可变形DETR的模型。在PIXray和OPIXray数据集上的大量实验表明,CSPCL可显著提高各种最新模型的性能,且不会增加复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- X光图像违禁品检测是安全检测的重要方法。
- X光图像中的前景背景特征耦合问题导致通用检测器效果不佳。
- 提出了CSPCL机制,通过类别语义先验对比学习提高模型对前景特征的敏感性。
- CSPCL机制包括ITA损失和IAR损失,优于N-pair损失和InfoNCE损失。
- ITA损失通过类原型吸引同类特定内容查询,保持必要差异性。
- IAR损失根据类原型之间的相似性,自适应排斥不同类别特定内容查询,有助于解开相似类别的特征。
点此查看论文截图
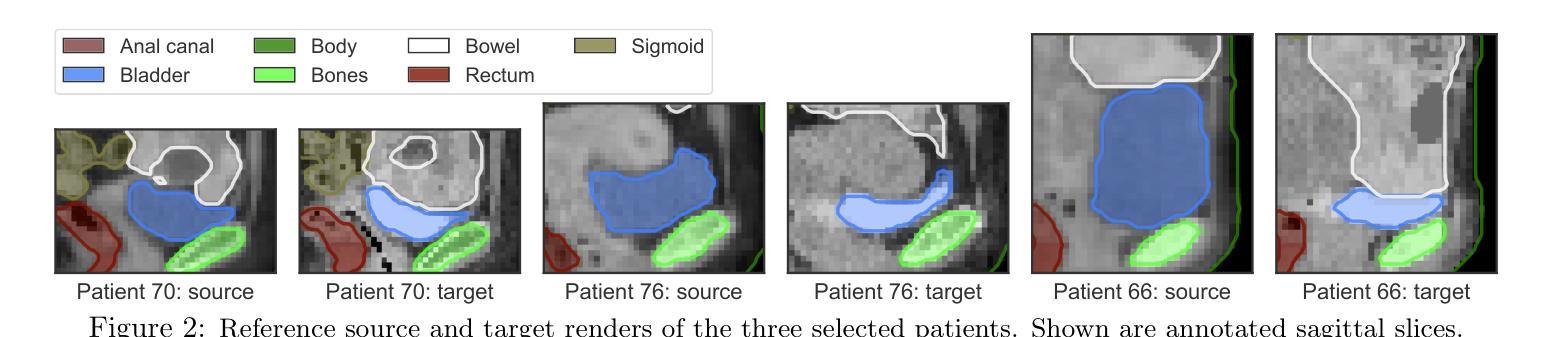
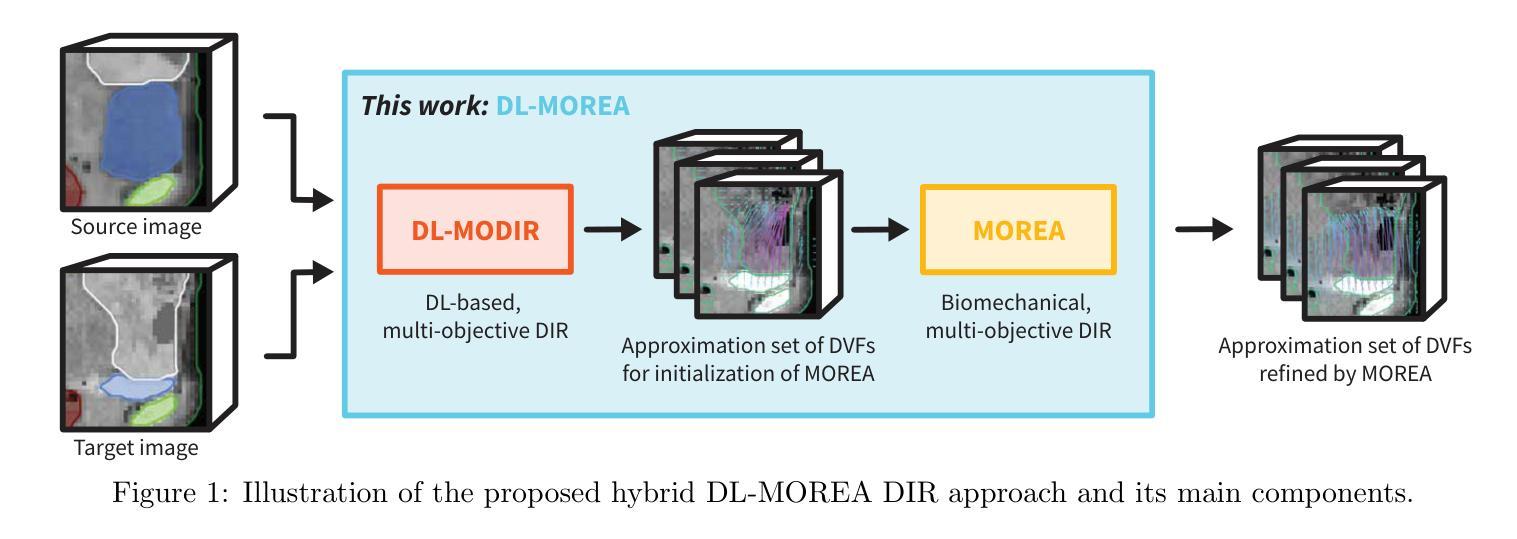
Multi-Objective Deep-Learning-based Biomechanical Deformable Image Registration with MOREA
Authors:Georgios Andreadis, Eduard Ruiz Munné, Thomas H. W. Bäck, Peter A. N. Bosman, Tanja Alderliesten
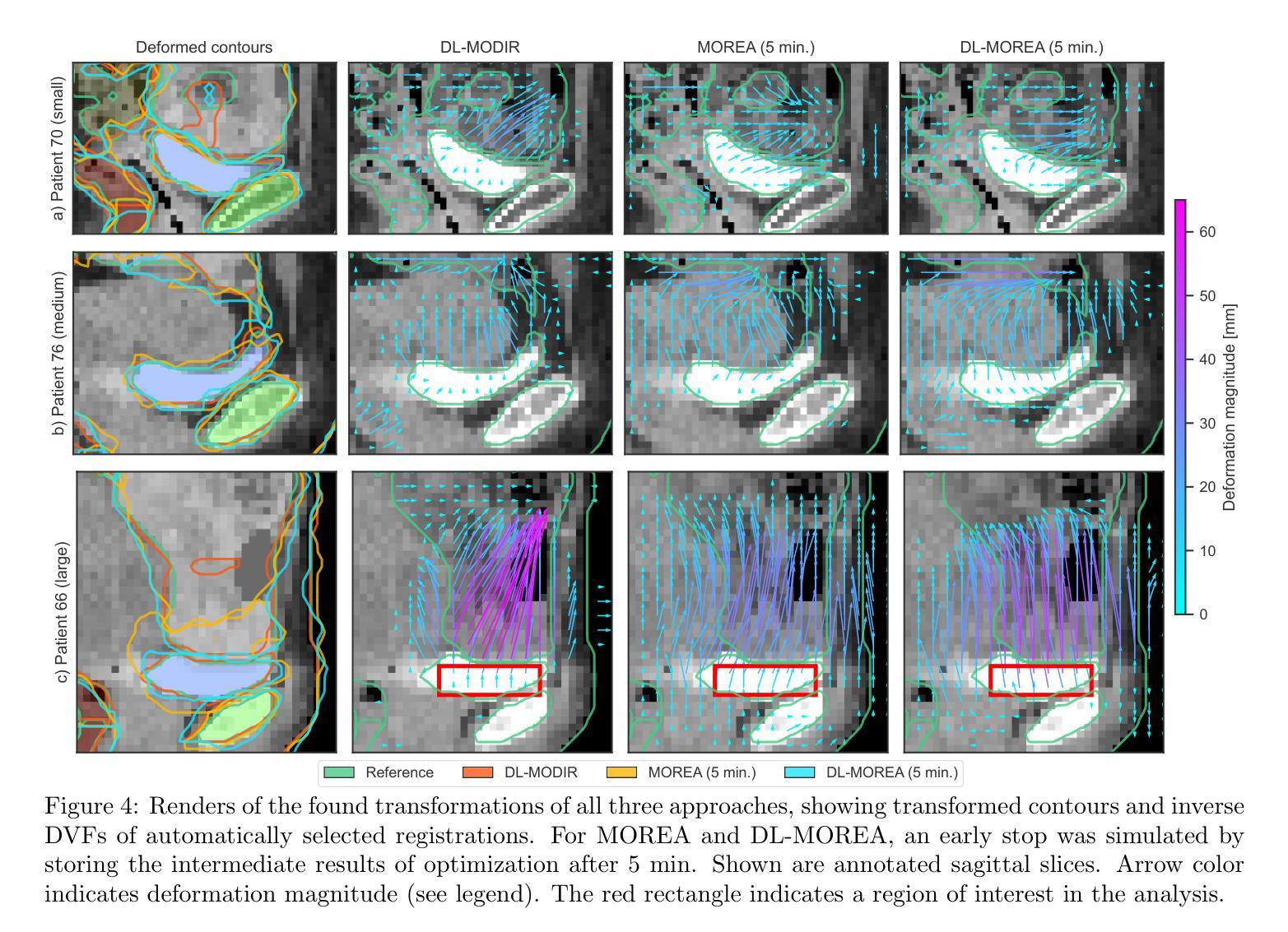
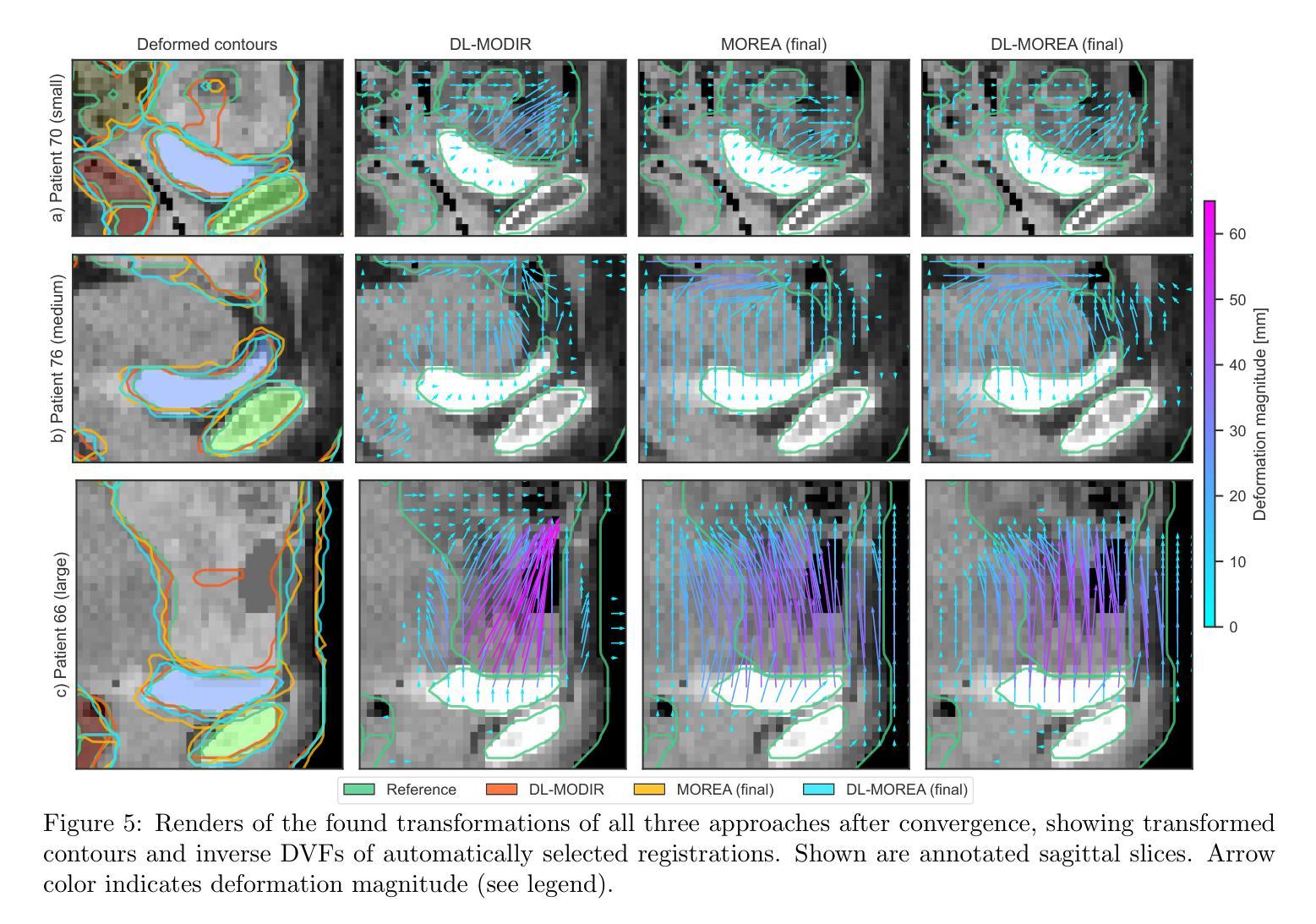
When choosing a deformable image registration (DIR) approach for images with large deformations and content mismatch, the realism of found transformations often needs to be traded off against the required runtime. DIR approaches using deep learning (DL) techniques have shown remarkable promise in instantly predicting a transformation. However, on difficult registration problems, the realism of these transformations can fall short. DIR approaches using biomechanical, finite element modeling (FEM) techniques can find more realistic transformations, but tend to require much longer runtimes. This work proposes the first hybrid approach to combine them, with the aim of getting the best of both worlds. This hybrid approach, called DL-MOREA, combines a recently introduced multi-objective DL-based DIR approach which leverages the VoxelMorph framework, called DL-MODIR, with MOREA, an evolutionary algorithm-based, multi-objective DIR approach in which a FEM-like biomechanical mesh transformation model is used. In our proposed hybrid approach, the DL results are used to smartly initialize MOREA, with the aim of more efficiently optimizing its mesh transformation model. We empirically compare DL-MOREA against its components, DL-MODIR and MOREA, on CT scan pairs capturing large bladder filling differences of 15 cervical cancer patients. While MOREA requires a median runtime of 45 minutes, DL-MOREA can already find high-quality transformations after 5 minutes. Compared to the DL-MODIR transformations, the transformations found by DL-MOREA exhibit far less folding and improve or preserve the bladder contour distance error.
在选择具有大变形和内容不匹配图像的形变图像配准(DIR)方法时,所找到的变换的真实性通常需要与所需的运行时间进行权衡。使用深度学习(DL)技术的DIR方法在预测变换方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,在复杂的注册问题上,这些变换的真实性可能会不足。使用生物力学、有限元建模(FEM)技术的DIR方法可以找到更真实的变换,但往往需要的运行时间更长。这项工作提出了将它们结合起来的第一个混合方法,旨在实现两者的最佳效果。这种混合方法称为DL-MOREA,它将最近引入的基于多目标的深度学习DIR方法与被称为DL-MODIR的VoxelMorph框架相结合,并与基于进化算法的多目标DIR方法MOREA相结合,其中使用FEM类似的生物力学网格变换模型。在我们提出的混合方法中,使用DL结果智能地初始化MOREA,旨在更有效地优化其网格变换模型。我们通过CT扫描对(捕捉15名宫颈癌患者膀胱充盈差异较大)实证比较DL-MOREA与其组件DL-MODIR和MOREA。虽然MOREA的中位运行时间为45分钟,但DL-MOREA在5分钟内就可以找到高质量的变换。与DL-MODIR变换相比,DL-MOREA找到的变换表现出较少的折叠,并改善或保持了膀胱轮廓距离误差。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-print for the SPIE Medical Imaging: Image Processing Conference
Summary
本文提出一种混合方法,名为DL-MOREA,结合了基于深度学习的可变形图像配准(DIR)方法和基于进化算法的多目标DIR方法。该方法旨在利用深度学习技术的优势快速预测变换,并结合有限元模型技术找到更真实的变换。通过智能初始化进化算法来优化网格变换模型,以实现更高效的优化。对15例宫颈癌患者的CT扫描数据进行实验比较,结果表明DL-MOREA能够在短时间内找到高质量的变换,减少了折叠现象,提高了膀胱轮廓距离误差的准确性和保留性。
Key Takeaways
- 文章介绍了混合方法DL-MOREA,结合了深度学习(DL)技术和进化算法的多目标可变形图像配准(DIR)。
- DL-MOREA旨在实现深度学习快速预测变换与有限元模型真实变换的结合。
- 进化算法被智能初始化以优化网格变换模型,提高优化效率。
- 实验比较显示DL-MOREA在短时间找到高质量的变换。
- 与仅使用深度学习的DL-MODIR相比,DL-MOREA找到的变换减少了折叠现象。
- DL-MOREA提高了膀胱轮廓距离误差的准确性和保留性。
点此查看论文截图

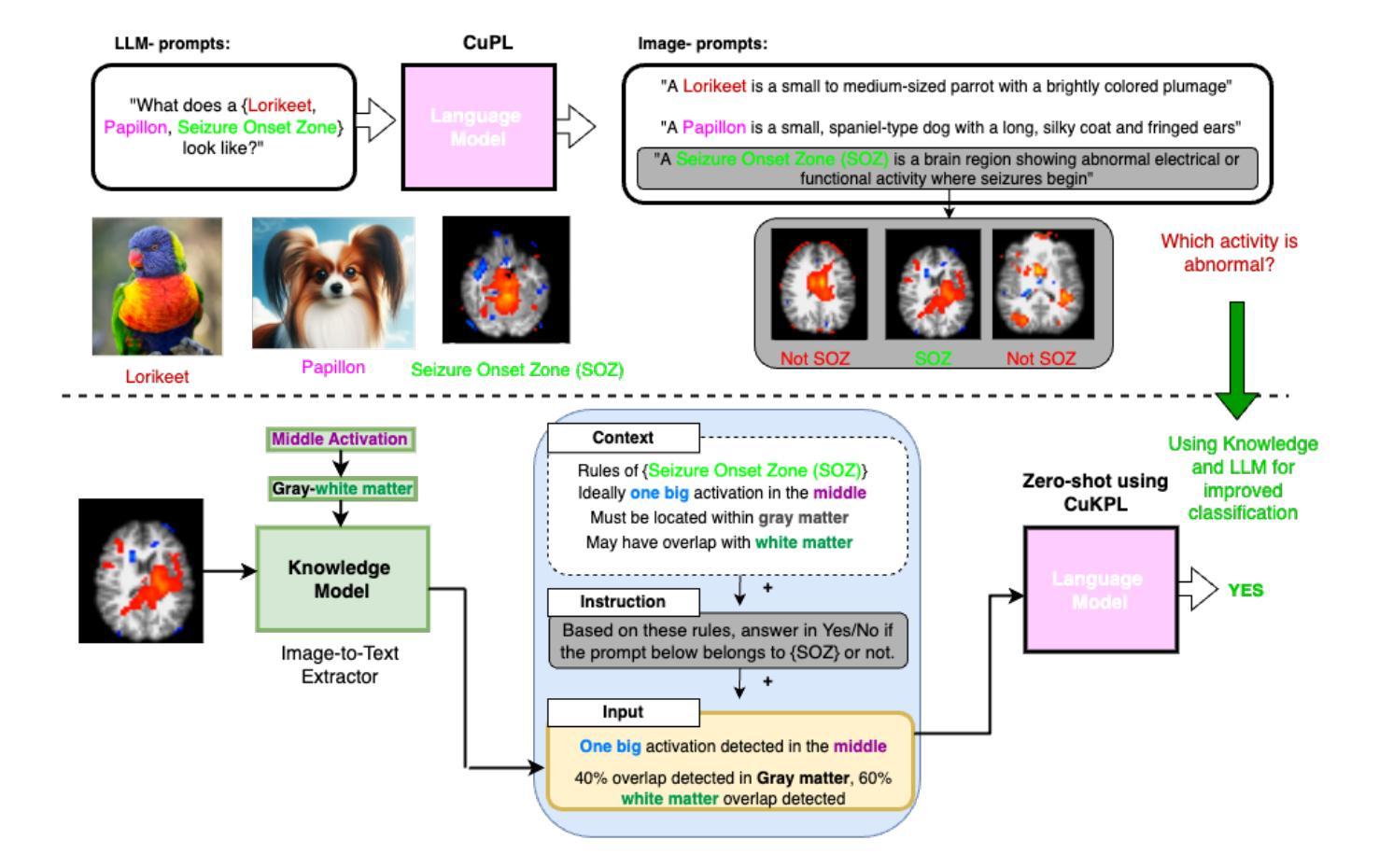
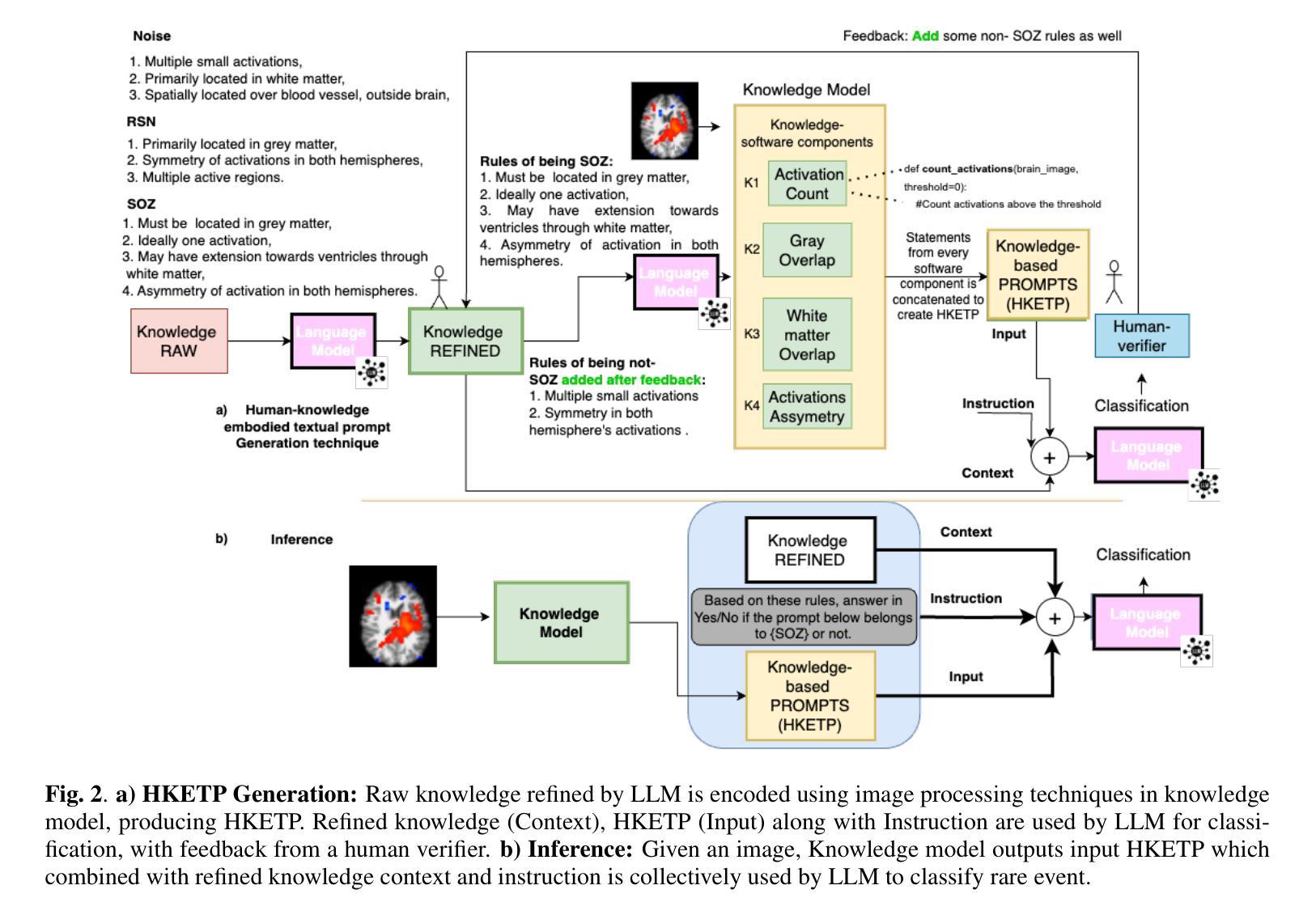
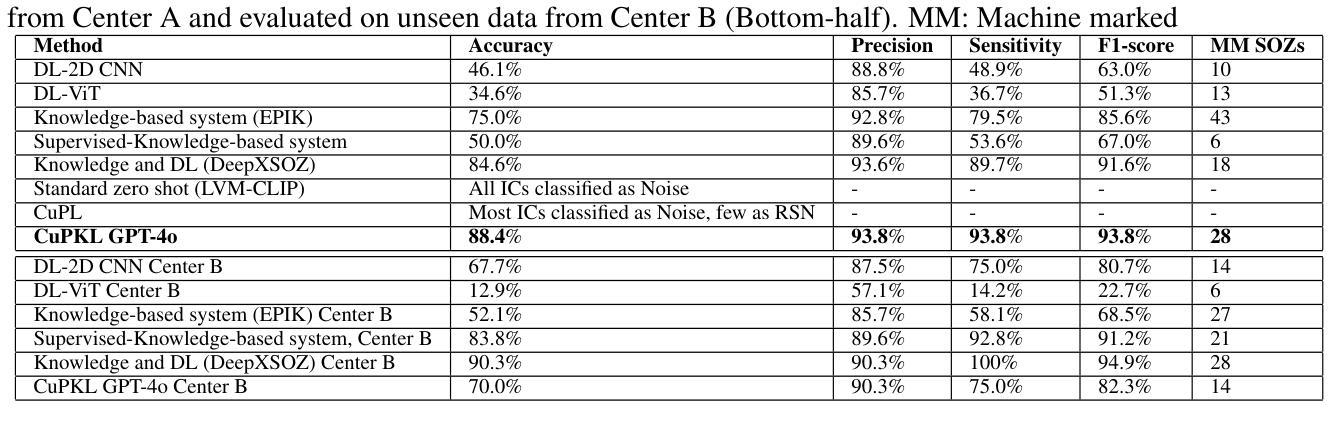
Generating customized prompts for Zero-Shot Rare Event Medical Image Classification using LLM
Authors:Payal Kamboj, Ayan Banerjee, Bin Xu, Sandeep Gupta
Rare events, due to their infrequent occurrences, do not have much data, and hence deep learning techniques fail in estimating the distribution for such data. Open-vocabulary models represent an innovative approach to image classification. Unlike traditional models, these models classify images into any set of categories specified with natural language prompts during inference. These prompts usually comprise manually crafted templates (e.g., ‘a photo of a {}’) that are filled in with the names of each category. This paper introduces a simple yet effective method for generating highly accurate and contextually descriptive prompts containing discriminative characteristics. Rare event detection, especially in medicine, is more challenging due to low inter-class and high intra-class variability. To address these, we propose a novel approach that uses domain-specific expert knowledge on rare events to generate customized and contextually relevant prompts, which are then used by large language models for image classification. Our zero-shot, privacy-preserving method enhances rare event classification without additional training, outperforming state-of-the-art techniques.
由于稀有事件发生的频率较低,因此没有大量数据,深度学习技术在此类数据的分布估计上表现不佳。开放词汇模型代表了图像分类的一种创新方法。与传统的模型不同,这些模型在推理期间将图像分类为用自然语言提示指定的任何类别集。这些提示通常包含手工制作的模板(例如,“一张……的照片”),在推理期间会填入每个类别的名称。本文介绍了一种简单有效的方法来生成包含辨别特征的准确且上下文描述性的提示。稀有事件检测,特别是在医学领域,由于类间低相似性和类内高差异性,更具挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种使用关于稀有事件的特定领域专业知识来生成定制和上下文相关的提示的新方法,然后将其用于大型语言模型进行图像分类。我们的零样本、保护隐私的方法在无需额外训练的情况下提高了稀有事件分类的性能,优于最新的技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in IEEE ISBI, 2025
Summary
本文提出一种简单有效的方法,用于生成高度准确且上下文描述性的提示,这些提示包含用于图像分类的判别特征。针对医学中的罕见事件检测,结合领域特定的专业知识生成定制且上下文相关的提示,然后由大型语言模型用于图像分类。该方法为零样本、保护隐私的方法,无需额外训练即可提高罕见事件的分类性能,优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 罕见事件由于数据稀少,深度学习技术在估计其分布时遭遇挑战。
- 开放词汇模型采用自然语言提示进行分类,与传统模型不同。
- 本文提出了一种生成包含判别特征的准确且上下文描述性提示的方法。
- 在医学领域的罕见事件检测中,存在低类间和高类内变异性问题。
- 结合领域专业知识生成定制提示,用于提高罕见事件的分类性能。
- 所提方法为零样本、保护隐私的方法,无需额外训练。
点此查看论文截图

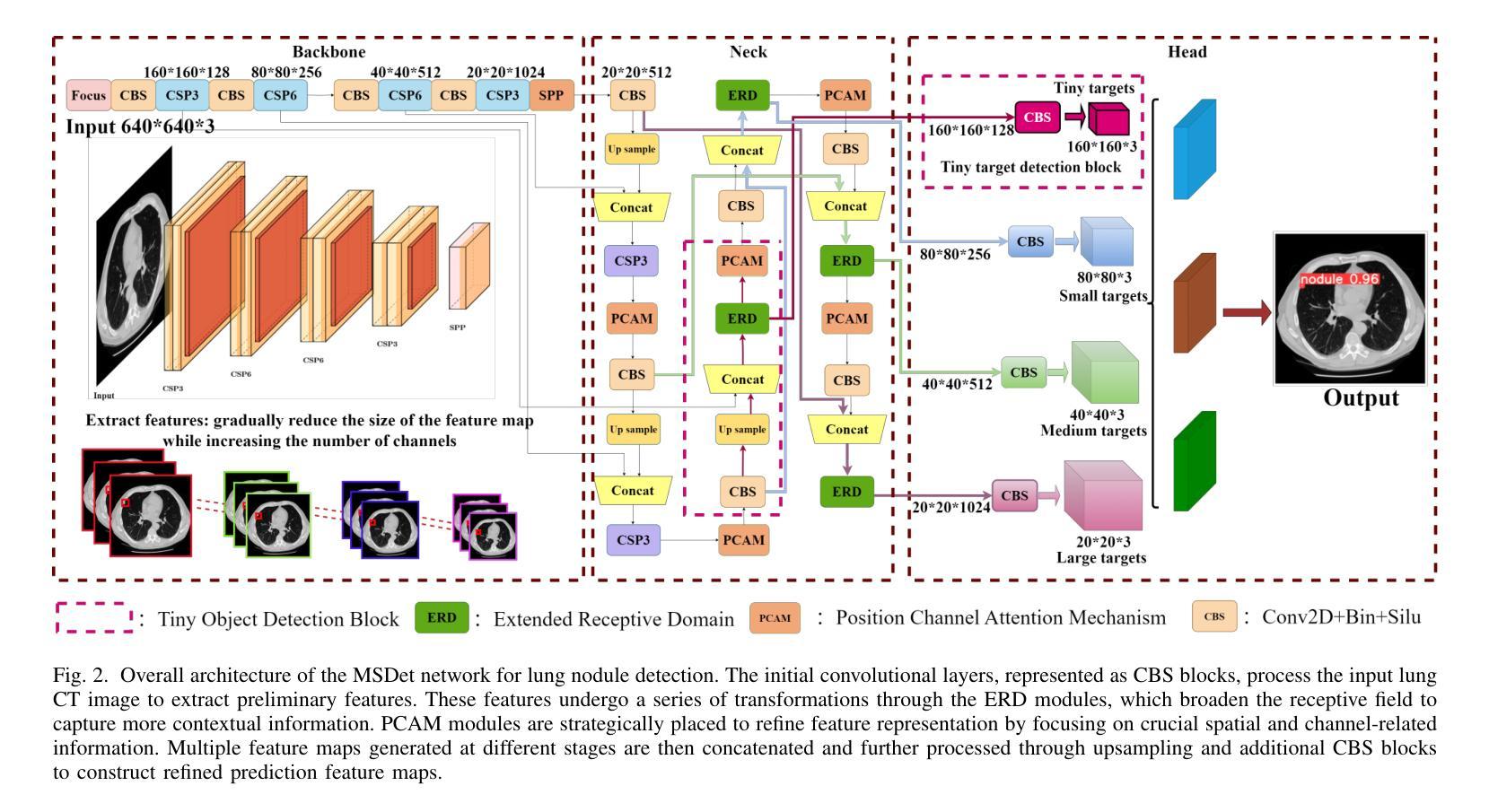
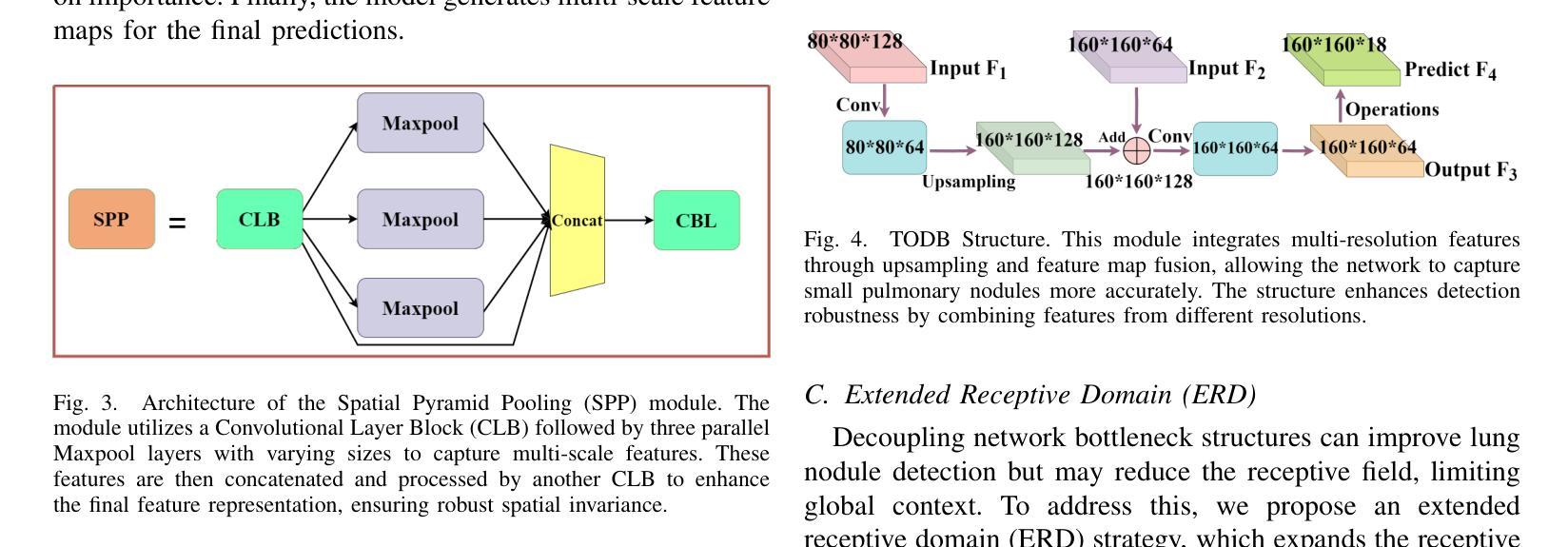
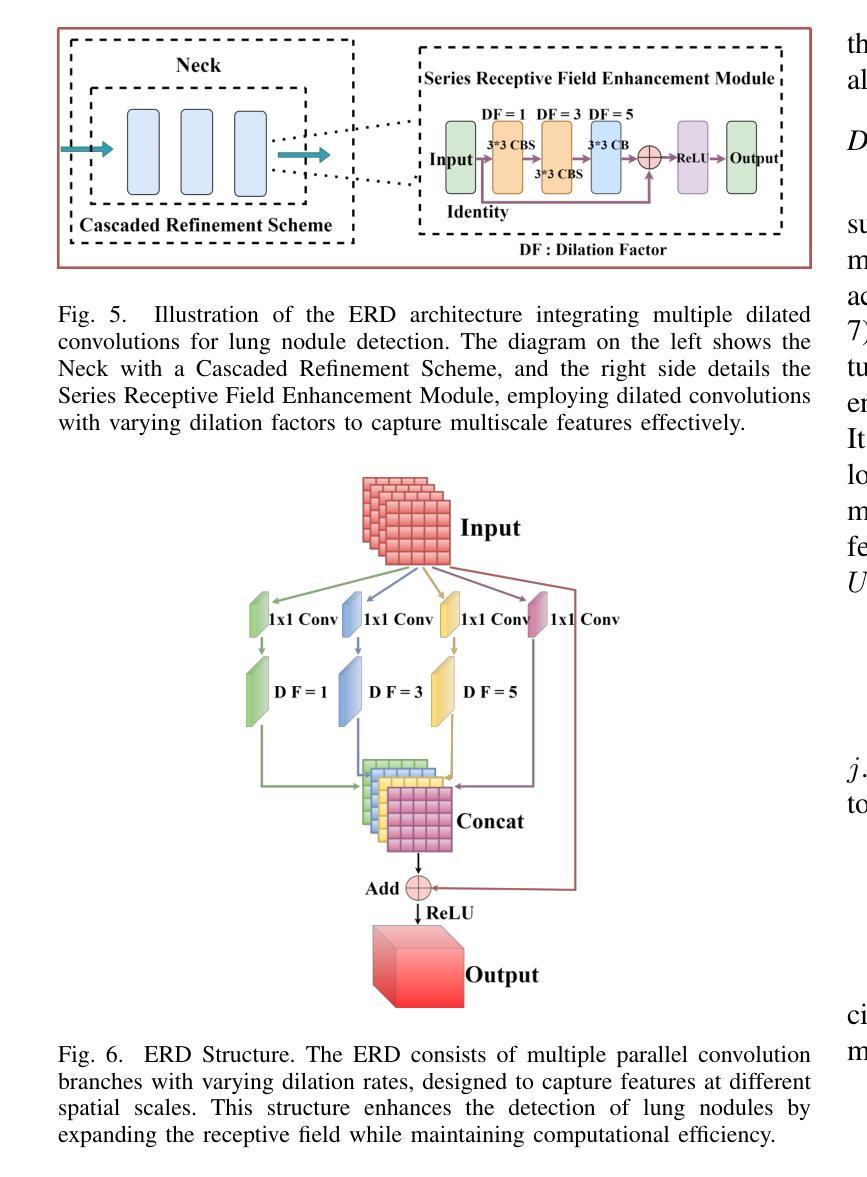
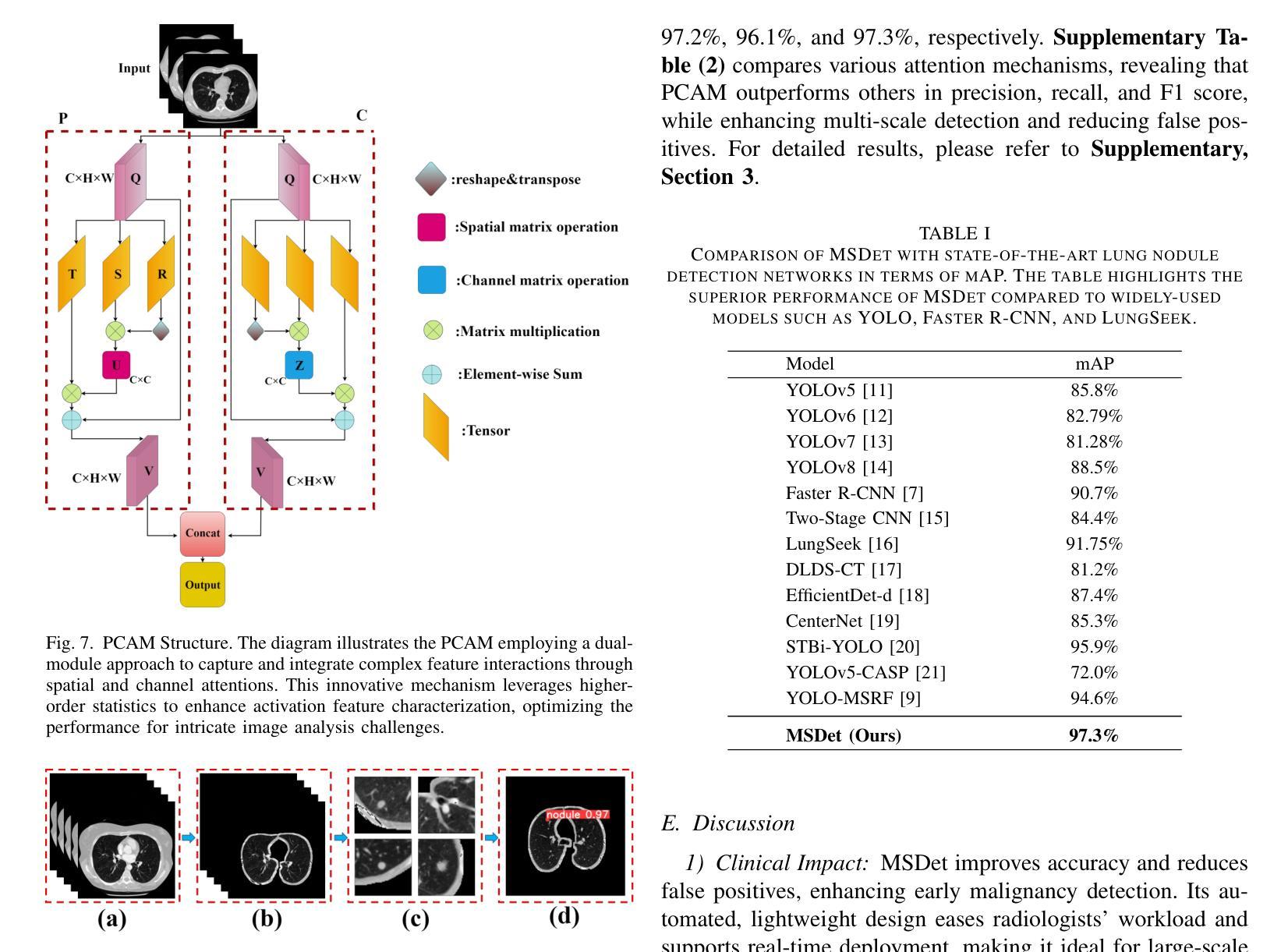
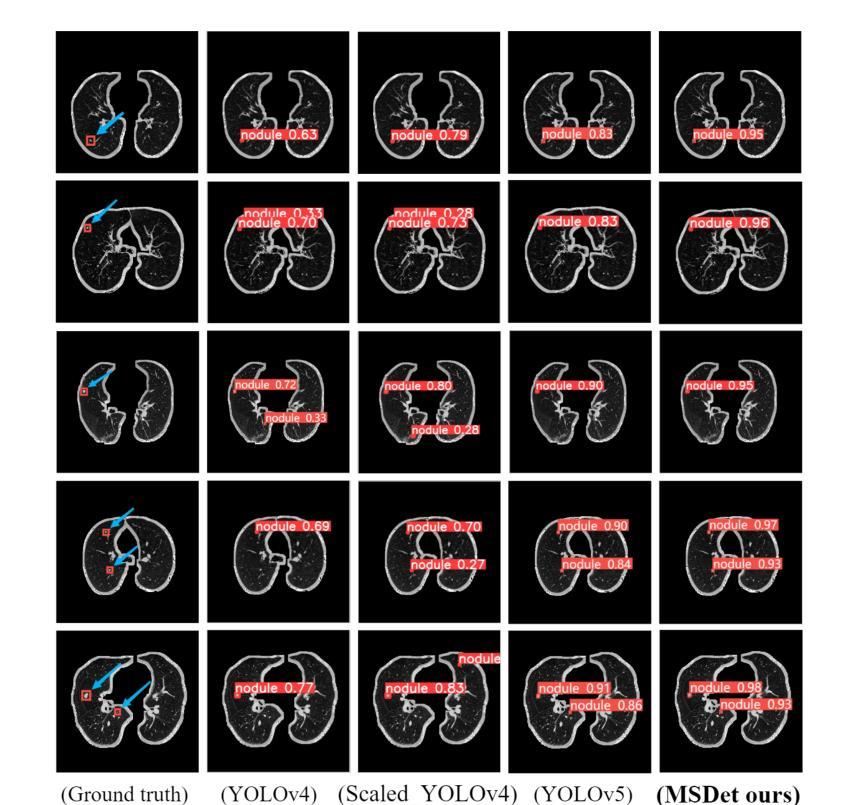
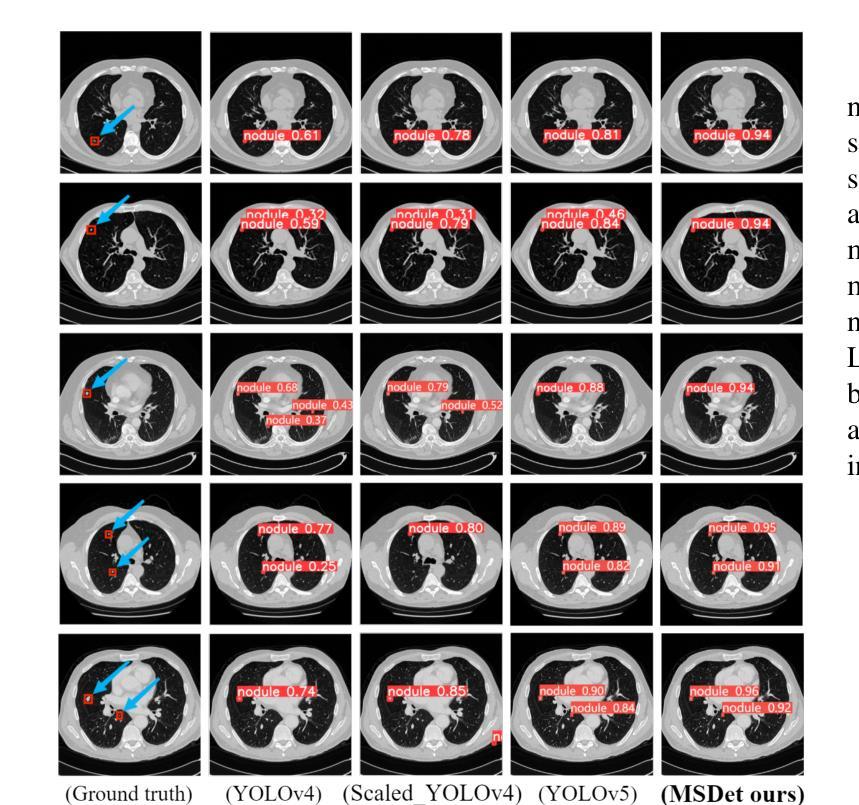
MSDet: Receptive Field Enhanced Multiscale Detection for Tiny Pulmonary Nodule
Authors:Guohui Cai, Ruicheng Zhang, Hongyang He, Zeyu Zhang, Daji Ergu, Yuanzhouhan Cao, Jinman Zhao, Binbin Hu, Zhinbin Liao, Yang Zhao, Ying Cai
Pulmonary nodules are critical indicators for the early diagnosis of lung cancer, making their detection essential for timely treatment. However, traditional CT imaging methods suffered from cumbersome procedures, low detection rates, and poor localization accuracy. The subtle differences between pulmonary nodules and surrounding tissues in complex lung CT images, combined with repeated downsampling in feature extraction networks, often lead to missed or false detections of small nodules. Existing methods such as FPN, with its fixed feature fusion and limited receptive field, struggle to effectively overcome these issues. To address these challenges, our paper proposed three key contributions: Firstly, we proposed MSDet, a multiscale attention and receptive field network for detecting tiny pulmonary nodules. Secondly, we proposed the extended receptive domain (ERD) strategy to capture richer contextual information and reduce false positives caused by nodule occlusion. We also proposed the position channel attention mechanism (PCAM) to optimize feature learning and reduce multiscale detection errors, and designed the tiny object detection block (TODB) to enhance the detection of tiny nodules. Lastly, we conducted thorough experiments on the public LUNA16 dataset, achieving state-of-the-art performance, with an mAP improvement of 8.8% over the previous state-of-the-art method YOLOv8. These advancements significantly boosted detection accuracy and reliability, providing a more effective solution for early lung cancer diagnosis. The code will be available at https://github.com/CaiGuoHui123/MSDet
肺部结节是肺癌早期诊断的关键指标,因此及时检测它们对于及时治疗至关重要。然而,传统的CT成像方法存在程序繁琐、检测率低和定位精度差的问题。在复杂的肺部CT图像中,肺部结节与周围组织的细微差异,以及在特征提取网络中的重复下采样,常常导致小结节被遗漏或错误检测。现有方法如FPN,其固定的特征融合和有限的感受野,难以有效克服这些问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们的论文提出了三个关键贡献:首先,我们提出了MSDet,这是一种多尺度注意力和感受野网络,用于检测微小的肺部结节。其次,我们提出了扩展感受域(ERD)策略,以捕获更丰富的上下文信息,并减少由结节遮挡引起的误报。我们还提出了位置通道注意机制(PCAM),以优化特征学习并减少多尺度检测错误,并设计了微小目标检测块(TODB)以增强微小结节的检测。最后,我们在公共LUNA16数据集上进行了全面的实验,取得了最先进的性能,与之前的最新方法YOLOv8相比,mAP提高了8.8%。这些进步显著提高了检测准确性和可靠性,为肺癌的早期诊断提供了更有效的解决方案。代码将在https://github.com/CaiGuoHui123/MSDet上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一系列针对肺部CT图像中微小肺结节检测的挑战和创新解决方案。通过引入多尺度注意力与感受野网络MSDet,扩展感受野策略ERD和位置通道注意力机制PCAM等技术,提高了肺结节检测的准确性和可靠性,为肺癌的早期诊断提供了更有效的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 肺部结节是肺癌早期诊断的关键指标,但其检测面临传统CT成像方法程序繁琐、检测率低和定位精度差的挑战。
- 现有方法如FPN在固定特征融合和有限感受野方面存在局限,难以有效应对上述问题。
- MSDet网络被提出,利用多尺度注意力和感受野来检测微小肺部结节。
- 引入扩展感受野(ERD)策略,以捕获更丰富的上下文信息,减少因结节遮挡导致的误报。
- 位置通道注意力机制(PCAM)被用于优化特征学习,减少多尺度检测错误。
- 设计了微小目标检测块(TODB),以增强对微小结节的检测。
点此查看论文截图

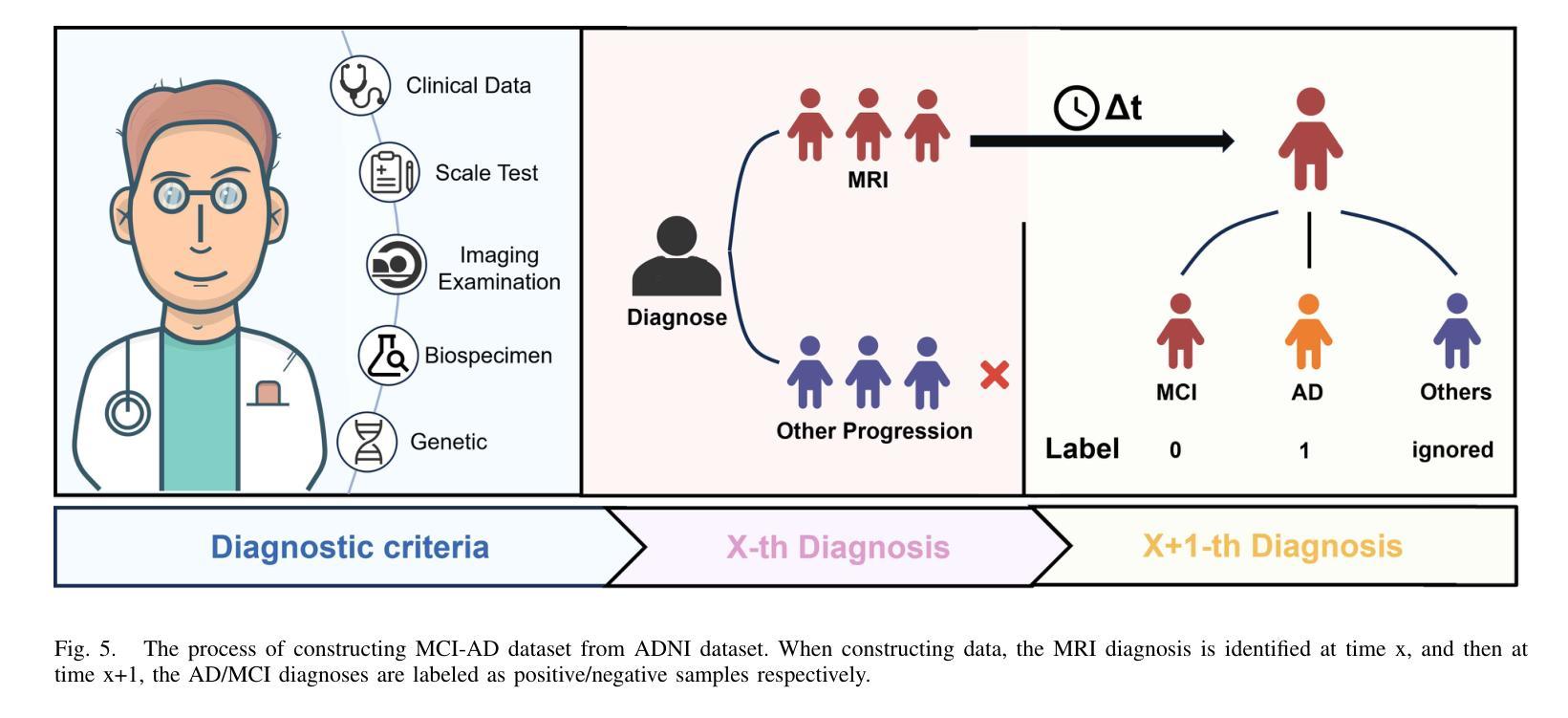
GFE-Mamba: Mamba-based AD Multi-modal Progression Assessment via Generative Feature Extraction from MCI
Authors:Zhaojie Fang, Shenghao Zhu, Yifei Chen, Binfeng Zou, Fan Jia, Linwei Qiu, Chang Liu, Xiang Feng, Changmiao Wang, Feiwei Qin, Jin Fan, Changbiao Chu
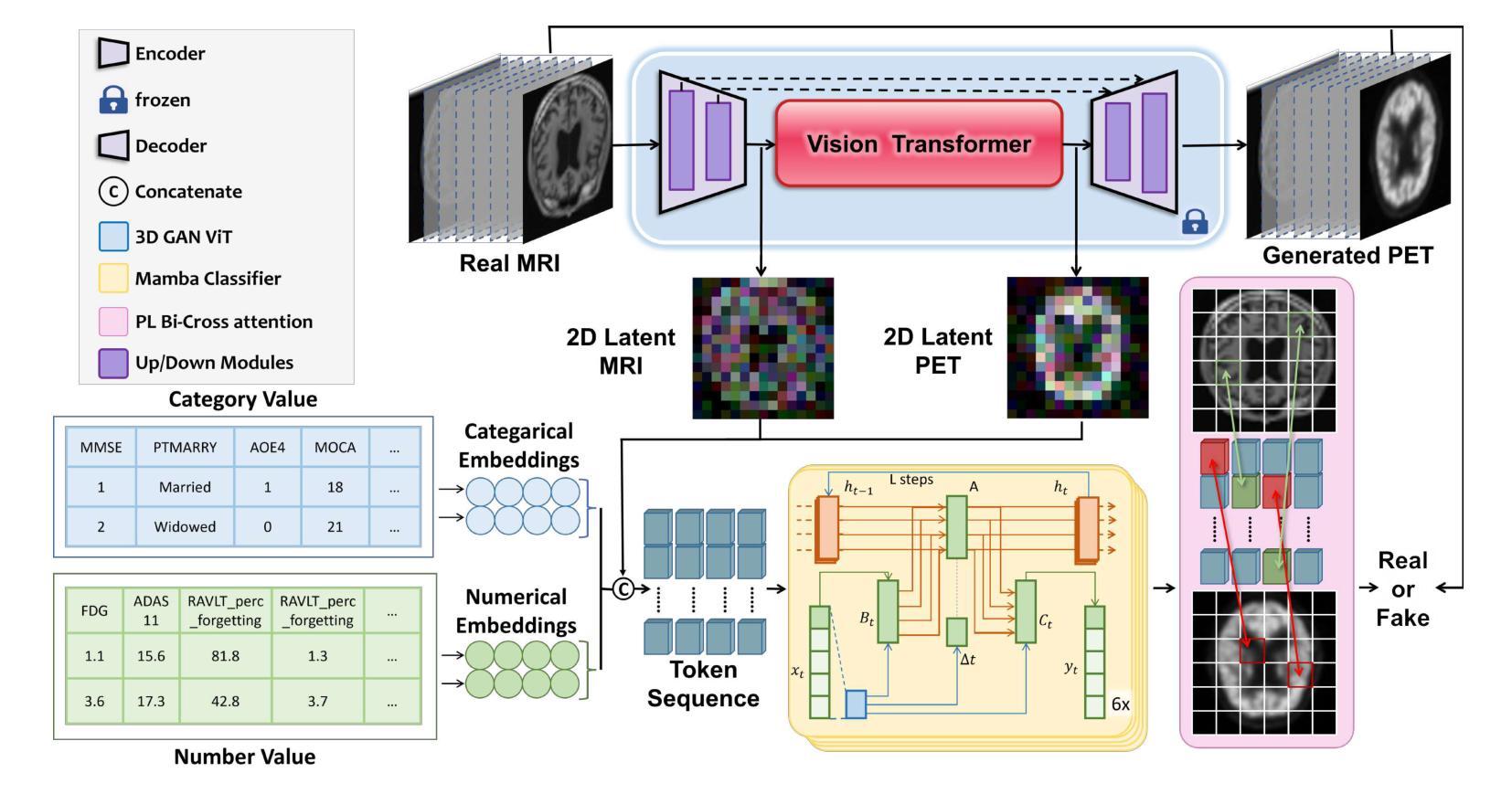
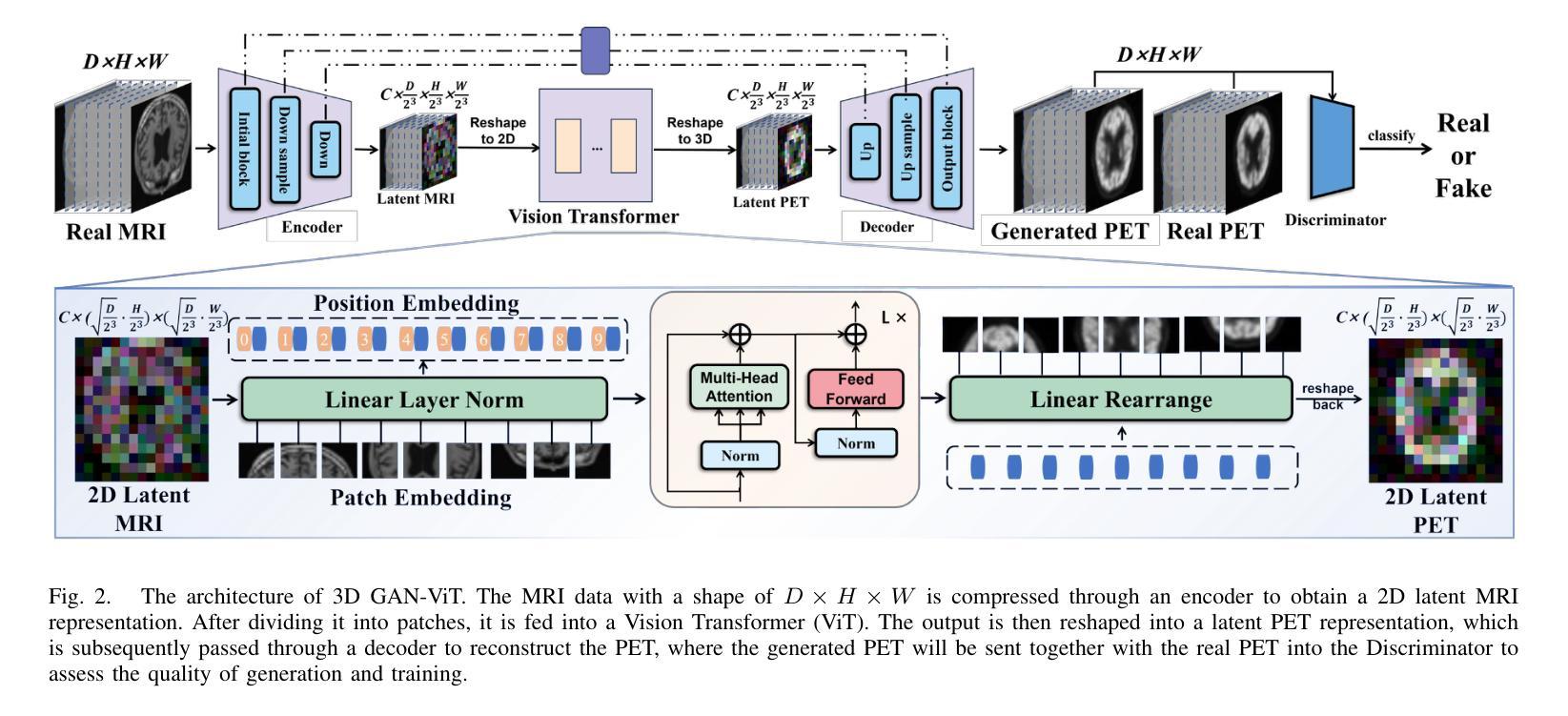
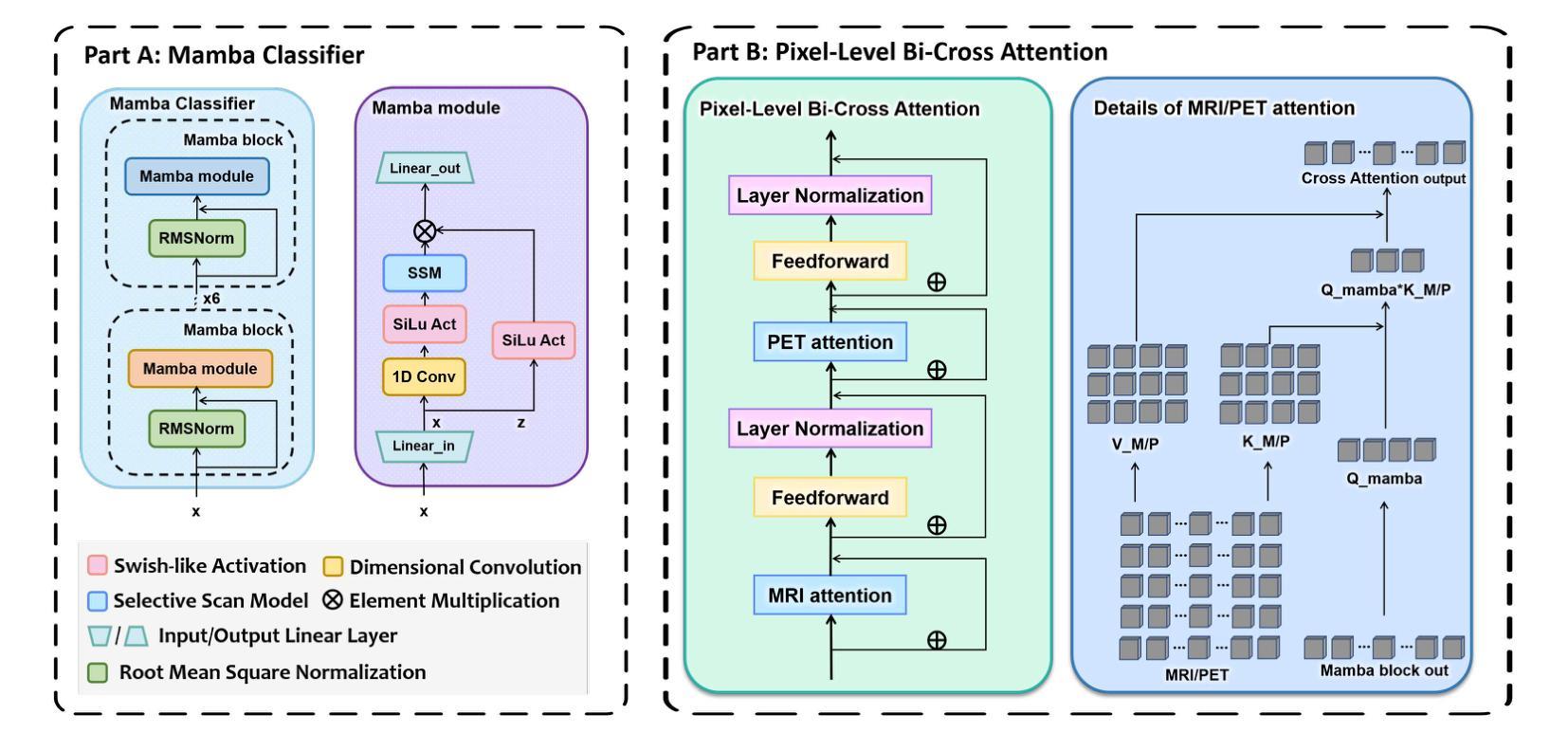
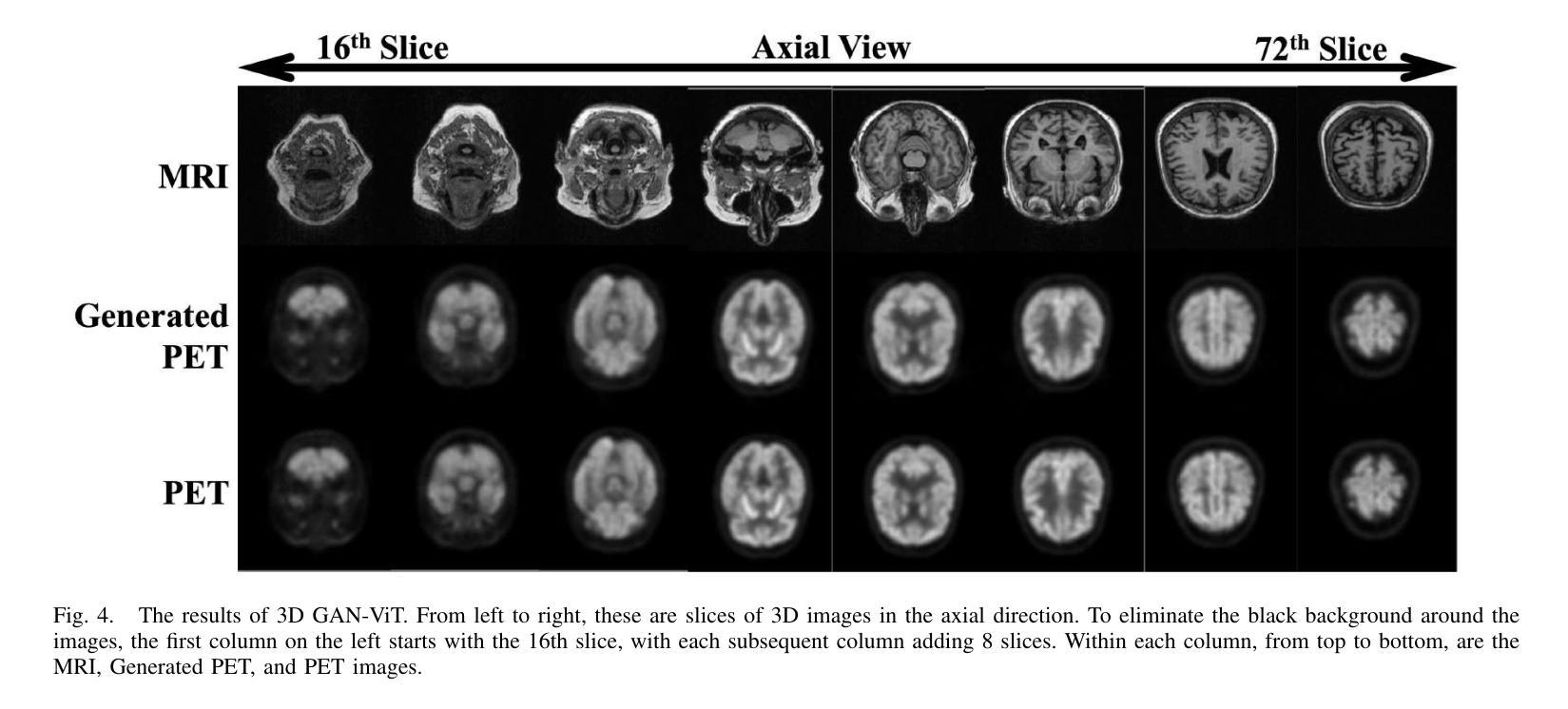
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a progressive, irreversible neurodegenerative disorder that often originates from Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). This progression results in significant memory loss and severely affects patients’ quality of life. Clinical trials have consistently shown that early and targeted interventions for individuals with MCI may slow or even prevent the advancement of AD. Research indicates that accurate medical classification requires diverse multimodal data, including detailed assessment scales and neuroimaging techniques like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). However, simultaneously collecting the aforementioned three modalities for training presents substantial challenges. To tackle these difficulties, we propose GFE-Mamba, a multimodal classifier founded on Generative Feature Extractor. The intermediate features provided by this Extractor can compensate for the shortcomings of PET and achieve profound multimodal fusion in the classifier. The Mamba block, as the backbone of the classifier, enables it to efficiently extract information from long-sequence scale information. Pixel-level Bi-cross Attention supplements pixel-level information from MRI and PET. We provide our rationale for developing this cross-temporal progression prediction dataset and the pre-trained Extractor weights. Our experimental findings reveal that the GFE-Mamba model effectively predicts the progression from MCI to AD and surpasses several leading methods in the field. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Tinysqua/GFE-Mamba.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种渐进性、不可逆的神经退行性疾病,通常起源于轻度认知障碍(MCI)。这种进展会导致明显的记忆力减退,严重影响患者的生活质量。临床试验反复表明,对MCI患者进行早期和有针对性的干预可以减缓甚至阻止AD的进展。研究表明,准确的医学分类需要包括详细评估量表和神经成像技术(如磁共振成像(MRI)和正电子发射断层扫描(PET))在内的多种模式数据。然而,同时收集上述三种模式进行培训存在相当大的挑战。为了应对这些困难,我们提出了基于生成特征提取器的多模式分类器GFE-Mamba。该提取器提供的中间特征可以弥补PET的不足,在分类器中实现深刻的多模式融合。作为分类器的骨干,“Mamba”块使其能够高效地从长序列尺度信息中提取信息。像素级双向交叉注意力补充了MRI和PET的像素级信息。我们阐述了建立这个跨时间进展预测数据集和开发预训练提取器权重的理由。我们的实验结果表明,GFE-Mamba模型有效地预测了从MCI到AD的进展,并超越了该领域的几种领先方法。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/Tinysqua/GFE-Mamba获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对阿尔茨海默病(AD)的早期干预和预测模型。研究指出,针对轻度认知障碍(MCI)的个体进行早期和有针对性的干预可能减缓甚至阻止AD的进展。为了准确进行医学分类,需要包括详细评估量表、磁共振成像(MRI)和正电子发射断层扫描(PET)等多模态数据。文章提出了一种基于生成特征提取器的多模态分类器GFE-Mamba,该分类器能够补偿PET的不足,实现深刻的跨模态融合,并有效地预测从MCI到AD的进展。
Key Takeaways
- 阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种不可逆的神经性退行性疾病,常由轻度认知障碍(MCI)发展而来。
- 早期针对MCI的干预可能减缓或阻止AD的进展。
- 准确医学分类需要多模态数据,包括详细评估量表、MRI和PET等技术。
- 提出了一种新的多模态分类器GFE-Mamba,基于生成特征提取器。
- GFE-Mamba能够通过中间特征补偿PET的不足,并实现跨模态融合。
- GFE-Mamba模型能够预测从MCI到AD的进展,并在实验中超越了领域内的几种领先方法。
点此查看论文截图