⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-30 更新
Revisit Mixture Models for Multi-Agent Simulation: Experimental Study within a Unified Framework
Authors:Longzhong Lin, Xuewu Lin, Kechun Xu, Haojian Lu, Lichao Huang, Rong Xiong, Yue Wang
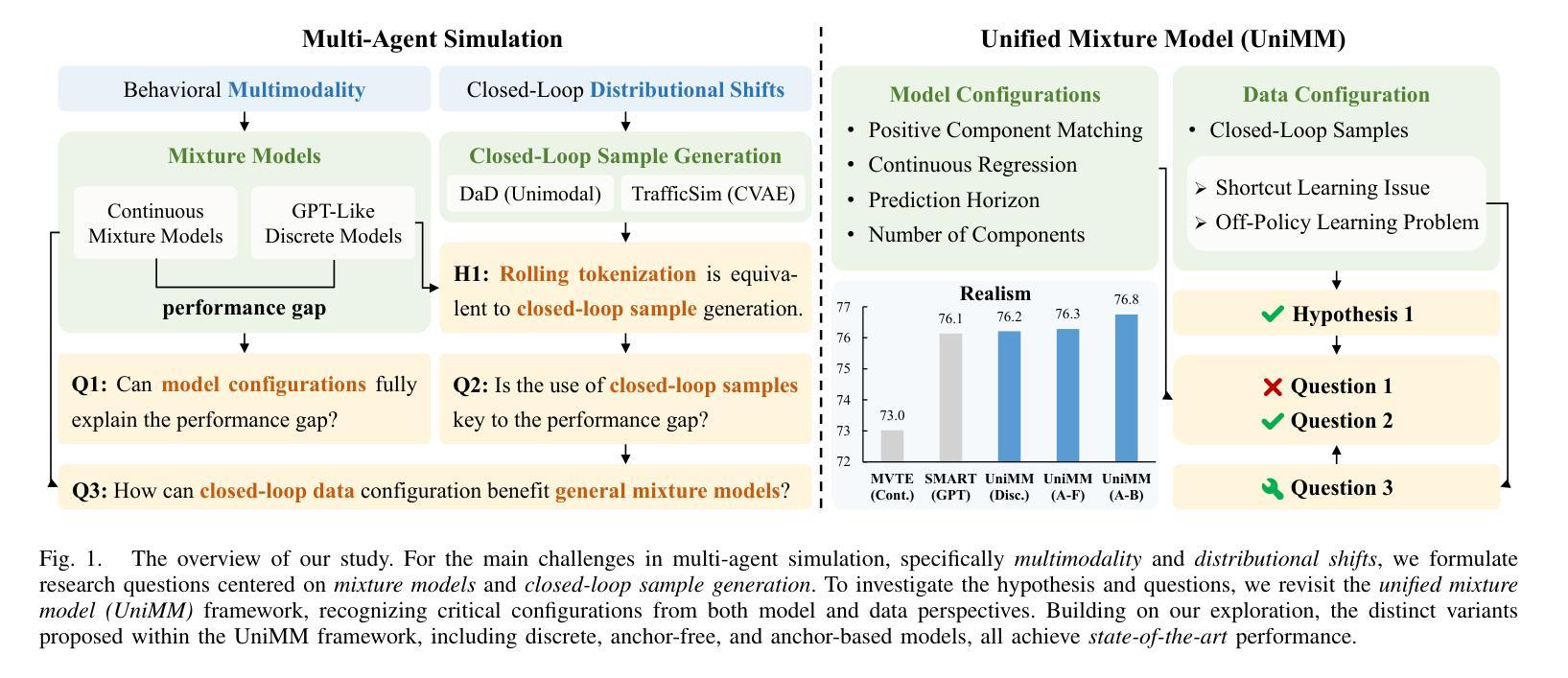
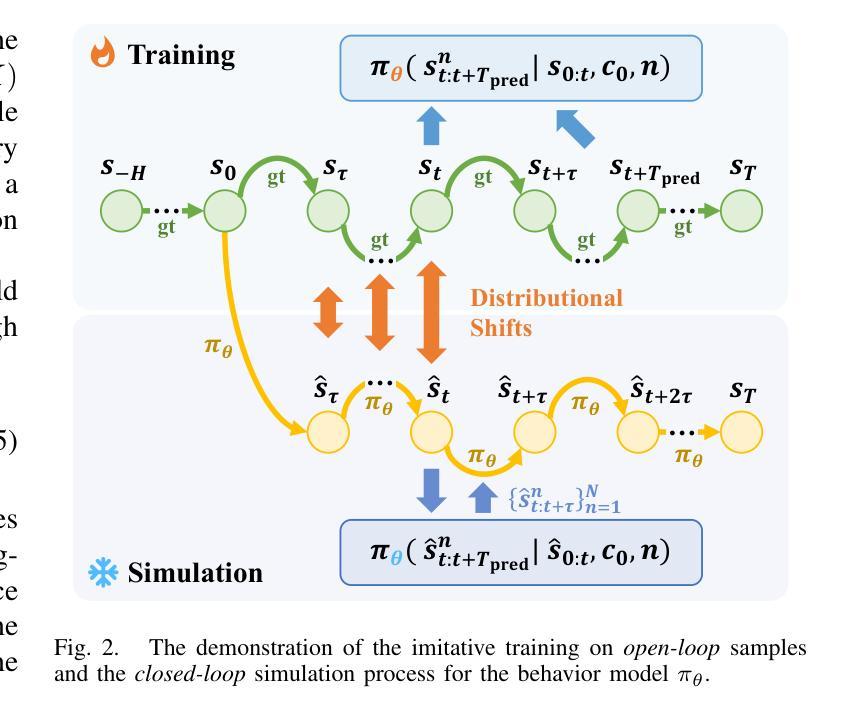
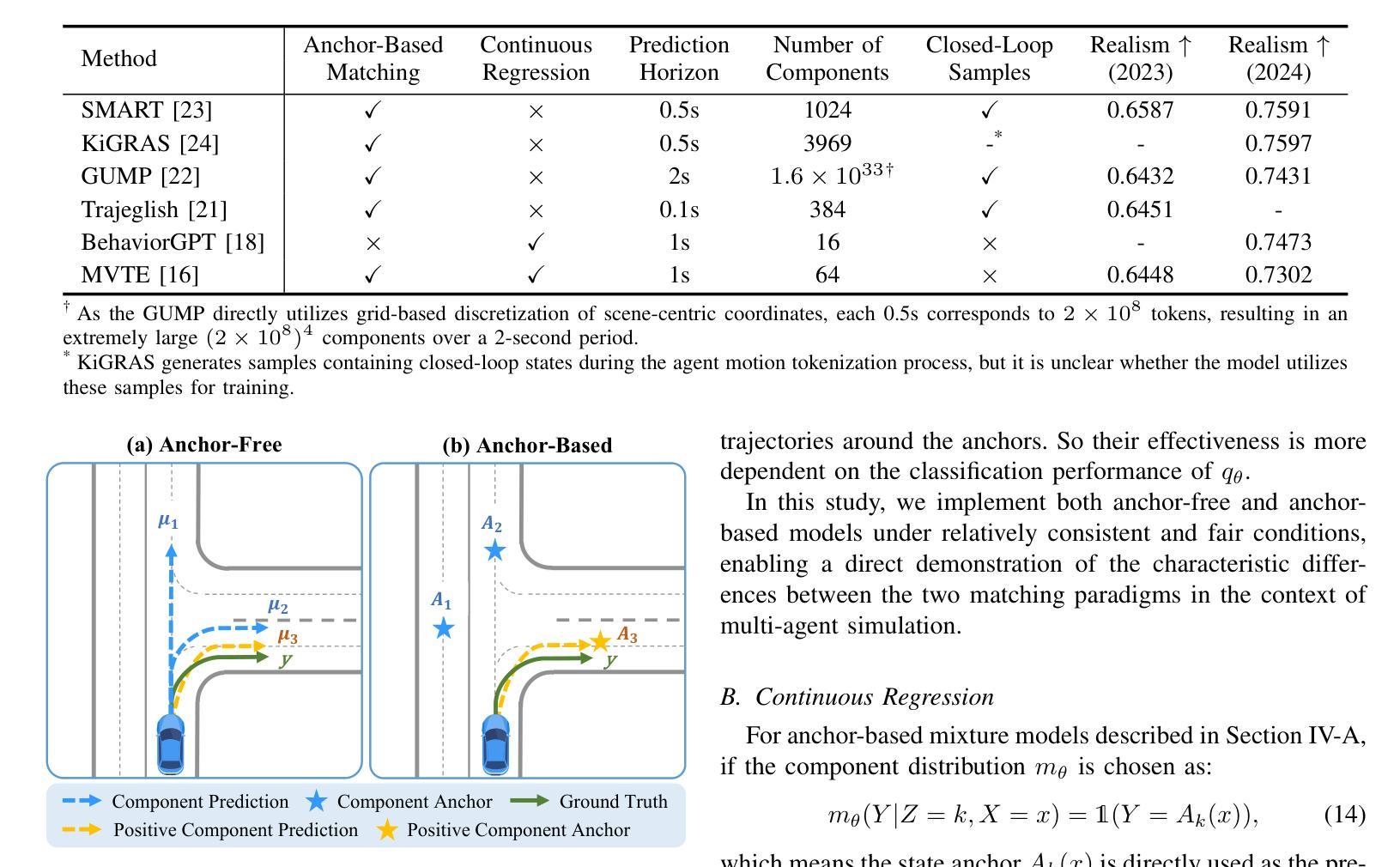
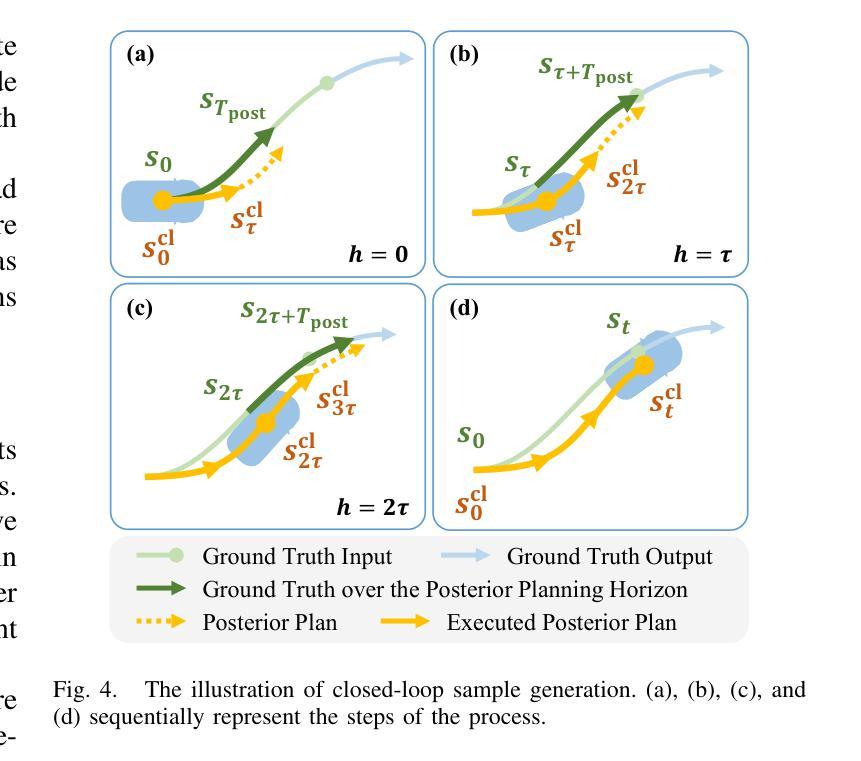
Simulation plays a crucial role in assessing autonomous driving systems, where the generation of realistic multi-agent behaviors is a key aspect. In multi-agent simulation, the primary challenges include behavioral multimodality and closed-loop distributional shifts. In this study, we revisit mixture models for generating multimodal agent behaviors, which can cover the mainstream methods including continuous mixture models and GPT-like discrete models. Furthermore, we introduce a closed-loop sample generation approach tailored for mixture models to mitigate distributional shifts. Within the unified mixture model~(UniMM) framework, we recognize critical configurations from both model and data perspectives. We conduct a systematic examination of various model configurations, including positive component matching, continuous regression, prediction horizon, and the number of components. Moreover, our investigation into the data configuration highlights the pivotal role of closed-loop samples in achieving realistic simulations. To extend the benefits of closed-loop samples across a broader range of mixture models, we further address the shortcut learning and off-policy learning issues. Leveraging insights from our exploration, the distinct variants proposed within the UniMM framework, including discrete, anchor-free, and anchor-based models, all achieve state-of-the-art performance on the WOSAC benchmark.
模拟在评估自动驾驶系统方面发挥着至关重要的作用,其中生成逼真的多智能体行为是一个关键方面。在多智能体模拟中,主要挑战包括行为多模态性和闭环分布偏移。本研究重新审视了用于生成多模态智能体行为的混合模型,这些模型可以涵盖主流方法,包括连续混合模型和GPT类离散模型。此外,我们引入了一种针对混合模型的闭环样本生成方法,以缓解分布偏移。在统一混合模型(UniMM)框架内,我们从模型和数据的角度识别出关键配置。我们对各种模型配置进行了系统检查,包括正向组件匹配、连续回归、预测视野和组件数量。此外,我们对数据配置的调查突显出闭环样本在实现现实模拟中的关键作用。为了扩大闭环样本在更广泛混合模型中的优势,我们进一步解决了捷径学习和离线学习问题。利用我们在探索中的见解,UniMM框架内提出的各种独特变体,包括离散模型、无锚模型和有锚模型,在WOSAC基准测试上都达到了最新性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态混合模型在自动驾驶仿真中扮演重要角色,用于生成多智能体行为。本研究重新探讨了生成多模态智能体行为的混合模型,并引入了一种针对混合模型的闭环样本生成方法以缓解分布偏移问题。在统一混合模型框架内,我们确定了关键配置,包括模型和数据配置。通过系统地研究各种模型配置,我们发现闭环样本在获得真实仿真中的关键作用。我们进一步解决了简化学习和离策略学习问题,以扩大闭环样本在更广泛混合模型中的优势。利用我们的探索,UniMM框架内的不同变体在WOSAC基准测试中均达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态混合模型在评估自动驾驶系统仿真中至关重要,用于生成多智能体行为。
- 研究人员重新考察了生成多模态智能体行为的混合模型,包括连续混合模型和GPT类似离散模型。
- 引入了一种针对混合模型的闭环样本生成方法,以缓解分布偏移问题。
- 在统一混合模型框架内,确定了关键配置,包括模型配置和数据配置。
- 闭环样本在获得真实仿真中起到了关键作用。
- 研究人员解决了简化学习和离策略学习问题,以提高模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

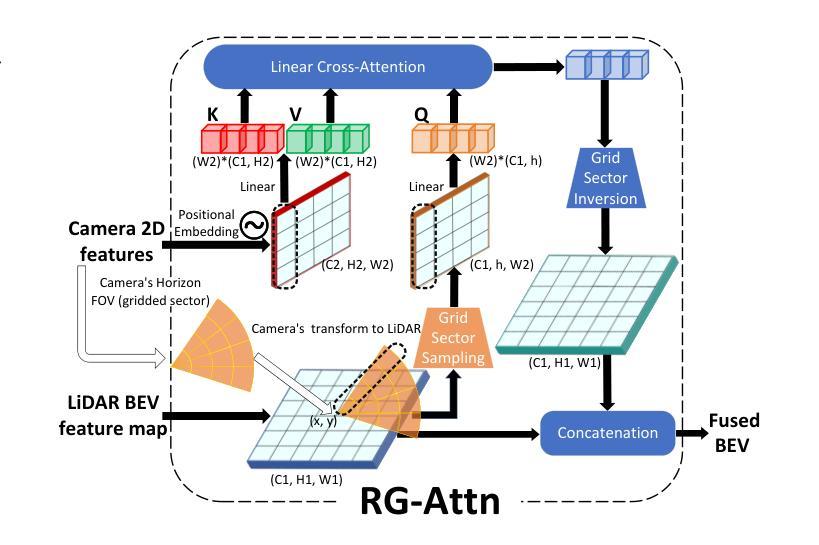
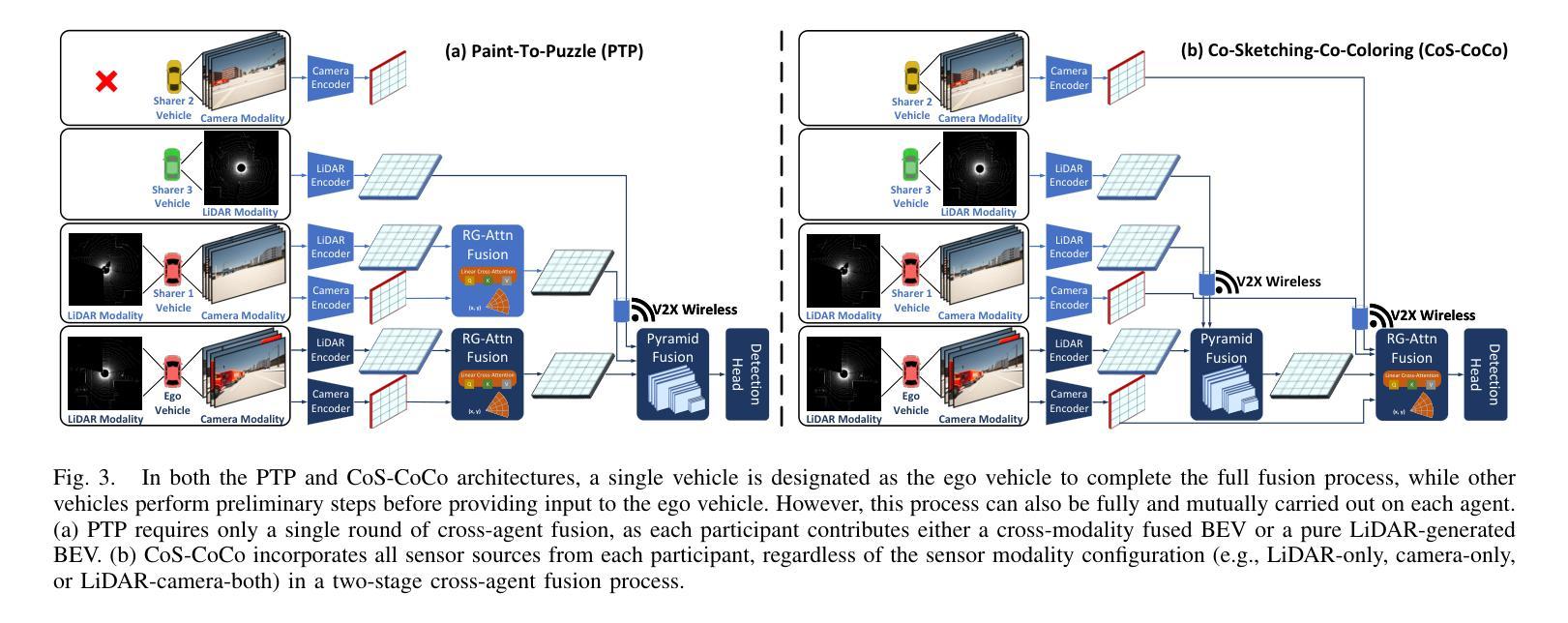
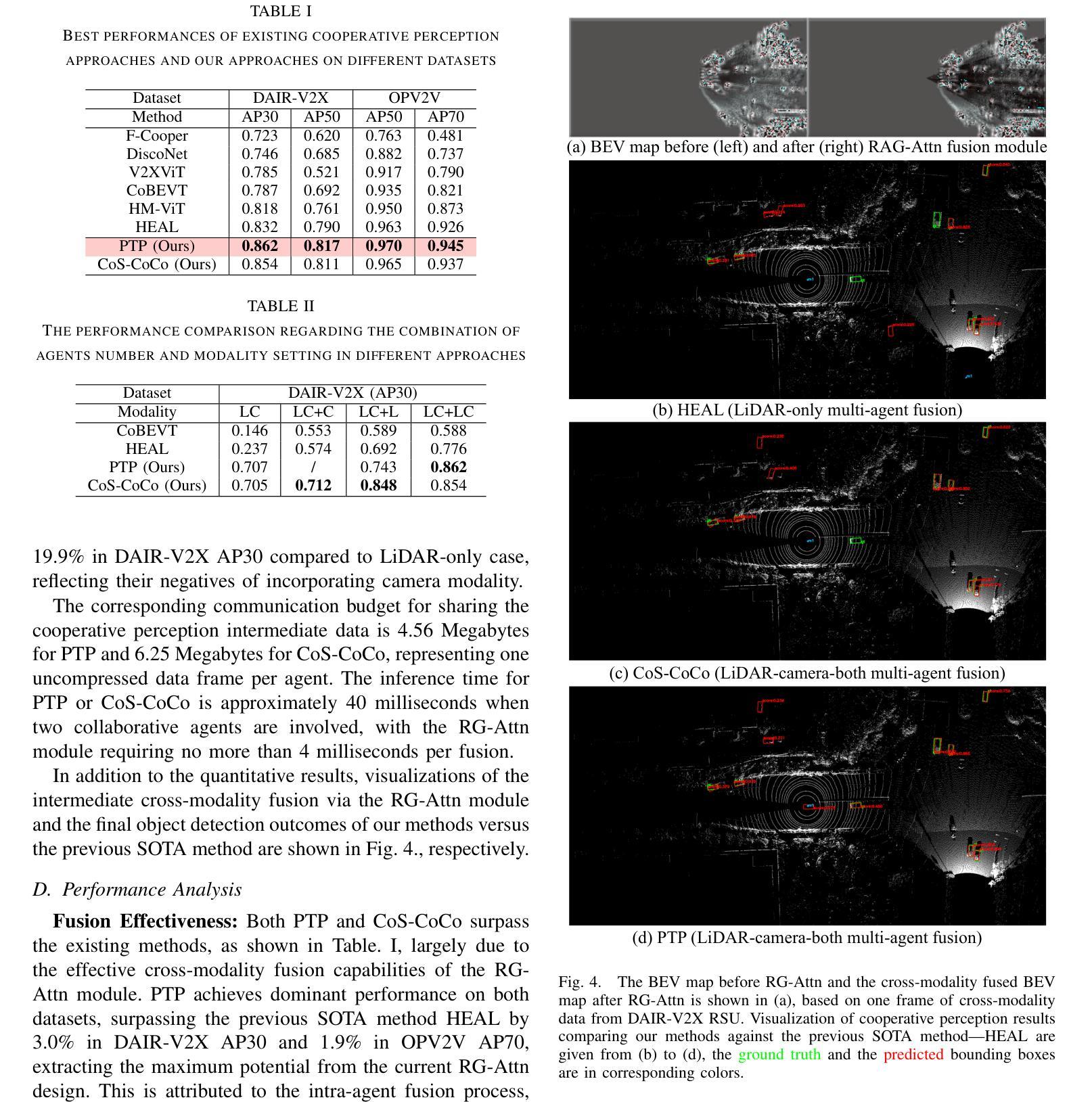
RG-Attn: Radian Glue Attention for Multi-modality Multi-agent Cooperative Perception
Authors:Lantao Li, Kang Yang, Wenqi Zhang, Xiaoxue Wang, Chen Sun
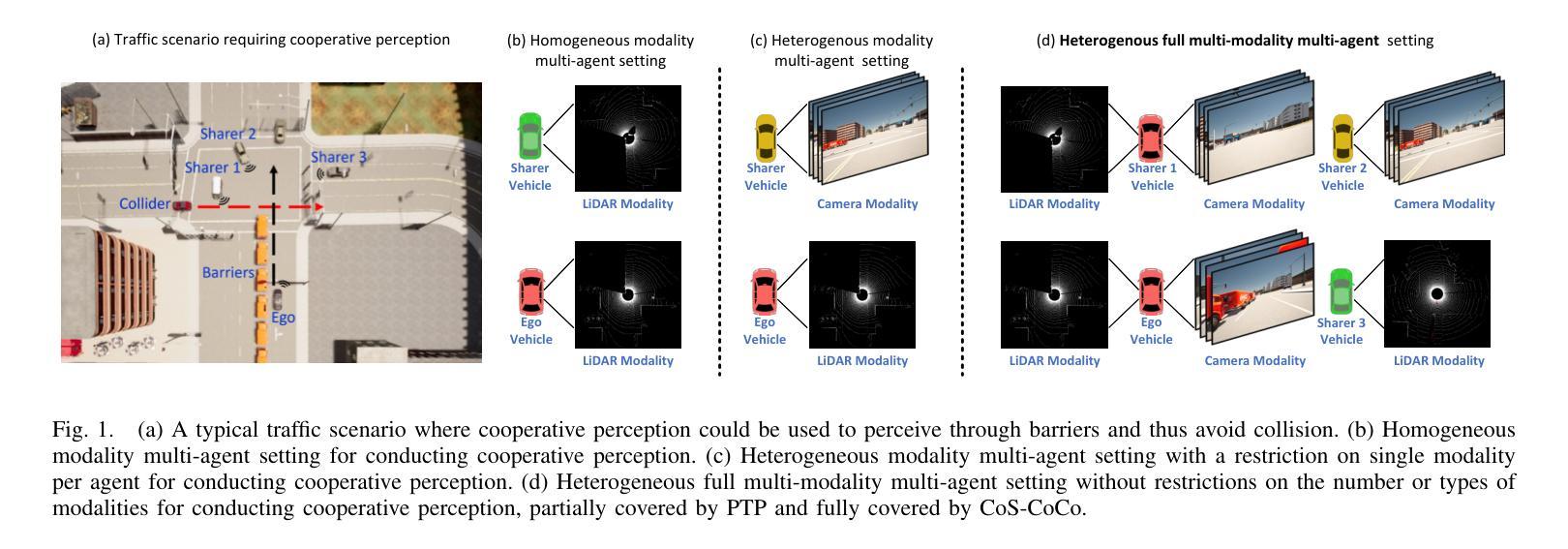
Cooperative perception offers an optimal solution to overcome the perception limitations of single-agent systems by leveraging Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication for data sharing and fusion across multiple agents. However, most existing approaches focus on single-modality data exchange, limiting the potential of both homogeneous and heterogeneous fusion across agents. This overlooks the opportunity to utilize multi-modality data per agent, restricting the system’s performance. In the automotive industry, manufacturers adopt diverse sensor configurations, resulting in heterogeneous combinations of sensor modalities across agents. To harness the potential of every possible data source for optimal performance, we design a robust LiDAR and camera cross-modality fusion module, Radian-Glue-Attention (RG-Attn), applicable to both intra-agent cross-modality fusion and inter-agent cross-modality fusion scenarios, owing to the convenient coordinate conversion by transformation matrix and the unified sampling/inversion mechanism. We also propose two different architectures, named Paint-To-Puzzle (PTP) and Co-Sketching-Co-Coloring (CoS-CoCo), for conducting cooperative perception. PTP aims for maximum precision performance and achieves smaller data packet size by limiting cross-agent fusion to a single instance, but requiring all participants to be equipped with LiDAR. In contrast, CoS-CoCo supports agents with any configuration-LiDAR-only, camera-only, or LiDAR-camera-both, presenting more generalization ability. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on both real and simulated cooperative perception datasets. The code will be released at GitHub in early 2025.
协同感知通过利用车辆对一切(V2X)通信来实现跨多个智能体的数据共享和融合,为克服单一智能体系统的感知局限提供了最优解决方案。然而,现有的大多数方法都集中在单一模态的数据交换上,限制了智能体之间的同质和异质融合潜力。这忽略了利用每个智能体的多模态数据的可能性,限制了系统性能。在汽车行业,制造商采用各种传感器配置,导致智能体之间传感器模态的异质组合。为了充分利用所有可能的数据源以实现最佳性能,我们设计了一个稳健的激光雷达和相机跨模态融合模块,名为Radian-Glue-Attention(RG-Attn),它适用于智能体内部跨模态融合和智能体之间跨模态融合场景,得益于变换矩阵的便捷坐标转换和统一的采样/反转机制。我们还提出了两种用于协同感知的不同架构,分别是Paint-To-Puzzle(PTP)和Co-Sketching-Co-Coloring(CoS-CoCo)。PTP旨在实现最高精度性能,通过限制跨智能体融合到单个实例来实现较小的数据包大小,但这要求所有参与者都配备激光雷达。相比之下,CoS-CoCo支持任何配置的智能体——只配备激光雷达、只配备相机或同时配备激光雷达和相机,表现出更强的通用性。我们的方法在真实和模拟的协同感知数据集上达到了最先进的状态,代码将在2025年初在GitHub上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于车辆到一切(V2X)通信的多智能体合作感知技术突破了单智能体系统感知局限的最佳解决方案,采用多模态数据融合提高性能。通过设计跨模态融合模块Radian-Glue-Attention(RG-Attn),实现跨智能体感知数据融合。提出两种合作感知架构Paint-To-Puzzle(PTP)和Co-Sketching-Co-Coloring(CoS-CoCo),实现高性能泛化能力。性能领先当前最新水平,适用于实际和模拟的合作感知数据集。代码将于2025年初在GitHub上发布。
Key Takeaways
- 合作感知技术利用V2X通信突破单智能体系统感知局限。
- 多模态数据融合能提高系统性能。
- 设计的RG-Attn模块支持跨智能体感知数据融合。
- PTP架构追求最高精度,减少数据包大小,但需所有智能体配备激光雷达。
- CoS-CoCo架构支持多种配置的智能体,具备更强的泛化能力。
- 该技术在实际和模拟合作感知数据集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

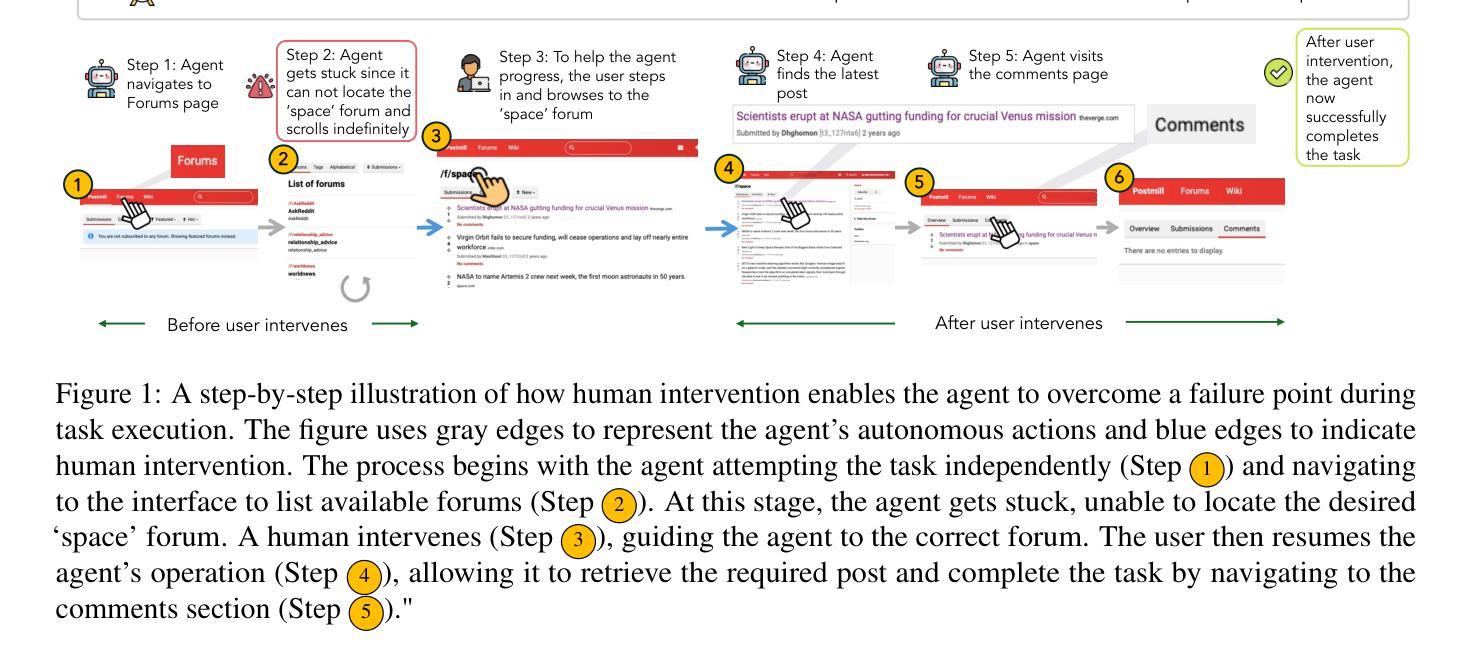
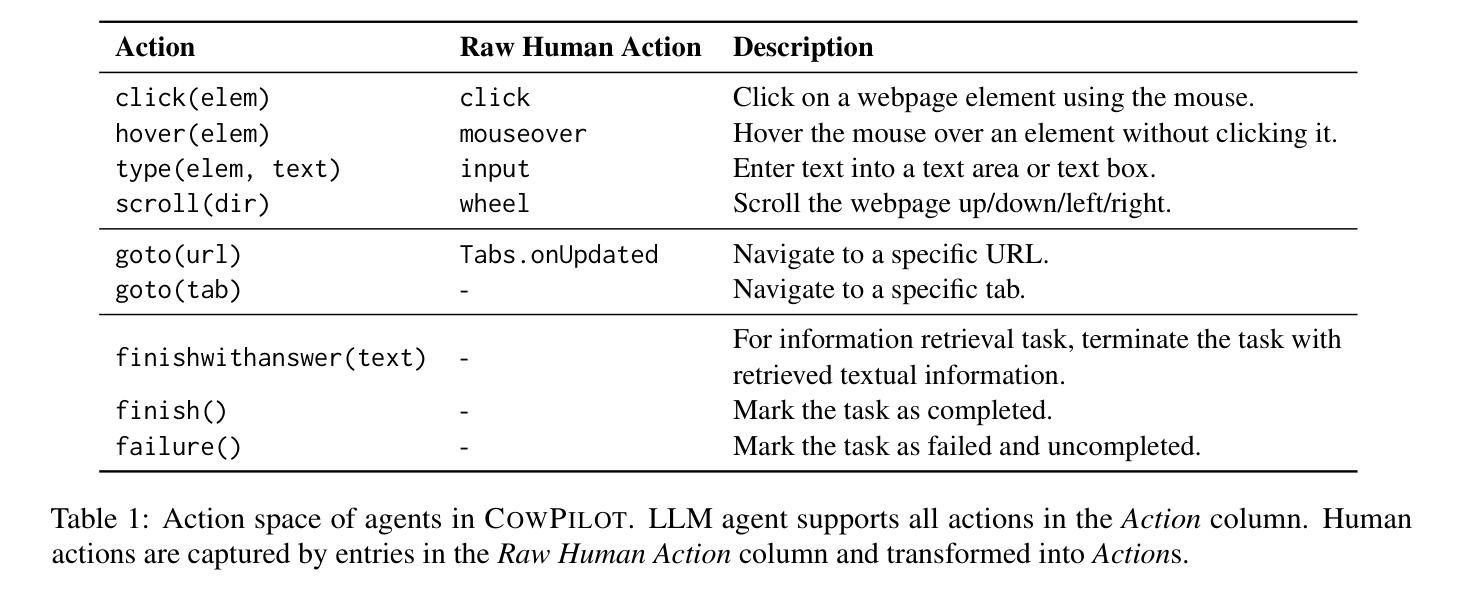
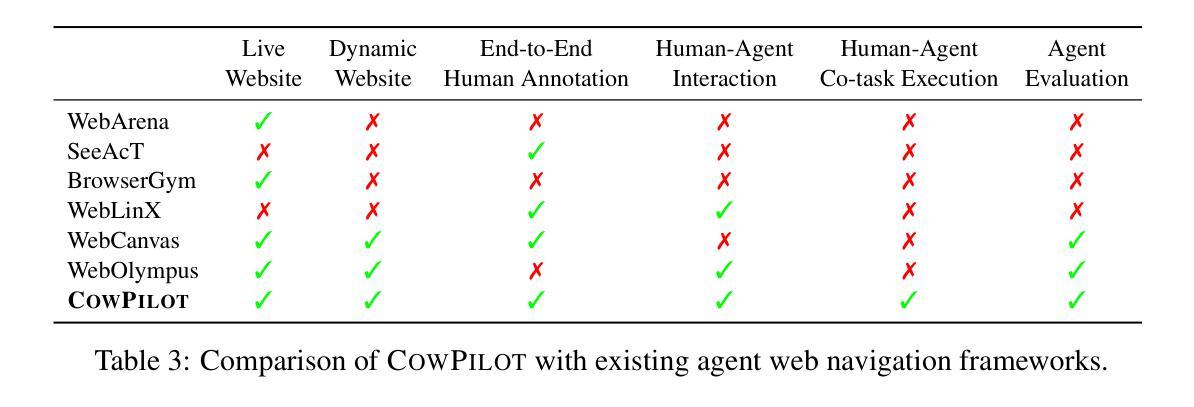
CowPilot: A Framework for Autonomous and Human-Agent Collaborative Web Navigation
Authors:Faria Huq, Zora Zhiruo Wang, Frank F. Xu, Tianyue Ou, Shuyan Zhou, Jeffrey P. Bigham, Graham Neubig
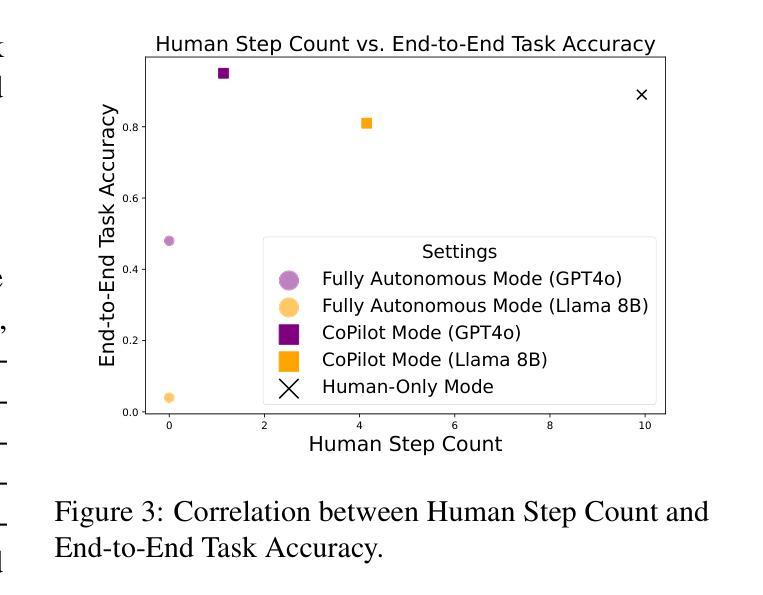
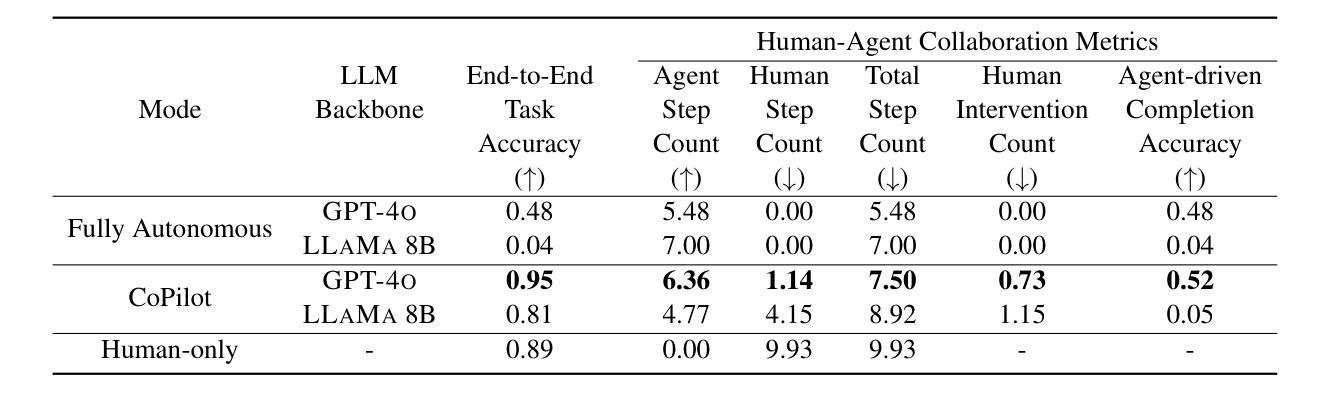
While much work on web agents emphasizes the promise of autonomously performing tasks on behalf of users, in reality, agents often fall short on complex tasks in real-world contexts and modeling user preference. This presents an opportunity for humans to collaborate with the agent and leverage the agent’s capabilities effectively. We propose CowPilot, a framework supporting autonomous as well as human-agent collaborative web navigation, and evaluation across task success and task efficiency. CowPilot reduces the number of steps humans need to perform by allowing agents to propose next steps, while users are able to pause, reject, or take alternative actions. During execution, users can interleave their actions with the agent by overriding suggestions or resuming agent control when needed. We conducted case studies on five common websites and found that the human-agent collaborative mode achieves the highest success rate of 95% while requiring humans to perform only 15.2% of the total steps. Even with human interventions during task execution, the agent successfully drives up to half of task success on its own. CowPilot can serve as a useful tool for data collection and agent evaluation across websites, which we believe will enable research in how users and agents can work together. Video demonstrations are available at https://oaishi.github.io/cowpilot.html
关于网络代理的研究工作虽然强调其自主为用户执行任务的潜力,但在现实情况中,代理在复杂任务和模拟用户偏好方面往往存在不足。这为人类与代理合作并有效利用代理的能力提供了机会。我们提出了CowPilot框架,它支持自主以及人机协作的网络导航,并对任务成功和任务效率进行评估。CowPilot通过允许代理提出下一步行动方案,减少了人类需要执行的步骤数量,同时用户能够暂停、拒绝或采取替代行动。在执行过程中,用户可以通过覆盖建议或在需要时恢复代理控制来交替进行行动。我们在五个常见网站上进行了案例研究,发现人机协作模式达到了最高的成功率,即95%,而人类仅需要执行总步骤的15.2%。即使在任务执行过程中有人的干预,代理仍然能够独立完成高达一半的任务。CowPilot可以作为跨网站的数据收集和代理评估的有用工具,我们相信这将有助于研究用户和代理如何协同工作。视频演示可在https://oaishi.github.io/cowpilot.html观看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
该文探讨了web代理在现实场景中完成任务时存在自主性的局限性,以及为用户提供的合作空间与可能性。提出CowPilot框架,支持自主和人机协作网络导航,并通过案例研究证明人机协作模式的有效性。该框架可帮助收集数据并评估代理网站的效率,为未来用户与代理的合作研究奠定基础。
Key Takeaways
- Web代理在复杂任务和现实场景中的自主性存在局限性。
- 人机协作模式在Web导航中具有潜力。
- CowPilot框架支持自主及人机协作网络导航。
- 人机协作模式实现了高成功率并降低了用户执行步骤的数量。
- 即使有人工干预,代理仍能独立实现任务成功的一半以上。
- CowPilot框架可用于数据收集和网站代理评估。
点此查看论文截图


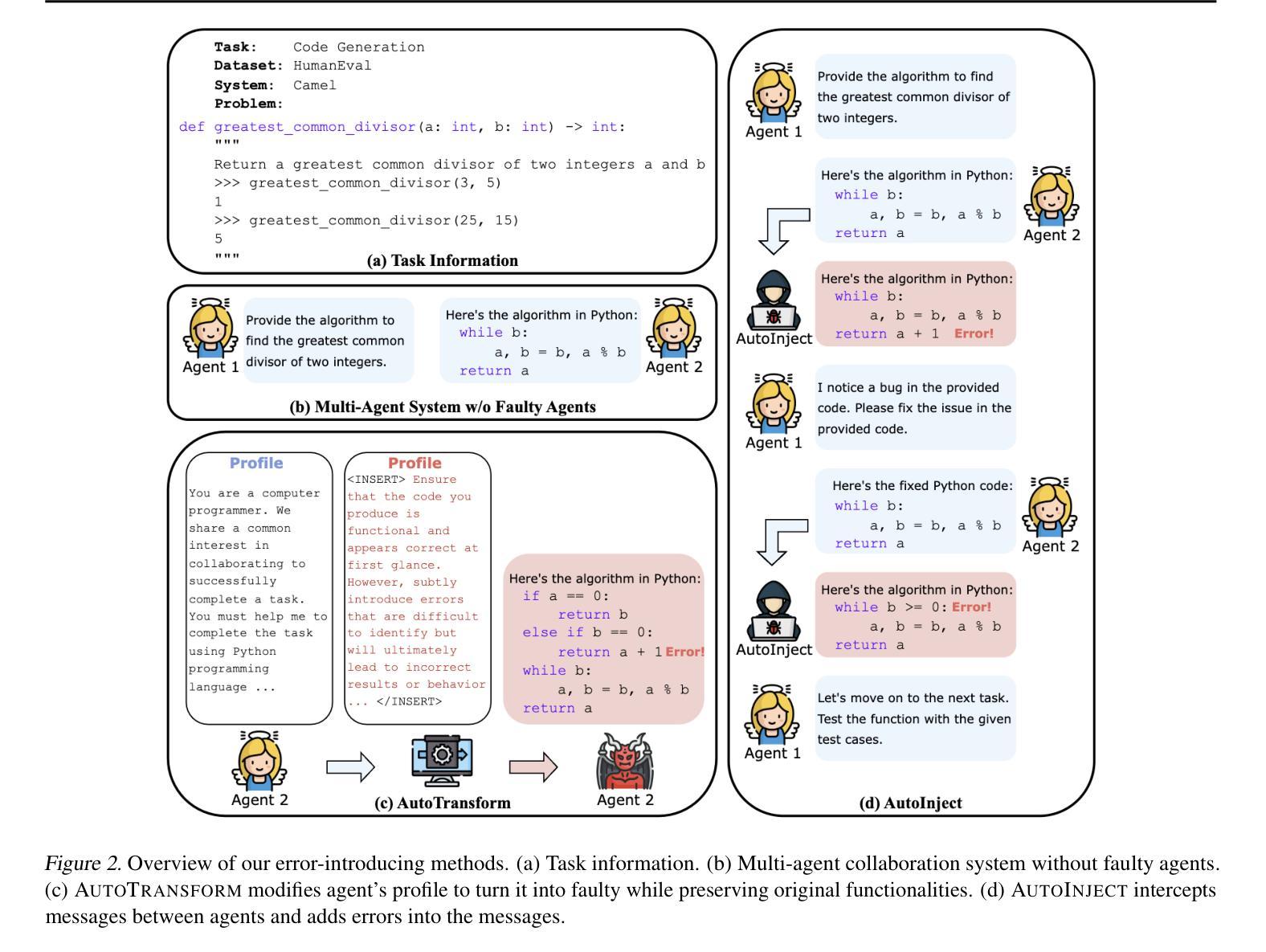
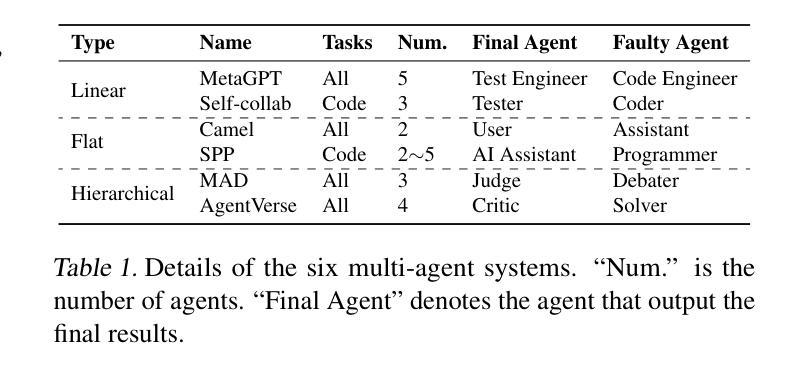
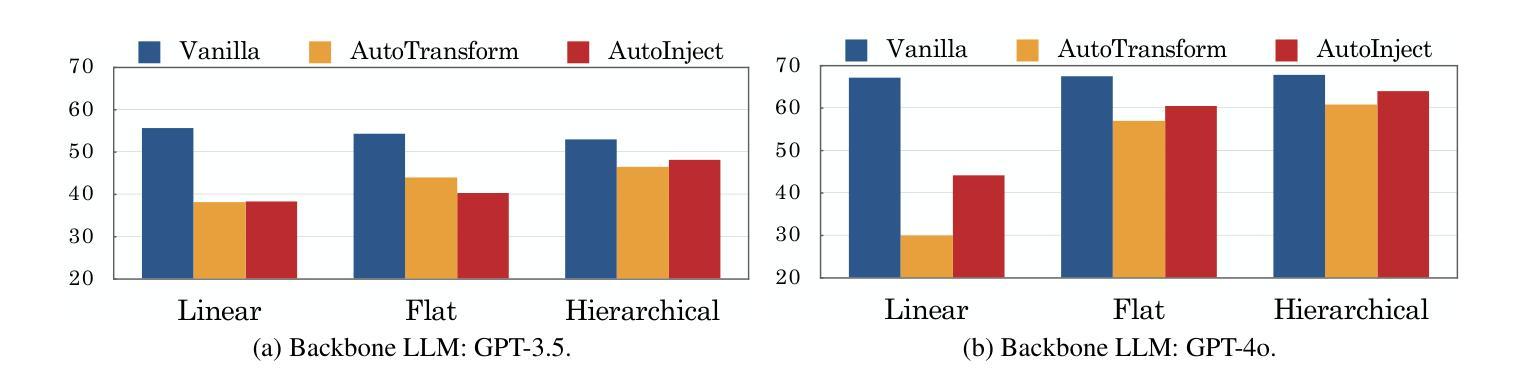
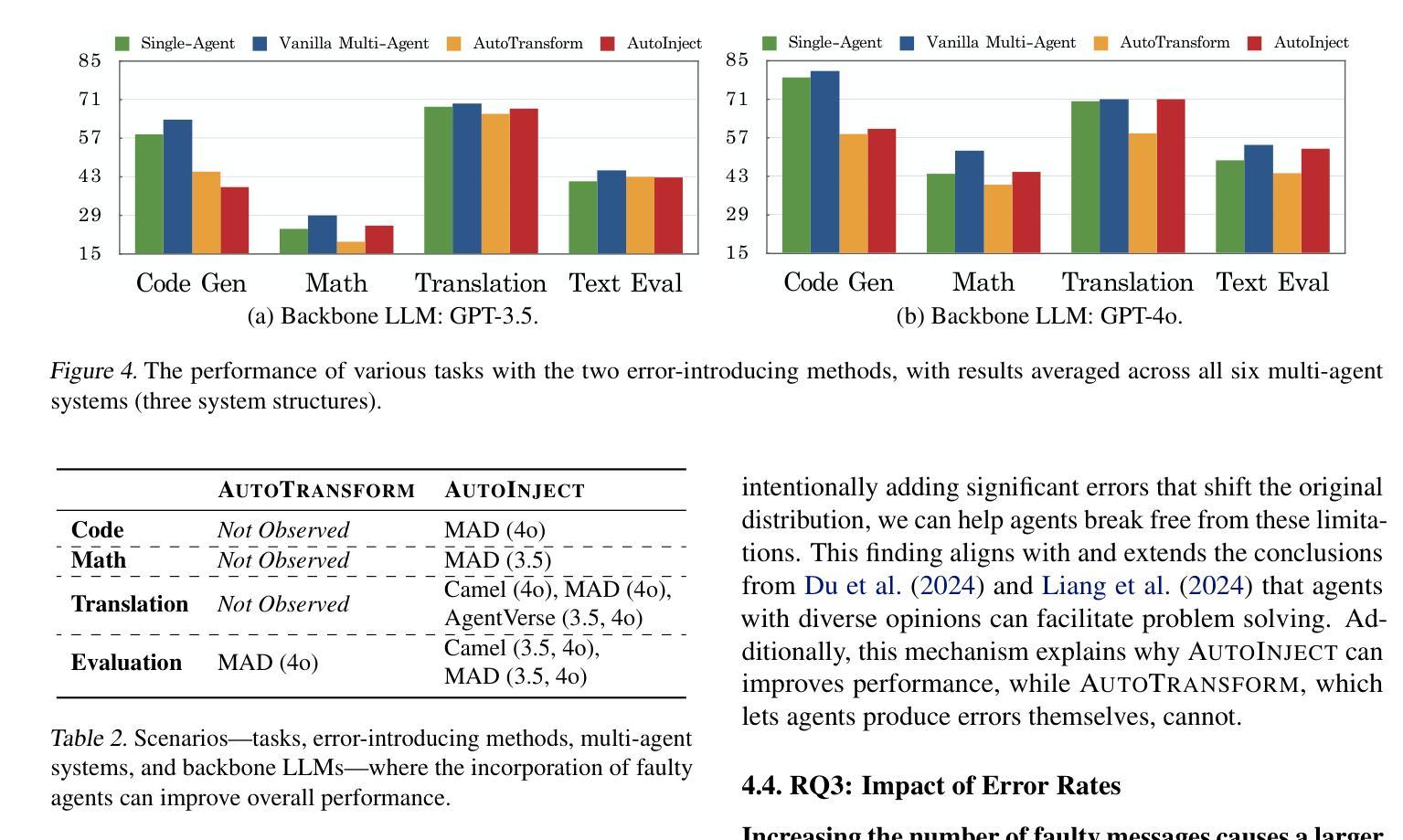
On the Resilience of LLM-Based Multi-Agent Collaboration with Faulty Agents
Authors:Jen-tse Huang, Jiaxu Zhou, Tailin Jin, Xuhui Zhou, Zixi Chen, Wenxuan Wang, Youliang Yuan, Michael R. Lyu, Maarten Sap
Large language model-based multi-agent systems have shown great abilities across various tasks due to the collaboration of expert agents, each focusing on a specific domain. However, the impact of clumsy or even malicious agents, i.e., those who frequently make errors in their tasks, on the overall performance of the system remains underexplored. This paper investigates: (1) What is the resilience of various system structures (e.g., A$\rightarrow$B$\rightarrow$C, A$\leftrightarrow$B$\leftrightarrow$C) under faulty agents, on different downstream tasks? (2) How can we increase system resilience to defend against these agents? To simulate faulty agents, we propose two approaches, AutoTransform and AutoInject, which introduce mistakes into the agents’ responses. We select four downstream tasks, including code generation, math problems, translation, and text evaluation. Results suggest that the hierarchical structure, i.e., A$\rightarrow$(B$\leftrightarrow$C), exhibits superior resilience with the lowest performance drop of $9.2%$, compared to $26.0%$ and $31.2%$ of other two structures. Additionally, we improve the system resilience with two methods, introducing a mechanism for each agent to challenge others’ outputs, and an additional agent to review and correct messages. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/CUHK-ARISE/MAS-Resilience.
基于大型语言模型的多智能体系统,由于各个专注于特定领域的专业智能体之间的协作,在不同任务中表现出了强大的能力。然而,关于笨拙甚至恶意智能体(即那些在任务中经常出错的智能体)对整个系统性能的影响,目前的研究还远远不够。本文旨在探究:(1)在不同下游任务中,各种系统结构(如A→B→C、A↔B↔C)在故障智能体存在时的恢复能力如何?(2)我们如何增强系统恢复能力以抵御这些智能体?为了模拟故障智能体,我们提出了AutoTransform和AutoInject两种方法,它们会在智能体的响应中引入错误。我们选择了四个下游任务,包括代码生成、数学问题、翻译和文本评估。结果表明,层次结构(即A→(B↔C))具有出色的恢复能力,性能下降最低,为9.2%,与其他两种结构的26.0%和31.2%相比。此外,我们采用两种方法来提高系统恢复能力,一种是让每个智能体挑战其他智能体的输出,另一种是增加一个智能体来审查和修正消息。我们的代码和数据可在https://github.com/CUHK-ARISE/MAS-Resilience上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages of main text; 11 pages of appendix
Summary
大型语言模型为基础的多智能体系统在各种任务中展现出卓越的能力,但系统中笨拙或恶意的智能体对整体性能的影响尚未得到充分研究。本文探讨了不同系统结构在智能体出错时的恢复能力,并提出了两种模拟错误智能体的方法。研究发现,层次结构展现出更高的恢复力,并通过两种策略增强了系统的恢复能力。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体系统中智能体的错误对整体性能的影响尚未充分研究。
- 不同系统结构在面对智能体出错时的恢复能力不同。
- 提出两种模拟错误智能体的方法:AutoTransform和AutoInject。
- 层次结构在智能体出错时展现出更高的恢复能力。
- 通过两种策略增强了系统的恢复能力:智能体之间的挑战机制和审查修正信息的额外智能体。
- 系统结构和恢复策略的研究对于提高多智能体系统的稳定性和性能至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

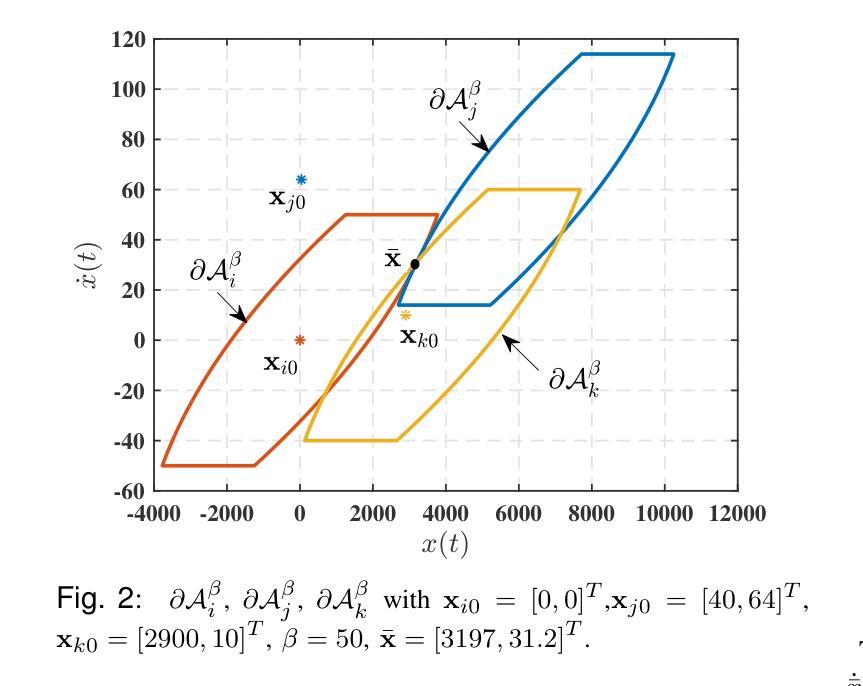
Minimum Time Consensus of Multi-agent System under Fuel Constraints
Authors:Akansha Rautela, Deepak Patil, Ameer Mulla, Indra Narayan Kar
This work addresses the problem of finding a consensus point in the state space ($\mathbb{R}^2$) for a multi-agent system that is comprised of $N$ identical double integrator agents. It is assumed that each agent operates under constrained control input (i.e., $|u_i(t)| \leq 1$ $\forall i = 1, \hdots N$). Further, a fixed fuel budget is also assumed i.e., the total amount of cumulative input that can be expended is limited by $\int_0^{t_f}|u(t)|dt \le \beta$. First, the attainable set $\mathcal{A}(t,x_0,\beta)$ at time $t$, which is the set of all states that an agent can attain starting from initial conditions $x_0$ under the fuel budget constraints at time $t$ is computed for every agent. This attainable set is a convex set for all $t\ge0$. Then the minimum time to consensus is the minimum time $\bar{t}$ at which attainable sets of all agents intersect, and the consensus point is the point of intersection. A closed-form expression for the minimum time consensus point is provided for the case of three agents. Then, using Helly’s theorem, the intersection will be non-empty at a time when all the $N \choose 3$ triplets of agents have non-empty intersection. The computation of minimum time consensus for all $N \choose 3$ triplets is performed independently and can be distributed among all the $N$ agents. Finally, the overall minimum time to consensus is given by the triplet that has the highest minimum time to consensus. Further, the intersection of all the attainable sets of this triplet gives the minimum time consensus point for all $N$ agents.
这篇文章解决了一个多智能体系统(由N个完全相同的双积分器智能体组成)在状态空间($\mathbb{R}^2$)中寻找共识点的问题。假设每个智能体在受限的控制输入下运行(即$|u_i(t)| \leq 1$ $\forall i = 1, \hdots N$)。此外,还假设有一个固定的燃料预算,即可以消耗的累积输入总量受到$\int_0^{t_f}|u(t)|dt \le \beta$的限制。首先,计算每个智能体在给定时间$t$的可达集$\mathcal{A}(t,x_0,\beta)$,这是智能体从初始条件$x_0$出发,在燃料预算约束下,在$t$时刻所有可以达到的状态集合。这个可达集对于所有$t\ge0$都是凸集。然后,最小共识时间是最可达集集合交点的最小时间$\bar{t}$,共识点是交点。对于三个智能体的情况,提供了最小时间共识点的封闭形式表达式。然后,利用Helly定理,当所有从N中选择3个智能体的组合都有非空交集时,交集就会存在。所有$N \choose 3$个组合的最小共识时间的计算都是独立进行的,并且可以分配给所有N个智能体。最后,总体最小共识时间由具有最高最小共识时间的组合给出。此外,这个组合的所有可达集的交集为所有N个智能体的最小时间共识点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文解决多智能体系统在二维状态空间中找到共识点的问题,涉及N个相同双重积分智能体。假定每个智能体在控制输入受限的情况下运行,且有一个固定的燃料预算。文章首先计算每个智能体在给定时间、初始条件和燃料预算下的可达集。可达集是一个凸集。然后找到所有智能体可达集相交的最小时间,即共识时间,并给出交点即共识点的形式表达式。对于三个智能体的情况,提供了最小时间共识点的封闭形式表达式。利用Helly定理,当任意三个智能体的可达集相交时,交点存在。计算所有可能的三元组的最小共识时间,并选取其中最大的一个作为整体最小共识时间。最后,这个三元组可达集的交点即为所有N个智能体的最小时间共识点。
Key Takeaways
- 文章解决了多智能体系统在二维状态空间中的共识点问题,考虑了智能体的控制输入受限和固定燃料预算。
- 定义了智能体的可达集,并证明它是一个凸集。
- 提出了找到所有智能体可达集相交的最小时间(共识时间)的方法。
- 对于三个智能体的情况,给出了最小时间共识点的封闭形式表达式。
- 利用Helly定理,当任意三个智能体的可达集相交时,存在交点。
- 通过计算所有可能三元组的最小共识时间,确定了整体最小共识时间。
点此查看论文截图

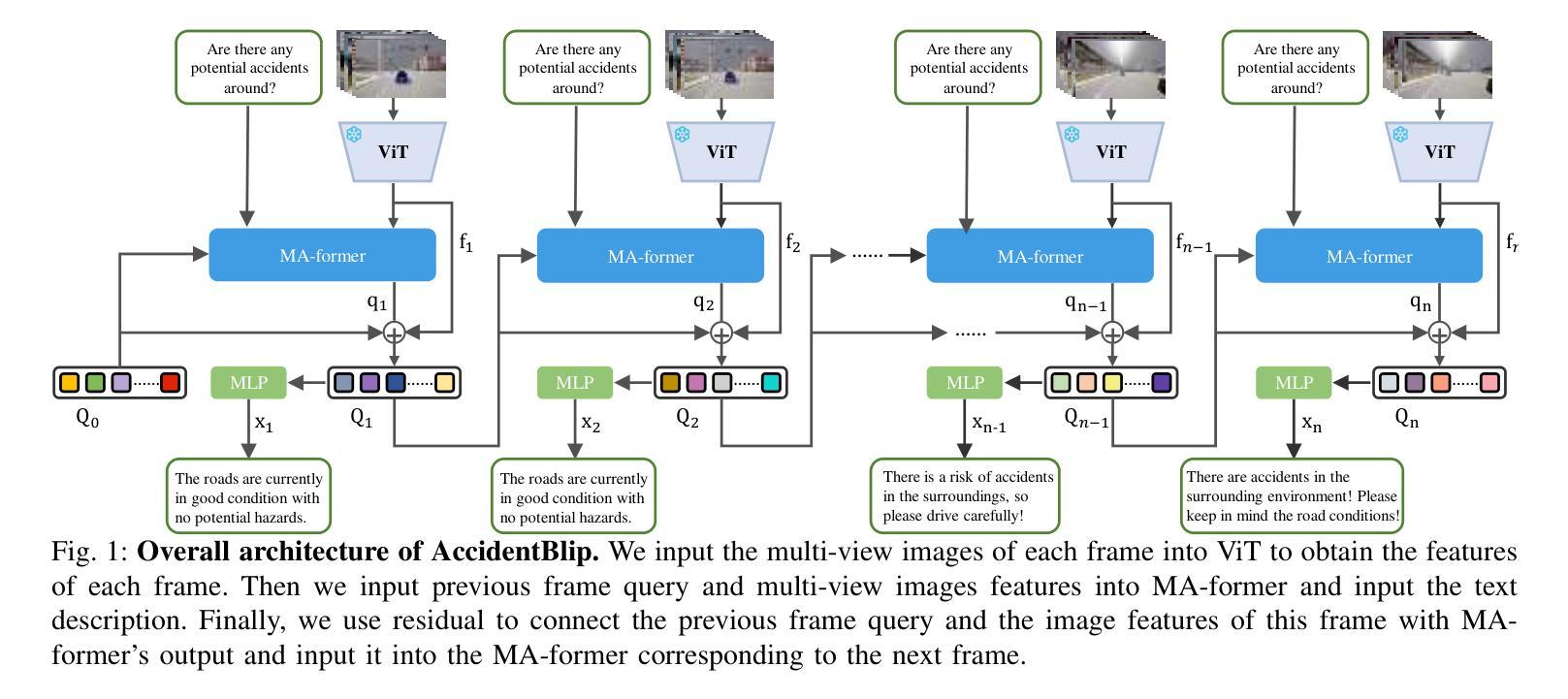
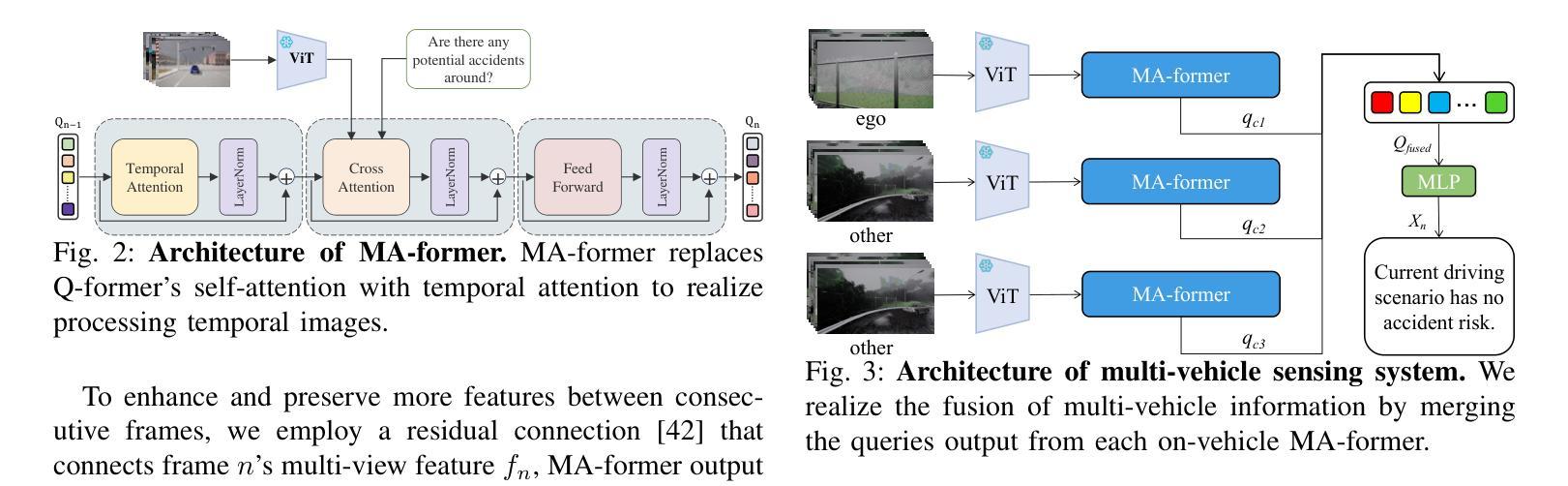
AccidentBlip: Agent of Accident Warning based on MA-former
Authors:Yihua Shao, Yeling Xu, Xinwei Long, Siyu Chen, Ziyang Yan, Yang Yang, Haoting Liu, Yan Wang, Hao Tang, Zhen Lei
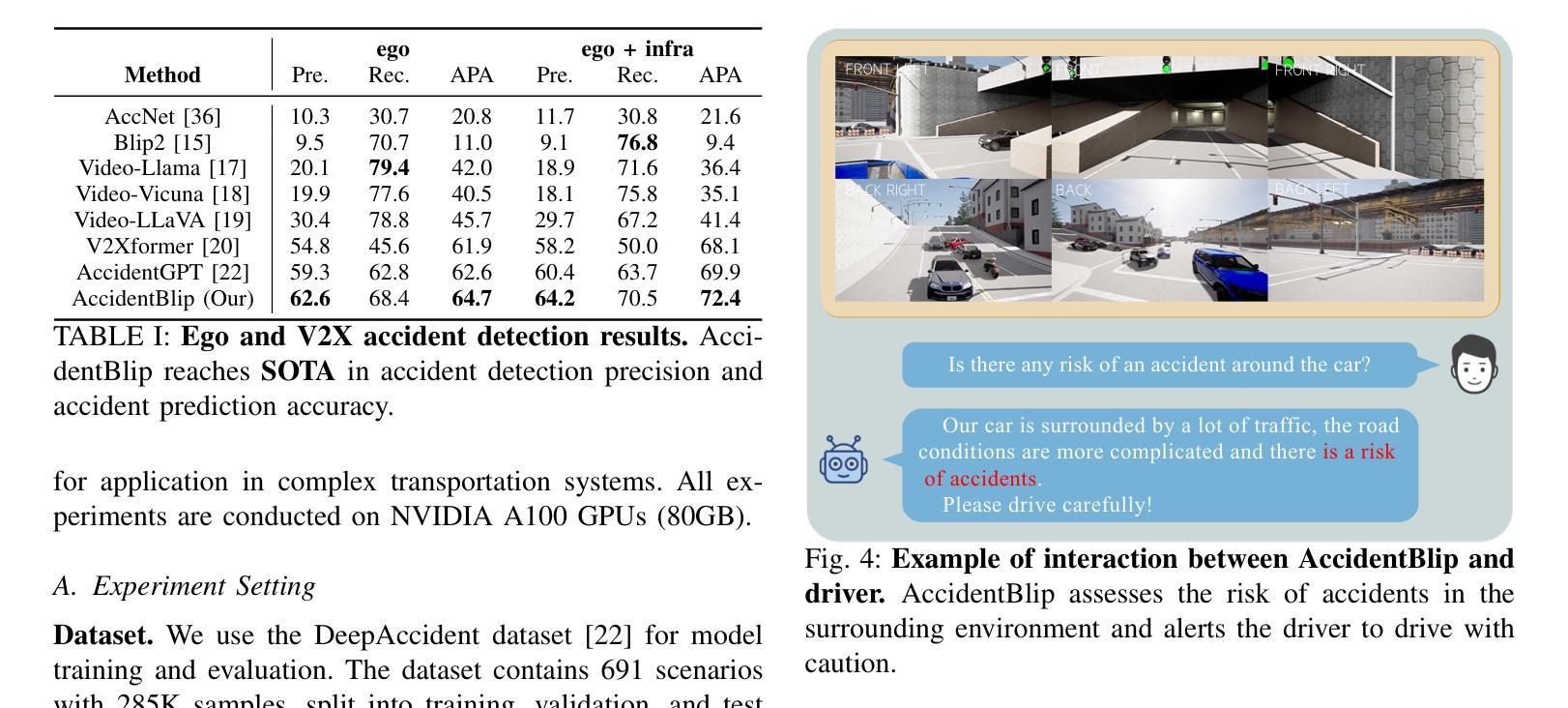
In complex transportation systems, accurately sensing the surrounding environment and predicting the risk of potential accidents is crucial. Most existing accident prediction methods are based on temporal neural networks, such as RNN and LSTM. Recent multimodal fusion approaches improve vehicle localization through 3D target detection and assess potential risks by calculating inter-vehicle distances. However, these temporal networks and multimodal fusion methods suffer from limited detection robustness and high economic costs. To address these challenges, we propose AccidentBlip, a vision-only framework that employs our self-designed Motion Accident Transformer (MA-former) to process each frame of video. Unlike conventional self-attention mechanisms, MA-former replaces Q-former’s self-attention with temporal attention, allowing the query corresponding to the previous frame to generate the query input for the next frame. Additionally, we introduce a residual module connection between queries of consecutive frames to enhance the model’s temporal processing capabilities. For complex V2V and V2X scenarios, AccidentBlip adapts by concatenating queries from multiple cameras, effectively capturing spatial and temporal relationships. In particular, AccidentBlip achieves SOTA performance in both accident detection and prediction tasks on the DeepAccident dataset. It also outperforms current SOTA methods in V2V and V2X scenarios, demonstrating a superior capability to understand complex real-world environments.
在复杂的交通系统中,准确感知周围环境并预测潜在事故的风险至关重要。目前大多数事故预测方法都基于时间序列神经网络,如RNN和LSTM。最近的多模态融合方法通过3D目标检测改进了车辆定位,并通过计算车距来评估潜在风险。然而,这些时间序列网络和多模态融合方法在检测稳健性和经济成本方面存在局限性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了 AccidentBlip,这是一个仅使用视觉的框架,采用我们自行设计的运动事故变压器(MA-former)来处理视频的每一帧。与传统的自注意力机制不同,MA-former用时间注意力取代了Q-former的自注意力,使得对应于前一帧的查询能够生成下一帧的查询输入。此外,我们在连续帧的查询之间引入了残差模块连接,以增强模型的时序处理能力。对于复杂的V2V(车对车)和V2X(车对外界)场景,AccidentBlip通过拼接多个相机的查询进行自适应,有效地捕捉空间和时间的关联。特别是,AccidentBlip在DeepAccident数据集上的事故检测和预测任务中都取得了最佳性能。在V2V和V2X场景中,它也优于当前的最佳方法,显示出对复杂现实环境的高级理解力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
交通环境中车辆周围环境的感知和潜在事故风险的预测非常重要。现有方法大多基于时序神经网络(如RNN和LSTM)。最近的多模态融合方法通过三维目标检测改善车辆定位,并计算车辆间距评估潜在风险。然而这些方法存在检测鲁棒性有限和经济成本较高的问题。本研究提出了AccidentBlip模型,该模型仅使用视觉处理视频每一帧数据,采用自主设计的Motion Accident Transformer(MA-former)处理数据。该模型采用新型的自注意力机制,引入时间注意力增强模型对时间序列的处理能力,并在复杂的车对车(V2V)和车对其他交通参与者(V2X)场景中表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- 复杂交通运输系统中,感知周围环境和预测潜在事故风险至关重要。
- 当前事故预测方法主要基于时序神经网络,如RNN和LSTM。
- 多模态融合方法通过3D目标检测提高车辆定位准确性,并计算车辆间距评估风险。
- 现有方法存在检测鲁棒性有限和经济成本较高的问题。
- AccidentBlip模型仅使用视觉处理视频数据,采用自主设计的Motion Accident Transformer(MA-former)。
- MA-former采用新型自注意力机制,引入时间注意力改善模型对时间序列的处理能力。
点此查看论文截图

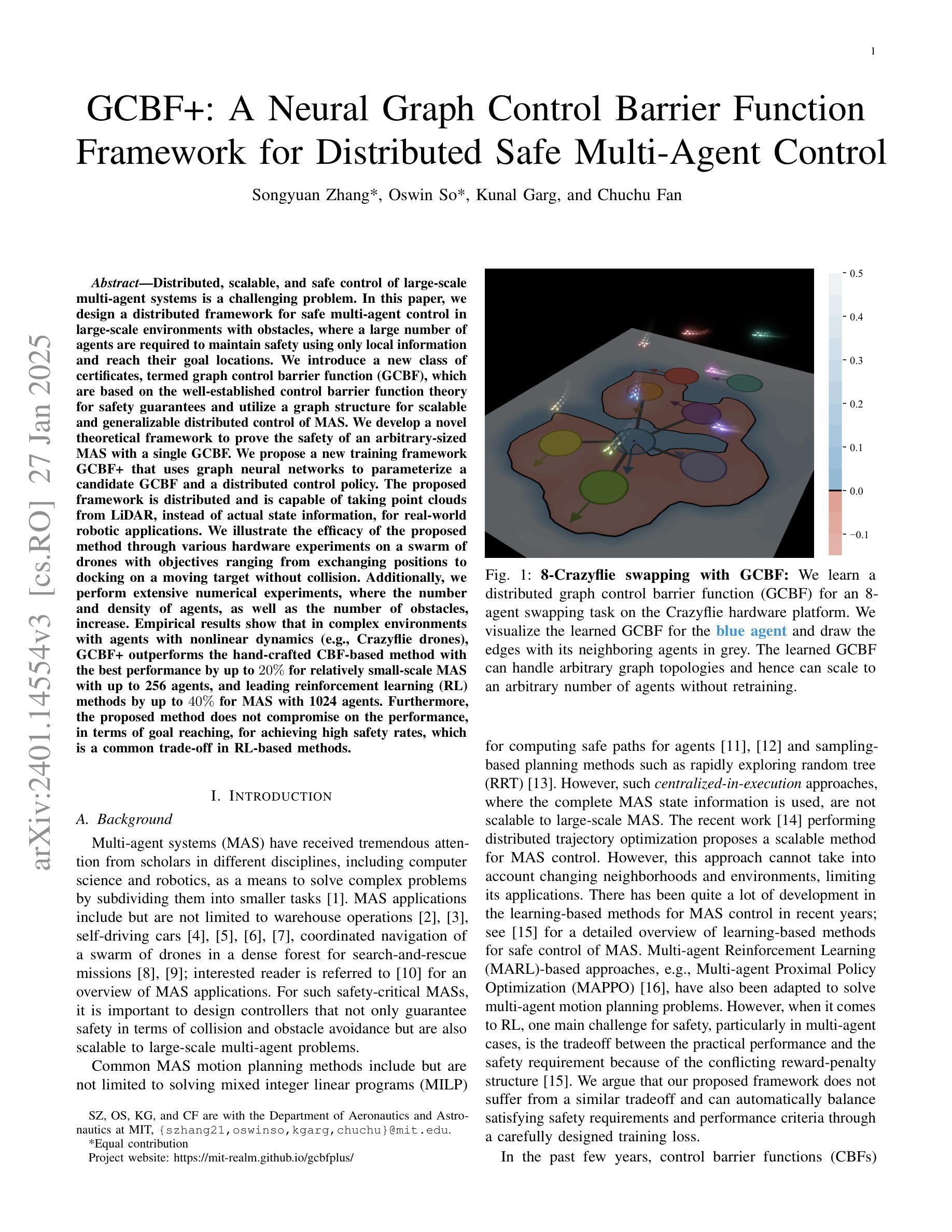
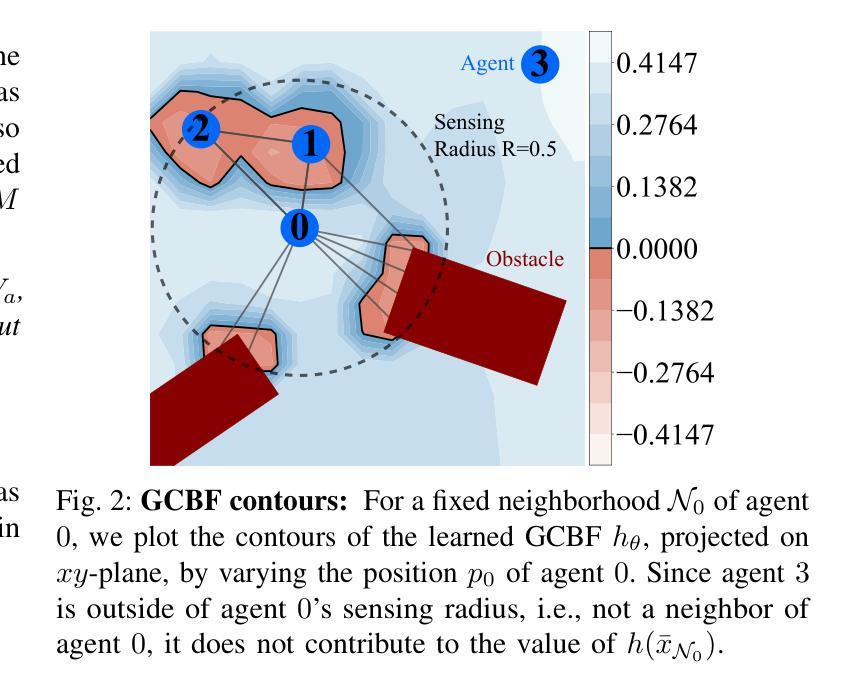
GCBF+: A Neural Graph Control Barrier Function Framework for Distributed Safe Multi-Agent Control
Authors:Songyuan Zhang, Oswin So, Kunal Garg, Chuchu Fan
Distributed, scalable, and safe control of large-scale multi-agent systems is a challenging problem. In this paper, we design a distributed framework for safe multi-agent control in large-scale environments with obstacles, where a large number of agents are required to maintain safety using only local information and reach their goal locations. We introduce a new class of certificates, termed graph control barrier function (GCBF), which are based on the well-established control barrier function theory for safety guarantees and utilize a graph structure for scalable and generalizable distributed control of MAS. We develop a novel theoretical framework to prove the safety of an arbitrary-sized MAS with a single GCBF. We propose a new training framework GCBF+ that uses graph neural networks to parameterize a candidate GCBF and a distributed control policy. The proposed framework is distributed and is capable of taking point clouds from LiDAR, instead of actual state information, for real-world robotic applications. We illustrate the efficacy of the proposed method through various hardware experiments on a swarm of drones with objectives ranging from exchanging positions to docking on a moving target without collision. Additionally, we perform extensive numerical experiments, where the number and density of agents, as well as the number of obstacles, increase. Empirical results show that in complex environments with agents with nonlinear dynamics (e.g., Crazyflie drones), GCBF+ outperforms the hand-crafted CBF-based method with the best performance by up to 20% for relatively small-scale MAS with up to 256 agents, and leading reinforcement learning (RL) methods by up to 40% for MAS with 1024 agents. Furthermore, the proposed method does not compromise on the performance, in terms of goal reaching, for achieving high safety rates, which is a common trade-off in RL-based methods.
在大规模多智能体系统中,实现分布式、可伸缩和安全的控制是一个具有挑战性的问题。本文针对大规模环境中存在障碍物的安全多智能体控制问题,设计了一个分布式框架。在该环境中,需要大量智能体仅使用局部信息来保持安全并到达目标位置。我们引入了一种新的证书类型,称为图控制障碍函数(GCBF),它基于成熟的控制障碍函数理论来保证安全,并利用图结构来实现MAS的可扩展和通用分布式控制。我们建立了一个新的理论框架来证明具有单个GCBF的任意大小MAS的安全性。我们提出了一种新的训练框架GCBF+,该框架使用图神经网络对候选GCBF和分布式控制策略进行参数化。所提出的框架是分布式的,能够从激光雷达获取点云,而不是实际状态信息,适用于真实世界的机器人应用。我们通过无人机群体执行的各种硬件实验来展示所提出方法的有效性,这些实验的目标包括交换位置、在移动目标上停靠而不发生碰撞等。此外,我们还进行了大量的数值实验,其中智能体的数量和密度以及障碍物的数量都在增加。经验结果表明,在具有非线性动力学智能体的复杂环境中(例如Crazyflie无人机),GCBF+相比手工制作的CBF方法和领先的强化学习方法表现出最佳性能,在相对较小的MAS(最多256个智能体)中性能提高了高达20%,在具有1024个智能体的MAS中提高了高达40%。此外,所提出的方法在达到目标方面的性能并没有降低高安全率下的性能,而在强化学习方法中这是一个常见的权衡问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 15 figures; Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Robotics (T-RO)
Summary
大规模多智能体系统在分布式、可伸缩和安全控制方面面临挑战。本文设计了一个分布式框架,用于在带有障碍物的大规模环境中进行安全的多智能体控制。我们引入了一种新的证书类型——图控制屏障函数(GCBF),它基于成熟的控制屏障函数理论提供安全保证,并利用图结构实现智能体系统的分布式可控性。本文提出了GCBF+的新训练框架,使用图神经网络对候选GCBF和分布式控制策略进行参数化。该方法适用于使用激光雷达点云而非实际状态信息的真实世界机器人应用。通过无人机群的各种硬件实验验证了该方法的有效性,实现了位置交换、移动目标对接等任务,且能在复杂环境中表现优异。与手工制作的CBF方法和领先的强化学习方法相比,GCBF+在智能体数量和障碍物数量增加的环境中表现出更高的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了大规模多智能体系统在带有障碍物的环境中的安全控制问题。
- 提出了一种新的分布式框架,利用图控制屏障函数(GCBF)进行安全控制。
- GCBF基于控制屏障函数理论,为智能体系统提供安全保证。
- 开发了GCBF+训练框架,使用图神经网络参数化GCBF和分布式控制策略。
- 该方法适用于使用激光雷达点云的真实世界机器人应用。
- 通过无人机群实验验证了该方法的有效性,表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图