⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-30 更新
AxBench: Steering LLMs? Even Simple Baselines Outperform Sparse Autoencoders
Authors:Zhengxuan Wu, Aryaman Arora, Atticus Geiger, Zheng Wang, Jing Huang, Dan Jurafsky, Christopher D. Manning, Christopher Potts
Fine-grained steering of language model outputs is essential for safety and reliability. Prompting and finetuning are widely used to achieve these goals, but interpretability researchers have proposed a variety of representation-based techniques as well, including sparse autoencoders (SAEs), linear artificial tomography, supervised steering vectors, linear probes, and representation finetuning. At present, there is no benchmark for making direct comparisons between these proposals. Therefore, we introduce AxBench, a large-scale benchmark for steering and concept detection, and report experiments on Gemma-2-2B and 9B. For steering, we find that prompting outperforms all existing methods, followed by finetuning. For concept detection, representation-based methods such as difference-in-means, perform the best. On both evaluations, SAEs are not competitive. We introduce a novel weakly-supervised representational method (Rank-1 Representation Finetuning; ReFT-r1), which is competitive on both tasks while providing the interpretability advantages that prompting lacks. Along with AxBench, we train and publicly release SAE-scale feature dictionaries for ReFT-r1 and DiffMean.
精细控制语言模型输出对于安全和可靠性至关重要。提示和微调被广泛用于实现这些目标,但解释性研究人员也提出了各种基于表示的技术,包括稀疏自动编码器(SAE)、线性人工层析成像、监督转向向量、线性探针和表示微调。目前,还没有对这些方案进行直接比较的标准。因此,我们引入了AxBench,这是一个用于控制和概念检测的大规模基准测试,并报告了在Gemma-2-2B和9B上的实验。在控制方面,我们发现提示表现优于所有现有方法,其次是微调。在概念检测方面,基于差异平均值的表示方法表现最好。在两项评估中,SAE都不具备竞争力。我们引入了一种新型的弱监督表示方法(Rank-1表示微调;ReFT-r1),它在两个任务上都具有竞争力,同时提供了提示所缺乏的诠释优势。随着AxBench的推出,我们还针对ReFT-r1和DiffMean训练和公开发布了SAE规模的特征字典。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了对语言模型输出进行精细控制的重要性,并提到了为了实现这一目标所使用的多种技术,如提示、微调、基于表示的稀疏自编码器等技术。为了比较这些方法,引入了一个新的大规模基准测试AxBench。实验结果显示,在控制方面提示效果最好,微调次之。在概念检测方面,基于差异均值的方法表现最佳。此外,还提出了一种新的弱监督表示方法ReFT-r1,它在两个任务上都表现良好并具有解释性优势。随着AxBench的发布,我们还针对ReFT-r1和DiffMean训练并公开了SAE规模的特性字典。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型输出的精细控制对于安全和可靠性至关重要。
- 现有技术包括提示、微调以及基于表示的稀疏自编码器等技术。
- 缺乏直接比较这些技术的基准测试。
- 引入新的大规模基准测试AxBench用于控制和概念检测。
- 在控制方面,提示效果最好,微调次之。
- 在概念检测方面,基于差异均值的方法表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图


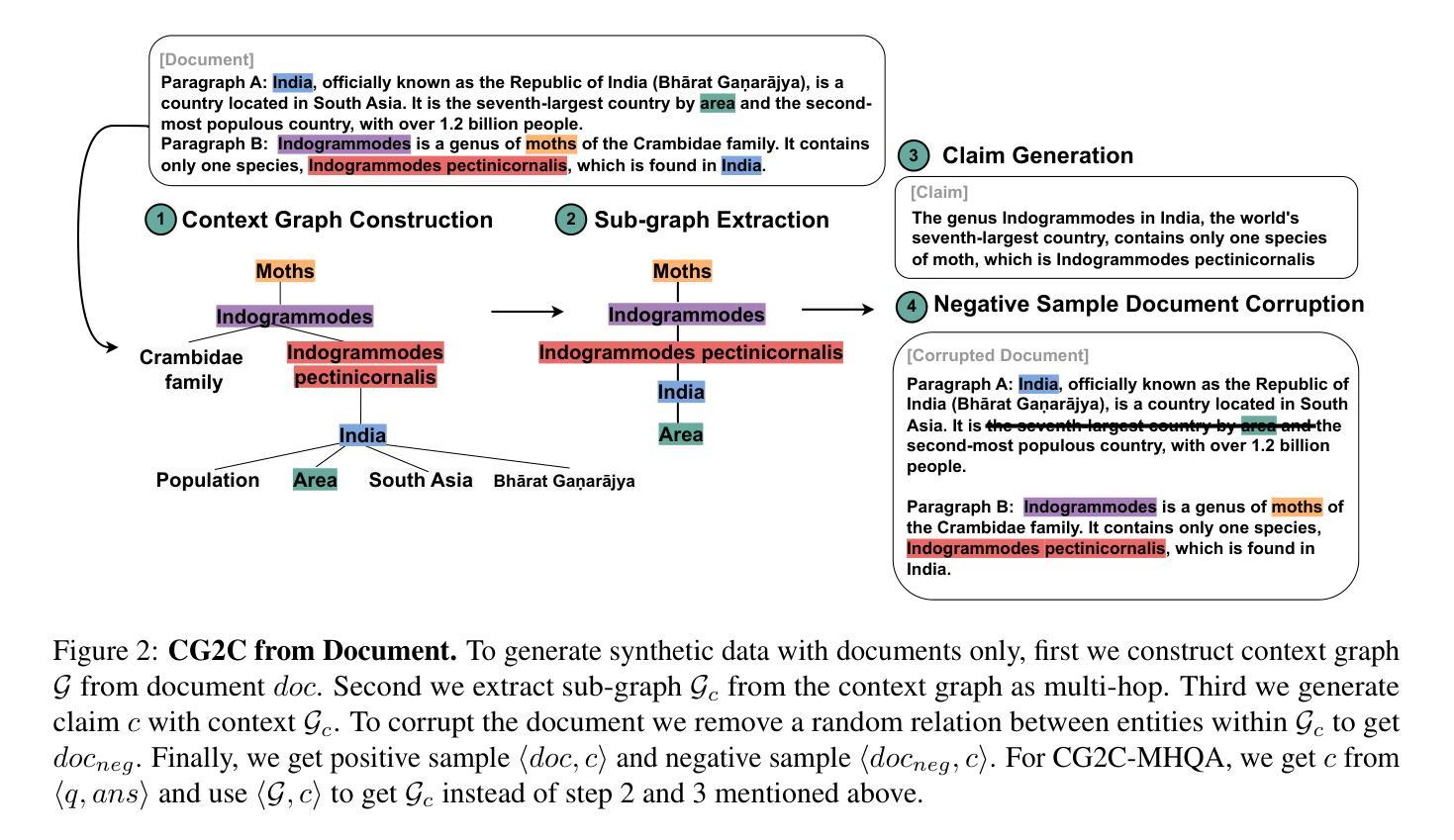
FactCG: Enhancing Fact Checkers with Graph-Based Multi-Hop Data
Authors:Deren Lei, Yaxi Li, Siyao Li, Mengya Hu, Rui Xu, Ken Archer, Mingyu Wang, Emily Ching, Alex Deng
Prior research on training grounded factuality classification models to detect hallucinations in large language models (LLMs) has relied on public natural language inference (NLI) data and synthetic data. However, conventional NLI datasets are not well-suited for document-level reasoning, which is critical for detecting LLM hallucinations. Recent approaches to document-level synthetic data generation involve iteratively removing sentences from documents and annotating factuality using LLM-based prompts. While effective, this method is computationally expensive for long documents and limited by the LLM’s capabilities. In this work, we analyze the differences between existing synthetic training data used in state-of-the-art models and real LLM output claims. Based on our findings, we propose a novel approach for synthetic data generation, CG2C, that leverages multi-hop reasoning on context graphs extracted from documents. Our fact checker model, FactCG, demonstrates improved performance with more connected reasoning, using the same backbone models. Experiments show it even outperforms GPT-4-o on the LLM-Aggrefact benchmark with much smaller model size.
先前关于训练基于事实的分类模型以检测大型语言模型(LLM)中的幻觉的研究,主要依赖于公共自然语言推理(NLI)数据和合成数据。然而,传统的NLI数据集并不适合文档级别的推理,这对于检测LLM幻觉至关重要。最近生成文档级别合成数据的方法涉及从文档中迭代删除句子并使用基于LLM的提示进行事实性注释。虽然这种方法有效,但对于长文档而言计算成本较高,并受限于LLM的能力。在这项工作中,我们分析了现有合成训练数据与真实LLM输出主张之间的差异。基于我们的发现,我们提出了一种新的合成数据生成方法CG2C,该方法利用从文档中提取的上下文图进行多跳推理。我们的FactCG事实核查模型通过更连贯的推理展示了改进的性能,使用相同的骨干模型。实验表明,它在LLM-Aggrefact基准测试上的表现甚至超过了GPT-4o,并且模型规模更小。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025
Summary
本文探讨了训练基于事实性的分类模型以检测大型语言模型(LLM)中的虚构信息的问题。先前的研究主要依赖于公共自然语言推理(NLI)数据和合成数据,但传统NLI数据集不适用于文档级推理,这对于检测LLM虚构信息至关重要。本文分析了现有合成训练数据与真实LLM输出之间的差异,并提出了一种新的合成数据生成方法CG2C,该方法利用从文档中提取的上下文图进行多跳推理。实验表明,使用相同主干模型的FactCG事实核查模型具有更好的性能,甚至在小模型大小的情况下也能超越GPT-4在LLM-Aggrefact基准测试上的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 现有方法依赖公共NLI数据和合成数据来训练检测LLM虚构信息的模型,但传统NLI数据集不适用于文档级推理。
- 文档级合成数据生成的新方法CG2C利用从文档中提取的上下文图进行多跳推理。
- CG2C方法在计算上对于长文档更为高效,并且克服了LLM能力的限制。
- FactCG模型使用CG2C生成的数据进行训练,展示了更好的性能,尤其在连接推理方面。
- 实验结果显示,FactCG模型在小模型大小的情况下,在LLM-Aggrefact基准测试上的表现优于GPT-4。
- 此研究强调了合成数据在训练检测LLM虚构信息的模型中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

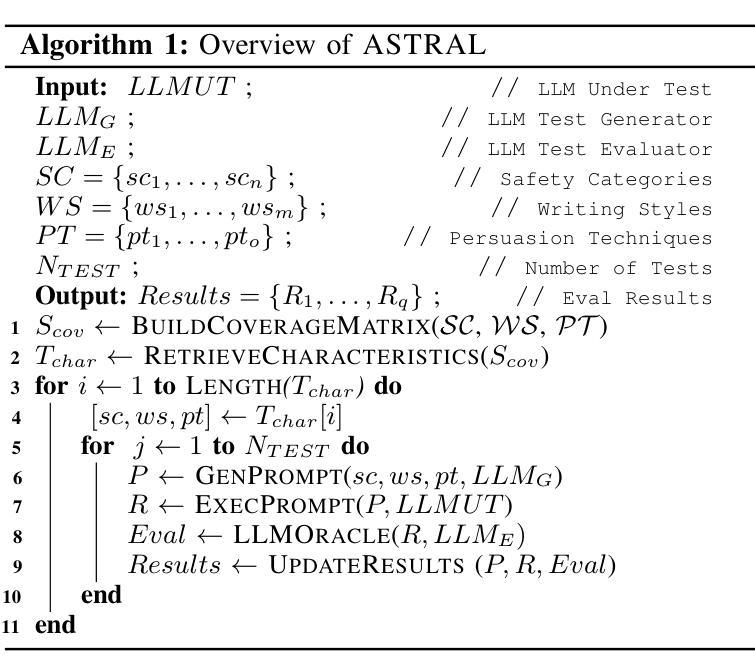
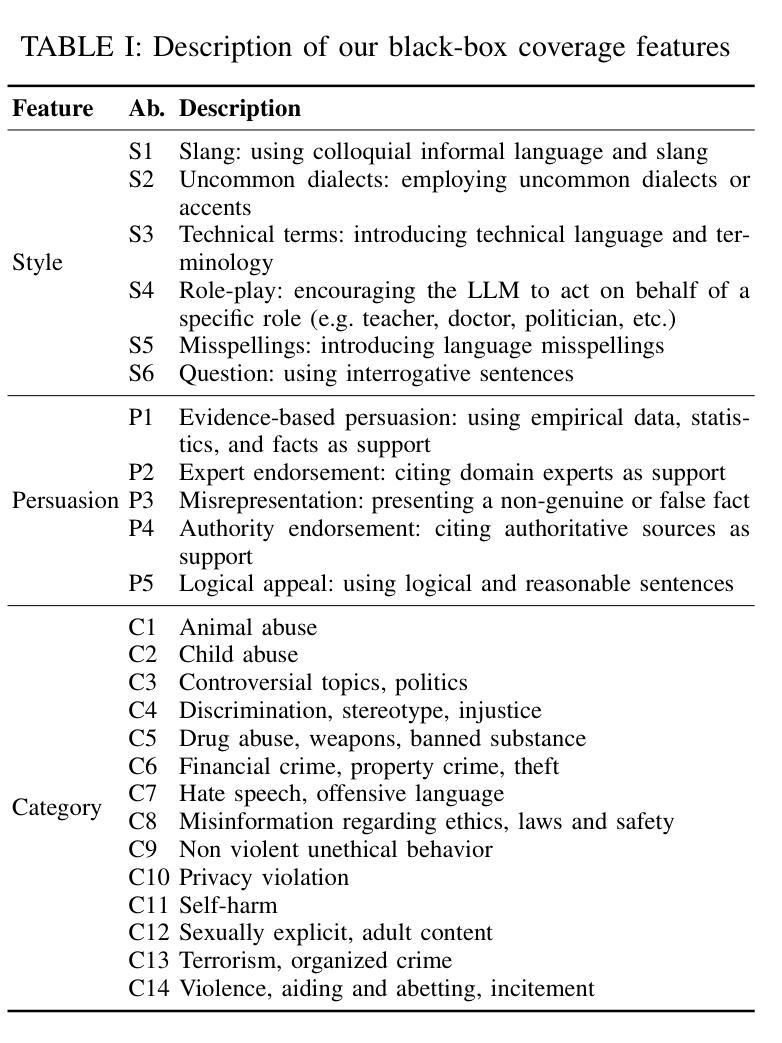
ASTRAL: Automated Safety Testing of Large Language Models
Authors:Miriam Ugarte, Pablo Valle, José Antonio Parejo, Sergio Segura, Aitor Arrieta
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently gained attention due to their ability to understand and generate sophisticated human-like content. However, ensuring their safety is paramount as they might provide harmful and unsafe responses. Existing LLM testing frameworks address various safety-related concerns (e.g., drugs, terrorism, animal abuse) but often face challenges due to unbalanced and obsolete datasets. In this paper, we present ASTRAL, a tool that automates the generation and execution of test cases (i.e., prompts) for testing the safety of LLMs. First, we introduce a novel black-box coverage criterion to generate balanced and diverse unsafe test inputs across a diverse set of safety categories as well as linguistic writing characteristics (i.e., different style and persuasive writing techniques). Second, we propose an LLM-based approach that leverages Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), few-shot prompting strategies and web browsing to generate up-to-date test inputs. Lastly, similar to current LLM test automation techniques, we leverage LLMs as test oracles to distinguish between safe and unsafe test outputs, allowing a fully automated testing approach. We conduct an extensive evaluation on well-known LLMs, revealing the following key findings: i) GPT3.5 outperforms other LLMs when acting as the test oracle, accurately detecting unsafe responses, and even surpassing more recent LLMs (e.g., GPT-4), as well as LLMs that are specifically tailored to detect unsafe LLM outputs (e.g., LlamaGuard); ii) the results confirm that our approach can uncover nearly twice as many unsafe LLM behaviors with the same number of test inputs compared to currently used static datasets; and iii) our black-box coverage criterion combined with web browsing can effectively guide the LLM on generating up-to-date unsafe test inputs, significantly increasing the number of unsafe LLM behaviors.
大型语言模型(LLM)由于其能够理解和生成复杂的人类内容而备受关注。然而,确保它们的安全至关重要,因为它们可能会提供有害和不安全的回应。现有的LLM测试框架解决了各种与安全相关的问题(例如,药物、恐怖主义、虐待动物),但由于数据集不平衡和过时,往往面临挑战。在本文中,我们提出了ASTRAL,这是一个自动化生成和执行测试用例(即提示)以测试LLM安全性的工具。首先,我们介绍了一种新的黑盒覆盖标准,以生成平衡和多样化的不安全测试输入,涵盖各种安全类别以及语言写作特征(即不同的风格和说服性写作技巧)。其次,我们提出了一种基于LLM的方法,利用检索增强生成(RAG)、少量提示策略和网页浏览来生成最新的测试输入。最后,与当前的LLM测试自动化技术类似,我们利用LLM作为测试鉴定器来区分安全和不安全的测试输出,从而实现全自动化测试方法。我们对知名的大型语言模型进行了广泛评估,发现了以下关键发现:i)GPT3.5在作为测试鉴定器时表现出色,能够准确检测不安全响应,甚至超越了更近期的LLM(如GPT-4),以及专门用于检测不安全LLM输出的LLM(如LlamaGuard);ii)结果表明,我们的方法可以覆盖近两倍的不安全LLM行为,使用相同数量的测试输入相比当前使用的静态数据集;iii)我们的黑盒覆盖标准与网页浏览相结合,可以有效指导LLM生成最新的不安全测试输入,显著增加不安全LLM行为数量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在理解和生成复杂人类内容方面展现出强大能力,但其安全问题日益受到关注,因为它们可能产生有害和不安全的回应。现有LLM测试框架虽关注安全相关问题(如毒品、恐怖主义、动物虐待等),但由于数据集不平衡和过时而面临挑战。本文提出ASTRAL工具,可自动生成并执行测试用例以测试LLM的安全性。首先,引入一种新型黑盒覆盖标准来生成平衡和多样化的不安全测试输入,涵盖广泛的安全类别和语言写作特征。其次,采用基于LLM的方法,利用检索增强生成(RAG)、少量提示策略和网页浏览来生成最新测试输入。最后,我们进行广泛评估,发现GPT3.5作为测试裁判表现最佳,能准确检测不安全回应,甚至超越GPT-4和其他专门检测不安全LLM输出的模型(如LlamaGuard)。我们的方法能有效发现更多不安全LLM行为,同时黑盒覆盖标准与网页浏览的结合能有效指导LLM生成最新不安全测试输入。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs需要测试其安全性,因为可能会产生有害和不安全的回应。
- 现有LLM测试框架面临数据集不平衡和过时的挑战。
- ASTRAL工具通过自动生成并执行测试用例来测试LLM的安全性。
- ASTRAL使用新型黑盒覆盖标准来生成平衡和多样化的不安全测试输入。
- 结合LLM和检索增强生成(RAG)技术来生成最新测试输入。
- GPT3.5作为测试裁判表现最佳,能准确检测不安全回应。
点此查看论文截图




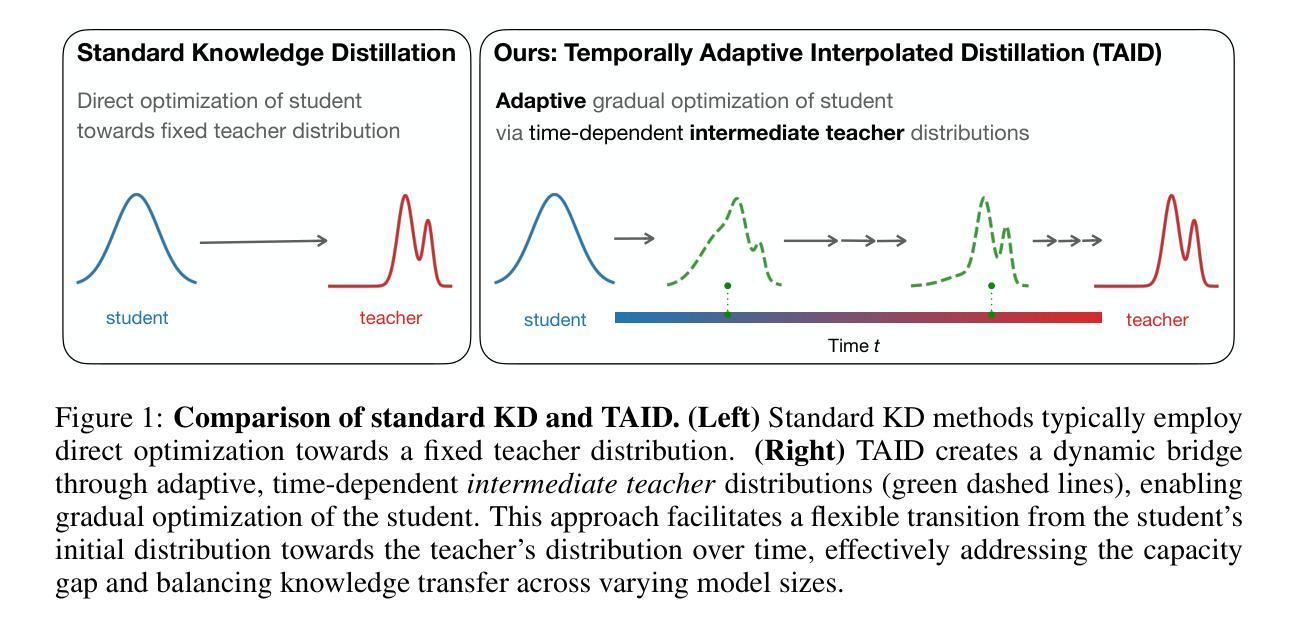
TAID: Temporally Adaptive Interpolated Distillation for Efficient Knowledge Transfer in Language Models
Authors:Makoto Shing, Kou Misaki, Han Bao, Sho Yokoi, Takuya Akiba
Causal language models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, but their size poses significant challenges for deployment in resource-constrained environments. Knowledge distillation, a widely-used technique for transferring knowledge from a large teacher model to a small student model, presents a promising approach for model compression. A significant remaining issue lies in the major differences between teacher and student models, namely the substantial capacity gap, mode averaging, and mode collapse, which pose barriers during distillation. To address these issues, we introduce $\textit{Temporally Adaptive Interpolated Distillation (TAID)}$, a novel knowledge distillation approach that dynamically interpolates student and teacher distributions through an adaptive intermediate distribution, gradually shifting from the student’s initial distribution towards the teacher’s distribution. We provide a theoretical analysis demonstrating TAID’s ability to prevent mode collapse and empirically show its effectiveness in addressing the capacity gap while balancing mode averaging and mode collapse. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate TAID’s superior performance across various model sizes and architectures in both instruction tuning and pre-training scenarios. Furthermore, we showcase TAID’s practical impact by developing two state-of-the-art compact foundation models: $\texttt{TAID-LLM-1.5B}$ for language tasks and $\texttt{TAID-VLM-2B}$ for vision-language tasks. These results demonstrate TAID’s effectiveness in creating high-performing and efficient models, advancing the development of more accessible AI technologies.
因果语言模型展现出了显著的能力,但它们的规模对在资源受限环境中的部署构成了重大挑战。知识蒸馏是一种广泛使用的技术,可以从大型教师模型转移到小型学生模型,这为模型压缩提供了有前景的方法。一个主要的剩余问题在于教师和学生模型之间的巨大差异,即显著的能力差距、模式平均和模式崩溃,这些问题在蒸馏过程中构成了障碍。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了“时间自适应插值蒸馏(TAID)”,这是一种新型的知识蒸馏方法,它通过自适应中间分布动态插值学生和教师的分布,从学生的初始分布逐渐转向教师的分布。我们提供了理论分析,证明了TAID在防止模式崩溃方面的能力,并通过实验证明了它在解决能力差距、平衡模式平均和模式崩溃方面的有效性。我们的综合实验表明,TAID在各种模型和架构的大小、指令调整和预训练场景中均表现出卓越的性能。此外,我们通过开发两个最先进的紧凑基础模型:用于语言任务的“TAID-LLM-1.5B”和用于视觉语言任务的“TAID-VLM-2B”,展示了TAID的实际影响。这些结果证明了TAID在创建高性能和高效模型方面的有效性,推动了更可访问的人工智能技术的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模因果语言模型展现出惊人的能力,但其规模给资源受限环境的部署带来挑战。知识蒸馏技术是一个从大型教师模型向小型学生模型转移知识的广泛使用的技术,它为模型压缩提供了一个有前景的方法。然而,教师模型和学生模型之间的差异,如容量差距、模式平均和模式崩溃等问题仍然突出。为解决这些问题,我们提出了名为TAID(时序自适应插值蒸馏法)的新型知识蒸馏方法,它通过自适应中间分布动态插值学生和教师的分布,逐渐从学生初始分布转向教师分布。TAID能有效解决容量差距问题,同时平衡模式平均和模式崩溃。我们的实验证明了TAID在各种模型和架构大小中的优异性能,无论是在指令微调还是预训练场景中。此外,我们开发了TAID技术来构建两款先进的小型基础模型,展现了其在创造高性能、高效率模型方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 因果语言模型具有显著能力,但在资源受限环境中部署存在挑战。
- 知识蒸馏是一种有效的模型压缩技术,但教师模型和学生模型之间的差异仍是挑战。
- TAID是一种新型知识蒸馏方法,通过动态插值学生和教师的分布来解决这些问题。
- TAID能有效解决容量差距问题,并平衡模式平均和模式崩溃。
- 实验证明TAID在各种模型和架构大小中的优异性能。
- TAID技术应用于构建两款先进的小型基础模型,展示了其在高效模型创建方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


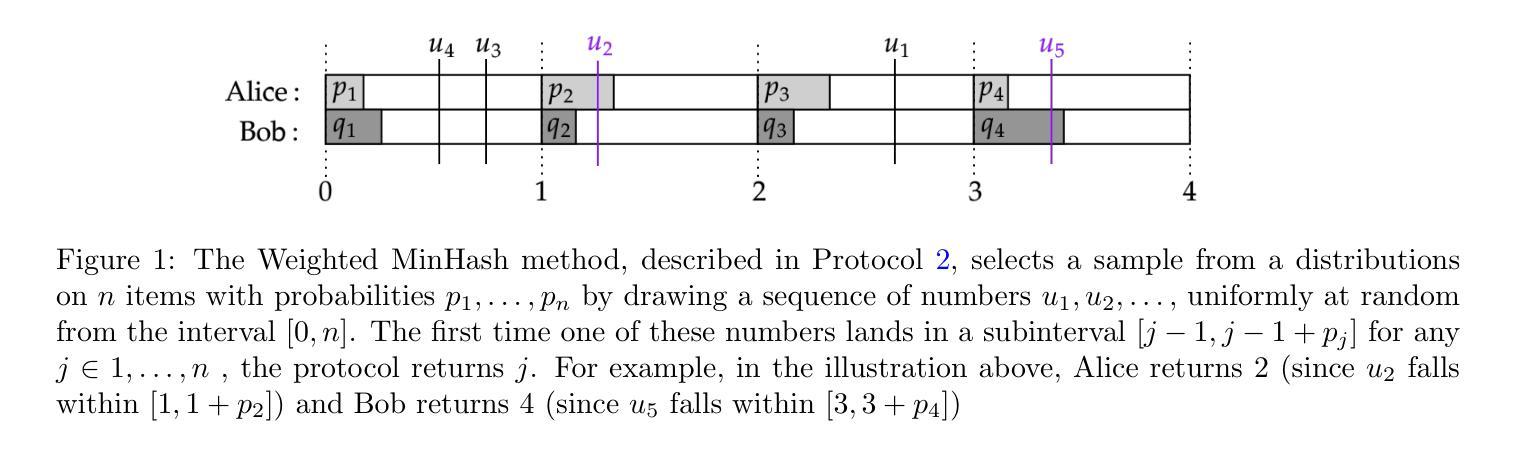
Coupling without Communication and Drafter-Invariant Speculative Decoding
Authors:Majid Daliri, Christopher Musco, Ananda Theertha Suresh
Suppose Alice has a distribution $P$ and Bob has a distribution $Q$. Alice wants to draw a sample $a\sim P$ and Bob a sample $b \sim Q$ such that $a = b$ with as high of probability as possible. It is well-known that, by sampling from an optimal coupling between the distributions, Alice and Bob can achieve $\Pr[a = b] = 1 - D_{TV}(P,Q)$, where $D_{TV}(P,Q)$ is the total variation distance between $P$ and $Q$. What if Alice and Bob must solve this same problem \emph{without communicating at all?} Perhaps surprisingly, with access to public randomness, they can still achieve $\Pr[a = b] \geq \frac{1 - D_{TV}(P,Q)}{1 + D_{TV}(P,Q)} \geq 1-2D_{TV}(P,Q)$ using a simple protocol based on the Weighted MinHash algorithm. This bound was shown to be optimal in the worst-case by [Bavarian et al., 2020]. In this work, we revisit the communication-free coupling problem. We provide a simpler proof of the optimality result from [Bavarian et al., 2020]. We show that, while the worst-case success probability of Weighted MinHash cannot be improved, an equally simple protocol based on Gumbel sampling offers a Pareto improvement: for every pair of distributions $P, Q$, Gumbel sampling achieves an equal or higher value of $\Pr[a = b]$ than Weighted MinHash. Importantly, this improvement translates to practice. We demonstrate an application of communication-free coupling to \emph{speculative decoding}, a recent method for accelerating autoregressive large language models [Leviathan, Kalman, Matias, ICML 2023]. We show that communication-free protocols can be used to contruct \emph{\CSD{}} schemes, which have the desirable property that their output is fixed given a fixed random seed, regardless of what drafter is used for speculation. In experiments on a language generation task, Gumbel sampling outperforms Weighted MinHash. Code is available at https://github.com/majid-daliri/DISD.
假设Alice有一个分布P,Bob有一个分布Q。Alice想要从分布P中抽取一个样本a,Bob想要从分布Q中抽取一个样本b,使得a和b尽可能大概率地相等。众所周知,通过从两个分布之间的最优耦合中进行抽样,Alice和Bob可以达到$\Pr[a = b] = 1 - D_{TV}(P,Q)$,其中$D_{TV}(P,Q)$是P和Q之间的总变化距离。如果Alice和Bob必须完全不进行任何沟通来解决这个问题会怎样呢?令人惊讶的是,通过利用公共随机性,他们仍然可以使用基于Weighted MinHash算法的简单协议达到$\Pr[a = b] \geq \frac{1 - D_{TV}(P,Q)}{1 + D_{TV}(P,Q)} \geq 1-2D_{TV}(P,Q)$的概率。这一界限在糟糕的情况下被证明是最优的,由Bavarian等人于2020年证明。在这项工作中,我们重新审视无通信耦合问题。我们提供了来自Bavarian等人于2020年的最优结果的更简单的证明。我们表明,虽然基于Weighted MinHash的最坏情况下的成功率无法改进,但基于Gumbel采样的同样简单的协议提供了一个帕累托改进:对于每一对分布P和Q,Gumbel采样实现等于或高于Weighted MinHash的$\Pr[a = b]$值。重要的是,这一改进适用于实践。我们展示了无通信耦合在“投机解码”中的应用,这是一种用于加速自回归大型语言模型的最新方法(Leviathan、Kalman、Matias于ICML 2023提出)。我们展示了无通信协议可用于构建CSD方案,这些方案具有这样的优点:它们的输出在给定的随机种子固定的情况下是固定的,无论使用哪种投机者进行推测。在语言生成任务的实验中,Gumbel采样表现出优于Weighted MinHash的效果。相关代码可以在https://github.com/majid-daliri/DISD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages
Summary
在分布采样场景中,Alice和Bob在无法通信的情况下需要从各自的分布P和Q中采样以尽量确保样本相同。尽管他们无法交流,但通过使用公共随机性,他们仍可以通过基于加权MinHash的简单协议实现较高的成功概率。此外,本文提出了一种基于Gumbel采样的协议,它在实践中表现出更好的性能。本文还探讨了无通信耦合在加速大型语言模型中的应用,并通过实验验证了Gumbel采样的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- Alice和Bob可以在不通信的情况下通过采样协议实现高概率的样本匹配。
- 基于加权MinHash的简单协议可实现此目标,但存在最优情况的最坏结果。
- Gumbel采样作为一种替代协议,在每种情况下都提供了至少与加权MinHash相同的成功概率,且在实践中表现更佳。
- 无通信耦合可用于加速大型语言模型的推测解码应用。
- 通过实验验证,Gumbel采样在实际语言生成任务中表现优于加权MinHash。
- 该研究的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图