⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-30 更新
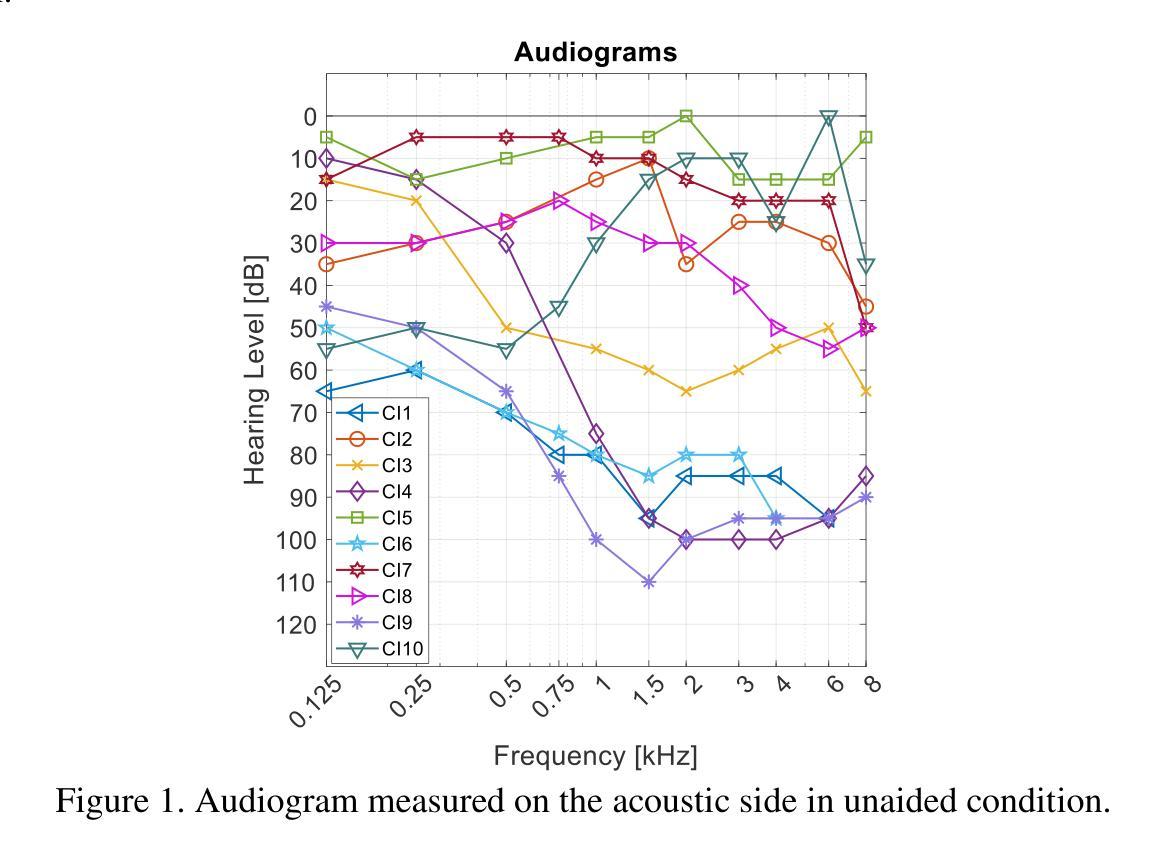
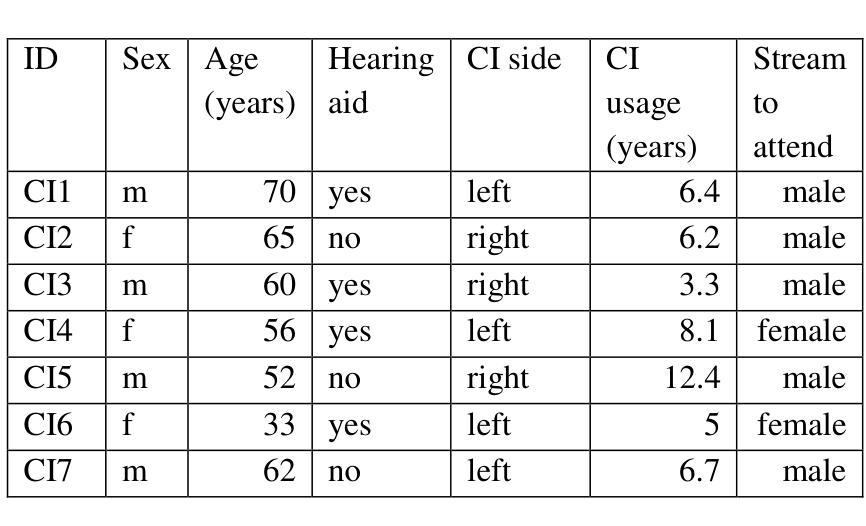
Cortical Temporal Mismatch Compensation in Bimodal Cochlear Implant Users: Selective Attention Decoding and Pupillometry Study
Authors:Hanna Dolhopiatenko, Waldo Nogueira
Bimodal stimulation, combining cochlear implant (CI) and acoustic input from the opposite ear, typically enhances speech perception but varies due to factors like temporal mismatch. Previously, we used cortical auditory evoked potentials (CAEPs) to estimate this mismatch based on N1 latency differences. This study expands on that by assessing the impact of temporal mismatch compensation on speech perception. We tested bimodal CI users in three conditions: clinical, compensated temporal mismatch, and a 50 ms mismatch. Measures included speech understanding, pupillometry, CAEPs, selective attention decoding, and parietal alpha power. Despite stable speech understanding across conditions, neural measures showed stronger effects. CAEP N1P2 amplitudes were highest in the compensated condition. Phase-locking value (PLV) and selective attention decoding improved but lacked significance. Parietal alpha power increased under 50 ms mismatch, suggesting cognitive resource allocation. Pupillometry correlated with speech understanding but showed limited sensitivity. Findings highlight that neural metrics are more sensitive than behavioral tests for detecting interaural mismatch. While CAEP N1P2 amplitudes significantly improved with compensation, other neural measures showed limited effects, suggesting the need for combined temporal and spectral compensation strategies.
双模态刺激结合了耳蜗植入物(CI)和对侧耳的声音输入,通常可以提高语音感知能力,但由于时间不匹配等因素会产生差异。以前,我们利用皮层听觉诱发电位(CAEPs)基于N1潜伏期差异来估计这种不匹配现象。本研究通过评估时间不匹配补偿对语音感知的影响来扩展这一领域的研究。我们对双模态CI用户进行了三项测试:临床测试、补偿时间不匹配测试以及50毫秒不匹配测试。测试指标包括语言理解、瞳孔测量法、皮层听觉诱发电位、选择性注意解码和顶叶α功率。尽管各条件下的语言理解能力保持稳定,但神经指标显示出了更强烈的影响。补偿条件下的CAEP N1P2振幅最高。相位锁定值(PLV)和选择性注意解码有所改善,但缺乏显著性。在50毫秒不匹配的情况下,顶叶α功率增加,表明认知资源的分配。瞳孔测量法与语言理解相关,但显示出有限的敏感性。研究结果强调,对于检测耳间不匹配现象,神经指标的敏感性高于行为测试。虽然CAEP N1P2振幅在补偿条件下显著改善,但其他神经指标的效应有限,这提示我们需要结合时间和光谱补偿策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 15 figures
Summary
本文研究了双模态刺激下,结合耳蜗植入器和另一侧耳朵的声学输入对语音感知的影响。研究通过评估时间不匹配补偿对语音感知的影响,发现尽管语音理解在三种条件下保持稳定,但神经测量显示出更强烈的效果。特别是皮质听觉诱发电位(CAEP)的N1P2振幅在补偿条件下最高。此外,还观察到顶叶α功率在50毫秒不匹配条件下增加,表明认知资源分配的变化。研究结果表明,神经度量比行为测试更能敏感地检测耳间不匹配,并且需要进一步结合时间和频谱补偿策略。
Key Takeaways
- Bimodal stimulation 通过结合耳蜗植入器和另一侧耳朵的声学输入增强语音感知。
- 时间不匹配是影响语音感知的重要因素之一。
- 神经度量(如皮质听觉诱发电位)比行为测试更能敏感地检测耳间不匹配。
- 在时间不匹配补偿条件下,皮质听觉诱发电位的N1P2振幅最高。
- 顶叶α功率在特定条件下增加,反映了认知资源分配的变化。
- 瞳孔测量与语音理解相关,但在检测时间不匹配方面的敏感性有限。
点此查看论文截图

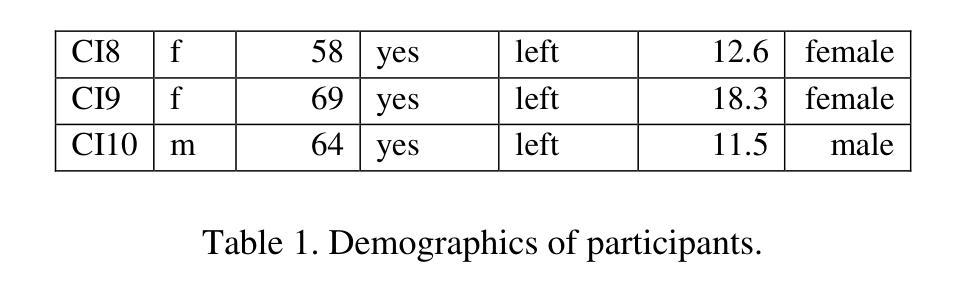
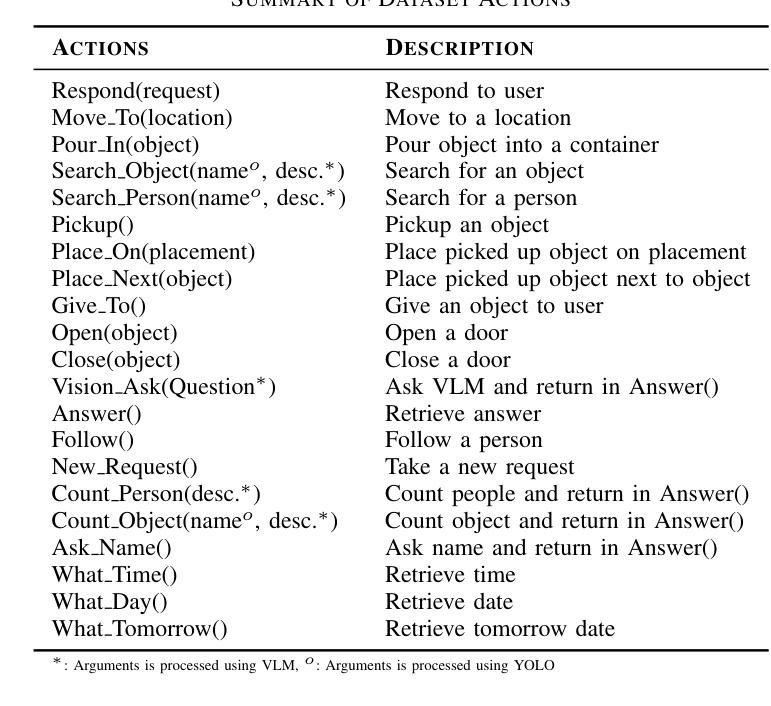
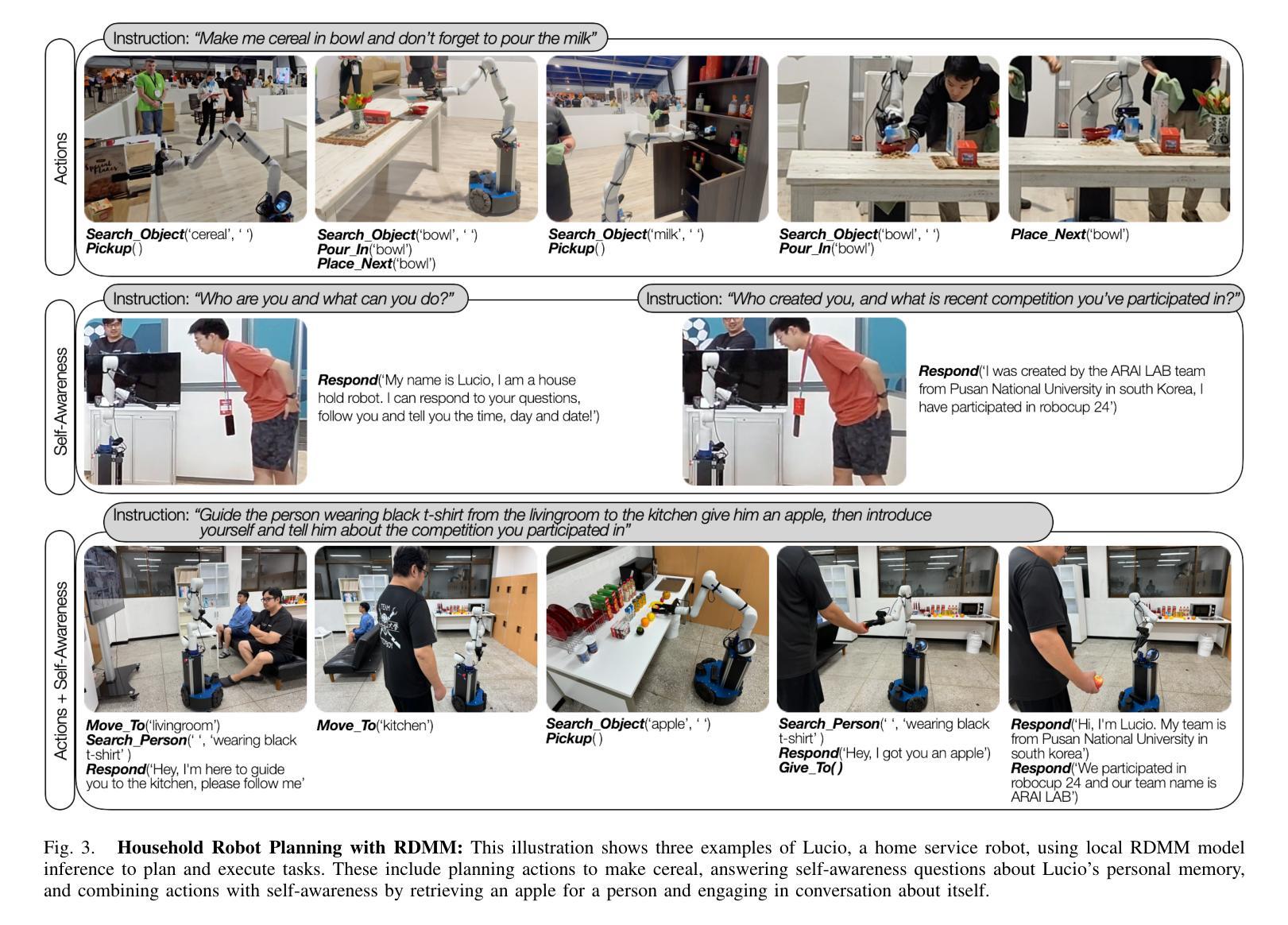
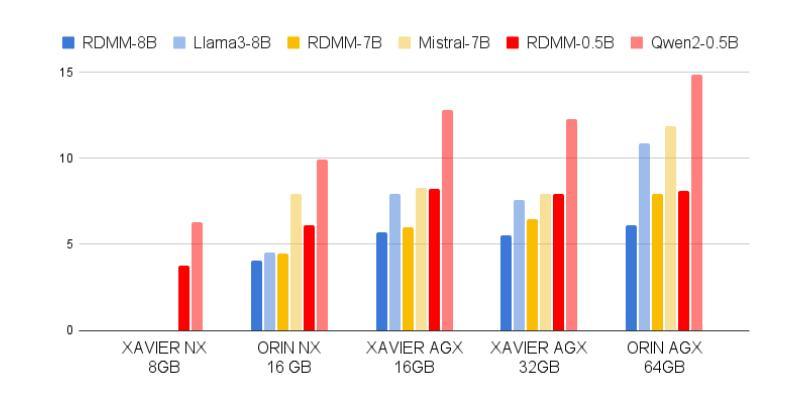
RDMM: Fine-Tuned LLM Models for On-Device Robotic Decision Making with Enhanced Contextual Awareness in Specific Domains
Authors:Shady Nasrat, Myungsu Kim, Seonil Lee, Jiho Lee, Yeoncheol Jang, Seung-joon Yi
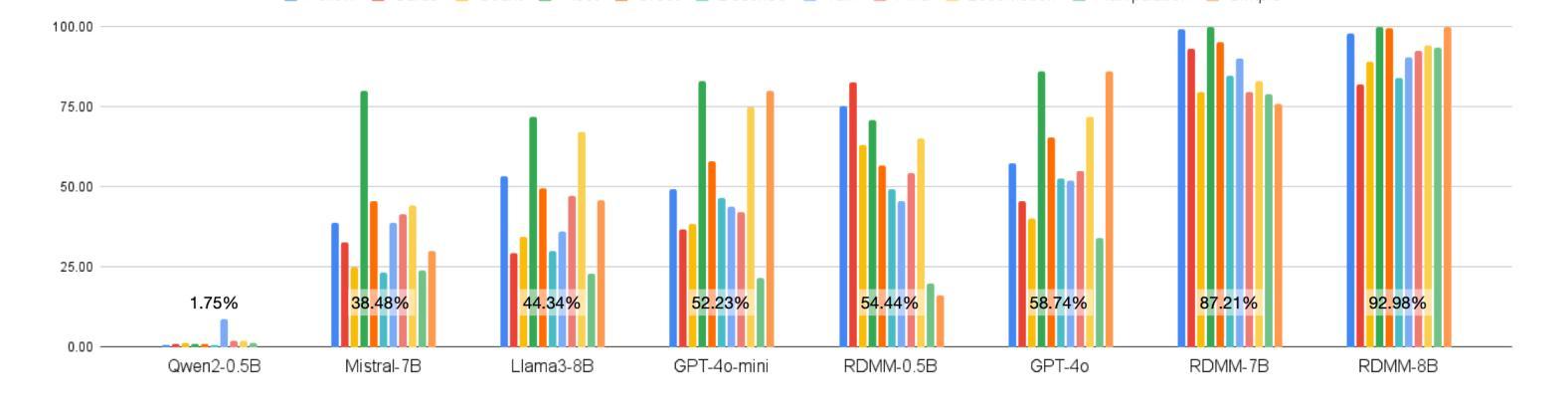
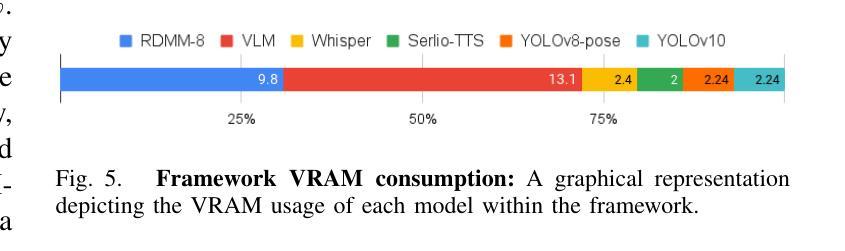
Large language models (LLMs) represent a significant advancement in integrating physical robots with AI-driven systems. We showcase the capabilities of our framework within the context of the real-world household competition. This research introduces a framework that utilizes RDMM (Robotics Decision-Making Models), which possess the capacity for decision-making within domain-specific contexts, as well as an awareness of their personal knowledge and capabilities. The framework leverages information to enhance the autonomous decision-making of the system. In contrast to other approaches, our focus is on real-time, on-device solutions, successfully operating on hardware with as little as 8GB of memory. Our framework incorporates visual perception models equipping robots with understanding of their environment. Additionally, the framework has integrated real-time speech recognition capabilities, thus enhancing the human-robot interaction experience. Experimental results demonstrate that the RDMM framework can plan with an 93% accuracy. Furthermore, we introduce a new dataset consisting of 27k planning instances, as well as 1.3k text-image annotated samples derived from the competition. The framework, benchmarks, datasets, and models developed in this work are publicly available on our GitHub repository at https://github.com/shadynasrat/RDMM.
大型语言模型(LLM)代表了将实体机器人与人工智能驱动系统相结合的重要进步。我们在现实世界的家庭竞赛背景下展示了我们的框架的能力。本研究介绍了一个利用RDMM(机器人决策模型)的框架,该框架在特定领域的上下文中具有决策能力,并意识到其个人知识和能力。该框架利用信息增强系统的自主决策能力。与其他方法相比,我们的重点是在实时设备上解决方案,可在仅有8GB内存的硬件上成功运行。我们的框架结合了视觉感知模型,赋予机器人理解其环境的能力。此外,该框架集成了实时语音识别功能,从而增强了人机互动体验。实验结果表明,RDMM框架的规划准确度可达93%。此外,我们引入了一个新的数据集,包含2.7万个规划实例以及来自竞赛的13万个文本图像注释样本。这项工作中的框架、基准测试、数据集和模型均可在我们的GitHub仓库(https://github.com/shadynasrat/RDMM)上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个利用大型语言模型(LLMs)的框架,该框架结合了物理机器人与人工智能系统。研究展示了一个使用RDMM(机器人决策模型)的框架,该框架能在特定领域进行决策,并意识到其个人知识和能力。框架利用信息提高系统的自主决策能力,关注实时、设备端解决方案,可在仅有8GB内存的硬件上成功运行。此外,框架融合了视觉感知模型,为机器人提供环境理解,并集成了实时语音识别能力,提升人机互动体验。实验结果显示RDMM框架的规划准确率达93%,同时公开了包含2.7万规划实例和一千余个文本图像标注样本的新数据集。相关框架、基准测试、数据集和模型可在GitHub上公开获取。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在集成物理机器人与人工智能系统中发挥了重要作用。
- 研究人员引入了RDMM(机器人决策模型)框架,具有特定领域的决策能力以及对个人知识和能力的意识。
- 该框架利用信息提高了系统的自主决策能力,注重实时、设备端解决方案。
- 框架融合了视觉感知模型,增强了机器人对环境的理解。
- 框架集成了实时语音识别能力,提升了人机互动体验。
- 实验结果显示RDMM框架的规划准确率为93%。
点此查看论文截图

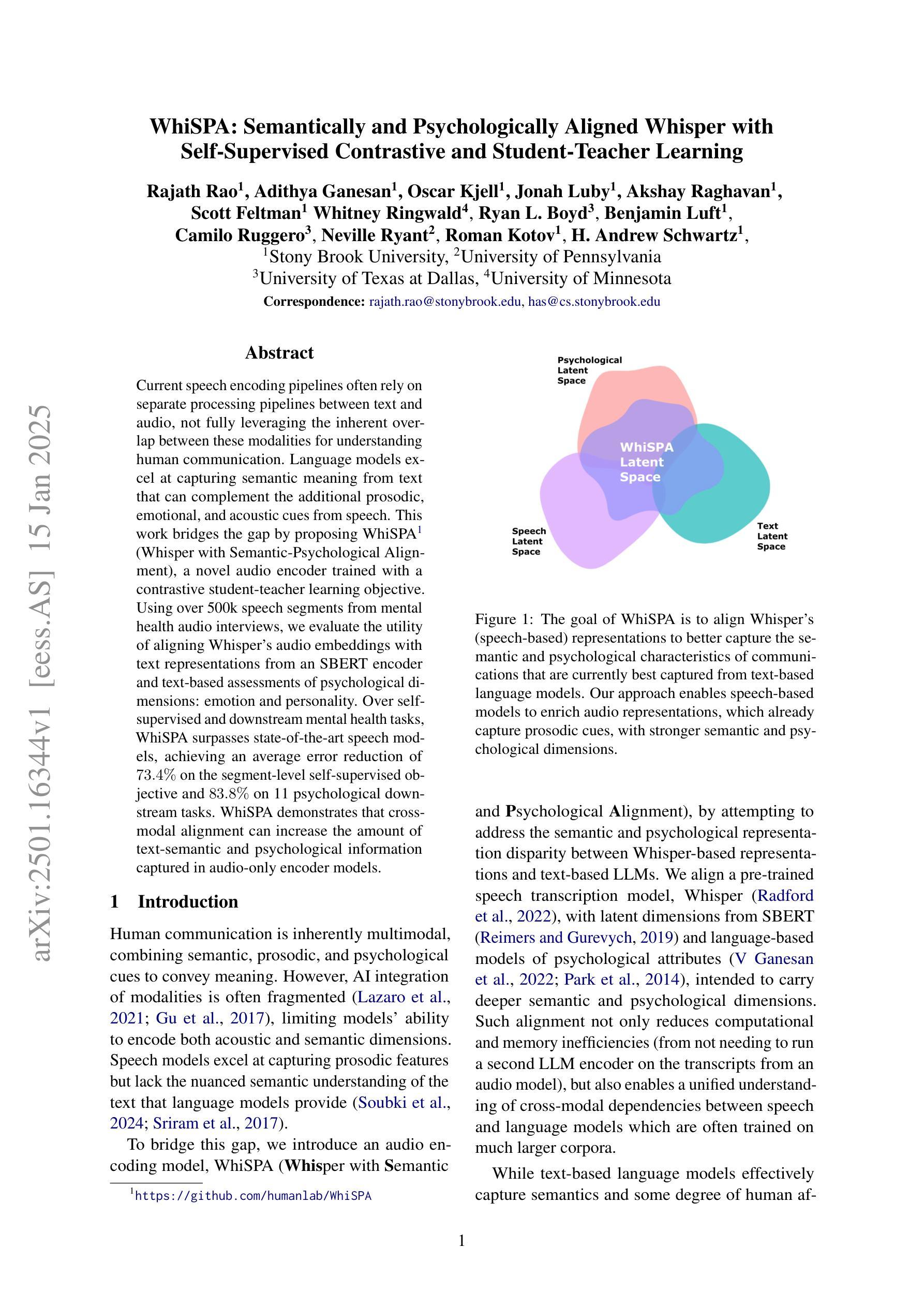
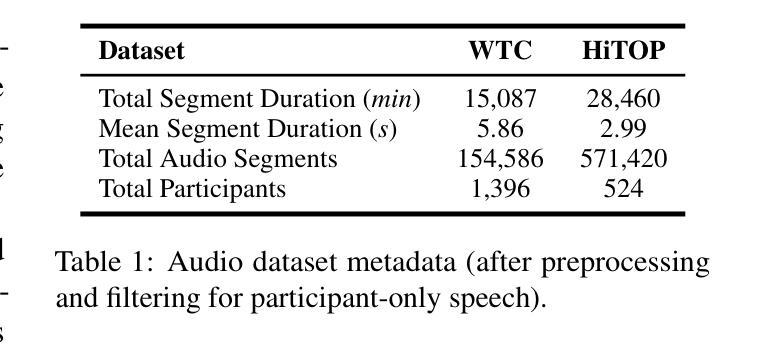
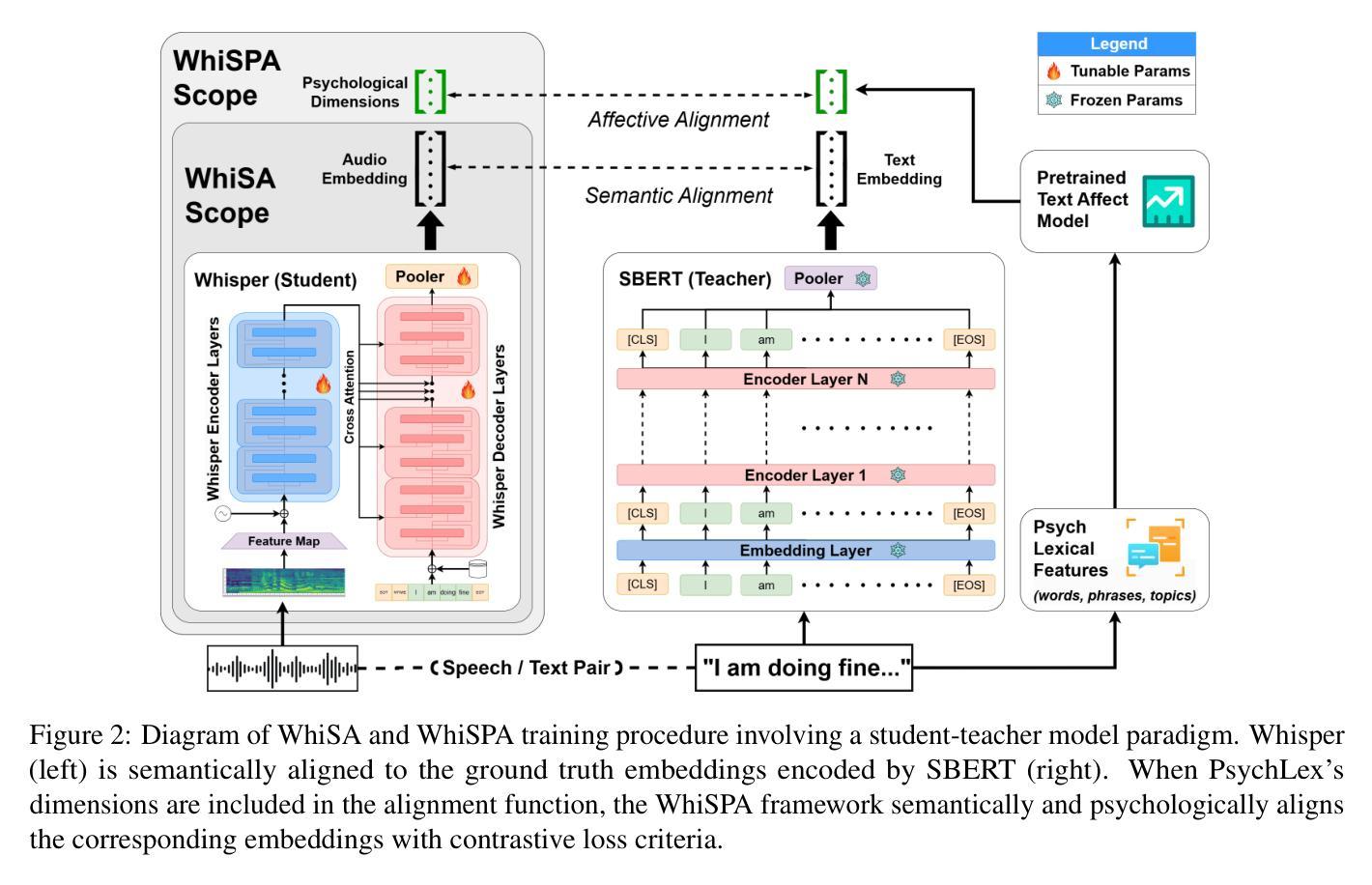
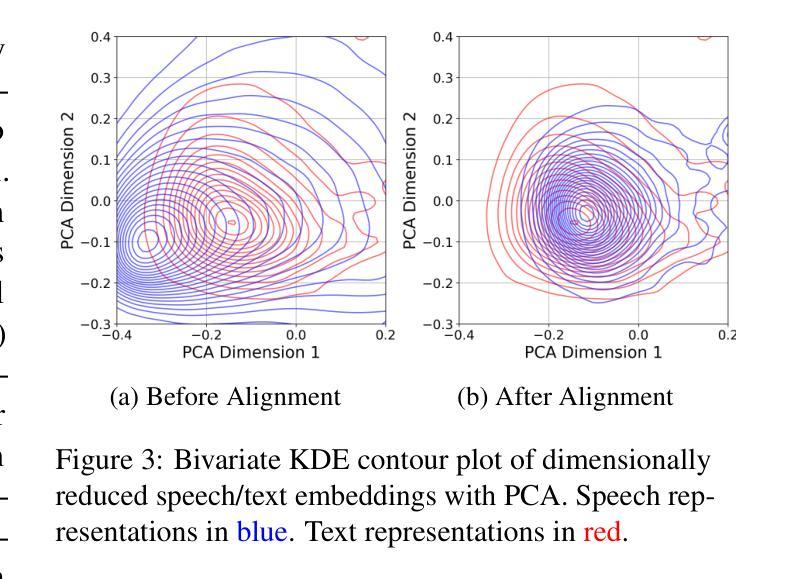
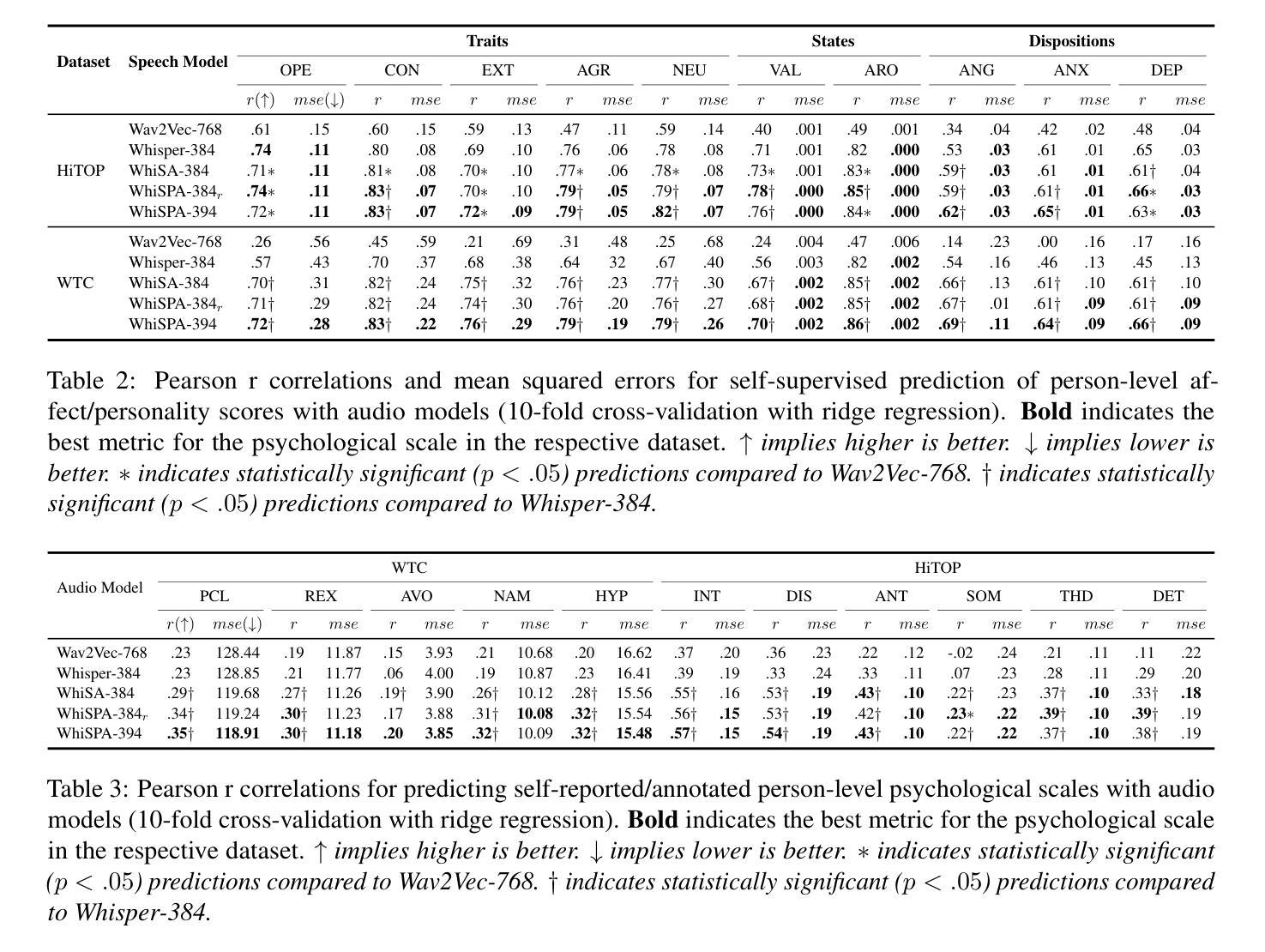
WhiSPA: Semantically and Psychologically Aligned Whisper with Self-Supervised Contrastive and Student-Teacher Learning
Authors:Rajath Rao, Adithya Ganesan, Oscar Kjell, Jonah Luby, Akshay Raghavan, Scott Feltman, Whitney Ringwald, Ryan L. Boyd, Benjamin Luft, Camilo Ruggero, Neville Ryant, Roman Kotov, H. Andrew Schwartz
Current speech encoding pipelines often rely on separate processing pipelines between text and audio, not fully leveraging the inherent overlap between these modalities for understanding human communication. Language models excel at capturing semantic meaning from text that can complement the additional prosodic, emotional, and acoustic cues from speech. This work bridges the gap by proposing WhiSPA (Whisper with Semantic-Psychological Alignment), a novel audio encoder trained with a contrastive student-teacher learning objective. Using over 500k speech segments from mental health audio interviews, we evaluate the utility of aligning Whisper audio embeddings with text representations from an SBERT encoder and text-based assessments of psychological dimensions: emotion and personality. Over self-supervised and downstream mental health tasks, WhiSPA surpasses state-of-the-art speech models, achieving an average error reduction of 73.4% on the segment-level self-supervised objective and 83.8% on 11 psychological downstream tasks. WhiSPA demonstrates that cross-modal alignment can increase the amount of text-semantic and psychological information captured in audio-only encoder models.
当前语音编码管道通常依赖于文本和音频之间的单独处理管道,没有充分利用这两种模式之间在理解人类交流方面的固有重叠。语言模型擅长从文本中捕获语义,可以弥补语音中的附加韵律、情感和声学线索。这项工作通过提出WhiSPA(带有语义心理对齐的耳语)来弥补这一差距,这是一种新型音频编码器,采用对比的学生-教师学习目标进行训练。我们利用来自心理健康音频访谈的超过50万段语音片段,评估将Whisper音频嵌入与来自SBERT编码器的文本表示以及基于文本的心理学维度评估(情感和个性)进行对齐的实用性。在自我监督和下游心理健康任务方面,WhiSPA超越了最先进的语音模型,在分段级别的自我监督目标上实现了平均误差降低73.4%,在11个心理学下游任务上实现了平均误差降低83.8%。WhiSPA证明跨模态对齐可以增加纯音频编码模型中捕获的文本语义和心理信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 6 figures, ACL ARR 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的语音编码管道WhiSPA(带有语义心理对齐的Whisper),该管道结合了文本和音频信息,充分利用两者之间的固有重叠,提高了对人类沟通的理解。通过使用超过50万段心理健康访谈的语音片段进行训练,WhiSPA在自监督学习和下游心理健康任务上的表现超越了现有语音模型。该研究展示了跨模态对齐能提高纯音频编码模型中捕捉文本语义和心理信息的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 当前语音编码管道在文本和音频处理之间存在分离,未能充分利用两者之间的固有重叠。
- 语言模型擅长捕捉文本语义,可补充语音中的语调、情感和声学线索。
- WhiSPA是一种新型音频编码器,通过对比学生-教师学习目进行训练。
- WhiSPA利用心理健康访谈的50万段语音片段进行训练。
- WhiSPA在自监督学习和下游心理健康任务上的表现优于现有语音模型。
- WhiSPA通过跨模态对齐提高了纯音频编码模型捕捉文本语义和心理信息的能力。
点此查看论文截图
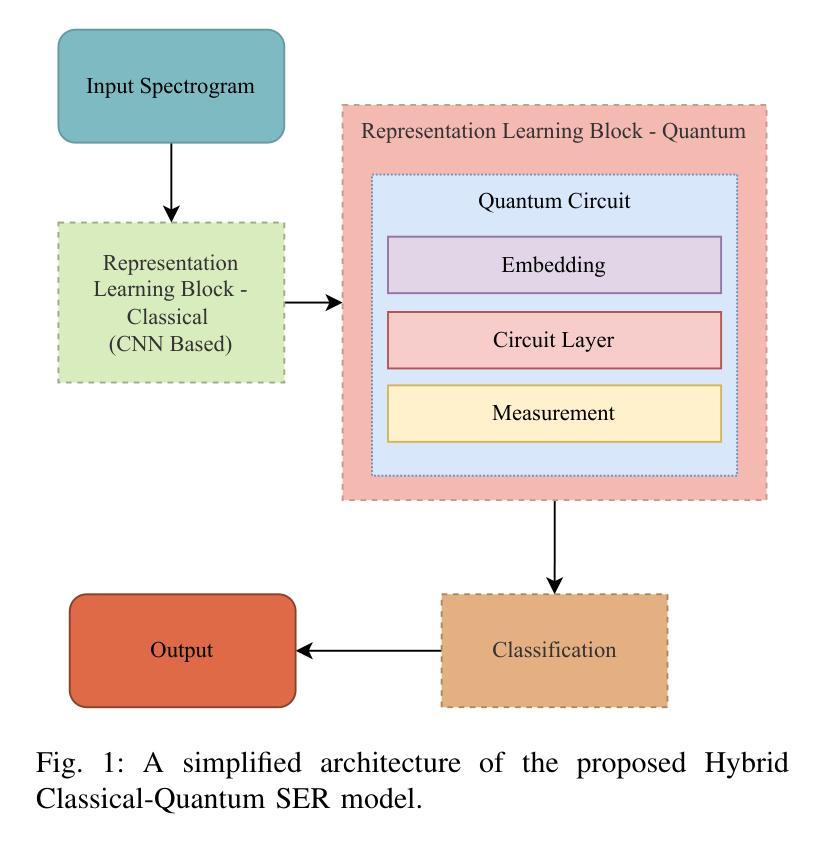
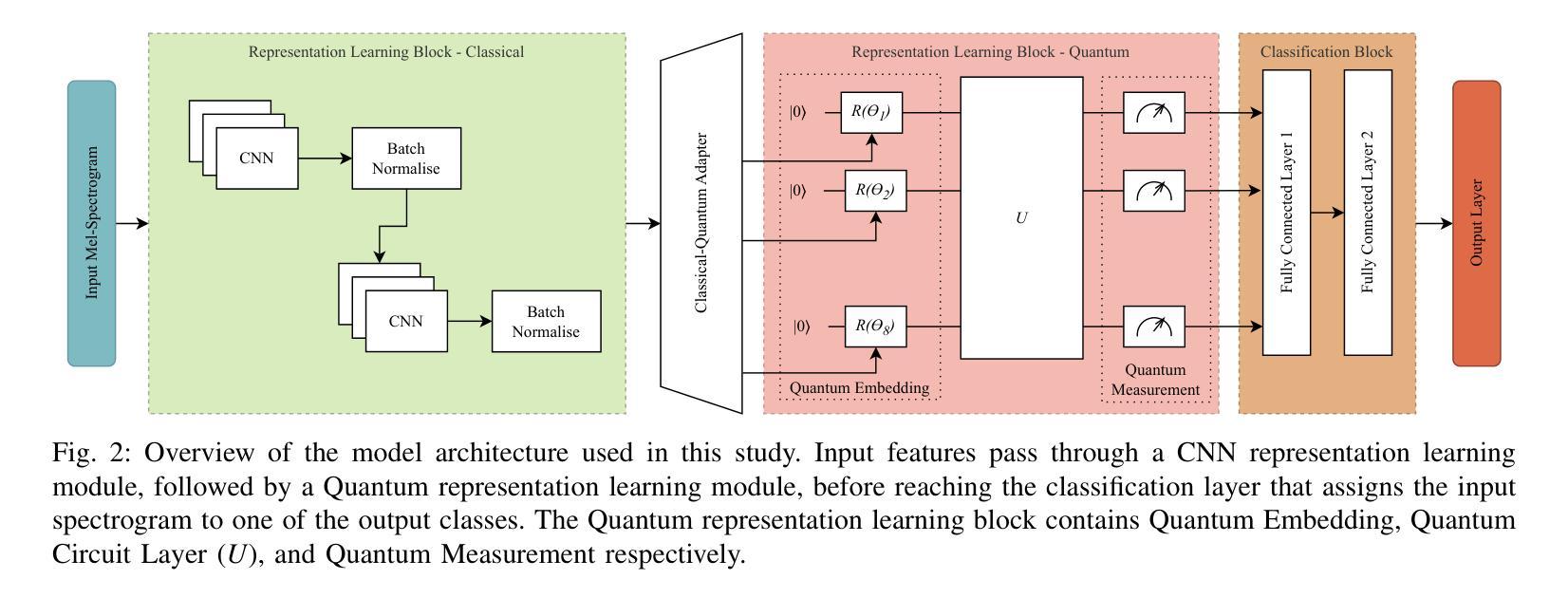
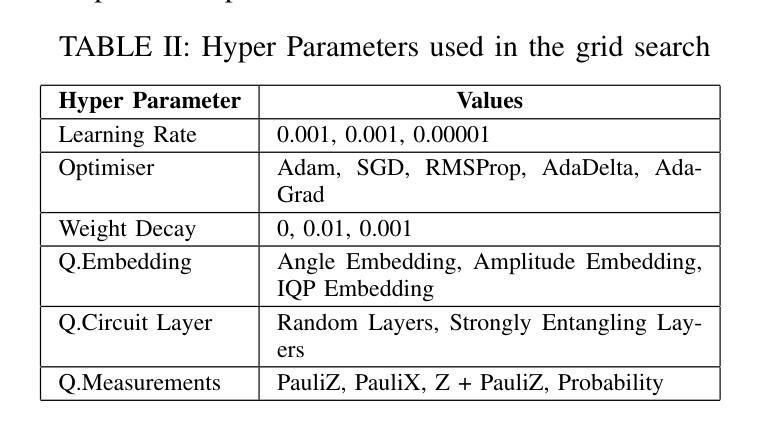
Representation Learning with Parameterised Quantum Circuits for Advancing Speech Emotion Recognition
Authors:Thejan Rajapakshe, Rajib Rana, Farina Riaz, Sara Khalifa, Björn W. Schuller
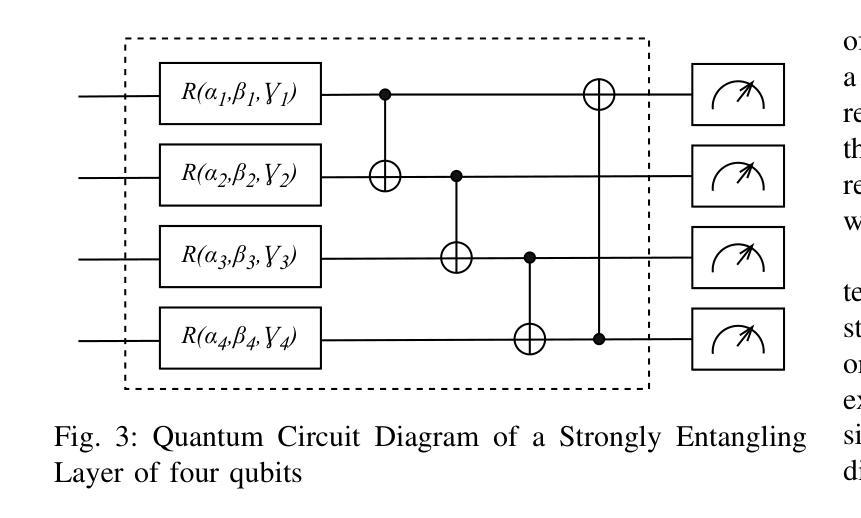
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) is a complex and challenging task in human-computer interaction due to the intricate dependencies of features and the overlapping nature of emotional expressions conveyed through speech. Although traditional deep learning methods have shown effectiveness, they often struggle to capture subtle emotional variations and overlapping states. This paper introduces a hybrid classical-quantum framework that integrates Parameterised Quantum Circuits (PQCs) with conventional Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures. By leveraging quantum properties such as superposition and entanglement, the proposed model enhances feature representation and captures complex dependencies more effectively than classical methods. Experimental evaluations conducted on benchmark datasets, including IEMOCAP, RECOLA, and MSP-Improv, demonstrate that the hybrid model achieves higher accuracy in both binary and multi-class emotion classification while significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters. While a few existing studies have explored the feasibility of using Quantum Circuits to reduce model complexity, none have successfully shown how they can enhance accuracy. This study is the first to demonstrate that Quantum Circuits has the potential to improve the accuracy of SER. The findings highlight the promise of QML to transform SER, suggesting a promising direction for future research and practical applications in emotion-aware systems.
语音情绪识别(SER)是人与计算机交互中的一个复杂且充满挑战的任务,原因在于语音特征之间的复杂依赖关系和情感表达的重叠性。虽然传统的深度学习方法已经显示出其有效性,但它们往往难以捕捉微妙的情感变化和重叠状态。本文介绍了一种混合的经典-量子框架,该框架将参数化量子电路(PQC)与传统卷积神经网络(CNN)架构相结合。通过利用量子特性,如叠加和纠缠,所提出的模型可以更好地表示特征并更有效地捕捉复杂的依赖关系,相比传统方法更具优势。在IEMOCAP、RECOLA和MSP-Improv等基准数据集上进行的实验评估表明,混合模型在二元和多元情感分类中都实现了更高的精度,同时显著减少了可训练参数的数量。虽然已有一些研究探讨了使用量子电路减少模型复杂性的可行性,但没有任何研究成功证明其可以提高精度。本研究首次证明了量子电路在提高SER精度方面的潜力。研究结果表明,量子机器学习(QML)在变革SER方面具有巨大潜力,为未来的研究和情感感知系统的实际应用指明了有前景的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语音情感识别是一项人机交互中的复杂任务,面临特征依赖复杂和情感表达重叠等挑战。本文提出了一种混合的经典-量子框架,将参数化量子电路与传统卷积神经网络架构相结合。利用量子叠加和纠缠等特性,该模型提高了特征表示能力,更有效地捕捉了复杂依赖关系。在IEMOCAP、RECOLA和MSP-Improv等基准数据集上的实验评估表明,混合模型在二元和多类情感分类中取得了更高的精度,并显著减少了可训练参数的数量。本研究首次展示了量子电路在提高语音情感识别准确率方面的潜力,突出了量子机器学习在该领域的希望。
Key Takeaways
- 语音情感识别是一项复杂的任务,因为特征依赖复杂且情感表达重叠。
- 传统深度学习方法在捕捉细微情感变化和重叠状态方面存在挑战。
- 本文提出了一种混合的经典-量子框架,结合了参数化量子电路和卷积神经网络。
- 利用量子叠加和纠缠特性,该模型提高了特征表示能力并更有效地捕捉复杂依赖关系。
- 实验评估表明,混合模型在情感分类上实现了更高的精度,并减少了可训练参数数量。
- 该研究首次展示了量子电路在语音情感识别中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图