⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-30 更新
Modulating CNN Features with Pre-Trained ViT Representations for Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Authors:Xiangyu Gao, Yu Dai, Benliu Qiu, Hongliang Li
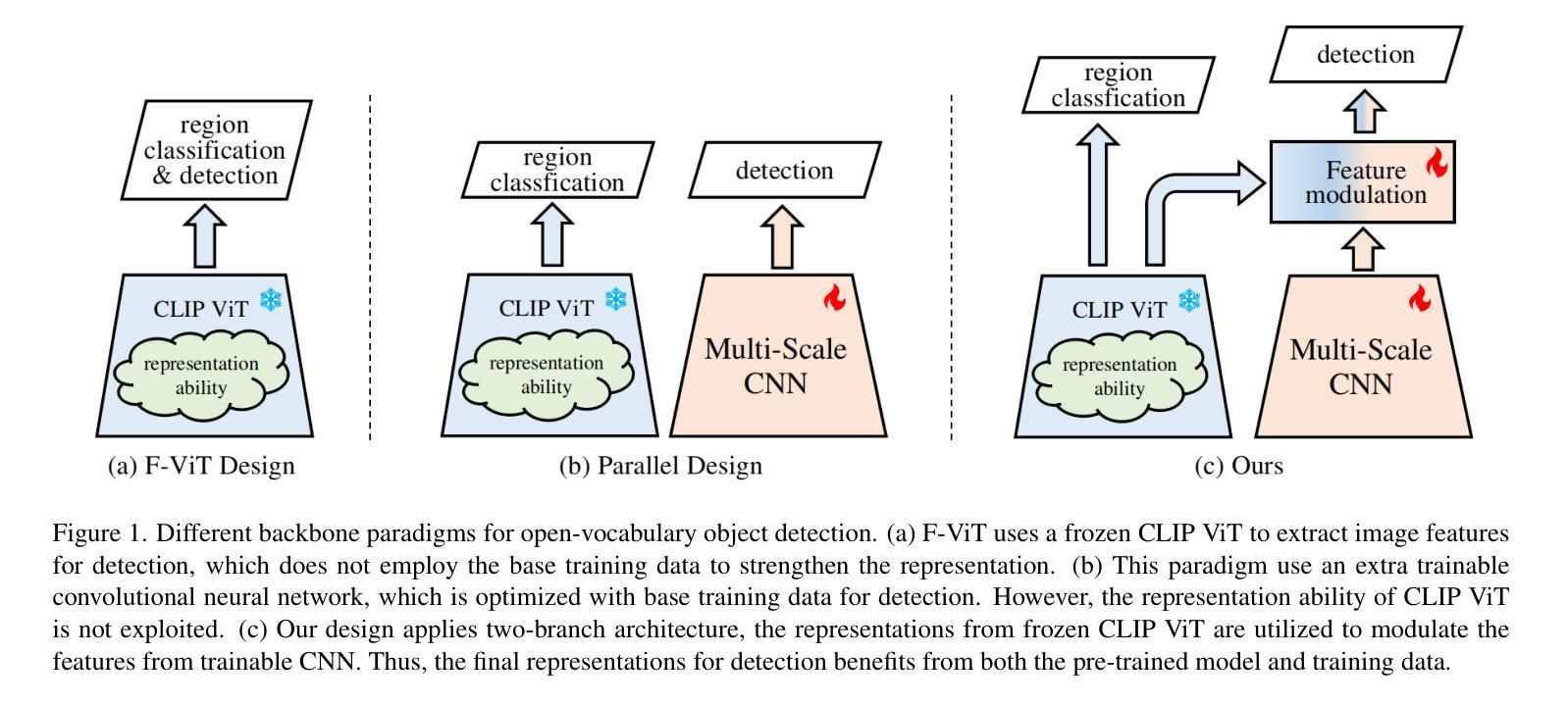
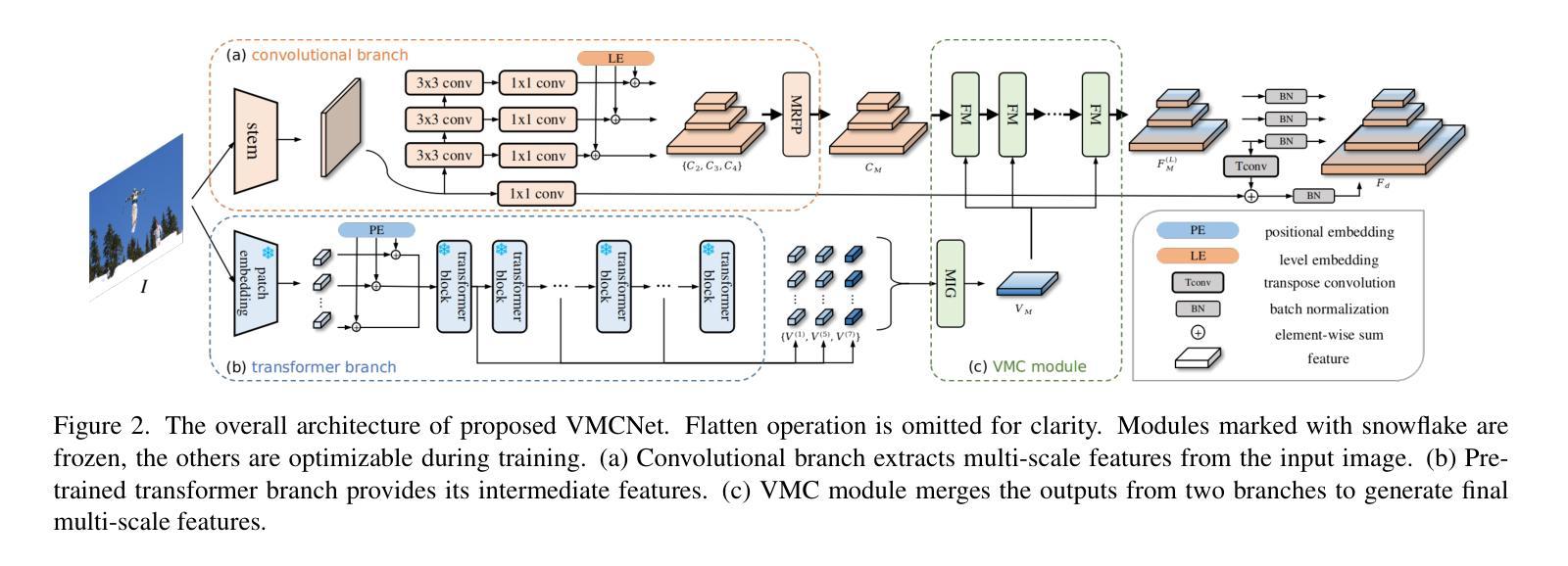
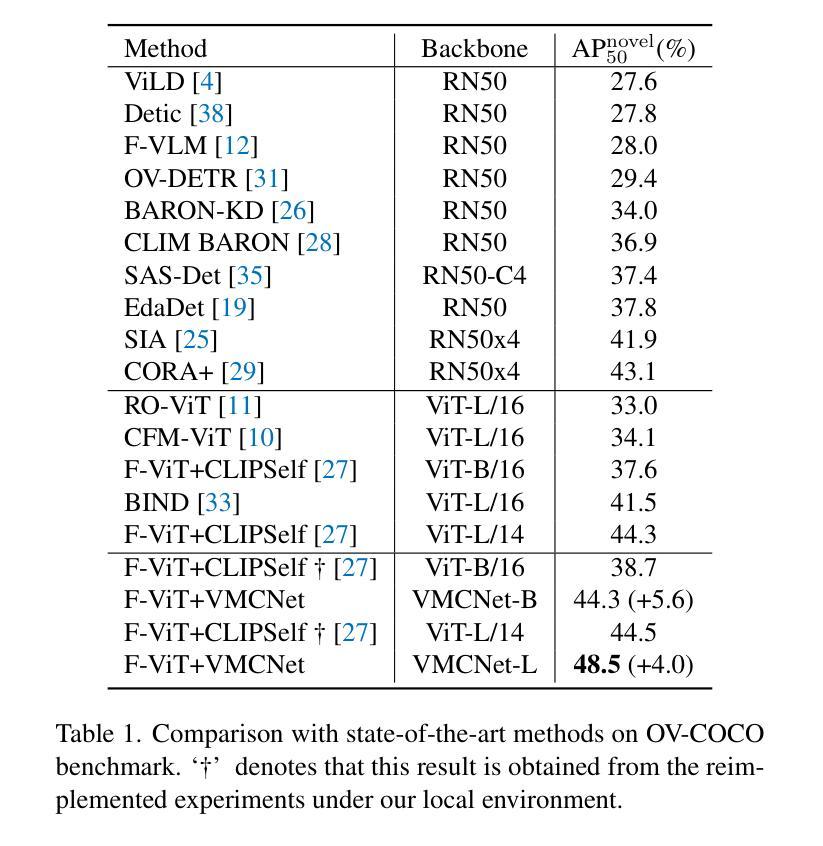
Owing to large-scale image-text contrastive training, pre-trained vision language model (VLM) like CLIP shows superior open-vocabulary recognition ability. Most existing open-vocabulary object detectors attempt to utilize the pre-trained VLM to attain generative representation. F-ViT uses the pre-trained visual encoder as the backbone network and freezes it during training. However, the frozen backbone doesn’t benefit from the labeled data to strengthen the representation. Therefore, we propose a novel two-branch backbone network design, named as ViT-Feature-Modulated Multi-Scale Convolutional network (VMCNet). VMCNet consists of a trainable convolutional branch, a frozen pre-trained ViT branch and a feature modulation module. The trainable CNN branch could be optimized with labeled data while the frozen pre-trained ViT branch could keep the representation ability derived from large-scale pre-training. Then, the proposed feature modulation module could modulate the multi-scale CNN features with the representations from ViT branch. With the proposed mixed structure, detector is more likely to discover novel categories. Evaluated on two popular benchmarks, our method boosts the detection performance on novel category and outperforms the baseline. On OV-COCO, the proposed method achieves 44.3 AP${50}^{\mathrm{novel}}$ with ViT-B/16 and 48.5 AP${50}^{\mathrm{novel}}$ with ViT-L/14. On OV-LVIS, VMCNet with ViT-B/16 and ViT-L/14 reaches 27.8 and 38.4 mAP$_{r}$.
由于大规模图像文本对比训练,预训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)表现出卓越的开放词汇识别能力。现有的大多数开放词汇对象检测器试图利用预训练的VLM来获得生成表示。F-ViT使用预训练的视觉编码器作为主干网络,并在训练过程中冻结它。然而,冻结的主干网络不能从标记数据中受益,无法加强表示能力。因此,我们提出了一种新的双分支主干网络设计,称为ViT特征调制多尺度卷积网络(VMCNet)。VMCNet由一个可训练的卷积分支、一个冻结的预训练ViT分支和一个特征调制模块组成。可训练的CNN分支可以优化标记数据,而冻结的预训练ViT分支可以保持从大规模预训练中获得的表示能力。然后,所提出的特征调制模块可以调制多尺度CNN特征与ViT分支的表示。通过混合结构,检测器更可能发现新类别。在两个流行的基准测试上,我们的方法在新型类别检测性能上有所提升并超越了基线。在OV-COCO上,所提方法使用ViT-B/16达到44.3 AP_{50}^{novel},使用ViT-L/14达到48.5 AP_{50}^{novel}。在OV-LVIS上,VMCNet与ViT-B/16和ViT-L/14分别达到了27.8和38.4的mAP_{r}。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于大规模图像文本对比训练的预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在开放词汇识别方面的优势。现有开放词汇对象检测器大多尝试利用预训练VLM来获得生成表示。F-ViT使用预训练的视觉编码器作为骨干网络并在训练期间冻结它。然而,冻结的骨干网络无法从标记数据中受益以增强表示能力。为此,本文提出了一种新的双分支骨干网络设计,名为ViT特征调制多尺度卷积网络(VMCNet)。VMCNet由一个可训练的卷积分支、一个冻结的预训练ViT分支和特征调制模块组成。可训练的CNN分支可以利用标记数据进行优化,而冻结的预训练ViT分支可以保持从大规模预训练中得到的表现能力。然后,所提出的特征调制模块可以调制多尺度CNN特征与ViT分支的表示。通过这种混合结构,检测器更可能发现新类别。在流行的基准测试中,我们的方法在新型类别检测性能上有所提升并超越了基线。在OV-COCO上,所提方法达到44.3 AP_{50}^{novel}(使用ViT-B/16)和48.5 AP_{50}^{novel}(使用ViT-L/14)。在OV-LVIS上,VMCNet使用ViT-B/16和ViT-L/14达到27.8和38.4 mAP_{r}。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)通过大规模图像文本对比训练展现出优秀的开放词汇识别能力。
- 现有开放词汇对象检测器倾向于利用预训练VLM来获得生成表示。
- F-ViT使用预训练视觉编码器作为骨干网络,但在训练期间冻结它,无法充分利用标记数据强化表示。
- 提出的VMCNet包含可训练的卷积分支、冻结的预训练ViT分支和特征调制模块。
- 可训练CNN分支利用标记数据优化,而预训练ViT分支保持从大规模预训练中获得的表现能力。
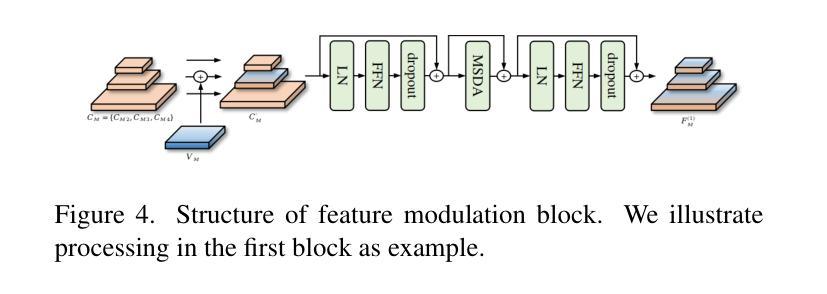
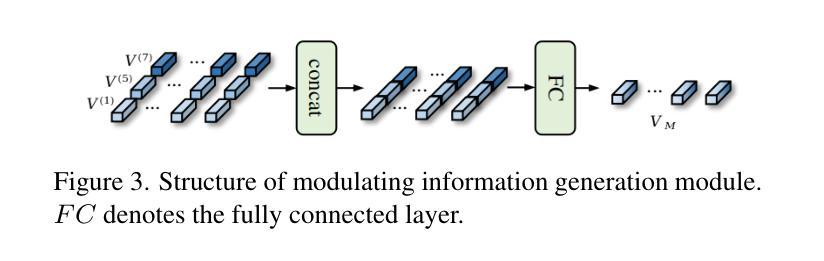
- 特征调制模块结合了多尺度CNN特征与ViT分支的表示。
点此查看论文截图

Privacy-Preserving Personalized Federated Prompt Learning for Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Linh Tran, Wei Sun, Stacy Patterson, Ana Milanova
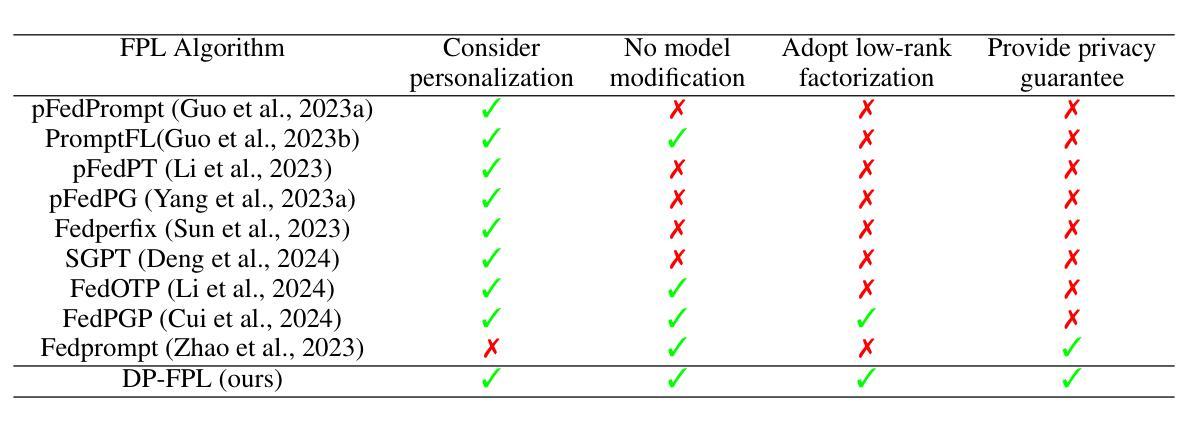
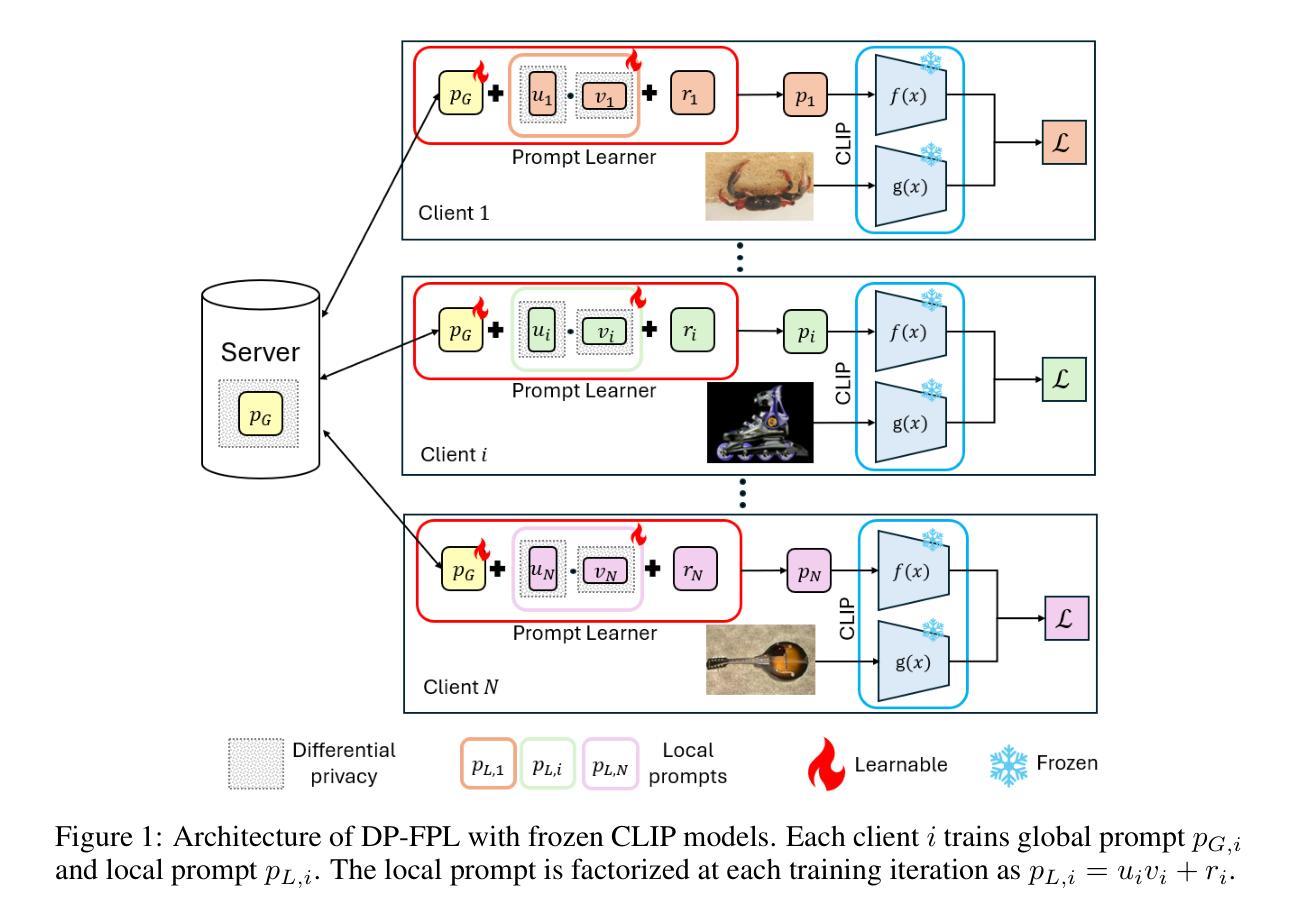
Multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) are pivotal in revolutionizing customer support and operations by integrating multiple modalities such as text, images, and audio. Federated Prompt Learning (FPL) is a recently proposed approach that combines pre-trained multimodal LLMs such as vision-language models with federated learning to create personalized, privacy-preserving AI systems. However, balancing the competing goals of personalization, generalization, and privacy remains a significant challenge. Over-personalization can lead to overfitting, reducing generalizability, while stringent privacy measures, such as differential privacy, can hinder both personalization and generalization. In this paper, we propose a Differentially Private Federated Prompt Learning (DP-FPL) approach to tackle this challenge by leveraging a low-rank adaptation scheme to capture generalization while maintaining a residual term that preserves expressiveness for personalization. To ensure privacy, we introduce a novel method where we apply local differential privacy to the two low-rank components of the local prompt, and global differential privacy to the global prompt. Our approach mitigates the impact of privacy noise on the model performance while balancing the tradeoff between personalization and generalization. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach over other benchmarks.
多模态大型语言模型(LLM)通过整合文本、图像和音频等多种模态,在革新客户支持和运营方面发挥着关键作用。联邦提示学习(FPL)是一种最近提出的方法,它将预训练的多模态LLM(如视觉语言模型)与联邦学习相结合,以创建个性化、保护隐私的人工智能系统。然而,在个性化、通用化和隐私之间取得平衡仍然是一个巨大的挑战。过度个性化可能导致过度拟合,降低通用性,而严格的隐私措施(如差分隐私)可能会阻碍个性化和通用化。在本文中,我们提出了一种差分私有联邦提示学习(DP-FPL)方法来解决这一挑战,该方法利用低阶适应方案来捕捉通用性,同时保持一个残余项,以保留个性化的表现力。为确保隐私,我们引入了一种新方法,对本地提示的两个低阶组件应用本地差分隐私,对全局提示应用全局差分隐私。我们的方法减轻了隐私噪声对模型性能的影响,在个性化与通用化之间取得了平衡。大量实验证明我们的方法在其他基准测试上的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025 main conference track
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)通过整合文本、图像和音频等多种模式,正在客户支持和运营领域掀起革命。联邦提示学习(FPL)是一种结合预训练的多模态LLMs(如视觉语言模型)和联邦学习的方法,可创建个性化、保护隐私的人工智能系统。然而,平衡个性化、通用化和隐私这三个相互竞争的目标仍然是一个巨大挑战。过度个性化可能导致过度拟合,降低通用性,而严格的隐私措施(如差分隐私)可能会阻碍个性化和通用化。本文提出了一种差分私有联邦提示学习(DP-FPL)方法,通过利用低秩适应方案来捕捉通用性,同时保持保留术语以保留个性化来解决这一挑战。为确保隐私,我们引入了一种新方法,对局部提示的两个低秩组件应用本地差分隐私,对全局提示应用全局差分隐私。我们的方法减轻了隐私噪声对模型性能的影响,并在个性化和通用化之间取得了平衡。大量实验证明我们的方法在其他基准测试上的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)整合文本、图像和音频,正在改变客户支持和运营。
- 联邦提示学习(FPL)结合预训练LLMs和联邦学习,实现个性化且保护隐私的AI系统。
- 平衡个性化、通用化和隐私是核心挑战,需避免过度个性化导致的过度拟合问题。
- 严格隐私措施如差分隐私可能阻碍个性化和通用化之间的平衡。
- 提出的DP-FPL方法利用低秩适应方案捕捉通用性并保留个性化表达。
- 通过将本地差分隐私应用于局部提示的低秩组件,同时应用全局差分隐私于全局提示来确保隐私。
点此查看论文截图

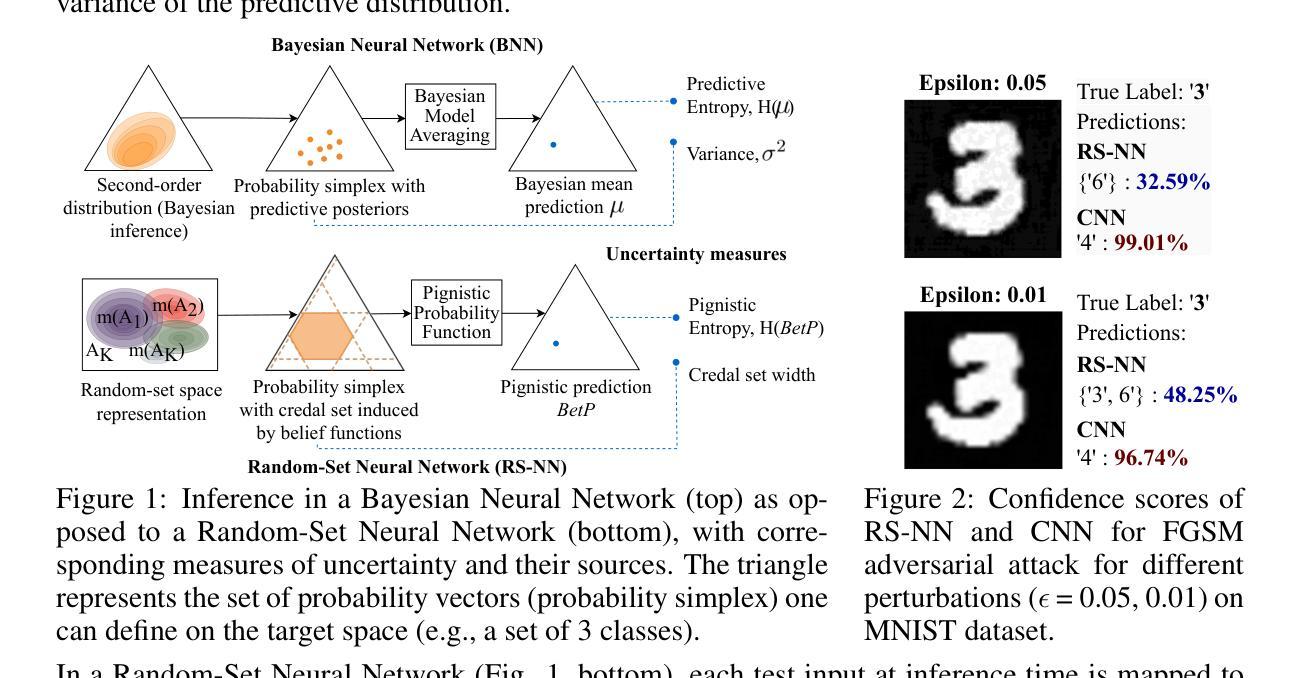
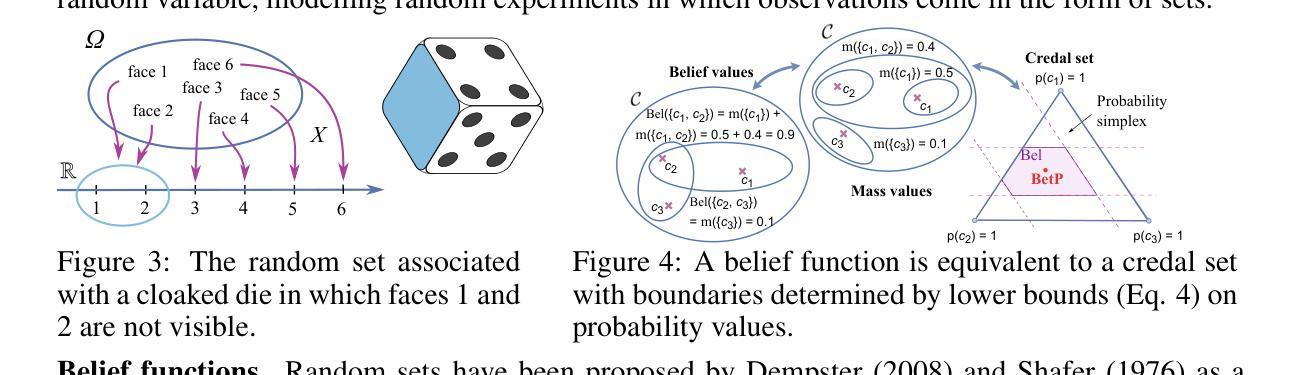
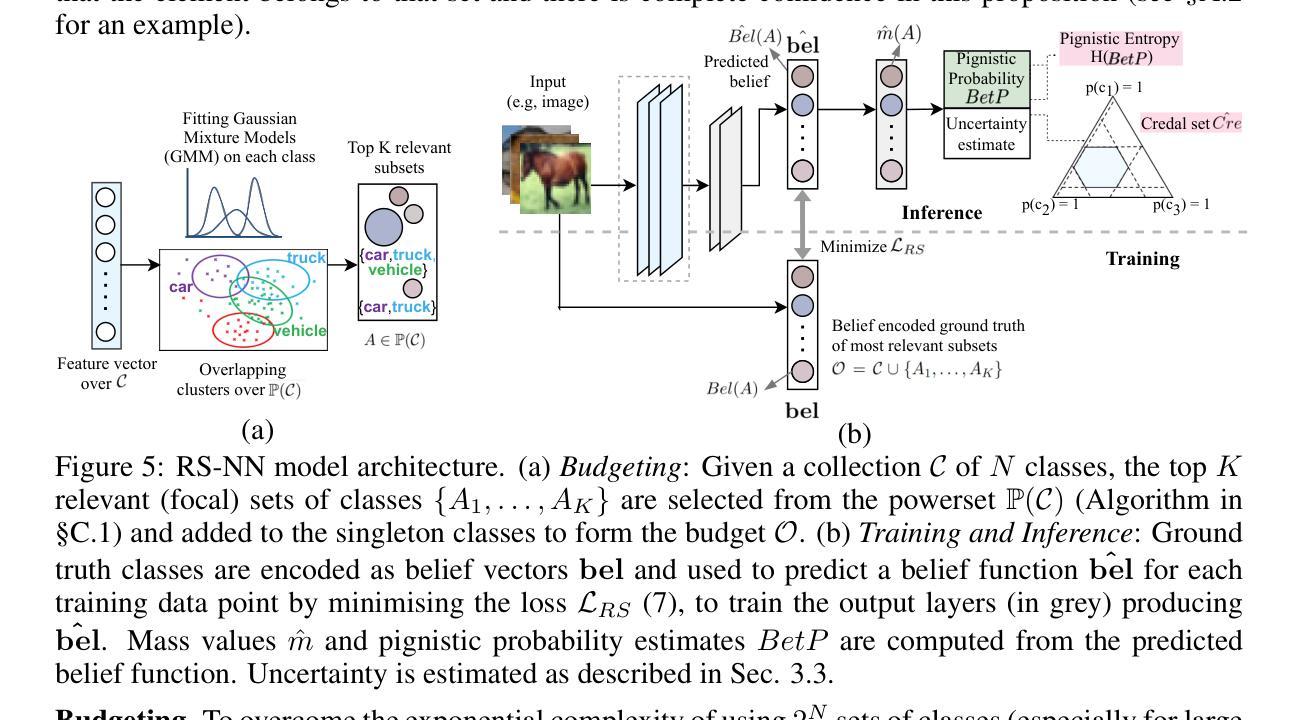
Random-Set Neural Networks (RS-NN)
Authors:Shireen Kudukkil Manchingal, Muhammad Mubashar, Kaizheng Wang, Keivan Shariatmadar, Fabio Cuzzolin
Machine learning is increasingly deployed in safety-critical domains where erroneous predictions may lead to potentially catastrophic consequences, highlighting the need for learning systems to be aware of how confident they are in their own predictions: in other words, ‘to know when they do not know’. In this paper, we propose a novel Random-Set Neural Network (RS-NN) approach to classification which predicts belief functions (rather than classical probability vectors) over the class list using the mathematics of random sets, i.e., distributions over the collection of sets of classes. RS-NN encodes the ‘epistemic’ uncertainty induced by training sets that are insufficiently representative or limited in size via the size of the convex set of probability vectors associated with a predicted belief function. Our approach outperforms state-of-the-art Bayesian and Ensemble methods in terms of accuracy, uncertainty estimation and out-of-distribution (OoD) detection on multiple benchmarks (CIFAR-10 vs SVHN/Intel-Image, MNIST vs FMNIST/KMNIST, ImageNet vs ImageNet-O). RS-NN also scales up effectively to large-scale architectures (e.g. WideResNet-28-10, VGG16, Inception V3, EfficientNetB2 and ViT-Base-16), exhibits remarkable robustness to adversarial attacks and can provide statistical guarantees in a conformal learning setting.
机器学习越来越多地应用在安全关键领域,错误预测可能导致灾难性后果,因此学习系统需要意识到自己对预测的信心程度变得至关重要,即“知道它们不知道的时候”。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的随机集神经网络(RS-NN)分类方法,该方法使用随机集的数学理论预测类别列表上的信念函数(而非传统的概率向量)。RS-NN通过预测信念函数相关的概率向量凸集的大小,对由训练集引起的不充分代表性或规模有限导致的“知识论”不确定性进行编码。我们的方法在多个基准测试(CIFAR-10与SVHN/Intel-Image、MNIST与FMNIST/KMNIST、ImageNet与ImageNet-O)上的准确性、不确定性估计和超出分布检测方面均优于最先进的贝叶斯和集成方法。RS-NN还能有效地扩展到大规模架构(如WideResNet-28-10、VGG16、Inception V3、EfficientNetB2和ViT-Base-16),对对抗性攻击表现出惊人的稳健性,并在符合学习环境中提供统计保证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at the Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)
Summary
本论文提出了一种新型的随机集神经网络(RS-NN)分类方法,该方法通过随机集的数学原理预测信念函数(而非传统的概率向量)。RS-NN通过训练集的不充分代表性或规模限制所导致的“认知”不确定性进行编码,通过预测的信念函数相关的概率向量凸集的大小来体现这种不确定性。RS-NN在多组基准测试(如CIFAR-10与SVHN/Intel-Image、MNIST与FMNIST/KMNIST、ImageNet与ImageNet-O)中的准确性、不确定性估计和域外检测等方面均优于现有的Bayesian和Ensemble方法。此外,RS-NN在大型架构(如WideResNet-28-10、VGG16、Inception V3、EfficientNetB2和ViT-Base-16)中可有效扩展,对对抗性攻击表现出惊人的稳健性,并在合规学习环境中提供统计保障。
Key Takeaways
- 本论文提出了随机集神经网络(RS-NN)分类方法,通过预测信念函数来处理机器学习中的不确定性。
- RS-NN利用随机集的数学原理,将预测建立在集合概率分布之上,而非单一的概率向量。
- RS-NN能有效编码由训练集的不充分代表性或规模限制所导致的认知不确定性。
- 在多个基准测试中,RS-NN在准确性、不确定性估计和域外检测方面均优于现有方法。
- RS-NN具有良好的可扩展性,适用于大型神经网络架构。
- RS-NN对对抗性攻击表现出强大的稳健性。
- RS-NN可在合规学习环境中提供统计保障。
点此查看论文截图