⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-31 更新
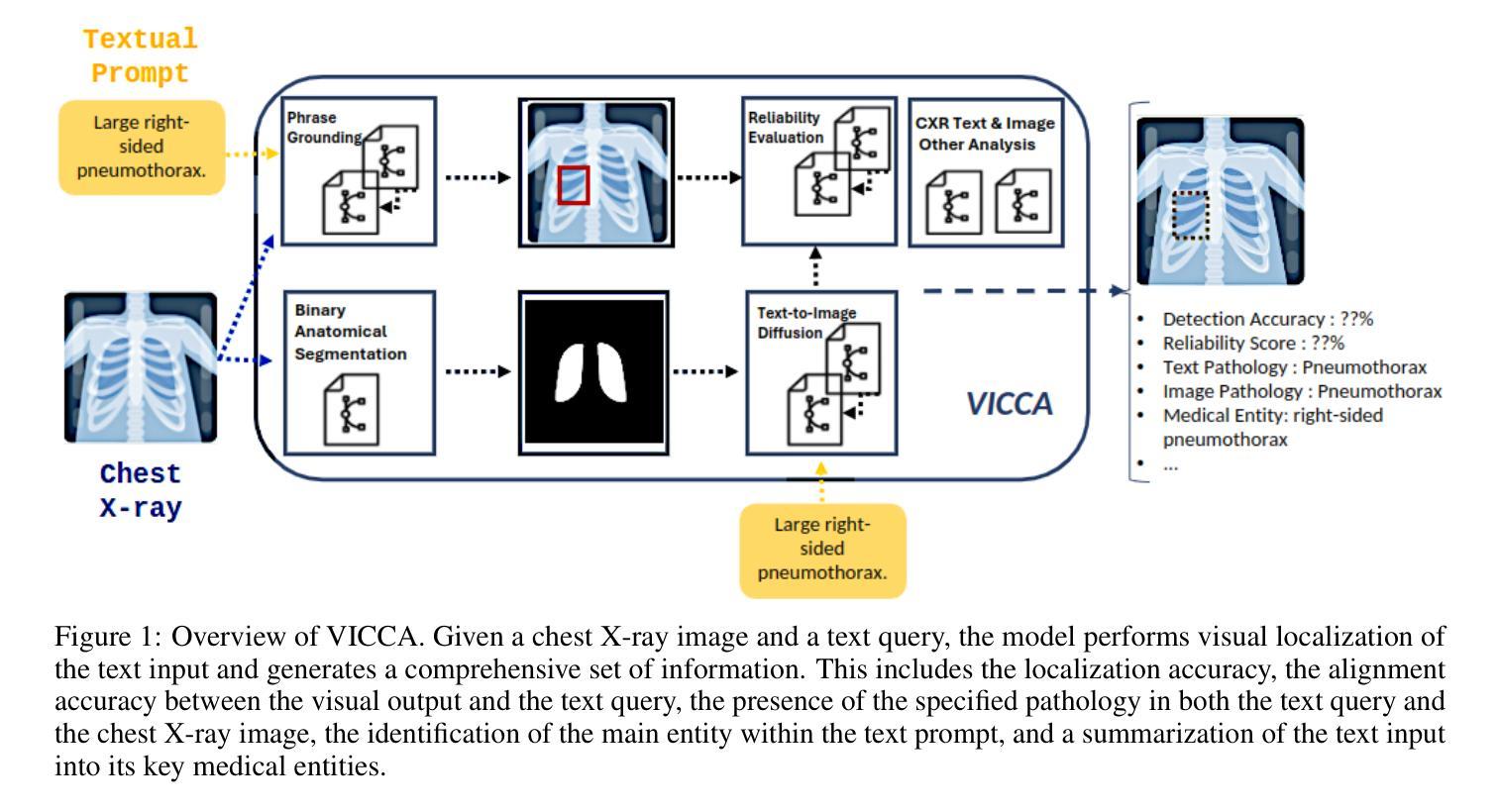
VICCA: Visual Interpretation and Comprehension of Chest X-ray Anomalies in Generated Report Without Human Feedback
Authors:Sayeh Gholipour Picha, Dawood Al Chanti, Alice Caplier
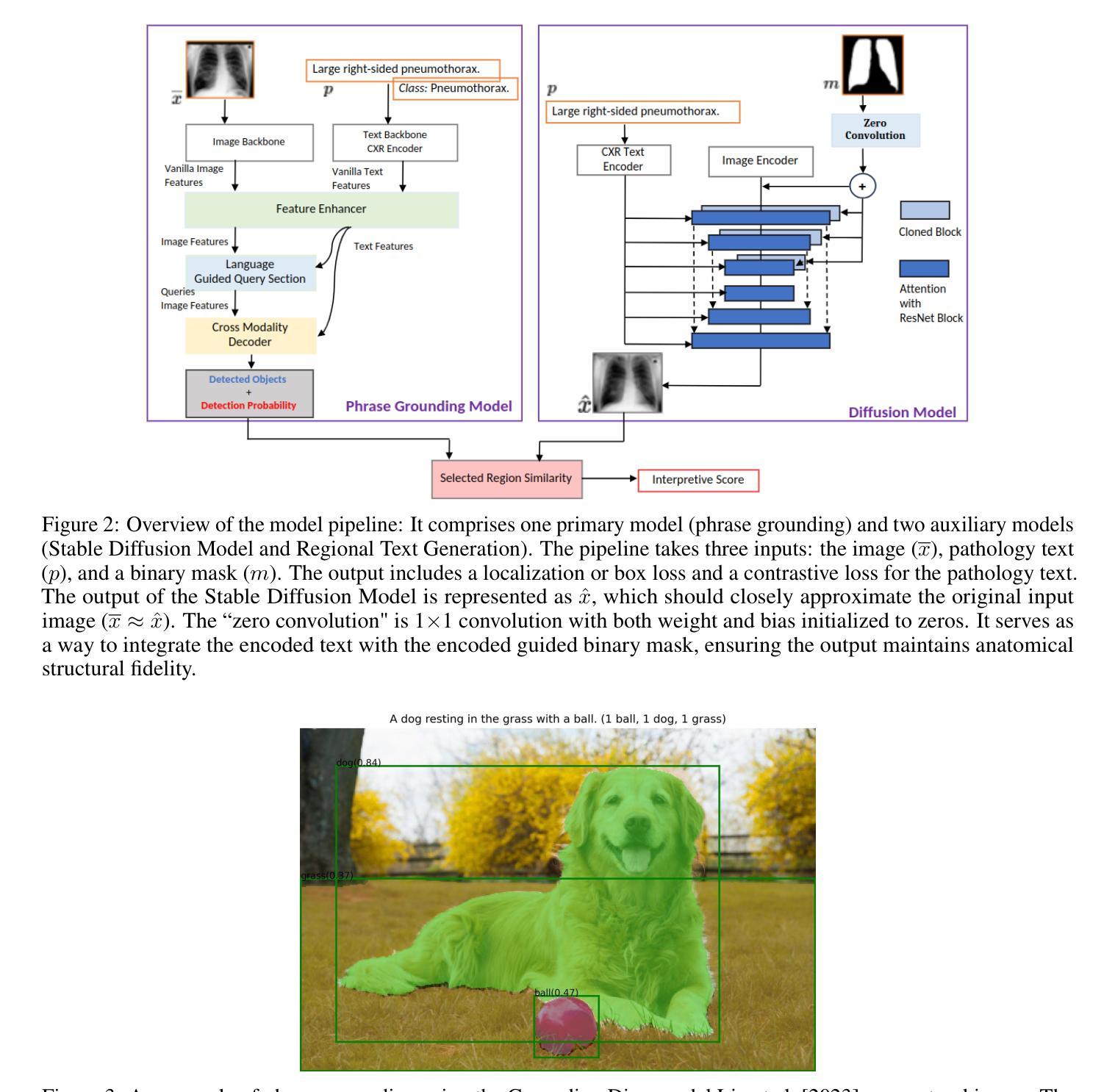
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes increasingly central to healthcare, the demand for explainable and trustworthy models is paramount. Current report generation systems for chest X-rays (CXR) often lack mechanisms for validating outputs without expert oversight, raising concerns about reliability and interpretability. To address these challenges, we propose a novel multimodal framework designed to enhance the semantic alignment and localization accuracy of AI-generated medical reports. Our framework integrates two key modules: a Phrase Grounding Model, which identifies and localizes pathologies in CXR images based on textual prompts, and a Text-to-Image Diffusion Module, which generates synthetic CXR images from prompts while preserving anatomical fidelity. By comparing features between the original and generated images, we introduce a dual-scoring system: one score quantifies localization accuracy, while the other evaluates semantic consistency. This approach significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in pathology localization and text-to-image alignment. The integration of phrase grounding with diffusion models, coupled with the dual-scoring evaluation system, provides a robust mechanism for validating report quality, paving the way for more trustworthy and transparent AI in medical imaging.
随着人工智能在医疗保健领域的应用日益普及,对解释性和可靠性的模型需求至关重要。目前用于胸部X射线(CXR)的报告生成系统由于缺乏在没有专家监督的情况下验证输出的机制,引发了人们对可靠性和可解释性的担忧。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的多模式框架,旨在提高人工智能生成医疗报告的语义对齐和定位准确性。我们的框架集成了两个关键模块:短语定位模型,该模型根据文本提示在CXR图像中识别和定位病理特征;文本到图像扩散模块,该模块从提示中生成合成CXR图像,同时保留解剖结构真实性。通过比较原始图像和生成图像的特征,我们引入了一种双重评分系统:一个评分量化定位准确性,另一个评分评估语义一致性。该方法显著优于现有方法,在病理定位和文本到图像对齐方面达到了最新结果。短语定位与扩散模型的集成以及双重评分评估系统的结合为验证报告质量提供了稳健的机制,为医学影像领域更可靠、更透明的AI铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
随着人工智能在医疗保健领域越来越重要,对解释性和可靠性的模型需求也越来越迫切。针对当前胸部X射线(CXR)报告生成系统缺乏验证输出的问题,我们提出了一种新型的多模态框架,旨在提高AI生成的医疗报告的语义对齐和定位精度。该框架集成了两个关键模块:短语定位模型和文本到图像扩散模块。短语定位模型根据文本提示识别和定位CXR图像中的病理,而文本到图像扩散模块则从提示生成合成CXR图像,保持解剖结构真实。通过比较原始和生成图像的特征,我们引入了一种双重评分系统:一个评分量化定位精度,另一个评分评估语义一致性。该方法显著优于现有方法,在病理定位和文本到图像对齐方面达到最新结果。短语定位与扩散模型的集成,加上双重评分评估系统,为验证报告质量提供了稳健的机制,为医疗成像领域更可靠、更透明的AI铺平了道路。
关键见解
- 随着人工智能在医疗保健领域的普及,对解释性和可靠性强的模型的需求增加。
- 当前胸部X射线报告生成系统存在验证输出的机制缺失问题。
- 提出了一种新型多模态框架,集成了短语定位模型和文本到图像扩散模块。
- 短语定位模型能根据文本提示在CXR图像中识别和定位病理。
- 文本到图像扩散模块从提示生成合成CXR图像,保持解剖结构真实。
- 引入了一种双重评分系统,一个评分量化定位精度,另一个评分评估语义一致性。
点此查看论文截图

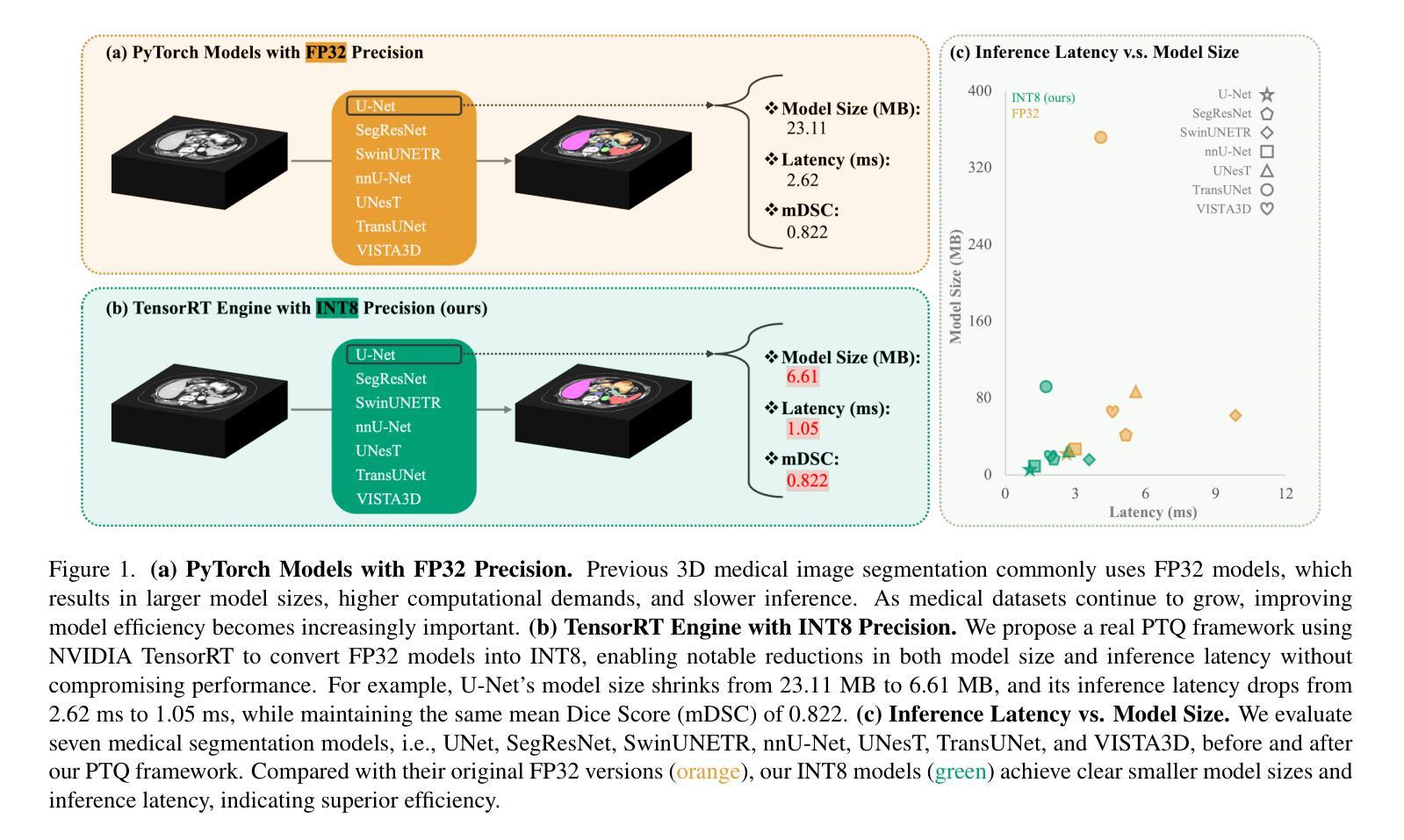
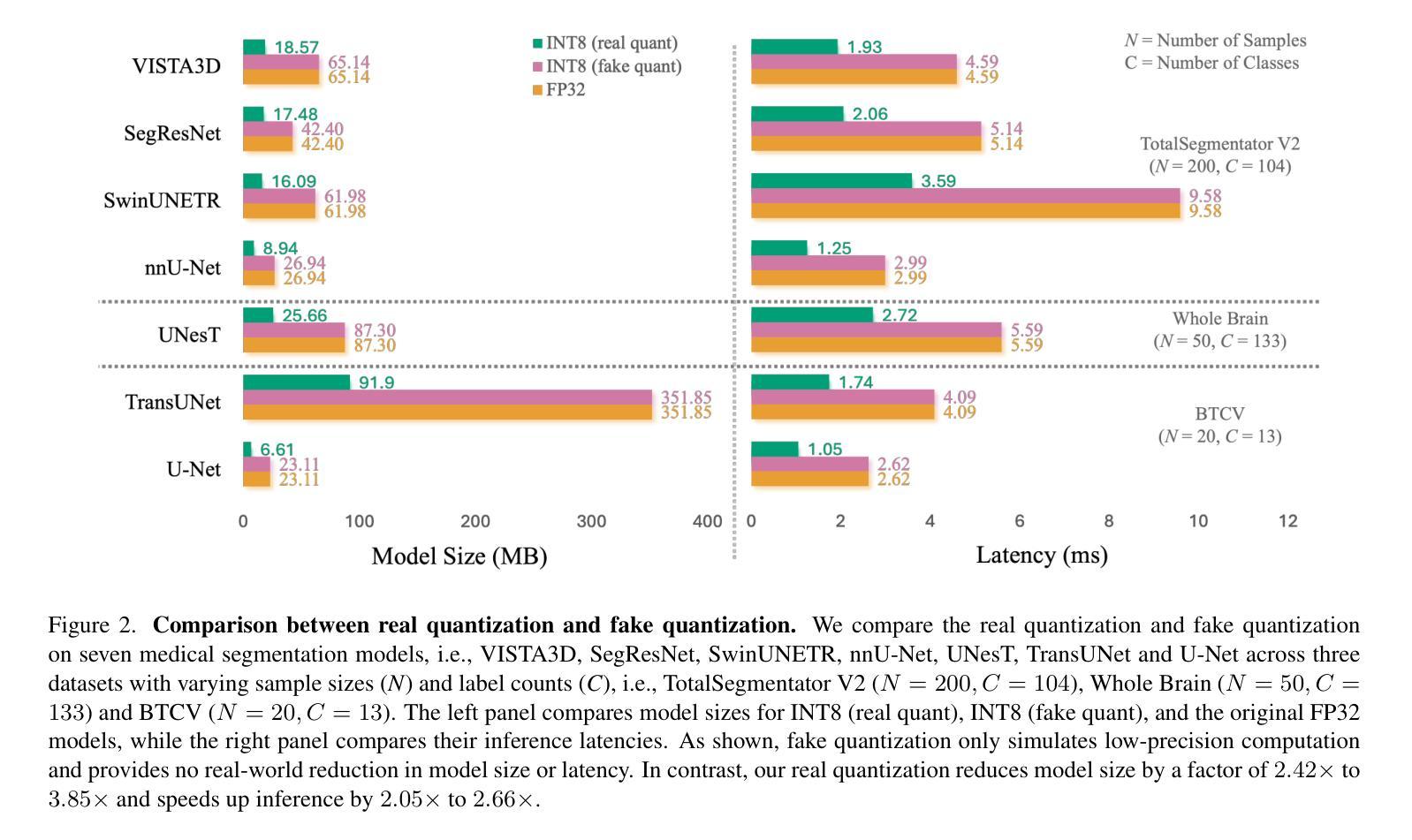
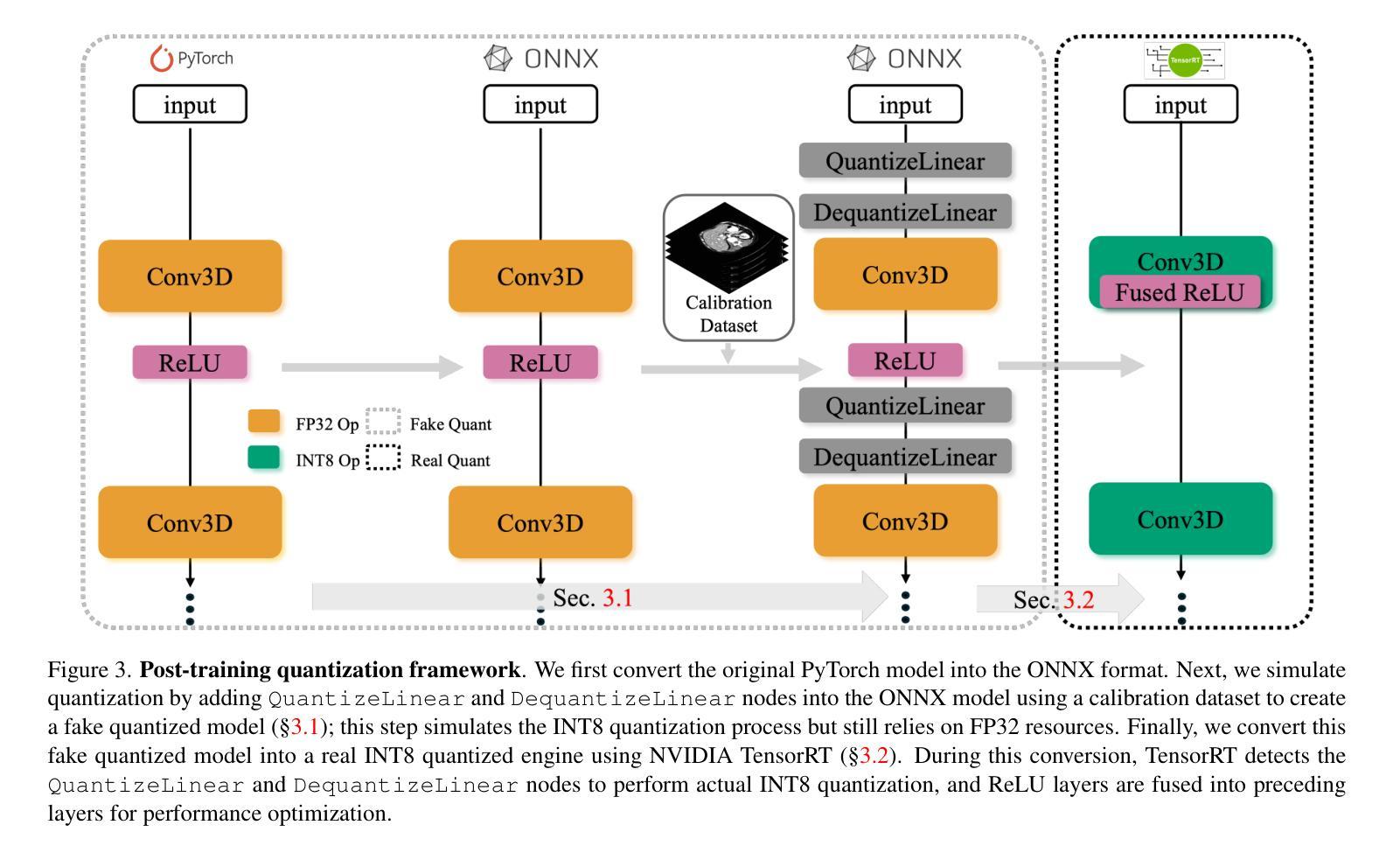
Post-Training Quantization for 3D Medical Image Segmentation: A Practical Study on Real Inference Engines
Authors:Chongyu Qu, Ritchie Zhao, Ye Yu, Bin Liu, Tianyuan Yao, Junchao Zhu, Bennett A. Landman, Yucheng Tang, Yuankai Huo
Quantizing deep neural networks ,reducing the precision (bit-width) of their computations, can remarkably decrease memory usage and accelerate processing, making these models more suitable for large-scale medical imaging applications with limited computational resources. However, many existing methods studied “fake quantization”, which simulates lower precision operations during inference, but does not actually reduce model size or improve real-world inference speed. Moreover, the potential of deploying real 3D low-bit quantization on modern GPUs is still unexplored. In this study, we introduce a real post-training quantization (PTQ) framework that successfully implements true 8-bit quantization on state-of-the-art (SOTA) 3D medical segmentation models, i.e., U-Net, SegResNet, SwinUNETR, nnU-Net, UNesT, TransUNet, ST-UNet,and VISTA3D. Our approach involves two main steps. First, we use TensorRT to perform fake quantization for both weights and activations with unlabeled calibration dataset. Second, we convert this fake quantization into real quantization via TensorRT engine on real GPUs, resulting in real-world reductions in model size and inference latency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework effectively performs 8-bit quantization on GPUs without sacrificing model performance. This advancement enables the deployment of efficient deep learning models in medical imaging applications where computational resources are constrained. The code and models have been released, including U-Net, TransUNet pretrained on the BTCV dataset for abdominal (13-label) segmentation, UNesT pretrained on the Whole Brain Dataset for whole brain (133-label) segmentation, and nnU-Net, SegResNet, SwinUNETR and VISTA3D pretrained on TotalSegmentator V2 for full body (104-label) segmentation. https://github.com/hrlblab/PTQ.
对深度神经网络进行量化,降低其计算的精度(位宽),可以显著降低内存使用并加速处理,使这些模型更适合于计算资源有限的大规模医学成像应用。然而,许多现有的方法研究了“假量化”,这只是在推理过程中模拟低精度操作,并没有真正减小模型大小或提高实际推理速度。此外,在现代GPU上实施真正的3D低位量化的潜力仍未被探索。在这项研究中,我们引入了一个真正的训练后量化(PTQ)框架,该框架成功地在最先进的3D医学分割模型上实现了真正的8位量化,包括U-Net、SegResNet、SwinUNETR、nnU-Net、UNesT、TransUNet、ST-UNet和VISTA3D。我们的方法涉及两个主要步骤。首先,我们使用TensorRT对权重和激活进行假量化处理,并使用未标记的校准数据集。其次,我们在真实的GPU上通过TensorRT引擎将假量化转化为真实量化,从而在现实中减小模型大小和推理延迟。大量实验表明,我们的框架能够在GPU上有效进行8位量化,而不会牺牲模型性能。这一进展使得能够在计算资源受限的医学成像应用中部署高效的深度学习模型。代码和模型已经发布,包括在BTCV数据集上预训练的用于腹部(13标签)分割的U-Net和TransUNet、用于全脑(133标签)分割的在Whole Brain Dataset上预训练的UNesT,以及在TotalSegmentator V2上预训练的nnU-Net、SegResNet、SwinUNETR和VISTA3D用于全身(104标签)分割。详情链接:https://github.com/hrlblab/PTQ。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
通过对深度神经网络进行量化,降低计算精度(位宽),可以显著降低内存使用并加速处理,使这些模型更适合计算资源有限的大规模医学成像应用。本研究引入了一个真正的训练后量化(PTQ)框架,成功实现了在先进的3D医学分割模型上的真实8位量化,并实现了模型大小和推理延迟的实际降低。
Key Takeaways
- 量化深度神经网络可以降低计算精度,从而减少内存使用并加速处理,尤其适用于计算资源有限的医学成像应用。
- 现有方法常常模拟低精度操作,并未真正实现模型大小减少或提高实际推理速度。
- 本研究引入了一个真正的训练后量化(PTQ)框架,成功在多个先进的3D医学分割模型上实现真实8位量化。
- 该框架使用TensorRT进行假量化,然后通过TensorRT引擎在真实GPU上进行转换,达到实际减少模型大小和推理延迟的效果。
- 实验表明,该框架能在GPU上有效进行8位量化,且不会牺牲模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

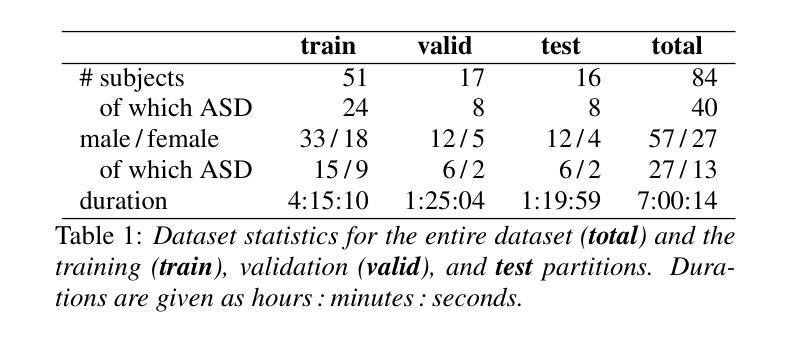
MADUV: The 1st INTERSPEECH Mice Autism Detection via Ultrasound Vocalization Challenge
Authors:Zijiang Yang, Meishu Song, Xin Jing, Haojie Zhang, Kun Qian, Bin Hu, Kota Tamada, Toru Takumi, Björn W. Schuller, Yoshiharu Yamamoto
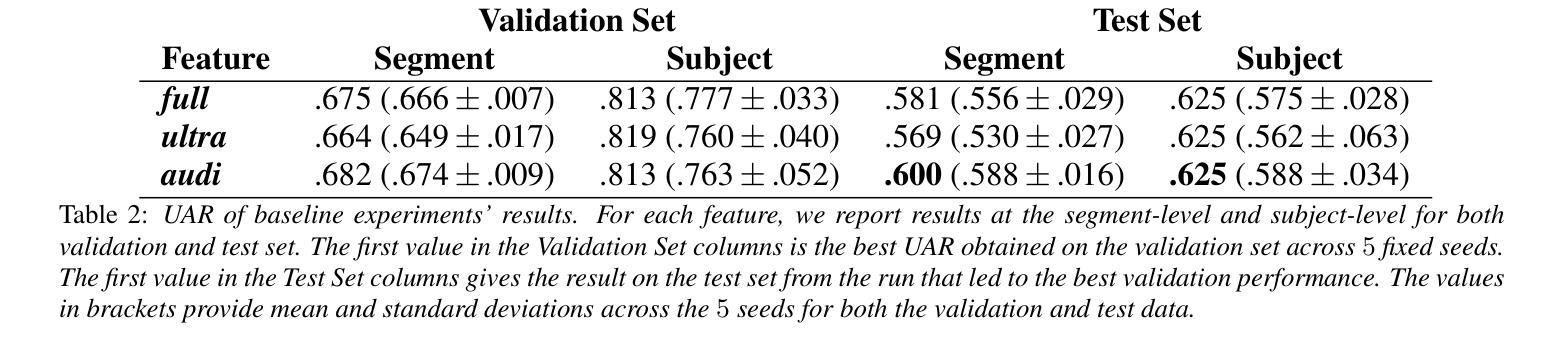
The Mice Autism Detection via Ultrasound Vocalization (MADUV) Challenge introduces the first INTERSPEECH challenge focused on detecting autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in mice through their vocalizations. Participants are tasked with developing models to automatically classify mice as either wild-type or ASD models based on recordings with a high sampling rate. Our baseline system employs a simple CNN-based classification using three different spectrogram features. Results demonstrate the feasibility of automated ASD detection, with the considered audible-range features achieving the best performance (UAR of 0.600 for segment-level and 0.625 for subject-level classification). This challenge bridges speech technology and biomedical research, offering opportunities to advance our understanding of ASD models through machine learning approaches. The findings suggest promising directions for vocalization analysis and highlight the potential value of audible and ultrasound vocalizations in ASD detection.
通过超声发声(MADUV)检测小鼠自闭症(Mice Autism Detection via Ultrasound Vocalization,简称MADUV)挑战引入了首个INTERSPEECH挑战,该挑战的重点是通过小鼠的发声来检测自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)。参赛者的任务是开发模型,根据高采样率的录音自动将小鼠分类为野生型或ASD模型。我们的基线系统采用基于简单卷积神经网络(CNN)的分类方法,使用三种不同的频谱特征。结果表明自动化检测ASD的可行性,所考虑的音频范围特征取得了最佳性能(分段级别为0.600的UAR,主题级别为0.625的分类)。本次挑战将语音技术与生物医学研究相结合,为通过机器学习方法深入了解ASD模型提供了机会。研究结果表明发声分析的希望方向,并突出了可听声和超声发声在ASD检测中的潜在价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figure and 2 tables. For MADUV Challenge 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了通过超声发声检测小鼠自闭症(MADUV)挑战,这是首个专注于通过小鼠发声检测自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)的INTERSPEECH挑战。参与者需开发模型自动将小鼠分类为野生型或ASD模型,基于高采样率录音。基线系统采用简单的CNN分类方法,使用三种不同的频谱特征。结果表明自动化ASD检测的可行性,所考虑的音频范围特征获得最佳性能(分段级别UAR为0.600,主题级别分类为0.625)。该挑战架起了语音技术与生物医学研究之间的桥梁,为通过机器学习方法深入了解ASD模型提供了机会,同时也暗示了发声分析的潜在前景以及在ASD检测中听觉和超声波发声的潜在价值。
Key Takeaways
- MADUV挑战旨在通过小鼠的超声发声来检测自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)。
- 参与者需要开发模型来自动分类小鼠是否为ASD模型或野生型。
- 基线系统采用CNN分类方法,并使用了三种不同的频谱特征。
- 音频范围特征在检测中表现最佳,分段级别的UAR为0.600,主题级别的分类为0.625。
- 该挑战结合了语音技术和生物医学研究,为理解ASD模型提供了新的视角。
- 结果显示了自动化ASD检测的可行性,为发声分析提供了潜在的前景。
点此查看论文截图

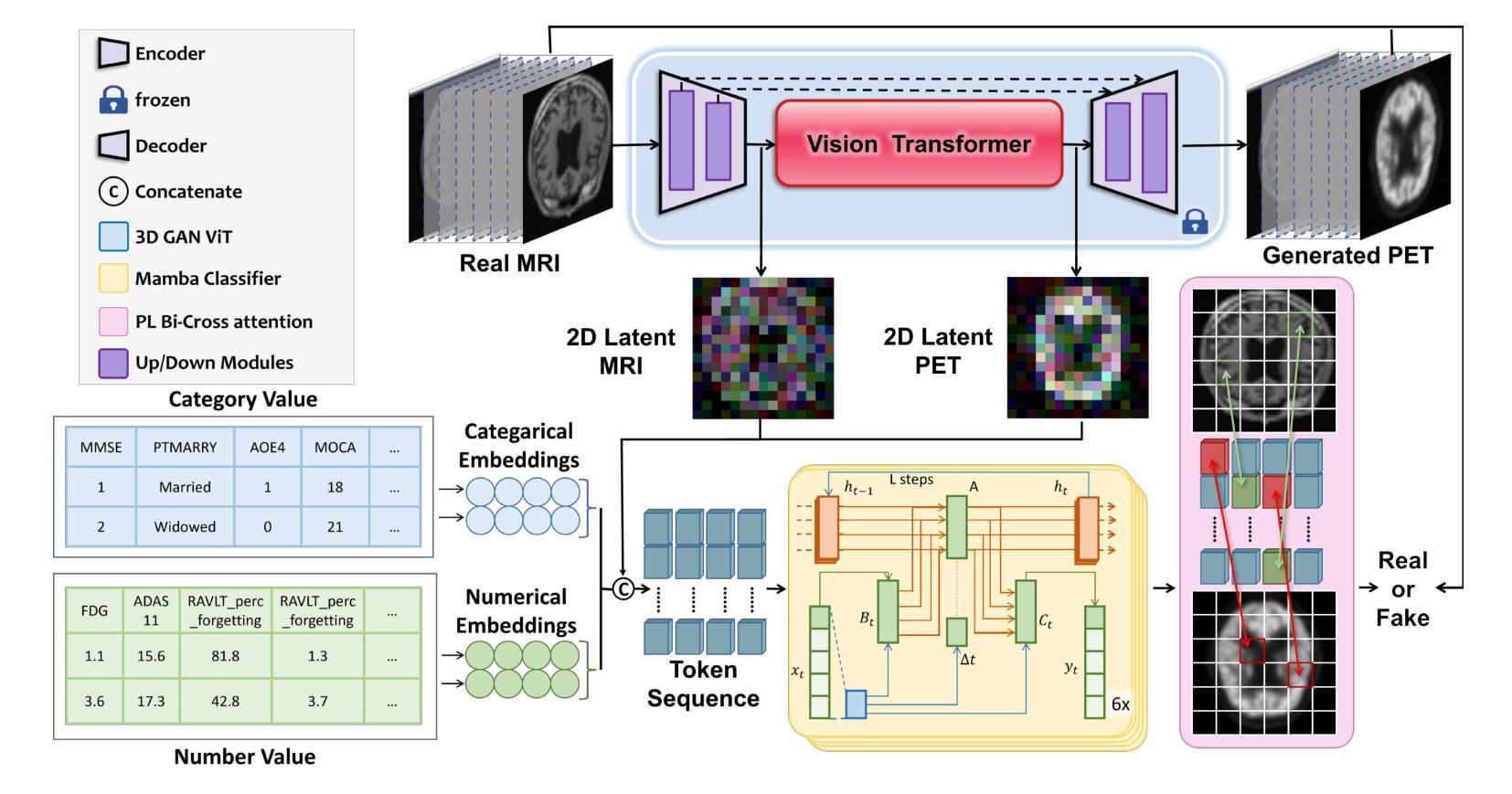
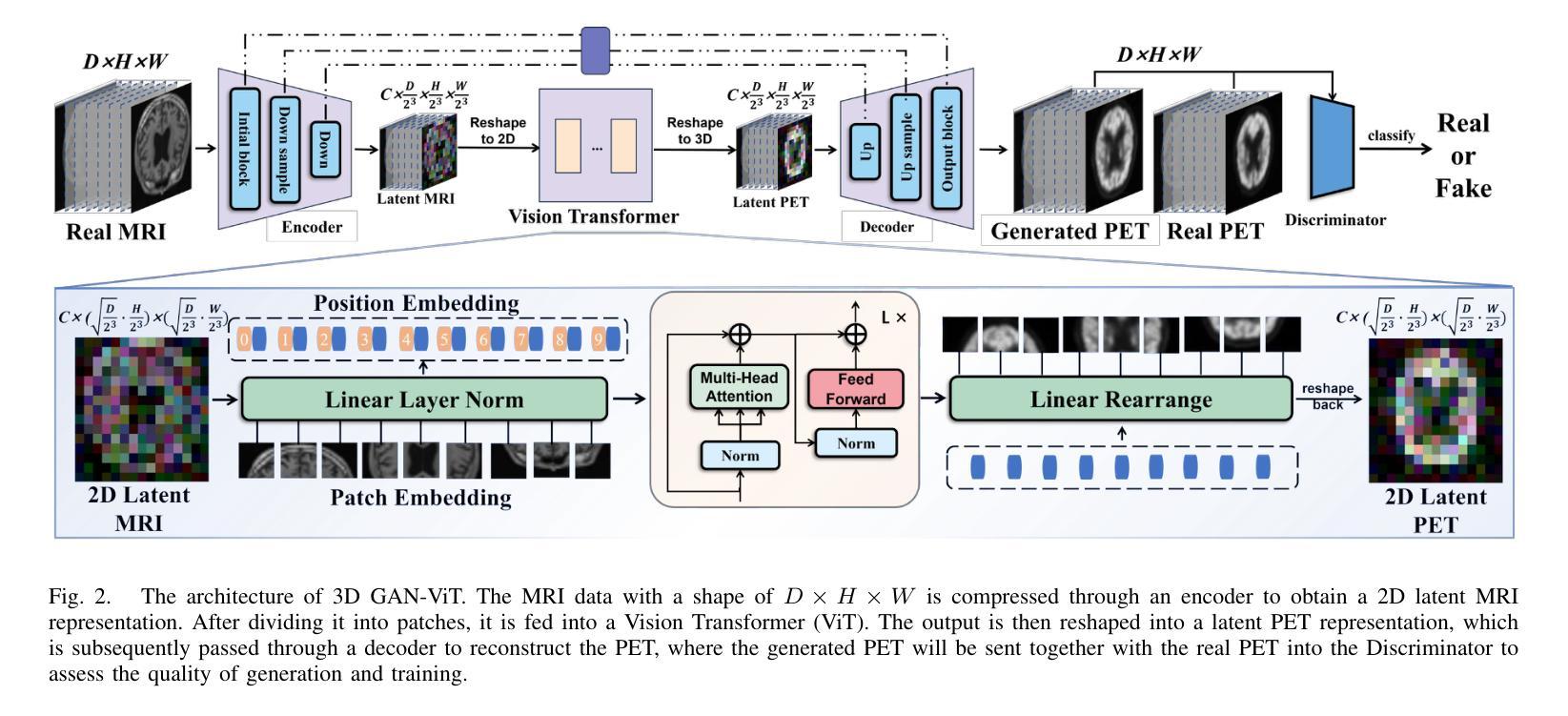
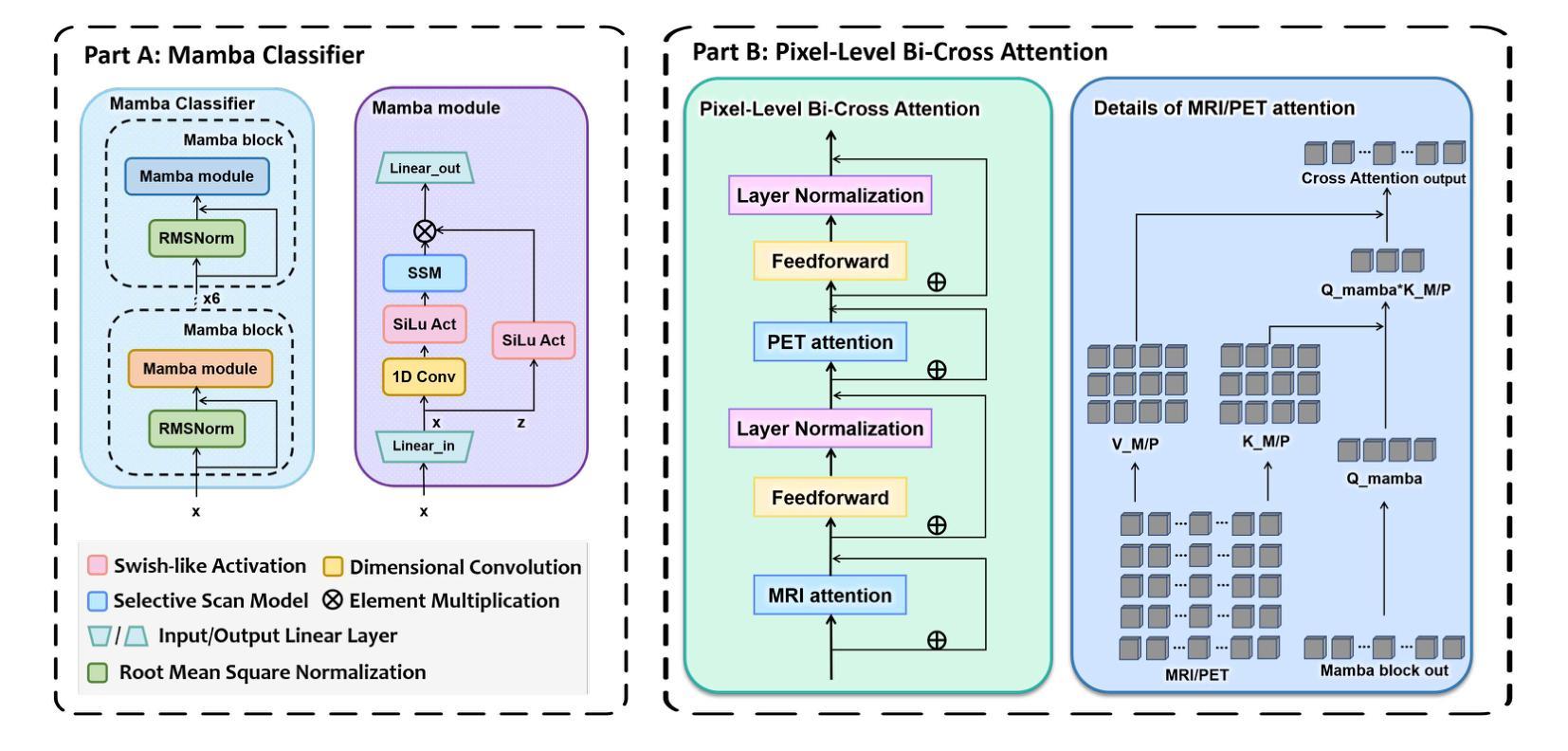
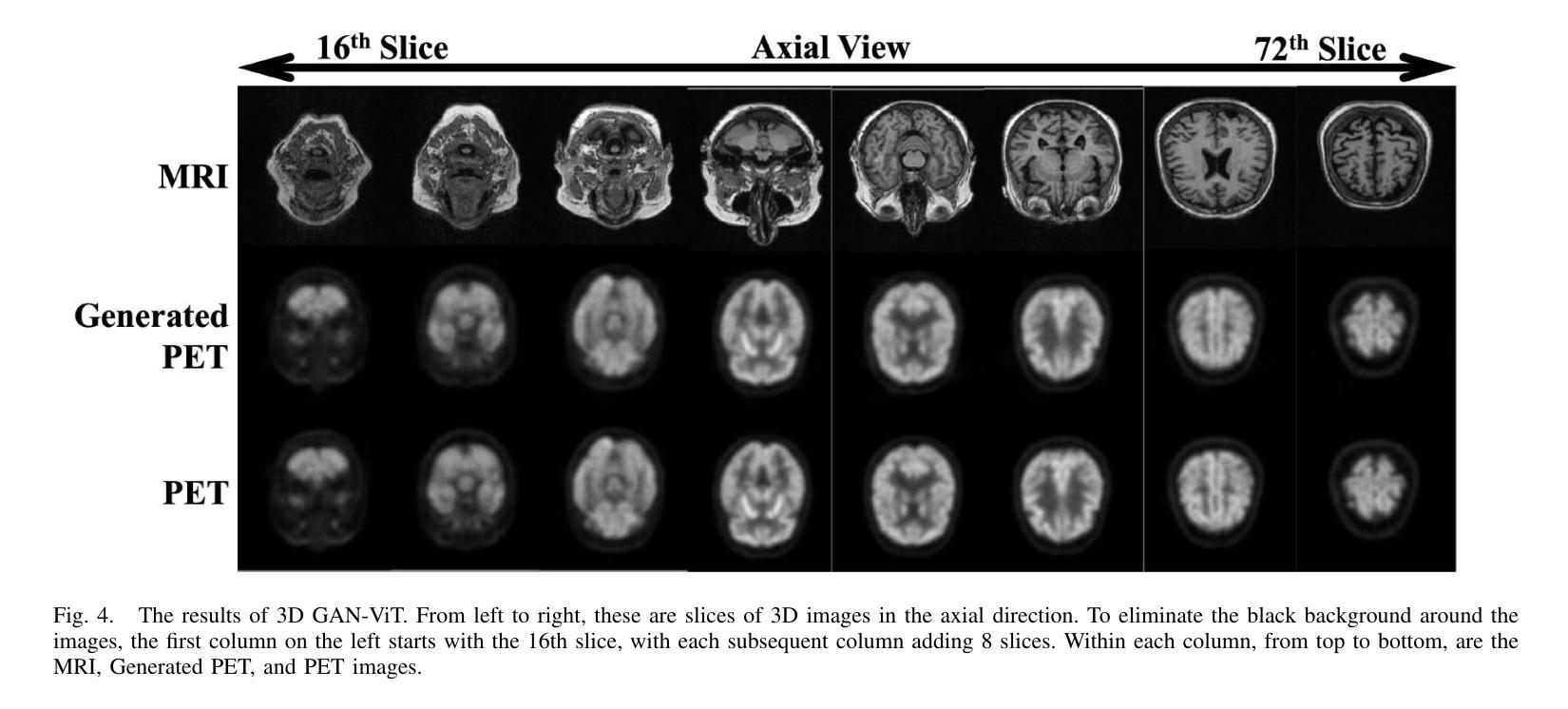
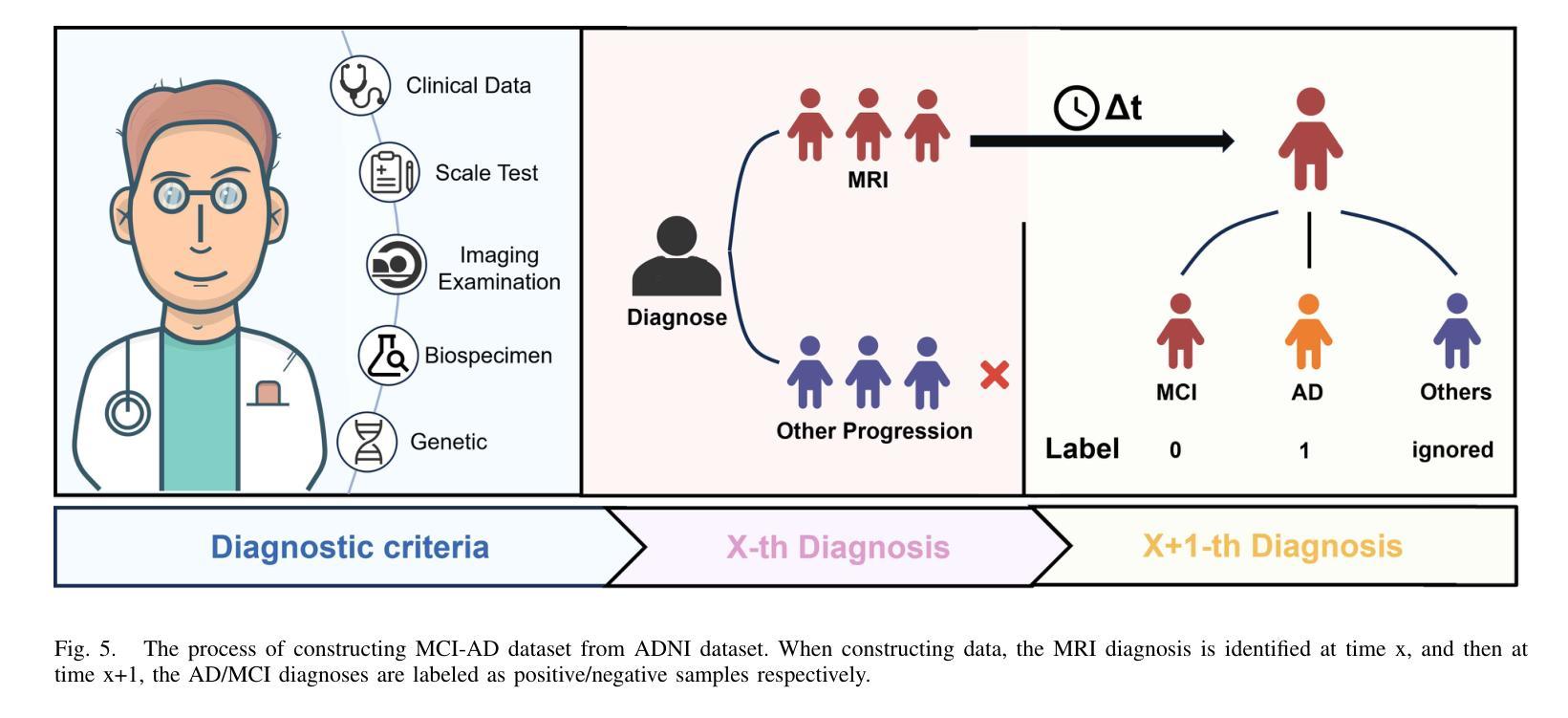
GFE-Mamba: Mamba-based AD Multi-modal Progression Assessment via Generative Feature Extraction from MCI
Authors:Zhaojie Fang, Shenghao Zhu, Yifei Chen, Binfeng Zou, Fan Jia, Chang Liu, Xiang Feng, Linwei Qiu, Feiwei Qin, Jin Fan, Changbiao Chu, Changmiao Wang
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a progressive, irreversible neurodegenerative disorder that often originates from Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). This progression results in significant memory loss and severely affects patients’ quality of life. Clinical trials have consistently shown that early and targeted interventions for individuals with MCI may slow or even prevent the advancement of AD. Research indicates that accurate medical classification requires diverse multimodal data, including detailed assessment scales and neuroimaging techniques like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). However, simultaneously collecting the aforementioned three modalities for training presents substantial challenges. To tackle these difficulties, we propose GFE-Mamba, a multimodal classifier founded on Generative Feature Extractor. The intermediate features provided by this Extractor can compensate for the shortcomings of PET and achieve profound multimodal fusion in the classifier. The Mamba block, as the backbone of the classifier, enables it to efficiently extract information from long-sequence scale information. Pixel-level Bi-cross Attention supplements pixel-level information from MRI and PET. We provide our rationale for developing this cross-temporal progression prediction dataset and the pre-trained Extractor weights. Our experimental findings reveal that the GFE-Mamba model effectively predicts the progression from MCI to AD and surpasses several leading methods in the field. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Tinysqua/GFE-Mamba.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种渐进性、不可逆的神经退行性疾病,通常起源于轻度认知障碍(MCI)。这一进程会导致显著的记忆力丧失,严重影响患者的生活质量。临床试验持续表明,对MCI患者进行早期和有针对性的干预可能会减缓甚至阻止AD的进展。研究表明,准确的医学分类需要包括详细评估量表和诸如磁共振成像(MRI)和正电子发射断层扫描(PET)等神经成像技术在内的多元多模态数据。然而,同时收集上述三种模式进行培训存在相当大的挑战。为了应对这些困难,我们提出了基于生成特征提取器的多模态分类器GFE-Mamba。该提取器提供的中间特征可以弥补PET的不足,实现分类器中的深刻多模态融合。作为分类器的骨干,“Mamba”块使其能够从长序列尺度信息中有效提取信息。像素级双向交叉注意力补充了MRI和PET的像素级信息。我们阐述了建立这个跨时间进程预测数据集和开发预训练提取器权重的理由。我们的实验结果表明,GFE-Mamba模型有效地预测了从MCI到AD的进展,并超越了该领域的几种领先方法。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/Tinysqua/GFE-Mamba获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文介绍了阿尔茨海默病(AD)的进展以及从轻度认知障碍(MCI)发展为AD的过程。研究表明,准确进行医学分类需要包括评估量表、磁共振成像(MRI)和正电子发射断层扫描(PET)在内的多种模式数据。为解决收集这些数据带来的挑战,提出了一种基于生成特征提取器的多模式分类器GFE-Mamba,该分类器可有效地从MRI和PET中提取信息,预测MCI向AD的进展,并超越了该领域的一些前沿方法。
Key Takeaways
- 阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种不可逆的神经性退行性疾病,常由轻度认知障碍(MCI)发展而来。
2.MCI的早期针对性干预可能减缓甚至阻止AD的发展。 - 准确医疗分类需要包括评估量表、MRI和PET在内的多种模式数据。
- 收集多种模式数据用于训练面临诸多挑战。
- 提出的GFE-Mamba模型基于生成特征提取器,可有效从MRI和PET中提取信息。
- GFE-Mamba模型能有效预测从MCI到AD的进展,并表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

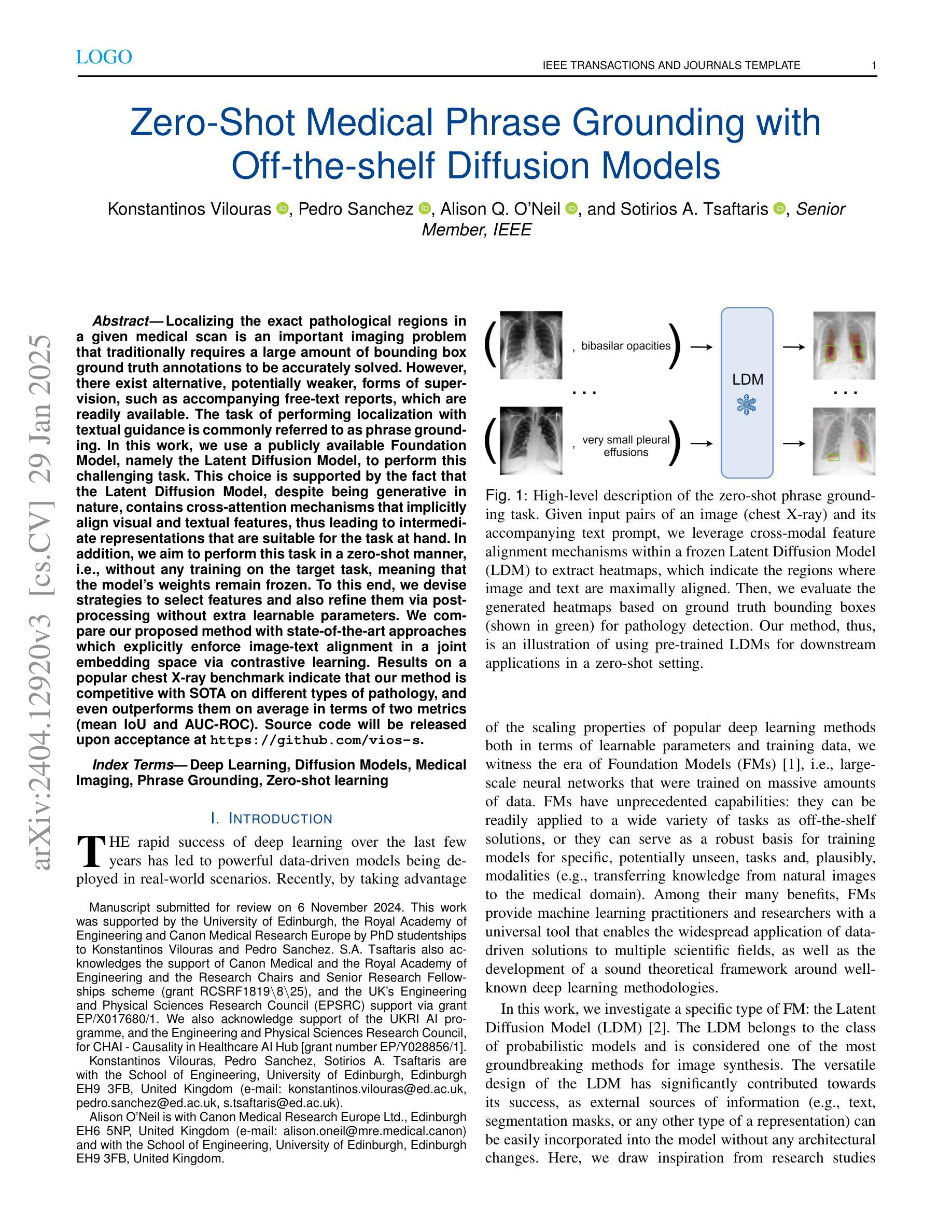
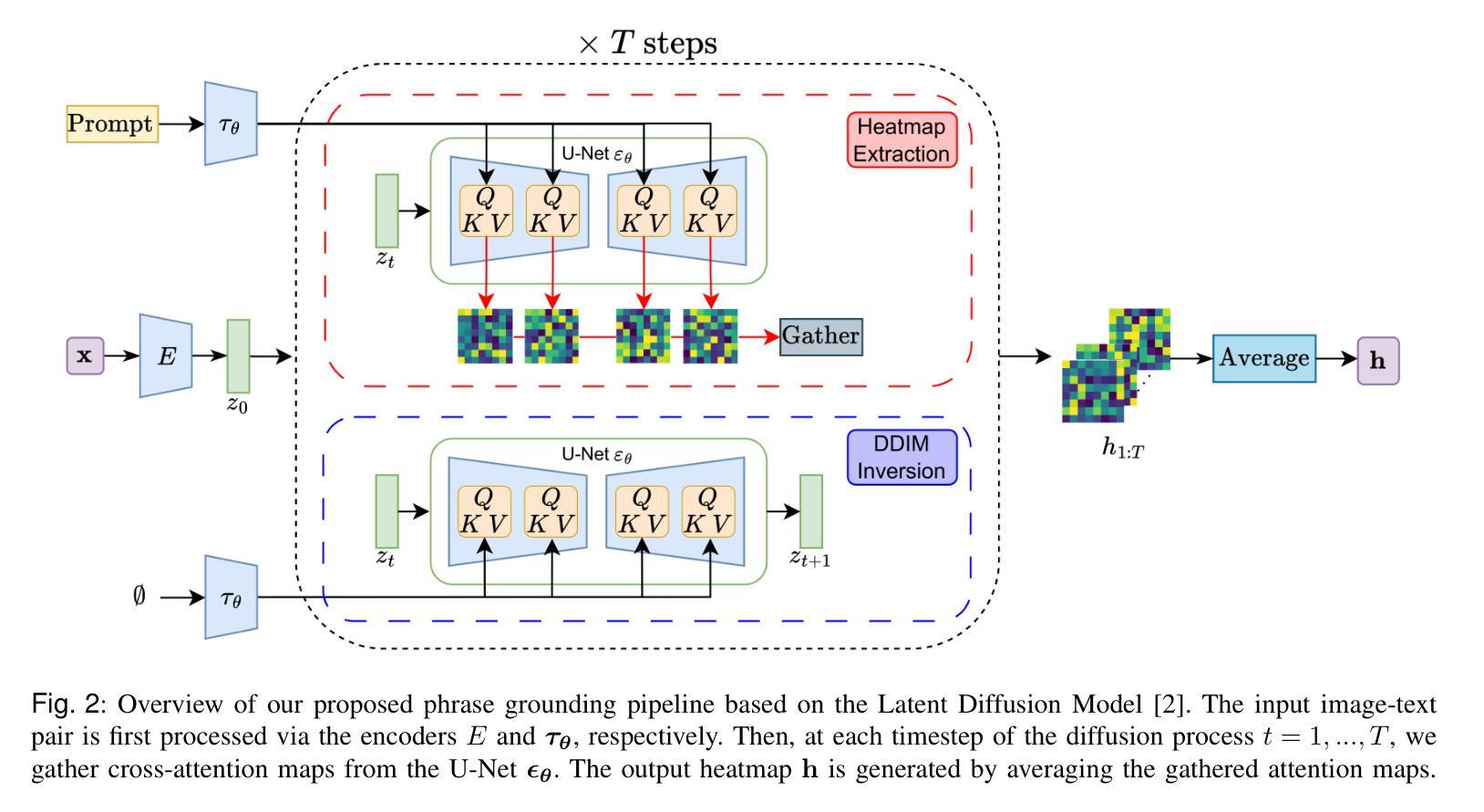
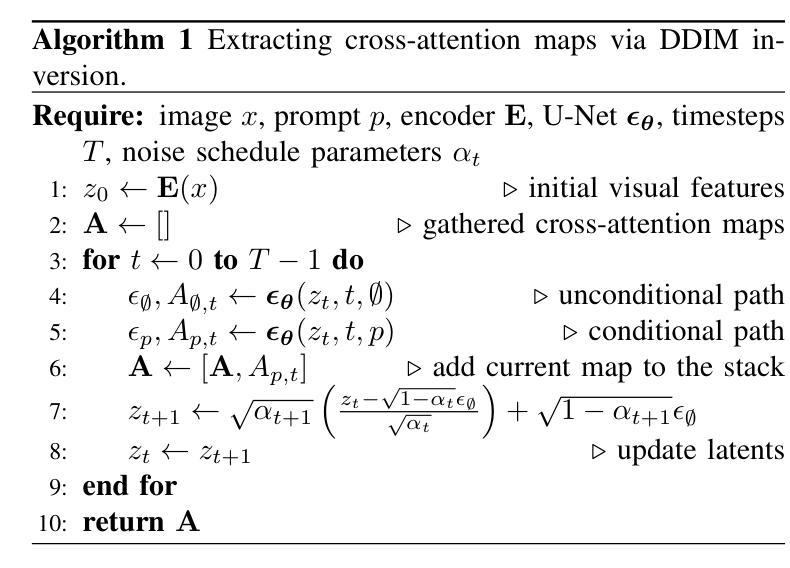
Zero-Shot Medical Phrase Grounding with Off-the-shelf Diffusion Models
Authors:Konstantinos Vilouras, Pedro Sanchez, Alison Q. O’Neil, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris
Localizing the exact pathological regions in a given medical scan is an important imaging problem that traditionally requires a large amount of bounding box ground truth annotations to be accurately solved. However, there exist alternative, potentially weaker, forms of supervision, such as accompanying free-text reports, which are readily available.The task of performing localization with textual guidance is commonly referred to as phrase grounding. In this work, we use a publicly available Foundation Model, namely the Latent Diffusion Model, to perform this challenging task. This choice is supported by the fact that the Latent Diffusion Model, despite being generative in nature, contains cross-attention mechanisms that implicitly align visual and textual features, thus leading to intermediate representations that are suitable for the task at hand. In addition, we aim to perform this task in a zero-shot manner, i.e., without any training on the target task, meaning that the model’s weights remain frozen. To this end, we devise strategies to select features and also refine them via post-processing without extra learnable parameters. We compare our proposed method with state-of-the-art approaches which explicitly enforce image-text alignment in a joint embedding space via contrastive learning. Results on a popular chest X-ray benchmark indicate that our method is competitive with SOTA on different types of pathology, and even outperforms them on average in terms of two metrics (mean IoU and AUC-ROC). Source code will be released upon acceptance at \url{https://github.com/vios-s}.
在给定医学扫描中定位精确病理区域是一个重要的成像问题,传统上需要大量边界框的地面真实注释才能准确解决。然而,存在替代的、潜在的较弱形式的监督方法,如伴随的自由文本报告,这些报告很容易获得。进行文本指导定位的任务通常被称为短语定位。在这项工作中,我们使用一个公开可用的基础模型——潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Model)来完成这项具有挑战性的任务。之所以选择该模型是因为尽管它是生成性的模型,但包含了跨注意力机制,能够隐式对齐视觉和文本特征,从而产生适合当前任务的中间表示。此外,我们旨在以零样本方式进行此任务,即无需对目标任务进行任何训练,这意味着模型的权重保持冻结状态。为此,我们制定了选择特征的策略并通过后处理对特征进行提炼,无需额外的可学习参数。我们将所提出的方法与最新前沿方法进行比较,这些方法通过对比学习在联合嵌入空间中显式执行图像文本对齐。在流行的胸部X射线基准测试上的结果表明,我们的方法在不同类型病理上的表现与最新前沿技术相当,甚至在两个指标(平均IoU和AUC-ROC)上平均表现优于它们。源代码在接受后将发布在https://github.com/vios-s上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures, IEEE J-BHI Special Issue on Foundation Models in Medical Imaging
Summary
本文利用公开的基础模型——潜在扩散模型,以零样本学习方式实现了借助文本指导进行医学图像病理区域定位的任务。该模型通过隐式对齐视觉和文本特征,产生适合任务的中间表示。在胸部X光射线基准测试上的结果表明,该方法与现有先进技术相比具有竞争力,并在两个指标上平均表现更优。
Key Takeaways
- 医学扫描中病理区域的定位是一个重要的成像问题,通常需要大量的边界框真实标注进行准确解决。
- 存在如伴随的自由文本报告等潜在的弱监督形式,可作为替代方案。
- 本文使用公开的基础模型——潜在扩散模型,该模型具有生成性质并含有跨注意机制,能隐式对齐视觉和文本特征。
- 任务以零样本学习方式进行,即无需对目标任务进行训练,模型权重保持冻结。
- 提出了通过策略选择特征并通过后处理进行细化的方法,无需额外可学习参数。
- 在流行的胸部X射线基准测试上,该方法与现有先进技术相比具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图