⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-31 更新
Efficient Redundancy Reduction for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Lin Chen, Qi Yang, Kun Ding, Zhihao Li, Gang Shen, Fei Li, Qiyuan Cao, Shiming Xiang
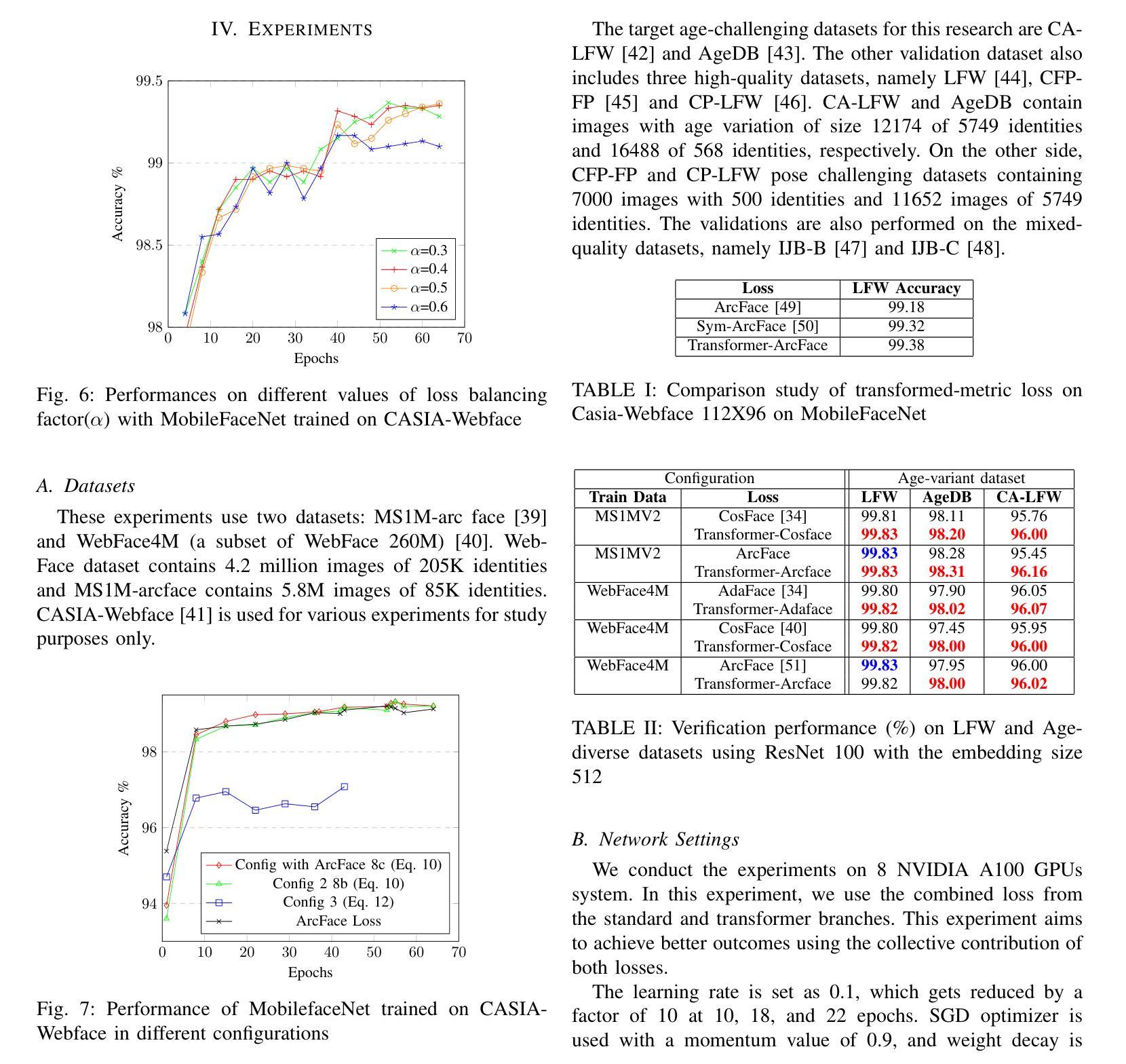
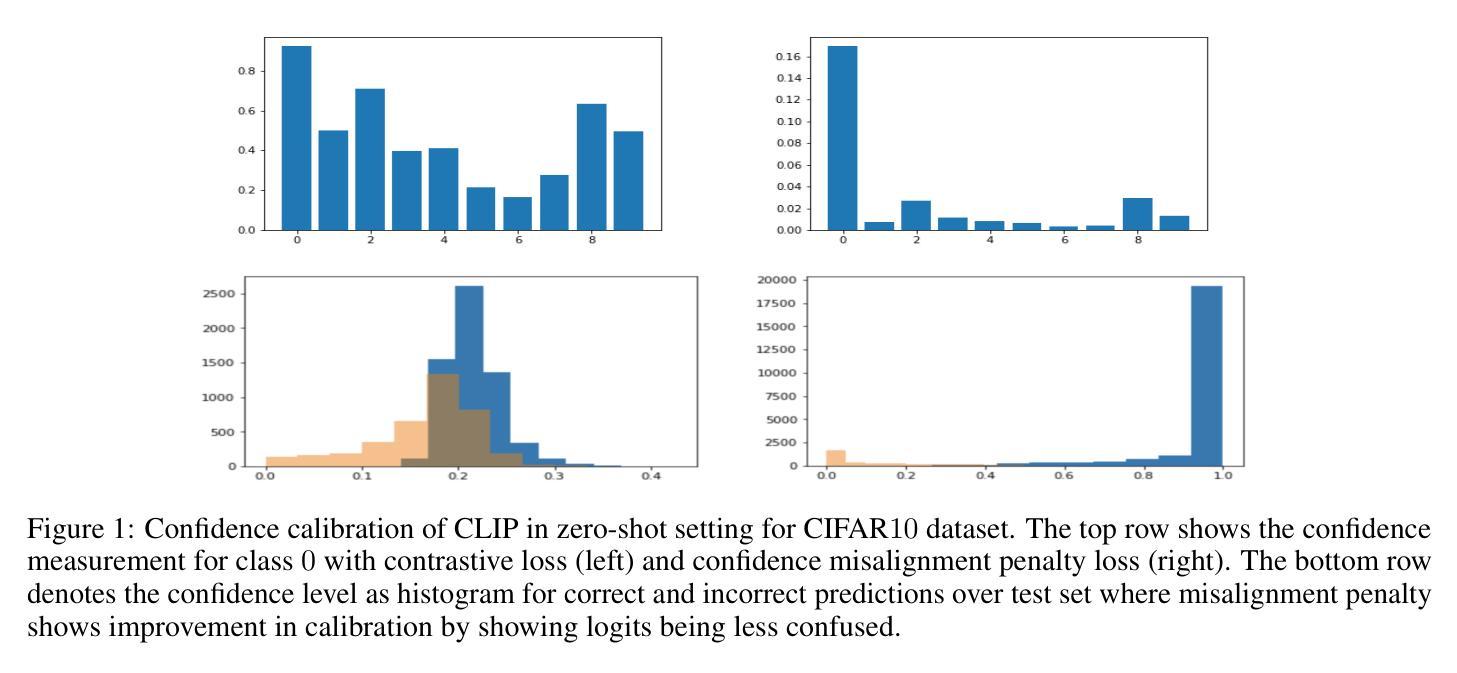
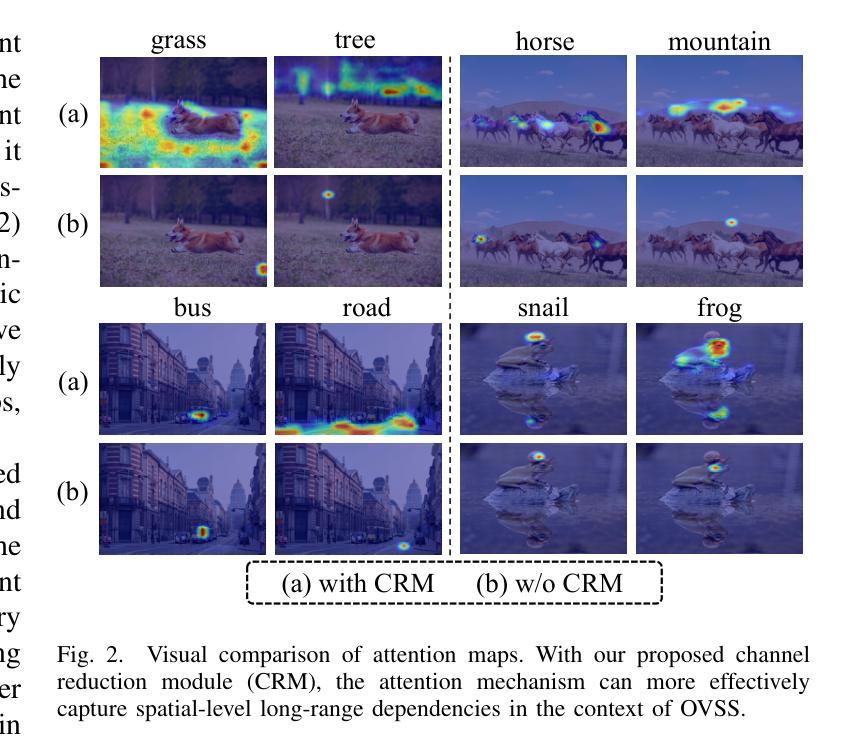
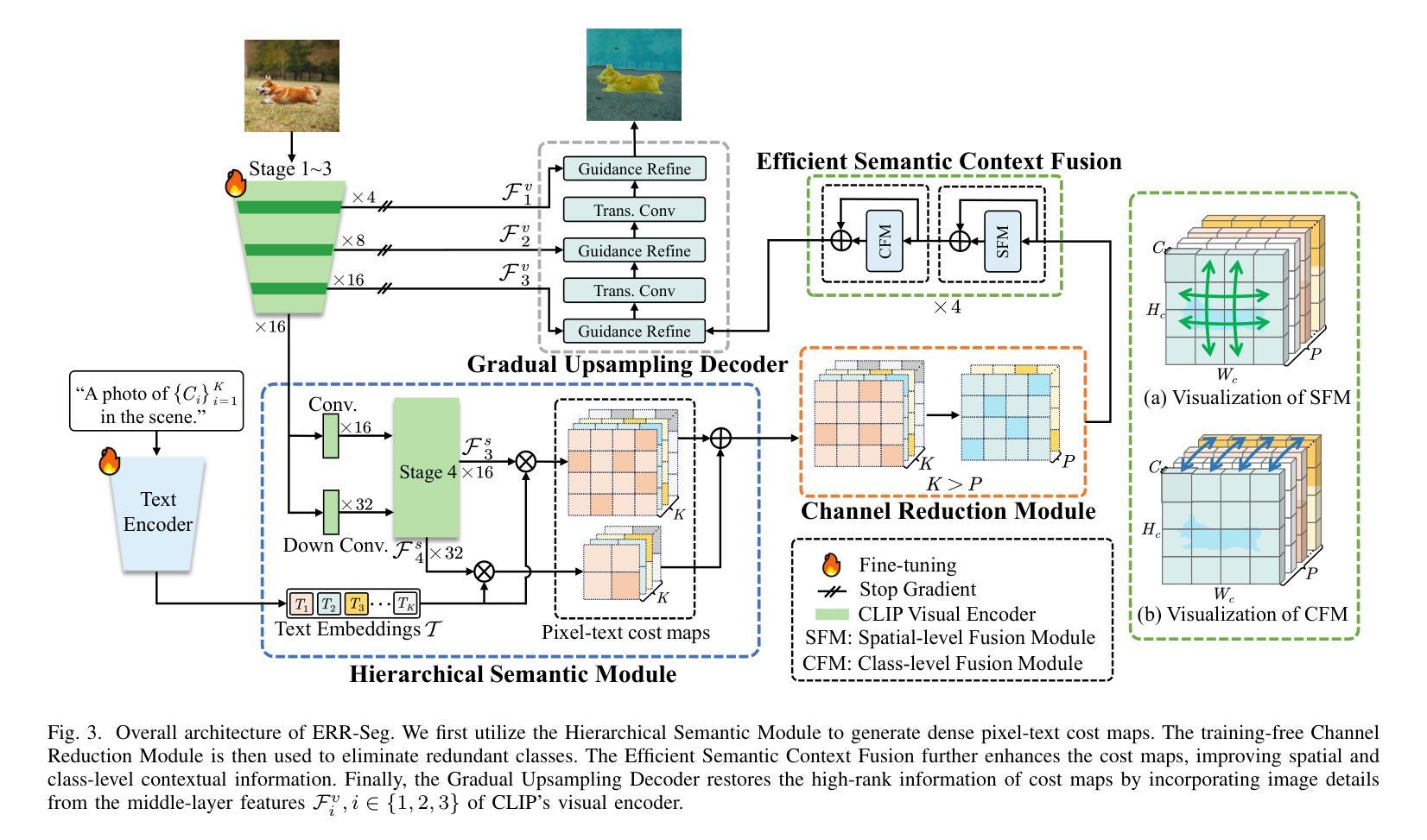
Open-vocabulary semantic segmentation (OVSS) is an open-world task that aims to assign each pixel within an image to a specific class defined by arbitrary text descriptions. Recent advancements in large-scale vision-language models have demonstrated their open-vocabulary understanding capabilities, significantly facilitating the development of OVSS. However, most existing methods suffer from either suboptimal performance or long latency. This study introduces ERR-Seg, a novel framework that effectively reduces redundancy to balance accuracy and efficiency. ERR-Seg incorporates a training-free Channel Reduction Module (CRM) that leverages prior knowledge from vision-language models like CLIP to identify the most relevant classes while discarding others. Moreover, it incorporates Efficient Semantic Context Fusion (ESCF) with spatial-level and class-level sequence reduction strategies. CRM and ESCF result in substantial memory and computational savings without compromising accuracy. Additionally, recognizing the significance of hierarchical semantics extracted from middle-layer features for closed-set semantic segmentation, ERR-Seg introduces the Hierarchical Semantic Module (HSM) to exploit hierarchical semantics in the context of OVSS. Compared to previous state-of-the-art methods under the ADE20K-847 setting, ERR-Seg achieves +$5.6%$ mIoU improvement and reduces latency by $67.3%$.
开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)是一项面向开放世界的任务,旨在将图像中的每个像素分配给由任意文本描述所定义的具体类别。大规模视觉语言模型的最新进展已经证明了其开放词汇理解的能力,极大地促进了OVSS的发展。然而,大多数现有方法都存在性能不佳或延迟过长的问题。本研究介绍了ERR-Seg,一种有效减少冗余以平衡准确性和效率的新型框架。ERR-Seg融入了一个无需训练即可工作的通道减少模块(CRM),该模块利用来自视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的先验知识来识别最相关的类别,同时忽略其他类别。此外,它结合了高效语义上下文融合(ESCF)与空间级和类别级序列减少策略。CRM和ESCF在不影响准确性的情况下,实现了大量的内存和计算节省。此外,ERR-Seg认识到从中层特征中提取的分层语义对于封闭集语义分割的重要性,因此在OVSS的上下文中引入了分层语义模块(HSM)来利用分层语义。与ADE20K-847设置下的先前最先进的方法相比,ERR-Seg实现了+ $5.6%$的mIoU改进,并将延迟时间减少了$67.3%$。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本研究提出了一种新的开放词汇语义分割框架ERR-Seg,旨在提高效率和准确性。ERR-Seg结合了基于CLIP的通道缩减模块(CRM)和高效语义上下文融合(ESCF),减少冗余,实现性能优化。此外,它引入了层次语义模块(HSM)来利用分层语义上下文的优势,有效改善闭集语义分割性能。最终成果为高效准确且无性能妥协。相比于其他最新技术,ERR-Seg在ADE20K-847环境下实现了更高的mIoU指标和更低的延迟时间。
Key Takeaways:
- 开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)是一种基于文本描述为每个像素分配特定类别的任务。
- ERR-Seg框架通过减少冗余来提高准确性和效率。
- ERR-Seg结合了通道缩减模块(CRM)和高效语义上下文融合(ESCF)。
- CRM基于CLIP识别最相关的类别并忽略其他类别,减少了不必要的计算负担。
- ESCF与空间级别和类别级别的序列缩减策略相结合提高了语义信息的有效传递。
- HSM模块的引入利用了中层特征的分层语义上下文,进一步改善了性能。在闭集语义分割任务上起到了很好的作用。
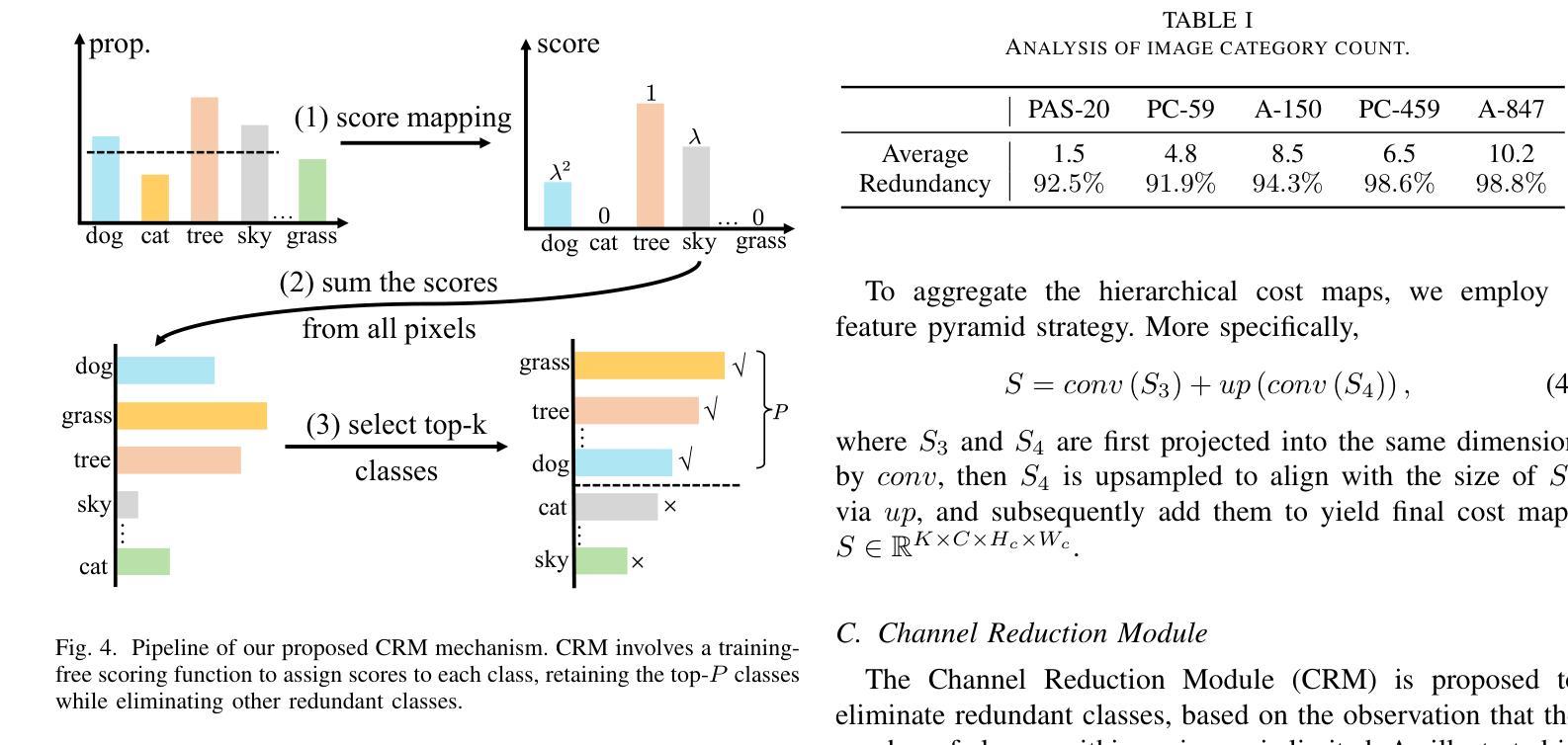
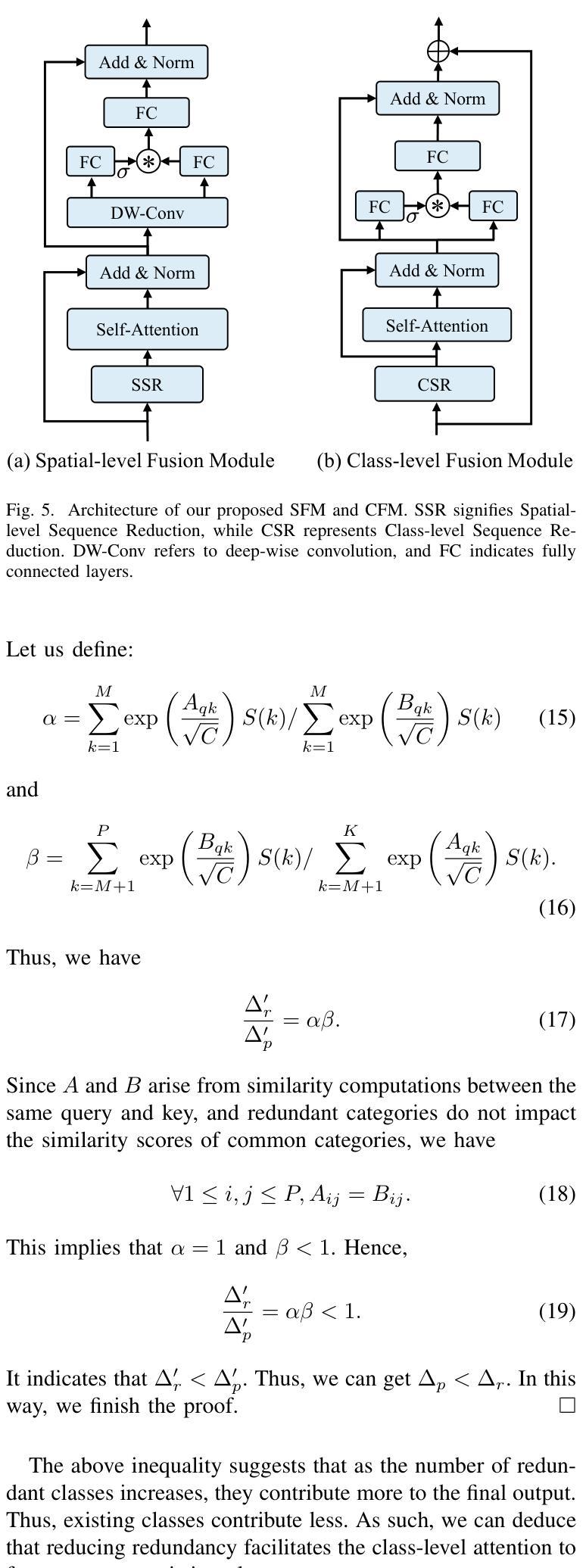
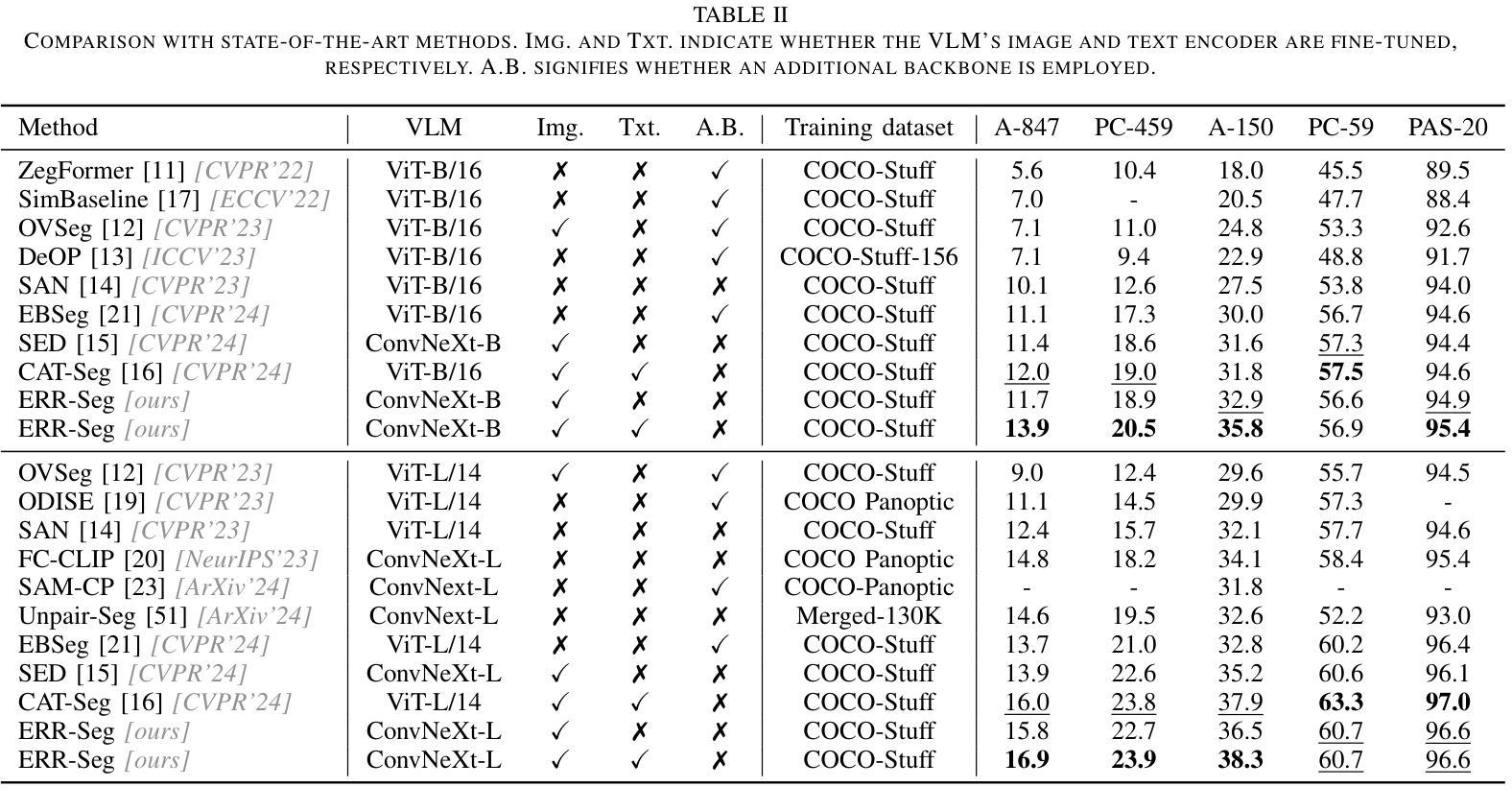
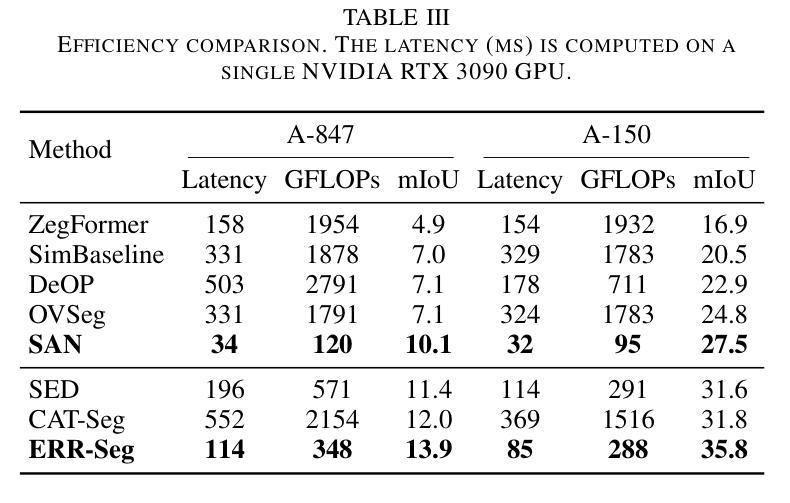
点此查看论文截图

Detection of Oscillation-like Patterns in Eclipsing Binary Light Curves using Neural Network-based Object Detection Algorithms
Authors:Burak Ulaş, Tamás Szklenár, Róbert Szabó
The primary aim of this research is to evaluate several convolutional neural network-based object detection algorithms for identifying oscillation-like patterns in light curves of eclipsing binaries. This involves creating a robust detection framework that can effectively process both synthetic light curves and real observational data. The study employs several state-of-the-art object detection algorithms, including Single Shot MultiBox Detector, Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network, You Only Look Once, and EfficientDet besides a custom non-pretrained model implemented from scratch. Synthetic light curve images and images derived from observational TESS light curves of known eclipsing binaries with a pulsating component were constructed with corresponding annotation files using custom scripts. The models were trained and validated on established datasets, followed by testing on unseen {\it{Kepler}} data to assess their generalization performance. The statistical metrics are also calculated to review the quality of each model. The results indicate that the pre-trained models exhibit high accuracy and reliability in detecting the targeted patterns. Faster R-CNN and You Only Look Once, in particular, showed superior performance in terms of object detection evaluation metrics on the validation dataset such as mAP value exceeding 99%. Single Shot MultiBox Detector, on the other hand, is the fastest although it shows slightly lower performance with a mAP of 97%. These findings highlight the potential of these models to contribute significantly to the automated determination of pulsating components in eclipsing binary systems, facilitating more efficient and comprehensive astrophysical investigations.
本文的主要目的是评估基于卷积神经网络的对象检测算法,用于识别食双星光曲线中的振荡模式。这涉及到创建一个稳健的检测框架,该框架可以有效处理合成光曲线和真实观测数据。该研究采用了多种最先进的目标检测算法,包括单发多框检测器(Single Shot MultiBox Detector)、快速区域卷积神经网络(Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network)、你只看一次(You Only Look Once)和EfficientDet,以及一个从头开始实现的自定义非预训练模型。使用自定义脚本构建了合成光曲线图像和来自已知具有脉动分量的食双星的观测TESS光曲线图像,并生成了相应的注释文件。这些模型在已建立的数据集上进行训练和验证,然后在未见过的开普勒数据上进行测试,以评估它们的泛化性能。还计算了统计指标以评估每个模型的质量。结果表明,预训练模型在检测目标模式方面表现出高准确性和可靠性。特别是Faster R-CNN和You Only Look Once在验证数据集上的目标检测评估指标(如mAP值超过99%)方面表现出卓越性能。另一方面,Single Shot MultiBox Detector虽然速度最快,但其性能略低,mAP为97%。这些发现表明这些模型在自动确定食双星系统中的脉动成分方面具有巨大潜力,有助于更高效和全面的天文研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Astronomy and Astrophysics (A&A). 27 pages, 35 figures, 5 tables
Summary:
本研究旨在评估基于卷积神经网络的对象检测算法,用于识别食双星光谱中振荡模式的性能。该研究实现了多个先进的目标检测算法,并在特定的数据集上进行训练和验证,测试在Kepler数据上的泛化性能。结果显示预训练模型在检测目标模式方面表现出高准确性和可靠性,其中Faster R-CNN和You Only Look Once表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究的目标是利用卷积神经网络评估对象检测算法在识别食双星光谱中的振荡模式方面的性能。
- 研究人员采用了多种先进的对象检测算法,包括Single Shot MultiBox Detector、Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network等。
- 研究使用定制脚本创建了合成光变曲线图像和基于观测的TESS光变曲线图像数据集,并附有相应的注释文件。
- 模型在特定数据集上进行训练和验证后,通过测试其未在训练中出现的Kepler数据来评估泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图
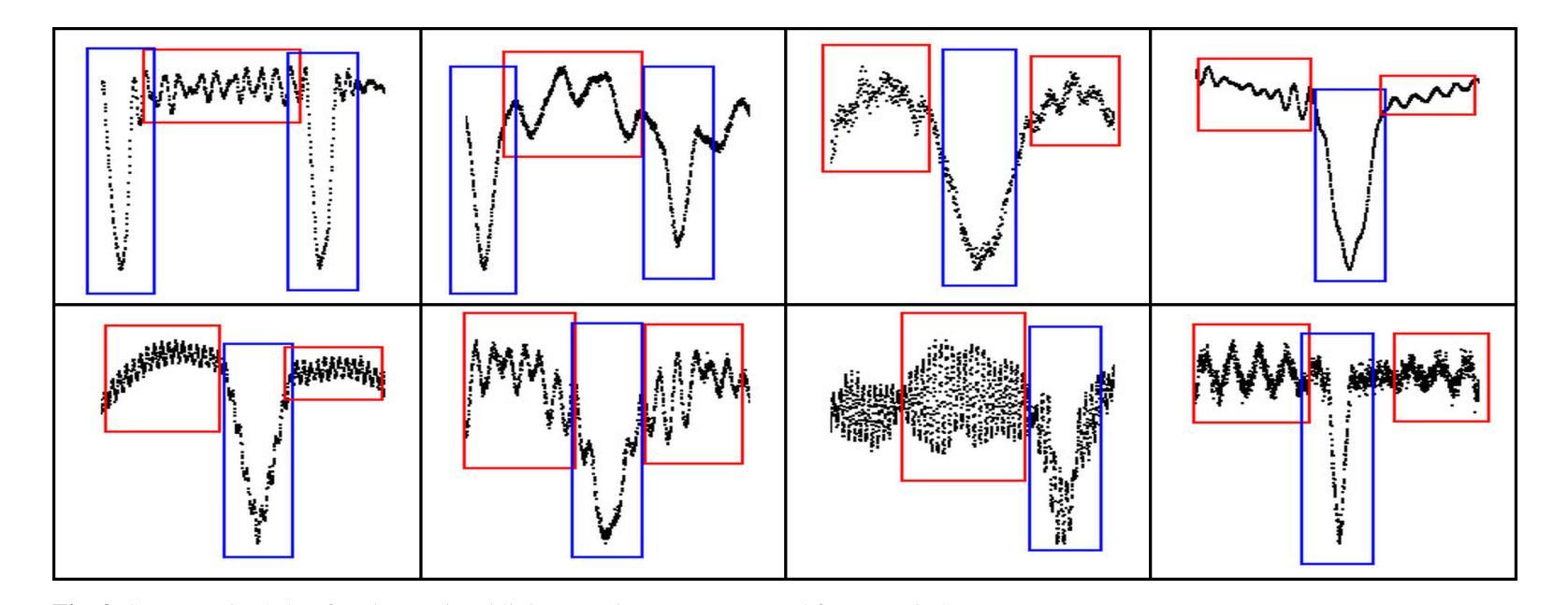
Assessing the Capability of YOLO- and Transformer-based Object Detectors for Real-time Weed Detection
Authors:Alicia Allmendinger, Ahmet Oğuz Saltık, Gerassimos G. Peteinatos, Anthony Stein, Roland Gerhards
Spot spraying represents an efficient and sustainable method for reducing the amount of pesticides, particularly herbicides, used in agricultural fields. To achieve this, it is of utmost importance to reliably differentiate between crops and weeds, and even between individual weed species in situ and under real-time conditions. To assess suitability for real-time application, different object detection models that are currently state-of-the-art are compared. All available models of YOLOv8, YOLOv9, YOLOv10, and RT-DETR are trained and evaluated with images from a real field situation. The images are separated into two distinct datasets: In the initial data set, each species of plants is trained individually; in the subsequent dataset, a distinction is made between monocotyledonous weeds, dicotyledonous weeds, and three chosen crops. The results demonstrate that while all models perform equally well in the metrics evaluated, the YOLOv9 models, particularly the YOLOv9s and YOLOv9e, stand out in terms of their strong recall scores (66.58 % and 72.36 %), as well as mAP50 (73.52 % and 79.86 %), and mAP50-95 (43.82 % and 47.00 %) in dataset 2. However, the RT-DETR models, especially RT-DETR-l, excel in precision with reaching 82.44 % on dataset 1 and 81.46 % in dataset 2, making them particularly suitable for scenarios where minimizing false positives is critical. In particular, the smallest variants of the YOLO models (YOLOv8n, YOLOv9t, and YOLOv10n) achieve substantially faster inference times down to 7.58 ms for dataset 2 on the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 GPU for analyzing one frame, while maintaining competitive accuracy, highlighting their potential for deployment in resource-constrained embedded computing devices as typically used in productive setups.
点喷技术是一种高效的可持续方法,可以减少农田中农药,特别是除草剂的用量。为实现这一点,在实时条件下可靠地区分作物和杂草,甚至区分个别杂草物种变得至关重要。为评估实时应用的适用性,对当前最先进的不同目标检测模型进行了比较。使用来自实际现场情况的图像对YOLOv8、YOLOv9、YOLOv10的所有可用模型以及RT-DETR进行了训练和评估。这些图像被分为两个独立的数据集:在初始数据集中,每种植物分别进行训练;在后续的数据集中,区分单子叶杂草、双子叶杂草和三种选择的作物。结果表明,在评估的指标中,所有模型的表现都相当出色,但YOLOv9模型,特别是YOLOv9s和YOLOv9e,在召回率方面表现出色(分别为66.58%和72.36%),以及mAP50(分别为73.52%和79.86%)和mAP50-95(分别为43.82%和47.00%)在数据集2中表现突出。然而,RT-DETR模型,特别是RT-DETR-l,在精确度方面表现出色,数据集1的精确率高达82.44%,数据集2的精确率为81.46%,使其成为在最小化误报至关重要的场景中特别合适的模型。特别是YOLO模型的最小变体(YOLOv8n、YOLOv9t和YOLOv10n),在NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 GPU上分析一帧的时间达到7.58毫秒的快速推理时间,同时保持具有竞争力的准确性,突显了它们在资源受限的嵌入式计算设备中部署的潜力,这些设备通常用于生产设置。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
实时作物与杂草识别技术在精准农业中的应用。对比了不同先进的目标检测模型,发现YOLOv9系列模型在杂草与作物的识别上具有更高的召回率和mAP(平均准确率),而RT-DETR系列模型则在精确度上表现优异,适合在需要减少误报的场景中应用。同时,小型YOLO模型具有更快的推理速度,适用于资源受限的嵌入式计算设备。
Key Takeaways
- 实时作物与杂草识别对减少农药使用至关重要。
- 对比了YOLOv8、YOLOv9、YOLOv10和RT-DETR等先进目标检测模型。
- YOLOv9系列模型在杂草与作物的识别上具有优秀的召回率和mAP。
- RT-DETR系列模型在精确度上表现突出,适用于减少误报的场景。
- 小型YOLO模型具有更快的推理速度。
- 这些模型在NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 GPU上的表现被评估。
点此查看论文截图

GMT: Guided Mask Transformer for Leaf Instance Segmentation
Authors:Feng Chen, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris, Mario Valerio Giuffrida
Leaf instance segmentation is a challenging multi-instance segmentation task, aiming to separate and delineate each leaf in an image of a plant. Accurate segmentation of each leaf is crucial for plant-related applications such as the fine-grained monitoring of plant growth and crop yield estimation. This task is challenging because of the high similarity (in shape and colour), great size variation, and heavy occlusions among leaf instances. Furthermore, the typically small size of annotated leaf datasets makes it more difficult to learn the distinctive features needed for precise segmentation. We hypothesise that the key to overcoming the these challenges lies in the specific spatial patterns of leaf distribution. In this paper, we propose the Guided Mask Transformer (GMT), which leverages and integrates leaf spatial distribution priors into a Transformer-based segmentor. These spatial priors are embedded in a set of guide functions that map leaves at different positions into a more separable embedding space. Our GMT consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art on three public plant datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/vios-s/gmt-leaf-ins-seg.
叶片实例分割是一项具有挑战性的多实例分割任务,旨在在一幅植物图像中分离和描绘每一片叶片。对于植物相关应用(如植物生长的精细监测和作物产量估算)而言,准确地对每片叶子进行分割至关重要。此任务之所以具有挑战性,是因为叶片实例之间在形状和颜色上的高度相似性、尺寸的巨大差异以及严重的遮挡问题。此外,通常带有注释的叶片数据集规模较小,这使得学习精确分割所需的区别特征变得更加困难。我们假设克服这些挑战的关键在于叶片分布的特定空间模式。在本文中,我们提出了导向掩膜转换器(GMT),它通过利用并整合叶片空间分布先验信息到一个基于转换器的分割器中来实现这一功能。这些空间先验信息嵌入一组引导函数中,该组函数可以将不同位置的叶子映射到一个更易分离的特征空间中。我们的GMT在三个公共植物数据集上均表现出卓越的性能。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/vios-s/gmt-leaf-ins-seg。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2025 (Oral Presentation)
Summary
本文介绍了叶实例分割任务的重要性和挑战性,提出了一种基于Transformer的引导掩膜转换器(GMT)来解决该问题。GMT利用叶片空间分布先验信息,通过引导函数将不同位置的叶片映射到可分离的嵌入空间。在三个公共植物数据集上,GMT表现优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 叶实例分割是植物图像中的一项挑战性任务,旨在分离和描绘每片叶子。
- 准确分割每片叶子对于植物生长精细监测和作物产量估算等植物相关应用至关重要。
- 叶实例分割面临的挑战包括高相似性(形状和颜色)、尺寸差异大以及叶片之间的严重遮挡。
- 叶片数据集标注样本量小,增加了学习精确分割所需特征识别的难度。
- 成功的关键在于利用叶片特定的空间分布模式。
- 提出了引导掩膜转换器(GMT),它利用叶片空间分布先验信息,并将其集成到基于Transformer的分割器中。
点此查看论文截图