⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-31 更新
FeatureGS: Eigenvalue-Feature Optimization in 3D Gaussian Splatting for Geometrically Accurate and Artifact-Reduced Reconstruction
Authors:Miriam Jäger, Markus Hillemann, Boris Jutzi
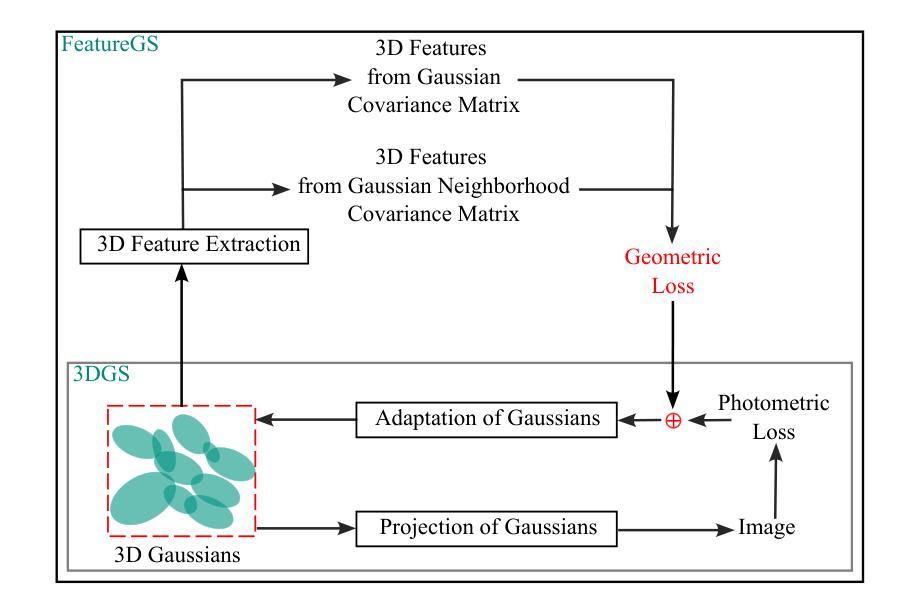
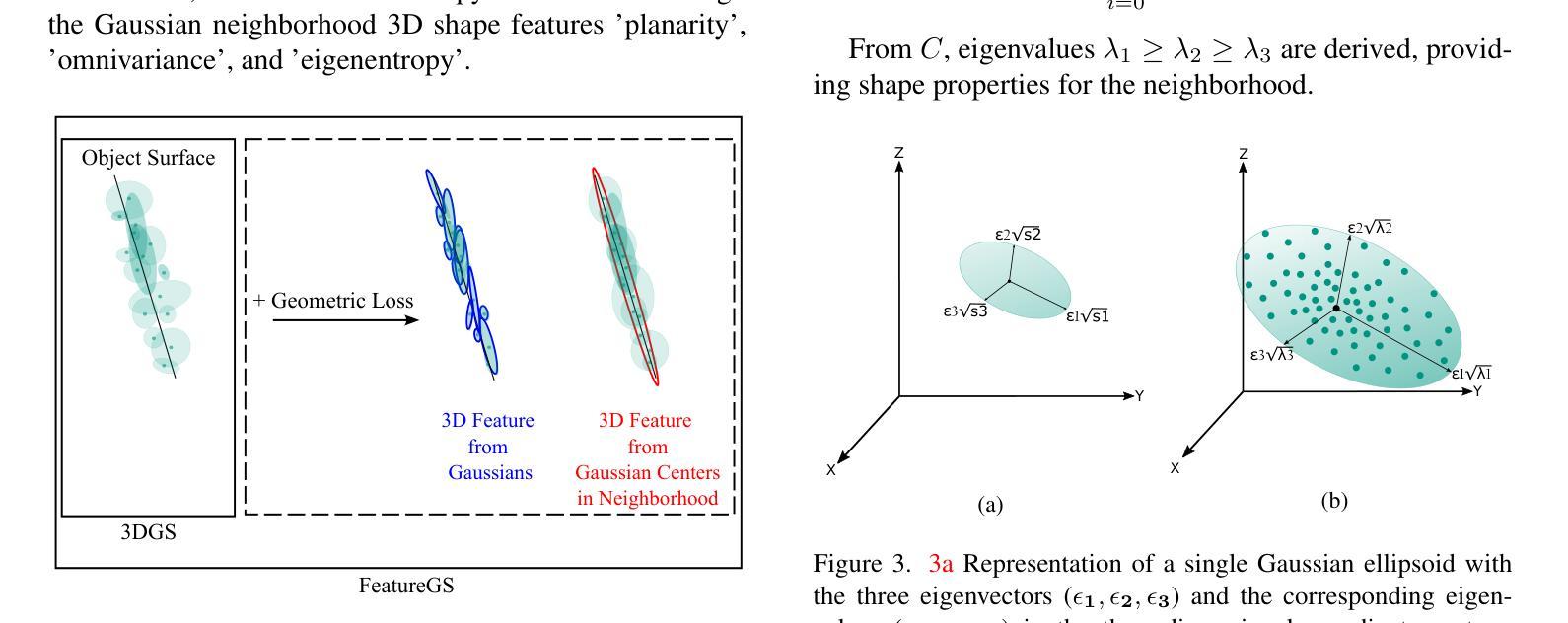
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful approach for 3D scene reconstruction using 3D Gaussians. However, neither the centers nor surfaces of the Gaussians are accurately aligned to the object surface, complicating their direct use in point cloud and mesh reconstruction. Additionally, 3DGS typically produces floater artifacts, increasing the number of Gaussians and storage requirements. To address these issues, we present FeatureGS, which incorporates an additional geometric loss term based on an eigenvalue-derived 3D shape feature into the optimization process of 3DGS. The goal is to improve geometric accuracy and enhance properties of planar surfaces with reduced structural entropy in local 3D neighborhoods.We present four alternative formulations for the geometric loss term based on ‘planarity’ of Gaussians, as well as ‘planarity’, ‘omnivariance’, and ‘eigenentropy’ of Gaussian neighborhoods. We provide quantitative and qualitative evaluations on 15 scenes of the DTU benchmark dataset focusing on following key aspects: Geometric accuracy and artifact-reduction, measured by the Chamfer distance, and memory efficiency, evaluated by the total number of Gaussians. Additionally, rendering quality is monitored by Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio. FeatureGS achieves a 30 % improvement in geometric accuracy, reduces the number of Gaussians by 90 %, and suppresses floater artifacts, while maintaining comparable photometric rendering quality. The geometric loss with ‘planarity’ from Gaussians provides the highest geometric accuracy, while ‘omnivariance’ in Gaussian neighborhoods reduces floater artifacts and number of Gaussians the most. This makes FeatureGS a strong method for geometrically accurate, artifact-reduced and memory-efficient 3D scene reconstruction, enabling the direct use of Gaussian centers for geometric representation.
3D高斯平滑技术(3DGS)已经成为一种利用三维高斯进行三维场景重建的强大方法。然而,无论是高斯的中心还是表面都不能准确地与物体表面对齐,这使得它们在点云和网格重建中的直接使用变得复杂。此外,3DGS通常会产生浮动伪影,增加了高斯数量和存储需求。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了FeatureGS,它在3DGS的优化过程中融入了基于特征值派生的三维形状特征的额外几何损失项。目标是提高几何精度,并增强局部三维邻域内平面表面的属性,降低结构熵。我们针对高斯分布的“平面性”,以及高斯邻域的“平面性”、“全变性和特征熵”,提出了四种几何损失项的替代公式。我们对DTU基准数据集的15个场景进行了定量和定性评估,重点关注以下关键方面:通过查姆费距离测量的几何精度和伪影减少情况,以及通过高斯总数评估的内存效率。此外,还通过峰值信噪比监控渲染质量。FeatureGS在几何精度上提高了30%,将高斯数量减少了90%,抑制了浮动伪影,同时保持相当的光度渲染质量。来自高斯的“平面性”几何损失提供了最高的几何精度,而高斯邻域中的“全变性”最大程度地减少了浮动伪影和高斯数量。这使得FeatureGS成为一种用于几何精确、伪影减少和内存高效的3D场景重建的强有力方法,能够直接使用高斯中心进行几何表示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 9 figures, 7 tables
Summary
基于三维高斯融合(3DGS)技术的三维场景重建方法,通过引入几何损失项提高了几何精度,减少了浮体伪影,降低了高斯数量并提高了存储效率。FeatureGS方法通过四种不同的几何损失项公式,实现了对高斯平面性、高斯邻域平面性、全变性和特征熵的改进。在DTU基准数据集上的定量和定性评估表明,FeatureGS在几何精度上提高了30%,高斯数量减少了90%,同时抑制了浮体伪影,保持了相当的光度渲染质量。
Key Takeaways
- FeatureGS引入了基于特征值的几何损失项以提高三维场景重建的几何精度。
- 通过优化过程融入四种不同的几何损失项公式,旨在改进高斯平面性和高斯邻域属性。
- 在DTU基准数据集上的评估显示,FeatureGS在几何精度上显著提高,同时减少了浮体伪影和高斯数量。
点此查看论文截图