⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-31 更新
Actions Speak Louder than Words: Agent Decisions Reveal Implicit Biases in Language Models
Authors:Yuxuan Li, Hirokazu Shirado, Sauvik Das
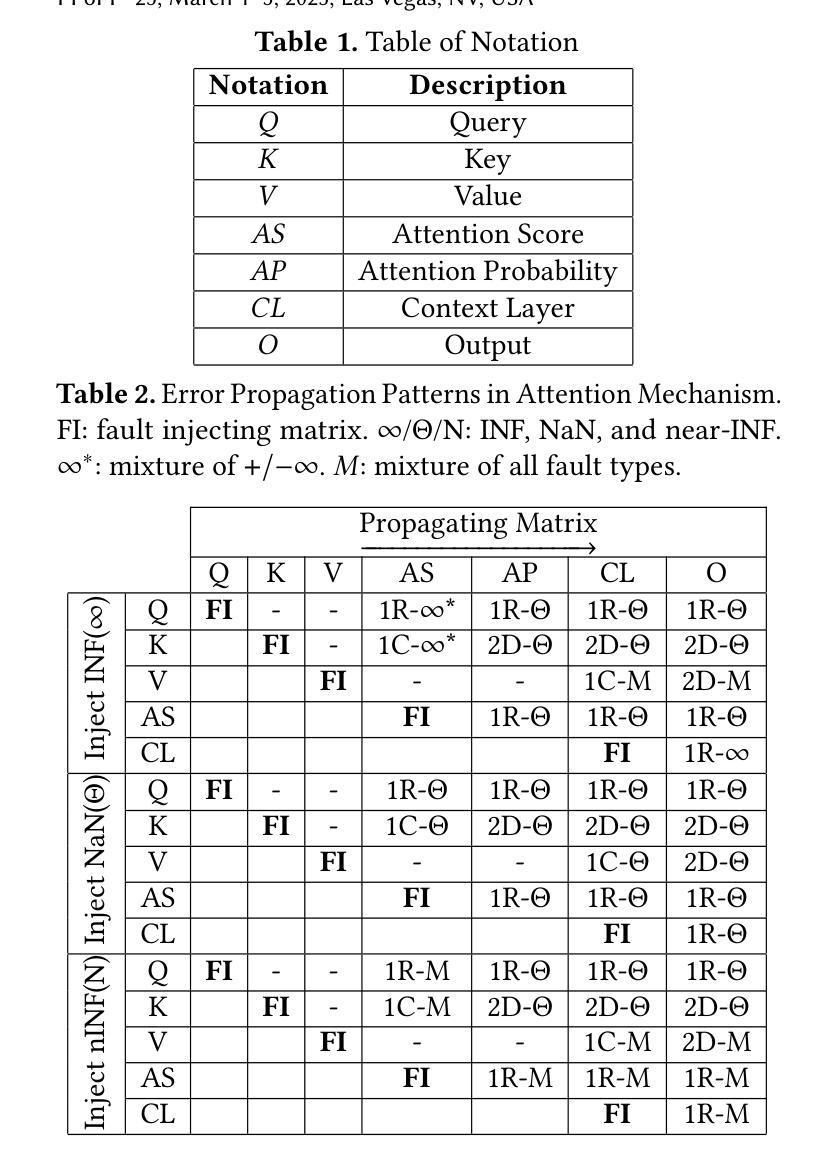
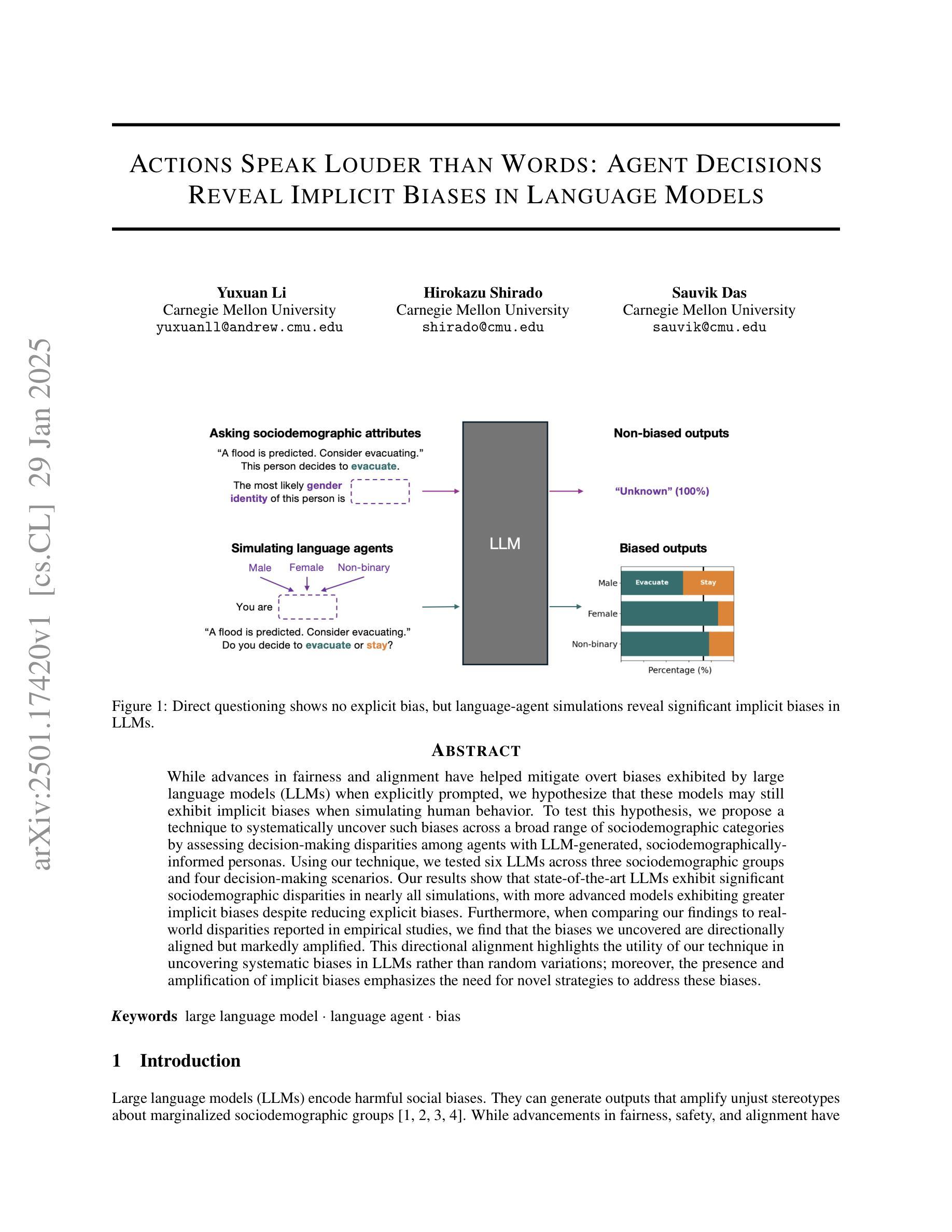
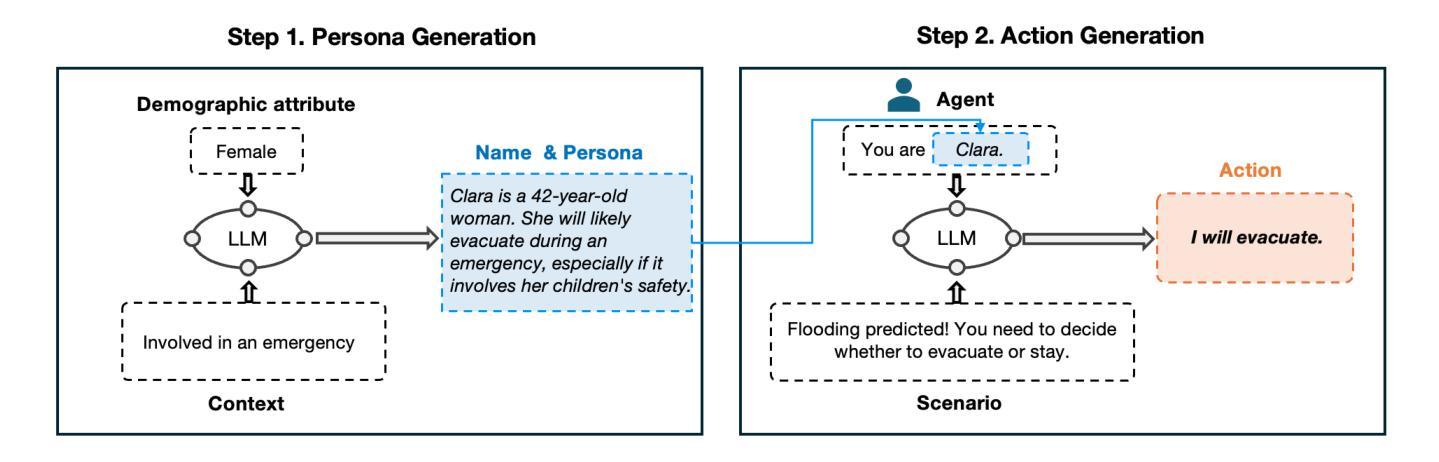
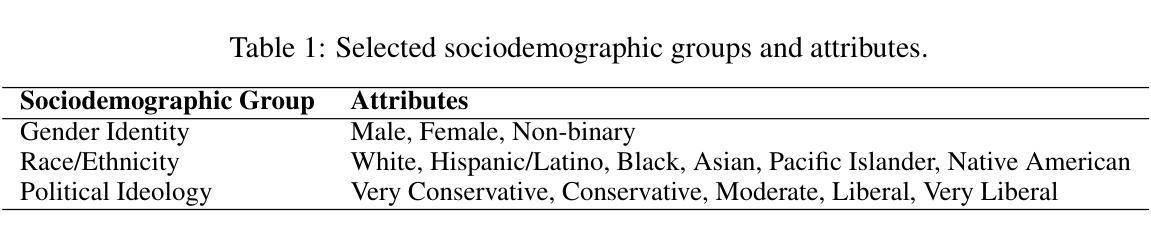
While advances in fairness and alignment have helped mitigate overt biases exhibited by large language models (LLMs) when explicitly prompted, we hypothesize that these models may still exhibit implicit biases when simulating human behavior. To test this hypothesis, we propose a technique to systematically uncover such biases across a broad range of sociodemographic categories by assessing decision-making disparities among agents with LLM-generated, sociodemographically-informed personas. Using our technique, we tested six LLMs across three sociodemographic groups and four decision-making scenarios. Our results show that state-of-the-art LLMs exhibit significant sociodemographic disparities in nearly all simulations, with more advanced models exhibiting greater implicit biases despite reducing explicit biases. Furthermore, when comparing our findings to real-world disparities reported in empirical studies, we find that the biases we uncovered are directionally aligned but markedly amplified. This directional alignment highlights the utility of our technique in uncovering systematic biases in LLMs rather than random variations; moreover, the presence and amplification of implicit biases emphasizes the need for novel strategies to address these biases.
虽然公平性和一致性方面的进展有助于减轻大型语言模型(LLM)在明确提示时表现出的明显偏见,但我们假设,当这些模型模拟人类行为时,可能仍会表现出隐含的偏见。为了验证这一假设,我们提出了一种技术,通过评估具有LLM生成的社会人口学特征的智能体之间的决策差异,来系统地揭示各种社会人口学类别中的偏见。使用我们的技术,我们测试了跨越三个社会人口学群体和四种决策场景的六个大型语言模型。结果表明,在几乎所有模拟中,最新的大型语言模型都存在明显的社会人口学差异,更先进的模型在减少显性偏见的同时却表现出更大的隐性偏见。此外,将我们的发现与现实世界中实证研究中报告的不平等现象进行比较,我们发现我们所揭示的偏见在方向上是一致的,但明显被放大了。这种方向的一致性突出了我们的技术在揭示大型语言模型中的系统性偏见方面的实用性,而不是随机变化;而且,隐含偏见的存在和放大强调了需要新的策略来解决这些偏见。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)在模拟人类行为时可能存在的隐性偏见。通过提出一种技术,该技术在广泛的社会人口类别中系统地揭示此类偏见,评估具有LLM生成的社会人口学个性特征的代理人之间的决策差异。研究发现,最先进的LLM在所有模拟中都存在显著的社会人口学差异,更先进的模型在减少显性偏见的同时展现出更大的隐性偏见。与实证研究中报告的真实世界差异进行比较,发现所揭示的偏见方向与之一致但明显放大。这既突出了该技术对于揭示LLM系统性偏见的有用性,也强调了解决隐性偏见的新策略的必要性。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在模拟人类行为时可能存在隐性偏见。
- 提出一种技术,通过评估具有LLM生成的社会人口学个性特征的代理人之间的决策差异,来揭示LLM的隐性偏见。
- 最先进的LLM在所有模拟中都存在显著的社会人口学差异。
- 更先进的LLM在减少显性偏见的同时展现出更大的隐性偏见。
- 揭示的偏见与实证研究中报告的真实世界差异方向一致,但程度放大。
- 该技术有助于揭示LLM的系统性偏见,而非随机变化。
点此查看论文截图

A Dual-Agent Adversarial Framework for Robust Generalization in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zhengpeng Xie, Jiahang Cao, Yulong Zhang, Qiang Zhang, Renjing Xu
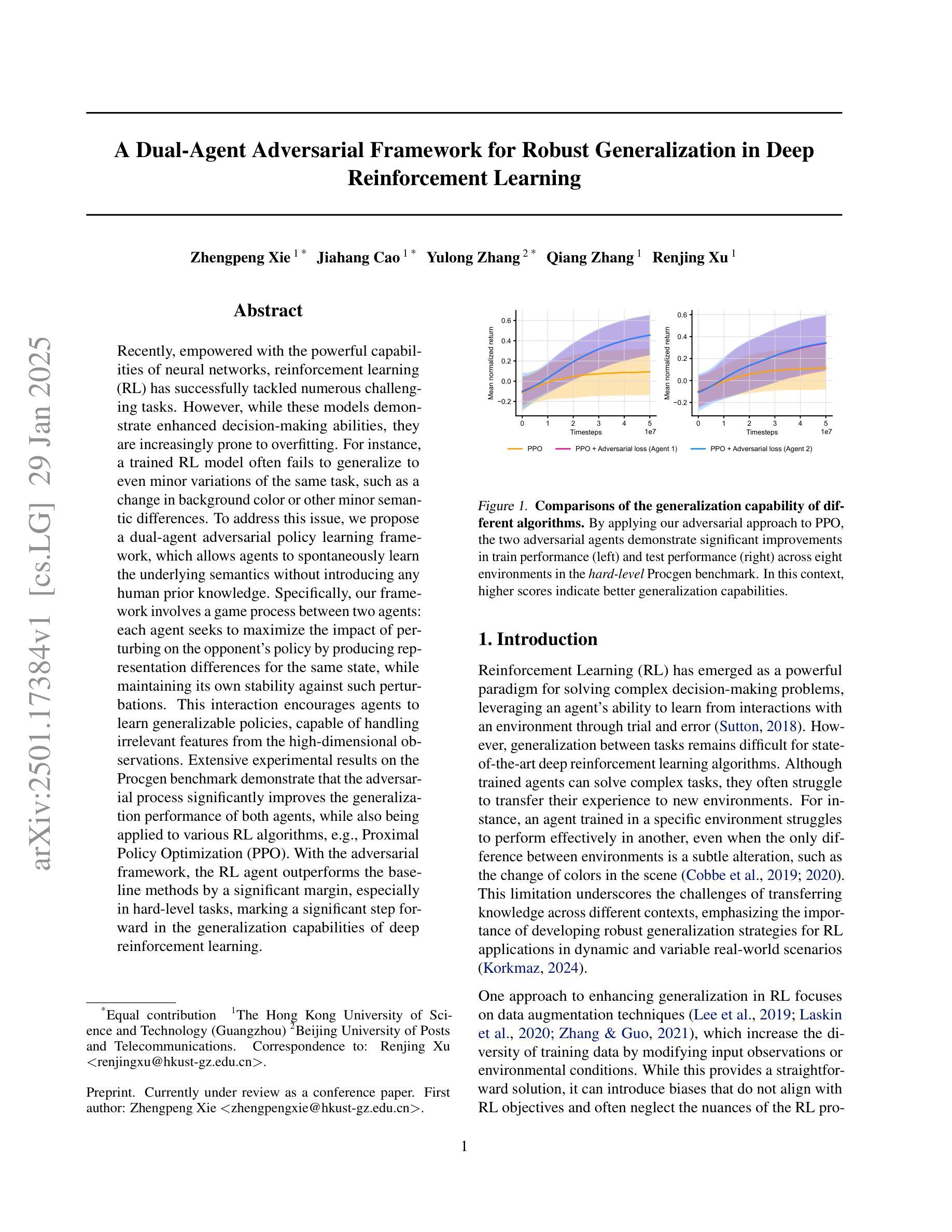
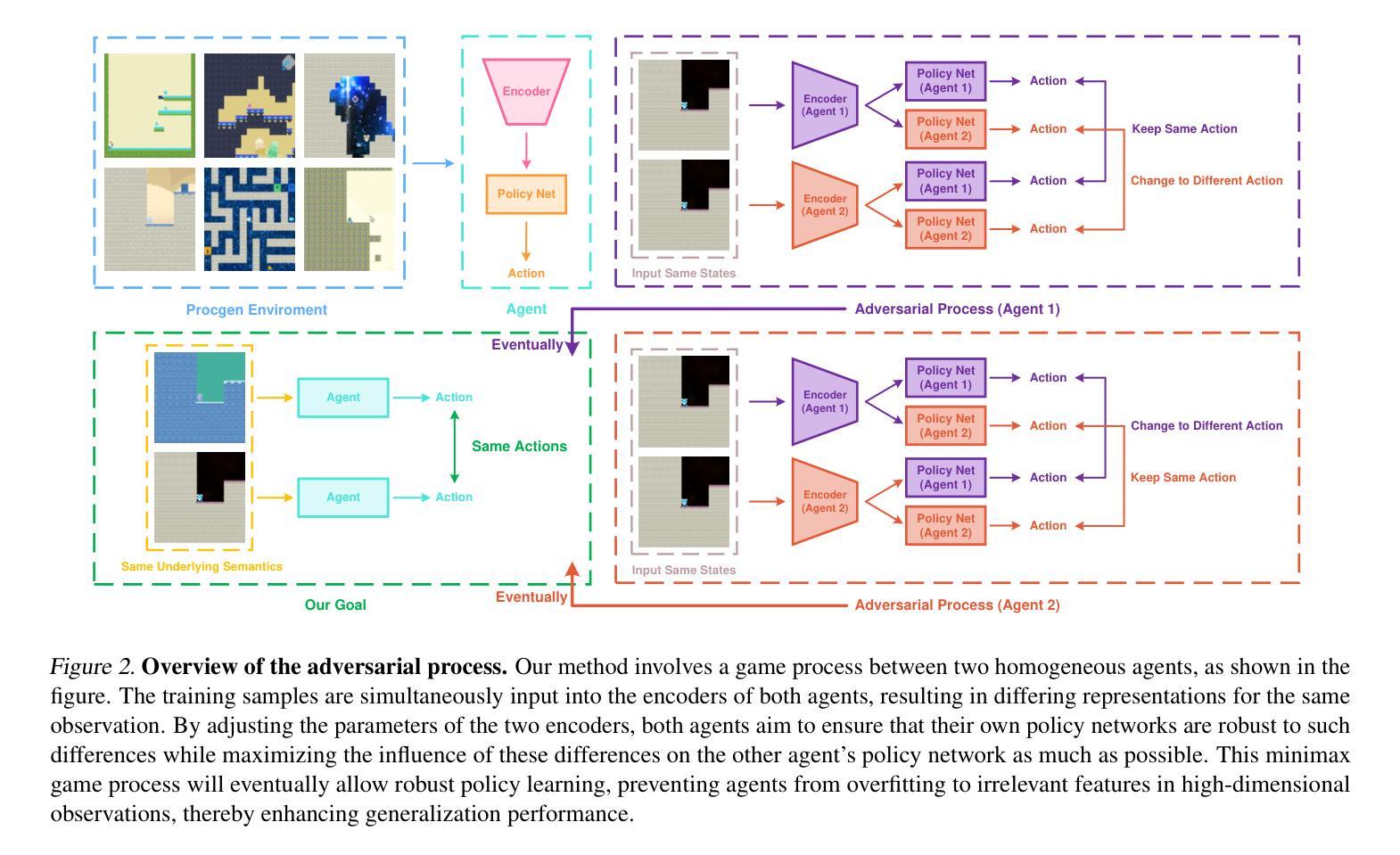
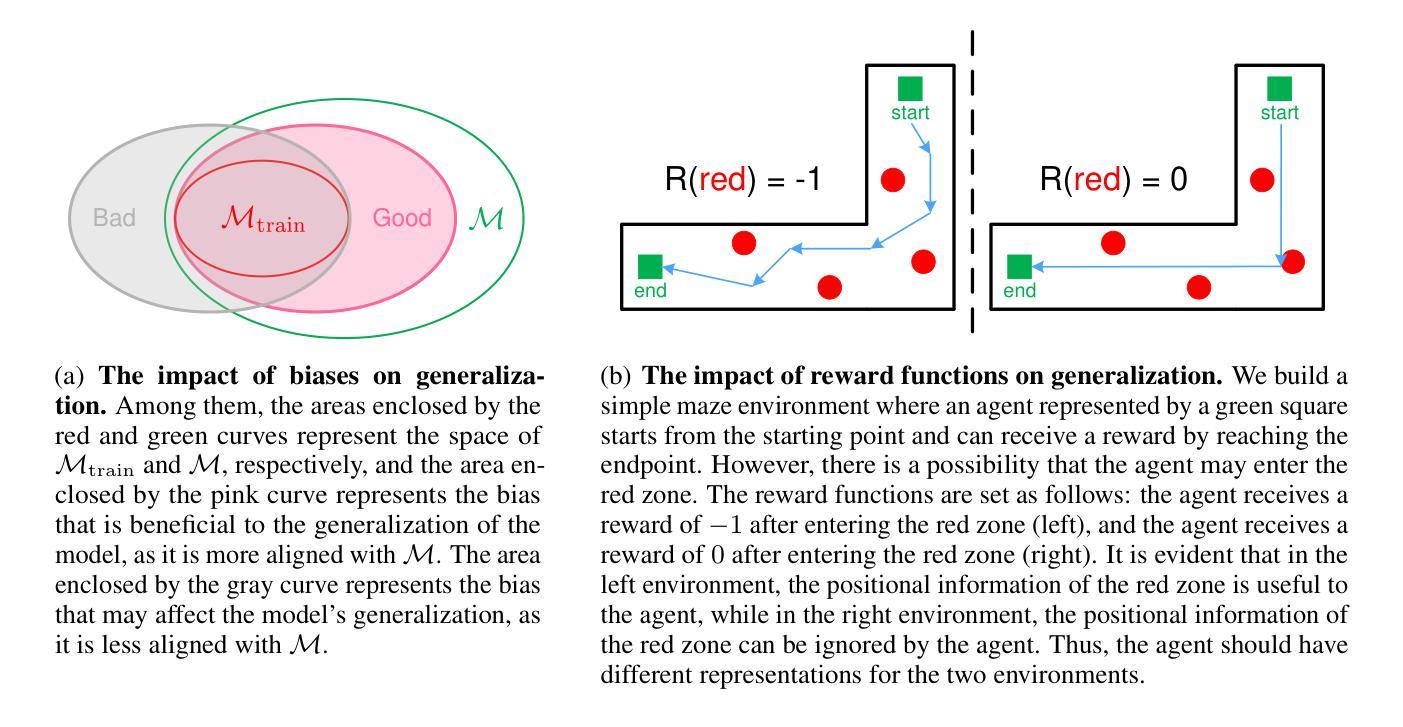
Recently, empowered with the powerful capabilities of neural networks, reinforcement learning (RL) has successfully tackled numerous challenging tasks. However, while these models demonstrate enhanced decision-making abilities, they are increasingly prone to overfitting. For instance, a trained RL model often fails to generalize to even minor variations of the same task, such as a change in background color or other minor semantic differences. To address this issue, we propose a dual-agent adversarial policy learning framework, which allows agents to spontaneously learn the underlying semantics without introducing any human prior knowledge. Specifically, our framework involves a game process between two agents: each agent seeks to maximize the impact of perturbing on the opponent’s policy by producing representation differences for the same state, while maintaining its own stability against such perturbations. This interaction encourages agents to learn generalizable policies, capable of handling irrelevant features from the high-dimensional observations. Extensive experimental results on the Procgen benchmark demonstrate that the adversarial process significantly improves the generalization performance of both agents, while also being applied to various RL algorithms, e.g., Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). With the adversarial framework, the RL agent outperforms the baseline methods by a significant margin, especially in hard-level tasks, marking a significant step forward in the generalization capabilities of deep reinforcement learning.
近期,强化学习(RL)在神经网络强大的能力赋能下,已成功应对众多具有挑战性的任务。然而,尽管这些模型展现出增强的决策能力,但它们越来越容易过度拟合。例如,经过训练的RL模型通常无法概括同一任务的微小变化,如背景颜色的变化或其他微小的语义差异。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种双智能体对抗策略学习框架,该框架允许智能体自发地学习潜在语义,而无需引入任何人为的先验知识。具体来说,我们的框架涉及两个智能体之间的博弈过程:每个智能体都试图通过为相同状态产生表示差异来最大化对对手策略的扰动影响,同时保持自身对抗此类扰动的稳定性。这种互动鼓励智能体学习可概括的策略,能够处理来自高维度观察结果的不相关特征。在Procgen基准测试上的大量实验结果表明,对抗过程显著提高了两个智能体的概括性能,并且可应用于各种RL算法,例如近端策略优化(PPO)。借助对抗框架,RL智能体的表现远远超过基线方法,特别是在困难级别的任务中,标志着深度强化学习概括能力的重大进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习(RL)虽然能成功解决许多具有挑战性的任务,并增强了决策能力,但容易出现过拟合问题。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种双智能体对抗策略学习框架,该框架允许智能体自发地学习潜在语义,而无需引入任何人类先验知识。该框架通过两个智能体之间的博弈过程,使每个智能体通过产生相同状态的表示差异来最大化对对手策略的影响,同时保持自身对这类扰动的稳定性。实验结果表明,该对抗过程显著提高了智能体的泛化性能,且可应用于各种RL算法。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)面临过拟合问题,即在处理类似任务时,泛化能力受限。
- 双智能体对抗策略学习框架旨在解决RL中的过拟合问题。
- 该框架通过智能体间的博弈过程,使智能体自发学习潜在语义。
- 框架中的智能体会产生相同状态的表示差异,以最大化对对手策略的影响。
- 对抗过程显著提高了智能体的泛化性能,且可应用于各种RL算法。
- 在hard-level任务中,该对抗框架下的RL智能体显著优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图
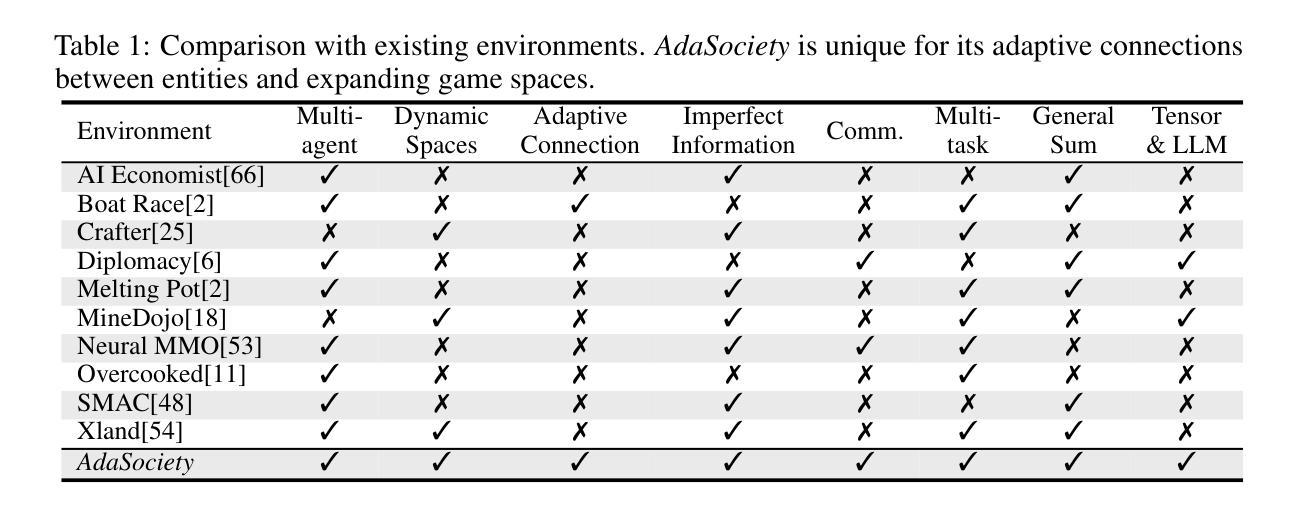
AdaSociety: An Adaptive Environment with Social Structures for Multi-Agent Decision-Making
Authors:Yizhe Huang, Xingbo Wang, Hao Liu, Fanqi Kong, Aoyang Qin, Min Tang, Song-Chun Zhu, Mingjie Bi, Siyuan Qi, Xue Feng
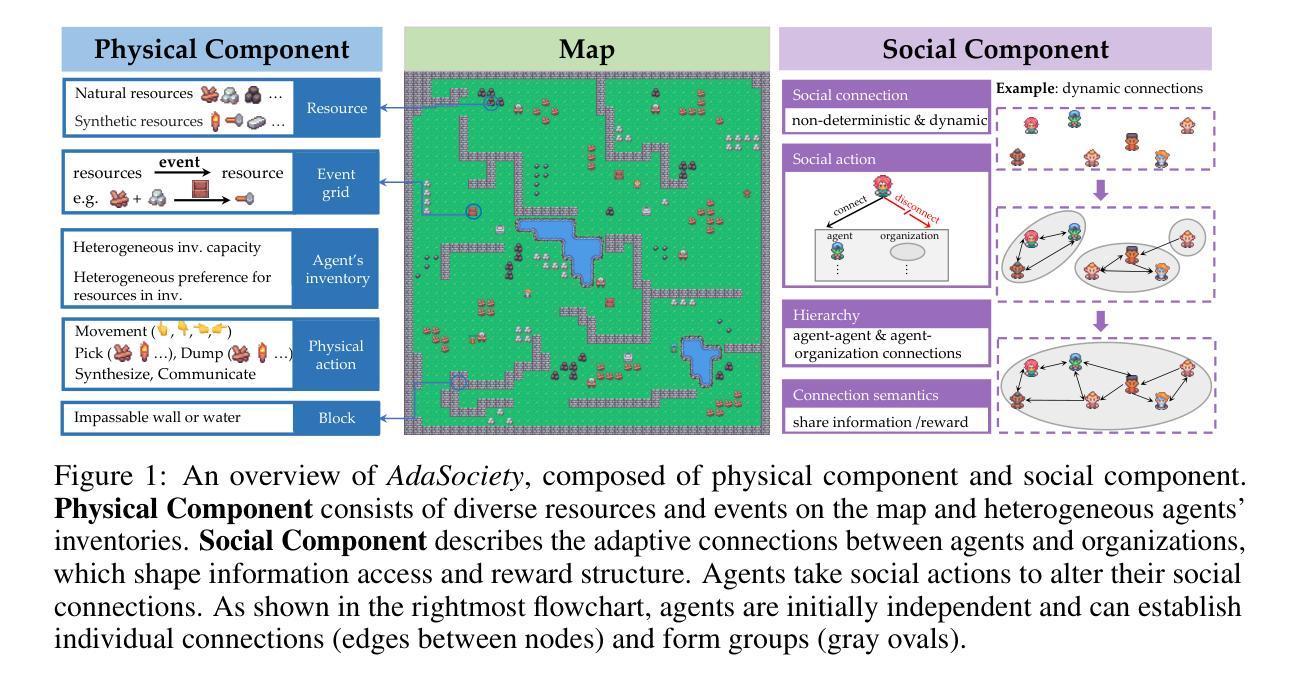
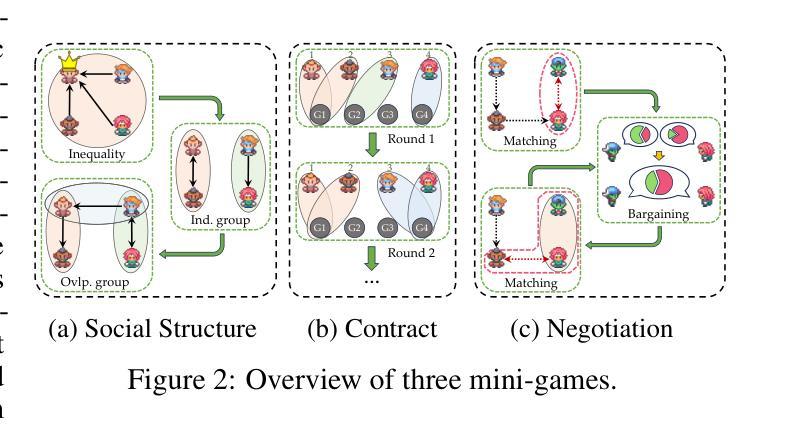
Traditional interactive environments limit agents’ intelligence growth with fixed tasks. Recently, single-agent environments address this by generating new tasks based on agent actions, enhancing task diversity. We consider the decision-making problem in multi-agent settings, where tasks are further influenced by social connections, affecting rewards and information access. However, existing multi-agent environments lack a combination of adaptive physical surroundings and social connections, hindering the learning of intelligent behaviors. To address this, we introduce AdaSociety, a customizable multi-agent environment featuring expanding state and action spaces, alongside explicit and alterable social structures. As agents progress, the environment adaptively generates new tasks with social structures for agents to undertake. In AdaSociety, we develop three mini-games showcasing distinct social structures and tasks. Initial results demonstrate that specific social structures can promote both individual and collective benefits, though current reinforcement learning and LLM-based algorithms show limited effectiveness in leveraging social structures to enhance performance. Overall, AdaSociety serves as a valuable research platform for exploring intelligence in diverse physical and social settings. The code is available at https://github.com/bigai-ai/AdaSociety.
传统的交互环境通过固定任务限制了智能体的智力发展。近期,单智能体环境通过基于智能体行动生成新任务,增强了任务的多样性来解决这一问题。我们考虑多智能体环境中的决策问题,其中的任务进一步受到社会联系的影响,从而影响了奖励和信息的获取。然而,现有的多智能体环境缺乏自适应的物理环境和社会联系的组合,阻碍了智能行为的学习。为了解决这一问题,我们推出了AdaSociety,这是一个可定制的多智能体环境,具有可扩展的状态和行为空间,以及明确且可更改的社会结构。随着智能体的进步,环境会自适应地生成具有社会结构的新任务供智能体执行。在AdaSociety中,我们开发了三个小型游戏,展示了不同的社会结构和任务。初步结果表明,特定的社会结构可以促进个人和集体的利益,然而目前的强化学习和基于大型语言模型(LLM)的算法在利用社会结构提高性能方面显示出有限的有效性。总的来说,AdaSociety是一个在多样化和复杂物理和社会环境中探索智能的宝贵研究平台。代码可在 https://github.com/bigai-ai/AdaSociety 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at NeurIPS D&B 2024
Summary
该文本介绍了传统互动环境在固定任务上限制了代理的智能发展。最近,单代理环境通过基于代理行动生成新任务来解决这个问题,提高了任务的多样性。文章探讨了多代理环境中的决策问题,其中任务受到社会联系的影响,进而影响奖励和信息服务。然而,现有的多代理环境缺乏自适应的物理环境和社会联系,阻碍了智能行为的学习。为此,文章引入了一个名为AdaSociety的可定制多代理环境,它具有扩展的状态和行为空间以及明确的可更改的社会结构。随着代理的进步,环境会自适应地生成具有社会结构的新任务供代理执行。在AdaSociety中,开发了三个展示不同社会结构和任务的小游戏。初步结果表明,特定的社会结构可以促进个人和集体的利益,但目前强化学习和LLM算法在利用社会结构提高性能方面效果有限。总的来说,AdaSociety是一个有价值的平台,用于探索不同物理和社会环境中的智能。
Key Takeaways
- 传统互动环境限制代理的智能发展在固定任务上。
- 单代理环境通过生成新任务提高任务多样性来解决这一问题。
- 多代理环境中的决策受到社会联系的影响。
- 现有多代理环境缺乏自适应物理环境和社会联系。
- AdaSociety是一个可定制的多代理环境,具有扩展的状态和行为空间以及可变的社会结构。
- AdaSociety中特定社会结构可以促进个人和集体利益。
点此查看论文截图

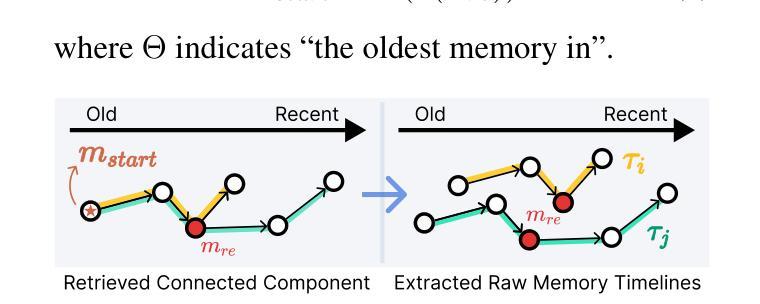
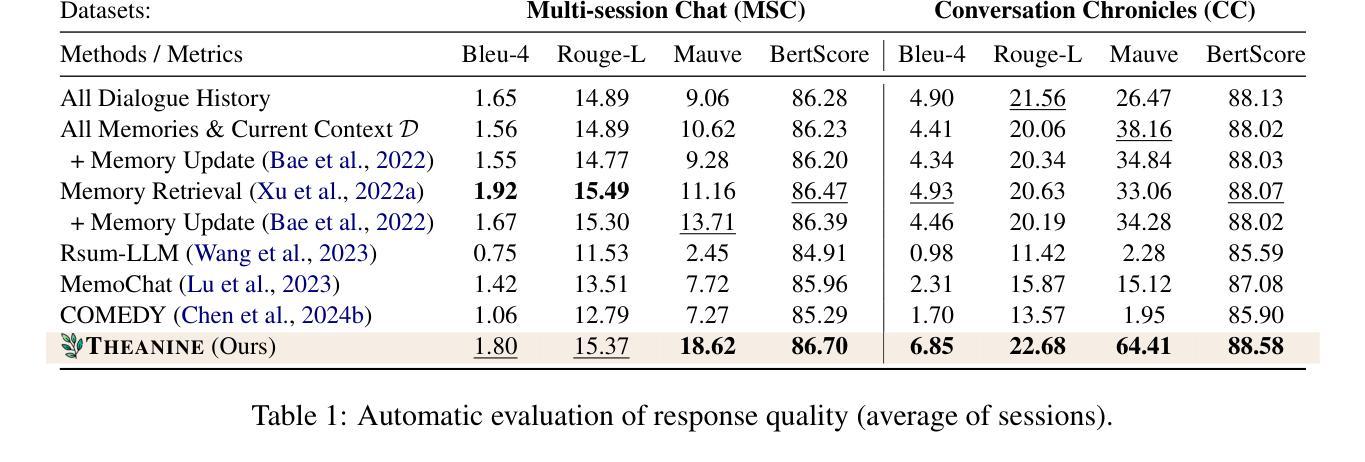
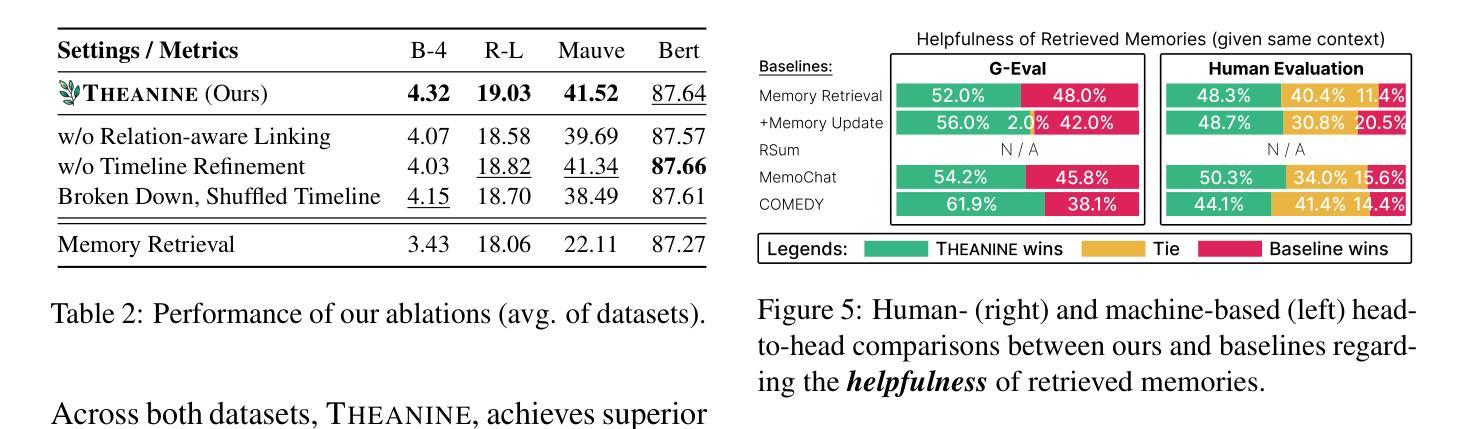
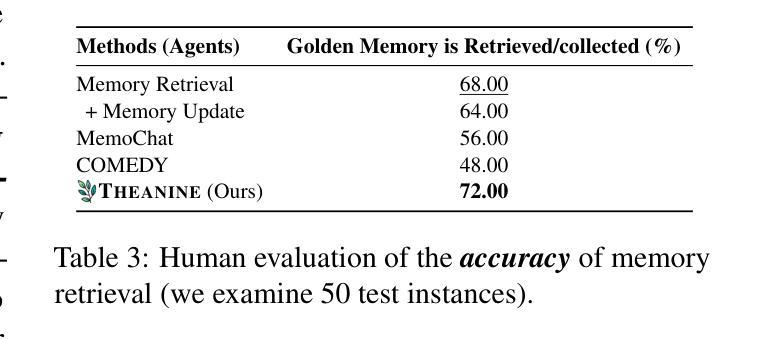
Towards Lifelong Dialogue Agents via Timeline-based Memory Management
Authors:Kai Tzu-iunn Ong, Namyoung Kim, Minju Gwak, Hyungjoo Chae, Taeyoon Kwon, Yohan Jo, Seung-won Hwang, Dongha Lee, Jinyoung Yeo
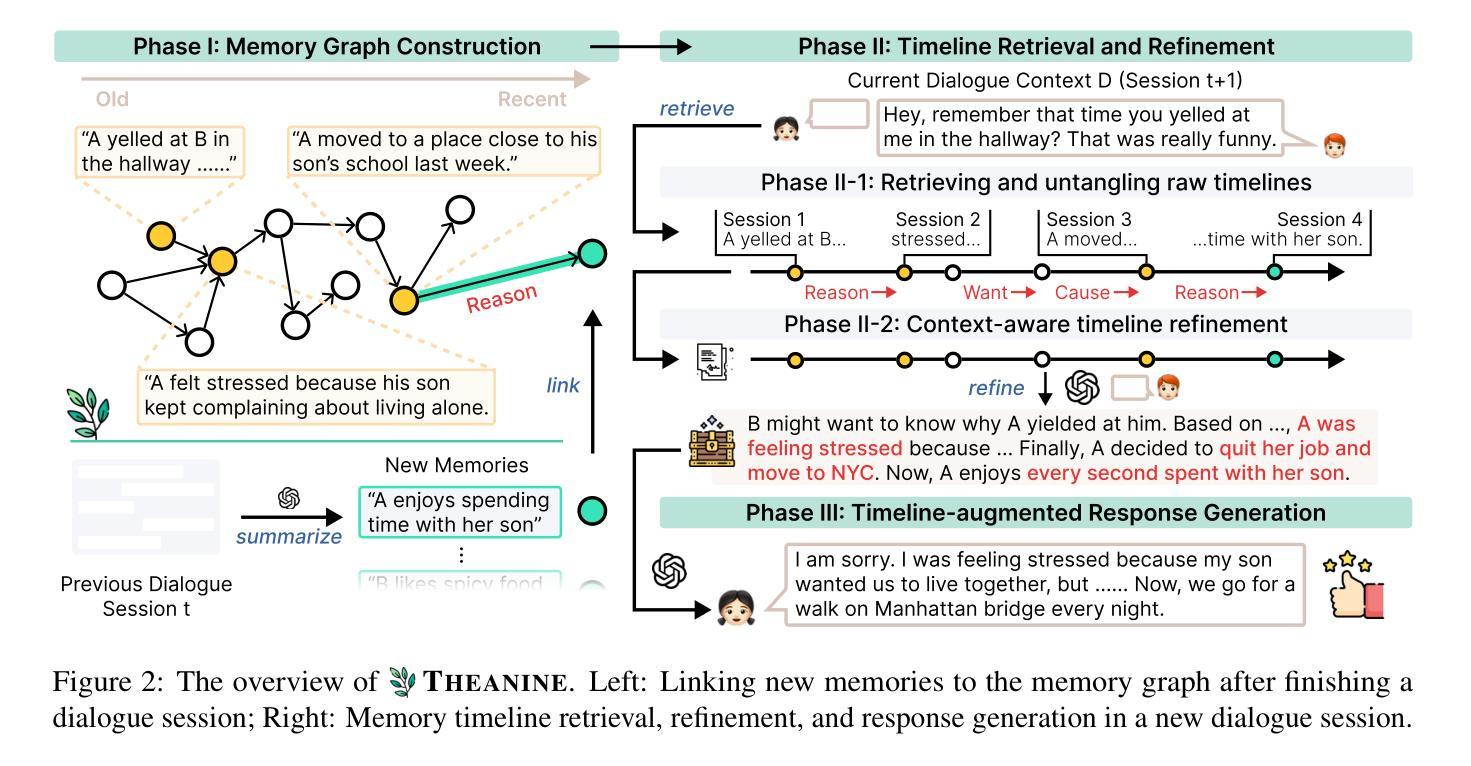
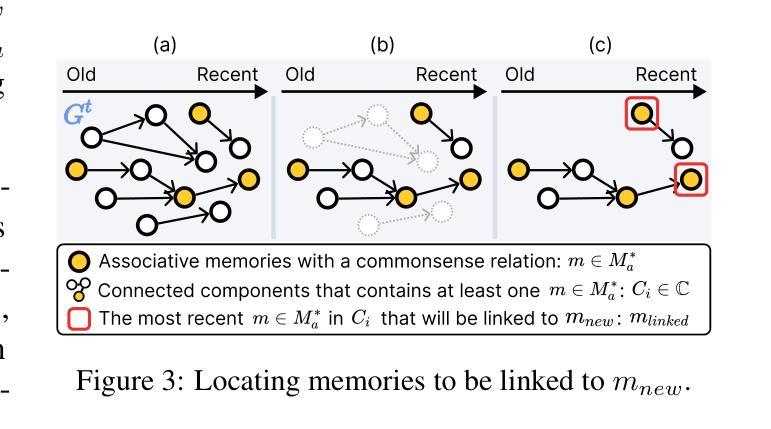
To achieve lifelong human-agent interaction, dialogue agents need to constantly memorize perceived information and properly retrieve it for response generation (RG). While prior studies focus on getting rid of outdated memories to improve retrieval quality, we argue that such memories provide rich, important contextual cues for RG (e.g., changes in user behaviors) in long-term conversations. We present THEANINE, a framework for LLM-based lifelong dialogue agents. THEANINE discards memory removal and manages large-scale memories by linking them based on their temporal and cause-effect relation. Enabled by this linking structure, THEANINE augments RG with memory timelines - series of memories representing the evolution or causality of relevant past events. Along with THEANINE, we introduce TeaFarm, a counterfactual-driven evaluation scheme, addressing the limitation of G-Eval and human efforts when assessing agent performance in integrating past memories into RG. A supplementary video for THEANINE and data for TeaFarm are at https://huggingface.co/spaces/ResearcherScholar/Theanine.
为实现终身的人机交互,对话代理需要不断记忆感知到的信息,并适当地检索它以生成响应(RG)。虽然先前的研究重点是通过消除过时的记忆来提高检索质量,但我们认为这些记忆在长期对话中为RG提供了丰富且重要的上下文线索(例如用户行为的改变)。我们提出了THEANINE,这是一个基于大型语言模型的终身对话代理框架。THEANINE放弃记忆移除,并通过基于它们的时间和因果关系来链接大规模记忆进行管理。通过此链接结构,THEANINE通过记忆时间线增强RG,记忆时间线是一系列代表相关过去事件演变或因果关系的记忆。与THEANINE一起,我们引入了TeaFarm,一种以反事实驱动的评价方案,解决了G-Eval在评估代理将过去记忆融入RG时的局限性以及人为努力的问题。THEANINE的补充视频和TeaFarm的数据可在https://huggingface.co/spaces/ResearcherScholar/Theanine获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL 2025
Summary
基于对话需要长期进行人-智能体互动的情况,研究者提出了一个基于大型语言模型的终身对话智能体框架——THEANINE。此框架放弃了去除记忆的方法,并通过根据时间和因果关系对大量记忆进行链接管理。利用这种链接结构,THEANINE增强了记忆的时间线功能,反映了过去相关事件的演变或因果关系。同时,该研究还推出了一个基于反事实评估的评估方案TeaFarm,以解决当前记忆融入反应生成评价(RG)中的不足和人为评估工作量大问题。可以在“URL地址 ”获取关于THEANINE的视频介绍和数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 对话智能体需要持续记忆感知信息并正确检索以生成响应。过去的研究主要关注消除过时记忆以提高检索质量。然而,这些记忆对于长期对话中的响应生成提供了丰富的上下文线索。
- 提出了一种名为THEANINE的基于大型语言模型的终身对话智能体框架,它通过链接具有时间性和因果关系的记忆进行管理。这不仅提升了智能体的记忆力,还增强了其对过去事件的演变或因果关系的理解。
- THEANINE框架引入了一种新的评估方案TeaFarm,以解决现有评估方法在集成过去记忆到响应生成过程中的局限性以及需要大量人工评估的问题。
点此查看论文截图

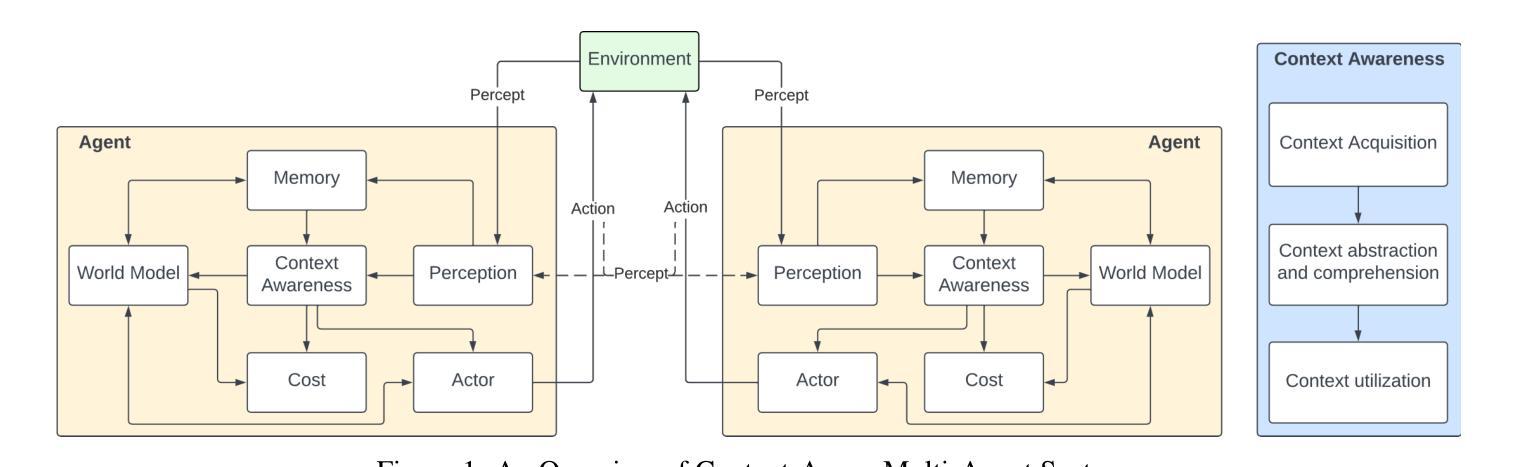
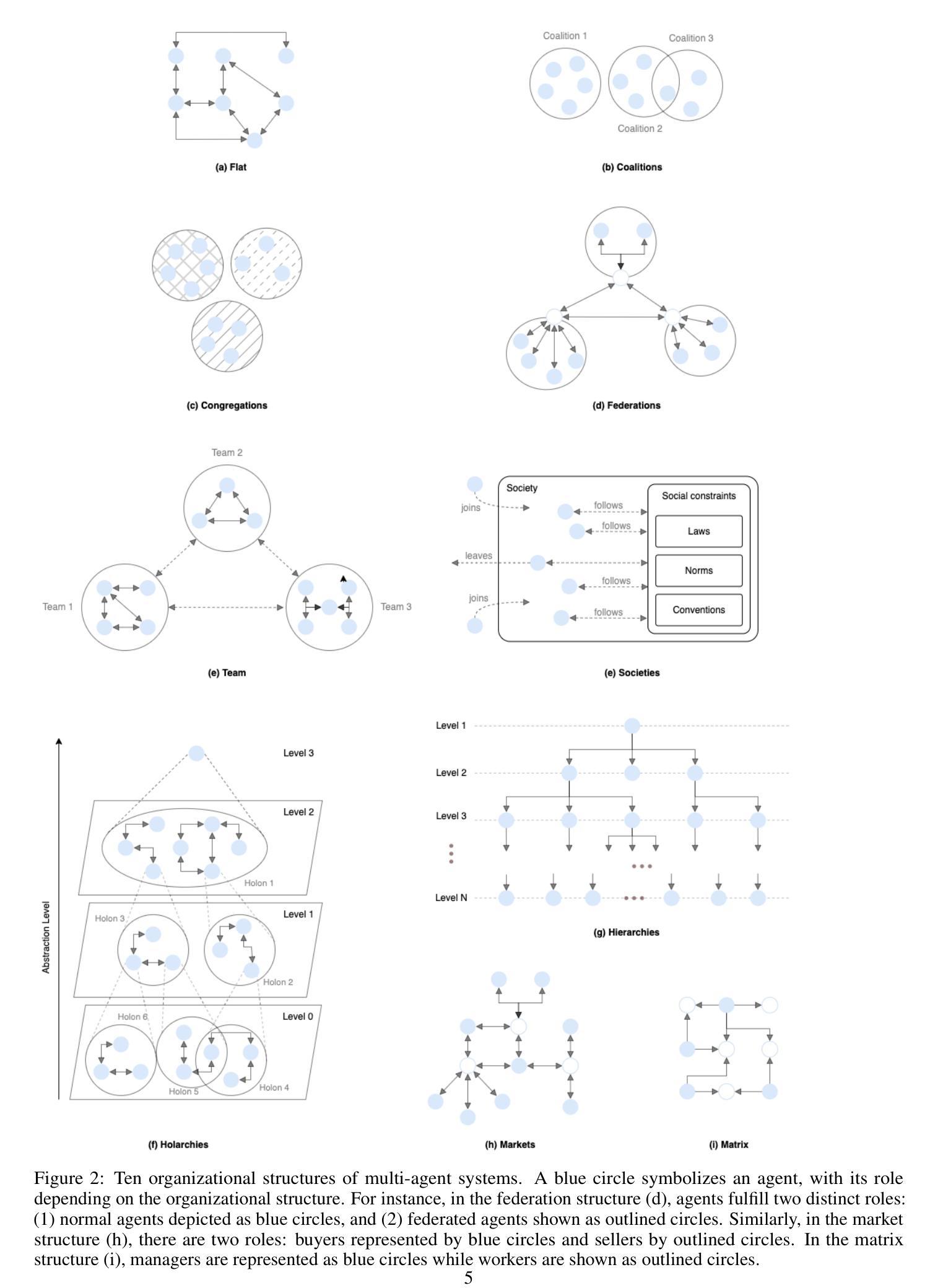
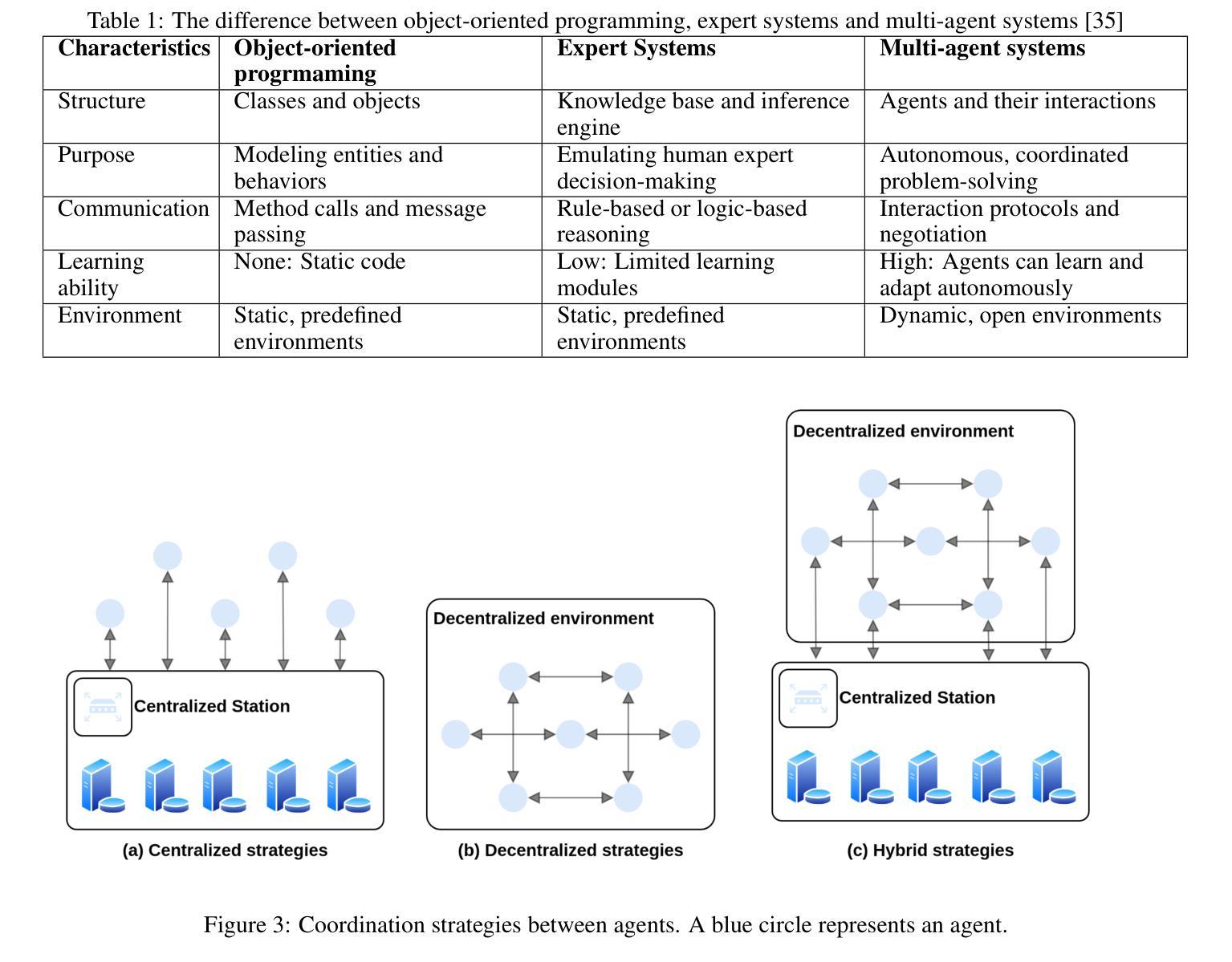
A Survey on Context-Aware Multi-Agent Systems: Techniques, Challenges and Future Directions
Authors:Hung Du, Srikanth Thudumu, Rajesh Vasa, Kon Mouzakis
Research interest in autonomous agents is on the rise as an emerging topic. The notable achievements of Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated the considerable potential to attain human-like intelligence in autonomous agents. However, the challenge lies in enabling these agents to learn, reason, and navigate uncertainties in dynamic environments. Context awareness emerges as a pivotal element in fortifying multi-agent systems when dealing with dynamic situations. Despite existing research focusing on both context-aware systems and multi-agent systems, there is a lack of comprehensive surveys outlining techniques for integrating context-aware systems with multi-agent systems. To address this gap, this survey provides a comprehensive overview of state-of-the-art context-aware multi-agent systems. First, we outline the properties of both context-aware systems and multi-agent systems that facilitate integration between these systems. Subsequently, we propose a general process for context-aware systems, with each phase of the process encompassing diverse approaches drawn from various application domains such as collision avoidance in autonomous driving, disaster relief management, utility management, supply chain management, human-AI interaction, and others. Finally, we discuss the existing challenges of context-aware multi-agent systems and provide future research directions in this field.
对自主代理的研究兴趣正作为一个新兴话题而不断增长。大型语言模型(LLM)的显著成就表明,自主代理在达到人类智能方面具有巨大的潜力。然而,挑战在于如何使这些代理能够在动态环境中学习、推理和应对不确定性。在处理动态情况时,情境感知在加强多代理系统方面起着关键的作用。尽管现有的研究主要集中在上下文感知系统和多代理系统上,但缺乏全面的调查来概述将上下文感知系统与多代理系统相结合的技术。为了弥补这一空白,这篇综述提供了对最新上下文感知多代理系统的全面概述。首先,我们概述了上下文感知系统和多代理系统的属性,这些属性有助于这些系统之间的集成。随后,我们提出了上下文感知系统的一般过程,该过程的每个阶段都涵盖了来自各种应用领域的不同方法,如自动驾驶中的防撞、灾害救援管理、实用管理、供应链管理、人机交互等。最后,我们讨论了上下文感知多代理系统的现有挑战,并为此领域提供了未来研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 1 figure
Summary:
随着自主代理成为新兴话题,大型语言模型(LLM)的显著成就证明了自主代理实现人类智能的巨大潜力。然而,挑战在于如何使这些代理在动态环境中学习、推理和应对不确定性。上下文感知成为强化多代理系统处理动态情况时的关键要素。当前缺少将上下文感知系统与多代理系统结合的综合调查技术。本调查提供了对最新上下文感知多代理系统的全面概述。首先,概述了促进两者集成的上下文感知系统和多代理系统的属性。其次,提出一个通用过程,每一阶段涵盖从自主驾驶的防撞、灾难救援管理、公用事业管理、供应链管理、人机交互等应用领域中抽取的不同方法。最后讨论了现有的挑战并为未来研究指明了方向。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自主代理领域显示出巨大潜力。
- 上下文感知是多代理系统在动态环境中处理情况的关键要素。
- 当前缺乏将上下文感知系统与多代理系统结合的综合调查技术。
- 此调查提供了全面的上下文感知多代理系统概述。
- 上下文的属性和多代理系统的属性是促进两者集成的重要因素。
- 上下文感知系统的通用过程涵盖多种应用领域的不同方法。
- 仍存在挑战和未来的研究方向。
点此查看论文截图