⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-01 更新
Diffusion Autoencoders are Scalable Image Tokenizers
Authors:Yinbo Chen, Rohit Girdhar, Xiaolong Wang, Sai Saketh Rambhatla, Ishan Misra
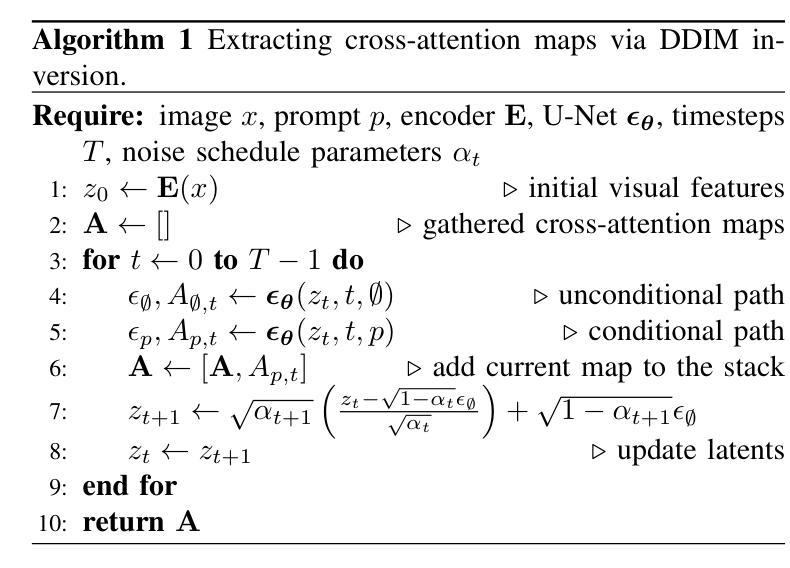
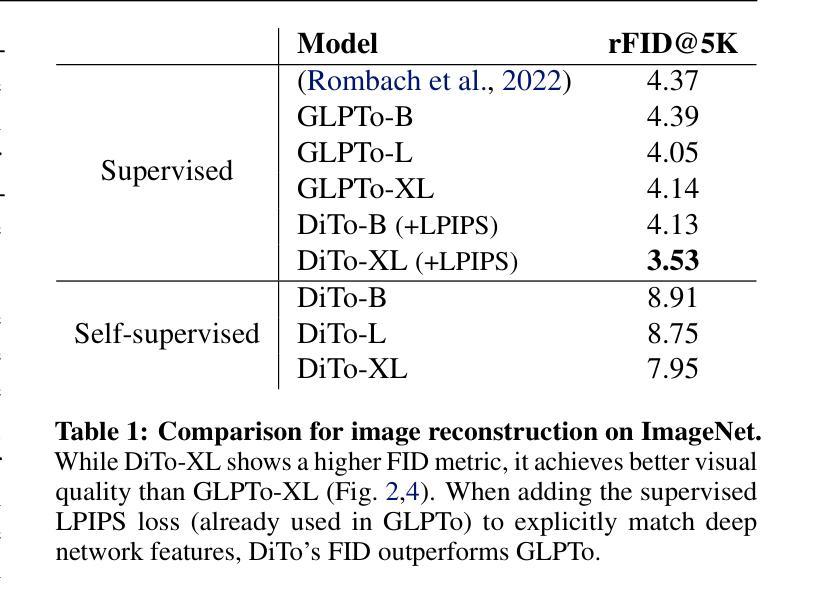
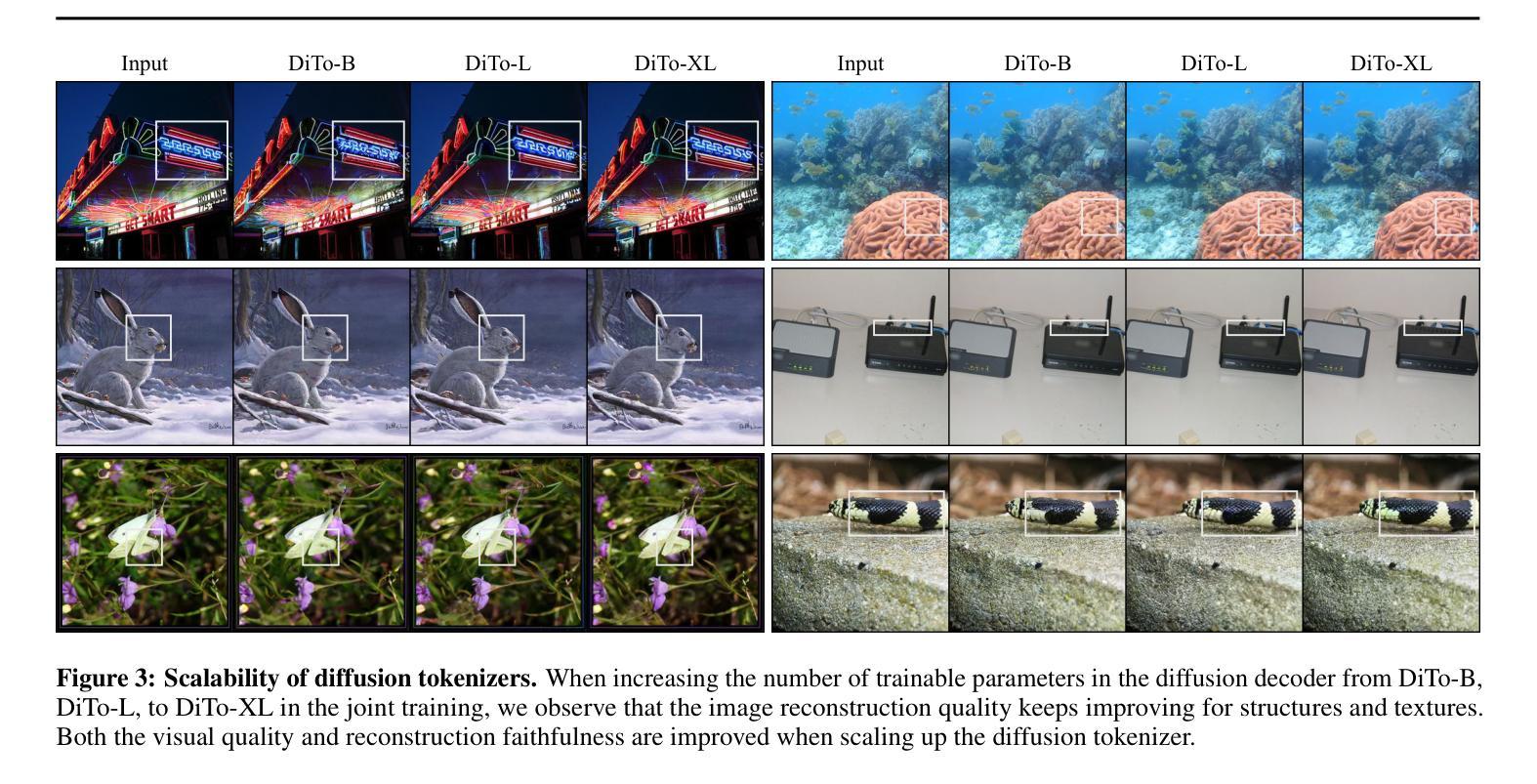
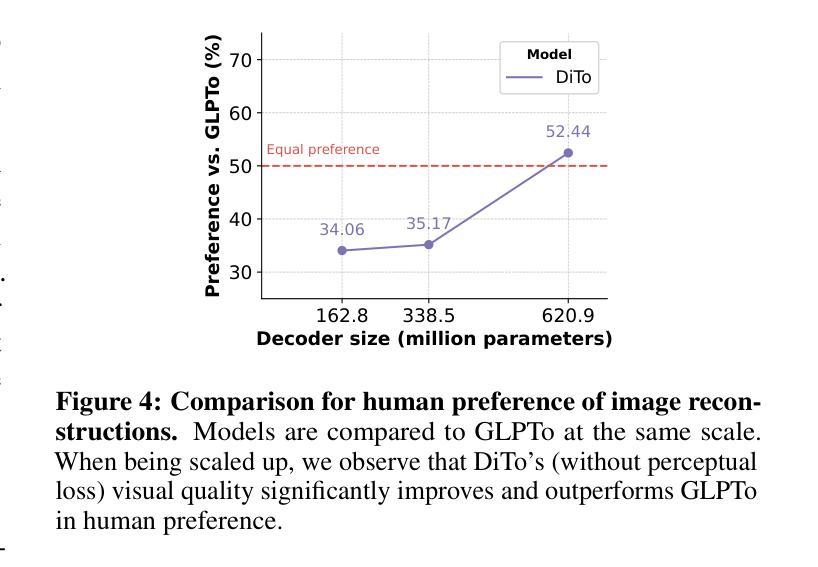
Tokenizing images into compact visual representations is a key step in learning efficient and high-quality image generative models. We present a simple diffusion tokenizer (DiTo) that learns compact visual representations for image generation models. Our key insight is that a single learning objective, diffusion L2 loss, can be used for training scalable image tokenizers. Since diffusion is already widely used for image generation, our insight greatly simplifies training such tokenizers. In contrast, current state-of-the-art tokenizers rely on an empirically found combination of heuristics and losses, thus requiring a complex training recipe that relies on non-trivially balancing different losses and pretrained supervised models. We show design decisions, along with theoretical grounding, that enable us to scale DiTo for learning competitive image representations. Our results show that DiTo is a simpler, scalable, and self-supervised alternative to the current state-of-the-art image tokenizer which is supervised. DiTo achieves competitive or better quality than state-of-the-art in image reconstruction and downstream image generation tasks.
将图像标记化为紧凑的视觉表示是学习高效且高质量图像生成模型的关键步骤。我们提出了一种简单的扩散标记器(DiTo),用于学习图像生成模型的紧凑视觉表示。我们的关键见解是,可以使用单个学习目标,即扩散L2损失,来训练可扩展的图像标记器。由于扩散已经广泛用于图像生成,因此我们的见解大大简化了此类标记器的训练。相反,当前最先进的标记器依赖于经验发现的启发式方法和损失的组合,因此需要复杂的训练配方,这依赖于不同损失的平衡和预训练的监督模型。我们展示了设计决策以及理论支撑,这些使我们能扩展DiTo来学习有竞争力的图像表示。我们的结果表明,DiTo是当前有监督的先进图像标记器的更简单、可扩展和自监督的替代品。DiTo在图像重建和下游图像生成任务中的表现具有竞争力或更好。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://yinboc.github.io/dito/
Summary
本文提出了一种简单的扩散分词器(DiTo),用于学习图像生成模型中的紧凑视觉表示。关键见解是使用单一的扩散L2损失作为训练可扩展图像分词器的学习目标,简化了训练过程。DiTo通过简单的自监督学习,实现了与当前最先进的图像分词器相当的图像重建和图像生成任务性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了简单的扩散分词器(DiTo)用于图像生成模型。
- 使用扩散L2损失作为训练图像分词器的单一学习目标。
- 扩散分词器(DiTo)简化了图像分词器的训练过程。
- 当前最先进的图像分词器需要结合多种启发式方法和损失,训练过程复杂。
- DiTo设计决策包括理论支撑,使其能够学习竞争性的图像表示。
- DiTo在图像重建和图像生成任务上实现了与当前最先进的图像分词器相当或更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


Waveform-Specific Performance of Deep Learning-Based Super-Resolution for Ultrasound Contrast Imaging
Authors:Rienk Zorgdrager, Nathan Blanken, Jelmer M. Wolterink, Michel Versluis, Guillaume Lajoinie
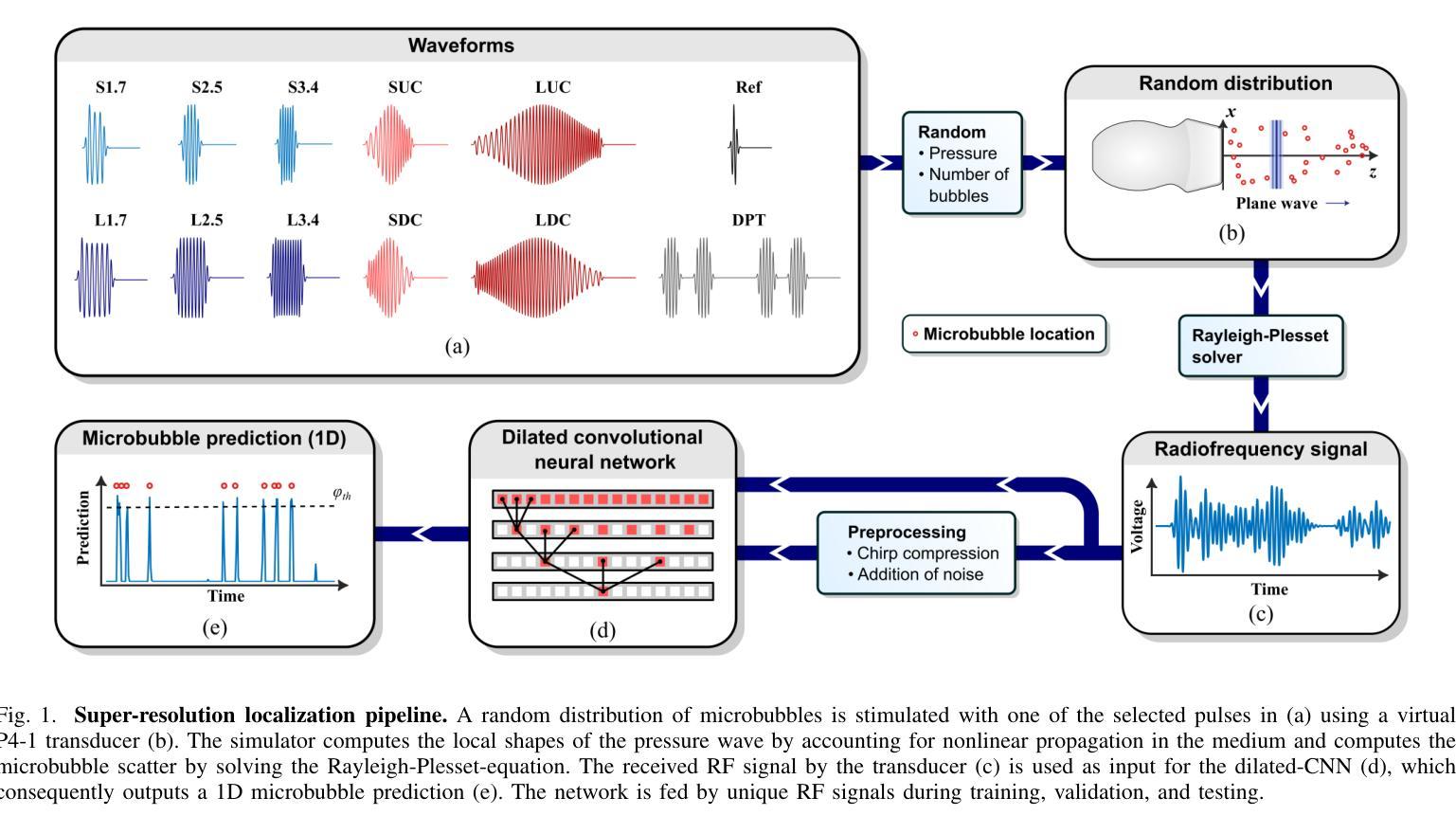
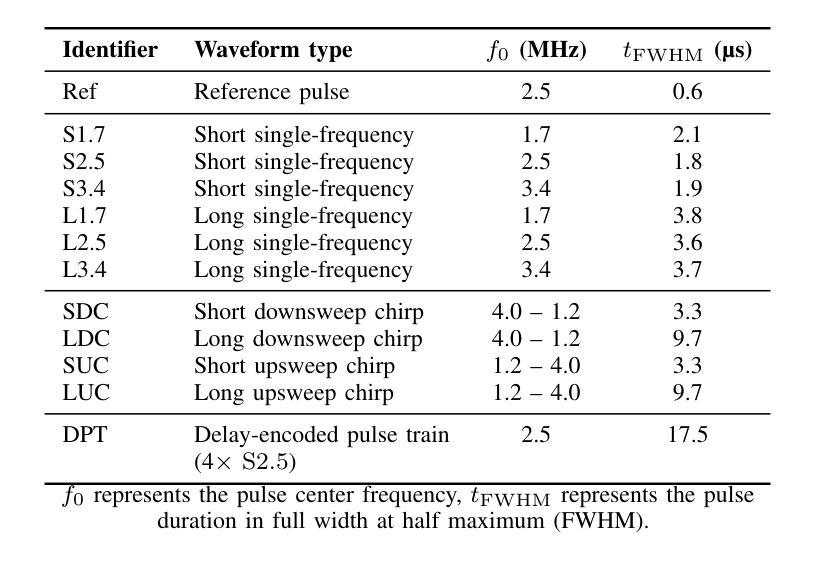
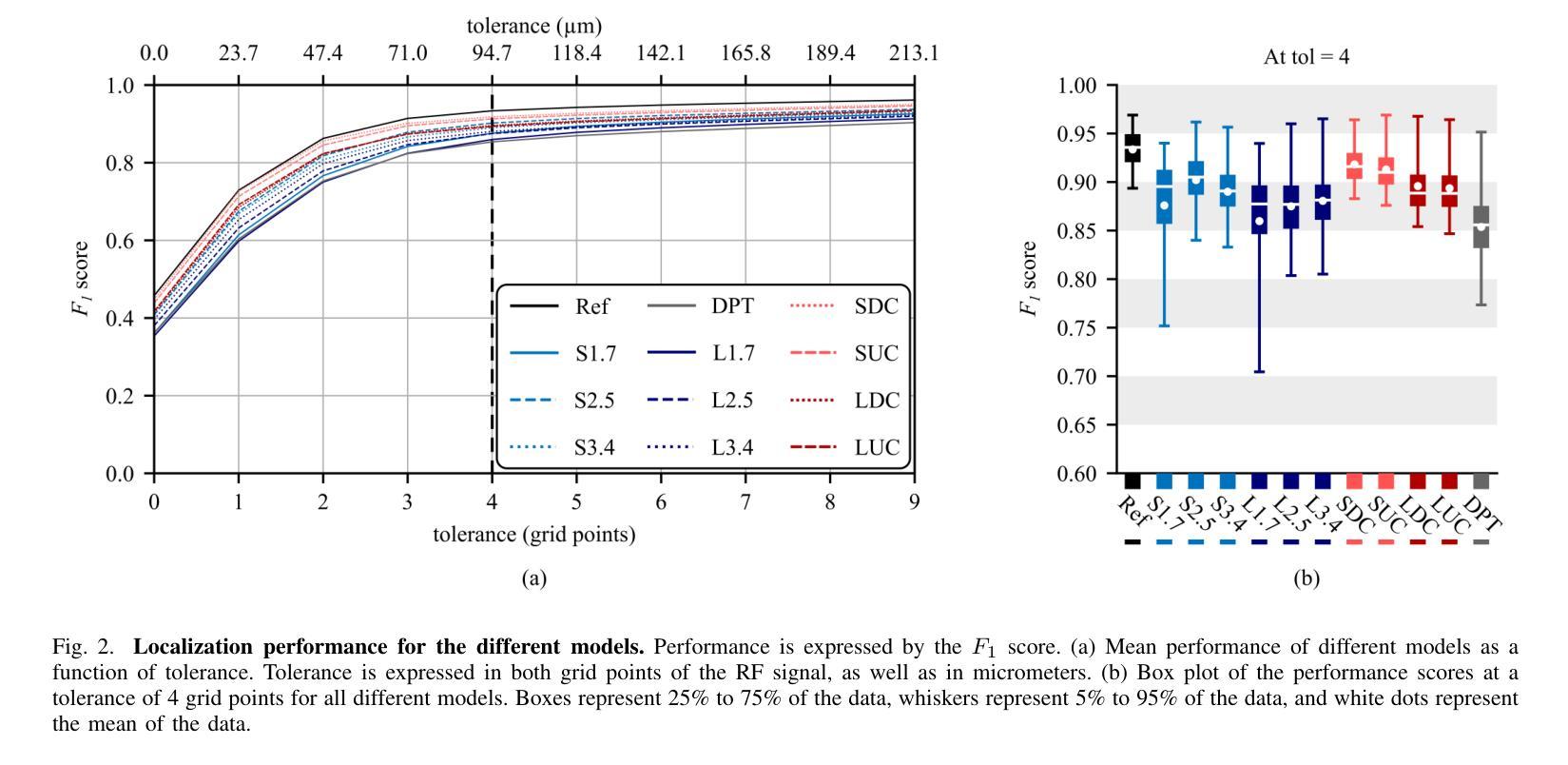
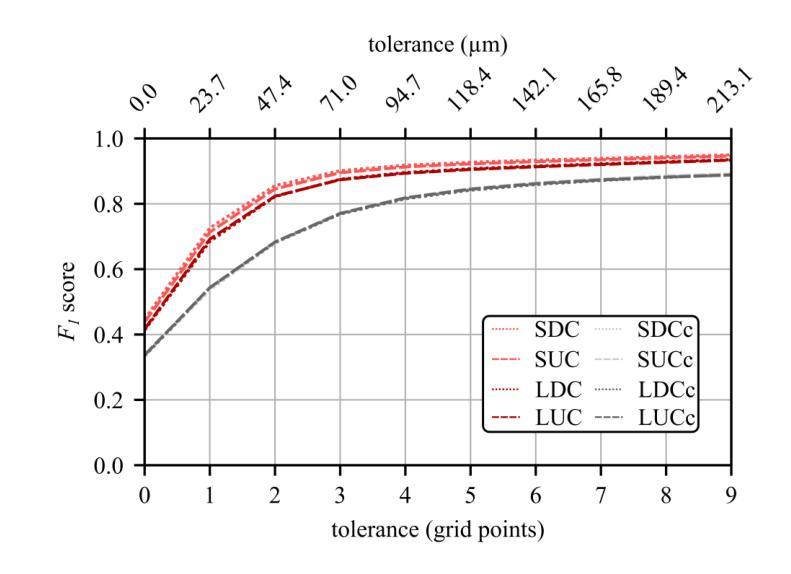
Resolving arterial flows is essential for understanding cardiovascular pathologies, improving diagnosis, and monitoring patient condition. Ultrasound contrast imaging uses microbubbles to enhance the scattering of the blood pool, allowing for real-time visualization of blood flow. Recent developments in vector flow imaging further expand the imaging capabilities of ultrasound by temporally resolving fast arterial flow. The next obstacle to overcome is the lack of spatial resolution. Super-resolved ultrasound images can be obtained by deconvolving radiofrequency (RF) signals before beamforming, breaking the link between resolution and pulse duration. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can be trained to locally estimate the deconvolution kernel and consequently super-localize the microbubbles directly within the RF signal. However, microbubble contrast is highly nonlinear, and the potential of CNNs in microbubble localization has not yet been fully exploited. Assessing deep learning-based deconvolution performance for non-trivial imaging pulses is therefore essential for successful translation to a practical setting, where the signal-to-noise ratio is limited, and transmission schemes should comply with safety guidelines. In this study, we train CNNs to deconvolve RF signals and localize the microbubbles driven by harmonic pulses, chirps, or delay-encoded pulse trains. Furthermore, we discuss potential hurdles for in-vitro and in-vivo super-resolution by presenting preliminary experimental results. We find that, whereas the CNNs can accurately localize microbubbles for all pulses, a short imaging pulse offers the best performance in noise-free conditions. However, chirps offer a comparable performance without noise, but are more robust to noise and outperform all other pulses in low-signal-to-noise ratio conditions.
解决动脉血流问题对于理解心血管病理、提高诊断水平以及监测病人状况至关重要。超声对比成像利用微气泡增强血液池的散射,从而可以实时可视化血流。向量流成像的近期发展进一步扩大了超声的成像能力,可以通过时间分辨率解析快速动脉血流。下一个需要克服的障碍是空间分辨率不足。通过在波束形成之前对射频(RF)信号进行反卷积,可以获得超级分辨率的超声图像,打破了分辨率和脉冲持续时间之间的联系。卷积神经网络(CNN)可以经过训练,局部估计反卷积核,从而直接在RF信号中超级定位微气泡。然而,微气泡对比高度非线性,CNN在微气泡定位方面的潜力尚未得到充分开发。因此,评估基于深度学习的反卷积在非平凡成像脉冲上的表现,对于成功应用于实际环境至关重要,因为在实践中信噪比有限,传输方案应遵守安全准则。在这项研究中,我们训练CNN对RF信号进行反卷积并定位由谐波脉冲、啁啾或延迟编码脉冲列驱动的微气泡。此外,我们还通过提供初步实验结果,讨论了体外和体内超分辨率的潜在障碍。我们发现,虽然CNN可以准确地对所有脉冲进行微气泡定位,但在无噪声条件下,短成像脉冲表现最佳。然而,啁啾在无噪声条件下表现相当,但在噪声方面更加稳健,在低信噪比条件下优于所有其他脉冲。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control
Summary
超声对比成像利用微气泡增强血液池散射,实现血流实时可视化。新近发展的矢量流成像技术提高了超声成像能力,可实时解析快速动脉血流。当前面临的挑战在于空间分辨率不足。通过射频信号解卷积预处理来获得超级分辨率超声图像,打破分辨率与脉冲持续时间之间的关联。卷积神经网络可训练局部估计解卷积核,进而直接在射频信号中超级定位微气泡。本研究训练卷积神经网络对射频信号进行解卷积和微气泡定位,并讨论体外和体内超分辨率的潜在障碍,初步实验结果指出,卷积神经网络在各种脉冲下能准确定位微气泡,短成像脉冲在无声噪条件下表现最佳,但短哌哌声在无噪声条件下表现相当且更抗噪声,在低信噪比条件下表现优于其他所有脉冲。
Key Takeaways
- 超声对比成像使用微气泡增强血流可视化。
- 矢量流成像提高了超声成像能力,但面临空间分辨率不足的挑战。
- 通过射频信号解卷积预处理可获得超级分辨率超声图像。
- 卷积神经网络可用于局部估计解卷积核并直接定位微气泡在射频信号中的位置。
- 训练卷积神经网络对射频信号进行解卷积和微气泡定位的实验结果展示了对不同脉冲的适应性。
- 在无声噪条件下,短成像脉冲表现最佳;而在低信噪比条件下,短哌哌声表现更稳健且优于其他脉冲。
点此查看论文截图

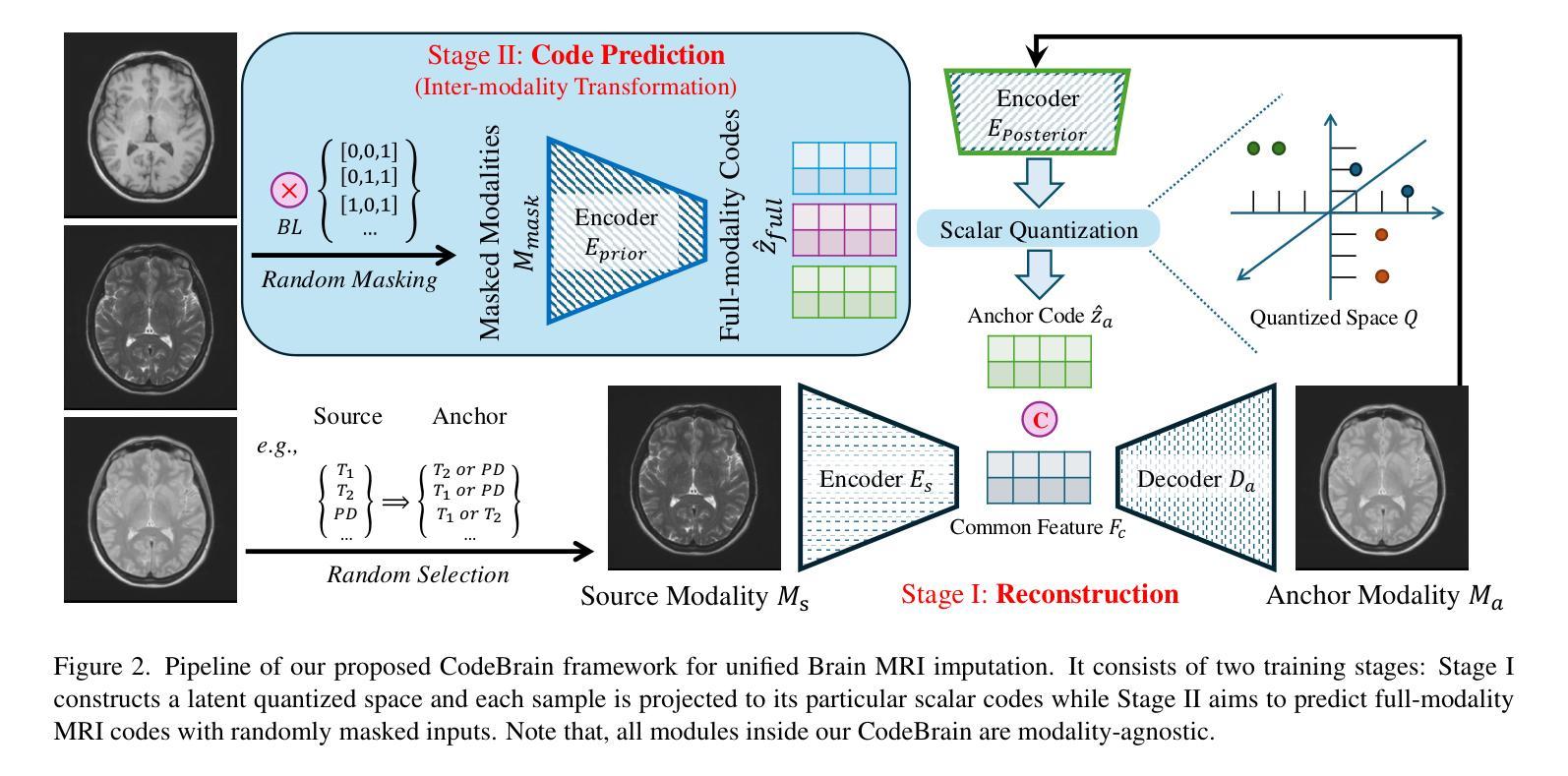
CodeBrain: Impute Any Brain MRI via Instance-specific Scalar-quantized Codes
Authors:Yicheng Wu, Tao Song, Zhonghua Wu, Zongyuan Ge, Zhaolin Chen, Jianfei Cai
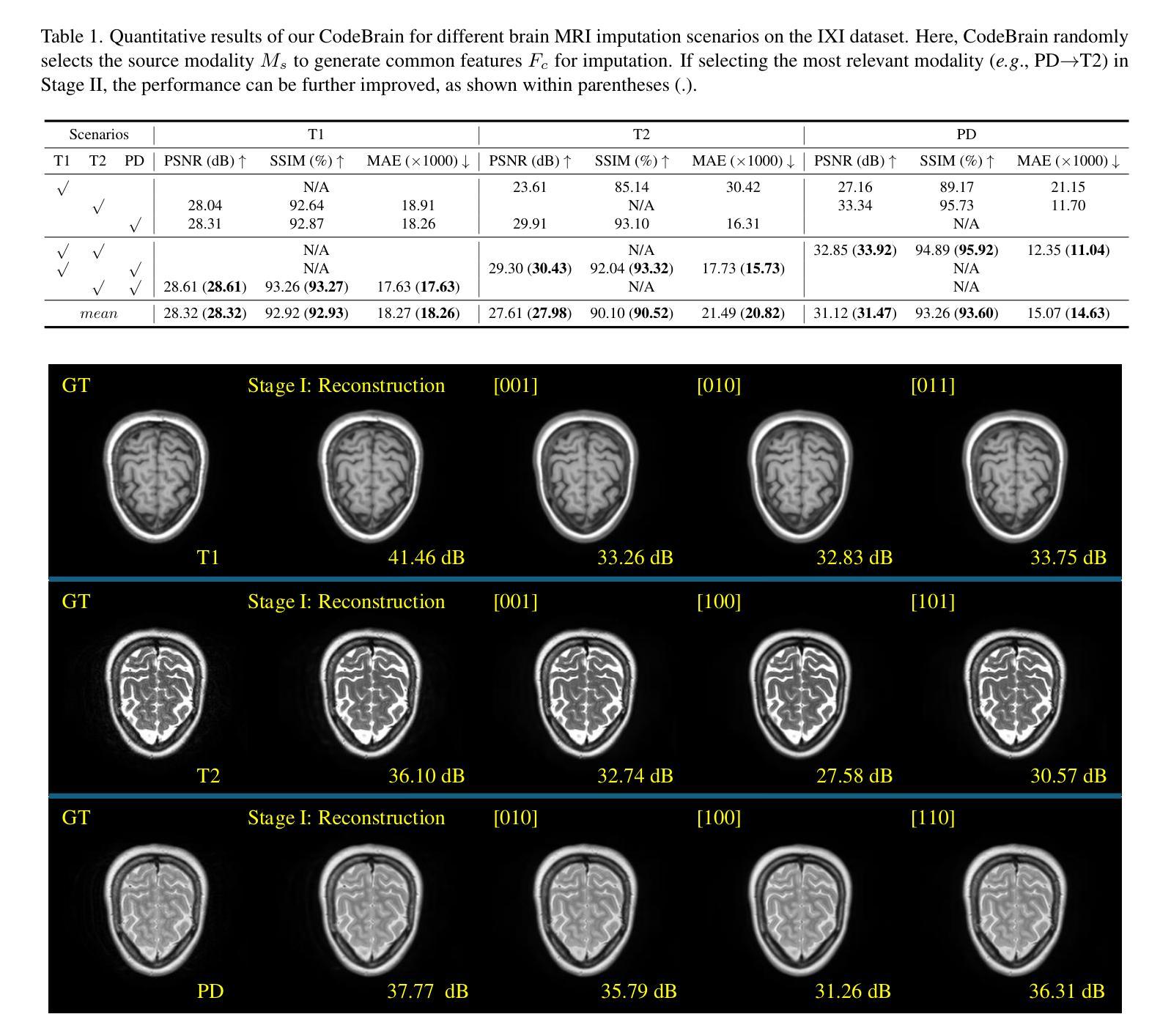
MRI imputation aims to synthesize the missing modality from one or more available ones, which is highly desirable since it reduces scanning costs and delivers comprehensive MRI information to enhance clinical diagnosis. In this paper, we propose a unified model, CodeBrain, designed to adapt to various brain MRI imputation scenarios. The core design lies in casting various inter-modality transformations as a full-modality code prediction task. To this end, CodeBrain is trained in two stages: Reconstruction and Code Prediction. First, in the Reconstruction stage, we reconstruct each MRI modality, which is mapped into a shared latent space followed by a scalar quantization. Since such quantization is lossy and the code is low dimensional, another MRI modality belonging to the same subject is randomly selected to generate common features to supplement the code and boost the target reconstruction. In the second stage, we train another encoder by a customized grading loss to predict the full-modality codes from randomly masked MRI samples, supervised by the corresponding quantized codes generated from the first stage. In this way, the inter-modality transformation is achieved by mapping the instance-specific codes in a finite scalar space. We evaluated the proposed CodeBrain model on two public brain MRI datasets (i.e., IXI and BraTS 2023). Extensive experiments demonstrate that our CodeBrain model achieves superior imputation performance compared to four existing methods, establishing a new state of the art for unified brain MRI imputation. Codes will be released.
MRI补全技术的目标是从一种或多种现有模态合成缺失的模态,这对于减少扫描成本并提供全面的MRI信息以增强临床诊断而言是非常理想的。在本文中,我们提出了一种统一的模型——CodeBrain,它旨在适应各种大脑MRI补全场景。核心设计在于将各种跨模态转换作为全模态代码预测任务。为此,CodeBrain分为两个阶段进行训练:重建和代码预测。首先,在重建阶段,我们重建每种MRI模态,将其映射到共享潜在空间然后进行标量量化。由于这种量化是有损的,并且代码是低维的,因此随机选择属于同一主体的另一种MRI模态来生成共同特征,以补充代码并促进目标重建。在第二阶段,我们使用定制的分级损失来训练另一个编码器,该编码器可以从随机遮挡的MRI样本中预测全模态代码,并由第一阶段生成的相应量化代码进行监督。通过这种方式,通过映射特定实例的代码在有限的标量空间中实现跨模态转换。我们在两个公共大脑MRI数据集(即IXI和BraTS 2023)上评估了所提出的CodeBrain模型。大量实验表明,我们的CodeBrain模型与四种现有方法相比实现了更优越的补全性能,为统一的脑部MRI补全建立了新的技术水平。相关代码将会发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出的CodeBrain模型用于大脑MRI缺失模态填补,通过两阶段训练,实现多种MRI模态的转换和补充,达到优异的填补性能,建立新的统一大脑MRI填补技术标杆。
Key Takeaways
- CodeBrain模型旨在适应各种大脑MRI缺失模态填补场景。
- 该模型通过两阶段训练,即重建和代码预测,实现MRI模态的转换。
- 在重建阶段,模型将每个MRI模态映射到共享潜在空间,然后进行标量量化,以补充代码并促进目标重建。
- 在代码预测阶段,模型通过定制的分级损失训练另一个编码器,从随机遮挡的MRI样本中预测全模态代码。
- CodeBrain模型通过映射特定实例代码在有限标量空间内实现模态间转换。
- 在IXI和BraTS 2023两个公开大脑MRI数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,CodeBrain模型取得了优于其他四种现有方法的填补性能。
点此查看论文截图

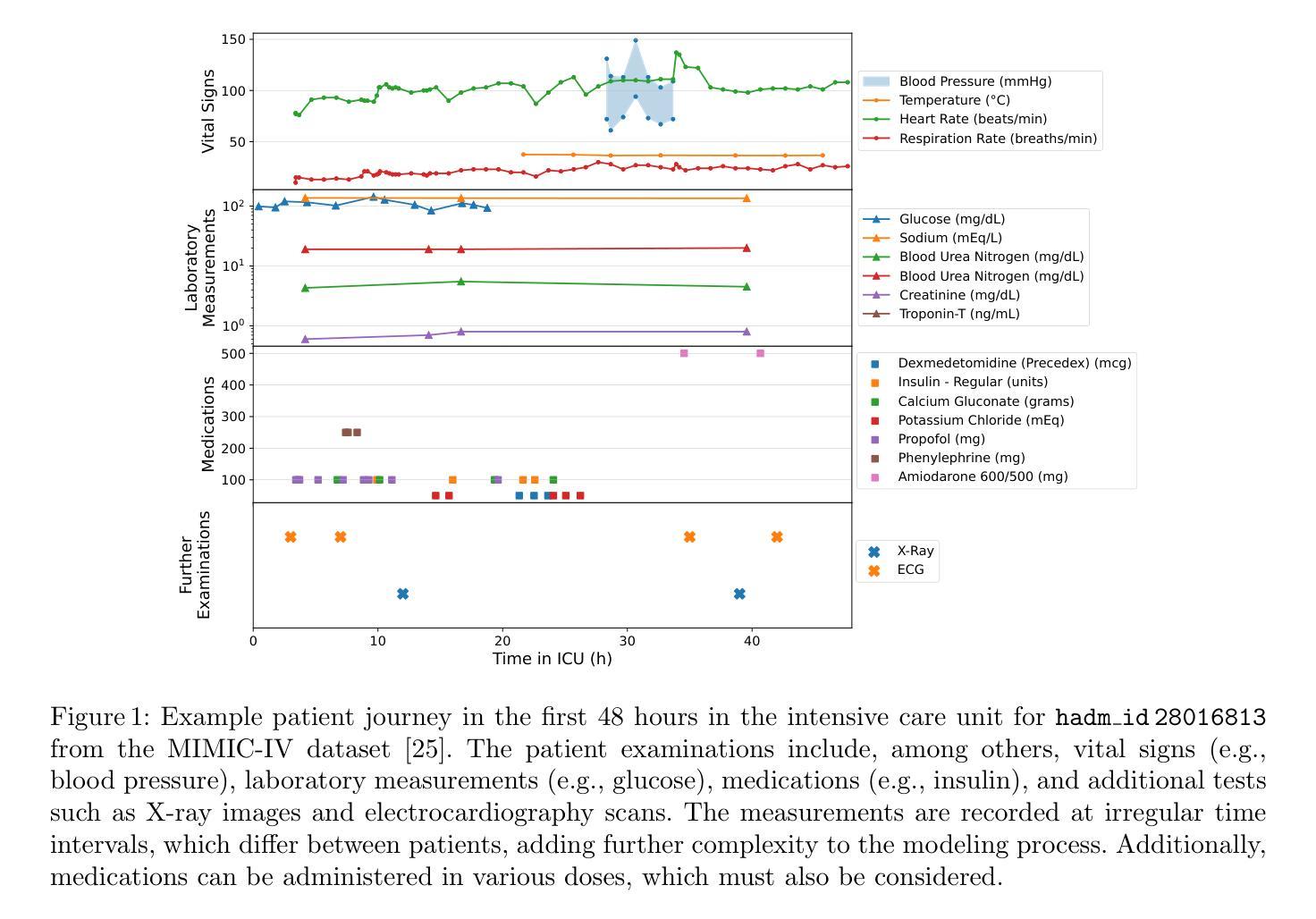
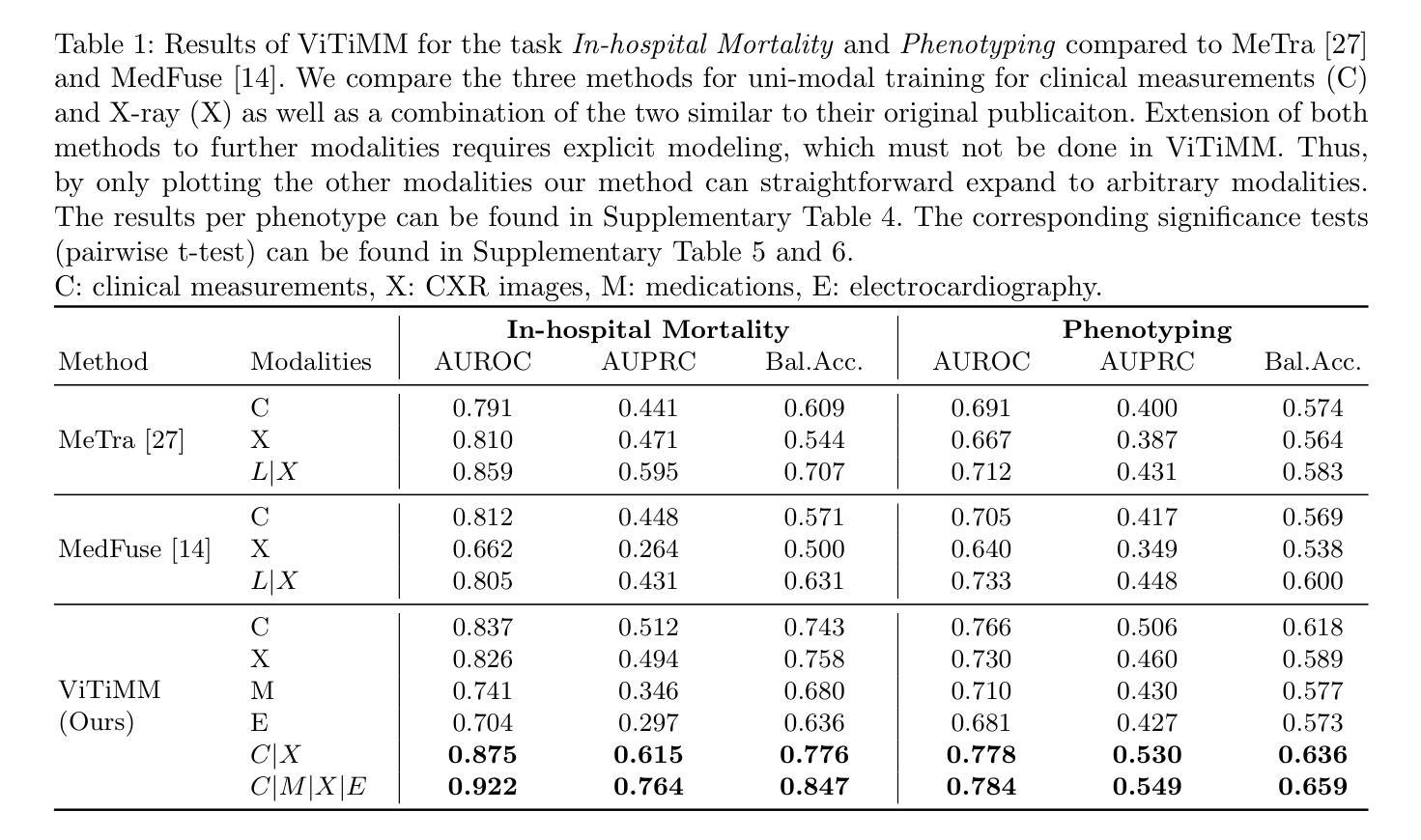
Arbitrary Data as Images: Fusion of Patient Data Across Modalities and Irregular Intervals with Vision Transformers
Authors:Malte Tölle, Mohamad Scharaf, Samantha Fischer, Christoph Reich, Silav Zeid, Christoph Dieterich, Benjamin Meder, Norbert Frey, Philipp Wild, Sandy Engelhardt
A patient undergoes multiple examinations in each hospital stay, where each provides different facets of the health status. These assessments include temporal data with varying sampling rates, discrete single-point measurements, therapeutic interventions such as medication administration, and images. While physicians are able to process and integrate diverse modalities intuitively, neural networks need specific modeling for each modality complicating the training procedure. We demonstrate that this complexity can be significantly reduced by visualizing all information as images along with unstructured text and subsequently training a conventional vision-text transformer. Our approach, Vision Transformer for irregular sampled Multi-modal Measurements (ViTiMM), not only simplifies data preprocessing and modeling but also outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in predicting in-hospital mortality and phenotyping, as evaluated on 6,175 patients from the MIMIC-IV dataset. The modalities include patient’s clinical measurements, medications, X-ray images, and electrocardiography scans. We hope our work inspires advancements in multi-modal medical AI by reducing the training complexity to (visual) prompt engineering, thus lowering entry barriers and enabling no-code solutions for training. The source code will be made publicly available.
病患在每次住院期间都会接受多次检查,每次检查提供健康状态的不同方面。这些评估包括具有不同采样率的时间数据、离散的单点测量、药物治疗等治疗干预以及图像。虽然医生能够直观地处理并整合多种模式,但神经网络需要为每种模式进行特定建模,从而复杂化训练程序。我们展示,通过将所有信息可视化为图像以及非结构化文本,可以大幅度减少这种复杂性,随后训练传统的视觉文本转换器。我们的方法——用于不规则采样多模式测量的视觉转换器(ViTiMM),不仅简化了数据预处理和建模,而且在预测住院死亡率和分型方面,表现出优于当前最先进方法的效果。评估数据来自MIMIC-IV数据集的6,175名患者。这些模式包括患者的临床测量、药物治疗、X光图像和心电图扫描。我们希望我们的工作能够通过简化训练复杂性,将(视觉)提示工程应用于多模式医疗人工智能,从而降低入门门槛并实现无代码解决方案的训练,以此激发多模式医疗人工智能的进步。源代码将公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种将多模态医疗数据(包括临床测量、药物、X光图像和心电图扫描等)可视化成图像,并结合非结构文本,通过训练常规视觉文本转换器(Vision Transformer)的方法来处理不规则采样的多模态测量数据。新方法简化了数据预处理和建模的复杂性,同时降低了对多模态医疗AI的入门门槛并有望激发更多相关研究的发展。实验结果显示,该方法在预测住院死亡率和疾病分型上优于现有技术。源代码将公开供公众使用。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了将多模态医疗数据可视化成图像的方法,包括临床测量、药物、X光图像和心电图扫描等。
- 通过训练常规视觉文本转换器(Vision Transformer)处理不规则采样的多模态测量数据。
- 简化了数据预处理和建模的复杂性,降低了多模态医疗AI的入门门槛。
- 提出了全新的ViTiMM模型框架在预测住院死亡率和疾病分型上具有出色表现。
- 实验结果优于现有技术。
- 源码将公开供公众使用,为未来的研究提供便利。
点此查看论文截图


Anatomy Might Be All You Need: Forecasting What to Do During Surgery
Authors:Gary Sarwin, Alessandro Carretta, Victor Staartjes, Matteo Zoli, Diego Mazzatenta, Luca Regli, Carlo Serra, Ender Konukoglu
Surgical guidance can be delivered in various ways. In neurosurgery, spatial guidance and orientation are predominantly achieved through neuronavigation systems that reference pre-operative MRI scans. Recently, there has been growing interest in providing live guidance by analyzing video feeds from tools such as endoscopes. Existing approaches, including anatomy detection, orientation feedback, phase recognition, and visual question-answering, primarily focus on aiding surgeons in assessing the current surgical scene. This work aims to provide guidance on a finer scale, aiming to provide guidance by forecasting the trajectory of the surgical instrument, essentially addressing the question of what to do next. To address this task, we propose a model that not only leverages the historical locations of surgical instruments but also integrates anatomical features. Importantly, our work does not rely on explicit ground truth labels for instrument trajectories. Instead, the ground truth is generated by a detection model trained to detect both anatomical structures and instruments within surgical videos of a comprehensive dataset containing pituitary surgery videos. By analyzing the interaction between anatomy and instrument movements in these videos and forecasting future instrument movements, we show that anatomical features are a valuable asset in addressing this challenging task. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first attempt to address this task for manually operated surgeries.
手术指导可以通过多种方式提供。在神经外科中,主要通过神经导航系统实现空间指导和定位,该系统参考术前MRI扫描。最近,通过分析来自工具如内窥镜的视频流提供实时指导的兴趣日益浓厚。现有方法,包括解剖检测、方向反馈、相位识别和视觉问答,主要侧重于帮助外科医生评估当前手术场景。本工作的目标是在更精细的层面上提供指导,旨在通过预测手术器械的轨迹来提供指导,本质上解决下一步该做什么的问题。为解决此任务,我们提出了一种模型,该模型不仅利用手术器械的历史位置,还整合了解剖特征。重要的是,我们的工作不需要依赖仪器轨迹的明确真实标签。相反,真实标签是由一个检测模型生成的,该模型经过训练,可检测综合数据集中手术视频内的解剖结构和仪器,该数据集包含垂体手术视频。通过分析这些视频中解剖结构与器械运动的相互作用,并预测未来器械的运动,我们证明了解剖特征是解决这一具有挑战性的宝贵资产。据我们所知,这是首次尝试解决手动手术的这一任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了外科手术指导的多种方式,特别是在神经外科中通过神经元导航系统实现空间指导和定位。最近,通过分析如内窥镜等工具的视频流提供实时指导的方法受到关注。现有方法主要关注评估当前手术场景,而本文旨在提供更精细的指导,通过预测手术器械的轨迹来解答下一步该如何操作的问题。为此,本文提出了一个模型,该模型不仅利用手术器械的历史位置,还整合了解剖特征。重要的是,我们的工作不需要仪器轨迹的明确真实标签,而是通过检测模型生成真实标签,该模型经过训练可检测综合数据集中的手术视频内的解剖结构和器械。通过分析这些视频中解剖结构和器械运动的相互作用并预测未来的器械运动,我们证明了解剖特征是解决这一具有挑战的任务的重要资源。据我们所知,这是首次尝试针对手动手术解决此问题。
Key Takeaways
- 外科手术指导有多种方式,包括神经元导航系统提供的空间指导和定位。
- 最近对通过视频流提供实时手术指导的兴趣正在增长。
- 现有方法主要关注评估当前手术场景,而本文旨在预测手术器械的轨迹以提供下一步操作指导。
- 本文提出的模型结合了手术器械的历史位置和解剖特征。
- 该工作不需要明确的仪器轨迹真实标签,而是通过检测模型生成真实标签。
- 通过分析解剖结构和器械运动的相互作用,证明了解剖特征对解决这一任务的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

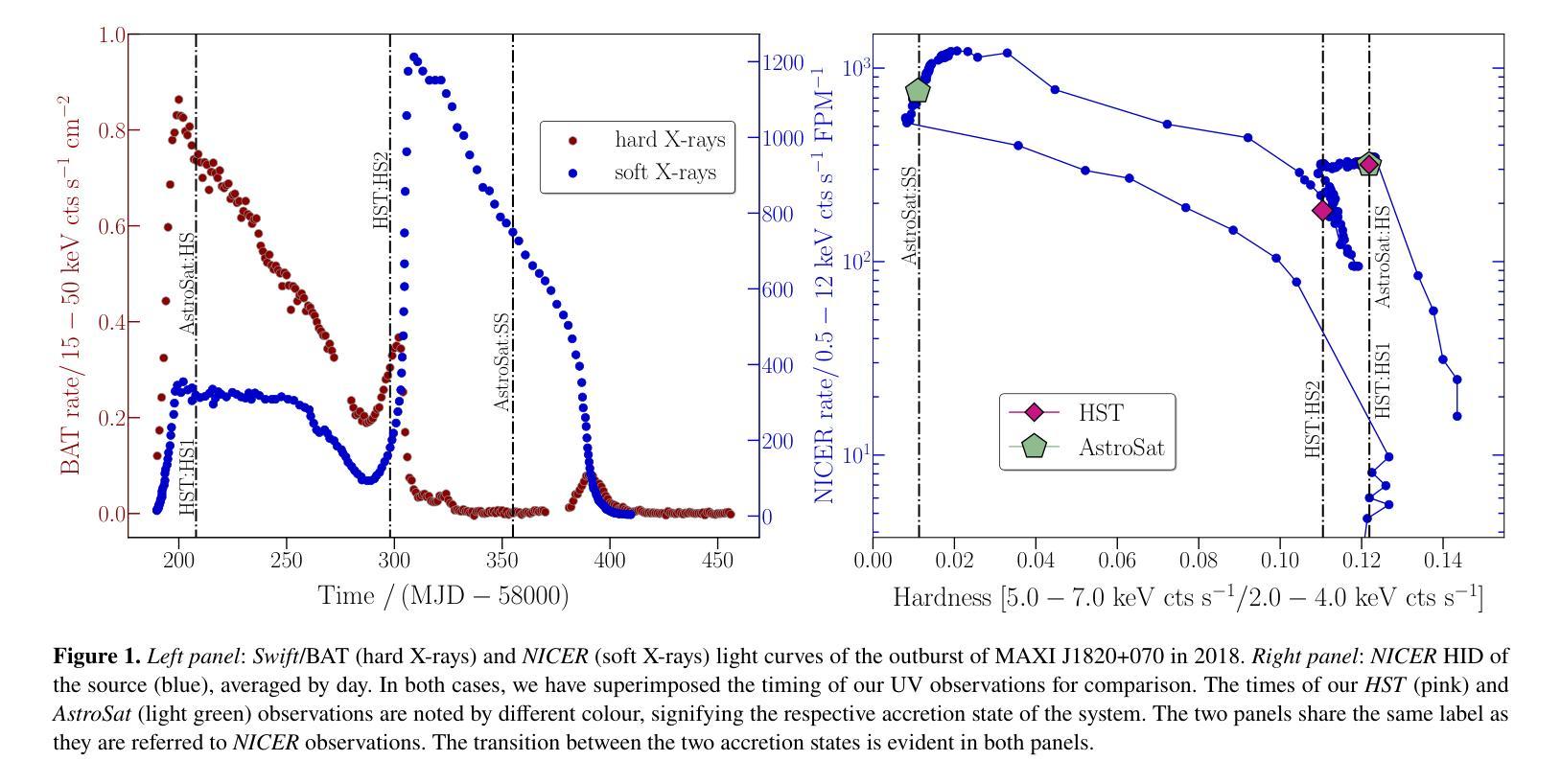
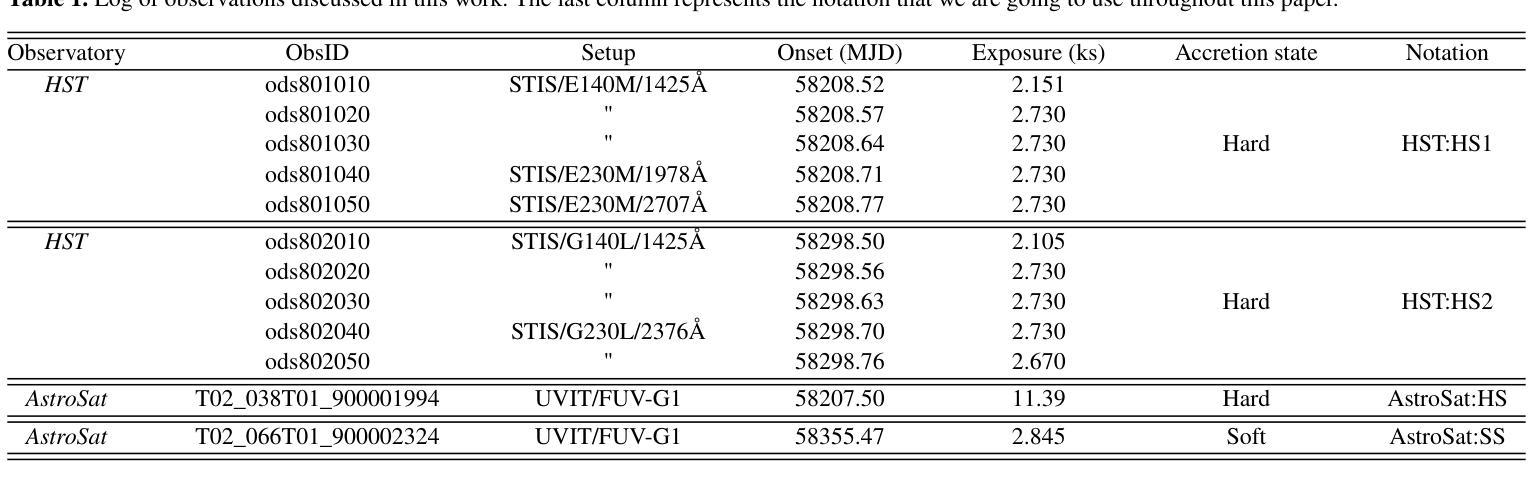
Ultraviolet spectroscopy of the black hole X-ray binary MAXI J1820+070 across a state transition
Authors:Maria Georganti, Christian Knigge, Noel Castro Segura, Knox S. Long, Gulab C. Dewangan, Srimanta Banerjee, Robert I. Hynes, Poshak Gandhi, Diego Altamirano, Joseph Patterson, David R. Zurek
We present ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopic observations covering three distinct accretion states of the low-mass X-ray binary (LMXB) MAXI J1820+070: the luminous hard state, a hard-intermediate state and the soft state. Our observations were obtained during the 2018 eruption of MAXI J1820+070 with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and AstroSat observatory. The extinction towards the source turns out to be low - $\rm E_{B-V} = 0.2 \pm 0.05$ - making it one of the best UV accretion laboratories among LMXBs. Remarkably, we observe only moderate differences between all three states, with all spectra displaying similar continuum shapes and emission lines. Moreover, the continua are not well-described by physically plausible irradiated disc models. All of this challenges the standard reprocessing picture for UV emission from erupting LMXBs. The UV emission lines are double-peaked, with high-ionization lines displaying higher peak-to-peak velocities. None of the lines display obvious outflow signatures, even though blue-shifted absorption features have been seen in optical and near-infrared lines during the hard state. The emission line ratios are consistent with normal abundances, suggesting that the donor mass at birth was low enough to avoid CNO processing ($\rm M_{2,i} \lesssim 1.0 - 1.5 {\mathrm M_{\odot}}$). Finally, we study the evolution of UV variability in our time-resolved HST observations (hard and hard-intermediate states). All UV power spectra can be modelled with a broken power-law, superposed on which we tentatively detect the $\simeq 18$s quasi-periodic oscillation (QPO) that has been seen in other spectral bands.
我们对低质量X射线双星(LMXB)MAXI J1820+070的三个不同积聚状态进行了紫外线(UV)光谱观测:发光硬态、硬中间态和软态。我们的观测数据是在MAXI J1820+070于2018年爆发期间使用哈勃太空望远镜(HST)和AstroSat天文台获得的。该源的消光结果较低——$\rm E_{B-V} = 0.2 \pm 0.05$——使其成为LMXB中最好的UV积聚实验室之一。值得注意的是,我们观察到三种状态之间的差异并不大,所有光谱都显示出相似的连续谱形状和发射线。此外,连续谱并不适合用物理上合理的辐照盘模型来描述。所有这些都对来自爆发的LMXB的UV发射的标准再处理图像提出了挑战。UV发射线是双峰的,高电离线的峰峰值速度较高。尽管在硬态期间观察到光学和近红外线具有蓝移吸收特征,但没有一条线显示出明显的流出特征。发射线比率与正常丰度一致,这表明捐赠者的初始质量足够低,避免了CNO加工($\rm M_{2,i} \leq 1.0 - 1.5 {\mathrm M_{\odot}}$)。最后,我们研究了时间分辨的HST观测中(硬态和硬中间态)UV可变性的演化。所有UV功率谱都可以用分段幂律模型来描述,在此基础上,我们初步检测到约为18秒的准周期性振荡(QPO),在其他光谱波段也观察到该振荡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 14 figures, submitted to MNRAS
摘要
本文报告了对低质量X射线双星MAXI J1820+070三种不同积聚状态的紫外线光谱观测结果。观测对象是在其2018年爆发期间的MAXI J1820+070,使用哈勃太空望远镜和AstroSat天文台进行观测。源头的消光较低,使其成为LMXB中最好的紫外线积聚实验室之一。尽管三个状态的差异不大,但光谱显示出相似的连续体和发射线。连续体不能用物理上合理的辐照盘模型很好地描述。这一切对标准紫外线发射的重处理图像提出了挑战。紫外线发射线是双峰的,高电离线的峰间速度较高。尽管硬态期间观察到光学和近红外线有蓝移吸收特征,但没有一条线显示出明显的流出迹象。发射线比率与正常丰度一致,暗示捐赠者的初始质量足够低,以避免CNO处理(M_{2,i} \lesssim 1.0 - 1.5 {\mathrm M_{\odot}})。最后,我们研究了紫外线可变性的演化。所有紫外线功率谱都可以用截断功率律模型进行建模,在此基础上我们检测到约为18秒的准周期性振荡(QPO)。
关键见解
- 报告了低质量X射线双星MAXI J1820+070在三种不同积聚状态的紫外线光谱观测结果。
- 源头的消光较低,使其成为LMXB中最佳的紫外线积聚实验室之一。
- 三个状态的光谱显示出相似的连续体和发射线,显示出适中的差异。
- 连续体不能用物理盘模型很好地描述,对标准紫外线发射的重处理图像提出了挑战。
- 紫外线发射线通常呈现双峰形态,高电离线的峰间速度较高。
- 没有观察到明显的流出迹象,尽管在硬态期间观察到蓝移吸收特征。
点此查看论文截图

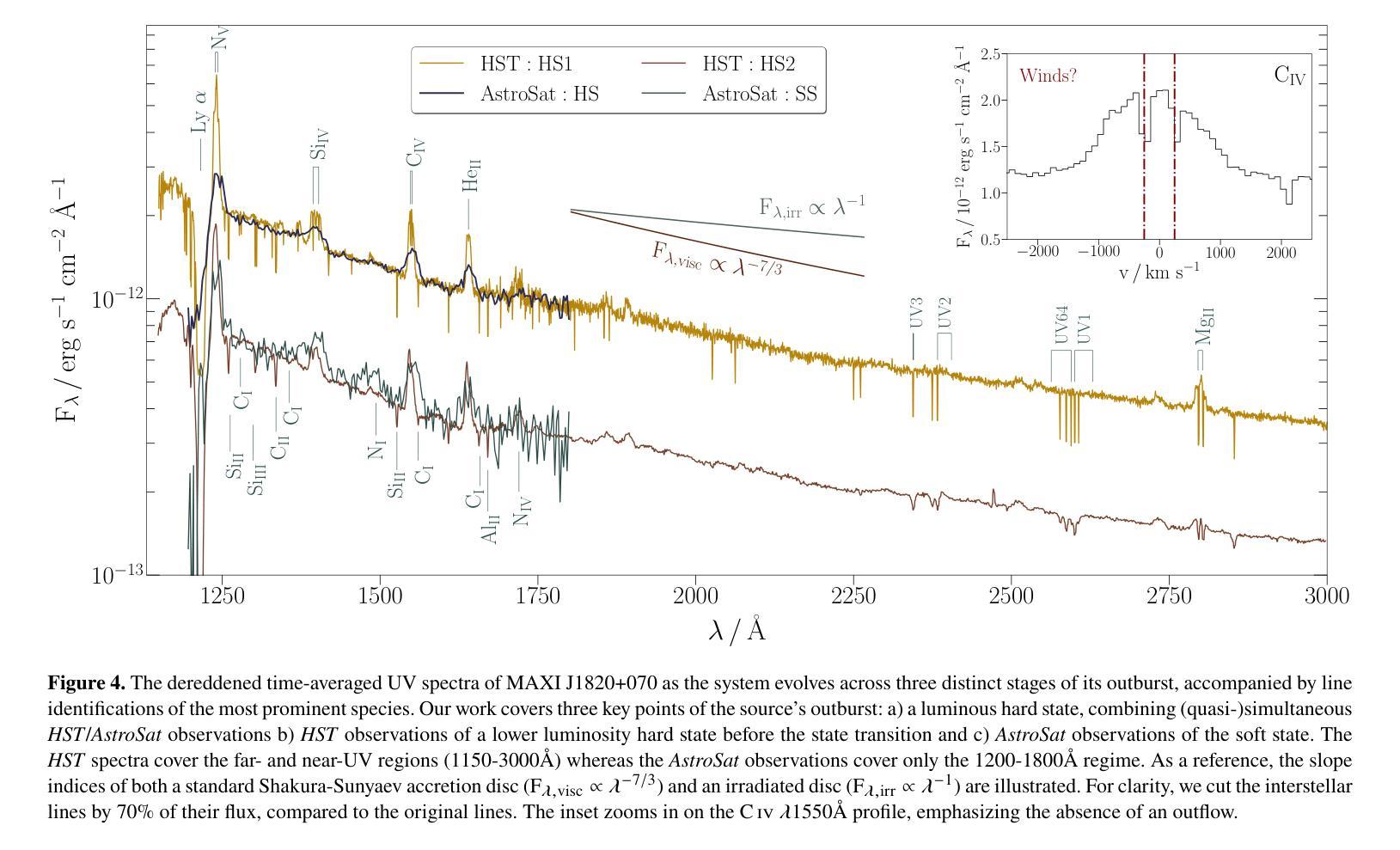
Unsupervised Patch-GAN with Targeted Patch Ranking for Fine-Grained Novelty Detection in Medical Imaging
Authors:Jingkun Chen, Guang Yang, Xiao Zhang, Jingchao Peng, Tianlu Zhang, Jianguo Zhang, Jungong Han, Vicente Grau
Detecting novel anomalies in medical imaging is challenging due to the limited availability of labeled data for rare abnormalities, which often display high variability and subtlety. This challenge is further compounded when small abnormal regions are embedded within larger normal areas, as whole-image predictions frequently overlook these subtle deviations. To address these issues, we propose an unsupervised Patch-GAN framework designed to detect and localize anomalies by capturing both local detail and global structure. Our framework first reconstructs masked images to learn fine-grained, normal-specific features, allowing for enhanced sensitivity to minor deviations from normality. By dividing these reconstructed images into patches and assessing the authenticity of each patch, our approach identifies anomalies at a more granular level, overcoming the limitations of whole-image evaluation. Additionally, a patch-ranking mechanism prioritizes regions with higher abnormal scores, reinforcing the alignment between local patch discrepancies and the global image context. Experimental results on the ISIC 2016 skin lesion and BraTS 2019 brain tumor datasets validate our framework’s effectiveness, achieving AUCs of 95.79% and 96.05%, respectively, and outperforming three state-of-the-art baselines.
在医学成像中检测新型异常是一个挑战,因为罕见异常的标注数据有限,而且这些异常通常表现出高度可变性和细微性。当较大的正常区域内嵌有小的异常区域时,这个挑战会进一步加剧,因为全图预测通常会忽略这些细微的偏差。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种无监督的Patch-GAN框架,该框架旨在通过捕捉局部细节和全局结构来检测和定位异常。我们的框架首先重建被遮挡的图像,以学习精细的、特定的正常特征,提高对正常细微偏差的敏感性。通过将这些重建的图像分成补丁并评估每个补丁的真实性,我们的方法可以在更精细的层面上识别异常,克服全图评估的限制。此外,补丁排名机制会优先考虑异常得分较高的区域,加强局部补丁差异与全局图像上下文之间的对齐。在ISIC 2016皮肤病变和BraTS 2019脑肿瘤数据集上的实验结果验证了我们的框架的有效性,分别实现了95.79%和96.05%的AUC,并超越了三种最先进的基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于无监督学习的Patch-GAN框架,用于解决医学图像中罕见异常检测的难题。通过重构图像学习正常特征的细节,并评估每个区域的真实性,以更精细地检测异常区域。框架采用排名机制,优先处理异常得分较高的区域,同时在局部补丁和全局图像之间保持一致性。在皮肤病变和脑肿瘤数据集上的实验验证了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像中罕见异常检测的挑战在于缺乏标记数据和异常的高变异性与微妙性。
- 提出的Patch-GAN框架旨在通过捕获局部细节和全局结构来解决这些问题。
- 框架通过重构图像学习正常特征的细节,提高对细微异常的敏感性。
- 通过评估每个图像补丁的真实性,在更精细的层面上检测异常。
- 采用排名机制优先处理异常得分较高的区域。
- 框架在皮肤病变和脑肿瘤数据集上的实验表现优异,分别实现了高AUC值。
点此查看论文截图




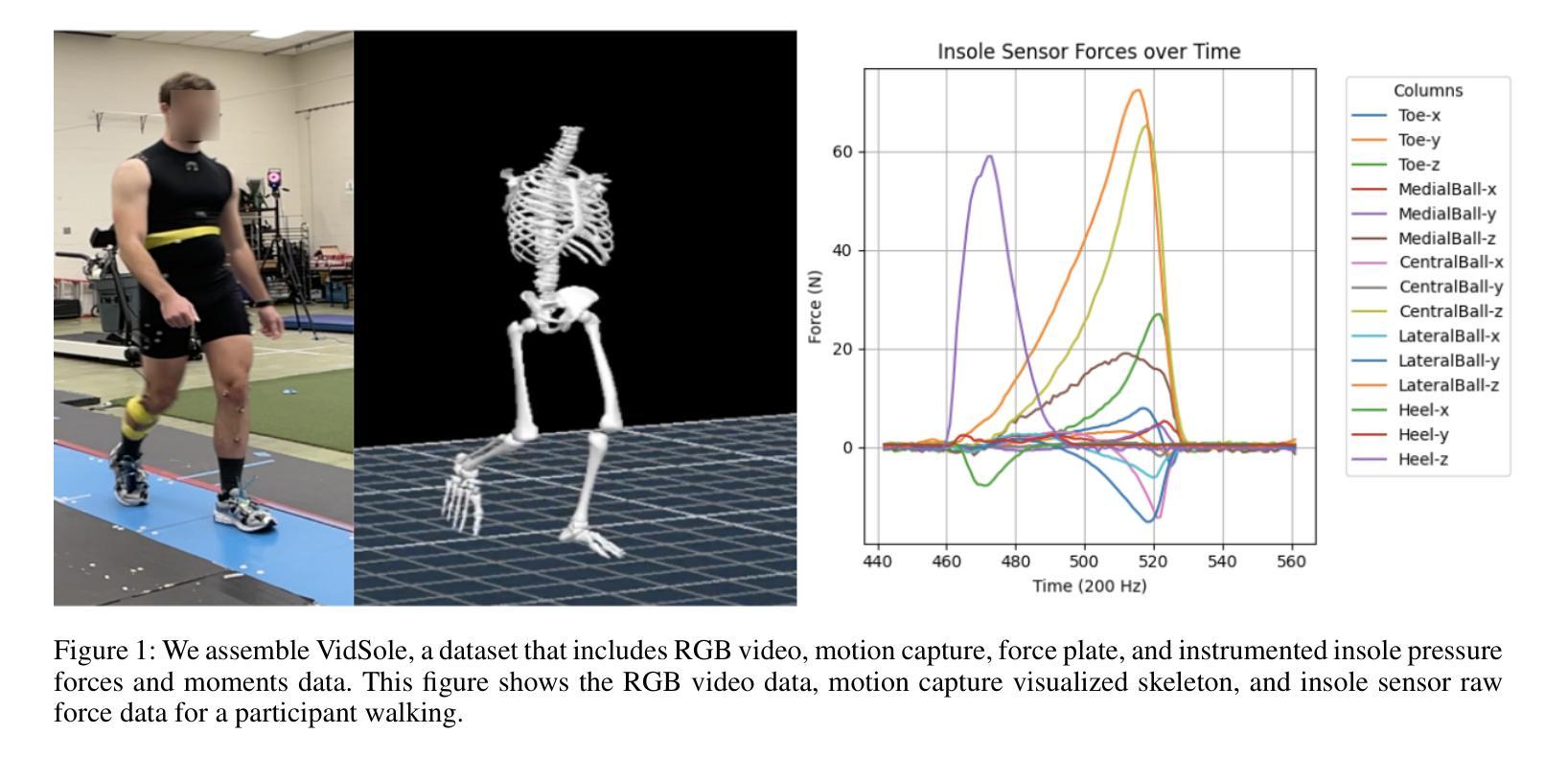
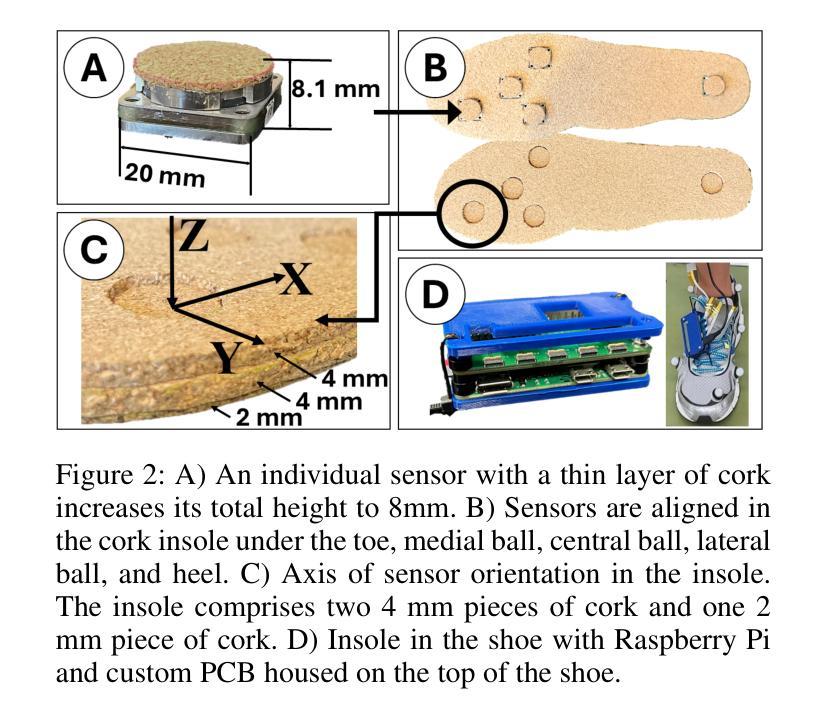
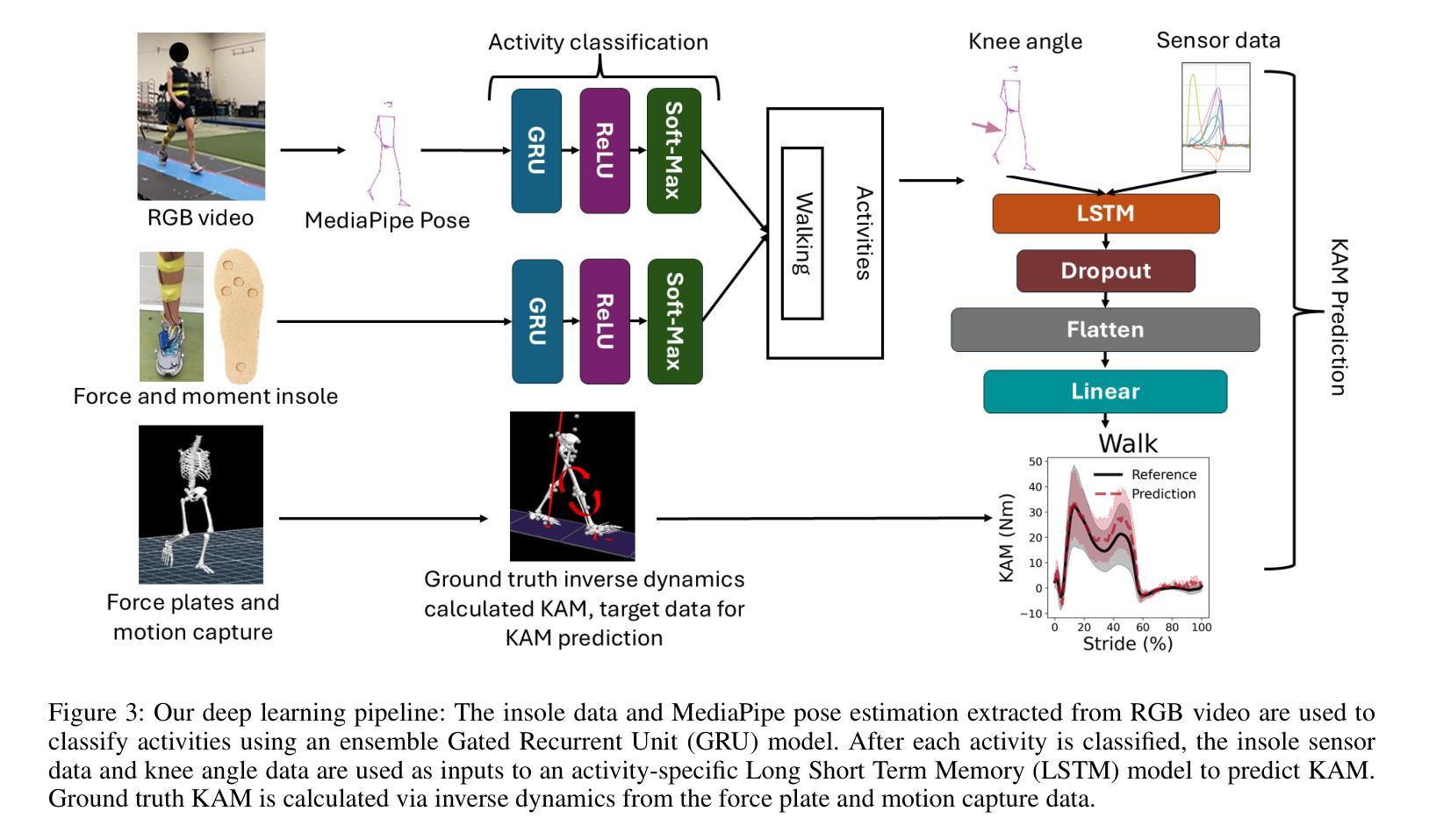
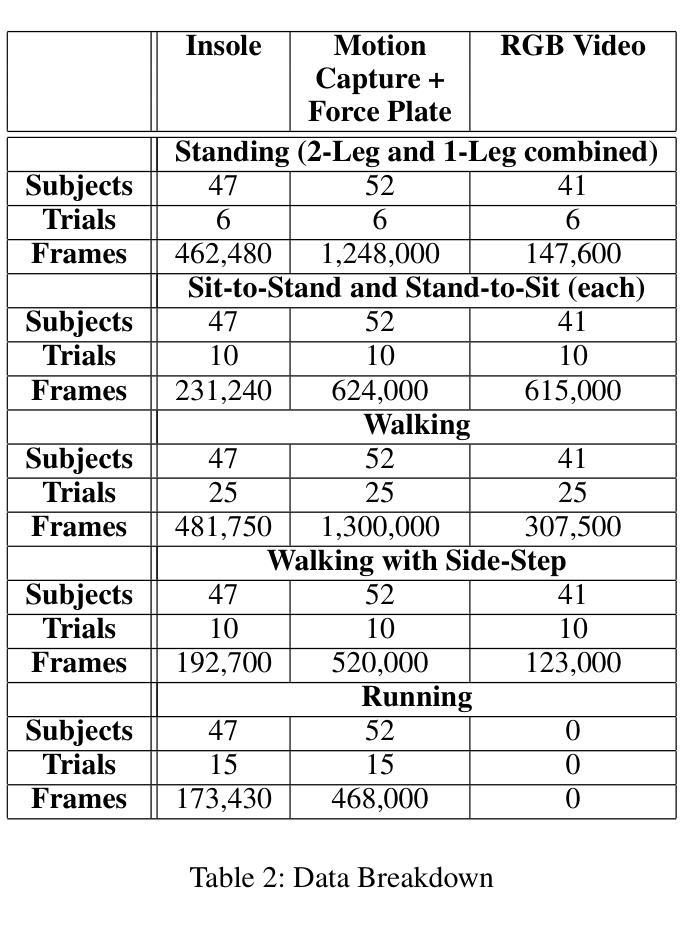
VidSole: A Multimodal Dataset for Joint Kinetics Quantification and Disease Detection with Deep Learning
Authors:Archit Kambhamettu, Samantha Snyder, Maliheh Fakhar, Samuel Audia, Ross Miller, Jae Kun Shim, Aniket Bera
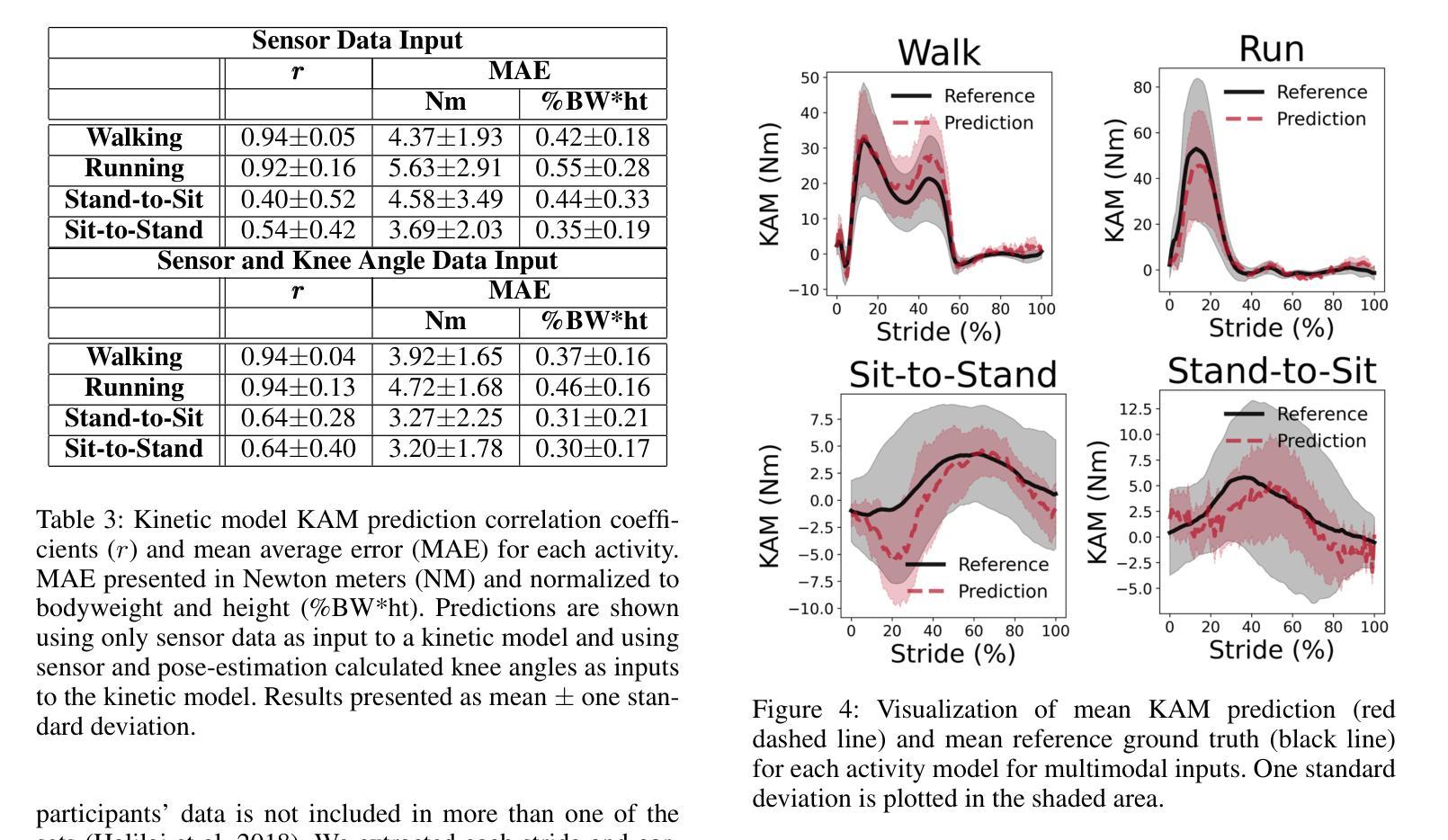
Understanding internal joint loading is critical for diagnosing gait-related diseases such as knee osteoarthritis; however, current methods of measuring joint risk factors are time-consuming, expensive, and restricted to lab settings. In this paper, we enable the large-scale, cost-effective biomechanical analysis of joint loading via three key contributions: the development and deployment of novel instrumented insoles, the creation of a large multimodal biomechanics dataset (VidSole), and a baseline deep learning pipeline to predict internal joint loading factors. Our novel instrumented insole measures the tri-axial forces and moments across five high-pressure points under the foot. VidSole consists of the forces and moments measured by these insoles along with corresponding RGB video from two viewpoints, 3D body motion capture, and force plate data for over 2,600 trials of 52 diverse participants performing four fundamental activities of daily living (sit-to-stand, stand-to-sit, walking, and running). We feed the insole data and kinematic parameters extractable from video (i.e., pose, knee angle) into a deep learning pipeline consisting of an ensemble Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) activity classifier followed by activity-specific Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) regression networks to estimate knee adduction moment (KAM), a biomechanical risk factor for knee osteoarthritis. The successful classification of activities at an accuracy of 99.02 percent and KAM estimation with mean absolute error (MAE) less than 0.5 percentbody weightheight, the current threshold for accurately detecting knee osteoarthritis with KAM, illustrates the usefulness of our dataset for future research and clinical settings.
理解关节内部受力对于诊断步态相关疾病(如膝关节骨关节炎)至关重要。然而,当前测量关节风险因素的方法耗时、昂贵,且仅限于实验室环境。在本文中,我们通过三个关键贡献实现了大规模、性价比高的关节加载生物力学分析:新型仪器化鞋垫的开发与部署、大型多模式生物力学数据集(VidSole)的创建,以及预测内部关节加载因素的深度学习管道基线。我们新型仪器化鞋垫可以测量五个高压力点下的三轴力和力矩。VidSole由这些鞋垫测量的力和力矩以及来自两个视角的相应RGB视频、3D人体运动捕捉和力量板数据组成,数据来自超过2600次试验,涉及52名不同参与者进行四项日常基本活动(从坐到站、从站到坐、行走和跑步)。我们将鞋垫数据和可从视频中提取的运动学参数(即姿势、膝关节角度)输入深度学习管道,该管道由集成门控循环单元(GRU)活动分类器组成,其次是特定活动的长短时记忆(LSTM)回归网络,用于估计膝关节内收力矩(KAM),这是膝关节骨关节炎的生物力学风险因素。活动分类的成功准确率为99.02%,膝关节内收力矩估计的平均绝对误差(MAE)低于体重身高的0.5%,这一数据准确检测膝关节骨关节炎的阈值说明了我们的数据集对未来研究和临床设置的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025 Special Track on AI for Social Impact
摘要
本文介绍了通过新型仪器化鞋垫、多模式生物力学数据集(VidSole)和深度学习管道,实现对关节载荷的大规模、成本效益高的生物力学分析。新型鞋垫可测量五个高压点下的三轴力和力矩。VidSole数据集包括鞋垫测量的力和力矩、两个视角的RGB视频、3D身体运动捕获以及超过2600次试验的数据,涉及52名不同参与者执行四项日常基本活动(坐立、站立、行走和跑步)。研究通过深度学习管道成功实现活动分类与膝关节加载力矩的估计,对于膝关节骨关节炎的诊断具有重要价值。活动分类准确率为99.02%,膝关节加载力矩估计误差低于体重乘以身高的百分比值(小于标准膝关节骨关节炎诊断阈值)。该数据集对后续研究和临床应用具有重要意义。
关键见解
一、利用新型仪器化鞋垫测量足部五个高压点的三轴力和力矩,为关节载荷分析提供新方法。
二、创建大型多模式生物力学数据集VidSole,涵盖多种活动和参与者数据,促进深入研究。
三、建立深度学习管道,以估计膝关节骨关节炎风险的关键因素——膝关节加载力矩。深度学习模型采用活动分类器结合长期记忆回归网络。
点此查看论文截图


Exploring AI-based System Design for Pixel-level Protected Health Information Detection in Medical Images
Authors:Tuan Truong, Ivo M. Baltruschat, Mark Klemens, Grit Werner, Matthias Lenga
Purpose: This study aims to evaluate different setups of an AI-based solution to detect Protected Health Information (PHI) in medical images. Materials and Methods: Text from eight PHI and eight non-PHI categories are simulated and incorporated into a curated dataset comprising 1,000 medical images across four modalities: CT, X-ray, bone scan, and MRI. The proposed PHI detection pipeline comprises three key components: text localization, extraction, and analysis. Three vision and language models, YOLOv11, EasyOCR, and GPT-4o, are benchmarked in different setups corresponding to three key components. The performance is evaluated with classification metrics, including precision, recall, F1 score, and accuracy. Results: All four setups demonstrate strong performance in detecting PHI imprints, with all metrics exceeding 0.9. The setup that utilizes YOLOv11 for text localization and GPT-4o for text extraction and analysis achieves the highest performance in PHI detection. However, this setup incurs the highest cost due to the increased number of generated tokens associated with GPT-4o model. Conversely, the setup using solely GPT-4o for the end-to-end pipeline exhibits the lowest performance but showcases the feasibility of multi-modal models in solving complex tasks. Conclusion: For optimal text localization and extraction, it is recommended to fine-tune an object detection model and utilize built-in Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software. Large language models like GPT-4o can be effectively leveraged to reason about and semantically analyze the PHI content. Although the vision capability of GPT-4o is promising for reading image crops, it remains limited for end-to-end pipeline applications with whole images.
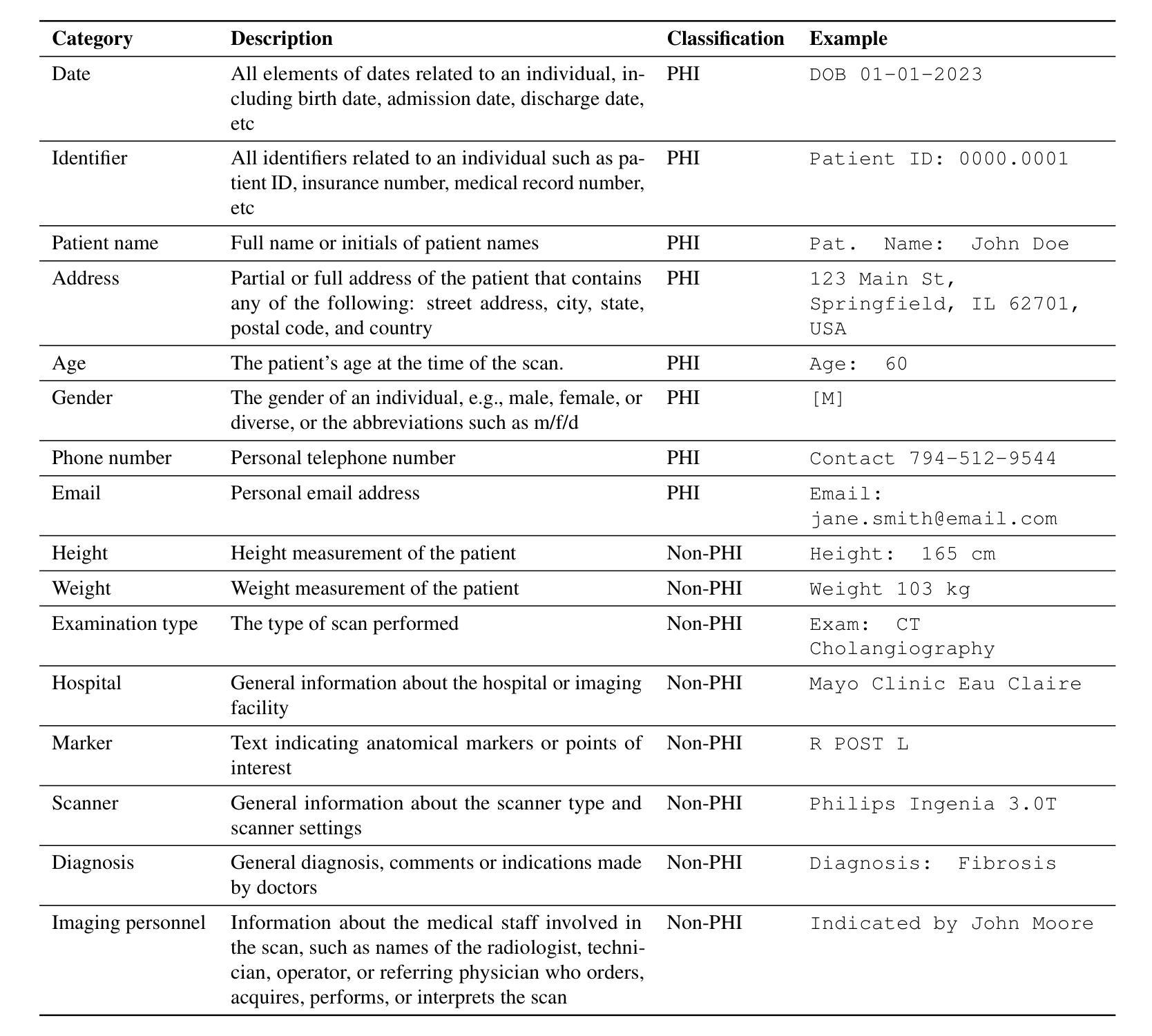
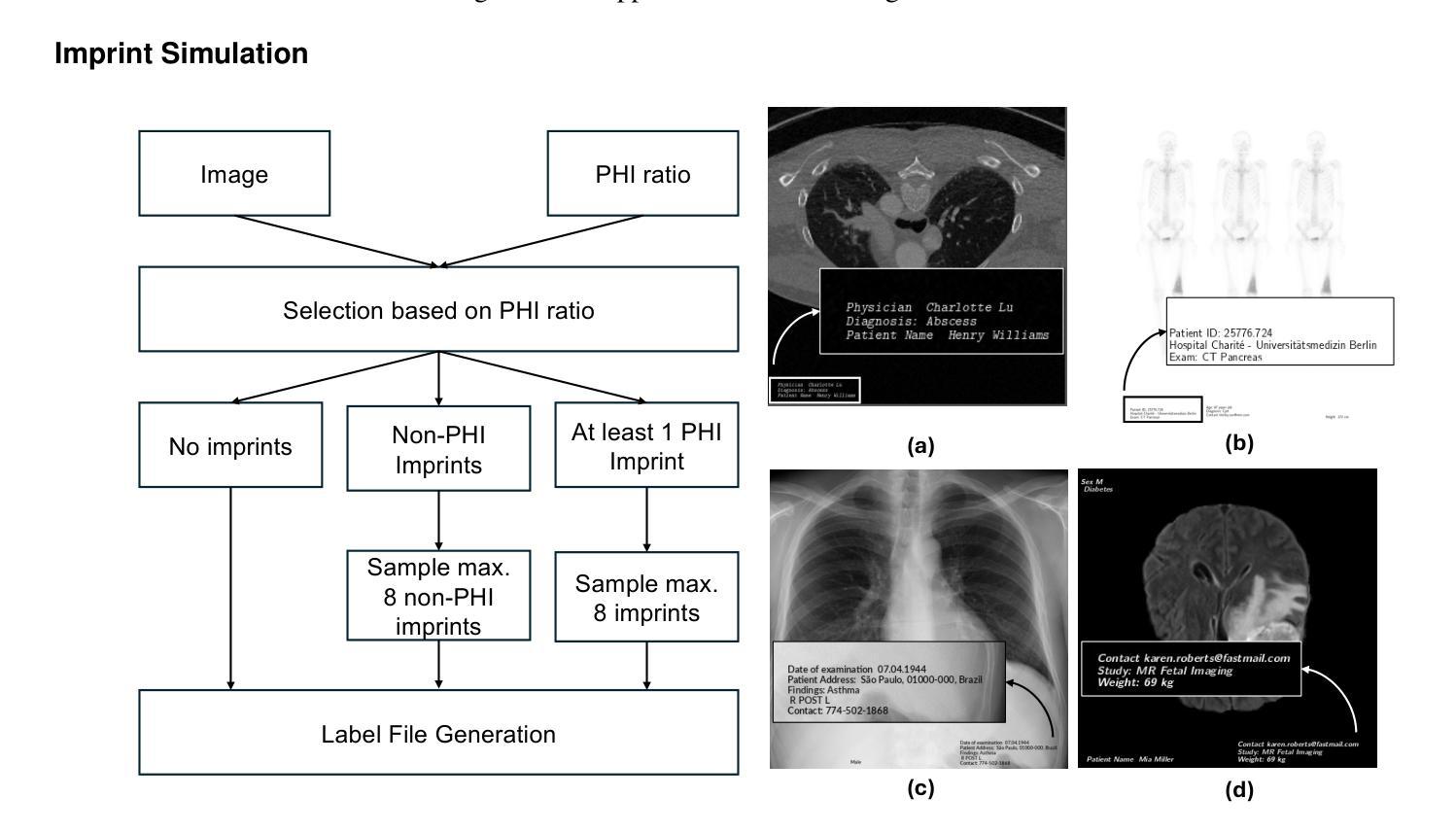
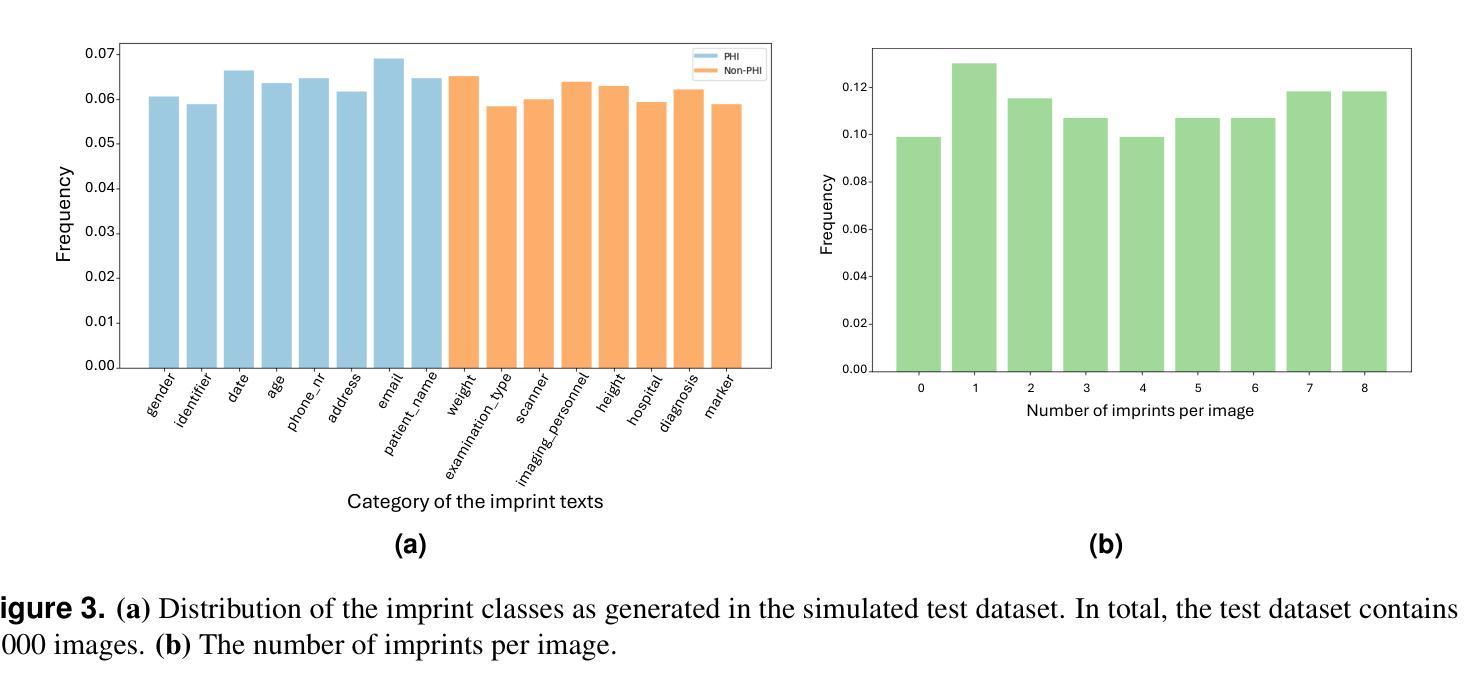
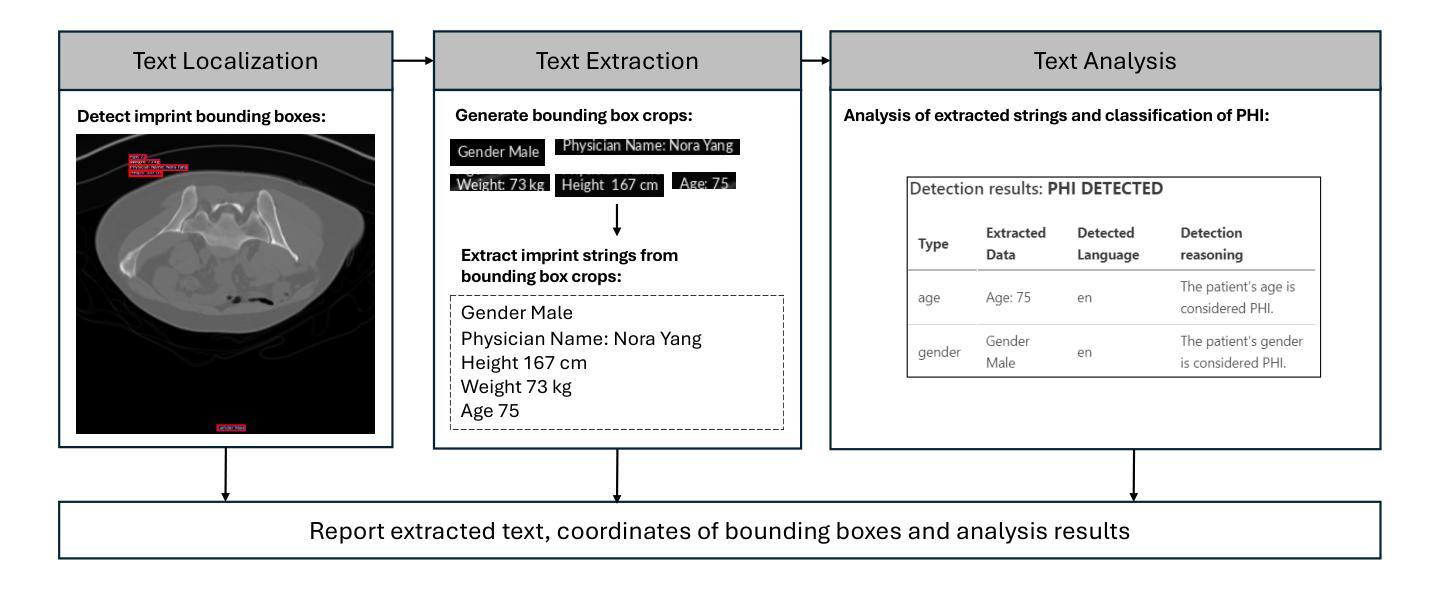
目的:本研究旨在评估基于人工智能的解决方案在不同配置下检测医学图像中的受保护健康信息(PHI)的能力。
材料与方法:模拟了来自八个PHI和八个非PHI类别的文本,并纳入包含1000张医学图像的定制数据集,涉及四种模态:CT、X光、骨扫描和MRI。提出的PHI检测流程包含三个关键组件:文本定位、提取和分析。三种视觉和语言模型,即YOLOv11、EasyOCR和GPT-4o,在不同的配置下进行了基准测试,分别对应于三个关键组件。性能评估采用分类指标,包括精确度、召回率、F1分数和准确率。
结果:所有四种配置在检测PHI印记方面都表现出强劲性能,各项指标均超过0.9。使用YOLOv11进行文本定位,GPT-4o进行文本提取和分析的配置在PHI检测方面表现最佳。然而,由于GPT-4o模型产生的令牌数量增加,该配置的成本也最高。相反,仅使用GPT-4o进行端到端管道的配置性能最低,但展示了多模态模型解决复杂任务的可行性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In progress
Summary
本研究旨在评估基于AI的解决方案在不同配置下检测医学图像中的受保护健康信息(PHI)的性能。该研究使用模拟的文本数据创建了包含一千张跨四种模态(CT、X光、骨扫描和MRI)的医学图像数据集。提出的PHI检测流程包含三个关键组件:文本定位、提取和分析。使用YOLOv11、EasyOCR和GPT-4o等视觉和语言模型在不同配置下进行基准测试。所有配置在检测PHI印记方面表现出强大的性能,各项指标均超过0.9。使用YOLOv11进行文本定位和GPT-4o进行文本提取和分析的配置在PHI检测方面表现最佳,但成本最高。仅使用GPT-4o进行端到端流程的配置性能最低,但证明了多模态模型在解决复杂任务中的可行性。建议对目标检测模型进行微调,并利用内置的光学字符识别(OCR)软件进行文本定位和提取。大型语言模型如GPT-4o可以有效地推理和语义分析PHI内容。尽管GPT-4o在读取图像裁剪方面的视觉能力令人鼓舞,但对于端到端管道应用来说仍然有限。
Key Takeaways
- 研究旨在评估不同配置的AI解决方案在医学图像中检测PHI的性能。
- 使用模拟文本数据创建了包含四种模态的医学图像数据集。
- PHI检测流程包含文本定位、提取和分析三个关键组件。
- 使用YOLOv11和GPT-4o等模型进行PHI检测表现出良好的性能。
- YOLOv11与GPT-4o结合在PHI检测方面表现最佳,但成本较高。
- GPT-4o在多模态任务中的可行性得到展示,但在处理整个图像时存在局限性。
点此查看论文截图


Quantum Down Sampling Filter for Variational Auto-encoder
Authors:Farina Riaz, Fakhar Zaman, Hajime Suzuki, Sharif Abuadbba, David Nguyen
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are essential tools in generative modeling and image reconstruction, with their performance heavily influenced by the encoder-decoder architecture. This study aims to improve the quality of reconstructed images by enhancing their resolution and preserving finer details, particularly when working with low-resolution inputs (16x16 pixels), where traditional VAEs often yield blurred or in-accurate results. To address this, we propose a hybrid model that combines quantum computing techniques in the VAE encoder with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in the decoder. By upscaling the resolution from 16x16 to 32x32 during the encoding process, our approach evaluates how the model reconstructs images with enhanced resolution while maintaining key features and structures. This method tests the model’s robustness in handling image reconstruction and its ability to preserve essential details despite training on lower-resolution data. We evaluate our proposed down sampling filter for Quantum VAE (Q-VAE) on the MNIST and USPS datasets and compare it with classical VAEs and a variant called Classical Direct Passing VAE (CDP-VAE), which uses windowing pooling filters in the encoding process. Performance is assessed using metrics such as the Frechet Inception Distance (FID) and Mean Squared Error (MSE), which measure the fidelity of reconstructed images. Our results demonstrate that the Q-VAE consistently outperforms both the Classical VAE and CDP-VAE, achieving significantly lower FID and MSE scores. Additionally, CDP-VAE yields better performance than C-VAE. These findings highlight the potential of quantum-enhanced VAEs to improve image reconstruction quality by enhancing resolution and preserving essential features, offering a promising direction for future applications in computer vision and synthetic data generation.
变分自编码器(VAEs)在生成建模和图像重建中扮演着重要角色,其性能在很大程度上受到编码器-解码器架构的影响。本研究旨在提高重建图像的质量,特别是在处理低分辨率输入(如16x16像素)时,通过提高分辨率并保持更精细的细节来提升图像质量,因为传统VAEs往往会产生模糊或不准确的结果。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种混合模型,该模型结合了变分自编码器编码器中的量子计算技术和解码器中的卷积神经网络(CNN)。我们的方法通过在编码过程中将分辨率从16x16提高到32x32来评估模型如何以更高的分辨率重建图像,同时保持关键特征的结构。这种方法测试了模型在处理图像重建方面的稳健性以及其在处理低分辨率数据时保留重要细节的能力。我们在MNIST和USPS数据集上评估了针对量子变分自编码器(Q-VAE)提出的下采样滤波器,并将其与经典变分自编码器(C-VAE)和一种称为经典直接传递变分自编码器(CDP-VAE)的变体进行了比较。后者在编码过程中使用窗口池化滤波器。性能评估使用了Frechet Inception Distance(FID)和均方误差(MSE)等度量指标,这些指标衡量了重建图像的保真度。我们的结果表明,Q-VAE始终优于经典VAE和CDP-VAE,获得了更低的FID和MSE分数。此外,CDP-VAE的性能也比C-VAE要好。这些发现突出了量子增强型VAE在提高图像重建质量方面的潜力,通过提高分辨率并保持关键特征来实现,为计算机视觉和合成数据生成领域的应用提供了有前途的研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 13 figures
摘要
本研究旨在提升变分自编码器(VAEs)在生成模型和图像重建中的性能,特别是针对低分辨率输入(16x16像素)的情况。传统VAE在处理此类输入时往往产生模糊或不准确的结果。本研究提出了一种结合量子计算和卷积神经网络(CNN)的混合模型。该模型在VAE编码器中使用量子计算技术,并在解码器中使用CNN。通过从16x16分辨率提升到32x32分辨率进行图像重建,评估模型在提升分辨率的同时保持关键特征和结构的能力。实验在MNIST和USPS数据集上对所提出的量子VAE(Q-VAE)进行下采样滤波器的测试,并与传统VAE和一种称为经典直接传递VAE(CDP-VAE)的变体进行比较。根据Frechet Inception Distance(FID)和Mean Squared Error(MSE)等度量指标,Q-VAE的性能表现最佳,取得了更低的FID和MSE分数。这些结果突显了量子增强VAE在提高图像重建质量和保持关键特征方面的潜力,为计算机视觉和合成数据生成等领域的未来应用提供了有前景的方向。
关键见解
- 本研究旨在提高变分自编码器(VAEs)在低分辨率输入下的图像重建质量。
- 提出了一种结合量子计算和卷积神经网络(CNN)的混合模型,即量子VAE(Q-VAE)。
- Q-VAE在编码过程中实现了从16x16到32x32的分辨率提升,以评估模型在提升分辨率同时保持关键特征的能力。
- 在MNIST和USPS数据集上的实验表明,Q-VAE在图像重建方面表现出卓越性能,优于传统VAE和CDP-VAE。
- Q-VAE在Frechet Inception Distance(FID)和Mean Squared Error(MSE)等度量指标上取得了更低的分数,证明了其优越性。
- 研究结果突显了量子增强VAE在图像重建和特征保持方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

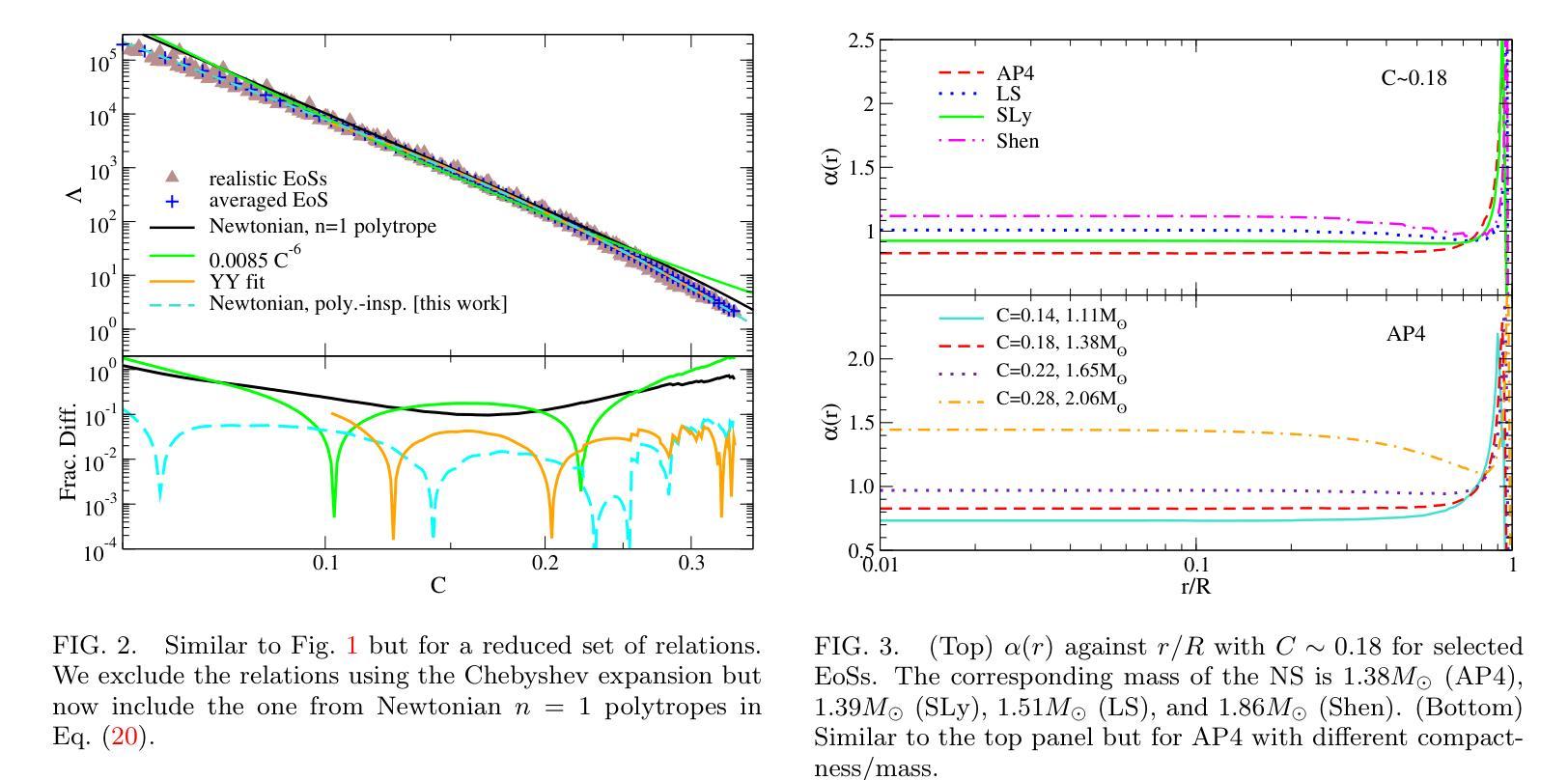
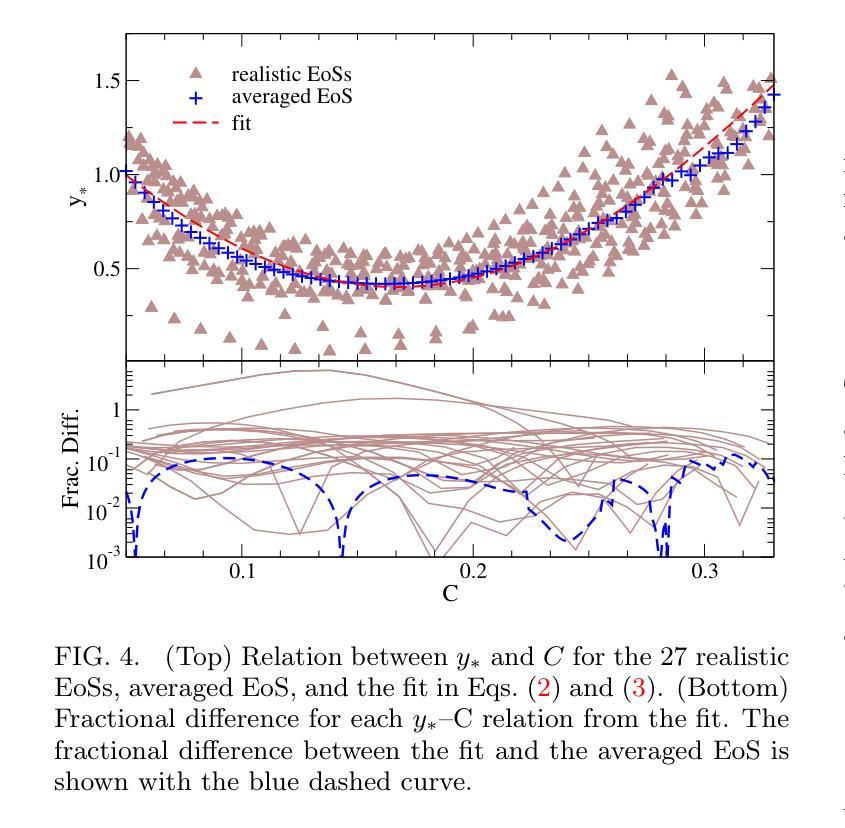
Improved Analytic Love-C Relations for Neutron Stars
Authors:Tristen Lowrey, Kent Yagi, Nicolás Yunes
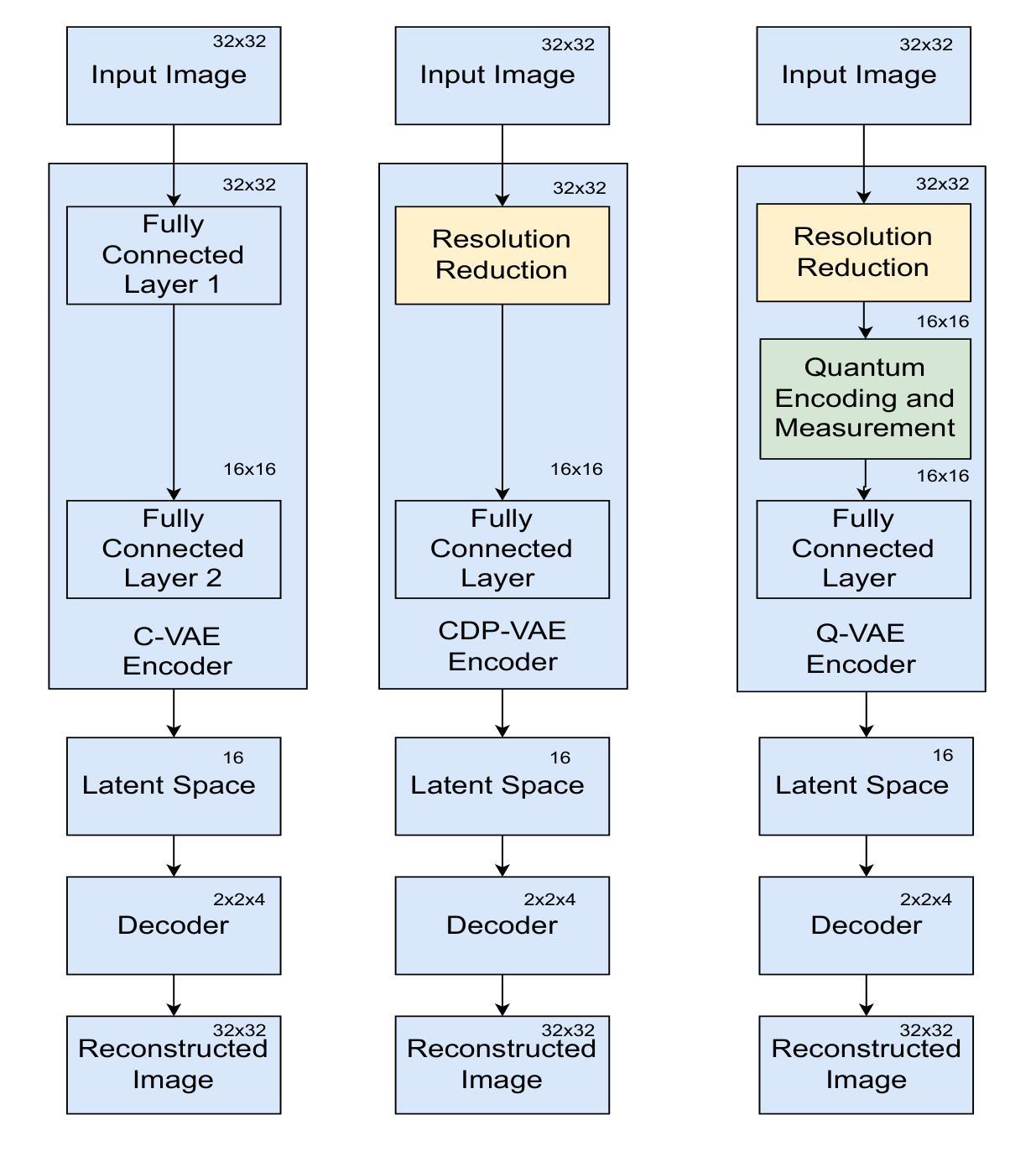
Precise measurements of neutron star observables (such as mass and radius) allow one to constrain the equations of state for supranuclear matter and develop a stronger understanding of nuclear physics. The Neutron star Interior Composition ExploreR (NICER) tracks X-ray hotspots on rotating NSs and is able to infer precise information about the compactness of the star. Gravitational waves carry information about the tidal deformability (related to the tidal Love number) of neutron stars, which has been measured by the LIGO/Virgo/KAGRA collaboration. These two observables enjoy an approximately universal property between each other that is insensitive to the equations of state (the “universal Love-C relation”). In this paper, we focus on deriving two analytic expressions for the Love-C relations that are ready-to-use and improve upon previous analytic expressions. The first model is inspired by a Newtonian polytrope, whose perturbation to the gravitational potential can be found analytically. We extend this Newtonian model to the relativistic regime by providing a quadratic fit to the gravitational potential perturbation against stellar compactness. The second model makes use of the Tolman VII model and adopts a spectral expansion with Chebyshev polynomials, which converges faster than the Taylor expansions used in previous work. We find that the first model provides a more accurate description of the Love-C relation for realistic neutron stars than the second model, and it provides the best expression among all other analytic relations studied here in terms of describing the averaged numerical Love-C relation. These new models are not only useful in practice, but they also show the power and importance of analytic modeling of neutron stars.
精确测量中子星的可观测值(如质量和半径)可以限制超核物质的物态方程,并加强对核物理的理解。中子星内部结构探测器(NICER)追踪旋转中子星上的X射线热点,并能够推断出关于恒星致密性的精确信息。引力波携带有关中子潮涨变形性的信息(与潮汐洛夫数有关),这是由LIGO/Virgo/KAGRA合作测量的。这两个可观测值之间具有彼此大致通用的属性,对物态方程不敏感(“通用洛夫-C关系”)。在本文中,我们专注于导出两个洛夫-C关系的解析表达式,这些表达式即学即用,并改进了先前的解析表达式。第一个模型受到牛顿多边形的启发,其引力势的扰动可以分析找到。我们通过将引力势扰动与恒星致密性进行二次拟合,将这一牛顿模型扩展到相对论领域。第二个模型利用Tolman VII模型,采用切比雪夫多项式的谱展开,其收敛速度比先前工作中使用的泰勒展开更快。我们发现,第一个模型为现实的中子星提供了更准确的洛夫-C关系描述,并且在描述平均数值洛夫-C关系方面,它在这里研究的所有其他解析关系中表现最佳。这些新模型不仅在实践中很有用,而且展示了中子星解析建模的力量和重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 9 figures
Summary
中子星观测数据的精确测量(如质量和半径)对于约束超核物质的物态方程以及增强对核物理的理解至关重要。NICER实验通过追踪旋转中子星上的X射线热点来推断关于星体紧致性的精确信息。引力波携带有关中子星潮汐变形性的信息,这一信息已经由LIGO/Virgo/KAGRA合作测量。中子星的潮汐爱与C关系(Love-C relation)具有一个大致的通用属性,该属性对物态方程不敏感。本文重点推导了两个用于Love-C关系的解析表达式,这些表达式使用方便并在之前的基础上进行了改进。第一个模型受到牛顿多边形的启发,其引力势扰动可找到解析解。我们通过将牛顿模型扩展为相对论模型,提供了一个引力势扰动相对于恒星紧致性的二次拟合。第二个模型利用Tolman VII模型并采用切比雪夫多项式进行谱展开,其收敛速度比之前的泰勒展开更快。研究发现,第一个模型在描述现实的中子星的Love-C关系时比第二个模型更准确,并且在描述平均数值Love-C关系方面,它提供了此处研究的所有其他解析关系中最佳的表达形式。这些新模型不仅在实践中具有实用性,而且还展示了中子星解析建模的力量和重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 中子星观测数据的精确测量对于理解核物理和超核物质的物态方程至关重要。
- NICER实验通过追踪旋转中子星上的X射线热点,能够推断出关于星体紧致性的精确信息。
- 引力波携带有关中子星潮汐变形性的信息,该信息已得到LIGO/Virgo/KAGRA合作的测量。
- 中子星的潮汐爱与C关系(Love-C relation)在物态方程上具有通用性。
- 文章提出了两个新的解析模型来描述Love-C关系,分别是基于牛顿多边形和Tolman VII模型的扩展。
- 第一个模型在描述现实的中子星的Love-C关系时表现出更高的准确性。
点此查看论文截图


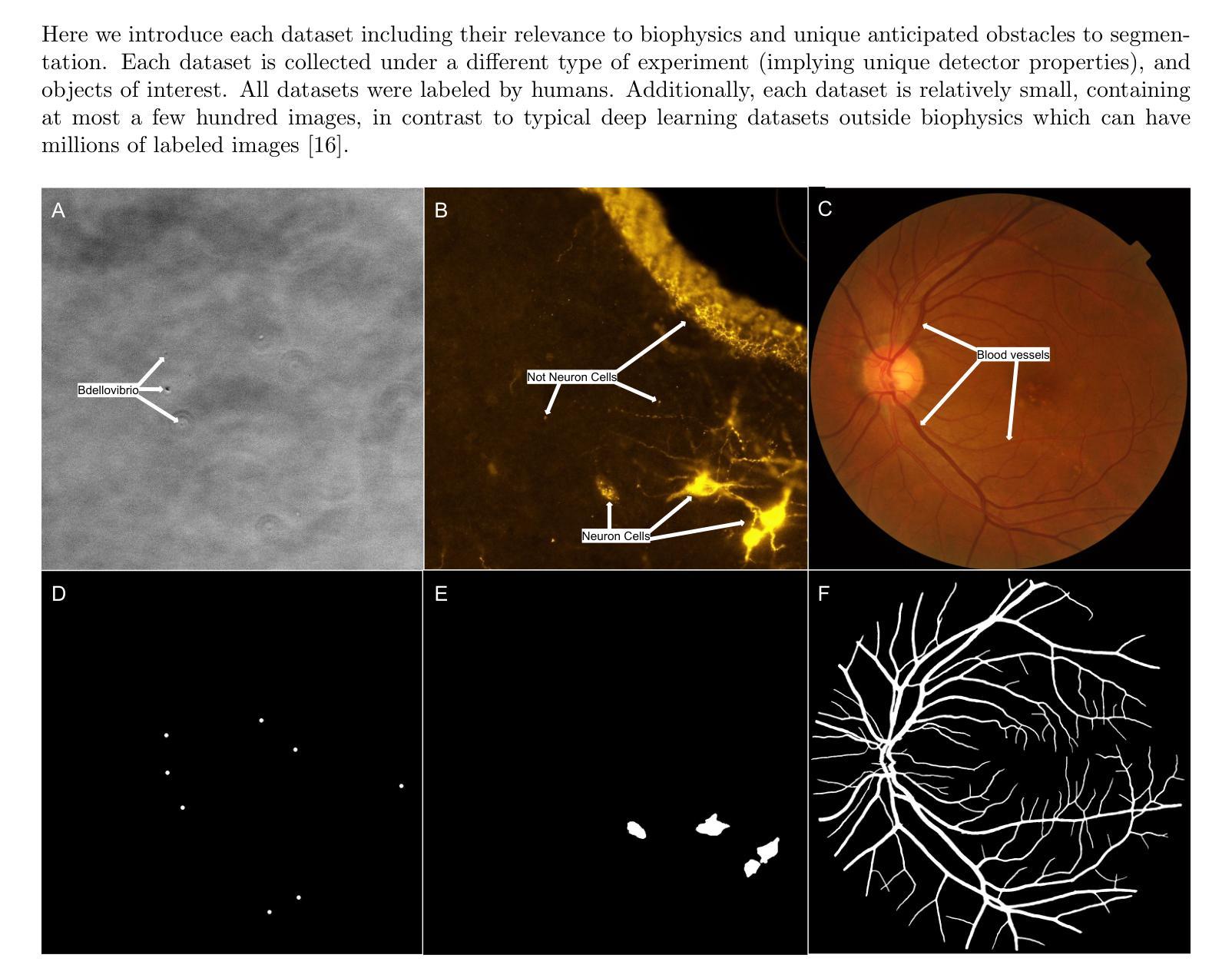
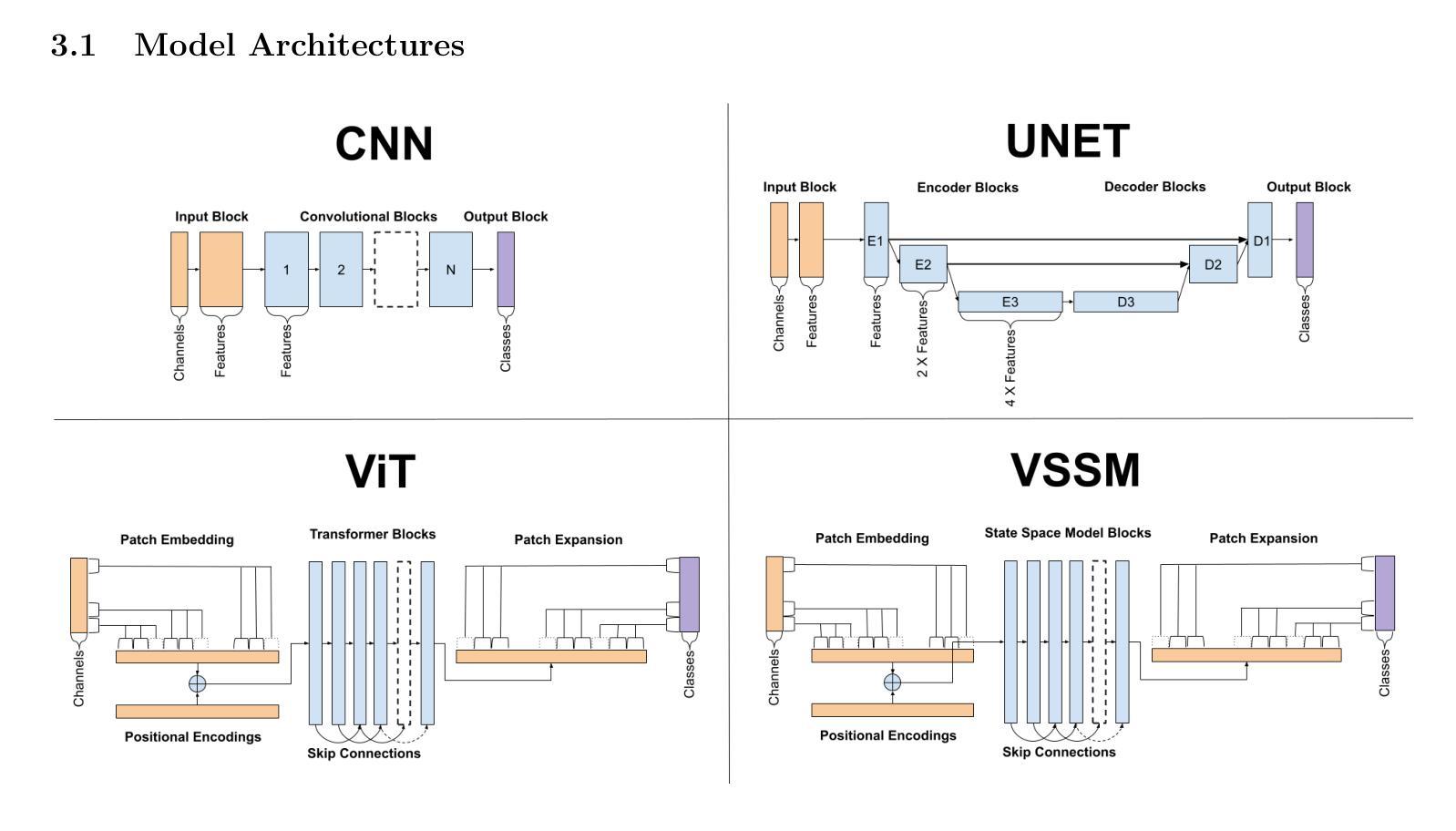
Perspectives: Comparison of Deep Learning Segmentation Models on Biophysical and Biomedical Data
Authors:J Shepard Bryan IV, Pedro Pessoa, Meyam Tavakoli, Steve Presse
Deep learning based approaches are now widely used across biophysics to help automate a variety of tasks including image segmentation, feature selection, and deconvolution. However, the presence of multiple competing deep learning architectures, each with its own unique advantages and disadvantages, makes it challenging to select an architecture best suited for a specific application. As such, we present a comprehensive comparison of common models. Here, we focus on the task of segmentation assuming the typically small training dataset sizes available from biophysics experiments and compare the following four commonly used architectures: convolutional neural networks, U-Nets, vision transformers, and vision state space models. In doing so, we establish criteria for determining optimal conditions under which each model excels, thereby offering practical guidelines for researchers and practitioners in the field.
基于深度学习的方法在生物物理学中得到了广泛的应用,用于自动化完成包括图像分割、特征选择和去卷积等任务。然而,多种竞争的深度学习架构的存在,每种架构都有其独特的优势和劣势,使得很难选择出最适合特定应用的架构。因此,我们对常见的模型进行了全面的比较。在这里,我们专注于分割任务,考虑到生物物理实验通常可用的小型训练数据集的大小,并比较了以下四种常用的架构:卷积神经网络、U-Net、视觉变压器和视觉状态空间模型。通过这样做,我们确定了每个模型在何种条件下表现最佳的标准,从而为该领域的研究人员和实践者提供了实用的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习在生物物理学中广泛应用于图像分割、特征选择和解卷积等任务。由于存在多种竞争的深度学习架构,选择适合特定应用的架构是一个挑战。本文全面比较了常见的模型,重点关注了假设生物物理实验可用训练数据集较小的分割任务,并比较了卷积神经网络、U-Nets、视觉变压器和视觉状态空间模型等四种常用架构。通过确定每个模型在何种条件下表现最佳,为研究人员和从业者提供了实用指南。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在生物物理学中有广泛的应用,包括图像分割、特征选择和解卷积等任务。
- 存在多种深度学习架构,每种架构都有其独特的优势和劣势。
- 选择适合特定应用的最佳架构是一个挑战。
- 本文比较了四种常用架构:卷积神经网络、U-Nets、视觉变压器和视觉状态空间模型。
- 在小训练数据集的情况下,不同架构的表现会有所不同。
- 通过实验确定了每个模型在何种条件下表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

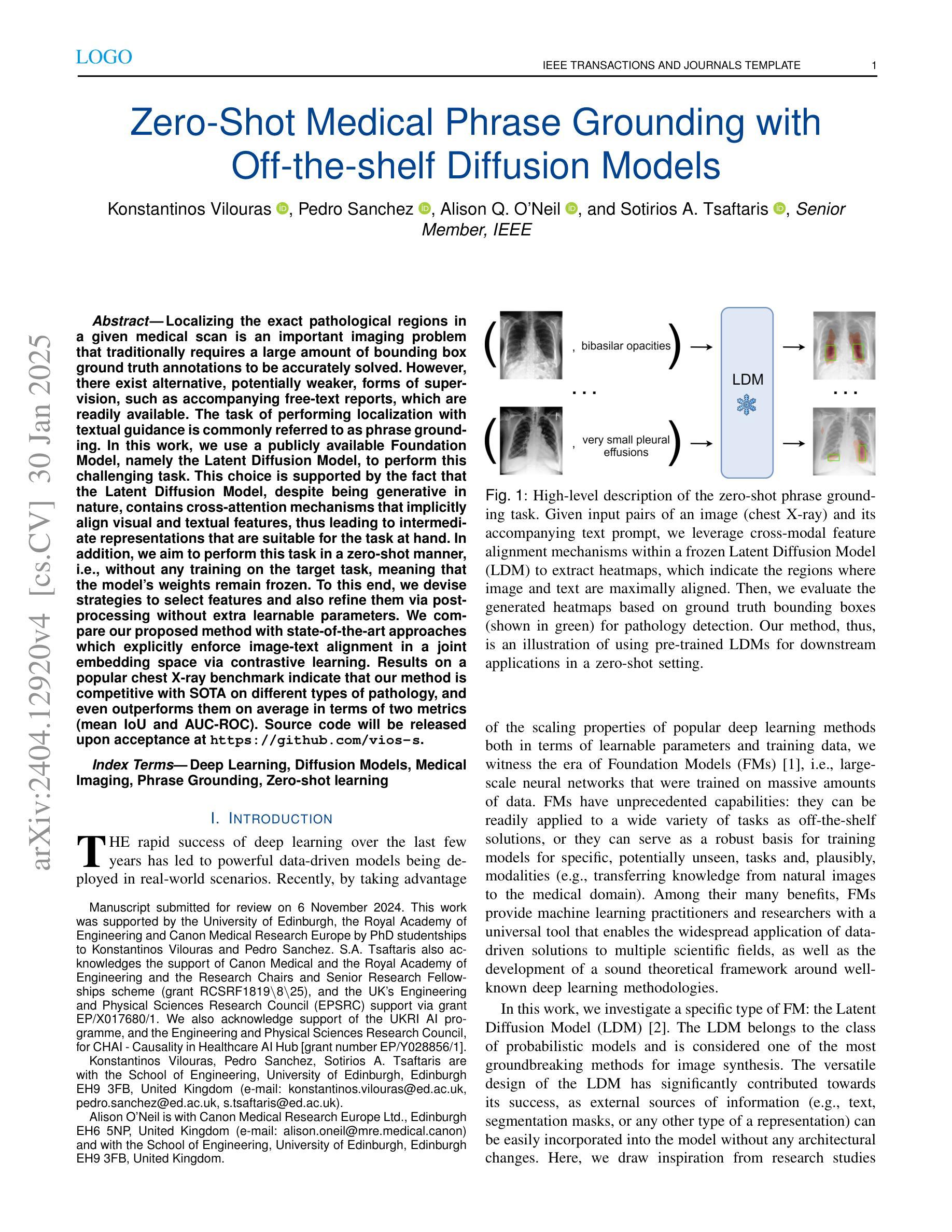
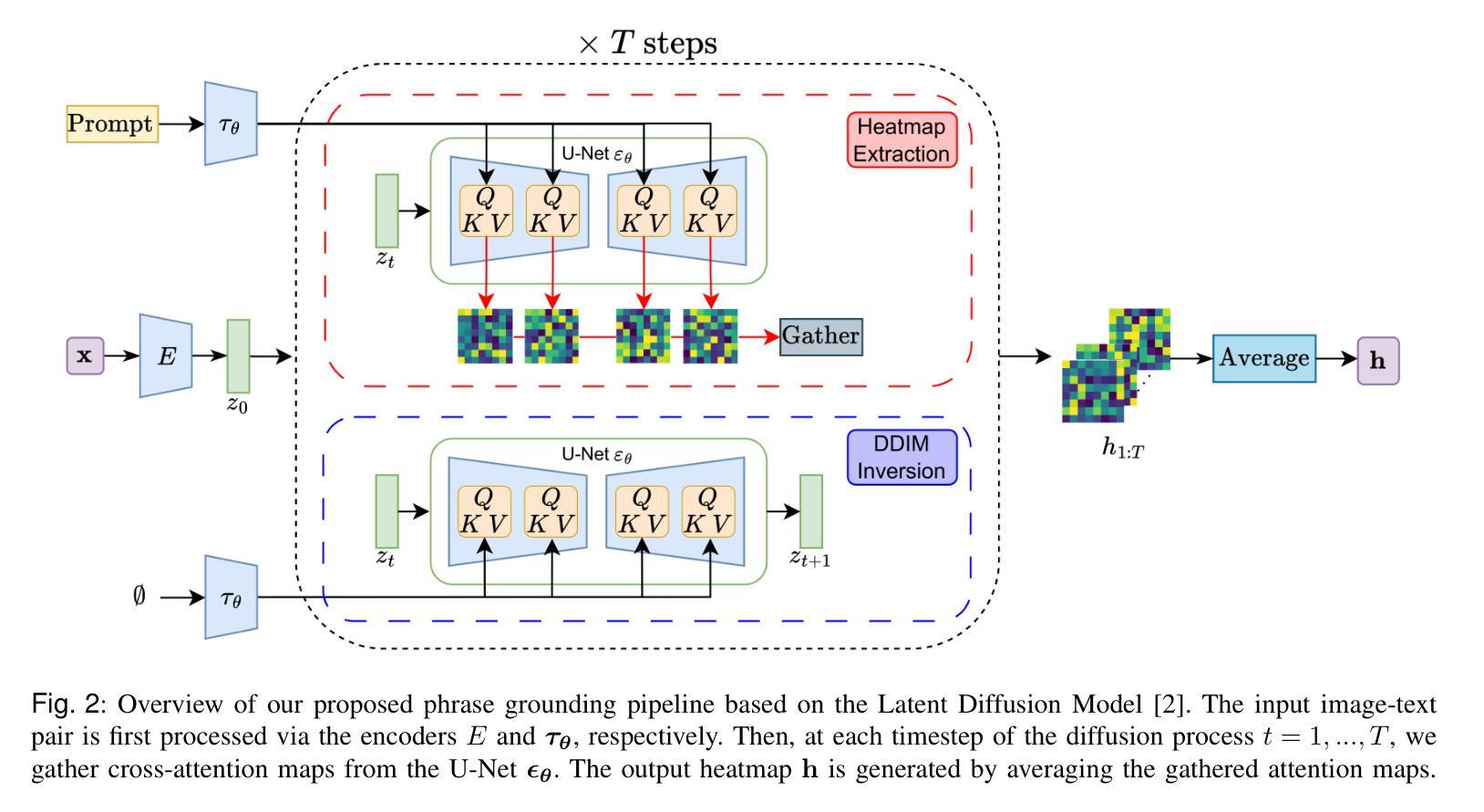
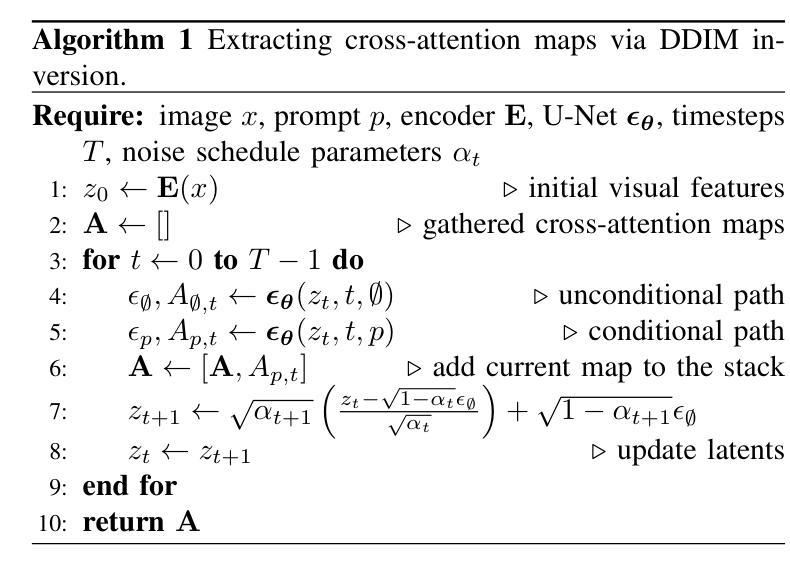
Zero-Shot Medical Phrase Grounding with Off-the-shelf Diffusion Models
Authors:Konstantinos Vilouras, Pedro Sanchez, Alison Q. O’Neil, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris
Localizing the exact pathological regions in a given medical scan is an important imaging problem that traditionally requires a large amount of bounding box ground truth annotations to be accurately solved. However, there exist alternative, potentially weaker, forms of supervision, such as accompanying free-text reports, which are readily available. The task of performing localization with textual guidance is commonly referred to as phrase grounding. In this work, we use a publicly available Foundation Model, namely the Latent Diffusion Model, to perform this challenging task. This choice is supported by the fact that the Latent Diffusion Model, despite being generative in nature, contains cross-attention mechanisms that implicitly align visual and textual features, thus leading to intermediate representations that are suitable for the task at hand. In addition, we aim to perform this task in a zero-shot manner, i.e., without any training on the target task, meaning that the model’s weights remain frozen. To this end, we devise strategies to select features and also refine them via post-processing without extra learnable parameters. We compare our proposed method with state-of-the-art approaches which explicitly enforce image-text alignment in a joint embedding space via contrastive learning. Results on a popular chest X-ray benchmark indicate that our method is competitive with SOTA on different types of pathology, and even outperforms them on average in terms of two metrics (mean IoU and AUC-ROC). Source code will be released upon acceptance at https://github.com/vios-s.
在给定医学扫描中定位精确病理区域是一个重要的成像问题,传统上需要大量的边界框真实标注来准确解决。然而,存在替代的、潜在的较弱形式的监督,如伴随的自由文本报告,这些报告很容易获得。进行带有文本指导的定位任务通常被称为短语定位。在这项工作中,我们使用一个公开可用的基础模型,即潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Model),来完成这项具有挑战性的任务。我们选择该模型是因为尽管它是生成性的,但它包含交叉注意机制,可以隐式地对齐视觉和文本特征,从而产生适合当前任务的中间表示。此外,我们旨在以零样本的方式进行这项任务,即不对目标任务进行任何训练,这意味着模型的权重保持不变。为此,我们制定了选择特征的策略,并通过后处理对特征进行提炼,无需额外的可学习参数。我们将所提出的方法与最新技术进行了比较,最新技术通过对比学习在联合嵌入空间中明确强制执行图像文本对齐。在流行的胸部X射线基准测试上的结果表明,我们的方法在不同类型病理上的表现与最新技术相当,甚至在两个指标(平均IoU和AUC-ROC)上的平均表现有所超越。源代码将在被接受后发布在https://github.com/vios-s。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures, IEEE J-BHI Special Issue on Foundation Models in Medical Imaging
摘要
基于医学扫描中准确的病理性区域定位是一项重要的医学图像问题。传统方法需要大量的边界框标注来解决这一问题。然而,存在潜在较弱的替代性监督方式,如伴随的自由文本报告。借助文本指导进行定位的任务被称为短语定位。在这项工作中,我们使用公开可用的基础模型——潜在扩散模型来解决这一挑战性问题。我们选择该模型是因为其生成性质中包含跨注意力机制,可以隐含地对齐视觉和文本特征,从而生成适合当前任务的中间表示形式。我们的目标是以零样本的方式进行此任务,即无需对目标任务进行任何训练,这意味着模型的权重保持冻结状态。为此,我们制定了选择特征并对其进行后处理的策略,而无需额外的可学习参数。我们将所提出的方法与最先进的方法进行了比较,后者通过对比学习在联合嵌入空间中明确执行图像文本对齐。在流行的胸部X射线基准测试上的结果表明,我们的方法在多种病理学上的表现与最先进的方法相当,并且在两个指标(平均IoU和AUC-ROC)上的平均表现更胜一筹。代码将在被接受后发布于 https://github.com/vios-s。
关键见解
- 定位医学扫描中的病理性区域是医学图像问题中的核心难点。
- 传统解决方式需要大批量边界框标注数据。
- 存在利用自由文本报告等替代监督方式的可能性。
- 采用短语定位任务借助文本指导进行定位。
- 选用潜在扩散模型作为基础模型,利用其生成性质和跨注意力机制解决此问题。
- 采用零样本方式进行任务执行,模型权重保持冻结状态。
- 通过后处理策略选择和精炼特征,无需额外可学习参数。
点此查看论文截图
Quantifying uncertainty in lung cancer segmentation with foundation models applied to mixed-domain datasets
Authors:Aneesh Rangnekar, Nishant Nadkarni, Jue Jiang, Harini Veeraraghavan
Medical image foundation models have shown the ability to segment organs and tumors with minimal fine-tuning. These models are typically evaluated on task-specific in-distribution (ID) datasets. However, reliable performance on ID datasets does not guarantee robust generalization on out-of-distribution (OOD) datasets. Importantly, once deployed for clinical use, it is impractical to have `ground truth’ delineations to assess ongoing performance drifts, especially when images fall into the OOD category due to different imaging protocols. Hence, we introduced a comprehensive set of computationally fast metrics to evaluate the performance of multiple foundation models (Swin UNETR, SimMIM, iBOT, SMIT) trained with self-supervised learning (SSL). All models were fine-tuned on identical datasets for lung tumor segmentation from computed tomography (CT) scans. The evaluation was performed on two public lung cancer datasets (LRAD: n = 140, 5Rater: n = 21) with different image acquisitions and tumor stages compared to training data (n = 317 public resource with stage III-IV lung cancers) and a public non-cancer dataset containing volumetric CT scans of patients with pulmonary embolism (n = 120). All models produced similarly accurate tumor segmentation on the lung cancer testing datasets. SMIT produced the highest F1-score (LRAD: 0.60, 5Rater: 0.64) and lowest entropy (LRAD: 0.06, 5Rater: 0.12), indicating higher tumor detection rate and confident segmentations. In the OOD dataset, SMIT misdetected the least number of tumors, marked by a median volume occupancy of 5.67 cc compared to the best method SimMIM of 9.97 cc. Our analysis shows that additional metrics such as entropy and volume occupancy may help better understand model performance on mixed domain datasets.
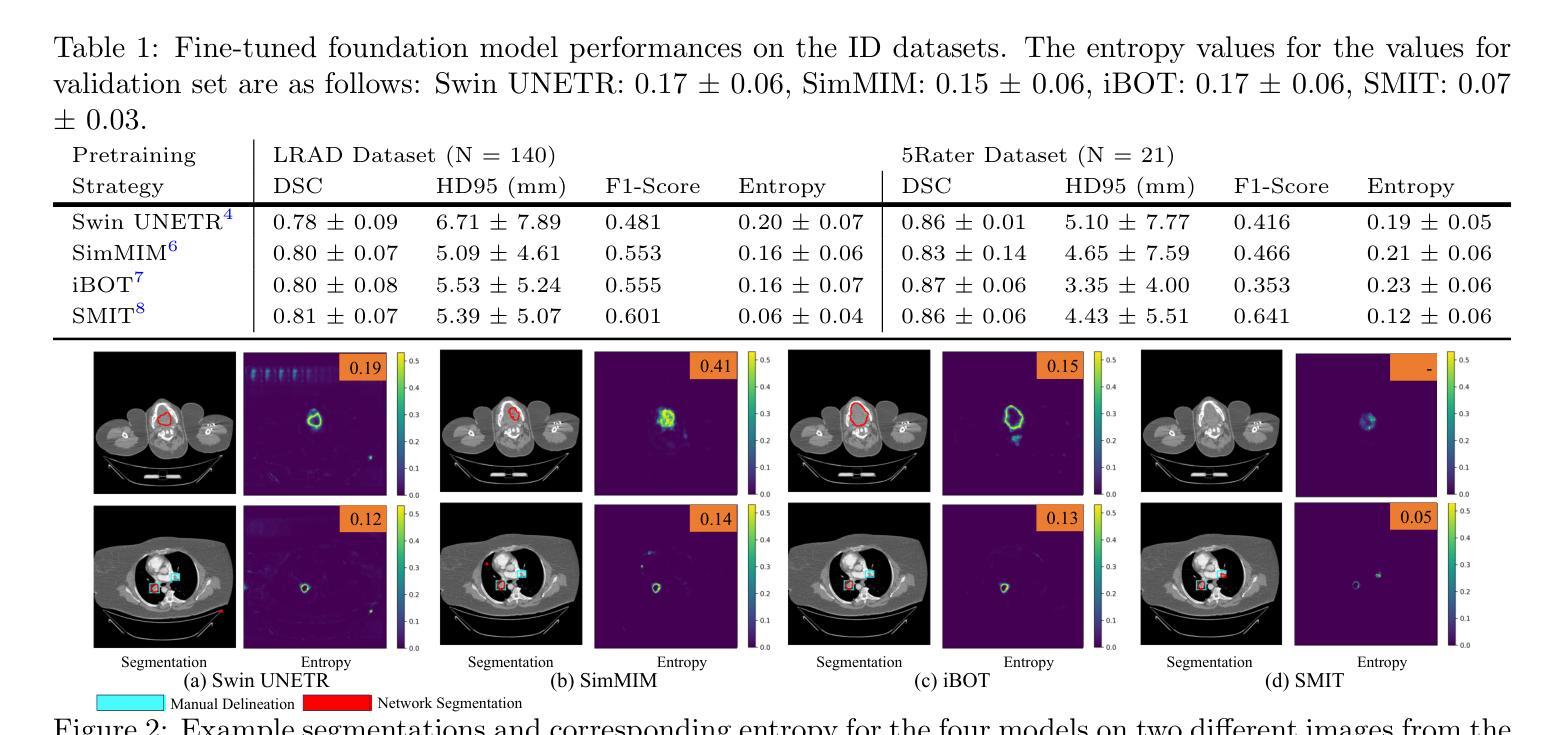
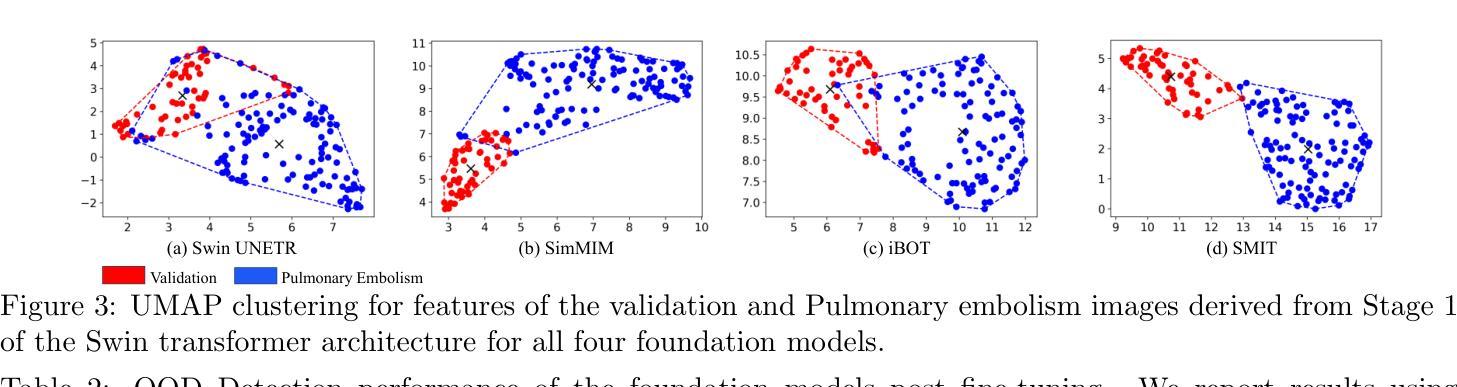
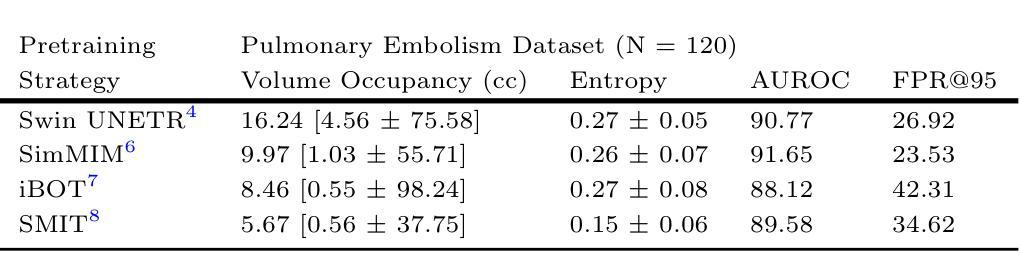
医学图像基础模型在轻微微调的情况下表现出了对器官和肿瘤的分割能力。这些模型通常在特定任务的内部数据集上进行评估。然而,在内部数据集上的可靠性能并不能保证在外部数据集上的稳健泛化能力。重要的是,一旦部署用于临床使用,很难获得“真实值”的轮廓来评估持续的性能漂移,尤其是当图像因不同的成像协议而落入异常值类别时。因此,我们引入了一套计算快速的指标来评估使用自监督学习训练的多基础模型(Swin UNETR、SimMIM、iBOT、SMIT)的性能。所有模型都在相同的肺部肿瘤分割数据集上进行微调,这些数据集来自计算机断层扫描(CT)。评估是在两个公共肺癌数据集(LRAD:n=140,5Rater:n=21)上进行的,这些数据集与训练数据(n=317个公共资源,包含III-IV期肺癌)相比,图像采集和肿瘤阶段有所不同,还有一个包含肺栓塞患者体积CT扫描的公共非癌症数据集(n=120)。所有模型在肺癌测试数据集上的肿瘤分割准确度相似。SMIT产生了最高的F1分数(LRAD:0.60,5Rater:0.64)和最低的熵值(LRAD:0.06,5Rater:0.12),表明其具有较高的肿瘤检测率和可靠的分割效果。在异常值数据集中,SMIT误检的肿瘤数量最少,以体积占有率中位数5.67cc表现最佳,相比之下SimMIM的最佳方法为9.97cc。我们的分析表明,额外的指标如熵和体积占有率可能有助于更好地了解混合域数据集上的模型性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at SPIE Medical Imaging 2025
Summary
医学图像基础模型在轻微精细调整后能够实现对器官和肿瘤的分割。这些模型通常在特定任务内部数据集上进行评估,但其在外部数据集上的泛化能力尚未得到保证。在实际临床应用中,难以获得真实分割来评估模型性能,特别是在图像属于外部数据集时。研究引入了快速计算指标集来评估采用自监督学习训练的基础模型性能。对所有模型在相同的肺部肿瘤分割数据集上进行微调,并在两个不同的公共肺癌数据集上进行评估,结果显示所有模型在肺癌测试数据集上的肿瘤分割准确性相似。SMIT模型在F1得分和熵值上表现最佳,表明其具有较高的肿瘤检测率和置信度分割。在外部数据集中,SMIT的误检肿瘤数量最少。分析表明,额外的指标如熵和体积占有率有助于更好地理解模型在混合域数据集上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像基础模型具备在轻微调整后分割器官和肿瘤的能力。
- 模型通常在特定任务内部数据集上评估,但泛化能力有限。
- 临床应用中评估模型性能面临困难,特别是在面对外部数据集时。
- 引入了一系列快速计算指标来评估自监督学习训练的基础模型性能。
- 所有模型在肺癌测试数据集上的肿瘤分割准确性相似。
- SMIT模型在F1得分和熵值上表现最佳,具有高的肿瘤检测率和置信度分割。
点此查看论文截图