⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-01 更新
Waveform-Specific Performance of Deep Learning-Based Super-Resolution for Ultrasound Contrast Imaging
Authors:Rienk Zorgdrager, Nathan Blanken, Jelmer M. Wolterink, Michel Versluis, Guillaume Lajoinie
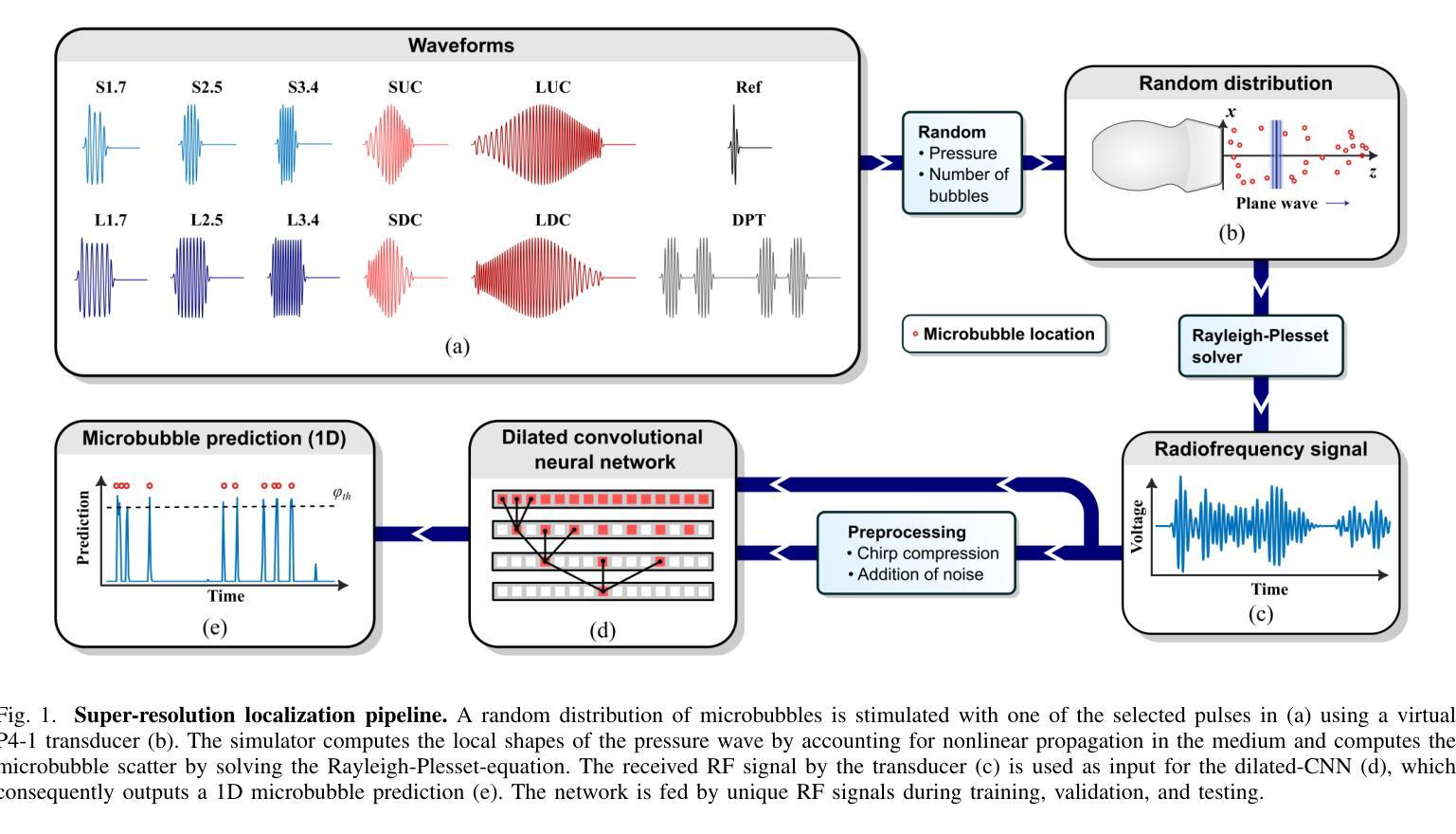
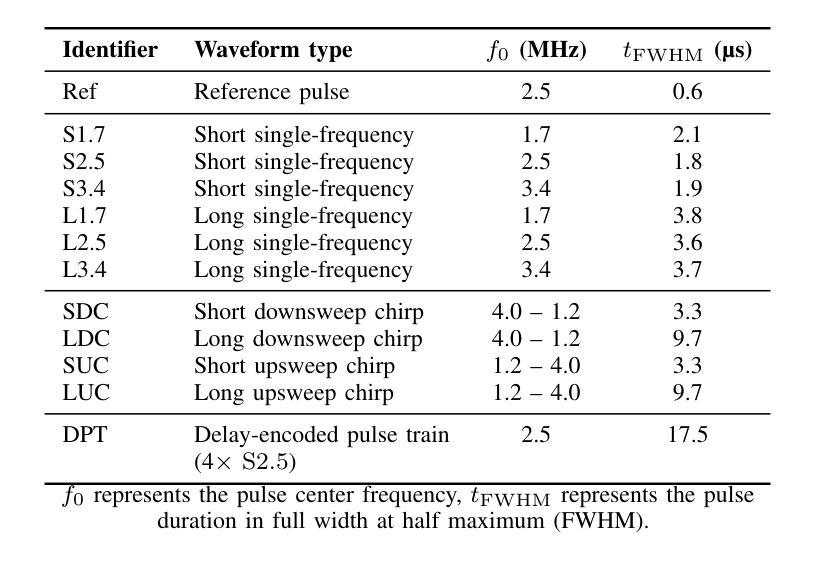
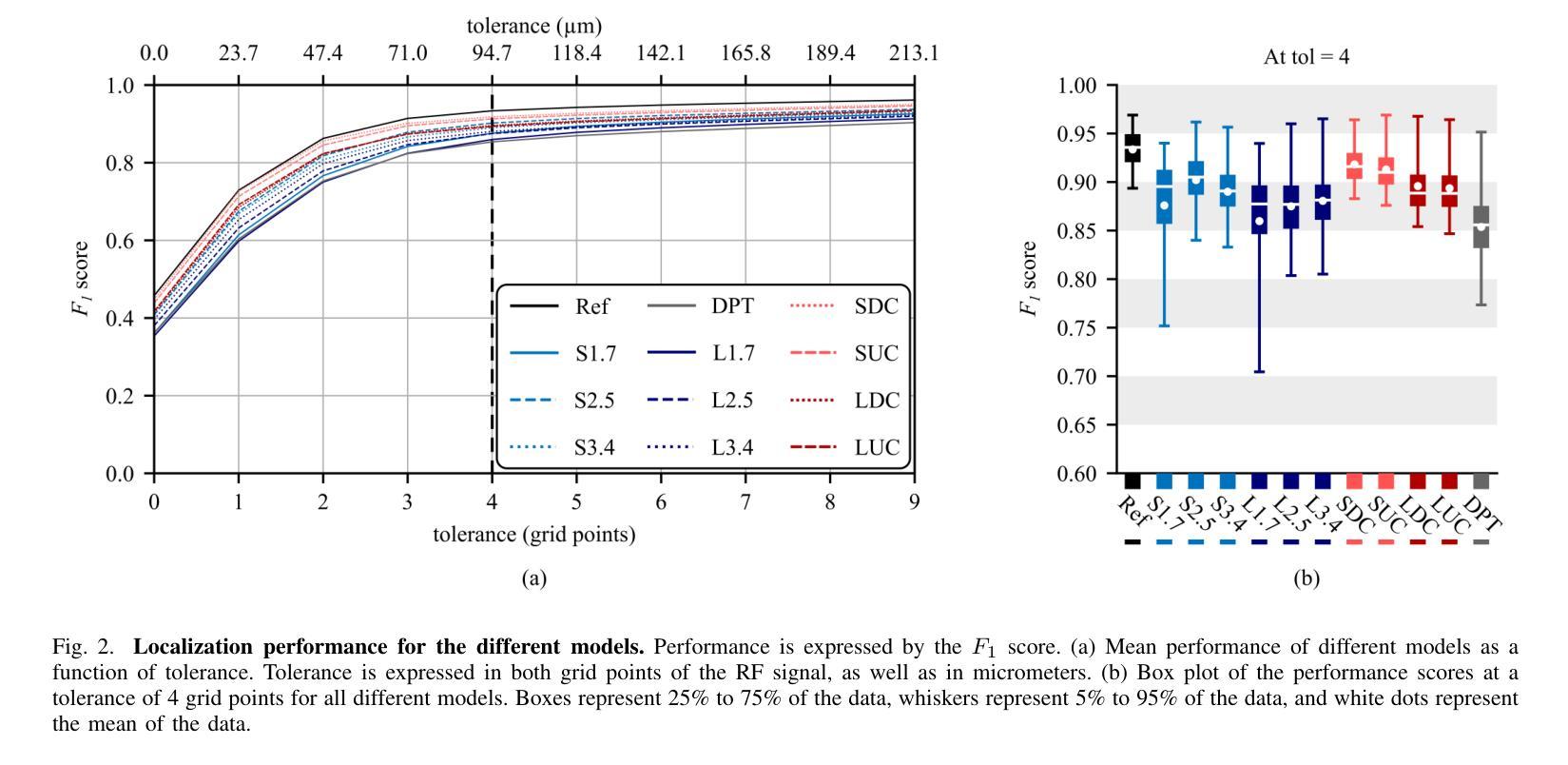
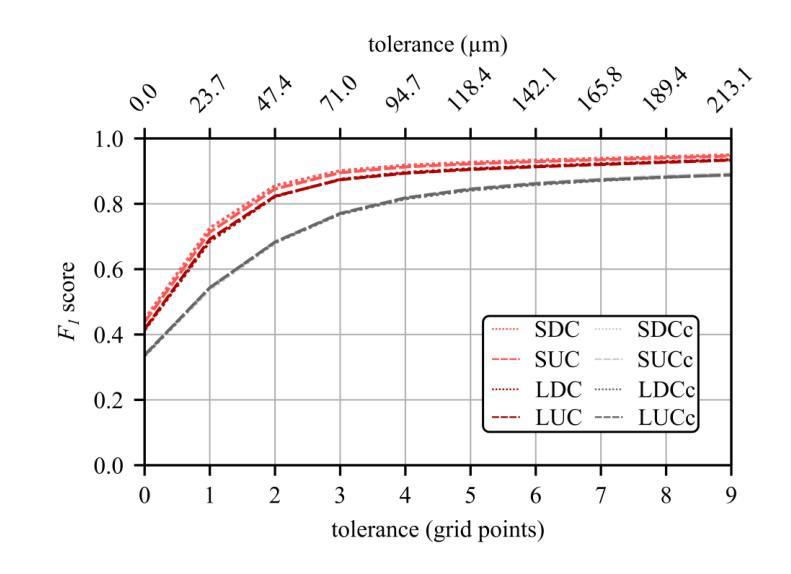
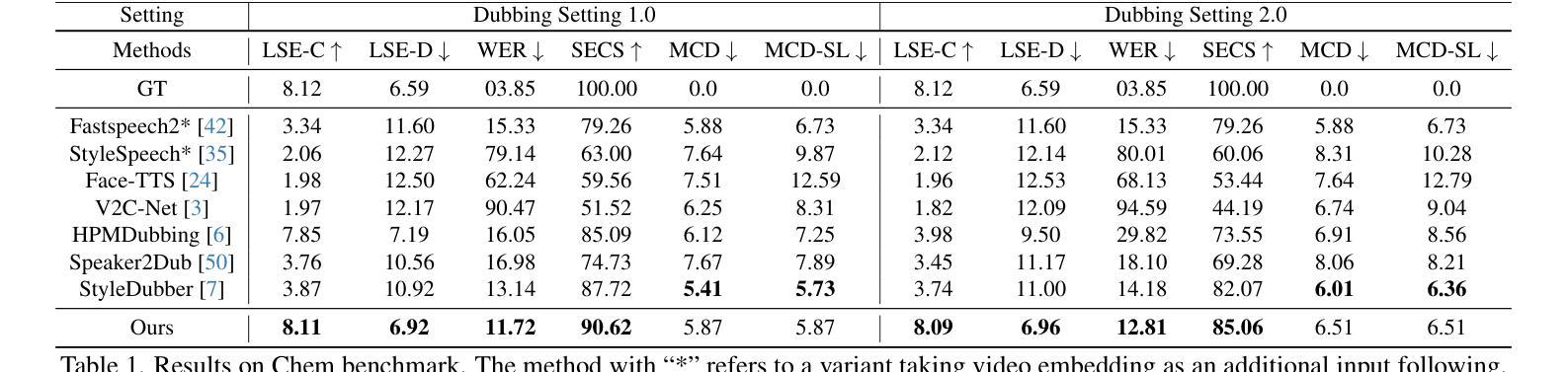
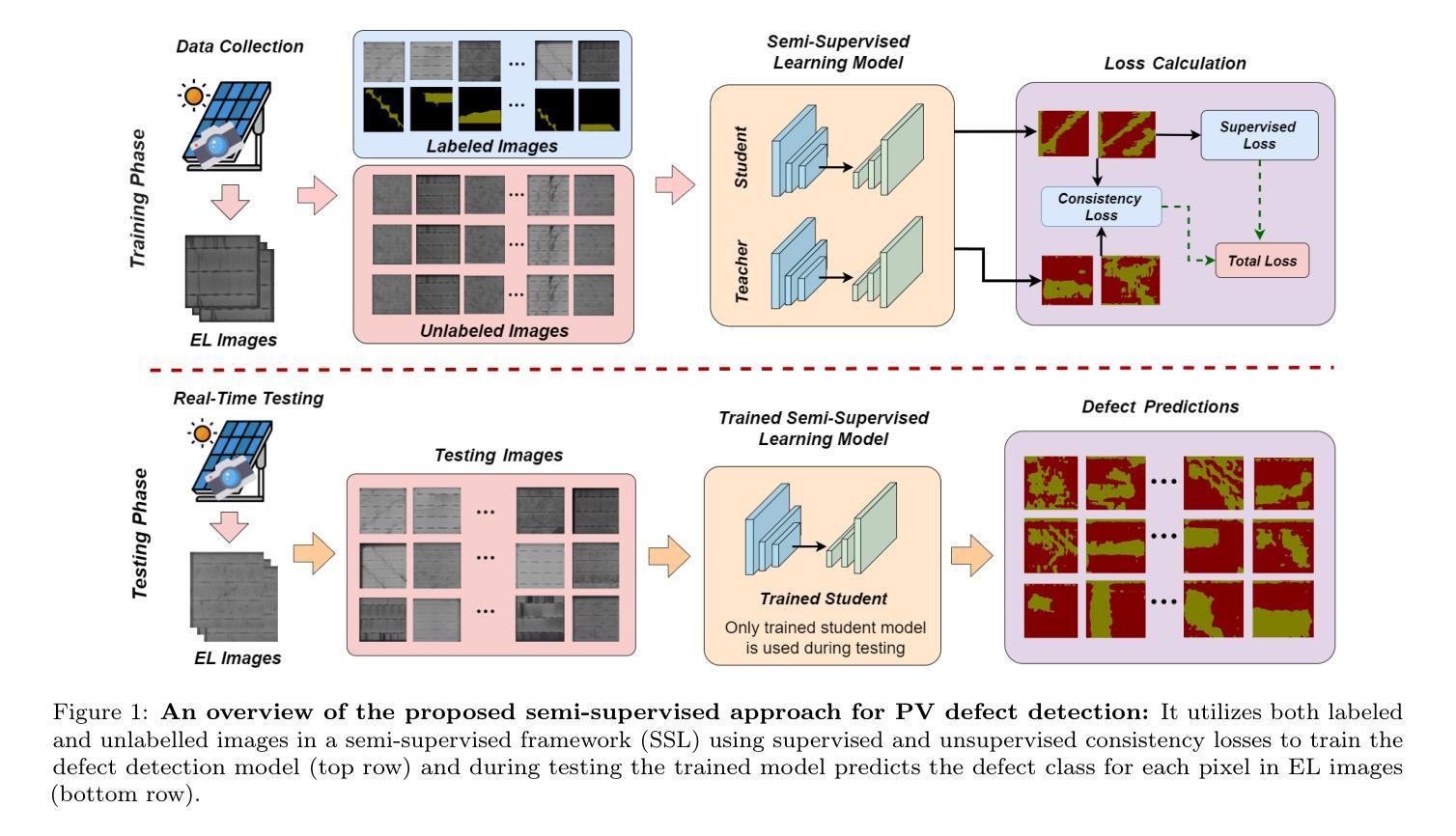
Resolving arterial flows is essential for understanding cardiovascular pathologies, improving diagnosis, and monitoring patient condition. Ultrasound contrast imaging uses microbubbles to enhance the scattering of the blood pool, allowing for real-time visualization of blood flow. Recent developments in vector flow imaging further expand the imaging capabilities of ultrasound by temporally resolving fast arterial flow. The next obstacle to overcome is the lack of spatial resolution. Super-resolved ultrasound images can be obtained by deconvolving radiofrequency (RF) signals before beamforming, breaking the link between resolution and pulse duration. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can be trained to locally estimate the deconvolution kernel and consequently super-localize the microbubbles directly within the RF signal. However, microbubble contrast is highly nonlinear, and the potential of CNNs in microbubble localization has not yet been fully exploited. Assessing deep learning-based deconvolution performance for non-trivial imaging pulses is therefore essential for successful translation to a practical setting, where the signal-to-noise ratio is limited, and transmission schemes should comply with safety guidelines. In this study, we train CNNs to deconvolve RF signals and localize the microbubbles driven by harmonic pulses, chirps, or delay-encoded pulse trains. Furthermore, we discuss potential hurdles for in-vitro and in-vivo super-resolution by presenting preliminary experimental results. We find that, whereas the CNNs can accurately localize microbubbles for all pulses, a short imaging pulse offers the best performance in noise-free conditions. However, chirps offer a comparable performance without noise, but are more robust to noise and outperform all other pulses in low-signal-to-noise ratio conditions.
解决动脉血流问题对于理解心血管病理、提高诊断水平和监测患者状况至关重要。超声对比成像利用微气泡增强血液池的散射,从而实现血流的实时可视化。向量流成像的近期发展通过时间分辨率快速动脉血流,进一步扩展了超声的成像能力。下一个需要克服的障碍是空间分辨率不足。通过在波束形成之前对射频(RF)信号进行反卷积,可以打破分辨率和脉冲持续时间之间的联系,从而获得超级分辨率的超声图像。卷积神经网络(CNN)可以经过训练,局部估计反卷积核,从而直接在RF信号中超级定位微气泡。然而,微气泡对比高度非线性,CNN在微气泡定位方面的潜力尚未得到充分开发。因此,评估基于深度学习的反卷积在非平凡成像脉冲上的表现,对于成功应用于实际环境至关重要,因为在实践环境中信噪比有限,传输方案应符合安全准则。在这项研究中,我们训练CNN对RF信号进行反卷积并定位由谐波脉冲、啁啾或延迟编码脉冲列驱动的微气泡。此外,我们还通过提供初步实验结果,讨论了体外和体内超分辨率的潜在障碍。我们发现,虽然CNN可以准确地对所有脉冲进行微气泡定位,但在无噪声条件下,短成像脉冲表现最佳。然而,啁啾在无噪声条件下表现相当,但对噪声更具鲁棒性,并在低信噪比条件下优于所有其他脉冲。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control
Summary
该文本介绍了超声对比成像中的微气泡对于理解心血管病变、提高诊断水平和监测患者状况的重要性。近期发展的矢量流成像技术提高了超声成像能力,在时间上解析快速动脉血流。然而,仍需克服空间分辨率的问题。通过射频信号去卷积和波束形成前的卷积神经网络训练,可以获得超级分辨率的超声图像,打破分辨率和脉冲持续时间之间的关联。尽管微气泡对比具有高度非线性,但CNN在微气泡定位方面的潜力尚未被完全发掘。本研究训练CNN对射频信号进行去卷积并定位由谐波脉冲、啁啾或延迟编码脉冲序列驱动的微气泡。初步实验结果表明,CNN能在各种脉冲下准确定位微气泡,短成像脉冲在无噪声条件下表现最佳,而啁啾在无噪声条件下表现相当,但在低信噪比条件下更具鲁棒性并表现优于其他所有脉冲。
Key Takeaways
- 超声对比成像利用微气泡增强血液池的散射,以实时可视化血流。
- 矢量流成像提高了超声在时间上解析快速动脉血流的能力。
- 目前面临的挑战是提高空间分辨率。
- 通过射频信号去卷积和卷积神经网络训练,可以获得超级分辨率的超声图像。
- 微气泡对比具有高度非线性,CNN在微气泡定位方面的潜力尚未完全发掘。
- 不同的成像脉冲影响超声成像效果,啁啾脉冲在低信噪比条件下表现较好。
点此查看论文截图