⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-01 更新
DiffusionRenderer: Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Ruofan Liang, Zan Gojcic, Huan Ling, Jacob Munkberg, Jon Hasselgren, Zhi-Hao Lin, Jun Gao, Alexander Keller, Nandita Vijaykumar, Sanja Fidler, Zian Wang
Understanding and modeling lighting effects are fundamental tasks in computer vision and graphics. Classic physically-based rendering (PBR) accurately simulates the light transport, but relies on precise scene representations–explicit 3D geometry, high-quality material properties, and lighting conditions–that are often impractical to obtain in real-world scenarios. Therefore, we introduce DiffusionRenderer, a neural approach that addresses the dual problem of inverse and forward rendering within a holistic framework. Leveraging powerful video diffusion model priors, the inverse rendering model accurately estimates G-buffers from real-world videos, providing an interface for image editing tasks, and training data for the rendering model. Conversely, our rendering model generates photorealistic images from G-buffers without explicit light transport simulation. Experiments demonstrate that DiffusionRenderer effectively approximates inverse and forwards rendering, consistently outperforming the state-of-the-art. Our model enables practical applications from a single video input–including relighting, material editing, and realistic object insertion.
理解和建模光照效果是计算机视觉和图形学中的基本任务。经典的基于物理的渲染(PBR)能准确模拟光传输,但依赖于精确的场景表示——明确的3D几何、高质量的材料属性和光照条件,这些在真实世界场景中往往难以获得。因此,我们引入了DiffusionRenderer,这是一种神经方法,在一个整体框架内解决了逆向和正向渲染的双重问题。利用强大的视频扩散模型先验知识,逆向渲染模型能准确地从真实视频估计G缓冲区,为图像编辑任务提供接口,并为渲染模型提供训练数据。相反,我们的渲染模型能够从G缓冲区生成逼真的图像,而无需显式模拟光传输。实验表明,DiffusionRenderer有效地近似了逆向和正向渲染,并始终优于当前最佳水平。我们的模型能够从单个视频输入中实现实际应用,包括重新照明、材料编辑和逼真的对象插入。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/DiffusionRenderer/
Summary
神经网络渲染器DiffusionRenderer结合了逆向和正向渲染,借助视频扩散模型先验准确估计G缓冲区,从真实视频生成图像编辑任务的接口和渲染模型的训练数据。渲染模型可直接从G缓冲区生成逼真的图像,无需显式模拟光线传输。实验证明,DiffusionRenderer在逆向和正向渲染方面的表现优于现有技术,并能从单一视频输入实现实用应用,如重新照明、材料编辑和真实对象插入。
Key Takeaways
- DiffusionRenderer结合了逆向和正向渲染。
- 利用视频扩散模型准确估计G缓冲区,有助于真实视频的图像编辑任务及渲染模型的训练。
- 无需模拟显式光线传输就能从G缓冲区生成逼真的图像。
- DiffusionRenderer在逆向和正向渲染方面的表现优于现有技术。
- 该模型可从单一视频输入实现实用应用,如重新照明、材料编辑和真实对象插入等。
- 该方法能应对复杂场景的渲染问题,提供更高的灵活性和逼真度。
点此查看论文截图


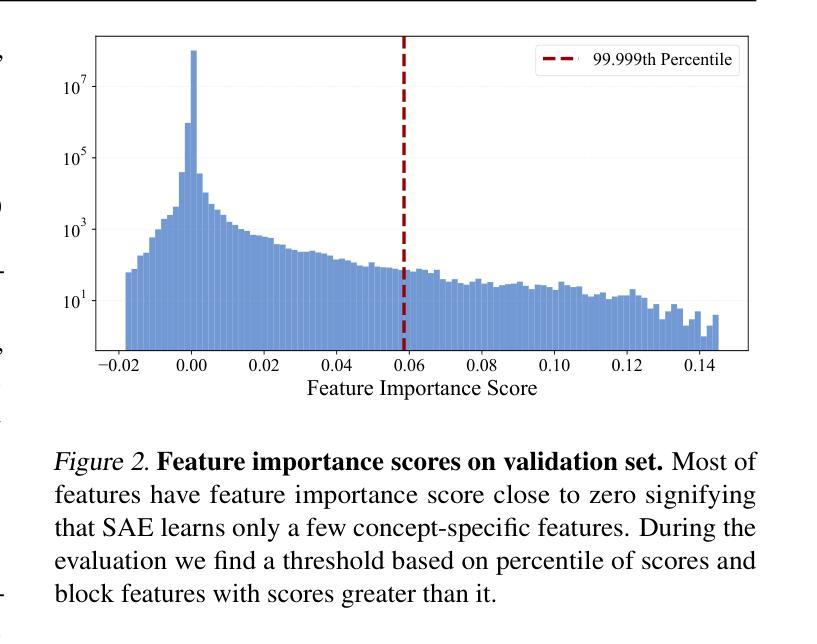
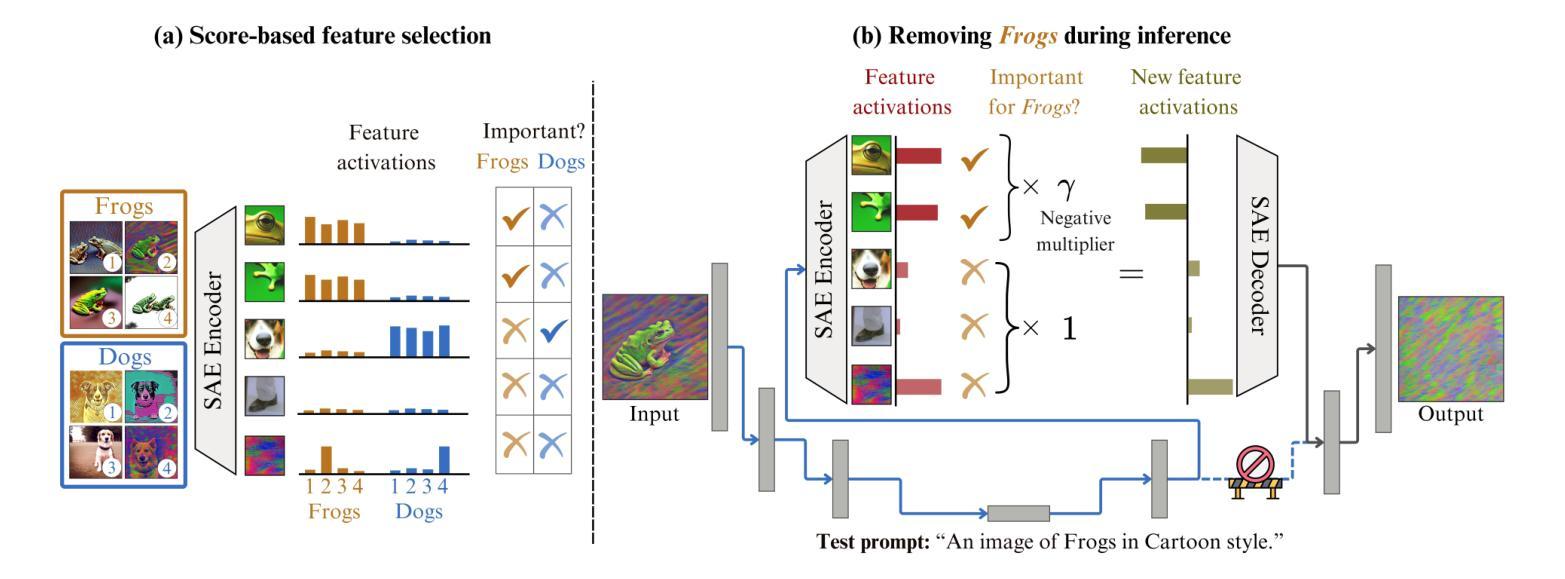
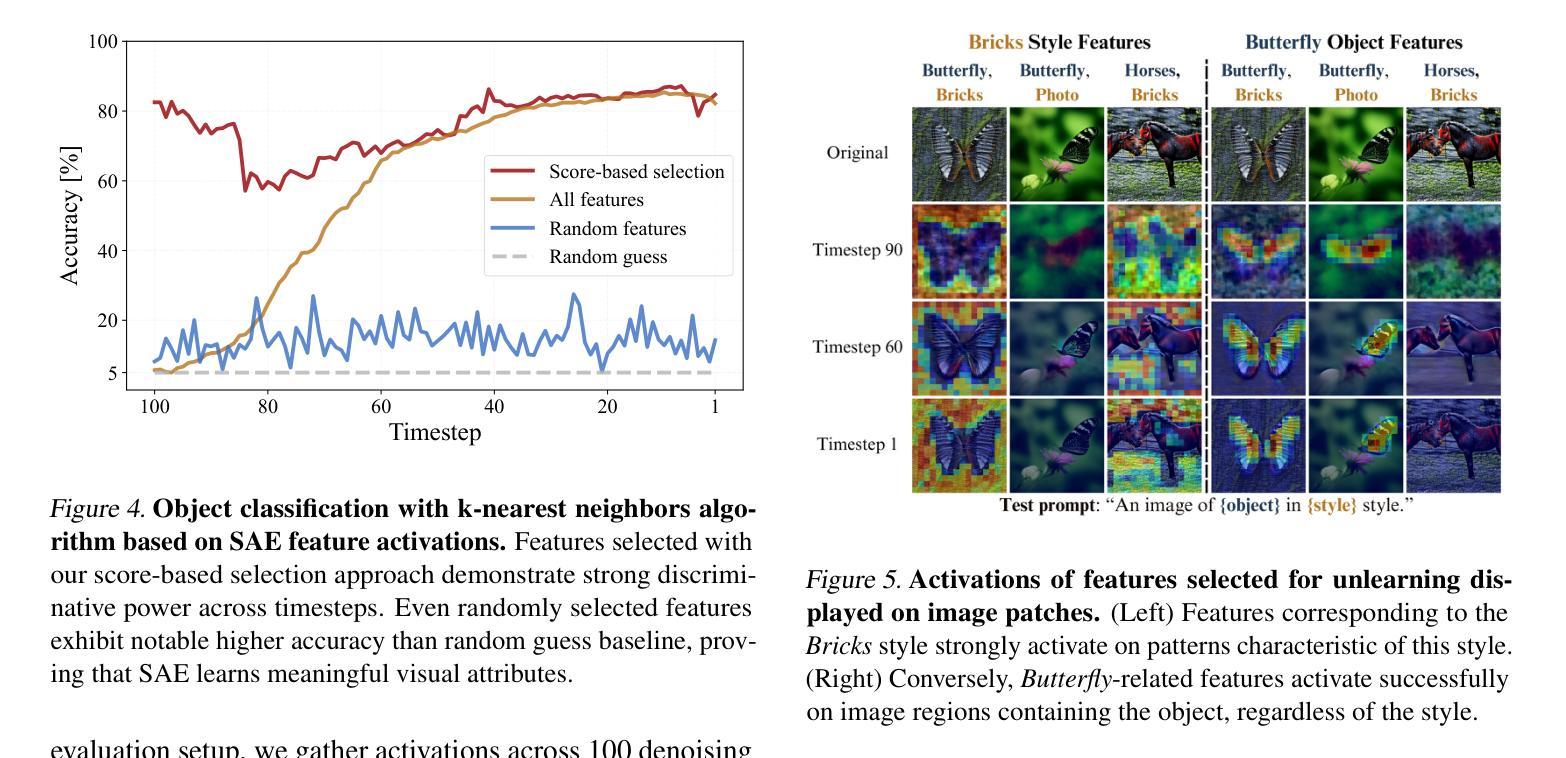
SAeUron: Interpretable Concept Unlearning in Diffusion Models with Sparse Autoencoders
Authors:Bartosz Cywiński, Kamil Deja
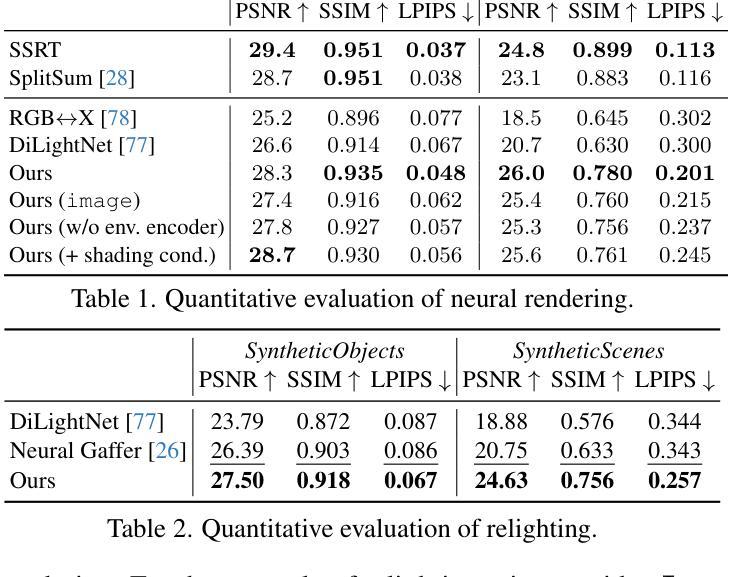
Recent machine unlearning approaches offer promising solution for removing unwanted concepts from diffusion models. However, traditional methods, which largely rely on fine-tuning, provide little insight into the changes they introduce to the base model, making it unclear whether concepts are truly removed or only masked. In this work, we introduce SAeUron, a novel method leveraging features learned by sparse autoencoders (SAEs) to unlearn unwanted concepts in text-to-image diffusion models. First, we demonstrate that SAEs, trained in an unsupervised manner on activations from multiple denoising timesteps of the diffusion model, capture sparse and interpretable features corresponding to specific concepts. Building on this, we propose a method of selecting concept-specific features. This enables precise interventions on the model’s activations to block targeted content while preserving the model’s overall performance. Evaluation on the competitive UnlearnCanvas benchmark on object and style unlearning highlights SAeUron’s state-of-the-art performance. Moreover, we show that with a single SAE, we can remove multiple concepts simultaneously and that in contrast to other methods, SAeUron dismisses the possibility of generating unwanted content, even under adversarial attack.
最近,机器学习去学习的技术为从扩散模型中移除不需要的概念提供了很有前景的解决方案。然而,传统的方法大多依赖于微调,对于它们给基础模型带来的改变并没有提供太多见解,因此不清楚概念是否真的被移除,还只是被掩盖了。在这项工作中,我们引入了SAeUron,这是一种利用稀疏自编码器(SAE)学习到的特征来去除文本到图像扩散模型中不需要的概念的新方法。首先,我们证明在扩散模型的多个去噪时间步长的激活上接受无监督训练的SAE能够捕获对应特定概念的特征,这些特征稀疏且可解释性强。在此基础上,我们提出了一种选择特定概念特征的方法。这能够对模型的激活进行精确干预,以阻止目标内容,同时保持模型的总体性能。在竞争性的UnlearnCanvas基准测试上进行的对象与风格去学习的评估凸显了SAeUron的卓越性能。此外,我们展示了使用一个单一的SAE可以同时移除多个概念,并且与其他方法相比,SAeUron消除了生成不需要内容的可能性,即使在对抗攻击下也是如此。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的方法SAeUron,利用稀疏自编码器(SAE)的特性,从文本到图像的扩散模型中去除不需要的概念。该方法能够在不干扰模型整体性能的情况下,精确干预模型的激活,以阻止特定内容的生成。在UnlearnCanvas基准测试上的表现突出,可以同时去除多个概念,且不会生成不需要的内容,具有领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- SAeUron是一种利用稀疏自编码器(SAE)去除扩散模型中不需要概念的新方法。
- SAE在多个去噪时间步长的扩散模型激活上进行无监督训练,能够捕获对应特定概念的特征。
- SAeUron可以精确干预模型的激活,以去除特定内容,同时保持模型的总体性能。
- 在UnlearnCanvas基准测试上,SAeUron表现出卓越的性能,可同时进行对象和风格的去除。
- SAeUron可以同时去除多个概念。
- 与其他方法相比,SAeUron在生成内容方面具有更高的可控性,不会生成不需要的内容。
点此查看论文截图
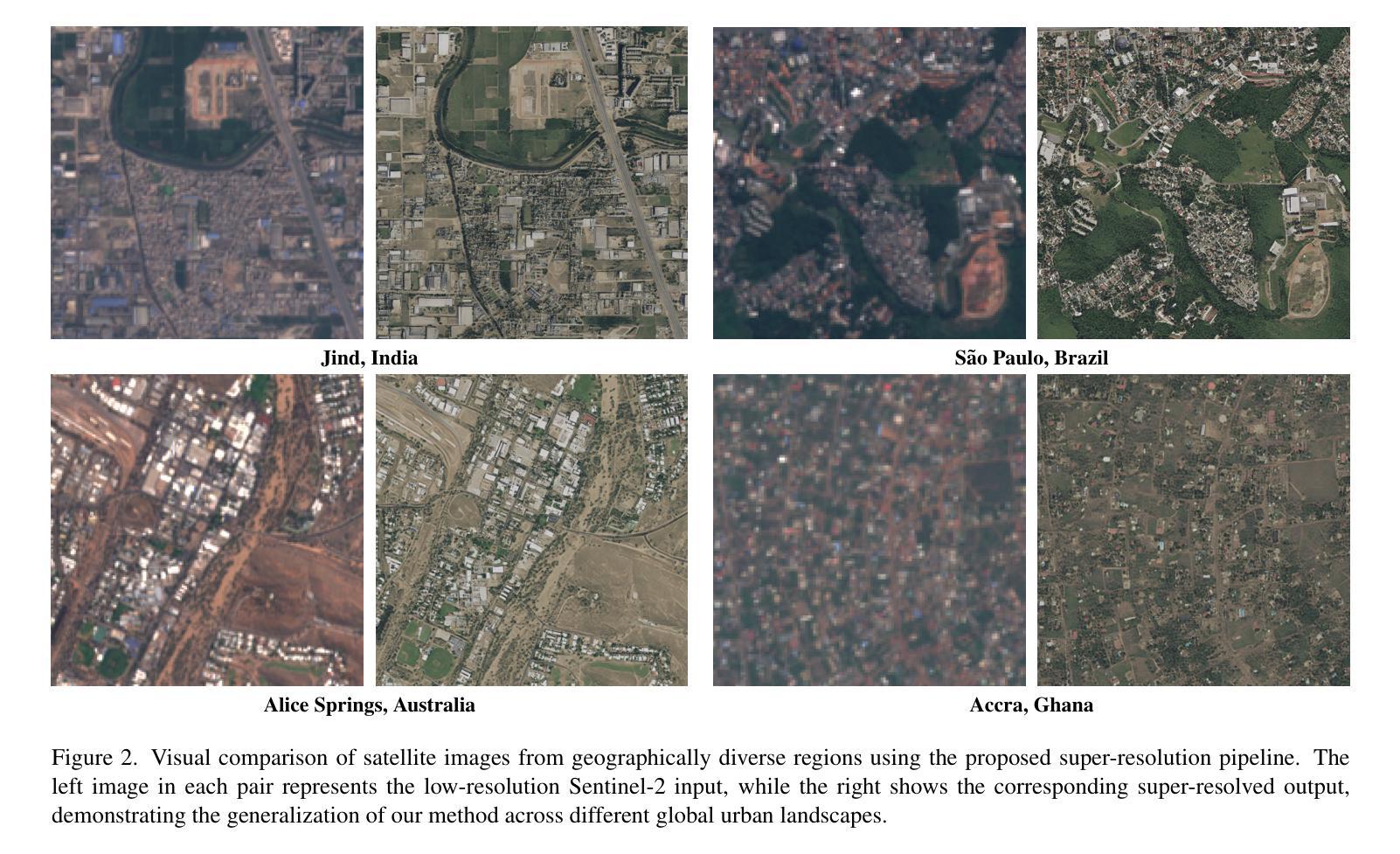
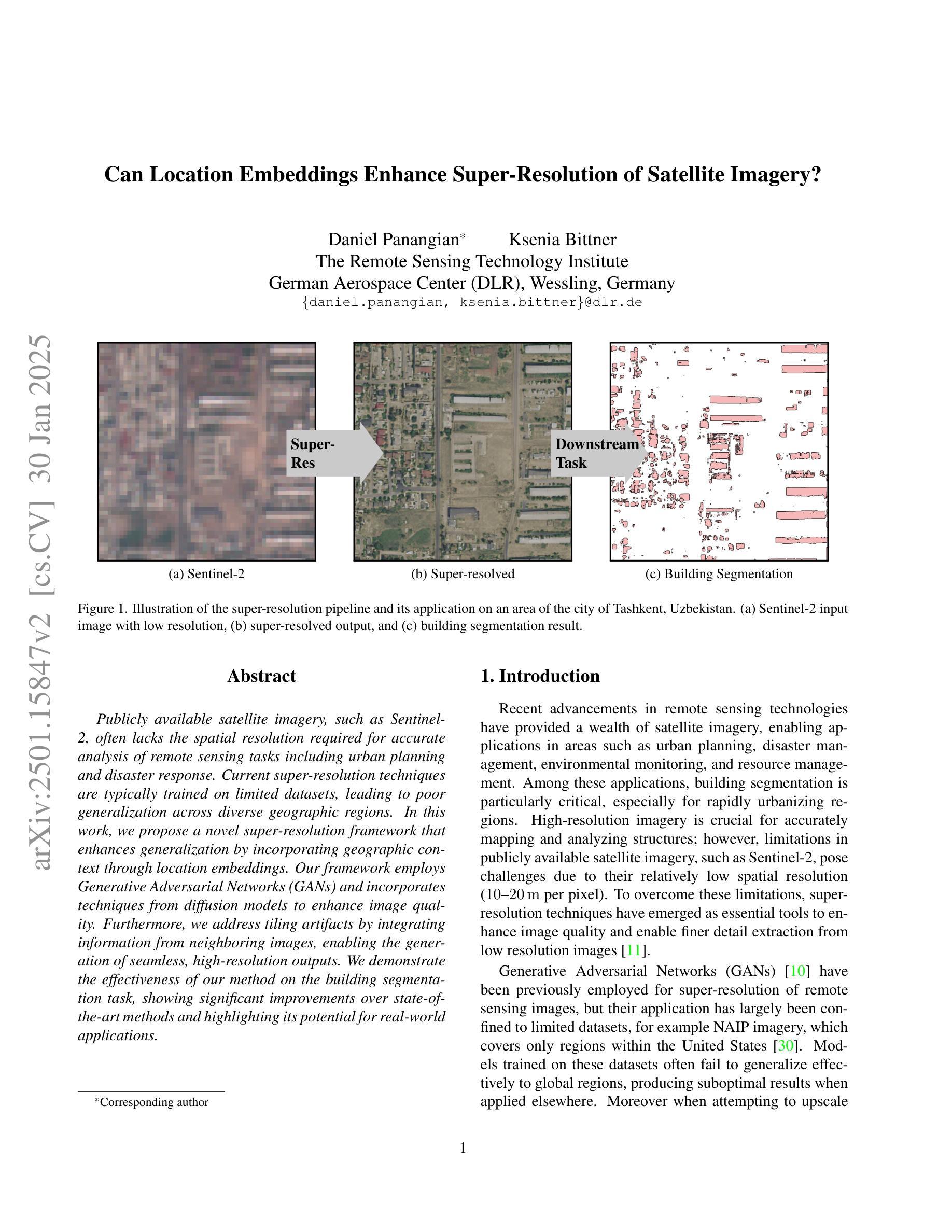
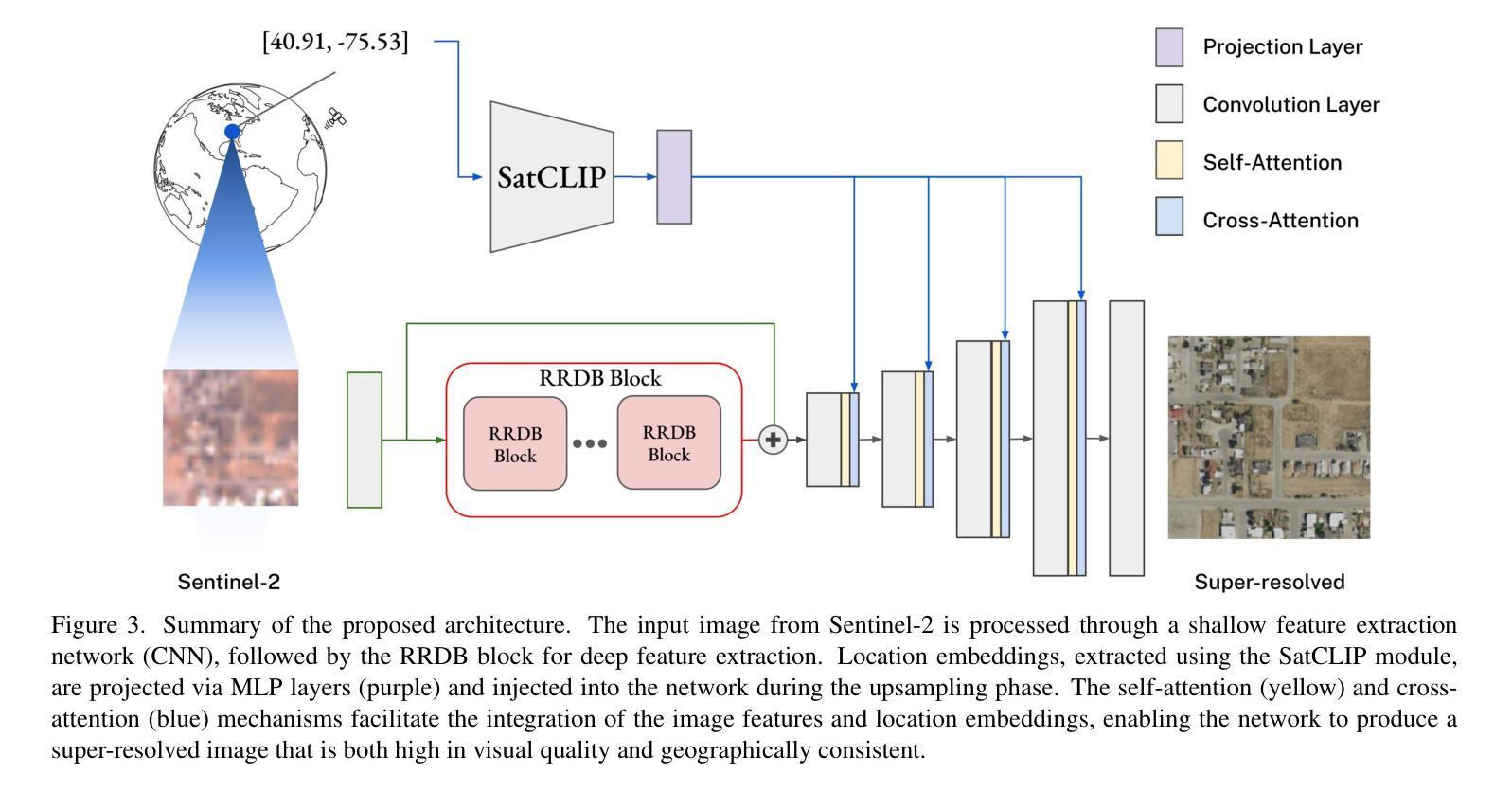
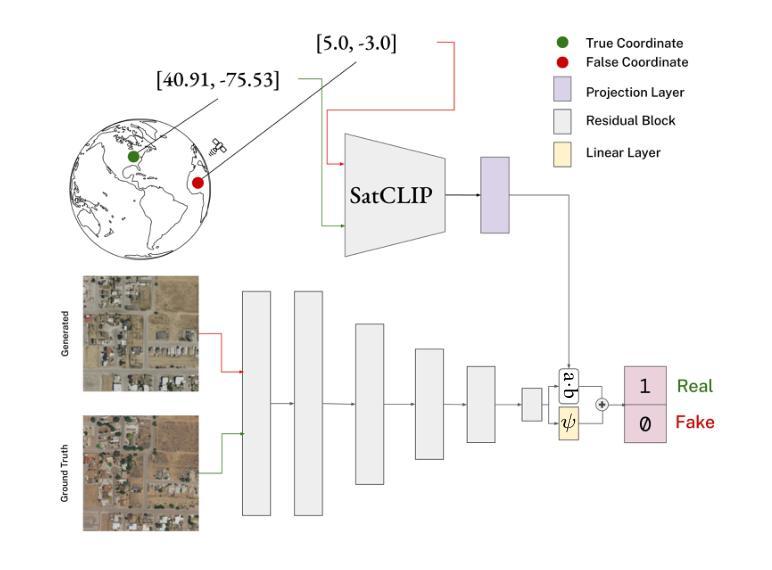
Can Location Embeddings Enhance Super-Resolution of Satellite Imagery?
Authors:Daniel Panangian, Ksenia Bittner
Publicly available satellite imagery, such as Sentinel- 2, often lacks the spatial resolution required for accurate analysis of remote sensing tasks including urban planning and disaster response. Current super-resolution techniques are typically trained on limited datasets, leading to poor generalization across diverse geographic regions. In this work, we propose a novel super-resolution framework that enhances generalization by incorporating geographic context through location embeddings. Our framework employs Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and incorporates techniques from diffusion models to enhance image quality. Furthermore, we address tiling artifacts by integrating information from neighboring images, enabling the generation of seamless, high-resolution outputs. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on the building segmentation task, showing significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods and highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
公开可用的卫星图像,如Sentinel-2,通常缺乏用于准确分析城市规划、灾害应对等遥感任务所需的空间分辨率。当前的超分辨率技术通常只在有限的数据集上进行训练,导致其在不同地理区域的泛化能力较差。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型超分辨率框架,它通过引入地理位置嵌入技术来提高地理上下文方面的泛化能力。我们的框架采用生成对抗网络(GANs),并结合扩散模型的技巧来提高图像质量。此外,我们还通过整合邻近图像的信息来解决拼贴痕迹问题,从而生成无缝、高分辨率的输出。我们在建筑分割任务上展示了该方法的有效性,相较于最先进的方法有明显的改进,并突出了其在现实世界应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)
Summary
本文提出一种新型的超分辨率框架,该框架结合地理上下文通过位置嵌入增强泛化能力。它采用生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型技术提高图像质量,并解决平铺伪影问题,通过整合邻近图像的信息来生成无缝、高分辨率的输出。在建筑物分割任务上,该方法效果显著,相较于现有方法有明显改进,并展现出在真实世界应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 公开卫星图像如Sentinel-2的空间分辨率通常不足以进行远程感应任务。
- 当前超分辨率技术通常在有限数据集上训练,导致在不同地理区域的泛化能力较差。
- 提出的新型超分辨率框架通过融入地理上下文和位置嵌入增强泛化能力。
- 框架采用生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型技术提高图像质量。
- 框架解决了由于图像分割产生的平铺伪影问题,通过整合邻近图像信息生成无缝高分辨率输出。
- 该方法在建筑物分割任务上表现出优异效果。
点此查看论文截图

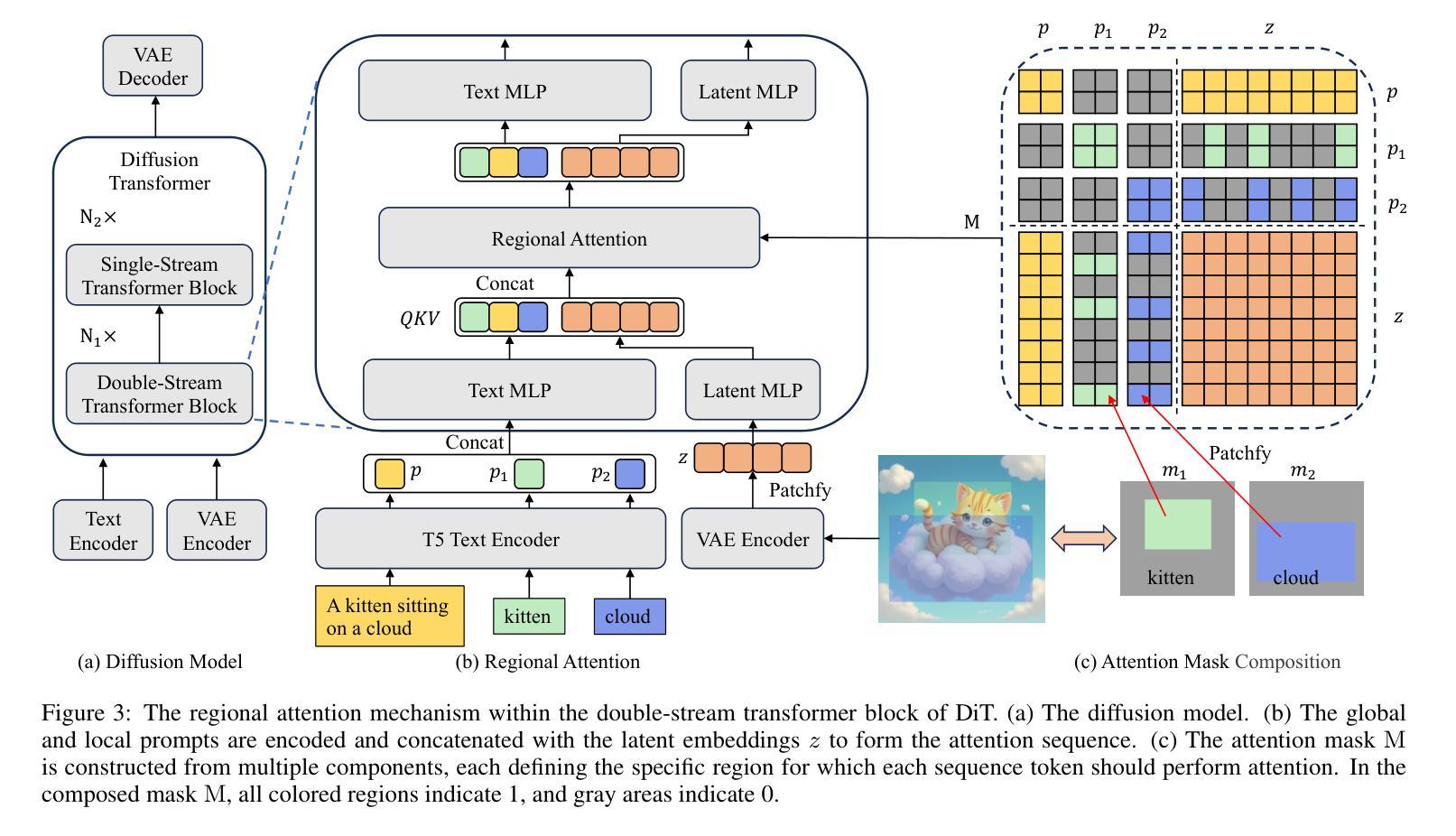
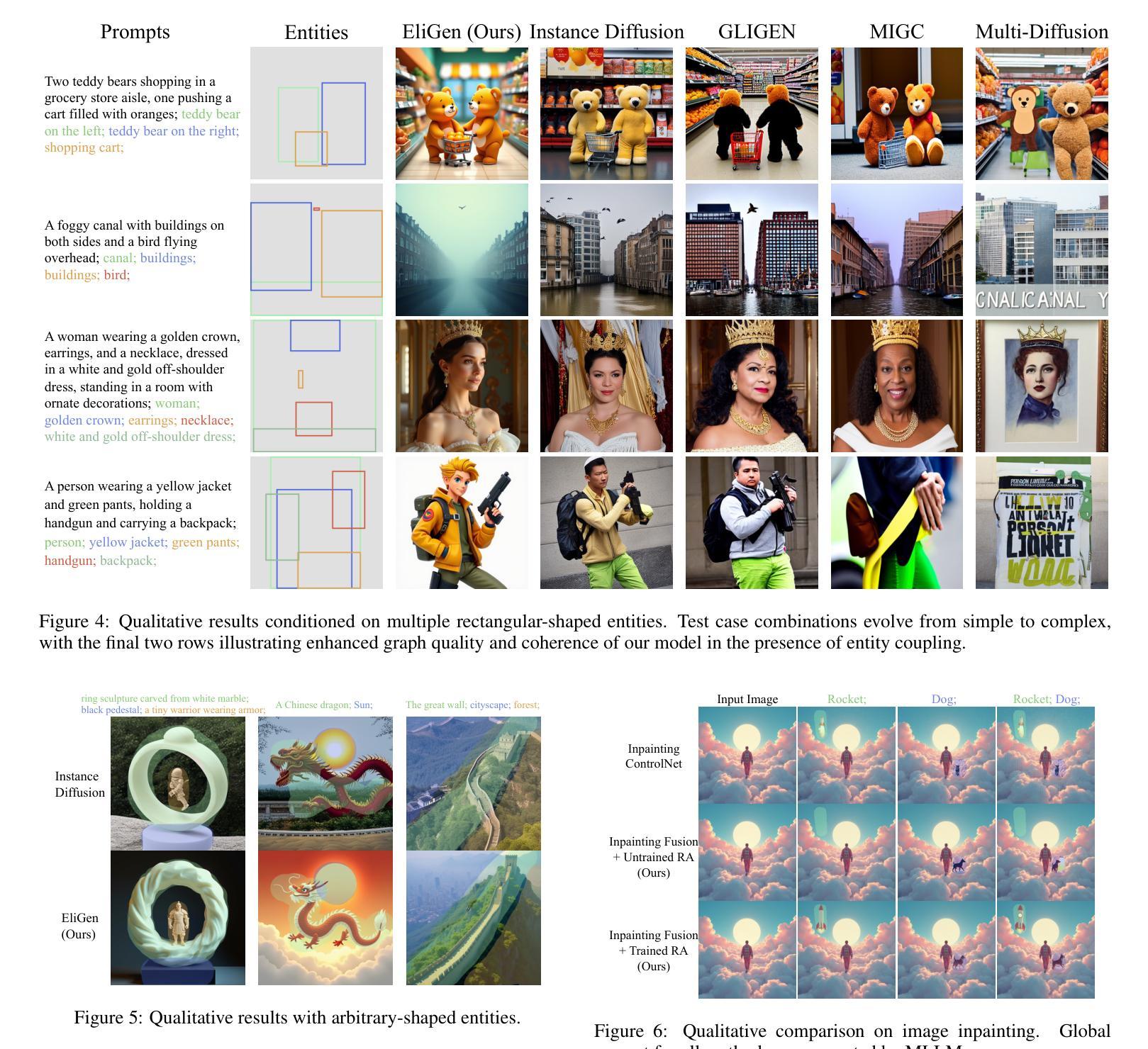
EliGen: Entity-Level Controlled Image Generation with Regional Attention
Authors:Hong Zhang, Zhongjie Duan, Xingjun Wang, Yingda Chen, Yu Zhang
Recent advancements in diffusion models have significantly advanced text-to-image generation, yet global text prompts alone remain insufficient for achieving fine-grained control over individual entities within an image. To address this limitation, we present EliGen, a novel framework for Entity-level controlled image Generation. Firstly, we put forward regional attention, a mechanism for diffusion transformers that requires no additional parameters, seamlessly integrating entity prompts and arbitrary-shaped spatial masks. By contributing a high-quality dataset with fine-grained spatial and semantic entity-level annotations, we train EliGen to achieve robust and accurate entity-level manipulation, surpassing existing methods in both spatial precision and image quality. Additionally, we propose an inpainting fusion pipeline, extending its capabilities to multi-entity image inpainting tasks. We further demonstrate its flexibility by integrating it with other open-source models such as IP-Adapter, In-Context LoRA and MLLM, unlocking new creative possibilities. The source code, model, and dataset are published at https://github.com/modelscope/DiffSynth-Studio.git.
最近扩散模型方面的进展极大地推动了文本到图像的生成,然而,仅使用全局文本提示仍不足以实现对图像内单个实体的精细控制。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了EliGen,这是一个用于实体级别控制图像生成的新型框架。首先,我们提出了区域注意力机制,这是一种无需额外参数的扩散变压器机制,无缝集成了实体提示和任意形状的空间掩码。通过提供一个具有精细空间语义和实体级注释的高质量数据集,我们训练EliGen实现稳健准确的实体级操作,在空间和图像质量方面都超越了现有方法。此外,我们提出了一种补全融合管道,将其能力扩展到多实体图像补全任务。我们通过将其与其他开源模型(如IP-Adapter、In-Context LoRA和MLLM)集成,进一步展示了其灵活性,解锁了新的创意可能性。源代码、模型和数据集已发布在https://github.com/modelscope/DiffSynth-Studio.git。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期扩散模型的新进展极大地推动了文本到图像的生成能力,然而,仅依赖全局文本提示无法实现图像内个体实体的精细控制。为解决这一局限,我们提出了EliGen框架,实现实体级别的图像生成控制。通过引入无需额外参数的区域注意力机制,扩散变压器能够无缝集成实体提示和任意形状的空间掩码。我们使用精细的空间和语义实体级注释的高质量数据集训练EliGen,实现在实体级别的稳健和精确操控,在空间精度和图像质量上超越现有方法。此外,我们提出了扩展其能力的补全融合管道,用于多实体图像补全任务。通过与其他开源模型(如IP-Adapter、In-Context LoRA和MLLM)的集成,展示了其灵活性,开启了新的创意可能性。相关源码、模型和数据集已发布在https://github.com/modelscope/DiffSynth-Studio.git。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的最新进展已显著改善文本到图像的生成能力。
- 现有方法依赖于全局文本提示,无法实现图像内个体实体的精细控制。
- 提出了EliGen框架,通过区域注意力机制实现实体级别的图像生成控制。
- 无需额外参数,扩散变压器能无缝集成实体提示和空间掩码。
- 使用高质量数据集进行训练,实现稳健和精确的实体级别操控。
- 在空间精度和图像质量上超越现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


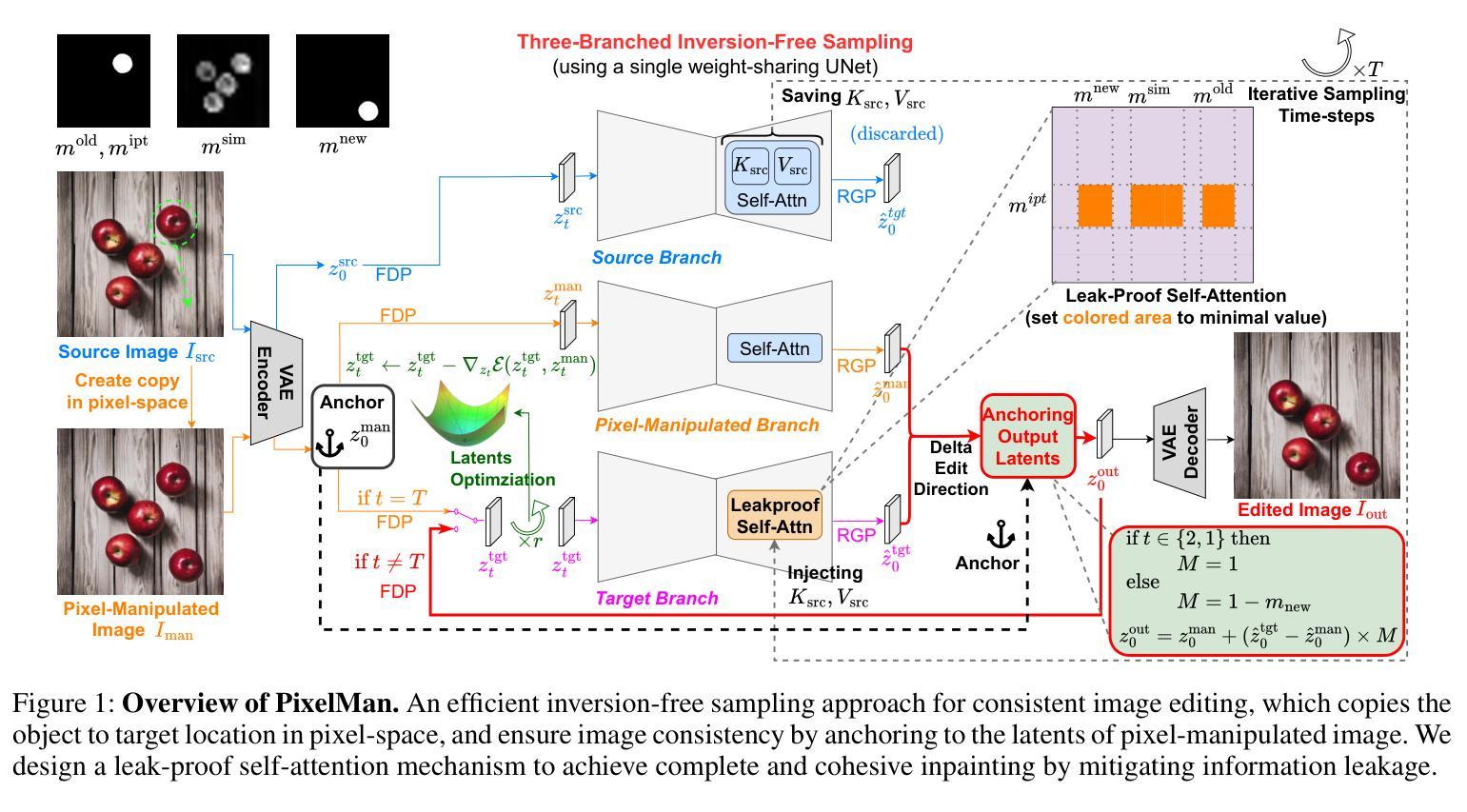
PixelMan: Consistent Object Editing with Diffusion Models via Pixel Manipulation and Generation
Authors:Liyao Jiang, Negar Hassanpour, Mohammad Salameh, Mohammadreza Samadi, Jiao He, Fengyu Sun, Di Niu
Recent research explores the potential of Diffusion Models (DMs) for consistent object editing, which aims to modify object position, size, and composition, etc., while preserving the consistency of objects and background without changing their texture and attributes. Current inference-time methods often rely on DDIM inversion, which inherently compromises efficiency and the achievable consistency of edited images. Recent methods also utilize energy guidance which iteratively updates the predicted noise and can drive the latents away from the original image, resulting in distortions. In this paper, we propose PixelMan, an inversion-free and training-free method for achieving consistent object editing via Pixel Manipulation and generation, where we directly create a duplicate copy of the source object at target location in the pixel space, and introduce an efficient sampling approach to iteratively harmonize the manipulated object into the target location and inpaint its original location, while ensuring image consistency by anchoring the edited image to be generated to the pixel-manipulated image as well as by introducing various consistency-preserving optimization techniques during inference. Experimental evaluations based on benchmark datasets as well as extensive visual comparisons show that in as few as 16 inference steps, PixelMan outperforms a range of state-of-the-art training-based and training-free methods (usually requiring 50 steps) on multiple consistent object editing tasks.
近期研究探讨了Diffusion Models(DMs)在对象一致性编辑方面的潜力。对象一致性编辑旨在修改对象的位置、大小、组成等,同时保持对象的连贯性和背景一致性,而不改变其纹理和属性。当前推理时间的方法通常依赖于DDIM反演,这固有的牺牲了效率和编辑图像的可实现一致性。近期的方法还使用能量引导,通过迭代更新预测噪声并可能驱动潜在空间远离原始图像,从而导致失真。在本文中,我们提出了PixelMan,这是一种无需反演和训练的方法,通过像素操作和生成实现对象的一致性编辑。我们直接在像素空间中创建源对象的目标位置副本,并引入高效的采样方法来迭代将操作对象和谐地融合到目标位置并对其原始位置进行填充,同时通过锚定生成的编辑图像到像素操作图像以及引入各种一致性保持优化技术在推理过程中确保图像的一致性。基于基准数据集的实验评估以及广泛的视觉比较表明,在仅16步推理的情况下,PixelMan在多个对象一致性编辑任务上的表现优于一系列最先进的基于训练和免训练的方法(通常需要50步推理)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025; version includes supplementary material; 27 Pages, 15 Figures, 6 Tables
Summary
本文研究了Diffusion Models在物体编辑方面的潜力,提出了一种名为PixelMan的方法,该方法无需反演和训练,即可通过像素操作和生成实现一致的物体编辑。它通过直接在目标位置创建源物体的副本,并采用高效的采样方法来迭代地将操作物体和谐地融入目标位置,同时保证图像的一致性。实验评估显示,PixelMan在少数推理步骤中就能优于一系列最先进的基于训练和非训练的方法。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Models (DMs) 在物体编辑方面具有潜力,能够修改物体位置、大小、组成等,同时保持物体和背景的连贯性。
- 当前的方法常常依赖DDIM反演,这影响了效率和图像的一致性。
- 现有方法使用能量引导,但可能导致预测噪声的更新和潜在偏离原始图像,造成失真。
- PixelMan方法通过像素操作和生成实现一致的物体编辑,无需反演和训练。
- PixelMan通过在目标位置创建源物体的副本,并迭代地将操作物体融入目标位置。
- PixelMan采用高效的采样方法来修复和和谐物体在原位置的形象,同时确保图像的一致性。
点此查看论文截图



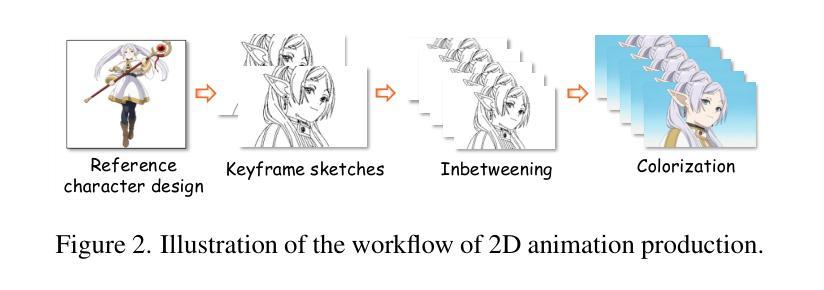
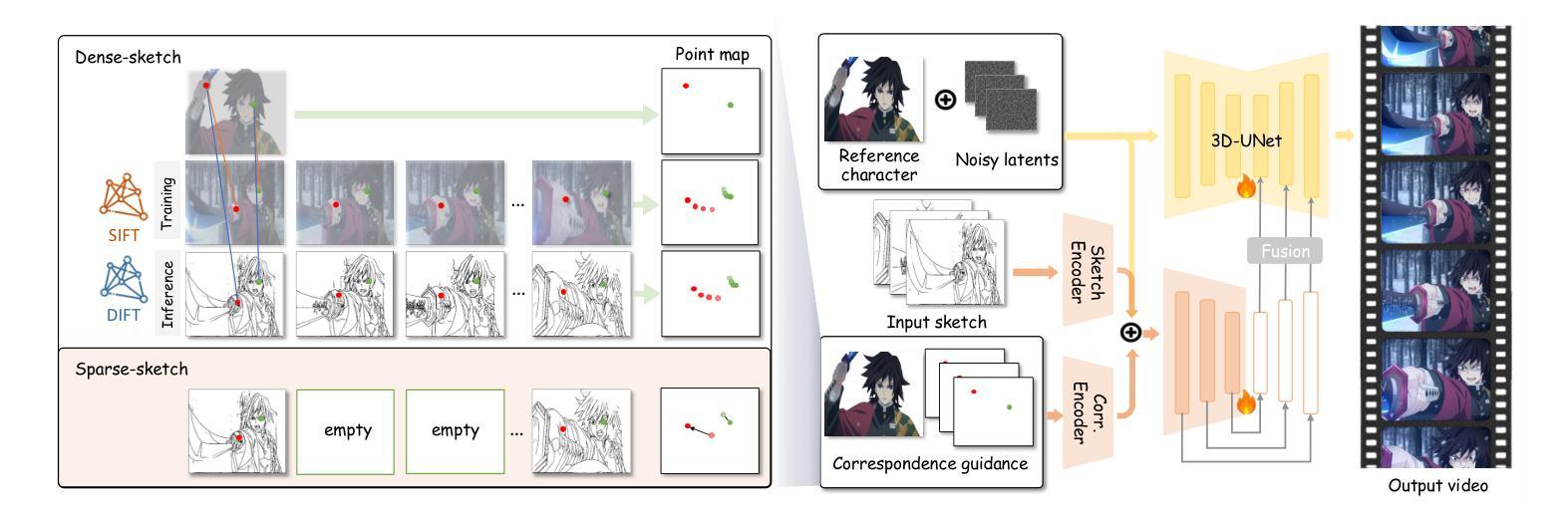
AniDoc: Animation Creation Made Easier
Authors:Yihao Meng, Hao Ouyang, Hanlin Wang, Qiuyu Wang, Wen Wang, Ka Leong Cheng, Zhiheng Liu, Yujun Shen, Huamin Qu
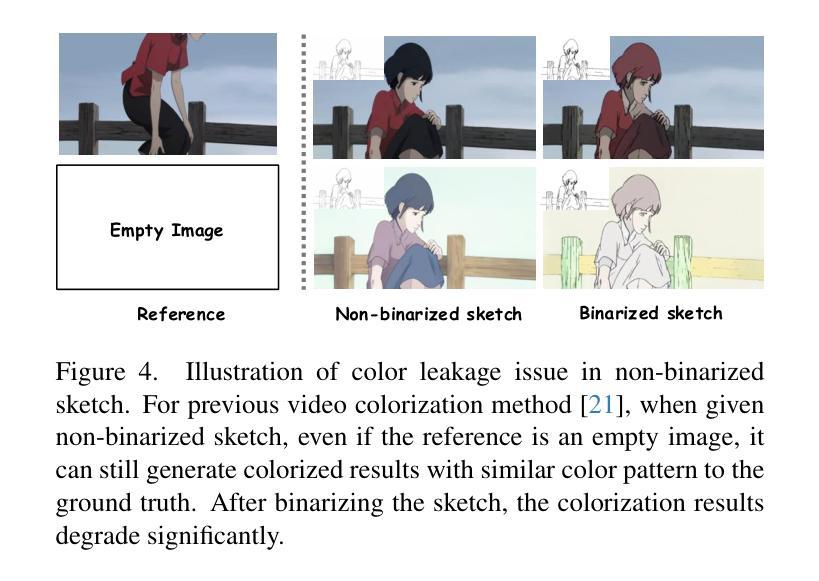
The production of 2D animation follows an industry-standard workflow, encompassing four essential stages: character design, keyframe animation, in-betweening, and coloring. Our research focuses on reducing the labor costs in the above process by harnessing the potential of increasingly powerful generative AI. Using video diffusion models as the foundation, AniDoc emerges as a video line art colorization tool, which automatically converts sketch sequences into colored animations following the reference character specification. Our model exploits correspondence matching as an explicit guidance, yielding strong robustness to the variations (e.g., posture) between the reference character and each line art frame. In addition, our model could even automate the in-betweening process, such that users can easily create a temporally consistent animation by simply providing a character image as well as the start and end sketches. Our code is available at: https://yihao-meng.github.io/AniDoc_demo.
二维动画的制作遵循行业标准的工作流程,包括四个基本阶段:角色设计、关键帧动画、中间帧生成和上色。我们的研究致力于通过利用日益强大的生成式人工智能的潜力来降低上述过程中的劳动力成本。以视频扩散模型为基础,AniDoc作为一种视频线艺术上色工具应运而生,它会自动将草图序列转换为彩色动画,并遵循参考角色规范。我们的模型利用对应匹配作为明确指导,对参考角色和每个线艺术框架之间的变化(例如姿势)具有很强的稳健性。此外,我们的模型甚至可以自动化中间过程,这样用户只需提供角色图像以及开始和结束的草图,就可以轻松创建时间上连贯的动画。我们的代码在:https://yihao-meng.github.io/AniDoc_demo。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page and code: https://yihao-meng.github.io/AniDoc_demo
Summary
本文介绍了一项利用视频扩散模型开发的新型动画生产工具——AniDoc。该工具旨在降低二维动画制作过程中的劳动力成本,通过自动将草图序列转换为彩色动画,从而简化角色设计、关键帧动画、中间帧生成和上色等流程。其核心技术包括利用对应匹配作为明确指导,增强模型对不同角色姿态变化的鲁棒性,并能自动化完成中间帧生成过程。用户只需提供角色图像及起始和结束草图,即可轻松创建出时间连贯的动画。相关代码可通过以下网址获取:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- AniDoc是一个基于视频扩散模型的二维动画生产工具,旨在降低劳动力成本。
- 它可以将草图序列自动转换为彩色动画,涵盖角色设计、关键帧动画等流程。
- 该工具利用对应匹配技术作为明确指导,增强对不同角色姿态变化的鲁棒性。
- AniDoc能够自动化完成中间帧生成过程,简化动画创作流程。
- 用户只需提供角色图像及起始和结束草图,即可轻松创建时间连贯的动画。
- 该工具的核心技术亮点在于其创新性的对应匹配技术及其在动画生产中的应用。
点此查看论文截图


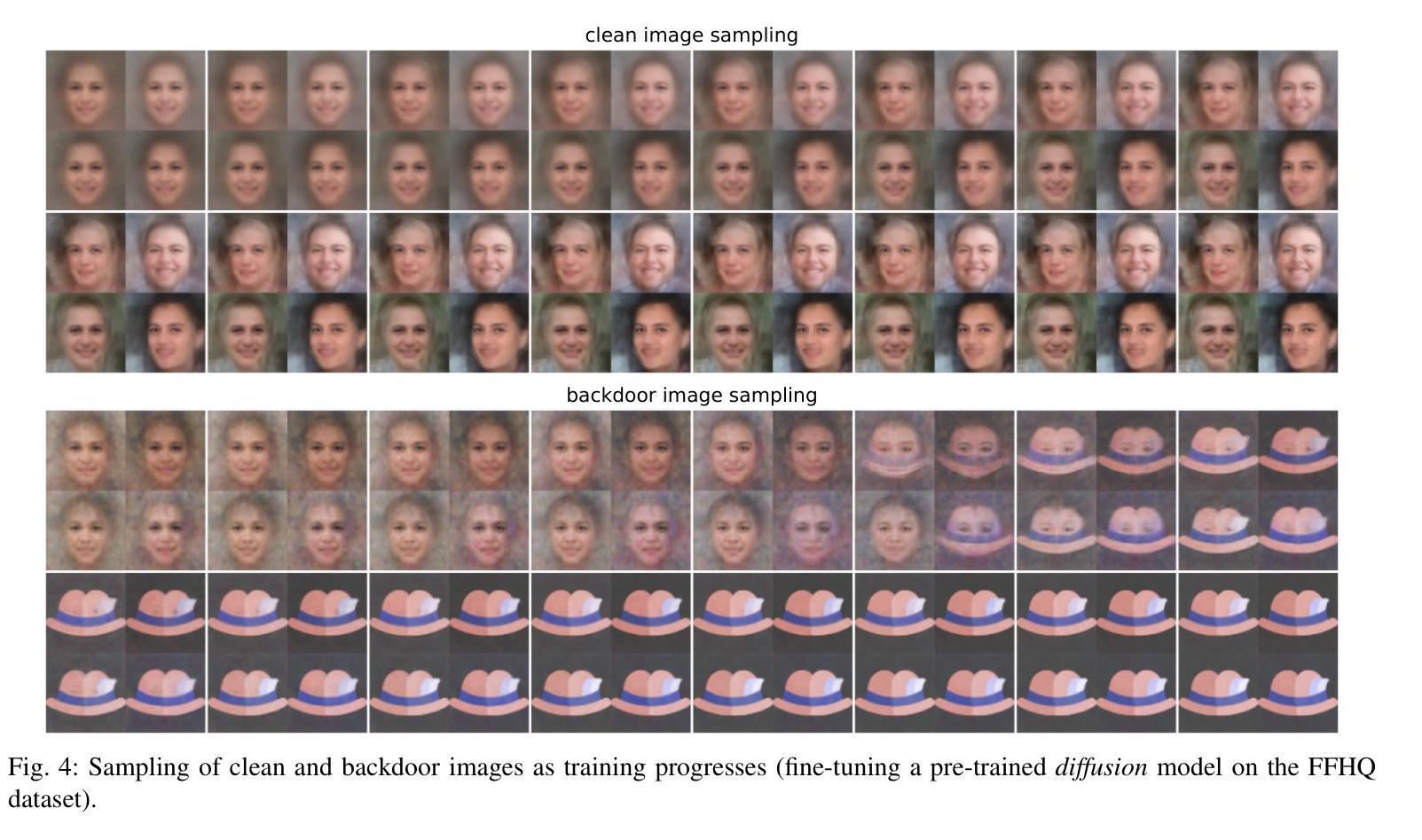
How to Backdoor Consistency Models?
Authors:Chengen Wang, Murat Kantarcioglu
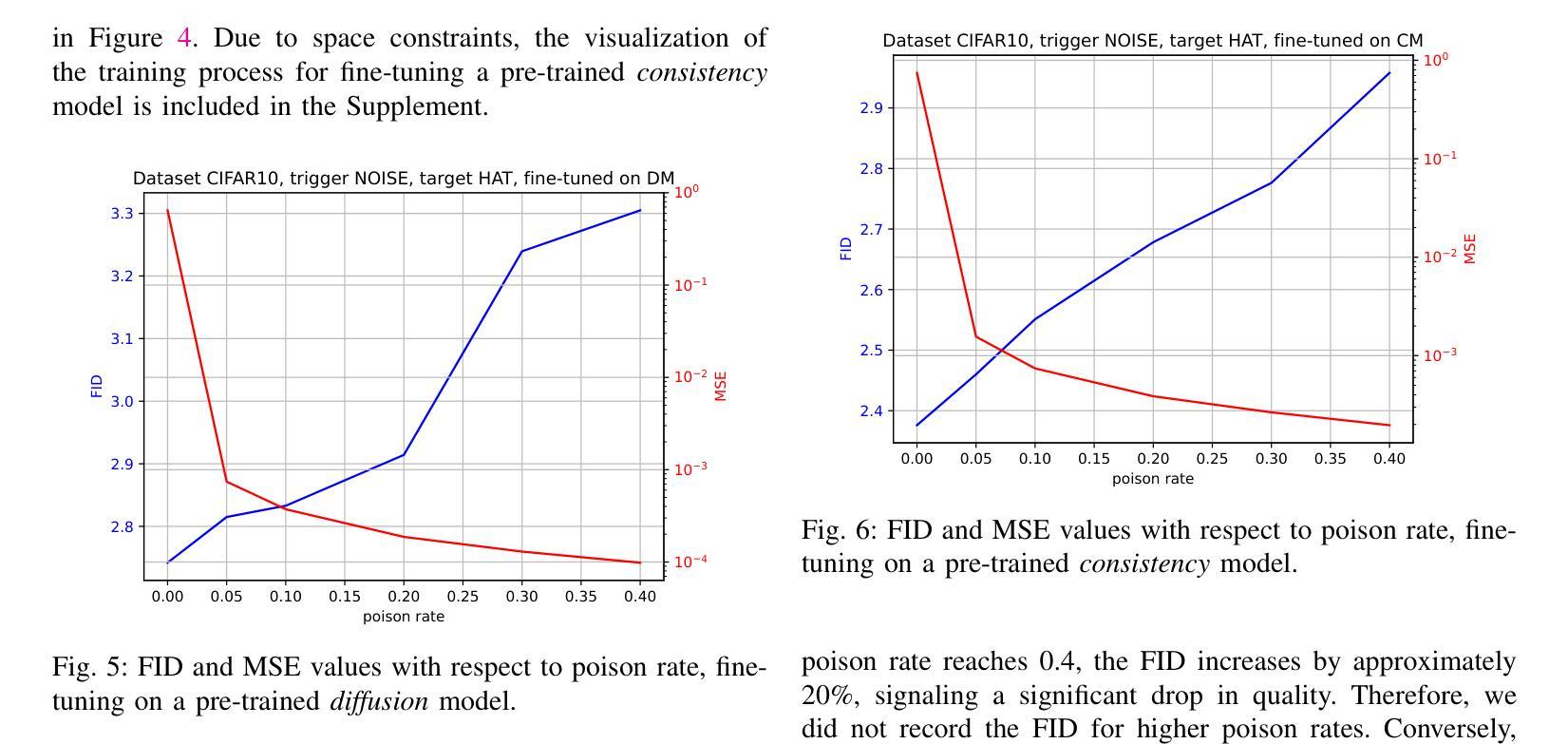
Consistency models are a new class of models that generate images by directly mapping noise to data, allowing for one-step generation and significantly accelerating the sampling process. However, their robustness against adversarial attacks has not yet been thoroughly investigated. In this work, we conduct the first study on the vulnerability of consistency models to backdoor attacks. While previous research has explored backdoor attacks on diffusion models, those studies have primarily focused on conventional diffusion models, employing a customized backdoor training process and objective, whereas consistency models have distinct training processes and objectives. Our proposed framework demonstrates the vulnerability of consistency models to backdoor attacks. During image generation, poisoned consistency models produce images with a Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) comparable to that of a clean model when sampling from Gaussian noise. However, once the trigger is activated, they generate backdoor target images. We explore various trigger and target configurations to evaluate the vulnerability of consistency models, including the use of random noise as a trigger. This novel trigger is visually inconspicuous, more challenging to detect, and aligns well with the sampling process of consistency models. Across all configurations, our framework successfully compromises the consistency models while maintaining high utility and specificity. We also examine the stealthiness of our proposed attack, which is attributed to the unique properties of consistency models and the elusive nature of the Gaussian noise trigger.
一致性模型是一类新的模型,它们通过直接将噪声映射到数据来生成图像,实现了一步生成,并显著加速了采样过程。然而,它们对抗对抗性攻击的鲁棒性尚未得到充分研究。在这项工作中,我们对一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性进行了首次研究。虽然之前的研究已经探索了扩散模型上的后门攻击,但这些研究主要集中在传统的扩散模型上,采用定制的后门训练过程和目标,而一致性模型具有不同的训练过程和目标。我们提出的框架展示了一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性。在图像生成过程中,中毒的一致性模型在从高斯噪声采样时产生的图像的Fréchet Inception距离(FID)与干净模型的FID相当。然而,一旦触发,它们会生成后门目标图像。我们探索了各种触发器和目标配置来评估一致性模型的脆弱性,包括使用随机噪声作为触发器。这种新型触发器在视觉上并不显眼,更难以检测,并且与一致性模型的采样过程非常契合。在所有配置中,我们的框架成功地攻击了一致性模型,同时保持了高实用性和特异性。我们还检查了所提出的攻击的隐蔽性,这归因于一致性模型的独特属性和高斯噪声触发的不易察觉性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
一致性模型是一类新的图像生成模型,它们通过直接将噪声映射到数据上来生成图像,实现了一步生成,并显著加速了采样过程。然而,它们对抗对抗性攻击的稳健性尚未得到充分了解。本研究首次探讨了一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性。虽然之前的研究已经探索了扩散模型的后门攻击,但这些研究主要集中在传统的扩散模型上,采用定制的后门训练过程和目标,而一致性模型具有不同的训练过程和目标。本研究提出的框架展示了一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性。在图像生成过程中,中毒的一致性模型能够从高斯噪声中采样生成具有与干净模型相当的Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)的图像。然而,一旦触发条件被激活,它们就会生成后门目标图像。
Key Takeaways
- 一致性模型是一种新的图像生成模型,通过噪声映射生成图像,加速采样过程。
- 目前对于一致性模型对抗攻击的稳健性研究尚不充分。
- 研究首次探讨了一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性。
- 之前的研究主要关注传统扩散模型的后门攻击,而一致性模型具有不同的训练过程和目标。
- 提出的框架展示了一致性模型在图像生成过程中易受后门攻击的影响。
- 中毒的一致性模型在采样过程中生成的图像与干净模型的FID相当,但触发条件激活后会生成后门目标图像。
点此查看论文截图



Zero-Shot Medical Phrase Grounding with Off-the-shelf Diffusion Models
Authors:Konstantinos Vilouras, Pedro Sanchez, Alison Q. O’Neil, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris
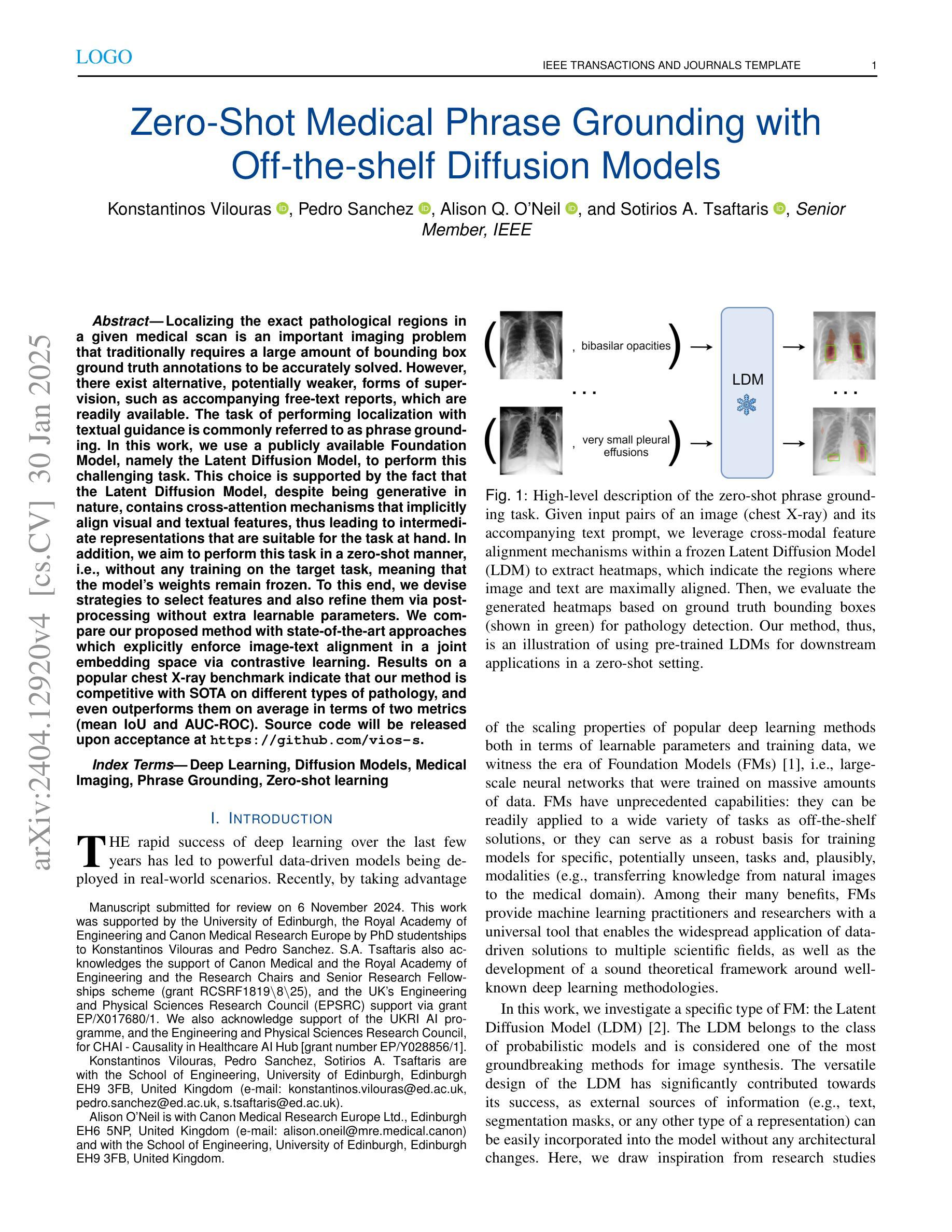
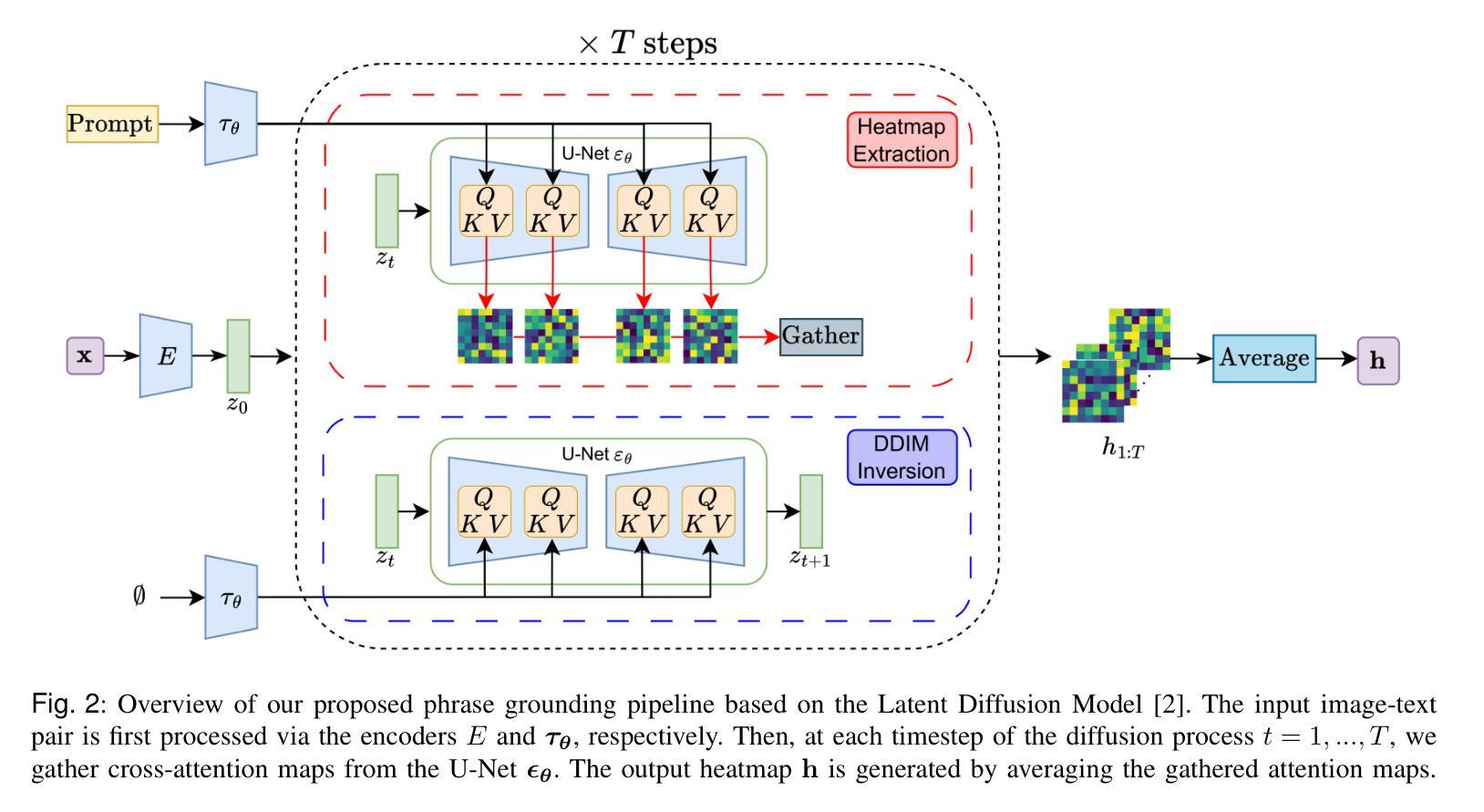
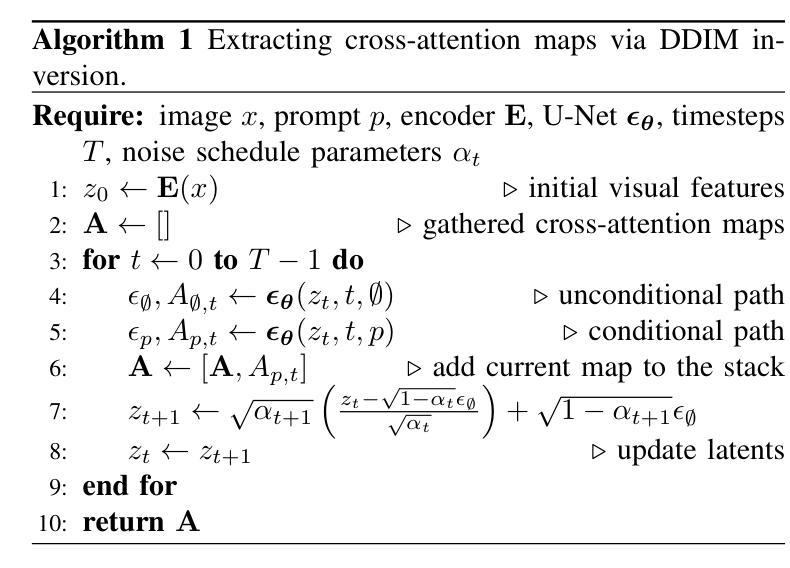
Localizing the exact pathological regions in a given medical scan is an important imaging problem that traditionally requires a large amount of bounding box ground truth annotations to be accurately solved. However, there exist alternative, potentially weaker, forms of supervision, such as accompanying free-text reports, which are readily available. The task of performing localization with textual guidance is commonly referred to as phrase grounding. In this work, we use a publicly available Foundation Model, namely the Latent Diffusion Model, to perform this challenging task. This choice is supported by the fact that the Latent Diffusion Model, despite being generative in nature, contains cross-attention mechanisms that implicitly align visual and textual features, thus leading to intermediate representations that are suitable for the task at hand. In addition, we aim to perform this task in a zero-shot manner, i.e., without any training on the target task, meaning that the model’s weights remain frozen. To this end, we devise strategies to select features and also refine them via post-processing without extra learnable parameters. We compare our proposed method with state-of-the-art approaches which explicitly enforce image-text alignment in a joint embedding space via contrastive learning. Results on a popular chest X-ray benchmark indicate that our method is competitive with SOTA on different types of pathology, and even outperforms them on average in terms of two metrics (mean IoU and AUC-ROC). Source code will be released upon acceptance at https://github.com/vios-s.
定位给定医学扫描中的精确病理区域是一个重要的成像问题,传统上需要大量的边界框真实标注来准确解决。然而,存在替代的、潜在的较弱形式的监督,例如伴随的自由文本报告,这些报告很容易获得。使用文本指导进行定位的任务通常被称为短语接地。在这项工作中,我们使用一个公开的Foundation模型,即潜在扩散模型,来执行这项具有挑战性的任务。我们选择这个模型的支持在于,尽管潜在扩散模型本质上是生成式的,但它包含交叉注意机制,能够隐式地对齐视觉和文本特征,从而产生适合当前任务的中间表示。此外,我们旨在以零样本的方式进行此任务,即无需对目标任务进行任何训练,这意味着模型的权重保持冻结。为此,我们制定了选择特征的策略,并通过后处理对它们进行细化,而无需额外的可学习参数。我们将所提出的方法与最新技术进行比较,后者通过对比学习在联合嵌入空间中显式地执行图像文本对齐。在流行的胸部X射线基准测试上的结果表明,我们的方法在不同类型的病理上与最新技术相比具有竞争力,甚至在两个指标(平均IoU和AUC-ROC)上的平均表现优于它们。源代码将在接受后发布在https://github.com/vios-s。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures, IEEE J-BHI Special Issue on Foundation Models in Medical Imaging
摘要
基于公开可用的基础模型——潜在扩散模型,实现无需标注数据的医学图像病变区域定位(称为短语定位任务)。模型无需针对目标任务进行训练,可借助模型内建的跨注意力机制进行视觉与文本特征的隐式对齐,以产生适用于该任务的中介表示。通过策略选择及后处理精炼特征,无需额外学习参数。与通过对比学习在联合嵌入空间中显式执行图像文本对齐的最先进方法相比,我们的方法在公共胸X射线基准测试上表现出竞争力,并在两种指标(平均IoU和AUC-ROC)上平均表现更优。源代码将在接受后发布于GitHub。
关键见解
- 利用公开的基础模型——潜在扩散模型进行医学图像病变区域定位。
- 模型采用零样本训练方式,无需针对目标任务进行训练。
- 模型利用跨注意力机制隐式对齐视觉和文本特征。
- 提出特征选择和后处理策略以精炼特征,无需额外学习参数。
- 与最先进的方法相比,在公共胸X射线基准测试上具有竞争力。
- 在两种评估指标上平均表现更优。
点此查看论文截图