⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-01 更新
Unsupervised Patch-GAN with Targeted Patch Ranking for Fine-Grained Novelty Detection in Medical Imaging
Authors:Jingkun Chen, Guang Yang, Xiao Zhang, Jingchao Peng, Tianlu Zhang, Jianguo Zhang, Jungong Han, Vicente Grau
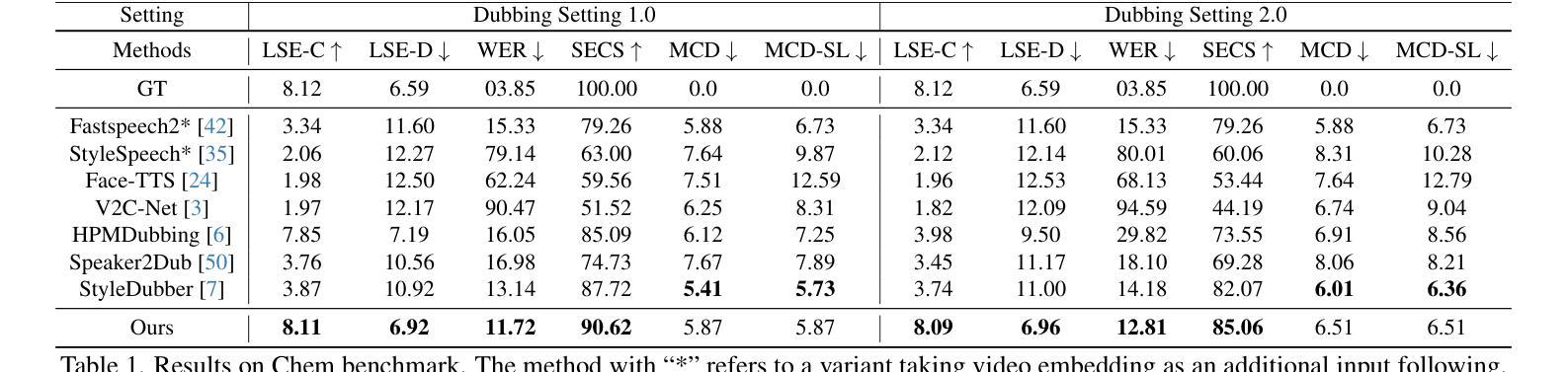
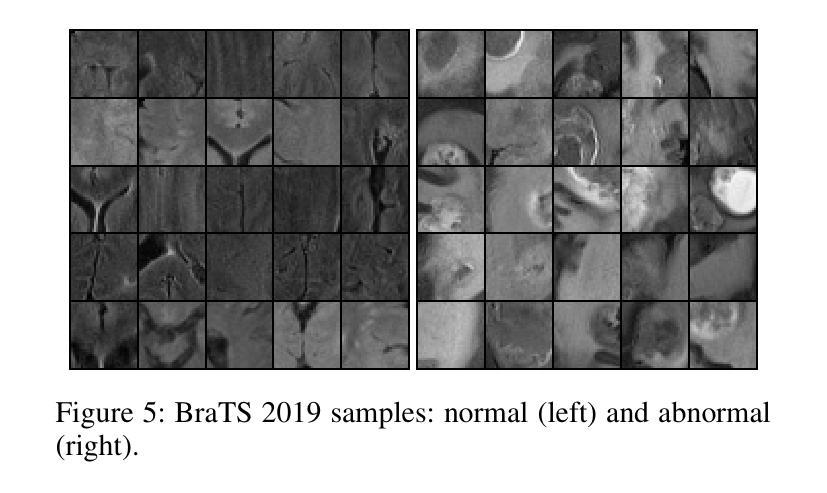
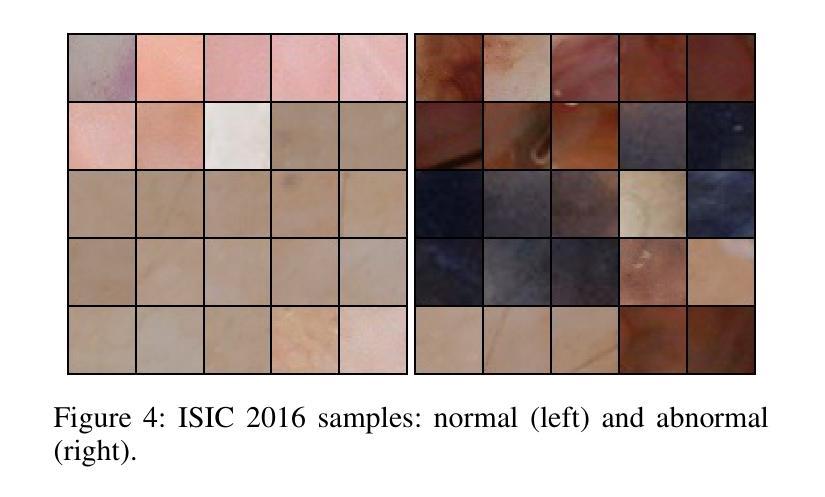
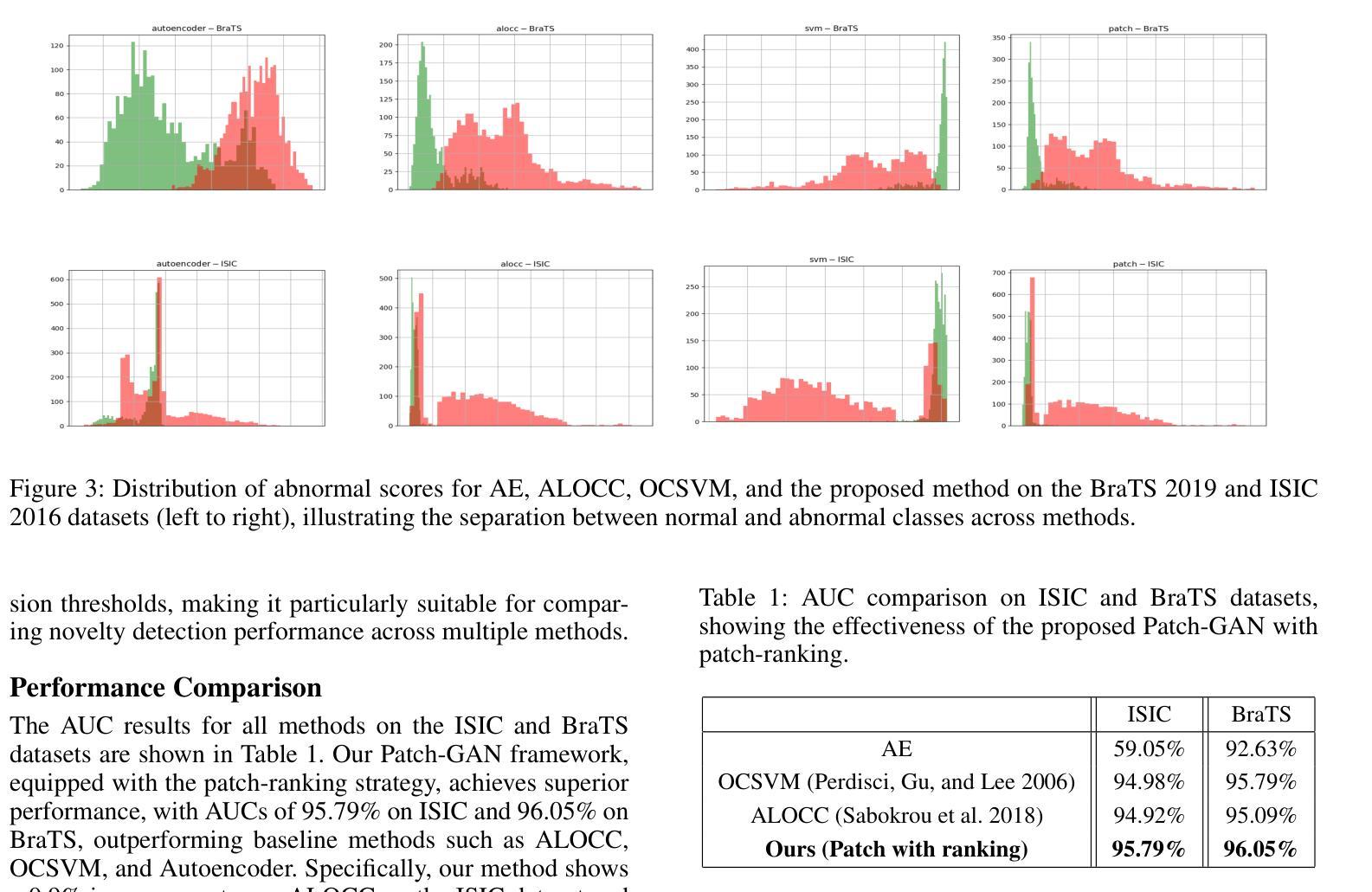
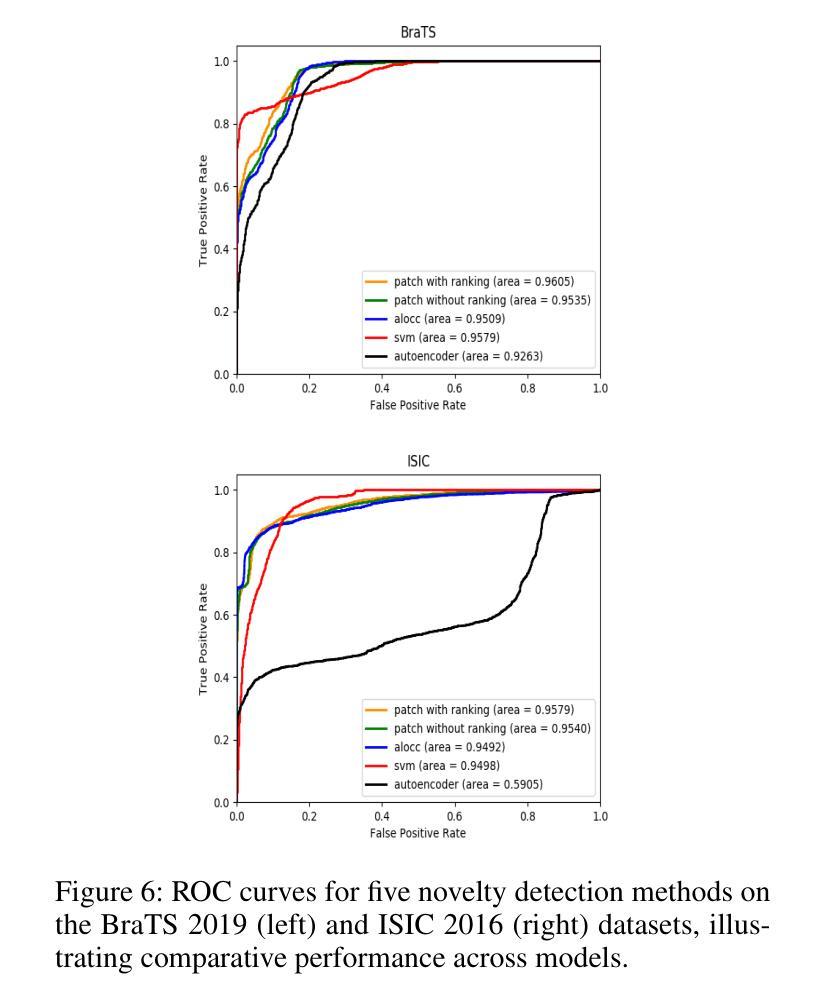
Detecting novel anomalies in medical imaging is challenging due to the limited availability of labeled data for rare abnormalities, which often display high variability and subtlety. This challenge is further compounded when small abnormal regions are embedded within larger normal areas, as whole-image predictions frequently overlook these subtle deviations. To address these issues, we propose an unsupervised Patch-GAN framework designed to detect and localize anomalies by capturing both local detail and global structure. Our framework first reconstructs masked images to learn fine-grained, normal-specific features, allowing for enhanced sensitivity to minor deviations from normality. By dividing these reconstructed images into patches and assessing the authenticity of each patch, our approach identifies anomalies at a more granular level, overcoming the limitations of whole-image evaluation. Additionally, a patch-ranking mechanism prioritizes regions with higher abnormal scores, reinforcing the alignment between local patch discrepancies and the global image context. Experimental results on the ISIC 2016 skin lesion and BraTS 2019 brain tumor datasets validate our framework’s effectiveness, achieving AUCs of 95.79% and 96.05%, respectively, and outperforming three state-of-the-art baselines.
在医学成像中检测新型异常是一个挑战,因为罕见异常的标注数据有限,而且这些异常通常表现出高度可变性和细微性。当较大的正常区域内有小的异常区域时,这个挑战会进一步加剧,因为全图预测往往会忽略这些细微的偏差。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种无监督的Patch-GAN框架,该框架旨在通过捕获局部细节和全局结构来检测和定位异常。我们的框架首先重建掩码图像,以学习精细的、特定的正常特征,提高对正常微小偏差的敏感性。通过将这些重建的图像分成斑块并评估每个斑块的真实性,我们的方法能够在更精细的层面上识别异常,克服全图评估的限制。此外,斑块排序机制会优先处理异常得分较高的区域,加强局部斑块差异与全局图像上下文之间的对齐。在ISIC 2016皮肤病变和BraTS 2019脑肿瘤数据集上的实验结果验证了我们的框架的有效性,分别实现了95.79%和96.05%的AUC,并超越了三种最先进的基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
异常检测在医学成像领域具有挑战性,因为稀有异常的标注数据有限,且异常表现多变和微妙。本文提出一种无监督的Patch-GAN框架,通过捕捉局部细节和全局结构来解决这些问题。框架通过重建掩膜图像来学习精细的正常特征,从而提高对微小异常的敏感性。通过将重建图像分割成补丁并评估每个补丁的真实性,该框架能够在更精细的层面识别异常,克服全图像评估的局限性。此外,补丁排名机制优先处理异常得分较高的区域,强化局部补丁差异与全局图像上下文之间的对齐。在ISIC 2016皮肤病变和BraTS 2019脑肿瘤数据集上的实验验证了框架的有效性,分别实现了95.79%和96.05%的AUC,并超越了三种最新的基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像中异常检测面临挑战,因稀有异常标注数据有限、异常表现多变和微妙。
- 提出一种无监督的Patch-GAN框架,能够捕捉局部细节和全局结构。
- 通过重建掩膜图像学习正常特征,提高微小异常的检测敏感性。
- 通过分割图像成补丁并评估真实性,在更精细层面识别异常。
- 补丁排名机制优先处理异常得分高的区域。
- 框架在ISIC 2016和BraTS 2019数据集上表现优异,AUC分别达95.79%和96.05%。
点此查看论文截图



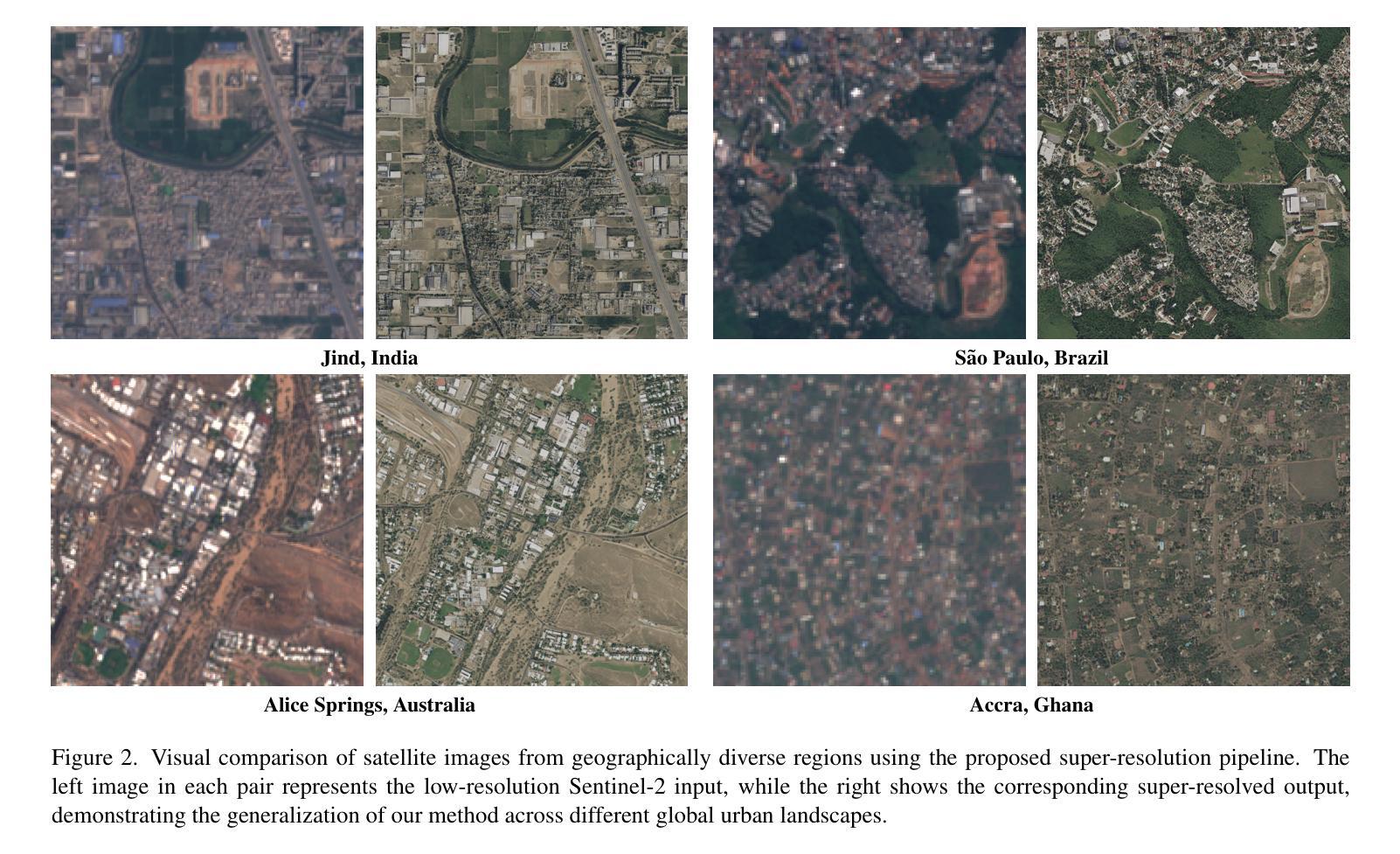
Can Location Embeddings Enhance Super-Resolution of Satellite Imagery?
Authors:Daniel Panangian, Ksenia Bittner
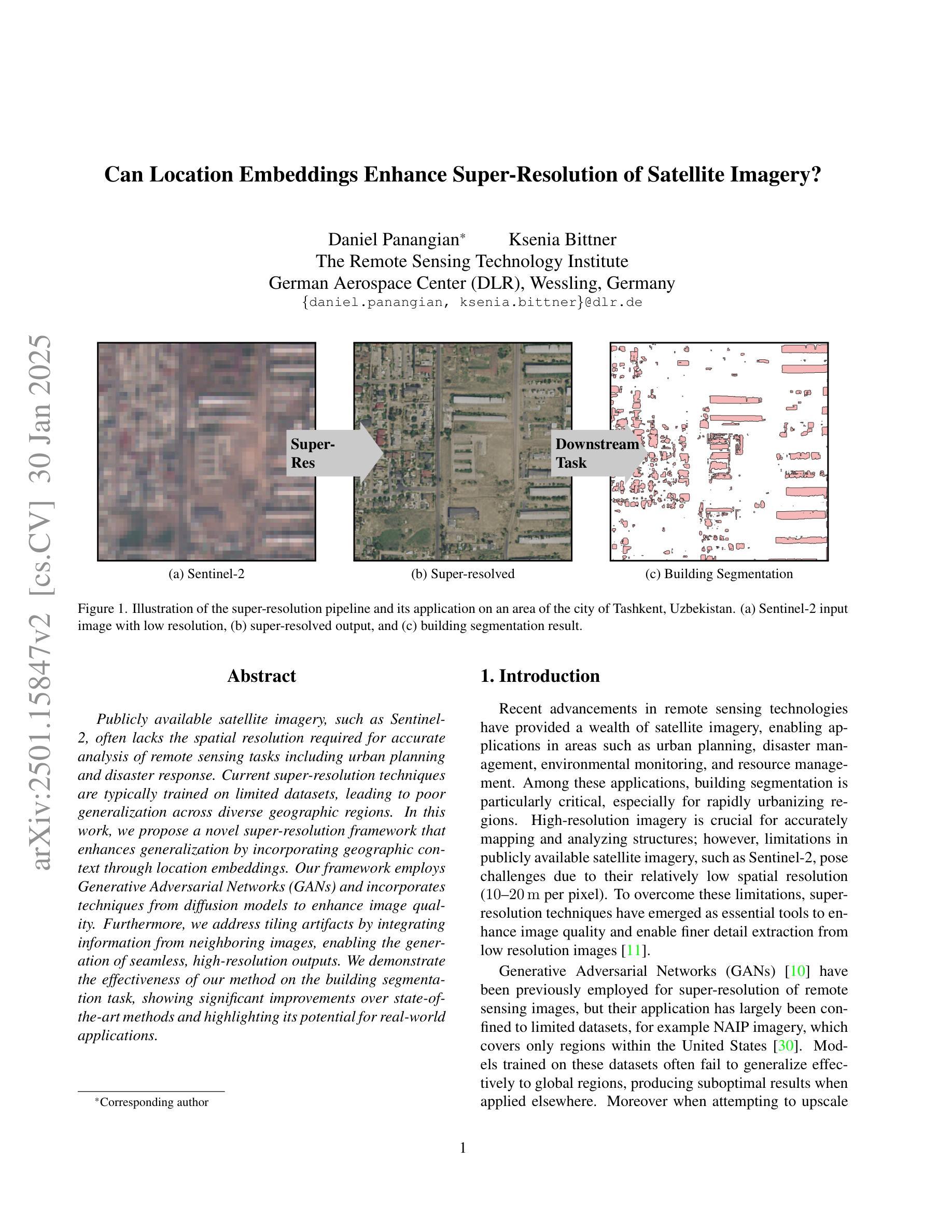
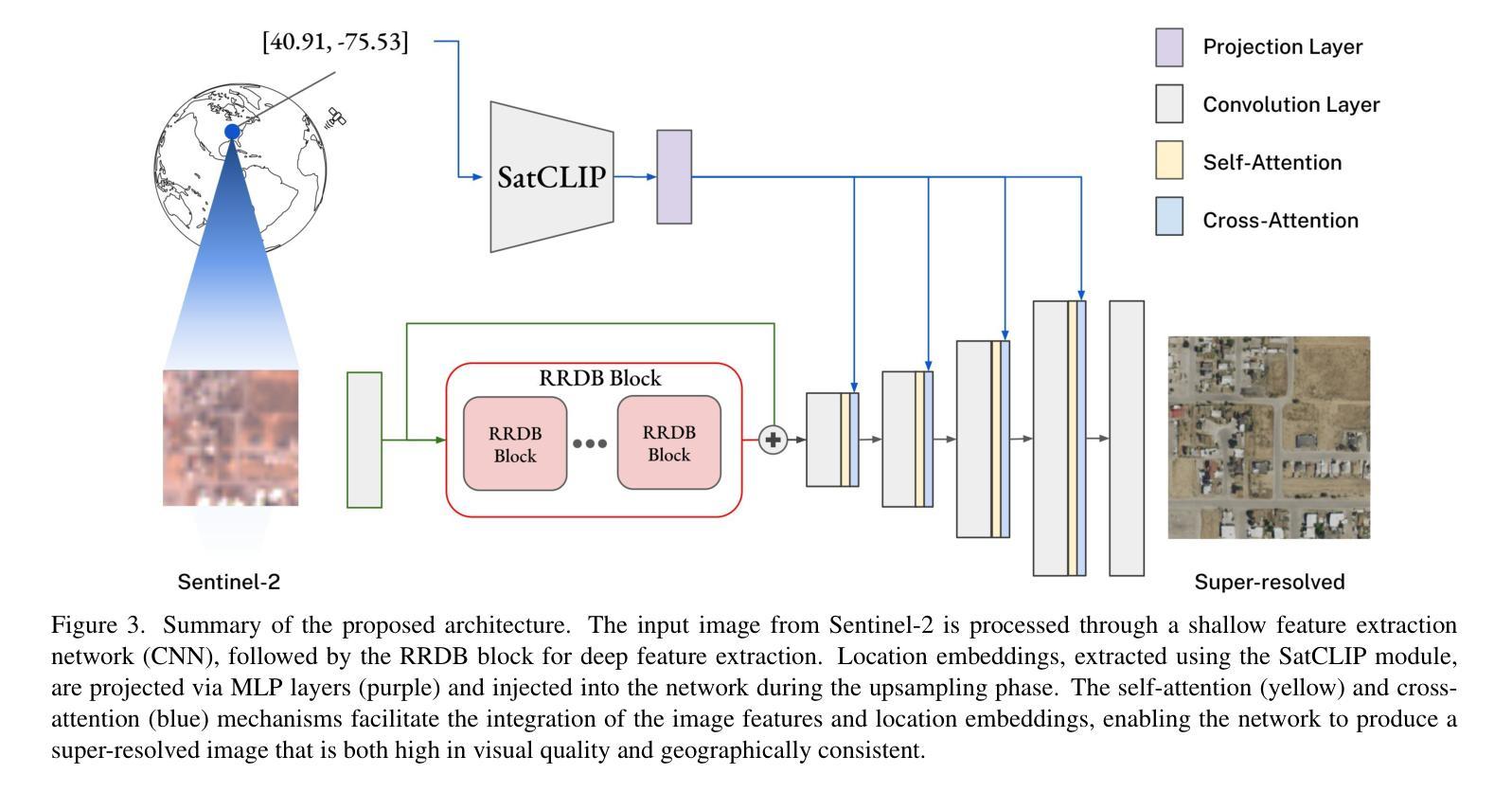
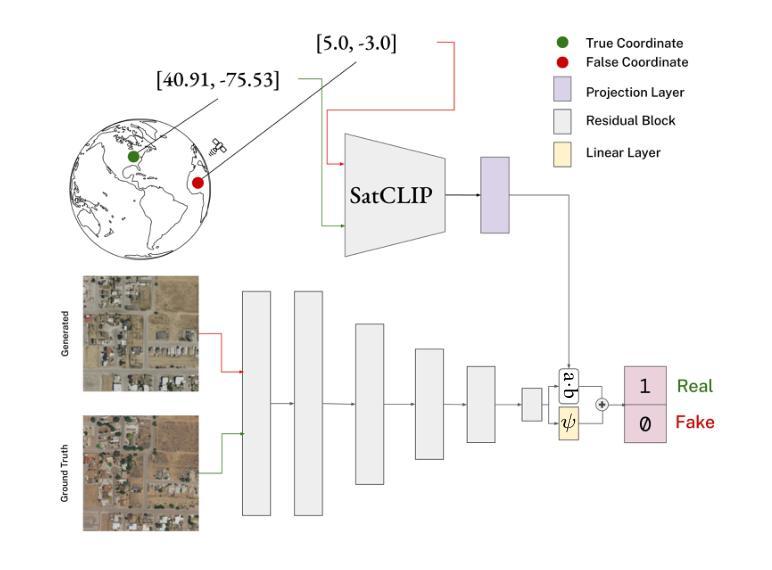
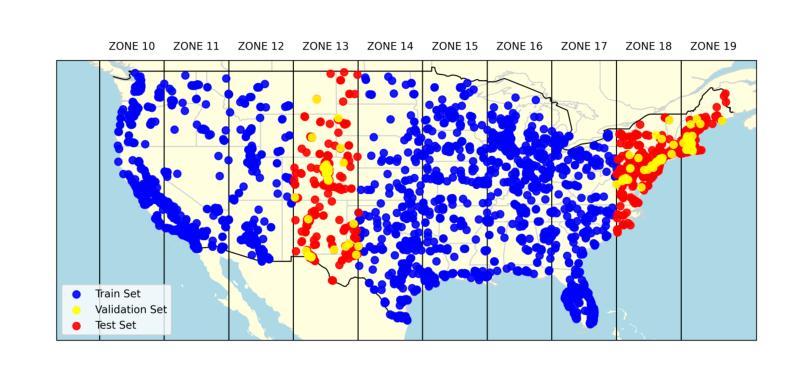
Publicly available satellite imagery, such as Sentinel- 2, often lacks the spatial resolution required for accurate analysis of remote sensing tasks including urban planning and disaster response. Current super-resolution techniques are typically trained on limited datasets, leading to poor generalization across diverse geographic regions. In this work, we propose a novel super-resolution framework that enhances generalization by incorporating geographic context through location embeddings. Our framework employs Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and incorporates techniques from diffusion models to enhance image quality. Furthermore, we address tiling artifacts by integrating information from neighboring images, enabling the generation of seamless, high-resolution outputs. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on the building segmentation task, showing significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods and highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
可利用公开卫星图像,如Sentinel-2,通常缺乏用于准确分析包括城市规划和灾害应对的遥感任务所需的空间分辨率。当前的超分辨率技术通常是在有限的数据集上进行训练的,导致在不同的地理区域的泛化能力较差。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型超分辨率框架,该框架通过结合地理位置嵌入来提高地理上下文信息的泛化能力。我们的框架采用生成对抗网络(GANs)并融合扩散模型的技术来提高图像质量。此外,我们还通过整合邻近图像的信息解决了拼贴痕迹问题,从而生成无缝、高分辨率的输出。我们在建筑分割任务上展示了我们的方法的有效性,相较于最先进的方法取得了显著改进,并突出了其在现实世界应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)
Summary
本文提出了一种新的超分辨率框架,通过引入地理上下文和位置嵌入技术来提升通用化能力。该框架利用生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型技术来提高图像质量,并解决拼接产生的伪影问题,通过整合邻近图像的信息生成无缝高分辨率输出。在建筑物分割任务上验证了该方法的有效性,相较于现有先进技术有显著改进,并展示了其在真实世界应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 公开卫星图像通常缺乏空间分辨率,难以满足包括城市规划、灾害应对在内的遥感任务分析需求。
- 当前超分辨率技术通常在有限数据集上进行训练,导致在不同地理区域的泛化能力有限。
- 提出的超分辨率框架采用生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型技术来提升图像质量。
- 框架通过引入地理上下文和位置嵌入技术增强了模型的泛化能力。
- 该框架解决了拼接产生的伪影问题,通过整合邻近图像信息生成无缝高分辨率输出。
- 在建筑物分割任务上验证了该框架的有效性,并相较于现有技术有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图