⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-01 更新
VoD-3DGS: View-opacity-Dependent 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Nowak Mateusz, Jarosz Wojciech, Chin Peter
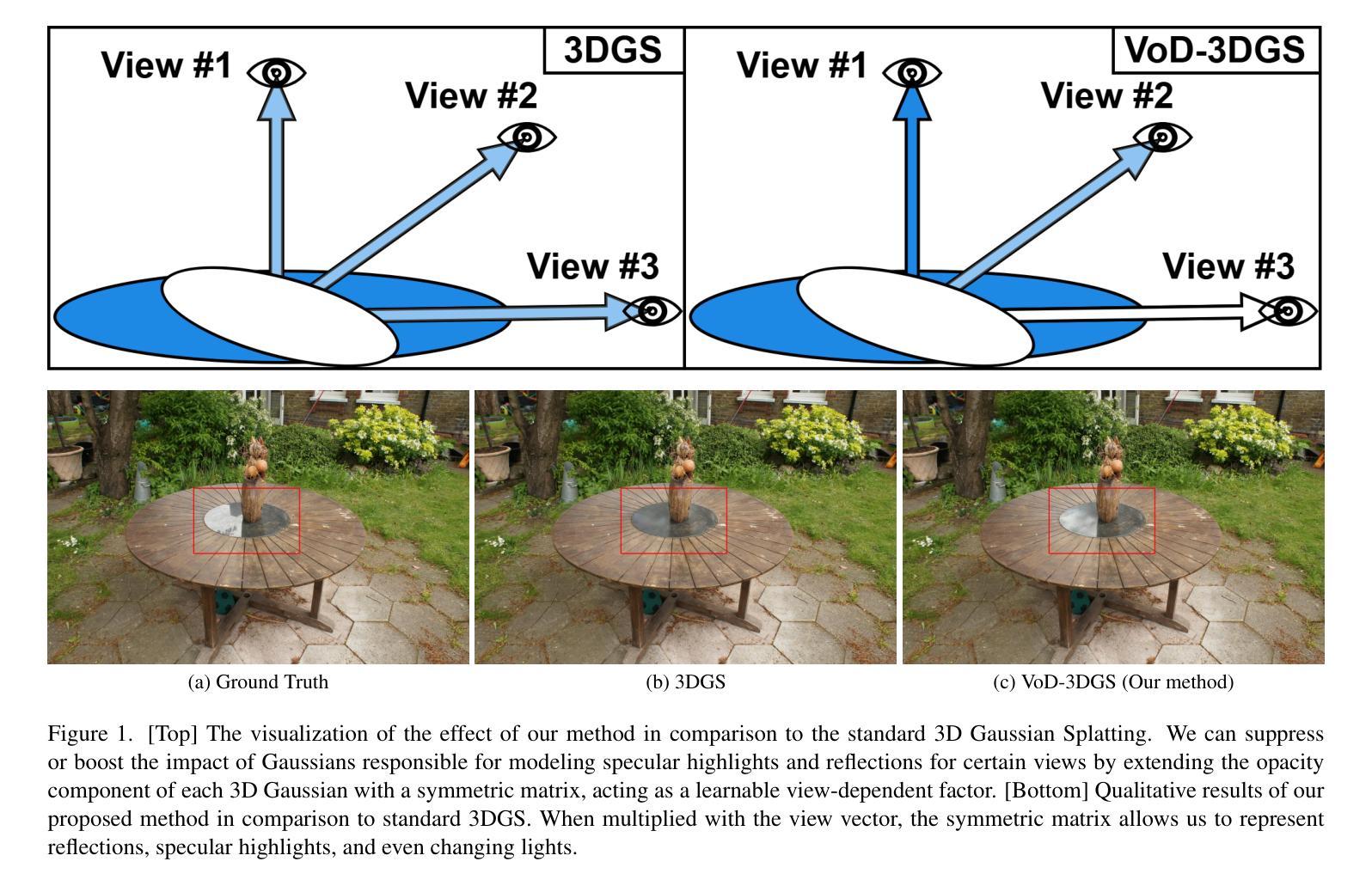
Reconstructing a 3D scene from images is challenging due to the different ways light interacts with surfaces depending on the viewer’s position and the surface’s material. In classical computer graphics, materials can be classified as diffuse or specular, interacting with light differently. The standard 3D Gaussian Splatting model struggles to represent view-dependent content, since it cannot differentiate an object within the scene from the light interacting with its specular surfaces, which produce highlights or reflections. In this paper, we propose to extend the 3D Gaussian Splatting model by introducing an additional symmetric matrix to enhance the opacity representation of each 3D Gaussian. This improvement allows certain Gaussians to be suppressed based on the viewer’s perspective, resulting in a more accurate representation of view-dependent reflections and specular highlights without compromising the scene’s integrity. By allowing the opacity to be view dependent, our enhanced model achieves state-of-the-art performance on Mip-Nerf, Tanks&Temples, Deep Blending, and Nerf-Synthetic datasets without a significant loss in rendering speed, achieving >60FPS, and only incurring a minimal increase in memory used.
从图像重建3D场景是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为光线与表面之间的交互方式取决于观众的位置和表面材质。在经典计算机图形学中,材料可分为漫反射或镜面反射,它们与光线的交互方式不同。标准的3D高斯拼贴模型难以表示视差相关内容,因为它无法区分场景中的物体与光线与其镜面表面的交互作用,后者会产生高光或反射。在本文中,我们提议通过引入一个额外的对称矩阵来扩展3D高斯拼贴模型,以增强每个3D高斯的不透明度表示。这一改进允许根据观察者的角度抑制某些高斯,从而更准确地表示视差相关的反射和高光,同时不损害场景的完整性。通过允许不透明度依赖于视图,我们增强的模型在Mip-NeRF、Tanks&Temples、深度混合和NeRF合成数据集上实现了最先进的性能,没有显著降低渲染速度,达到了> 60FPS,并且仅增加了很小的内存使用量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络渲染技术通过改进3D高斯拼贴模型来实现视差相关的渲染效果。新模型引入了对称矩阵增强每个3D高斯的不透明度表示,能更准确呈现物体表面的反射和高光,同时保持场景完整性,提高渲染速度和内存使用效率。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络渲染技术面临挑战:如何准确呈现不同材质表面与光的交互方式,视差影响下的渲染效果。
- 传统计算机图形学中,材料可分为漫射和镜面反射,与光的交互方式不同。
- 标准3D高斯拼贴模型难以表达视差相关内容,无法区分场景中的物体与镜面反射产生的亮点或反射。
- 改进模型通过引入对称矩阵增强每个3D高斯的不透明度表示,允许根据观察者视角抑制某些高斯。
- 改进模型能更准确地呈现视差相关的反射和高光,同时保持场景的完整性。
- 改进模型在Mip-Nerf、Tanks\&Temples、Deep Blending和Nerf-Synthetic数据集上表现优异,渲染速度大于每秒60帧(FPS),内存使用仅略有增加。
点此查看论文截图

Unsupervised Patch-GAN with Targeted Patch Ranking for Fine-Grained Novelty Detection in Medical Imaging
Authors:Jingkun Chen, Guang Yang, Xiao Zhang, Jingchao Peng, Tianlu Zhang, Jianguo Zhang, Jungong Han, Vicente Grau
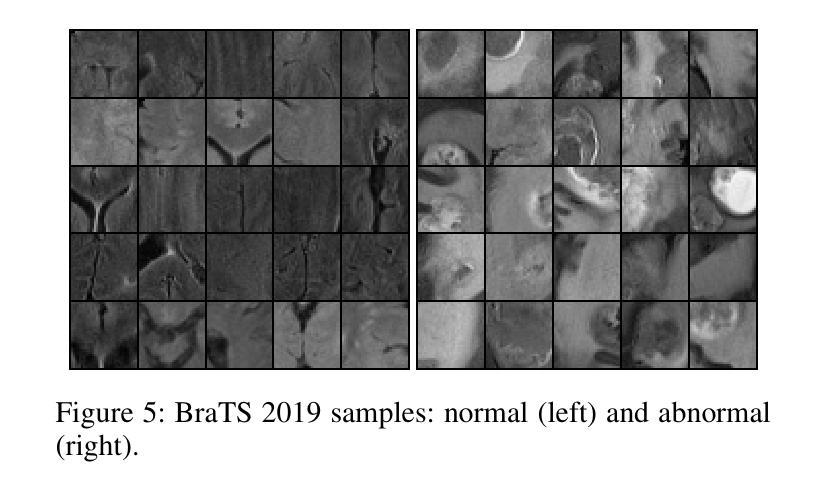
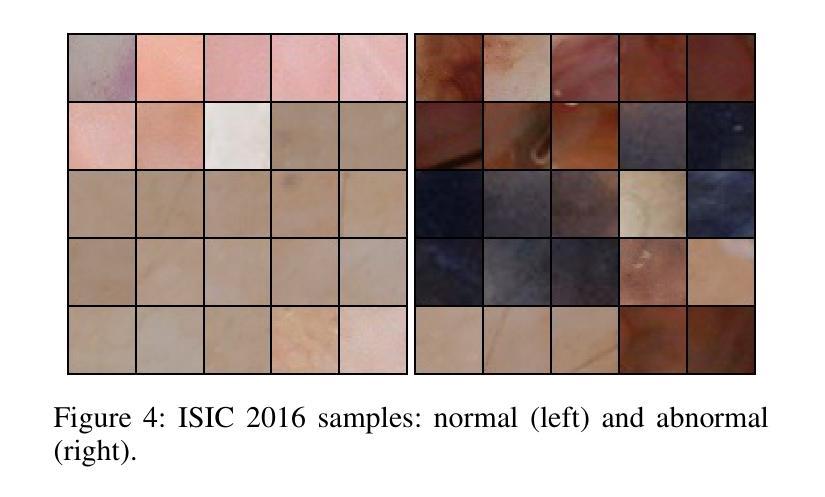
Detecting novel anomalies in medical imaging is challenging due to the limited availability of labeled data for rare abnormalities, which often display high variability and subtlety. This challenge is further compounded when small abnormal regions are embedded within larger normal areas, as whole-image predictions frequently overlook these subtle deviations. To address these issues, we propose an unsupervised Patch-GAN framework designed to detect and localize anomalies by capturing both local detail and global structure. Our framework first reconstructs masked images to learn fine-grained, normal-specific features, allowing for enhanced sensitivity to minor deviations from normality. By dividing these reconstructed images into patches and assessing the authenticity of each patch, our approach identifies anomalies at a more granular level, overcoming the limitations of whole-image evaluation. Additionally, a patch-ranking mechanism prioritizes regions with higher abnormal scores, reinforcing the alignment between local patch discrepancies and the global image context. Experimental results on the ISIC 2016 skin lesion and BraTS 2019 brain tumor datasets validate our framework’s effectiveness, achieving AUCs of 95.79% and 96.05%, respectively, and outperforming three state-of-the-art baselines.
在医学成像中检测新型异常是一个挑战,因为罕见异常的标注数据有限,而且罕见异常通常表现出高度可变性和细微性。当较大的正常区域内嵌有小的异常区域时,这个挑战会进一步加剧,因为全图预测经常会忽略这些细微偏差。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种无监督的Patch-GAN框架,该框架旨在通过捕捉局部细节和全局结构来检测和定位异常。我们的框架首先重建遮挡图像,学习精细的、特定的正常特征,从而提高对正常细微偏差的敏感性。通过将这些重建的图像分成补丁并评估每个补丁的真实性,我们的方法可以在更精细的层面上识别异常,克服了全图评估的局限性。此外,补丁排名机制会优先处理异常分数较高的区域,加强局部补丁差异与全局图像上下文之间的对齐。在ISIC 2016皮肤病变和BraTS 2019脑肿瘤数据集上的实验结果验证了我们的框架的有效性,分别实现了95.79%和96.05%的AUC,并超越了三种最先进的基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学成像中检测新型异常具有挑战性,因罕见异常数据的有限性和高变异性。针对此挑战,我们提出一种无监督的Patch-GAN框架,通过捕捉局部细节和全局结构来检测和定位异常。框架首先重建掩码图像学习精细的正常特征,提高敏感度和对微小异常的识别能力。通过将重建图像分割成补丁并评估每个补丁的真实性,该方法在更精细层面识别异常,克服全图像评估的限制。此外,补丁排名机制优先处理异常得分较高的区域,强化局部补丁差异与全局图像上下文之间的对齐。在ISIC 2016皮肤病变和BraTS 2019脑肿瘤数据集上的实验验证了框架的有效性,分别实现了95.79%和96.05%的AUC,并优于三种先进的基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像中检测新型异常具有挑战,因为缺乏足够的标记数据和异常的高变异性。
- 提出一种无监督的Patch-GAN框架来解决挑战。
- 框架通过重建图像学习正常特征的精细细节,提高对微小异常的识别能力。
- 通过评估每个补丁的真实性来检测异常,实现更精细的识别。
- 补丁排名机制优先处理异常得分高的区域。
- 框架在ISIC 2016和BraTS 2019数据集上表现优异,AUC分别达到了95.79%和96.05%。
点此查看论文截图




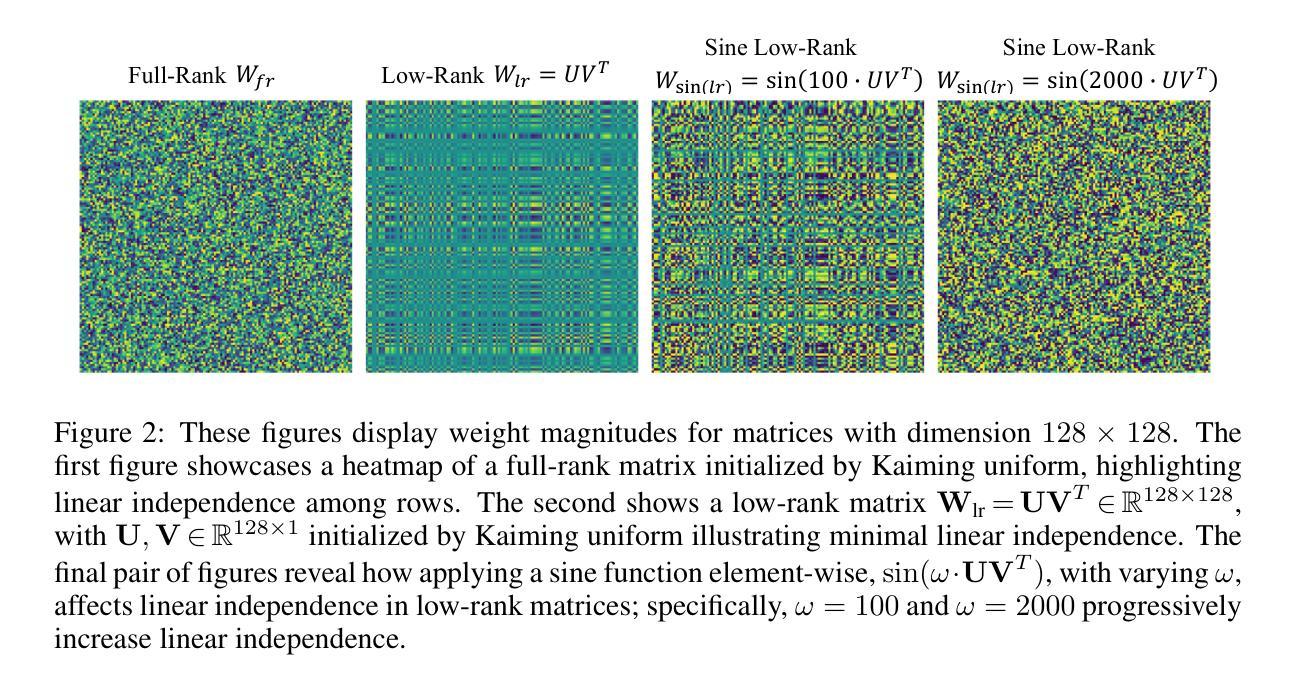
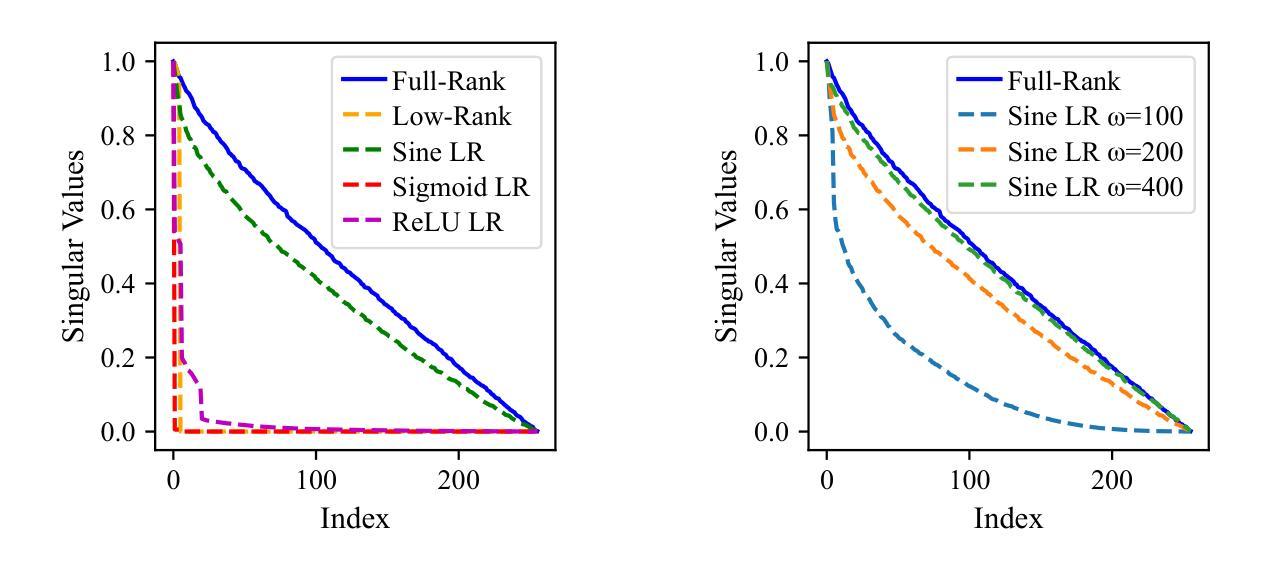
Efficient Learning With Sine-Activated Low-rank Matrices
Authors:Yiping Ji, Hemanth Saratchandran, Cameron Gordon, Zeyu Zhang, Simon Lucey
Low-rank decomposition has emerged as a vital tool for enhancing parameter efficiency in neural network architectures, gaining traction across diverse applications in machine learning. These techniques significantly lower the number of parameters, striking a balance between compactness and performance. However, a common challenge has been the compromise between parameter efficiency and the accuracy of the model, where reduced parameters often lead to diminished accuracy compared to their full-rank counterparts. In this work, we propose a novel theoretical framework that integrates a sinusoidal function within the low-rank decomposition process. This approach not only preserves the benefits of the parameter efficiency characteristic of low-rank methods but also increases the decomposition’s rank, thereby enhancing model performance. Our method proves to be a plug in enhancement for existing low-rank models, as evidenced by its successful application in Vision Transformers (ViT), Large Language Models (LLMs), Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D shape modelling.
低秩分解作为提高神经网络架构参数效率的重要工具,在机器学习各种应用中受到广泛关注。这些技术大大降低了参数数量,在紧凑性和性能之间取得了平衡。然而,参数效率和模型精度之间的权衡是一个常见的挑战,减少的参数往往会导致与全秩模型相比精度下降。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的理论框架,该框架将正弦函数整合到低秩分解过程中。这种方法不仅保留了低秩方法参数效率的优点,还提高了分解的秩,从而增强了模型性能。我们的方法被证明是对现有低秩模型的增强插件,其在视觉转换器(ViT)、大型语言模型(LLM)、神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D形状建模中的应用都取得了成功。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally. Paper accepted at ICLR 2025
Summary
低秩分解在提升神经网络架构的参数效率方面表现出关键作用,广泛应用于机器学习中的多个领域。然而,参数效率与模型准确性的权衡成为一大挑战。本研究提出了一种新型理论框架,该框架将正弦函数融入低秩分解过程中,既保留了低秩方法的参数效率优势,又提升了模型的性能表现。此方法可应用于现有的低秩模型,成功应用于图像转换器(ViT)、大型语言模型(LLMs)、神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维建模等领域。
Key Takeaways
- 低秩分解在神经网络架构中扮演重要角色,有助于提升参数效率。
- 参数效率与模型准确性之间存在权衡挑战。
- 研究提出的新型理论框架结合了正弦函数,在低秩分解中提升了模型的性能。
- 该方法提高了分解的秩数,保留了低秩方法的参数效率优势。
- 方法可应用于多种领域,包括图像转换器(ViT)、大型语言模型(LLMs)、神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维建模等。
- 此方法可以作为现有低秩模型的插件增强功能。
点此查看论文截图