⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
Pathological MRI Segmentation by Synthetic Pathological Data Generation in Fetuses and Neonates
Authors:Misha P. T Kaandorp, Damola Agbelese, Hosna Asma-ull, Hyun-Gi Kim, Kelly Payette, Patrice Grehten, Gennari Antonio Giulio, Levente István Lánczi, Andras Jakab
Developing new methods for the automated analysis of clinical fetal and neonatal MRI data is limited by the scarcity of annotated pathological datasets and privacy concerns that often restrict data sharing, hindering the effectiveness of deep learning models. We address this in two ways. First, we introduce Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM, a novel diffusion model framework designed to generate high-quality synthetic pathological fetal and neonatal MRIs from semantic label images. Second, we enhance training data by modifying healthy label images through morphological alterations to simulate conditions such as ventriculomegaly, cerebellar and pontocerebellar hypoplasia, and microcephaly. By leveraging Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM, we synthesize realistic pathological MRIs from these modified pathological label images. Radiologists rated the synthetic MRIs as significantly (p < 0.05) superior in quality and diagnostic value compared to real MRIs, demonstrating features such as blood vessels and choroid plexus, and improved alignment with label annotations. Synthetic pathological data enhanced state-of-the-art nnUNet segmentation performance, particularly for severe ventriculomegaly cases, with the greatest improvements achieved in ventricle segmentation (Dice scores: 0.9253 vs. 0.7317). This study underscores the potential of generative AI as transformative tool for data augmentation, offering improved segmentation performance in pathological cases. This development represents a significant step towards improving analysis and segmentation accuracy in prenatal imaging, and also offers new ways for data anonymization through the generation of pathologic image data.
针对临床胎儿和新生儿MRI数据的自动化分析新方法的开发受限于标注病理数据集的稀缺性以及隐私担忧,这经常限制数据共享,阻碍了深度学习模型的有效性。我们通过两种方式来解决这个问题。首先,我们引入了Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM,这是一种新型扩散模型框架,旨在从语义标签图像中生成高质量合成病理胎儿和新生儿MRIs。其次,我们通过形态学改变来修改健康标签图像,以模拟诸如脑积水、小脑和桥小脑发育不良以及小头畸形等状况,增强训练数据。我们利用Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM从这些修改后的病理标签图像中合成逼真的病理性MRI。放射科医生评估认为,合成的MRI在质量和诊断价值上显著优于真实的MRI(p < 0.05),显示出血管和脉络丛等特征,与标签注释的吻合度更高。合成病理数据增强了最先进的前端分割性能,特别是在严重的脑积水病例中,在脑室分割方面取得了最大的改进(Dice得分:0.9253对比0.7317)。该研究突出了生成人工智能作为数据增强工具所具备的潜力,为病例分割性能带来了改进。这一发展代表了产前成像分析和分割准确性的一大进步,并且通过病理性图像数据的生成提供了新的数据匿名化方式。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables
摘要
针对临床胎儿和新生儿MRI数据的自动化分析新方法受限于标注病理数据集的稀缺性和隐私担忧,阻碍了深度学习模型的有效性。本研究通过两个方面解决这一问题。首先,我们引入Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM新型扩散模型框架,该框架能从语义标签图像生成高质量合成病理胎儿和新生儿MRI。其次,我们通过形态学改变健康标签图像来模拟诸如脑积水、小脑和脑桥小脑发育不良和小头畸形等状况,以增强训练数据。利用Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM模型从这些经过修改的病标签图像中合成现实病理MRI。医生评价合成的MRI在质量和诊断价值上显著优于真实MRI(p < 0.05),能呈现血管、脉络丛等特征,与标签注释对齐。合成病理数据提高了最先进分割网络nnUNet的性能,特别是在严重脑积水病例中,脑室分割的Dice得分从0.7317提高到0.9253。本研究突显生成人工智能作为数据扩充工具的潜力,在提高病理情况下的分割性能方面表现优异。这一进展对提高产前成像的分析和分割精度具有重要意义,并提供了通过生成病理图像数据进行匿名化的新方法。
关键见解
- 临床胎儿和新生儿MRI数据自动化分析受限于标注病理数据稀缺和隐私担忧的问题。
- 引入Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM扩散模型框架,可从语义标签图像生成高质量合成病理MRI。
- 通过形态学改变健康标签图像模拟病理状况,增强训练数据。
- 合成的MRI在质量和诊断价值上优于真实MRI,具有血管、脉络丛等特征。
- 合成病理数据提高了nnUNet分割性能,尤其在脑室分割方面表现显著。
- 生成人工智能在数据扩充方面展现潜力,有助于提高病理情况的分割性能。
点此查看论文截图

Strong geometry dependence of the X-ray Thomson Scattering Spectrum in single crystal silicon
Authors:Thomas Gawne, Zhandos A. Moldabekov, Oliver S. Humphries, Karen Appel, Carsten Baehtz, Victorien Bouffetier, Erik Brambrink, Attila Cangi, Celine Crépisson, Sebastian Göde, Zuzana Konôpková, Mikako Makita, Mikhail Mishchenko, Motoaki Nakatsutsumi, Lisa Randolph, Sebastian Schwalbe, Jan Vorberger, Ulf Zastrau, Tobias Dornheim, Thomas R. Preston
We report on results from an experiment at the European XFEL where we measured the x-ray Thomson scattering (XRTS) spectrum of single crystal silicon with ultrahigh resolution. Compared to similar previous experiments, we consider a more complex scattering setup, in which the scattering vector changes orientation through the crystal lattice. In doing so, we are able to observe strong geometric dependencies in the inelastic scattering spectrum of silicon at low scattering angles. Furthermore, the high quality of the experimental data allows us to benchmark state-of-the-art TDDFT calculations, and demonstrate TDDFT’s ability to accurately predict these geometric dependencies. Finally, we note that this experimental data was collected at a much faster rate than another recently reported dataset using the same setup, demonstrating that ultrahigh resolution XRTS data can be collected in more general experimental scenarios.
我们报告了在欧洲XFEL进行的一项实验的结果,在该实验中,我们以超高的分辨率测量了单晶硅的X射线汤姆森散射(XRTS)光谱。与之前类似的实验相比,我们考虑了一个更复杂的散射设置,其中散射矢量通过晶格改变方向。通过这样做,我们能够观察到在较小的散射角度下硅的非弹性散射光谱中强烈的几何依赖性。此外,实验数据的高质量使我们能够评估最先进的TDDFT计算,并证明TDDFT能够准确预测这些几何依赖性。最后,我们注意到此实验数据是在比最近使用相同设置报道的另一数据集更快的速率下收集的,这表明在更一般的实验场景中也可以收集超高分辨率的XRTS数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文报道了在欧洲XFEL实验室进行的实验,测量了单晶硅的X射线汤姆森散射(XRTS)光谱,具有超高的分辨率。实验采用更复杂的散射装置,观察到硅在较低散射角下的强几何依赖性。高质量的实验数据验证了TDDFT计算的可靠性,并展示了其预测几何依赖性的能力。此外,实验数据收集速度比使用相同设置的最近报道的数据集更快,表明在更一般的实验场景中也可以收集到超高分辨率的XRTS数据。
Key Takeaways
- 报道了使用超高分辨率测量单晶硅X射线汤姆森散射光谱的实验结果。
- 采用更复杂的散射装置,观察到硅在较低散射角下的强几何依赖性。
- 高质量的实验数据验证了TDDFT计算的准确性。
- TDDFT能够准确预测几何依赖性。
- 实验数据收集速度比先前报道的数据更快。
- 表明在更一般的实验场景中也可以收集到超高分辨率的XRTS数据。
点此查看论文截图

Medical Semantic Segmentation with Diffusion Pretrain
Authors:David Li, Anvar Kurmukov, Mikhail Goncharov, Roman Sokolov, Mikhail Belyaev
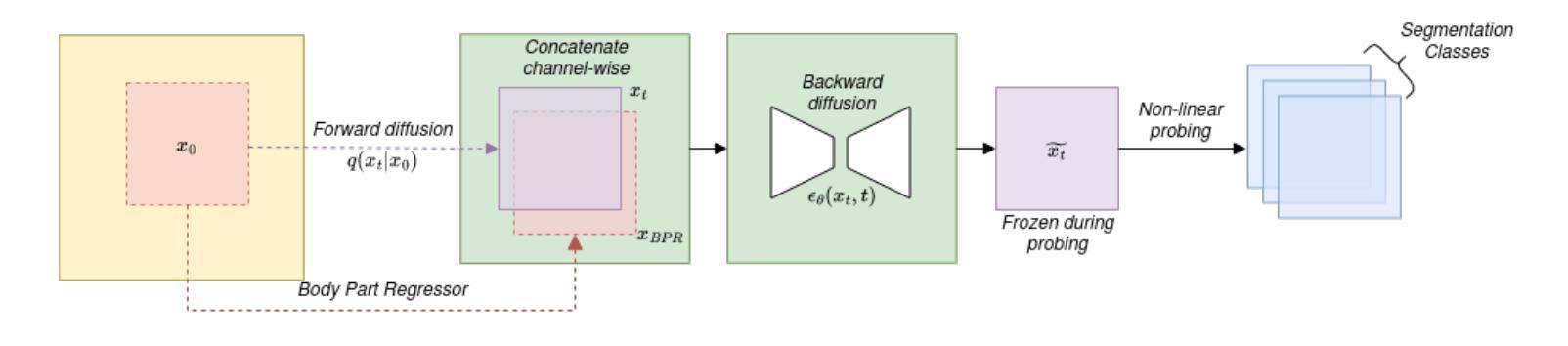
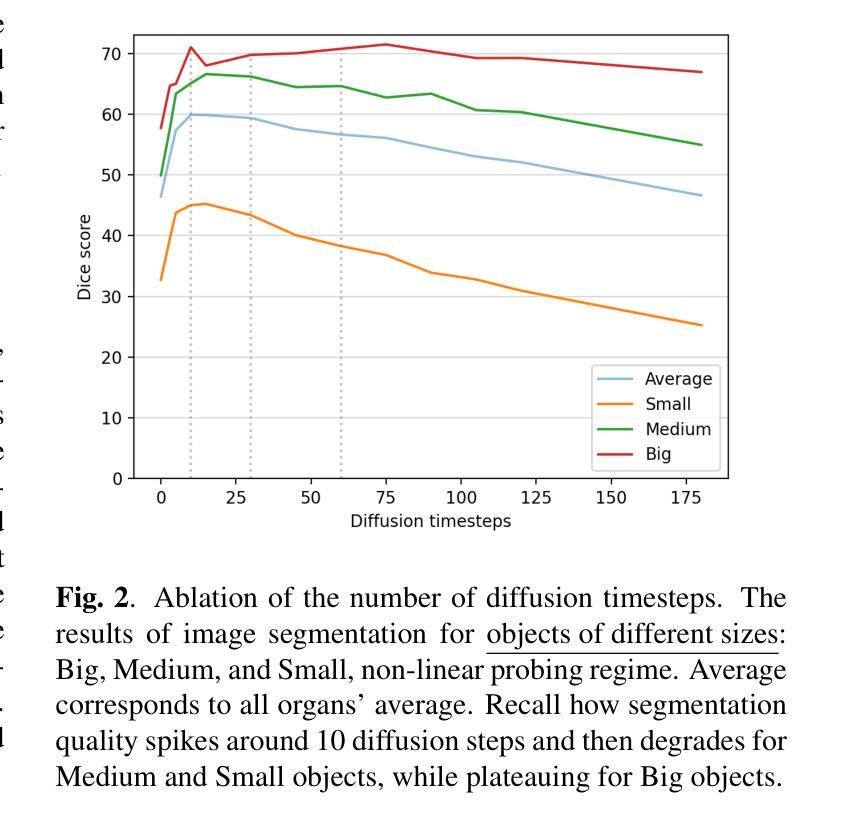
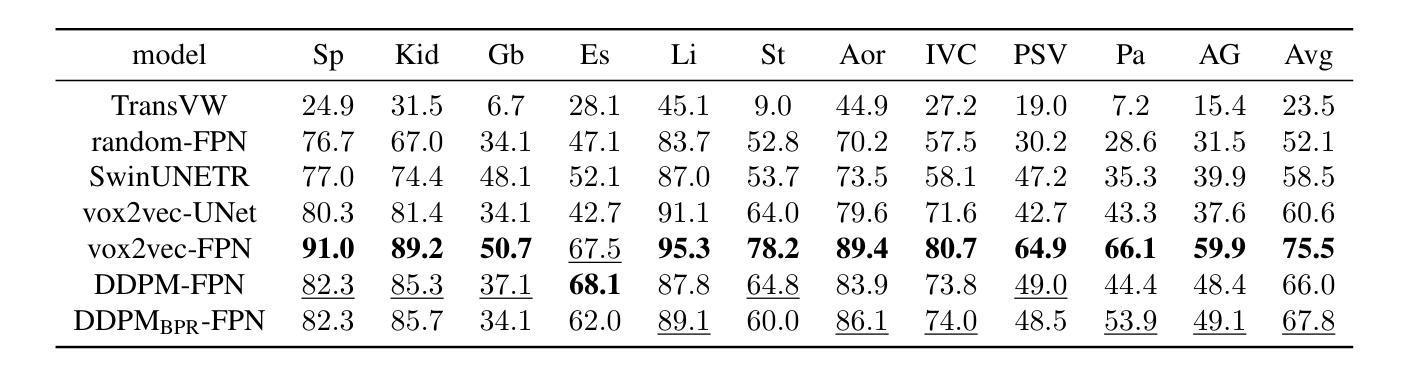
Recent advances in deep learning have shown that learning robust feature representations is critical for the success of many computer vision tasks, including medical image segmentation. In particular, both transformer and convolutional-based architectures have benefit from leveraging pretext tasks for pretraining. However, the adoption of pretext tasks in 3D medical imaging has been less explored and remains a challenge, especially in the context of learning generalizable feature representations. We propose a novel pretraining strategy using diffusion models with anatomical guidance, tailored to the intricacies of 3D medical image data. We introduce an auxiliary diffusion process to pretrain a model that produce generalizable feature representations, useful for a variety of downstream segmentation tasks. We employ an additional model that predicts 3D universal body-part coordinates, providing guidance during the diffusion process and improving spatial awareness in generated representations. This approach not only aids in resolving localization inaccuracies but also enriches the model’s ability to understand complex anatomical structures. Empirical validation on a 13-class organ segmentation task demonstrate the effectiveness of our pretraining technique. It surpasses existing restorative pretraining methods in 3D medical image segmentation by $7.5%$, and is competitive with the state-of-the-art contrastive pretraining approach, achieving an average Dice coefficient of 67.8 in a non-linear evaluation scenario.
最近深度学习的发展表明,学习鲁棒的特征表示对包括医学图像分割在内的许多计算机视觉任务的成功至关重要。特别是,基于transformer和卷积的架构都受益于利用预文本任务进行预训练。然而,在3D医学影像中采用预文本任务的研究相对较少,仍然是一个挑战,特别是在学习可泛化的特征表示方面。我们提出了一种使用扩散模型的新预训练策略,该策略具有解剖导向,针对3D医学图像数据的复杂性进行了定制。我们引入了一个辅助扩散过程来预训练一个模型,该模型能够产生可泛化的特征表示,对于各种下游分割任务都很有用。我们采用了另一个预测3D通用身体部位坐标的模型,在扩散过程中提供指导,提高了生成表示中的空间感知能力。这种方法不仅有助于解决定位不准确的问题,还丰富了模型理解复杂解剖结构的能力。在13类器官分割任务上的经验验证表明我们的预训练技术非常有效。与现有的3D医学图像分割的修复预训练方法相比,我们的方法提高了7.5%,并与最先进的对比预训练方法具有竞争力,在非线性评价场景中达到了平均Dice系数为67.8。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的新型预训练策略,结合解剖学指导,用于处理复杂的3D医学图像数据。通过引入辅助扩散过程和预测3D通用身体部位坐标的附加模型,提高模型的通用特征表示能力,有助于解决下游分割任务中的定位不准确问题,并增强对复杂解剖结构的理解能力。在13类器官分割任务上的实证验证显示,该预训练技术优于现有的恢复性预训练方法,在非线性评价场景中平均Dice系数为67.8,具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割等计算机视觉任务中的成功关键在于学习鲁棒的特征表示。
- 变种和卷积神经网络架构都受益于利用预文本任务进行预训练。
- 3D医学成像中的预文本任务采用较少,学习通用特征表示具有挑战性。
- 提出一种新型的基于扩散模型的预训练策略,结合解剖学指导,针对3D医学图像数据的特性。
- 引入辅助扩散过程以产生通用的特征表示,有助于多种下游分割任务。
- 通过预测3D通用身体部位坐标的附加模型,提高模型的空间感知能力,解决定位不准确的问题。
点此查看论文截图

Analysis of the sensitivity of tumor control probability in molecular radiotherapy to uncertainties in the dose rate curves
Authors:Pedro Otero-Casal, Aldán Baliño, Sara Neira, Faustino Gómez, Juan Pardo-Montero
In this work, we have investigated the sensitivity of the effectiveness (TCP) of molecular radiotherapy (MRT) treatment to uncertainties of the dose rate curves that may appear when reconstructing those curves. We generated different dose rate curves from experimental data, imposing the constraint of equal dose for each of them. Then, we computed TCPs and looked for correlations between metrics measuring the differences between the dose rate curves and differences in TCP. Finally, according to these results, we estimated the range of tolerable uncertainties in the dose rate curves. The study was performed for different radiopharmaceuticals and different radiosensitive parameters that can affect the dose rate response ($\alpha/\beta$, sub-lethal repair rate). The best correlation between differences in the dose rate curves and TCP was found for a metric that computes averaged linear differences between the curves. With this metric, we quantified differences in dose rate curves that would lead to differences in TCP of 0.02, a parameter denoted $m_{1,: 0.02}$ that is a surrogate of the dependence of the TCP on the dose rate profile. The results showed that the sensitivity of the TCP to dose rate variations decreases (i.e. larger values of $m_{1,: 0.02}$) with increasing $\alpha/\beta$ and sub-lethal damage repair rate of the tumor cells, and increasing biological half-life of the dose rate curves. The radiobiological effect of a MRT treatment on a tumor depends on the absorbed dose and the dose rate profile. Ideally, both magnitudes should be measured with accuracy in order to progress towards the optimization of individualized MRT treatments. Our study suggests that this would be more important for tumors with low $\alpha/\beta$ and moderately slow sub-lethal damage repair treated with fast-decaying radiopharmaceuticals.
在这项工作中,我们研究了分子放射治疗(MRT)治疗的效果(TCP)对不精确重建剂量率曲线时可能出现的不确定性的敏感度。我们从实验数据中生成了不同的剂量率曲线,并施加相等的剂量限制。然后,我们计算TCP,并寻找剂量率曲线差异测量指标与TCP差异之间的相关性。最后,根据这些结果,我们估计了剂量率曲线中可容忍的不确定性范围。该研究的对象为影响剂量率响应的不同放射药物和不同辐射敏感参数($\alpha/\beta$,亚致死修复率)。在剂量率曲线与TCP之间的差异之间,找到的最佳相关性是一个计算曲线之间平均线性差异的指标。使用该指标,我们量化了导致TCP差异为0.02的剂量率曲线的差异,该参数表示为$m_{1,: 0.02}$,作为TCP对剂量率分布的依赖性的替代物。结果表明,TCP对剂量率变化的敏感性随着$\alpha/\beta$的增加、肿瘤细胞亚致死性损伤修复速率的增加以及剂量率曲线的生物半衰期的延长而降低。分子放射治疗对肿瘤的生物效应取决于吸收剂量和剂量率分布。理想情况下,应准确测量这两个参数,以实现个体化MRT治疗的优化。我们的研究提示,对于具有低$\alpha/\beta$和中等缓慢亚致死损伤修复且使用快速衰变放射药物的肿瘤,这一点更为重要。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究探讨了分子放射治疗(MRT)的治疗效果(TCP)对剂量率曲线重构时可能出现的不确定性敏感度。通过生成不同的剂量率曲线并计算TCP,研究不同剂量率曲线之间的差异与TCP差异之间的相关性,进而估算剂量率曲线可容忍的不确定性范围。研究针对多种放射性药物和不同辐射敏感参数(如α/β比率、亚致死修复速率)进行。最佳相关性出现在一个计算曲线之间平均线性差异的指标上。利用这一指标,我们量化了导致TCP差异0.02的剂量率曲线差异,一个参数标记为m1,0.02,作为TCP对剂量率曲线的依赖性的替代指标。结果表明,TCP对剂量率变化的敏感性随着α/β比率的增加、肿瘤细胞亚致死性损伤修复速率的增加以及剂量率曲线的生物半衰期的增加而降低。分子放射治疗对肿瘤的生物效应取决于吸收剂量和剂量率分布。为了优化个体化MRT治疗,应准确测量两者。本研究提示,对于具有低α/β比率和中等缓慢亚致死性损伤的肿瘤,使用快速衰变的放射性药物时更应重视准确测量。
关键见解
- 研究了分子放射治疗(MRT)治疗效果(TCP)对剂量率曲线不确定性的敏感度。
- 通过不同指标评估了剂量率曲线之间的差异,并与TCP变化进行了关联。
- 发现一个计算曲线间平均线性差异的指标与TCP变化最佳相关。
- 定义了m1,0.02参数,作为TCP对剂量率曲线依赖性的替代指标。
- TCP对剂量率变化的敏感性随α/β比率、肿瘤细胞亚致死修复速率及剂量率曲线生物半衰期的变化而变化。
- MRT治疗肿瘤的生物效应涉及吸收剂量和剂量率分布,二者都应准确测量以优化个体化治疗。
点此查看论文截图

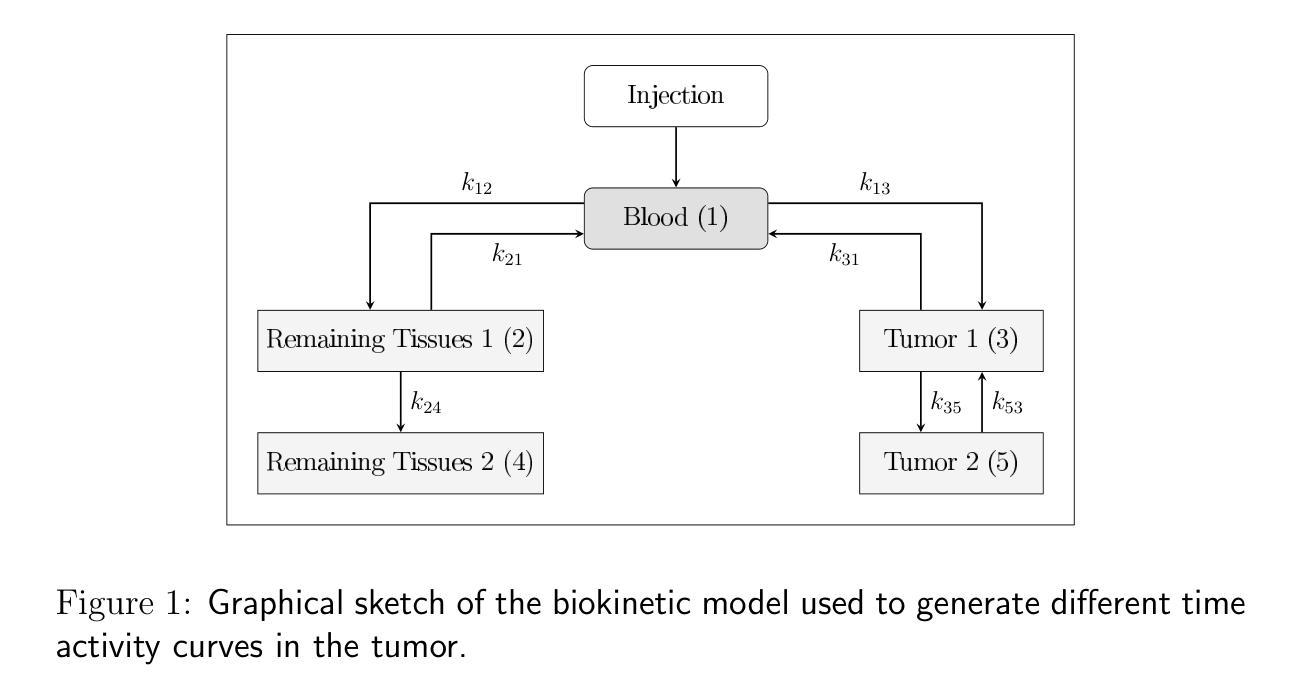
Ambient Denoising Diffusion Generative Adversarial Networks for Establishing Stochastic Object Models from Noisy Image Data
Authors:Xichen Xu, Wentao Chen, Weimin Zhou
It is widely accepted that medical imaging systems should be objectively assessed via task-based image quality (IQ) measures that ideally account for all sources of randomness in the measured image data, including the variation in the ensemble of objects to be imaged. Stochastic object models (SOMs) that can randomly draw samples from the object distribution can be employed to characterize object variability. To establish realistic SOMs for task-based IQ analysis, it is desirable to employ experimental image data. However, experimental image data acquired from medical imaging systems are subject to measurement noise. Previous work investigated the ability of deep generative models (DGMs) that employ an augmented generative adversarial network (GAN), AmbientGAN, for establishing SOMs from noisy measured image data. Recently, denoising diffusion models (DDMs) have emerged as a leading DGM for image synthesis and can produce superior image quality than GANs. However, original DDMs possess a slow image-generation process because of the Gaussian assumption in the denoising steps. More recently, denoising diffusion GAN (DDGAN) was proposed to permit fast image generation while maintain high generated image quality that is comparable to the original DDMs. In this work, we propose an augmented DDGAN architecture, Ambient DDGAN (ADDGAN), for learning SOMs from noisy image data. Numerical studies that consider clinical computed tomography (CT) images and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) images are conducted. The ability of the proposed ADDGAN to learn realistic SOMs from noisy image data is demonstrated. It has been shown that the ADDGAN significantly outperforms the advanced AmbientGAN models for synthesizing high resolution medical images with complex textures.
普遍认为,医疗成像系统应通过基于任务的图像质量(IQ)措施进行客观评估,这些措施理想情况下应考虑到测量图像数据中所有随机性的来源,包括待成像对象集合的变异。能够从对象分布中随机抽取样本的随机对象模型(SOMs)可用于表征对象变异性。为了为基于任务的IQ分析建立现实的SOMs,使用实验图像数据是理想的。然而,从医疗成像系统获得的实验图像数据受到测量噪声的影响。早期的研究调查了深度生成模型(DGMs)使用增强生成对抗网络(GAN)即AmbientGAN从噪声测量图像数据中建立SOMs的能力。最近,降噪扩散模型(DDMs)作为领先的DGM图像合成技术已经出现,并能产生比GAN更高的图像质量。然而,原始DDMs由于降噪步骤中的高斯假设而具有较慢的图像生成过程。最近,提出了降噪扩散GAN(DDGAN)以实现快速图像生成并保持与原始DDMs相当的高生成图像质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种增强的DDGAN架构,即Ambient DDGAN(ADDGAN),用于从噪声图像数据中学习SOMs。考虑了临床计算机断层扫描(CT)图像和数字乳腺断层合成(DBT)图像的数值研究已经开展。已经证明了所提出的ADDGAN从噪声图像数据中学习现实SOMs的能力。研究表明,在处理具有复杂纹理的高分辨率医学图像合成时,ADDGAN显著优于先进的AmbientGAN模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SPIE Medical Imaging 2025
摘要
基于任务质量的医学成像系统评估应考虑到图像数据中的所有随机性来源,包括成像对象集合的变异性。本文提出了使用增强型DDGAN架构(Ambient DDGAN,简称ADDGAN)从含噪图像数据中学习随机对象模型(SOMs)的方法。通过对临床计算机断层扫描(CT)和数字化乳腺断层合成(DBT)图像的研究,展示了ADDGAN从含噪图像数据中学习现实SOMs的能力。结果表明,ADDGAN在合成具有复杂纹理的高分辨率医学图像方面显著优于先进的AmbientGAN模型。
关键见解
- 医学成像系统的评估应使用任务基础的图像质量(IQ)度量,该度量应考虑到图像数据中的所有随机性来源。
- 随机对象模型(SOMs)可用于表征对象变异性,可从对象分布中随机抽样。
- 使用实验图像数据建立现实的SOMs对于任务基础的IQ分析至关重要。
- 由于测量噪声的影响,从医学成像系统获得的实验图像数据可能不准确。
- 深度生成模型(DGM),特别是使用增强型生成对抗网络(GAN)的AmbientGAN,已被用于从含噪测量图像数据中建立SOMs。
- 最近的数值研究表明,对于合成具有复杂纹理的高分辨率医学图像,ADDGAN显著优于原始的AmbientGAN模型。
点此查看论文截图

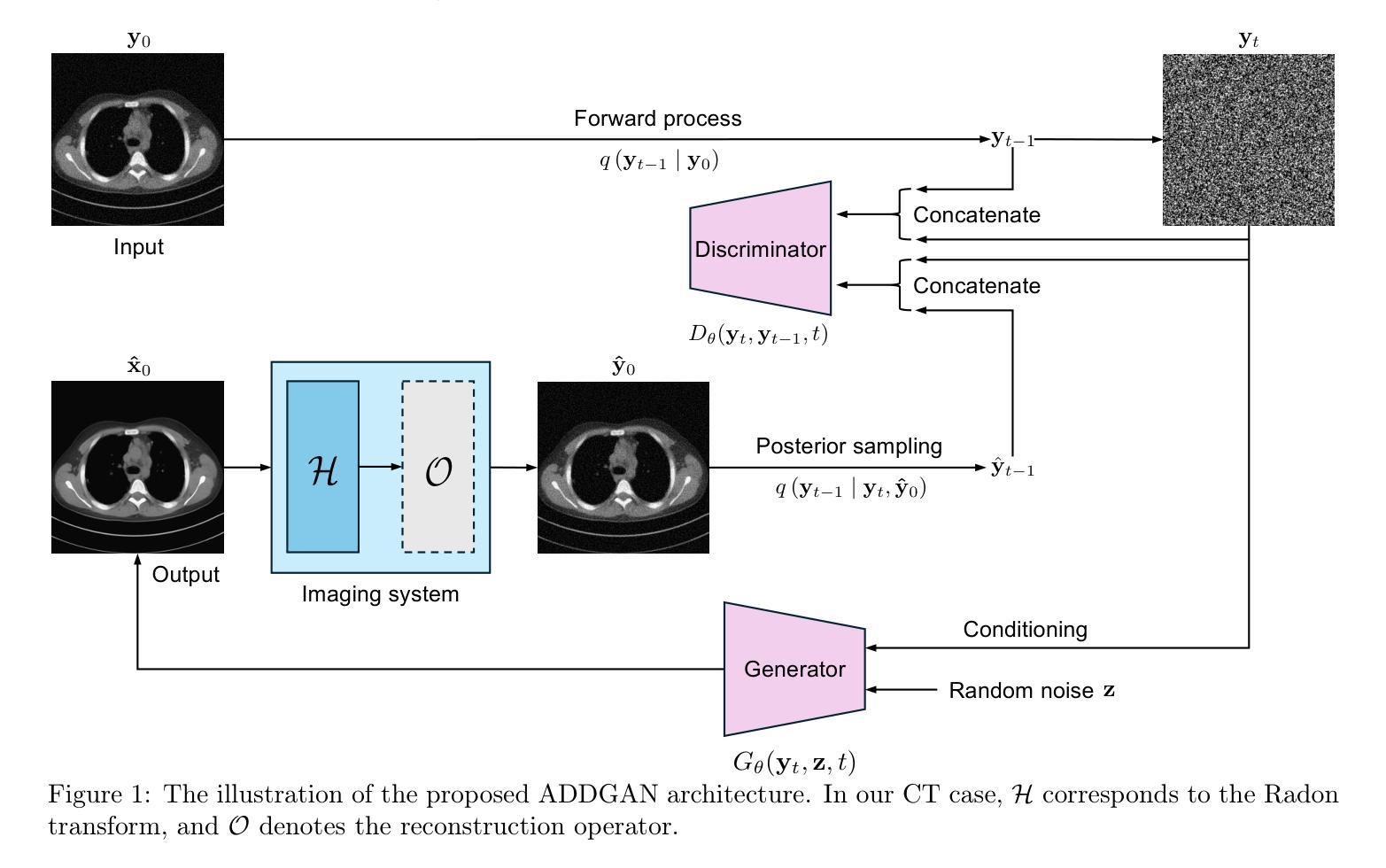

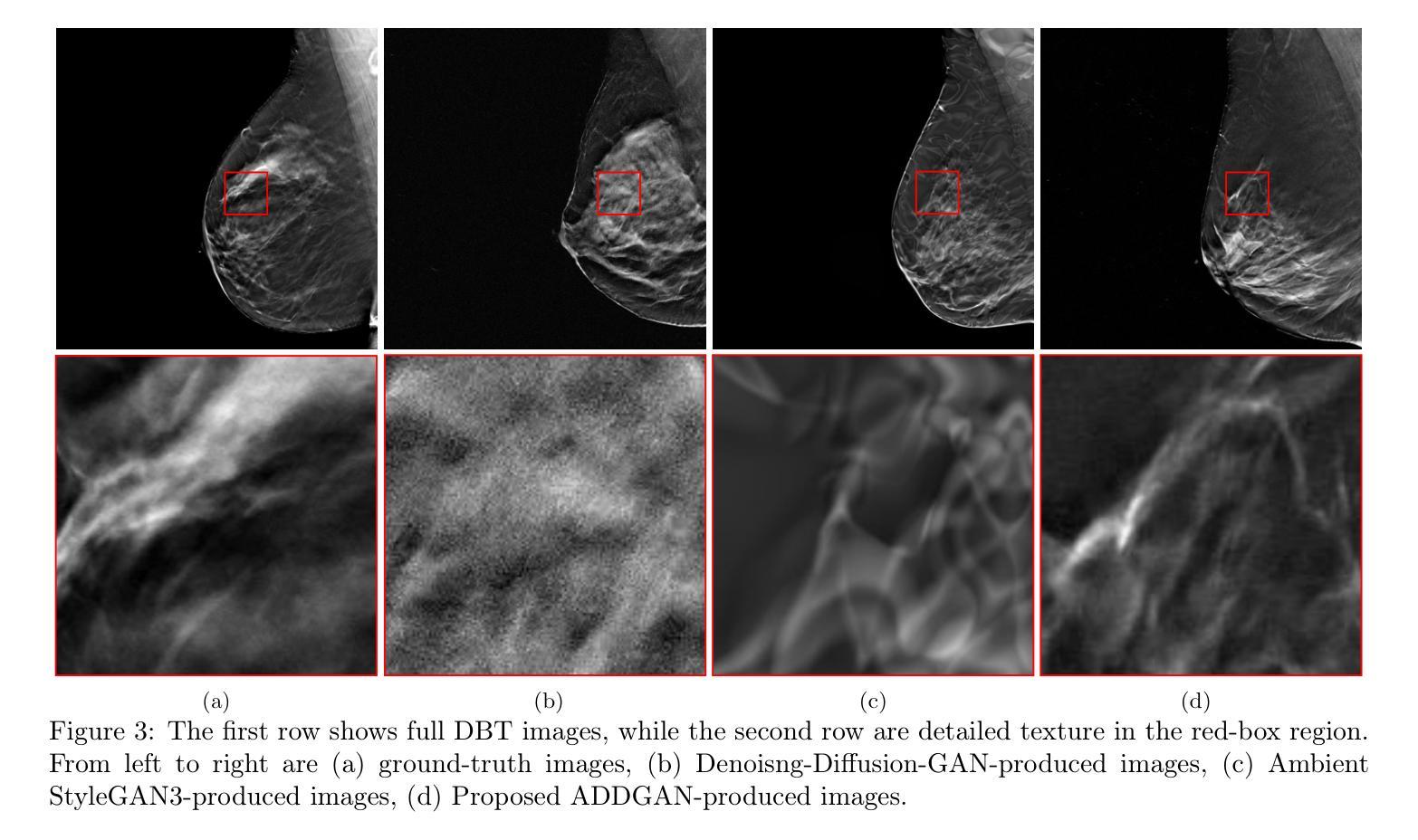
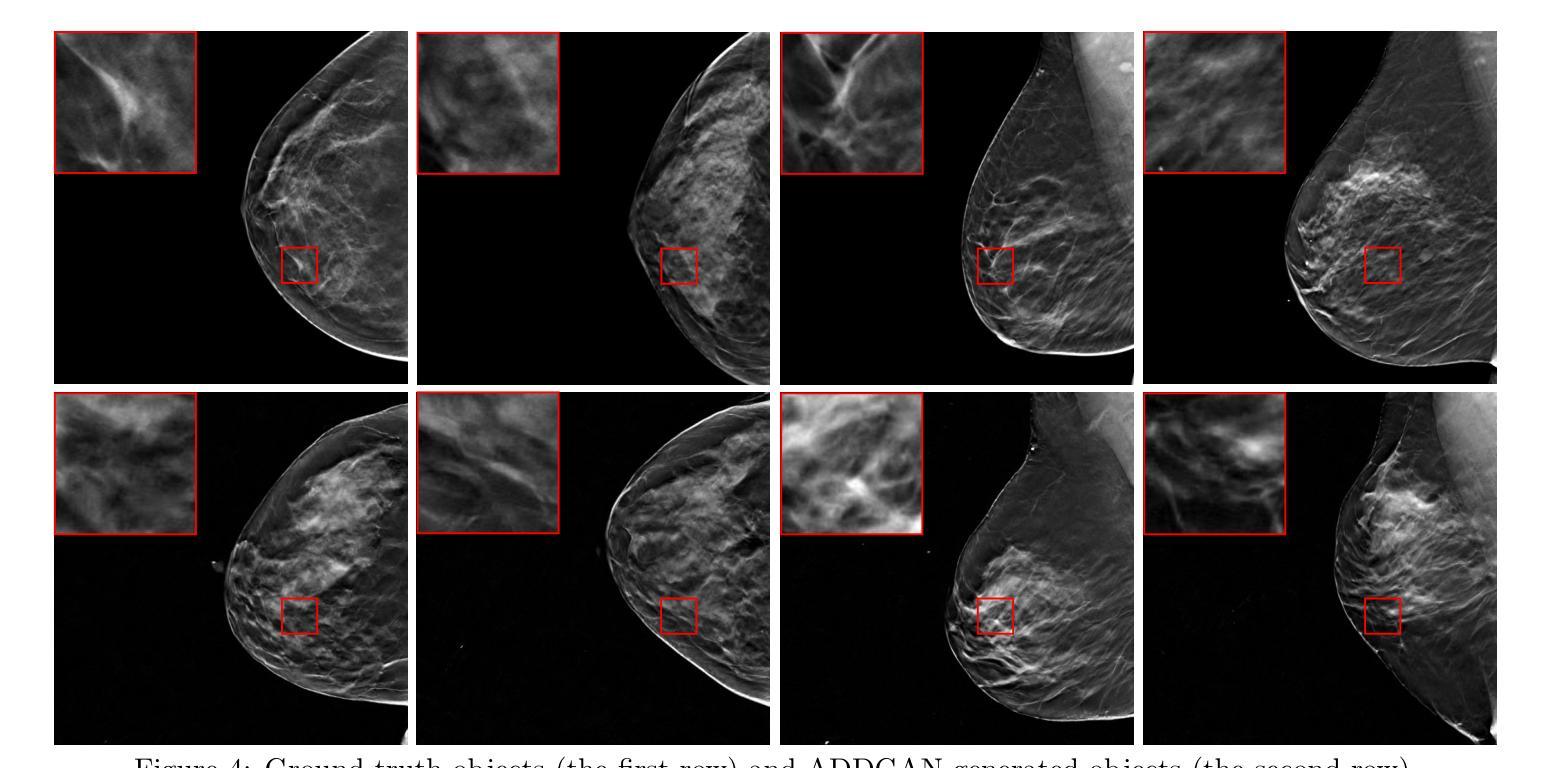


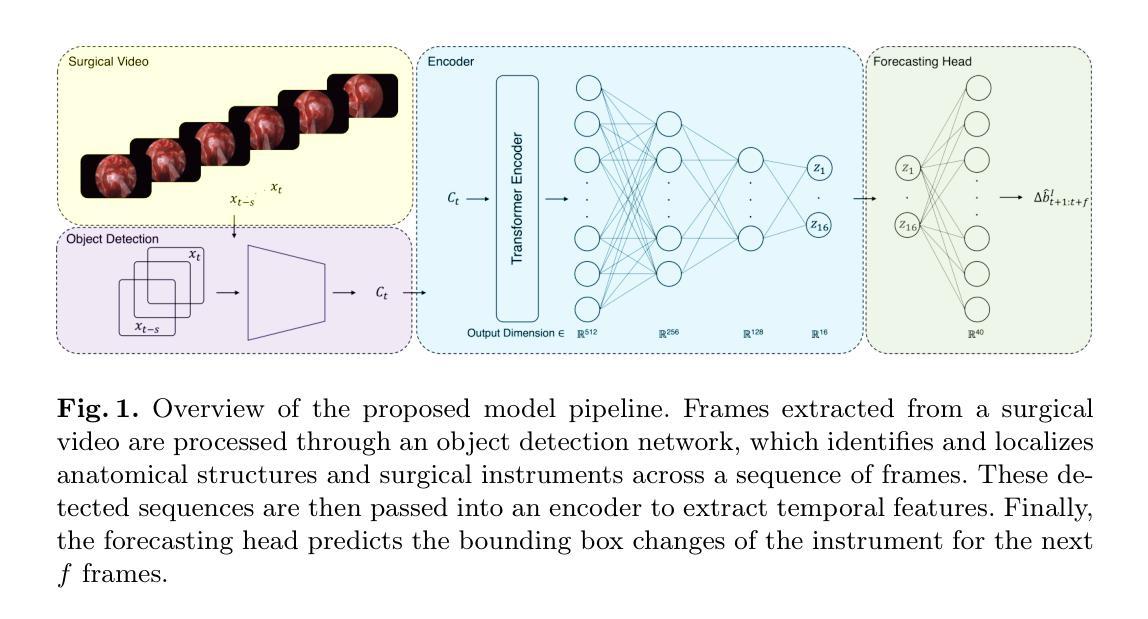
Anatomy Might Be All You Need: Forecasting What to Do During Surgery
Authors:Gary Sarwin, Alessandro Carretta, Victor Staartjes, Matteo Zoli, Diego Mazzatenta, Luca Regli, Carlo Serra, Ender Konukoglu
Surgical guidance can be delivered in various ways. In neurosurgery, spatial guidance and orientation are predominantly achieved through neuronavigation systems that reference pre-operative MRI scans. Recently, there has been growing interest in providing live guidance by analyzing video feeds from tools such as endoscopes. Existing approaches, including anatomy detection, orientation feedback, phase recognition, and visual question-answering, primarily focus on aiding surgeons in assessing the current surgical scene. This work aims to provide guidance on a finer scale, aiming to provide guidance by forecasting the trajectory of the surgical instrument, essentially addressing the question of what to do next. To address this task, we propose a model that not only leverages the historical locations of surgical instruments but also integrates anatomical features. Importantly, our work does not rely on explicit ground truth labels for instrument trajectories. Instead, the ground truth is generated by a detection model trained to detect both anatomical structures and instruments within surgical videos of a comprehensive dataset containing pituitary surgery videos. By analyzing the interaction between anatomy and instrument movements in these videos and forecasting future instrument movements, we show that anatomical features are a valuable asset in addressing this challenging task. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first attempt to address this task for manually operated surgeries.
手术指导可以通过多种方式实现。在神经外科中,空间指导和定位主要通过参考术前MRI扫描的神经导航系统来实现。最近,通过分析来自内窥镜等工具的视频流提供实时指导的兴趣日益浓厚。现有方法,包括解剖学检测、方向反馈、相位识别和视觉问答,主要侧重于帮助外科医生评估当前手术场景。这项工作旨在提供更精细的指导,目标是预测手术器械的轨迹,基本解决下一步该做什么的问题。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种模型,该模型不仅利用手术器械的历史位置,还整合了解剖特征。重要的是,我们的工作不依赖于仪器轨迹的明确真实标签。相反,真实值是由一个检测模型生成的,该模型经过训练,能够检测综合数据集中的垂体手术视频等手术视频中的解剖结构和器械。通过分析这些视频中解剖结构和器械运动的相互作用,并预测未来器械的运动,我们证明了解剖特征是解决这一具有挑战性的宝贵资产。据我们所知,这是首次尝试解决手动手术的这一任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了神经外科手术指导的新方法,该方法通过结合神经导航系统和内镜视频反馈,实现手术器械轨迹的预测,为医生提供精细化指导。新方法利用历史手术器械位置与解剖特征,无需明确的器械轨迹真实标签,通过检测模型自动生成真实轨迹。
Key Takeaways
- 神经外科手术指导方式多样,包括神经导航系统提供的空间指导和内镜视频反馈分析。
- 当前方法主要关注评估手术现场,而本文旨在提供更精细的指导,预测手术器械的轨迹。
- 所提模型利用历史手术器械位置和解剖特征,自动生成器械轨迹的真实标签。
- 本文工作不依赖明确的器械轨迹真实标签,降低了对标注数据的需求。
- 通过分析解剖结构和器械运动之间的相互作用,证明了解剖特征在预测器械轨迹中的价值。
- 本文是首次尝试为手动操作的手术提供此类指导。
- 此方法有望提高神经外科手术的精确性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

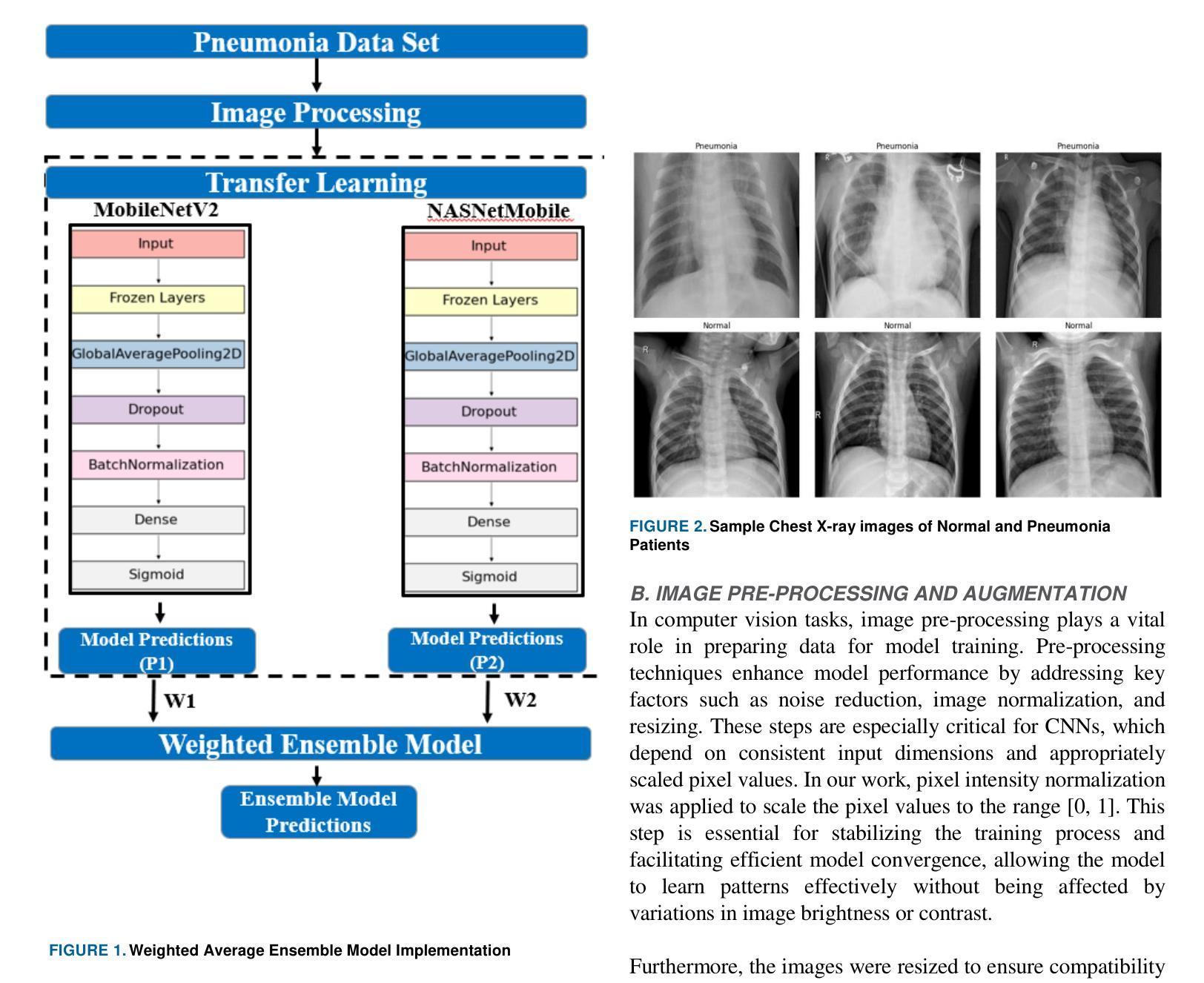
Lightweight Weighted Average Ensemble Model for Pneumonia Detection in Chest X-Ray Images
Authors:Suresh Babu Nettur, Shanthi Karpurapu, Unnati Nettur, Likhit Sagar Gajja, Sravanthy Myneni, Akhil Dusi, Lalithya Posham
Pneumonia is a leading cause of illness and death in children, underscoring the need for early and accurate detection. In this study, we propose a novel lightweight ensemble model for detecting pneumonia in children using chest X-ray images. This ensemble model integrates two pre-trained convolutional neural networks (CNNs), MobileNetV2 and NASNetMobile, selected for their balance of computational efficiency and accuracy. These models were fine-tuned on a pediatric chest X-ray dataset and combined to enhance classification performance. Our proposed ensemble model achieved a classification accuracy of 98.63%, significantly outperforming individual models such as MobileNetV2 (97.10%) and NASNetMobile(96.25%) in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. Moreover, the ensemble model outperformed state-of-the-art architectures, including ResNet50, InceptionV3, and DenseNet201, while maintaining computational efficiency. The proposed lightweight ensemble model presents a highly effective and resource-efficient solution for pneumonia detection, making it particularly suitable for deployment in resource-constrained settings.
肺炎是儿童疾病和死亡的主要原因之一,强调了对早期和准确检测的需求。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种新型的轻量级集成模型,用于利用胸部X射线图像检测儿童肺炎。该集成模型集成了两个经过预训练的卷积神经网络(CNN),即MobileNetV2和NASNetMobile,它们被选中是因为在计算效率和准确性之间达到了平衡。这些模型在一个儿童胸部X射线数据集上进行微调,并结合使用以提高分类性能。我们提出的集成模型达到了98.63%的分类准确率,在准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数方面显著优于单独的模型,如MobileNetV2(97.10%)和NASNetMobile(96.25%)。此外,该集成模型在保持计算效率的同时,还优于最新的架构,包括ResNet50、InceptionV3和DenseNet201。所提出的轻量级集成模型为肺炎检测提供了一种高效且资源利用率的解决方案,特别适用于资源受限的环境中进行部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Corresponding authors: Shanthi Karpurapu (shanthi.karpurapu@gmail.com), Suresh Babu Nettur (nettursuresh@gmail.com) Shanthi Karpurapu and Suresh Babu Nettur are co-first authors
Summary
本研究提出一种用于儿童肺炎检测的轻量级集成模型,该模型结合MobileNetV2和NASNetMobile两个预训练卷积神经网络,实现对儿童胸部X光图像的肺炎检测。集成模型在分类性能上取得了显著的提升,达到了98.63%的分类准确率,且在准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数上均优于单独使用MobileNetV2和NASNetMobile模型。同时,该集成模型在计算效率上超过了当前最先进的架构,如ResNet50、InceptionV3和DenseNet201,适用于资源受限环境下的部署。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一个轻量级的集成模型,用于儿童肺炎的检测。
- 集成模型结合了MobileNetV2和NASNetMobile两个预训练的卷积神经网络。
- 集成模型在儿科胸部X光图像数据集上进行微调,增强了分类性能。
- 该模型的分类准确率达到了98.63%,优于单独的MobileNetV2和NASNetMobile模型以及其他最先进的架构。
- 集成模型在准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数上均有优异表现。
- 该模型在计算效率上表现出色,适用于资源受限的环境。
点此查看论文截图

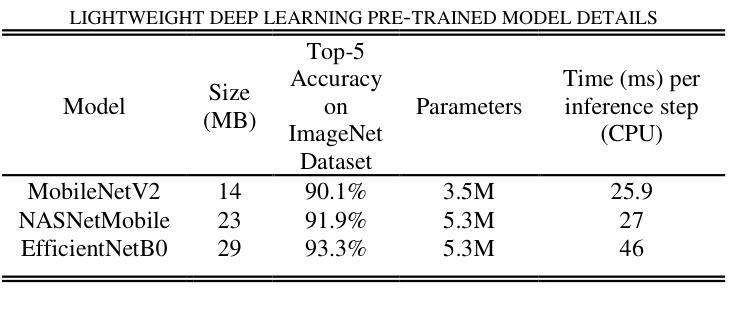
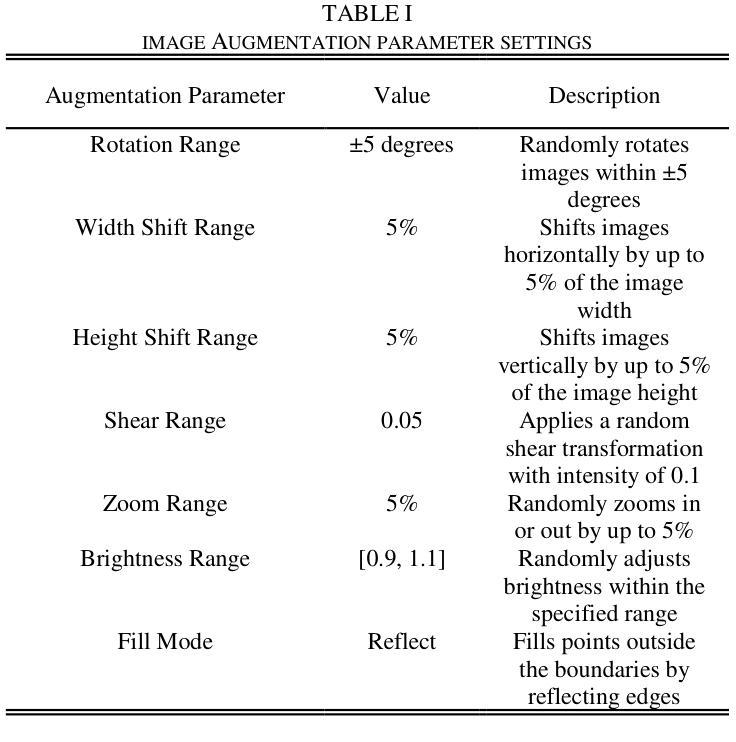
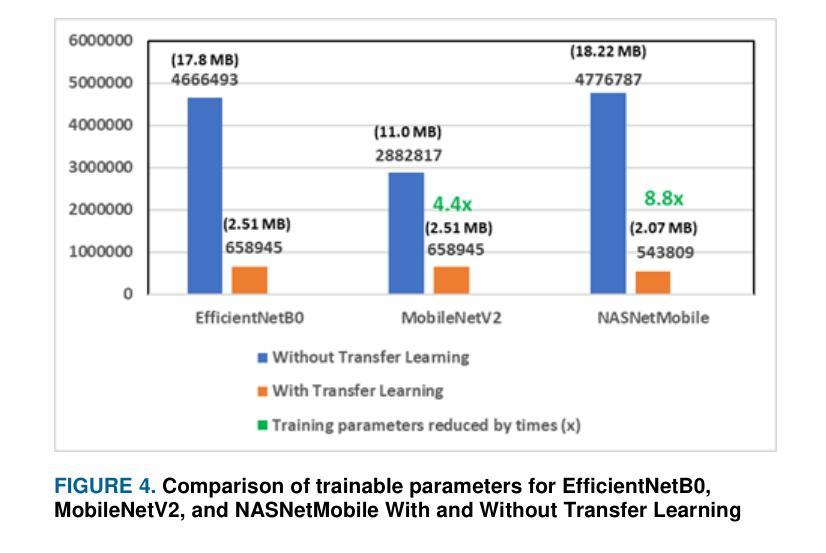
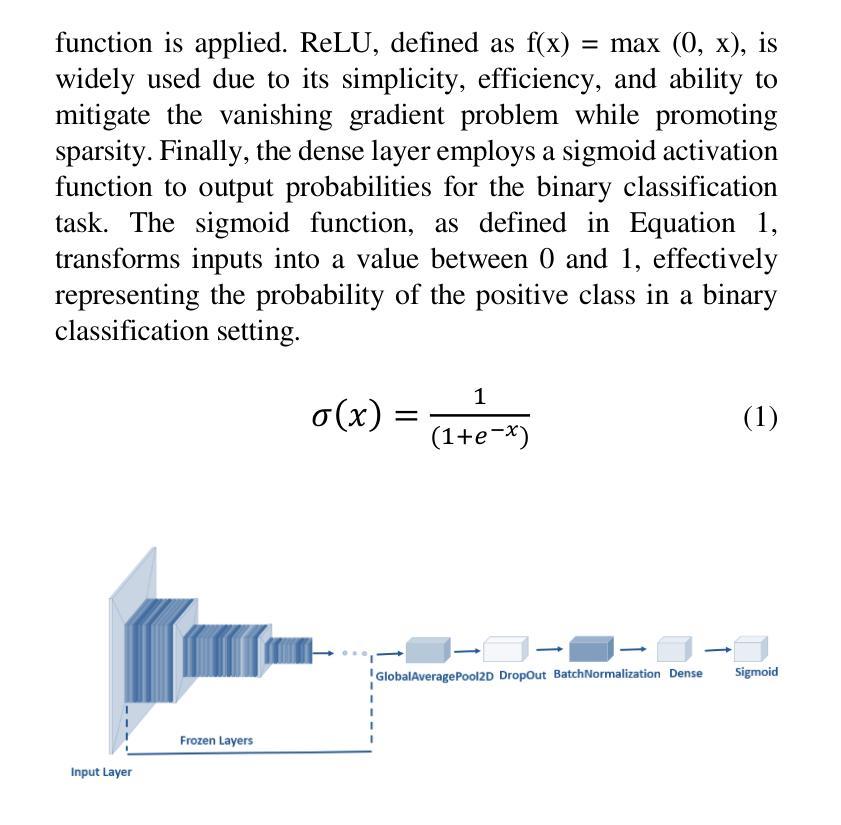
Advancing MRI Reconstruction: A Systematic Review of Deep Learning and Compressed Sensing Integration
Authors:Mojtaba Safari, Zach Eidex, Chih-Wei Chang, Richard L. J. Qiu, Xiaofeng Yang
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging modality and provides comprehensive anatomical and functional insights into the human body. However, its long acquisition times can lead to patient discomfort, motion artifacts, and limiting real-time applications. To address these challenges, strategies such as parallel imaging have been applied, which utilize multiple receiver coils to speed up the data acquisition process. Additionally, compressed sensing (CS) is a method that facilitates image reconstruction from sparse data, significantly reducing image acquisition time by minimizing the amount of data collection needed. Recently, deep learning (DL) has emerged as a powerful tool for improving MRI reconstruction. It has been integrated with parallel imaging and CS principles to achieve faster and more accurate MRI reconstructions. This review comprehensively examines DL-based techniques for MRI reconstruction. We categorize and discuss various DL-based methods, including end-to-end approaches, unrolled optimization, and federated learning, highlighting their potential benefits. Our systematic review highlights significant contributions and underscores the potential of DL in MRI reconstruction. Additionally, we summarize key results and trends in DL-based MRI reconstruction, including quantitative metrics, the dataset, acceleration factors, and the progress of and research interest in DL techniques over time. Finally, we discuss potential future directions and the importance of DL-based MRI reconstruction in advancing medical imaging. To facilitate further research in this area, we provide a GitHub repository that includes up-to-date DL-based MRI reconstruction publications and public datasets-https://github.com/mosaf/Awesome-DL-based-CS-MRI.
磁共振成像(MRI)是一种非侵入性的成像技术,能够提供人体全面的解剖和功能性信息。然而,其较长的采集时间可能导致患者不适、运动伪影,并限制了实时应用。为了解决这些挑战,已经应用了诸如并行成像等策略,其使用多个接收器线圈来加速数据采集过程。此外,压缩感知(CS)是一种方法,可以从稀疏数据中促进图像重建,通过最小化所需的数据收集量来显著减少图像采集时间。最近,深度学习(DL)已经成为改进MRI重建的强大工具。它已经与并行成像和CS原理相结合,实现了更快、更准确的MRI重建。本文全面审查了基于深度学习的MRI重建技术。我们分类并讨论了各种基于深度学习的方法,包括端到端方法、解开优化和联邦学习,突出了它们的潜在优势。我们的系统评价突出了重大贡献,并强调了深度学习在MRI重建中的潜力。此外,我们总结了基于深度学习的MRI重建的关键结果和趋势,包括定量指标、数据集、加速因子以及DL技术的进展和研究兴趣随时间的变化。最后,我们讨论了潜在的未来方向以及基于深度学习的MRI重建在推动医学成像方面的重要性。为了方便该领域的研究,我们提供了一个GitHub仓库,其中包括最新的基于深度学习的MRI重建出版物和公开数据集:https://github.com/mosaf/Awesome-DL-based-CS-MRI。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2405.00241
Summary
MRI技术在医学图像领域具有重要应用,但其数据采集时间长会导致患者不适和运动伪影等问题。为此,采用并行成像等策略加快数据采集过程。此外,压缩感知和深度学习等方法能够减少数据采集量,实现快速MRI重建。本文全面综述了基于深度学习的MRI重建技术,包括各种方法的特点和潜在优势。
Key Takeaways
- MRI是一种重要的非侵入性成像技术,但数据采集时间长会带来挑战。
- 并行成像利用多个接收器线圈可加快数据采集过程。
- 压缩感知方法可从稀疏数据中重建图像,减少数据采集量。
- 深度学习在MRI重建中展现出强大潜力,可与并行成像和压缩感知结合实现更快更准确的重建。
- 本文综述了基于深度学习的MRI重建的各种方法,包括端到端、滚动优化和联邦学习等。
- 文章总结了关键结果和趋势,包括定量指标、数据集、加速因子以及深度学习技术的进步和兴趣。
点此查看论文截图

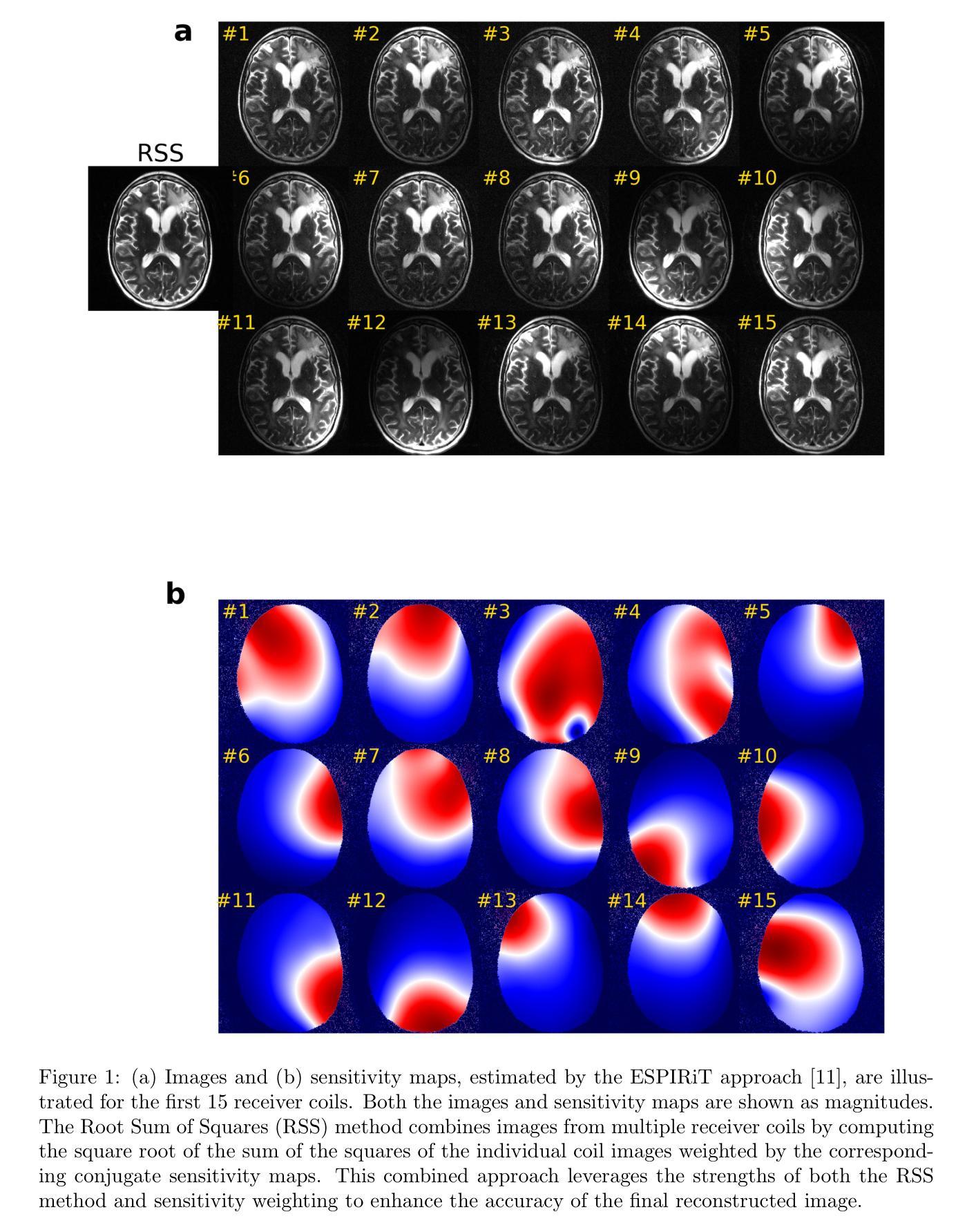
Regulating radiology AI medical devices that evolve in their lifecycle
Authors:Camila González, Moritz Fuchs, Daniel Pinto dos Santos, Philipp Matthies, Manuel Trenz, Maximilian Grüning, Akshay Chaudhari, David B. Larson, Ahmed Othman, Moon Kim, Felix Nensa, Anirban Mukhopadhyay
Over time, the distribution of medical image data drifts due to factors such as shifts in patient demographics, acquisition devices, and disease manifestations. While human radiologists can adjust their expertise to accommodate such variations, deep learning models cannot. In fact, such models are highly susceptible to even slight variations in image characteristics. Consequently, manufacturers must conduct regular updates to ensure that they remain safe and effective. Performing such updates in the United States and European Union required, until recently, obtaining re-approval. Given the time and financial burdens associated with these processes, updates were infrequent, and obsolete systems remained in operation for too long. During 2024, several regulatory developments promised to streamline the safe rollout of model updates: The European Artificial Intelligence Act came into effect last August, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued final marketing submission recommendations for a Predetermined Change Control Plan (PCCP) in December. We provide an overview of these developments and outline the key building blocks necessary for successfully deploying dynamic systems. At the heart of these regulations - and as prerequisites for manufacturers to conduct model updates without re-approval - are clear descriptions of data collection and re-training processes, coupled with robust real-world quality monitoring mechanisms.
随着时间的推移,由于患者人口统计、采集设备和疾病表现等因素的变化,医学图像数据的分布会发生漂移。虽然人类放射科医生可以调整他们的专业知识以适应这种变化,但深度学习模型却无法做到。事实上,这些模型对图像特征中的细微变化也非常敏感。因此,制造商必须进行定期更新,以确保其安全性和有效性。最近在美国和欧盟进行的此类更新,都需要重新获得批准。考虑到这些流程所带来的时间和财务负担,更新并不频繁,过时的系统运营时间过长。在2024年期间,多项监管发展有望简化模型更新的安全推出:去年八月,《欧洲人工智能法案》开始生效,十二月美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)针对预定的变更控制计划(PCCP)发布了最终营销提交建议。本文概述了这些发展动态,并概述了成功部署动态系统的关键构建块。这些法规的核心——以及制造商无需重新批准即可进行模型更新的先决条件——是对数据采集和再训练过程的清晰描述,以及强大的现实世界质量监测机制。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这段文本主要讨论了医学图像数据分布随时间的变化对深度学习模型的影响,强调了更新模型以确保其安全性和有效性的重要性。针对美国及欧盟的监管发展,提供了概述并指出了成功部署动态系统的关键构建要素,包括数据收集、再训练过程的清晰描述以及强大的现实世界质量监测机制。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像数据分布随时间变化,导致深度学习模型性能受到影响。
- 人类放射科医生可以适应这种变化,但深度学习模型无法做到。
- 制造商必须对深度学习模型进行定期更新以确保其安全性和有效性。
- 在美国及欧盟,更新模型需重新获得批准,这带来了时间和财务负担。
- 2024年期间,欧洲人工智能法案和FDA的预定变更控制计划最终营销提交建议为简化模型更新的安全推出提供了机会。
- 成功部署动态系统的关键要素包括清晰描述的数据收集、再训练过程和强大的现实世界质量监测机制。
点此查看论文截图

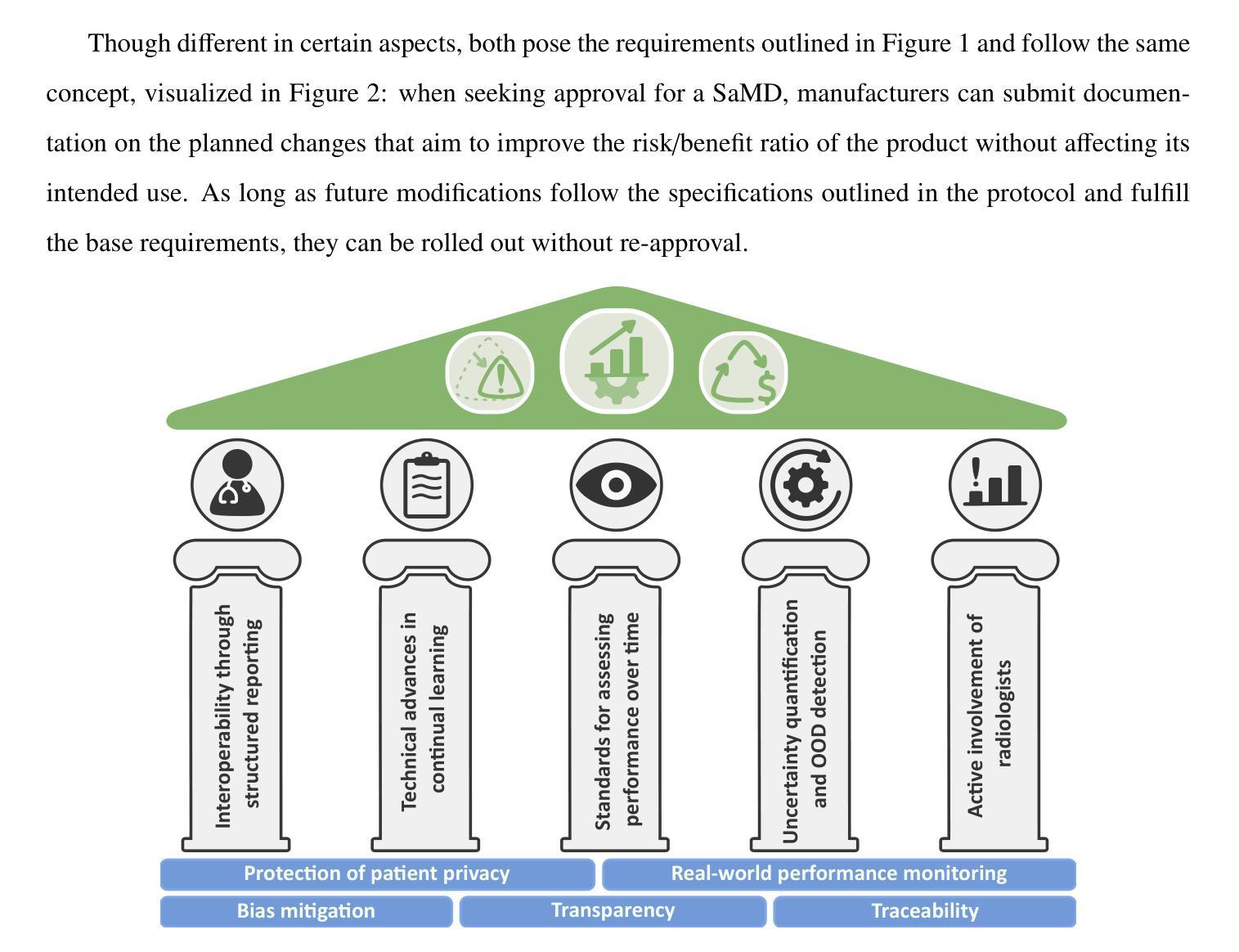
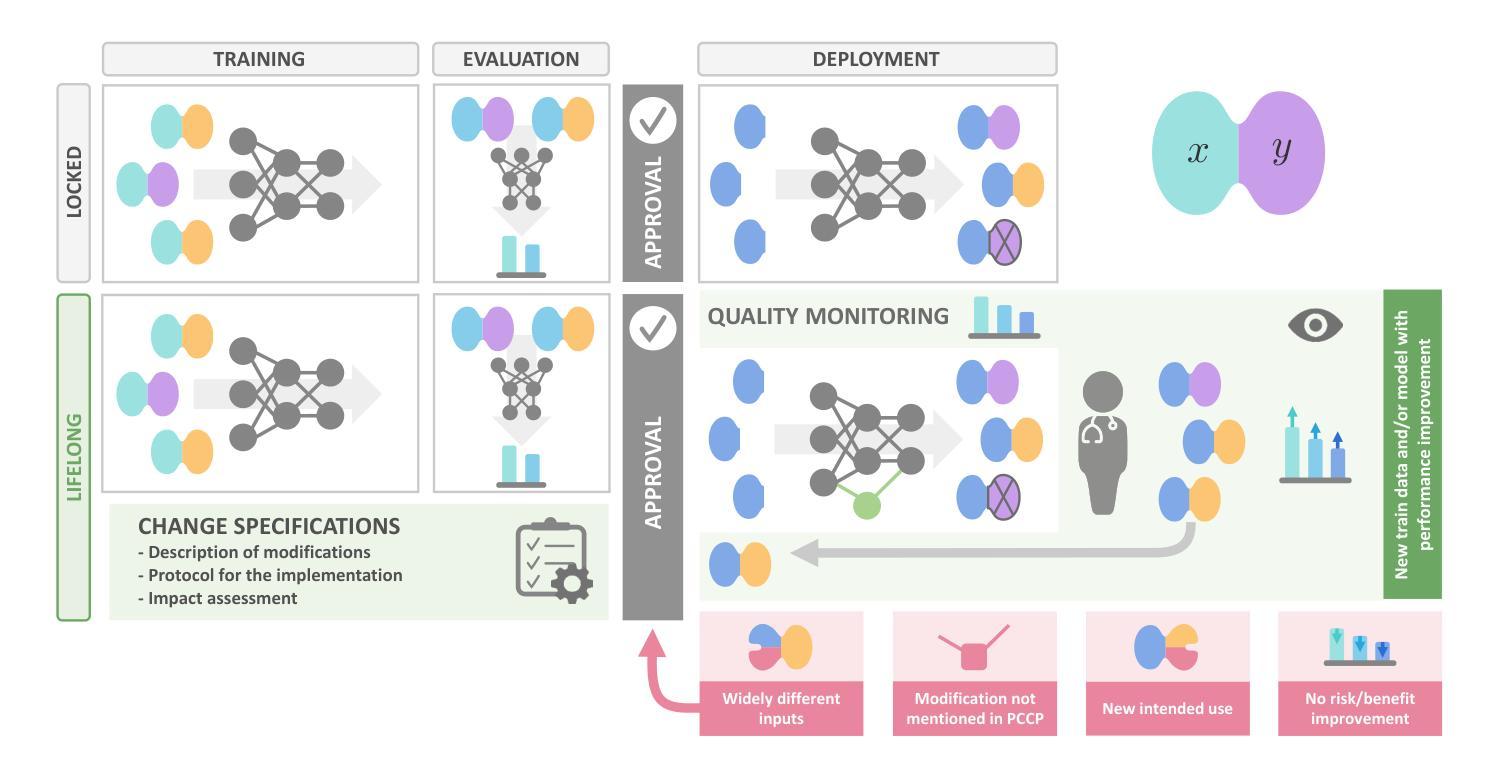
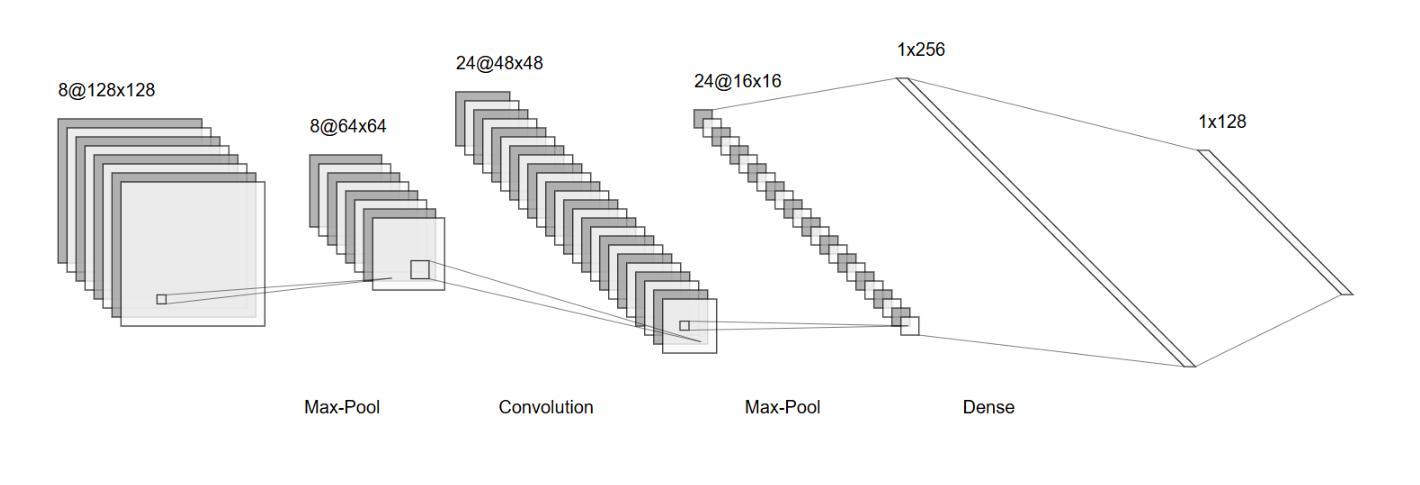
The Potential of Convolutional Neural Networks for Cancer Detection
Authors:Hossein Molaeian, Kaveh Karamjani, Sina Teimouri, Saeed Roshani, Sobhan Roshani
Early detection is a prime requisite for successful cancer treatment and increasing its survivability rates, particularly in the most common forms. CNNs (Convolutional Neural Networks) are very potent tools for the analysis and classification of medical images, with particular reference to the early detection of different types of cancer. Ten different cancers have been identified in most of these advances that use CNN techniques for classification. The unique architectures of CNNs employed in each study are focused on pattern recognition for each type of cancer through different datasets. By comparing and analyzing these architectures, the strengths and drawbacks of each approach are pointed out in terms of their efforts toward improving the earlier detection of cancer. The opportunity to embrace CNNs within the clinical sphere was interrogated as support or potential substitution of traditional diagnostic techniques. Furthermore, challenges such as integrating diverse data, how to interpret the results, and ethical dilemmas continue to stalk this field with inconceivable hindrances. This study identifies those CNN architectures that carry out the best work and offers a comparative analysis that reveals to researchers the impact of CNNs on cancer detection in the leap toward boosting diagnostic capabilities in health.
早期检测是癌症治疗成功的关键要素,有助于提高患者的存活率,特别是在最常见的癌症类型中。卷积神经网络(CNN)是用于分析和分类医学图像的强大工具,尤其适用于不同类型的癌症的早期检测。在利用CNN技术进行分类的这些进展中,已经确定了十种不同的癌症。每项研究中采用的CNN的独特架构都专注于通过不同数据集识别每种癌症的模式。通过比较和分析这些架构,指出了每种方法在改进癌症早期检测方面的优点和缺点。探讨了将CNN纳入临床实践的机会,以支持或可能取代传统诊断技术。此外,该领域还面临着诸如整合多样化数据、如何解释结果和道德困境等挑战,这些挑战带来了难以想象的阻碍。本研究确定了表现最佳的CNN架构,并提供了一项比较分析,向研究人员揭示了CNN在癌症检测中对提升诊断能力的巨大影响及其在健康领域的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
卷积神经网络(CNN)在医学图像分析和分类中具有强大潜力,尤其对于常见癌症的早期检测至关重要。通过对比不同CNN架构在癌症检测方面的应用,研究指出了各自的优势和局限性,并探讨了将CNN纳入临床实践以支持或可能替代传统诊断技术的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- CNNs在医学图像分析和分类中具有强大潜力,尤其在癌症早期检测方面。
- CNN的独特架构专注于每种癌症的模式识别,通过不同的数据集进行分类。
- 对比和分析这些CNN架构揭示了各自在改进早期癌症检测方面的优势和局限性。
- CNN有潜力成为临床实践中的传统诊断技术的支持或替代品。
- 集成多样化数据、结果解读和伦理困境等挑战仍是该领域面临的主要难题。
- 该研究确定了表现最佳的CNN架构,并为研究人员提供了关于CNN在癌症检测中对诊断能力影响的比较分析。
点此查看论文截图

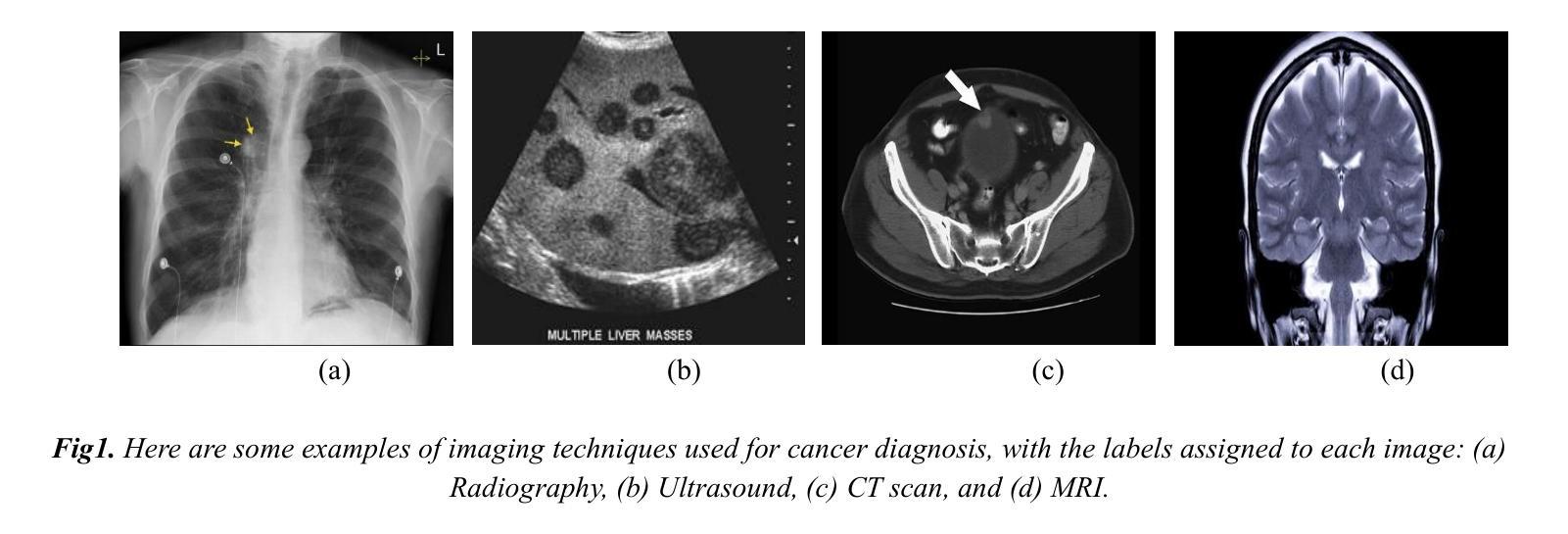
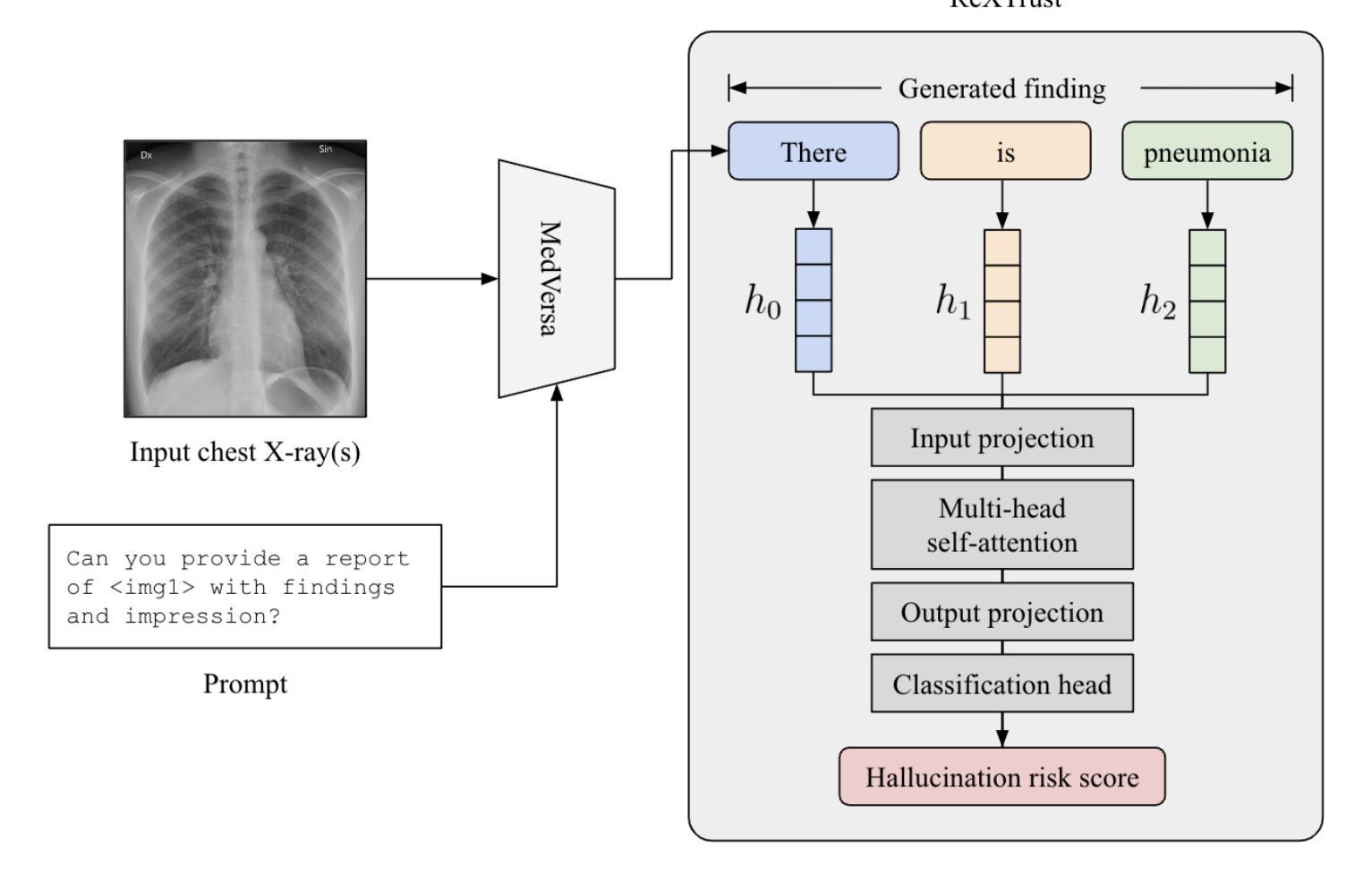
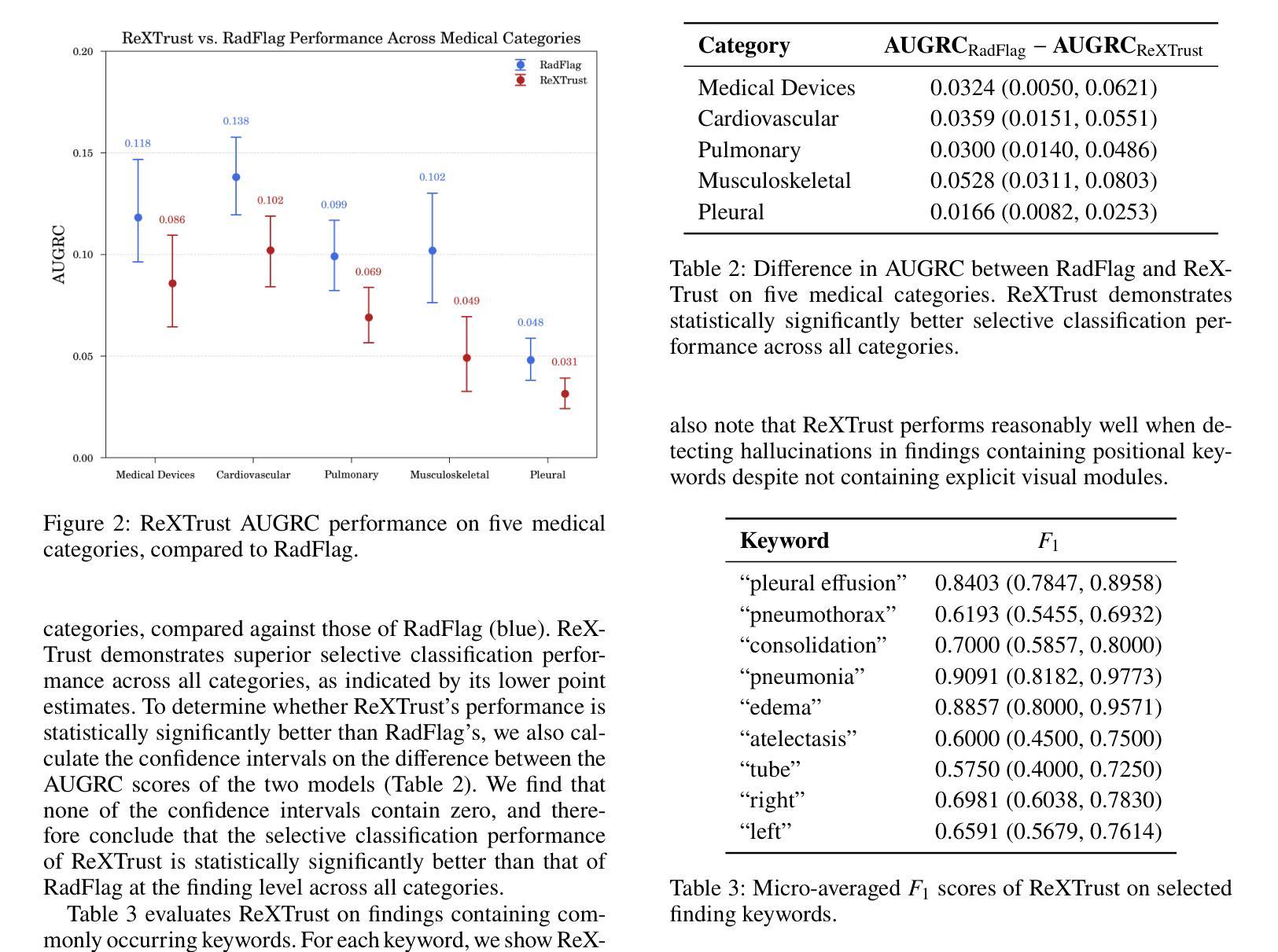
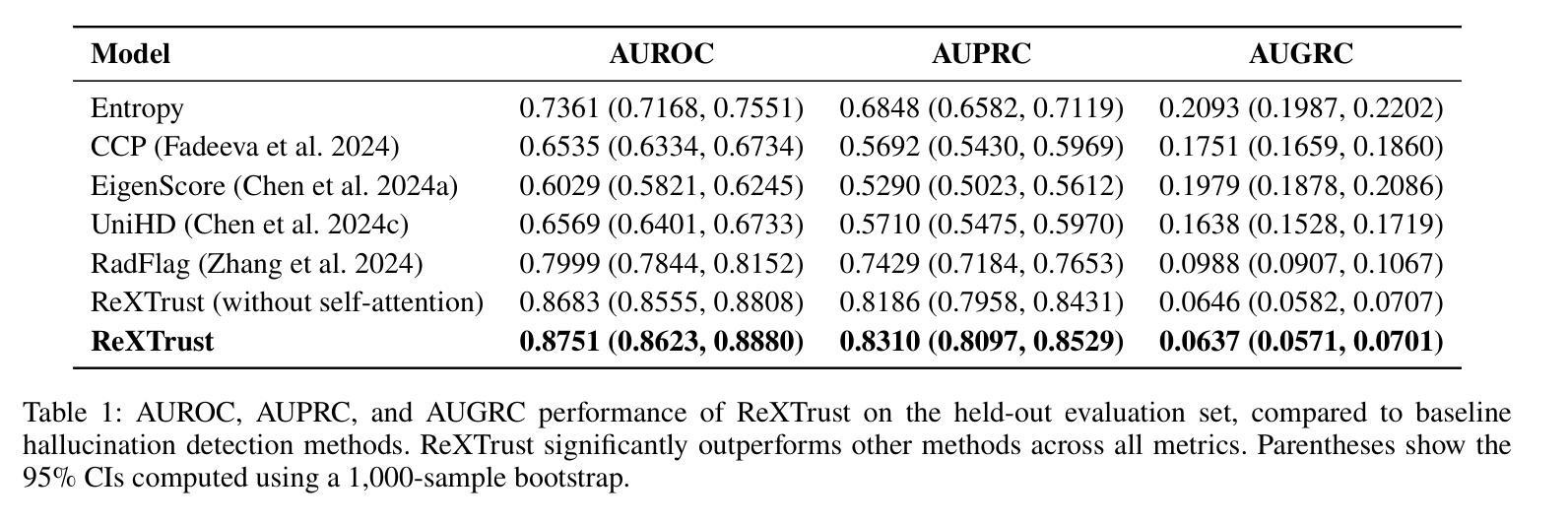
ReXTrust: A Model for Fine-Grained Hallucination Detection in AI-Generated Radiology Reports
Authors:Romain Hardy, Sung Eun Kim, Du Hyun Ro, Pranav Rajpurkar
The increasing adoption of AI-generated radiology reports necessitates robust methods for detecting hallucinations–false or unfounded statements that could impact patient care. We present ReXTrust, a novel framework for fine-grained hallucination detection in AI-generated radiology reports. Our approach leverages sequences of hidden states from large vision-language models to produce finding-level hallucination risk scores. We evaluate ReXTrust on a subset of the MIMIC-CXR dataset and demonstrate superior performance compared to existing approaches, achieving an AUROC of 0.8751 across all findings and 0.8963 on clinically significant findings. Our results show that white-box approaches leveraging model hidden states can provide reliable hallucination detection for medical AI systems, potentially improving the safety and reliability of automated radiology reporting.
随着越来越多地使用人工智能生成的放射学报告,我们需要强大的方法来检测幻觉——可能影响患者护理的虚假或没有根据的陈述。我们提出了ReXTrust,这是一个用于精细粒度幻觉检测的新型框架,适用于人工智能生成的放射学报告。我们的方法利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列来生成发现级别的幻觉风险分数。我们在MIMIC-CXR数据集的一个子集上评估了ReXTrust,并展示了相比现有方法的优越性能,在所有发现上的AUROC达到0.8751,在具有临床意义的发现上达到0.8963。我们的结果表明,利用模型隐藏状态的white-box方法可以为医疗人工智能系统提供可靠的幻觉检测,有可能提高自动放射学报告的安全性和可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AIMedHealth 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
AI生成的放射学报告中的虚假陈述检测问题日益受到关注。本文提出一种名为ReXTrust的精细粒度虚假陈述检测框架,通过利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列生成针对发现的虚假陈述风险评分。在MIMIC-CXR数据集子集上进行的评估显示,相较于现有方法,ReXTrust表现出卓越的性能,在所有发现上的AUROC为0.8751,在具有临床意义发现上的AUROC为0.8963。结果证明,利用模型隐藏状态的透明方法可为医学AI系统提供可靠的虚假陈述检测能力,有望提高自动化放射学报告的安全性及可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的放射学报告中存在虚假陈述问题,对病人护理产生影响。
- 提出了一种名为ReXTrust的精细粒度虚假陈述检测框架。
- ReXTrust利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列生成针对发现的虚假陈述风险评分。
- 在MIMIC-CXR数据集子集上的评估显示ReXTrust性能卓越。
- ReXTrust在所有发现上的AUROC为0.8751,在具有临床意义发现上的AUROC为0.8963。
- 利用模型隐藏状态的透明方法可以提供可靠的虚假陈述检测能力。
点此查看论文截图

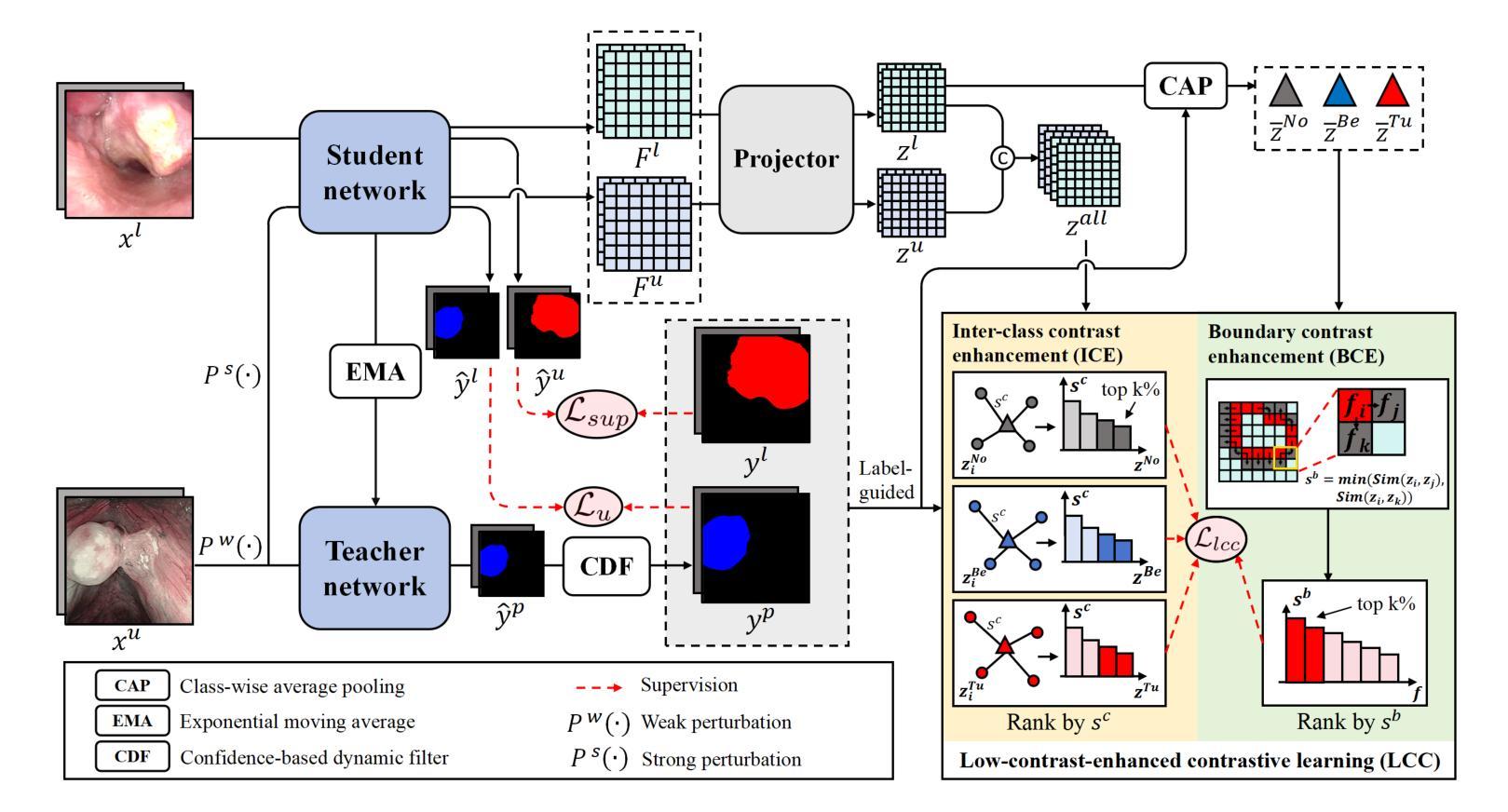
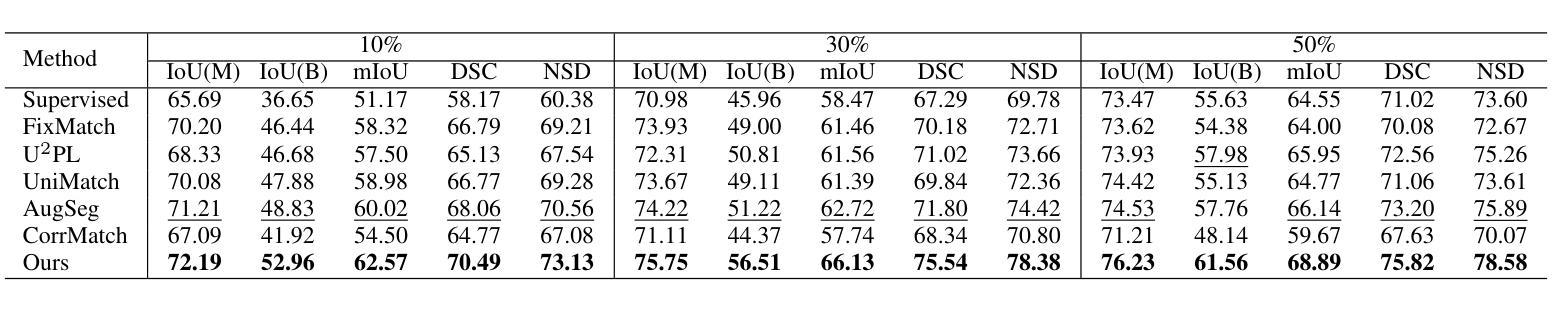
Low-Contrast-Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Endoscopic Image Segmentation
Authors:Lingcong Cai, Yun Li, Xiaomao Fan, Kaixuan Song, Ruxin Wang, Wenbin Lei
The segmentation of endoscopic images plays a vital role in computer-aided diagnosis and treatment. The advancements in deep learning have led to the employment of numerous models for endoscopic tumor segmentation, achieving promising segmentation performance. Despite recent advancements, precise segmentation remains challenging due to limited annotations and the issue of low contrast. To address these issues, we propose a novel semi-supervised segmentation framework termed LoCo via low-contrast-enhanced contrastive learning (LCC). This innovative approach effectively harnesses the vast amounts of unlabeled data available for endoscopic image segmentation, improving both accuracy and robustness in the segmentation process. Specifically, LCC incorporates two advanced strategies to enhance the distinctiveness of low-contrast pixels: inter-class contrast enhancement (ICE) and boundary contrast enhancement (BCE), enabling models to segment low-contrast pixels among malignant tumors, benign tumors, and normal tissues. Additionally, a confidence-based dynamic filter (CDF) is designed for pseudo-label selection, enhancing the utilization of generated pseudo-labels for unlabeled data with a specific focus on minority classes. Extensive experiments conducted on two public datasets, as well as a large proprietary dataset collected over three years, demonstrate that LoCo achieves state-of-the-art results, significantly outperforming previous methods. The source code of LoCo is available at the URL of \href{https://github.com/AnoK3111/LoCo}{https://github.com/AnoK3111/LoCo}.
内镜图像的分割在计算机辅助诊断和治疗中起着至关重要的作用。深度学习的进步导致了多种内镜肿瘤分割模型的应用,并实现了有前景的分割性能。尽管最近有进展,但由于标注有限和对比度低的问题,精确分割仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型半监督分割框架,称为LoCo,通过低对比度增强对比学习(LCC)。这种创新的方法有效地利用了内镜图像分割中大量可用的未标记数据,提高了分割过程的准确性和稳健性。具体来说,LCC结合了两种先进策略,以提高低对比度像素的辨别力:类间对比度增强(ICE)和边界对比度增强(BCE),使模型能够在恶性肿瘤、良性肿瘤和正常组织之间分割低对比度像素。此外,还设计了一种基于置信度的动态滤波器(CDF)进行伪标签选择,提高了生成的伪标签在针对未标记数据的利用,特别关注少数类别。在两个公共数据集以及三年收集的大规模专有数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,LoCo达到了最新水平的结果,显著优于以前的方法。LoCo的源代码可在https://github.com/AnoK3111/LoCo的URL处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习在內視鏡影像分割上的应用已取得了显著进展,但仍面临标注有限和对比度低的问题。为此,提出一种新型半监督分割框架LoCo,通过低对比度增强对比学习(LCC)有效利用大量未标记数据,提高分割准确性和稳健性。框架包含两种策略:类间对比度增强(ICE)和边界对比度增强(BCE),能区分恶性、良性肿瘤和正常组织的低对比度像素。同时,设计基于置信度的动态过滤器(CDF)进行伪标签筛选,提高未标记数据的利用率,特别关注少数类。在多个数据集上的实验显示,LoCo表现卓越,显著超越其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 内窥镜图像分割在计算机辅助诊断和治疗中起重要作用。
- 深度学习在许多内窥镜肿瘤分割模型中的应用已经取得了显著的进步。
- 存在标注有限和对比度低的问题,仍需要精确分割。
- 提出了一种新型半监督分割框架LoCo,通过低对比度增强对比学习(LCC)解决上述问题。
- LoCo利用未标记数据提高分割的准确性和稳健性。
- LoCo包含两种策略:ICE和BCE,以区分低对比度像素。
- LoCo设计CDF进行伪标签筛选,提高未标记数据的利用率,特别是在少数类中。
点此查看论文截图

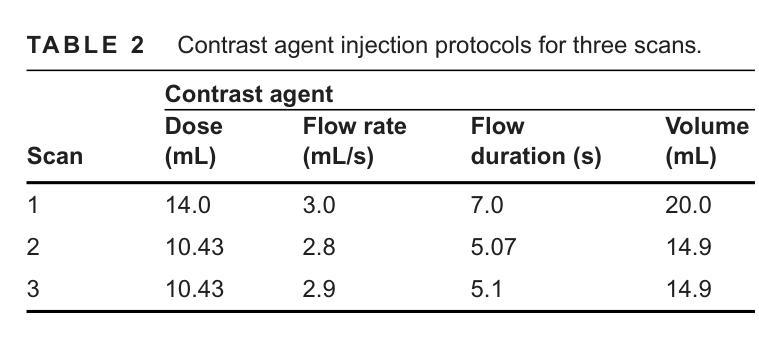
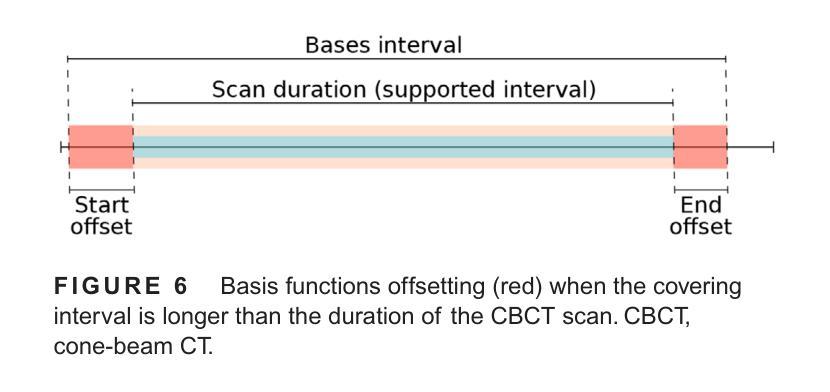
Model-Based Perfusion Reconstruction with Time Separation Technique in Cone-Beam CT Dynamic Liver Perfusion Imaging
Authors:Hana Haseljić, Robert Frysch, Vojtěch Kulvait, Thomas Werncke, Inga Brusch, Oliver Speck, Jessica Schulz, Michael Manhart, Georg Rose
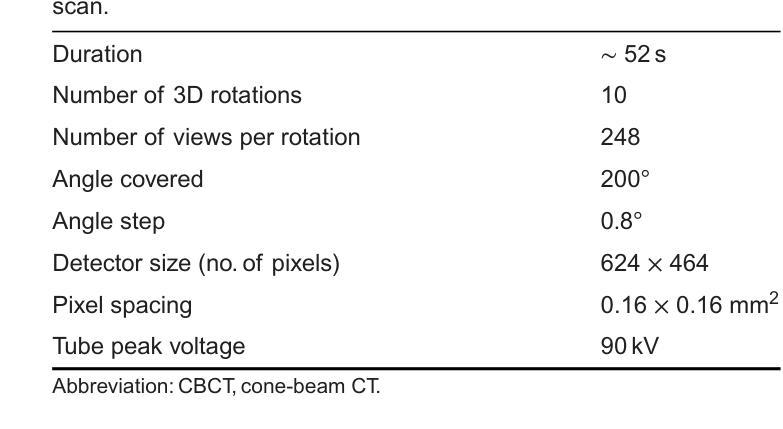
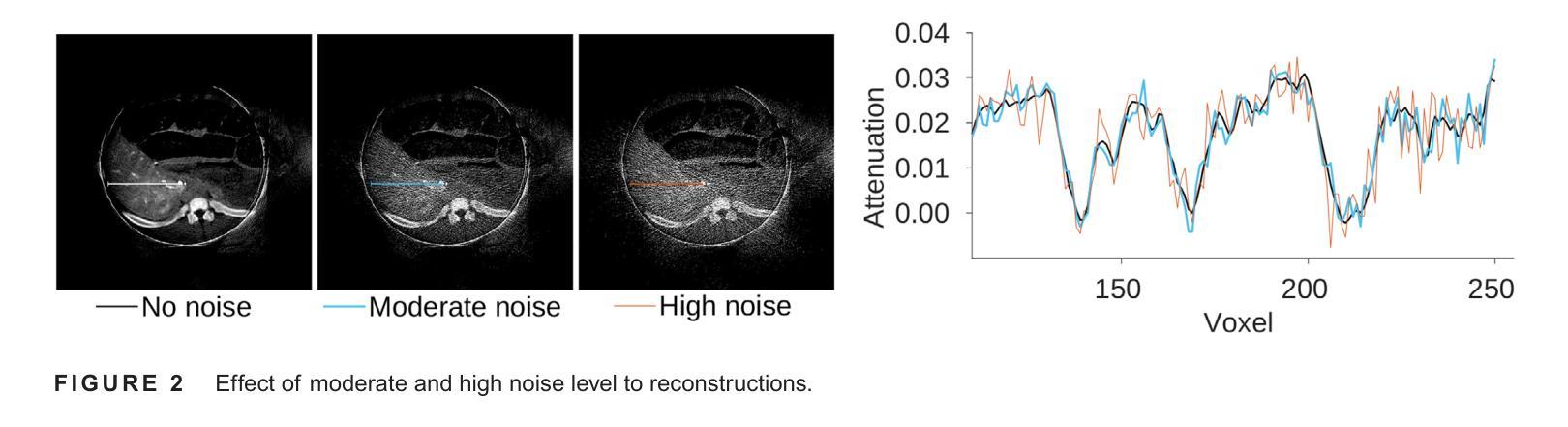
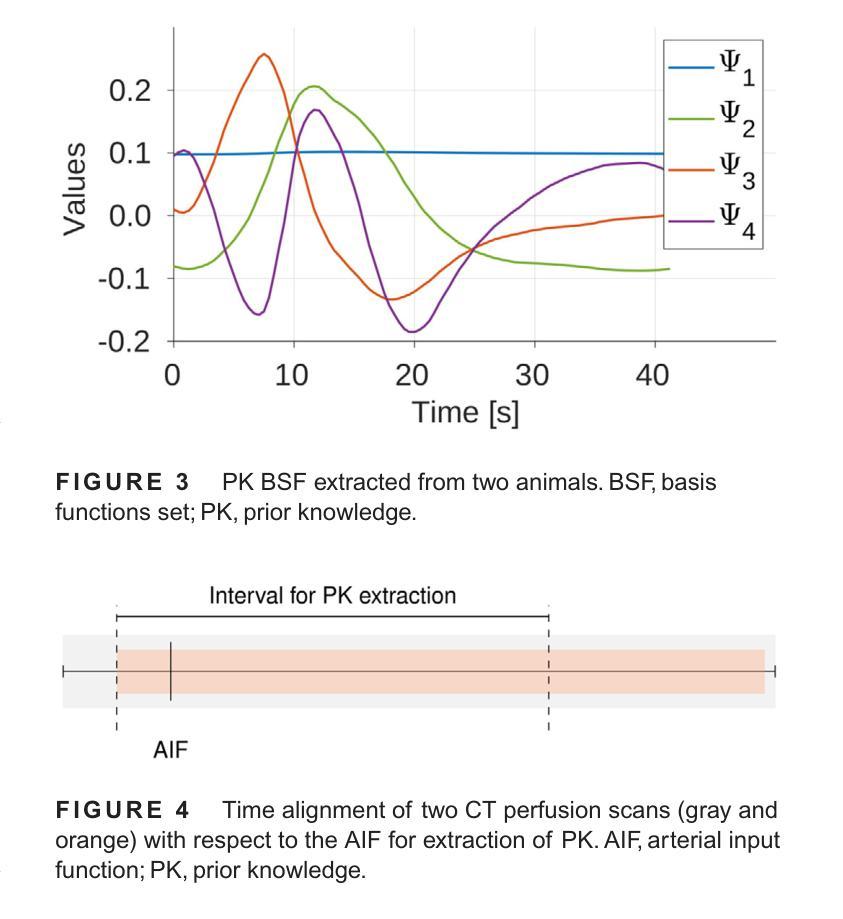
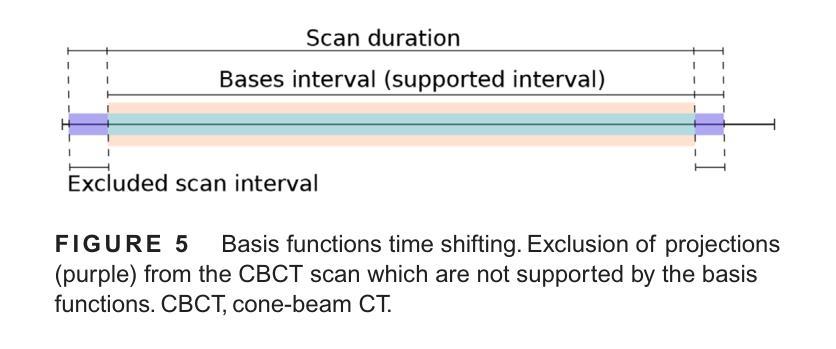
The success of embolisation, a minimally invasive treatment of liver cancer, could be evaluated in the operational room with cone-beam CT by acquiring a dynamic perfusion scan. The reconstruction algorithm must address the issues of low temporal sampling and higher noise levels inherent in cone-beam CT systems, compared to conventional CT. Therefore, a model-based perfusion reconstruction based on the time separation technique (TST) was applied. TST uses basis functions to model time attenuation curves. These functions are either analytical or based on prior knowledge, extracted using singular value decomposition from CT perfusion data. To explore how well the prior knowledge can model perfusion dynamics and what the potential limitations are, the dynamic CBCT perfusion scan was simulated under different noise levels. The TST method was compared to static reconstruction. It was demonstrated that a set consisting of only four basis functions results in perfusion maps that preserve relevant information, denoises the data, and outperforms static reconstruction under higher noise levels. TST with prior knowledge would not only outperform static reconstruction, but also the TST with analytical basis functions. Furthermore, it has been shown that only eight CBCT rotations, unlike previously assumed ten, are sufficient to obtain the perfusion maps comparable to the reference CT perfusion maps. This contributes to saving dose and reconstruction time. The real dynamic CBCT perfusion scan, reconstructed under the same conditions as the simulated scan, shows potential for maintaining the accuracy of the perfusion maps. By visual inspection, the embolised region was matching to that in corresponding CT perfusion maps. Further analysis of a larger cohort of patient data is needed to draw final conclusions regarding the expected advantages of the time separation technique.
肝脏癌症的栓塞治疗作为一种微创手术,其成功性可以通过手术室中的锥形束CT进行动态灌注扫描来评估。与传统的CT相比,锥形束CT系统存在时间采样较低和噪声水平较高的问题,因此重建算法必须解决这些问题。因此,应用了一种基于时间分离技术(TST)的模型灌注重建。TST使用基础函数来模拟时间衰减曲线。这些函数是分析的,或者是基于先验知识,通过奇异值分解从CT灌注数据中提取。为了探讨先验知识能够模拟灌注动力学的程度以及潜在局限性,在不同噪声水平下模拟了动态CBCT灌注扫描。将TST方法与静态重建进行比较,结果表明,由四个基础函数组成的集合产生的灌注图保留了相关信息,去除了数据噪声,并在较高噪声水平下优于静态重建。具有先验知识的TST不仅优于静态重建,而且优于使用分析基础函数的TST。此外,研究表明,只需八个CBCT旋转(与以前假设的十个不同)就足以获得与参考CT灌注图相当的灌注图。这有助于减少剂量和重建时间。在相同条件下重建的实际动态CBCT灌注扫描显示出保持灌注图准确性的潜力。通过目测,栓塞区域与相应的CT灌注图相匹配。需要对更大的患者群体进行进一步分析,以得出时间分离技术的预期优势的最终结论。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Medical Physics Received: 2 August 2024 Revised: 20 November 2024 Accepted: 27 December 2024
Summary
基于时间分离技术(TST)的模型基础灌注重建用于评价肝癌栓塞治疗的成功。使用锥束CT进行动态灌注扫描,并通过重建算法解决其固有的时间采样低和噪声水平高的问题。模拟动态CBCT灌注扫描以探索先验知识对灌注动力学的建模效果及潜在限制。结果显示,仅由四个基函数组成的集合能够保留相关信息、去除噪声,并在高噪声水平下优于静态重建。此外,只需八个CBCT旋转即可获得与参考CT灌注地图相当的灌注地图,有助于节省剂量和重建时间。真实动态CBCT灌注扫描显示维持灌注地图准确性的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 栓塞治疗肝癌症效可通过操作室的锥束CT动态灌注扫描进行评估。
- 锥束CT系统相较于传统CT存在时间采样低和噪声水平高的问题。
- 采用基于时间分离技术(TST)的模型基础灌注重建算法来解决这些问题。
- TST使用先验知识或分析基础函数来建模时间衰减曲线。
- 在不同噪声水平下模拟动态CBCT灌注扫描,以测试TST的效果和潜在限制。
- TST在仅使用四个基函数时表现优异,优于静态重建,尤其是在高噪声环境下。
点此查看论文截图

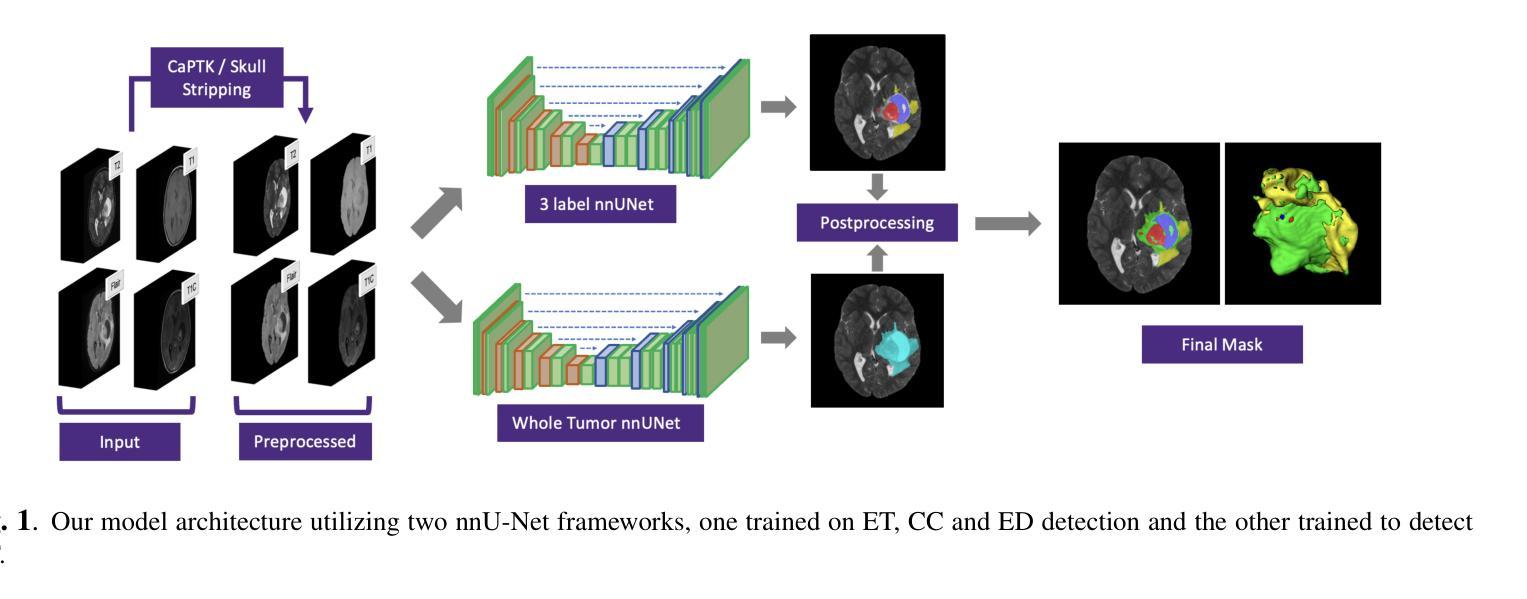
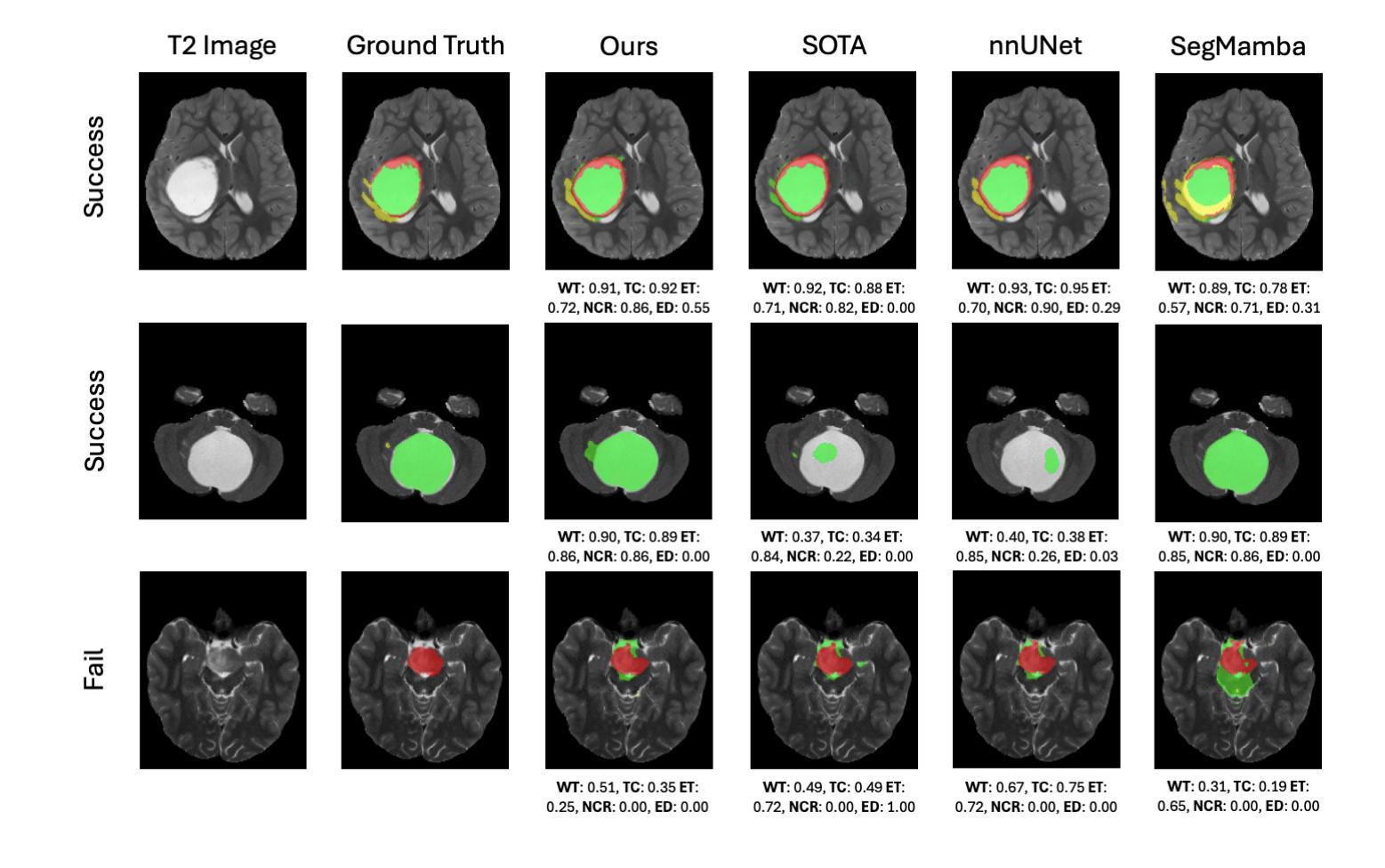
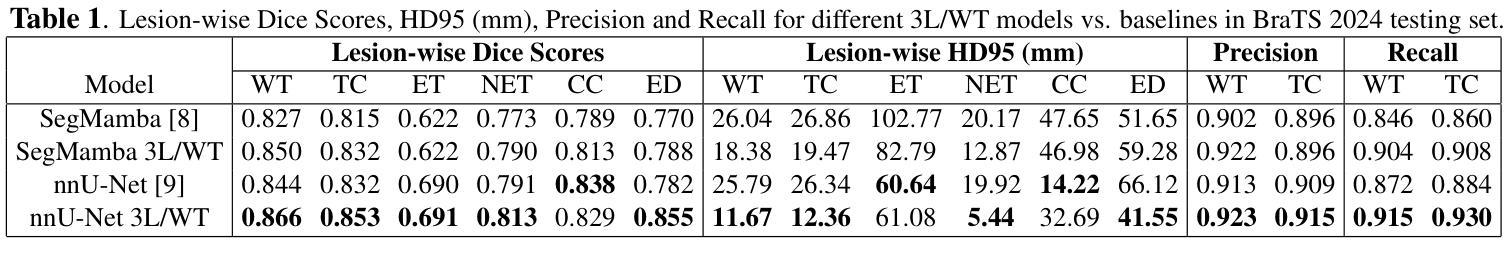
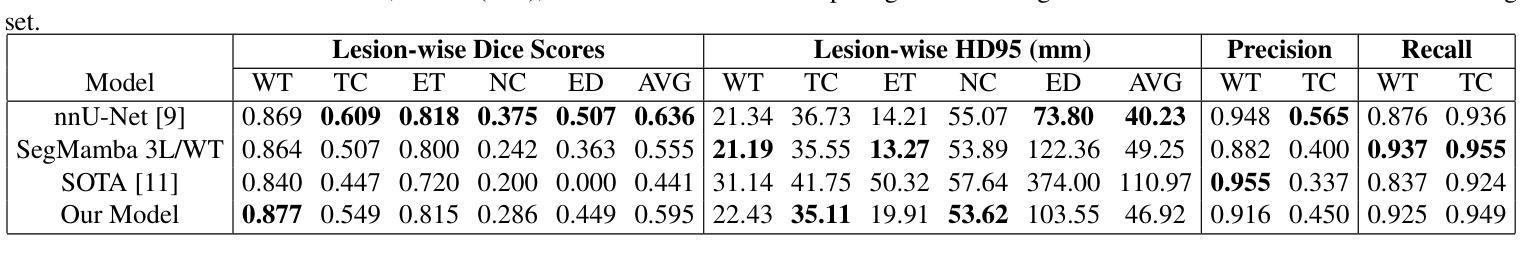
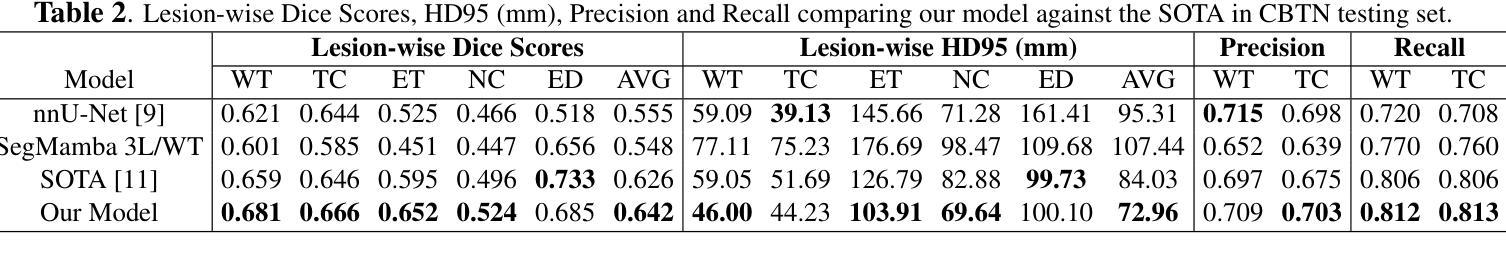
A New Logic For Pediatric Brain Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Max Bengtsson, Elif Keles, Gorkem Durak, Syed Anwar, Yuri S. Velichko, Marius G. Linguraru, Angela J. Waanders, Ulas Bagci
In this paper, we present a novel approach for segmenting pediatric brain tumors using a deep learning architecture, inspired by expert radiologists’ segmentation strategies. Our model delineates four distinct tumor labels and is benchmarked on a held-out PED BraTS 2024 test set (i.e., pediatric brain tumor datasets introduced by BraTS). Furthermore, we evaluate our model’s performance against the state-of-the-art (SOTA) model using a new external dataset of 30 patients from CBTN (Children’s Brain Tumor Network), labeled in accordance with the PED BraTS 2024 guidelines and 2023 BraTS Adult Glioma dataset. We compare segmentation outcomes with the winning algorithm from the PED BraTS 2023 challenge as the SOTA model. Our proposed algorithm achieved an average Dice score of 0.642 and an HD95 of 73.0 mm on the CBTN test data, outperforming the SOTA model, which achieved a Dice score of 0.626 and an HD95 of 84.0 mm. Moreover, our model exhibits strong generalizability, attaining a 0.877 Dice score in whole tumor segmentation on the BraTS 2023 Adult Glioma dataset, surpassing existing SOTA. Our results indicate that the proposed model is a step towards providing more accurate segmentation for pediatric brain tumors, which is essential for evaluating therapy response and monitoring patient progress.
本文介绍了一种受专家放射科医生分割策略启发的新型深度学习架构,用于分割儿童脑肿瘤。我们的模型能够区分四种不同的肿瘤标签,并在BraTS推出的PED BraTS 2024测试集上进行了评估。此外,我们使用来自儿童脑肿瘤网络(CBTN)的30名患者的新外部数据集和根据PED BraTS 2024准则以及BraTS成人胶质瘤数据集进行模型性能评估。我们将分割结果与来自PED BraTS 2023挑战的获胜算法作为当前最前沿模型进行比较。我们提出的算法在CBTN测试数据上取得了平均Dice系数为0.642和HD95为73.0毫米的成绩,超过了当前最前沿模型,其Dice系数为0.626和HD95为84.0毫米。此外,我们的模型具有很强的泛化能力,在BraTS 2023成人胶质瘤数据集的全肿瘤分割上取得了Dice系数达到0.877的成绩,超过了现有最前沿模型。我们的结果表明,所提出的模型是朝着为儿童脑肿瘤提供更准确分割的方向迈出的一步,这对于评估治疗反应和监测患者进展至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的新方法,用于分割儿童脑肿瘤。此方法受放射科医生分割策略的启发,可区分四种不同的肿瘤标签。它在独立的PED BraTS 2024测试集上与先进模型相比较,表现出较高的性能。在来自CBTN的外部数据集上,新算法的Dice系数平均为0.642,高于SOTA模型的0.626。此外,该算法还展示了良好的泛化能力,在BraTS 2023成人胶质瘤数据集上的全肿瘤分割Dice系数达到0.877。研究结果表明,该模型为儿童脑肿瘤的准确分割提供了重要进展,有助于评估治疗效果和监测患者进展。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种用于分割儿童脑肿瘤的深度学习新方法。
- 方法基于专家放射学家的分割策略,能区分四种不同的肿瘤标签。
- 在独立的PED BraTS 2024测试集上进行了性能验证。
- 在CBTN外部数据集上的新算法性能优于当前最佳模型。
- 新算法的Dice系数平均为0.642,高于SOTA模型的0.626。
- 算法在BraTS 2023成人胶质瘤数据集上表现出良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

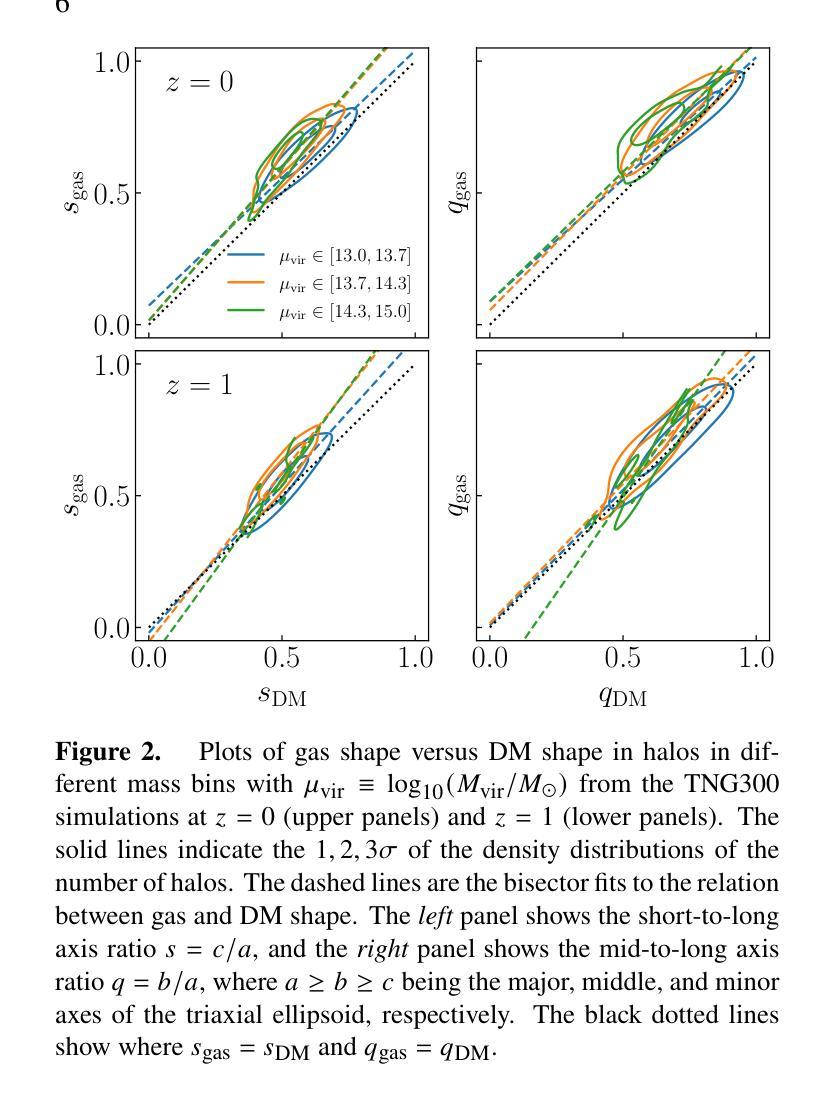
Baryon Pasting the Uchuu Lightcone Simulation
Authors:Erwin T. Lau, Daisuke Nagai, Arya Farahi, Tomoaki Ishiyama, Hironao Miyatake, Ken Osato, Masato Shirasaki
We present the Baryon Pasted (BP) X-ray and thermal Sunyaev-Zel’dovich (tSZ) maps derived from the half-sky Uchuu Lightcone simulation. These BP-Uchuu maps are constructed using more than $75$ million dark matter halos with masses $M_{500c} \geq 10^{13} M_\odot$ within the redshift range $0 \leq z \leq 2$. A distinctive feature of our BP-Uchuu Lightcone maps is their capability to assess the influence of both extrinsic and intrinsic scatter caused by triaxial gaseous halos and internal gas characteristics, respectively, at the map level. We show that triaxial gas drives substantial scatter in X-ray luminosities of clusters and groups, accounting for nearly half of the total scatter in core-excised measurements. Additionally, scatter in the thermal pressure and gas density profiles of halos enhances the X-ray and SZ power spectra, leading to biases in cosmological parameter estimates. These findings are statistically robust due to the extensive sky coverage and large halo sample in the BP-Uchuu maps. The BP-Uchuu maps are publicly available on https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=cf8dadb7-b6e9-4e2c-abc1-0813877efc13 .
我们展示了基于半天空Uchuu Lightcone模拟的Baryon Pasted(BP)X射线和热Sunyaev-Zel’dovich(tSZ)映射。这些BP-Uchuu映射是使用红移范围内$M_{500c} \geq 10^{13} M_\odot$的超过$75$万个暗物质晕构建的,红移范围在$0 \leq z \leq 2$。BP-Uchuu Lightcone映射的一个显著特点是,它们能够在映射层面评估由三轴气体晕和外部气体特性分别引起的外在和内在散射的影响。我们表明,三轴气体驱动了集群和星系团X射线光度的大量散射,占核心切除测量中总散射的近一半。此外,晕热压和气密度分布的散射增加了X射线和SZ功率谱,导致宇宙学参数估计出现偏差。这些发现由于BP-Uchuu映射中的广阔天空覆盖范围和大量的晕样本而具有统计稳健性。BP-Uchuu映射可在https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=cf8dadb7-b6e9-4e2c-abc1-0813877efc13上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 12 figures, ApJ accepted. The BP-Uchuu maps are publicly available on https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=cf8dadb7-b6e9-4e2c-abc1-0813877efc13
摘要
本文介绍了基于Uchuu Lightcone模拟的Baryon Pasted(BP)X射线和热Sunyaev-Zel’dovich(tSZ)图。这些BP-Uchuu图是由红移范围在0至2之间,质量大于10^13M_odot的7500多万个暗物质晕构建的。BP-Uchuu Lightcone图的独特之处在于,它们能够评估三轴气晕和内部气体特性造成的外在和内在散射在地图层面的影响。研究发现,三轴气体导致了集群和星团X射线光度的大量散射,在核心切除测量中约占总散射的一半。此外,晕的热压和气密度分布轮廓的散射增强了X射线和SZ功率谱,导致宇宙学参数估计出现偏差。这些发现由于BP-Uchuu图的广阔天空覆盖范围和大量晕样本而具有统计稳健性。BP-Uchuu图可在https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=cf8dadb7-b6e9-4e2c-abc1-0813877efc13上公开获取。
关键见解
- 介绍了基于Uchuu Lightcone模拟的BP X射线和tSZ图。
- BP图是由大量暗物质晕构建的,这些晕在特定的红移范围内且具有特定的质量。
- BP图能够评估三轴气晕和内部气体特性造成的外在和内在散射的影响。
- 三轴气体对集群和星团的X射线光度产生显著散射。
- 晕的热压和气密度分布轮廓的散射会导致X射线和SZ功率谱增强。
- 散射现象可能影响宇宙学参数的估计,导致偏差。
点此查看论文截图


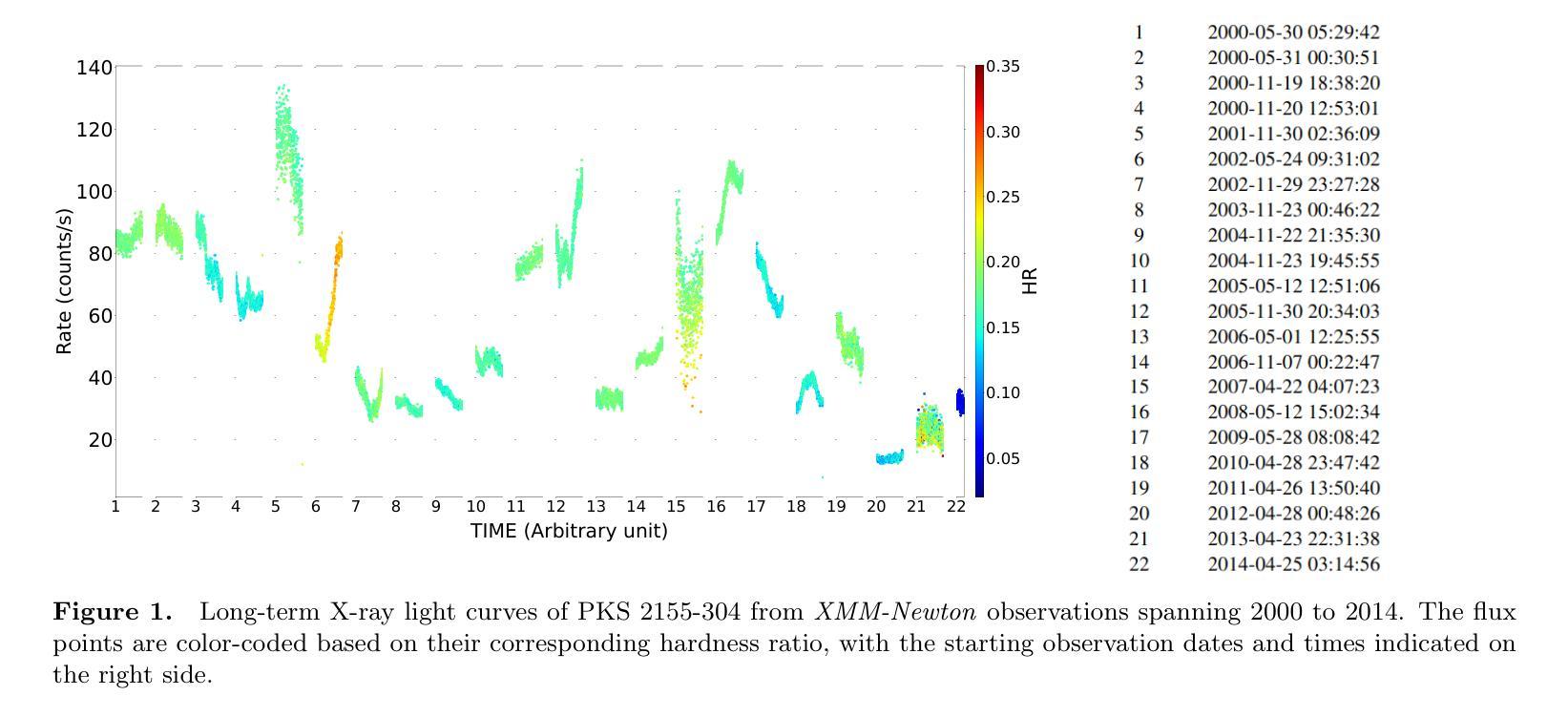
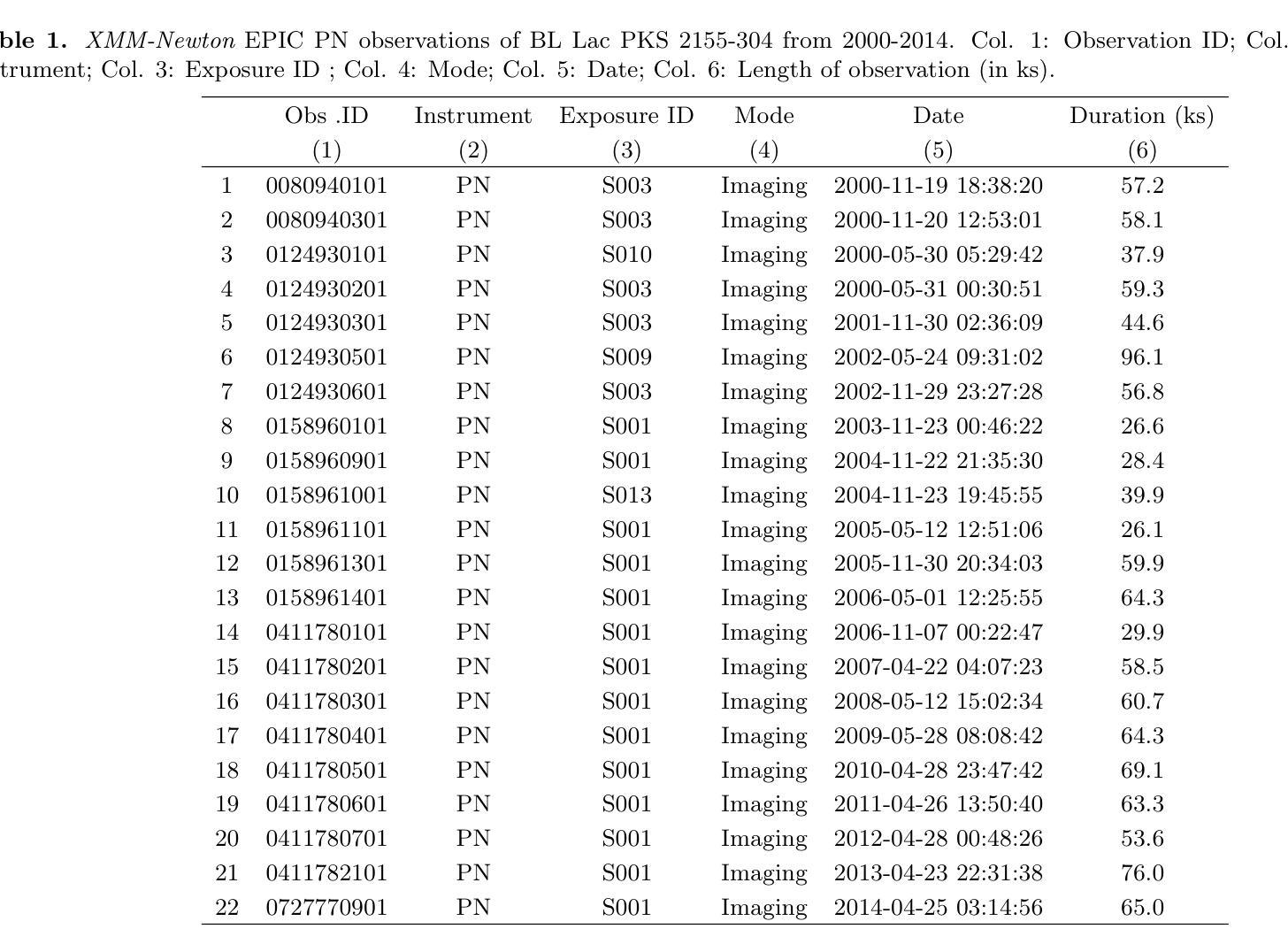
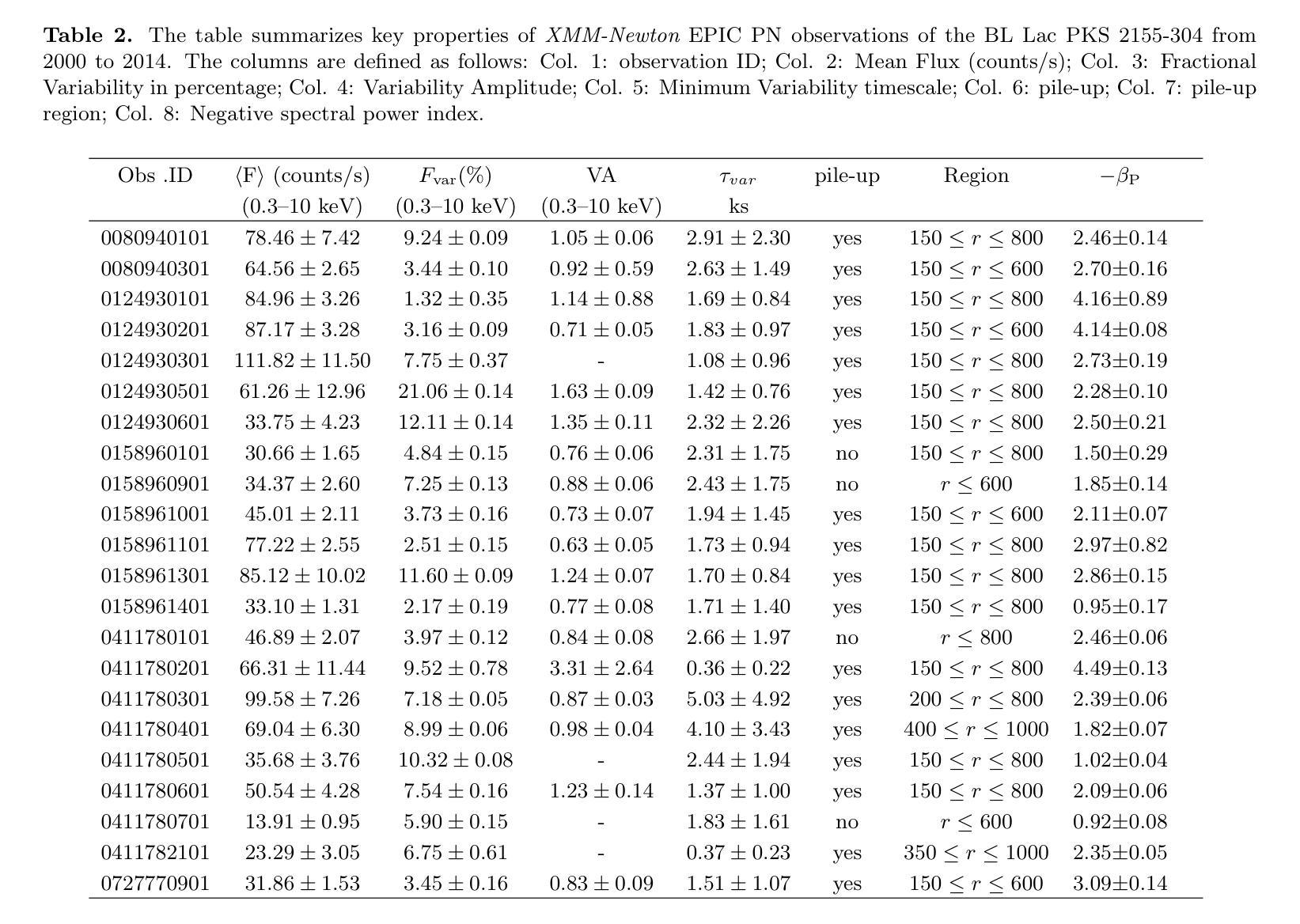
Probing X-ray Timing and Spectral Variability in the Blazar PKS 2155-304 Over a Decade of XMM-Newton Observations
Authors:Gopal Bhatta, Suvas C. Chaudhary, Niraj Dhital, Tek P. Adhikari, Maksym Mohorian, Radim Pánis, Raghav Neupane, Yogesh Singh Maharjan
Blazars, a class of active galactic nuclei (AGN) powered by supermassive black holes, are known for their remarkable variability across multiple timescales and wavelengths. Despite significant advancements in our understanding of AGN central engines, thanks to both ground- and space-based telescopes, the details of the mechanisms driving this variability remain elusive. The primary objective of this study is to constrain the X-ray variability properties of the TeV blazar PKS 2155-304. We conducted a comprehensive X-ray spectral and timing analysis, focusing on both long-term and intra-day variability (IDV), using data from 22 epochs of {\it XMM-Newton} observations collected over 15 years (2000 to 2014). For the timing analysis, we estimated the fractional variability, variability amplitude, minimum variability timescales, flux distribution, and power spectral density. In the spectral analysis, we fitted the X-ray spectra using power-law, log-parabola, and broken power-law models to determine the best-fitting parameters. We observed moderate IDV in the majority of the light curves. Seven out of the 22 observations showed a clear bimodal flux distribution, indicating the presence of two distinct flux states. Our analysis revealed a variable power spectral slope. Most hardness ratio plots did not show significant variation with flux, except for two observations, where the hardness ratio changed considerably with flux. The fitted X-ray spectra favored the broken power law model for the majority of observations, indicating break in the spectral profiles. The findings of this work shed light on the IDV of blazars, providing insights into the non-thermal jet processes that drive the observed flux variations.
耀斑(Blazars)是一类由超大质量黑洞驱动的活跃星系核(Active Galactic Nuclei,简称AGN),以其跨越多个时间尺度和波长的显著可变性而闻名。尽管得益于地面和空间望远镜的显著进步,我们对活跃星系核中心引擎的理解有所加深,但推动这种可变性的机制细节仍然难以捉摸。本研究的主要目的是约束TeV耀斑PKS 2155-304的X射线可变特性。我们对X射线光谱和时间进行了全面的分析,重点关注长期和日内变化(IDV),使用的是从跨越长达近十五年的XM牛顿观测仪所收集的数据,包括数据自时间较长达数年以至为期数天的大量观察周期共计近一期的观察。在时序分析中,我们估计了分数的变异性、变化幅度以及最短变异期时间段的长短(针对一定时间内峰值活动时间开始到来的情况的解析),频率的分布和功率谱密度。在光谱分析中,我们使用幂律、对数抛物线以及断裂幂律模型拟合X射线光谱,以确定最佳的拟合参数。我们在大多数的光变曲线中都观察到适度的日内变化。在这其中超过七个光变曲线呈现明显双峰型态的分布情况,这也揭示出两种不同的流量状态存在的事实。我们的分析发现功率谱斜率的起伏非常大并且会不时产生不稳定因素的结果也随时间流逝而不同方向地进行演化;另外观察到,绝大多数的光变特征图中并没有显示出硬度比会随着流量而发生显著变化的情况,然而有两张观测图则呈现出相当不同的结果。通过拟合得到的X射线光谱模型的结果偏向于大部分观察期间的断裂幂律模型,该结果意味着其谱面出现了断裂或断开的现象发生的结果亦昭示出部分群体的某些较为突出的断裂型态以及分布的实质影响等等情况的变化特点或显著因素皆一一得到了相当显著的验证与展现。这项工作的发现揭示了耀斑的日内变化,为理解驱动观测流量变化的非热喷射过程提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
研究PKS 2155-304变体的X射线特性,对其进行了全面的X射线光谱及时序分析。观察其长期与日内变化特性,采用XMM-牛顿观测数据,跨度长达15年。分析其变化特性,如变化率、振幅、最小变化时间尺度、流量分布及功率谱密度。在光谱分析中,使用幂律、对数抛物线及分段幂律模型拟合X射线光谱,观察到了日内变化及流量分布的二态性。结果揭示了功率谱斜率的可变性及部分观测中硬度比随流量的显著变化。多数观测数据支持分段幂律模型,表明光谱特征的转变。该研究对Blazars的日内变化提供了洞见,揭示非热喷流过程驱动流量变化的机制。
关键见解
- 研究对象为TeV Blazar PKS 2155-304的X射线变化特性。
- 对长达15年的22个时期的XMM-Newton观测数据进行了综合X射线光谱及时序分析。
- 观察到日内变化(IDV)在多数光变曲线中表现适中。
- 七次观测显示明显的双峰流量分布,表明存在两种截然不同的流量状态。
- 分析发现功率谱斜率有所变化。
- 在部分观测中,硬度比随流量显著变化。
点此查看论文截图

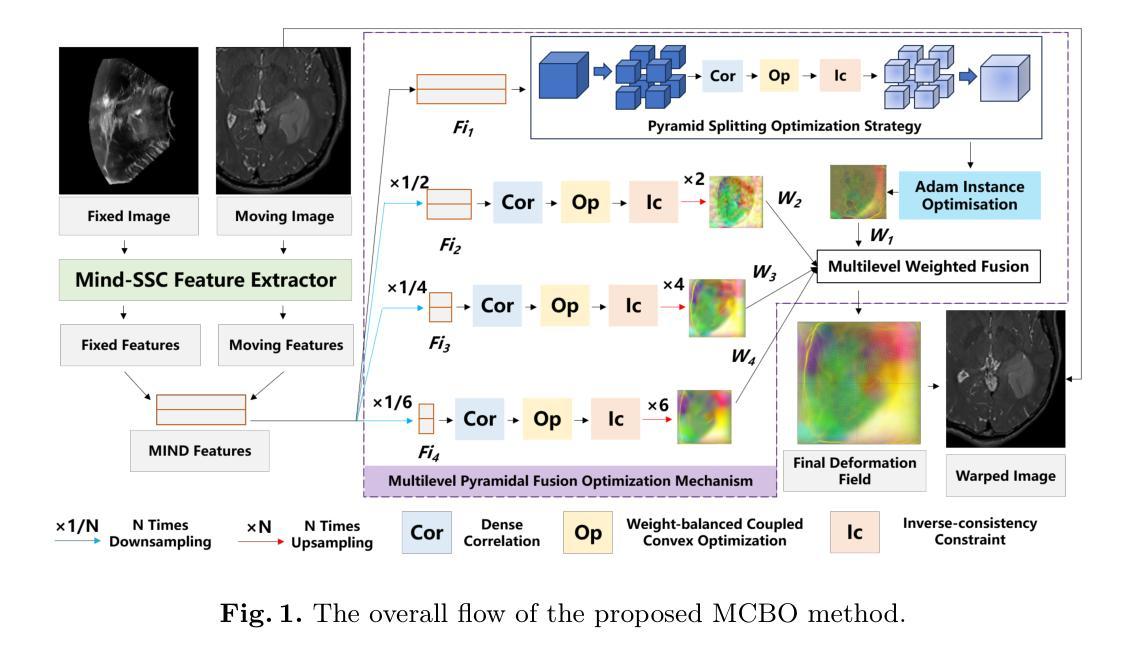
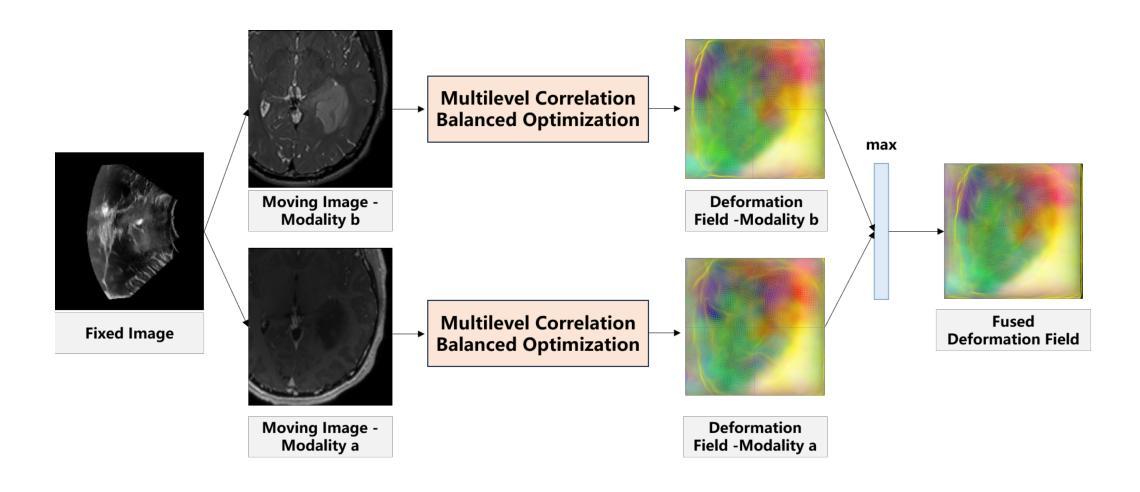
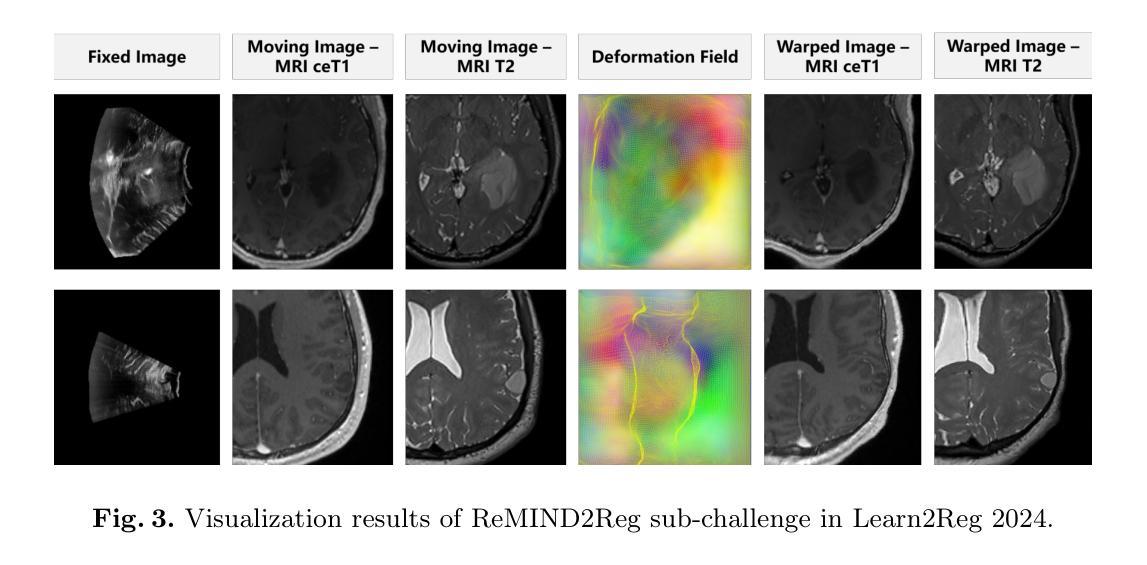
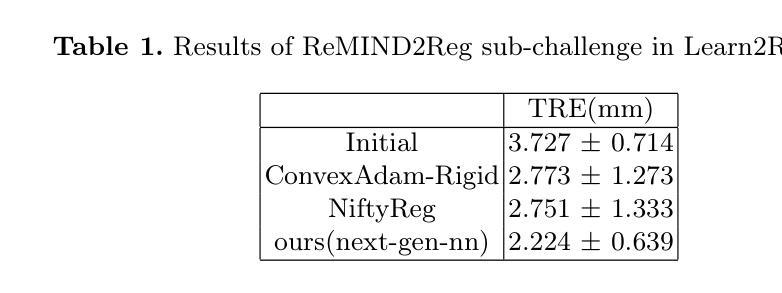
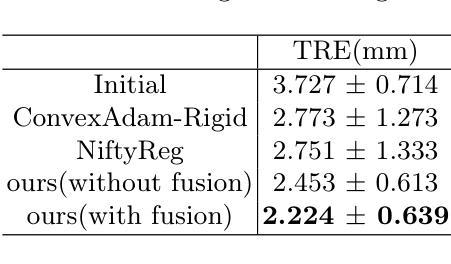
Unsupervised Multimodal 3D Medical Image Registration with Multilevel Correlation Balanced Optimization
Authors:Jiazheng Wang, Xiang Chen, Yuxi Zhang, Min Liu, Yaonan Wang, Hang Zhang
Surgical navigation based on multimodal image registration has played a significant role in providing intraoperative guidance to surgeons by showing the relative position of the target area to critical anatomical structures during surgery. However, due to the differences between multimodal images and intraoperative image deformation caused by tissue displacement and removal during surgery, effective registration of preoperative and intraoperative multimodal images faces significant challenges. To address the multimodal image registration challenges in Learn2Reg 2024, an unsupervised multimodal medical image registration method based on multilevel correlation balanced optimization (MCBO) is designed to solve these problems. First, the features of each modality are extracted based on the modality independent neighborhood descriptor, and the multimodal images are mapped to the feature space. Second, a multilevel pyramidal fusion optimization mechanism is designed to achieve global optimization and local detail complementation of the deformation field through dense correlation analysis and weight-balanced coupled convex optimization for input features at different scales. For preoperative medical images in different modalities, the alignment and stacking of valid information between different modalities is achieved by the maximum fusion between deformation fields. Our method focuses on the ReMIND2Reg task in Learn2Reg 2024, and to verify the generality of the method, we also tested it on the COMULIS3DCLEM task. Based on the results, our method achieved second place in the validation of both two tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/wjiazheng/MCBO.
基于多模态图像配准的手术导航在手术中起到了重要作用,它展示了目标区域相对于关键解剖结构的位置,为外科医生提供了术中指导。然而,由于多模态图像之间的差异以及手术过程中组织移位和移除所导致的术中图像变形,对术前和术中的多模态图像进行有效配准面临着重大挑战。为了解决Learn2Reg 2024中的多模态图像配准挑战,设计了一种基于多层次相关性平衡优化(MCBO)的无监督多模态医学图像配准方法。首先,基于模态独立邻域描述符提取每种模态的特征,并将多模态图像映射到特征空间。其次,设计了一种多层次金字塔融合优化机制,通过密集的相关性分析和权重平衡耦合凸优化,对不同尺度的输入特征实现变形场的全局优化和局部细节补充。对于不同模态的术前医学图像,通过变形场之间的最大融合实现不同模态之间有效信息的对齐和堆叠。我们的方法主要关注Learn2Reg 2024中的ReMIND2Reg任务,为了验证方法的通用性,我们还对COMULIS3DCLEM任务进行了测试。基于结果,我们的方法在两项任务的验证中均获得第二名。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/wjiazheng/MCBO。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Method description for MICCAI Learn2Reg 2024 challenge
Summary
基于多模态图像配准的手术导航在术中为外科医生提供目标区域与关键解剖结构的相对位置的指导。然而,由于多模态图像之间的差异以及术中图像变形带来的挑战,如组织位移和移除,有效的术前与术中的多模态图像配准仍面临困难。为解决Learn2Reg 2024中的多模态图像配准挑战,设计了一种基于多层次相关性平衡优化(MCBO)的无监督多模态医学图像配准方法。该方法首先基于模态独立邻域描述符提取各模态的特征,并将多模态图像映射到特征空间。其次,设计了一种多层次金字塔融合优化机制,通过密集相关性分析和权重平衡耦合凸优化,在不同尺度上对输入特征实现全局优化和局部细节补充的变形场。该方法实现了不同模态的术前医学图像之间的有效信息对齐和堆叠,并验证了其在ReMIND2Reg和COMULIS3DCLEM任务上的通用性。在两项任务的验证中,该方法取得了第二名。
Key Takeaways
- 手术导航基于多模态图像配准,为外科医生提供术中目标区域与解剖结构的相对位置指导。
- 多模态图像配准面临差异和术中图像变形的挑战。
- 提出了基于多层次相关性平衡优化(MCBO)的无监督多模态医学图像配准方法。
- 该方法通过特征提取和映射、多层次金字塔融合优化机制解决配准问题。
- 方法实现了不同模态医学图像的有效信息对齐和堆叠。
- 方法在ReMIND2Reg和COMULIS3DCLEM任务上进行了验证,取得了第二名。
点此查看论文截图


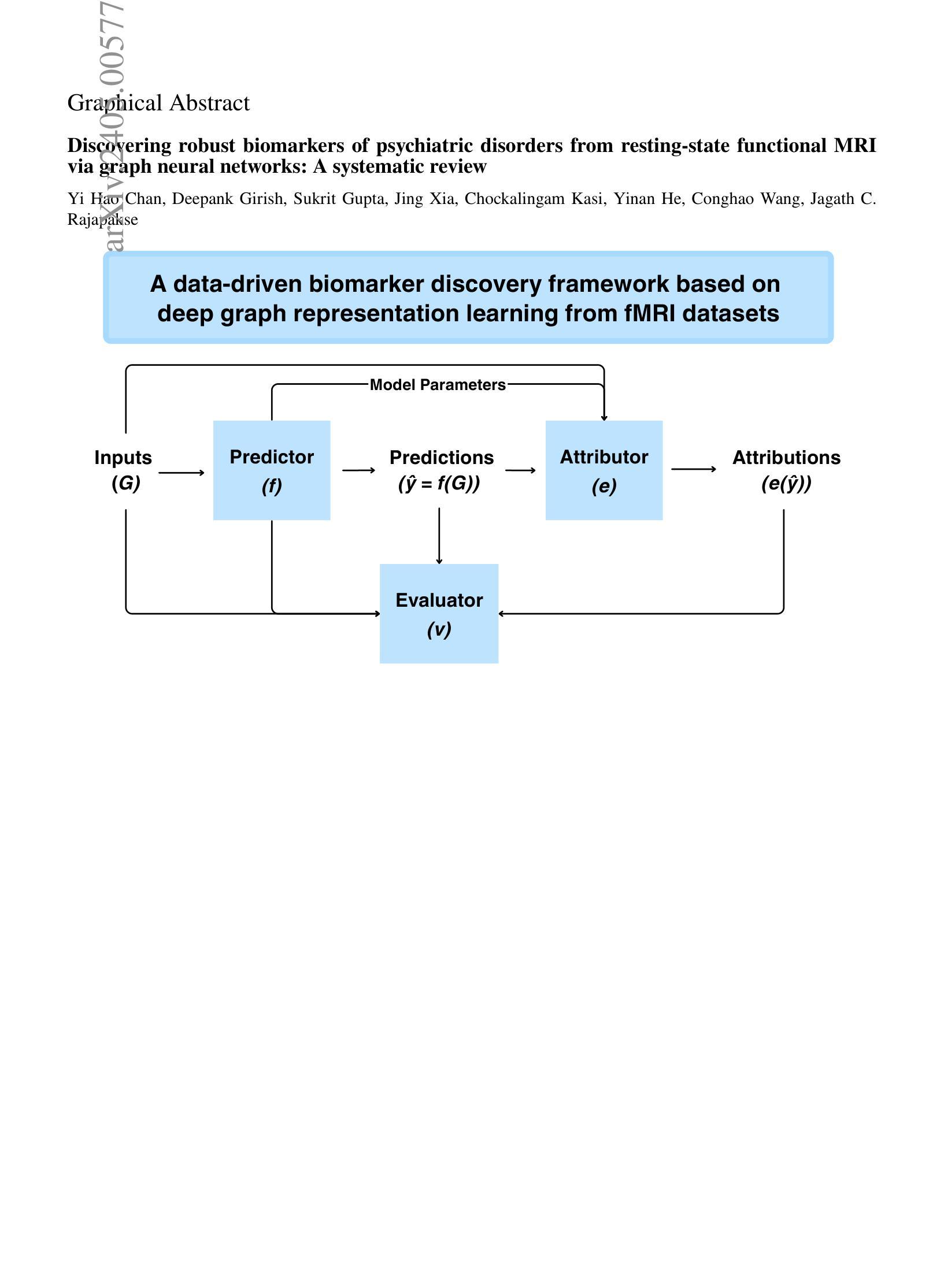
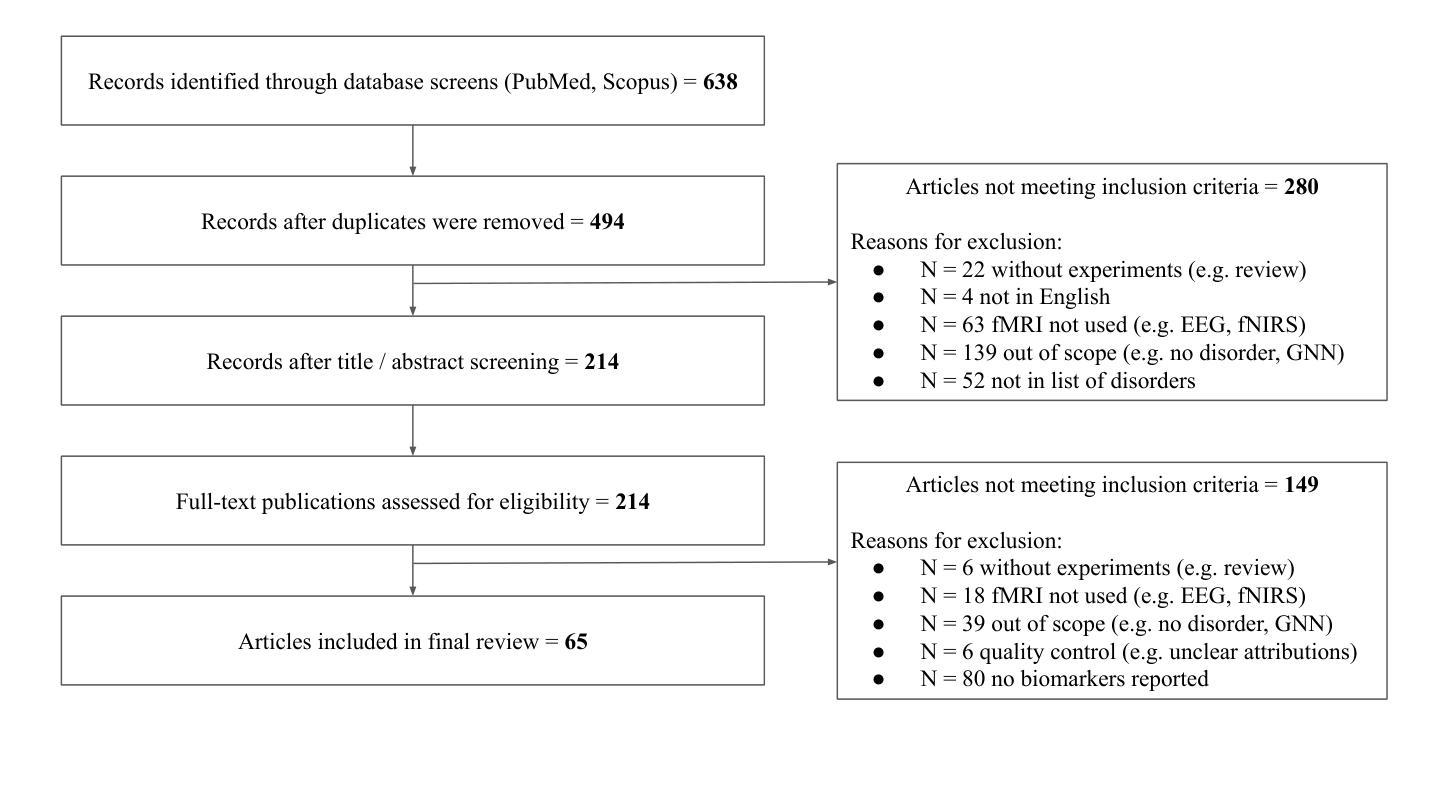
Discovering robust biomarkers of psychiatric disorders from resting-state functional MRI via graph neural networks: A systematic review
Authors:Yi Hao Chan, Deepank Girish, Sukrit Gupta, Jing Xia, Chockalingam Kasi, Yinan He, Conghao Wang, Jagath C. Rajapakse
Graph neural networks (GNN) have emerged as a popular tool for modelling functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) datasets. Many recent studies have reported significant improvements in disorder classification performance via more sophisticated GNN designs and highlighted salient features that could be potential biomarkers of the disorder. However, existing methods of evaluating their robustness are often limited to cross-referencing with existing literature, which is a subjective and inconsistent process. In this review, we provide an overview of how GNN and model explainability techniques (specifically, feature attributors) have been applied to fMRI datasets for disorder prediction tasks, with an emphasis on evaluating the robustness of potential biomarkers produced for psychiatric disorders. Then, 65 studies using GNNs that reported potential fMRI biomarkers for psychiatric disorders (attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, autism spectrum disorder, major depressive disorder, schizophrenia) published before 9 October 2024 were identified from 2 online databases (Scopus, PubMed). We found that while most studies have performant models, salient features highlighted in these studies (as determined by feature attribution scores) vary greatly across studies on the same disorder. Reproducibility of biomarkers is only limited to a small subset at the level of regions and few transdiagnostic biomarkers were identified. To address these issues, we suggest establishing new standards that are based on objective evaluation metrics to determine the robustness of these potential biomarkers. We further highlight gaps in the existing literature and put together a prediction-attribution-evaluation framework that could set the foundations for future research on discovering robust biomarkers of psychiatric disorders via GNNs.
图神经网络(GNN)已经成为处理功能磁共振成像(fMRI)数据集的一种流行工具。许多最近的研究报告指出,通过更复杂的GNN设计,疾病分类性能得到了显著提高,并突出了可能是疾病潜在生物标志物的特征。然而,现有的评估其稳健性的方法通常仅限于与现有文献进行交叉引用,这是一个主观且不一致的过程。在这篇综述中,我们概述了如何将图神经网络和模型解释性技术(特别是特征归因者)应用于fMRI数据集以进行疾病预测任务,重点评估了针对精神病学疾病所产生的潜在生物标志物的稳健性。然后,我们从两个在线数据库(Scopus和PubMed)中确定了65项在截至日期前发布的关于精神病学疾病(注意力缺陷多动障碍、自闭症谱系障碍、重度抑郁症和精神分裂症)的潜在fMRI生物标志物的GNN研究。我们发现,虽然大多数研究都取得了不错的成绩,但这些研究中突出强调的特征(由特征归属分数决定)在同一疾病的不同研究中存在很大差异。生物标志物的可重复性仅限于少数几个区域和几个跨诊断生物标志物。为了解决这些问题,我们建议使用基于客观评估指标的新标准来确定这些潜在生物标志物的稳健性。我们还强调了现有文献中的空白,并构建了一个预测-归因-评估框架,该框架可以为通过GNN发现精神病学疾病的稳健生物标志物的研究奠定未来基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图神经网络(GNN)在功能磁共振成像(fMRI)数据集建模中受到广泛关注。本研究综述了GNN及模型解释性技术在fMRI数据集上用于精神疾病预测任务的应用,并强调了评估潜在生物标志物稳健性的重要性。通过对65项研究进行分析,发现不同研究之间潜在特征差异较大,跨研究重现性有限。建议建立基于客观评估指标的新标准来确定生物标志物的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- GNN已成为建模fMRI数据集的流行工具,用于精神疾病分类并识别潜在生物标志物。
- 现有评估生物标志物稳健性的方法通常仅限于参考文献,这一过程主观且不一致。
- 研究发现,针对同一疾病的不同研究之间,所强调的潜在特征差异较大。
- 生物标志物的跨研究重现性仅限于少数区域和跨诊断生物标志物。
- 建议建立基于客观评估指标的新标准来确定潜在生物标志物的稳健性。
- 现有文献存在空白,需要建立预测-归因-评估框架。
点此查看论文截图
Identification of the superconductivity in bilayer nickelate La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$ upon 100 GPa
Authors:Jingyuan Li, Di Peng, Peiyue Ma, Hengyuan Zhang, Zhenfang Xing, Xing Huang, Chaoxin Huang, Mengwu Huo, Deyuan Hu, Zixian Dong, Xiang Chen, Tao Xie, Hongliang Dong, Hualei Sun, Qiaoshi Zeng, Ho-kwang Mao, Meng Wang
Identification of superconductivity in the Ruddlesden-Popper phases of nickelates under high pressure remains challenging. Here, we report a comprehensive study of the crystal structure, resistance, and Meissner effect in single crystals of La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$ with hydrostatic pressures up to 104 GPa. X-ray diffraction measurements reveal a structural transition from the orthorhombic to a tetragonal phase above 40 GPa. Zero resistance of the superconductivity was achieved with a maximum onset $T_c^{onset}$ of 83 K at 18.0 GPa. Superconductivity is gradually suppressed until it disappears above 80 GPa, resulting in a right-triangle-like superconducting region. The direct-current magnetic susceptibility technique successfully detected the Meissner effect in La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$ under pressure; the maximum superconducting volume fraction is estimated to be 62.7% at 22.0 GPa. Thus, we demonstrate the bulk nature of superconductivity in the bilayer nickelate La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$ single crystals under high pressure. The results reveal intimate connections among the superconductivity, oxygen content, and structure in La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$.
在高压下识别镍酸盐的Ruddlesden-Popper相的超导性仍然是一个挑战。在这里,我们报告了一项关于La3Ni2O7单晶的晶体结构、电阻和迈斯纳效应的全面研究,该研究在高达104 GPa的静水压力下进行。X射线衍射测量显示,在超过40 GPa时,结构从正交晶系转变为四方晶系。在18.0 GPa时,达到超导性的零电阻,起始临界温度Tconset最高为83 K。超导性在超过80 GPa时逐渐受到抑制直至消失,形成一个类似直角三角形的超导区域。直流磁化率技术成功地检测到了压力下的La3Ni2O7中的迈斯纳效应;估计在22.0 GPa时,超导体积分数最大,为62.7%。因此,我们证实了高压下双层镍酸盐La3Ni2O7单晶中的超导性是体性质。结果揭示了La3Ni2O7中超导性、氧含量和结构之间的密切联系。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is a renewed version with Meissner effect measurements
摘要
在高压环境下对镍酸镧的Ruddlesden-Popper相中的超导性进行研究是一个巨大的挑战。本论文针对单晶La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$的晶体结构、电阻和迈斯纳效应进行了全面的研究,压力高达104 GPa。X射线衍射测量显示,在高于40 GPa时,其结构从正交转变为四方相。在高压下观察到超导电性具有零电阻状态,最大起始转变温度($T_c^{onset}$)在18.0 GPa下达到83 K。超导性在高于80 GPa时逐渐受到抑制直至消失,形成类似直角三角形的高温超导区域。采用直流磁化率技术成功检测到压力下的La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$的迈斯纳效应;在22.0 GPa下估计的最大超导体积分数为62.7%。因此,我们证明了双层镍酸盐La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$单晶在高压下的超导性是体相性质。结果表明,超导性与氧含量和结构在La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$中存在密切联系。
关键要点
- 通过对单晶La$_3$Ni$_2$O$_7$在高压下的研究,观察到超导现象。
- 在特定压力下观察到零电阻状态,起始转变温度达到83 K。
- 超导性在压力超过一定值后逐渐受到抑制直至消失,形成特定的高压超导区域。
- 通过直流磁化率技术成功检测到超导的迈斯纳效应,证明超导是体相性质。
- 最大超导体积分数达到62.7%。
- X射线衍射测量显示高压下晶体结构从正交到四方的转变。
- 研究结果表明超导性与氧含量和结构有密切联系。
点此查看论文截图