⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
Improving Multi-Label Contrastive Learning by Leveraging Label Distribution
Authors:Ning Chen, Shen-Huan Lyu, Tian-Shuang Wu, Yanyan Wang, Bin Tang
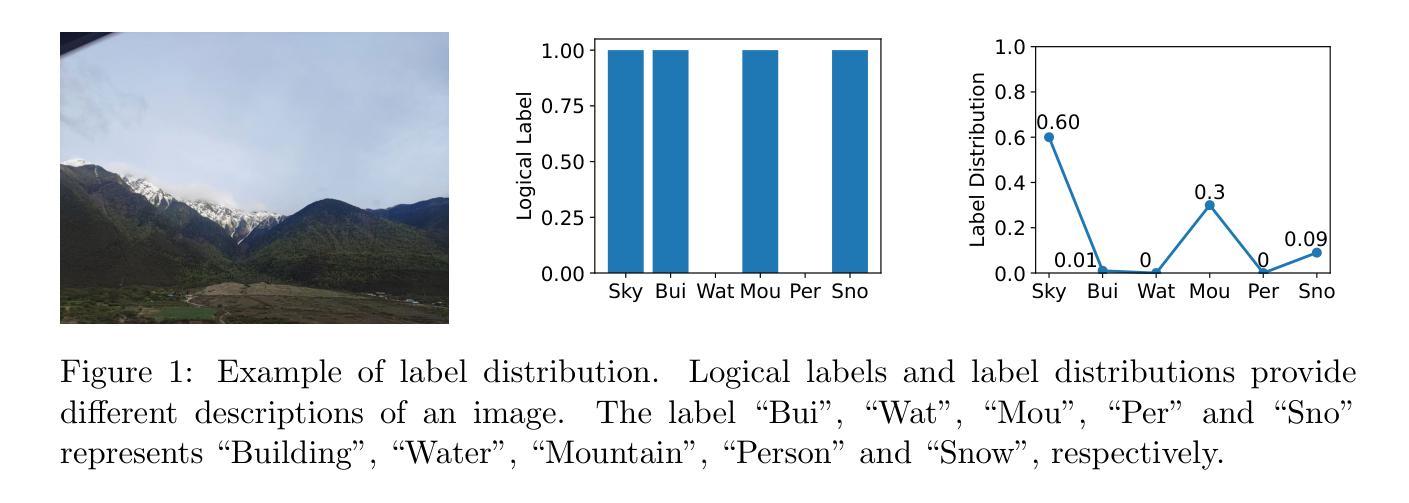
In multi-label learning, leveraging contrastive learning to learn better representations faces a key challenge: selecting positive and negative samples and effectively utilizing label information. Previous studies selected positive and negative samples based on the overlap between labels and used them for label-wise loss balancing. However, these methods suffer from a complex selection process and fail to account for the varying importance of different labels. To address these problems, we propose a novel method that improves multi-label contrastive learning through label distribution. Specifically, when selecting positive and negative samples, we only need to consider whether there is an intersection between labels. To model the relationships between labels, we introduce two methods to recover label distributions from logical labels, based on Radial Basis Function (RBF) and contrastive loss, respectively. We evaluate our method on nine widely used multi-label datasets, including image and vector datasets. The results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in six evaluation metrics.
在多标签学习中,利用对比学习来学习更好的表示面临一个关键挑战:选择正样本和负样本,并有效利用标签信息。早期研究基于标签之间的重叠来选择正样本和负样本,并将其用于标签损失平衡。然而,这些方法遭受着复杂的选择过程,并且未能考虑到不同标签的不同重要性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种通过标签分布改进多标签对比学习的新方法。具体来说,在选择正样本和负样本时,我们只需要考虑标签之间是否存在交集。为了建模标签之间的关系,我们引入两种基于径向基函数(RBF)和对比损失分别从逻辑标签中恢复标签分布的方法。我们在九个广泛使用的多标签数据集上评估了我们的方法,包括图像和向量数据集。结果表明,我们的方法在六个评估指标上优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了基于标签分布改进多标签对比学习的新方法。通过考虑标签间的逻辑关系,该方法在选取正、负样本时只需关注标签间是否有交集,并引入两种从逻辑标签恢复标签分布的方法,基于径向基函数(RBF)和对比损失分别实现。在多个多标签数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在六个评估指标上优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 多标签对比学习在选取正、负样本时面临挑战,需要解决标签重叠的问题,并有效利用标签信息。
- 现有方法存在复杂的选择过程和忽略不同标签不同重要性的问题。
- 本文提出了一种基于标签分布改进多标签对比学习的新方法,通过考虑标签间的逻辑关系简化样本选择过程。
- 引入两种从逻辑标签恢复标签分布的方法,分别基于径向基函数(RBF)和对比损失实现。
- 该方法在九个广泛应用的多标签数据集上进行实验验证,包括图像和向量数据集。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在六个评估指标上优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

Low-Contrast-Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Endoscopic Image Segmentation
Authors:Lingcong Cai, Yun Li, Xiaomao Fan, Kaixuan Song, Ruxin Wang, Wenbin Lei
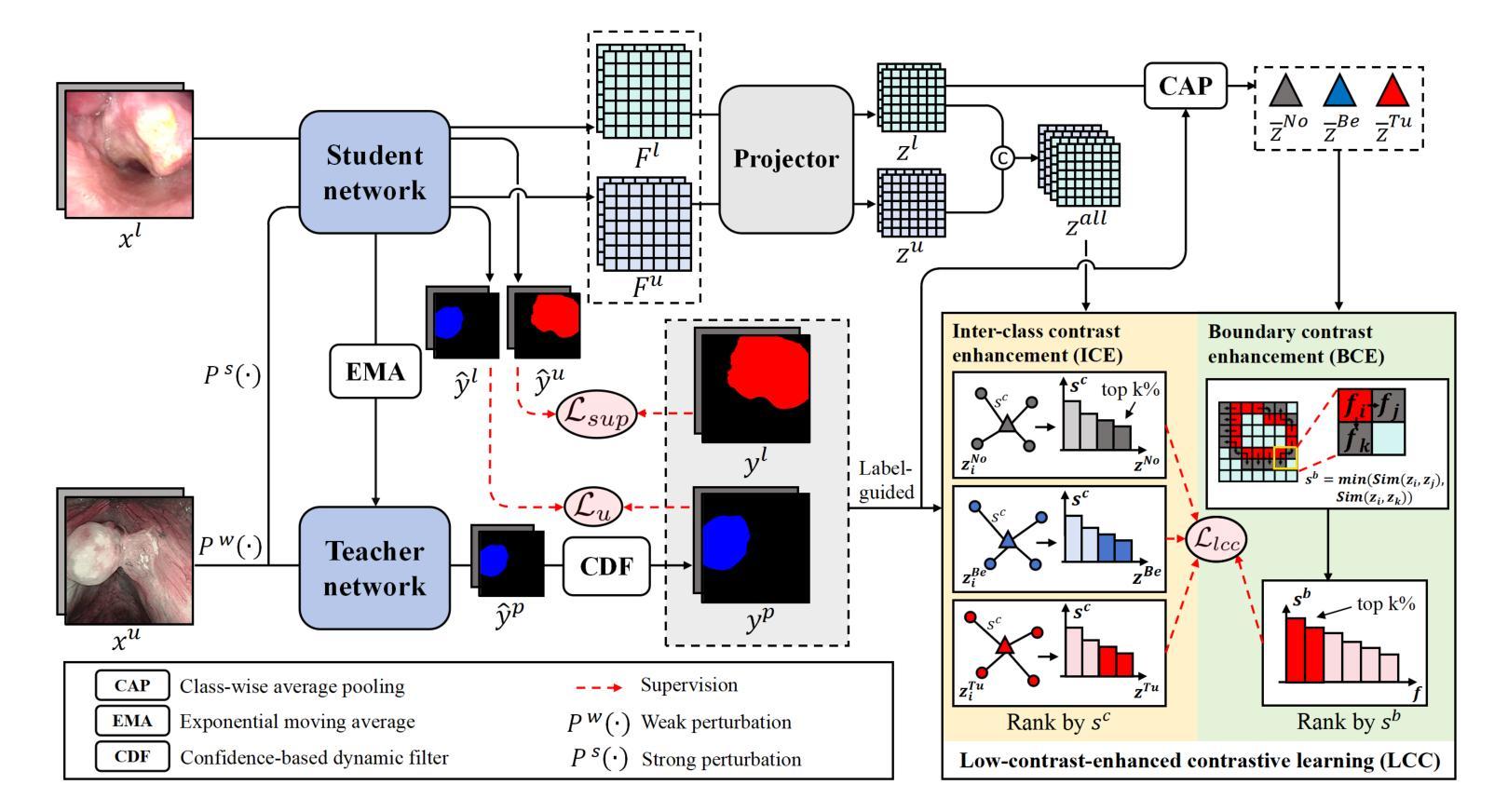
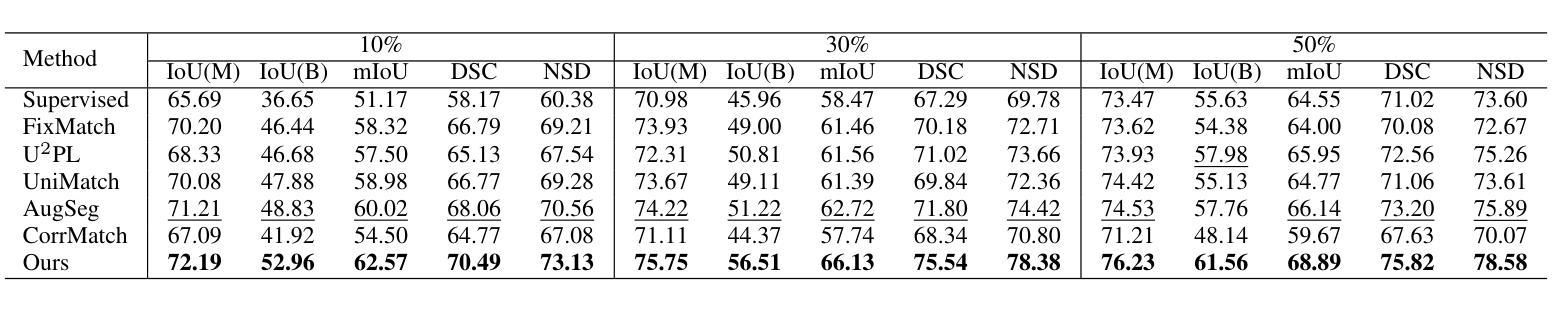
The segmentation of endoscopic images plays a vital role in computer-aided diagnosis and treatment. The advancements in deep learning have led to the employment of numerous models for endoscopic tumor segmentation, achieving promising segmentation performance. Despite recent advancements, precise segmentation remains challenging due to limited annotations and the issue of low contrast. To address these issues, we propose a novel semi-supervised segmentation framework termed LoCo via low-contrast-enhanced contrastive learning (LCC). This innovative approach effectively harnesses the vast amounts of unlabeled data available for endoscopic image segmentation, improving both accuracy and robustness in the segmentation process. Specifically, LCC incorporates two advanced strategies to enhance the distinctiveness of low-contrast pixels: inter-class contrast enhancement (ICE) and boundary contrast enhancement (BCE), enabling models to segment low-contrast pixels among malignant tumors, benign tumors, and normal tissues. Additionally, a confidence-based dynamic filter (CDF) is designed for pseudo-label selection, enhancing the utilization of generated pseudo-labels for unlabeled data with a specific focus on minority classes. Extensive experiments conducted on two public datasets, as well as a large proprietary dataset collected over three years, demonstrate that LoCo achieves state-of-the-art results, significantly outperforming previous methods. The source code of LoCo is available at the URL of \href{https://github.com/AnoK3111/LoCo}{https://github.com/AnoK3111/LoCo}.
内镜图像的分割在计算机辅助诊断和治疗中起着至关重要的作用。深度学习的发展推动了内镜肿瘤分割模型的应用,并实现了有希望的分割性能。尽管最近有进展,但由于标注有限和对比度低的问题,精确分割仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的半监督分割框架,名为LoCo,通过低对比度增强对比学习(LCC)。这种创新的方法有效地利用了内镜图像分割中大量可用的未标记数据,提高了分割过程的准确性和稳健性。具体来说,LCC结合了两种先进策略,以提高低对比度像素的区分性:类间对比度增强(ICE)和边界对比度增强(BCE),使模型能够在恶性、良性肿瘤和正常组织之间分割低对比度像素。此外,还设计了一种基于信心的动态过滤器(CDF)进行伪标签选择,提高了对生成伪标签的利用,重点关注少数类。在两个公共数据集以及三年收集的大型专有数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,LoCo达到了最先进的性能,显著优于以前的方法。LoCo的源代码可在https://github.com/AnoK3111/LoCo的URL上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于低对比度增强对比学习(LCC)的半监督分割框架LoCo,用于内镜图像分割。该框架通过利用大量未标注数据,提高了分割的准确性和鲁棒性。其中,采用两种策略增强低对比度像素的区分度:类间对比度增强(ICE)和边界对比度增强(BCE)。此外,还设计了一种基于置信度的动态滤波器(CDF)用于伪标签选择。在多个公共和自有数据集上的实验表明,LoCo取得了最新结果,显著优于之前的方法。代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- LoCo是一个基于低对比度增强对比学习(LCC)的半监督分割框架,用于内镜图像分割。
- LCC框架通过利用大量未标注数据,提高了分割准确性和鲁棒性。
- 采用类间对比度增强(ICE)和边界对比度增强(BCE)策略,增强了低对比度像素的区分度。
- 基于置信度的动态滤波器(CDF)用于伪标签选择,提高了未标注数据的利用率,特别关注少数类。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,LoCo显著优于之前的方法,取得了最新结果。
点此查看论文截图

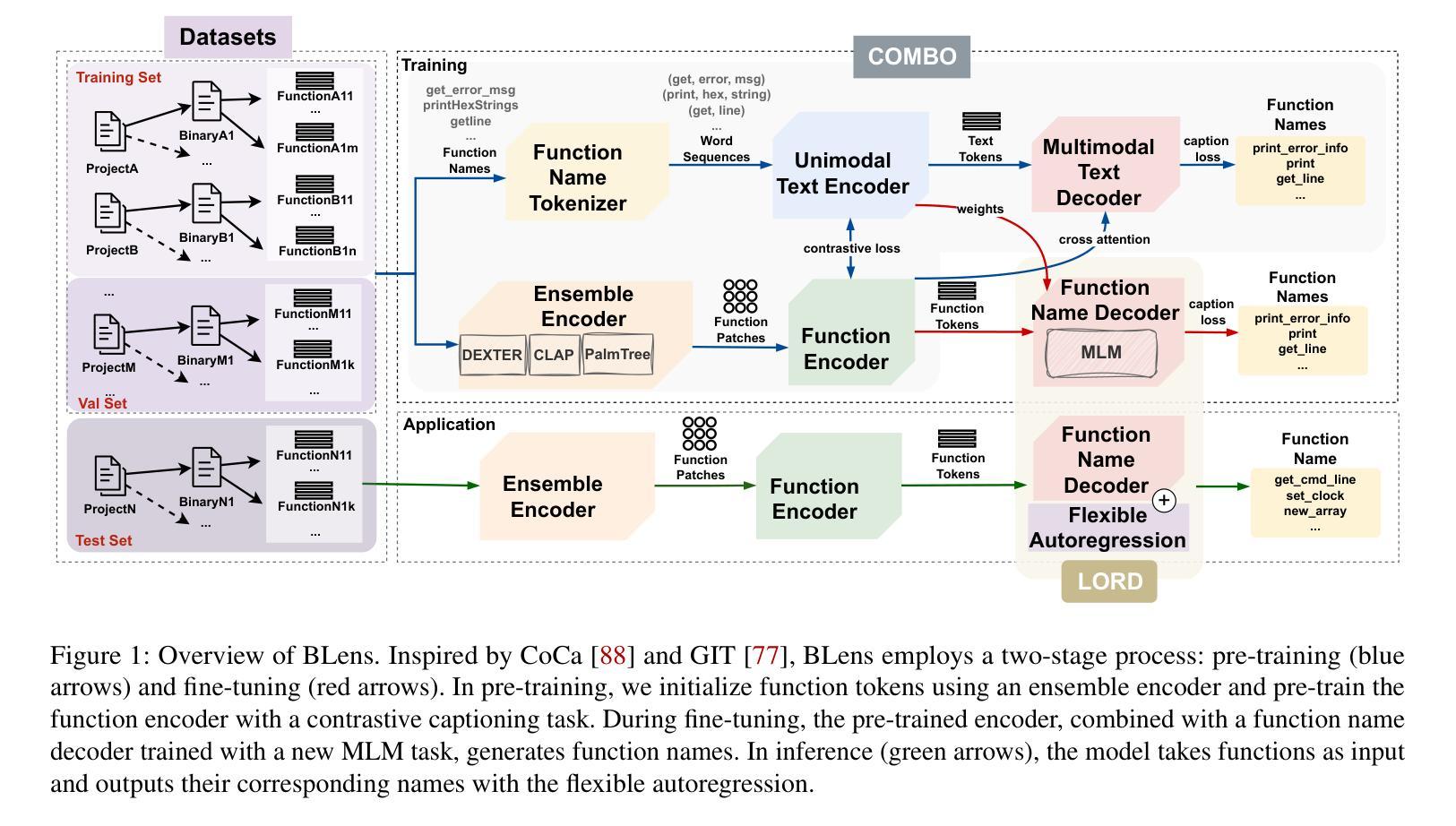
BLens: Contrastive Captioning of Binary Functions using Ensemble Embedding
Authors:Tristan Benoit, Yunru Wang, Moritz Dannehl, Johannes Kinder
Function names can greatly aid human reverse engineers, which has spurred the development of machine learning-based approaches to predicting function names in stripped binaries. Much current work in this area now uses transformers, applying a metaphor of machine translation from code to function names. Still, function naming models face challenges in generalizing to projects unrelated to the training set. In this paper, we take a completely new approach by transferring advances in automated image captioning to the domain of binary reverse engineering, such that different parts of a binary function can be associated with parts of its name. We propose BLens, which combines multiple binary function embeddings into a new ensemble representation, aligns it with the name representation latent space via a contrastive learning approach, and generates function names with a transformer architecture tailored for function names. Our experiments demonstrate that BLens significantly outperforms the state of the art. In the usual setting of splitting per binary, we achieve an $F_1$ score of 0.79 compared to 0.70. In the cross-project setting, which emphasizes generalizability, we achieve an $F_1$ score of 0.46 compared to 0.29. Finally, in an experimental setting reducing shared components across projects, we achieve an $F_1$ score of $0.32$ compared to $0.19$.
函数名可以极大地帮助人类逆向工程师,这刺激了基于机器学习的方法在剥离二进制文件中预测函数名的发展。目前该领域的许多工作都使用了变压器(transformers),采用了一种从代码到函数名的机器翻译隐喻。然而,函数命名模型在面对与训练集不相关的项目时,普遍存在着泛化挑战。
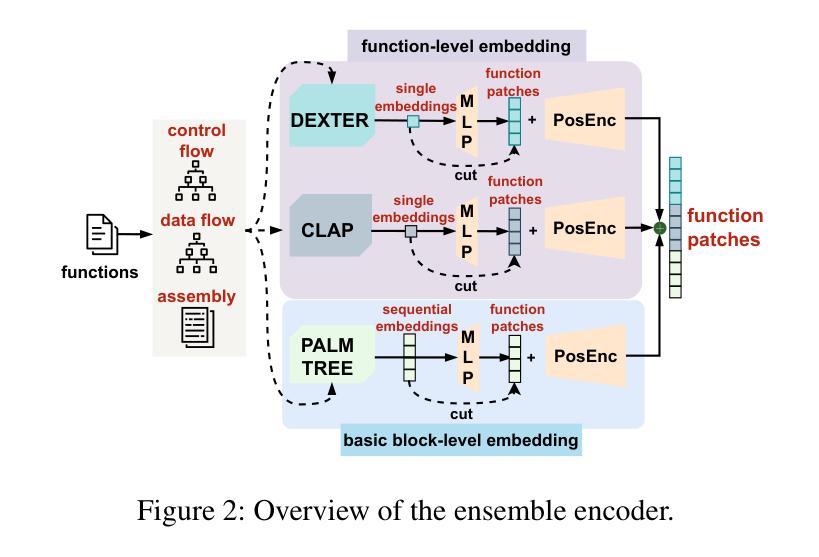
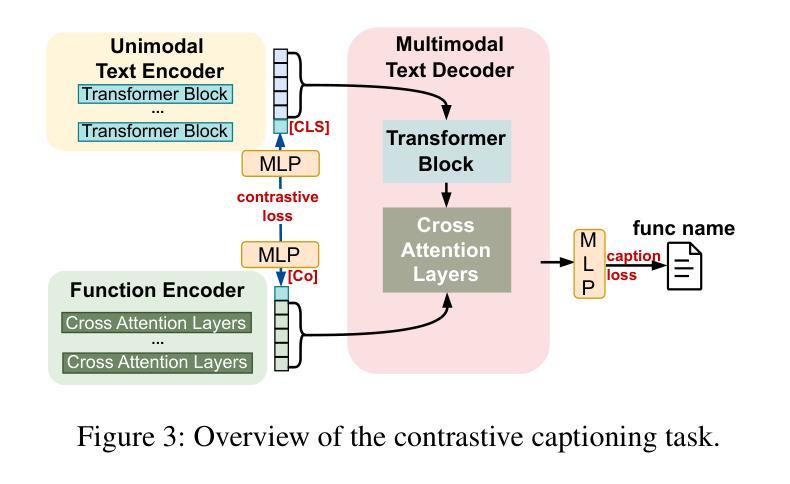
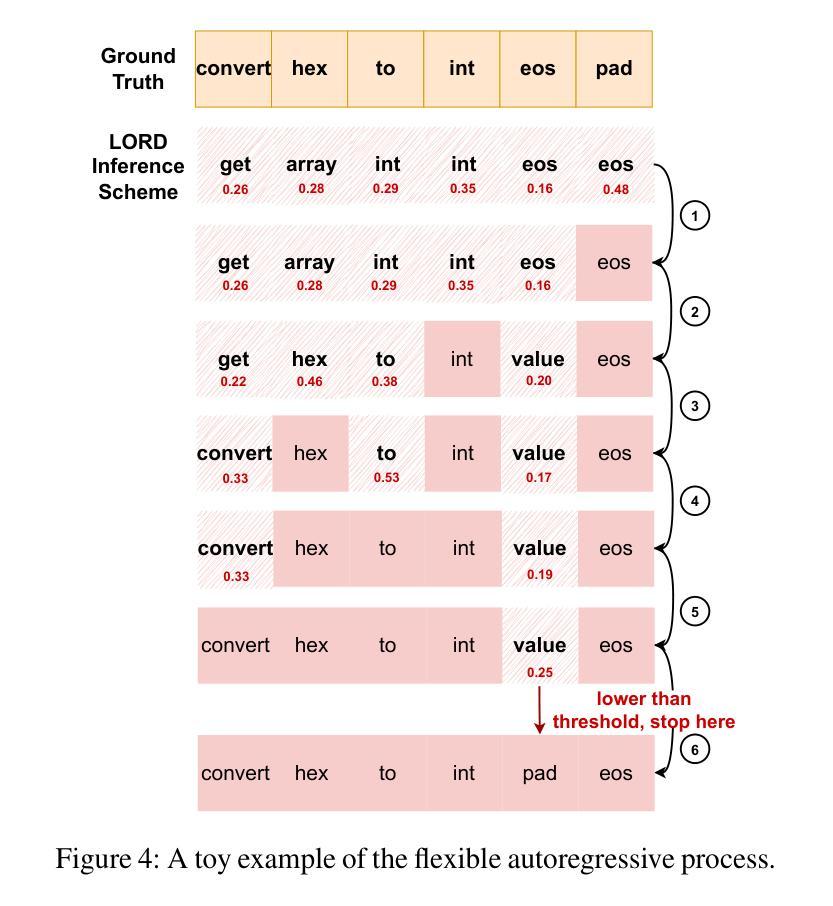
在本文中,我们采用了全新的方法,将自动图像描述领域的先进技术转移到二进制逆向工程领域,使得二进制函数的不同部分可以与它的名称部分相关联。我们提出了BLens,它将多个二进制函数嵌入组合成一个新的集成表示,通过对比学习方法将其与名称表示潜在空间对齐,并使用针对函数名称定制的变压器架构生成函数名称。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 34th USENIX Security Symposium (Usenix 2025). 20 pages, 5 figures. Tristan Benoit and Yunru Wang made equal contributions to this work
Summary
本文提出了一种新的方法BLens,将图像自动描述技术应用于二进制反向工程领域,将二进制函数的不同部分与其名称部分相关联。BLens结合多个二进制函数嵌入到一个新的集合表示中,通过对比学习方法将其与名称表示潜在空间对齐,并使用针对函数名称定制的变压器架构生成函数名称。实验表明,BLens显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了一种新的方法BLens,利用图像自动描述技术为二进制反向工程领域提供新的解决方案。
- BLens结合多个二进制函数嵌入到一个新的集合表示中,这种表示方式有助于更好地理解和分析二进制函数。
- 文章采用对比学习方法,将二进制函数与名称表示潜在空间对齐,这是该方法的创新点之一。
- 使用针对函数名称定制的变压器架构生成函数名称,这是BLens的另一个重要特点。
- 实验表明,BLens在标准二进制分割设置中实现了较高的F1分数,达到了0.79,优于现有技术的0.70。
- 在强调通用性的跨项目设置中,BLens也表现出较高的性能,实现了F1分数为0.46,优于现有技术的0.29。
点此查看论文截图