⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
Medical Semantic Segmentation with Diffusion Pretrain
Authors:David Li, Anvar Kurmukov, Mikhail Goncharov, Roman Sokolov, Mikhail Belyaev
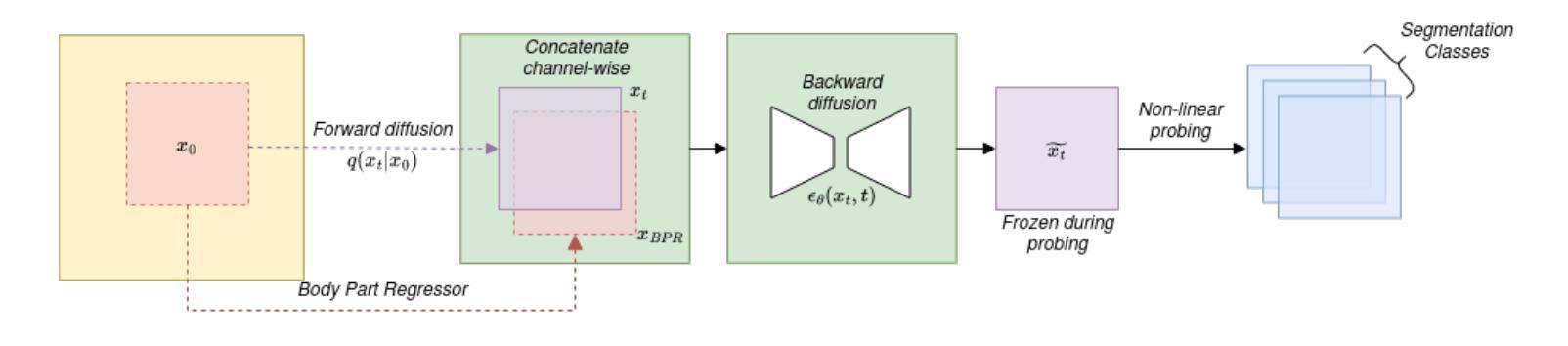
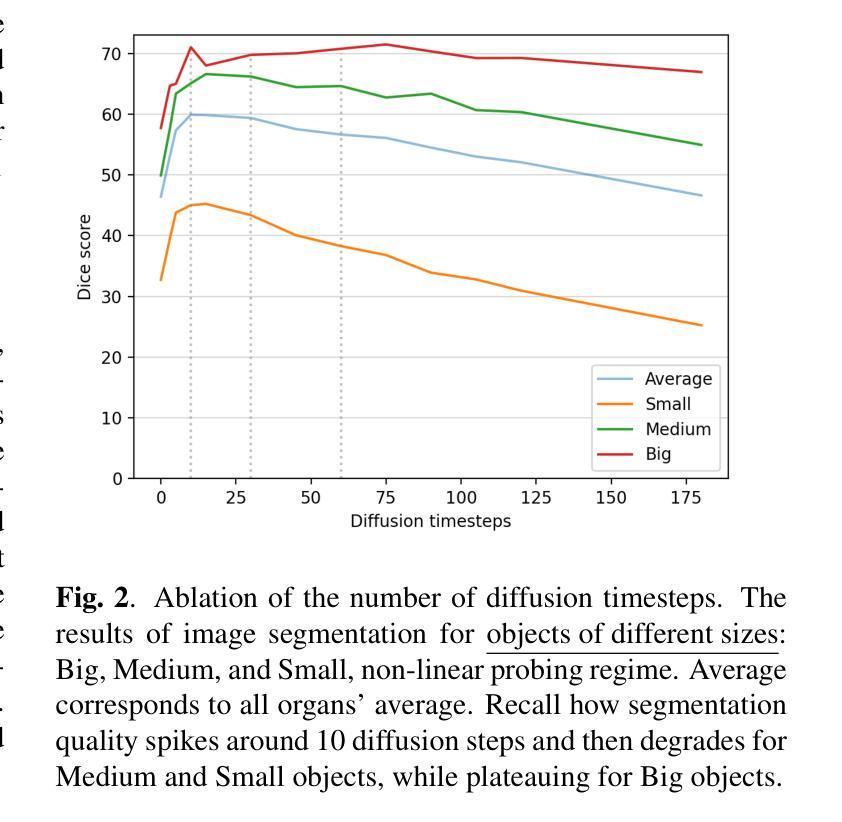
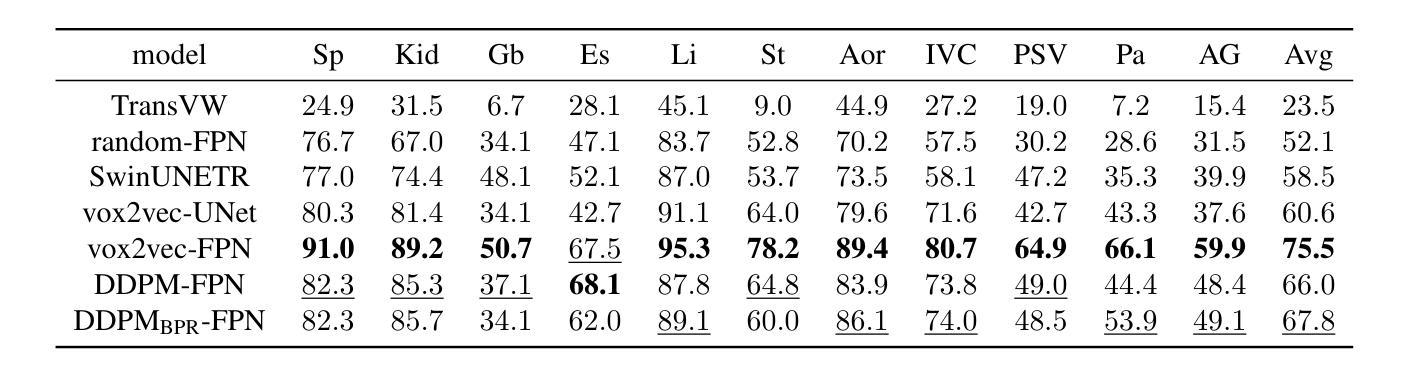
Recent advances in deep learning have shown that learning robust feature representations is critical for the success of many computer vision tasks, including medical image segmentation. In particular, both transformer and convolutional-based architectures have benefit from leveraging pretext tasks for pretraining. However, the adoption of pretext tasks in 3D medical imaging has been less explored and remains a challenge, especially in the context of learning generalizable feature representations. We propose a novel pretraining strategy using diffusion models with anatomical guidance, tailored to the intricacies of 3D medical image data. We introduce an auxiliary diffusion process to pretrain a model that produce generalizable feature representations, useful for a variety of downstream segmentation tasks. We employ an additional model that predicts 3D universal body-part coordinates, providing guidance during the diffusion process and improving spatial awareness in generated representations. This approach not only aids in resolving localization inaccuracies but also enriches the model’s ability to understand complex anatomical structures. Empirical validation on a 13-class organ segmentation task demonstrate the effectiveness of our pretraining technique. It surpasses existing restorative pretraining methods in 3D medical image segmentation by $7.5%$, and is competitive with the state-of-the-art contrastive pretraining approach, achieving an average Dice coefficient of 67.8 in a non-linear evaluation scenario.
最近的深度学习进展表明,学习鲁棒的特征表示对于包括医学图像分割在内的许多计算机视觉任务的成功至关重要。特别是,基于transformer和卷积的架构都受益于利用预训练中的预文本任务。然而,在3D医学影像中使用预文本任务的实践尚未得到充分探索,并且在学习可推广的特征表示方面仍然存在挑战。我们提出了一种使用扩散模型进行预训练的新型策略,该策略针对3D医学图像数据的复杂性进行了定制。我们引入了一个辅助扩散过程来预训练一个模型,该模型能够产生可用于各种下游分割任务的通用特征表示。我们还采用了另一个预测3D通用身体部位坐标的模型,在扩散过程中提供指导,并提高了生成表示中的空间感知能力。这种方法不仅有助于解决定位不准确的问题,而且还丰富了模型理解复杂解剖结构的能力。在13类器官分割任务上的经验验证表明了我们预训练技术的有效性。与现有的3D医学图像分割的修复预训练方法相比,我们的技术超越了其7.5%,并且在非线性评估场景中与最新的对比预训练方法具有竞争力,达到了平均Dice系数为67.8。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习的新进展表明,学习鲁棒的特征表示对于包括医学图像分割在内的计算机视觉任务的成功至关重要。本文提出了一种利用扩散模型进行预训练的新型策略,该策略具有解剖导向,针对3D医学图像数据的复杂性。通过引入辅助扩散过程和预测3D通用身体部位坐标的附加模型,该方法可产生用于各种下游分割任务的通用特征表示。这提高了模型的空间感知能力,并改善了定位不准确的问题。在13类器官分割任务上的经验验证表明,我们的预训练技术超越了现有的3D医学图像分割的修复预训练方法,并处于与最新的对比预训练方法的竞争水平。在非线性评价标准下,平均Dice系数为67.8。这是一种创新的方法,极大地提升了分割跟踪的准确度与效率。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割中的应用日益重要,学习鲁棒的特征表示是关键。
- 文中提出了一种新型的预训练策略,利用扩散模型并结合解剖导向,针对3D医学图像数据的复杂性进行优化。
- 通过引入辅助扩散过程和预测身体部位坐标的模型,提高了模型的空间感知能力。
- 该方法解决了定位不准确的问题,提升了分割跟踪的准确度。
- 在多个器官分割任务上的实验验证显示其效果超越现有方法,平均Dice系数较高。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用前景,可应用于多种下游分割任务。
点此查看论文截图

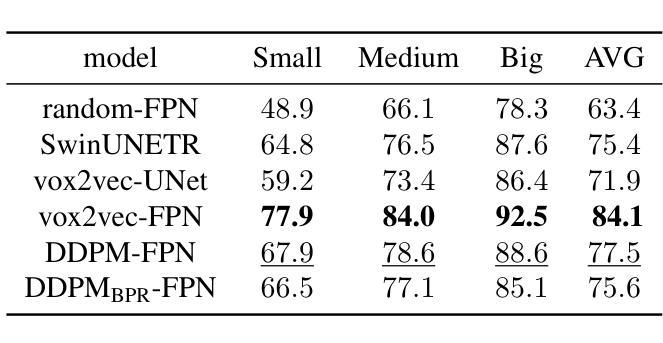
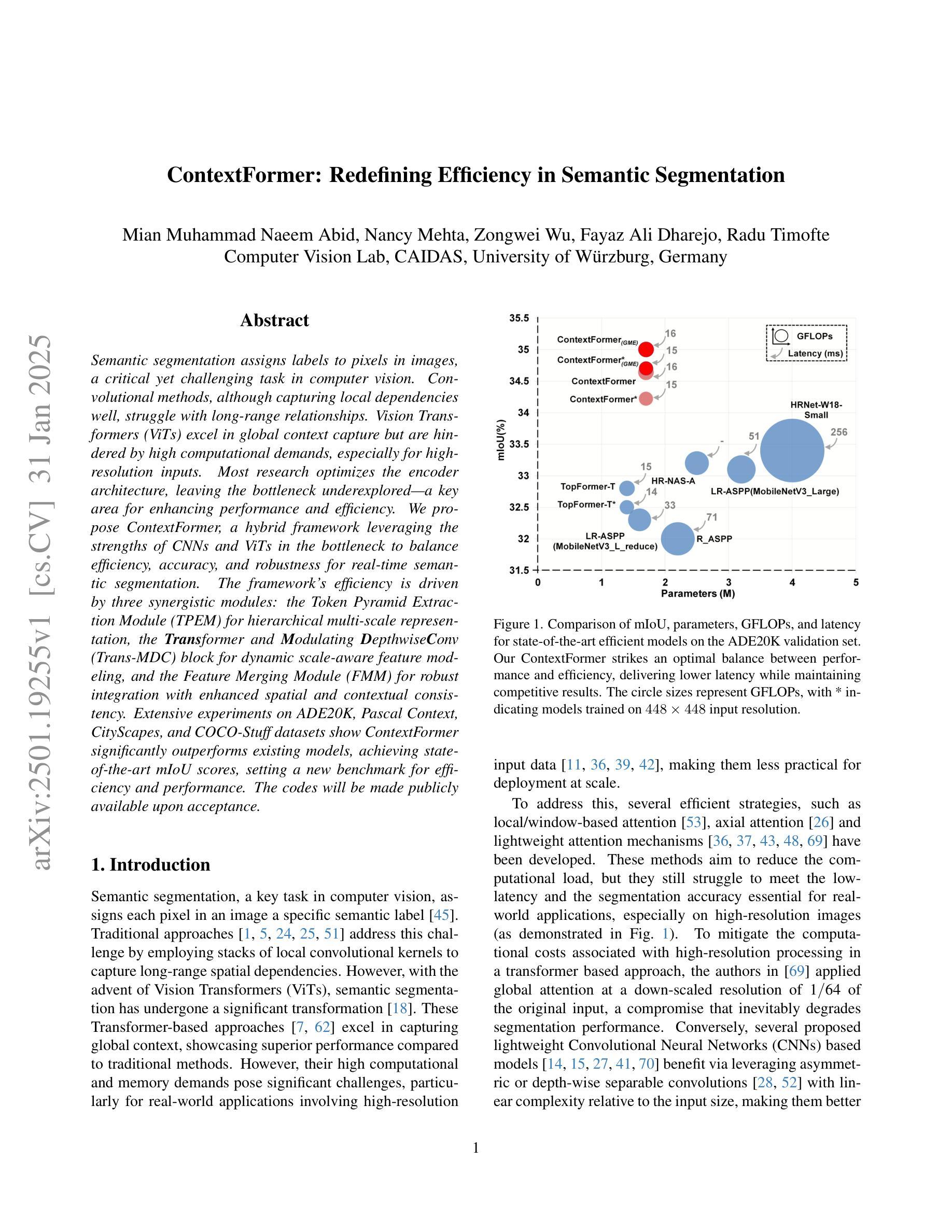
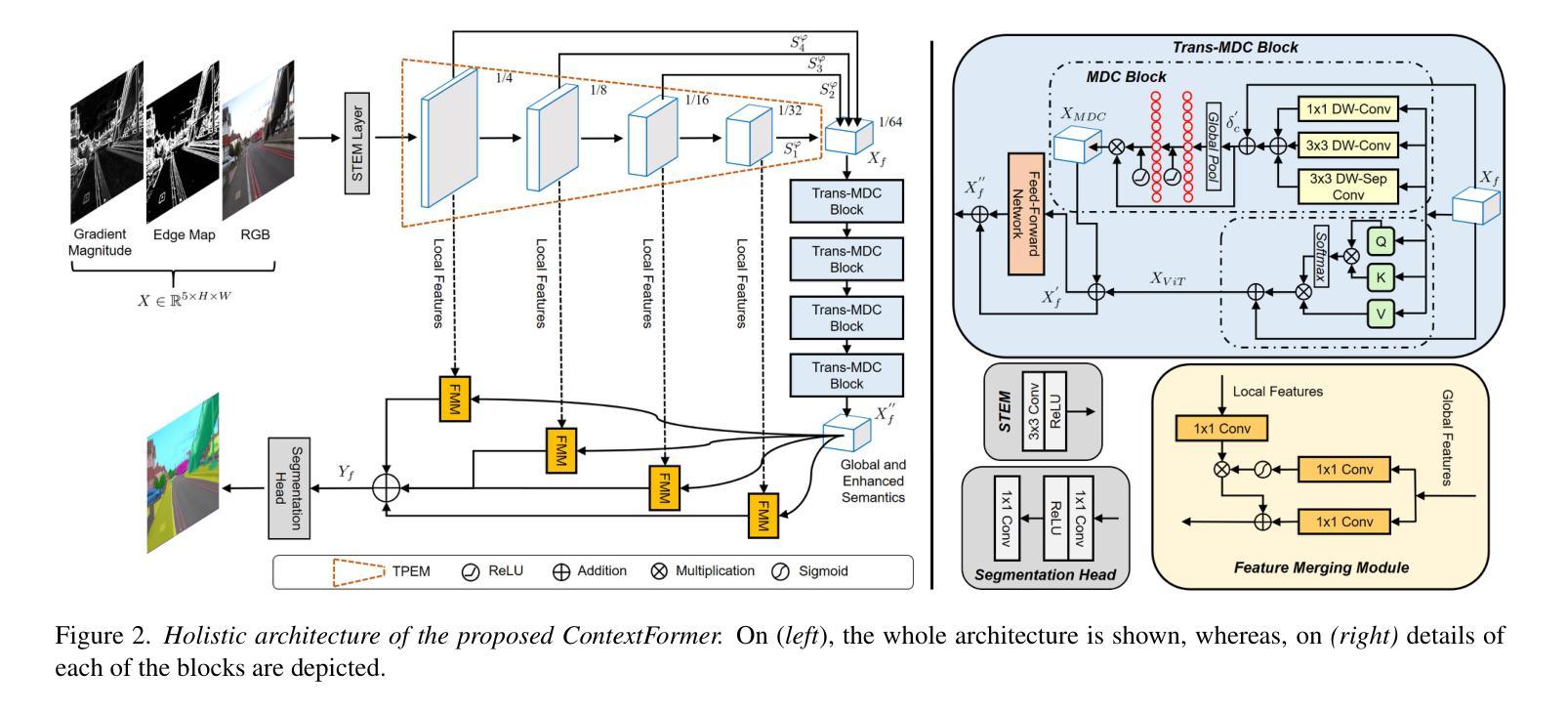
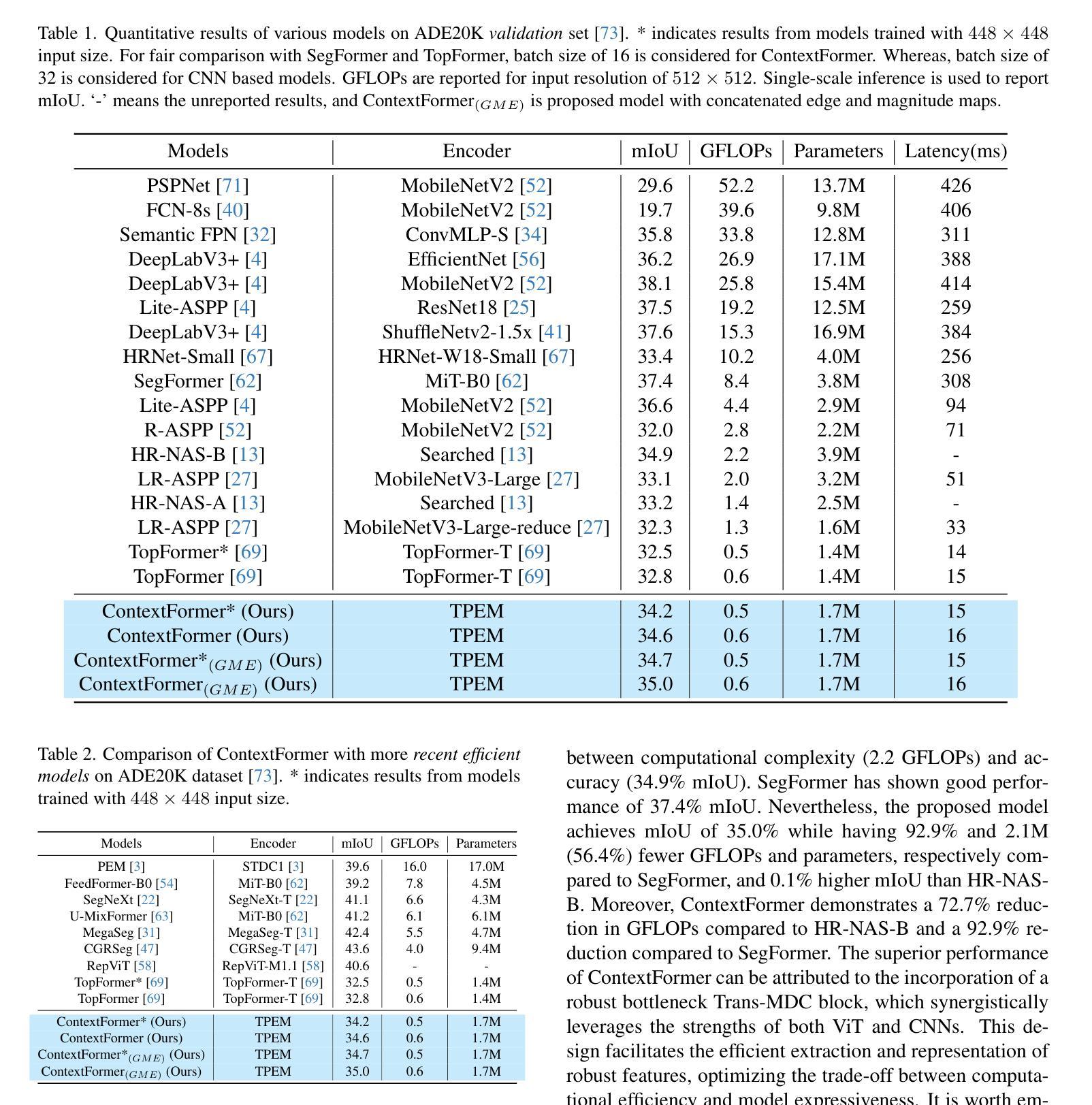
ContextFormer: Redefining Efficiency in Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Mian Muhammad Naeem Abid, Nancy Mehta, Zongwei Wu, Fayaz Ali Dharejo, Radu Timofte
Semantic segmentation assigns labels to pixels in images, a critical yet challenging task in computer vision. Convolutional methods, although capturing local dependencies well, struggle with long-range relationships. Vision Transformers (ViTs) excel in global context capture but are hindered by high computational demands, especially for high-resolution inputs. Most research optimizes the encoder architecture, leaving the bottleneck underexplored - a key area for enhancing performance and efficiency. We propose ContextFormer, a hybrid framework leveraging the strengths of CNNs and ViTs in the bottleneck to balance efficiency, accuracy, and robustness for real-time semantic segmentation. The framework’s efficiency is driven by three synergistic modules: the Token Pyramid Extraction Module (TPEM) for hierarchical multi-scale representation, the Transformer and Modulating DepthwiseConv (Trans-MDC) block for dynamic scale-aware feature modeling, and the Feature Merging Module (FMM) for robust integration with enhanced spatial and contextual consistency. Extensive experiments on ADE20K, Pascal Context, CityScapes, and COCO-Stuff datasets show ContextFormer significantly outperforms existing models, achieving state-of-the-art mIoU scores, setting a new benchmark for efficiency and performance. The codes will be made publicly available.
语义分割是计算机视觉领域中的一项重要且具有挑战性的任务,它需要对图像中的像素进行标注。卷积方法虽然能够很好地捕捉局部依赖性,但在处理长距离关系方面存在困难。视觉转换器(ViTs)擅长捕捉全局上下文,但计算需求较高,尤其是对于高分辨率输入。大多数研究都在优化编码器架构,而忽略了一个关键的性能提升和效率提升的区域。我们提出了ContextFormer,这是一个混合框架,利用CNN和ViT在瓶颈处的优势,在实时语义分割中平衡效率、准确性和鲁棒性。该框架的效率由三个协同模块驱动:用于层次化多尺度表示的Token金字塔提取模块(TPEM)、用于动态尺度感知特征建模的Transformer和调制深度卷积(Trans-MDC)块、以及用于稳健集成、增强空间一致性和上下文一致性的特征合并模块(FMM)。在ADE20K、Pascal Context、CityScapes和COCO-Stuff数据集上的大量实验表明,ContextFormer显著优于现有模型,达到了最先进的mIoU分数,为效率和性能设定了新的基准。相关代码将会公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语义分割是对图像中的像素进行标注的关键任务,在计算机视觉中极具挑战性。卷积方法擅长捕捉局部依赖性,但在处理长距离关系时遇到困难。Vision Transformers(ViTs)擅长捕捉全局上下文,但计算成本高昂,尤其是处理高分辨率输入时。大多数研究优化了编码器架构,而忽略了对瓶颈的优化,这是提高性能和效率的关键领域。本研究提出ContextFormer框架,利用CNN和ViT在瓶颈上的优势,平衡效率、准确性和鲁棒性,实现实时语义分割。该框架的效率得益于三个协同模块:用于分层多尺度表示的Token Pyramid Extraction Module(TPEM)、用于动态尺度感知特征建模的Transformer和Modulating DepthwiseConv(Trans-MDC)块以及用于稳健集成的Feature Merging Module(FMM),增强了空间一致性。在ADE20K、Pascal Context、CityScapes和COCO-Stuff数据集上的大量实验表明,ContextFormer显著优于现有模型,实现了最先进的mIoU得分,为效率和性能设定了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割是计算机视觉中的关键任务,但具有挑战性。
- 卷积方法和Vision Transformers(ViTs)在语义分割中有各自的优势和劣势。
- 当前研究多关注优化编码器架构,而瓶颈的优化被忽略。
- ContextFormer是一个混合框架,结合CNN和ViT的优势,旨在平衡效率、准确性和鲁棒性。
- ContextFormer框架包含三个协同模块:TPEM、Trans-MDC和FMM。
- ContextFormer在多个数据集上实现了先进的mIoU得分,显著优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图
SynthmanticLiDAR: A Synthetic Dataset for Semantic Segmentation on LiDAR Imaging
Authors:Javier Montalvo, Pablo Carballeira, Álvaro García-Martín
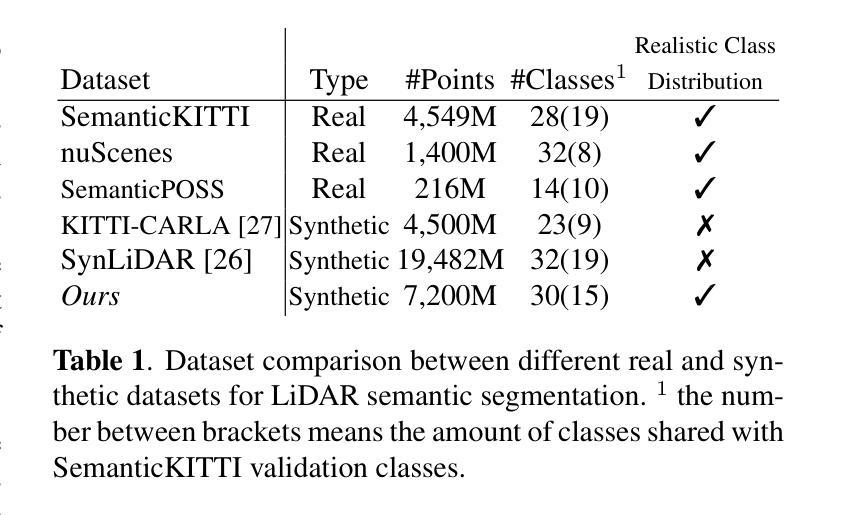
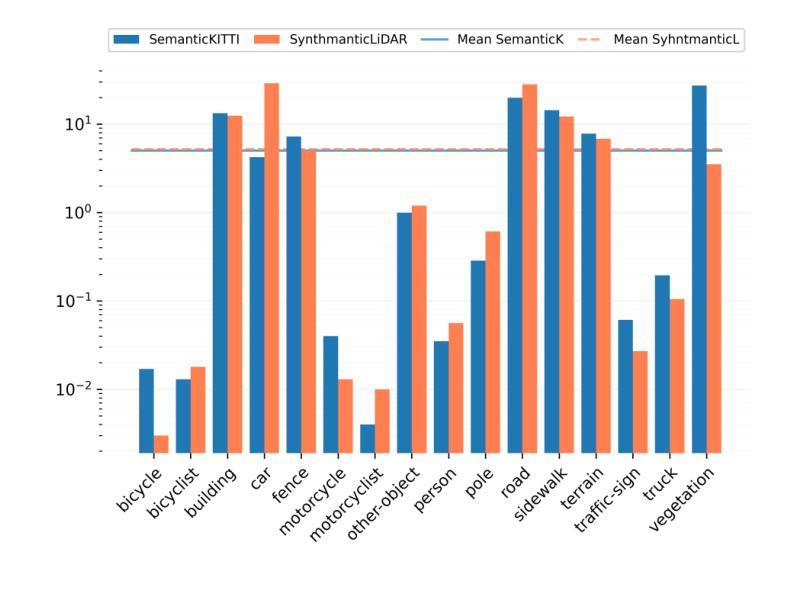
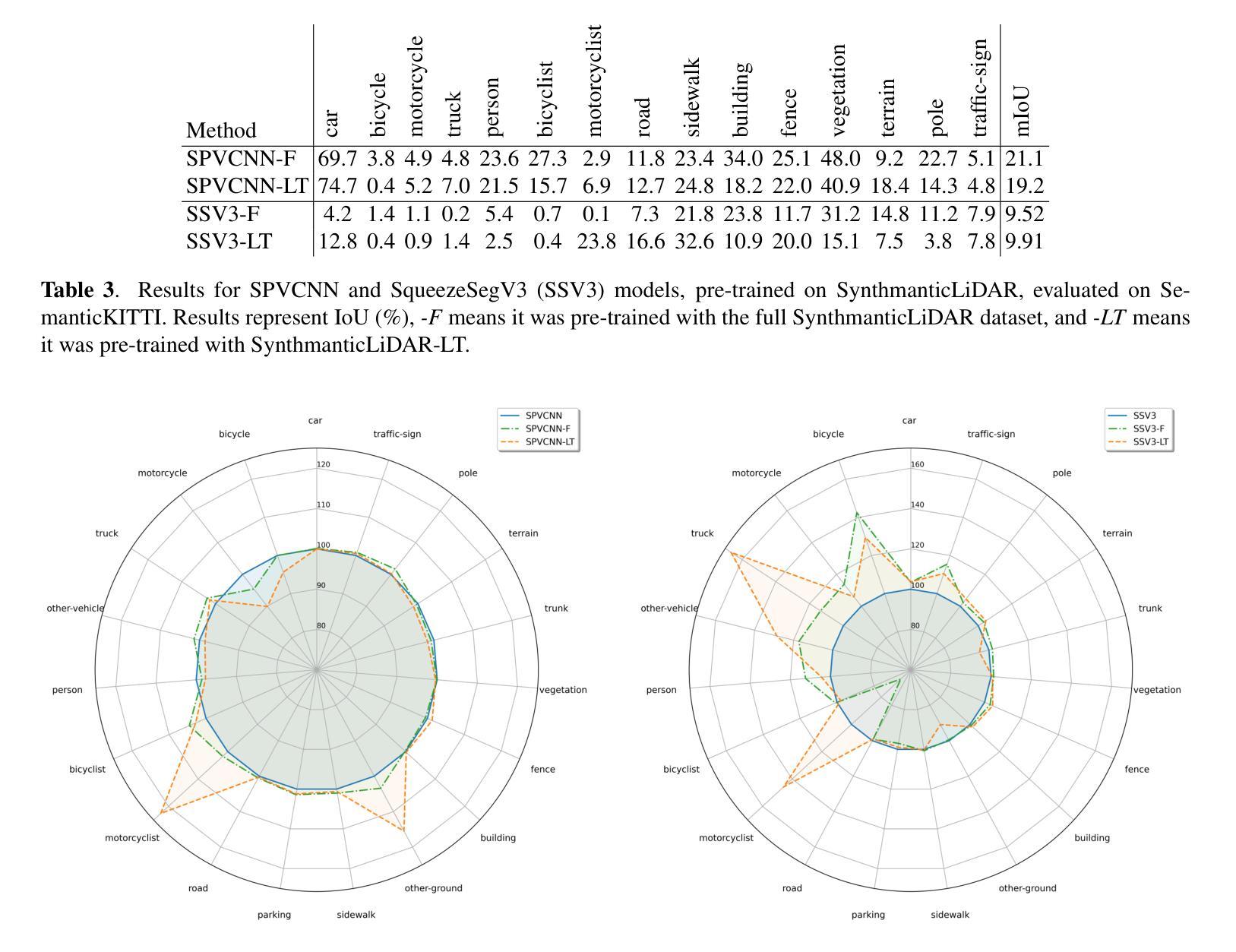
Semantic segmentation on LiDAR imaging is increasingly gaining attention, as it can provide useful knowledge for perception systems and potential for autonomous driving. However, collecting and labeling real LiDAR data is an expensive and time-consuming task. While datasets such as SemanticKITTI have been manually collected and labeled, the introduction of simulation tools such as CARLA, has enabled the creation of synthetic datasets on demand. In this work, we present a modified CARLA simulator designed with LiDAR semantic segmentation in mind, with new classes, more consistent object labeling with their counterparts from real datasets such as SemanticKITTI, and the possibility to adjust the object class distribution. Using this tool, we have generated SynthmanticLiDAR, a synthetic dataset for semantic segmentation on LiDAR imaging, designed to be similar to SemanticKITTI, and we evaluate its contribution to the training process of different semantic segmentation algorithms by using a naive transfer learning approach. Our results show that incorporating SynthmanticLiDAR into the training process improves the overall performance of tested algorithms, proving the usefulness of our dataset, and therefore, our adapted CARLA simulator. The dataset and simulator are available in https://github.com/vpulab/SynthmanticLiDAR.
激光雷达成像的语义分割越来越受到关注,因为它可以为感知系统和自动驾驶提供有用的知识。然而,收集和标记真实的激光雷达数据是一项昂贵且耗时的任务。虽然像SemanticKITTI这样的数据集已经被手动收集和标记,但CARLA等仿真工具的出现,使得能够按需创建合成数据集成为可能。在这项工作中,我们展示了经过修改的CARLA模拟器,它是专门针对激光雷达语义分割而设计的,包含新的类别、更一致的对象标记,以及能够与如SemanticKITTI等真实数据集相对应的对象类别的可能性,还可以调整对象类别分布。使用这个工具,我们生成了SynthmanticLiDAR数据集,这是一个用于激光雷达成像语义分割的合成数据集,设计得类似于SemanticKITTI。我们通过使用简单的迁移学习方法来评估其对不同语义分割算法训练过程的贡献。结果表明,在训练过程中加入SynthmanticLiDAR能提高测试算法的整体性能,这证明了我们的数据集以及经过修改的CARLA模拟器的实用性。数据集和模拟器可在https://github.com/vpulab/SynthmanticLiDAR获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)
Summary
语义分割在激光雷达成像领域正受到越来越多的关注,因为它能为感知系统和自动驾驶提供有价值的知识。然而,收集和标注真实的激光雷达数据是一项昂贵且耗时的工作。尽管像SemanticKITTI这样的数据集已经被手动收集和标注,但CARLA仿真器的出现使得可以按需创建合成数据集成为可能。在这项研究中,我们展示了针对激光雷达语义分割设计的改进版CARLA仿真器,包括新的类别、更一致的物体标注以及与真实数据集如SemanticKITTI的对应物标注匹配,以及可调整物体类别分布的功能。利用此工具,我们生成了用于激光雷达成像语义分割的合成数据集SynthmanticLiDAR,其设计类似于SemanticKITTI。我们通过使用简单的迁移学习方法评估了其对不同语义分割算法训练过程的贡献。结果表明,将SynthmanticLiDAR纳入训练过程提高了测试算法的整体性能,证明了我们的数据集和适应性CARLA仿真器的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在激光雷达成像领域日益受到关注,因为它有助于提升感知系统和自动驾驶技术的性能。
- 真实激光雷达数据的收集与标注成本高昂且耗时。
- CARLA仿真器的改进版本被设计用于激光雷达语义分割,具备新的类别、更一致的物体标注以及与真实数据集的匹配性。
- 利用改进版CARLA仿真器生成了名为SynthmanticLiDAR的合成数据集,用于激光雷达成像的语义分割。
- SynthmanticLiDAR的设计类似于SemanticKITTI数据集。
- 通过迁移学习方法评估,将SynthmanticLiDAR纳入训练过程提高了语义分割算法的性能。
- 结果证明了SynthmanticLiDAR数据集和适应性CARLA仿真器的实用价值。
点此查看论文截图