⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
Advancing Dense Endoscopic Reconstruction with Gaussian Splatting-driven Surface Normal-aware Tracking and Mapping
Authors:Yiming Huang, Beilei Cui, Long Bai, Zhen Chen, Jinlin Wu, Zhen Li, Hongbin Liu, Hongliang Ren
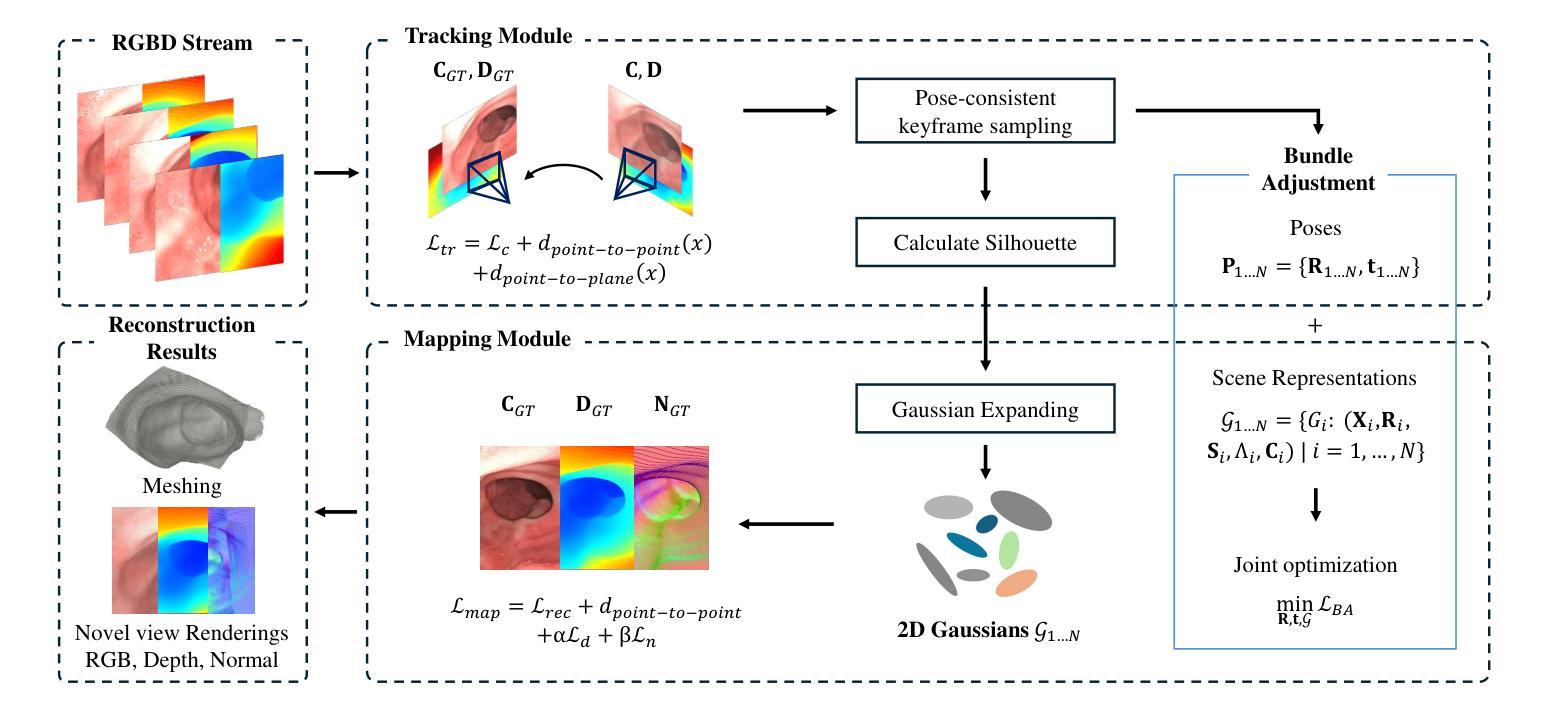
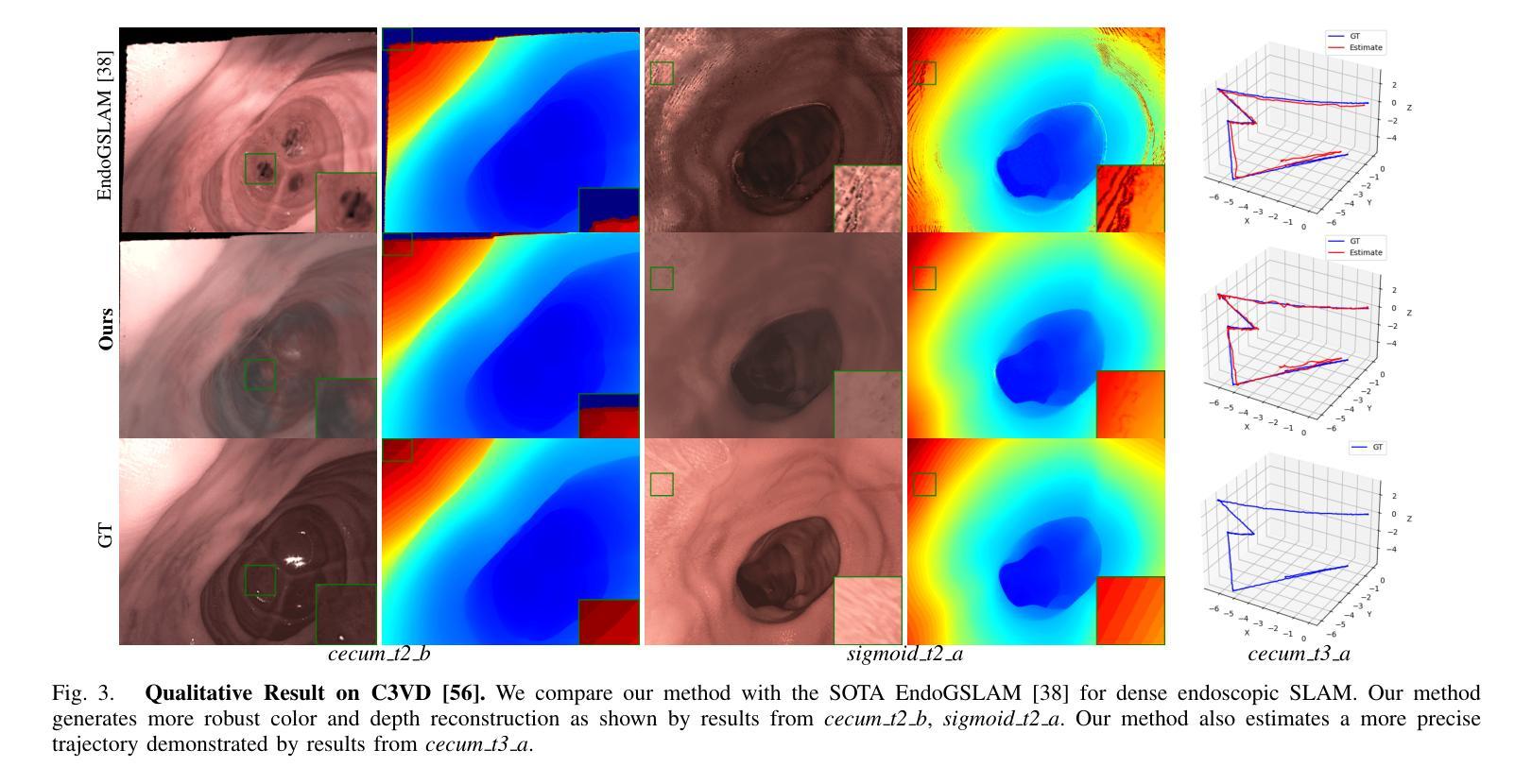
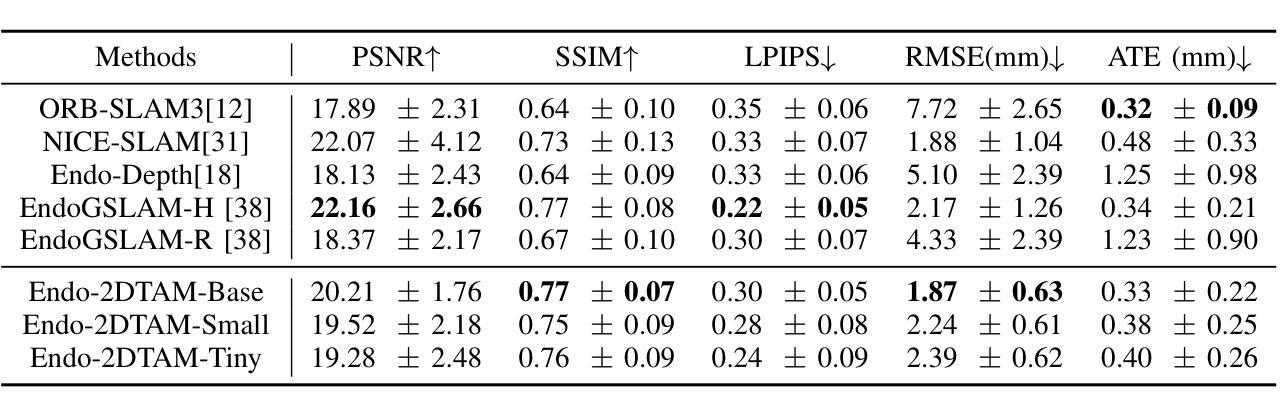
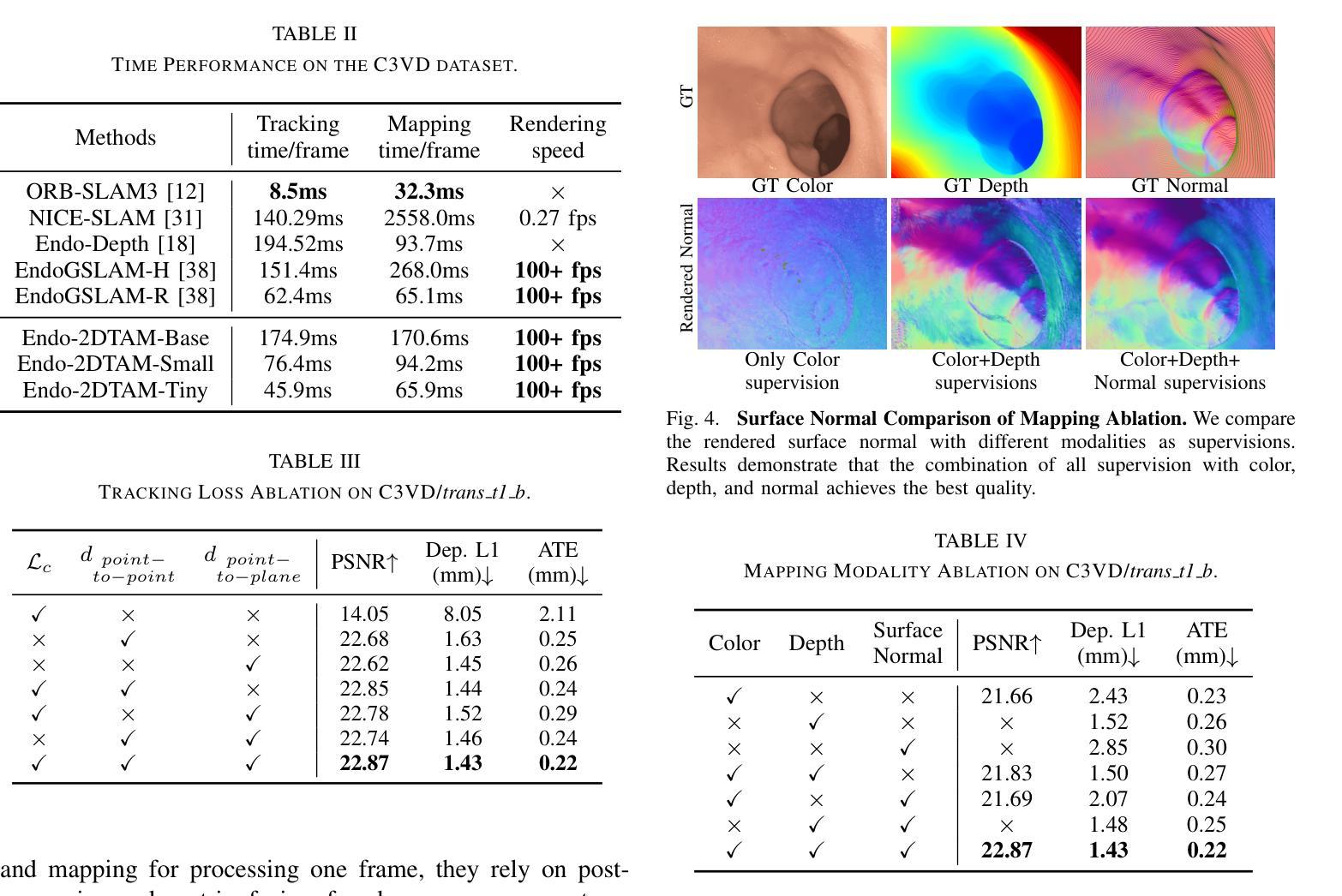
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is essential for precise surgical interventions and robotic tasks in minimally invasive procedures. While recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have improved SLAM with high-quality novel view synthesis and fast rendering, these systems struggle with accurate depth and surface reconstruction due to multi-view inconsistencies. Simply incorporating SLAM and 3DGS leads to mismatches between the reconstructed frames. In this work, we present Endo-2DTAM, a real-time endoscopic SLAM system with 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) to address these challenges. Endo-2DTAM incorporates a surface normal-aware pipeline, which consists of tracking, mapping, and bundle adjustment modules for geometrically accurate reconstruction. Our robust tracking module combines point-to-point and point-to-plane distance metrics, while the mapping module utilizes normal consistency and depth distortion to enhance surface reconstruction quality. We also introduce a pose-consistent strategy for efficient and geometrically coherent keyframe sampling. Extensive experiments on public endoscopic datasets demonstrate that Endo-2DTAM achieves an RMSE of $1.87\pm 0.63$ mm for depth reconstruction of surgical scenes while maintaining computationally efficient tracking, high-quality visual appearance, and real-time rendering. Our code will be released at github.com/lastbasket/Endo-2DTAM.
同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)在微创手术中的精确手术干预和机器人任务中至关重要。虽然最近在3D高斯喷射(3DGS)方面的最新进展已通过高质量的新型视图合成和快速渲染功能改进了SLAM,但这些系统在深度与表面重建方面仍存在准确性问题,这是由于多视图的不一致性所导致的。仅仅将SLAM和3DGS相结合会导致重建帧之间的不匹配。在这项工作中,我们提出了Endo-2DTAM,这是一种具有实时功能的内窥镜SLAM系统,结合了二维高斯喷射(2DGS)来解决这些挑战。Endo-2DTAM采用了一种表面法线感知管道,该管道包含跟踪、映射和捆绑调整模块,用于实现几何准确的重建。我们的稳健跟踪模块结合了点到点和点到平面的距离度量,而映射模块则利用法线一致性和深度失真来增强表面重建质量。我们还介绍了一种姿态一致的策略,以实现高效且几何连贯的关键帧采样。在公共内窥镜数据集上的大量实验表明,Endo-2DTAM实现了手术场景深度重建的RMSE为$ 1.87±0.63$毫米,同时保持计算高效的跟踪、高质量视觉效果和实时渲染。我们的代码将在github.com/lastbasket/Endo-2DTAM上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICRA 2025
Summary
基于实时内镜SLAM系统的Endo-2DTAM,结合了三维高斯分裂(3DGS)技术,解决了在微创手术中的精确定位和映射问题。通过引入表面正常感知管道,实现了几何准确的重建。通过稳健的跟踪模块和映射模块的结合,提高了表面重建质量,同时引入姿态一致性策略以实现高效且几何连贯的关键帧采样。在公共内镜数据集上的实验表明,Endo-2DTAM实现了深度重建的均方根误差(RMSE)为±mm 1.87,同时具备高效计算跟踪、高质量视觉外观和实时渲染功能。代码将在github.com/lastbasket/Endo-2DTAM发布。
Key Takeaways
以下是七个关键要点:
- Endo-2DTAM解决了Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)在微创手术中的精准定位和地图构建问题。
点此查看论文截图

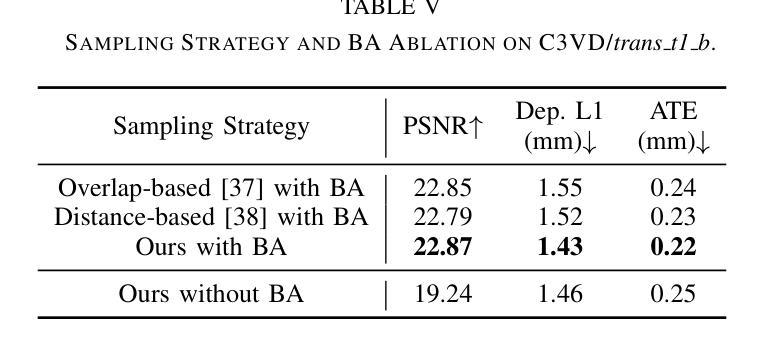
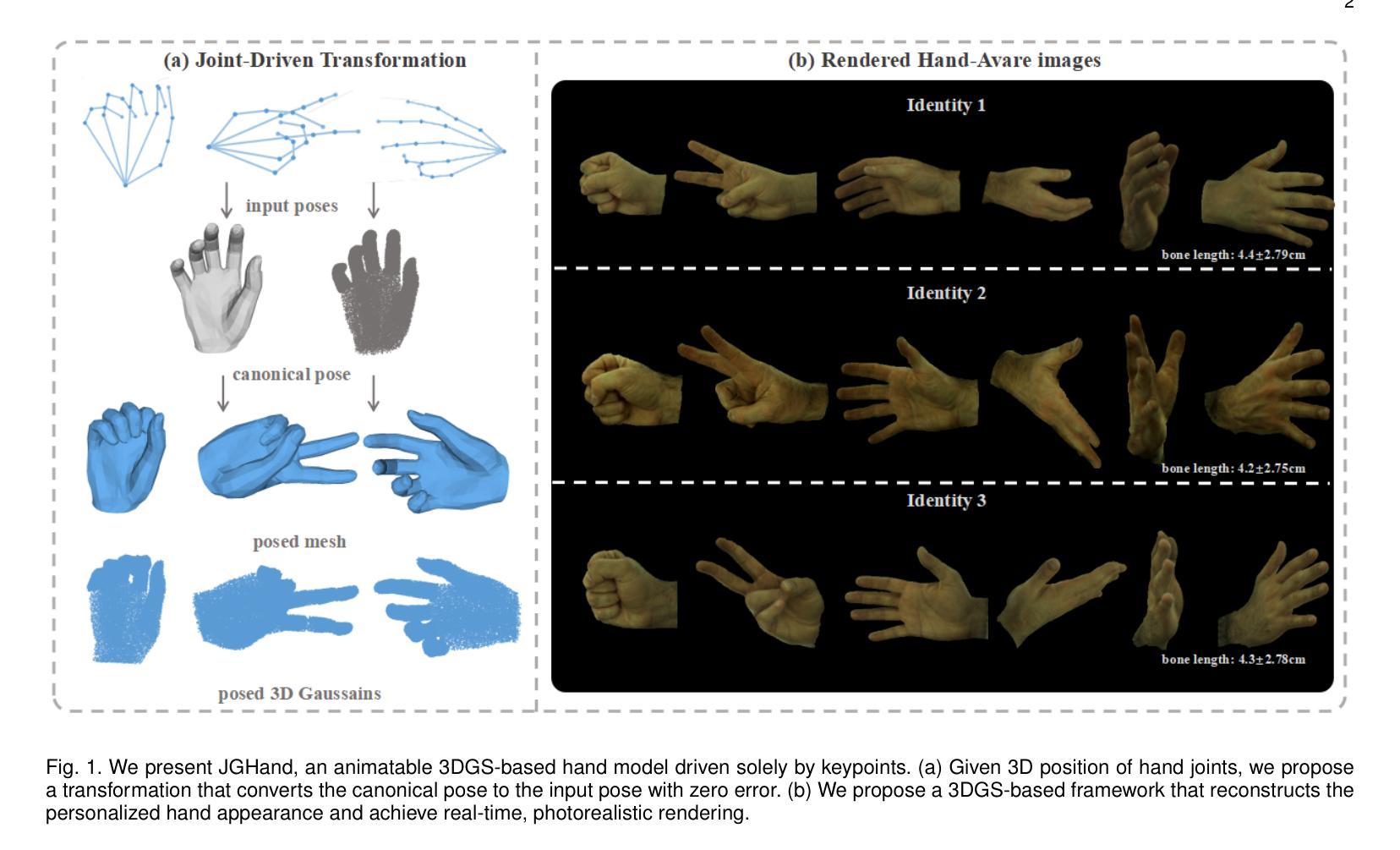
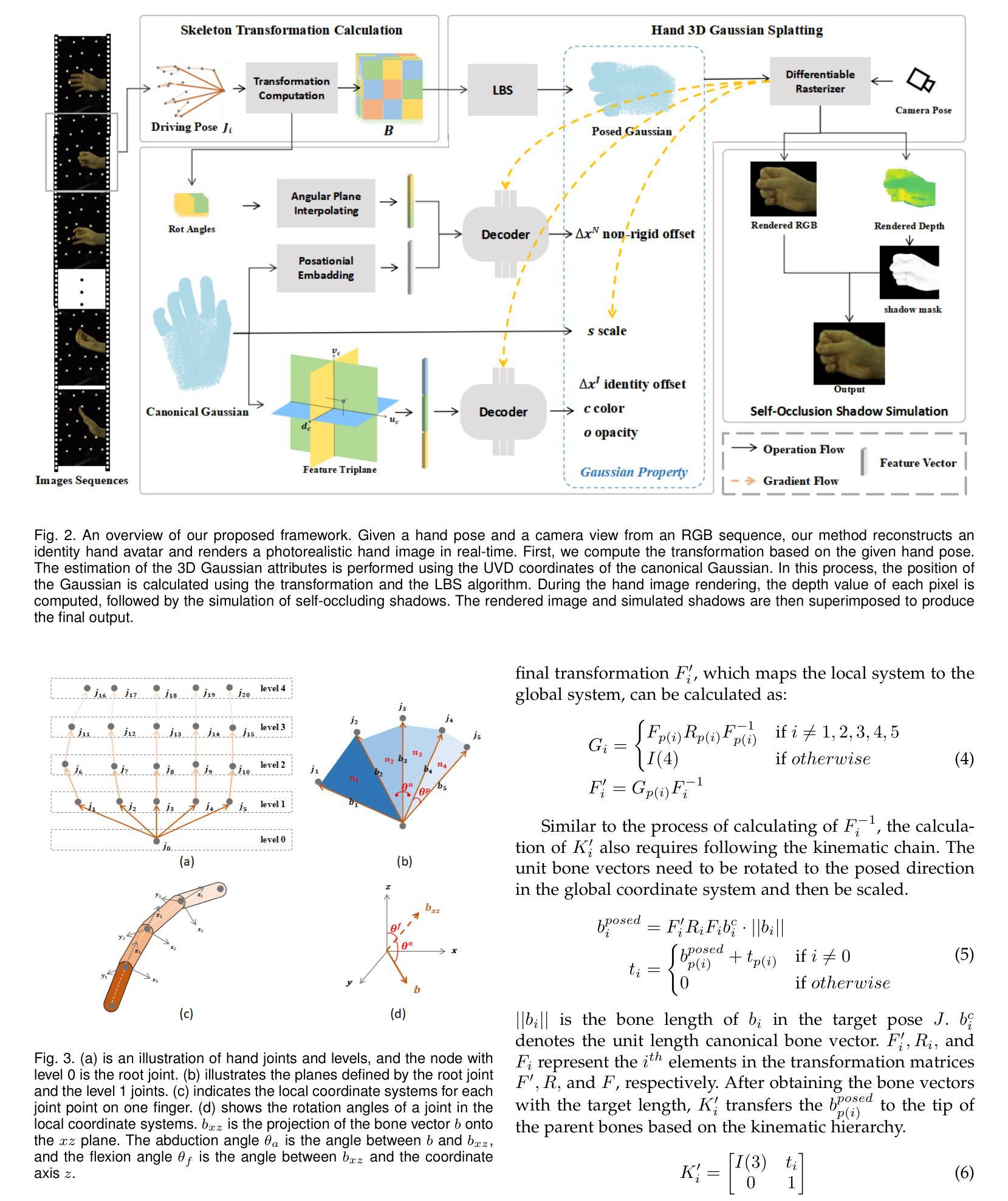
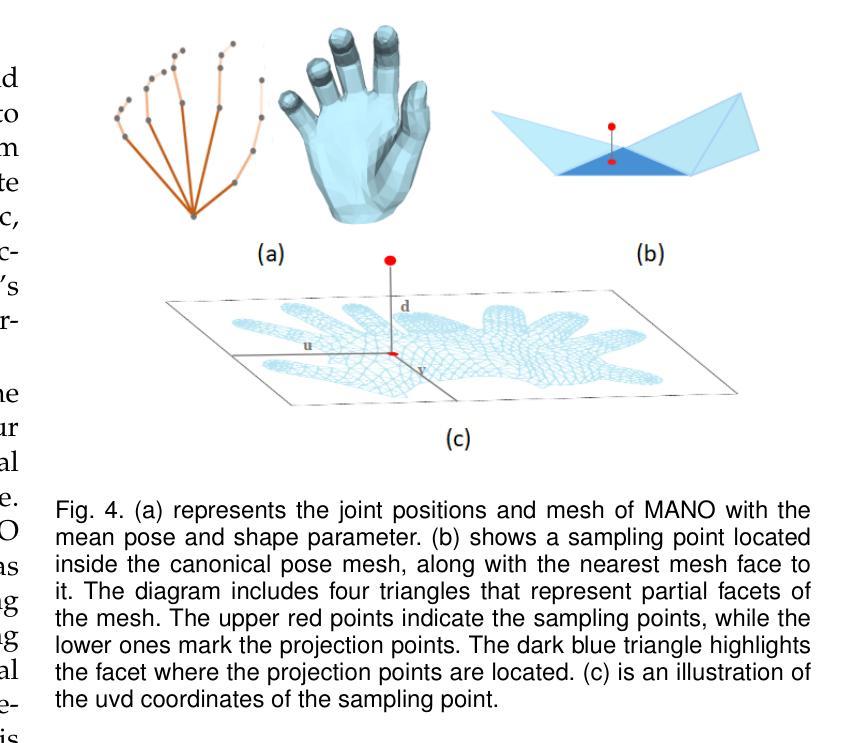
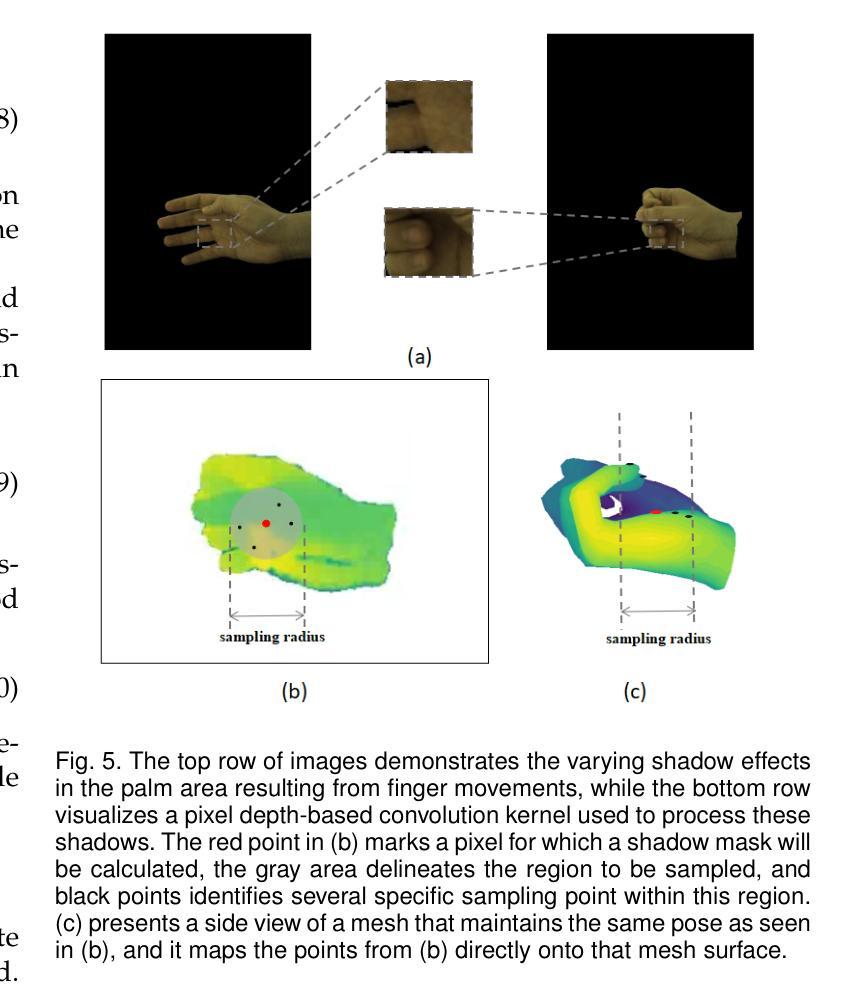
JGHand: Joint-Driven Animatable Hand Avater via 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zhoutao Sun, Xukun Shen, Yong Hu, Yuyou Zhong, Xueyang Zhou
Since hands are the primary interface in daily interactions, modeling high-quality digital human hands and rendering realistic images is a critical research problem. Furthermore, considering the requirements of interactive and rendering applications, it is essential to achieve real-time rendering and driveability of the digital model without compromising rendering quality. Thus, we propose Jointly 3D Gaussian Hand (JGHand), a novel joint-driven 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)-based hand representation that renders high-fidelity hand images in real-time for various poses and characters. Distinct from existing articulated neural rendering techniques, we introduce a differentiable process for spatial transformations based on 3D key points. This process supports deformations from the canonical template to a mesh with arbitrary bone lengths and poses. Additionally, we propose a real-time shadow simulation method based on per-pixel depth to simulate self-occlusion shadows caused by finger movements. Finally, we embed the hand prior and propose an animatable 3DGS representation of the hand driven solely by 3D key points. We validate the effectiveness of each component of our approach through comprehensive ablation studies. Experimental results on public datasets demonstrate that JGHand achieves real-time rendering speeds with enhanced quality, surpassing state-of-the-art methods.
由于手是日常交互中的主要界面,因此建立高质量的数字人手模型并呈现逼真的图像是一个关键的研究问题。此外,考虑到交互和渲染应用的要求,必须在不损害渲染质量的前提下实现数字模型的实时渲染和可驱动性。因此,我们提出了Jointly 3D Gaussian Hand(JGHand),这是一种基于关节驱动的新型3D高斯展平(3DGS)手部表示方法,可实时呈现各种姿势和角色的高保真手部图像。与现有的关节神经渲染技术不同,我们引入了一种基于3D关键点的空间转换的可微过程。这个过程支持从标准模板到具有任意骨骼长度和姿势的网格的变形。此外,我们提出了一种基于像素深度的实时阴影模拟方法,以模拟由手指移动引起的自遮挡阴影。最后,我们嵌入手部先验知识,并提出一种仅由3D关键点驱动的可动画3DGS手部表示方法。我们通过全面的消融研究验证了我们的方法每个组件的有效性。在公共数据集上的实验结果表明,JGHand实现了高质量的实时渲染速度,超越了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的联合3D手部模型(JGHand),可实时渲染高质量的手部图像。该模型支持多种姿势和角色的手部模拟,具有可驱动性和实时渲染能力。通过引入基于3D关键点的可微分空间变换过程,支持从标准模板到具有任意骨长度和姿势的网格的变形。同时,还提出了基于像素深度的实时阴影模拟方法,模拟手指移动产生的自遮挡阴影。最后,通过嵌入手部先验知识,提出一种仅由3D关键点驱动的可动画3DGS手部表示。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的联合3D手部模型(JGHand),用于高质量手部图像的实时渲染。
- 支持多种姿势和角色的手部模拟,具有可驱动性。
- 引入基于3D关键点的可微分空间变换过程,实现从标准模板到任意骨长度和姿势的网格的变形。
- 提出了实时阴影模拟方法,基于像素深度模拟手指移动产生的自遮挡阴影。
- 嵌入手部先验知识,提出一种仅由3D关键点驱动的可动画3D手部表示。
- 通过综合的消融研究验证了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

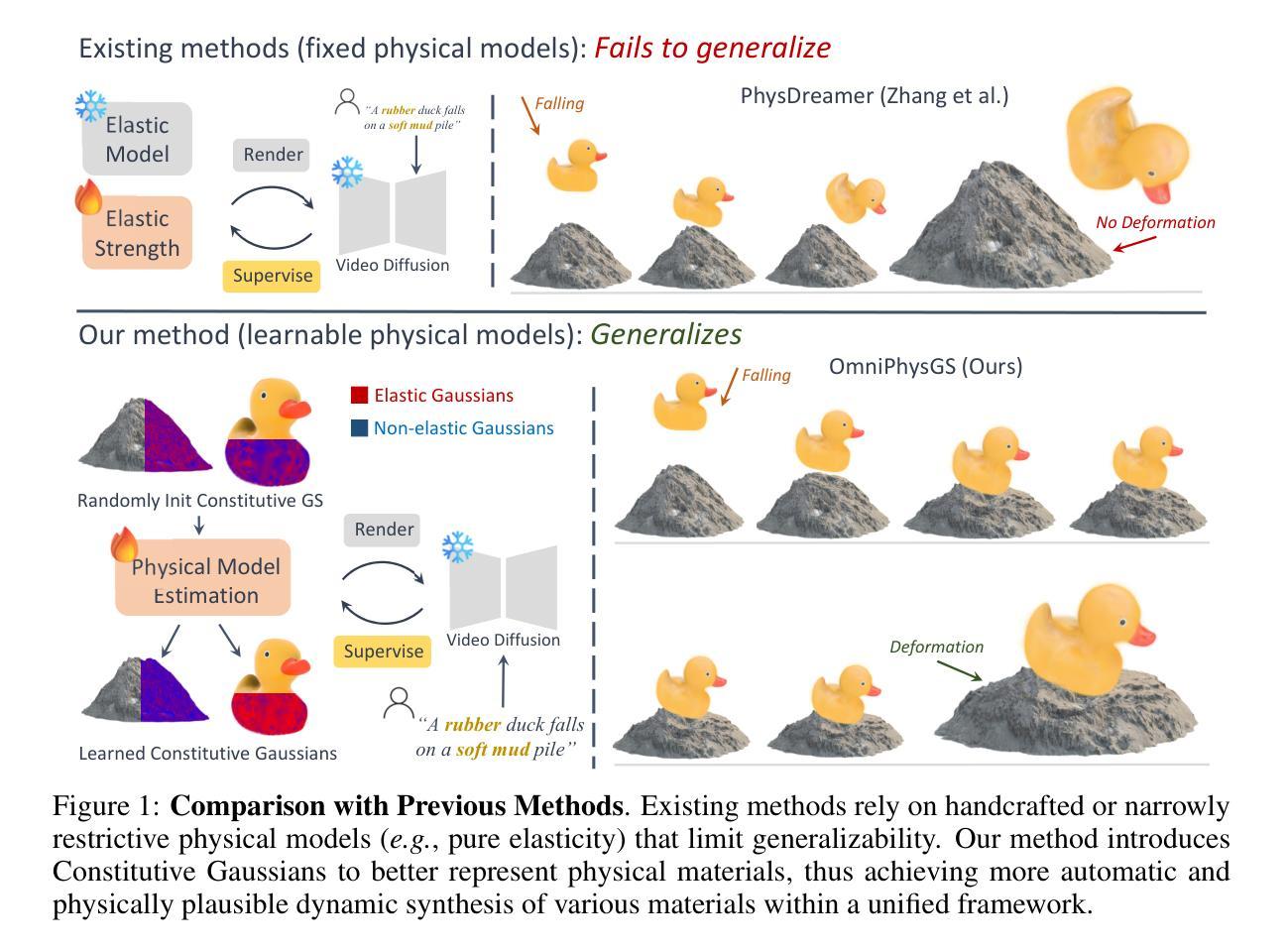
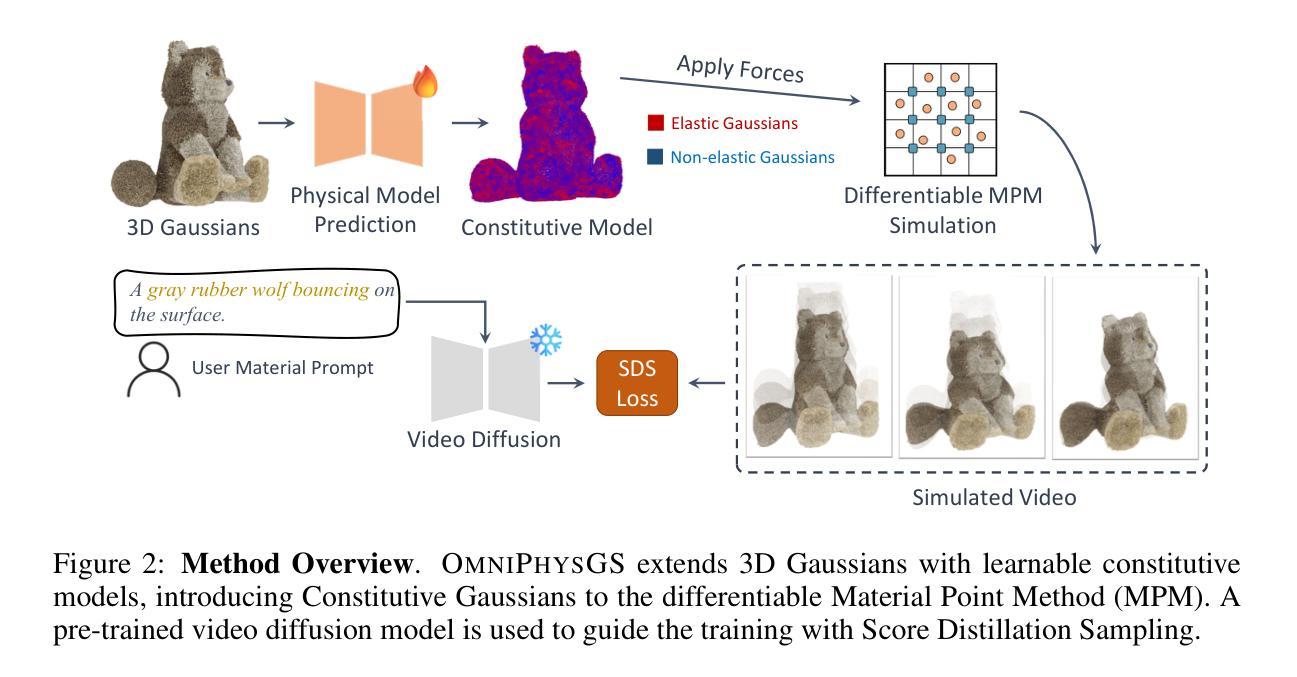
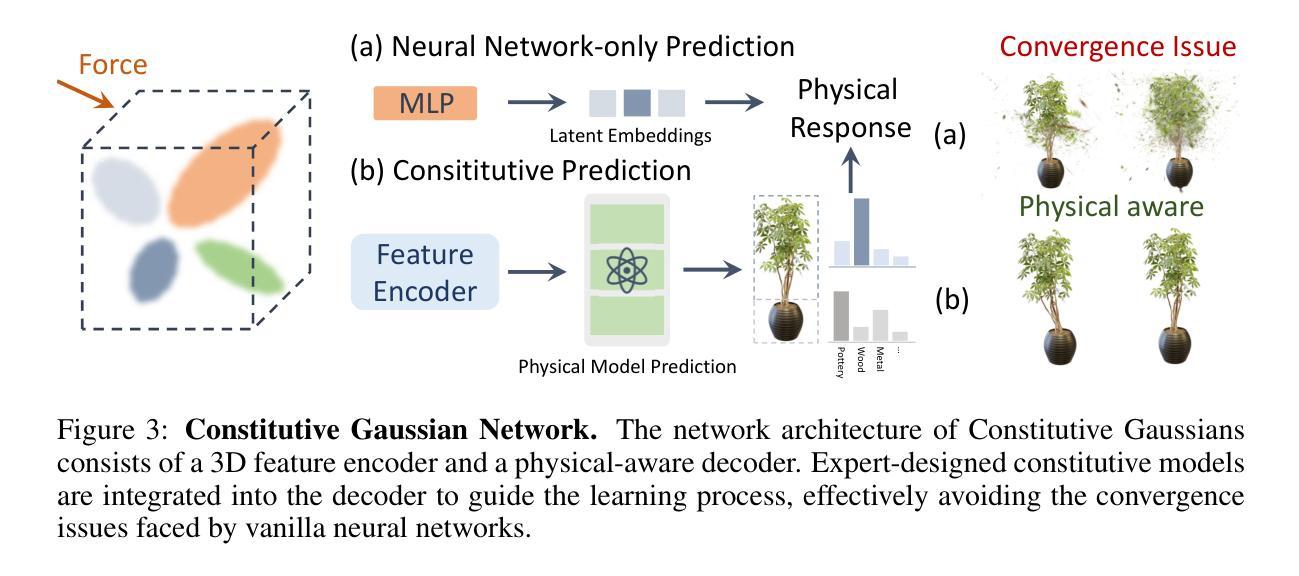
OmniPhysGS: 3D Constitutive Gaussians for General Physics-Based Dynamics Generation
Authors:Yuchen Lin, Chenguo Lin, Jianjin Xu, Yadong Mu
Recently, significant advancements have been made in the reconstruction and generation of 3D assets, including static cases and those with physical interactions. To recover the physical properties of 3D assets, existing methods typically assume that all materials belong to a specific predefined category (e.g., elasticity). However, such assumptions ignore the complex composition of multiple heterogeneous objects in real scenarios and tend to render less physically plausible animation given a wider range of objects. We propose OmniPhysGS for synthesizing a physics-based 3D dynamic scene composed of more general objects. A key design of OmniPhysGS is treating each 3D asset as a collection of constitutive 3D Gaussians. For each Gaussian, its physical material is represented by an ensemble of 12 physical domain-expert sub-models (rubber, metal, honey, water, etc.), which greatly enhances the flexibility of the proposed model. In the implementation, we define a scene by user-specified prompts and supervise the estimation of material weighting factors via a pretrained video diffusion model. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that OmniPhysGS achieves more general and realistic physical dynamics across a broader spectrum of materials, including elastic, viscoelastic, plastic, and fluid substances, as well as interactions between different materials. Our method surpasses existing methods by approximately 3% to 16% in metrics of visual quality and text alignment.
近期,3D资产的重建和生成方面取得了重大进展,包括静态案例和具有物理交互的案例。为了恢复3D资产的物理特性,现有方法通常假设所有材料都属于特定的预定义类别(例如,弹性)。然而,这样的假设忽略了真实场景中多个异质对象的复杂组合,并且在面对更广泛的对象时,往往呈现出物理上不太可能的动画。我们提出OmniPhysGS来合成由更一般对象组成的基于物理的3D动态场景。OmniPhysGS的一个关键设计是将每个3D资产视为一组构成的三维高斯分布。对于每个高斯分布,其物理材料由一组由12个物理领域专家子模型(橡胶、金属、蜂蜜、水等)组成,这极大地增强了所提出模型的灵活性。在实现中,我们通过用户指定的提示来定义场景,并通过预训练的视频扩散模型来监督材料权重因子的估计。综合实验表明,OmniPhysGS在更广泛的材料范围内实现了更通用和更现实的物理动态,包括弹性、粘弹性、塑料和流体物质,以及不同材料之间的交互。我们的方法在视觉质量和文本对齐的指标上比现有方法高出约3%到16%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025; Project page: https://wgsxm.github.io/projects/omniphysgs/
Summary
该研究提出一种名为OmniPhysGS的基于物理的3D动态场景合成方法,用于生成包含更通用对象的物理场景。该方法将每个3D资产视为一系列三维高斯分布的集合,并为每个高斯分布的物理材质采用一组由物理领域专家提供的子模型表示。通过用户指定的提示和监督预训练视频扩散模型来估计材料权重因子。OmniPhysGS能够生成更为广泛且逼真的物理动态效果,涵盖弹性、粘性弹性、塑性以及流体等多种材质,并实现不同材质间的交互。相较于现有方法,OmniPhysGS在视觉质量和文本对齐方面的指标有所提升,约提升3%至16%。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决了现有方法在重建和生成具有物理交互的3D资产时的局限性,尤其是关于材料类别假设的问题。不同于现有的依赖于预先定义的材料类别的方法,它更注重物体的复杂性和异质性。
- 研究提出了OmniPhysGS方法,通过用户指定的提示来定义场景,并使用预训练的视频扩散模型来估计材料权重因子。这使得场景的合成更为灵活且高效。
- OmniPhysGS能够实现更广泛和逼真的物理动态效果,包括弹性、粘性弹性、塑性以及流体等不同材质的交互效果。这意味着它能够模拟更真实的物理世界场景。
- 该方法能够在多种材质之间实现交互效果,这在现有的研究中是较为罕见的。这种能力使得生成的场景更加多样化和复杂。
- 与现有方法相比,OmniPhysGS在视觉质量和文本对齐方面的性能有所提升。这表明它在生成高质量和真实感的场景方面表现出优势。
- OmniPhysGS的设计将每个3D资产视为一系列三维高斯分布的集合,这为模型的灵活性提供了重要的支持。此外,它为每个高斯分布的物理材质采用一组由物理领域专家提供的子模型表示,这增强了模型的物理准确性。
点此查看论文截图

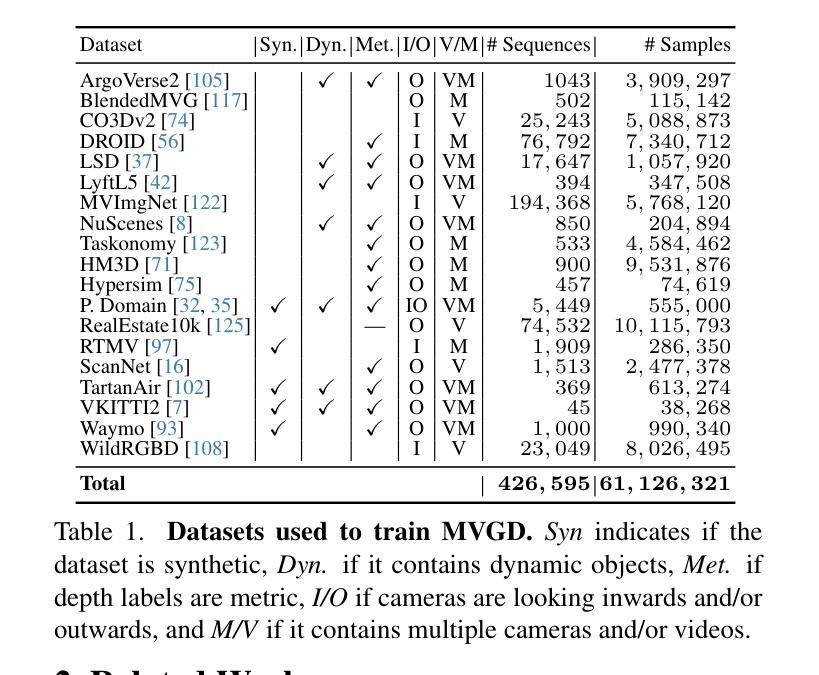
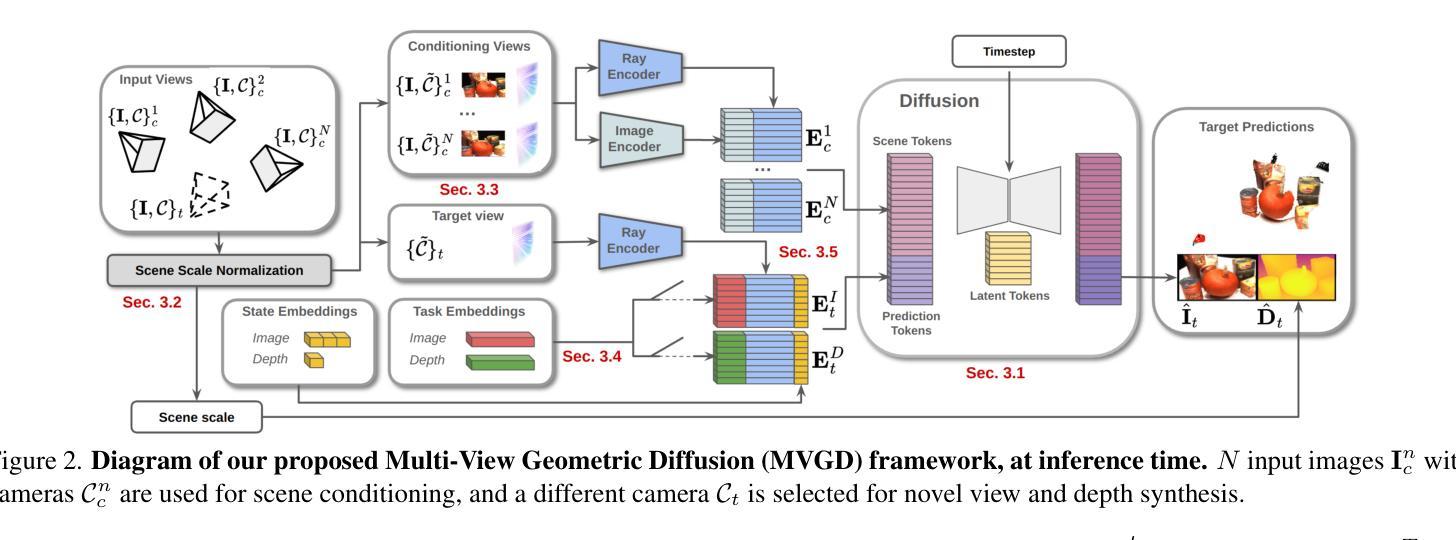
Zero-Shot Novel View and Depth Synthesis with Multi-View Geometric Diffusion
Authors:Vitor Guizilini, Muhammad Zubair Irshad, Dian Chen, Greg Shakhnarovich, Rares Ambrus
Current methods for 3D scene reconstruction from sparse posed images employ intermediate 3D representations such as neural fields, voxel grids, or 3D Gaussians, to achieve multi-view consistent scene appearance and geometry. In this paper we introduce MVGD, a diffusion-based architecture capable of direct pixel-level generation of images and depth maps from novel viewpoints, given an arbitrary number of input views. Our method uses raymap conditioning to both augment visual features with spatial information from different viewpoints, as well as to guide the generation of images and depth maps from novel views. A key aspect of our approach is the multi-task generation of images and depth maps, using learnable task embeddings to guide the diffusion process towards specific modalities. We train this model on a collection of more than 60 million multi-view samples from publicly available datasets, and propose techniques to enable efficient and consistent learning in such diverse conditions. We also propose a novel strategy that enables the efficient training of larger models by incrementally fine-tuning smaller ones, with promising scaling behavior. Through extensive experiments, we report state-of-the-art results in multiple novel view synthesis benchmarks, as well as multi-view stereo and video depth estimation.
当前用于从稀疏定位图像重建3D场景的方法采用中间3D表示,如神经场、体素网格或3D高斯,以实现多视角一致的场景外观和几何。在本文中,我们介绍了MVGD,这是一种基于扩散的架构,能够从任意数量的输入视角直接生成像素级的图像和深度图。我们的方法使用射线图条件来增强视觉特征,并加入从不同视角获取的空间信息,以指导从新颖视角生成图像和深度图。我们方法的关键方面在于图像和深度图的多任务生成,利用可学习的任务嵌入来引导扩散过程朝着特定的模式进行。我们在来自公开数据集的超过6000万个多视角样本上训练此模型,并提出了一些技术,以实现在这种多样条件下的高效且一致的学习。我们还提出了一种新的策略,通过逐步微调较小的模型来有效地训练更大的模型,具有良好的扩展性。通过广泛的实验,我们在多个新颖视图合成基准测试中取得了最新结果,以及在多视角立体和视频深度估计方面也取得了成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://mvgd.github.io
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散架构的MVGD方法,能够直接从多个视角的图像和深度图中生成像素级的多视角一致场景。该方法使用射线映射条件增强视觉特征,并引导从新颖视角生成图像和深度图。通过多任务生成图像和深度图,利用可学习的任务嵌入引导扩散过程针对特定模态。实验结果表明,该方法在多视角合成、立体视频和多视角深度估计等多个基准测试中达到最佳状态。
Key Takeaways
- MVGD是一种基于扩散架构的方法,可直接从稀疏定位的图像生成像素级的多视角一致场景。
- 使用射线映射条件同时增强视觉特征和空间信息,以生成多视角图像和深度图。
- 多任务生成图像和深度图,利用可学习的任务嵌入引导扩散过程针对特定模态,实现更精细的生成。
- 在超过6000万多个多视角样本上进行训练,提出在多样条件下实现高效一致学习的技术。
- 提出一种有效策略,通过逐步微调较小的模型来训练更大的模型,具有良好的扩展性。
- 在多个基准测试中达到最佳性能,包括多视角合成、立体视频和多视角深度估计等。
点此查看论文截图


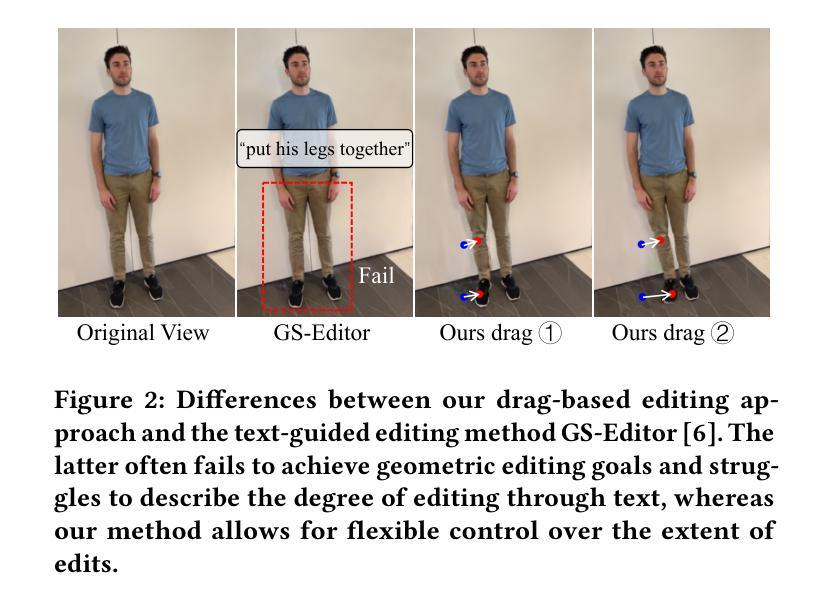
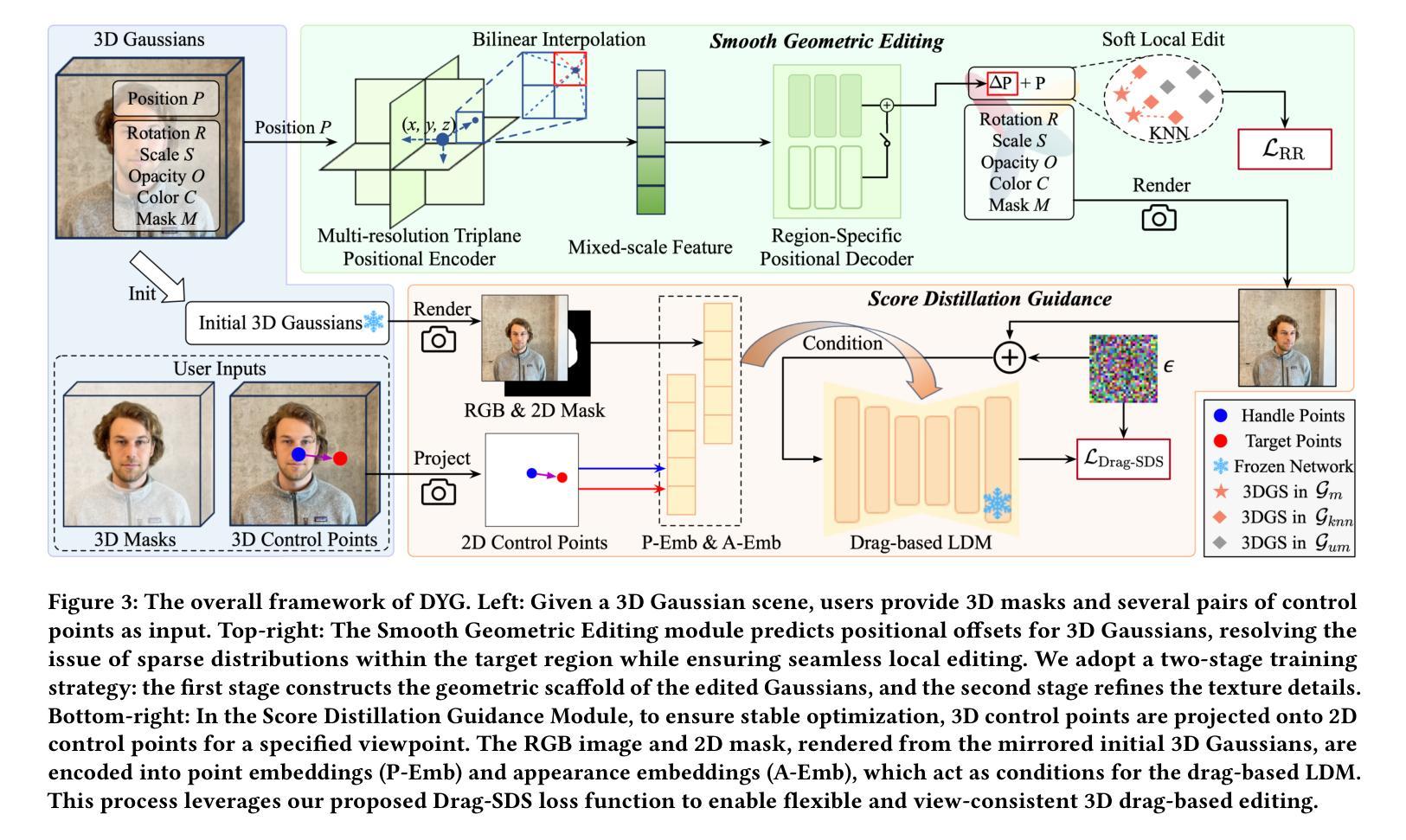
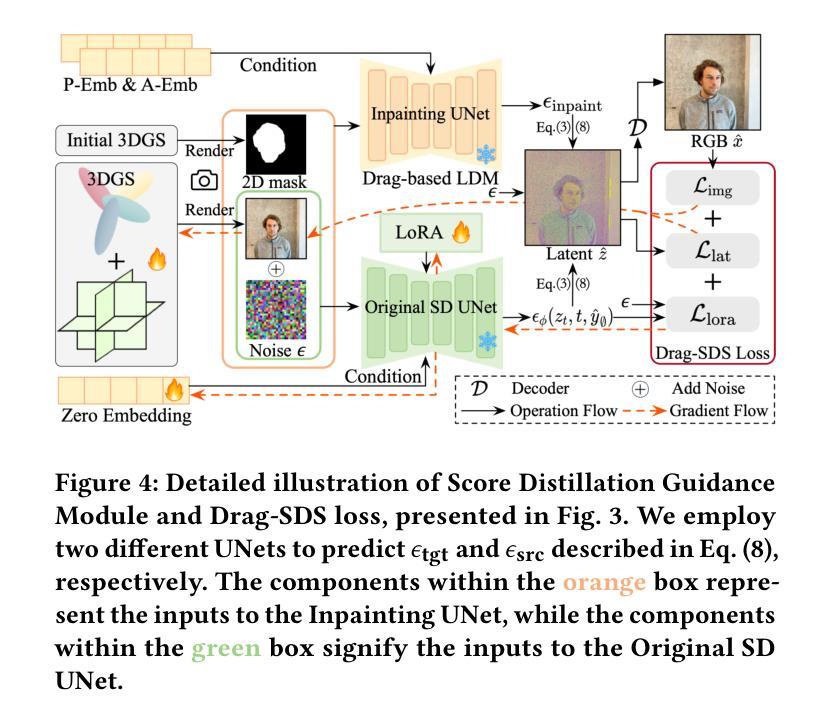
Drag Your Gaussian: Effective Drag-Based Editing with Score Distillation for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yansong Qu, Dian Chen, Xinyang Li, Xiaofan Li, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
Recent advancements in 3D scene editing have been propelled by the rapid development of generative models. Existing methods typically utilize generative models to perform text-guided editing on 3D representations, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). However, these methods are often limited to texture modifications and fail when addressing geometric changes, such as editing a character’s head to turn around. Moreover, such methods lack accurate control over the spatial position of editing results, as language struggles to precisely describe the extent of edits. To overcome these limitations, we introduce DYG, an effective 3D drag-based editing method for 3D Gaussian Splatting. It enables users to conveniently specify the desired editing region and the desired dragging direction through the input of 3D masks and pairs of control points, thereby enabling precise control over the extent of editing. DYG integrates the strengths of the implicit triplane representation to establish the geometric scaffold of the editing results, effectively overcoming suboptimal editing outcomes caused by the sparsity of 3DGS in the desired editing regions. Additionally, we incorporate a drag-based Latent Diffusion Model into our method through the proposed Drag-SDS loss function, enabling flexible, multi-view consistent, and fine-grained editing. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DYG conducts effective drag-based editing guided by control point prompts, surpassing other baselines in terms of editing effect and quality, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Visit our project page at https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian.
最近的三维场景编辑进展得益于生成模型的快速发展。现有方法通常利用生成模型对三维表示进行文本引导编辑,例如三维高斯贴图(3DGS)。然而,这些方法通常仅限于纹理修改,在应对几何变化时往往会失效,例如编辑角色头部以使其旋转。此外,这些方法在控制编辑结果的空间位置方面不够精确,因为语言很难精确描述编辑的程度。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了DYG,这是一种针对三维高斯贴图的有效基于拖拽的三维编辑方法。它使用户可以通过输入三维遮罩和控制点对,方便地指定所需的编辑区域和拖拽方向,从而实现对编辑程度的精确控制。DYG结合了隐式triplane表示的优点,建立编辑结果的三维骨架,有效克服了在所需编辑区域中3DGS稀疏导致的次优编辑结果。此外,我们通过提出的Drag-SDS损失函数,将基于拖拽的潜在扩散模型融入我们的方法,实现灵活、多视角一致、精细的编辑。大量实验表明,DYG通过控制点提示进行有效的基于拖拽的编辑,在编辑效果和品质方面超越其他基线方法,定性和定量评估均如此。请访问我们的项目页面:https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Visit our project page at https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian
摘要
最近,三维场景编辑技术的进展得益于生成模型的快速发展。现有方法通常利用生成模型对三维表示进行文本引导编辑,如三维高斯喷溅(3DGS)。然而,这些方法主要局限于纹理修改,在几何变化方面表现不足,如角色头部的旋转编辑。此外,由于缺乏精确的空间位置控制,语言难以精确描述编辑的程度。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了基于拖放的3D编辑方法DYG,用于3D高斯喷溅。它使用户可以通过输入3D遮罩和控制点对来方便地指定所需的编辑区域和拖动方向,从而实现精确的编辑程度控制。DYG结合隐式triplane表示建立编辑结果几何框架的优势,有效克服了3DGS在所需编辑区域稀疏导致的次优编辑结果。此外,我们通过在提出的Drag-SDS损失函数中融入基于拖放的潜在扩散模型,实现了灵活、多视角一致、精细的编辑。大量实验表明,DYG通过控制点提示进行有效的拖放编辑,在编辑效果和品质上超越了其他基线方法。请访问我们的项目页面https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian了解更多。
关键见解
- 生成模型推动3D场景编辑技术的新进展。
- 现有方法主要局限于纹理修改,在几何变化方面存在局限。
- 提出基于拖放的3D编辑方法DYG,用于3D高斯喷溅。
- DYG允许用户通过3D遮罩和控制点方便指定编辑区域和拖动方向。
- DYG结合隐式triplane表示实现精确几何编辑结果。
- 融入基于拖放的潜在扩散模型,实现灵活、多视角一致、精细的编辑。
点此查看论文截图


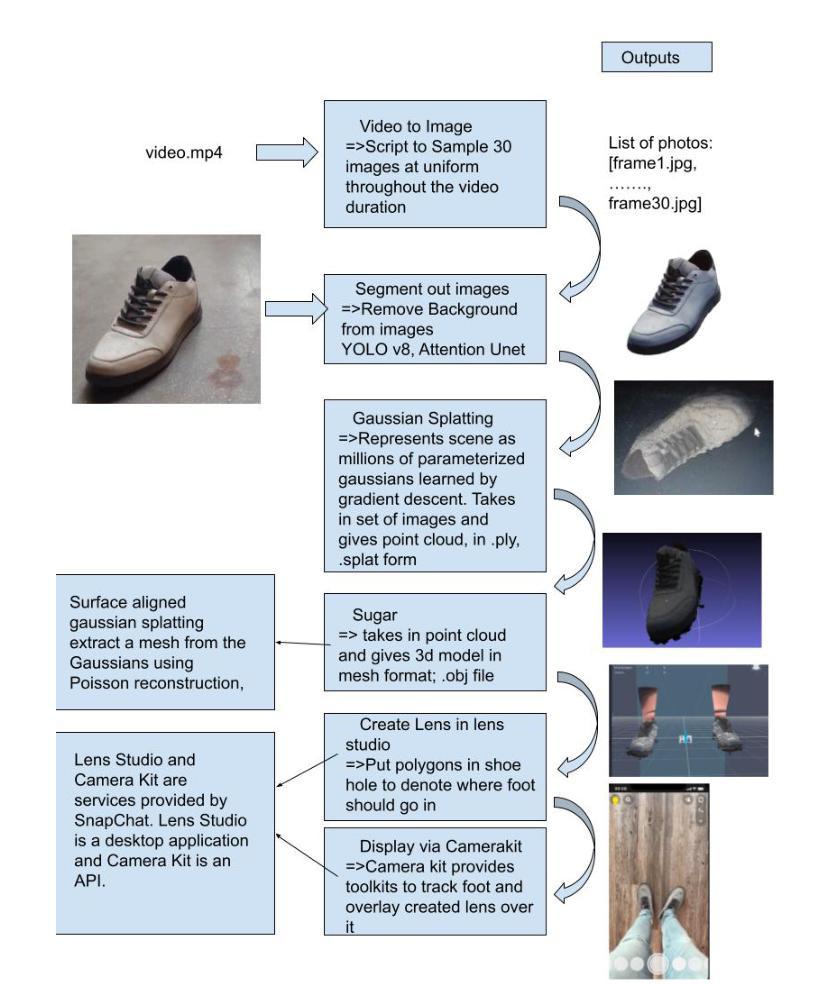
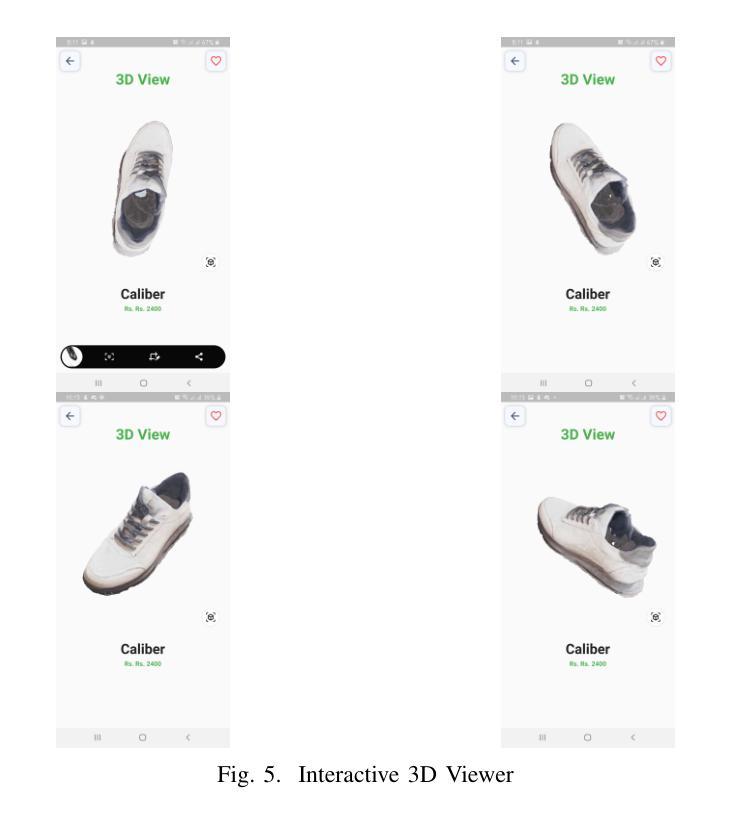
3D Reconstruction of Shoes for Augmented Reality
Authors:Pratik Shrestha, Sujan Kapali, Swikar Gautam, Vishal Pokharel, Santosh Giri
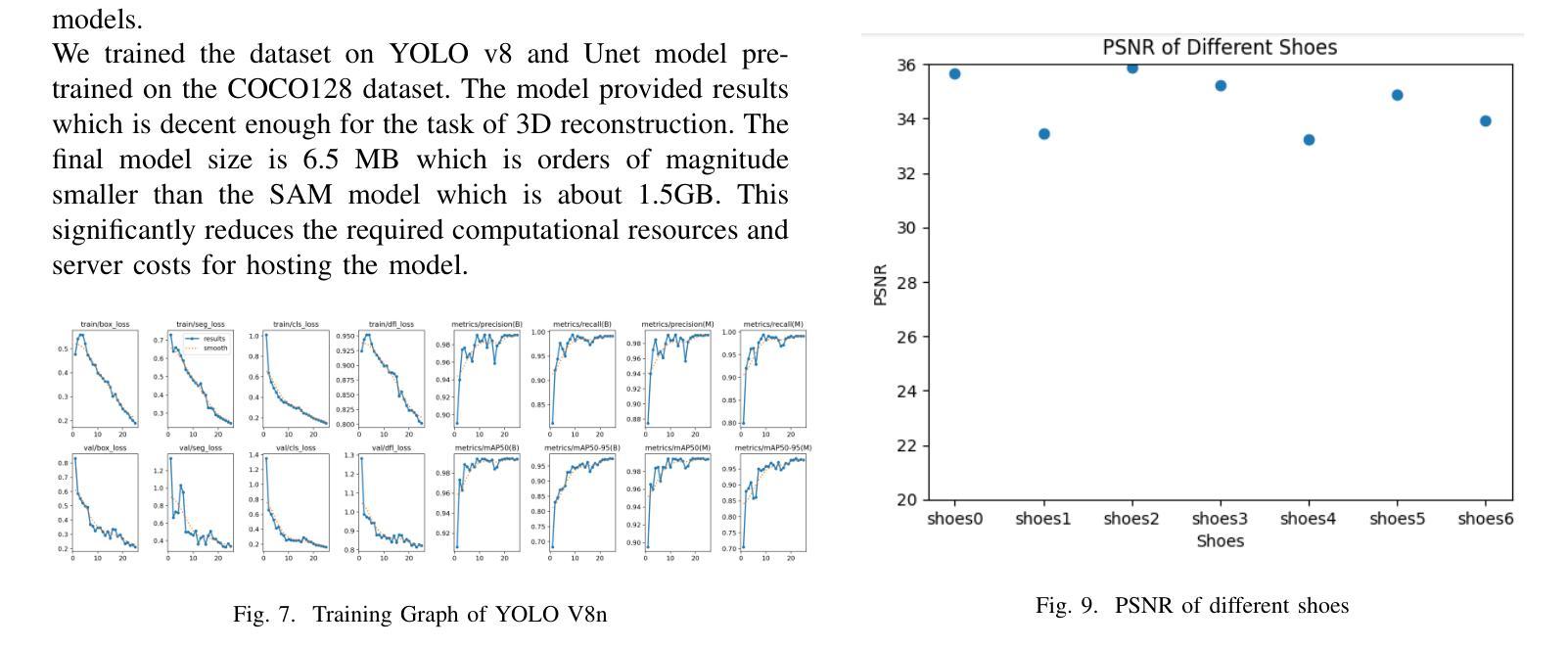
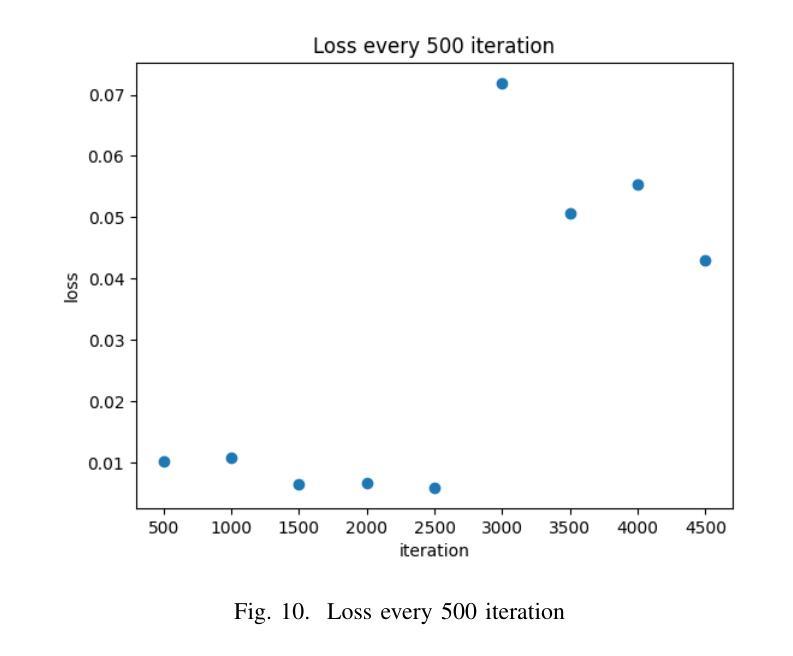
This paper introduces a mobile-based solution that enhances online shoe shopping through 3D modeling and Augmented Reality (AR), leveraging the efficiency of 3D Gaussian Splatting. Addressing the limitations of static 2D images, the framework generates realistic 3D shoe models from 2D images, achieving an average Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) of 0.32, and enables immersive AR interactions via smartphones. A custom shoe segmentation dataset of 3120 images was created, with the best-performing segmentation model achieving an Intersection over Union (IoU) score of 0.95. This paper demonstrates the potential of 3D modeling and AR to revolutionize online shopping by offering realistic virtual interactions, with applicability across broader fashion categories.
本文介绍了一种基于移动设备的解决方案,通过3D建模和增强现实(AR)技术提高网上购鞋体验,利用3D高斯拼贴技术的效率。该框架解决了静态2D图像的限制,能够从2D图像生成逼真的3D鞋模,平均峰值信噪比(PSNR)达到0.32,并通过智能手机实现沉浸式AR交互。创建了一个包含3120张图片的自定义鞋类分割数据集,最佳分割模型达到交并比(IoU)分数为0.95。本文展示了3D建模和AR技术在在线购物中的潜力,通过提供逼真的虚拟交互,可广泛应用于更广泛的时尚类别。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于移动设备的解决方案,通过3D建模和增强现实(AR)技术提升在线购鞋体验。该方案利用3D高斯喷绘技术,克服静态2D图像的局限性,通过2D图像生成逼真的3D鞋模,平均峰值信噪比(PSNR)达到0.32,并通过智能手机实现沉浸式AR交互。研究创建了一个包含3120张图片的自定义鞋类分割数据集,最佳分割模型的交并比(IoU)分数达到0.95。本文展示了3D建模和AR技术在在线购物中的潜力,通过提供逼真的虚拟交互,有望改变消费者的购物体验,并且具有更广泛的应用于时尚领域。
Key Takeaways
- 利用移动设备和3D建模技术提升在线购鞋体验。
- 通过3D高斯喷绘技术从2D图像生成3D鞋模。
- 平均峰值信噪比(PSNR)达到0.32,保证模型的真实性。
- 实现沉浸式AR交互,增强购物体验。
- 创建了一个自定义鞋类分割数据集,用于训练和测试模型。
- 最佳分割模型的交并比(IoU)分数达到0.95,显示模型的良好性能。
点此查看论文截图





Deformable Beta Splatting
Authors:Rong Liu, Dylan Sun, Meida Chen, Yue Wang, Andrew Feng
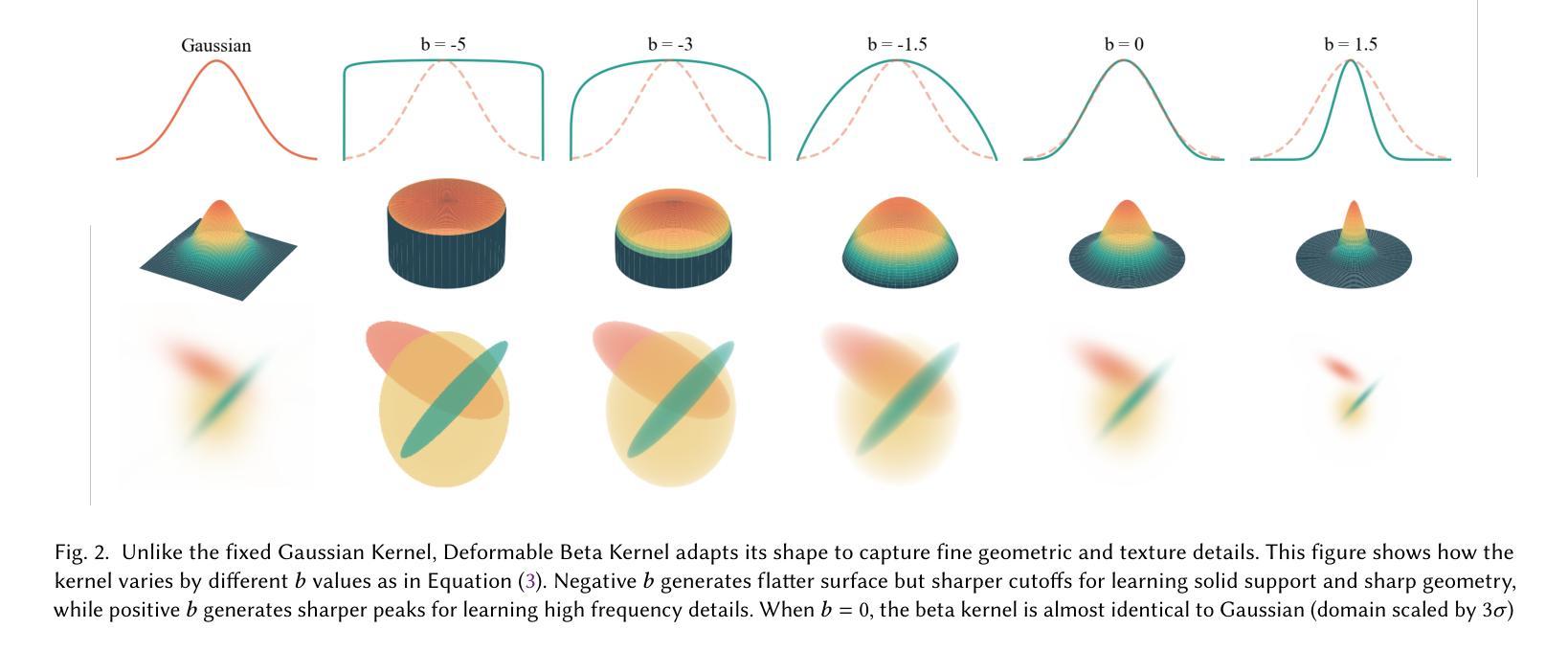
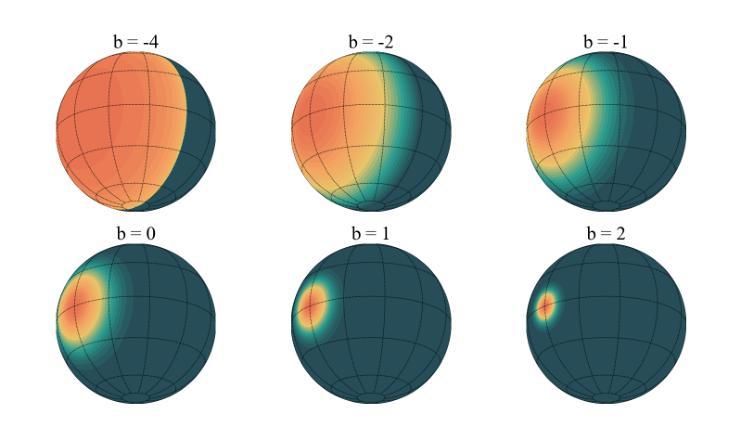
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has advanced radiance field reconstruction by enabling real-time rendering. However, its reliance on Gaussian kernels for geometry and low-order Spherical Harmonics (SH) for color encoding limits its ability to capture complex geometries and diverse colors. We introduce Deformable Beta Splatting (DBS), a deformable and compact approach that enhances both geometry and color representation. DBS replaces Gaussian kernels with deformable Beta Kernels, which offer bounded support and adaptive frequency control to capture fine geometric details with higher fidelity while achieving better memory efficiency. In addition, we extended the Beta Kernel to color encoding, which facilitates improved representation of diffuse and specular components, yielding superior results compared to SH-based methods. Furthermore, Unlike prior densification techniques that depend on Gaussian properties, we mathematically prove that adjusting regularized opacity alone ensures distribution-preserved Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), independent of the splatting kernel type. Experimental results demonstrate that DBS achieves state-of-the-art visual quality while utilizing only 45% of the parameters and rendering 1.5x faster than 3DGS-based methods. Notably, for the first time, splatting-based methods outperform state-of-the-art Neural Radiance Fields, highlighting the superior performance and efficiency of DBS for real-time radiance field rendering.
3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)通过实现实时渲染,推动了辐射场重建的发展。然而,它依赖于几何高斯核和低阶球面谐波(SH)进行颜色编码,这限制了其捕捉复杂几何和多样颜色的能力。我们引入了可变形Beta Splatting(DBS),这是一种可变形且紧凑的方法,能够增强几何和颜色的表示。DBS用可变形的Beta核替换高斯核,提供有界支持和自适应频率控制,以更高的保真度捕捉精细的几何细节,同时实现更好的内存效率。此外,我们将Beta核扩展到颜色编码,这有助于改进漫反射和镜面成分的表示,与基于SH的方法相比,产生更优越的结果。此外,与以往依赖高斯属性的密集化技术不同,我们从数学上证明,仅调整正则化不透明度就能确保分布保留的马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗(MCMC)方法独立于Splatting核类型。实验结果表明,DBS达到了最先进的视觉质量,同时仅使用3DGS方法的45%参数,并且渲染速度提高了1.5倍。值得注意的是,基于Splatting的方法首次超越了最先进的神经辐射场技术,突显了DBS在实时辐射场渲染方面的卓越性能和效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
3DGS在实时渲染中推动了辐射场重建的发展,但受限于高斯核和低阶球面谐波的颜色编码。现在引入可变形Beta Splatting(DBS),提高了几何和颜色表示的精度和效率。DBS使用可变形Beta核替代高斯核,支持有界支持和自适应频率控制,更准确地捕捉精细几何细节,同时实现更好的内存效率。此外,将Beta核扩展到颜色编码,改进了漫反射和镜面成分表示,获得优于基于SH的方法的结果。实验证明,DBS实现了卓越的可视化质量,仅使用45%的参数,渲染速度比基于3DGS的方法快1.5倍。重要的是,基于劈绘的方法首次超越了最先进的神经辐射场,突显了DBS在实时辐射场渲染中的卓越性能和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS推动了实时渲染中的辐射场重建,但存在对复杂几何和多彩色的捕捉限制。
- 引入DBS,一种可变形和紧凑的方法,增强几何和颜色表示。
- DBS使用可变形Beta核替代高斯核,更好地捕捉精细几何细节,提高内存效率。
- 扩展Beta核用于颜色编码,改进漫反射和镜面成分表示,优于球面谐波方法。
- 实验证明DBS在可视化质量、参数使用和渲染速度上优于3DGS。
点此查看论文截图


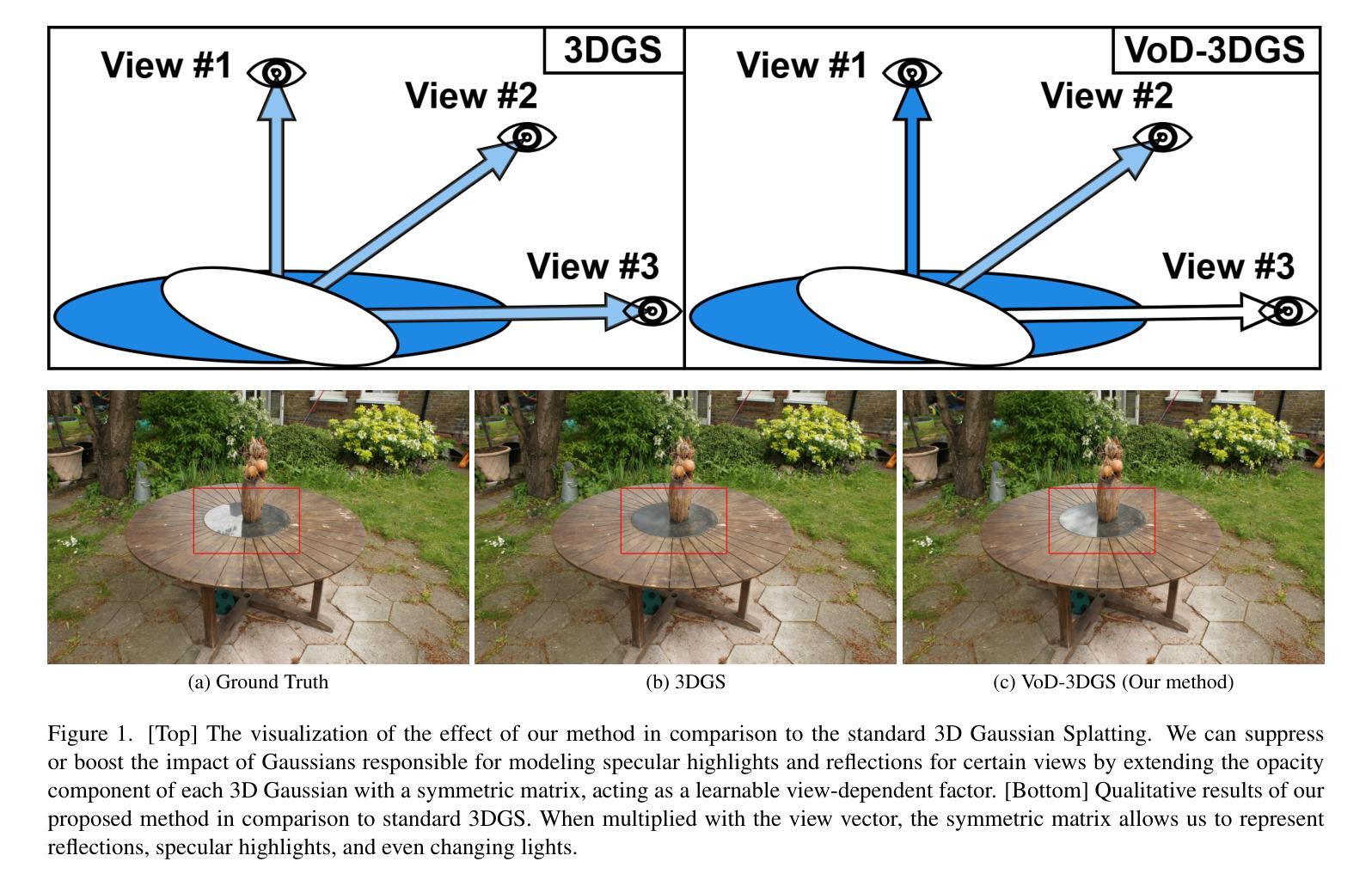
VoD-3DGS: View-opacity-Dependent 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Mateusz Nowak, Wojciech Jarosz, Peter Chin
Reconstructing a 3D scene from images is challenging due to the different ways light interacts with surfaces depending on the viewer’s position and the surface’s material. In classical computer graphics, materials can be classified as diffuse or specular, interacting with light differently. The standard 3D Gaussian Splatting model struggles to represent view-dependent content, since it cannot differentiate an object within the scene from the light interacting with its specular surfaces, which produce highlights or reflections. In this paper, we propose to extend the 3D Gaussian Splatting model by introducing an additional symmetric matrix to enhance the opacity representation of each 3D Gaussian. This improvement allows certain Gaussians to be suppressed based on the viewer’s perspective, resulting in a more accurate representation of view-dependent reflections and specular highlights without compromising the scene’s integrity. By allowing the opacity to be view dependent, our enhanced model achieves state-of-the-art performance on Mip-Nerf, Tanks&Temples, Deep Blending, and Nerf-Synthetic datasets without a significant loss in rendering speed, achieving >60FPS, and only incurring a minimal increase in memory used.
从图像重建3D场景是一个具有挑战性的任务,因为光线与表面互动的方式取决于观察者的位置和表面材质。在经典计算机图形学中,材料可分为漫反射或镜面反射,与光线的互动方式不同。标准的3D高斯拼贴模型在表示视角相关内容时遇到困难,因为它无法区分场景中的物体与其与镜面表面交互的光线,从而产生高光或反射。在本文中,我们提出通过引入一个额外的对称矩阵来扩展3D高斯拼贴模型,以增强每个3D高斯的不透明度表示。这一改进允许根据观察者的角度抑制某些高斯,从而更准确地表示视角相关的反射和高光,同时不损害场景的完整性。通过允许不透明度依赖于视角,我们增强的模型在Mip-Nerf、Tanks&Temples、Deep Blending和Nerf-Synthetic数据集上实现了最先进的性能,渲染速度没有明显损失,达到>60FPS,并且只增加了很少的内存使用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出扩展3D高斯散斑模型,通过引入额外的对称矩阵以增强每个3D高斯的不透明度表示。改进允许根据观察者的视角抑制某些高斯,从而更准确地表示视差相关的反射和高光,同时保持场景的完整性。增强模型在不显著降低渲染速度(达到>60FPS)和仅增加极小内存使用的情况下,实现了Mip-Nerf、Tanks&Temples、Deep Blending和Nerf-Synthetic数据集上的业界领先性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入对称矩阵扩展了3D高斯散斑模型。
- 增强模型能更准确地表示视差相关的反射和高光。
- 改进允许根据观察者的视角抑制某些高斯。
- 增强模型在不牺牲场景完整性的情况下实现上述效果。
- 渲染速度保持>60FPS,且内存使用仅略有增加。
- 扩展模型在多个数据集上实现了业界领先的性能。
点此查看论文截图

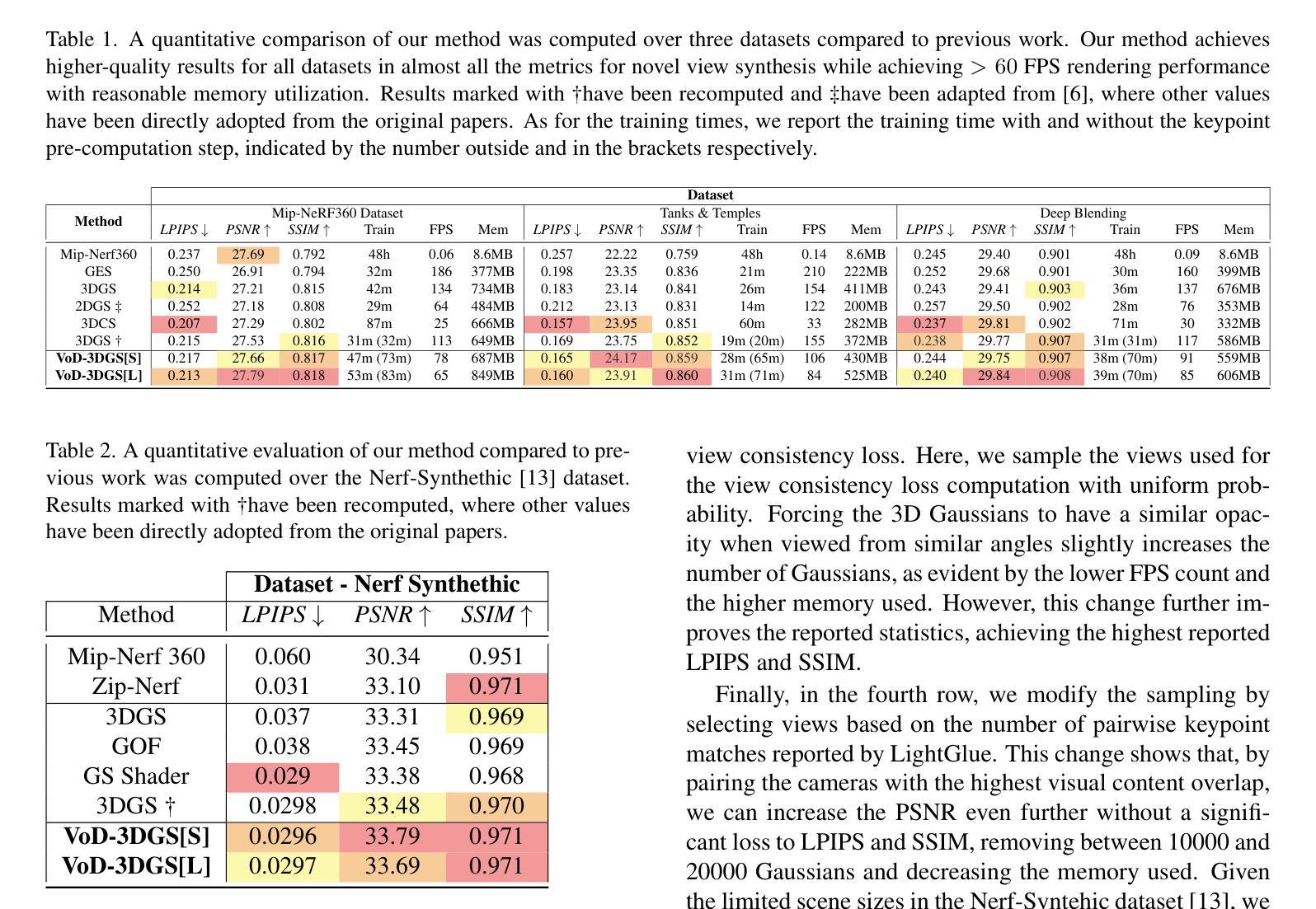
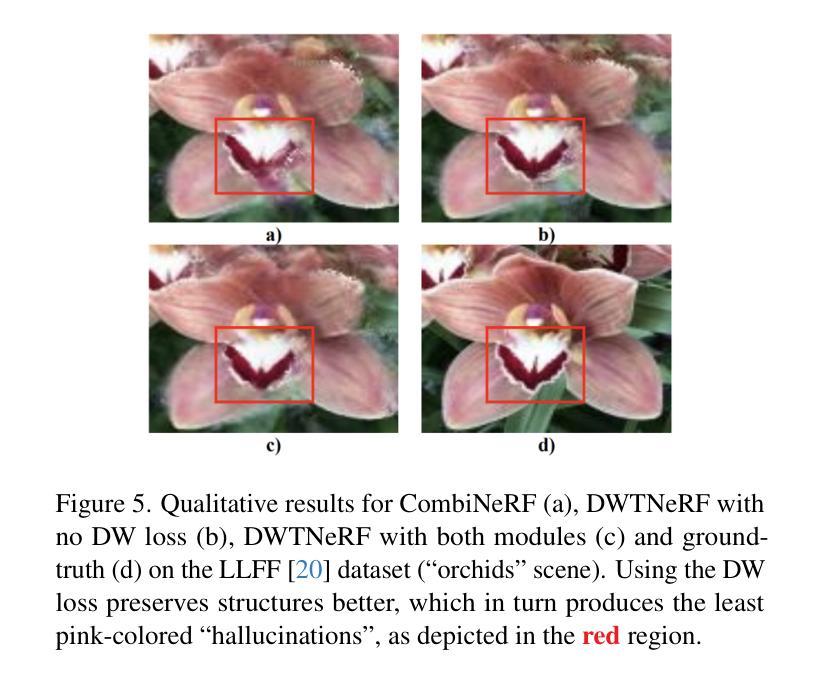
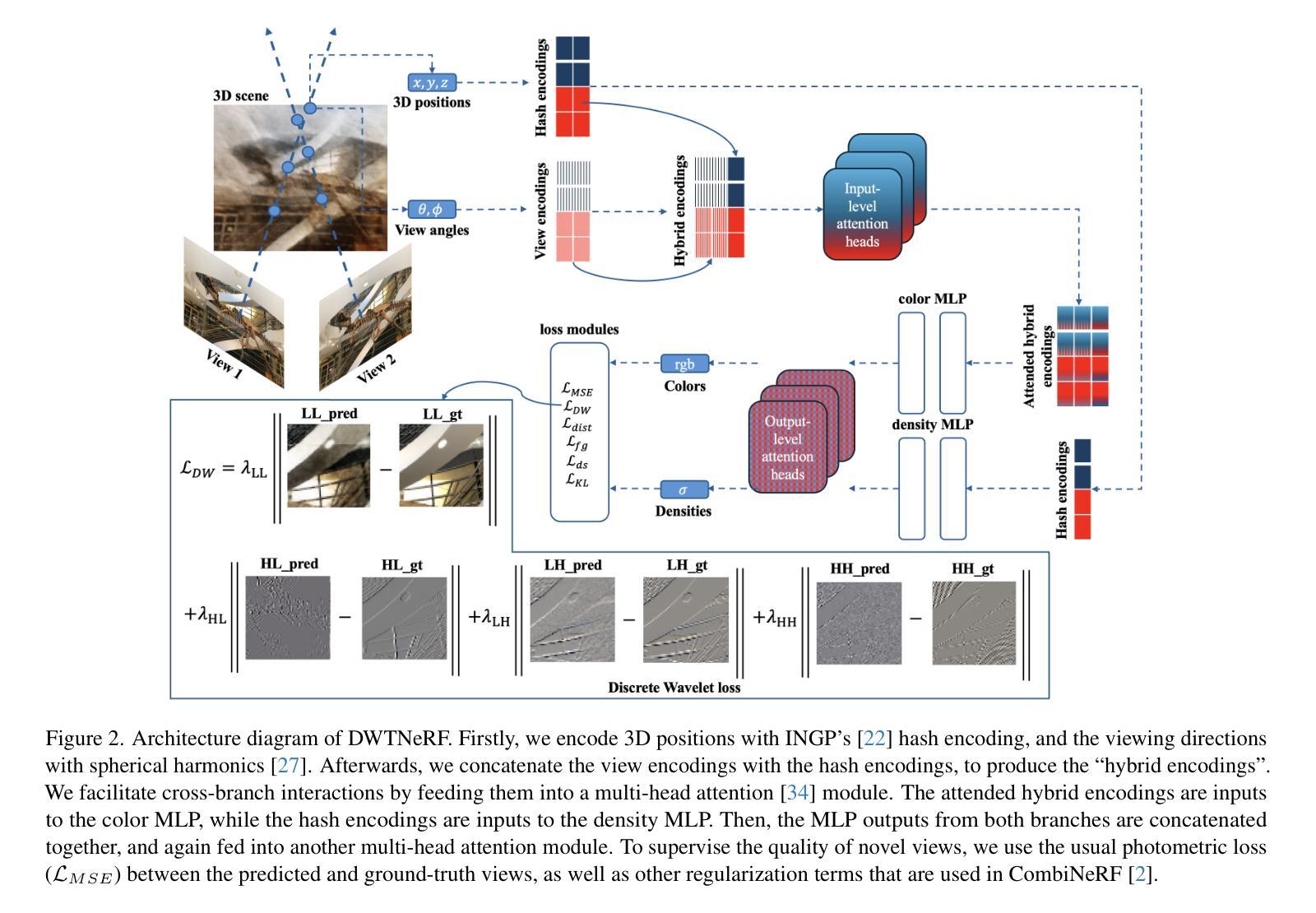
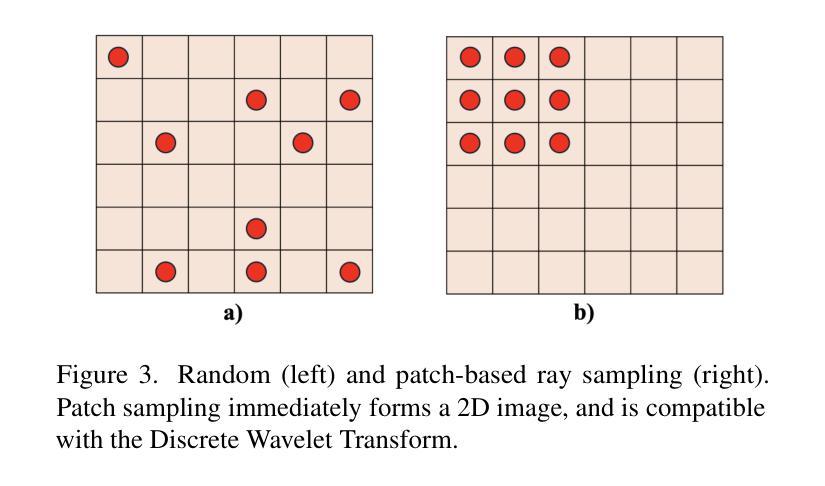
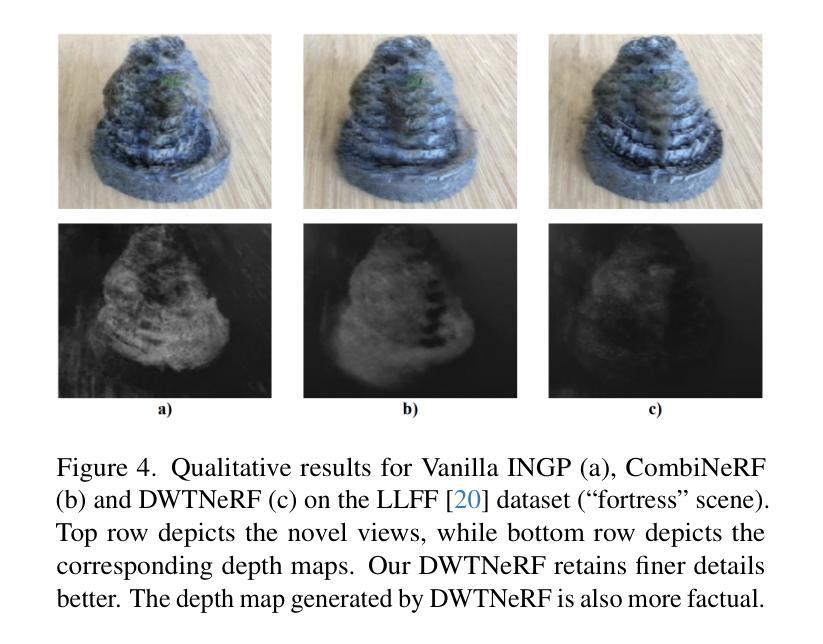
DWTNeRF: Boosting Few-shot Neural Radiance Fields via Discrete Wavelet Transform
Authors:Hung Nguyen, Blark Runfa Li, Truong Nguyen
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) has achieved superior performance in novel view synthesis and 3D scene representation, but its practical applications are hindered by slow convergence and reliance on dense training views. To this end, we present DWTNeRF, a unified framework based on Instant-NGP’s fast-training hash encoding. It is coupled with regularization terms designed for few-shot NeRF, which operates on sparse training views. Our DWTNeRF additionally includes a novel Discrete Wavelet loss that allows explicit prioritization of low frequencies directly in the training objective, reducing few-shot NeRF’s overfitting on high frequencies in earlier training stages. We also introduce a model-based approach, based on multi-head attention, that is compatible with INGP, which are sensitive to architectural changes. On the 3-shot LLFF benchmark, DWTNeRF outperforms Vanilla INGP by 15.07% in PSNR, 24.45% in SSIM and 36.30% in LPIPS. Our approach encourages a re-thinking of current few-shot approaches for fast-converging implicit representations like INGP or 3DGS.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在新型视图合成和3D场景表示方面取得了卓越的性能,但其实际应用受到了收敛速度慢和依赖密集训练视图的影响。为此,我们提出了DWTNeRF,这是一个基于Instant-NGP快速训练哈希编码的统一框架。它与针对少射NeRF设计的正则化术语相结合,在稀疏训练视图上运行。我们的DWTNeRF还包括一种新型离散小波损失,允许在训练目标中直接明确优先处理低频,从而减少早期训练阶段中少射NeRF对高频的过拟合。我们还介绍了一种基于多头注意力机制的模型方法,该方法与INGP兼容,对架构变化敏感。在3次拍摄的LLFF基准测试中,DWTNeRF在PSNR上较Vanilla INGP高出15.07%,在SSIM上高出24.45%,在LPIPS上高出36.30%。我们的方法鼓励对现有的少射方法进行重新思考,以寻找如INGP或3DGS这样的快速收敛隐式表示方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 13 figures, 8 tables
Summary
NeRF技术在新型视图合成和3D场景表示方面表现出卓越性能,但其实际应用中存在收敛速度慢和依赖密集训练视图的问题。为此,提出了DWTNeRF统一框架,它基于Instant-NGP的快速训练哈希编码,并设计了针对少量射击NeRF的正则化项,可在稀疏训练视图上运行。DWTNeRF还包括一种新型离散小波损失,允许直接在训练目标中明确优先处理低频信息,从而减少早期训练阶段中少量射击NeRF对高频信息的过度拟合。在3次射击LLFF基准测试上,DWTNeRF较Vanilla INGP在PSNR上提高了15.07%,在SSIM上提高了24.45%,在LPIPS上提高了36.30%。我们的方法鼓励对当前少量射击的快速收敛隐式表示方法(如INGP或3DGS)进行重新审视。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术在视图合成和3D场景表示方面表现出卓越性能,但存在收敛慢和依赖密集训练视图的问题。
- DWTNeRF框架基于Instant-NGP的快速训练哈希编码,能在稀疏训练视图上运行。
- DWTNeRF引入了一种新型离散小波损失,能优先处理低频信息,减少过度拟合。
- 在基准测试中,DWTNeRF较原有方法有明显性能提升。
- DWTNeRF方法对于隐式表示的快速收敛具有启示意义。
- DWTNeRF方法为少量射击情况下的NeRF技术提供了新的思考方向。
点此查看论文截图


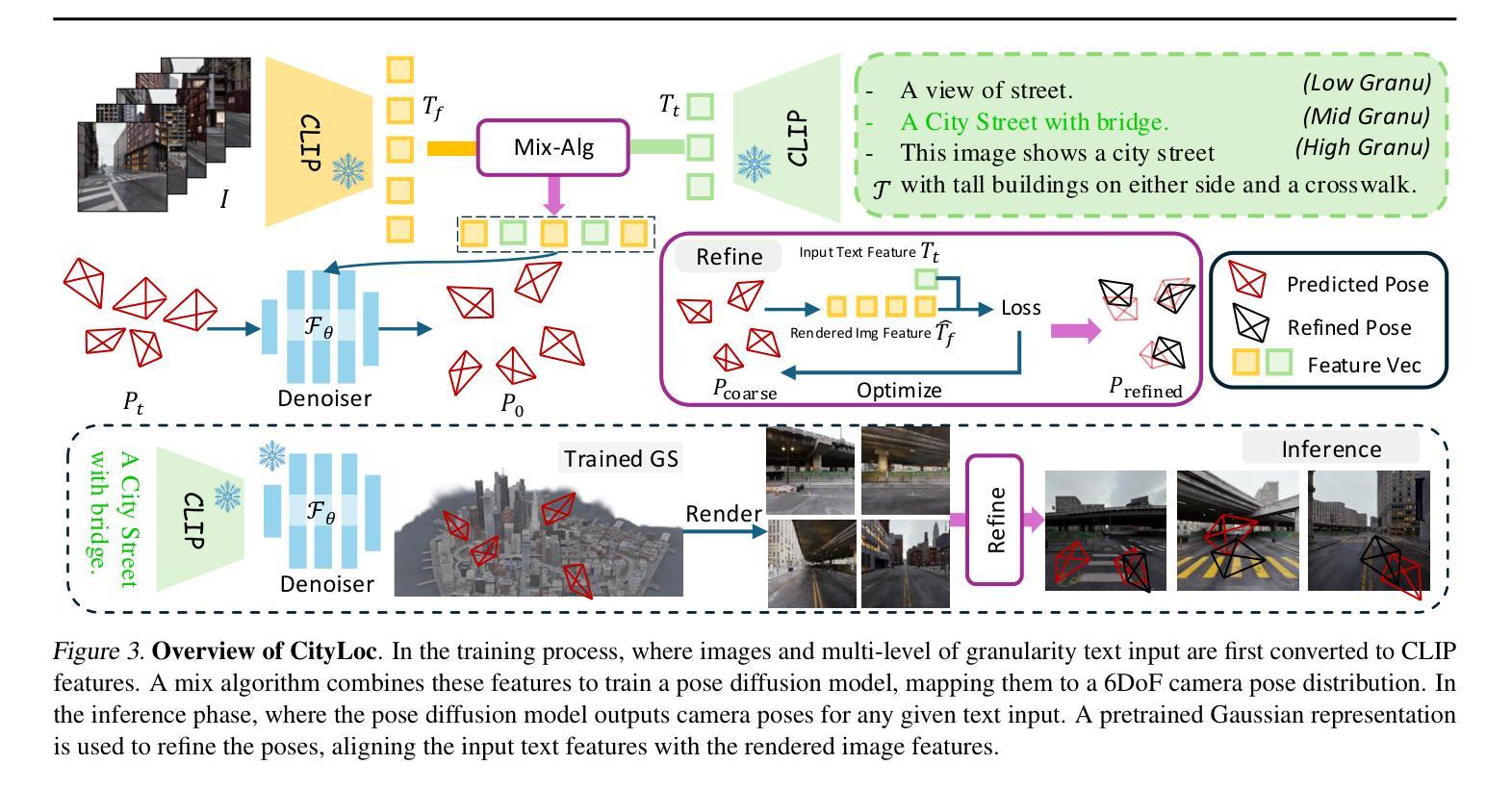
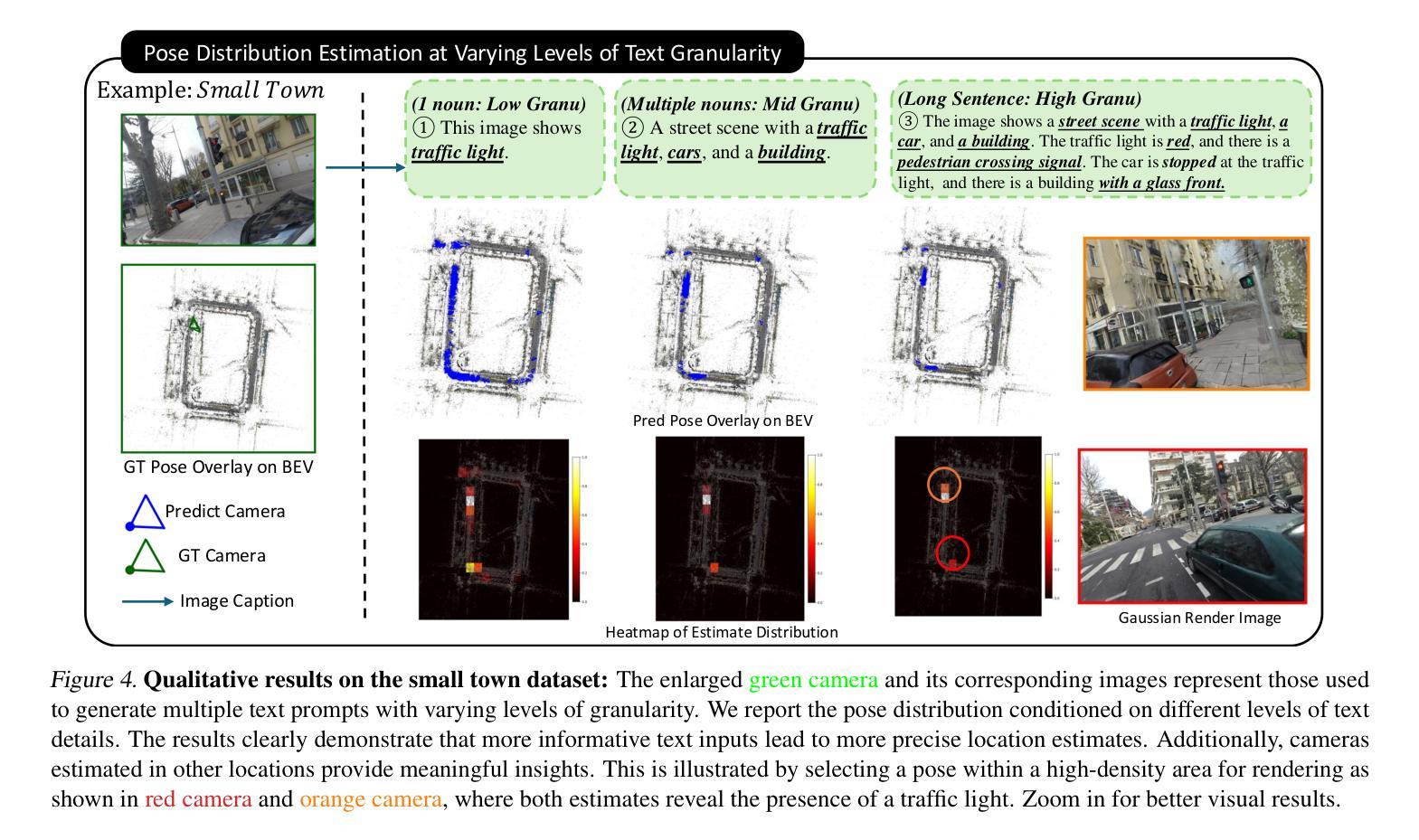
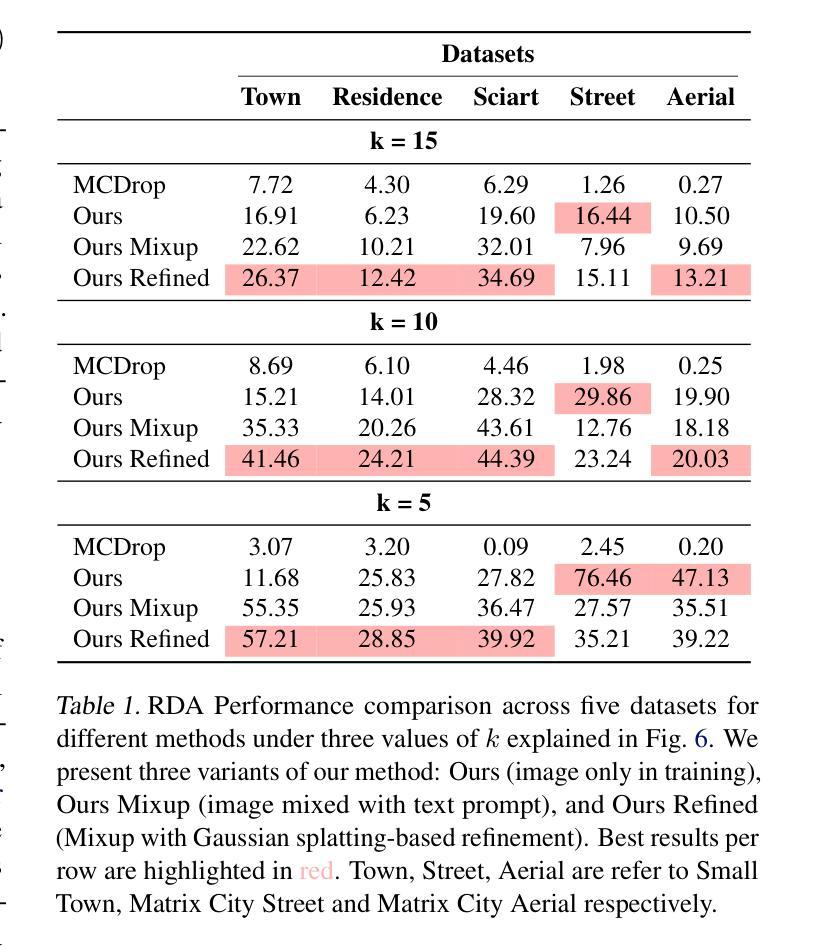
CityLoc: 6DoF Pose Distributional Localization for Text Descriptions in Large-Scale Scenes with Gaussian Representation
Authors:Qi Ma, Runyi Yang, Bin Ren, Nicu Sebe, Ender Konukoglu, Luc Van Gool, Danda Pani Paudel
Localizing textual descriptions within large-scale 3D scenes presents inherent ambiguities, such as identifying all traffic lights in a city. Addressing this, we introduce a method to generate distributions of camera poses conditioned on textual descriptions, facilitating robust reasoning for broadly defined concepts. Our approach employs a diffusion-based architecture to refine noisy 6DoF camera poses towards plausible locations, with conditional signals derived from pre-trained text encoders. Integration with the pretrained Vision-Language Model, CLIP, establishes a strong linkage between text descriptions and pose distributions. Enhancement of localization accuracy is achieved by rendering candidate poses using 3D Gaussian splatting, which corrects misaligned samples through visual reasoning. We validate our method’s superiority by comparing it against standard distribution estimation methods across five large-scale datasets, demonstrating consistent outperformance. Code, datasets and more information will be publicly available at our project page.
在大规模三维场景中对文本描述进行定位存在固有的模糊性,例如识别城市中的所有交通灯。为解决这一问题,我们引入了一种方法,根据文本描述生成相机姿态分布,促进对广义概念的稳健推理。我们的方法采用基于扩散的架构,将嘈杂的6DoF相机姿态细化到合理位置,条件信号来源于预训练的文本编码器。与预训练的视觉语言模型CLIP的结合,在文本描述和姿态分布之间建立了强有力的联系。通过采用三维高斯摊铺渲染候选姿态,实现了定位精度的提升,通过视觉推理纠正了错位样本。我们在五个大规模数据集上将我们的方法与标准分布估计方法进行了比较,展示了持续超越对手的性能。我们的项目页面将公开提供代码、数据集和更多信息。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种方法,通过生成基于文本描述的相机姿态分布来解决大规模三维场景中本地化文本描述的内生歧义问题。该方法利用扩散架构优化噪声6DoF相机姿态,使其朝向合理位置,并使用预训练文本编码器生成条件信号。结合预训练的视觉语言模型CLIP,在文本描述和姿态分布之间建立强链接。通过3D高斯喷绘技术渲染候选姿态,提高定位精度,并可通过视觉推理修正错位样本。本文方法在五个大规模数据集上与其他分布估计方法进行比较,展现了优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种解决大规模三维场景中本地化文本描述的内生歧义问题的方法。
- 通过生成基于文本描述的相机姿态分布,促进对广泛定义概念的理解。
- 利用扩散架构优化相机姿态,使其朝向合理位置。
- 结合预训练的文本编码器和视觉语言模型CLIP,建立文本描述与姿态分布之间的强链接。
- 采用3D高斯喷绘技术渲染候选姿态,增强定位准确性。
- 通过视觉推理修正错位样本。
- 在五个大规模数据集上验证了方法的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图



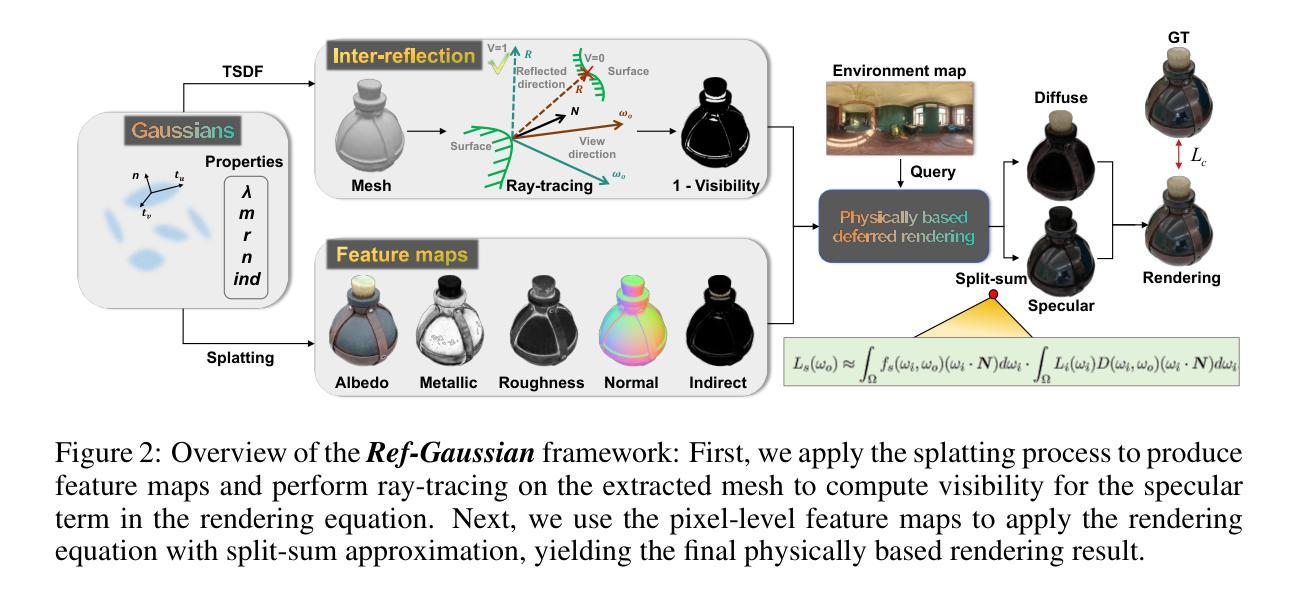
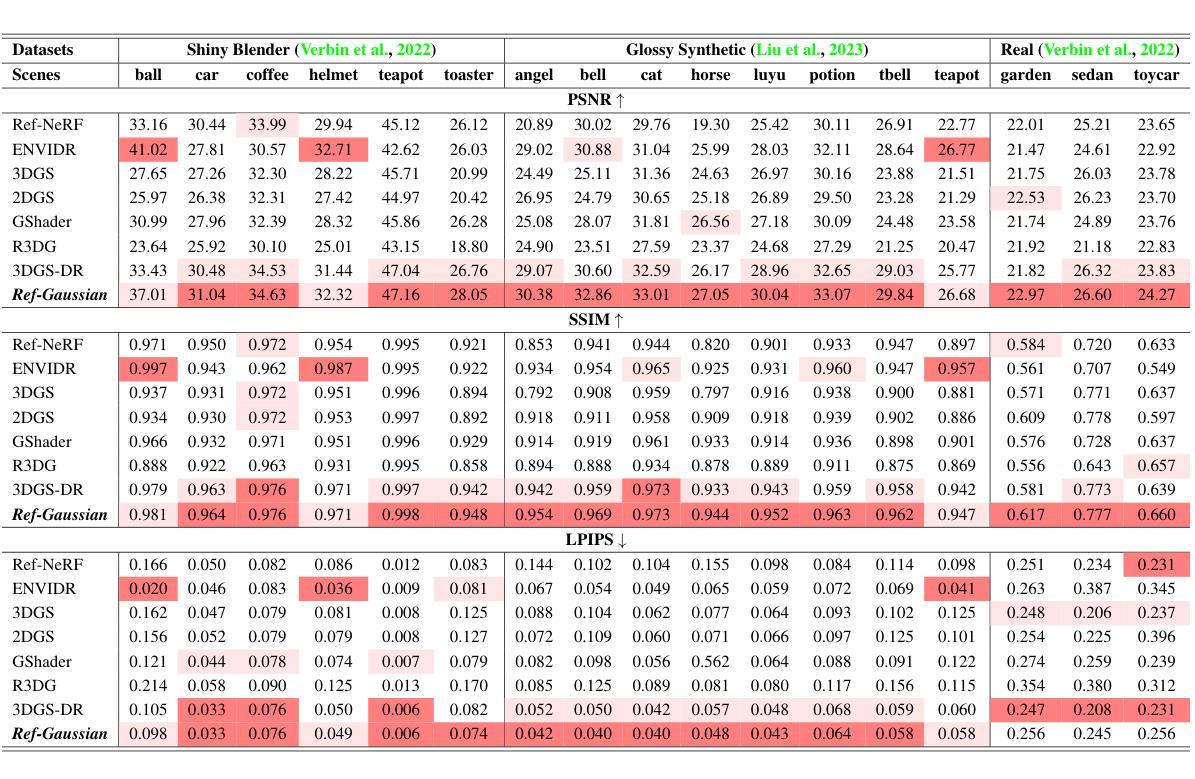
Reflective Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yuxuan Yao, Zixuan Zeng, Chun Gu, Xiatian Zhu, Li Zhang
Novel view synthesis has experienced significant advancements owing to increasingly capable NeRF- and 3DGS-based methods. However, reflective object reconstruction remains challenging, lacking a proper solution to achieve real-time, high-quality rendering while accommodating inter-reflection. To fill this gap, we introduce a Reflective Gaussian splatting (Ref-Gaussian) framework characterized with two components: (I) Physically based deferred rendering that empowers the rendering equation with pixel-level material properties via formulating split-sum approximation; (II) Gaussian-grounded inter-reflection that realizes the desired inter-reflection function within a Gaussian splatting paradigm for the first time. To enhance geometry modeling, we further introduce material-aware normal propagation and an initial per-Gaussian shading stage, along with 2D Gaussian primitives. Extensive experiments on standard datasets demonstrate that Ref-Gaussian surpasses existing approaches in terms of quantitative metrics, visual quality, and compute efficiency. Further, we show that our method serves as a unified solution for both reflective and non-reflective scenes, going beyond the previous alternatives focusing on only reflective scenes. Also, we illustrate that Ref-Gaussian supports more applications such as relighting and editing.
基于新型视图合成方法,尤其是日益强大的NeRF和3DGS方法,已经取得了重大进展。然而,反射物体的重建仍然是一个挑战,缺乏一种能在实时实现高质量渲染的同时处理相互反射的适当解决方案。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了基于反射高斯点涂(Ref-Gaussian)的框架,该框架由两个组件构成:(I)基于物理的延迟渲染技术,它通过公式化分割求和近似法为渲染方程赋予像素级材料属性;(II)基于高斯理论的相互反射技术,首次在高斯点涂范式内实现了所需的相互反射功能。为了提高几何建模能力,我们还引入了感知材料的法线传播和初始的高斯阴影阶段,以及二维高斯基本体。在标准数据集上的大量实验表明,Ref-Gaussian在定量指标、视觉质量和计算效率方面超过了现有方法。此外,我们证明我们的方法可以作为反射和非反射场景的统一解决方案,超越了之前只关注反射场景的替代方案。我们还说明Ref-Gaussian支持更多应用,如重新照明和编辑。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for ICLR 2025
Summary
基于NeRF和3DGS的方法,新型视图合成技术取得了显著进展,但反射物体重建仍面临挑战,缺乏实现实时高质量渲染同时兼顾互反射的适当解决方案。为解决此问题,我们提出了基于反射高斯拼贴(Ref-Gaussian)的框架,包含两个关键组成部分:(I)基于物理的延迟渲染,通过公式化分割和求和近似,为渲染方程提供像素级材料属性;(II)基于高斯拼贴的互反射实现。为提高几何建模能力,我们还引入了感知材料的正常传播、初始的高斯着色阶段以及二维高斯基本元素。在标准数据集上的广泛实验表明,Ref-Gaussian在定量指标、视觉质量和计算效率方面均超越了现有方法。此外,我们的方法成为反射和非反射场景的统一解决方案,超越了之前仅关注反射场景的替代方案。同时,Ref-Gaussian还支持重新照明和编辑等更多应用。
Key Takeaways
- 新型视图合成技术取得显著进展,反射物体重建仍是挑战。
- 引入Reflective Gaussian splatting(Ref-Gaussian)框架,包含基于物理的延迟渲染和Gaussian拼贴实现互反射两个关键部分。
- Ref-Gaussian提升几何建模能力,引入材料感知的正常传播和初始高斯着色阶段。
- 在标准数据集上,Ref-Gaussian在定量指标、视觉质量和计算效率方面超越现有方法。
- Ref-Gaussian成为反射和非反射场景的统一解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

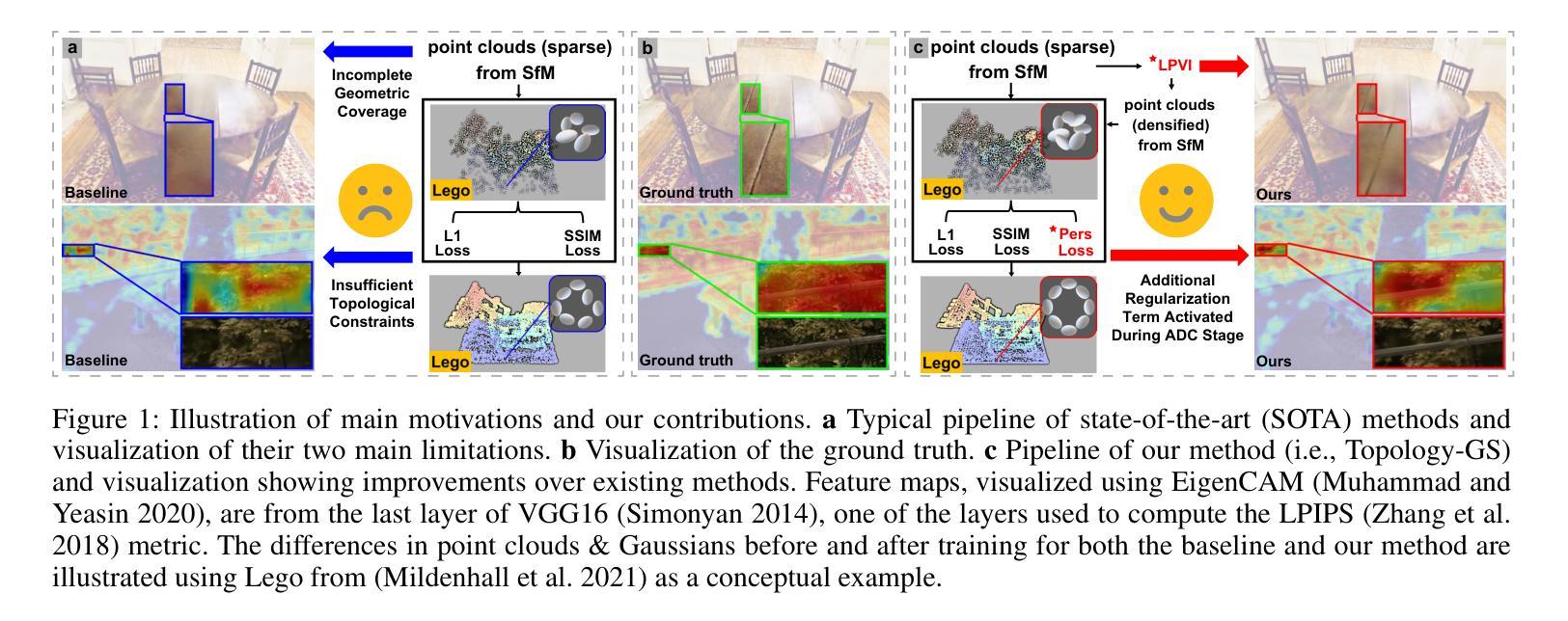
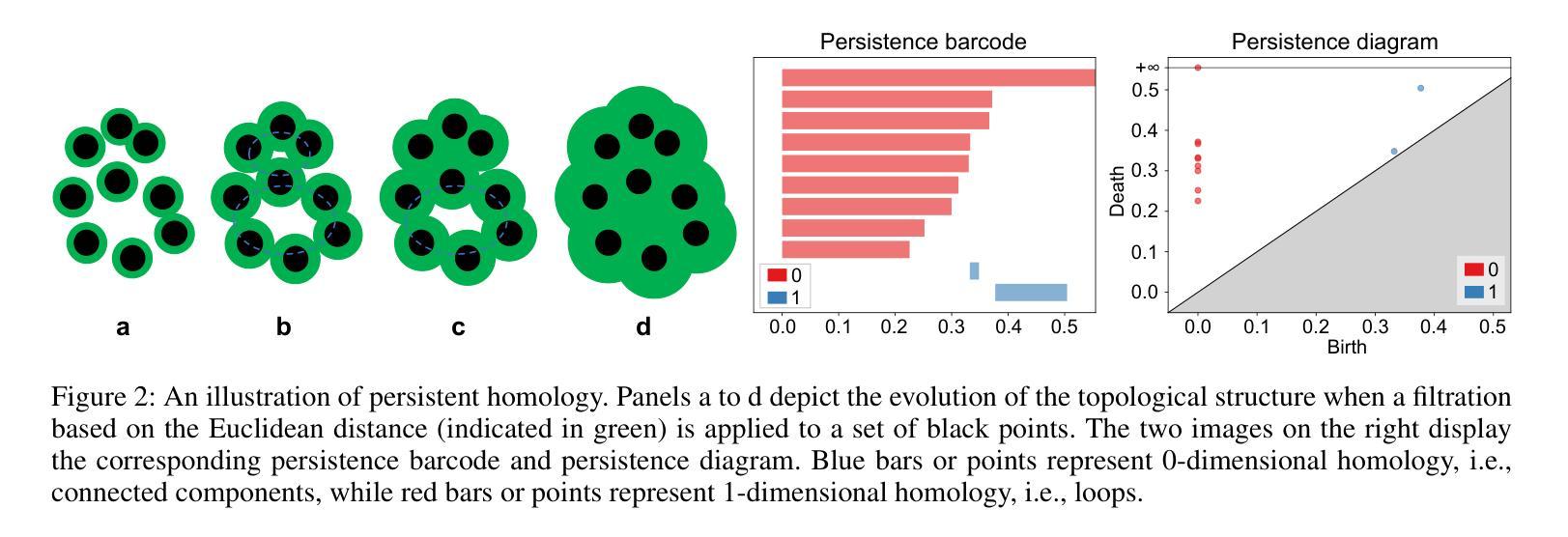
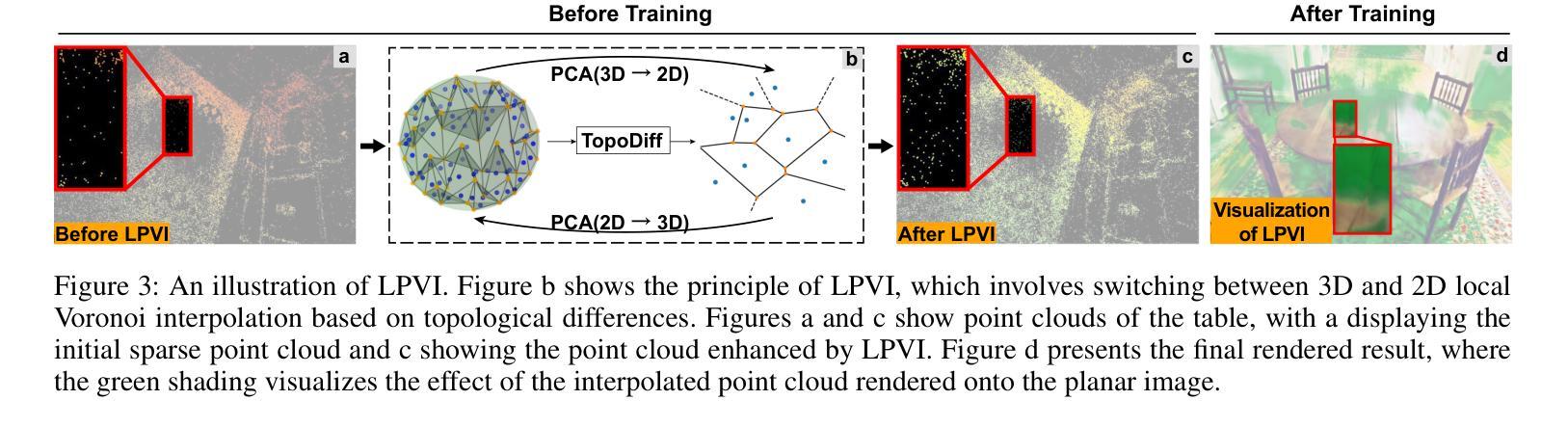
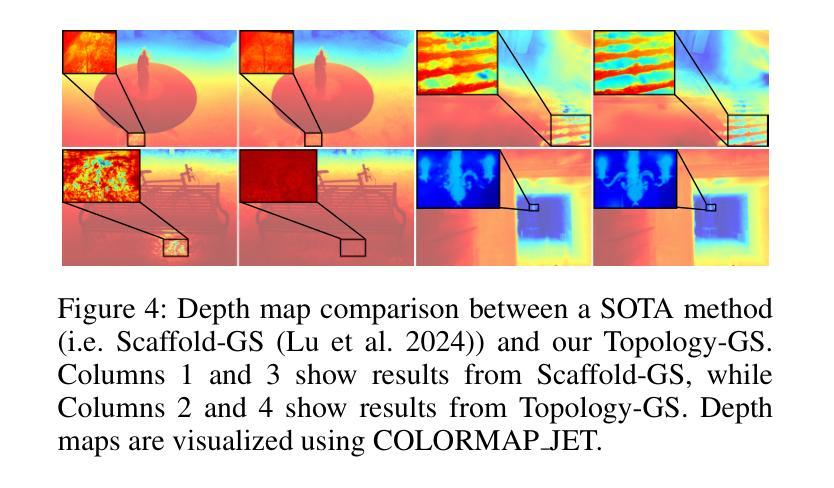
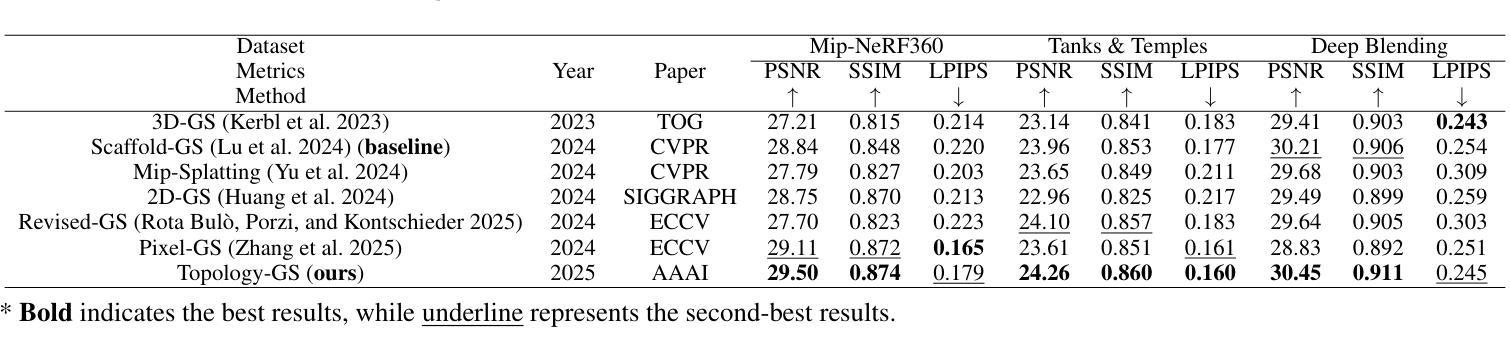
Topology-Aware 3D Gaussian Splatting: Leveraging Persistent Homology for Optimized Structural Integrity
Authors:Tianqi Shen, Shaohua Liu, Jiaqi Feng, Ziye Ma, Ning An
Gaussian Splatting (GS) has emerged as a crucial technique for representing discrete volumetric radiance fields. It leverages unique parametrization to mitigate computational demands in scene optimization. This work introduces Topology-Aware 3D Gaussian Splatting (Topology-GS), which addresses two key limitations in current approaches: compromised pixel-level structural integrity due to incomplete initial geometric coverage, and inadequate feature-level integrity from insufficient topological constraints during optimization. To overcome these limitations, Topology-GS incorporates a novel interpolation strategy, Local Persistent Voronoi Interpolation (LPVI), and a topology-focused regularization term based on persistent barcodes, named PersLoss. LPVI utilizes persistent homology to guide adaptive interpolation, enhancing point coverage in low-curvature areas while preserving topological structure. PersLoss aligns the visual perceptual similarity of rendered images with ground truth by constraining distances between their topological features. Comprehensive experiments on three novel-view synthesis benchmarks demonstrate that Topology-GS outperforms existing methods in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS metrics, while maintaining efficient memory usage. This study pioneers the integration of topology with 3D-GS, laying the groundwork for future research in this area.
高斯贴图(GS)已成为表示离散体积辐射场的关键技术。它利用独特的参数化方法,以减轻场景优化中的计算需求。本文介绍了拓扑感知三维高斯贴图(Topology-GS),解决了当前方法中的两个关键局限性:由于初始几何覆盖不完整而损害像素级结构完整性,以及在优化过程中由于拓扑约束不足而导致特征级完整性不足。为了克服这些局限性,Topology-GS融入了一种新型插值策略——局部持久Voronoi插值(LPVI)和一种基于持久条码的专注于拓扑的正则化项,称为PersLoss。LPVI利用持久同源性来引导自适应插值,在低曲率区域增强点覆盖,同时保留拓扑结构。PersLoss通过对拓扑特征之间的距离进行约束,使渲染图像的视觉感知相似性符合真实情况。在三个全新视图合成基准测试上的综合实验表明,在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS指标方面,Topology-GS优于现有方法,同时保持高效的内存使用。本研究首创了拓扑与3D-GS的集成,为这一领域的未来研究奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了高斯采样(GS)在表示离散体积辐射场中的关键作用,并通过独特的参数化方法减轻了场景优化中的计算负担。为此工作引入的拓扑感知三维高斯采样(Topology-GS)解决了当前方法中的两个关键局限:由于初始几何覆盖不完整而导致的像素级结构完整性受损,以及在优化过程中因拓扑约束不足而导致的特征级完整性不足。为了克服这些局限性,Topology-GS采用了一种新颖的内插策略——局部持久Voronoi内插(LPVI)和基于持久条码的拓扑重点正则化术语——PersLoss。LPVI利用持久同源性引导自适应内插,增强了低曲率区域的点覆盖,同时保持拓扑结构。PersLoss通过对拓扑特征之间的距离进行约束,使渲染图像的视觉感知相似性与地面真实情况保持一致。在三个全新视图合成基准测试上的综合实验表明,Topology-GS在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS指标上优于现有方法,同时保持高效的内存使用。该研究开创了拓扑与3D-GS的集成,为未来该领域的研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯采样(GS)是表示离散体积辐射场的重要技术,通过参数化减轻场景优化计算负担。
- 拓扑感知三维高斯采样(Topology-GS)解决了当前方法的两个关键局限:像素级结构完整性的妥协和特征级完整性的不足。
- Topology-GS采用局部持久Voronoi内插(LPVI)和基于持久条码的拓扑重点正则化术语——PersLoss来克服这些局限性。
- LPVI利用持久同源性增强低曲率区域的点覆盖,并保持拓扑结构。
- PersLoss约束渲染图像与地面真实情况之间的拓扑特征距离,提高视觉感知相似性。
- 在全新视图合成基准测试上,Topology-GS在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS指标上表现优越,且内存使用高效。
点此查看论文截图



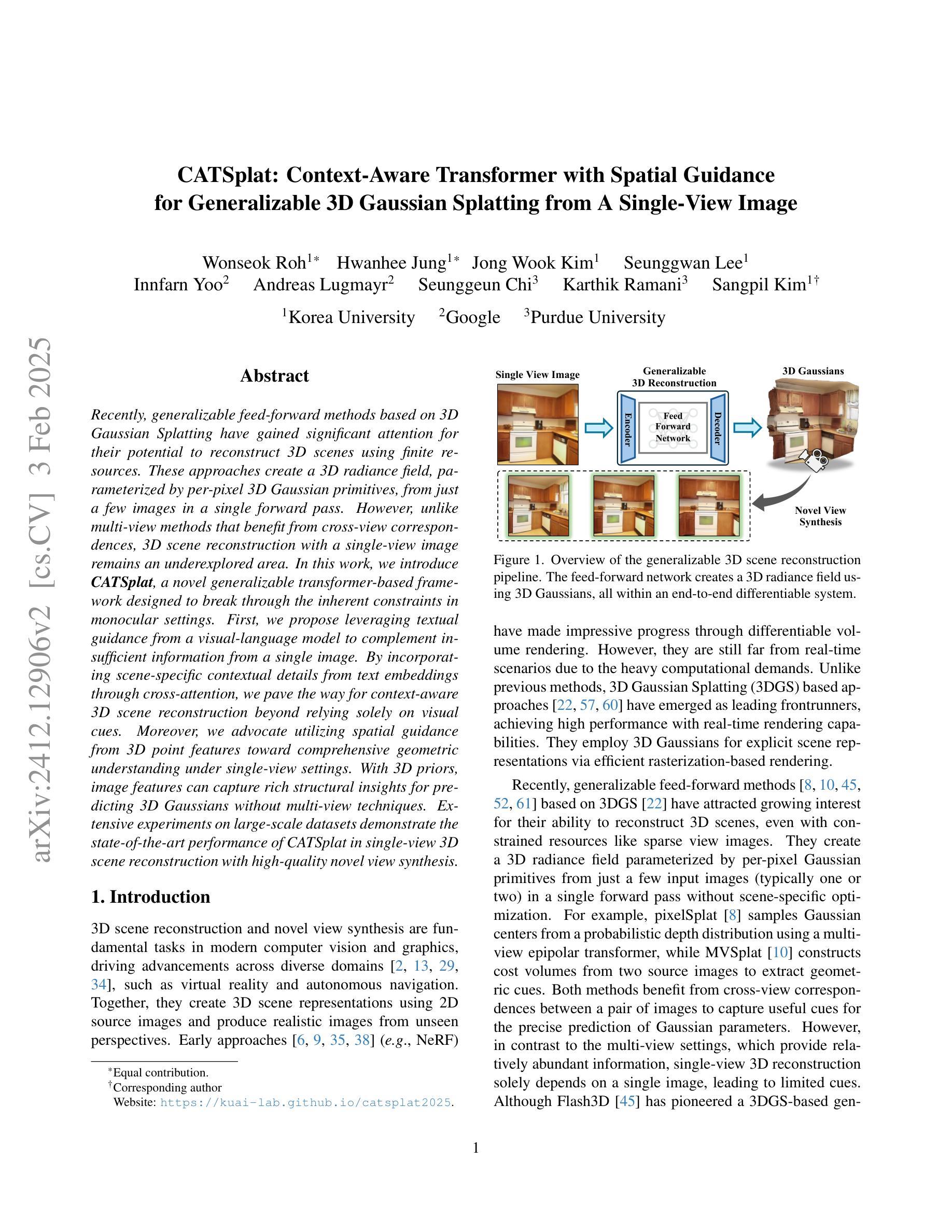
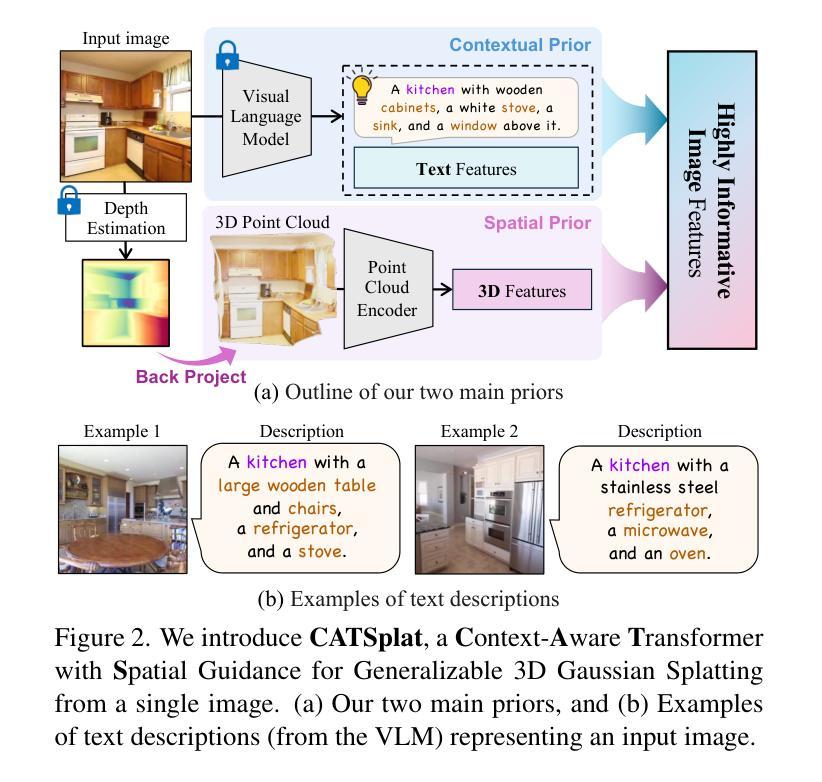
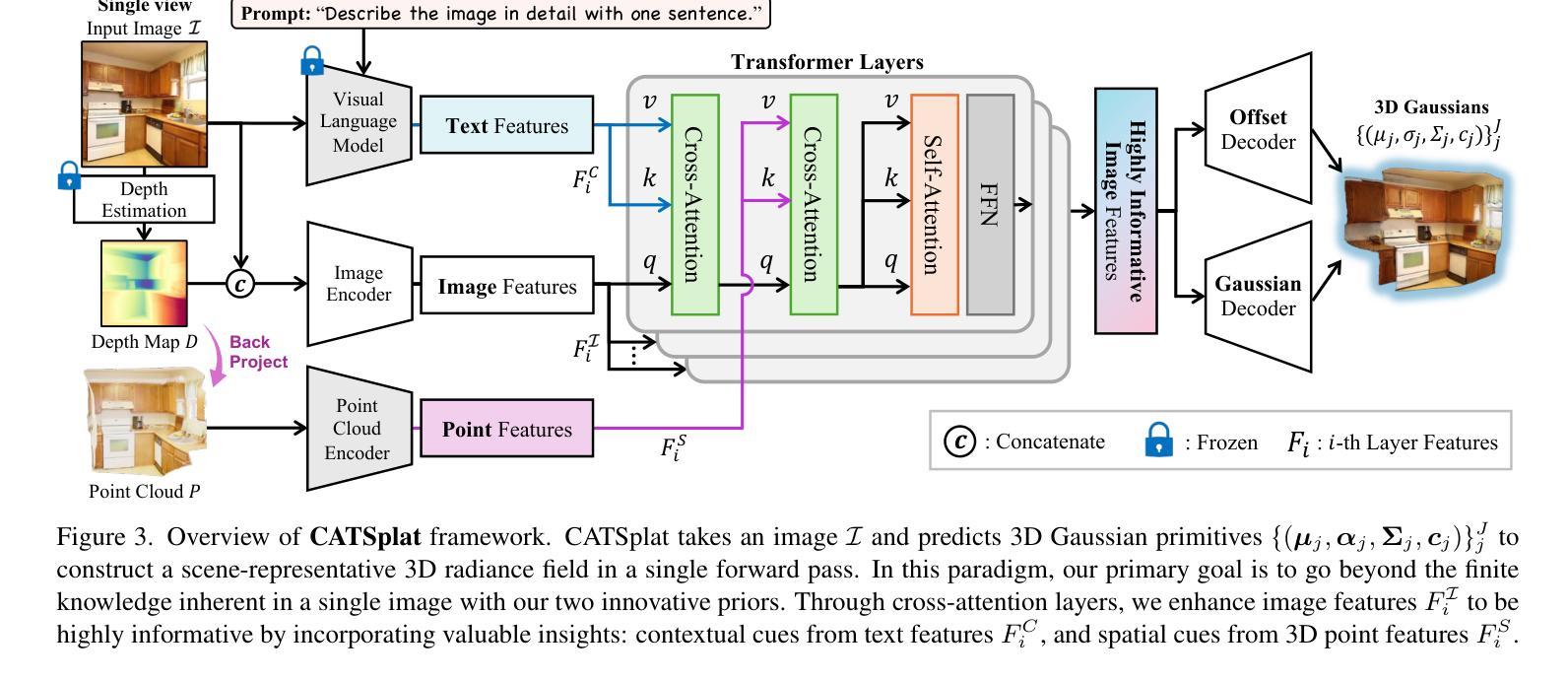
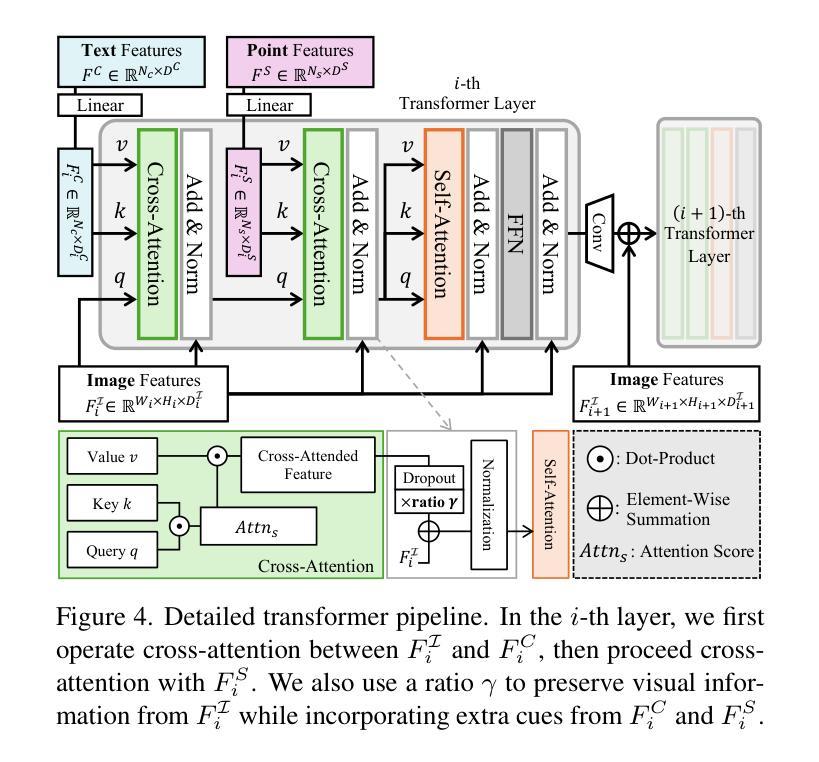
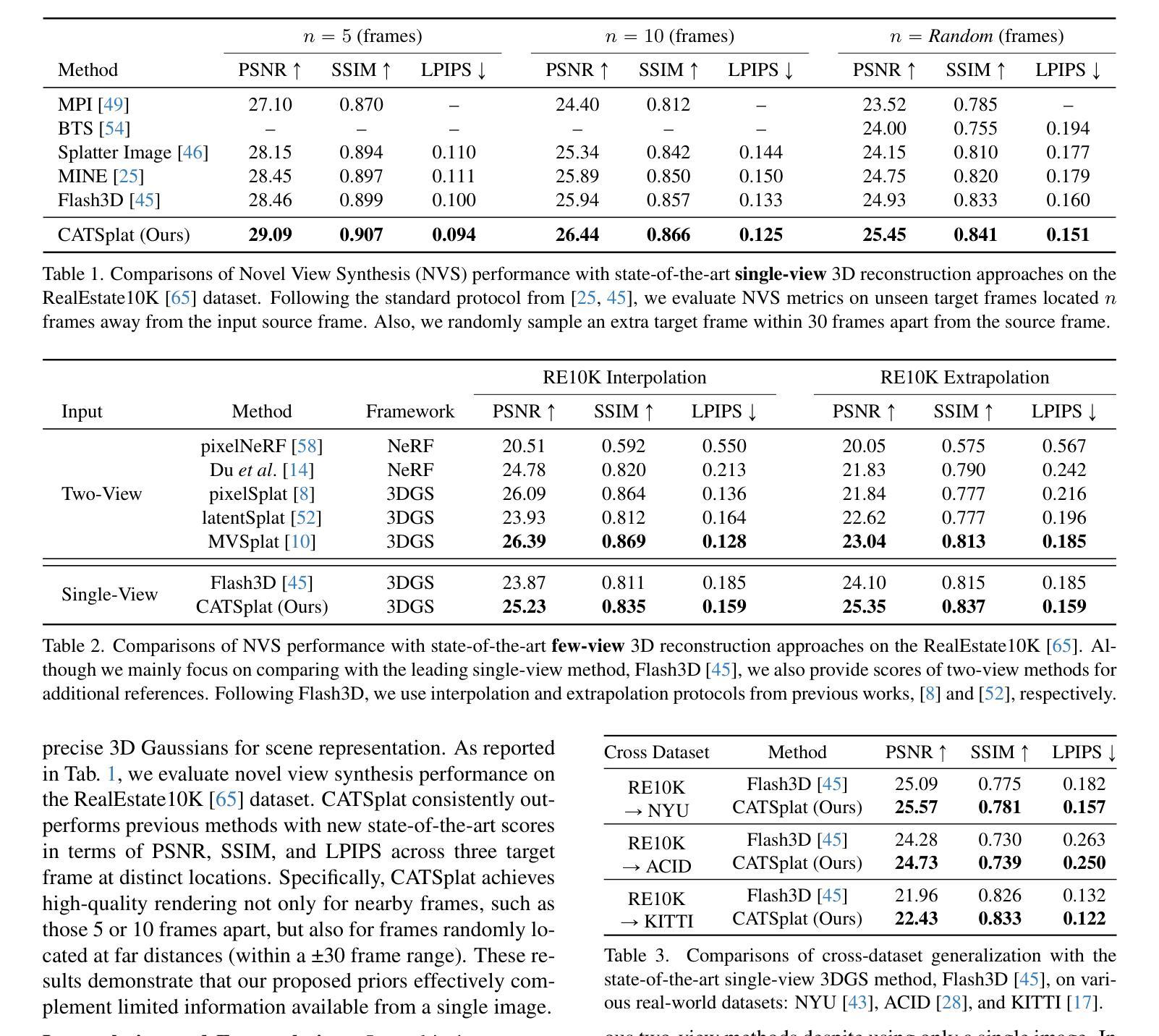
CATSplat: Context-Aware Transformer with Spatial Guidance for Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting from A Single-View Image
Authors:Wonseok Roh, Hwanhee Jung, Jong Wook Kim, Seunggwan Lee, Innfarn Yoo, Andreas Lugmayr, Seunggeun Chi, Karthik Ramani, Sangpil Kim
Recently, generalizable feed-forward methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting have gained significant attention for their potential to reconstruct 3D scenes using finite resources. These approaches create a 3D radiance field, parameterized by per-pixel 3D Gaussian primitives, from just a few images in a single forward pass. However, unlike multi-view methods that benefit from cross-view correspondences, 3D scene reconstruction with a single-view image remains an underexplored area. In this work, we introduce CATSplat, a novel generalizable transformer-based framework designed to break through the inherent constraints in monocular settings. First, we propose leveraging textual guidance from a visual-language model to complement insufficient information from a single image. By incorporating scene-specific contextual details from text embeddings through cross-attention, we pave the way for context-aware 3D scene reconstruction beyond relying solely on visual cues. Moreover, we advocate utilizing spatial guidance from 3D point features toward comprehensive geometric understanding under single-view settings. With 3D priors, image features can capture rich structural insights for predicting 3D Gaussians without multi-view techniques. Extensive experiments on large-scale datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of CATSplat in single-view 3D scene reconstruction with high-quality novel view synthesis.
最近,基于三维高斯拼贴(3D Gaussian Splatting)的通用前馈方法因其利用有限资源重建三维场景的潜力而受到广泛关注。这些方法在单次前向传递中仅使用少数图像即可创建一个三维辐射场,该辐射场由像素级三维高斯基元参数化。然而,与受益于跨视图对应的多视角方法不同,基于单视图图像的三维场景重建仍然是一个尚未得到充分探索的领域。在这项工作中,我们引入了CATSplat,这是一个新型的可推广的基于transformer的框架,旨在突破单目视觉设置中的固有约束。首先,我们提出利用视觉语言模型的文本指导来补充单一图像中的不足信息。通过跨注意力融入场景特定的上下文细节和文本嵌入,我们为仅在视觉线索之外进行上下文感知的三维场景重建铺平了道路。此外,我们主张利用三维点特征的空间指导,以实现单视角设置下的全面几何理解。借助三维先验知识,图像特征可以捕捉丰富的结构洞察力,无需多视角技术即可预测三维高斯分布。在大型数据集上的广泛实验表明,CATSplat在单视角三维场景重建中具有最先进的性能,并能实现高质量的新视角合成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本描述的辅助和单视角图像特征的空间指导,CATSplat框架实现了突破单目场景固有约束的通用可变形态建模,完成了超越视觉线索的单视角上下文感知的三维场景重建任务。该方法展示了卓越的单视角三维场景重建性能,实现了高质量的新视角合成。
Key Takeaways
- CATSplat是一种基于通用可变形态的框架,旨在突破单目场景重建的固有约束。
- 利用文本指导来补充单一图像的信息不足,实现上下文感知的三维场景重建。
- 通过结合视觉语言模型的文本嵌入和跨注意力机制,将场景特定的上下文细节融入重建过程。
- 利用空间指导进行单视角下的全面几何理解,通过三维先验图像特征捕捉丰富的结构信息。
- 在大规模数据集上的实验证明了CATSplat在单视角三维场景重建领域的优越性。
- 该方法可实现高质量的新视角合成。
点此查看论文截图
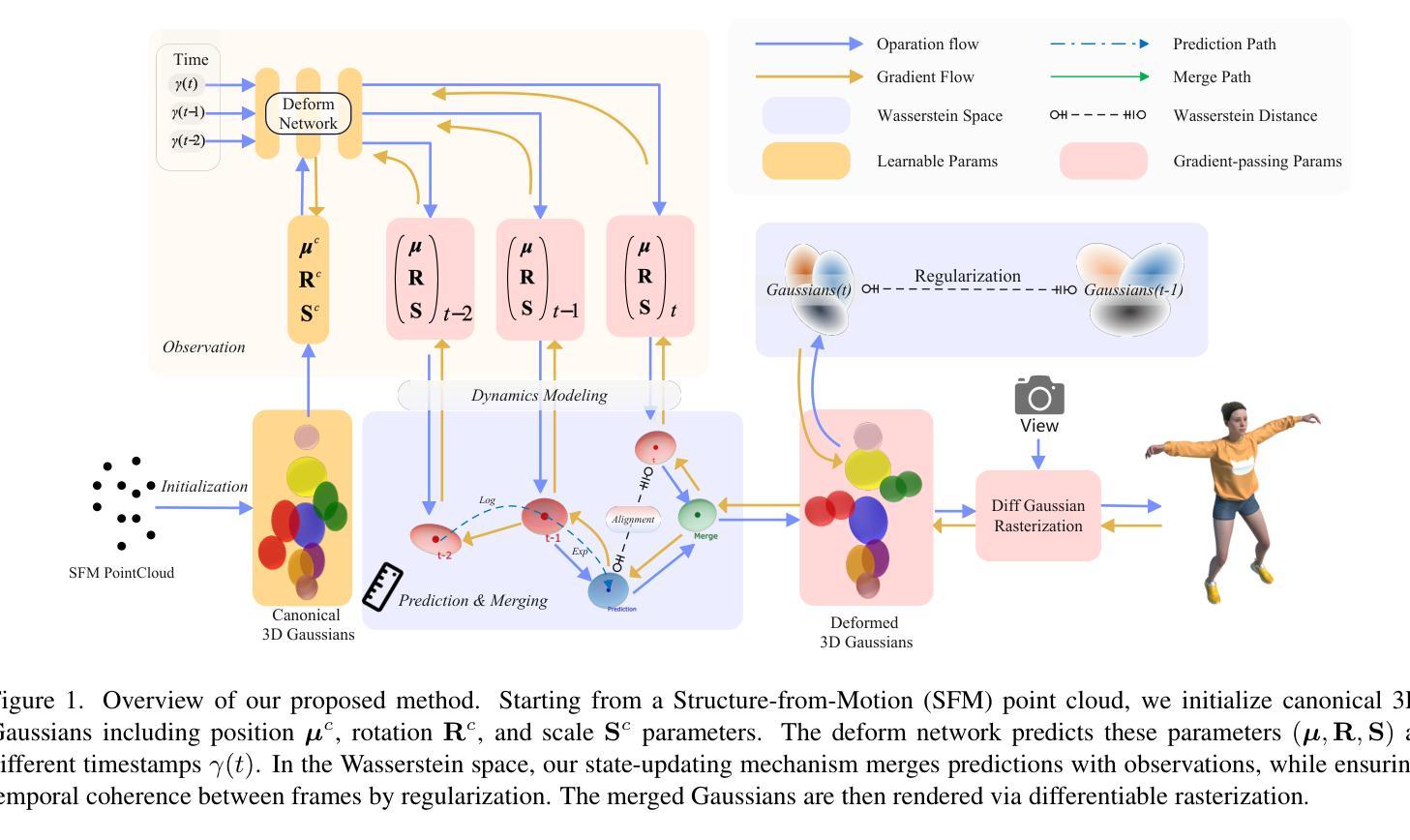
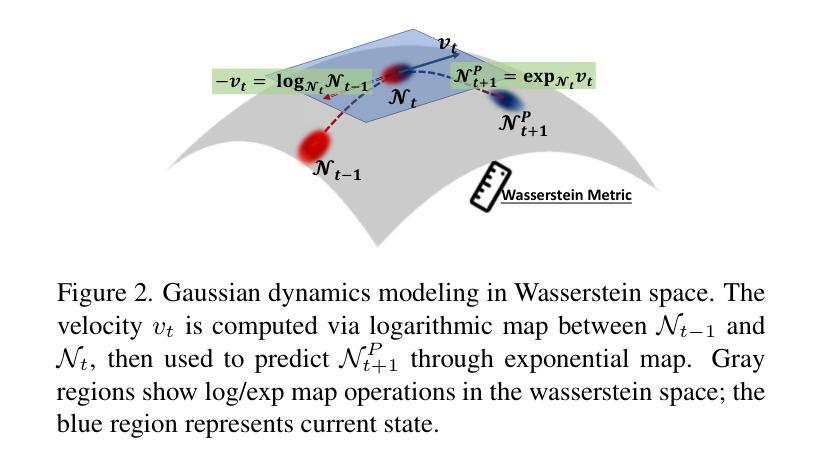
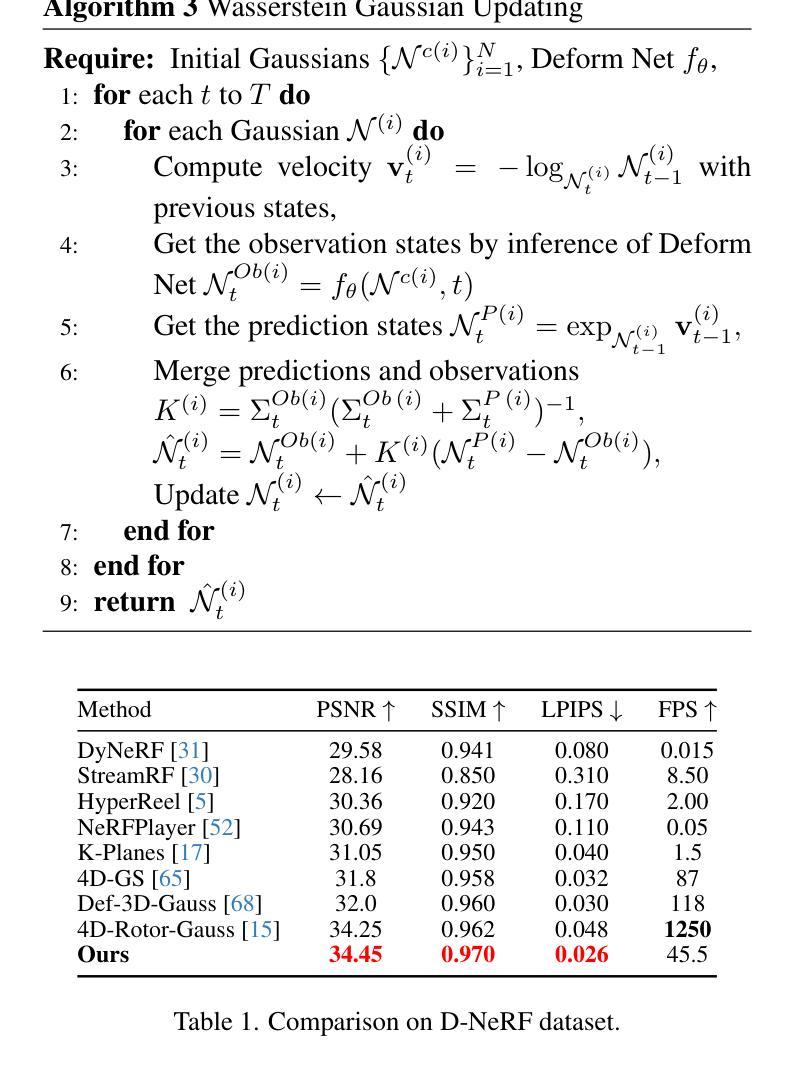
Gaussians on their Way: Wasserstein-Constrained 4D Gaussian Splatting with State-Space Modeling
Authors:Junli Deng, Yihao Luo
Dynamic scene rendering has taken a leap forward with the rise of 4D Gaussian Splatting, but there’s still one elusive challenge: how to make 3D Gaussians move through time as naturally as they would in the real world, all while keeping the motion smooth and consistent. In this paper, we unveil a fresh approach that blends state-space modeling with Wasserstein geometry, paving the way for a more fluid and coherent representation of dynamic scenes. We introduce a State Consistency Filter that merges prior predictions with the current observations, enabling Gaussians to stay true to their way over time. We also employ Wasserstein distance regularization to ensure smooth, consistent updates of Gaussian parameters, reducing motion artifacts. Lastly, we leverage Wasserstein geometry to capture both translational motion and shape deformations, creating a more physically plausible model for dynamic scenes. Our approach guides Gaussians along their natural way in the Wasserstein space, achieving smoother, more realistic motion and stronger temporal coherence. Experimental results show significant improvements in rendering quality and efficiency, outperforming current state-of-the-art techniques.
动态场景渲染随着四维高斯贴图技术的兴起取得了长足的发展,但仍面临一个难以捉摸的挑战:如何在保持运动平滑一致的同时,让三维高斯随时间变化像真实世界那样自然移动。在本文中,我们提出了一种将状态空间建模与Wasserstein几何相结合的新方法,为动态场景的表达开辟了更加流畅和连贯的道路。我们引入了一种状态一致性滤波器,它将先前的预测与当前观测相结合,使高斯随着时间的推移保持其真实性。我们还采用Wasserstein距离正则化,以确保高斯参数的平滑一致更新,减少运动伪影。最后,我们利用Wasserstein几何来捕捉平移运动和形状变形,为动态场景创建了一个更物理上合理的模型。我们的方法引导高斯在Wasserstein空间内沿着自然路径移动,实现更平滑、更逼真的运动以及更强的时间连贯性。实验结果表明,在渲染质量和效率方面都有显著提高,超越了当前最先进的技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文提出了一种将状态空间模型与Wasserstein几何相结合的新方法,以更流畅、连贯地表现动态场景。新方法通过使用状态一致性滤波器来融合先前的预测和当前观察结果,确保Gaussians随时间推移保持一致性。此外,采用Wasserstein距离正则化确保Gaussian参数平滑、一致地更新,减少运动伪影。最后,利用Wasserstein几何捕捉平移运动和形状变形,建立更贴近物理现实的动态场景模型。此方法在Wasserstein空间中引导Gaussians沿自然路径运动,实现了更平滑、更逼真的运动效果,并提高了渲染质量和效率,优于当前先进技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 引入状态空间模型与Wasserstein几何结合的新方法,以改善动态场景的渲染质量。
- 通过状态一致性滤波器融合先前预测和当前观察结果,使Gaussians保持一致性。
- 采用Wasserstein距离正则化确保Gaussian参数平滑、一致更新,减少运动伪影。
- 利用Wasserstein几何捕捉运动和形状变形,建立更物理现实的动态场景模型。
- 方法实现了更平滑、更逼真的运动效果。
- 提高了渲染效率和质量。
点此查看论文截图