⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
Multi-agent Multi-armed Bandit with Fully Heavy-tailed Dynamics
Authors:Xingyu Wang, Mengfan Xu
We study decentralized multi-agent multi-armed bandits in fully heavy-tailed settings, where clients communicate over sparse random graphs with heavy-tailed degree distributions and observe heavy-tailed (homogeneous or heterogeneous) reward distributions with potentially infinite variance. The objective is to maximize system performance by pulling the globally optimal arm with the highest global reward mean across all clients. We are the first to address such fully heavy-tailed scenarios, which capture the dynamics and challenges in communication and inference among multiple clients in real-world systems. In homogeneous settings, our algorithmic framework exploits hub-like structures unique to heavy-tailed graphs, allowing clients to aggregate rewards and reduce noises via hub estimators when constructing UCB indices; under $M$ clients and degree distributions with power-law index $\alpha > 1$, our algorithm attains a regret bound (almost) of order $O(M^{1 -\frac{1}{\alpha}} \log{T})$. Under heterogeneous rewards, clients synchronize by communicating with neighbors, aggregating exchanged estimators in UCB indices; With our newly established information delay bounds on sparse random graphs, we prove a regret bound of $O(M \log{T})$. Our results improve upon existing work, which only address time-invariant connected graphs, or light-tailed dynamics in dense graphs and rewards.
我们研究在完全重尾环境中分散的多智能体多臂赌博问题。在此环境中,客户端通过稀疏随机图进行通信,这些图的度分布具有重尾特性,并且观察到重尾(同质或异质)的奖励分布,可能存在无限方差。我们的目标是最大化系统性能,通过拉动所有客户中具有最高全局奖励均值的最佳全局手臂。我们是第一个解决这种完全重尾场景的研究团队,这捕捉了现实世界中多个客户端之间的通信和推断的动力学和挑战。在同质环境中,我们的算法框架利用重尾图中独有的中心结构,允许客户端在构建UCB指数时通过中心估计器来聚合奖励并减少噪声;在拥有幂律指数α> 1的M个客户端和度分布的情况下,我们的算法达到了几乎为O(M^{1 -\frac{1}{\alpha}} log{T})的后悔界。在异质奖励下,客户端通过与邻居通信进行同步,在UCB指数中聚合交换的估计器;根据我们在稀疏随机图上新建立的信息延迟界限,我们证明了O(M log{T})的后悔界。我们的研究结果改进了现有工作,这些工作仅针对时间不变的连通图或密集图中的轻尾动态和奖励进行研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 40 pages
Summary:
在完全重尾分布的环境中,研究了分散式多智能体多臂老虎机问题。在稀疏随机图中通信时,通信客户之间的节点度数分布和奖励分布呈现重尾特性。目标是最大化系统性能,通过拉动全局最优臂获得最高全局平均奖励。首次解决此类完全重尾场景问题,捕捉了现实系统中多个客户端之间的通信和推断动态和挑战。在奖励分布均匀的环境下,算法框架利用重尾图的中心结构特点,构建UCB指数时通过中心估计器聚合奖励并减少噪声;在M个客户端和幂律指数α>1的情况下,算法达到几乎为O(M^{1-\frac{1}{\alpha}} log{T})的后悔界。在奖励分布不均的环境下,客户端通过与邻居同步通信并在UCB指数中聚合估计器;根据新建立的信息延迟边界在稀疏随机图上,我们证明了后悔界为O(M log{T})。结果优于现有只处理时间不变连通图或密集图中轻尾动力学的解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究了分散式多智能体多臂老虎机在完全重尾分布环境下的表现。
- 在稀疏随机图中通信时,节点度数分布和奖励分布呈现重尾特性。
- 目标是通过最大化系统性能来拉动全局最优臂以获取最高全局平均奖励。
- 该研究首次解决此类完全重尾场景问题,反映现实系统中多个客户端间的通信和推断动态和挑战。
- 在均匀奖励环境下,算法利用重尾图的中心结构特点来优化性能。
- 在不同环境下,算法有不同的后悔界表现。在M个客户端和特定幂律指数下,算法达到特定的后悔界。
点此查看论文截图

An Empirical Game-Theoretic Analysis of Autonomous Cyber-Defence Agents
Authors:Gregory Palmer, Luke Swaby, Daniel J. B. Harrold, Matthew Stewart, Alex Hiles, Chris Willis, Ian Miles, Sara Farmer
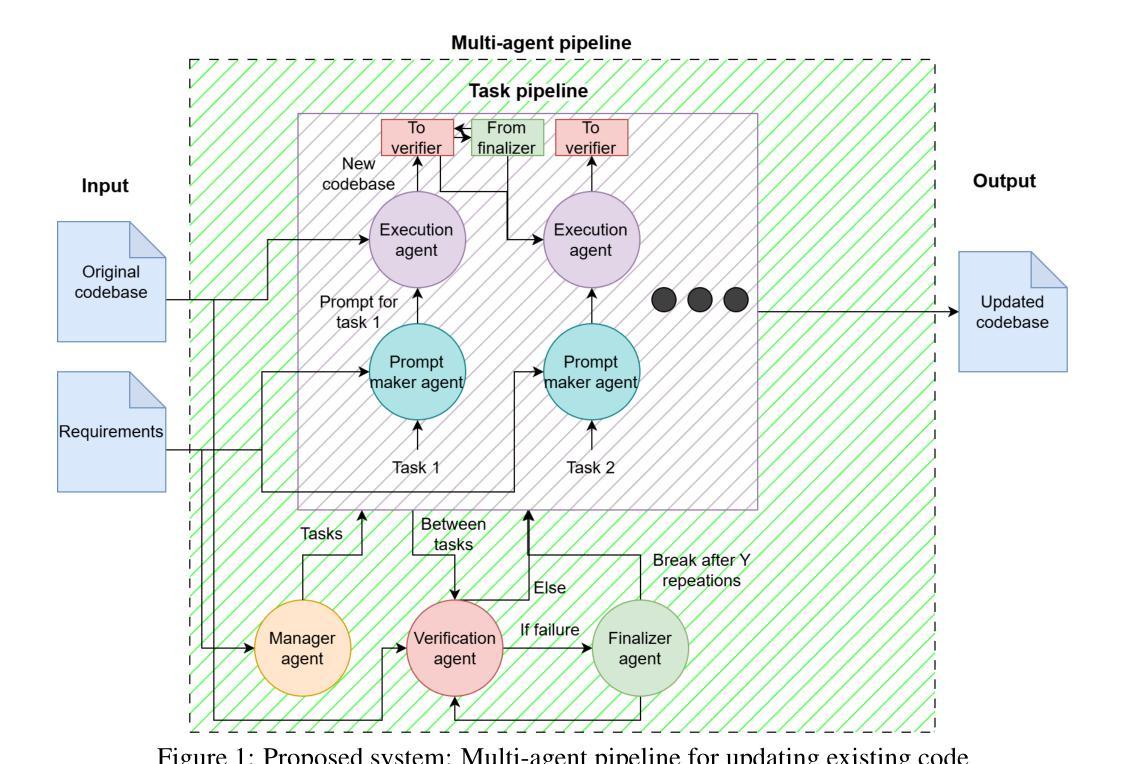
The recent rise in increasingly sophisticated cyber-attacks raises the need for robust and resilient autonomous cyber-defence (ACD) agents. Given the variety of cyber-attack tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) employed, learning approaches that can return generalisable policies are desirable. Meanwhile, the assurance of ACD agents remains an open challenge. We address both challenges via an empirical game-theoretic analysis of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approaches for ACD using the principled double oracle (DO) algorithm. This algorithm relies on adversaries iteratively learning (approximate) best responses against each others’ policies; a computationally expensive endeavour for autonomous cyber operations agents. In this work we introduce and evaluate a theoretically-sound, potential-based reward shaping approach to expedite this process. In addition, given the increasing number of open-source ACD-DRL approaches, we extend the DO formulation to allow for multiple response oracles (MRO), providing a framework for a holistic evaluation of ACD approaches.
近期日益复杂的网络攻击的增加,使得对强大且坚韧的自主网络安全防御(ACD)代理的需求愈发迫切。考虑到所使用的网络攻击策略、技术和程序(TTPs)的多样性,学习能够回归通用策略的方法是非常理想的。同时,ACD代理的保证仍然是一个开放性的挑战。我们通过深度强化学习(DRL)方法来解决这两个挑战,并对ACD进行实证博弈论分析,采用有原则的Double Oracle(DO)算法。该算法依赖于对手之间针对彼此的决策进行迭代学习(近似)最佳响应,对于自主网络操作代理来说是一项计算成本高昂的工作。在这项工作中,我们引入并评估了一种基于理论的奖励塑形方法,以加快这一过程。此外,鉴于开源ACD-DRL方法的数量不断增加,我们将DO公式扩展到允许多重响应Oracle(MRO),为全面评估ACD方法提供了一个框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 17 figures, 10 tables
Summary
随着网络攻击手段日益复杂,对自主网络安全防御(ACD)智能体的需求愈发迫切。由于网络攻击战术、技术和程序(TTPs)的种类多样,学习通用化策略至关重要。针对ACD智能体的可信度问题以及学习策略的泛化问题,本研究采用基于博弈论深度强化学习(DRL)的方法,利用原则性双盲算法(DO算法)进行分析。为提高计算效率,本研究引入了一种基于理论的奖励塑造方法。此外,考虑到开源ACD-DRL方法的数量不断增加,本研究将DO算法扩展到多重响应双盲(MRO),为全面评估ACD方法提供框架。
Key Takeaways
- 自主网络安全防御(ACD)智能体因网络攻击复杂性而越发重要。
- 需要开发可学习通用化策略的网络安全防御策略。
- 研究通过深度强化学习的博弈论分析来解决策略泛化问题。
- 采用原则性双盲算法(DO算法)进行分析。
- 为提高计算效率,引入基于理论的奖励塑造方法。
- 针对日益增长的开源ACD方法,扩展了多重响应双盲算法框架。
点此查看论文截图

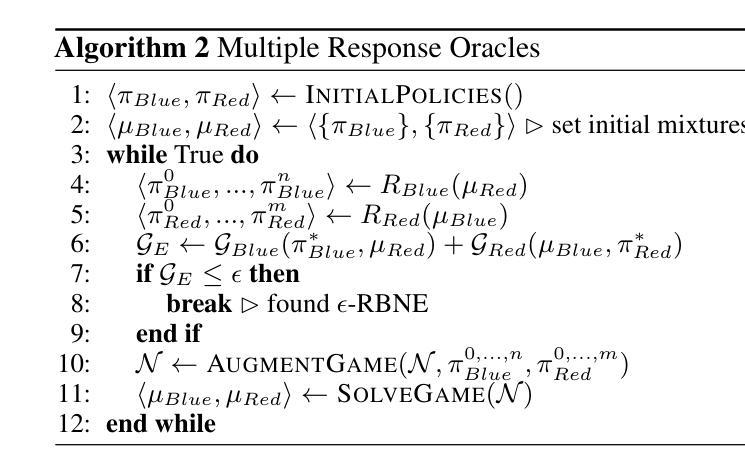

Autonomous Legacy Web Application Upgrades Using a Multi-Agent System
Authors:Valtteri Ala-Salmi, Zeeshan Rasheed, Abdul Malik Sami, Zheying Zhang, Kai-Kristian Kemell, Jussi Rasku, Shahbaz Siddeeq, Mika Saari, Pekka Abrahamsson
The use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for autonomous code generation is gaining attention in emerging technologies. As LLM capabilities expand, they offer new possibilities such as code refactoring, security enhancements, and legacy application upgrades. Many outdated web applications pose security and reliability challenges, yet companies continue using them due to the complexity and cost of upgrades. To address this, we propose an LLM-based multi-agent system that autonomously upgrades legacy web applications to the latest versions. The system distributes tasks across multiple phases, updating all relevant files. To evaluate its effectiveness, we employed Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL) and One-Shot Learning (OSL) prompts, applying identical instructions in both cases. The evaluation involved updating view files and measuring the number and types of errors in the output. For complex tasks, we counted the successfully met requirements. The experiments compared the proposed system with standalone LLM execution, repeated multiple times to account for stochastic behavior. Results indicate that our system maintains context across tasks and agents, improving solution quality over the base model in some cases. This study provides a foundation for future model implementations in legacy code updates. Additionally, findings highlight LLMs’ ability to update small outdated files with high precision, even with basic prompts. The source code is publicly available on GitHub: https://github.com/alasalm1/Multi-agent-pipeline.
使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行自主代码生成正受到新兴技术的关注。随着LLM能力的扩展,它们提供了新的可能性,例如代码重构、安全增强和遗留应用程序升级。许多过时的web应用程序带来了安全和可靠性挑战,但由于升级复杂性和成本,公司仍继续使用它们。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于LLM的多智能体系统,该系统可自主将遗留web应用程序升级到最新版本。该系统将任务分布到多个阶段,并更新所有相关文件。为了评估其有效性,我们采用了零样本学习(ZSL)和单样本学习(OSL)提示,在两种情况下均应用相同的指令。评估过程包括更新视图文件并测量输出中的错误数量和类型。对于复杂任务,我们计算成功满足的要求数量。实验将所提出系统与独立LLM执行进行了比较,多次重复以考虑随机行为。结果表明,我们的系统在任务和智能体之间保持了上下文,在某些情况下提高了解决方案的质量。这项研究为未来模型在遗留代码更新中的实现提供了基础。此外,研究结果还强调了LLM更新小过时文件的高精度能力,即使使用基本的提示也能实现。源代码已在GitHub上公开可用:https://github.com/alasalm1/Multi-agent-pipeline。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 2 figures
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主代码生成技术正受到新兴技术的关注。随着LLM能力的扩展,它们为代码重构、安全增强和遗留应用升级等提供了新的可能性。为应对遗留web应用存在的安全和可靠性挑战,提出了一种基于LLM的多智能体系统,可自主将遗留web应用升级到最新版本。通过分布任务在多阶段更新所有相关文件。实验表明,该系统在维持语境跨任务和智能体的情况下,在某些情况下提高了解决方案的质量。此研究为未来模型在遗留代码更新中的应用提供了基础。LLM即使使用基本提示,也能高精度地更新小型过时文件。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)正被用于自主代码生成,为代码重构、安全增强和遗留应用升级提供新可能性。
- 遗留web应用存在安全和可靠性挑战,公司因升级复杂性和成本而继续使用。
- 提出一种基于LLM的多智能体系统,可自主升级遗留web应用到最新版本,通过分布任务在多阶段更新文件。
- 通过Zero-Shot Learning(ZSL)和One-Shot Learning(OSL)提示评估系统有效性。
- 实验表明,该系统在维持语境跨任务和智能体的情况下,提高解决方案质量。
- LLMs能够更新小型过时文件,且精度高,即使使用基本提示也能实现。
点此查看论文截图

O-MAPL: Offline Multi-agent Preference Learning
Authors:The Viet Bui, Tien Mai, Hong Thanh Nguyen
Inferring reward functions from demonstrations is a key challenge in reinforcement learning (RL), particularly in multi-agent RL (MARL), where large joint state-action spaces and complex inter-agent interactions complicate the task. While prior single-agent studies have explored recovering reward functions and policies from human preferences, similar work in MARL is limited. Existing methods often involve separate stages of supervised reward learning and MARL algorithms, leading to unstable training. In this work, we introduce a novel end-to-end preference-based learning framework for cooperative MARL, leveraging the underlying connection between reward functions and soft Q-functions. Our approach uses a carefully-designed multi-agent value decomposition strategy to improve training efficiency. Extensive experiments on SMAC and MAMuJoCo benchmarks show that our algorithm outperforms existing methods across various tasks.
从演示中推断奖励函数是强化学习(RL)中的一项关键挑战,特别是在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中,联合状态动作空间的大规模和智能体间的复杂交互使任务复杂化。虽然之前的单智能体研究已经探索了从人类偏好中恢复奖励函数和政策,但类似的多智能体研究受到限制。现有方法通常涉及监督奖励学习和MARL算法的独立阶段,导致训练不稳定。在这项工作中,我们为合作型多智能体强化学习引入了一种新型端到端的基于偏好的学习框架,利用奖励函数和软Q函数之间的内在联系。我们的方法采用精心设计的多智能体价值分解策略来提高训练效率。在SMAC和MAMuJoCo基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的算法在各种任务上的表现优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了强化学习(RL)中的关键挑战——从演示中推断奖励函数,特别是在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中。由于联合状态动作空间庞大和智能体间复杂交互,这项工作更具挑战性。尽管先前单智能体研究已探索从人类偏好中恢复奖励函数和策略,但多智能体强化学习中的类似工作仍有限。现有方法通常涉及监督奖励学习和MARL算法的单独阶段,导致训练不稳定。本研究介绍了一种新型基于偏好的端到端学习框架,用于合作型MARL,利用奖励函数和软Q函数之间的内在联系。通过精心设计的多智能体值分解策略,提高了训练效率。在SMAC和MAMuJoCo基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的算法在各项任务中的表现均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体强化学习(MARL)在推断奖励函数方面面临挑战,主要由于联合状态动作空间庞大和智能体间的复杂交互。
- 现有方法在监督奖励学习和MARL算法分离阶段存在训练不稳定的问题。
- 研究提出了一种新型的基于偏好的端到端学习框架,该框架针对合作型MARL,并融合了奖励函数和软Q函数之间的联系。
- 通过精心设计的多智能体值分解策略,提高了训练效率。
- 在SMAC和MAMuJoCo基准测试上进行的实验表明,该算法在多种任务中的表现均优于现有方法。
- 该框架可能为解决多智能体系统中的奖励函数推断问题提供新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

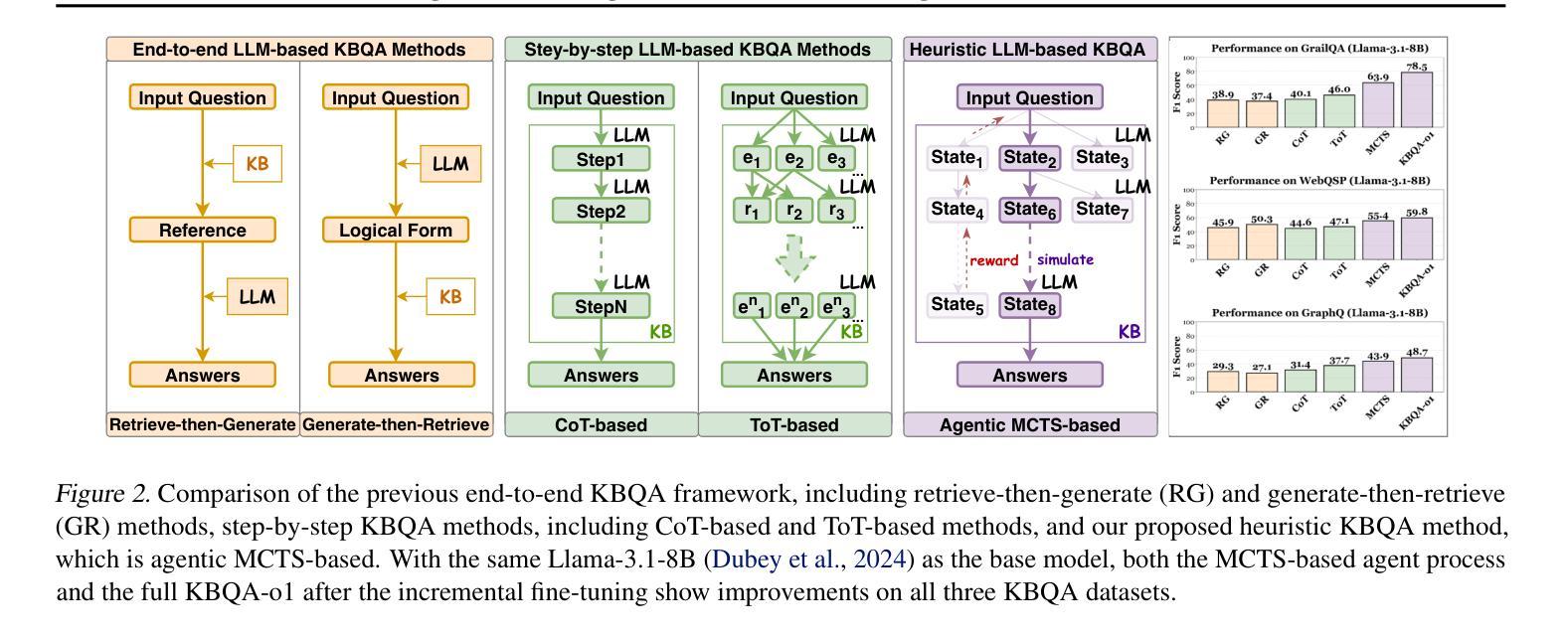
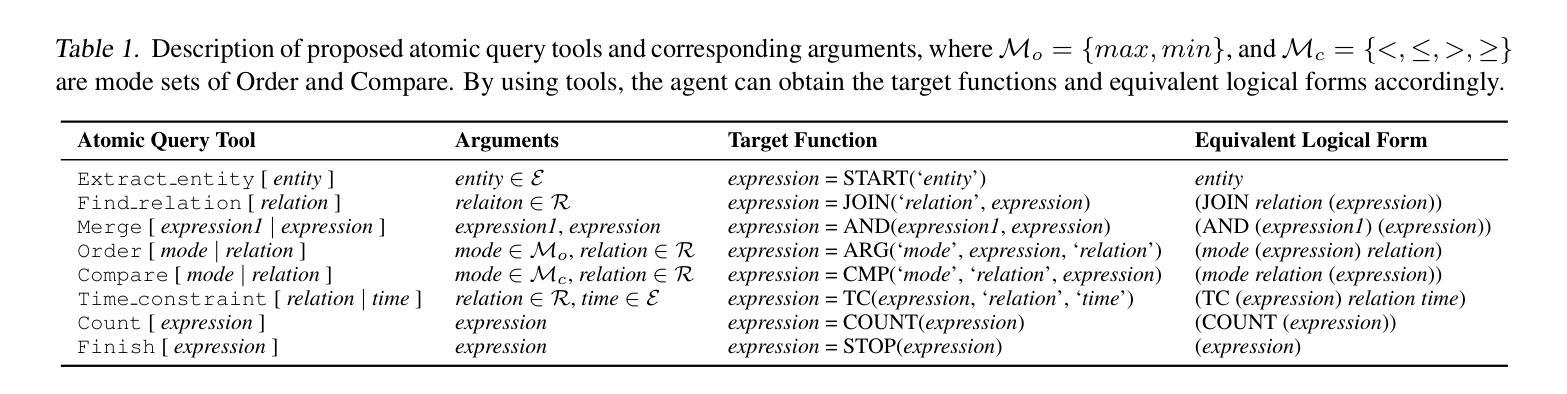
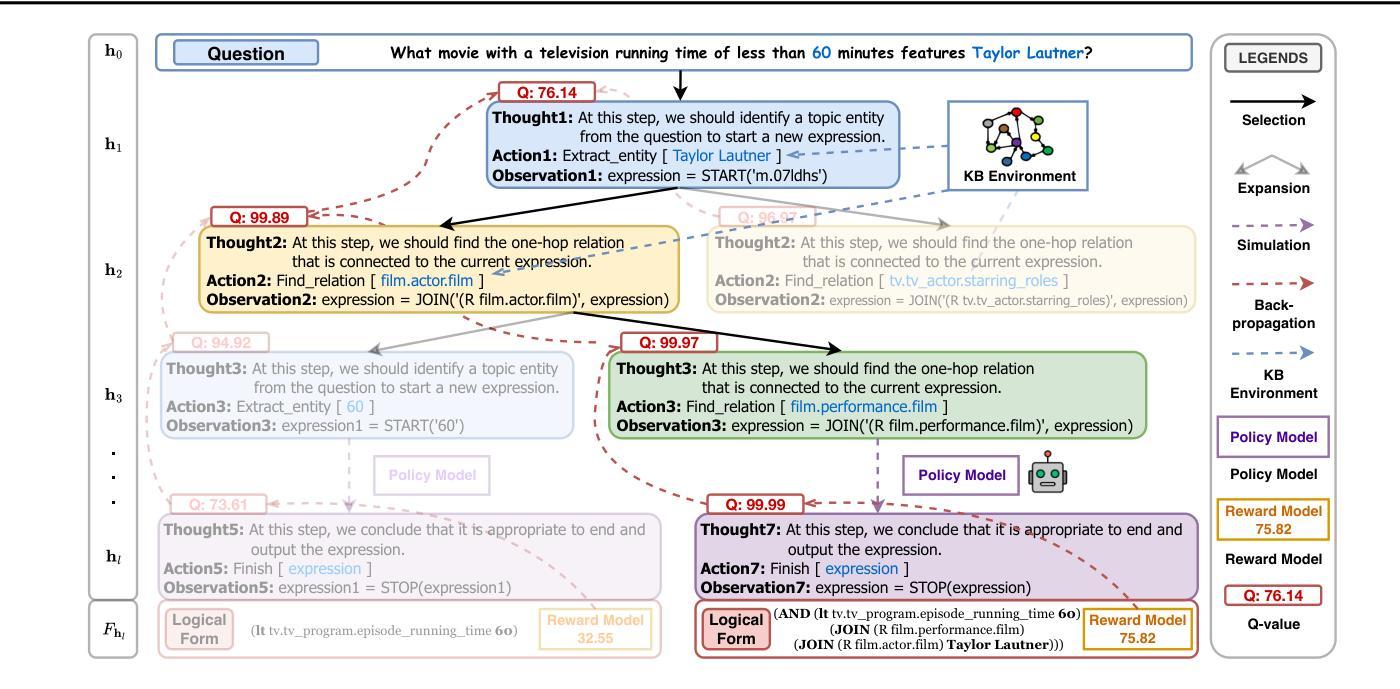
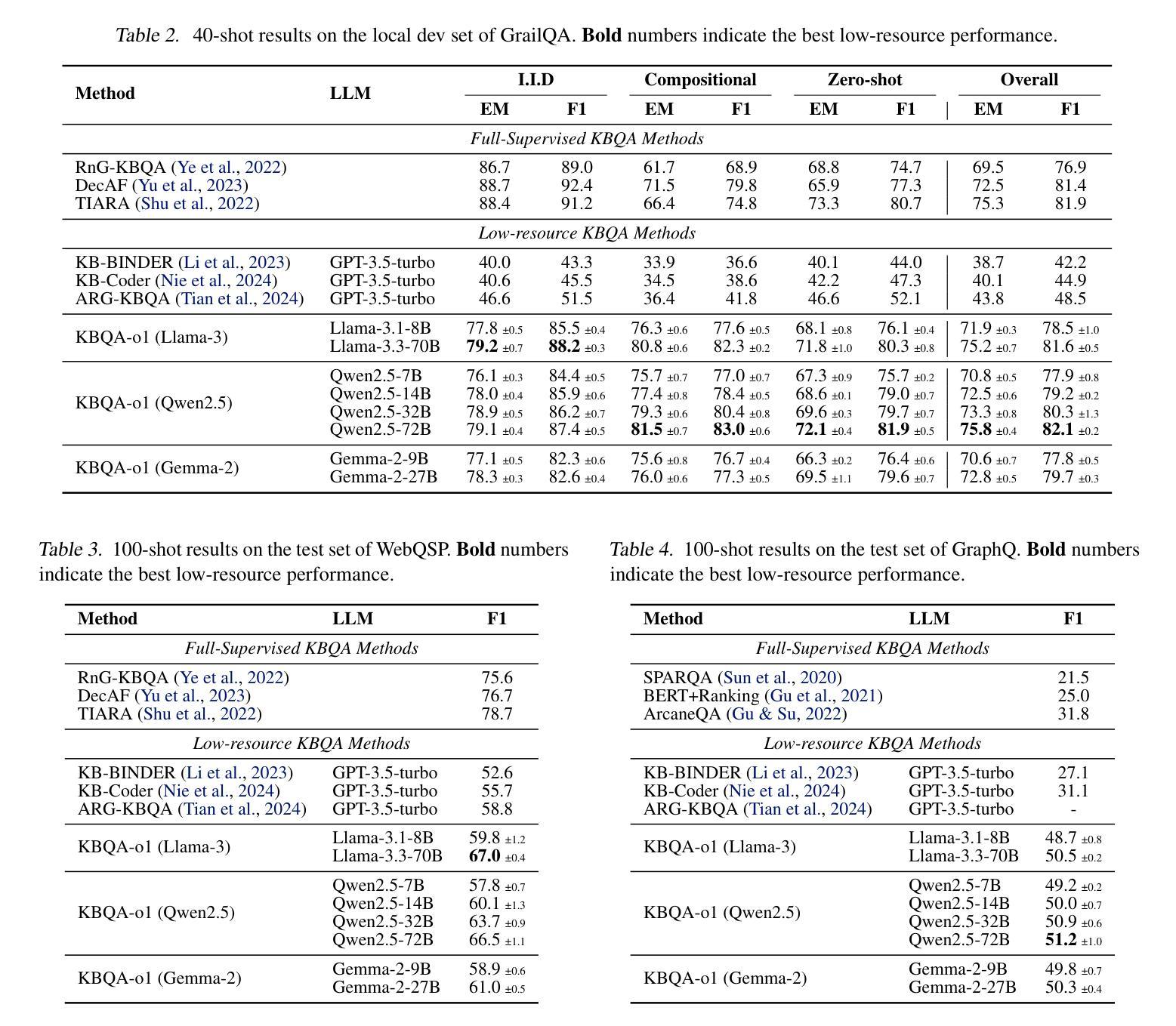
KBQA-o1: Agentic Knowledge Base Question Answering with Monte Carlo Tree Search
Authors:Haoran Luo, Haihong E, Yikai Guo, Qika Lin, Xiaobao Wu, Xinyu Mu, Wenhao Liu, Meina Song, Yifan Zhu, Luu Anh Tuan
Knowledge Base Question Answering (KBQA) aims to answer natural language questions with a large-scale structured knowledge base (KB). Despite advancements with large language models (LLMs), KBQA still faces challenges in weak KB awareness, imbalance between effectiveness and efficiency, and high reliance on annotated data. To address these challenges, we propose KBQA-o1, a novel agentic KBQA method with Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). It introduces a ReAct-based agent process for stepwise logical form generation with KB environment exploration. Moreover, it employs MCTS, a heuristic search method driven by policy and reward models, to balance agentic exploration’s performance and search space. With heuristic exploration, KBQA-o1 generates high-quality annotations for further improvement by incremental fine-tuning. Experimental results show that KBQA-o1 outperforms previous low-resource KBQA methods with limited annotated data, boosting Llama-3.1-8B model’s GrailQA F1 performance to 78.5% compared to 48.5% of the previous sota method with GPT-3.5-turbo.
知识库问答(KBQA)旨在利用大规模结构化知识库(KB)回答自然语言问题。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)有所进步,但KBQA仍然面临对知识库了解不足、效率和效果之间的不平衡以及高度依赖标注数据的挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了KBQA-o1,这是一种新型的基于蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)的智能KBQA方法。它引入了一种基于ReAct的代理过程,用于逐步生成逻辑形式并进行知识库环境探索。此外,它采用MCTS(一种受策略和奖励模型驱动的自适应搜索方法)来平衡智能探索的性能和搜索空间。通过启发式探索,KBQA-o1可以生成高质量标注,通过增量微调进一步改进。实验结果表明,KBQA-o1优于之前低资源KBQA方法,这些方法依赖于有限的标注数据,它使得Llama-3.1-8B模型的GrailQA F1性能提升到78.5%,而之前最佳方法GPT-3.5-turbo的该指标为48.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
KBQA系统旨在通过大规模结构化知识库回答自然语言问题。为应对KBQA的挑战,如弱知识库意识、效率和有效性之间的不平衡以及高度依赖标注数据的问题,我们提出了KBQA-o1这一新型智能体知识库问答方法,结合蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)。它引入基于ReAct的智能体过程,进行逐步逻辑形式生成和知识库环境探索。此外,利用MCTS这一受政策和奖励模型驱动的策略性搜索方法,实现智能体探索性能与搜索空间的平衡。通过启发式探索,KBQA-o1可生成高质量标注用于进一步增量微调。实验结果显示,KBQA-o1在有限标注数据的情况下,优于先前低资源KBQA方法,将Llama-3.1-8B模型的GrailQA F1性能提升至78.5%,远超先前最佳方法GPT-3.5-turbo的48.5%。
Key Takeaways
- KBQA系统通过大规模结构化知识库回答自然语言问题。
- KBQA面临弱知识库意识、效率和有效性之间的不平衡以及依赖标注数据等挑战。
- KBQA-o1是应对这些挑战的新型智能体知识库问答方法,结合了蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)。
- KBQA-o1通过基于ReAct的智能体过程进行逐步逻辑形式生成和知识库环境探索。
- MCTS平衡了智能体探索的性能和搜索空间。
- KBQA-o1能生成高质量标注用于增量微调。
点此查看论文截图

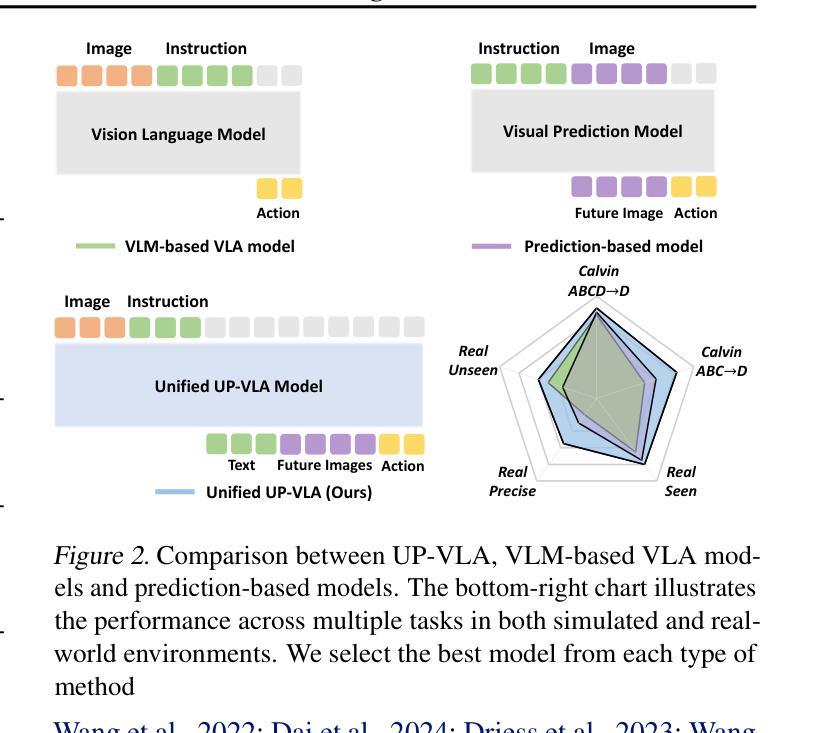
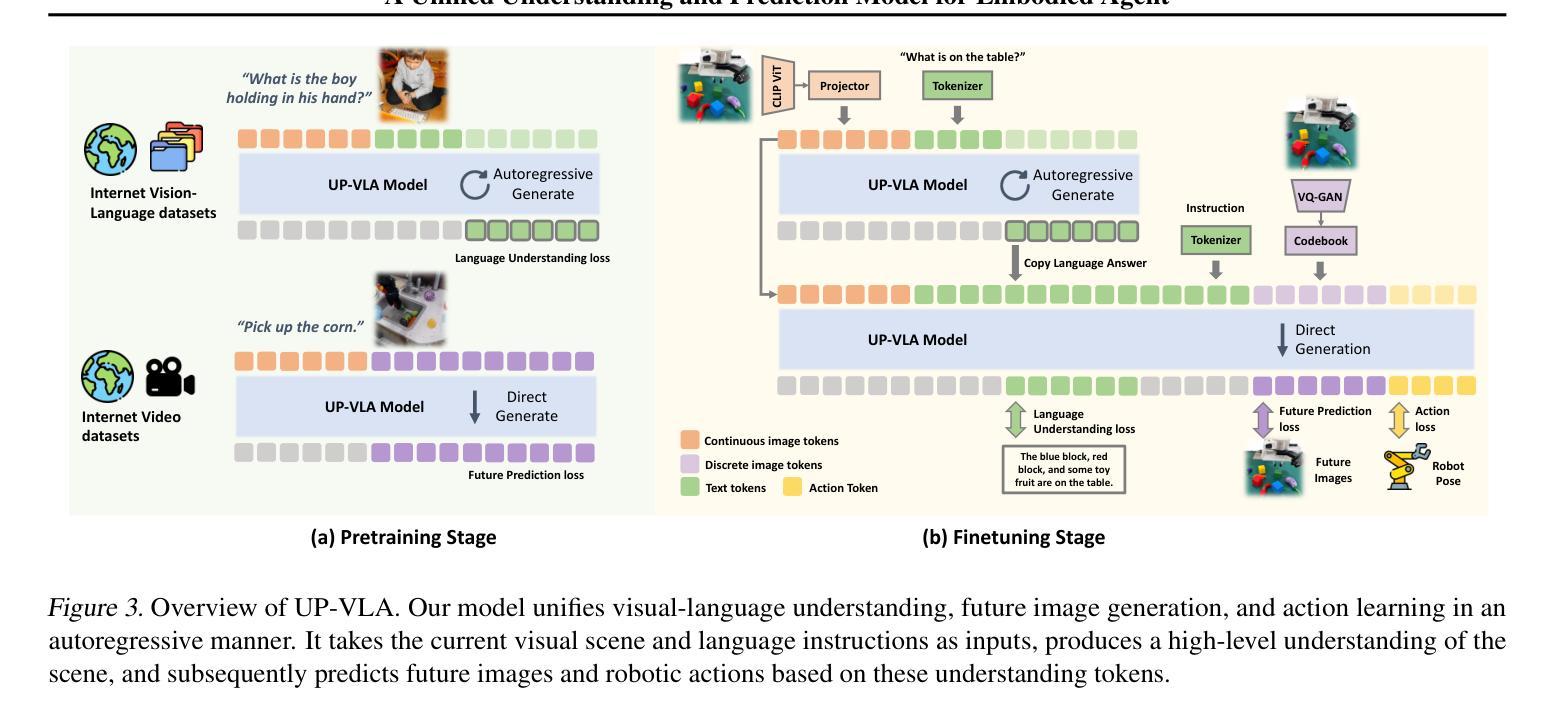
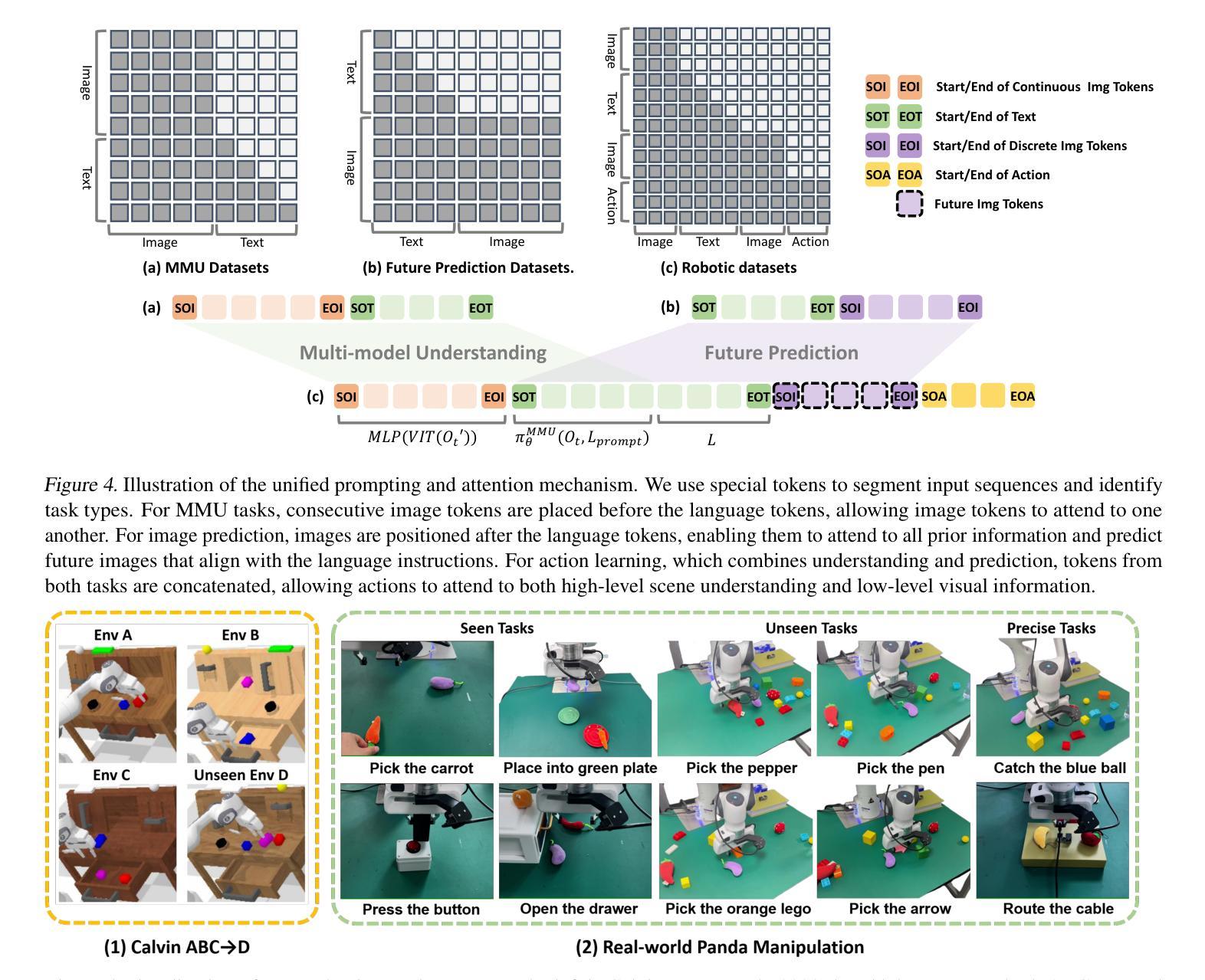
UP-VLA: A Unified Understanding and Prediction Model for Embodied Agent
Authors:Jianke Zhang, Yanjiang Guo, Yucheng Hu, Xiaoyu Chen, Xiang Zhu, Jianyu Chen
Recent advancements in Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have leveraged pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to improve the generalization capabilities. VLMs, typically pre-trained on vision-language understanding tasks, provide rich semantic knowledge and reasoning abilities. However, prior research has shown that VLMs often focus on high-level semantic content and neglect low-level features, limiting their ability to capture detailed spatial information and understand physical dynamics. These aspects, which are crucial for embodied control tasks, remain underexplored in existing pre-training paradigms. In this paper, we investigate the training paradigm for VLAs, and introduce \textbf{UP-VLA}, a \textbf{U}nified VLA model training with both multi-modal \textbf{U}nderstanding and future \textbf{P}rediction objectives, enhancing both high-level semantic comprehension and low-level spatial understanding. Experimental results show that UP-VLA achieves a 33% improvement on the Calvin ABC-D benchmark compared to the previous state-of-the-art method. Additionally, UP-VLA demonstrates improved success rates in real-world manipulation tasks, particularly those requiring precise spatial information.
最近,Vision-Language-Action(VLA)模型的进步利用了预训练的Vision-Language Models(VLMs)来提高模型的泛化能力。通常,VLMs在视觉语言理解任务上进行预训练,提供了丰富的语义知识和推理能力。然而,先前的研究表明,VLMs往往关注高级语义内容而忽视低级特征,限制了它们在捕捉详细的空间信息和理解物理动态方面的能力。对于实体控制任务来说,这些方面至关重要,但在现有的预训练范式中仍然探索不足。在本文中,我们研究了VLA的训练范式,并引入了UP-VLA,这是一个统一的VLA模型训练,具有多模式理解(multi-modal understanding)和未来预测(future prediction)目标,增强了高级语义理解和低级空间理解。实验结果表明,与先前最先进的方法相比,UP-VLA在Calvin ABC-D基准测试上实现了33%的改进。此外,UP-VLA在现实世界操作任务上的成功率也有所提高,尤其是那些需要精确空间信息的任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于最新视觉语言动作(VLA)模型的进展,研究引入了预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)以提升泛化能力。然而,现有研究指出VLM模型常常忽略低层次特征,限制了捕捉详细空间信息和理解物理动态的能力。本研究调查了VLA的训练模式,并提出了统一VLA模型训练范例UP-VLA,旨在提高多模态理解与未来预测目标,以增强高层次语义理解和低层次空间理解。在Calvin ABC-D基准测试中,UP-VLA相比之前的方法取得了33%的改进,并在现实操作任务中显示出更高的成功率,特别是在需要精确空间信息的任务中。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs虽能提供丰富的语义知识和推理能力,但常常忽略低层次特征,限制了空间信息和物理动态的理解。
- 本研究调查了VLA模型的训练范式,并引入了UP-VLA模型,该模型结合了多模态理解和未来预测目标。
- UP-VLA模型旨在增强高层次语义理解和低层次空间理解。
- 在Calvin ABC-D基准测试中,UP-VLA模型相比之前的方法有显著改进。
- UP-VLA模型在现实操作任务中表现出更高的成功率,特别是在需要精确空间信息的任务中。
点此查看论文截图

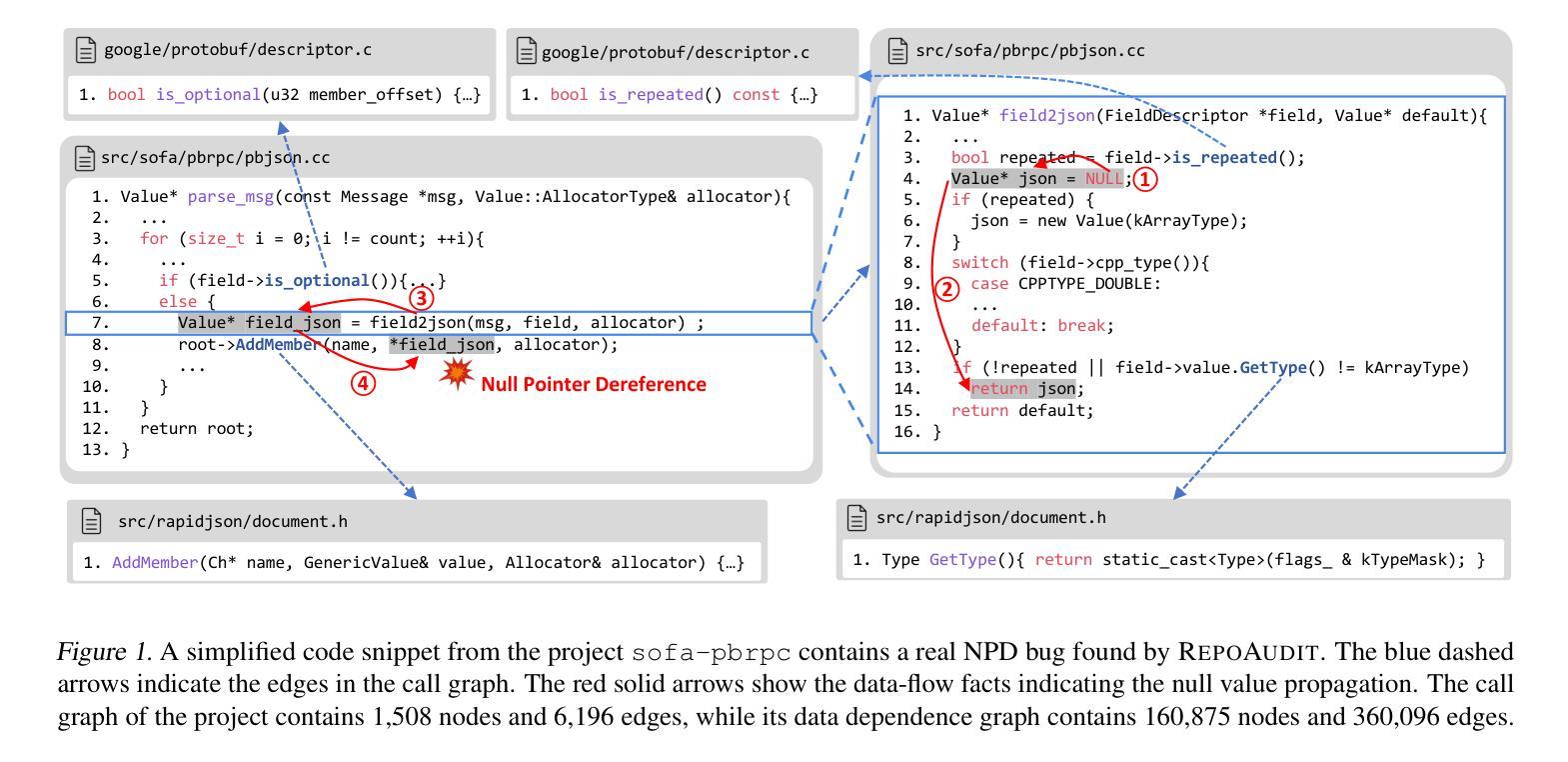
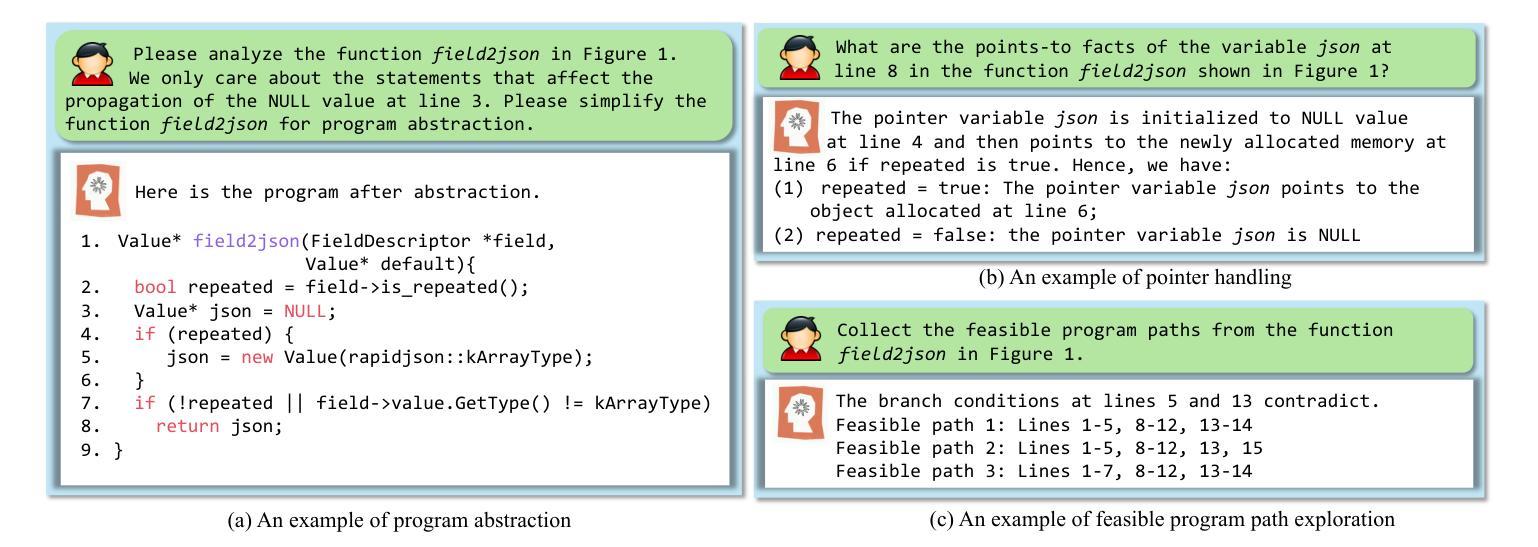
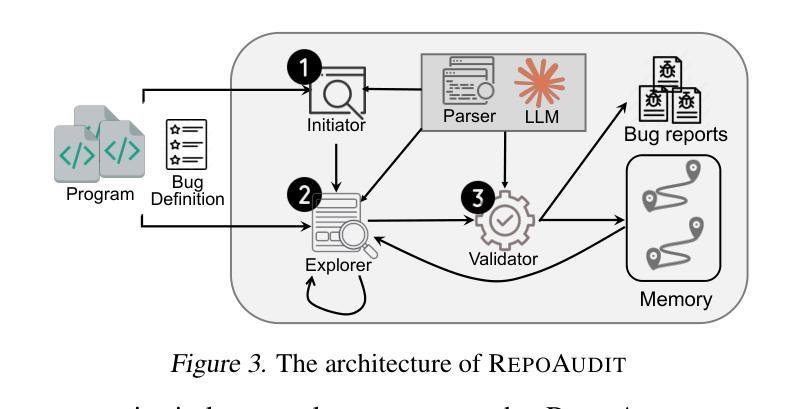
RepoAudit: An Autonomous LLM-Agent for Repository-Level Code Auditing
Authors:Jinyao Guo, Chengpeng Wang, Xiangzhe Xu, Zian Su, Xiangyu Zhang
Code auditing is a code review process with the goal of finding bugs. Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown substantial potential in this task, offering the ability to analyze programs without compilation and enabling customized bug detection following specified prompts. However, applying LLMs to repository-level code auditing presents notable challenges. The inherent context limits and hallucinations of LLMs can lead to the low quality of bug reports. Meanwhile, the large size of software repositories introduces substantial time and token costs, hindering efficiency and scalability in real-world scenarios. This work introduces an autonomous LLM-agent, RepoAudit, designed to enable precise and efficient repository-level code auditing. Equipped with the agent memory, RepoAudit explores the code repository on demand, analyzing data-flow facts along different feasible program paths in individual functions. It also introduces the validator to check the data-flow facts for hallucination mitigation and examine the satisfiability of path conditions of potential buggy paths, which enables RepoAudit to discard false positives in the code auditing. Our experiment shows that RepoAudit powered by Claude 3.5 Sonnet successfully finds 38 true bugs in 15 real-world systems, consuming 0.44 hours and $2.54 per project on average.
代码审计是一种寻找错误的代码审查过程。大型语言模型(LLM)在这一任务中表现出了巨大的潜力,它们能够在不编译的情况下分析程序,并根据特定提示进行定制化的错误检测。然而,将LLM应用于仓库级别的代码审计存在显著的挑战。LLM的固有上下文限制和幻觉可能导致错误报告的质量低下。同时,软件仓库的大规模性引入了大量的时间和令牌成本,阻碍了现实世界场景中的效率和可扩展性。这项工作引入了一个自主的语言模型代理RepoAudit,旨在实现精确高效的仓库级代码审计。配备有代理内存的RepoAudit按需探索代码仓库,分析单个函数中不同可行程序路径的数据流事实。它还引入了验证器,以减轻幻觉并检查数据流事实,并检查潜在错误路径的路径条件的可满足性,这使得RepoAudit能够在代码审计中剔除误报。我们的实验表明,由Claude 3.5 Sonnet驱动的RepoAudit成功在15个真实系统中找到了38个真实错误,平均每个项目消耗0.44小时和2.54美元。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 8 tables, 5 figures, 3 listings
Summary
代码审计旨在发现错误,大型语言模型(LLM)在此任务中显示出巨大潜力,可分析程序而无需编译,并能根据特定提示进行定制化的错误检测。然而,将LLM应用于仓库级代码审计存在挑战。LLM的固有上下文限制和幻想可能导致错误报告质量低下。同时,软件仓库的大规模引入了大量时间和令牌成本,阻碍了现实世界场景中的效率和可扩展性。本研究引入了一种自主LLM代理RepoAudit,旨在实现精确高效的仓库级代码审计。RepoAudit配备了代理内存,可按需探索代码仓库,分析单个函数中不同可行程序路径的数据流事实。它还引入了验证器,以减轻幻想并检查数据流事实,并检查潜在错误路径的满足性,使RepoAudit能够在代码审计中剔除误报。实验表明,由Claude 3.5 Sonnet驱动的RepoAudit成功在15个真实系统中找到38个真实错误,平均每个项目消耗0.44小时和2.54美元。
Key Takeaways
- 代码审计目标是发现错误,大型语言模型在此任务中显示出潜力。
- LLM应用于仓库级代码审计存在挑战,如上下文限制和幻想问题。
- RepoAudit是一个自主LLM代理,可实现精确高效的仓库级代码审计。
- RepoAudit配备了代理内存,可按需探索代码仓库,并分析数据流事实。
- 验证器的引入用于检查数据流事实并减少幻想,同时检查潜在错误路径的满足性。
- 实验显示RepoAudit成功在多个真实系统中发现真实错误,且效率较高。
点此查看论文截图

B3C: A Minimalist Approach to Offline Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Woojun Kim, Katia Sycara
Overestimation arising from selecting unseen actions during policy evaluation is a major challenge in offline reinforcement learning (RL). A minimalist approach in the single-agent setting – adding behavior cloning (BC) regularization to existing online RL algorithms – has been shown to be effective; however, this approach is understudied in multi-agent settings. In particular, overestimation becomes worse in multi-agent settings due to the presence of multiple actions, resulting in the BC regularization-based approach easily suffering from either over-regularization or critic divergence. To address this, we propose a simple yet effective method, Behavior Cloning regularization with Critic Clipping (B3C), which clips the target critic value in policy evaluation based on the maximum return in the dataset and pushes the limit of the weight on the RL objective over BC regularization, thereby improving performance. Additionally, we leverage existing value factorization techniques, particularly non-linear factorization, which is understudied in offline settings. Integrated with non-linear value factorization, B3C outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms on various offline multi-agent benchmarks.
在离线强化学习(RL)中,由于在策略评估时选择未观察到的动作而导致的过度估计是主要挑战。在单智能体环境中,一种极简主义的方法——向现有的在线RL算法添加行为克隆(BC)正则化已被证明是有效的;然而,在多智能体环境中,这种方法的研究还不够。特别是在多智能体环境中,由于存在多种动作,过度估计的情况变得更糟,导致基于BC正则化的方法很容易受到过度正则化或评论家发散的影响。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种简单有效的方法,即带有评论家裁剪的行为克隆正则化(B3C),该方法基于数据集的最大回报来裁剪目标评论家值,并提高了在策略评估中RL目标上权重的限制,从而提高了性能。此外,我们利用现有的值分解技术,特别是在离线环境中尚未充分研究的非线性分解技术。与非线性值分解相结合,B3C在各种离线多智能体基准测试上优于最新算法。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
离线强化学习中的主要挑战在于选择未知动作时产生的过估计问题。在单智能体环境中,通过向现有在线强化学习算法添加行为克隆(BC)正则化这种极简方案已被证明是有效的。然而,在多智能体环境中,该方案的研究相对较少。特别是由于存在多个动作,过估计问题在多智能体环境中变得更加严重,导致基于BC正则化的方法容易遭受过度正则化或评论家发散的问题。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种简单有效的方法——行为克隆正则化与评论家裁剪(B3C)。该方法基于数据集的最大回报来裁剪目标评论家值,并在政策评估中改进性能。此外,我们利用现有的价值分解技术,特别是离线环境中研究较少的非线性分解技术。结合非线性价值分解,B3C在多种离线多智能体基准测试上超越了现有算法。
关键见解
- 离线强化学习面临的主要挑战是选择未知动作时导致的过估计问题。
- 在多智能体环境中,由于多个动作的存在,过估计问题变得更加严重。
- 行为克隆(BC)正则化是一种有效的单智能体强化学习优化方法,但在多智能体环境中其效果有待提高。
- 行为克隆正则化与评论家裁剪(B3C)方法旨在解决多智能体环境中的过估计问题,通过裁剪目标评论家值来改善性能。
- B3C方法结合了非线性价值分解技术,以提高在离线多智能体环境中的性能。
- B3C在各种离线多智能体基准测试上的表现超越了现有算法。
- 该研究为多智能体离线强化学习提供了一个新的、有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

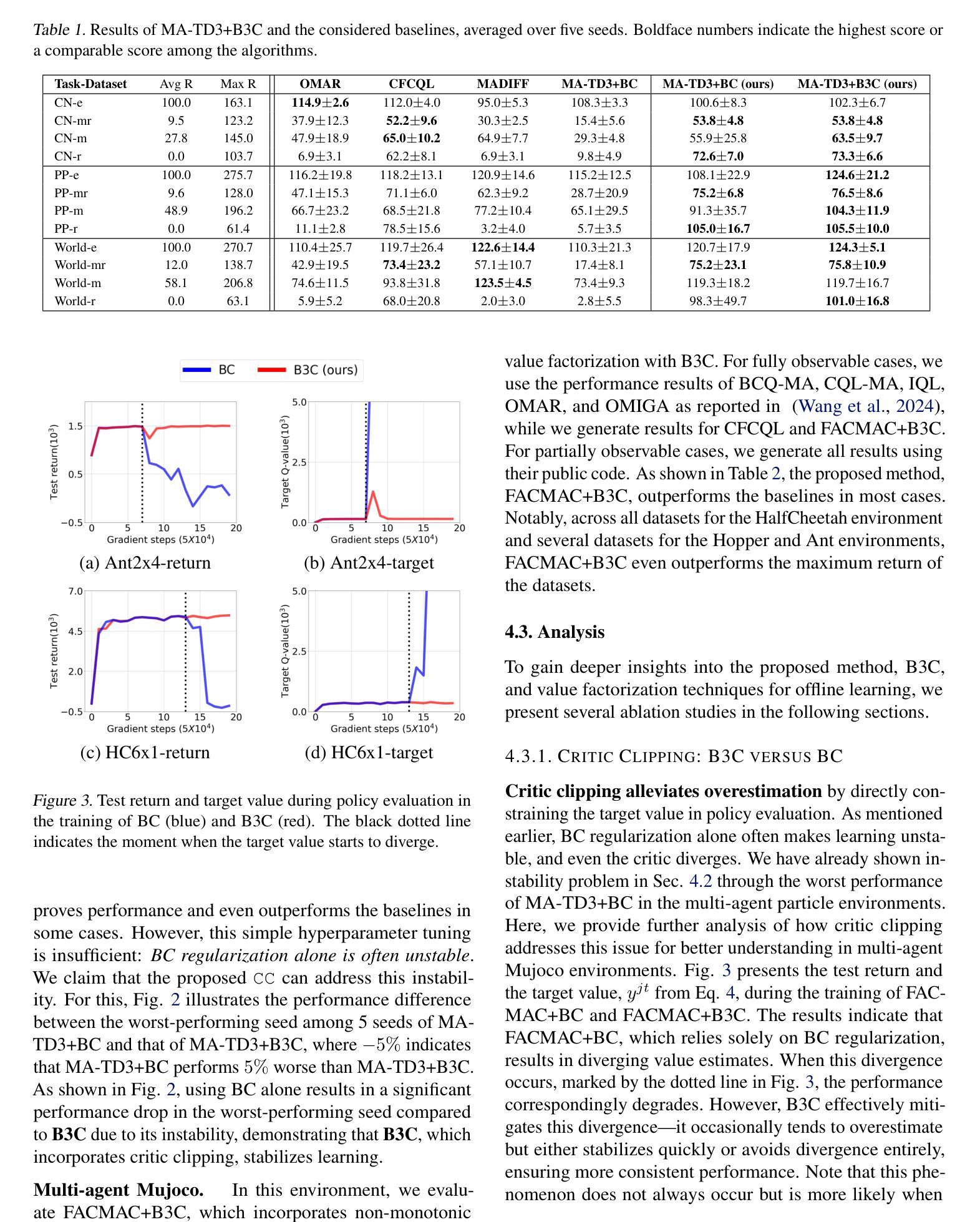
Fortran2CPP: Automating Fortran-to-C++ Translation using LLMs via Multi-Turn Dialogue and Dual-Agent Integration
Authors:Le Chen, Bin Lei, Dunzhi Zhou, Pei-Hung Lin, Chunhua Liao, Caiwen Ding, Ali Jannesari
Translating legacy Fortran code into C++ is a crucial step in modernizing high-performance computing (HPC) applications. However, the scarcity of high-quality, parallel Fortran-to-C++ datasets and the limited domain-specific expertise in large language models (LLMs) present significant challenges for automated translation. In this paper, we introduce Fortran2CPP, a multi-turn dialogue dataset generated by a novel LLM agent-based approach that integrates a dual-LLM Questioner-Solver module to enhance translation accuracy. Our dataset comprises 11.7k dialogues capturing iterative feedback-decision workflows including code translation, compilation, execution, unit testing, and error-fixing. Using this dataset, we fine-tune several open-weight LLMs and achieve up to a 3.31x improvement in CodeBLEU scores and a 92% increase in compilation success rate, demonstrating enhanced syntactic accuracy and functional reliability. Our findings highlight the value of dialogue-based LLM training for complex code translation tasks. The dataset and model have been open-sourced and are available on our public GitHub repository\footnote{\url{https://github.com/HPC-Fortran2CPP/Fortran2Cpp}}.
将传统Fortran代码转换为C++代码是现代高性能计算(HPC)应用现代化过程中的关键步骤。然而,高质量并行Fortran到C++数据集缺乏以及大型语言模型(LLM)中特定领域的专业知识有限,给自动化翻译带来了重大挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了Fortran2CPP,这是一个通过基于新型LLM代理的方法生成的多轮对话数据集,集成了双LLM问答解决模块,以提高翻译准确性。我们的数据集包含11.7k个对话,捕捉了包括代码翻译、编译、执行、单元测试和错误修复在内的迭代反馈决策工作流程。使用该数据集,我们对几个开源LLM进行了微调,实现了高达3.31倍的CodeBLEU得分提升和92%的编译成功率提升,证明了其在语法准确性和功能可靠性方面的提升。我们的研究突出了基于对话的LLM训练在复杂代码翻译任务中的价值。数据集和模型已开源,可在我们的GitHub公共存储库中找到(https://github.com/HPC-Fortran2CPP/Fortran2Cpp)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了将旧版Fortran代码翻译成C++的重要性,并指出由于缺乏高质量并行Fortran到C++的数据集以及大型语言模型(LLM)的特定领域专业知识所带来的挑战。为此,本文提出了一种基于多轮对话的新方法Fortran2CPP,该方法集成了双LLM问答解决模块以提高翻译准确性。数据集包含捕获迭代反馈决策工作流的对话,包括代码翻译、编译、执行、单元测试和错误修复。使用此数据集微调开放权重LLM,可提高代码BLEU得分并增加编译成功率,显示出增强的语法准确性和功能可靠性。研究结果表明对话式LLM训练对于复杂的代码翻译任务的价值。数据集和模型已开源,可在公共GitHub存储库中找到。
Key Takeaways
- Fortran代码向C++的转换是高性能计算应用现代化的重要步骤。
- 缺乏高质量并行Fortran到C++的数据集以及大型语言模型的特定领域专业知识给自动化翻译带来了挑战。
- 介绍了Fortran2CPP方法,这是一种基于多轮对话的方法,集成了双LLM问答解决模块以提高翻译准确性。
- Fortran2CPP数据集包含用于代码翻译任务的迭代反馈决策工作流对话。
- 使用此数据集对开放权重LLM进行微调,提高了语法准确性和功能可靠性。
- Fortran2CPP方法实现了高达3.31倍的代码BLEU得分改进和92%的编译成功率增加。
点此查看论文截图

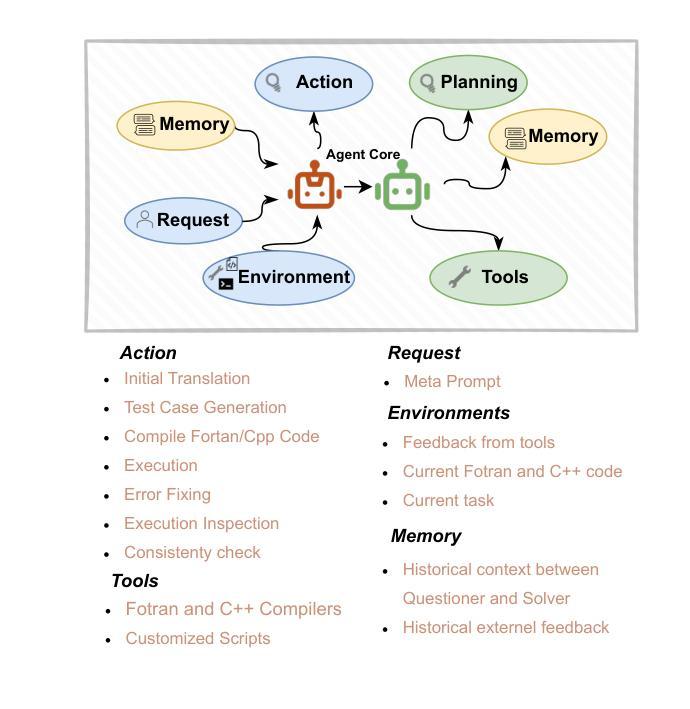

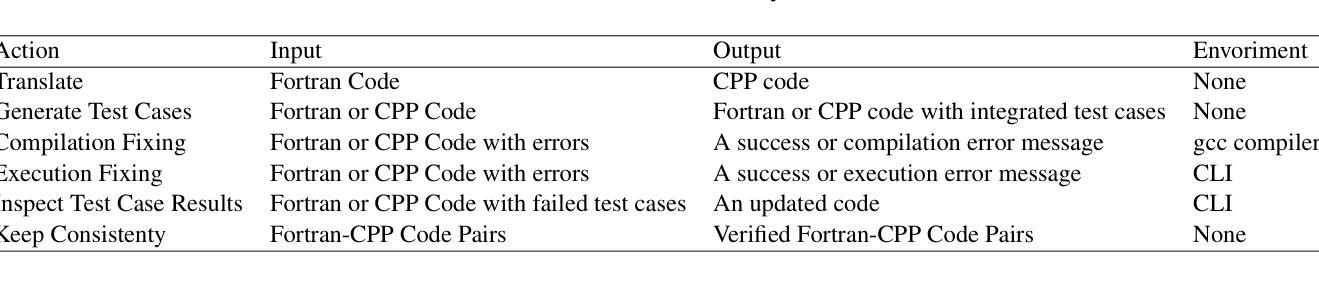
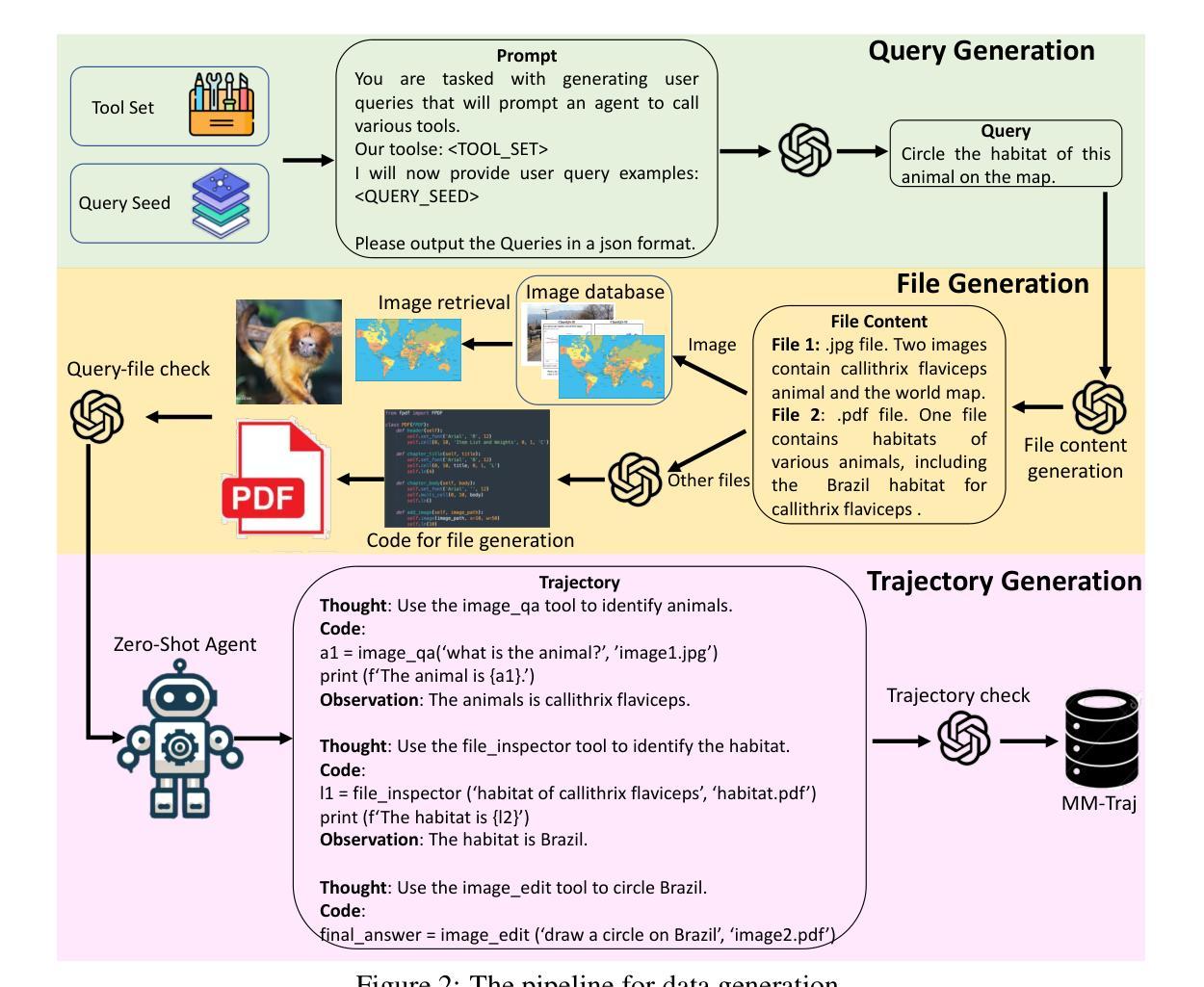
Multi-modal Agent Tuning: Building a VLM-Driven Agent for Efficient Tool Usage
Authors:Zhi Gao, Bofei Zhang, Pengxiang Li, Xiaojian Ma, Tao Yuan, Yue Fan, Yuwei Wu, Yunde Jia, Song-Chun Zhu, Qing Li
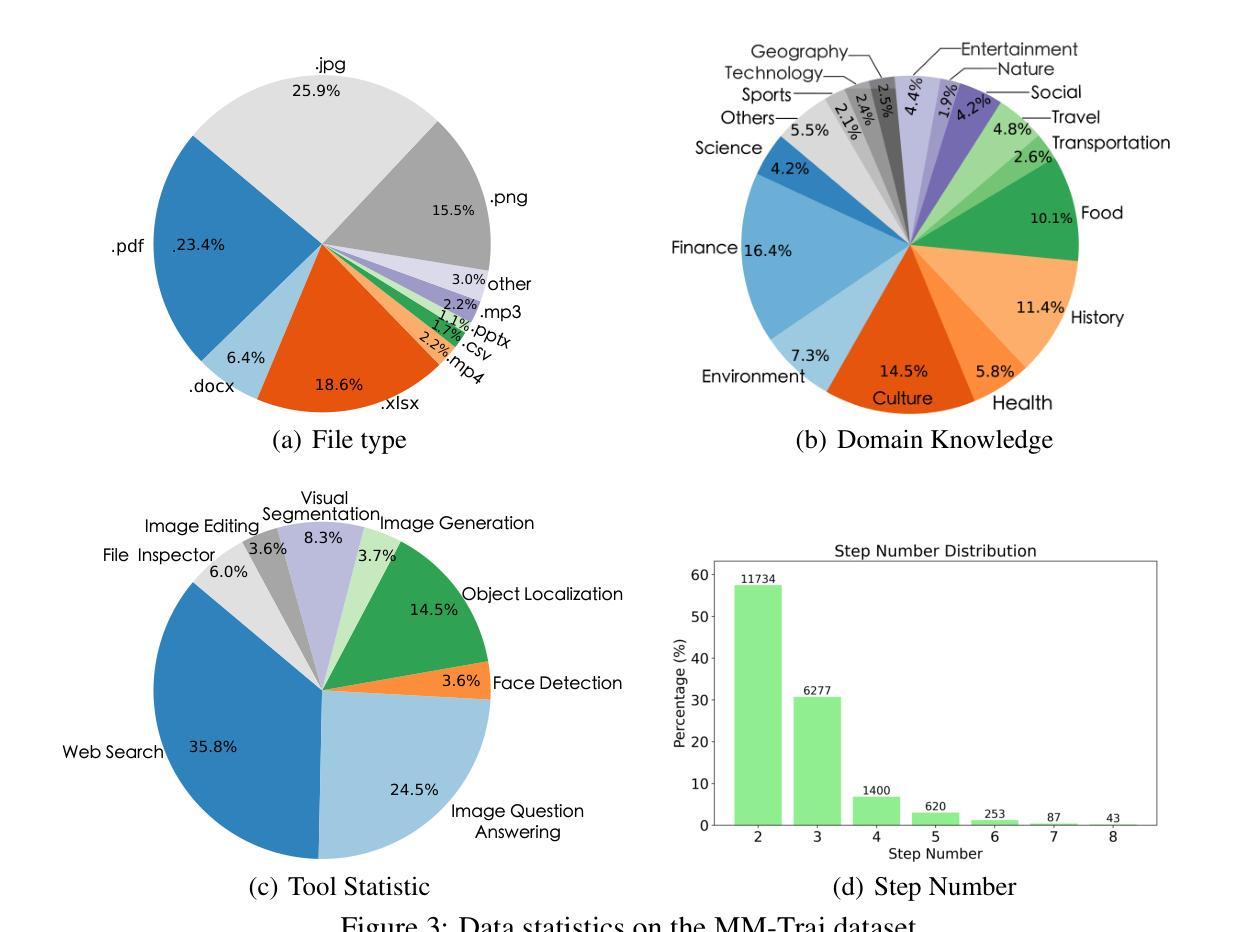
The advancement of large language models (LLMs) prompts the development of multi-modal agents, which are used as a controller to call external tools, providing a feasible way to solve practical tasks. In this paper, we propose a multi-modal agent tuning method that automatically generates multi-modal tool-usage data and tunes a vision-language model (VLM) as the controller for powerful tool-usage reasoning. To preserve the data quality, we prompt the GPT-4o mini model to generate queries, files, and trajectories, followed by query-file and trajectory verifiers. Based on the data synthesis pipeline, we collect the MM-Traj dataset that contains 20K tasks with trajectories of tool usage. Then, we develop the T3-Agent via \underline{T}rajectory \underline{T}uning on VLMs for \underline{T}ool usage using MM-Traj. Evaluations on the GTA and GAIA benchmarks show that the T3-Agent consistently achieves improvements on two popular VLMs: MiniCPM-V-8.5B and {Qwen2-VL-7B}, which outperforms untrained VLMs by $20%$, showing the effectiveness of the proposed data synthesis pipeline, leading to high-quality data for tool-usage capabilities.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的进展,多模态代理的发展得到了推动,这些代理被用作控制器来调用外部工具,为解决实际任务提供了可行的方法。在本文中,我们提出了一种多模态代理调整方法,该方法可自动生成多模态工具使用数据,并调整视觉语言模型(VLM)作为控制器,以实现强大的工具使用推理。为了保持数据质量,我们提示GPT-4o小型模型生成查询、文件和轨迹,随后进行查询文件验证器和轨迹验证器。基于数据合成管道,我们收集了包含2万个任务使用轨迹的MM-Traj数据集。然后,我们通过使用MM-Traj的轨迹调整VLM来开发T3代理。在GTA和GAIA基准测试上的评估表明,T3代理在两款流行的VLM(MiniCPM-V-8.5B和Qwen2-VL-7B)上均实现了持续改进,其性能比未训练的VLM高出20%,证明了所提出的数据合成管道的有效性,为工具使用能力提供了高质量的数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025, https://mat-agent.github.io/
Summary
大型语言模型的进步推动了多模态代理的发展,本文提出了一种多模态代理调节方法,该方法可自动生成多模态工具使用数据,并调节视觉语言模型作为控制器来进行工具使用推理。通过数据合成管道,我们收集了MM-Traj数据集,并在此基础上开发了T3-Agent。评估表明,T3-Agent在两种流行的VLM上实现了改进,并优于未训练的VLM,证明了数据合成管道的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的进步促进了多模态代理的发展,多模态代理能够作为控制器调用外部工具,为解决实际任务提供了可行方法。
- 本文提出了一种多模态代理调节方法,可以自动生成多模态工具使用数据。
- 采用了数据合成管道来收集MM-Traj数据集,该数据集包含2万项任务及工具使用轨迹。
- 开发了一种基于MM-Traj的T3-Agent,通过轨迹调节视觉语言模型进行工具使用。
- 评估结果显示T3-Agent在两种流行的VLM上表现优异,优于未训练的VLM。
- 数据合成管道的有效性得到了验证,能够生成高质量的工具使用数据。
点此查看论文截图

Large Language Model-Brained GUI Agents: A Survey
Authors:Chaoyun Zhang, Shilin He, Jiaxu Qian, Bowen Li, Liqun Li, Si Qin, Yu Kang, Minghua Ma, Guyue Liu, Qingwei Lin, Saravan Rajmohan, Dongmei Zhang, Qi Zhang
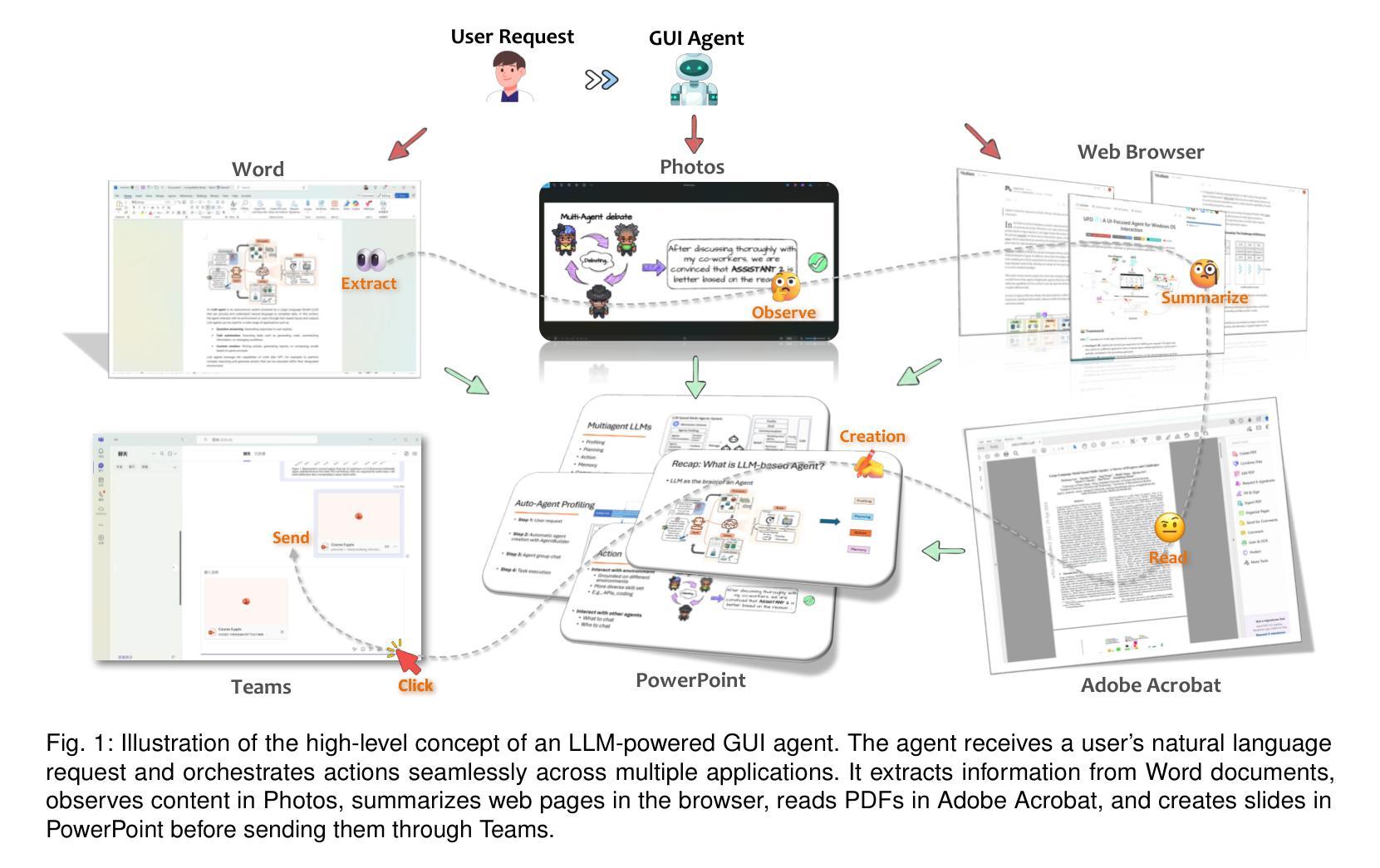
GUIs have long been central to human-computer interaction, providing an intuitive and visually-driven way to access and interact with digital systems. The advent of LLMs, particularly multimodal models, has ushered in a new era of GUI automation. They have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in natural language understanding, code generation, and visual processing. This has paved the way for a new generation of LLM-brained GUI agents capable of interpreting complex GUI elements and autonomously executing actions based on natural language instructions. These agents represent a paradigm shift, enabling users to perform intricate, multi-step tasks through simple conversational commands. Their applications span across web navigation, mobile app interactions, and desktop automation, offering a transformative user experience that revolutionizes how individuals interact with software. This emerging field is rapidly advancing, with significant progress in both research and industry. To provide a structured understanding of this trend, this paper presents a comprehensive survey of LLM-brained GUI agents, exploring their historical evolution, core components, and advanced techniques. We address research questions such as existing GUI agent frameworks, the collection and utilization of data for training specialized GUI agents, the development of large action models tailored for GUI tasks, and the evaluation metrics and benchmarks necessary to assess their effectiveness. Additionally, we examine emerging applications powered by these agents. Through a detailed analysis, this survey identifies key research gaps and outlines a roadmap for future advancements in the field. By consolidating foundational knowledge and state-of-the-art developments, this work aims to guide both researchers and practitioners in overcoming challenges and unlocking the full potential of LLM-brained GUI agents.
图形用户界面(GUIs)长期以来一直是人机交互的核心,提供了一种直观且视觉驱动的方式来访问和与数字系统交互。大语言模型(LLMs)的出现,特别是多模态模型,已经开启了GUI自动化的新时代。它们在自然语言理解、代码生成和视觉处理方面表现出了卓越的能力。这为新一代基于LLM的GUI代理铺平了道路,这些代理能够解释复杂的GUI元素,并基于自然语言指令自主执行操作。这些代理代表了范式转变,使用户能够通过简单的命令执行复杂的多步骤任务。它们的应用范围涵盖网页导航、移动应用交互和桌面自动化,提供变革性的用户体验,彻底改变个人与软件的交互方式。这个新兴领域正在迅速发展,在研究和工业方面都取得了重大进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The collection of papers reviewed in this survey will be hosted and regularly updated on the GitHub repository: https://github.com/vyokky/LLM-Brained-GUI-Agents-Survey Additionally, a searchable webpage is available at https://aka.ms/gui-agent for easier access and exploration
Summary
本文介绍了GUI在人机交互中的长期重要地位,以及大型语言模型(LLM)特别是多模态模型的出现所带来的GUI自动化新时代。LLM展现出在理解自然语言、生成代码和视觉处理方面的卓越能力,为新一代基于LLM的GUI代理的发展铺平了道路。这些代理可以解释复杂的GUI元素并根据自然语言指令自主执行操作。它们的应用范围广泛,包括网页导航、移动应用交互和桌面自动化,为用户提供了一种变革性的体验,彻底改变了个人与软件的交互方式。本文全面概述了基于LLM的GUI代理的历史演变、核心组件和先进技术,并探讨了该领域的关键研究问题。
Key Takeaways
- GUI在人机交互中占据重要地位,大型语言模型(LLM)的引入为GUI自动化带来了新的发展机会。
- LLM在理解自然语言、生成代码和视觉处理方面表现出卓越能力。
- 基于LLM的GUI代理能够解释复杂的GUI元素并根据自然语言指令自主执行操作。
- 这些代理的应用范围广泛,包括网页导航、移动应用交互和桌面自动化。
- 基于LLM的GUI代理代表了用户与软件交互方式的重大转变。
- 当前研究问题包括GUI代理框架、数据收集和利用、针对GUI任务的特殊动作模型开发等。
点此查看论文截图

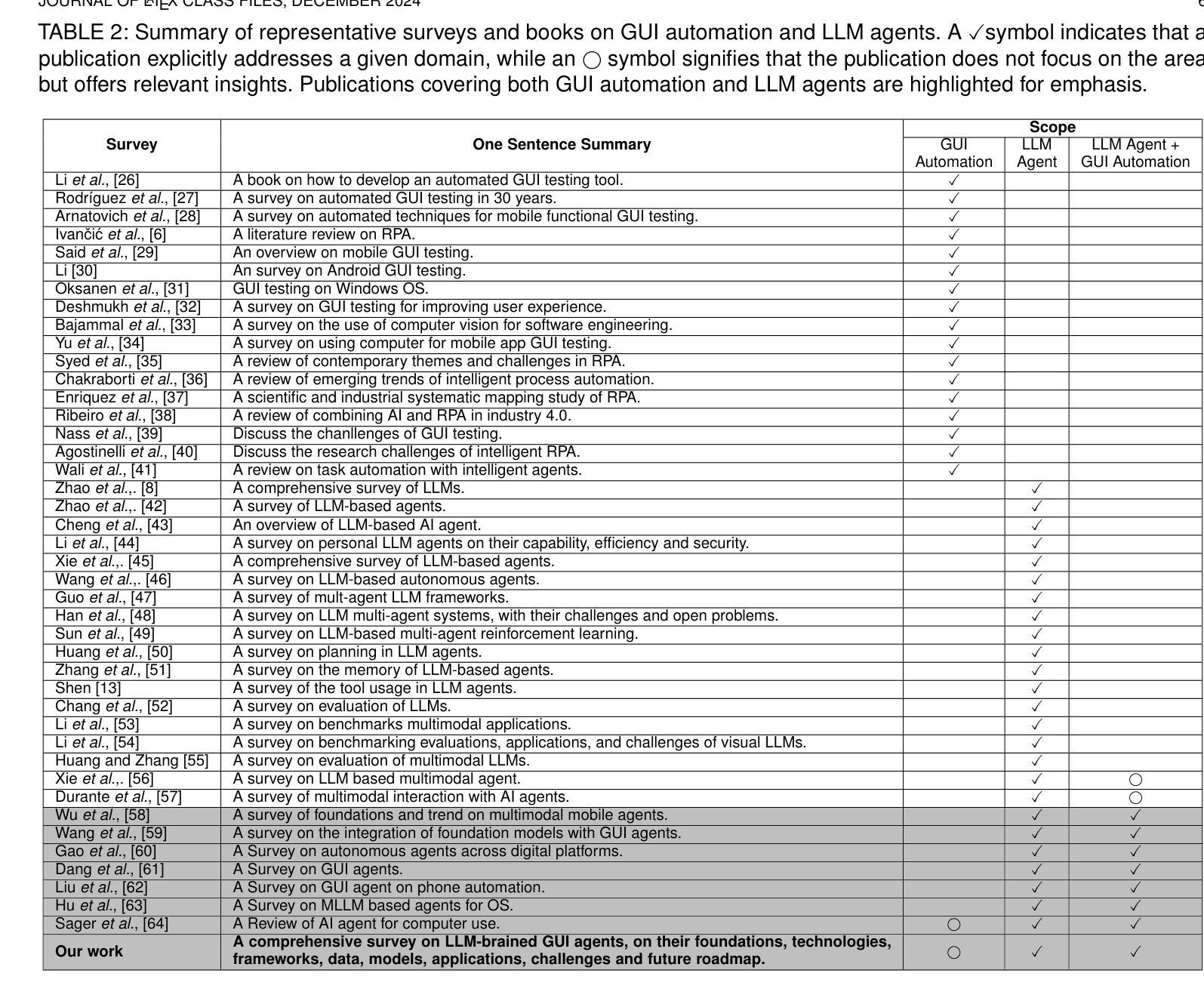
LLM-Consensus: Multi-Agent Debate for Visual Misinformation Detection
Authors:Kumud Lakara, Georgia Channing, Juil Sock, Christian Rupprecht, Philip Torr, John Collomosse, Christian Schroeder de Witt
One of the most challenging forms of misinformation involves the out-of-context (OOC) use of images paired with misleading text, creating false narratives. Existing AI-driven detection systems lack explainability and require expensive finetuning. We address these issues with LLM-Consensus, a multi-agent debate system for OOC misinformation detection. LLM-Consensus introduces a novel multi-agent debate framework where multimodal agents collaborate to assess contextual consistency and request external information to enhance cross-context reasoning and decision-making. Our framework enables explainable detection with state-of-the-art accuracy even without domain-specific fine-tuning. Extensive ablation studies confirm that external retrieval significantly improves detection accuracy, and user studies demonstrate that LLM-Consensus boosts performance for both experts and non-experts. These results position LLM-Consensus as a powerful tool for autonomous and citizen intelligence applications.
误解信息最具挑战性的形式之一涉及脱离上下文(OOC)使用与误导性文本配对的图像,从而创造错误的叙事。现有的AI驱动的检测系统缺乏解释性,并需要昂贵的微调。我们通过LLM-Consensus解决这些问题,这是一种用于OOC误解信息检测的基于多智能体的辩论系统。LLM-Consensus引入了一种新型的多智能体辩论框架,其中多模态智能体相互协作以评估上下文一致性并请求外部信息以增强跨上下文推理和决策制定。我们的框架在无需特定领域微调的情况下,即可实现具有前沿准确性的可解释检测。广泛的消融研究证实,外部检索显着提高了检测准确性,用户研究也表明LLM-Consensus可提升专家和非专家的性能。这些结果将LLM-Consensus定位为自主和公民智能应用的强大工具。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出了一种基于多模态对话框架的OOC虚假信息检测模型LLM-Consensus。该模型通过引入外部信息提高跨上下文推理和决策制定能力,支持可解释性检测并实现了较高准确度,无需特定领域微调。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-Consensus解决了现有AI驱动检测系统中存在的解释性不足和昂贵微调成本的问题。
- LLM-Consensus采用多模态对话框架,实现跨上下文推理和决策制定。
- 该模型引入外部信息检索功能,显著提高检测准确性。
- LLM-Consensus的检测具有可解释性,并达到业界领先水平。
- 用户研究表明,LLM-Consensus对于专家和非专家用户都有性能提升。
点此查看论文截图


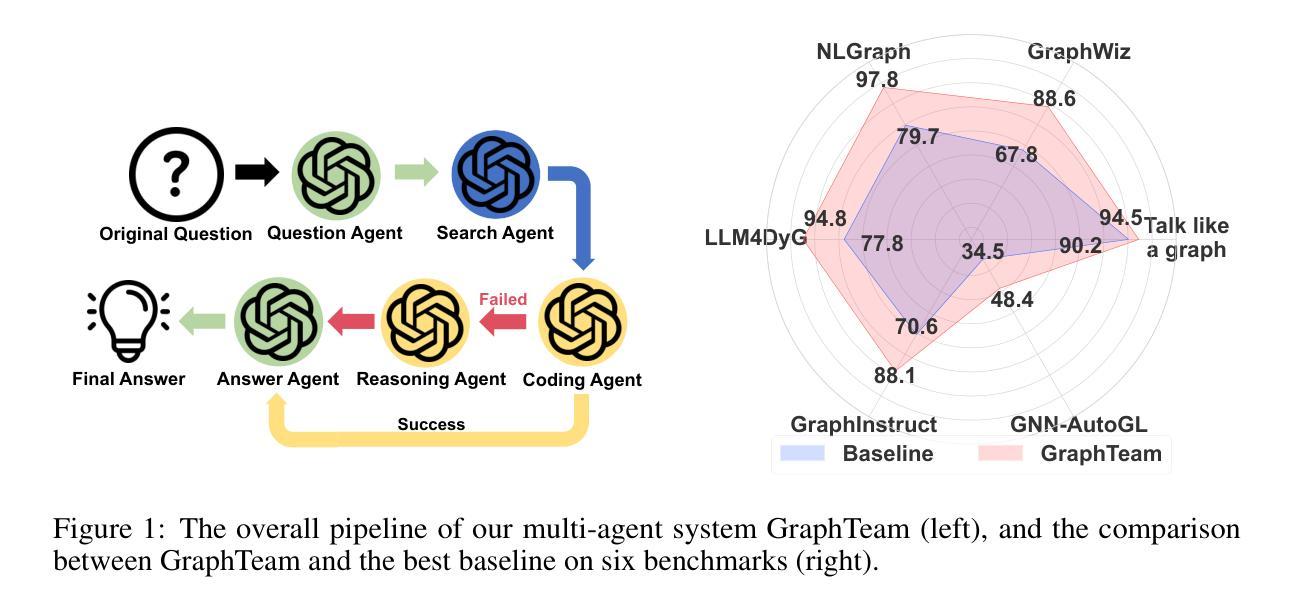
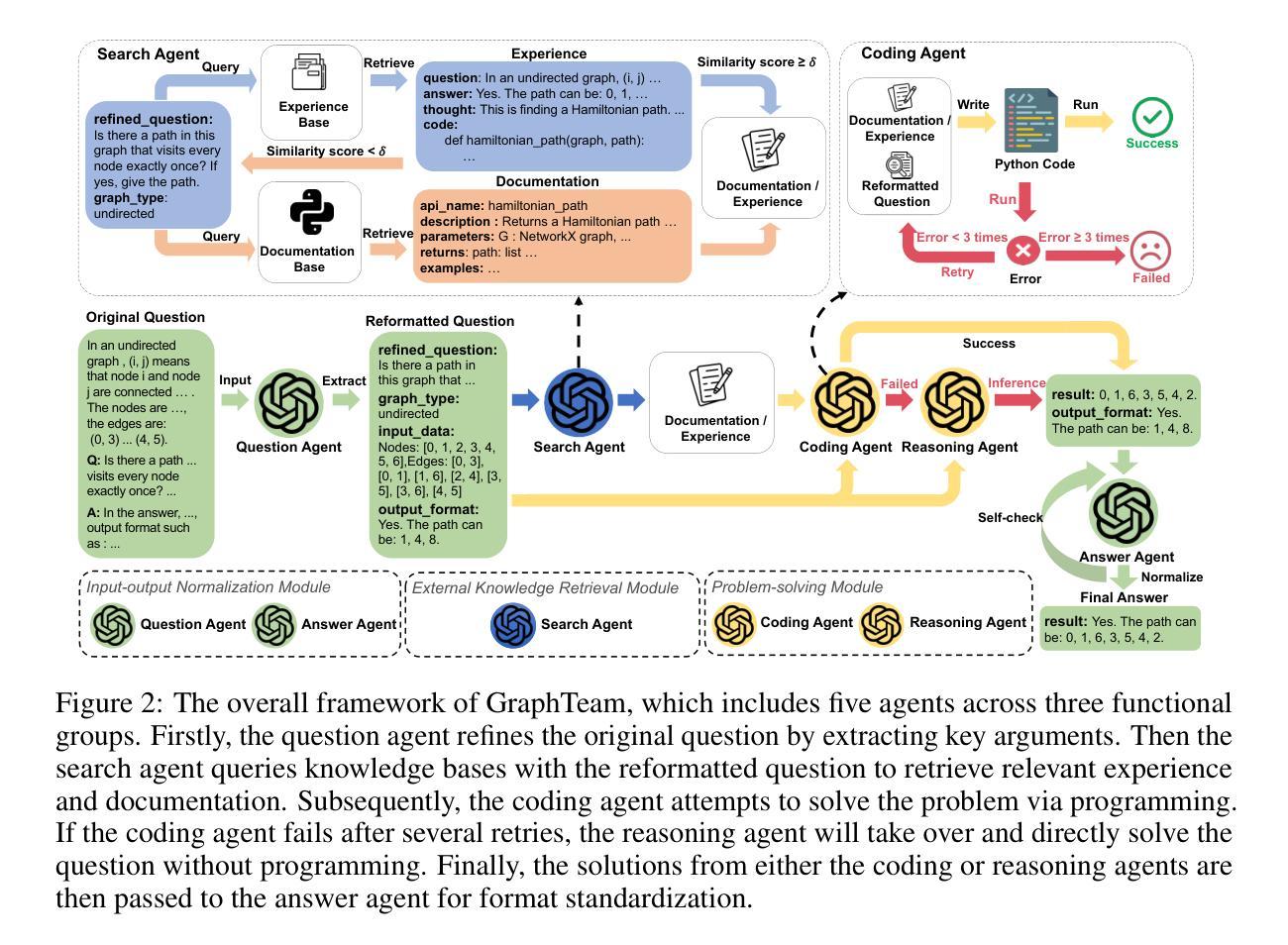
GraphTeam: Facilitating Large Language Model-based Graph Analysis via Multi-Agent Collaboration
Authors:Xin Li, Qizhi Chu, Yubin Chen, Yang Liu, Yaoqi Liu, Zekai Yu, Weize Chen, Chen Qian, Chuan Shi, Cheng Yang
Graphs are widely used for modeling relational data in real-world scenarios, such as social networks and urban computing. Existing LLM-based graph analysis approaches either integrate graph neural networks (GNNs) for specific machine learning tasks, limiting their transferability, or rely solely on LLMs’ internal reasoning ability, resulting in suboptimal performance. To address these limitations, we take advantage of recent advances in LLM-based agents, which have shown capabilities of utilizing external knowledge or tools for problem solving. By simulating human problem-solving strategies such as analogy and collaboration, we propose a multi-agent system based on LLMs named GraphTeam, for graph analysis. GraphTeam consists of five LLM-based agents from three modules, and the agents with different specialities can collaborate with each other to address complex problems. Specifically, (1) input-output normalization module: the question agent extracts and refines four key arguments from the original question, facilitating the problem understanding, and the answer agent organizes the results to meet the output requirement; (2) external knowledge retrieval module: we first build a knowledge base consisting of relevant documentation and experience information, and then the search agent retrieves the most relevant entries for each question. (3) problem-solving module: given the retrieved information from search agent, the coding agent uses established algorithms via programming to generate solutions, and in case the coding agent does not work, the reasoning agent will directly compute the results without programming. Extensive experiments on six graph analysis benchmarks demonstrate that GraphTeam achieves state-of-the-art performance with an average 25.85% improvement over the best baseline in terms of accuracy. The code and data are available at https://github.com/BUPT-GAMMA/GraphTeam.
图被广泛用于现实场景中的关系数据建模,如社交网络和城市计算。现有的基于大型语言模型(LLM)的图分析方法的不足之处在于,它们要么将图神经网络(GNNs)集成到特定的机器学习任务中,限制了其可迁移性,要么仅依赖于LLMs的内部推理能力,导致性能不佳。为了解决这些局限性,我们利用基于LLM的代理的最新进展,这些代理已显示出利用外部知识或工具解决问题的能力。通过模拟人类的解决问题策略,如类比和协作,我们提出了一种基于LLM的多代理系统,名为GraphTeam,用于图分析。GraphTeam由三个模块中的五个基于LLM的代理组成,不同专业的代理可以相互协作来解决复杂问题。具体来说,(1)输入输出归一化模块:问题代理从原始问题中提取并优化四个关键参数,促进对问题的理解,答案代理则负责按输出要求组织结果;(2)外部知识检索模块:我们首先建立一个包含相关文档和经验信息的知识库,然后搜索代理根据每个问题检索最相关的条目。(3)问题解决模块:给定来自搜索代理的检索信息,编码代理通过编程使用既定算法来生成解决方案;如果编码代理无法工作,推理代理将直接进行计算以得出结果。在六个图分析基准测试上的广泛实验表明,GraphTeam在准确度方面达到了最先进的性能,与最佳基线相比平均提高了25.85%。相关代码和数据可以在https://github.com/BUPT-GAMMA/GraphTeam获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用大型语言模型(LLM)构建名为GraphTeam的多智能体系统,用于图分析。该系统由三个模块组成,包含输入输出的规范处理、外部知识的检索、问题求解。该系统的智能体能通过协同合作解决复杂问题,对六种图分析基准测试的实验结果表明,GraphTeam实现了卓越的性能,平均准确率相较于最佳基线提高了25.85%。相关代码和数据在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- GraphTeam是一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统,用于图分析。
- GraphTeam解决了现有LLM-based图分析方法的局限性,如缺乏转移性和性能不足。
- GraphTeam包含三个模块:输入输出的规范处理、外部知识的检索和问题求解。
- 输入输出规范处理模块包含问题理解和结果组织。
- 外部知识检索模块建立了包含相关文档和经验信息的知识库,并能够通过搜索智能体检索最相关的信息。
- 问题求解模块能够通过编程智能体利用已建立的算法生成解决方案,如果不适用编程方式,推理智能体会直接计算结果。
点此查看论文截图

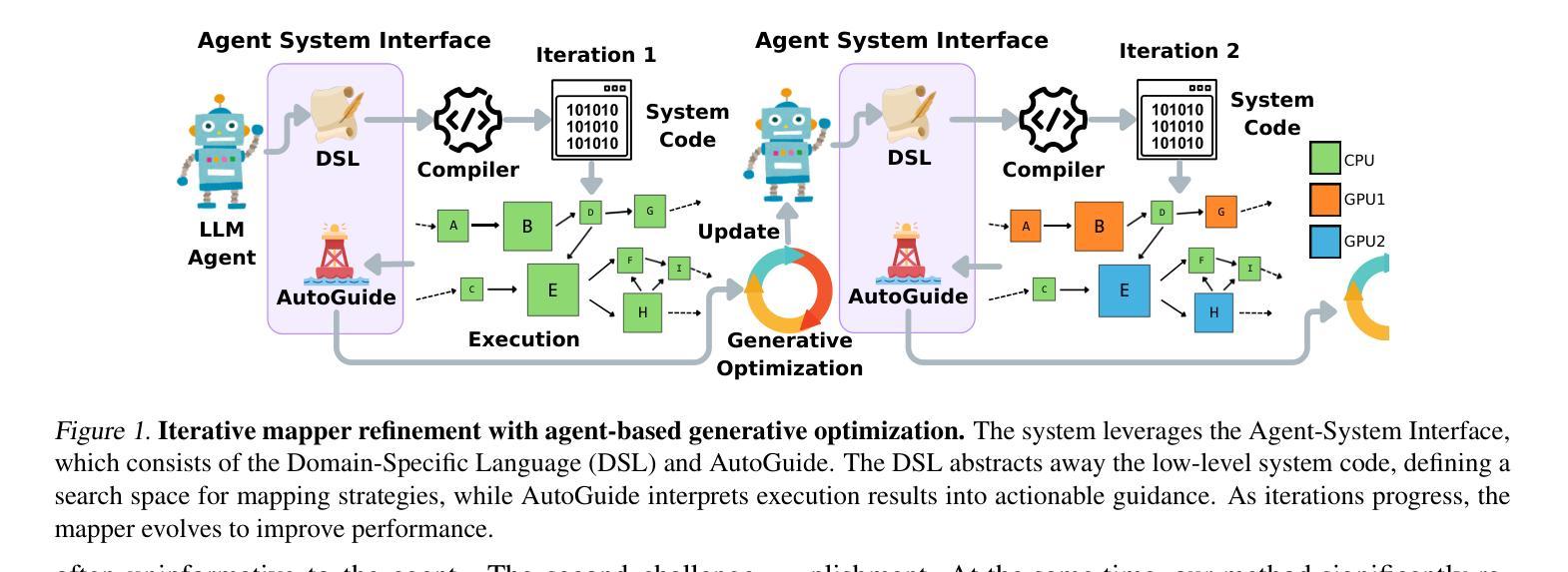
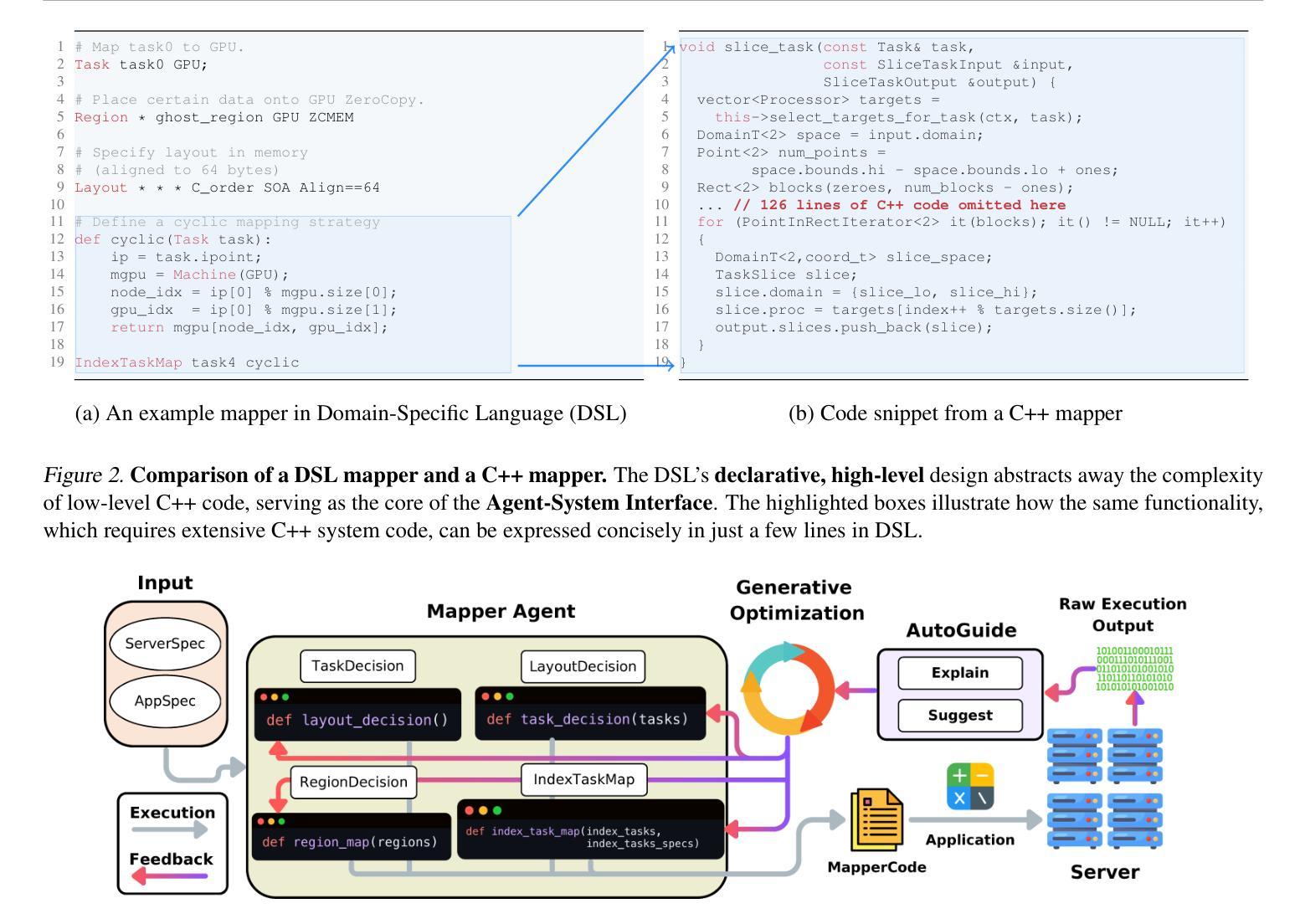
Improving Parallel Program Performance with LLM Optimizers via Agent-System Interface
Authors:Anjiang Wei, Allen Nie, Thiago S. F. X. Teixeira, Rohan Yadav, Wonchan Lee, Ke Wang, Alex Aiken
Modern scientific discovery increasingly relies on high-performance computing for complex modeling and simulation. A key challenge in improving parallel program performance is efficiently mapping tasks to processors and data to memory, a process dictated by intricate, low-level system code known as mappers. Developing high-performance mappers demands days of manual tuning, posing a significant barrier for domain scientists without systems expertise. We introduce a framework that automates mapper development with generative optimization, leveraging richer feedback beyond scalar performance metrics. Our approach features the Agent-System Interface, which includes a Domain-Specific Language (DSL) to abstract away low-level complexity of system code and define a structured search space, as well as AutoGuide, a mechanism that interprets raw execution output into actionable feedback. Unlike traditional reinforcement learning methods such as OpenTuner, which rely solely on scalar feedback, our method finds superior mappers in far fewer iterations. With just 10 iterations, it outperforms OpenTuner even after 1000 iterations, achieving 3.8X faster performance. Our approach finds mappers that surpass expert-written mappers by up to 1.34X speedup across nine benchmarks while reducing tuning time from days to minutes.
现代科学发现越来越依赖于高性能计算进行复杂的建模和模拟。提高并行程序性能的关键挑战在于有效地将任务映射到处理器并将数据映射到内存,这一过程由复杂的低级系统代码(称为映射器)决定。开发高性能映射器需要数天的手动调整,这对没有系统专业知识的领域科学家来说是一个重大障碍。我们引入了一个框架,该框架使用生成优化来自动进行映射器开发,并利用标量性能指标之外的更丰富反馈。我们的方法具有Agent-System接口,它包括一个领域特定语言(DSL),以消除系统代码的底层复杂性并定义结构化的搜索空间,以及AutoGuide,它是一种解释原始执行输出为可操作反馈的机制。与传统的强化学习方法(如OpenTuner)不同,后者仅依赖于标量反馈,我们的方法在较少的迭代次数中找到更优的映射器。仅需10次迭代,即使在1000次迭代后,它的性能也优于OpenTuner,达到了3.8倍的速度提升。我们的方法找到的映射器在九个基准测试中实现了高达1.34倍的速度提升,并将调整时间从数天缩短到数分钟。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了现代科学发现中高性能计算在复杂建模和仿真中的重要作用。为提高并行程序性能的关键挑战是有效映射任务到处理器和数据到内存,这一过程由称为映射器的低级系统代码控制。开发高性能映射器需要数天的手动调整,对没有系统专业知识的领域科学家构成重大障碍。本文引入了一个使用生成优化自动映射器开发的框架,该框架利用丰富的反馈超越了标量性能度量。其特点包括Agent-System接口和AutoGuide机制,分别通过领域特定语言(DSL)抽象系统代码的低级复杂性并定义结构化搜索空间,以及将原始执行输出解释为可操作的反馈。该方法在较少的迭代次数中找到高性能映射器,优于仅依赖标量反馈的传统强化学习方法(如OpenTuner),并在仅10次迭代中实现了高达3.8倍的性能提升。此外,该方法找到了超过专家编写的映射器在九个基准测试中的速度提升高达1.34倍,并将调整时间从数天缩短到数分钟。
Key Takeaways
- 现代科学发现依赖于高性能计算进行复杂建模和仿真。
- 开发高性能映射器是一项挑战,需要数天的手动调整,对没有系统专业知识的领域科学家构成挑战。
- 介绍了一种使用生成优化自动映射器开发的框架。
- 该框架利用丰富的反馈超越了标量性能度量,通过Agent-System接口和AutoGuide机制实现了高效映射器的开发。
- Agent-System接口包括一个领域特定语言(DSL),可以抽象系统代码的低级复杂性并定义结构化搜索空间。
- 该方法在较少的迭代次数中找到高性能映射器,优于传统强化学习方法(如OpenTuner)。
点此查看论文截图


Breaking the Curse of Multiagency in Robust Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Laixi Shi, Jingchu Gai, Eric Mazumdar, Yuejie Chi, Adam Wierman
Standard multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) algorithms are vulnerable to sim-to-real gaps. To address this, distributionally robust Markov games (RMGs) have been proposed to enhance robustness in MARL by optimizing the worst-case performance when game dynamics shift within a prescribed uncertainty set. RMGs remains under-explored, from reasonable problem formulation to the development of sample-efficient algorithms. Two notorious and open challenges are the formulation of the uncertainty set and whether the corresponding RMGs can overcome the curse of multiagency, where the sample complexity scales exponentially with the number of agents. In this work, we propose a natural class of RMGs inspired by behavioral economics, where each agent’s uncertainty set is shaped by both the environment and the integrated behavior of other agents. We first establish the well-posedness of this class of RMGs by proving the existence of game-theoretic solutions such as robust Nash equilibria and coarse correlated equilibria (CCE). Assuming access to a generative model, we then introduce a sample-efficient algorithm for learning the CCE whose sample complexity scales polynomially with all relevant parameters. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first algorithm to break the curse of multiagency for RMGs, regardless of the uncertainty set formulation.
标准的多智能体强化学习(MARL)算法容易受到仿真到现实的差距影响。为解决这一问题,提出了分布鲁棒马尔可夫博弈(RMGs),通过优化在规定的不确定性集内游戏动态变化时的最坏情况性能,增强MARL中的稳健性。RMGs的研究仍然不足,从合理的问题公式化到样本高效算法的开发都是如此。两个著名且公开的挑战是不确定性集合的公式化以及相应的RMGs是否能够克服多智能体的诅咒,即样本复杂度随智能体数量的增加而呈指数级增长。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种受行为经济学启发的自然RMGs类别,其中每个智能体的不确定性集是由环境和其它智能体的综合行为共同塑造的。我们首先通过建立这类RMGs的适定性来证明博弈论解的存在性,如鲁棒纳什均衡和粗糙相关均衡(CCE)。假设能够访问生成模型,我们然后介绍了一种学习CCE的样本高效算法,其样本复杂度与所有相关参数呈多项式增长。据我们所知,这是第一个打破了RMGs的多智能体诅咒的算法,无论不确定性集的公式化如何。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一类受行为经济学启发的分布稳健性马尔可夫游戏(RMGs),旨在增强多智能体强化学习(MARL)的稳健性。通过考虑环境和其他智能体的综合行为来构建每个智能体的不确定性集,进而优化最坏情况下的性能。本文证明了这类RMGs的游戏理论解的存在性,如稳健的纳什均衡和粗糙相关均衡。在假设有生成模型的情况下,提出了一种样本效率高的学习CCE的算法,其样本复杂度与所有相关参数呈多项式增长,打破了RMGs中的多智能体诅咒,无论不确定性集的形式如何。
Key Takeaways
- RMGs旨在增强MARL的稳健性,对抗模拟到实际的差距。
- 本文提出了受行为经济学启发的RMGs,构建智能体的不确定性集时考虑了环境和其他智能体的行为。
- 证明了这类RMGs的游戏理论解的存在性,如稳健的纳什均衡和CCE。
- 引入了一种样本效率高的算法来学习CCE,其样本复杂度与所有相关参数呈多项式增长。
- 该算法打破了RMGs中的多智能体诅咒,即样本复杂度不会随着智能体数量的增加而指数增长。
- 该算法对不确定性集的具体形式具有鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图

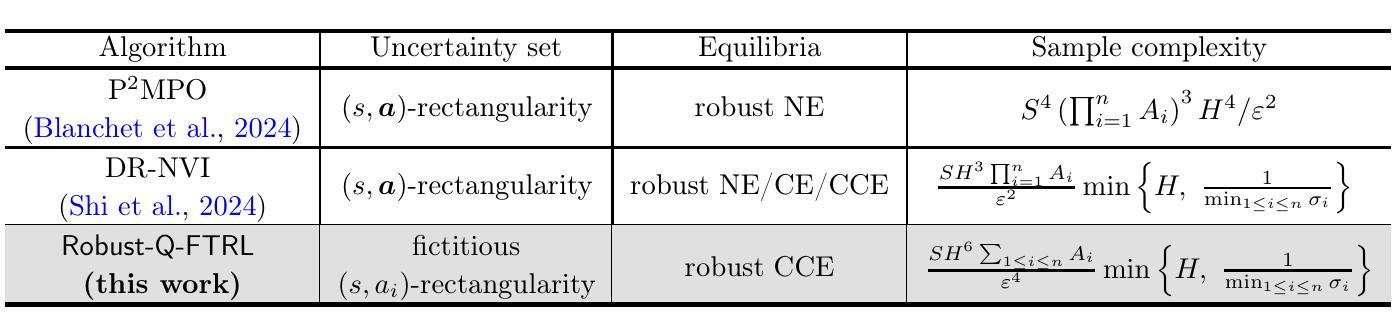
InvAgent: A Large Language Model based Multi-Agent System for Inventory Management in Supply Chains
Authors:Yinzhu Quan, Zefang Liu
Supply chain management (SCM) involves coordinating the flow of goods, information, and finances across various entities to deliver products efficiently. Effective inventory management is crucial in today’s volatile and uncertain world. Previous research has demonstrated the superiority of heuristic methods and reinforcement learning applications in inventory management. However, the application of large language models (LLMs) as autonomous agents in multi-agent systems for inventory management remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel approach using LLMs to manage multi-agent inventory systems. Leveraging their zero-shot learning capabilities, our model, InvAgent, enhances resilience and improves efficiency across the supply chain network. Our contributions include utilizing LLMs for zero-shot learning to enable adaptive and informed decision-making without prior training, providing explainability and clarity through chain-of-thought, and demonstrating dynamic adaptability to varying demand scenarios while reducing costs and preventing stockouts. Extensive evaluations across different scenarios highlight the efficiency of our model in SCM.
供应链管理(SCM)涉及协调各实体之间的货物、信息和财务流动,以实现高效的产品交付。在如今这个波动和不确定的世界中,有效的库存管理至关重要。先前的研究已经证明了启发式方法和强化学习应用在库存管理中的优越性。然而,将大型语言模型(LLM)作为多智能体系统中的自主智能体应用于库存管理仍然未被充分探索。本研究介绍了一种使用LLM管理多智能体库存系统的新方法。利用他们的零样本学习能力,我们的模型InvAgent增强了供应链的弹性并提高了效率。我们的贡献包括利用LLM进行零样本学习,以实现未经训练的自适应和基于信息的决策制定,通过思维链提供解释性和清晰度,并展示对不断变化的需求场景的动态适应性,同时降低成本并防止缺货。在不同场景下的广泛评估突出了我们模型在供应链管理中的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于供应链管理的有效库存管理在现代动荡和不确定的世界中尤为关键。过去的研究已显示启发式方法和强化学习在库存管理中的应用优势。然而,关于在多智能体系统中使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行库存管理的自主性智能体的应用仍然鲜有研究。本研究采用了一种新型方法,即利用LLM管理多智能体库存系统。借助其零样本学习能力,我们的模型InvAgent提高了供应链网络的弹性和效率。其贡献包括利用LLM进行零样本学习以实现无需预先训练的适应性和智能决策制定,通过思维链提供解释性和清晰度,并展示对不断变化的需求场景的适应力,同时降低成本并避免缺货情况。在不同场景下的广泛评估凸显了我们的模型在供应链管理中的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 供应链管理中有效的库存管理对于现代不稳定环境中的企业至关重要。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在多智能体系统中的库存管理应用尚未得到充分探索。
- 本研究提出了一种使用LLM管理多智能体库存系统的创新方法。
- LLM的零样本学习能力增强了供应链网络的弹性和效率。
- 模型InvAgent实现了无需预先训练的适应性和智能决策制定。
- 模型提供了清晰的解释性,能够展示对不断变化需求的适应力,并降低成本和避免缺货情况。
点此查看论文截图

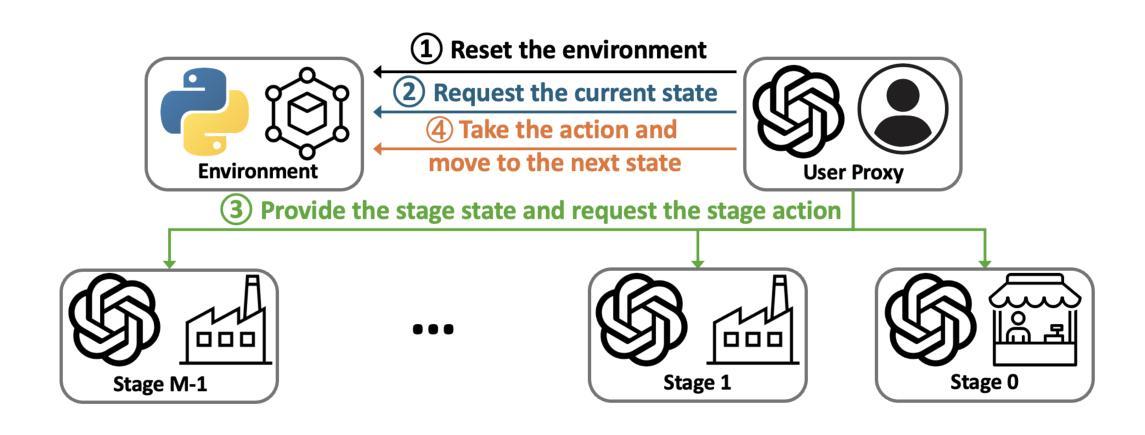
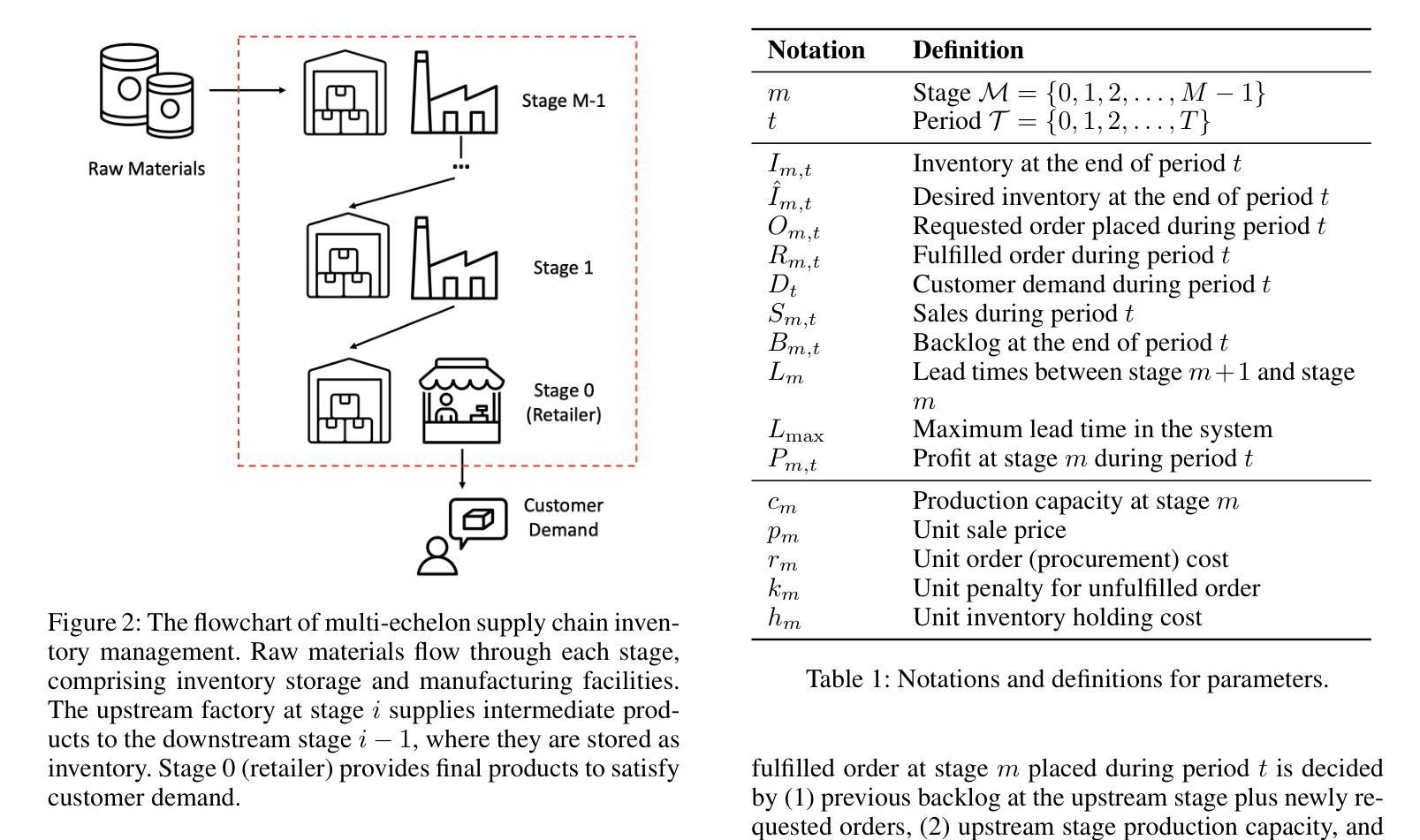
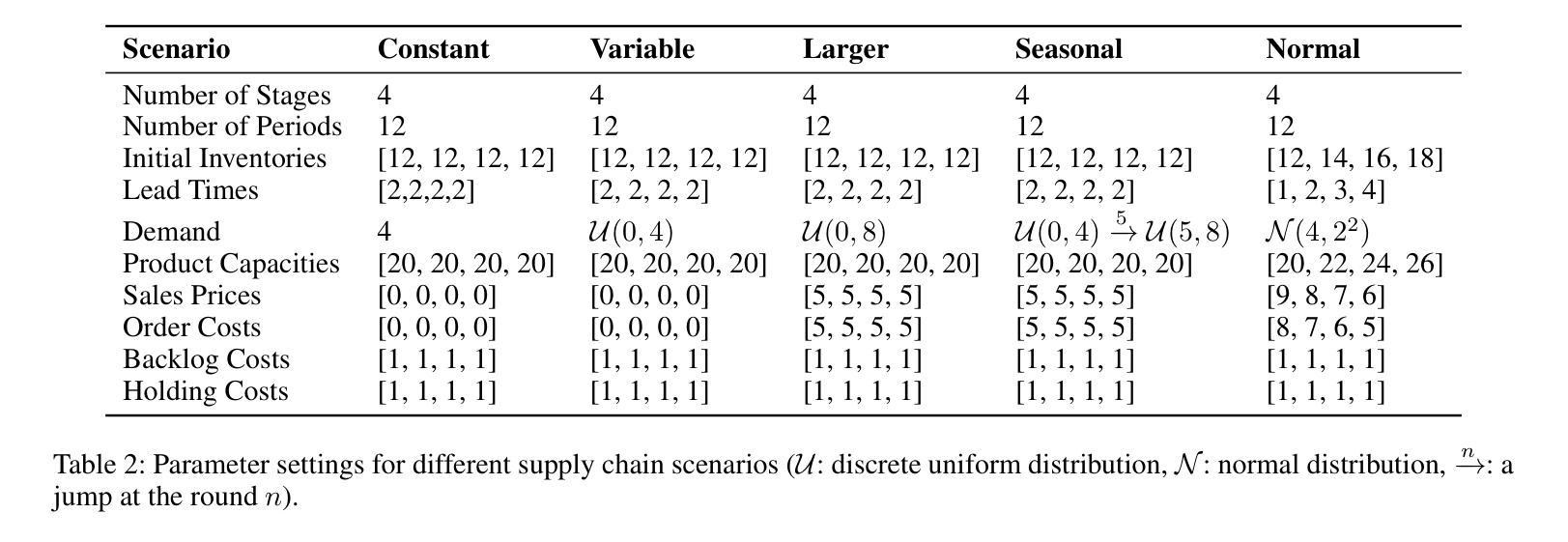
LNS2+RL: Combining Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Large Neighborhood Search in Multi-Agent Path Finding
Authors:Yutong Wang, Tanishq Duhan, Jiaoyang Li, Guillaume Sartoretti
Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) is a critical component of logistics and warehouse management, which focuses on planning collision-free paths for a team of robots in a known environment. Recent work introduced a novel MAPF approach, LNS2, which proposed to repair a quickly obtained set of infeasible paths via iterative replanning, by relying on a fast, yet lower-quality, prioritized planning (PP) algorithm. At the same time, there has been a recent push for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) based MAPF algorithms, which exhibit improved cooperation over such PP algorithms, although inevitably remaining slower. In this paper, we introduce a new MAPF algorithm, LNS2+RL, which combines the distinct yet complementary characteristics of LNS2 and MARL to effectively balance their individual limitations and get the best from both worlds. During early iterations, LNS2+RL relies on MARL for low-level replanning, which we show eliminates collisions much more than a PP algorithm. There, our MARL-based planner allows agents to reason about past and future information to gradually learn cooperative decision-making through a finely designed curriculum learning. At later stages of planning, LNS2+RL adaptively switches to PP algorithm to quickly resolve the remaining collisions, naturally trading off solution quality (number of collisions in the solution) and computational efficiency. Our comprehensive experiments on high-agent-density tasks across various team sizes, world sizes, and map structures consistently demonstrate the superior performance of LNS2+RL compared to many MAPF algorithms, including LNS2, LaCAM, EECBS, and SCRIMP. In maps with complex structures, the advantages of LNS2+RL are particularly pronounced, with LNS2+RL achieving a success rate of over 50% in nearly half of the tested tasks, while that of LaCAM, EECBS and SCRIMP falls to 0%.
多智能体路径查找(MAPF)是物流管理和仓库管理的重要组成部分,主要关注在已知环境中为机器人团队规划无碰撞路径。最近的工作引入了一种新的MAPF方法LNS2,它依靠一种快速但质量较低的优先规划(PP)算法,通过迭代重新规划来修复一组快速获得的不可行路径。与此同时,基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的MAPF算法也备受关注,它们在合作方面表现出比PP算法更好的性能,但不可避免地速度较慢。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新的MAPF算法LNS2+RL,它结合了LNS2和MARL的独特且互补的特性,有效地平衡了各自的局限性,并融合了两者最好的部分。在早期迭代中,LNS2+RL依赖于MARL进行低级重新规划,我们证明这消除了比PP算法更多的碰撞。我们的基于MARL的规划器允许智能体根据过去和未来信息进行推理,并通过精心设计的学习课程逐步学习合作决策。在规划后期阶段,LNS2+RL自适应地切换到PP算法,快速解决剩余的碰撞问题,自然地平衡解决方案质量(解决方案中的碰撞次数)和计算效率。我们在各种任务规模、世界规模和地图结构上的全面实验显示,在高密度智能体任务中,LNS2+RL的性能始终优于许多MAPF算法,包括LNS2、LaCAM、EECBS和SCRIMP等。在具有复杂结构的地图上,LNS2+RL的优势尤为突出,在几乎一半的实验任务中成功率超过50%,而LaCAM、EECBS和SCRIMP等的成功率则在测试任务中降为0%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at AAAI 2025
Summary
多智能体路径查找(MAPF)是物流及仓库管理的关键部分,涉及在已知环境中为机器人团队规划无碰撞路径。本文提出一种新的MAPF算法LNS2+RL,结合了LNS2和基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的特性,有效平衡两者的局限,实现优势互补。早期迭代使用MARL进行低级重规划,后期则采用优先级规划(PP)快速解决剩余碰撞问题。相比其他MAPF算法,LNS2+RL在复杂地图结构中表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- LNS2+RL结合了LNS2和MARL的特点,旨在平衡解决方案质量和计算效率。
- 在早期迭代中,LNS2+RL使用MARL进行低级重规划,能有效减少碰撞。
- MARL允许智能体考虑过去和未来信息,通过精心设计的课程学习逐步学习合作决策。
- 在后期规划阶段,LNS2+RL自适应切换到PP算法,以快速解决剩余碰撞问题。
- LNS2+RL在高性能智能体密度的任务中表现出卓越的性能,尤其在复杂地图结构中表现更突出。
- LNS2+RL成功率为超过一半的任务中超过一半以上,而其他算法如LaCAM、EECBS和SCRIMP在复杂地图中的成功率降低至零。
点此查看论文截图


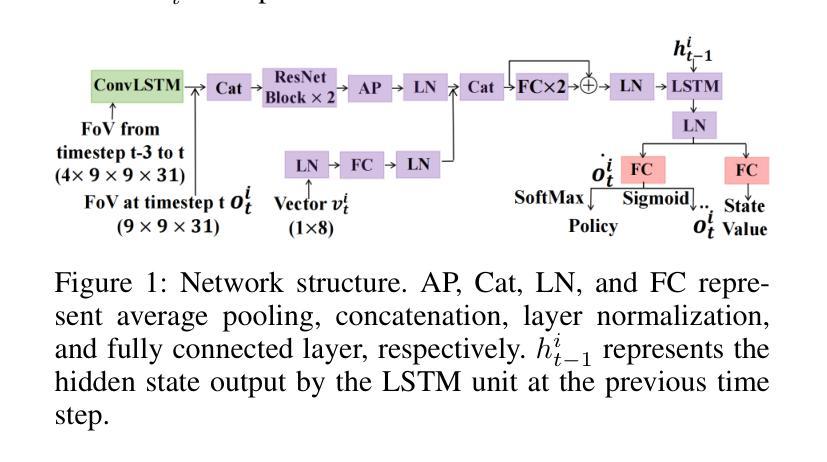
Exploring Prosocial Irrationality for LLM Agents: A Social Cognition View
Authors:Xuan Liu, Jie Zhang, Song Guo, Haoyang Shang, Chengxu Yang, Quanyan Zhu
Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to face hallucination issues due to the data they trained on often containing human bias; whether this is reflected in the decision-making process of LLM Agents remains under-explored. As LLM Agents are increasingly employed in intricate social environments, a pressing and natural question emerges: Can we utilize LLM Agents’ systematic hallucinations to mirror human cognitive biases, thus exhibiting irrational social intelligence? In this paper, we probe the irrational behavior among contemporary LLM Agents by melding practical social science experiments with theoretical insights. Specifically, We propose CogMir, an open-ended Multi-LLM Agents framework that utilizes hallucination properties to assess and enhance LLM Agents’ social intelligence through cognitive biases. Experimental results on CogMir subsets show that LLM Agents and humans exhibit high consistency in irrational and prosocial decision-making under uncertain conditions, underscoring the prosociality of LLM Agents as social entities and highlighting the significance of hallucination properties. Additionally, the CogMir framework demonstrates its potential as a valuable platform for encouraging more research into the social intelligence of LLM Agents.
大型语言模型(LLM)由于训练数据常含有人类偏见,已出现幻觉问题;然而,这一问题是否反映在LLM代理的决策过程中尚未得到充分探索。随着LLM代理越来越多地被应用于复杂的社会环境,一个紧迫而自然的问题出现了:我们能否利用LLM代理的系统性幻觉来反映人类认知偏见,从而表现出非理性的社会智能?在本文中,我们通过结合实用的社会科学实验和理论见解,探究了当代LLM代理的非理性行为。具体来说,我们提出了CogMir,这是一个开放的多LLM代理框架,利用幻觉属性通过认知偏见来评估和增强LLM代理的社会智能。在CogMir子集上的实验结果表明,LLM代理和人类在不确定条件下的非理性亲社会决策表现出高度一致性,这强调了LLM代理作为社会实体的亲社会性,并突出了幻觉属性的重要性。此外,CogMir框架展示了一个有价值的平台潜力,可以鼓励更多关于LLM代理社会智能的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)面临的幻觉问题反映在人类偏见上。本研究探讨LLM代理人在社会环境中展现的不理性行为,并提出CogMir框架,利用幻觉属性评估并提升LLM代理人的社会智能。实验结果显示,LLM代理人在不确定条件下的决策与人类行为高度一致,凸显了幻觉属性的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在决策过程中会展现出幻觉问题,这源于训练数据中包含的人类偏见。
- LLM代理人在社会环境中展现出不理性行为,这与人有一定的相似性。
- CogMir框架旨在利用LLM代理人的幻觉属性来评估并提升其社会智能。
- 实验证明,LLM代理人在不确定条件下的决策与人类行为高度一致。
- 幻觉属性对于展示LLM代理人的社会智能具有重要意义。
- CogMir框架有助于鼓励更多关于LLM代理人社会智能的研究。
点此查看论文截图

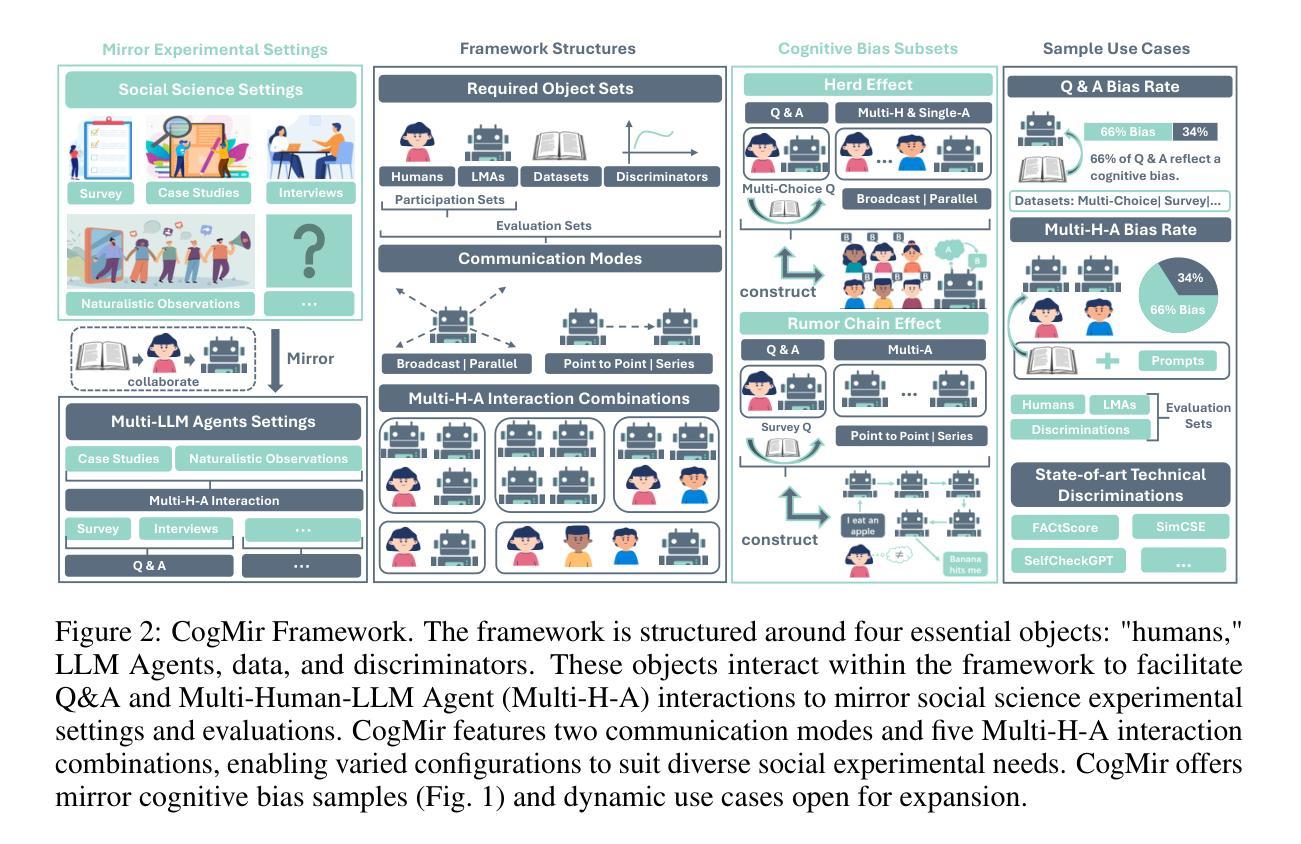
RH20T-P: A Primitive-Level Robotic Dataset Towards Composable Generalization Agents
Authors:Zeren Chen, Zhelun Shi, Xiaoya Lu, Lehan He, Sucheng Qian, Zhenfei Yin, Wanli Ouyang, Jing Shao, Yu Qiao, Cewu Lu, Lu Sheng
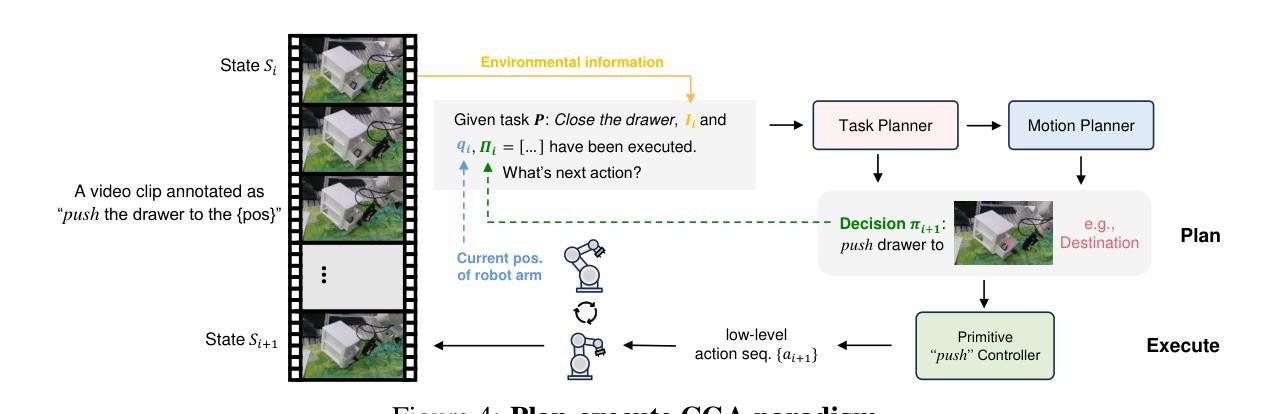
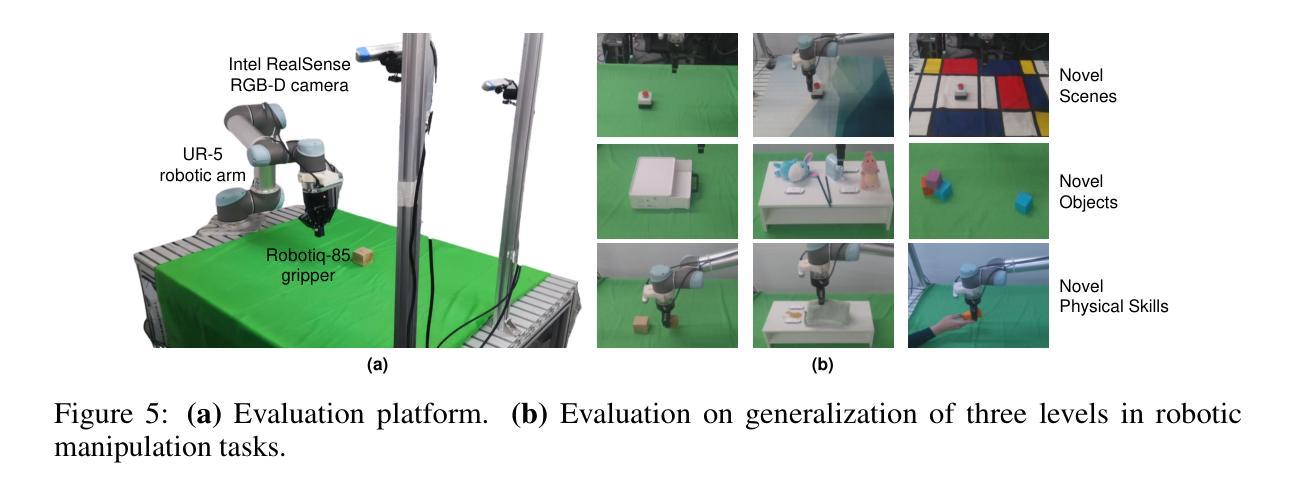
Achieving generalizability in solving out-of-distribution tasks is one of the ultimate goals of learning robotic manipulation. Recent progress of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) has shown that VLM-based task planners can alleviate the difficulty of solving novel tasks, by decomposing the compounded tasks as a plan of sequentially executing primitive-level skills that have been already mastered. It is also promising for robotic manipulation to adapt such composable generalization ability, in the form of composable generalization agents (CGAs). However, the community lacks of reliable design of primitive skills and a sufficient amount of primitive-level data annotations. Therefore, we propose RH20T-P, a primitive-level robotic manipulation dataset, which contains about 38k video clips covering 67 diverse manipulation tasks in real-world scenarios. Each clip is manually annotated according to a set of meticulously designed primitive skills that are common in robotic manipulation. Furthermore, we standardize a plan-execute CGA paradigm and implement an exemplar baseline called RA-P on our RH20T-P, whose positive performance on solving unseen tasks validates that the proposed dataset can offer composable generalization ability to robotic manipulation agents.
实现通用性来解决分布式外的任务是学习机器人操作的一个终极目标。最近的视觉语言模型(VLM)进展表明,基于VLM的任务规划器可以通过将复杂的任务分解为一系列已掌握的原始技能来减轻解决新任务的难度。对于机器人操作来说,采用可组合通用代理(CGA)的形式适应这种可组合通用能力也很有前景。然而,社区缺乏可靠的原始技能设计和足够的原始级别数据注释。因此,我们提出了RH20T-P,这是一个原始级别的机器人操作数据集,包含约3.8万个视频剪辑,涵盖现实场景中67种多样的操作任务。每个剪辑都根据精心设计的在机器人操作中常见的原始技能集进行手动注释。此外,我们对CGA范式进行了标准化,并在我们的RH20T-P上实施了RA-P示例基线,其在解决未见任务上的积极表现证明了我们提出的数据集可以为机器人操作代理提供可组合通用能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 11 figures, 7 tables. Accepted by NeurIPS 2024 Workshop
Summary
视觉语言模型(VLM)具备分解复杂任务并依次执行已掌握的基础技能的能力,这为解决新型任务提供了一种新的策略。这种策略在机器人操作领域展现出巨大潜力,有助于构建具有组合泛化能力的代理(CGAs)。当前领域面临基础技能设计和数据标注不足的问题,为此我们提出RH20T-P数据集,包含约3.8万条涵盖现实场景中67种不同操作任务的视频片段。每个片段都依据一套经过精心设计的通用基础技能进行手动标注。我们确定了CGA的标准范例并实现RA-P范例用于基准测试。它在解决未知任务上的积极表现验证了数据集可以为机器人操作代理提供组合泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- VLM能够分解复杂任务为一系列基础技能执行计划,为解决新型任务提供新思路。
- VLM在机器人操作领域具备巨大潜力,有助于构建具有组合泛化能力的代理(CGAs)。但现实中仍缺乏可靠的基础技能设计和充足的基础级数据标注。为解决这一问题,我们提出了RH20T-P数据集。该数据集包含涵盖多种现实操作任务的手动标注视频片段,依据一套精心设计的通用基础技能进行标注。
点此查看论文截图


Replication-proof Bandit Mechanism Design with Bayesian Agents
Authors:Suho Shin, Seyed A. Esmaeili, MohammadTaghi Hajiaghayi
We study the problem of designing replication-proof bandit mechanisms when agents strategically register or replicate their own arms to maximize their payoff. Specifically, we consider Bayesian agents who only know the distribution from which their own arms’ mean rewards are sampled, unlike the original setting of by Shin et al. 2022. Interestingly, with Bayesian agents in stark contrast to the previous work, analyzing the replication-proofness of an algorithm becomes significantly complicated even in a single-agent setting. We provide sufficient and necessary conditions for an algorithm to be replication-proof in the single-agent setting, and present an algorithm that satisfies these properties. These results center around several analytical theorems that focus on \emph{comparing the expected regret of multiple bandit instances}, and therefore might be of independent interest since they have not been studied before to the best of our knowledge. We expand this result to the multi-agent setting, and provide a replication-proof algorithm for any problem instance. We finalize our result by proving its sublinear regret upper bound which matches that of Shin et al. 2022.
我们研究了在设计复制证明的多臂赌博机制时,代理人为了最大化收益而策略性地注册或复制自己的手臂的问题。具体来说,我们考虑的是贝叶斯代理人,他们只知道自己的手臂平均奖励的采样分布,这与Shin等人2022年的原始设置不同。有趣的是,与之前的作品相比,带有贝叶斯代理人的分析,即使在单代理设置中,分析算法的防复制性也变得非常复杂。我们为算法在单代理设置中提供防复制的充分必要条件,并展示满足这些属性的算法。这些结果围绕几个分析定理展开,这些定理侧重于比较多个赌博实例的预期遗憾,因此它们可能是独立感兴趣的,因为据我们所知,之前没有人研究过。我们将结果扩展到多代理设置,并为任何问题实例提供防复制算法。最后,我们通过证明其匹配的次线性遗憾上限来完善我们的结果,这与Shin等人2022年的结果相符。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了设计防止策略性复制的多臂赌博机机制的问题,特别考虑了战略性代理如何注册或复制自己的臂以最大化收益。与Shin et al. 2022的原始设置不同,我们考虑了仅知道自身手臂奖励均值分布采样的贝叶斯代理的情况。有趣的是,即使在单代理设置中,与之前的分析相比,分析算法的防复制性也变得更加复杂。我们提供了算法在单代理设置中具备防复制性的充分必要条件,并给出了满足这些属性的算法。这些结果集中在几个分析定理上,重点在于比较多个赌博机的预期遗憾,这可能是独立兴趣的研究主题,因为在现有知识范围内尚未进行过类似研究。我们将结果扩展到多代理设置,并为任何问题实例提供了防复制的算法。最后,我们证明了其匹配的遗憾上界是次线性的,与Shin et al. 2022的结果相符。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了设计防止代理战略性复制的多臂赌博机机制的问题。
- 分析了贝叶斯代理在单代理设置中的防复制性,与之前的分析相比更加复杂。
- 提供了算法在单代理设置中具备防复制性的充分必要条件。
- 提出了一种满足这些属性的算法。
- 研究结果集中在比较多个赌博机的预期遗憾的分析定理上,这可能是独立兴趣的研究主题。
- 将研究结果扩展到多代理设置,并为任何问题实例提供了防复制的算法。
点此查看论文截图