⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
Pathological MRI Segmentation by Synthetic Pathological Data Generation in Fetuses and Neonates
Authors:Misha P. T Kaandorp, Damola Agbelese, Hosna Asma-ull, Hyun-Gi Kim, Kelly Payette, Patrice Grehten, Gennari Antonio Giulio, Levente István Lánczi, Andras Jakab
Developing new methods for the automated analysis of clinical fetal and neonatal MRI data is limited by the scarcity of annotated pathological datasets and privacy concerns that often restrict data sharing, hindering the effectiveness of deep learning models. We address this in two ways. First, we introduce Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM, a novel diffusion model framework designed to generate high-quality synthetic pathological fetal and neonatal MRIs from semantic label images. Second, we enhance training data by modifying healthy label images through morphological alterations to simulate conditions such as ventriculomegaly, cerebellar and pontocerebellar hypoplasia, and microcephaly. By leveraging Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM, we synthesize realistic pathological MRIs from these modified pathological label images. Radiologists rated the synthetic MRIs as significantly (p < 0.05) superior in quality and diagnostic value compared to real MRIs, demonstrating features such as blood vessels and choroid plexus, and improved alignment with label annotations. Synthetic pathological data enhanced state-of-the-art nnUNet segmentation performance, particularly for severe ventriculomegaly cases, with the greatest improvements achieved in ventricle segmentation (Dice scores: 0.9253 vs. 0.7317). This study underscores the potential of generative AI as transformative tool for data augmentation, offering improved segmentation performance in pathological cases. This development represents a significant step towards improving analysis and segmentation accuracy in prenatal imaging, and also offers new ways for data anonymization through the generation of pathologic image data.
针对临床胎儿和新生儿MRI数据的自动化分析新方法的开发受限于标注病理数据集的稀缺性以及隐私担忧,后者经常限制数据共享,阻碍了深度学习模型的有效性。我们通过两种方式来解决这个问题。首先,我们引入了Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM这一新型扩散模型框架,旨在从语义标签图像生成高质量合成病理胎儿和新生儿MRIs。其次,我们通过形态改变修改健康标签图像来增强训练数据,以模拟脑室扩大、小脑和桥小脑萎缩以及小头畸形等状况。通过利用Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM,我们从这些修改后的病理标签图像中合成出逼真的病理性MRI。放射科医生评价合成的MRI在质量和诊断价值上显著高于真实MRI(p<0.05),显示出血管和脉络丛等特征,与标签注释对齐度更高。合成病理数据提高了最先进分割网络的分割性能(nnUNet),特别是对于严重的脑室扩大病例,在脑室分割方面取得了最大的改进(Dice分数:0.9253 vs. 0.7317)。这项研究强调了生成人工智能作为数据增强工具的潜力,在病理情况下提高了分割性能。这一发展代表了产前成像分析和分割精度改进的重要一步,同时也提供了新的方法来通过生成病理图像数据进行数据匿名处理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种解决临床胎儿和新生儿MRI数据自动化分析难题的新方法。针对病理性数据集稀缺和隐私担忧限制数据共享的问题,研究团队采取了两种策略。他们提出了一种新型扩散模型框架Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM,能够从语义标签图像生成高质量合成病理性胎儿和新生儿MRI。同时,通过对健康标签图像进行形态学改变以模拟诸如脑积水、小脑和脑桥小脑发育不良和小头畸形等状况,增强训练数据。合成的MRI图像被放射科医生评价为具有较高的质量和诊断价值。此外,合成病理性数据提高了nnUNet分割的性能,特别是在严重脑积水病例中,脑室分割的Dice得分显著提高。该研究凸显了生成式人工智能在数据增强方面的巨大潜力,为提高病理情况下的分析和分割精度提供了新的途径,并可通过生成病理性图像数据实现数据匿名化。
Key Takeaways
- 胎儿和新生儿MRI数据自动化分析面临病理性数据集稀缺和隐私担忧的挑战。
- 引入Fetal&Neonatal-DDPM扩散模型框架,从语义标签图像生成高质量合成病理性MRI。
- 通过形态学改变健康标签图像以模拟病理性状况,增强训练数据。
- 合成的MRI图像被放射科医生评价为具有较高的质量和诊断价值。
- 合成病理性数据提高了nnUNet分割性能,特别是在脑室分割方面。
- 研究凸显了生成式人工智能在数据增强方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

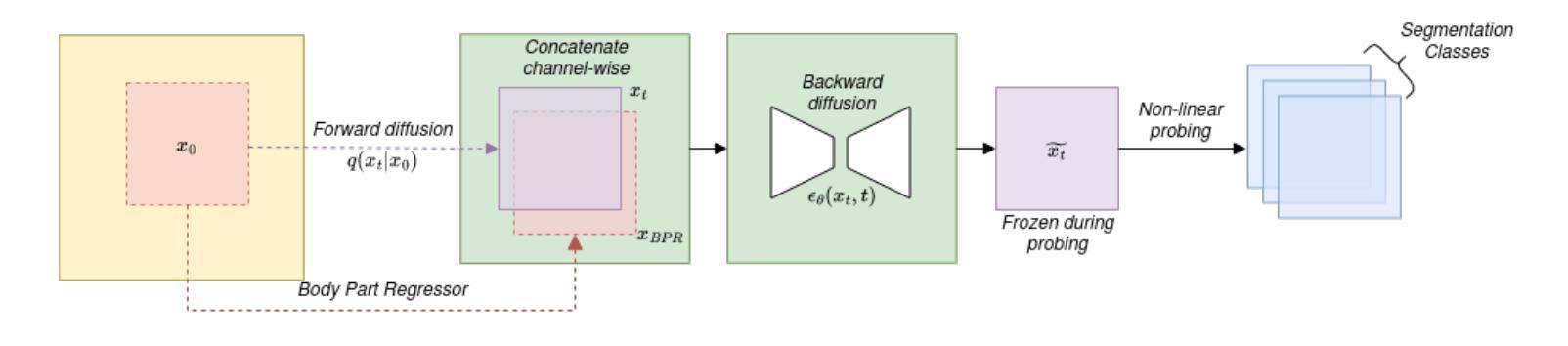
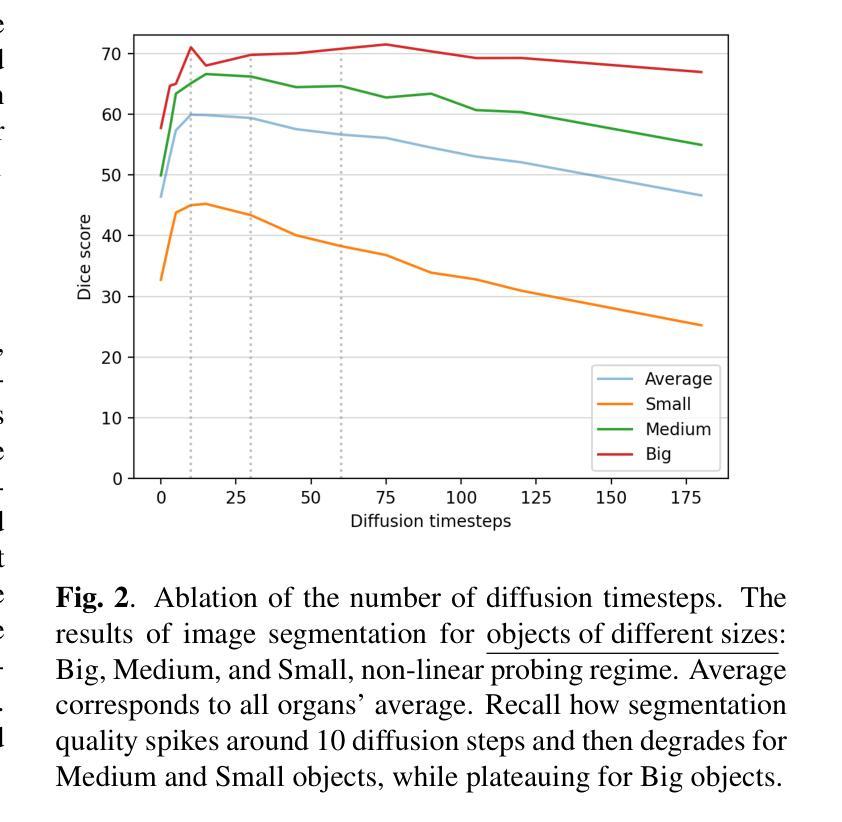
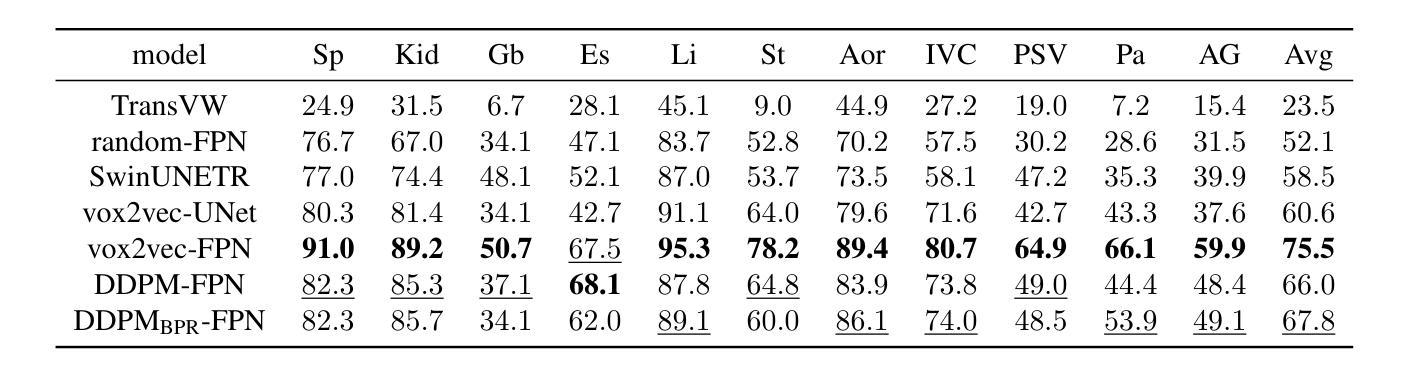
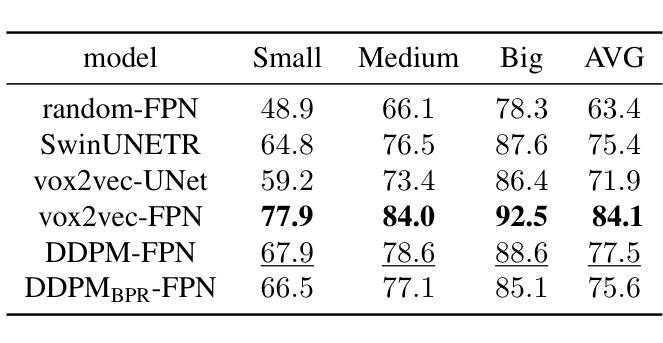
Medical Semantic Segmentation with Diffusion Pretrain
Authors:David Li, Anvar Kurmukov, Mikhail Goncharov, Roman Sokolov, Mikhail Belyaev
Recent advances in deep learning have shown that learning robust feature representations is critical for the success of many computer vision tasks, including medical image segmentation. In particular, both transformer and convolutional-based architectures have benefit from leveraging pretext tasks for pretraining. However, the adoption of pretext tasks in 3D medical imaging has been less explored and remains a challenge, especially in the context of learning generalizable feature representations. We propose a novel pretraining strategy using diffusion models with anatomical guidance, tailored to the intricacies of 3D medical image data. We introduce an auxiliary diffusion process to pretrain a model that produce generalizable feature representations, useful for a variety of downstream segmentation tasks. We employ an additional model that predicts 3D universal body-part coordinates, providing guidance during the diffusion process and improving spatial awareness in generated representations. This approach not only aids in resolving localization inaccuracies but also enriches the model’s ability to understand complex anatomical structures. Empirical validation on a 13-class organ segmentation task demonstrate the effectiveness of our pretraining technique. It surpasses existing restorative pretraining methods in 3D medical image segmentation by $7.5%$, and is competitive with the state-of-the-art contrastive pretraining approach, achieving an average Dice coefficient of 67.8 in a non-linear evaluation scenario.
最近的深度学习进展表明,学习稳健的特征表示对于许多计算机视觉任务(包括医学图像分割)的成功至关重要。特别是基于transformer和卷积的架构都从利用预训练任务中获益。然而,在3D医学影像中采用预训练任务的研究相对较少,仍然是一个挑战,特别是在学习通用特征表示方面。我们提出了一种使用扩散模型进行预训练的新策略,该策略具有解剖导向性,针对3D医学图像数据的复杂性进行了定制。我们引入了一个辅助扩散过程来预训练一个模型,该模型可以产生可用于各种下游分割任务的通用特征表示。我们还采用另一个模型预测3D通用身体部位坐标,在扩散过程中提供指导,提高了生成表示的空间感知能力。这种方法不仅有助于解决定位不准确的问题,还丰富了模型理解复杂解剖结构的能力。在13类器官分割任务上的经验验证表明我们预训练技术的有效性。与现有的3D医学图像分割恢复预训练方法相比,我们的技术提高了7.5%,并且在非线性评估场景中与最先进的对比预训练方法相竞争,平均Dice系数为67.8。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的新型预训练策略,结合解剖学指导,针对3D医学图像数据的特性进行定制。通过引入辅助扩散过程和预测3D通用身体部位坐标的附加模型,提高模型在多种下游分割任务中的通用特征表示能力。实验验证显示,该方法不仅解决了定位不准确的问题,还提高了模型理解复杂解剖结构的能力。在13类器官分割任务上的表现优于现有的恢复性预训练方法,并与最新的对比预训练方法具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习中的先进进展表明,学习鲁棒的特征表示对于包括医学图像分割在内的许多计算机视觉任务的成功至关重要。
- 尽管预训练在图像识别和其他NLP任务中已经证明了其价值,但在医学成像领域,尤其是学习通用特征表示方面仍存在挑战。
- 本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新型预训练策略,特别适用于3D医学图像数据。
- 通过引入辅助扩散过程和预测身体部位坐标的模型,提高了模型的空间感知能力和通用特征表示能力。
- 与现有方法相比,该策略在多种下游任务中的表现均有显著提升,解决了定位不准确的问题。
- 在复杂的解剖结构理解方面,该策略表现出了显著的改进和优越性。
点此查看论文截图

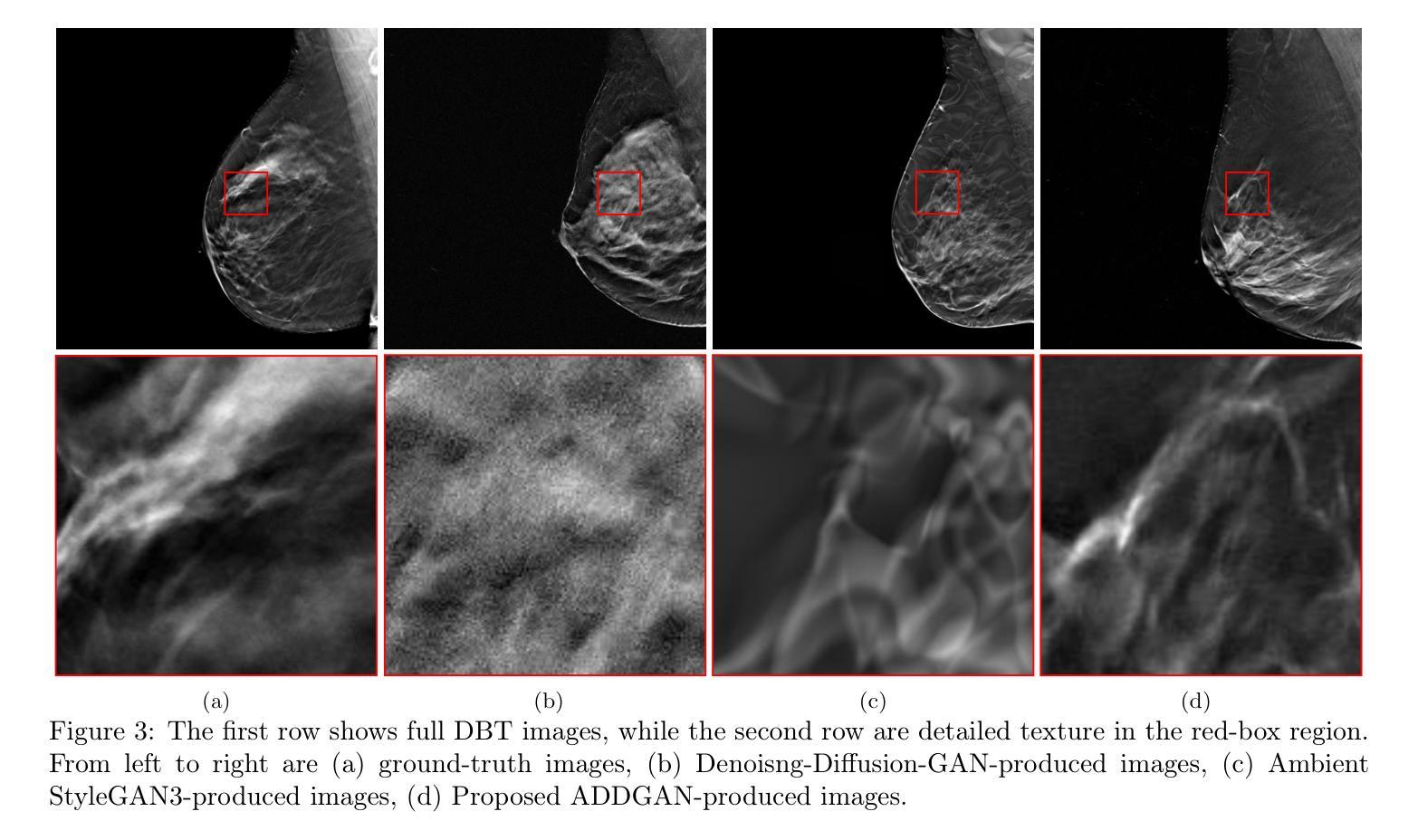
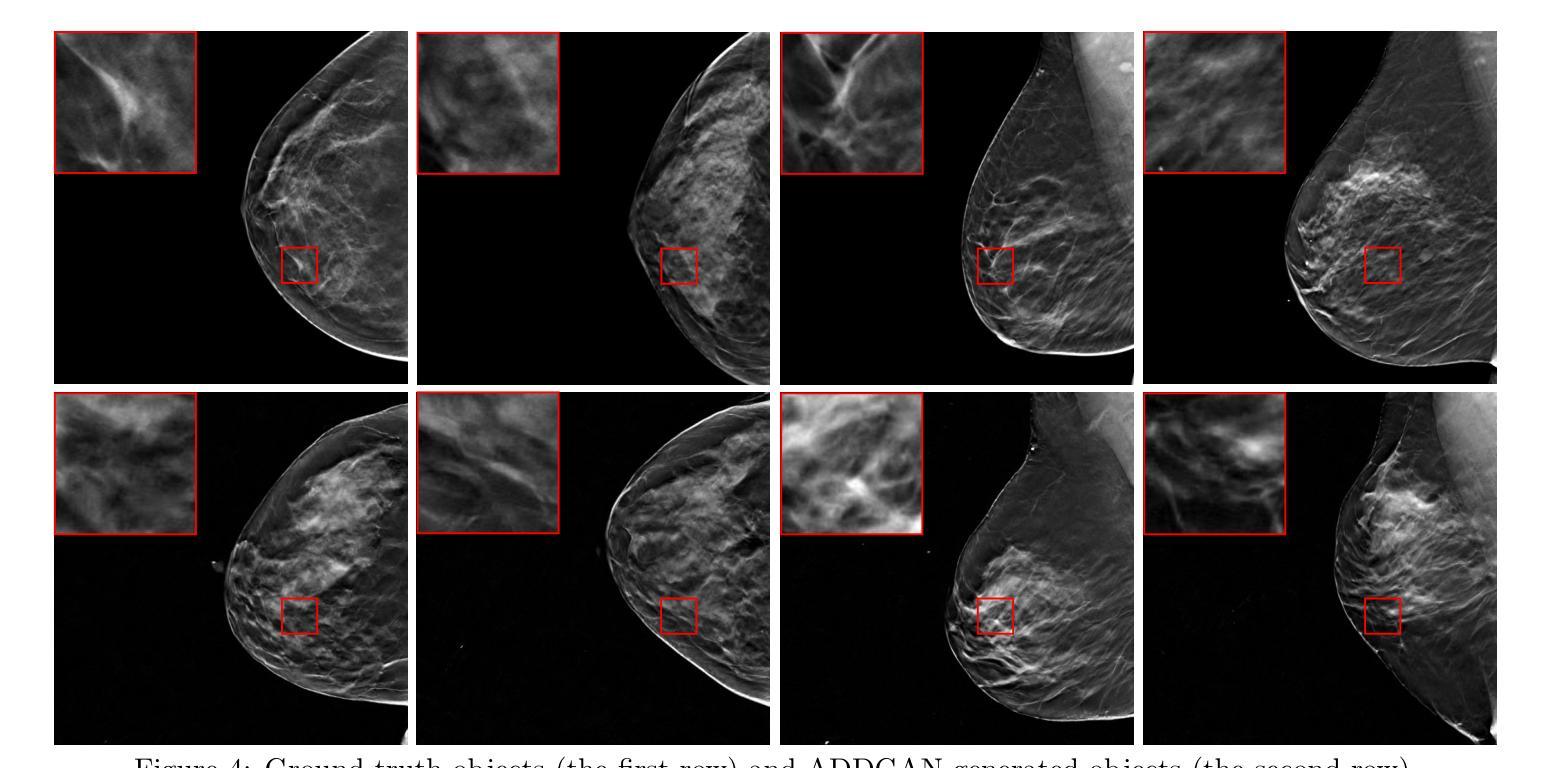
Ambient Denoising Diffusion Generative Adversarial Networks for Establishing Stochastic Object Models from Noisy Image Data
Authors:Xichen Xu, Wentao Chen, Weimin Zhou
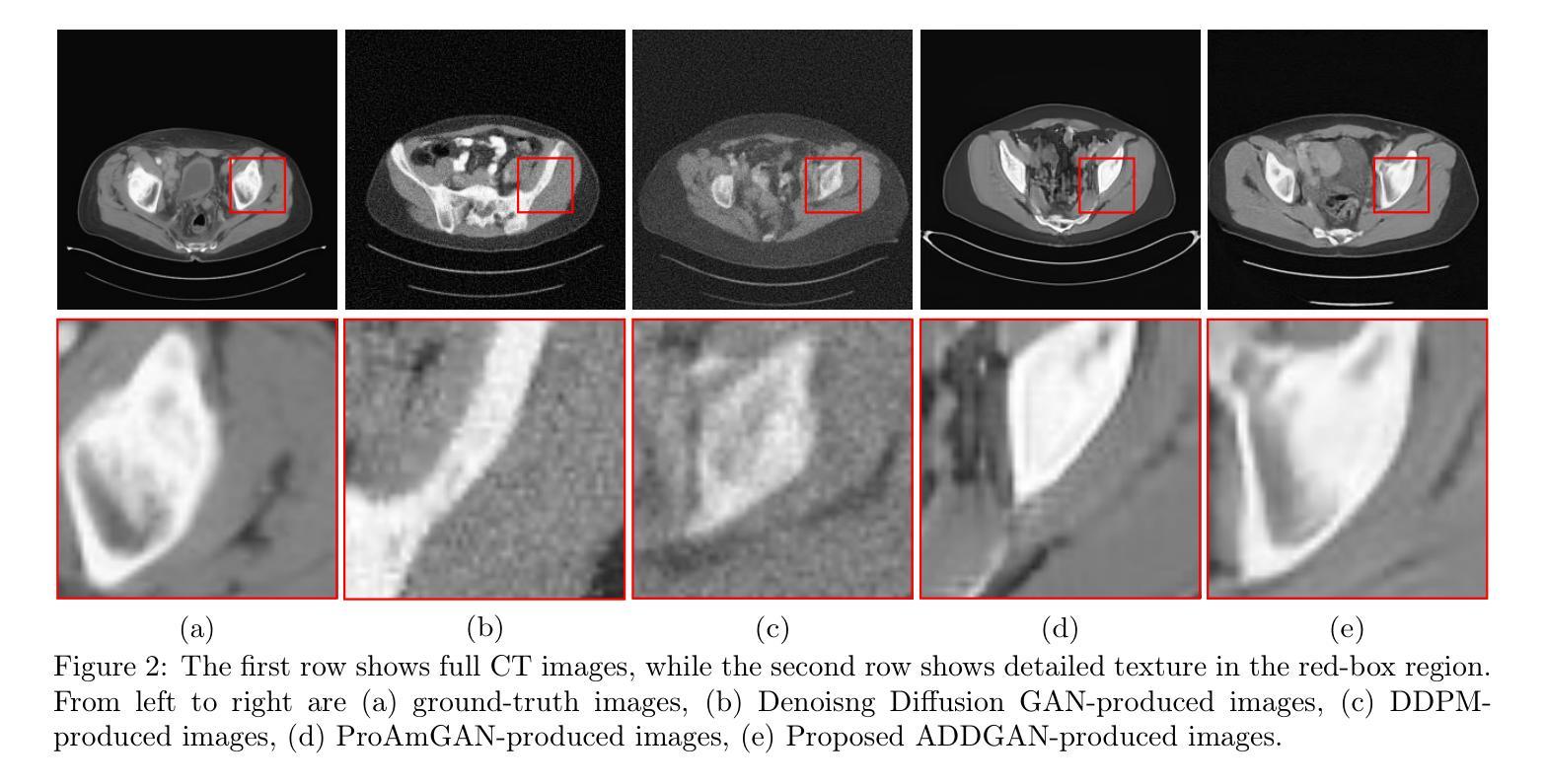
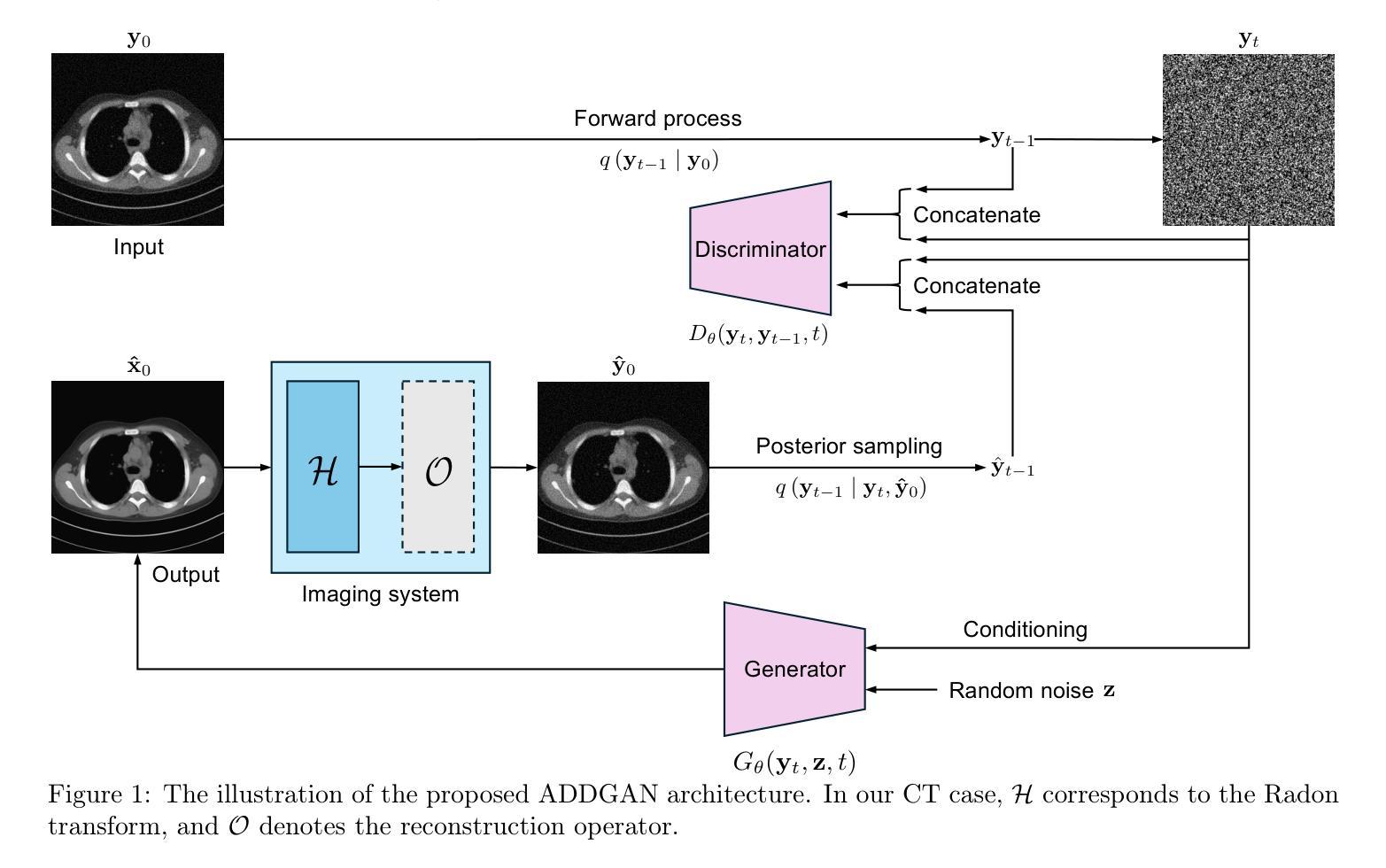
It is widely accepted that medical imaging systems should be objectively assessed via task-based image quality (IQ) measures that ideally account for all sources of randomness in the measured image data, including the variation in the ensemble of objects to be imaged. Stochastic object models (SOMs) that can randomly draw samples from the object distribution can be employed to characterize object variability. To establish realistic SOMs for task-based IQ analysis, it is desirable to employ experimental image data. However, experimental image data acquired from medical imaging systems are subject to measurement noise. Previous work investigated the ability of deep generative models (DGMs) that employ an augmented generative adversarial network (GAN), AmbientGAN, for establishing SOMs from noisy measured image data. Recently, denoising diffusion models (DDMs) have emerged as a leading DGM for image synthesis and can produce superior image quality than GANs. However, original DDMs possess a slow image-generation process because of the Gaussian assumption in the denoising steps. More recently, denoising diffusion GAN (DDGAN) was proposed to permit fast image generation while maintain high generated image quality that is comparable to the original DDMs. In this work, we propose an augmented DDGAN architecture, Ambient DDGAN (ADDGAN), for learning SOMs from noisy image data. Numerical studies that consider clinical computed tomography (CT) images and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) images are conducted. The ability of the proposed ADDGAN to learn realistic SOMs from noisy image data is demonstrated. It has been shown that the ADDGAN significantly outperforms the advanced AmbientGAN models for synthesizing high resolution medical images with complex textures.
普遍认同医学影像系统应通过基于任务的图像质量(IQ)措施进行客观评估,这些措施理想情况下应考虑到测量图像数据中所有随机性的来源,包括待成像物体集合的变异。可以使用随机对象模型(SOMs)从物体分布中随机抽取样本以表征物体变异性。为了建立基于任务的IQ分析的现实SOMs,使用实验图像数据是理想的。然而,从医学影像系统获得的实验图像数据会受到测量噪声的影响。早期的工作研究了使用增强生成对抗网络(GAN)的深生成模型(DGM)建立噪声测量图像数据的SOMs的能力。最近,去噪扩散模型(DDM)作为领先的图像合成DGM而出现,可以产生比GAN更高的图像质量。然而,原始DDMs由于去噪步骤中的高斯假设而具有缓慢的图像处理过程。最近,提出了去噪扩散GAN(DDGAN)以允许快速图像生成并保持与原始DDMs相当的高质量图像。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种增强的DDGAN架构,即环境DDGAN(ADDGAN),用于从噪声图像数据中学习SOMs。我们进行了考虑临床计算机断层扫描(CT)图像和数字乳腺断层合成(DBT)图像的数值研究。证明了所提出的ADDGAN从噪声图像数据中学习现实SOMs的能力。已经显示,ADDGAN在合成具有复杂纹理的高分辨率医学图像方面显著优于先进的AmbientGAN模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SPIE Medical Imaging 2025
摘要
本研究探讨了利用增强型去噪扩散生成对抗网络(DDGAN)从含噪医学图像数据中建立随机对象模型(SOMs)的方法。通过数值研究,证明所提出的ADDGAN(Ambient DDGAN)能从含噪的医学图像数据中学习真实的SOMs,并在合成具有复杂纹理的高分辨率医学图像方面显著优于先进的AmbientGAN模型。
关键见解
- 研究强调了通过任务基础图像质量(IQ)措施对医学成像系统进行客观评估的重要性,考虑了图像数据中的所有随机性来源,包括要成像的对象集合的变异性。
- 随机对象模型(SOMs)可用于表征对象变异性,可从对象分布中随机抽取样本。
- 使用实验图像数据进行任务基础IQ分析时,需要注意数据受测量噪声影响的问题。
- 之前的研究已调查了使用深度生成模型(DGM)如增强型生成对抗网络(GAN)的AmbientGAN从含噪测量图像数据中建立SOMs的能力。
- 去噪扩散模型(DDM)作为领先的图像合成DGM,能产生比GAN更优质的图像。然而,原始DDMs由于去噪步骤中的高斯假设,图像生成过程较慢。
- 新提出的去噪扩散生成对抗网络(DDGAN)允许快速图像生成,同时保持与原始DDMs相当的图像质量。
点此查看论文截图




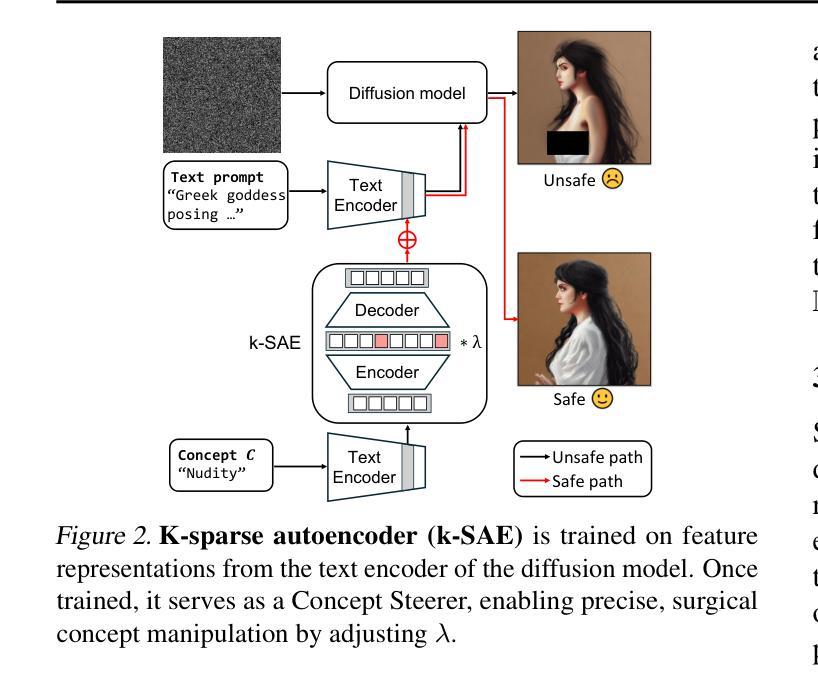
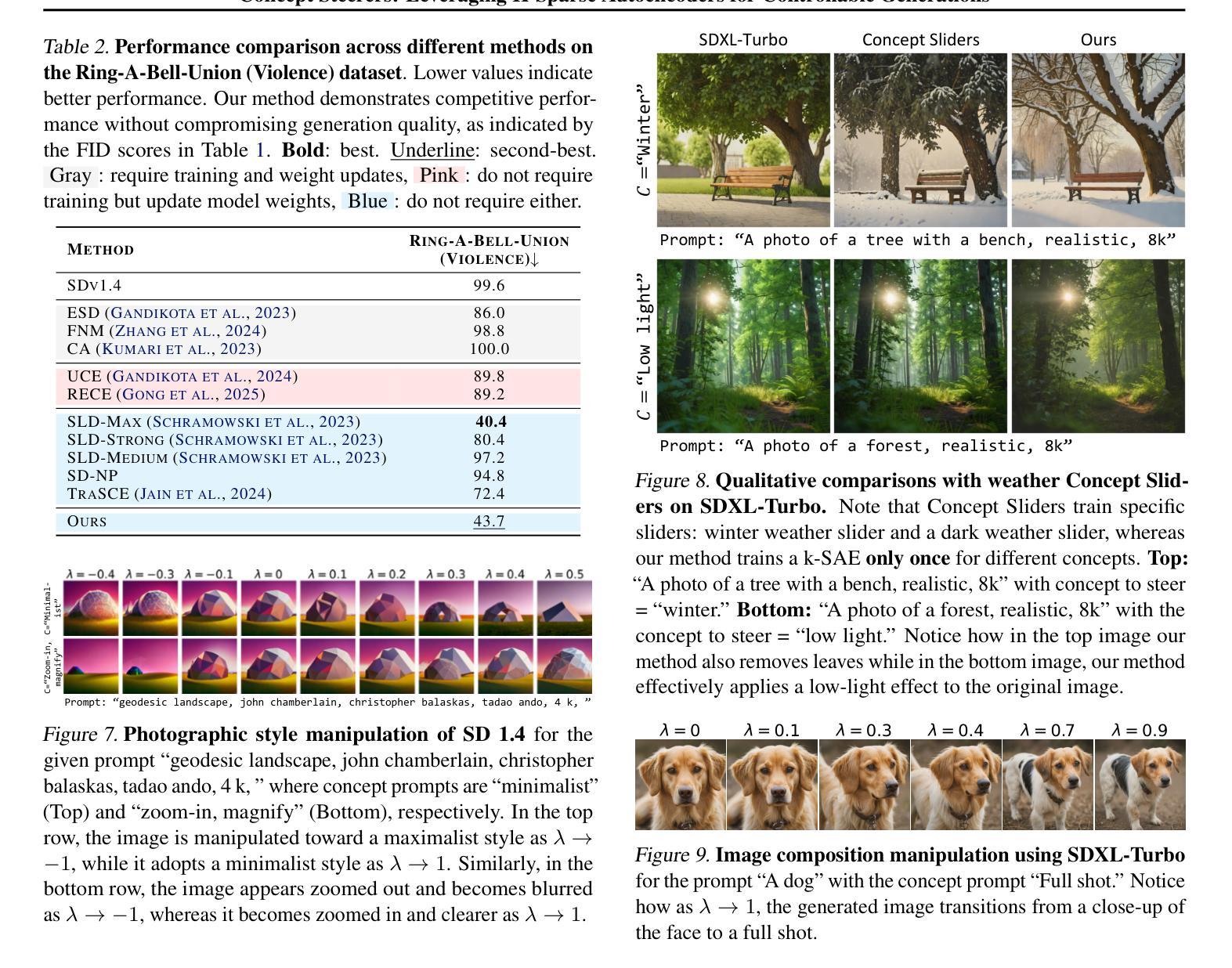
Concept Steerers: Leveraging K-Sparse Autoencoders for Controllable Generations
Authors:Dahye Kim, Deepti Ghadiyaram
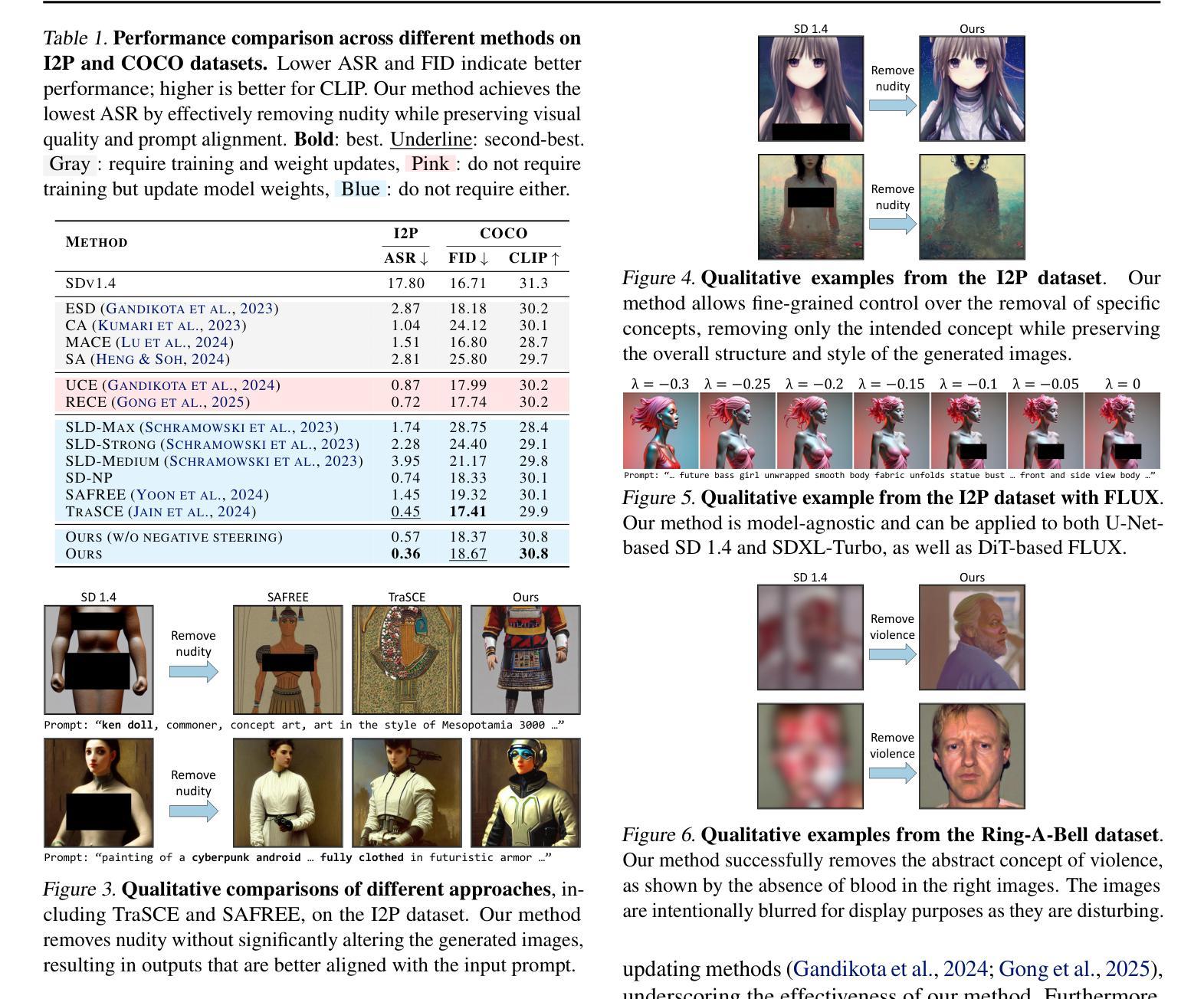
Despite the remarkable progress in text-to-image generative models, they are prone to adversarial attacks and inadvertently generate unsafe, unethical content. Existing approaches often rely on fine-tuning models to remove specific concepts, which is computationally expensive, lack scalability, and/or compromise generation quality. In this work, we propose a novel framework leveraging k-sparse autoencoders (k-SAEs) to enable efficient and interpretable concept manipulation in diffusion models. Specifically, we first identify interpretable monosemantic concepts in the latent space of text embeddings and leverage them to precisely steer the generation away or towards a given concept (e.g., nudity) or to introduce a new concept (e.g., photographic style). Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our approach is very simple, requires no retraining of the base model nor LoRA adapters, does not compromise the generation quality, and is robust to adversarial prompt manipulations. Our method yields an improvement of $\mathbf{20.01%}$ in unsafe concept removal, is effective in style manipulation, and is $\mathbf{\sim5}$x faster than current state-of-the-art.
尽管文本到图像生成模型取得了显著的进步,但它们容易受到对抗性攻击,并可能无意中生成不安全、不符合伦理的内容。现有方法通常依赖于微调模型来消除特定概念,这计算成本高、缺乏可扩展性,并且/或损害生成质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个利用k稀疏自编码器(k-SAEs)的新框架,以实现扩散模型中高效且可解释的概念操作。具体来说,我们首先在文本嵌入的潜在空间中识别可解释的单语义概念,并利用它们来精确控制生成远离或朝向给定概念(例如,裸体),或引入新概念(例如,摄影风格)。通过大量实验,我们证明我们的方法非常简单,无需重新训练基础模型或使用LoRA适配器,不会损害生成质量,并且对对抗性提示操作具有鲁棒性。我们的方法在不安全概念删除方面提高了20.01%,在风格操作方面非常有效,并且是当前最先进的技术的约5倍速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 16 figures
Summary
本文提出利用k-稀疏自编码器(k-SAEs)构建新型框架,实现在扩散模型中的高效且可解释的概念操控。通过识别文本嵌入潜在空间中的可解释单语义概念,该框架能够精准地引导生成结果远离或靠近特定概念,或引入新概念,如避免不安全的内容生成。实验证明,该方法简单高效,无需重新训练基础模型或使用LoRA适配器,不降低生成质量,且对对抗性提示操控具有鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像生成模型虽然取得显著进展,但仍易受到对抗性攻击,会无意中生成不安全、不道德的内容。
- 现有方法通常依赖对模型进行微调以去除特定概念,但这种方法计算成本高、缺乏可扩展性且可能影响生成质量。
- 本文提出利用k-稀疏自编码器(k-SAEs)的新框架,实现在扩散模型中的概念操控。
- 该框架能够识别文本嵌入潜在空间中的可解释单语义概念,并精准地引导生成结果远离或靠近特定概念或引入新概念。
- 实验表明,该方法在不妥协生成质量的前提下,提高了不安全概念移除的效果,达到20.01%的改进,且在风格操控方面有效。
- 与当前先进技术相比,该方法速度提高了约5倍。
点此查看论文截图

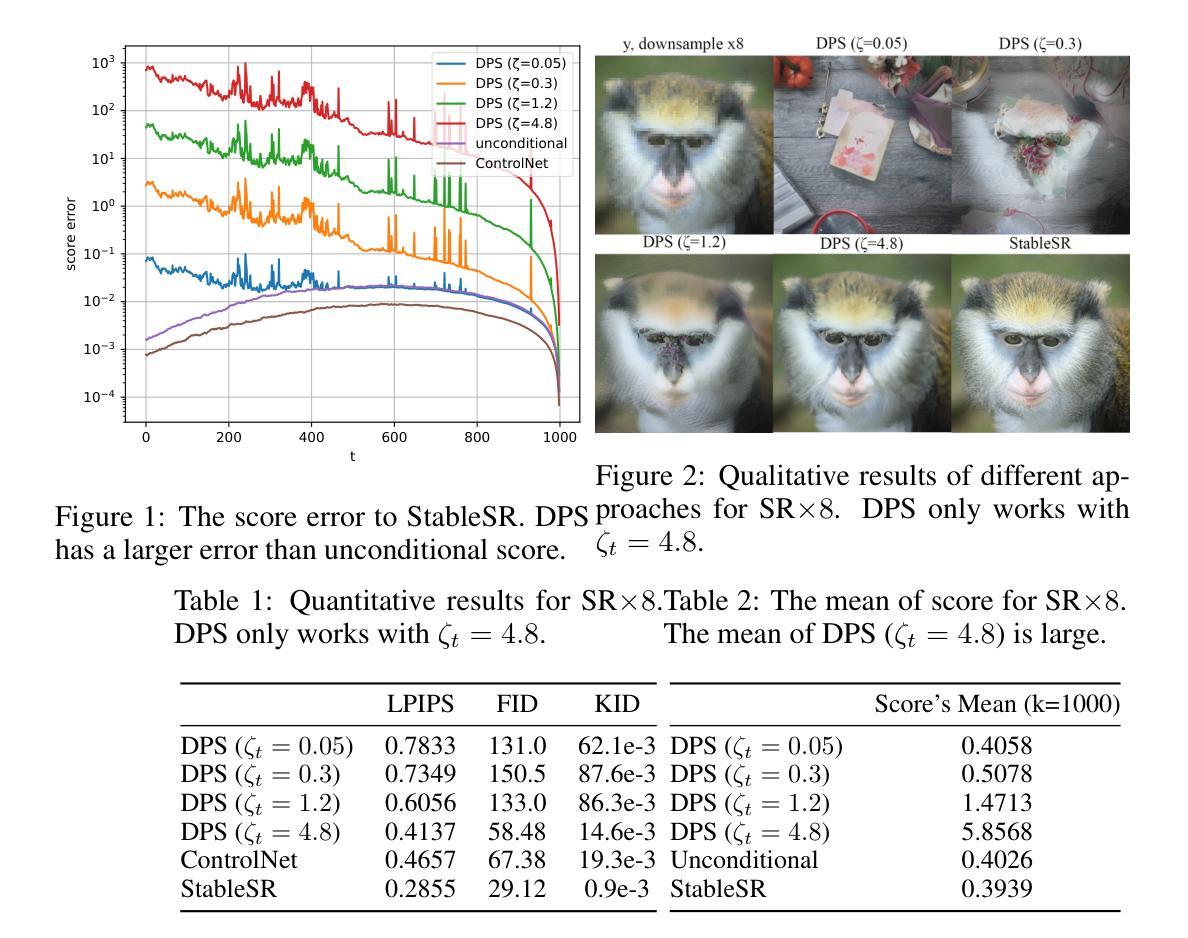
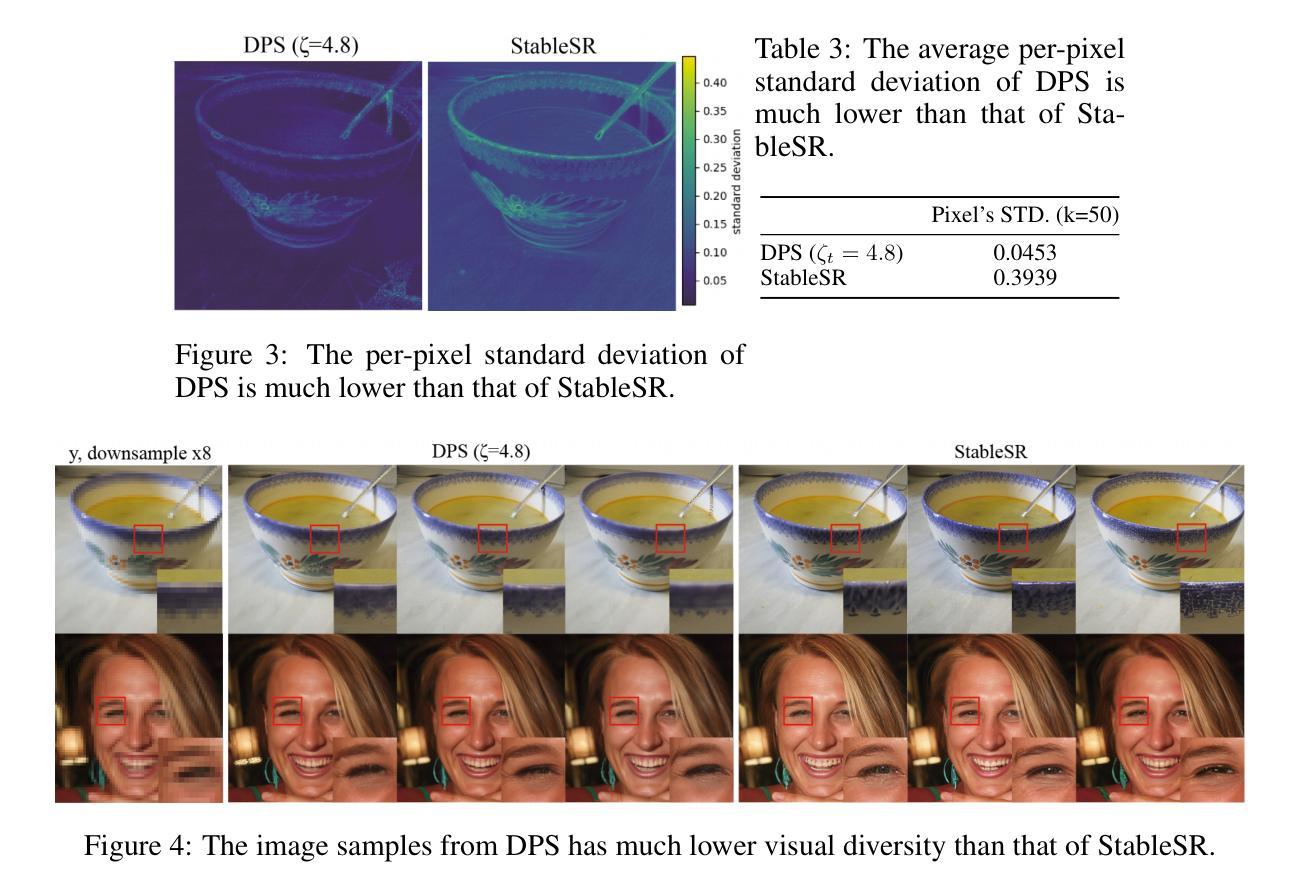
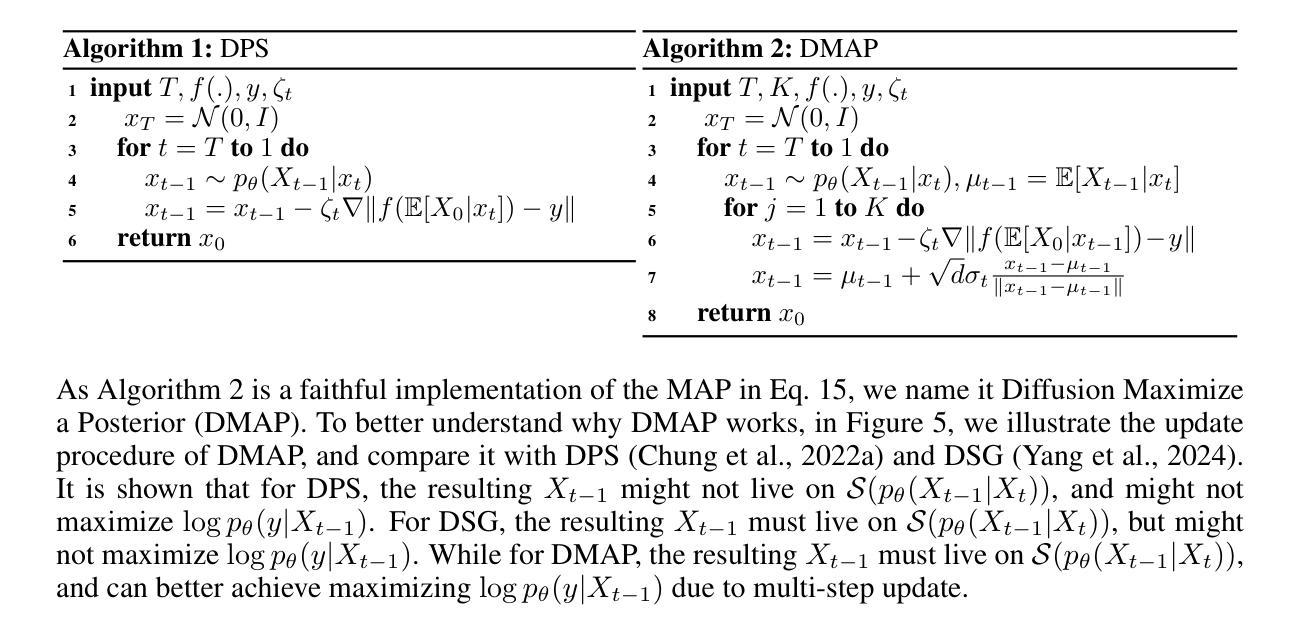
Rethinking Diffusion Posterior Sampling: From Conditional Score Estimator to Maximizing a Posterior
Authors:Tongda Xu, Xiyan Cai, Xinjie Zhang, Xingtong Ge, Dailan He, Ming Sun, Jingjing Liu, Ya-Qin Zhang, Jian Li, Yan Wang
Recent advancements in diffusion models have been leveraged to address inverse problems without additional training, and Diffusion Posterior Sampling (DPS) (Chung et al., 2022a) is among the most popular approaches. Previous analyses suggest that DPS accomplishes posterior sampling by approximating the conditional score. While in this paper, we demonstrate that the conditional score approximation employed by DPS is not as effective as previously assumed, but rather aligns more closely with the principle of maximizing a posterior (MAP). This assertion is substantiated through an examination of DPS on 512x512 ImageNet images, revealing that: 1) DPS’s conditional score estimation significantly diverges from the score of a well-trained conditional diffusion model and is even inferior to the unconditional score; 2) The mean of DPS’s conditional score estimation deviates significantly from zero, rendering it an invalid score estimation; 3) DPS generates high-quality samples with significantly lower diversity. In light of the above findings, we posit that DPS more closely resembles MAP than a conditional score estimator, and accordingly propose the following enhancements to DPS: 1) we explicitly maximize the posterior through multi-step gradient ascent and projection; 2) we utilize a light-weighted conditional score estimator trained with only 100 images and 8 GPU hours. Extensive experimental results indicate that these proposed improvements significantly enhance DPS’s performance. The source code for these improvements is provided in https://github.com/tongdaxu/Rethinking-Diffusion-Posterior-Sampling-From-Conditional-Score-Estimator-to-Maximizing-a-Posterior.
近期扩散模型的新进展已被用于解决无需额外训练的反问题,其中Diffusion Posterior Sampling(DPS)(Chung等人,2022a)是最受欢迎的方法之一。之前的分析表明,DPS通过近似条件分数来实现后验采样。然而,本文中我们证明DPS所采用的条件分数近似并不像之前假设的那样有效,而更接近于最大后验(MAP)原则。这一主张通过对DPS在512x512 ImageNet图像上的检查得到了证实,结果显示:1)DPS的条件分数估计与训练良好的条件扩散模型的分数存在显著差异,甚至不如无条件分数;2)DPS的条件分数估计均值偏离零,使其成为无效的分数估计;3)DPS生成的样本质量虽高,但多样性显著降低。鉴于上述发现,我们认为DPS更类似于MAP而非条件分数估计器,并据此对DPS提出以下改进:1)我们通过多步梯度上升和投影显式地最大化后验;2)我们使用仅使用100张图像和8个GPU小时训练的轻量级条件分数估计器。大量的实验结果表明,这些改进显著提高了DPS的性能。这些改进的代码源可在https://github.com/tongdaxu/Rethinking-Diffusion-Posterior-Sampling-From-Conditional-Score-Estimator-to-Maximizing-a-Posterior找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
摘要
近期扩散模型的新进展被用来解决逆向问题而无需额外训练,其中Diffusion Posterior Sampling(DPS)是最受欢迎的方法之一。本研究发现,DPS所采用的条件分数近似并非如先前假设般有效,而是更贴近最大化后验(MAP)原理。通过对DPS在512x512 ImageNet图像上的研究,我们发现:1)DPS的条件分数估计与训练良好的条件扩散模型的分数存在显著差异,甚至不及无条件分数;2)DPS的条件分数估计均值偏离零,使其成为一个无效的分数估计;3)DPS生成的样本质量高,但多样性显著降低。鉴于以上发现,我们认为DPS更类似于MAP而非条件分数估计器,并据此提出以下增强措施:1)通过多步梯度上升和投影显式最大化后验;2)使用轻量级的条件分数估计器,仅使用100张图像和8 GPU小时进行训练。实验结果表明,这些改进显著提高了DPS的性能。
关键见解
- Diffusion Posterior Sampling (DPS) 在处理逆向问题时,其条件分数估计并不如先前研究所示有效。
- DPS的条件分数估计与良好的条件扩散模型的分数存在显著差异,甚至不如无条件分数估计。
- DPS的条件分数估计均值显著偏离零,表明其分数估计无效。
- DPS虽然能生成高质量样本,但样本多样性显著降低。
- DPS更接近最大化后验(MAP)原理而非条件分数估计。
- 提出了通过多步梯度上升和投影来显式最大化后验的方法,以提高DPS性能。
- 使用轻量级的条件分数估计器,仅需要少量图像和计算资源就能进行有效训练,进一步提升了DPS的性能。
点此查看论文截图

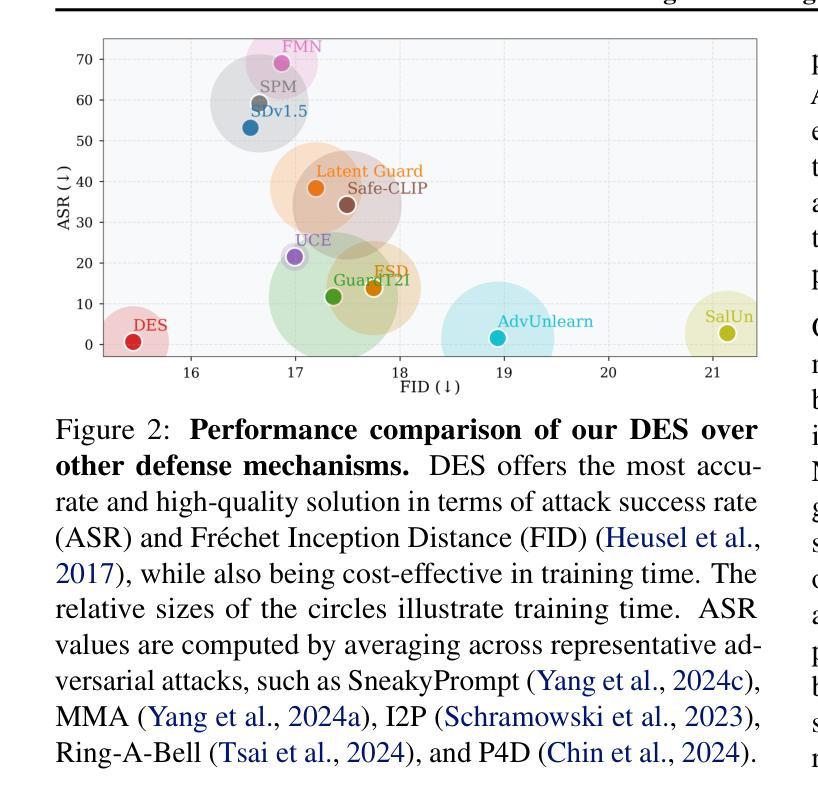
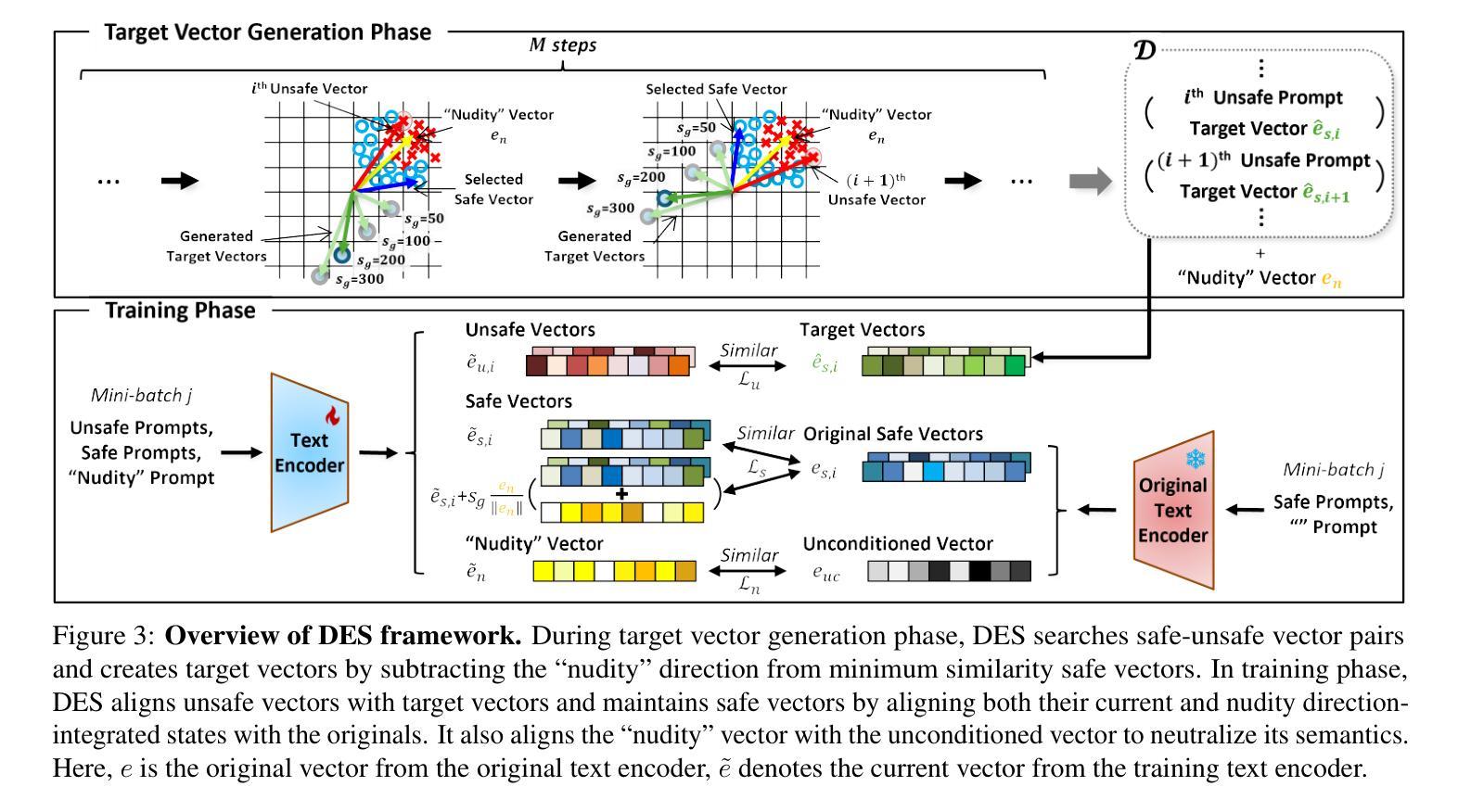
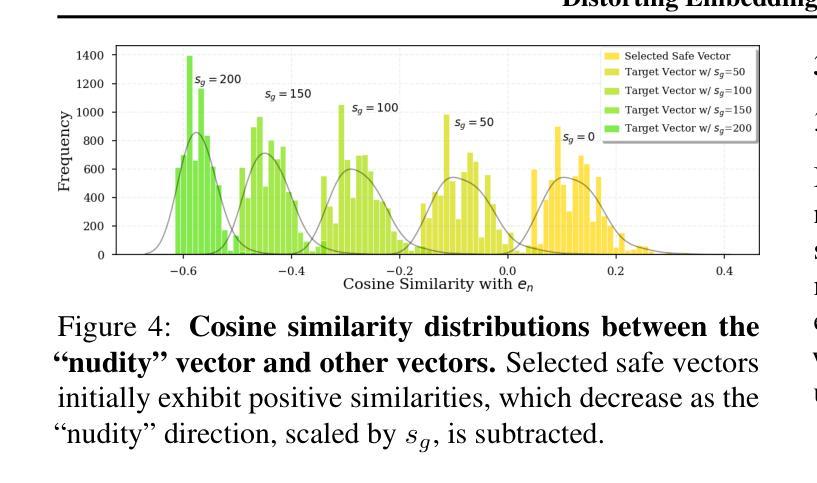
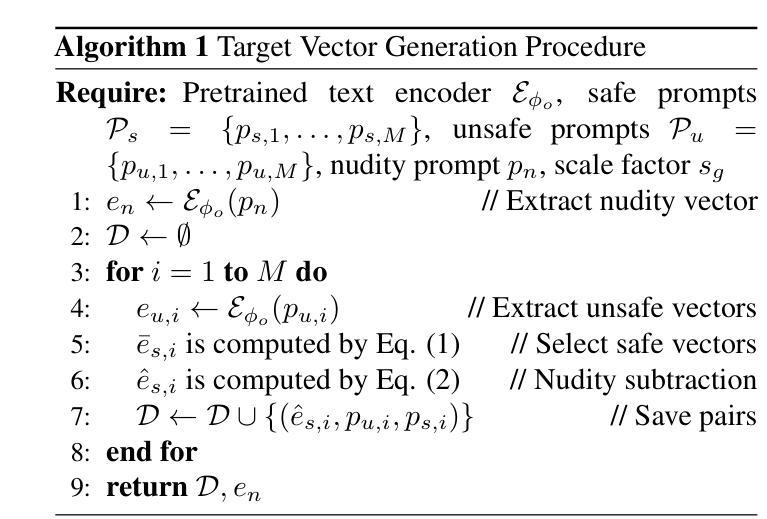
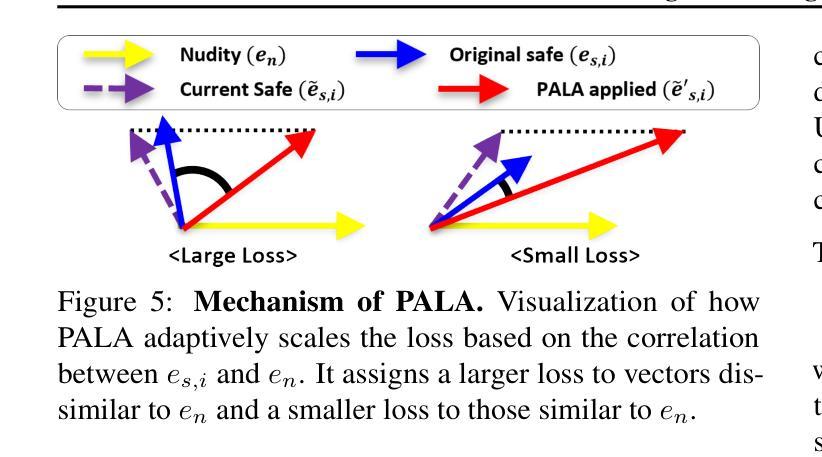
Distorting Embedding Space for Safety: A Defense Mechanism for Adversarially Robust Diffusion Models
Authors:Jaesin Ahn, Heechul Jung
Text-to-image diffusion models show remarkable generation performance following text prompts, but risk generating Not Safe For Work (NSFW) contents from unsafe prompts. Existing approaches, such as prompt filtering or concept unlearning, fail to defend against adversarial attacks while maintaining benign image quality. In this paper, we propose a novel approach called Distorting Embedding Space (DES), a text encoder-based defense mechanism that effectively tackles these issues through innovative embedding space control. DES transforms unsafe embeddings, extracted from a text encoder using unsafe prompts, toward carefully calculated safe embedding regions to prevent unsafe contents generation, while reproducing the original safe embeddings. DES also neutralizes the nudity embedding, extracted using prompt ``nudity”, by aligning it with neutral embedding to enhance robustness against adversarial attacks. These methods ensure both robust defense and high-quality image generation. Additionally, DES can be adopted in a plug-and-play manner and requires zero inference overhead, facilitating its deployment. Extensive experiments on diverse attack types, including black-box and white-box scenarios, demonstrate DES’s state-of-the-art performance in both defense capability and benign image generation quality. Our model is available at https://github.com/aei13/DES.
文本到图像的扩散模型在文本提示下显示出显著的生成性能,但存在从不安全提示生成不适合工作场所(NSFW)内容的风险。现有方法,如提示过滤或概念遗忘,未能有效对抗攻击同时保持良性图像质量。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为“扭曲嵌入空间”(DES)的新方法,这是一种基于文本编码器的防御机制,通过创新的嵌入空间控制有效地解决了这些问题。DES将不安全嵌入(通过文本编码器使用不安全提示提取)转换为精心计算的安全嵌入区域,以防止不安全内容的生成,同时重现原始的安全嵌入。DES通过对齐使用“裸露”提示提取的裸露嵌入到中性嵌入中,增强了对对抗性攻击的稳健性。这些方法确保了强大的防御和高质量的图像生成。此外,DES采用即插即用方式,无需任何推理开销,便于部署。对各种攻击类型进行的广泛实验,包括黑箱和白箱场景,证明了DES在防御能力和良性图像生成质量方面的卓越性能。我们的模型可在https://github.com/aei13/DES找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像的扩散模型能够根据文本提示生成出色的图像,但存在从不安全提示生成不适合工作场合(NSFW)内容的风险。现有方法如提示过滤或概念遗忘,无法在对抗攻击中防御同时保持良性图像质量。本文提出了一种名为“扭曲嵌入空间(DES)”的新方法,通过创新的嵌入空间控制技术有效解决这些问题。DES通过文本编码器提取不安全嵌入,并将其向精心计算的安全嵌入区域转变,防止不安全内容的生成,同时再现原始安全嵌入。DES还通过将“裸露”嵌入与中性嵌入对齐,增强了对对抗攻击的稳健性。这些方法确保了强大的防御能力和高质量图像生成。此外,DES采用即插即用方式,无需推理延迟,便于部署。在不同类型的攻击场景,包括黑箱和白箱场景中,DES在防御能力和良性图像生成质量方面都表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的扩散模型能够根据文本提示生成图像,但存在生成NSFW内容的风险。
- 现有方法在对抗攻击中的防御能力有限,无法同时保持良性图像质量。
- 提出了一种新方法“扭曲嵌入空间(DES)”,通过控制嵌入空间来解决这一问题。
- DES通过文本编码器提取不安全嵌入,然后将其转变向安全嵌入区域,防止不安全内容的生成。
- DES能够增强对对抗攻击的稳健性,通过对齐“裸露”嵌入与中性嵌入实现。
- DES方法既具有强大的防御能力,又能保持高质量图像生成。
点此查看论文截图

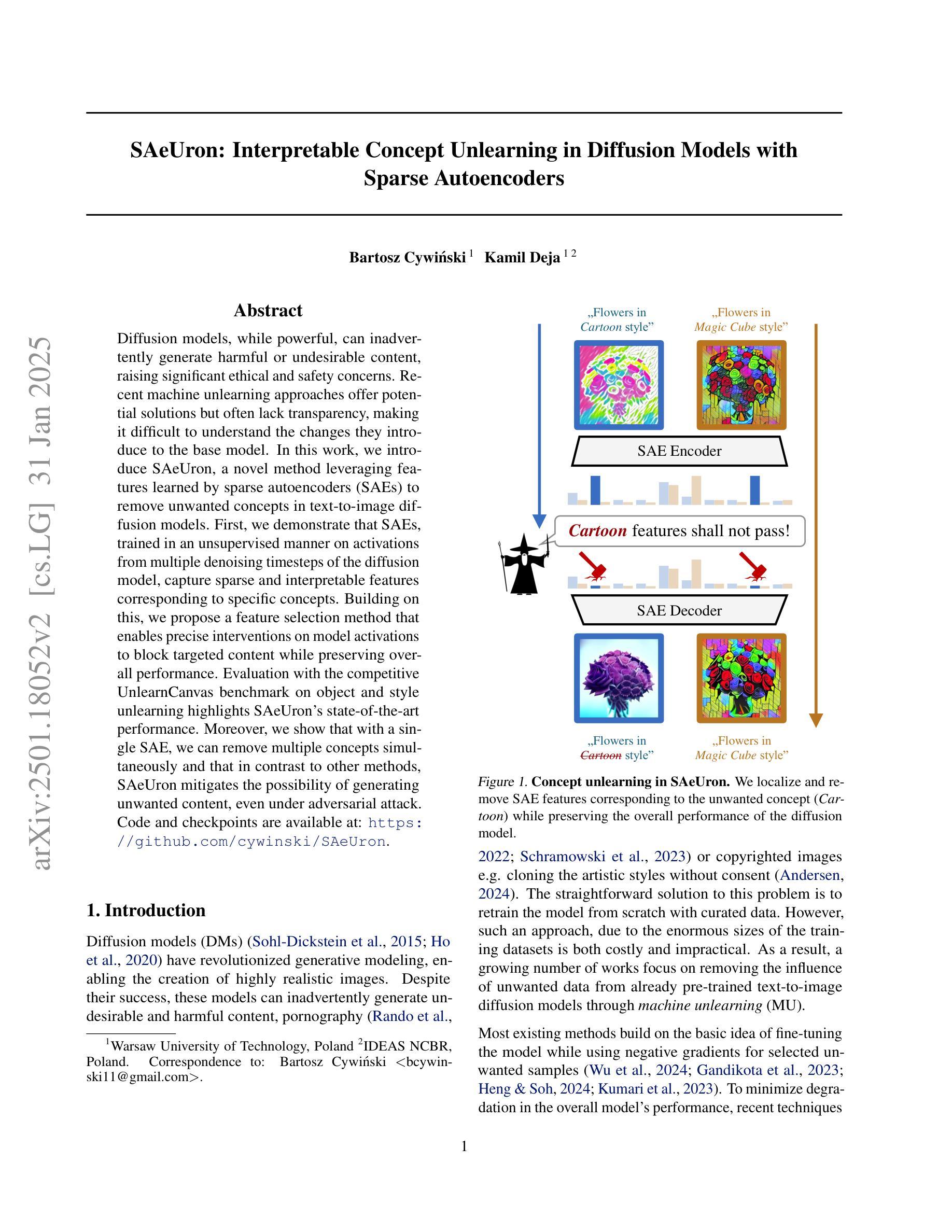
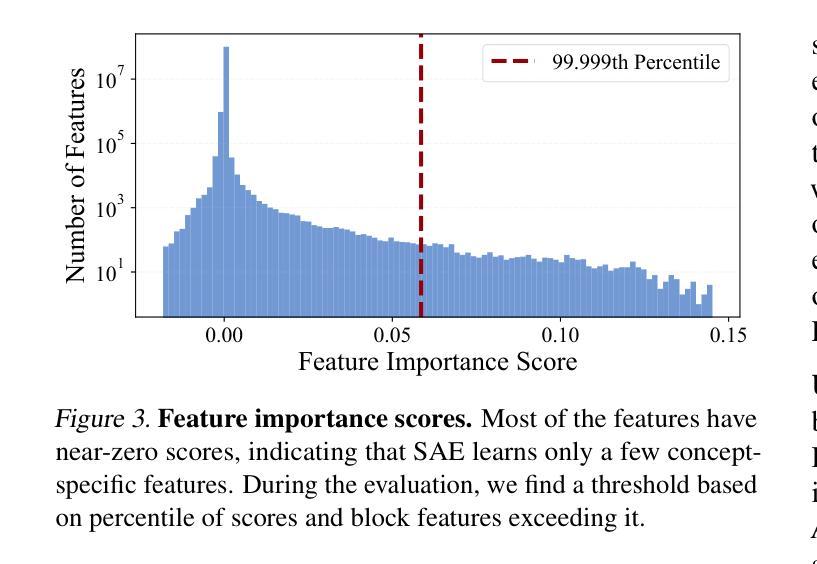
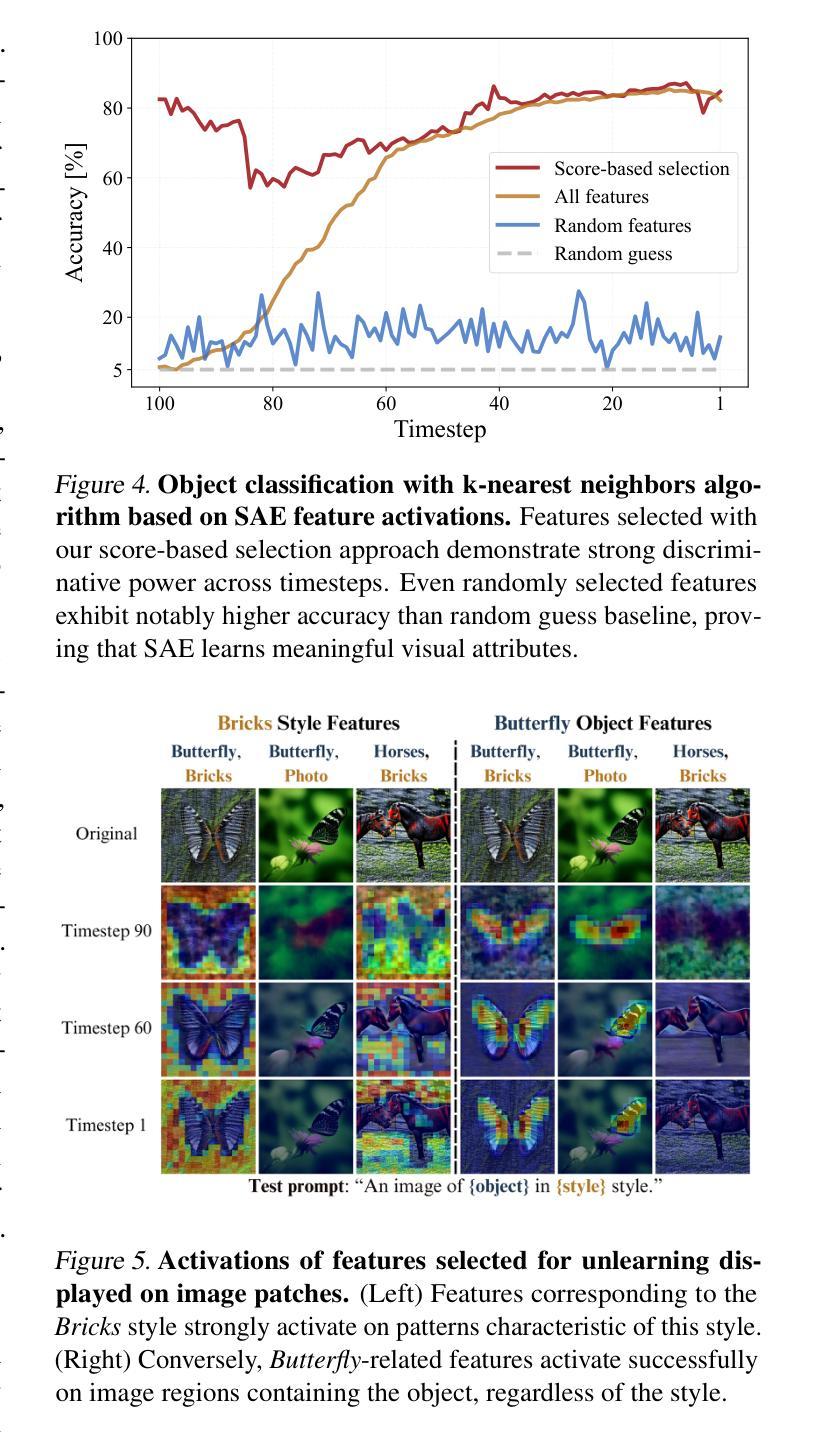
SAeUron: Interpretable Concept Unlearning in Diffusion Models with Sparse Autoencoders
Authors:Bartosz Cywiński, Kamil Deja
Diffusion models, while powerful, can inadvertently generate harmful or undesirable content, raising significant ethical and safety concerns. Recent machine unlearning approaches offer potential solutions but often lack transparency, making it difficult to understand the changes they introduce to the base model. In this work, we introduce SAeUron, a novel method leveraging features learned by sparse autoencoders (SAEs) to remove unwanted concepts in text-to-image diffusion models. First, we demonstrate that SAEs, trained in an unsupervised manner on activations from multiple denoising timesteps of the diffusion model, capture sparse and interpretable features corresponding to specific concepts. Building on this, we propose a feature selection method that enables precise interventions on model activations to block targeted content while preserving overall performance. Evaluation with the competitive UnlearnCanvas benchmark on object and style unlearning highlights SAeUron’s state-of-the-art performance. Moreover, we show that with a single SAE, we can remove multiple concepts simultaneously and that in contrast to other methods, SAeUron mitigates the possibility of generating unwanted content, even under adversarial attack. Code and checkpoints are available at: https://github.com/cywinski/SAeUron.
扩散模型虽然功能强大,但可能会不经意地生成有害或不良内容,引发严重的伦理和安全担忧。最近的机器非学习(unlearning)方法提供了潜在的解决方案,但通常缺乏透明度,使得难以了解它们对基础模型所做的改变。在这项工作中,我们介绍了SAeUron,这是一种利用稀疏自动编码器(Sparse Autoencoders,SAE)学习到的特征来去除文本到图像扩散模型中不需要的概念的新方法。首先,我们证明了在扩散模型的多个去噪时间步长的激活上采用无监督方式训练的SAE能够捕获对应于特定概念的稀疏和可解释的特征。在此基础上,我们提出了一种特征选择方法,通过对模型激活进行精确干预来阻止目标内容,同时保持整体性能。使用针对对象和风格非学习的竞争性UnlearnCanvas基准测试,突出了SAeUron的顶尖性能。此外,我们证明了一个SAE可以同时去除多个概念,而且与其他方法相比,SAeUron减轻了生成不需要内容的风险,即使在对抗性攻击下也是如此。代码和检查点可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/cywinski/SAeUron。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型虽然强大,但可能无意中生成有害或不可取的内容,引发严重的伦理和安全担忧。虽然最近的机器遗忘方法提供了潜在的解决方案,但它们通常缺乏透明度,难以了解它们对基础模型所做的改变。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种新的方法SAeUron,它利用稀疏自动编码器(SAE)的特征,去除文本到图像扩散模型中的不想要的概念。首先,我们证明,在扩散模型的多步去噪时间的激活上,以无监督的方式训练的SAE可以捕获对应特定概念稀疏且可解释的特征。在此基础上,我们提出了一种特征选择方法,可以对模型激活进行精确干预,以阻止目标内容,同时保持整体性能。在对象和风格遗忘方面,使用竞争性的UnlearnCanvas基准测试突出了SAeUron的先进性能。此外,我们证明了一个SAE可以同时去除多个概念,而且与其他方法相比,SAeUron减轻了生成不想要内容的可能性,即使在敌对攻击下也是如此。代码和检查点可用于:https://github.com/cywinski/SAeUron。
关键见解
- 扩散模型可能生成有害或不可取的内容,引发伦理和安全担忧。
- 最近的机器遗忘方法虽为解决此问题提供方案,但普遍缺乏透明度。
- SAeUron方法利用稀疏自动编码器的特征来去除扩散模型中的不想要的概念。
- SAE能够在无监督方式下捕获对应特定概念的稀疏且可解释的特征。
- SAeUron通过特征选择方法进行精确干预,能阻止目标内容生成同时保持模型性能。
- SAeUron在UnlearnCanvas基准测试中表现优异,展示其先进性能。
点此查看论文截图
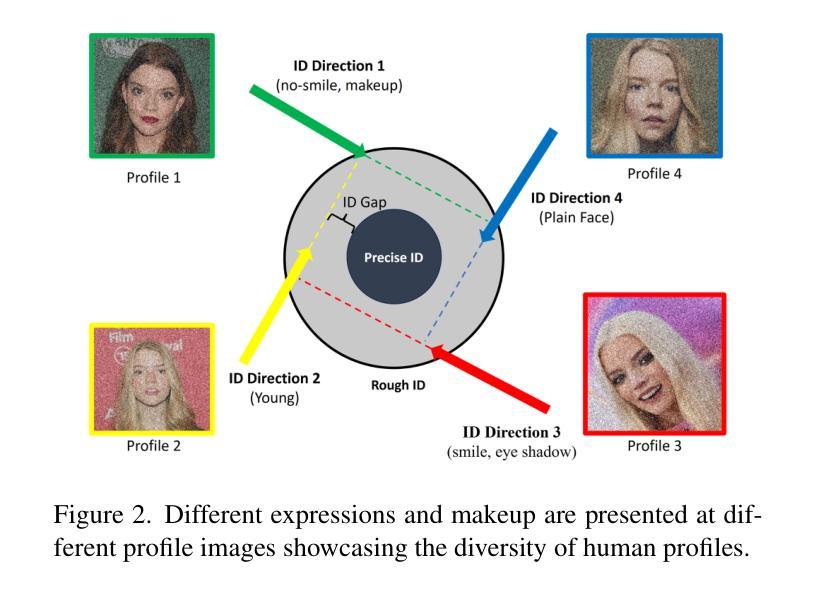
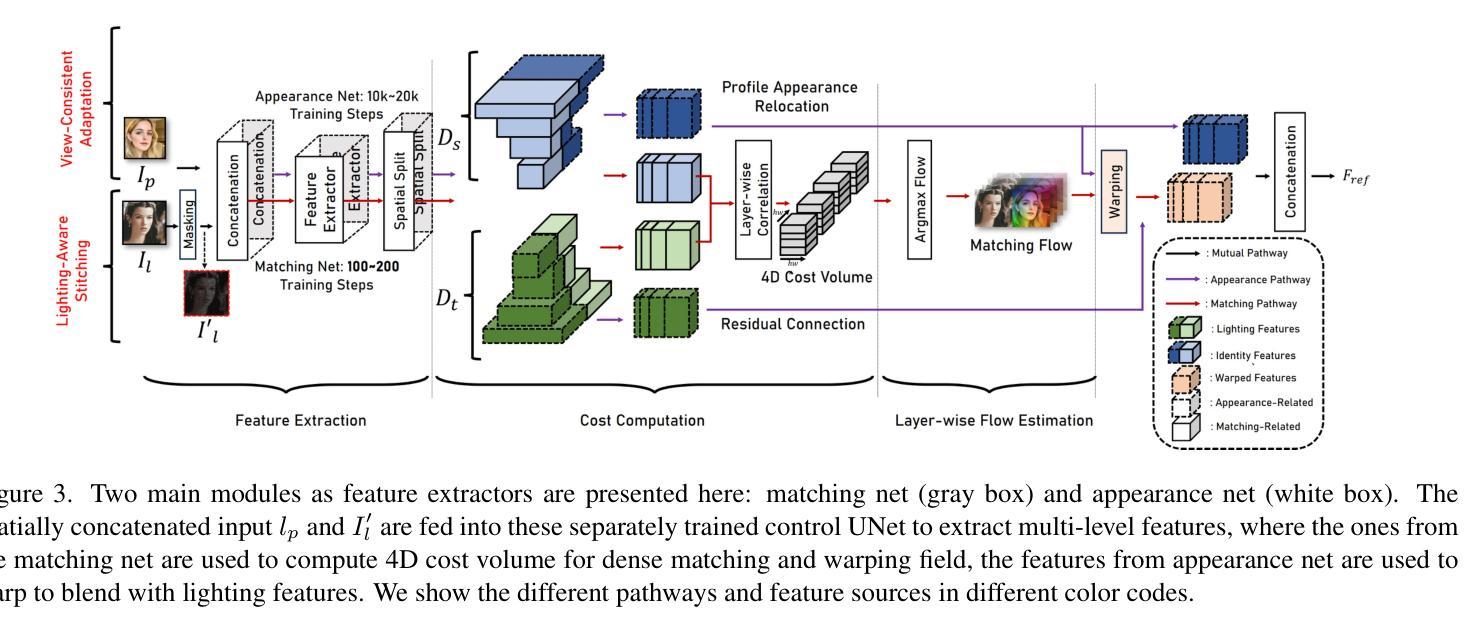
IC-Portrait: In-Context Matching for View-Consistent Personalized Portrait
Authors:Han Yang, Enis Simsar, Sotiris Anagnostidis, Yanlong Zang, Thomas Hofmann, Ziwei Liu
Existing diffusion models show great potential for identity-preserving generation. However, personalized portrait generation remains challenging due to the diversity in user profiles, including variations in appearance and lighting conditions. To address these challenges, we propose IC-Portrait, a novel framework designed to accurately encode individual identities for personalized portrait generation. Our key insight is that pre-trained diffusion models are fast learners (e.g.,100 ~ 200 steps) for in-context dense correspondence matching, which motivates the two major designs of our IC-Portrait framework. Specifically, we reformulate portrait generation into two sub-tasks: 1) Lighting-Aware Stitching: we find that masking a high proportion of the input image, e.g., 80%, yields a highly effective self-supervisory representation learning of reference image lighting. 2) View-Consistent Adaptation: we leverage a synthetic view-consistent profile dataset to learn the in-context correspondence. The reference profile can then be warped into arbitrary poses for strong spatial-aligned view conditioning. Coupling these two designs by simply concatenating latents to form ControlNet-like supervision and modeling, enables us to significantly enhance the identity preservation fidelity and stability. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that IC-Portrait consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods both quantitatively and qualitatively, with particularly notable improvements in visual qualities. Furthermore, IC-Portrait even demonstrates 3D-aware relighting capabilities.
现有的扩散模型在身份保留生成方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,由于用户资料的多样性,包括外观和光照条件的差异,个性化肖像生成仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了IC-Portrait,这是一个旨在准确编码个人身份用于个性化肖像生成的新型框架。我们的关键见解是,预训练的扩散模型对于上下文中的密集对应匹配是快速学习者(例如,100〜200步),这激发了我们IC-Portrait框架的两个主要设计。具体来说,我们将肖像生成重新定义为两个子任务:1)光照感知拼接:我们发现,遮挡输入图像的高比例部分(例如80%),可以有效地进行参考图像光照的自我监督表示学习。2)视图一致适应:我们利用合成视图一致的轮廓数据集来学习上下文中的对应关系。然后可以将参考轮廓变形为任意姿势,以实现强大的空间对齐视图条件。通过简单地连接潜在空间以形成ControlNet类似的监督和建模,可以大大增强身份保留的保真度和稳定性。大量评估表明,IC-Portrait在定量和定性上均优于现有先进技术,在视觉品质上有特别显著的改进。此外,IC-Portrait甚至展示了3D感知的重照明能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF technical report
Summary
本文提出了一种名为IC-Portrait的新型框架,用于解决个性化肖像生成中的身份保留挑战。该框架利用预训练的扩散模型,通过两个子任务:光照感知拼接和视图一致适应,实现准确编码个体身份。这种方法通过高度有效的自监督学习,以及对参考图像光照和视角一致性的适应,显著提高了身份保留的保真度和稳定性。IC-Portrait在视觉质量上表现出显著的提升,并且具有3D感知的重新照明能力。
Key Takeaways
- IC-Portrait框架利用预训练的扩散模型,针对个性化肖像生成中的身份保留挑战。
- 框架包括两个子任务:光照感知拼接和视图一致适应,以准确编码个体身份。
- 通过高度有效的自监督学习,实现参考图像光照的自我学习。
- 利用合成视图一致的轮廓数据集进行上下文对应学习,使参考轮廓可以变形为任意姿态,实现空间对齐视图条件。
- 简单的潜在连接方法(如ControlNet)显著提高身份保留的保真度和稳定性。
- IC-Portrait在视觉质量上表现出显著的提升,并具备3D感知的重新照明能力。
点此查看论文截图



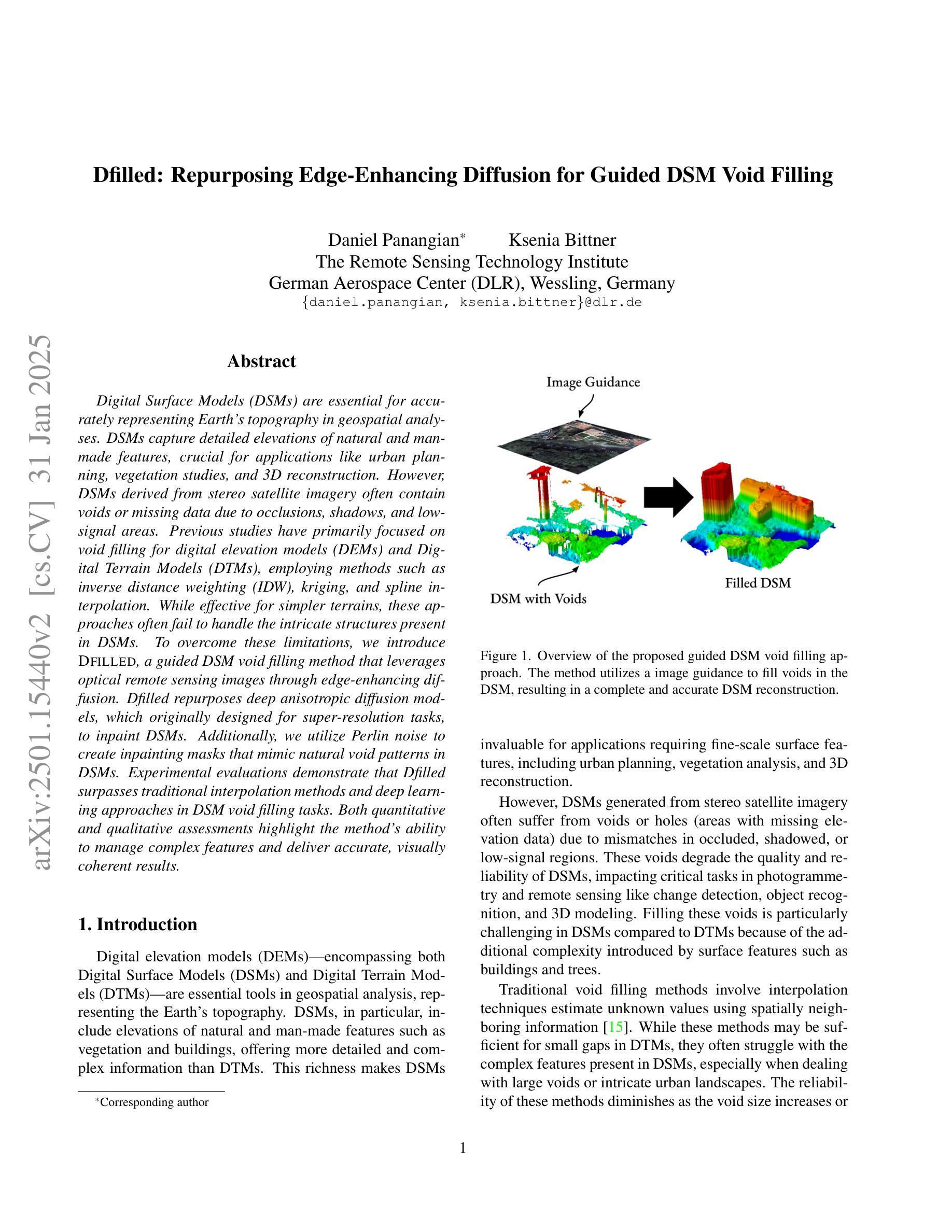
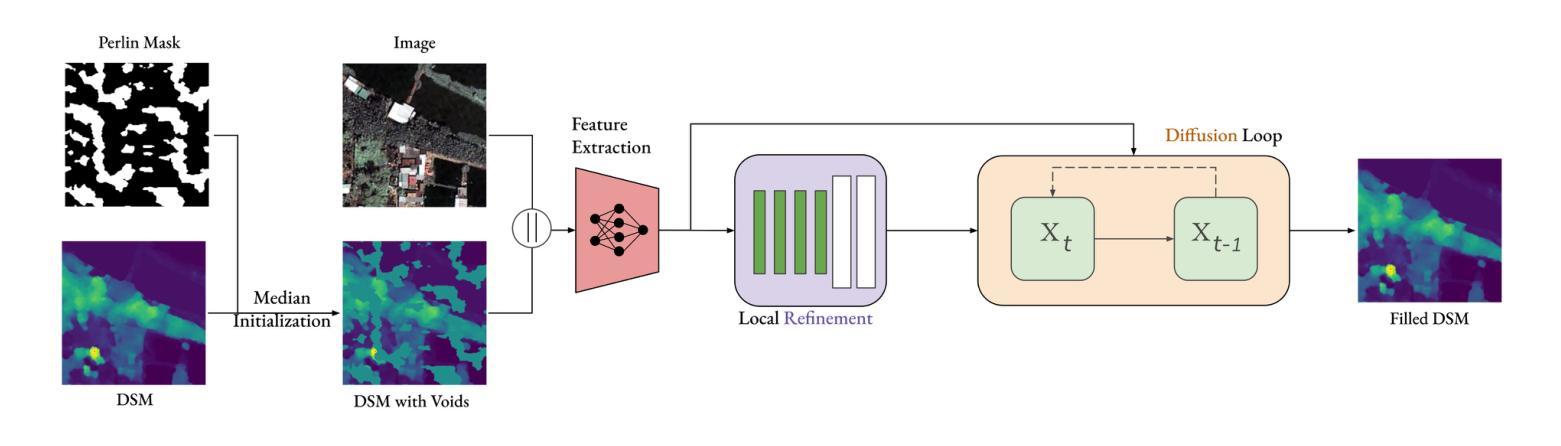
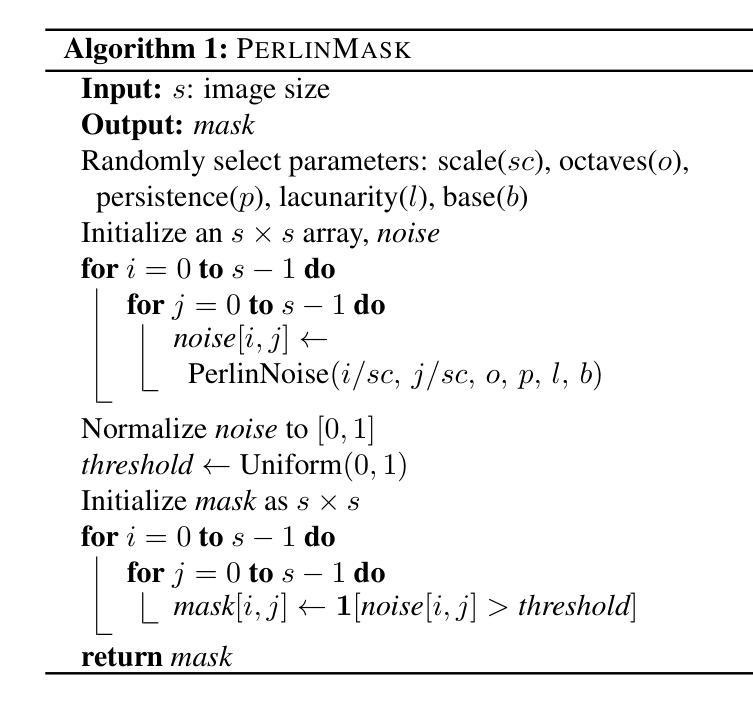
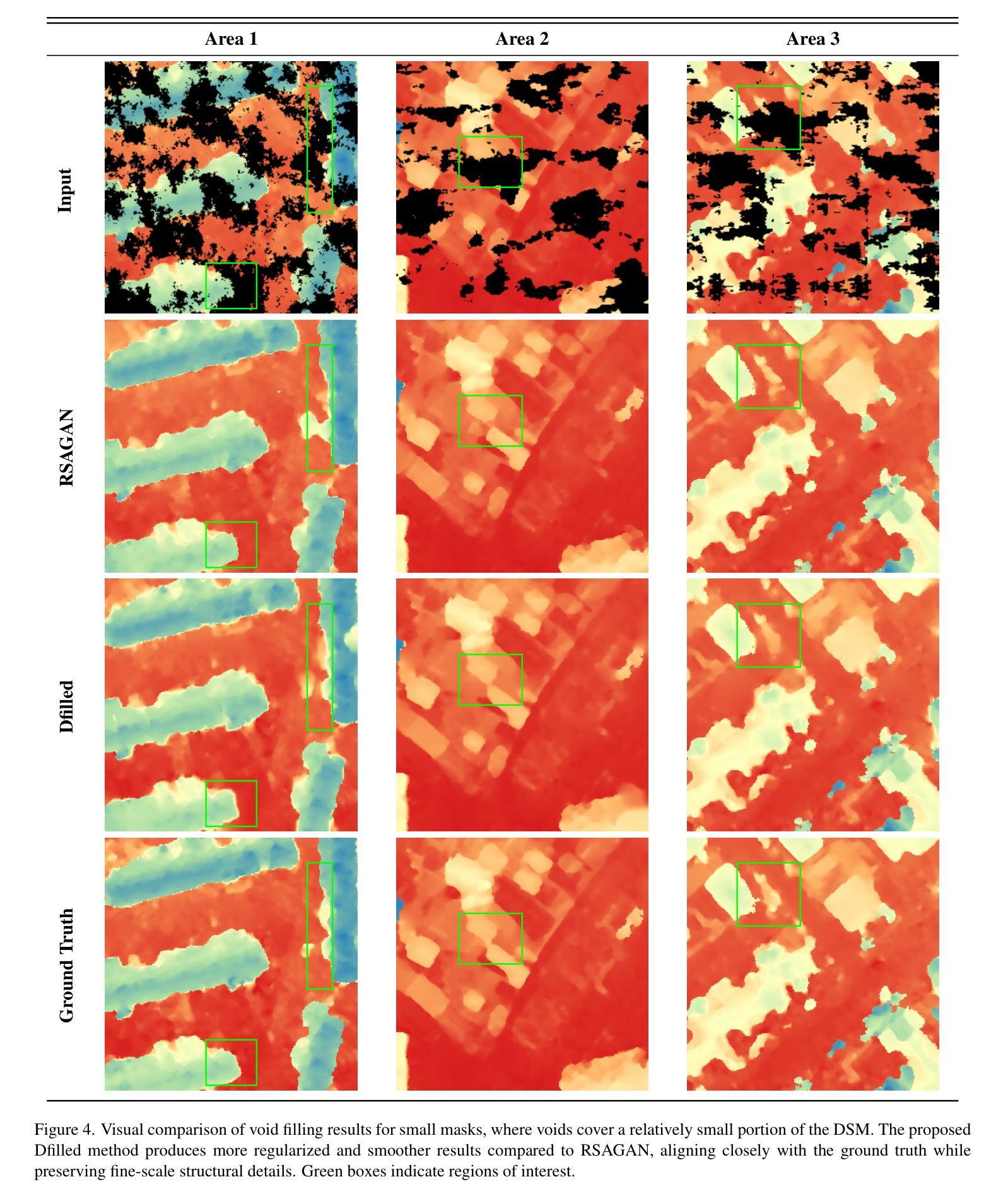
Dfilled: Repurposing Edge-Enhancing Diffusion for Guided DSM Void Filling
Authors:Daniel Panangian, Ksenia Bittner
Digital Surface Models (DSMs) are essential for accurately representing Earth’s topography in geospatial analyses. DSMs capture detailed elevations of natural and manmade features, crucial for applications like urban planning, vegetation studies, and 3D reconstruction. However, DSMs derived from stereo satellite imagery often contain voids or missing data due to occlusions, shadows, and lowsignal areas. Previous studies have primarily focused on void filling for digital elevation models (DEMs) and Digital Terrain Models (DTMs), employing methods such as inverse distance weighting (IDW), kriging, and spline interpolation. While effective for simpler terrains, these approaches often fail to handle the intricate structures present in DSMs. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Dfilled, a guided DSM void filling method that leverages optical remote sensing images through edge-enhancing diffusion. Dfilled repurposes deep anisotropic diffusion models, which originally designed for super-resolution tasks, to inpaint DSMs. Additionally, we utilize Perlin noise to create inpainting masks that mimic natural void patterns in DSMs. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that Dfilled surpasses traditional interpolation methods and deep learning approaches in DSM void filling tasks. Both quantitative and qualitative assessments highlight the method’s ability to manage complex features and deliver accurate, visually coherent results.
数字表面模型(DSMs)在地理空间分析中准确表示地球地形方面起着至关重要的作用。DSM捕捉自然和人为特征的详细高程,对于城市规划、植被研究和3D重建等应用至关重要。然而,从立体卫星影像派生的DSMs通常由于遮挡、阴影和低信号区域而包含空洞或缺失数据。先前的研究主要集中在数字高程模型(DEM)和数字地形模型(DTM)的空洞填充上,采用的方法包括反距离加权(IDW)、克里金法和样条插值。这些方法在简单地形上虽然有效,但往往难以处理DSM中存在的复杂结构。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了Dfilled,这是一种有指导的DSM空洞填充方法,它通过边缘增强扩散利用光学遥感图像。Dfilled重新设计了原本用于超分辨率任务的深度各向异性扩散模型,用于填充DSM。此外,我们还使用Perlin噪声生成填充掩膜,以模仿DSM中的自然空洞模式。实验评估表明,在DSM空洞填充任务中,Dfilled超越了传统的插值方法和深度学习方法。定量和定性评估都突出了该方法管理复杂特征的能力,并能提供准确、视觉连贯的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW)
Summary:
数字表面模型(DSMs)在地理空间分析中准确表示地球地形至关重要。DSMs捕捉自然和人造特征的详细高程,对于城市规划、植被研究和3D重建等应用至关重要。然而,从立体卫星影像派生的DSMs通常由于遮挡、阴影和低信号区域而包含空洞或缺失数据。以往的研究主要集中在数字高程模型(DEMs)和数字地形模型(DTMs)的空洞填充上,采用反距离加权(IDW)、克里格和样条插值等方法。这些方法对于简单地形有效,但难以处理DSM中的复杂结构。为解决这些问题,我们引入了Dfilled,一种利用边缘增强扩散引导DSM空洞填充的方法。Dfilled利用光学遥感图像,并重新设计深度各向异性扩散模型以填充DSM。此外,我们还利用Perlin噪声创建模仿DSM中自然空洞模式的插值掩模。实验评估表明,Dfilled在DSM空洞填充任务上超越了传统插值方法和深度学习方法。定量和定性评估均证明该方法能够管理复杂特征并提供准确、视觉连贯的结果。
Key Takeaways:
- 数字表面模型(DSMs)在地理空间分析中非常重要,能准确表示地球地形特征。
- 从立体卫星影像生成的DSMs常含有空洞或缺失数据,这会影响其准确性。
- 传统方法如反距离加权(IDW)、克里格和样条插值在简单地形中有效,但难以处理复杂的DSM结构。
- 引入的Dfilled方法利用光学遥感图像和深度各向异性扩散模型进行DSM空洞填充。
- Dfilled使用Perlin噪声来模仿DSM中的自然空洞模式,提高了填充的准确度。
- 实验评估显示,Dfilled在DSM空洞填充任务上的表现优于传统方法和深度学习。
点此查看论文截图

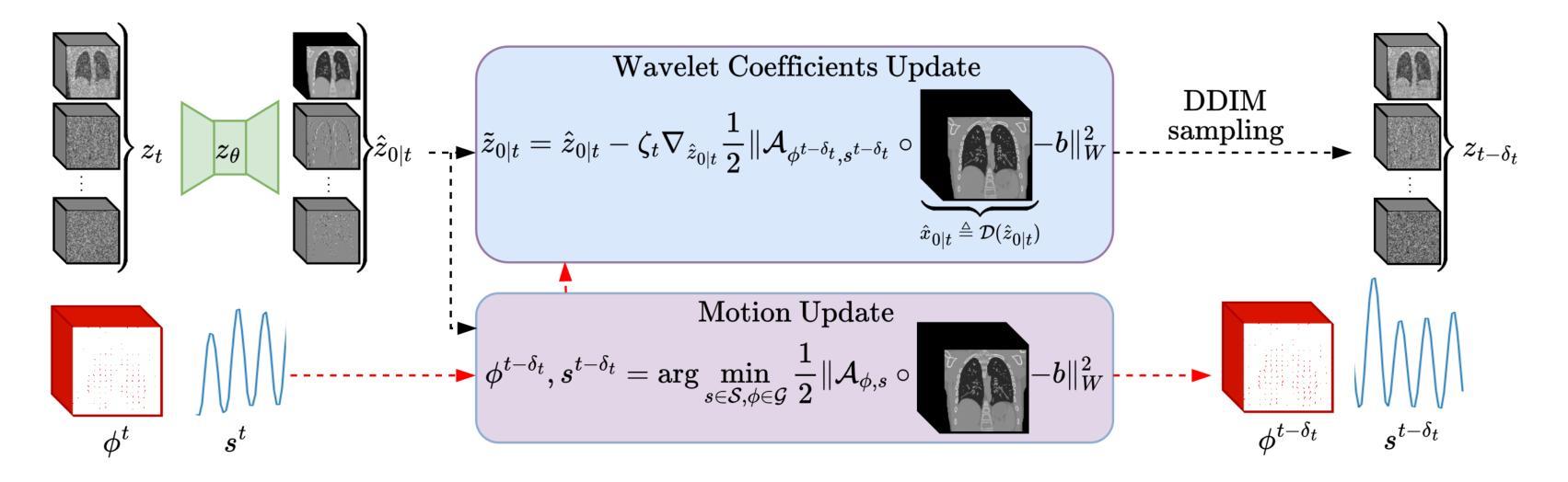
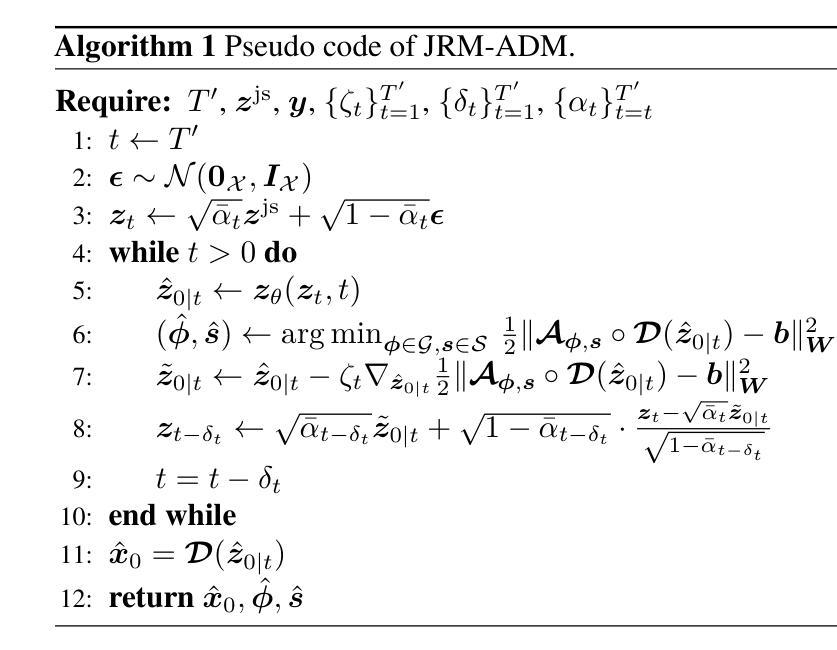
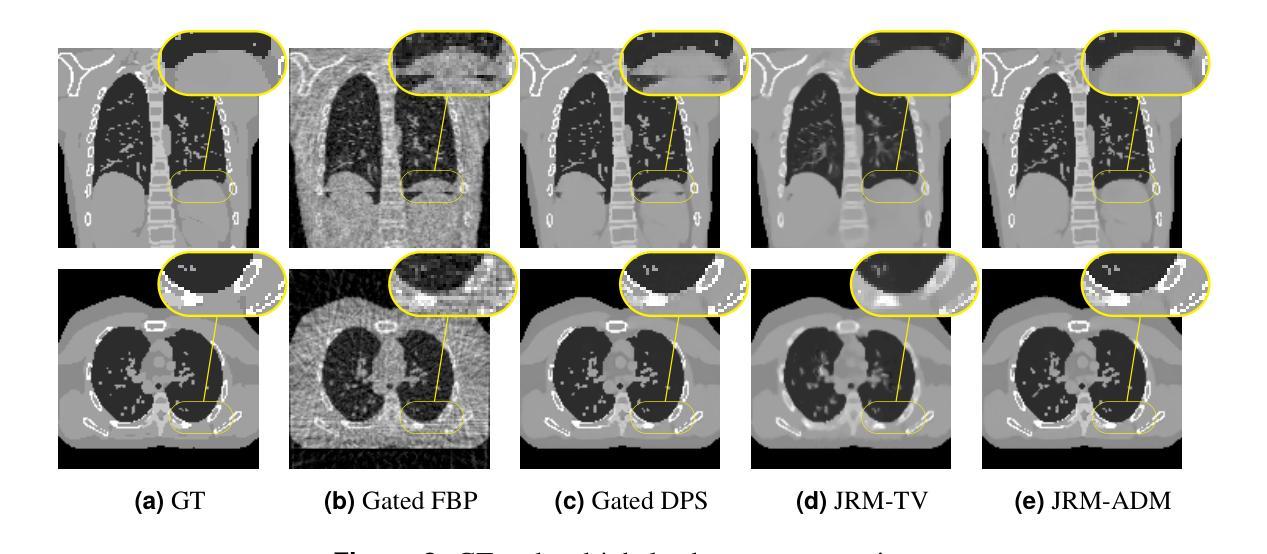
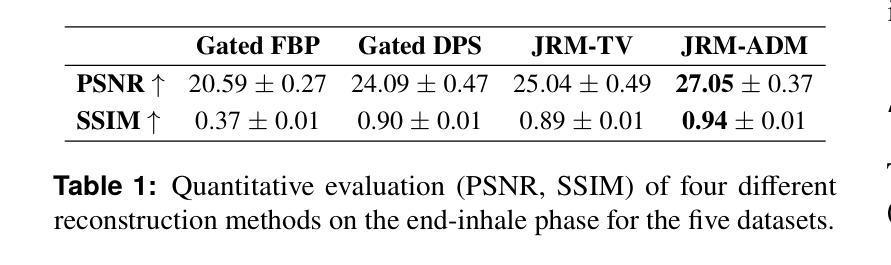
Solving Blind Inverse Problems: Adaptive Diffusion Models for Motion-corrected Sparse-view 4DCT
Authors:Antoine De Paepe, Alexandre Bousse, Clémentine Phung-Ngoc, Dimitris Visvikis
Four-dimensional computed tomography (4DCT) is essential for medical imaging applications like radiotherapy, which demand precise respiratory motion representation. Traditional methods for reconstructing 4DCT data suffer from artifacts and noise, especially in sparse-view, low-dose contexts. Motion-corrected (MC) reconstruction is a blind inverse problem that we propose to solve with a novel diffusion model (DM) framework that calibrates an adaptive unknown forward model for motion correction. Furthermore, we used a wavelet diffusion model (WDM) to address computational cost and memory usage. By leveraging the prior probability distribution function (PDF) from the DMs, we enhance the joint reconstruction and motion estimation (JRM) process, improving image quality and preserving resolution. Experiments on extended cardiac-torso (XCAT) phantom data demonstrate that our method outperforms existing techniques, yielding artifact-free, high-resolution reconstructions even under irregular breathing conditions. These results showcase the potential of combining DMs with motion correction to advance sparse-view 4DCT imaging.
四维计算机断层扫描(4DCT)在医学成像应用(如放射治疗)中至关重要,这要求精确表示呼吸运动。传统的重建4DCT数据的方法在稀疏视角、低剂量环境下会出现伪影和噪声。运动校正(MC)重建是一个盲逆问题,我们建议使用一种新型扩散模型(DM)框架来解决这个问题,该框架可以校准用于运动校正的自适应未知前向模型。此外,我们还使用小波扩散模型(WDM)来解决计算成本和内存使用问题。通过利用扩散模型的先验概率分布函数(PDF),我们增强了联合重建和运动估计(JRM)过程,提高了图像质量并保持了分辨率。在扩展的心脏体模(XCAT)数据上的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有技术,即使在不规则呼吸条件下也能产生无伪影、高分辨率的重建结果。这些结果展示了将扩散模型与运动校正相结合在稀疏视角的4DCT成像中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 2 figures, 1 table
Summary
本文介绍了四维计算机断层扫描(4DCT)在医疗成像应用中的重要性,特别是在放射治疗领域中对精确呼吸运动表示的需求。针对传统重建4DCT数据的方法存在的伪影和噪声问题,特别是在稀疏视角和低剂量情况下,提出了一种基于扩散模型(DM)框架的运动校正(MC)重建方法。利用小波扩散模型(WDM)解决计算成本和内存使用问题,通过利用扩散模型的先验概率分布函数(PDF)来增强联合重建和运动估计(JRM)过程,从而提高图像质量和保持分辨率。在XCAT Phantom数据上的实验表明,该方法优于现有技术,即使在不规则呼吸条件下也能实现无伪影、高分辨率重建。这些结果展示了将扩散模型与运动校正相结合在稀疏视角4DCT成像中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 四维计算机断层扫描(4DCT)在医疗成像中至关重要,特别是在精确呼吸运动表示的放射治疗领域。
- 传统重建4DCT数据的方法在稀疏视角和低剂量情况下存在伪影和噪声问题。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型(DM)框架的运动校正(MC)重建方法来解决这一问题。
- 利用小波扩散模型(WDM)以提高计算效率和降低内存使用。
- 通过利用扩散模型的先验概率分布函数(PDF)来增强联合重建和运动估计(JRM)过程。
- 在XCAT Phantom数据上的实验表明,该方法优于现有技术,实现了无伪影、高分辨率重建。
点此查看论文截图

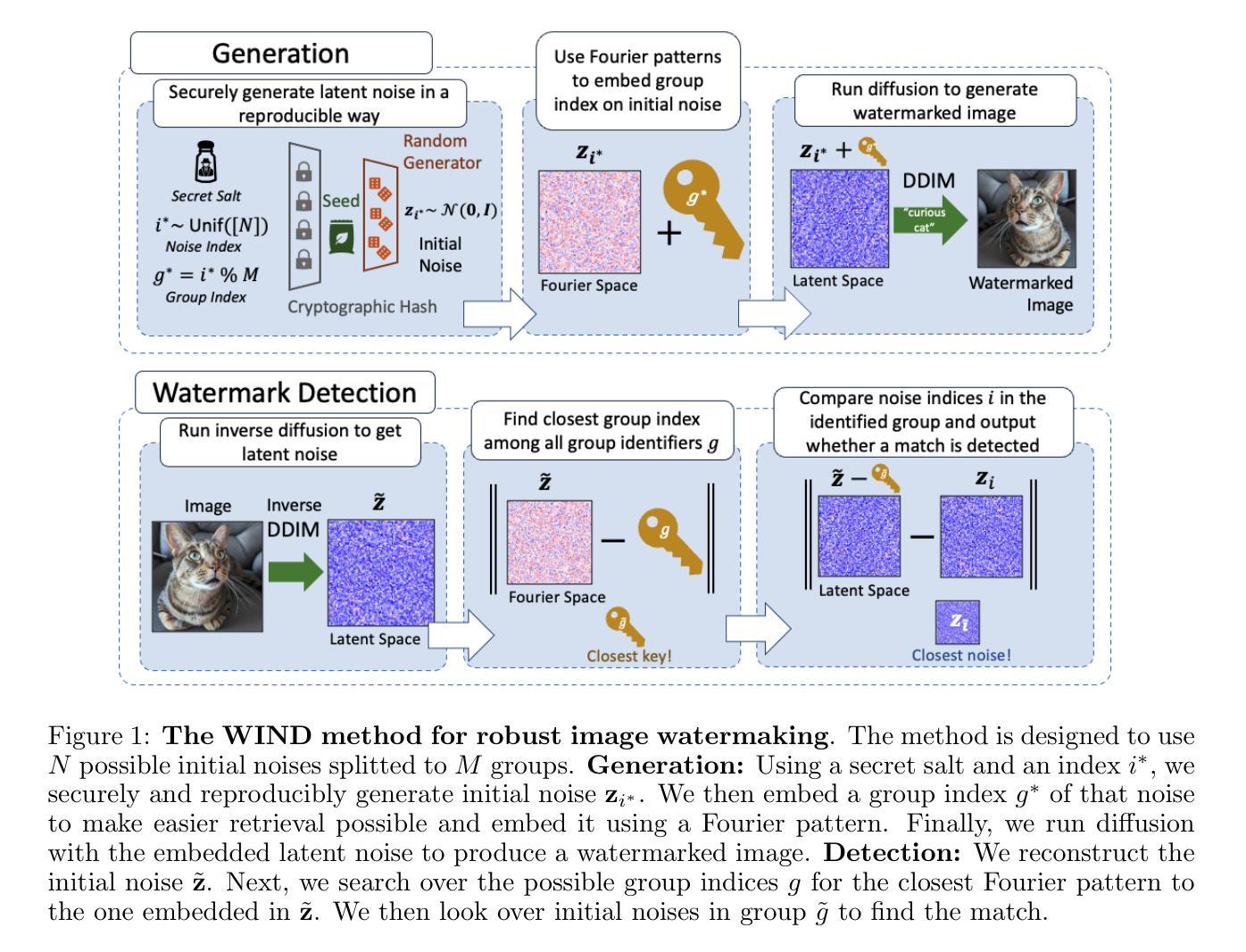
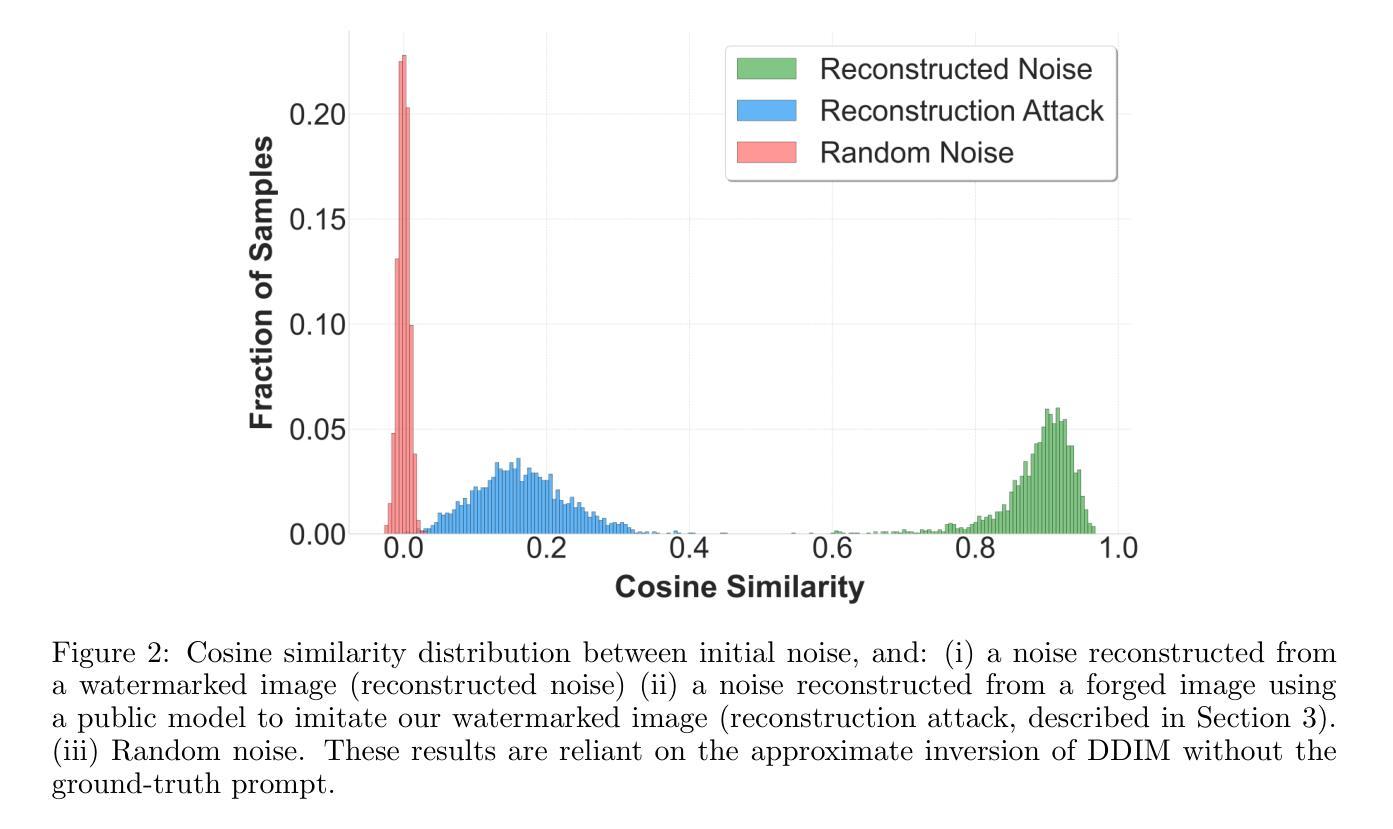
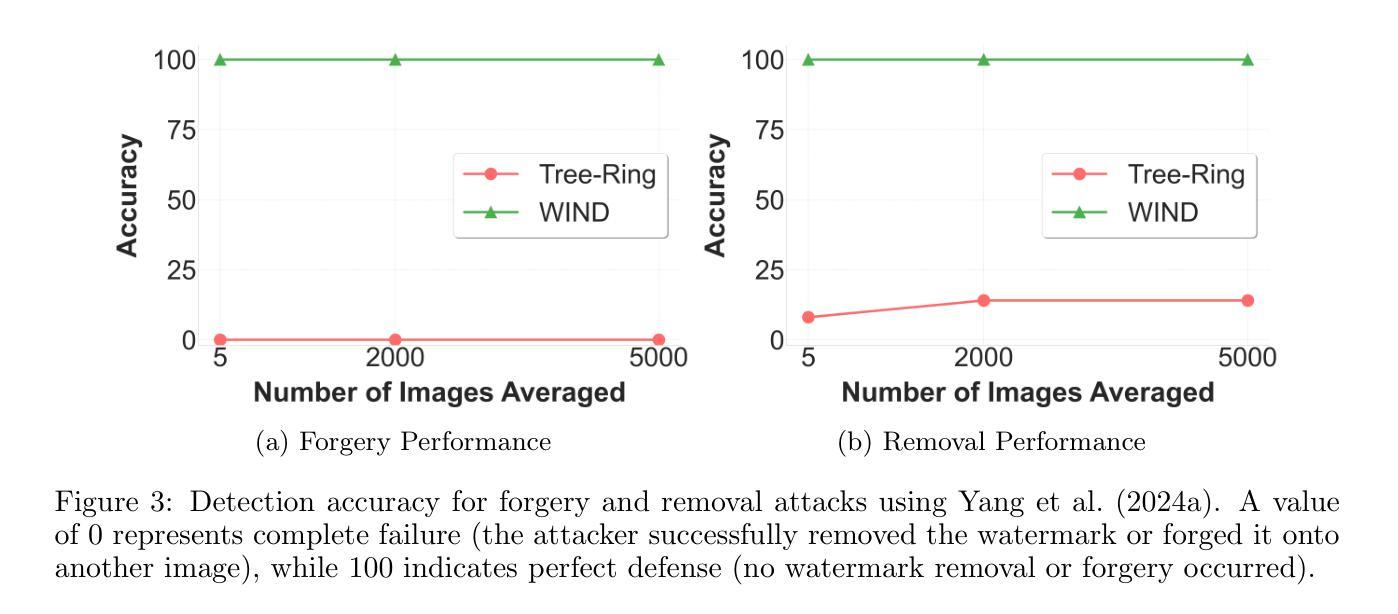
Hidden in the Noise: Two-Stage Robust Watermarking for Images
Authors:Kasra Arabi, Benjamin Feuer, R. Teal Witter, Chinmay Hegde, Niv Cohen
As the quality of image generators continues to improve, deepfakes become a topic of considerable societal debate. Image watermarking allows responsible model owners to detect and label their AI-generated content, which can mitigate the harm. Yet, current state-of-the-art methods in image watermarking remain vulnerable to forgery and removal attacks. This vulnerability occurs in part because watermarks distort the distribution of generated images, unintentionally revealing information about the watermarking techniques. In this work, we first demonstrate a distortion-free watermarking method for images, based on a diffusion model’s initial noise. However, detecting the watermark requires comparing the initial noise reconstructed for an image to all previously used initial noises. To mitigate these issues, we propose a two-stage watermarking framework for efficient detection. During generation, we augment the initial noise with generated Fourier patterns to embed information about the group of initial noises we used. For detection, we (i) retrieve the relevant group of noises, and (ii) search within the given group for an initial noise that might match our image. This watermarking approach achieves state-of-the-art robustness to forgery and removal against a large battery of attacks.
随着图像生成器的质量不断提高,深度伪造成为社会热议的话题。图像水印允许负责任的模型所有者检测和标记其AI生成的内容,这可以减轻损害。然而,当前图像水印的最先进方法仍然容易受到伪造和移除攻击。这种脆弱性部分是因为水印会扭曲生成图像的分布,从而无意间泄露有关水印技术的信息。在这项工作中,我们首先展示了一种基于扩散模型的初始噪声的无损水印方法。然而,检测水印需要比较图像的重建初始噪声与所有之前使用的初始噪声。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于高效检测的两阶段水印框架。在生成过程中,我们通过使用生成的傅立叶模式增强初始噪声,以嵌入有关我们所用初始噪声组的信息。对于检测,我们(i)检索相关的噪声组,(ii)在给定组内搜索可能与我们的图像匹配的初始噪声。这种水印方法实现了对一系列攻击的高度稳健性和防伪性,且在去除攻击方面达到了最先进水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了图像水印技术在防止深度伪造图像方面的应用及其面临的挑战。针对当前图像水印技术易被篡改和移除的问题,提出了一种基于扩散模型初始噪声的无损水印方法。该方法通过两个阶段实现高效检测,第一阶段在生成时增强初始噪声嵌入信息,第二阶段在检测时搜索匹配的初始噪声。该方法实现了对大量攻击的鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像生成器质量的提升引发了深度伪造的社会议题,图像水印技术允许模型所有者对其AI生成内容进行检测和标记,减轻潜在危害。
- 当前图像水印技术存在易被篡改和移除的缺陷,部分原因是水印会干扰生成图像的分布,泄露水印技术信息。
- 基于扩散模型的初始噪声,提出了一种无损水印方法,该方法在生成图像时利用扩散模型的特性嵌入水印信息。
- 水印检测需要比较图像的初始噪声与所有已使用的初始噪声,因此提出了一个两阶段的水印检测框架以提高效率。
- 在第一阶段,通过生成的傅里叶模式嵌入关于使用的初始噪声组的信息。
- 在第二阶段,首先检索相关的噪声组,然后在给定的噪声组内搜索可能与图像匹配的初始噪声。
点此查看论文截图


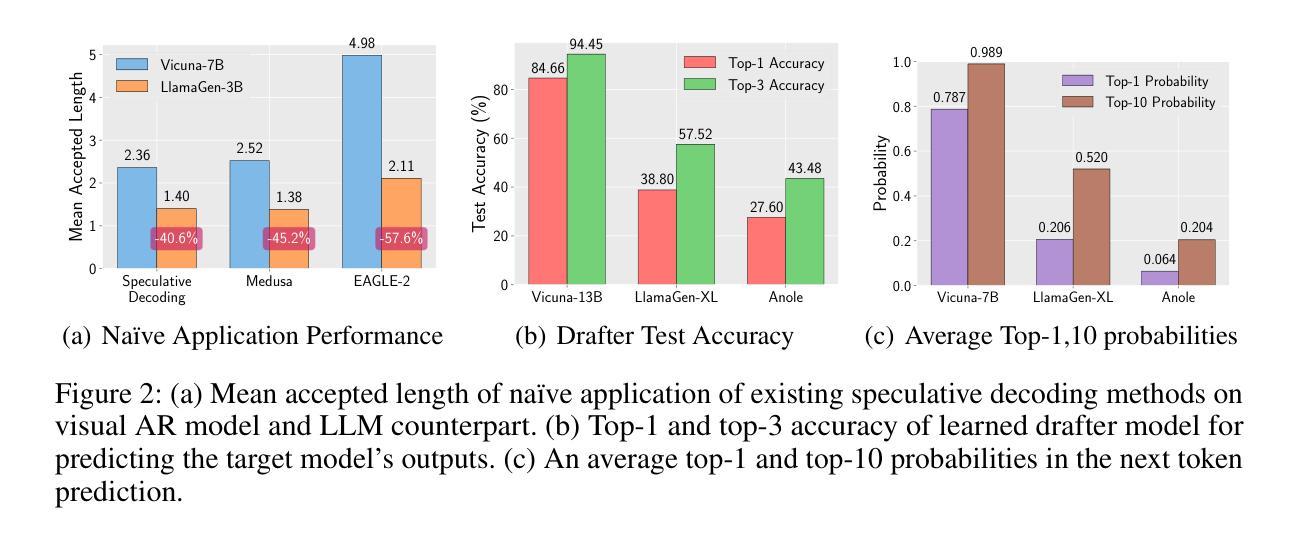
LANTERN: Accelerating Visual Autoregressive Models with Relaxed Speculative Decoding
Authors:Doohyuk Jang, Sihwan Park, June Yong Yang, Yeonsung Jung, Jihun Yun, Souvik Kundu, Sung-Yub Kim, Eunho Yang
Auto-Regressive (AR) models have recently gained prominence in image generation, often matching or even surpassing the performance of diffusion models. However, one major limitation of AR models is their sequential nature, which processes tokens one at a time, slowing down generation compared to models like GANs or diffusion-based methods that operate more efficiently. While speculative decoding has proven effective for accelerating LLMs by generating multiple tokens in a single forward, its application in visual AR models remains largely unexplored. In this work, we identify a challenge in this setting, which we term \textit{token selection ambiguity}, wherein visual AR models frequently assign uniformly low probabilities to tokens, hampering the performance of speculative decoding. To overcome this challenge, we propose a relaxed acceptance condition referred to as LANTERN that leverages the interchangeability of tokens in latent space. This relaxation restores the effectiveness of speculative decoding in visual AR models by enabling more flexible use of candidate tokens that would otherwise be prematurely rejected. Furthermore, by incorporating a total variation distance bound, we ensure that these speed gains are achieved without significantly compromising image quality or semantic coherence. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of our method in providing a substantial speed-up over speculative decoding. In specific, compared to a na"ive application of the state-of-the-art speculative decoding, LANTERN increases speed-ups by $\mathbf{1.75}\times$ and $\mathbf{1.82}\times$, as compared to greedy decoding and random sampling, respectively, when applied to LlamaGen, a contemporary visual AR model.
自回归(AR)模型最近在图像生成领域获得了显著的重要性,其性能经常与扩散模型相匹配甚至超越。然而,AR模型的一个主要局限性是它们的顺序性,即一次只处理一个标记,导致与生成对抗网络(GAN)或基于扩散的方法等更高效的模型相比,生成速度较慢。尽管猜测解码已经证明可以通过一次前向生成多个标记来加速大型语言模型,但其在视觉AR模型中的应用仍然未被广泛探索。在这项工作中,我们确定了在这种情况下的一项挑战,我们称之为“标记选择歧义”,其中视觉AR模型经常为标记分配均匀且低的概率,阻碍了猜测解码的性能。为了克服这一挑战,我们提出了一种称为LANTERN的放宽接受条件的方法,该方法利用潜在空间中标记的可互换性。这种放松恢复了猜测解码在视觉AR模型中的有效性,通过更灵活地利用候选标记(否则会被过早拒绝)。此外,通过引入总变异距离界限,我们确保这些速度提升是在不损害图像质量或语义连贯性的情况下实现的。实验结果表明我们的方法对于提供猜测解码的实质性加速非常有效。具体来说,与对最先进的猜测解码的朴素应用相比,LANTERN在应用于当代视觉AR模型LlamaGen时,与贪心解码和随机采样相比,分别将速度提高了1.75倍和1.82倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 13 figures
Summary
近期自回归(AR)模型在图像生成领域受到广泛关注,其性能甚至可与扩散模型相媲美。然而,AR模型存在顺序处理标记的局限性,导致生成速度较慢。本研究中,我们遇到了一种名为“标记选择模糊性”的挑战,视觉AR模型经常为标记分配均匀的低概率,阻碍了解码速度的提升。为了克服这一挑战,我们提出了一种称为LANTERN的宽松接受条件,利用潜在空间中标记的可互换性。通过引入总变异距离边界,确保了这些加速并不会损害图像质量或语义连贯性。实验证明,该方法在加速解码方面效果显著。与当前最佳策略相比,LANTERN在应用于视觉AR模型LlamaGen时,速度提升分别达到1.75倍和1.82倍。此方法的实施显著提升了视觉AR模型的性能与效率。
**Key Takeaways**
1. AR模型在图像生成中表现出良好的性能。然而,由于其顺序处理标记的特性,其生成速度较慢。这限制了其在某些应用中的使用效率。
2. 在视觉AR模型中出现了“标记选择模糊性”的挑战,即模型经常为标记分配均匀的低概率,导致解码效率低下。这成为提高解码速度的关键难题。为应对这一问题需要一种新型的解决方案来提高模型的效率并降低对解算资源的消耗需求。这个问题的解决将成为推动图像生成技术发展的重要一步。对于该问题尚未有充分的探索与研究目前对于如何解决这一问题的研究还处于初级阶段对于未来可能出现的研究方向具有极高的潜力以及探讨空间巨大的实用价值意味着这项研究的进步有望大幅提升整个图像生成领域的性能并带动其向前发展对于视觉AR模型的性能提升具有深远影响未来的研究需要进一步探索和改进该领域的相关技术以实现更高效的图像生成这也是该技术研究的深远意义所在希望通过进一步研究能够帮助优化标记选择和决策机制同时充分研究各个性能指标以期优化图像生成技术并推动相关领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图



Zero-Shot Video Restoration and Enhancement Using Pre-Trained Image Diffusion Model
Authors:Cong Cao, Huanjing Yue, Xin Liu, Jingyu Yang
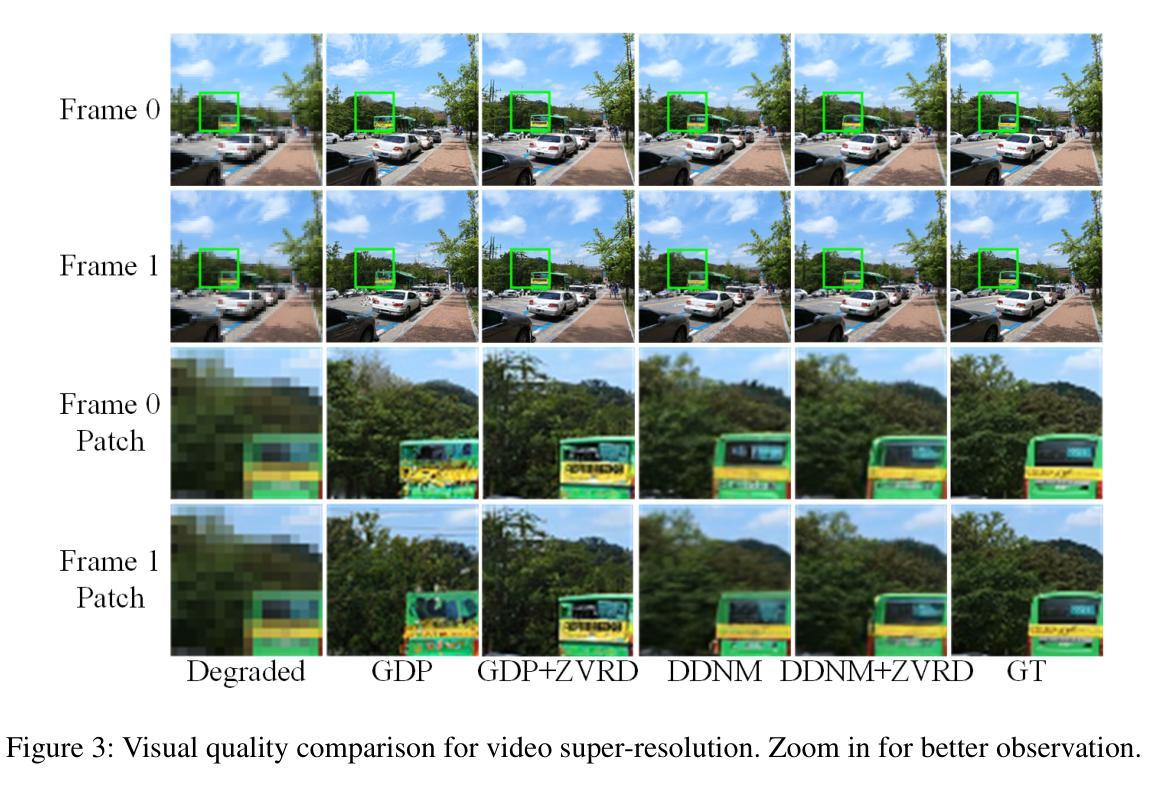
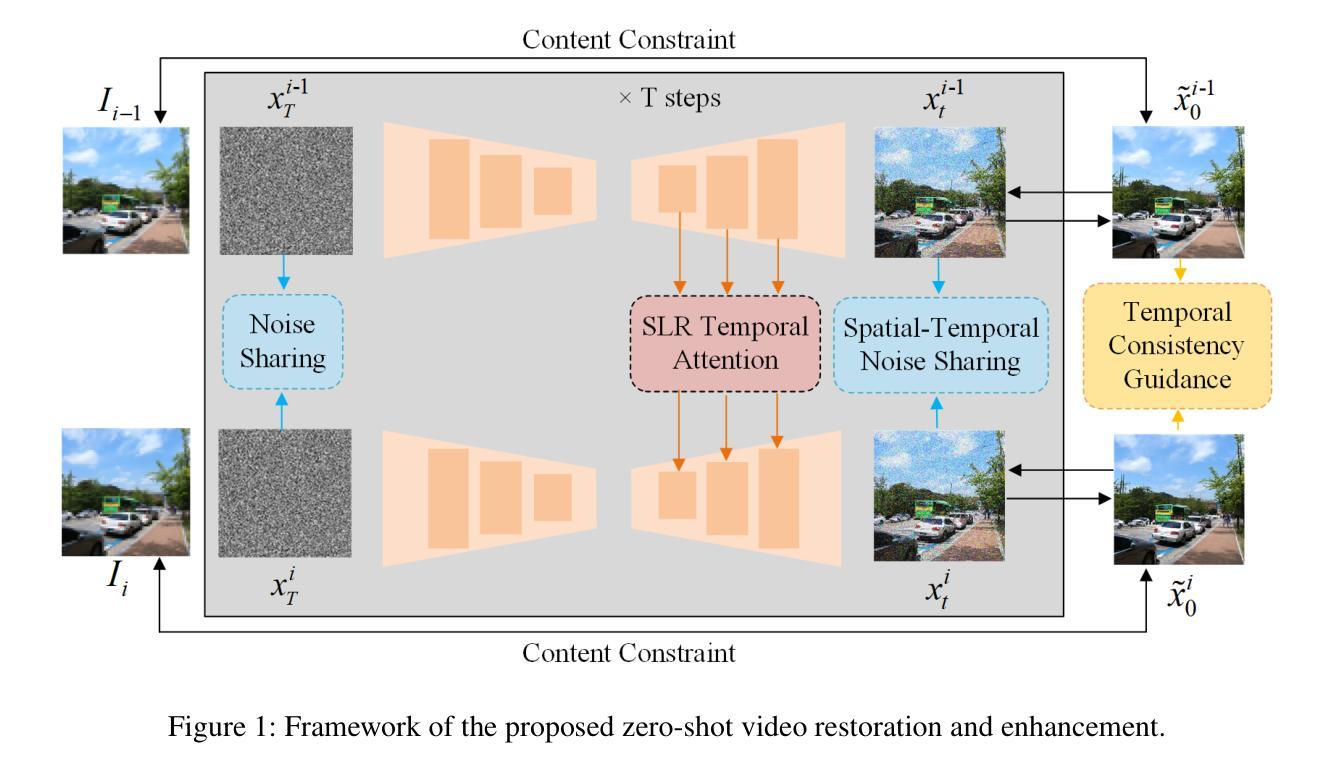
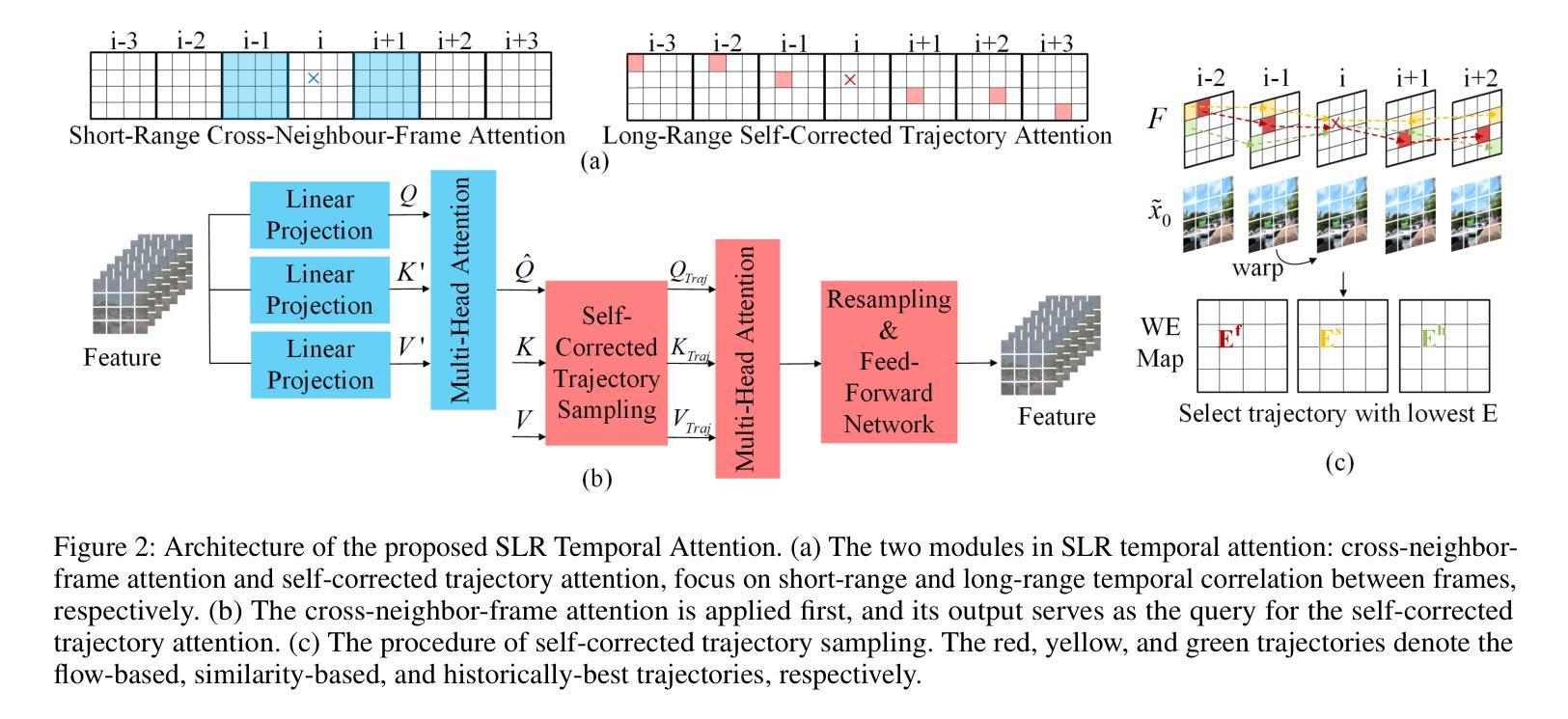
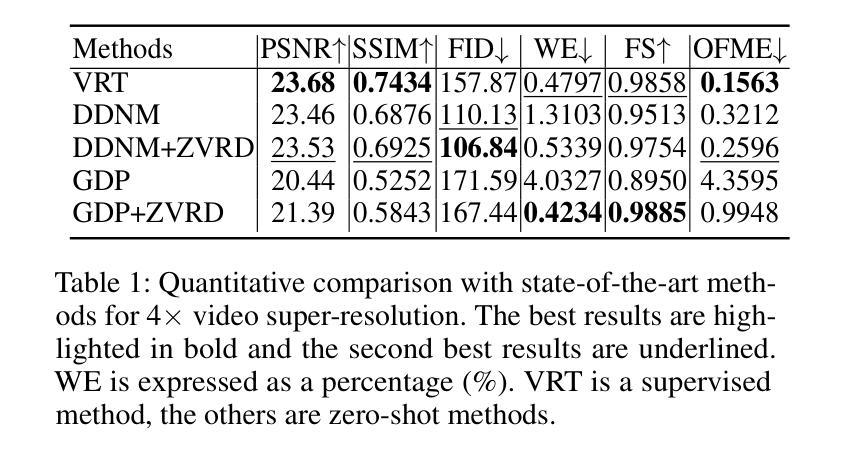
Diffusion-based zero-shot image restoration and enhancement models have achieved great success in various tasks of image restoration and enhancement. However, directly applying them to video restoration and enhancement results in severe temporal flickering artifacts. In this paper, we propose the first framework for zero-shot video restoration and enhancement based on the pre-trained image diffusion model. By replacing the spatial self-attention layer with the proposed short-long-range (SLR) temporal attention layer, the pre-trained image diffusion model can take advantage of the temporal correlation between frames. We further propose temporal consistency guidance, spatial-temporal noise sharing, and an early stopping sampling strategy to improve temporally consistent sampling. Our method is a plug-and-play module that can be inserted into any diffusion-based image restoration or enhancement methods to further improve their performance. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method. Our code is available at https://github.com/cao-cong/ZVRD.
基于扩散的零样本图像修复和增强模型在图像修复和增强的各种任务中取得了巨大的成功。然而,将其直接应用于视频修复和增强会导致严重的临时闪烁伪影。在本文中,我们提出了基于预训练图像扩散模型的首个零样本视频修复和增强框架。通过用所提出的短长程(SLR)临时注意力层替换空间自注意力层,预训练的图像扩散模型可以利用帧之间的临时相关性。我们还提出了临时一致性指导、时空噪声共享和早期停止采样策略,以改善时间一致的采样。我们的方法是一个即插即用的模块,可以插入任何基于扩散的图像修复或增强方法来进一步提高其性能。实验结果证明了我们的方法优越性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/cao-cong/ZVRD上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
扩散模型在零样本图像修复和增强任务中取得了巨大成功,但直接应用于视频修复和增强会产生严重的时空闪烁伪影。本文首次提出了基于预训练图像扩散模型的零样本视频修复和增强框架。通过替换空间自注意力层为所提出的长短程(SLR)时间注意力层,利用帧间的时序相关性。进一步提出了时间一致性指导、时空噪声共享和早期停止采样策略来改善时序一致性采样。该方法是一个即插即用的模块,可插入任何基于扩散的图像修复或增强方法中,进一步提高其性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在零样本图像修复和增强任务中表现优异,但直接应用于视频会出现时空闪烁问题。
- 本文提出了首个基于预训练图像扩散模型的零样本视频修复和增强框架。
- 通过引入长短程(SLR)时间注意力层,利用帧间的时序相关性。
- 提出了时间一致性指导、时空噪声共享和早期停止采样策略来改善时序一致性。
- 该方法可作为插件模块,适用于任何基于扩散的图像修复或增强方法。
- 实验结果证明该方法具有优越性。
点此查看论文截图

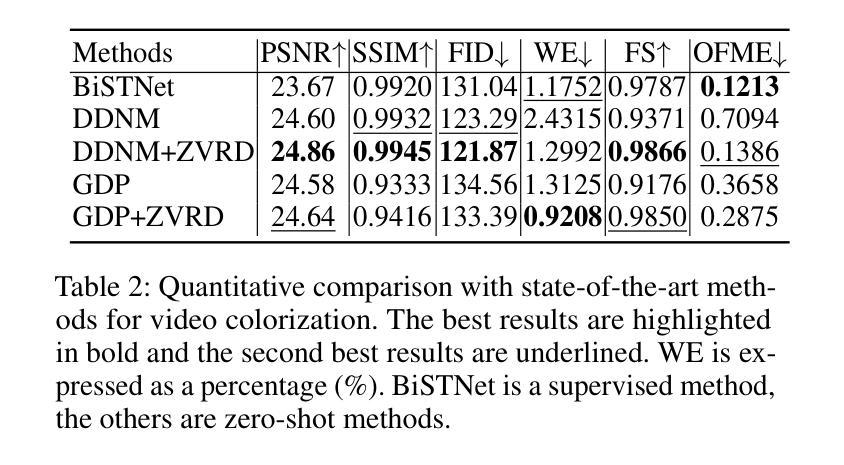

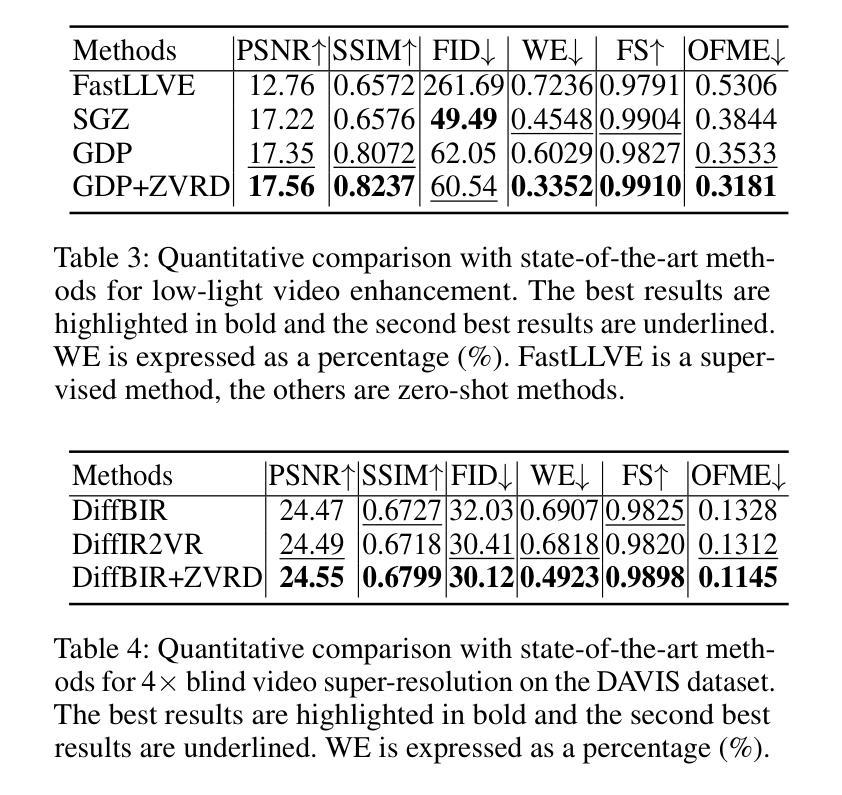
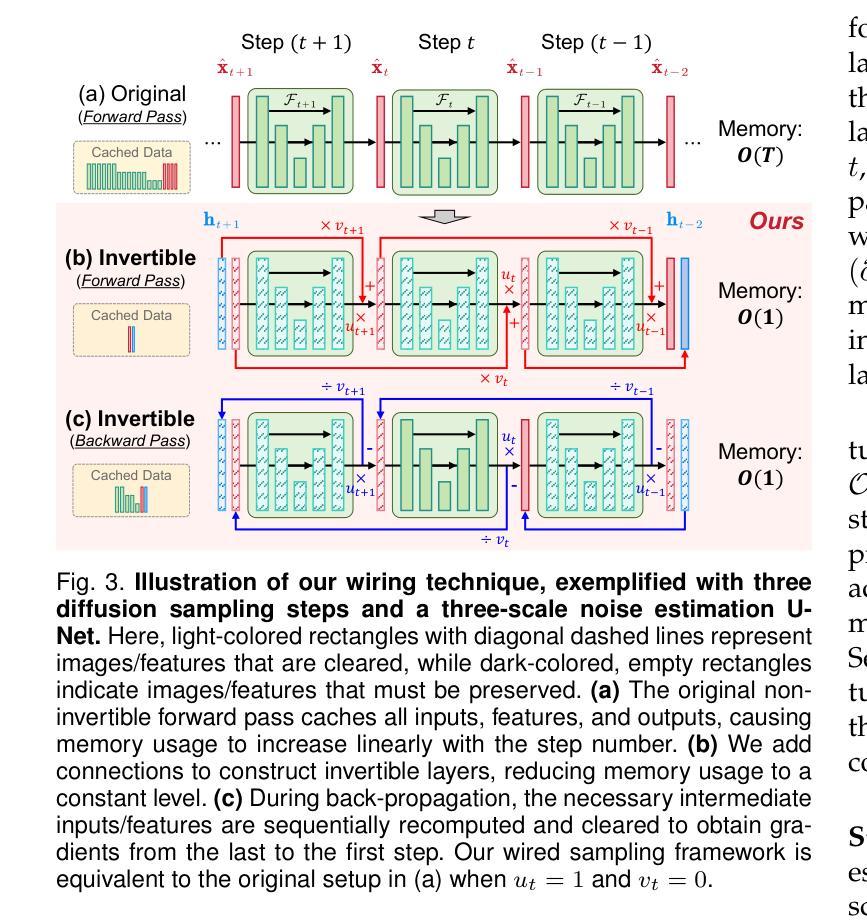
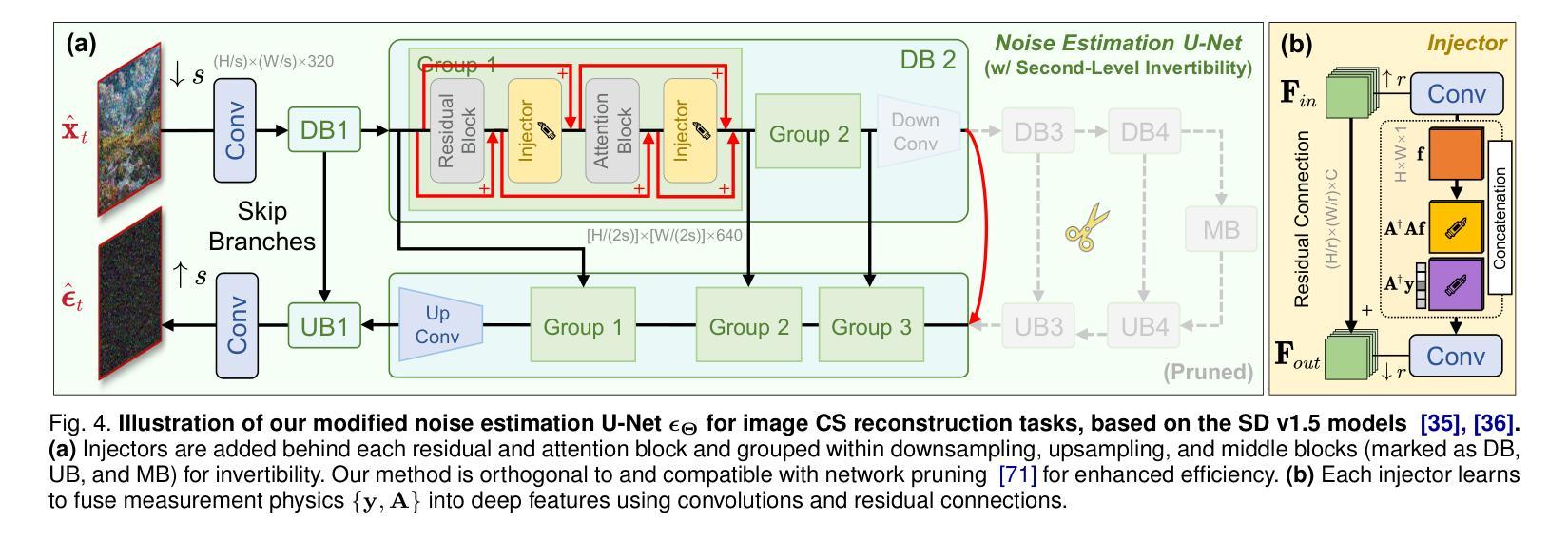
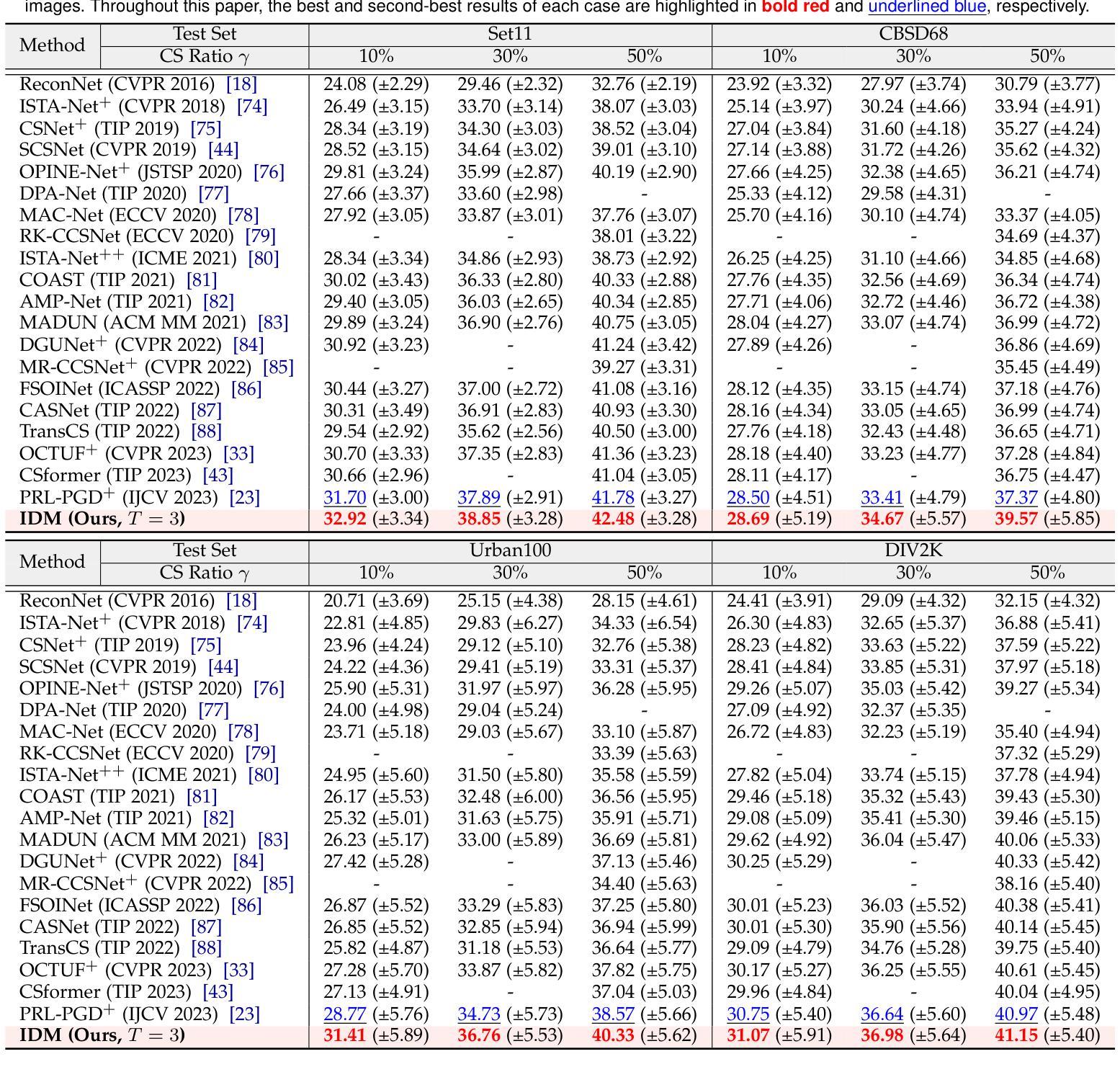
Invertible Diffusion Models for Compressed Sensing
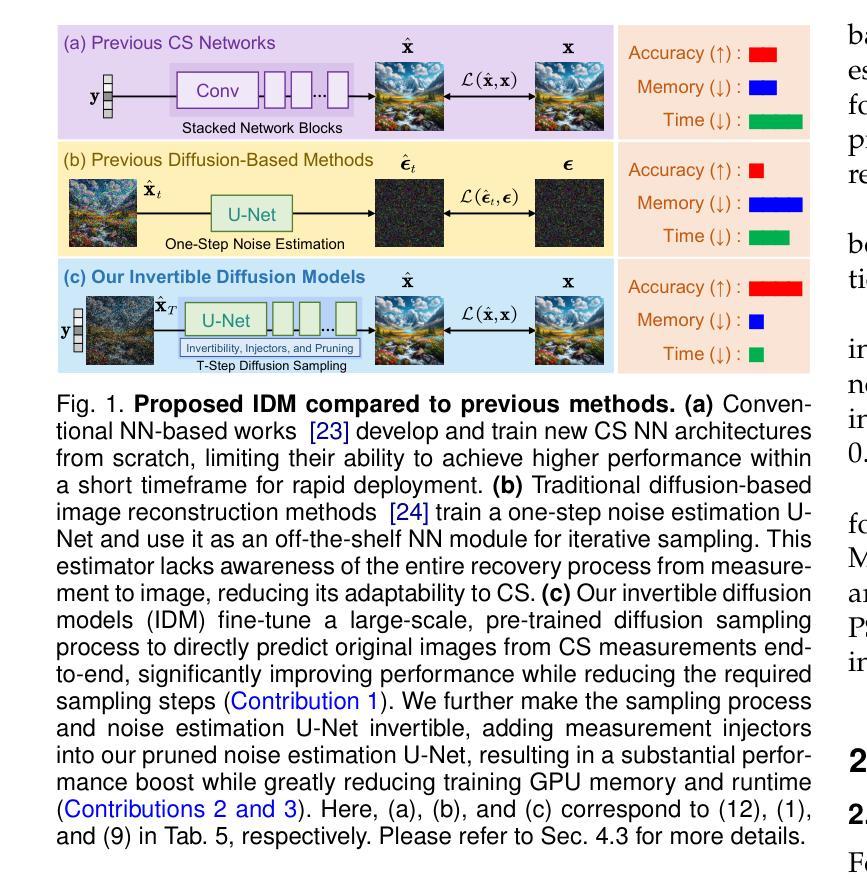
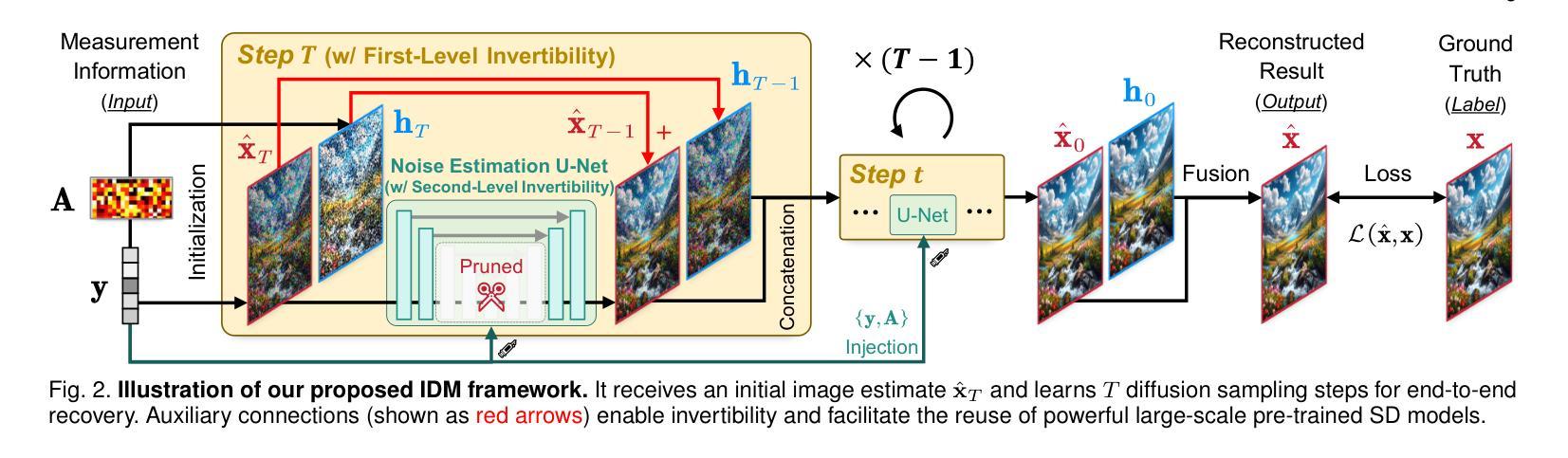
Authors:Bin Chen, Zhenyu Zhang, Weiqi Li, Chen Zhao, Jiwen Yu, Shijie Zhao, Jie Chen, Jian Zhang
While deep neural networks (NN) significantly advance image compressed sensing (CS) by improving reconstruction quality, the necessity of training current CS NNs from scratch constrains their effectiveness and hampers rapid deployment. Although recent methods utilize pre-trained diffusion models for image reconstruction, they struggle with slow inference and restricted adaptability to CS. To tackle these challenges, this paper proposes Invertible Diffusion Models (IDM), a novel efficient, end-to-end diffusion-based CS method. IDM repurposes a large-scale diffusion sampling process as a reconstruction model, and fine-tunes it end-to-end to recover original images directly from CS measurements, moving beyond the traditional paradigm of one-step noise estimation learning. To enable such memory-intensive end-to-end fine-tuning, we propose a novel two-level invertible design to transform both (1) multi-step sampling process and (2) noise estimation U-Net in each step into invertible networks. As a result, most intermediate features are cleared during training to reduce up to 93.8% GPU memory. In addition, we develop a set of lightweight modules to inject measurements into noise estimator to further facilitate reconstruction. Experiments demonstrate that IDM outperforms existing state-of-the-art CS networks by up to 2.64dB in PSNR. Compared to the recent diffusion-based approach DDNM, our IDM achieves up to 10.09dB PSNR gain and 14.54 times faster inference. Code is available at https://github.com/Guaishou74851/IDM.
虽然深度神经网络(NN)通过提高重建质量来显著推进图像压缩感知(CS)的发展,但当前需要从头开始训练CS神经网络,这限制了其有效性并阻碍了快速部署。尽管最近的方法利用预训练的扩散模型进行图像重建,但它们面临推理速度慢和适应压缩感知的能力有限的问题。为了解决这些挑战,本文提出了可逆扩散模型(IDM),这是一种基于扩散的高效、端到端的压缩感知新方法。IDM将大规模的扩散采样过程重新用作重建模型,并对其进行端到端的微调,直接从压缩感知测量中恢复原始图像,超越了传统的一步噪声估计学习范式。为了实现这种内存密集型的端到端微调,我们提出了一种新型的两级可逆设计,将(1)多步采样过程和(2)每一步中的噪声估计U-Net转化为可逆网络。因此,在训练过程中清除了大多数中间特征,以减少高达93.8%的GPU内存。此外,我们开发了一系列轻量级模块,将测量值注入噪声估计器,以进一步促进重建。实验表明,IDM在峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面优于现有的先进CS网络,提高了高达2.64dB。与最近的扩散模型DDNM相比,我们的IDM在PSNR上实现了高达10.09dB的增益,推理速度提高了14.54倍。代码可通过https://github.com/Guaishou74851/IDM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)
摘要
深度神经网络(NN)在图像压缩感知(CS)领域取得了显著进展,但现有CS NN需要从头开始训练,这限制了其有效性并阻碍了快速部署。尽管已有方法利用预训练的扩散模型进行图像重建,但它们面临着推理速度慢和适应CS能力有限的问题。本文提出可逆扩散模型(IDM),这是一种基于扩散的高效端到端CS方法。IDM将大规模的扩散采样过程重新用作重建模型,并将其端到端微调,直接从CS测量中恢复原始图像,超越了传统的一步噪声估计学习范式。为实现这种内存密集型的端到端微调,我们提出了一种新型的两级可逆设计,将(1)多步采样过程和(2)每一步中的噪声估计U-Net转换为可逆网络。结果,大多数中间特征在训练过程中被清除,以减少高达93.8%的GPU内存。此外,我们开发了一系列轻量级模块,将测量值注入噪声估计器,以进一步促进重建。实验表明,IDM在峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面比现有先进的CS网络高出2.64dB。与最近的扩散方法DDNM相比,我们的IDM实现了高达10.09dB的PSNR增益和14.54倍的推理速度提升。相关代码可在XXX中获得。
关键见解
- 本文提出了一种新的图像压缩感知方法——可逆扩散模型(IDM),该方法基于扩散采样过程进行重建。
- IDM通过端到端微调直接从CS测量中恢复原始图像,超越了传统的一步噪声估计学习。
- 提出了一种新型的两级可逆设计,以优化内存使用并加速训练过程。这种设计能够减少GPU内存使用高达93.8%。
- IDm采用了轻量级模块来注入测量值到噪声估计过程中以促进重建。
- 实验结果表明,IDM在PSNR指标上显著提高,相比现有网络有高达2.64dB的提升。
- 与现有扩散模型DDNM相比,IDM在PSNR上实现了更高的增益并显著提高了推理速度。
点此查看论文截图

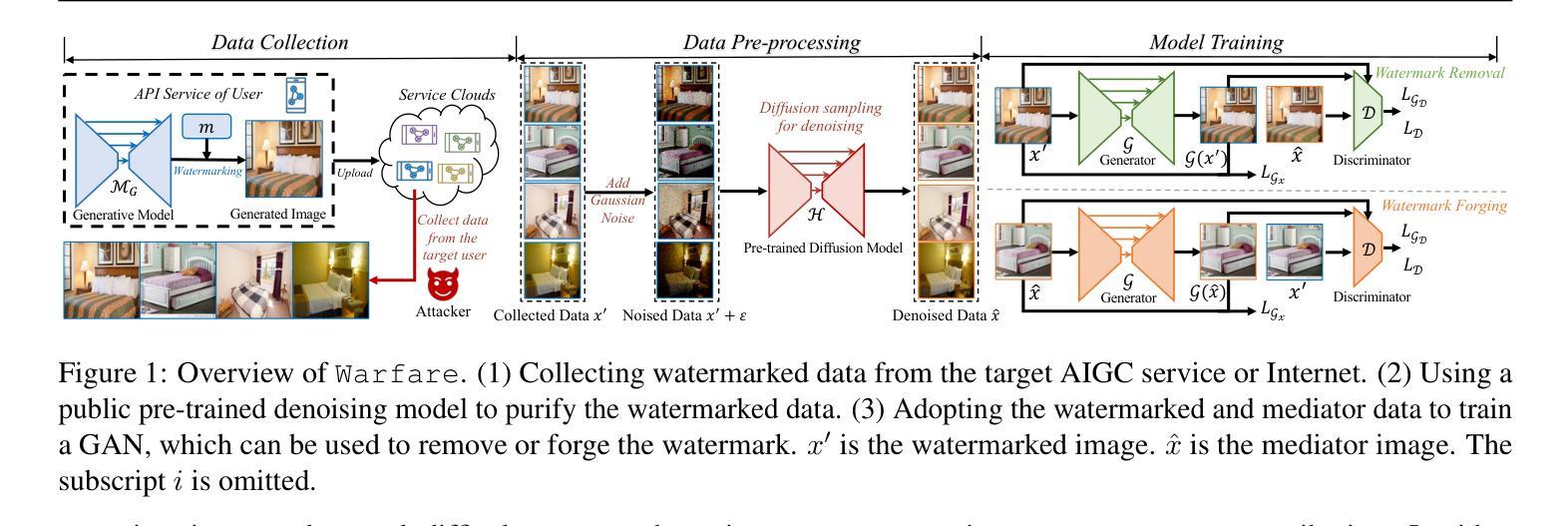
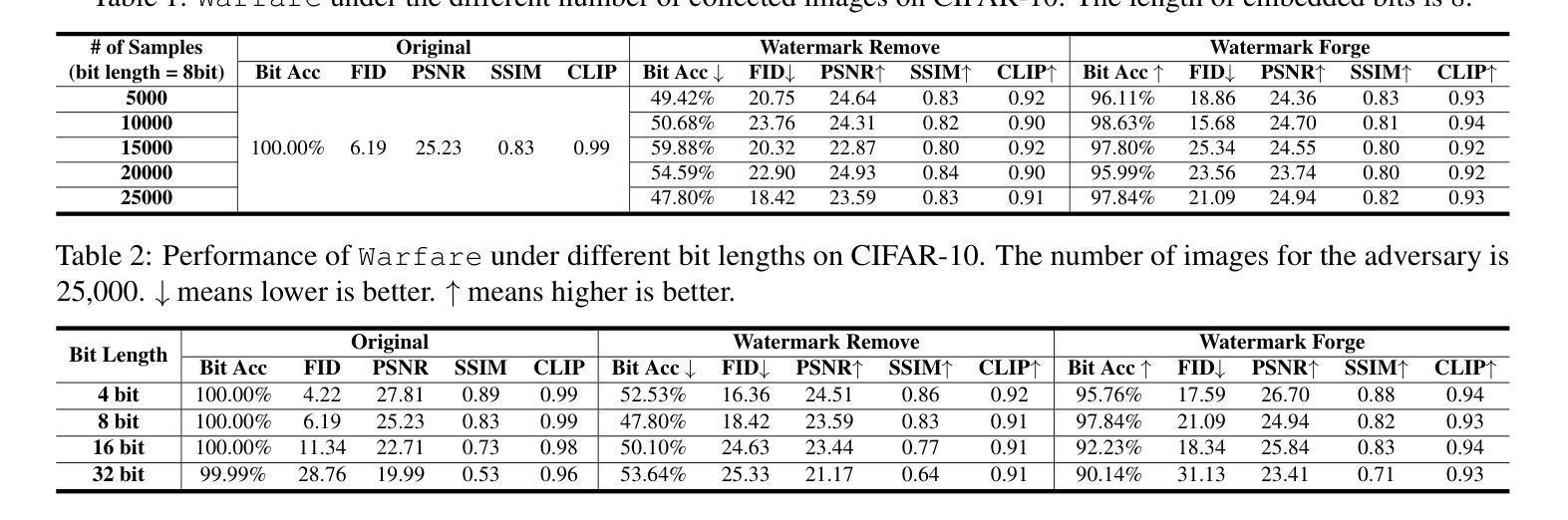
Warfare:Breaking the Watermark Protection of AI-Generated Content
Authors:Guanlin Li, Yifei Chen, Jie Zhang, Shangwei Guo, Han Qiu, Guoyin Wang, Jiwei Li, Tianwei Zhang
AI-Generated Content (AIGC) is rapidly expanding, with services using advanced generative models to create realistic images and fluent text. Regulating such content is crucial to prevent policy violations, such as unauthorized commercialization or unsafe content distribution. Watermarking is a promising solution for content attribution and verification, but we demonstrate its vulnerability to two key attacks: (1) Watermark removal, where adversaries erase embedded marks to evade regulation, and (2) Watermark forging, where they generate illicit content with forged watermarks, leading to misattribution. We propose Warfare, a unified attack framework leveraging a pre-trained diffusion model for content processing and a generative adversarial network for watermark manipulation. Evaluations across datasets and embedding setups show that Warfare achieves high success rates while preserving content quality. We further introduce Warfare-Plus, which enhances efficiency without compromising effectiveness. The code can be found in https://github.com/GuanlinLee/warfare.
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)正在迅速扩张,服务中使用先进的生成模型来创建逼真的图像和流畅的文本。对这类内容进行监管对于防止政策违规行为至关重要,例如未经授权的商业化或不安全的内容传播。水印是一种具有前景的内容归属和验证解决方案,但我们展示了其面临两种主要攻击的脆弱性:(1)水印移除,其中对手删除嵌入的标记以逃避监管;(2)水印伪造,他们使用伪造的水印生成非法内容,导致归属错误。我们提出了Warfare,一个统一的攻击框架,利用预训练的扩散模型进行内容处理,并使用生成对抗网络进行水印操作。在数据集和嵌入设置上的评估表明,Warfare在保持内容质量的同时实现了较高的成功率。我们还介绍了提高效率而不妥协效果的Warfare-Plus。代码可在https://github.com/GuanlinLee/warfare中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
AIGC内容生成技术快速发展,需要监管以防止政策违规。水印是解决内容归属和验证的有效方法,但存在两大攻击威胁:一是去除水印以逃避监管,二是伪造水印导致内容误归属。提出利用预训练扩散模型和生成对抗网络构建的 Warfare 攻击框架来应对,并在数据集和嵌入设置上的评估显示其高成功率且内容质量不受影响。同时推出增强版 Warfare-Plus,提高效率且不降低效果。
Key Takeaways
- AIGC内容生成技术迅速发展,引发监管需求,以防止政策违规。
- 水印是解决内容归属和验证的可行方法,但存在被移除和伪造的风险。
- 水印移除和伪造是两大攻击威胁,可能导致逃避监管和误归属。
- 提出利用预训练扩散模型和生成对抗网络的 Warfare 攻击框架。
- Warfare框架在数据集和嵌入设置上的评估表现出高成功率和内容质量保留。
- 推出Warfare-Plus,提高效率和效果。
点此查看论文截图