⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
A Survey on Class-Agnostic Counting: Advancements from Reference-Based to Open-World Text-Guided Approaches
Authors:Luca Ciampi, Ali Azmoudeh, Elif Ecem Akbaba, Erdi Sarıtaş, Ziya Ata Yazıcı, Hazım Kemal Ekenel, Giuseppe Amato, Fabrizio Falchi
Object counting has recently shifted towards class-agnostic counting (CAC), which addresses the challenge of counting objects across arbitrary categories, tackling a critical need in versatile counting systems. While humans effortlessly identify and count objects from diverse categories without prior knowledge, most counting methods remain restricted to enumerating instances of known classes, requiring extensive labeled datasets for training, and struggling under open-vocabulary settings. Conversely, CAC aims to count objects belonging to classes never seen during training, typically operating in a few-shot setting. In this paper, for the first time, we review advancements in CAC methodologies, categorizing them into three paradigms based on how target object classes can be specified: reference-based, reference-less, and open-world text-guided. Reference-based approaches have set performance benchmarks using exemplar-guided mechanisms. Reference-less methods eliminate exemplar dependency by leveraging inherent image patterns. Finally, open-world text-guided methods utilize vision-language models, enabling object class descriptions through textual prompts, representing a flexible and appealing solution. We analyze state-of-the-art techniques and we report their results on existing gold standard benchmarks, comparing their performance and identifying and discussing their strengths and limitations. Persistent challenges – such as annotation dependency, scalability, and generalization – are discussed, alongside future directions. We believe this survey serves as a valuable resource for researchers to understand the progressive developments and contributions over time and the current state-of-the-art of CAC, suggesting insights for future directions and challenges to be addressed.
对象计数最近已经转向类别未知计数(CAC),这解决了跨任意类别计数对象的挑战,满足了通用计数系统的迫切需求。虽然人类能够毫不费力地识别并计算来自不同类别的对象数量,而无需事先知识,但大多数计数方法仍然仅限于计算已知类别的实例数量,需要广泛的有标签数据集进行训练,并且在开放词汇设置下遇到挑战。相反,CAC旨在计算属于在训练期间未见过的类别的对象数量,通常运行在少量样本设置下。在本文中,我们首次回顾了CAC方法的发展,根据目标对象类别的指定方式将它们分为三种范式:基于参考、无参考和开放世界文本引导。基于参考的方法使用示例引导机制设定了性能基准。无参考方法通过利用固有的图像模式来消除对示例的依赖。最后,开放世界文本引导的方法利用视觉语言模型,通过文本提示实现对象类别描述,代表了一种灵活且有吸引力的解决方案。我们分析了最新技术,并在现有的黄金标准基准测试上报告了它们的成果,比较了它们的性能,并讨论和分析了它们的优缺点。还讨论了持续的挑战,如注释依赖性、可扩展性和泛化性,以及未来的研究方向。我们相信这份综述对于研究人员了解CAC的渐进发展、贡献和当前最新状态非常有价值,并为未来的研究方向和挑战提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文综述了类未知计数(CAC)方法的最新进展,将其分为三种基于目标类别指定方式的范式:基于参考的、无参考的和开放世界文本引导的方法。基于参考的方法使用范例引导机制设定性能基准,无参考方法则利用图像内在模式消除范例依赖性,而开放世界文本引导的方法则利用视觉语言模型,通过文本提示实现目标类别描述,为CAC提供了一个灵活且具吸引力的解决方案。文章分析了最新技术并在现有标准基准上报告了结果,比较了性能,同时讨论和识别了各自的优缺点。
Key Takeaways
- 类未知计数(CAC)是对象计数领域的新趋势,旨在解决跨任意类别计数对象的挑战。
- CAC方法分为三个基于目标类别指定方式的范式:基于参考、无参考和开放世界文本引导。
- 基于参考的方法使用范例引导机制,设定了性能基准。
- 无参考方法利用图像内在模式,消除对范例的依赖。
- 开放世界文本引导的方法使用视觉语言模型,通过文本提示实现目标类别描述,为CAC提供灵活解决方案。
- 现有技术面临持续挑战,如注释依赖性、可扩展性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图



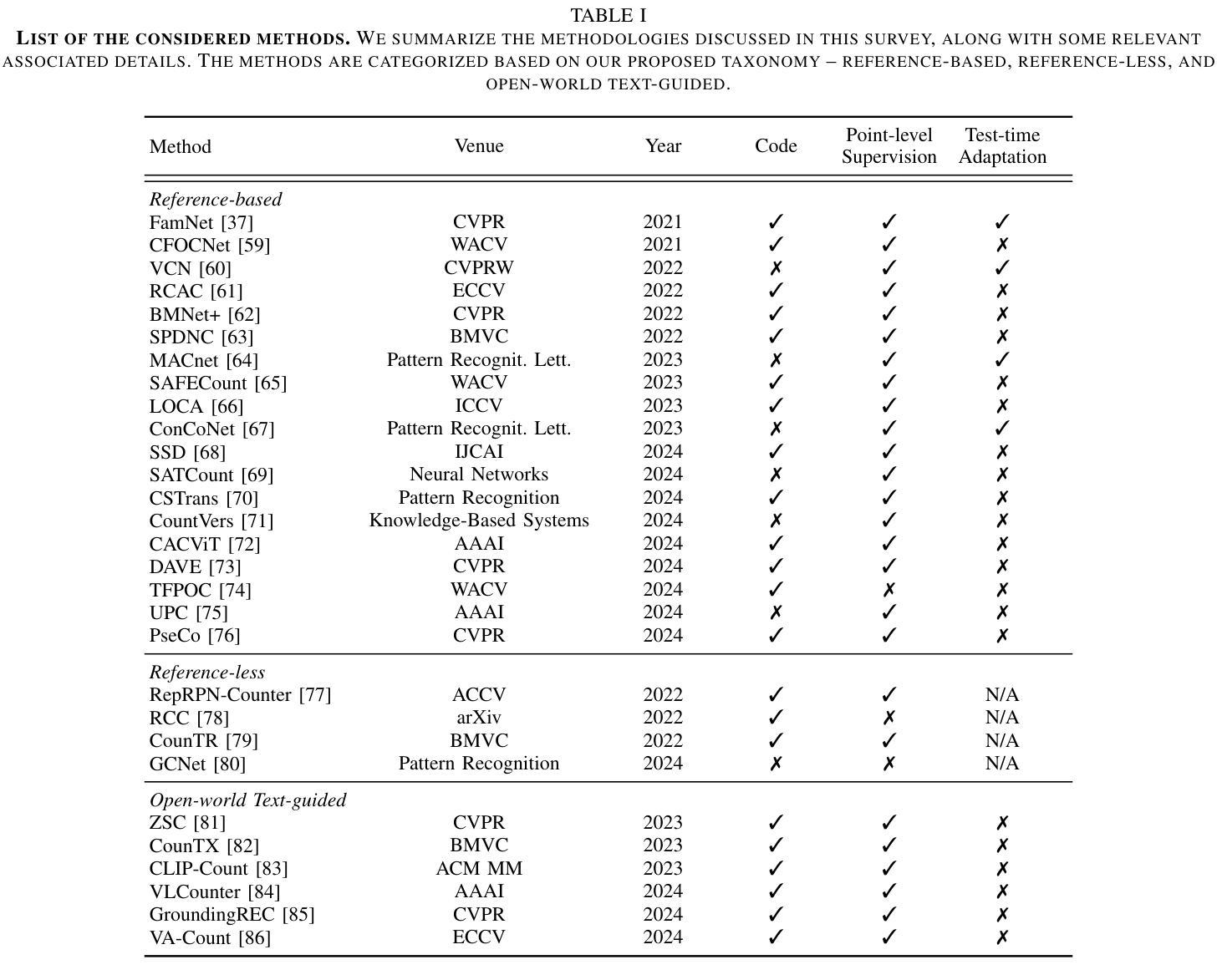
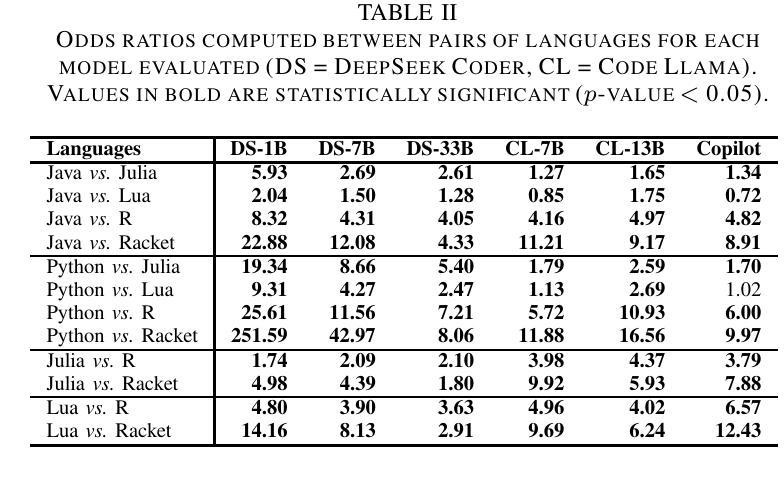
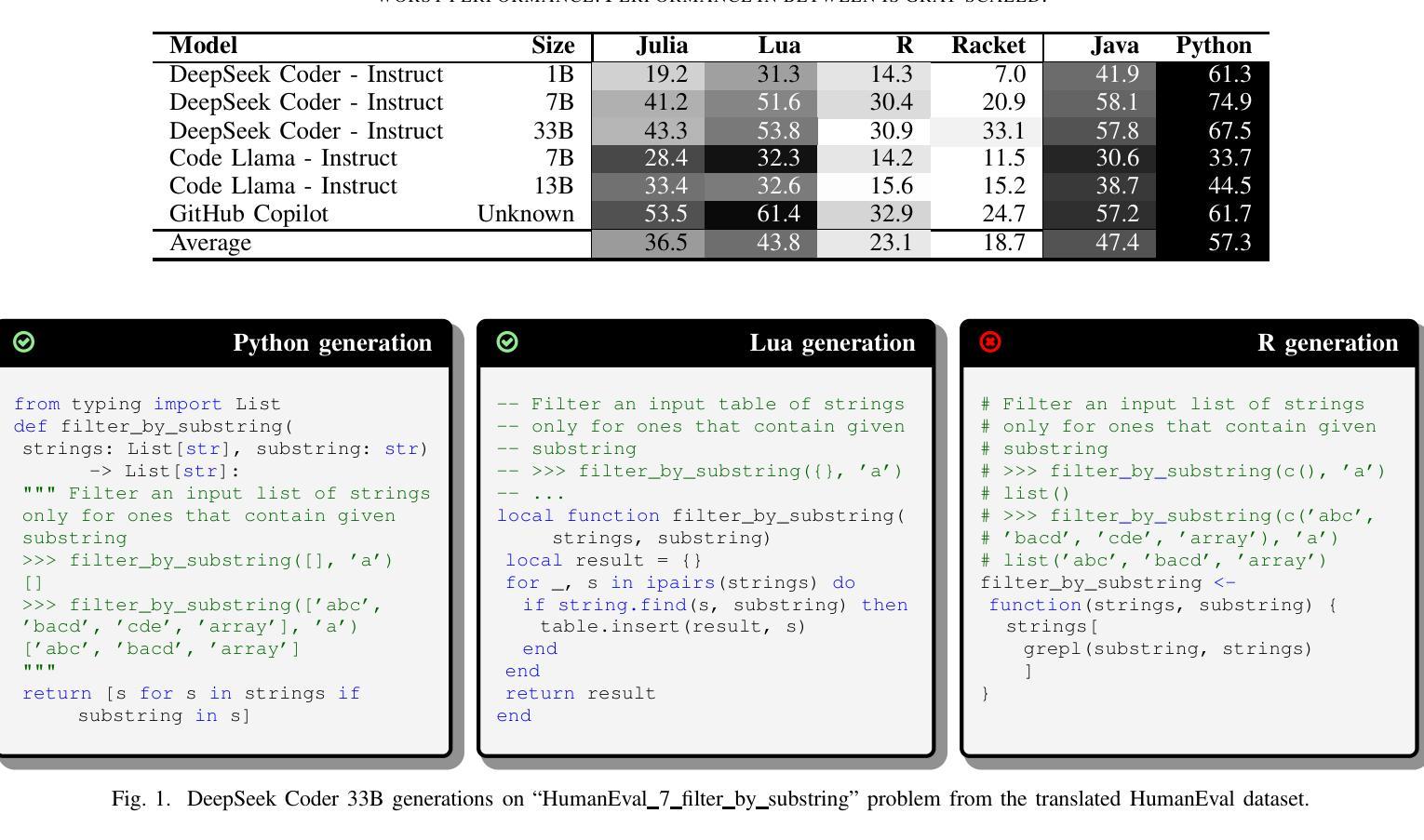
Enhancing Code Generation for Low-Resource Languages: No Silver Bullet
Authors:Alessandro Giagnorio, Alberto Martin-Lopez, Gabriele Bavota
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has significantly advanced the field of automated code generation. LLMs rely on large and diverse datasets to learn syntax, semantics, and usage patterns of programming languages. For low-resource languages (i.e., niche programming languages characterized by the scarcity of training data), the limited availability of such data hampers the models’ ability to generalize effectively, resulting in poorer code generation performance as compared to high-resource languages. For this reason, there is a quest for techniques able to close this performance gap. We present an empirical study investigating the effectiveness of several approaches for boosting LLMs’ performance on low-resource languages, namely: (i) a classic fine-tuning, which is however capped in size by the scarcity of training data; (ii) three variants of in-context learning, with prompts crafted to provide the LLM with additional information about the low-resource language (e.g., few-shot examples showcasing features of the targeted language); and (iii) a pre-training objective teaching the model how to translate between high- and low-resource languages. The context of our study are two low-resource languages (R and Racket) and six LLMs having different architectures and sizes. Our findings reveal that a fine-tuning is usually the best choice for smaller LLMs, possibly due to the fact that even a small dataset is sufficient to train their limited number of parameters. With the increase in size of the models, in-context learning becomes more and more effective, representing a safe and cheap bet (i.e., it always helps, but with different magnitudes). Differently, very large LLMs may deteriorate their performance on low-resource languages when fine-tuning is performed, possibly due to the lack of enough data needed to effectively update their weights.
大型语言模型(LLM)的出现,极大地推动了自动化代码生成领域的发展。LLM依赖于大型和多样化的数据集来学习编程语言的语法、语义和使用模式。对于资源匮乏的语言(即训练数据稀缺的专有编程语言),此类数据的有限可用性阻碍了模型有效地推广,与资源丰富的语言相比,导致较差的代码生成性能。因此,人们正在寻找能够缩小这一性能差距的技术。我们进行了一项实证研究,探讨了提高LLM在资源匮乏的语言上的性能的几种方法的有效性,即:(i)经典的微调,但受限于训练数据的稀缺性;(ii)三种上下文学习变体,通过提示为LLM提供有关低资源语言的额外信息(例如,展示目标语言特征的几个示例);(iii)一个预训练目标,教会模型如何在高资源和低资源语言之间进行翻译。我们研究的背景是两种资源匮乏的语言(R和Racket)和六种具有不同架构和规模的LLM。我们的研究结果表明,对于较小的LLM,微调通常是最佳选择,这可能是由于即使小数据集也足以训练其有限数量的参数。随着模型规模的增加,上下文学习变得越来越有效,是一个安全且经济的选择(即它总是有帮助,但程度不同)。不同的是,对于非常大的LLM,当进行微调时,其在资源匮乏的语言上的性能可能会下降,这可能是由于缺乏足够的数据来有效地更新其权重。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICPC’25
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自动代码生成领域取得了显著进展,但在处理低资源语言时面临挑战。针对这一问题,本文探讨了提升LLM在低资源语言上性能的方法,包括微调、上下文学习和预训练目标等策略。研究发现,对于小型LLM,微调通常是最佳选择;随着模型规模的增加,上下文学习变得更加有效;而对于非常大的LLM,过度微调可能导致性能下降。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自动代码生成上表现卓越,但在处理低资源语言时面临挑战。
- 有限的训练数据限制了LLM在低资源语言上的性能。
- 经典微调受限于训练数据的稀缺性,但对于小型LLM可能仍是最优选择。
- 随着模型规模的增加,上下文学习变得更加有效。
- 预训练目标可以帮助模型在低资源语言上进行翻译。
- 对于非常大的LLM,过度微调可能导致性能下降。
点此查看论文截图

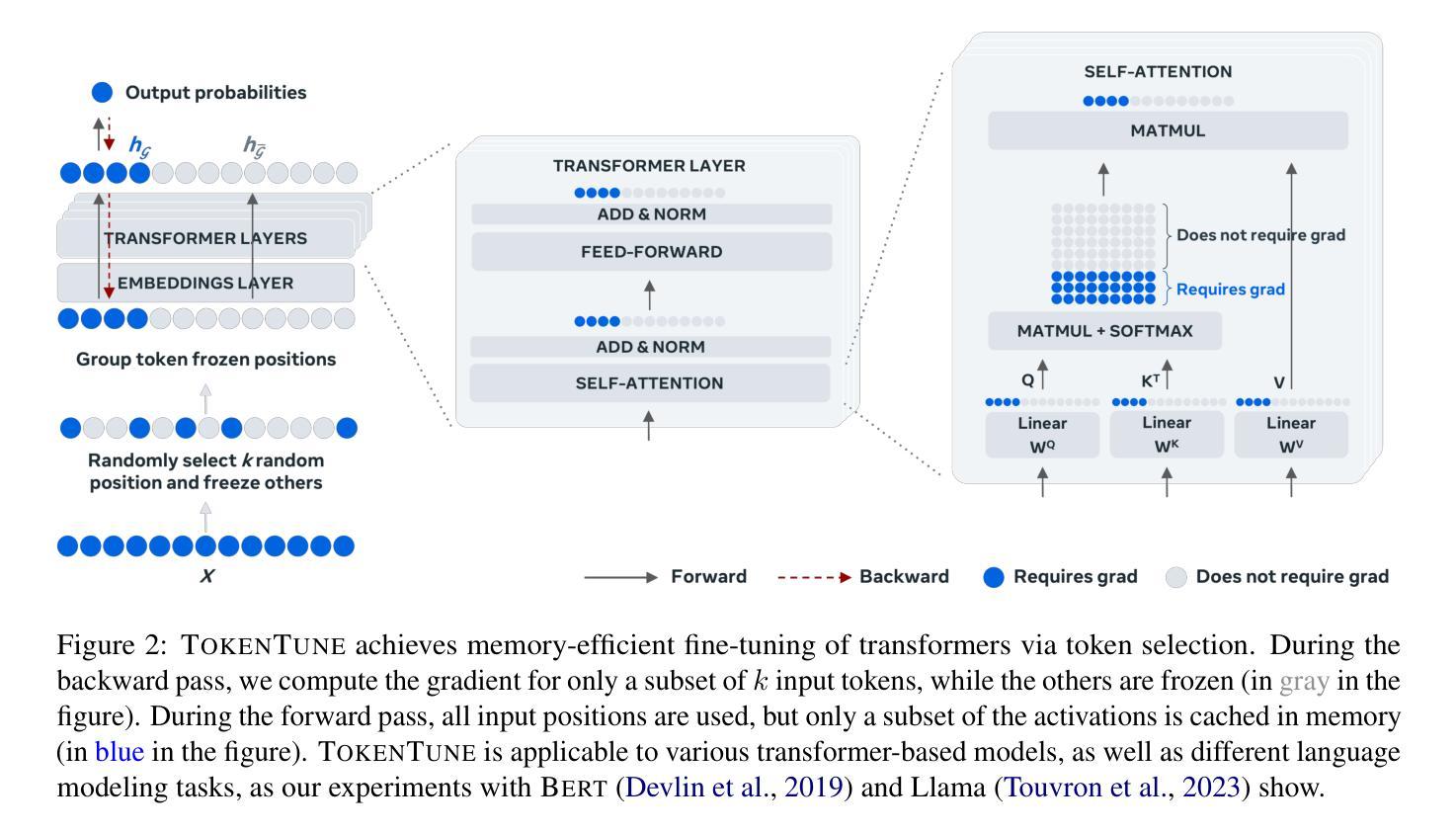
Memory-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Transformers via Token Selection
Authors:Antoine Simoulin, Namyong Park, Xiaoyi Liu, Grey Yang
Fine-tuning provides an effective means to specialize pre-trained models for various downstream tasks. However, fine-tuning often incurs high memory overhead, especially for large transformer-based models, such as LLMs. While existing methods may reduce certain parts of the memory required for fine-tuning, they still require caching all intermediate activations computed in the forward pass to update weights during the backward pass. In this work, we develop TokenTune, a method to reduce memory usage, specifically the memory to store intermediate activations, in the fine-tuning of transformer-based models. During the backward pass, TokenTune approximates the gradient computation by backpropagating through just a subset of input tokens. Thus, with TokenTune, only a subset of intermediate activations are cached during the forward pass. Also, TokenTune can be easily combined with existing methods like LoRA, further reducing the memory cost. We evaluate our approach on pre-trained transformer models with up to billions of parameters, considering the performance on multiple downstream tasks such as text classification and question answering in a few-shot learning setup. Overall, TokenTune achieves performance on par with full fine-tuning or representative memory-efficient fine-tuning methods, while greatly reducing the memory footprint, especially when combined with other methods with complementary memory reduction mechanisms. We hope that our approach will facilitate the fine-tuning of large transformers, in specializing them for specific domains or co-training them with other neural components from a larger system. Our code is available at https://github.com/facebookresearch/tokentune.
微调(Fine-tuning)为针对各种下游任务的专业化预训练模型提供了有效的手段。然而,微调通常会引起较高的内存开销,尤其是对于基于大型变换模型的预训练模型(如大型语言模型)。尽管现有方法可能减少了微调所需的某些内存部分,但它们仍然需要在前向传播过程中缓存所有中间激活的计算结果,以在反向传播过程中更新权重。在这项工作中,我们开发了TokenTune,一种旨在减少基于变换模型的微调过程中的内存使用量的方法,特别是用于存储中间激活值的内存。在反向传播过程中,TokenTune通过仅通过输入令牌的一个子集进行反向传播来近似梯度计算。因此,使用TokenTune时,仅在正向传播过程中缓存一小部分中间激活值。此外,TokenTune还可以轻松地与LoRA等现有方法相结合,进一步降低内存成本。我们在具有数十亿参数的预训练变换模型上评估了我们的方法,并考虑了其在多个下游任务(如文本分类和问题回答)上的性能表现。总体而言,TokenTune的性能与完全微调或代表性内存高效的微调方法相当,同时大大降低了内存占用空间,尤其是与其他具有互补内存减少机制的方法相结合时。我们希望我们的方法能够促进大型转换器的微调工作,在特定领域对其进行专业化处理或与其他神经网络组件从更大的系统进行协同训练。我们的代码可在https://github.com/facebookresearch/tokentune获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2024
Summary
本文提出了TokenTune方法,用于减少微调基于转换器模型时的内存使用。通过仅缓存输入令牌子集的部分中间激活值,TokenTune能够在微调过程中降低内存消耗。此方法可与现有方法(如LoRA)结合使用,进一步降低内存成本。在多项下游任务(如文本分类和问答)的少量学习设置中,TokenTune实现了与完全微调或代表性内存高效微调方法相当的性能,同时大大减少了内存占用。我们的代码已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- TokenTune方法专注于减少微调基于转换器模型时的内存使用。
- 通过仅缓存输入令牌子集的部分中间激活值,降低了内存消耗。
- TokenTune可以与现有方法(如LoRA)结合使用,以进一步提高内存效率。
- 在多项下游任务中,TokenTune实现了与完全微调或内存高效微调方法相当的性能。
- TokenTune特别适用于大型转换模型的微调。
- TokenTune有助于在少量学习设置中进行模型微调。
点此查看论文截图


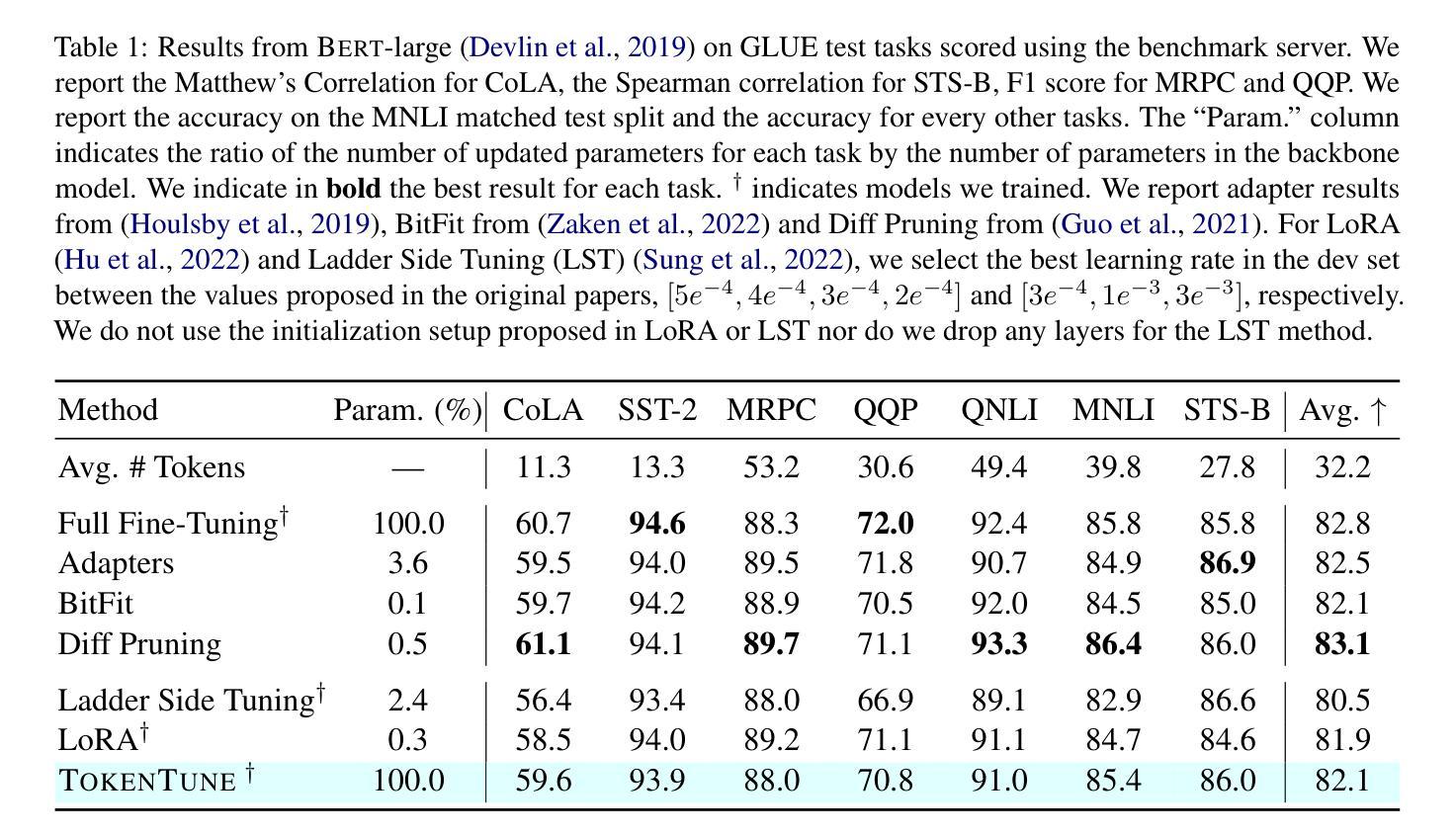
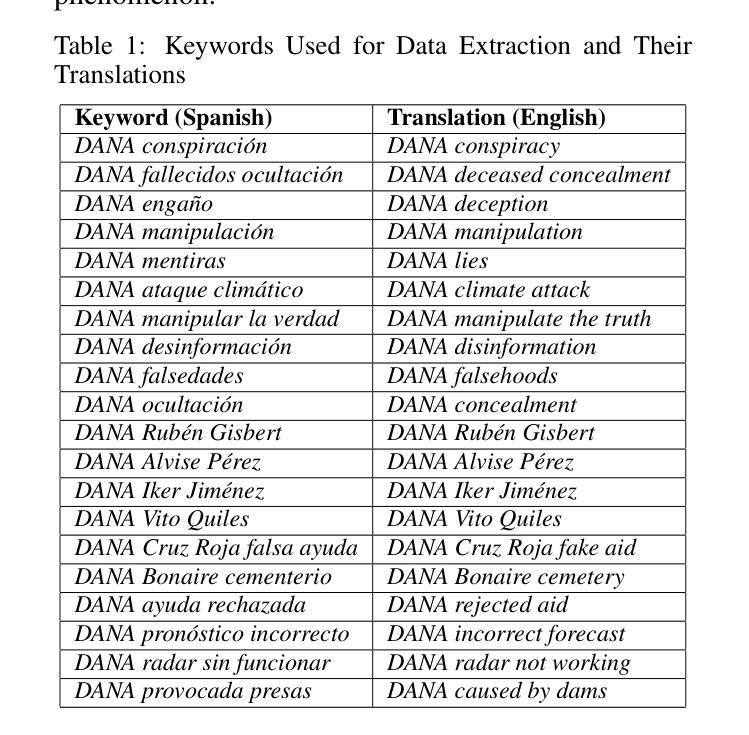
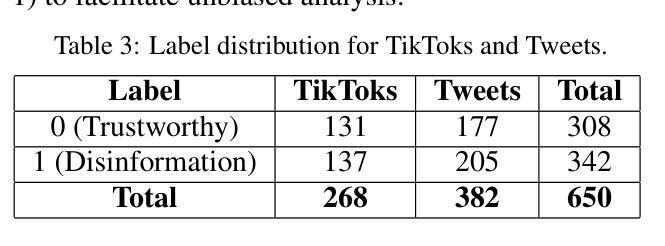
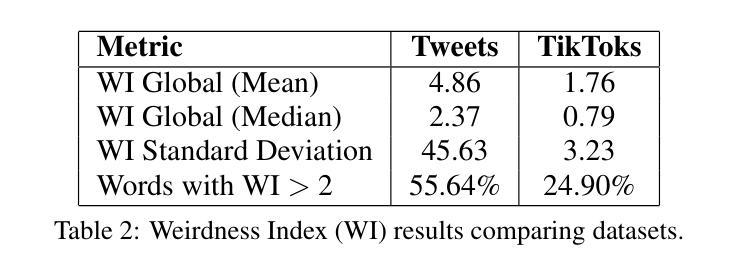
Divergent Emotional Patterns in Disinformation on Social Media? An Analysis of Tweets and TikToks about the DANA in Valencia
Authors:Iván Arcos, Paolo Rosso, Ramón Salaverría
This study investigates the dissemination of disinformation on social media platforms during the DANA event (DANA is a Spanish acronym for Depresion Aislada en Niveles Altos, translating to high-altitude isolated depression) that resulted in extremely heavy rainfall and devastating floods in Valencia, Spain, on October 29, 2024. We created a novel dataset of 650 TikTok and X posts, which was manually annotated to differentiate between disinformation and trustworthy content. Additionally, a Few-Shot annotation approach with GPT-4o achieved substantial agreement (Cohen’s kappa of 0.684) with manual labels. Emotion analysis revealed that disinformation on X is mainly associated with increased sadness and fear, while on TikTok, it correlates with higher levels of anger and disgust. Linguistic analysis using the LIWC dictionary showed that trustworthy content utilizes more articulate and factual language, whereas disinformation employs negations, perceptual words, and personal anecdotes to appear credible. Audio analysis of TikTok posts highlighted distinct patterns: trustworthy audios featured brighter tones and robotic or monotone narration, promoting clarity and credibility, while disinformation audios leveraged tonal variation, emotional depth, and manipulative musical elements to amplify engagement. In detection models, SVM+TF-IDF achieved the highest F1-Score, excelling with limited data. Incorporating audio features into roberta-large-bne improved both Accuracy and F1-Score, surpassing its text-only counterpart and SVM in Accuracy. GPT-4o Few-Shot also performed well, showcasing the potential of large language models for automated disinformation detection. These findings demonstrate the importance of leveraging both textual and audio features for improved disinformation detection on multimodal platforms like TikTok.
本研究调查了在DANA事件(DANA是西班牙语中Depresion Aislada en Niveles Altos的缩写,意为高海拔孤立性抑郁症)期间社交媒体平台上传播的错误信息。该事件导致2024年10月29日西班牙瓦伦西亚出现极端强降雨和破坏性洪水。我们创建了包含650个TikTok和X帖子的新型数据集,并进行了手动注释,以区分错误信息和可靠内容。另外,使用GPT-4o的Few-Shot标注方法达到了与手动标签的实质一致性(Cohen的kappa值为0.684)。情绪分析显示,X上的错误信息主要与悲伤和恐惧感增加有关,而在TikTok上,它与愤怒和厌恶程度较高相关。使用LIWC词典进行的语言分析表明,可靠的内容使用更艺术和事实性的语言,而错误信息则使用否定词、感知词汇和个人轶事来显得可信。对TikTok帖子的音频分析突显了明显的模式:可靠音频的音调更明亮,采用机器人或单调的叙述,以促进清晰度和可信度;而错误信息的音频则利用音调变化、情感深度和操纵性的音乐元素来增强参与度。在检测模型中,SVM+TF-IDF获得了最高的F1分数,在有限的数据下表现卓越。将音频特性融入roberta-large-bne中提高了准确率和F1分数,超越了其纯文本对应模型和SVM的准确率。GPT-4o的Few-Shot表现也相当不错,展示了大型语言模型在自动错误信息检测中的潜力。这些发现表明,利用文本和音频特征对于改进TikTok等多模式平台上的错误信息检测至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究探讨了DANA事件(高海拔孤立性抑郁症的缩写,该事件导致西班牙瓦伦西亚于2024年10月29日发生极端强降雨和破坏性洪水)期间社交媒体平台上假消息的扩散。研究者创建了一个包含650篇TikTok和X平台的帖子的数据集,并进行手动标注以区分假消息和可靠内容。情感分析发现,X平台上的假消息主要与悲伤和恐惧感增加有关,而TikTok上的假消息则与愤怒和厌恶情绪更高相关。语言分析显示,可靠内容使用更艺术和事实性的语言,而假消息则使用否定词、感知词汇和个人轶事来显得可信。音频分析表明,可信的音频具有更明亮的音调和机器人或单调的叙述,而假消息的音频则利用音调变化和操纵性音乐元素来增加参与度。检测模型中,SVM+TF-IDF达到最高F1分数,结合音频特征的roberta-large-bne在准确率和F1分数上有所提升。GPT-4o的Few-Shot表现也良好,突显大型语言模型在自动假消息检测中的潜力。研究结果表明,利用文本和音频特征对于改进TikTok等多模式平台上的假消息检测至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 研究聚焦于DANA事件期间社交媒体上的假消息传播。
- 创建了包含TikTok和X平台帖子的数据集,并进行手动标注。
- 情感分析显示不同平台上假消息与不同情绪的相关性。
- 语言分析揭示可靠内容和假消息在语言使用上的差异。
- 音频分析显示,假消息的音频具有特定的特征和模式。
- SVM+TF-IDF和结合音频特征的roberta-large-bne在检测模型中表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图


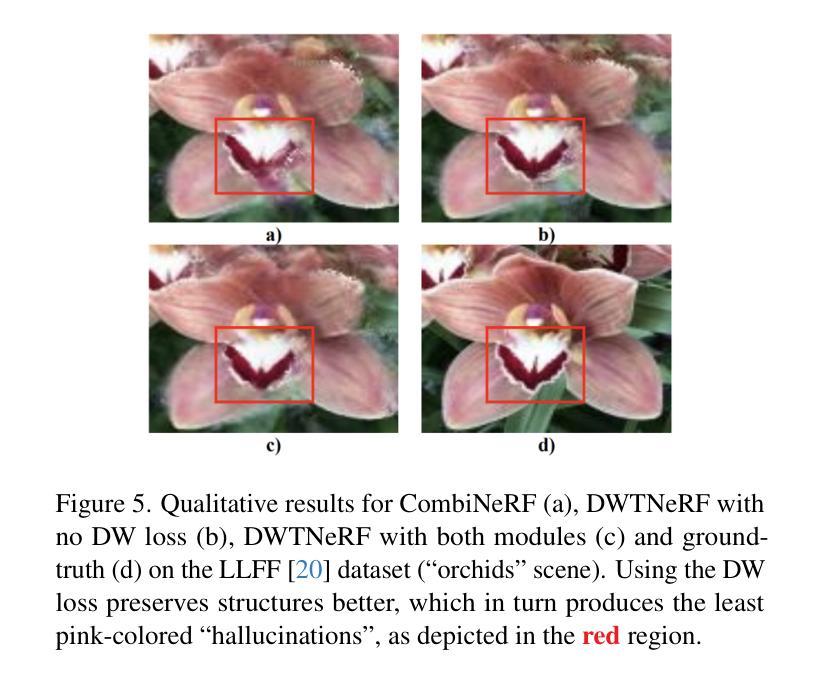
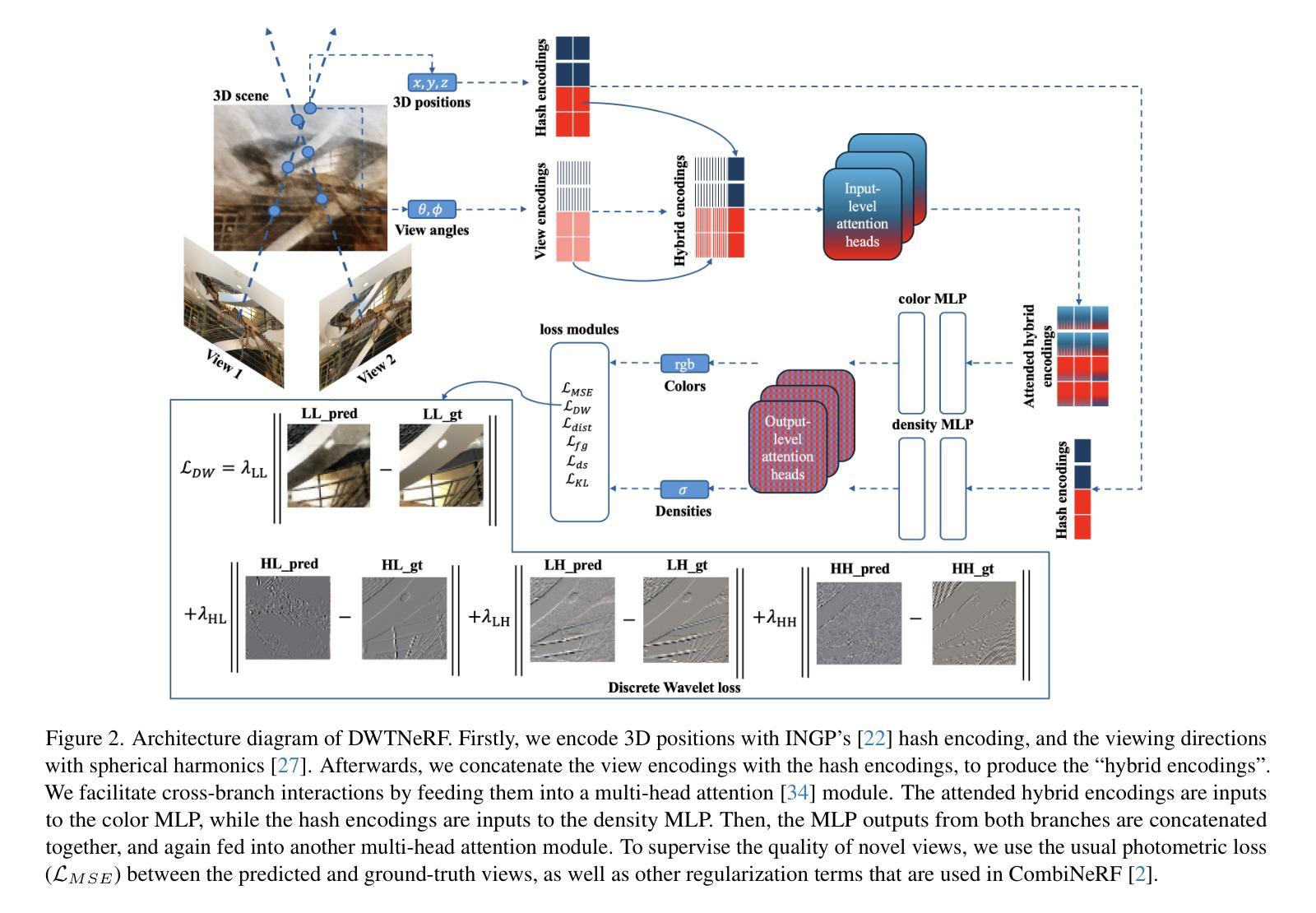
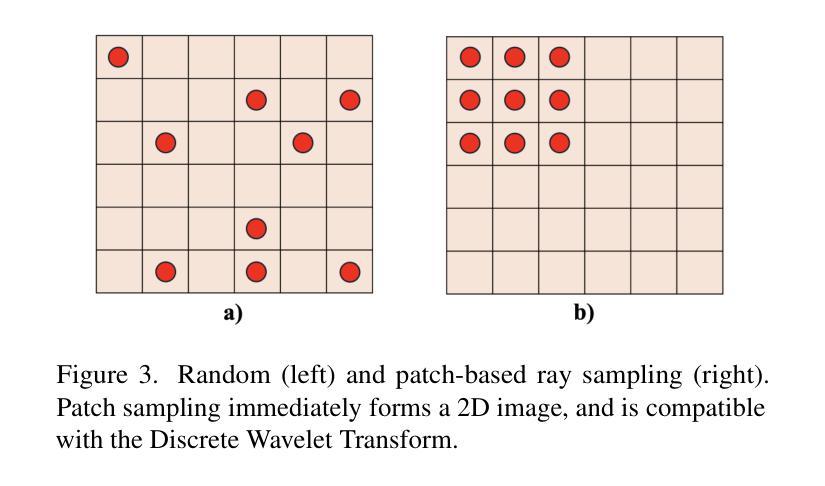
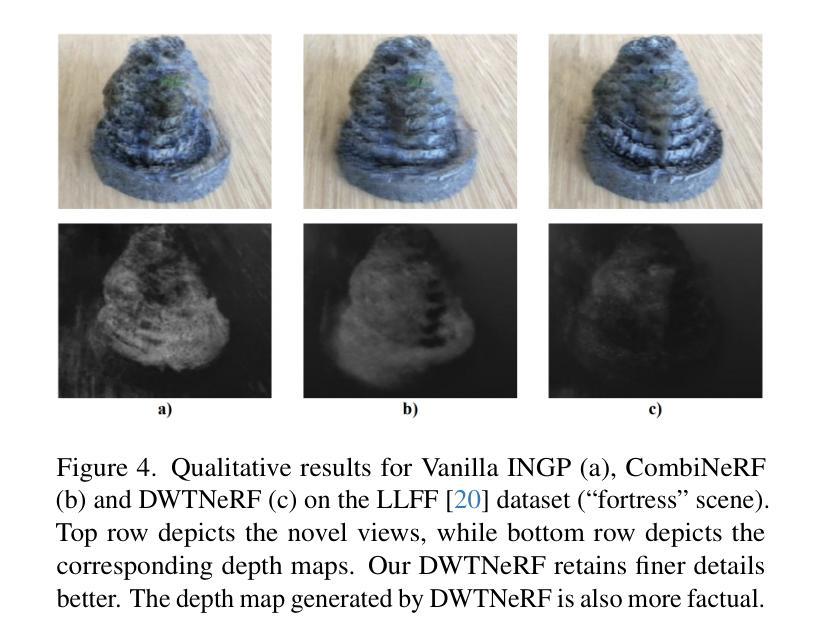
DWTNeRF: Boosting Few-shot Neural Radiance Fields via Discrete Wavelet Transform
Authors:Hung Nguyen, Blark Runfa Li, Truong Nguyen
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) has achieved superior performance in novel view synthesis and 3D scene representation, but its practical applications are hindered by slow convergence and reliance on dense training views. To this end, we present DWTNeRF, a unified framework based on Instant-NGP’s fast-training hash encoding. It is coupled with regularization terms designed for few-shot NeRF, which operates on sparse training views. Our DWTNeRF additionally includes a novel Discrete Wavelet loss that allows explicit prioritization of low frequencies directly in the training objective, reducing few-shot NeRF’s overfitting on high frequencies in earlier training stages. We also introduce a model-based approach, based on multi-head attention, that is compatible with INGP, which are sensitive to architectural changes. On the 3-shot LLFF benchmark, DWTNeRF outperforms Vanilla INGP by 15.07% in PSNR, 24.45% in SSIM and 36.30% in LPIPS. Our approach encourages a re-thinking of current few-shot approaches for fast-converging implicit representations like INGP or 3DGS.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在新型视图合成和3D场景表示方面取得了卓越的性能,但其实际应用受到了收敛速度慢和依赖密集训练视图的影响。为此,我们提出了DWTNeRF,这是一个基于Instant-NGP快速训练哈希编码的统一框架。它与针对少量射击NeRF设计的正则化术语相结合,在稀疏训练视图上运行。我们的DWTNeRF还包括一种新型离散小波损失,允许在训练目标中直接明确优先处理低频,从而减少早期训练阶段中少量射击NeRF对高频的过拟合。我们还介绍了一种基于多头注意力的模型方法,该方法与INGP兼容,对架构变化敏感。在3次拍摄的LLFF基准测试中,DWTNeRF在PSNR上比Vanilla INGP高出15.07%,在SSIM上高出24.45%,在LPIPS上高出36.30%。我们的方法鼓励重新思考当前的少量射击方法,以快速收敛隐式表示形式,如INGP或3DGS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 13 figures, 8 tables
Summary
NeRF技术在新视角合成和三维场景表示方面表现出卓越性能,但其实际应用受到缓慢收敛和依赖密集训练视图的限制。为解决这些问题,提出了DWTNeRF统一框架,结合Instant-NGP的快速训练哈希编码,设计用于少量射击NeRF的正则化术语,并在稀疏训练视图上运行。DWTNeRF还包括一种新的离散小波损失,允许在训练目标中显式优先考虑低频信息,减少早期训练阶段对高频的过拟合。在3次拍摄的LLFF基准测试中,DWTNeRF在PSNR上较Vanilla INGP高出15.07%,在SSIM上高出24.45%,在LPIPS上高出36.30%。DWTNeRF为当前少量拍摄隐式表示方法的快速收敛提供了一个新的思考方向。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术在处理和展示三维场景上具有优越性能,但存在收敛慢和依赖密集训练视图的问题。
- DWTNeRF是一个基于Instant-NGP的快速训练哈希编码的统一框架,解决了NeRF技术的收敛问题。它能在稀疏的训练视图上运行。
- DWTNeRF框架包括一种新颖的离散小波损失技术,能够在训练目标中显式优先考虑低频信息,减少了早期训练阶段对高频的过拟合。
- 在基准测试中,DWTNeRF的性能显著优于传统的NeRF技术。具体来说,它在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS等关键指标上取得了显著的提升。
点此查看论文截图


Self-Instruct Few-Shot Jailbreaking: Decompose the Attack into Pattern and Behavior Learning
Authors:Jiaqi Hua, Wanxu Wei
Recently, several works have been conducted on jailbreaking Large Language Models (LLMs) with few-shot malicious demos. In particular, Zheng et al. focus on improving the efficiency of Few-Shot Jailbreaking (FSJ) by injecting special tokens into the demos and employing demo-level random search, known as Improved Few-Shot Jailbreaking (I-FSJ). Nevertheless, we notice that this method may still require a long context to jailbreak advanced models e.g. 32 shots of demos for Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct (Llama-3) \cite{llama3modelcard}. In this paper, we discuss the limitations of I-FSJ and propose Self-Instruct Few-Shot Jailbreaking (Self-Instruct-FSJ) facilitated with the demo-level greedy search. This framework decomposes the FSJ attack into pattern and behavior learning to exploit the model’s vulnerabilities in a more generalized and efficient way. We conduct elaborate experiments to evaluate our method on common open-source models and compare it with baseline algorithms. Our code is available at https://github.com/iphosi/Self-Instruct-FSJ.
最近,有若干研究利用少量恶意演示来破解大型语言模型(LLM)。特别是,Zheng等人专注于通过向演示中注入特殊令牌并采用演示级随机搜索来提高少量演示破解(FSJ)的效率,这被称为改进型少量演示破解(I-FSJ)。然而,我们注意到此方法可能仍需要较长的上下文来破解高级模型,例如在Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct(Llama-3)中需要32个演示镜头 \cite{llama3modelcard}。在本文中,我们讨论了I-FSJ的局限性,并提出了借助演示级贪心搜索的辅助自我指令少量演示破解(Self-Instruct-FSJ)框架。此框架将FSJ攻击分解为模式学习和行为学习,以更通用和高效的方式利用模型的漏洞。我们进行了精心设计的实验,以评估我们的方法在常用开源模型上的表现,并与基线算法进行了比较。我们的代码位于 https://github.com/iphosi/Self-Instruct-FSJ。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本聚焦于如何通过破解大型语言模型来提升模型效率的问题。文章讨论了现有的Improved Few-Shot Jailbreaking方法在某些高级模型上的局限性,并介绍了Self-Instruct Few-Shot Jailbreaking框架,该框架通过分解FSJ攻击的模式和行为学习,以更通用和高效的方式利用模型的漏洞。通过实验验证该方法的性能并公开了源代码。
Key Takeaways
- Large Language Models (LLMs)的破解方法一直是研究热点,但现有的Improved Few-Shot Jailbreaking方法在破解高级模型时仍有局限性。
- Self-Instruct Few-Shot Jailbreaking框架被提出,通过分解FSJ攻击的模式和行为学习,以更通用和高效的方式利用模型的漏洞。
- 该框架包括在演示中注入特殊令牌并采用演示级别的贪婪搜索来提高效率。
- 实验验证了该框架在公共开源模型上的性能,并与基线算法进行了比较。
- 文章的源代码已公开,可供进一步研究和参考。
- Self-Instruct Few-Shot Jailbreaking可能有助于提升大型语言模型的效率和安全性。
点此查看论文截图



Transforming Role Classification in Scientific Teams Using LLMs and Advanced Predictive Analytics
Authors:Wonduk Seo, Yi Bu
Scientific team dynamics are critical in determining the nature and impact of research outputs. However, existing methods for classifying author roles based on self-reports and clustering lack comprehensive contextual analysis of contributions. Thus, we present a transformative approach to classifying author roles in scientific teams using advanced large language models (LLMs), which offers a more refined analysis compared to traditional clustering methods. Specifically, we seek to complement and enhance these traditional methods by utilizing open source and proprietary LLMs, such as GPT-4, Llama3 70B, Llama2 70B, and Mistral 7x8B, for role classification. Utilizing few-shot prompting, we categorize author roles and demonstrate that GPT-4 outperforms other models across multiple categories, surpassing traditional approaches such as XGBoost and BERT. Our methodology also includes building a predictive deep learning model using 10 features. By training this model on a dataset derived from the OpenAlex database, which provides detailed metadata on academic publications – such as author-publication history, author affiliation, research topics, and citation counts – we achieve an F1 score of 0.76, demonstrating robust classification of author roles.
科研团队的动态在决定研究成果的性质和影响方面至关重要。然而,现有的基于自我报告和聚类的作者角色分类方法缺乏对贡献的全面上下文分析。因此,我们提出了一种利用先进的大型语言模型(LLMs)对科研团队中的作者角色进行分类的变革性方法,与传统聚类方法相比,它提供了更精细的分析。具体来说,我们希望通过利用开源和专有的大型语言模型(如GPT-4、Llama 3 70B、Llama 2 70B和Mistral 7x8B)来分类角色,以补充和增强这些方法。通过少量的提示,我们对作者角色进行了分类,并证明GPT-4在多个类别中优于其他模型,超越了传统的XGBoost和BERT等方法。我们的方法还包括建立一个使用10个特征的预测深度学习模型。通过在OpenAlex数据库衍生的数据集上训练模型(该数据库提供有关学术出版物(如作者出版历史、作者归属关系、研究主题和引用计数)的详细元数据),我们实现了F1分数为0.76,证明了作者角色分类的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables
摘要
科研团队内部的动态对研究产出的性质和影响力起关键作用。现有的基于自我报告和聚类的作者角色分类方法缺乏全面的贡献上下文分析。因此,我们提出了一种利用先进的大型语言模型(LLM)对科研团队中的作者角色进行分类的变革性方法,相比传统的聚类方法,它提供了更为精细的分析。我们旨在结合并优化这些传统方法,利用开源和专有LLM(如GPT-4、Llama3 70B、Llama2 70B和Mistral 7x8B)进行角色分类。通过小样本提示的方法,我们对作者角色进行了分类,并证明GPT-4在多个类别中表现优于其他模型,超越了传统的如XGBoost和BERT的方法。我们的方法还包括利用OpenAlex数据库提供的详细元数据构建预测深度学习模型,对作者角色进行分类,实现了F1分数为0.76。该模型训练数据集包含作者出版历史、作者隶属关系、研究主题和引用计数等特征。
关键见解
- 科研团队动态对研究输出的性质和影响力至关重要。
- 现有作者角色分类方法主要基于自我报告和聚类,缺乏全面的贡献上下文分析。
- 利用先进的大型语言模型(LLM)进行作者角色分类是一种更精细的方法。
- GPT-4在多个类别中表现优于其他模型,用于角色分类。
- GPT-4的优越性能超越了传统的如XGBoost和BERT的方法。
- 利用OpenAlex数据库的详细元数据构建了预测深度学习模型,实现了F1分数为0.76的作者角色分类。
- 模型训练数据集包含丰富的特征,如作者出版历史、作者隶属关系、研究主题和引用计数等。
点此查看论文截图


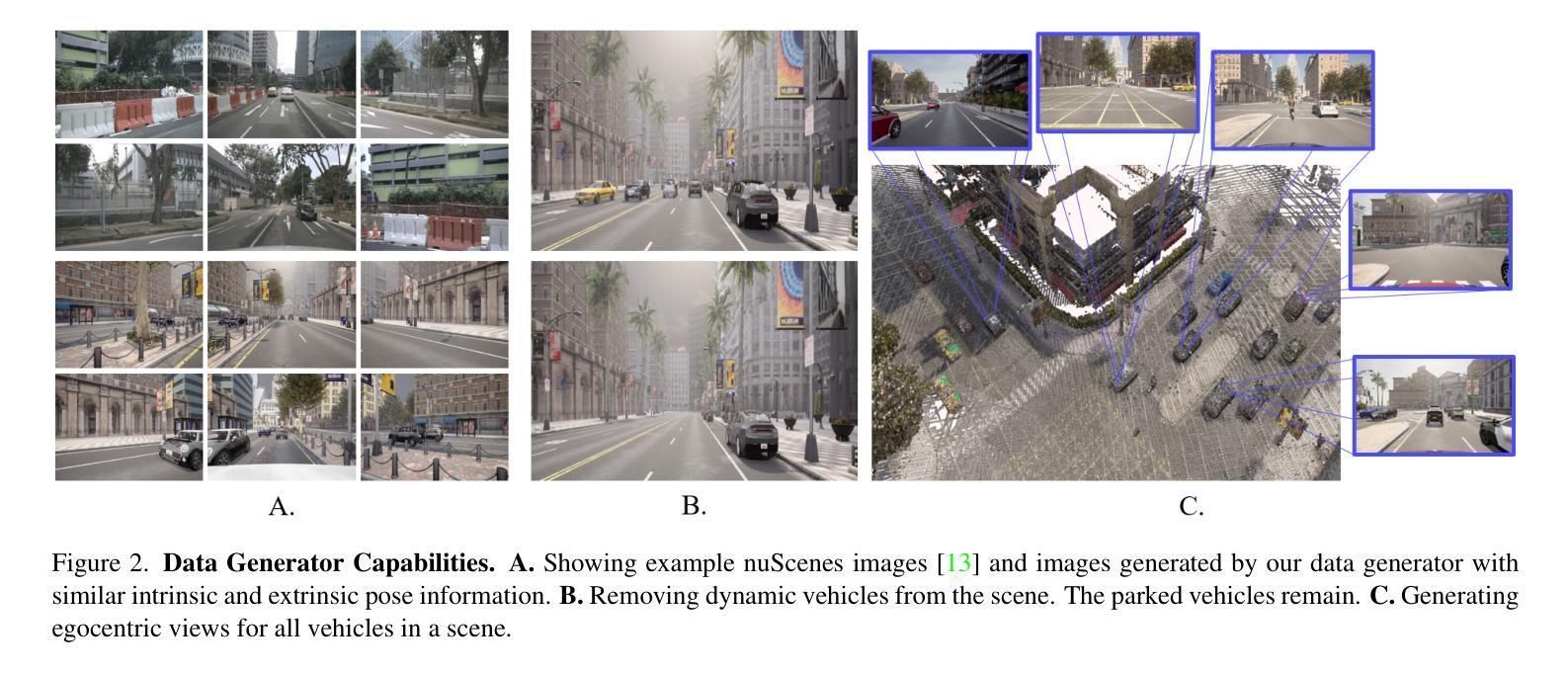
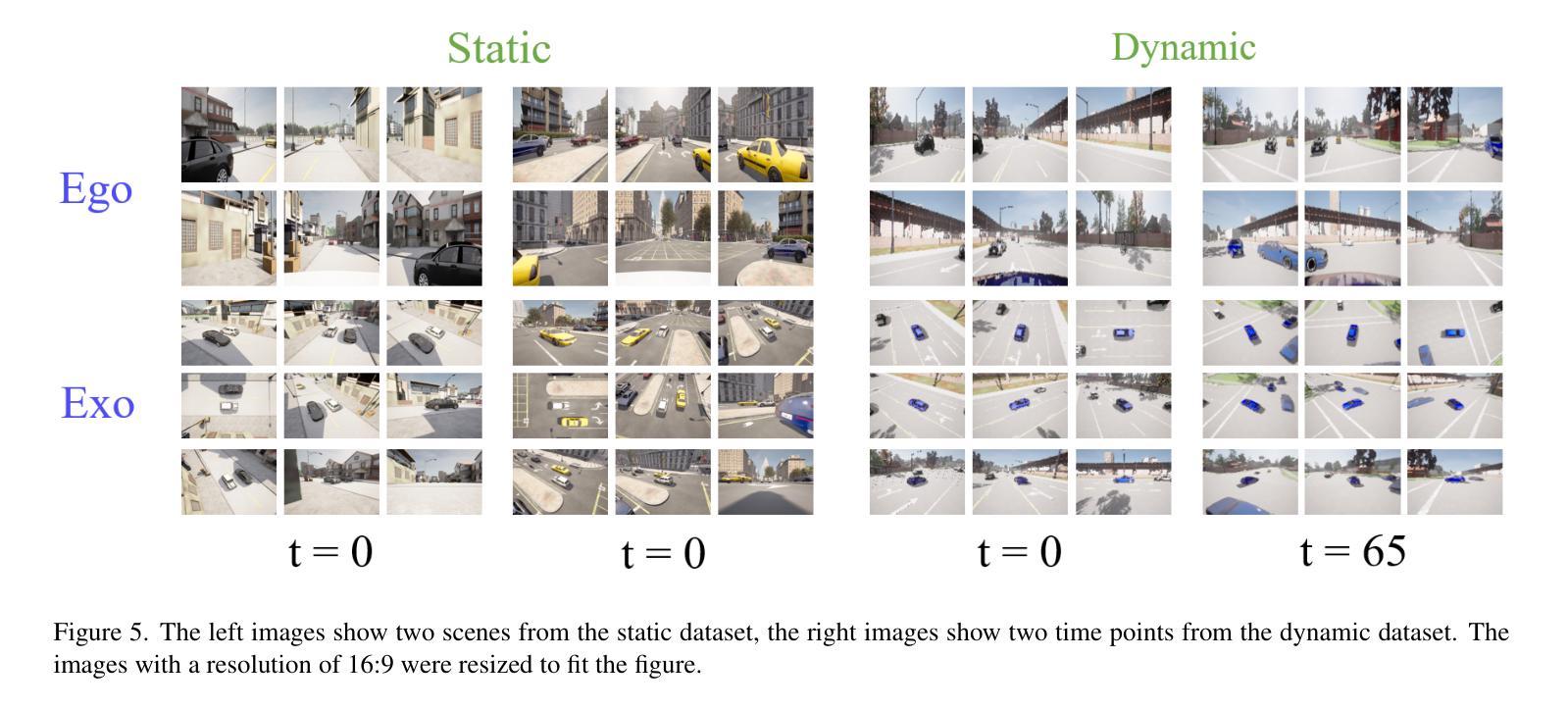
SEED4D: A Synthetic Ego–Exo Dynamic 4D Data Generator, Driving Dataset and Benchmark
Authors:Marius Kästingschäfer, Théo Gieruc, Sebastian Bernhard, Dylan Campbell, Eldar Insafutdinov, Eyvaz Najafli, Thomas Brox
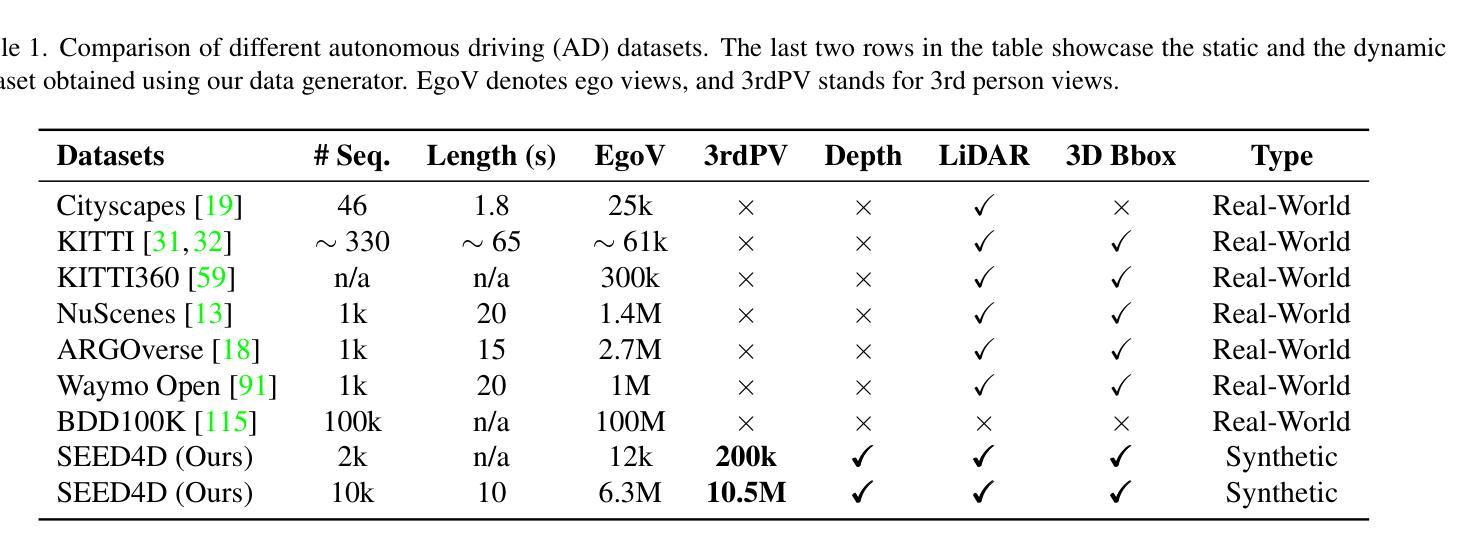
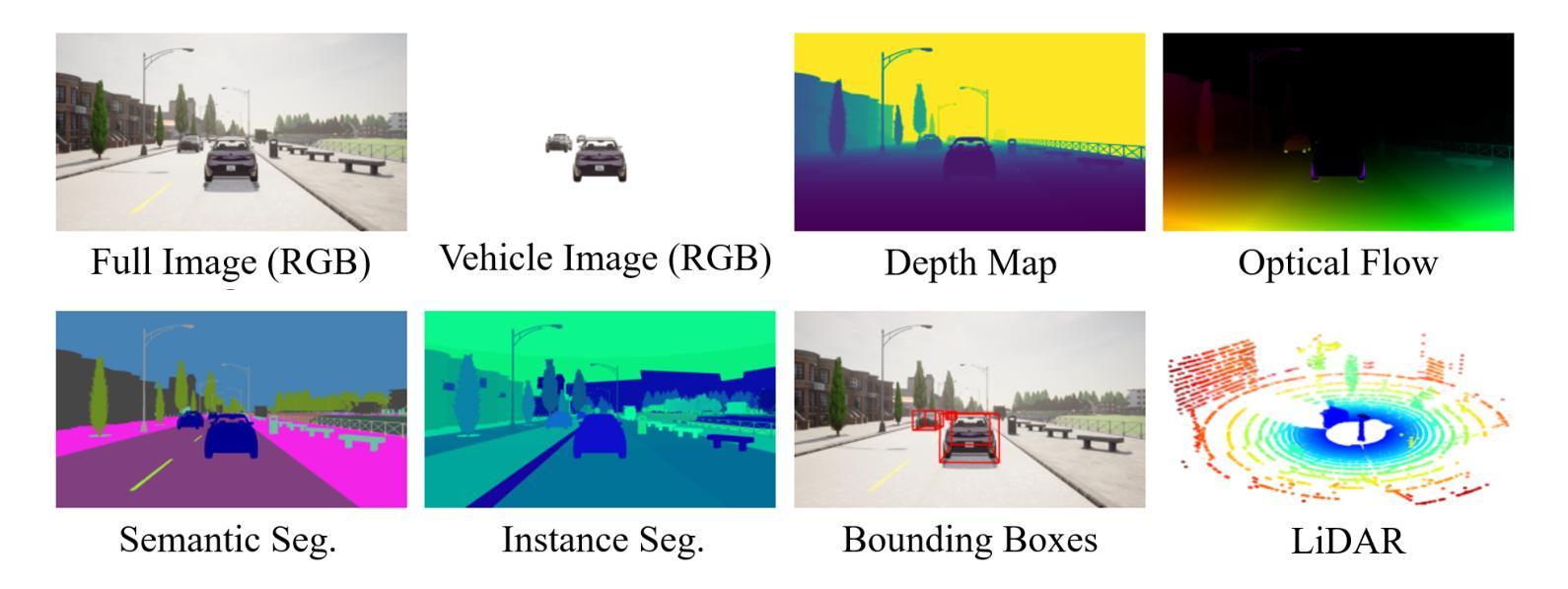
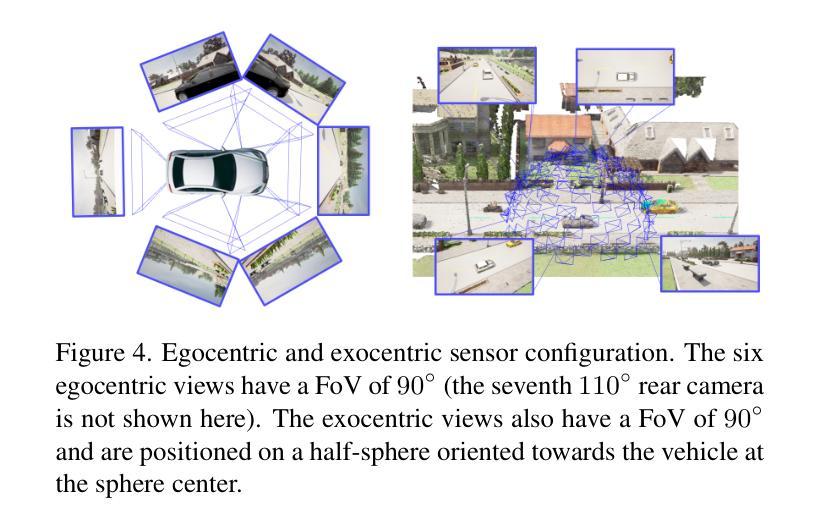
Models for egocentric 3D and 4D reconstruction, including few-shot interpolation and extrapolation settings, can benefit from having images from exocentric viewpoints as supervision signals. No existing dataset provides the necessary mixture of complex, dynamic, and multi-view data. To facilitate the development of 3D and 4D reconstruction methods in the autonomous driving context, we propose a Synthetic Ego–Exo Dynamic 4D (SEED4D) data generator and dataset. We present a customizable, easy-to-use data generator for spatio-temporal multi-view data creation. Our open-source data generator allows the creation of synthetic data for camera setups commonly used in the NuScenes, KITTI360, and Waymo datasets. Additionally, SEED4D encompasses two large-scale multi-view synthetic urban scene datasets. Our static (3D) dataset encompasses 212k inward- and outward-facing vehicle images from 2k scenes, while our dynamic (4D) dataset contains 16.8M images from 10k trajectories, each sampled at 100 points in time with egocentric images, exocentric images, and LiDAR data. The datasets and the data generator can be found at https://seed4d.github.io/.
对于以自我为中心(egocentric)的3D和4D重建模型,包括小样本插值和外推设置,可以从异位视角的图像中获得监督信号,从而受益。目前没有数据集能够提供复杂、动态和多视角数据所必需的混合。为了促进在自动驾驶背景下3D和4D重建方法的发展,我们提出了合成自我异位动态四维(SEED4D)数据生成器和数据集。我们展示了一个可定制的、易于使用的多视角时空数据生成器。我们的开源数据生成器可以创建常用于NuScenes、KITTI360和Waymo数据集的相机设置合成数据。此外,SEED4D包含两个大规模的多视角合成城市场景数据集。我们的静态(3D)数据集包含来自2k场景的21.2万张车内和车外车辆图像,而我们的动态(4D)数据集包含来自10k轨迹的1680万张图像,每条轨迹在时间上采样100个点,包括以自我为中心的图像、以异位为中心的图像和激光雷达数据。数据集和数据生成器可在https://seed4d.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV 2025. Project page: https://seed4d.github.io/. Code: https://github.com/continental/seed4d
Summary
该文本介绍了一个名为SEED4D的合成数据集生成器,它能生成适用于自动驾驶场景的egocentric 3D和4D重建模型所需的合成数据。该生成器可以为复杂的动态多视角数据创建混合体,从而促进模型的训练和发展。SEED4D包含两个大规模的多视角合成城市场景数据集,涵盖了静态的3D数据集和动态的4D数据集。此外,数据生成器易于使用且可定制,适用于NuScenes、KITTI360和Waymo等常用的相机设置。数据集和生成器可在SEED4D官方网站下载和使用。
Key Takeaways
- SEED4D是一个合成数据集生成器,用于生成适用于自动驾驶场景的egocentric 3D和4D重建模型的数据。
- 生成的数据包括复杂的动态多视角数据,有助于提高模型的训练效果。
- SEED4D包含静态的3D数据集和动态的4D数据集,涵盖大规模的多视角合成城市场景。
- 数据生成器适用于常见的相机设置,如NuScenes、KITTI360和Waymo。
- 数据生成器具有可定制性和易用性。
- SEED4D官网提供数据集和生成器的下载和使用。
点此查看论文截图



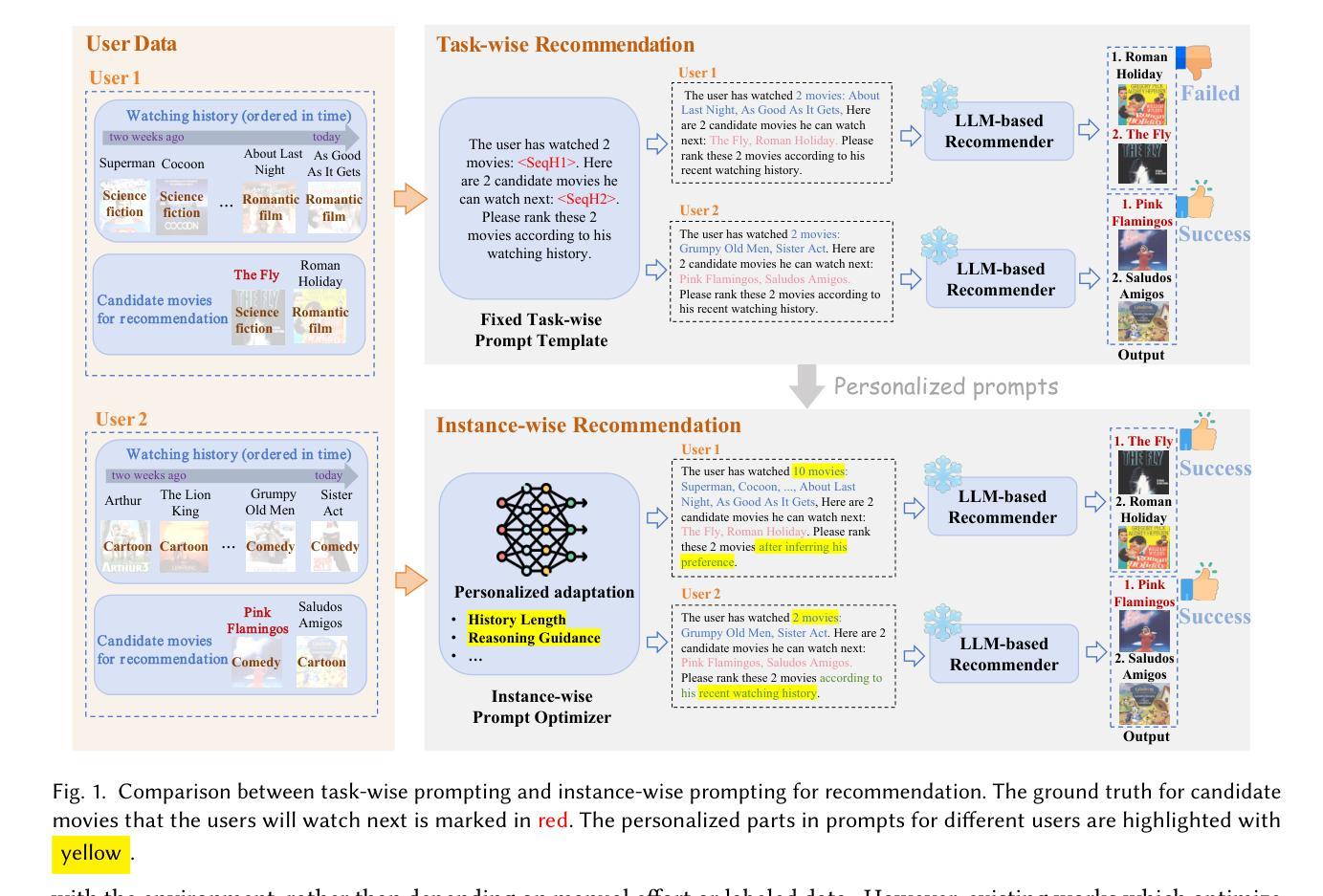
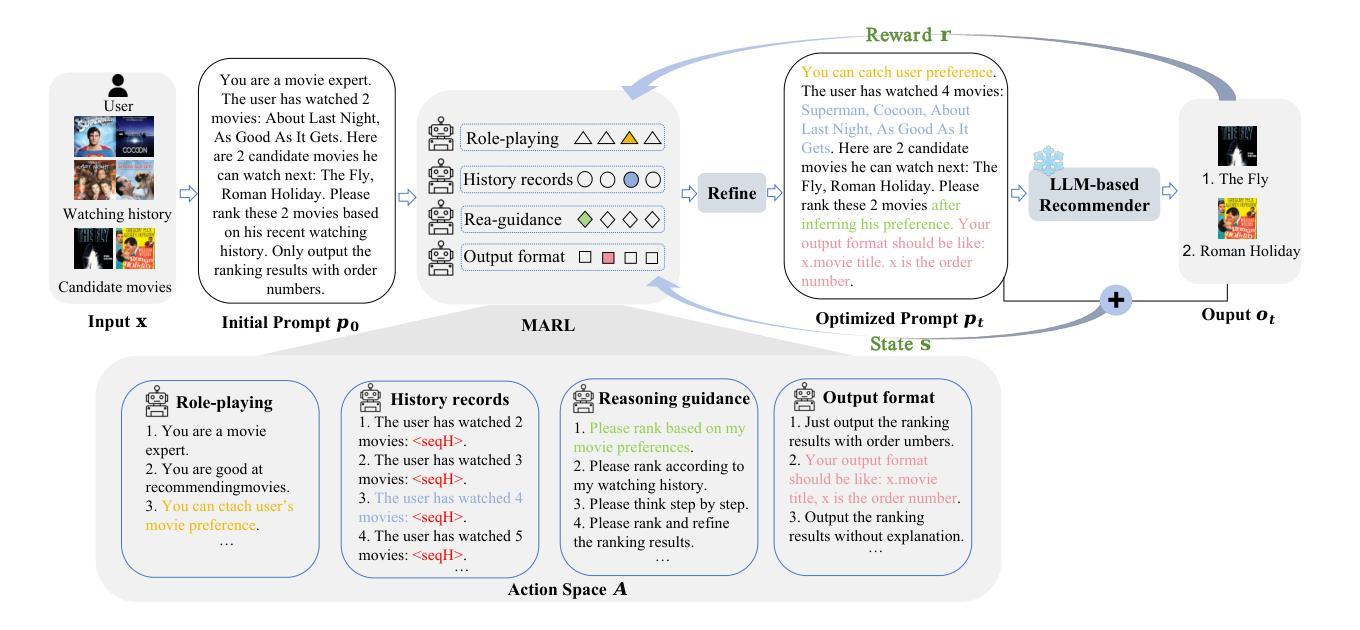
Reinforced Prompt Personalization for Recommendation with Large Language Models
Authors:Wenyu Mao, Jiancan Wu, Weijian Chen, Chongming Gao, Xiang Wang, Xiangnan He
Designing effective prompts can empower LLMs to understand user preferences and provide recommendations with intent comprehension and knowledge utilization capabilities. Nevertheless, recent studies predominantly concentrate on task-wise prompting, developing fixed prompt templates shared across all users in a given recommendation task (e.g., rating or ranking). Although convenient, task-wise prompting overlooks individual user differences, leading to inaccurate analysis of user interests. In this work, we introduce the concept of instance-wise prompting, aiming at personalizing discrete prompts for individual users. Toward this end, we propose Reinforced Prompt Personalization (RPP) to realize it automatically. To improve efficiency and quality, RPP personalizes prompts at the sentence level rather than searching in the vast vocabulary word-by-word. Specifically, RPP breaks down the prompt into four patterns, tailoring patterns based on multi-agent and combining them. Then the personalized prompts interact with LLMs (environment) iteratively, to boost LLMs’ recommending performance (reward). In addition to RPP, to improve the scalability of action space, our proposal of RPP+ dynamically refines the selected actions with LLMs throughout the iterative process. Extensive experiments on various datasets demonstrate the superiority of RPP/RPP+ over traditional recommender models, few-shot methods, and other prompt-based methods, underscoring the significance of instance-wise prompting in LLMs for recommendation. Our code is available at https://github.com/maowenyu-11/RPP.
设计有效的提示可以赋能大型语言模型(LLMs),使其能够理解用户偏好,并提供具有意图理解和知识利用能力的推荐。然而,最近的研究主要集中在任务式的提示上,即在给定的推荐任务(如评分或排名)中,为所有用户开发固定的提示模板。虽然方便,但任务式的提示忽视了单个用户之间的差异,导致对用户兴趣的不准确分析。在这项工作中,我们引入了实例级提示的概念,旨在针对单个用户进行个性化的离散提示。为此,我们提出了强化提示个性化(RPP)的方法来实现其自动化。为了提高效率和质量,RPP在句子级别个性化提示,而不是在庞大的词汇表中逐字搜索。具体来说,RPP将提示分解为四种模式,基于多代理定制模式并将其组合。然后,个性化的提示与LLMs(环境)进行迭代交互,以提高LLMs的推荐性能(奖励)。除了RPP之外,为了提高动作空间的可扩展性,我们提出的RPP+在迭代过程中动态优化所选动作与LLMs的配合。在多种数据集上的大量实验表明,RPP/RPP+优于传统推荐模型、少样本方法和其他基于提示的方法,突显了实例级提示在LLMs推荐中的重要性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/maowenyu-11/RPP获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了设计有效提示语可以赋能大型语言模型(LLMs)以理解用户偏好并提供个性化推荐的能力。针对当前主要研究的任务式提示方法忽略用户个体差异的问题,本文提出了实例式提示的概念,旨在针对每个用户个性化定制提示语。为此,本文提出了强化提示个性化(RPP)方法,可以在句子级别个性化提示语,提高效率和质量。此外,为了改善行动空间的扩展性,还提出了RPP+方法,在迭代过程中动态优化所选行动。实验证明,RPP和RPP+在推荐性能上优于传统推荐模型、少样本方法和其它提示语方法,突显实例式提示在LLMs推荐中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 设计有效提示语能增强LLMs理解用户偏好并提供个性化推荐的能力。
- 当前任务式提示方法忽略用户个体差异,导致对用户兴趣分析不准确。
- 实例式提示旨在针对每个用户个性化定制提示语。
- 强化提示个性化(RPP)方法能在句子级别个性化提示语,提高效率。
- RPP+方法动态优化所选行动,改善行动空间的扩展性。
- 实验证明RPP和RPP+在推荐性能上优于传统和其它方法。
- 实例式提示在LLMs推荐中具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

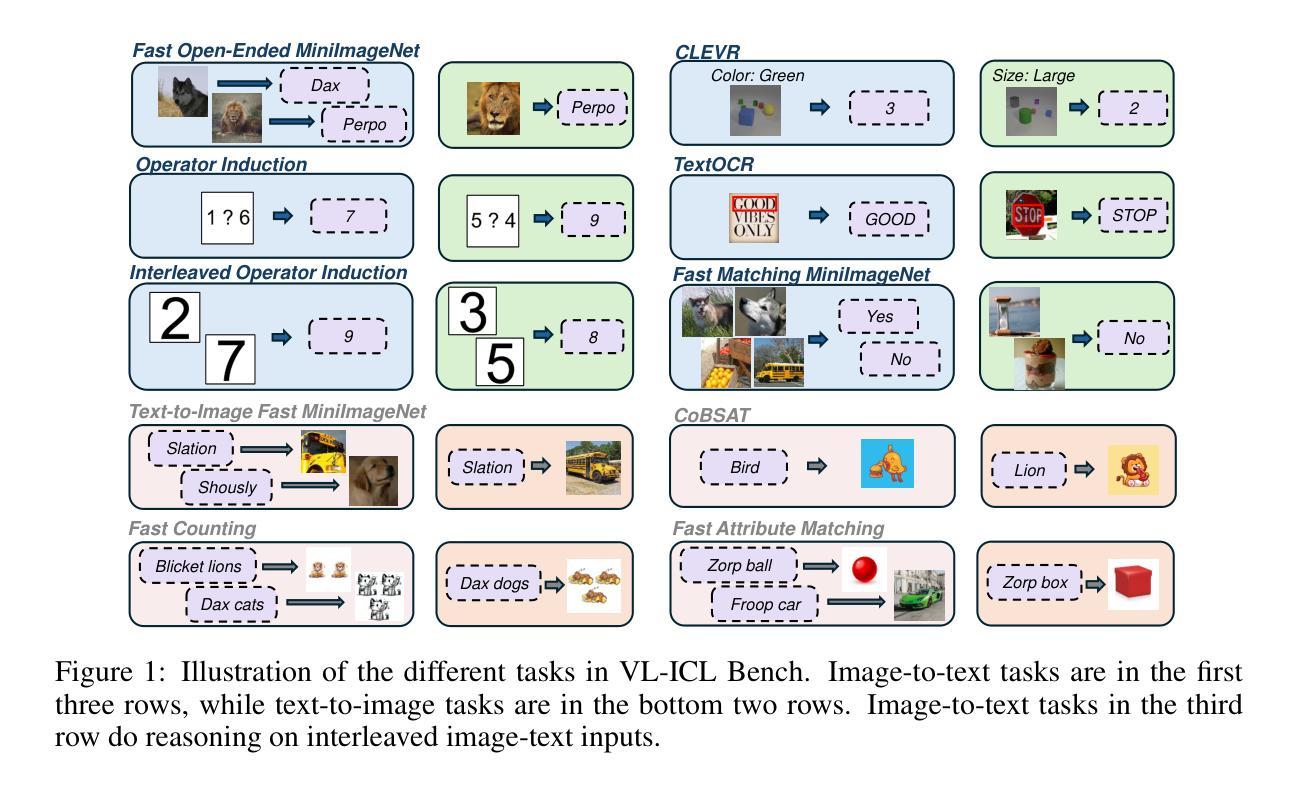
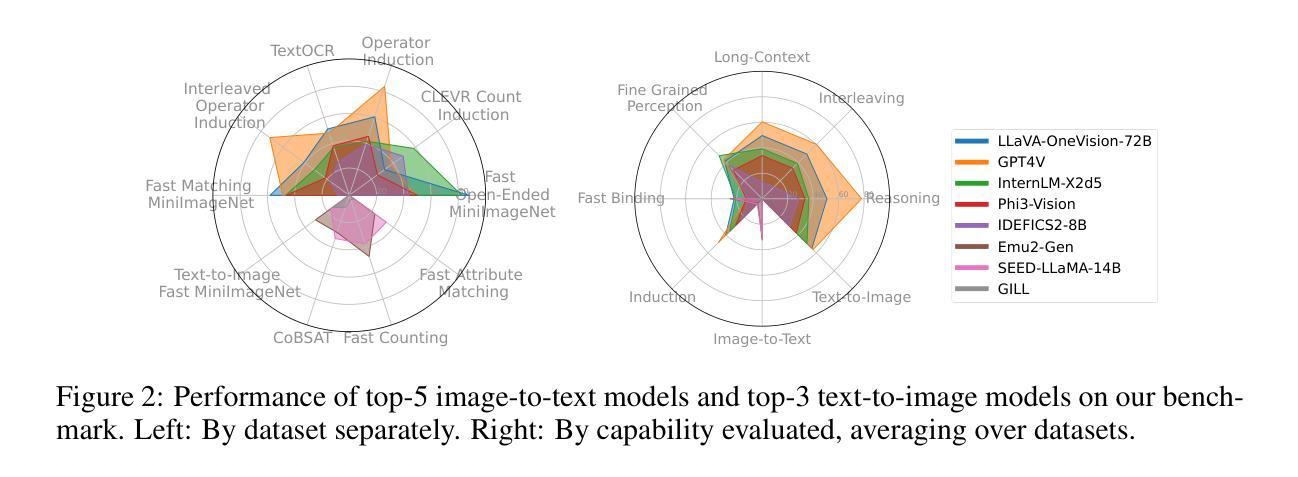
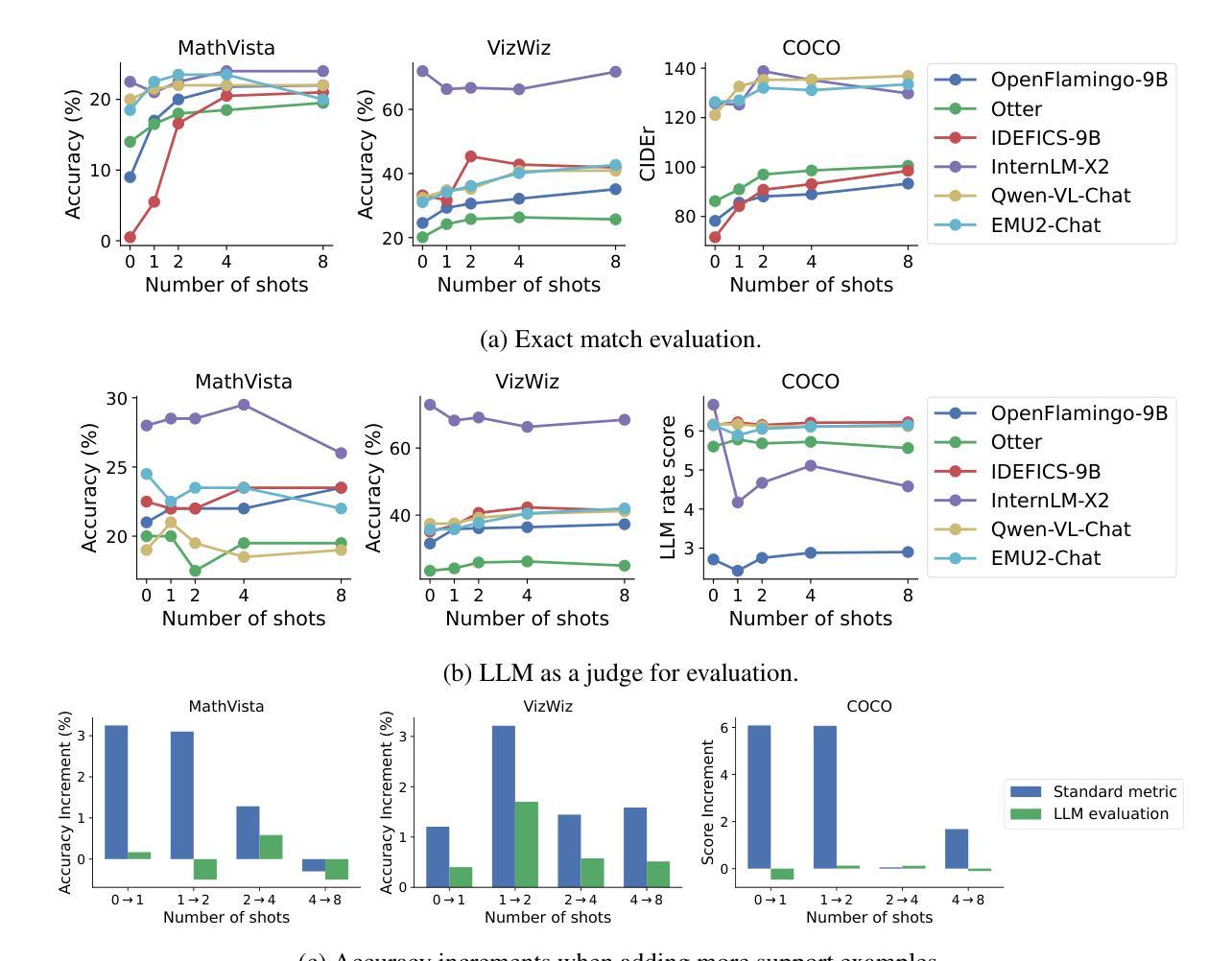
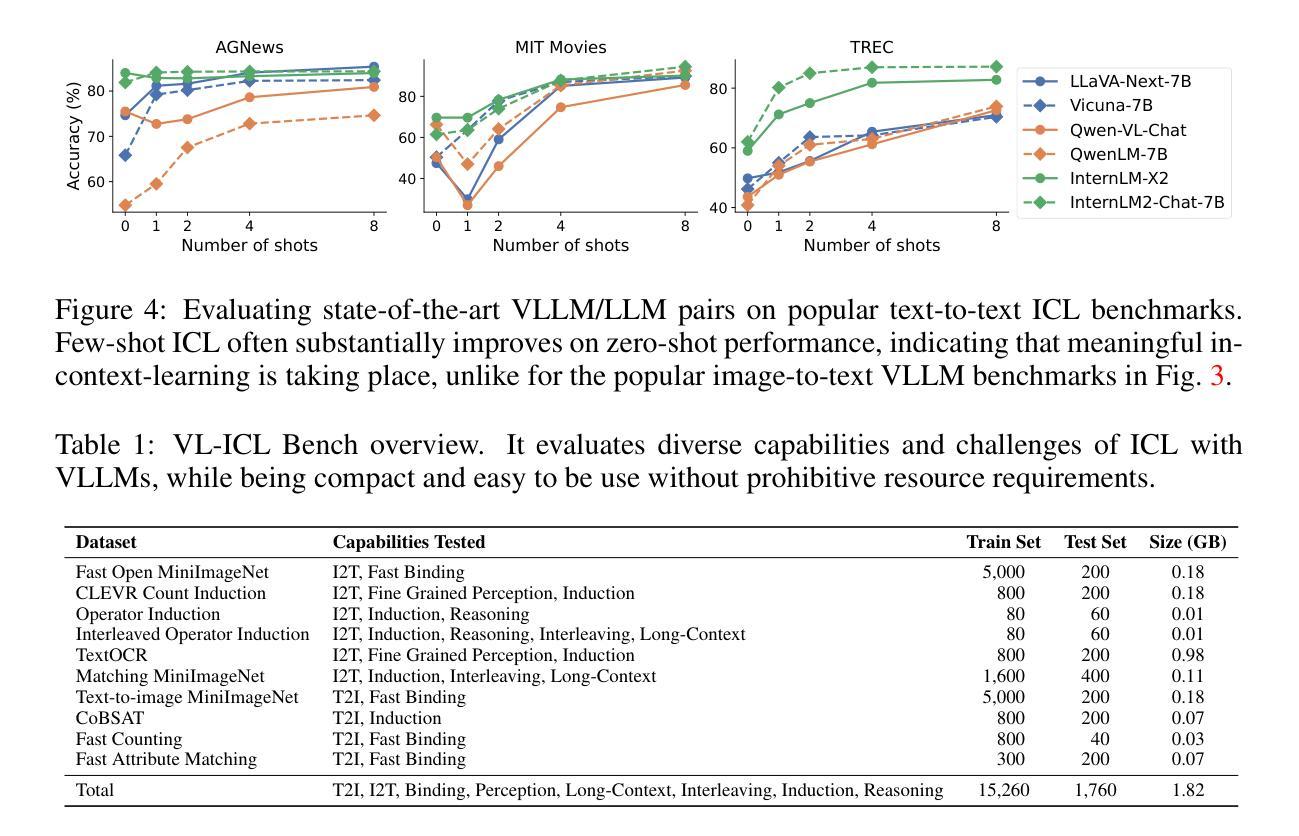
VL-ICL Bench: The Devil in the Details of Multimodal In-Context Learning
Authors:Yongshuo Zong, Ondrej Bohdal, Timothy Hospedales
Large language models (LLMs) famously exhibit emergent in-context learning (ICL) – the ability to rapidly adapt to new tasks using few-shot examples provided as a prompt, without updating the model’s weights. Built on top of LLMs, vision large language models (VLLMs) have advanced significantly in areas such as recognition, reasoning, and grounding. However, investigations into \emph{multimodal ICL} have predominantly focused on few-shot visual question answering (VQA), and image captioning, which we will show neither exploit the strengths of ICL, nor test its limitations. The broader capabilities and limitations of multimodal ICL remain under-explored. In this study, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark VL-ICL Bench for multimodal in-context learning, encompassing a broad spectrum of tasks that involve both images and text as inputs and outputs, and different types of challenges, from {perception to reasoning and long context length}. We evaluate the abilities of state-of-the-art VLLMs against this benchmark suite, revealing their diverse strengths and weaknesses, and showing that even the most advanced models, such as GPT-4, find the tasks challenging. By highlighting a range of new ICL tasks, and the associated strengths and limitations of existing models, we hope that our dataset will inspire future work on enhancing the in-context learning capabilities of VLLMs, as well as inspire new applications that leverage VLLM ICL. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ys-zong/VL-ICL.
大型语言模型(LLM)展现出了突出的上下文突发学习(ICL)能力——即使用少量示例进行提示即可快速适应新任务,而无需更新模型权重。建立在大型语言模型之上的视觉大型语言模型(VLLM)在识别、推理和接地等领域取得了显著进展。然而,对于多模式ICL的研究主要集中在基于视觉的少量问答(VQA)和图像描述上,我们将展示它们都没有充分利用ICL的优势,也没有测试其局限性。多模式ICL的更广泛的能力和局限性尚未得到充分探索。本研究中,我们引入了全面的基准测试VL-ICL Bench,用于多模式上下文学习,涵盖了一系列涉及图像和文本作为输入和输出的任务,涵盖了从感知到推理和长上下文长度的不同类型挑战。我们针对这个基准测试套件评估了最先进的大型视觉语言模型的能力,揭示了它们的各种优势和劣势,并表明即使是最先进的模型,如GPT-4,也发现这些任务具有挑战性。通过突出一系列新的ICL任务以及现有模型的关联优势和局限性,我们希望我们的数据集能够激发未来关于增强大型视觉语言模型的上下文学习能力的相关工作,并激发利用大型视觉语言模型ICL的新应用。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/ys-zong/VL-ICL上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
大型语言模型展现出基于上下文的快速学习能力,而视觉大型语言模型在识别、推理和定位等领域有了显著进展。然而,对于多模态的基于上下文的学习的研究主要集中在视觉问答和图像描述生成上,其未能充分利用和测试这种学习的优势。本研究引入了一个全面的多模态基于上下文学习的基准测试VL-ICL Bench,涵盖一系列任务和挑战,从感知到推理和长文本上下文。我们评估了最先进的视觉大型语言模型在该基准测试上的表现,揭示了其多样化的优势和弱点,并显示即使是最先进的模型如GPT-4也面临挑战。我们希望这一数据集能激励未来增强视觉大型语言模型的基于上下文的学习能力的研究,并激发利用这种学习能力的新应用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型展现出基于上下文的快速学习能力。
- 视觉大型语言模型在识别、推理和定位等领域有显著进展。
- 当前多模态基于上下文的学习研究主要集中在视觉问答和图像描述生成,未能充分利用和测试这种学习的优势。
- 引入了一个全面的多模态基于上下文学习的基准测试VL-ICL Bench。
- 评估了最先进的视觉大型语言模型在该基准测试上的表现。
- 揭示了视觉大型语言模型在基于上下文学习上的多样化优势和弱点。
点此查看论文截图

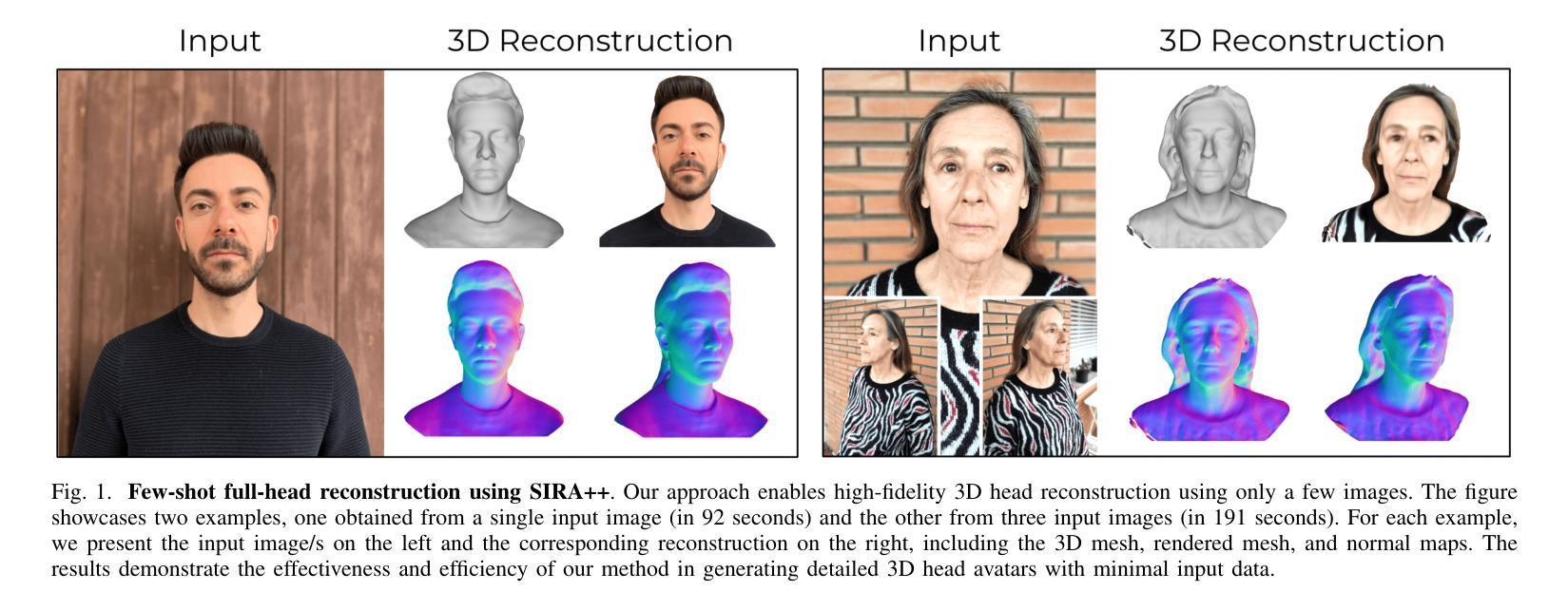
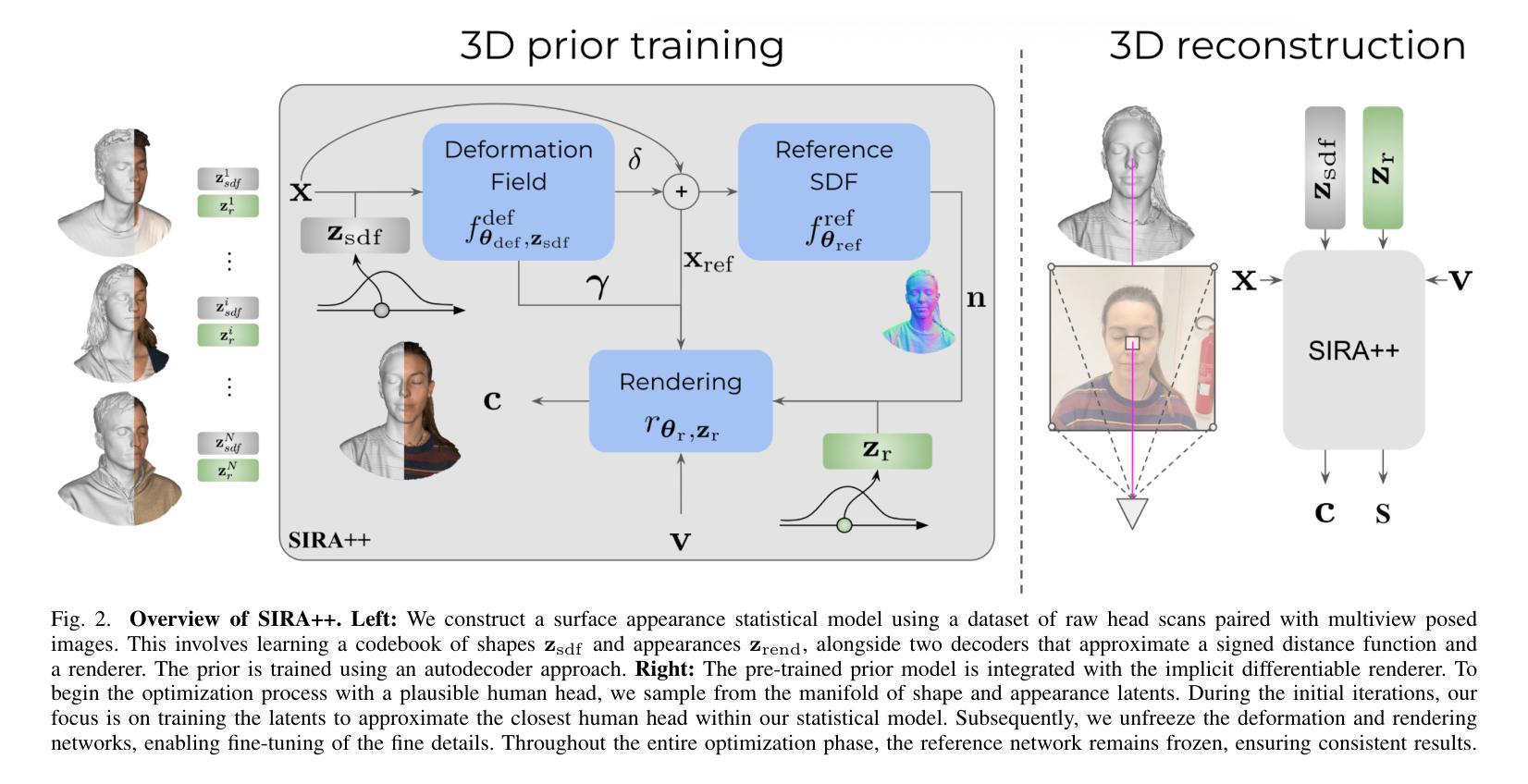
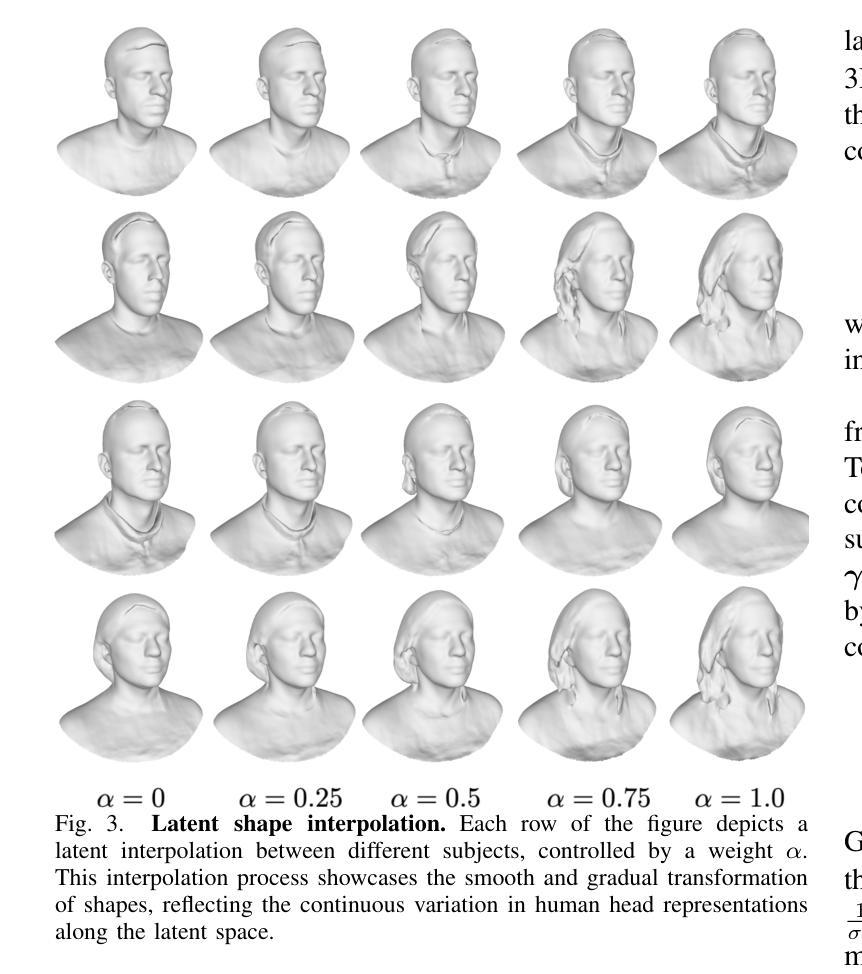
Implicit Shape and Appearance Priors for Few-Shot Full Head Reconstruction
Authors:Pol Caselles, Eduard Ramon, Jaime Garcia, Gil Triginer, Francesc Moreno-Noguer
Recent advancements in learning techniques that employ coordinate-based neural representations have yielded remarkable results in multi-view 3D reconstruction tasks. However, these approaches often require a substantial number of input views (typically several tens) and computationally intensive optimization procedures to achieve their effectiveness. In this paper, we address these limitations specifically for the problem of few-shot full 3D head reconstruction. We accomplish this by incorporating a probabilistic shape and appearance prior into coordinate-based representations, enabling faster convergence and improved generalization when working with only a few input images (even as low as a single image). During testing, we leverage this prior to guide the fitting process of a signed distance function using a differentiable renderer. By incorporating the statistical prior alongside parallelizable ray tracing and dynamic caching strategies, we achieve an efficient and accurate approach to few-shot full 3D head reconstruction. Moreover, we extend the H3DS dataset, which now comprises 60 high-resolution 3D full head scans and their corresponding posed images and masks, which we use for evaluation purposes. By leveraging this dataset, we demonstrate the remarkable capabilities of our approach in achieving state-of-the-art results in geometry reconstruction while being an order of magnitude faster than previous approaches.
近期,采用坐标基神经网络表示的学习技术在多视角3D重建任务中取得了显著成果。然而,这些方法通常需要大量的输入视角(通常是数十个)和计算密集型的优化程序才能发挥其作用。在本文中,我们针对少样本全3D头部重建问题解决了这些限制。我们通过将概率形状和外观先验知识融入坐标基表示,仅使用少量输入图像(甚至低至单张图像)即可实现更快的收敛和更好的泛化能力。在测试过程中,我们利用此先验知识,通过可微分渲染器引导有符号距离函数的拟合过程。通过将统计先验知识与可并行化的光线追踪和动态缓存策略相结合,我们实现了高效且精准的少样本全3D头部重建方法。此外,我们扩展了H3DS数据集,现在包含60个高分辨率的3D全头扫描及其相应的姿态图像和蒙版,用于评估目的。我们利用此数据集,展示了我们的方法在几何重建方面达到最新技术成果,同时比以前的方法快一个数量级。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) 2025
Summary
近期基于坐标的神经网络表示学习方法在多视角3D重建任务中取得了显著成果,但在处理少量输入图像时面临挑战。本文提出了一种针对少视角头部重建的方法,通过引入概率形状和外观先验信息,提高了收敛速度和泛化能力。此外,利用并行光线追踪和动态缓存策略实现了高效准确的重建方法。本文还扩展了H3DS数据集,用于评估重建效果。
Key Takeaways
- 引入概率形状和外观先验信息,提高少视角头部重建的收敛速度和泛化能力。
- 利用可微分的渲染器将先验信息应用于符号距离函数的拟合过程。
- 通过并行光线追踪和动态缓存策略实现高效准确的重建方法。
- 扩展了H3DS数据集,包含60个高分辨率的3D头部扫描数据及其对应的姿态图像和掩码。
- 方法在几何重建方面取得了最新成果,且运行速度比先前的方法快一个数量级。
- 方法在少视角或单视角的输入条件下仍然表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图