⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
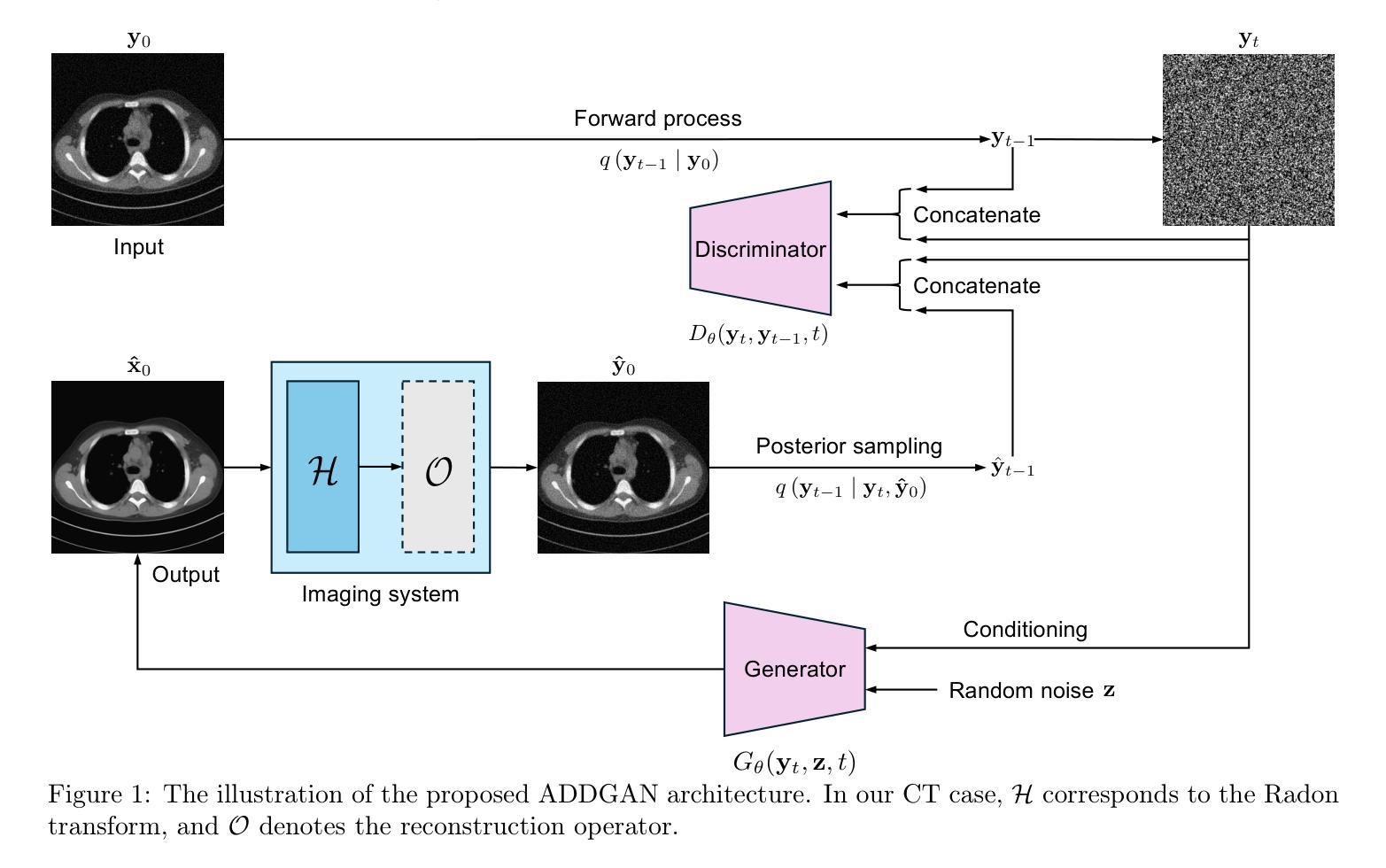
Ambient Denoising Diffusion Generative Adversarial Networks for Establishing Stochastic Object Models from Noisy Image Data
Authors:Xichen Xu, Wentao Chen, Weimin Zhou
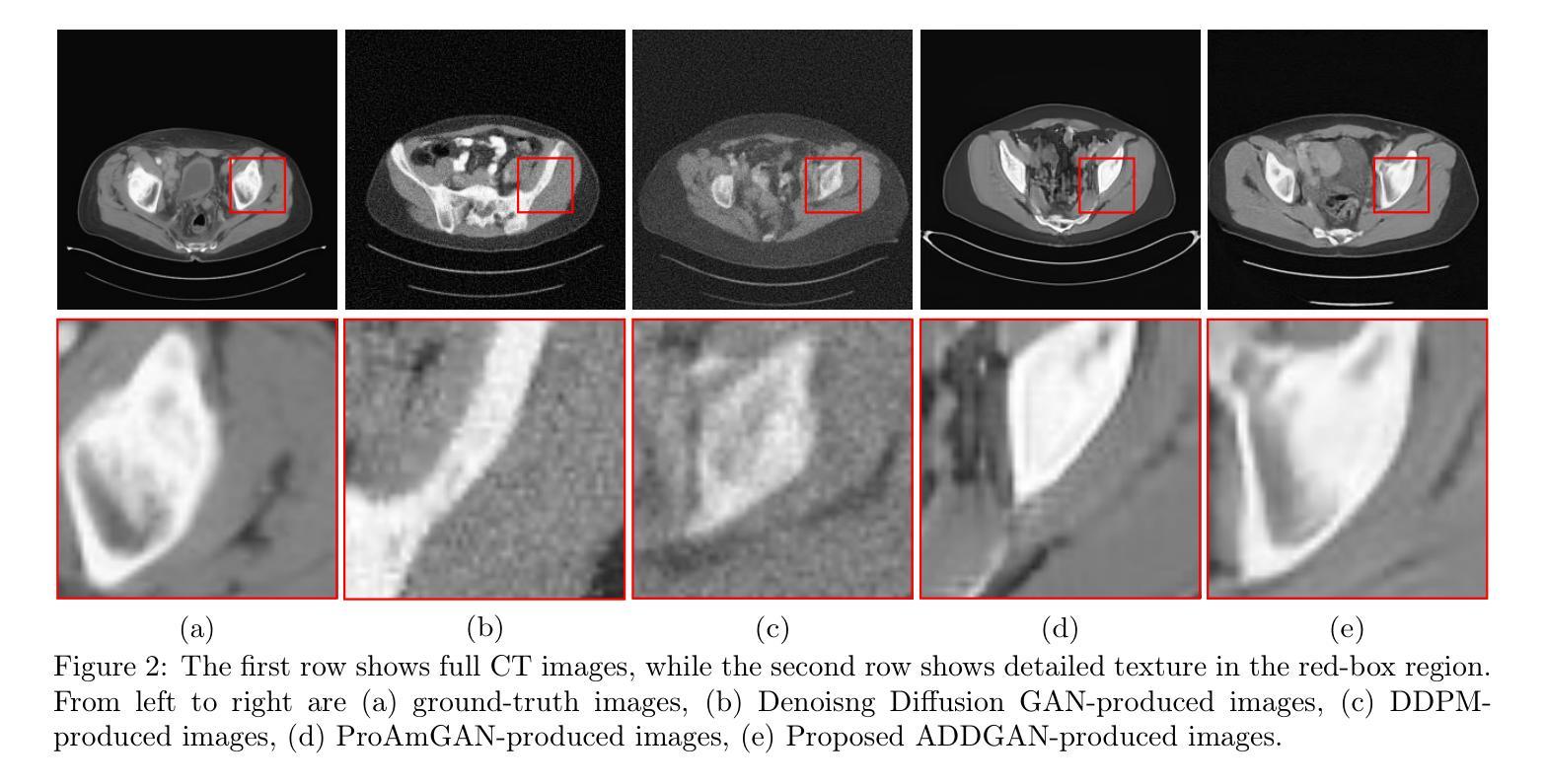
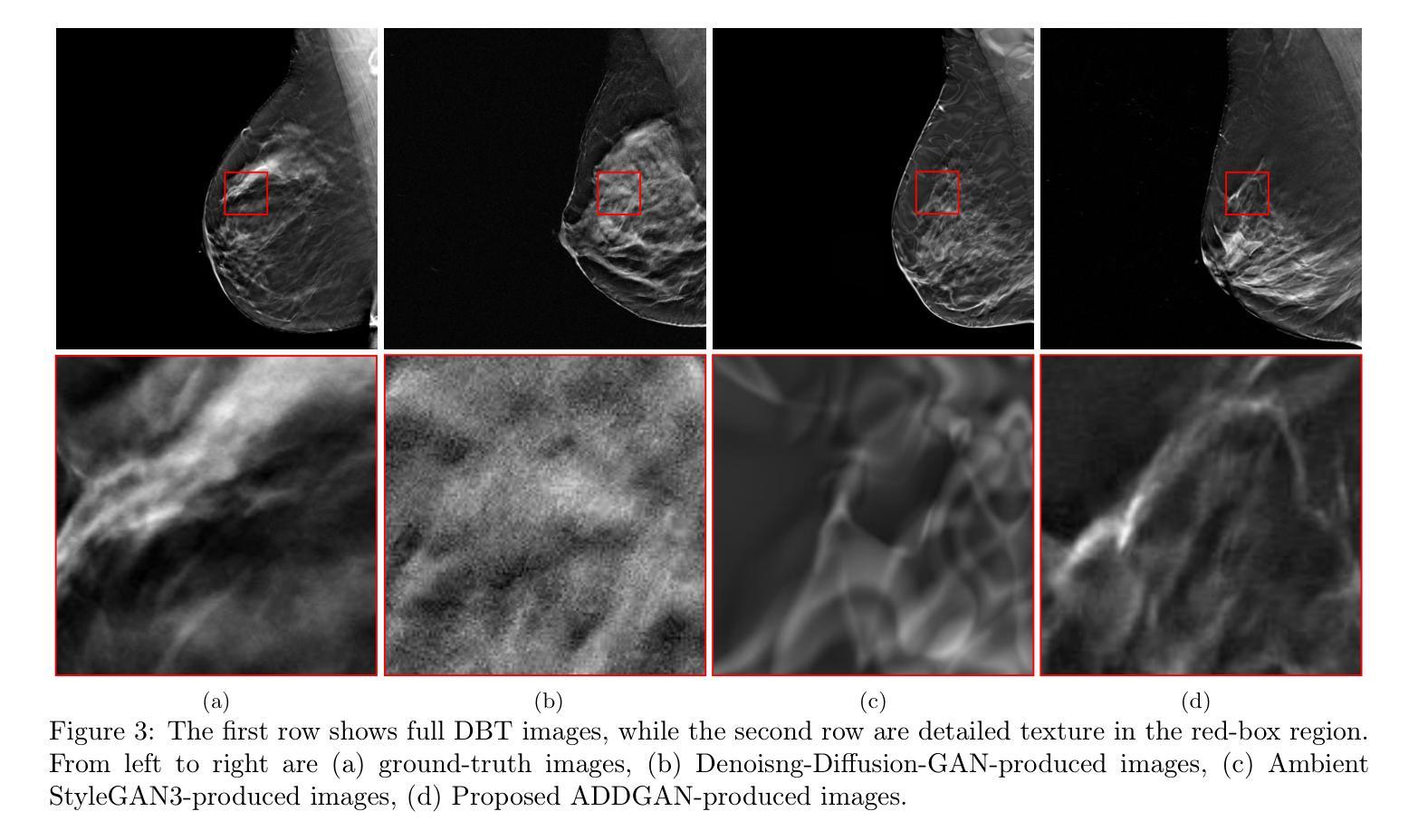
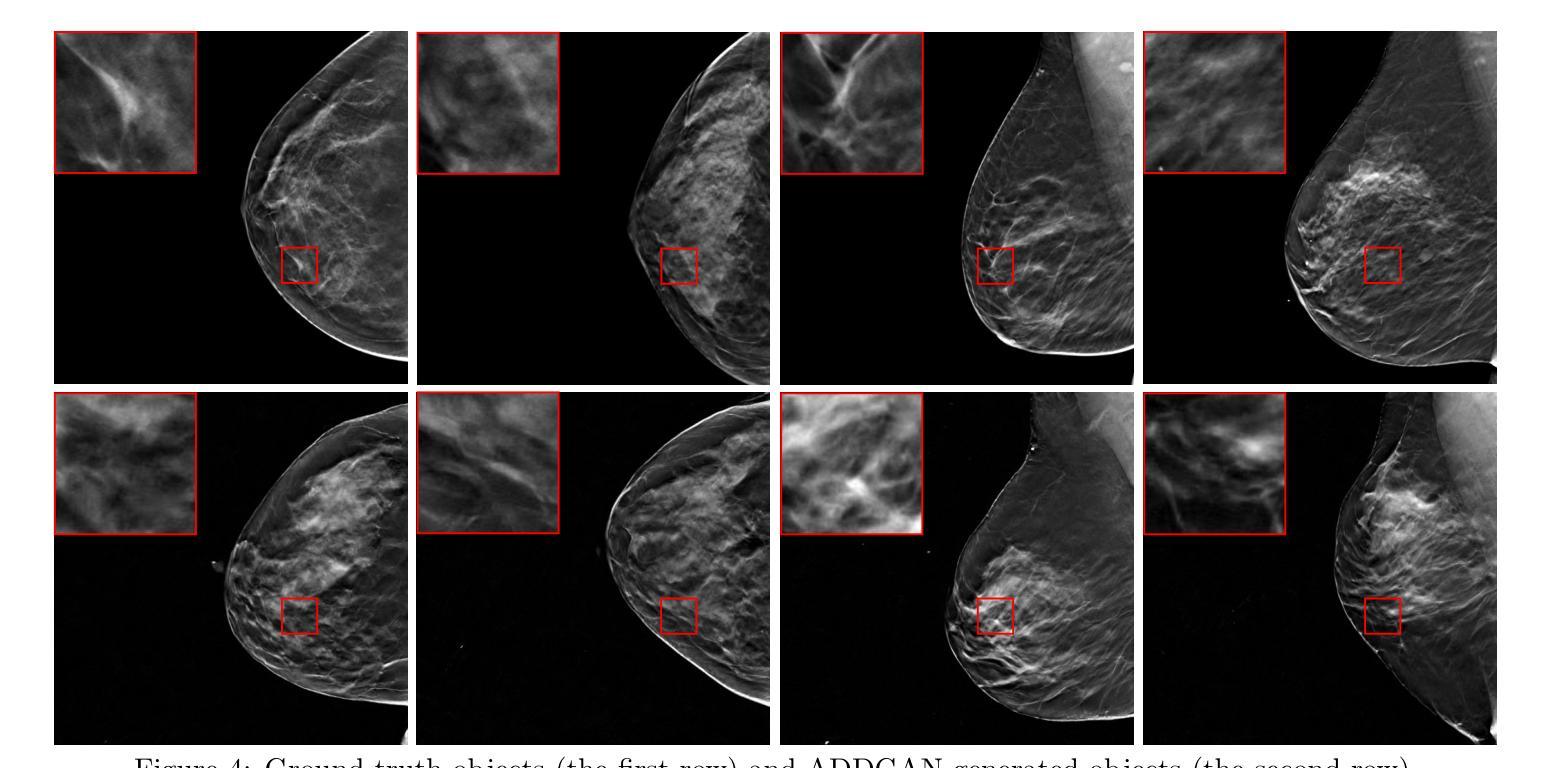
It is widely accepted that medical imaging systems should be objectively assessed via task-based image quality (IQ) measures that ideally account for all sources of randomness in the measured image data, including the variation in the ensemble of objects to be imaged. Stochastic object models (SOMs) that can randomly draw samples from the object distribution can be employed to characterize object variability. To establish realistic SOMs for task-based IQ analysis, it is desirable to employ experimental image data. However, experimental image data acquired from medical imaging systems are subject to measurement noise. Previous work investigated the ability of deep generative models (DGMs) that employ an augmented generative adversarial network (GAN), AmbientGAN, for establishing SOMs from noisy measured image data. Recently, denoising diffusion models (DDMs) have emerged as a leading DGM for image synthesis and can produce superior image quality than GANs. However, original DDMs possess a slow image-generation process because of the Gaussian assumption in the denoising steps. More recently, denoising diffusion GAN (DDGAN) was proposed to permit fast image generation while maintain high generated image quality that is comparable to the original DDMs. In this work, we propose an augmented DDGAN architecture, Ambient DDGAN (ADDGAN), for learning SOMs from noisy image data. Numerical studies that consider clinical computed tomography (CT) images and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) images are conducted. The ability of the proposed ADDGAN to learn realistic SOMs from noisy image data is demonstrated. It has been shown that the ADDGAN significantly outperforms the advanced AmbientGAN models for synthesizing high resolution medical images with complex textures.
普遍认为,医学成像系统应通过基于任务的图像质量(IQ)度量进行客观评估,这些度量理想情况下应考虑测量图像数据中所有随机性的来源,包括要成像的对象集合的变化。可以随机从对象分布中抽取样本的随机对象模型(SOMs)可用于表征对象变量。为了建立基于任务IQ分析的现实SOMs,使用实验图像数据是理想的。然而,从医学成像系统获得的实验图像数据存在测量噪声。先前的工作研究了使用增强生成对抗网络(GAN)的深生成模型(DGM)建立噪声测量图像数据的SOMs的能力。最近,去噪扩散模型(DDM)作为领先的图像合成DGM出现,可以产生比GAN更高的图像质量。然而,原始DDMs由于去噪步骤中的高斯假设而具有较慢的图像生成过程。最近,提出了去噪扩散GAN(DDGAN)以实现快速图像生成,同时保持与原始DDMs相当的生成图像质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种增强的DDGAN架构,即环境DDGAN(ADDGAN),用于从噪声图像数据中学习SOMs。我们进行了考虑临床计算机断层扫描(CT)图像和数字乳腺断层合成(DBT)图像的数值研究。展示了所提出的ADDGAN从噪声图像数据中学习现实SOMs的能力。研究表明,ADDGAN在合成具有复杂纹理的高分辨率医学图像方面显著优于先进的AmbientGAN模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SPIE Medical Imaging 2025
摘要
本文探讨了在医学成像系统中,利用增强型去噪扩散生成对抗网络(DDGAN)从含噪图像数据中学习随机对象模型(SOM)的方法。通过临床计算机断层扫描(CT)和数字化乳腺断层合成(DBT)图像的数值研究,展示了ADDGAN学习现实SOM并从含噪图像数据中合成高分辨率医学图像的能力。相较于传统的生成对抗网络(GAN),DDGAN能够在快速生成图像的同时保持高图像质量。
关键见解
- 医学成像系统的客观评估需要通过任务基础上的图像质量(IQ)度量来进行,这需要考虑图像数据中所有来源的随机性,包括成像对象的集合变化。
- 可以用随机对象模型(SOMs)来刻画对象的变化性,这可以通过从对象分布中随机抽取样本来实现。
- 为了进行任务基础的IQ分析,建立现实的SOM,实验图像数据是必要的,但是这些数据会受到测量噪声的影响。
- 深度生成模型(DGMs),特别是增强型生成对抗网络(GAN),被用于从含噪测量图像数据中建立SOMs。
- 去噪扩散模型(DDMs)是一种领先的DGM用于图像合成,并能产生比GAN更高的图像质量。然而,原始的DDMs拥有较慢的图像生成过程。
- 为了快速生成图像并保持高图像质量,提出了去噪扩散生成对抗网络(DDGAN)。
点此查看论文截图




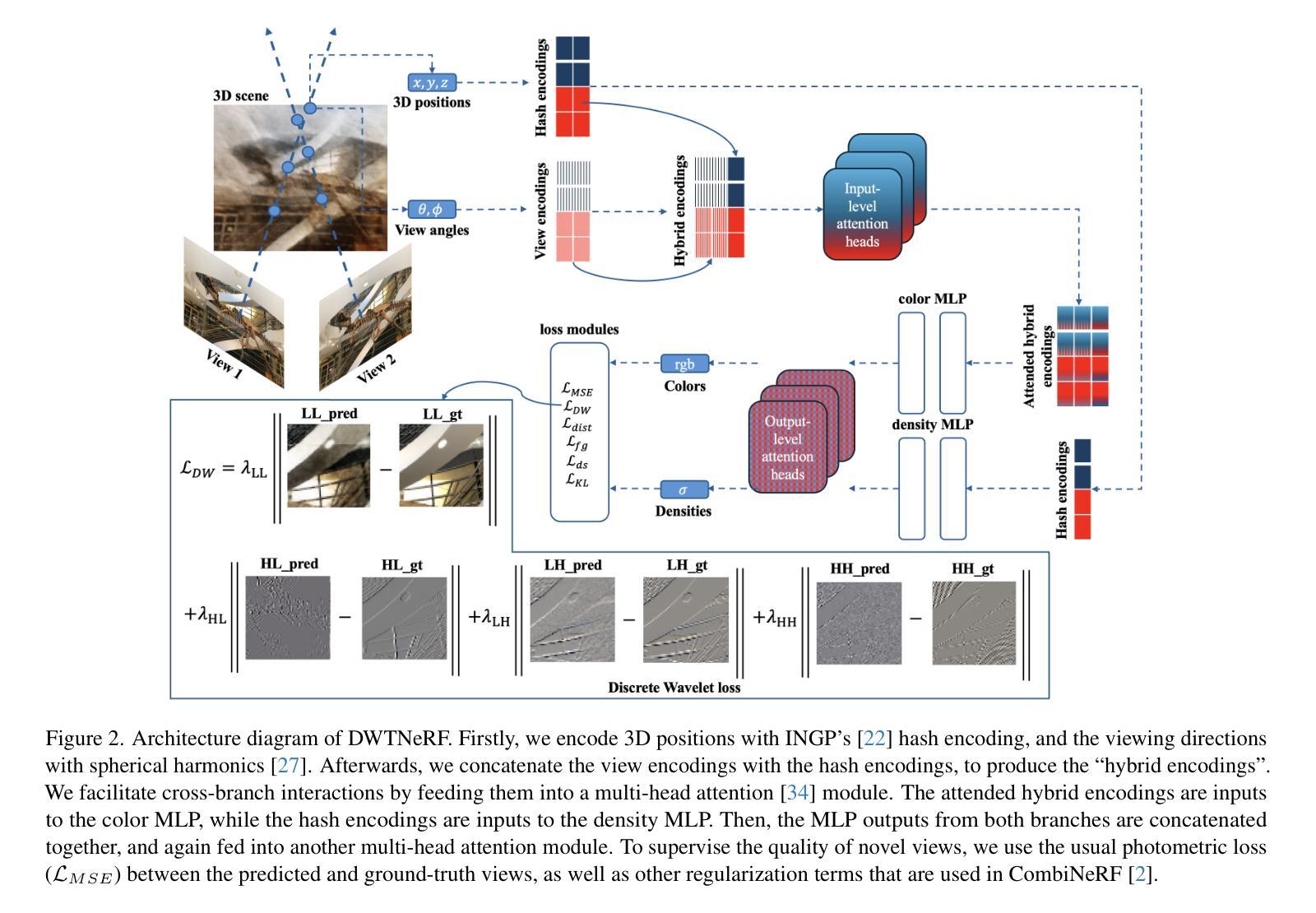
LANTERN: Accelerating Visual Autoregressive Models with Relaxed Speculative Decoding
Authors:Doohyuk Jang, Sihwan Park, June Yong Yang, Yeonsung Jung, Jihun Yun, Souvik Kundu, Sung-Yub Kim, Eunho Yang
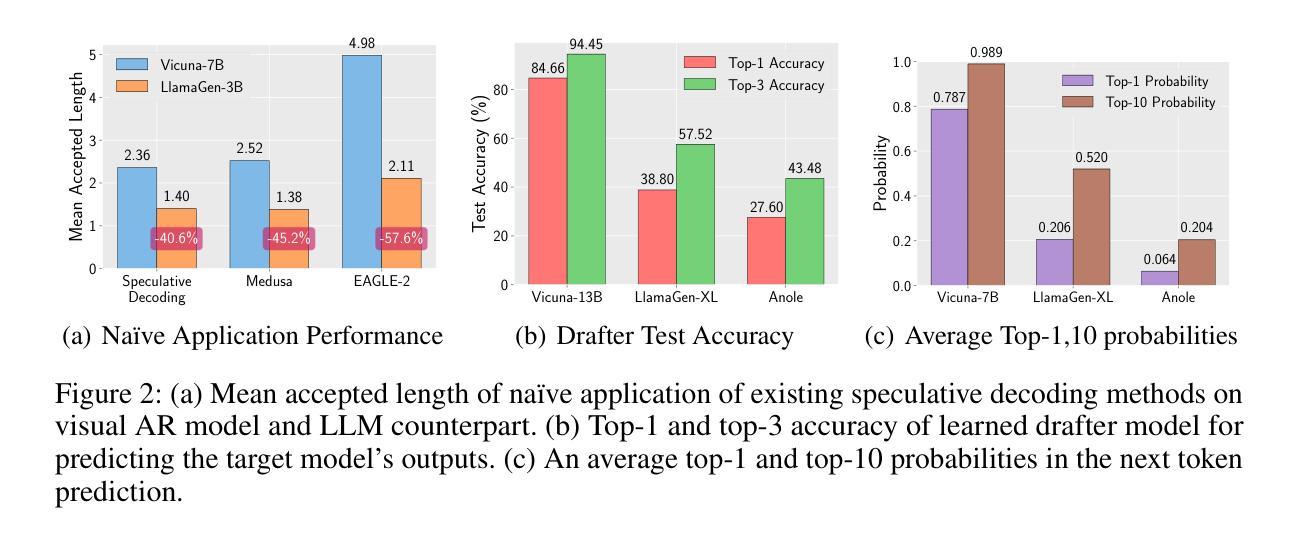
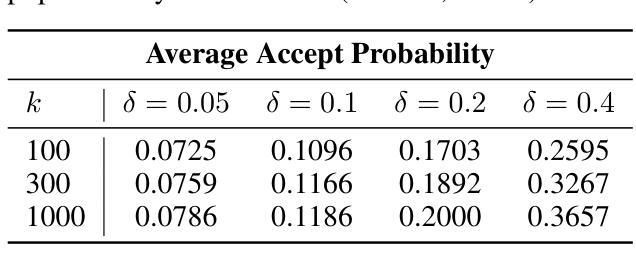
Auto-Regressive (AR) models have recently gained prominence in image generation, often matching or even surpassing the performance of diffusion models. However, one major limitation of AR models is their sequential nature, which processes tokens one at a time, slowing down generation compared to models like GANs or diffusion-based methods that operate more efficiently. While speculative decoding has proven effective for accelerating LLMs by generating multiple tokens in a single forward, its application in visual AR models remains largely unexplored. In this work, we identify a challenge in this setting, which we term \textit{token selection ambiguity}, wherein visual AR models frequently assign uniformly low probabilities to tokens, hampering the performance of speculative decoding. To overcome this challenge, we propose a relaxed acceptance condition referred to as LANTERN that leverages the interchangeability of tokens in latent space. This relaxation restores the effectiveness of speculative decoding in visual AR models by enabling more flexible use of candidate tokens that would otherwise be prematurely rejected. Furthermore, by incorporating a total variation distance bound, we ensure that these speed gains are achieved without significantly compromising image quality or semantic coherence. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of our method in providing a substantial speed-up over speculative decoding. In specific, compared to a na"ive application of the state-of-the-art speculative decoding, LANTERN increases speed-ups by $\mathbf{1.75}\times$ and $\mathbf{1.82}\times$, as compared to greedy decoding and random sampling, respectively, when applied to LlamaGen, a contemporary visual AR model.
自回归(AR)模型最近在图像生成领域受到了广泛关注,其性能往往与扩散模型相匹配甚至更胜一筹。然而,AR模型的一个主要局限性在于它们的序列性质,即一次只处理一个令牌,与像GAN或基于扩散的方法等更高效的模型相比,生成速度较慢。虽然猜测解码已经证明可以通过单次前向生成多个令牌来加速大型语言模型,但其在视觉AR模型中的应用仍然未被广泛探索。在这项工作中,我们确定了一个在此环境中的挑战,我们称之为“令牌选择歧义”,其中视觉AR模型经常为令牌分配统一的低概率,阻碍猜测解码的性能。为了克服这一挑战,我们提出了一种放宽的接受条件,称为LANTERN,它利用潜在空间中令牌的互换性。这种放松恢复了猜测解码在视觉AR模型中的有效性,通过更灵活地利用候选令牌,这些令牌通常会被过早地拒绝。此外,通过引入总变异距离界限,我们确保在加速的同时不会显著降低图像质量或语义连贯性。实验结果表明我们的方法提供了对猜测解码的有效加速。具体来说,与对最新猜测解码的朴素应用相比,LANTERN在应用于当代视觉AR模型LlamaGen时,速度提高了1.75倍和1.82倍,分别与贪婪解码和随机采样相比。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 13 figures
Summary
本文探讨了自回归(AR)模型在图像生成领域面临的挑战,并提出了一个名为LANTERN的新方法来解决这些问题。通过利用潜在空间中令牌的互换性,该方法解决了被称为“令牌选择歧义”的问题,恢复了投机解码在视觉AR模型中的有效性。实验结果表明,该方法在加速图像生成方面效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- AR模型在图像生成中受到广泛关注,但其顺序处理令牌的特性导致生成速度较慢。
- 投机解码在加速大型语言模型方面的应用已被证实,但在视觉AR模型中的应用尚未得到充分探索。
- 视觉AR模型面临“令牌选择歧义”问题,即经常对令牌分配均匀的低概率,阻碍投机解码的性能。
- LANTERN方法通过放松接受条件来解决这个问题,利用潜在空间中令牌的互换性,使视觉AR模型能够更灵活地利用候选令牌。
- LANTERN方法结合总变差距离界来保证加速效果的同时不损害图像质量或语义连贯性。
- 实验结果表明,与现有的投机解码方法相比,LANTERN方法提供了显著的速度提升,最高可达1.75倍和1.82倍。
点此查看论文截图



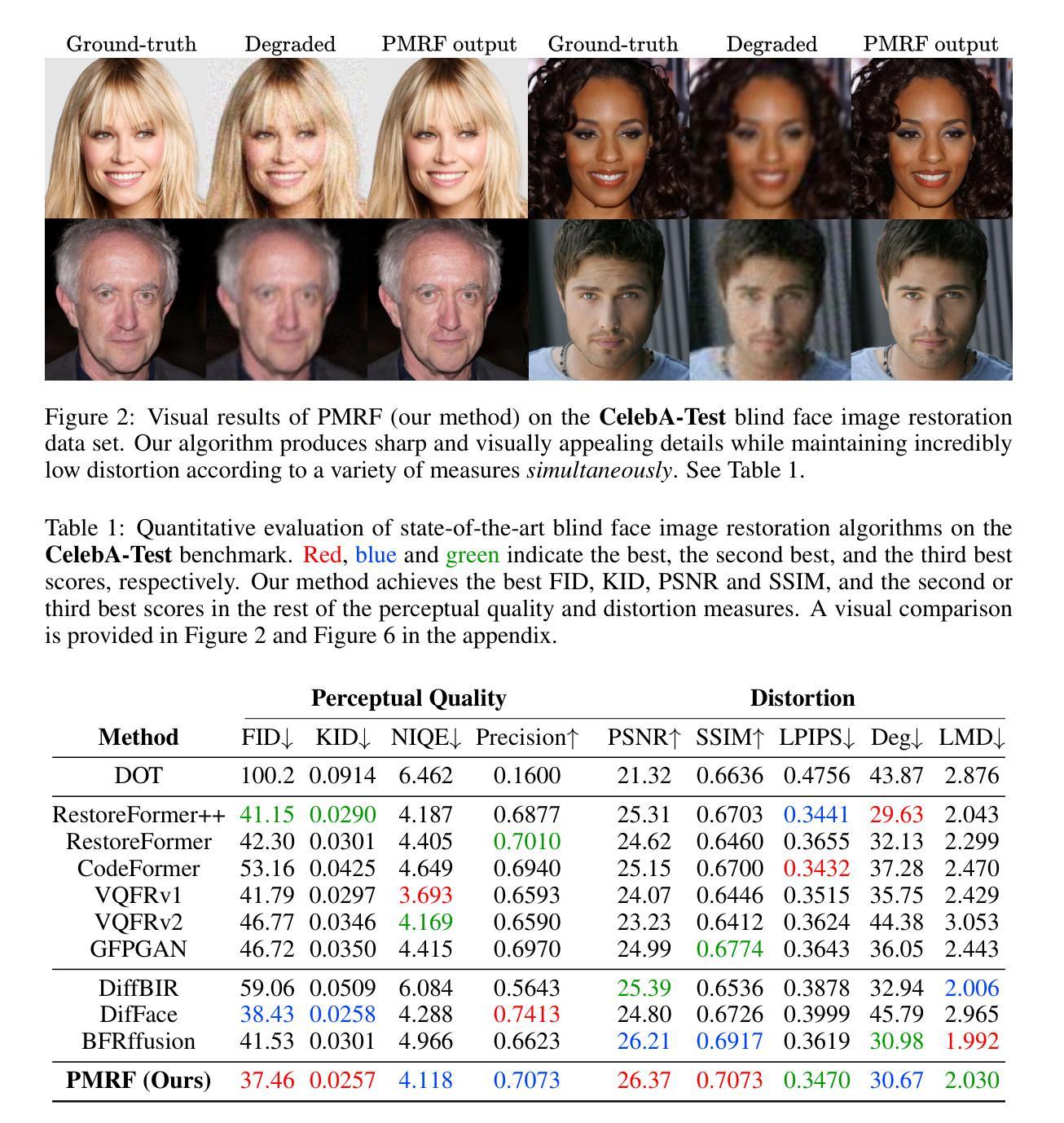
Posterior-Mean Rectified Flow: Towards Minimum MSE Photo-Realistic Image Restoration
Authors:Guy Ohayon, Tomer Michaeli, Michael Elad
Photo-realistic image restoration algorithms are typically evaluated by distortion measures (e.g., PSNR, SSIM) and by perceptual quality measures (e.g., FID, NIQE), where the desire is to attain the lowest possible distortion without compromising on perceptual quality. To achieve this goal, current methods commonly attempt to sample from the posterior distribution, or to optimize a weighted sum of a distortion loss (e.g., MSE) and a perceptual quality loss (e.g., GAN). Unlike previous works, this paper is concerned specifically with the optimal estimator that minimizes the MSE under a constraint of perfect perceptual index, namely where the distribution of the reconstructed images is equal to that of the ground-truth ones. A recent theoretical result shows that such an estimator can be constructed by optimally transporting the posterior mean prediction (MMSE estimate) to the distribution of the ground-truth images. Inspired by this result, we introduce Posterior-Mean Rectified Flow (PMRF), a simple yet highly effective algorithm that approximates this optimal estimator. In particular, PMRF first predicts the posterior mean, and then transports the result to a high-quality image using a rectified flow model that approximates the desired optimal transport map. We investigate the theoretical utility of PMRF and demonstrate that it consistently outperforms previous methods on a variety of image restoration tasks.
基于照片真实的图像恢复算法通常通过失真度量(例如PSNR、SSIM)和感知质量度量(例如FID、NIQE)进行评估。目标是尽可能降低失真,同时不妥协感知质量。为了达到这个目标,当前的方法通常尝试从后验分布中采样,或者优化失真损失(例如MSE)和感知质量损失的加权和(例如GAN)。与以前的工作不同,本文专注于在完美感知指数约束下最小化MSE的最优估计器,即在重建图像的分布与真实图像的分布相等的情况下。最近的理论结果表明,可以通过最佳传输后验均值预测(MMSE估计)到真实图像的分布来构建这样的估计器。受此结果的启发,我们引入了后均值校正流(PMRF),这是一种简单而高效的方法,可以近似这种最优估计器。具体而言,PMRF首先预测后验均值,然后使用校正流模型将结果传输到高质量图像,该模型近似于所需的最佳传输映射。我们研究了PMRF的理论效用,并证明在各种图像恢复任务上,它始终优于以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025. Code and demo are available at https://https://pmrf-ml.github.io/
Summary
本文关注于在完美感知指数约束下最小化均方误差的最优估计器。研究展示了通过优化传输后验均值预测到真实图像分布的方法,并据此提出了名为PMRF的算法,该算法通过模拟期望的最优传输映射,将预测的后验均值转化为高质量图像。经理论验证和多项图像恢复任务的实践对比,PMRF表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 文章关注于在完美感知质量下最小化均方误差的最优估计器。
- 现有理论结果启发,通过优化传输后验均值预测到真实图像分布的方法。
- 引入PMRF算法,模拟期望的最优传输映射,将预测的后验均值转化为高质量图像。
- PMRF在多种图像恢复任务上表现优于前人的方法。
- 文章探索了PMRF的理论效用。
- 该研究强调了感知质量和失真度量的平衡在图像恢复中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图
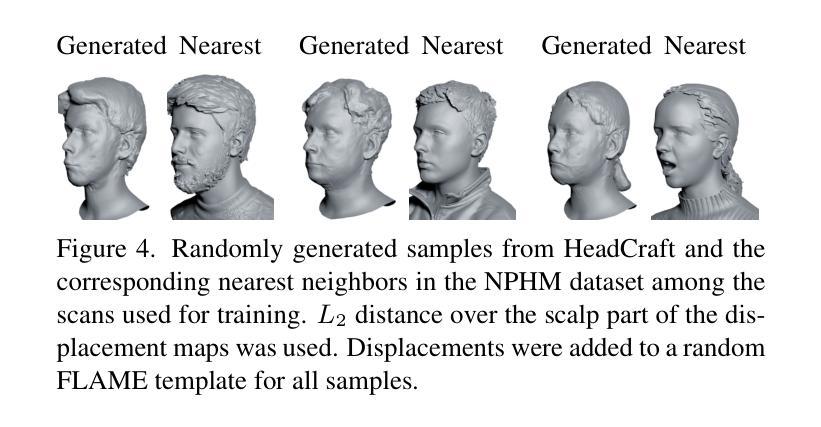
HeadCraft: Modeling High-Detail Shape Variations for Animated 3DMMs
Authors:Artem Sevastopolsky, Philip-William Grassal, Simon Giebenhain, ShahRukh Athar, Luisa Verdoliva, Matthias Niessner
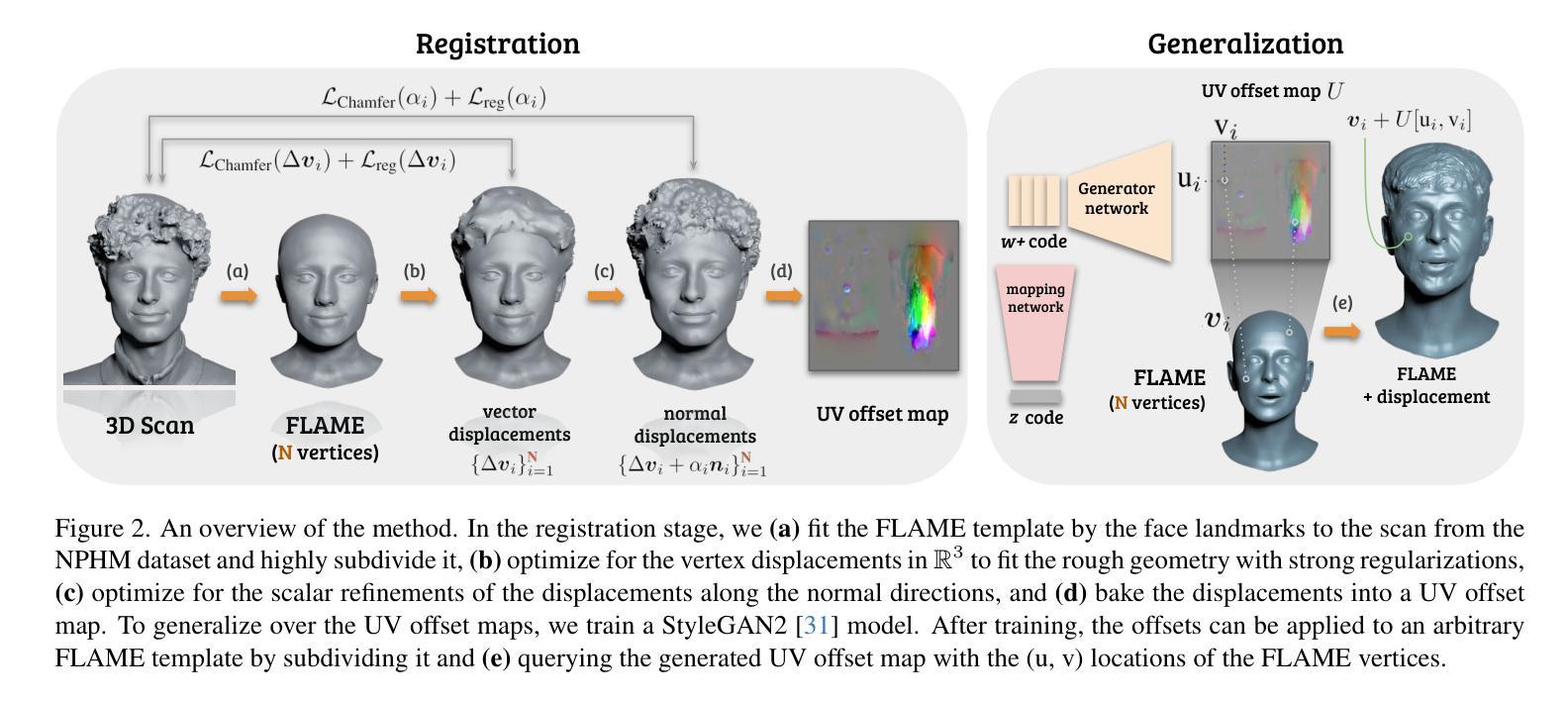
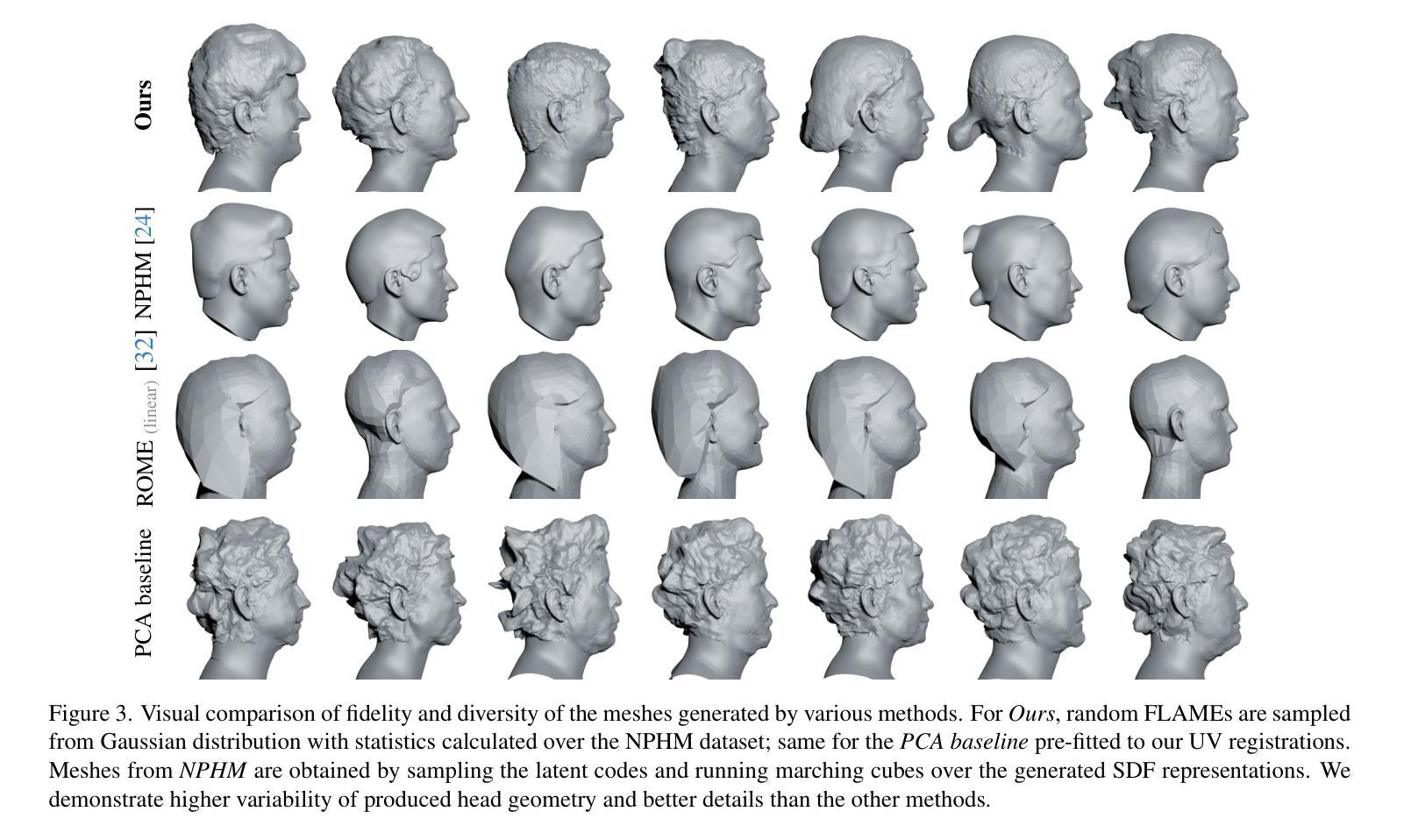
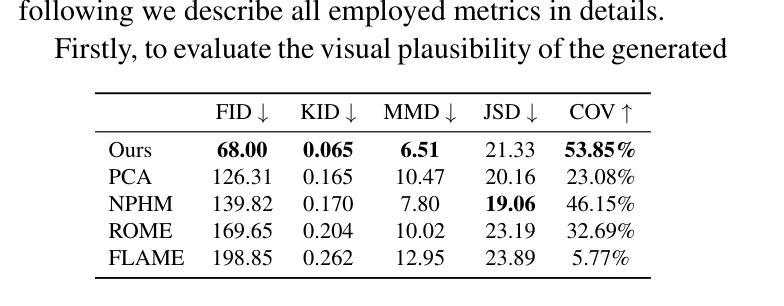
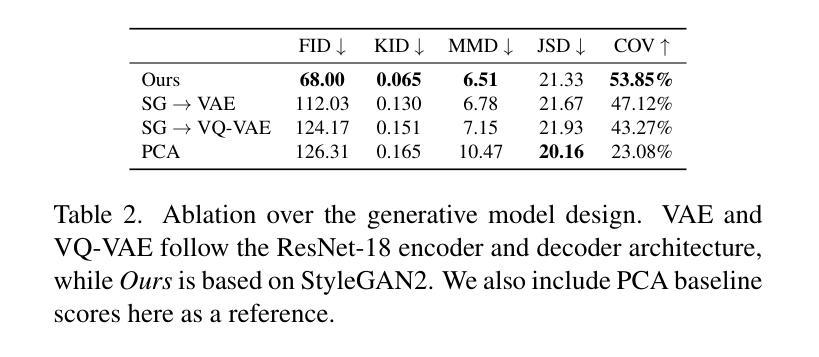
Current advances in human head modeling allow the generation of plausible-looking 3D head models via neural representations, such as NeRFs and SDFs. Nevertheless, constructing complete high-fidelity head models with explicitly controlled animation remains an issue. Furthermore, completing the head geometry based on a partial observation, e.g., coming from a depth sensor, while preserving a high level of detail is often problematic for the existing methods. We introduce a generative model for detailed 3D head meshes on top of an articulated 3DMM, simultaneously allowing explicit animation and high-detail preservation. Our method is trained in two stages. First, we register a parametric head model with vertex displacements to each mesh of the recently introduced NPHM dataset of accurate 3D head scans. The estimated displacements are baked into a hand-crafted UV layout. Second, we train a StyleGAN model to generalize over the UV maps of displacements, which we later refer to as HeadCraft. The decomposition of the parametric model and high-quality vertex displacements allows us to animate the model and modify the regions semantically. We demonstrate the results of unconditional sampling, fitting to a scan and editing. The project page is available at https://seva100.github.io/headcraft.
当前的人头建模技术进展允许通过神经表示(如NeRF和SDF)生成逼真的3D头模型。然而,构建具有明确控制动画的高保真头模型仍然是一个问题。此外,根据部分观察(例如来自深度传感器的数据)完成头几何结构,同时保持高水平细节对于现有方法来说常常是有问题的。我们引入了一种基于关节式3DMM的详细3D头网格生成模型,可以同时实现明确的动画和高细节保存。我们的方法分为两个阶段进行训练。首先,我们将参数化头模型与顶点位移注册到最近引入的NPHM数据集的每个网格上,该数据集包含准确的3D头部扫描。估计的位移被烘焙到手工制作的UV布局中。其次,我们训练StyleGAN模型以概括位移的UV地图,我们稍后将其称为HeadCraft。参数模型的分解和高质量顶点位移使我们能够动画化模型并语义地修改区域。我们展示了无条件采样的结果、扫描适配和编辑。项目页面可在https://seva100.github.io/headcraft访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2nd version includes updated method and results. Project page: https://seva100.github.io/headcraft. Video: https://youtu.be/uBeBT2f1CL0. 24 pages, 21 figures, 3 tables
Summary
基于当前的人头建模技术,可以通过神经表示(如NeRF和SDF)生成逼真的3D人头模型。然而,构建具有明确控制的完整高保真人头模型仍然是一个问题。我们引入了一种基于关节式3DMM的详细3D人头网格生成模型,可以同时实现明确的动画和高细节保存。我们的方法分为两个阶段进行训练,首先是注册参数化人头模型与NPHM数据集的准确3D头部扫描网格的顶点位移,然后将估计的位移烘焙到手工制作的UV布局中。其次,我们训练StyleGAN模型以概括UV地图的位移,我们称之为HeadCraft。参数模型和高品质顶点位移的分解使我们能够动画模型和语义上修改区域。我们展示了无条件采样的结果、扫描适配和编辑示例。
Key Takeaways
- 当前的人头建模技术能够通过神经表示生成逼真的3D人头模型。
- 构建具有明确控制的完整高保真人头模型仍存在挑战。
- 引入了一种基于关节式3DMM的详细3D人头网格生成模型,支持明确的动画和高细节保存。
- 方法分为两个阶段:注册参数化人头模型与NPHM数据集的头部扫描,然后训练StyleGAN模型以概括UV地图的位移。
- 参数模型和高品质顶点位移的分解使动画和区域修改成为可能。
- 展示了无条件采样的结果、扫描适配和编辑示例。
点此查看论文截图