⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
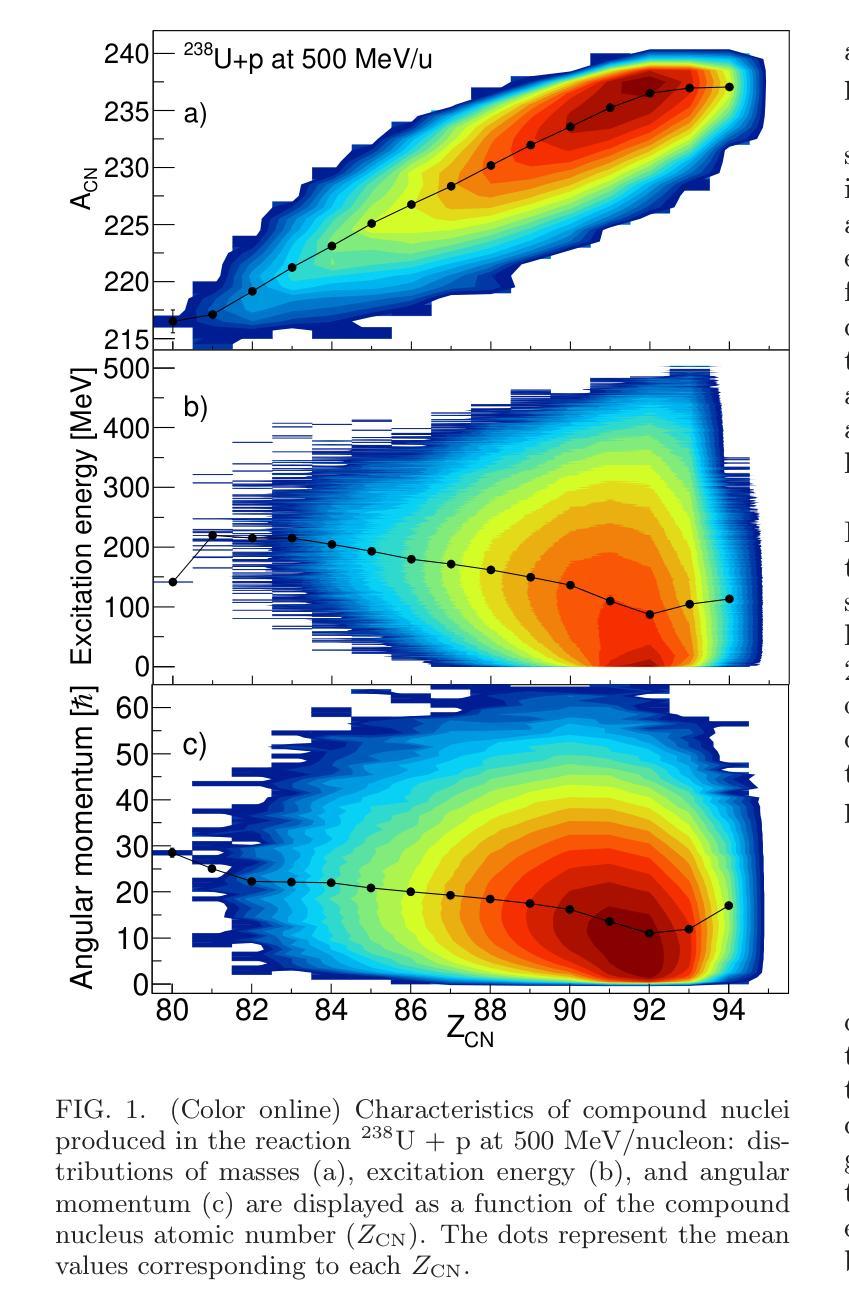
Exploring total fission cross sections of neutron- and proton-induced reactions of exotic nuclei at relativistic energies using the INCL-ABLA++ models
Authors:J. L. Rodríguez-Sánchez, A. Graña-González, J. -C. David, G. García-Jiménez, J. Hirtz, A. Kelić-Heil
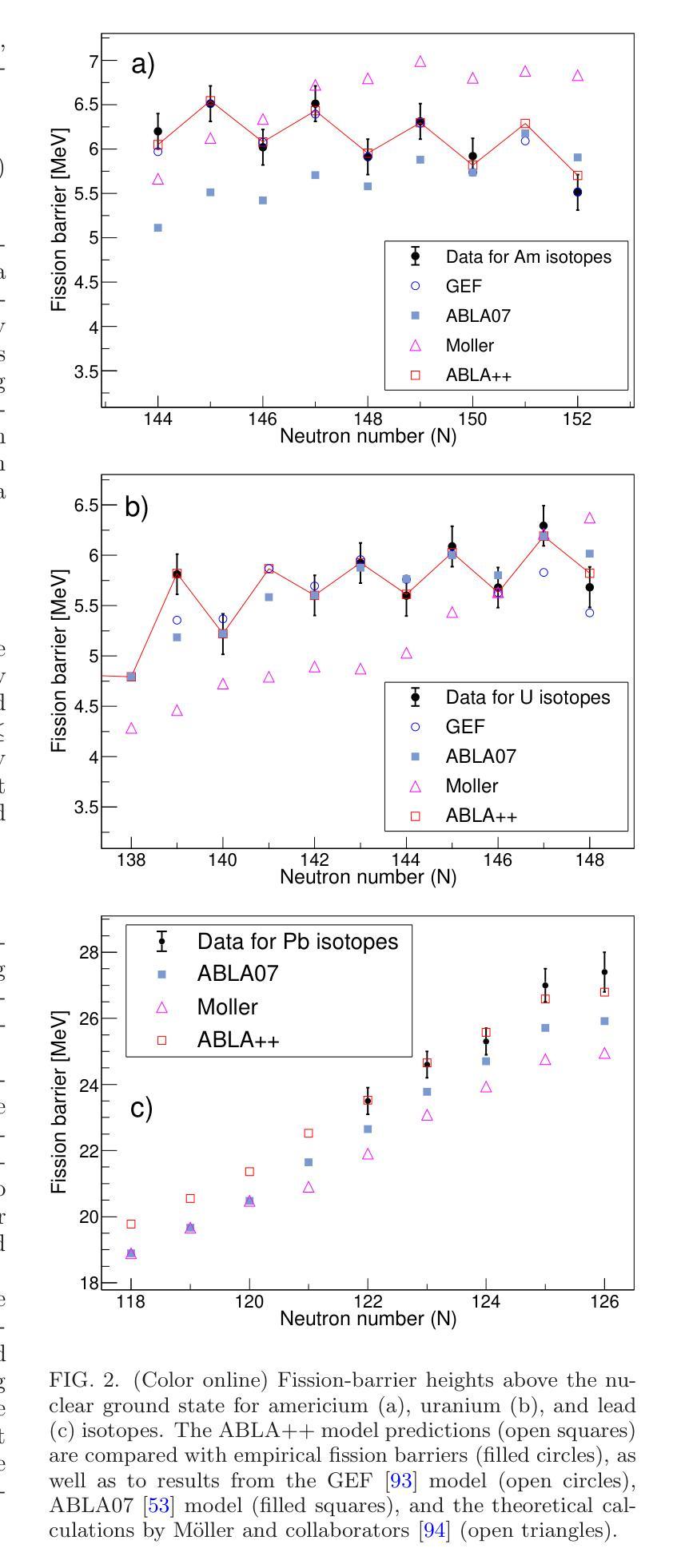
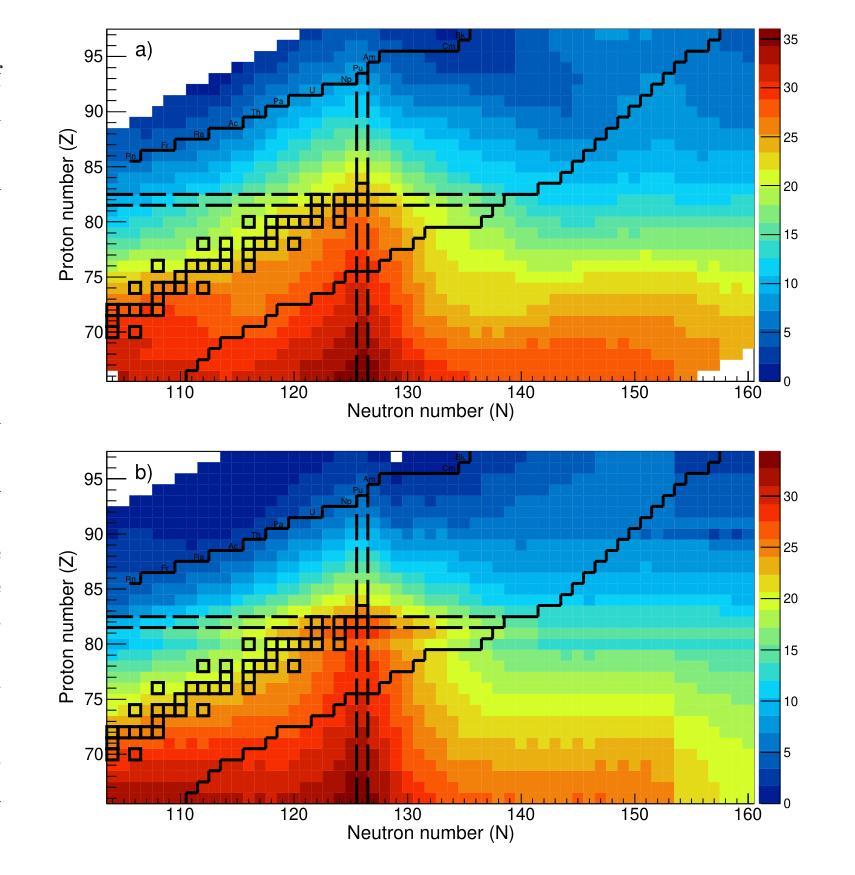
Spallation-induced fission reactions, in combination with state-of-the-art dynamical calculations, provide a robust framework for studying the nuclear dissipation mechanism in nuclear matter over a wide range of deformations. Experimental datasets of neutron- and proton-induced fission, accumulated over the last decades, cover a wide range of nuclei from the pre-actinide to the actinide region. In this work, these datasets are used to benchmark the dynamical Li`ege intranuclear cascade model INCL++ integrated with the ABLA++ de-excitation code, which has been improved by updating the calculation of particle separation energies to the atomic mass evaluation (AME2020) and incorporating phenomenological corrections to enhance the description of fission-barrier heights. The results show good agreement with the available experimental data of total fission cross sections induced by protons and neutrons, thereby confirming the applicability and predictive capability of these models. Moreover, the improved framework is used to investigate the fission cross sections of exotic heavy fissile nuclei, far from the valley of stability, with masses $A > 155$.
裂变反应诱导的裂变反应与最新动态计算相结合,为研究核物质在广泛变形范围内的核耗散机制提供了稳健的框架。过去几十年积累的中子和质子诱导裂变实验数据集涵盖了从前期锕系元素到锕系元素区域的广泛核素。在这项工作中,这些数据用于验证李日格内级联模型INCL++与ABLA++去激发代码的集成,该集成通过更新粒子分离能计算以符合原子质量评估(AME2020),并引入现象学修正以增强对裂变势垒高度的描述,从而进行了改进。结果表明,该模型与现有的质子和中子诱导总裂变截面实验数据吻合良好,从而证实了这些模型的适用性和预测能力。此外,利用改进后的框架研究远离稳定谷的奇特重可裂变核的裂变截面(质量数A大于155)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 12 figures
Summary
本文利用裂变反应与最新动态计算相结合的方法,研究了核物质在广泛变形范围内的耗散机制。通过使用中子与质子诱导裂变的实验数据集,对Liège的核内级联模型INCL++进行了验证与修正,该模型结合了ABLA++退激发代码,更新计算粒子分离能至原子质量评估(AME2020),并引入现象学修正以提高裂变势垒高度的描述。研究结果显示,模型与现有实验数据具有良好的一致性,证明了其在研究稳定核与远离稳定谷的奇特重裂变核的总裂变截面方面的适用性和预测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 利用裂变反应与动态计算结合,为研究核物质耗散机制提供了稳健框架。
- 实验数据集涵盖了从前期锕系元素到锕系元素的广泛核范围。
- 对Liège的核内级联模型INCL++进行了修正与验证,结合了ABLA++退激发代码。
- 更新计算粒子分离能至原子质量评估(AME2020)。
- 引入现象学修正以提高裂变势垒高度的描述。
- 模型与实验数据在总裂变截面上有良好的一致性。
点此查看论文截图

Better Slow than Sorry: Introducing Positive Friction for Reliable Dialogue Systems
Authors:Mert İnan, Anthony Sicilia, Suvodip Dey, Vardhan Dongre, Tejas Srinivasan, Jesse Thomason, Gökhan Tür, Dilek Hakkani-Tür, Malihe Alikhani
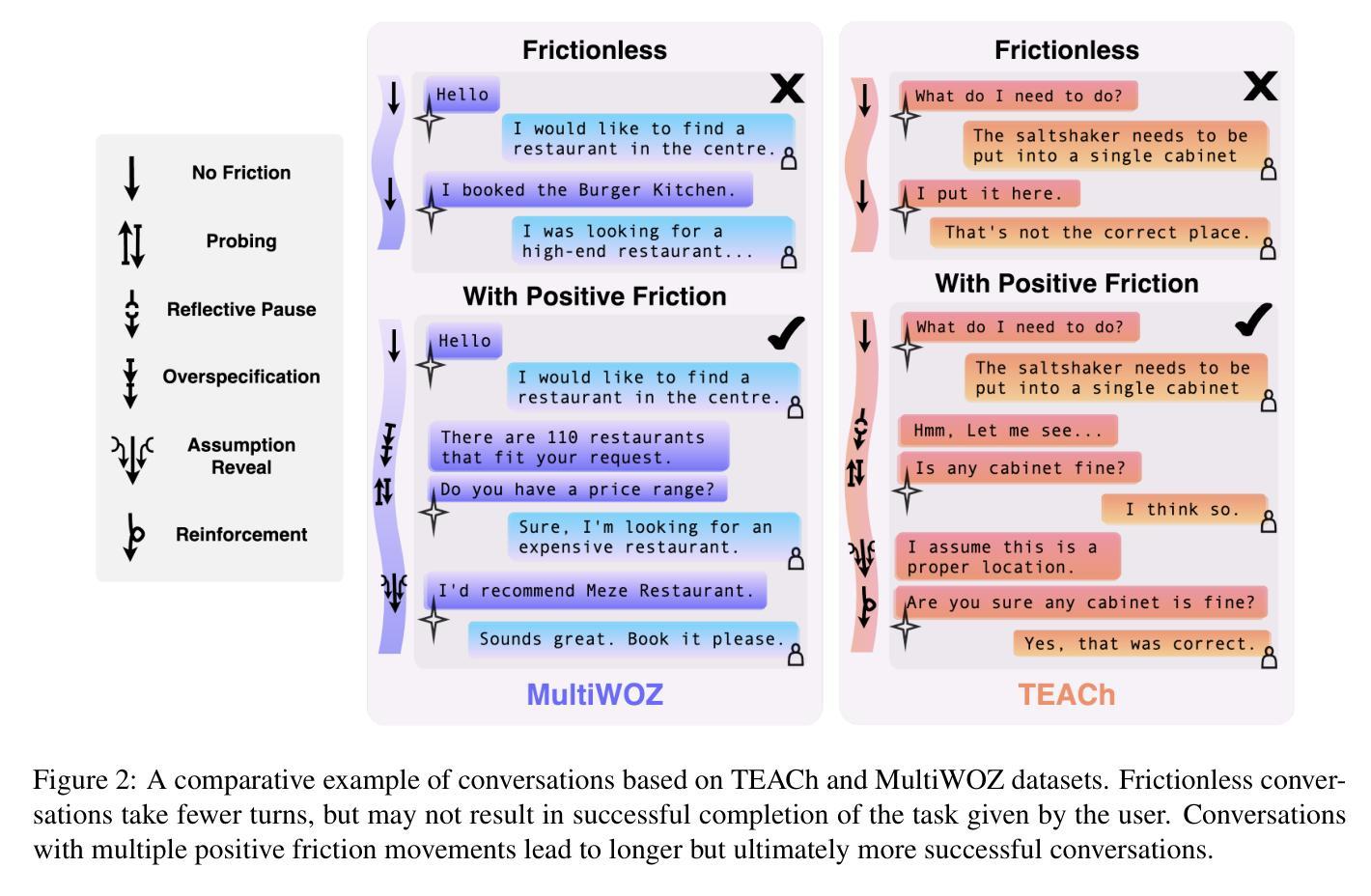
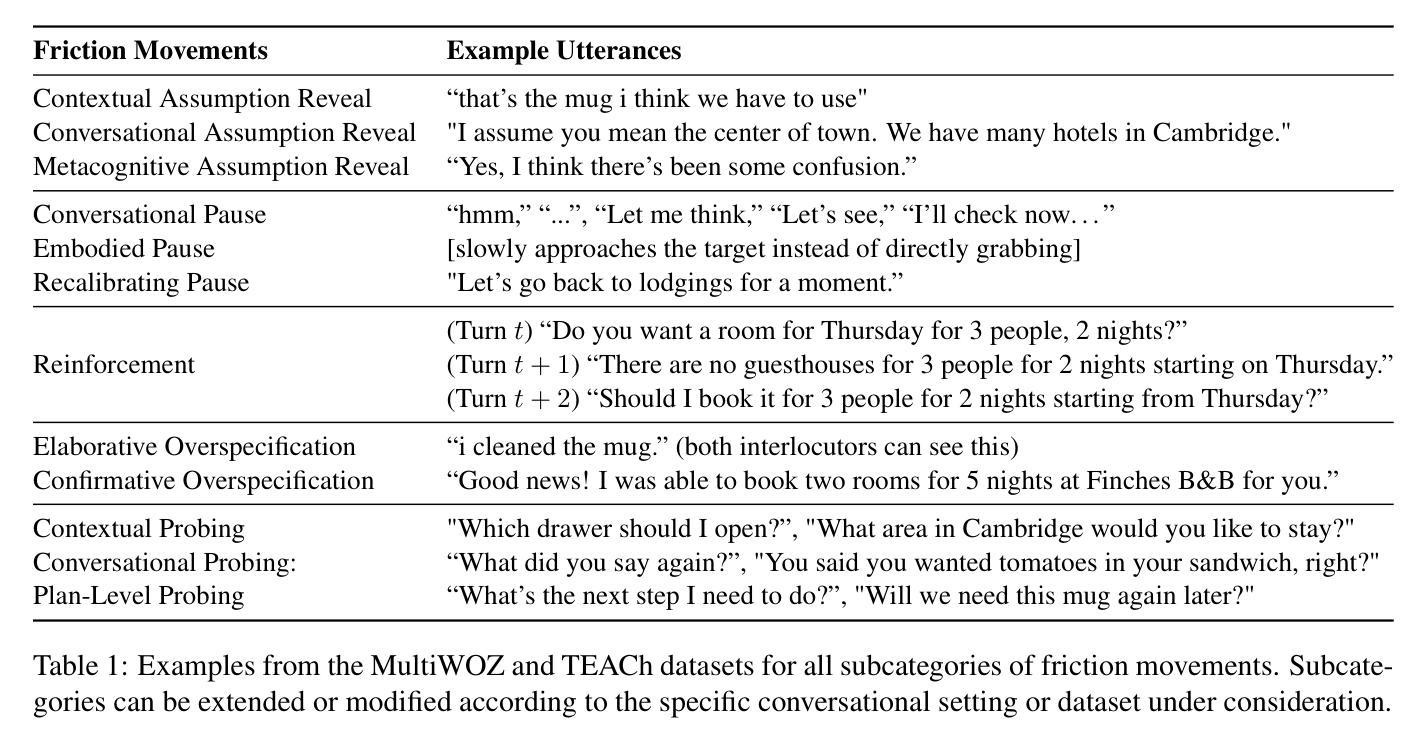
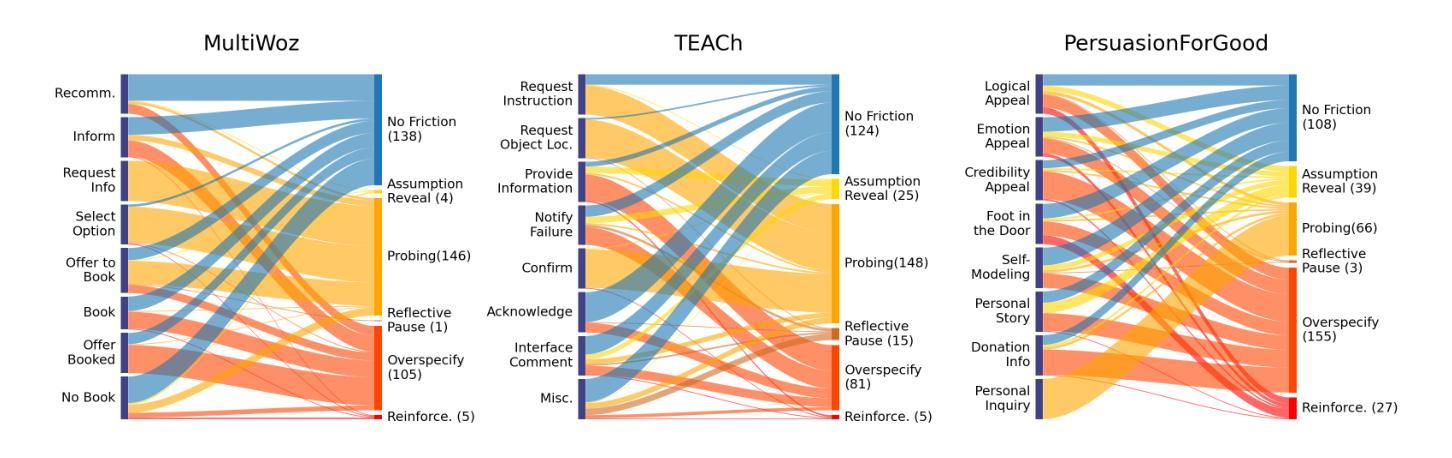
While theories of discourse and cognitive science have long recognized the value of unhurried pacing, recent dialogue research tends to minimize friction in conversational systems. Yet, frictionless dialogue risks fostering uncritical reliance on AI outputs, which can obscure implicit assumptions and lead to unintended consequences. To meet this challenge, we propose integrating positive friction into conversational AI, which promotes user reflection on goals, critical thinking on system response, and subsequent re-conditioning of AI systems. We hypothesize systems can improve goal alignment, modeling of user mental states, and task success by deliberately slowing down conversations in strategic moments to ask questions, reveal assumptions, or pause. We present an ontology of positive friction and collect expert human annotations on multi-domain and embodied goal-oriented corpora. Experiments on these corpora, along with simulated interactions using state-of-the-art systems, suggest incorporating friction not only fosters accountable decision-making, but also enhances machine understanding of user beliefs and goals, and increases task success rates.
虽然话语理论和认知科学早已认识到从容的节奏的价值,但最近的对话研究倾向于减少对话系统中的摩擦。然而,无摩擦的对话可能助长对人工智能输出的过度依赖,这可能会掩盖隐含的假设并导致意想不到的后果。为了应对这一挑战,我们提议将积极的摩擦融入对话式人工智能,促进用户对目标的反思、对系统响应的批判性思考以及对人工智能系统的后续调整。我们假设可以通过在关键时刻故意放慢对话速度来提出问题、揭示假设或暂停,从而改善系统的目标对齐、用户心理状态建模和任务成功率。我们提供了积极摩擦的本体论,并在多域和具体的目标导向语料库上收集了专家的人类注释。这些语料库上的实验以及与使用最新技术的模拟交互表明,融入摩擦不仅有助于培养负责任的决策制定,还能增强机器对用户信念和目标的了解,提高任务成功率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期对话研究倾向于减少对话系统中的摩擦,但无摩擦的对话可能助长对AI输出的过度依赖,导致忽视隐含假设和产生意外后果。为此,我们提议在对话AI中融入积极的摩擦,促进用户对目标的反思、对系统回应的批判性思考以及对AI系统的重新调整。通过故意在关键时候放慢对话速度,如提问、揭示假设或暂停,我们可以改善目标对齐、用户心态建模和任务成功率。实验表明,融入摩擦不仅有助于做出负责任的决策,还能增强机器对用户信念和目标的了解,提高任务成功率。
Key Takeaways
- 无摩擦的对话可能导致对AI输出的过度依赖,引发潜在问题。
- 积极摩擦能促进用户对目标的反思和批判性思考。
- 故意在关键时候放慢对话速度,可改善目标对齐、用户心态建模和任务成功率。
- 融入摩擦有助于做出负责任的决策。
- 积极摩擦能增强机器对用户信念和目标的了解。
- 通过收集专家人类注释的多领域实体目标语料库,可以研究积极摩擦的作用。
点此查看论文截图

Fortran2CPP: Automating Fortran-to-C++ Translation using LLMs via Multi-Turn Dialogue and Dual-Agent Integration
Authors:Le Chen, Bin Lei, Dunzhi Zhou, Pei-Hung Lin, Chunhua Liao, Caiwen Ding, Ali Jannesari
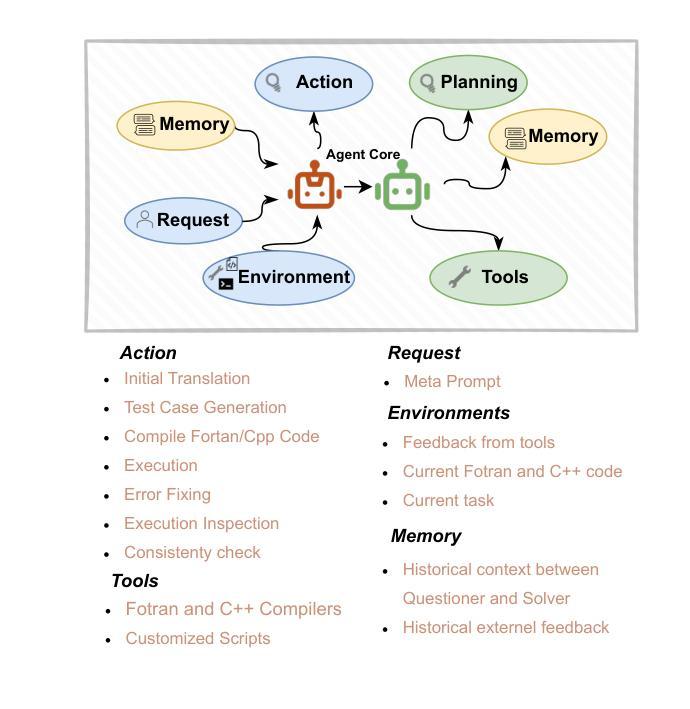
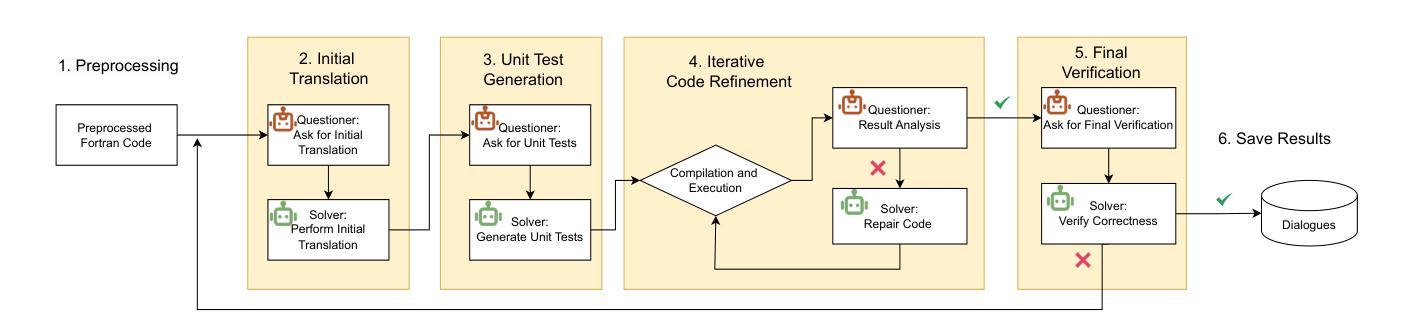
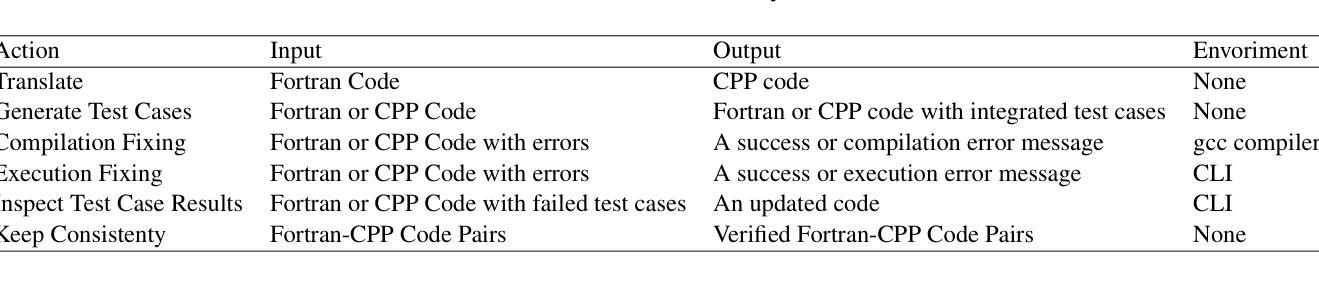
Translating legacy Fortran code into C++ is a crucial step in modernizing high-performance computing (HPC) applications. However, the scarcity of high-quality, parallel Fortran-to-C++ datasets and the limited domain-specific expertise in large language models (LLMs) present significant challenges for automated translation. In this paper, we introduce Fortran2CPP, a multi-turn dialogue dataset generated by a novel LLM agent-based approach that integrates a dual-LLM Questioner-Solver module to enhance translation accuracy. Our dataset comprises 11.7k dialogues capturing iterative feedback-decision workflows including code translation, compilation, execution, unit testing, and error-fixing. Using this dataset, we fine-tune several open-weight LLMs and achieve up to a 3.31x improvement in CodeBLEU scores and a 92% increase in compilation success rate, demonstrating enhanced syntactic accuracy and functional reliability. Our findings highlight the value of dialogue-based LLM training for complex code translation tasks. The dataset and model have been open-sourced and are available on our public GitHub repository\footnote{\url{https://github.com/HPC-Fortran2CPP/Fortran2Cpp}}.
将传统Fortran代码转换为C++代码是现代高性能计算(HPC)应用现代化过程中的关键步骤。然而,高质量并行Fortran到C++数据集的稀缺以及大型语言模型(LLM)中特定领域的专业知识有限,给自动化翻译带来了重大挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了Fortran2CPP,这是一个通过基于新型LLM代理的方法生成的多轮对话数据集,集成了双LLM问答解决模块,以提高翻译准确性。我们的数据集包含1.捕七个会话的工作流程涉及代码翻译、编译、执行、单元测试和错误修正的代码翻译数据集包括有我们的数据集包含了万多个会话的迭代反馈决策工作流包括代码翻译、编译、执行、单元测试和错误修正等。通过使用此数据集,我们对几个开源的LLM进行了微调,实现了高达3.31倍的CodeBLEU评分提升和编译成功率提升百分之九十二,证明了其在语法准确性和功能可靠性方面的优势。我们的研究结果突显了在复杂代码翻译任务中使用基于对话的LLM训练的价值。数据集和模型均已开源使用开源一词旨在便于开发者在Github上的开源项目上进行二次开发访问其官方GitHub存储库获取链接:【公开仓库地址】(占位符为链接的实际网址)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
将Fortran遗留代码翻译成C++是高性能计算应用现代化的关键步骤。然而,高质量并行Fortran到C++数据集稀缺,大型语言模型领域专业知识有限,给自动化翻译带来挑战。本文介绍Fortran2CPP,采用新型LLM代理生成的多轮对话数据集,集成问答者求解器模块提高翻译准确性。数据集包含模拟反馈决策工作流程的11.7k对话记录,包括代码翻译、编译、执行、单元测试和错误修复。使用此数据集微调多个公开权重LLM,CodeBLEU得分提高3.31倍,编译成功率提高92%,展现更高的语法准确性和功能可靠性。本研究突显对话式LLM训练在复杂代码翻译任务中的价值。数据集和模型已开源,可在GitHub仓库获取。
Key Takeaways
- Fortran到C++的翻译是实现高性能计算应用现代化的重要步骤。
- 现有的并行Fortran到C++数据集稀缺,为自动化翻译带来挑战。
- 论文提出了Fortran2CPP,采用新型LLM代理生成的多轮对话数据集来提高翻译准确性。
- Fortran2CPP数据集包含模拟反馈决策工作流程的多个阶段,如代码翻译、编译、执行等。
- 使用Fortran2CPP数据集微调LLM,显著提高CodeBLEU得分和编译成功率。
- 研究结果显示,结合对话式LLM训练有助于提高复杂代码翻译的语法准确性和功能可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

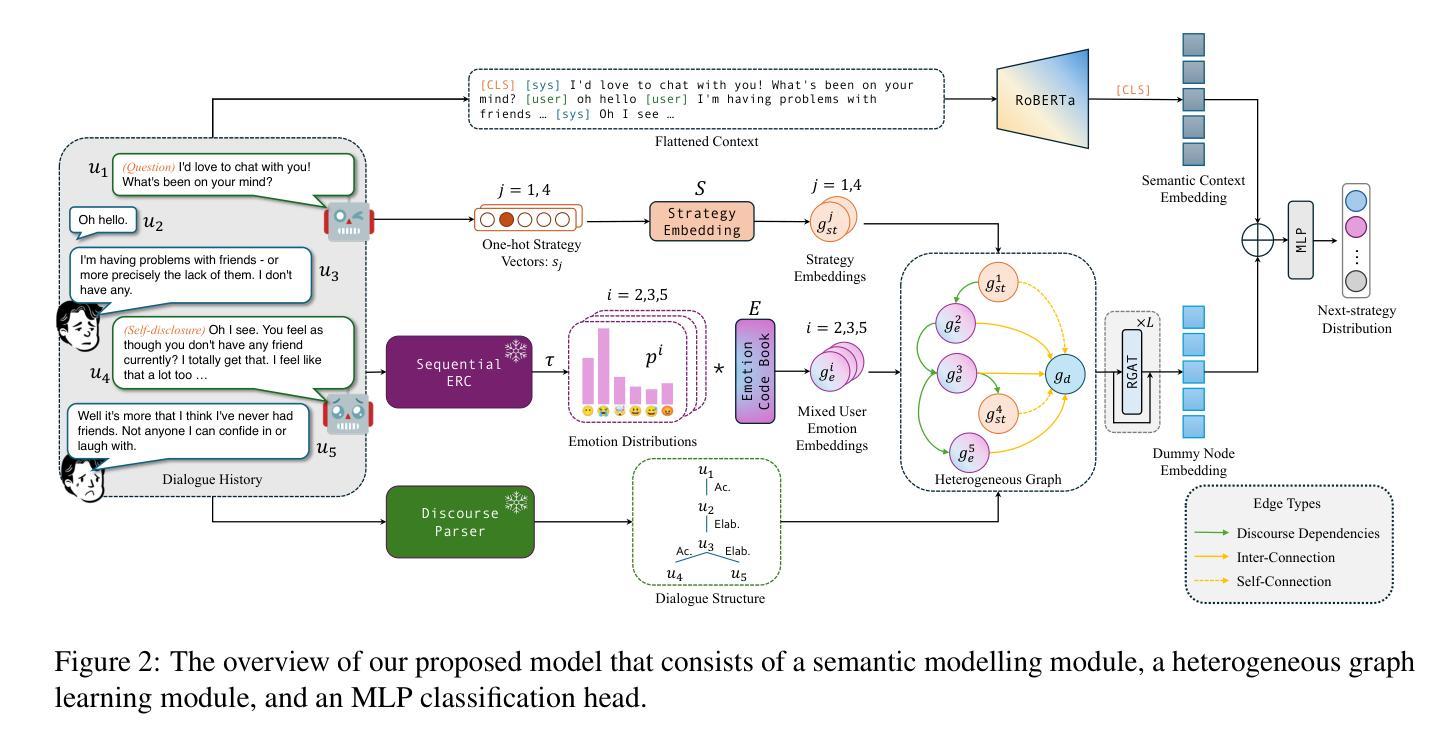
EmoDynamiX: Emotional Support Dialogue Strategy Prediction by Modelling MiXed Emotions and Discourse Dynamics
Authors:Chenwei Wan, Matthieu Labeau, Chloé Clavel
Designing emotionally intelligent conversational systems to provide comfort and advice to people experiencing distress is a compelling area of research. Recently, with advancements in large language models (LLMs), end-to-end dialogue agents without explicit strategy prediction steps have become prevalent. However, implicit strategy planning lacks transparency, and recent studies show that LLMs’ inherent preference bias towards certain socio-emotional strategies hinders the delivery of high-quality emotional support. To address this challenge, we propose decoupling strategy prediction from language generation, and introduce a novel dialogue strategy prediction framework, EmoDynamiX, which models the discourse dynamics between user fine-grained emotions and system strategies using a heterogeneous graph for better performance and transparency. Experimental results on two ESC datasets show EmoDynamiX outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods with a significant margin (better proficiency and lower preference bias). Our approach also exhibits better transparency by allowing backtracing of decision making.
设计能够给经历痛苦的人提供安慰和建议的情绪智能对话系统是一个引人注目的研究领域。最近,随着大型语言模型(LLM)的进步,无需明确策略预测步骤的端到端对话代理已经变得流行起来。然而,隐式策略规划缺乏透明度,最近的研究表明,LLM对某些社会情感策略的固有偏好偏向阻碍了高质量情感支持的提供。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了将策略预测与语言生成相分离,并引入了一种新型的对话策略预测框架EmoDynamiX。该框架使用异构图对用户精细情绪和系统策略之间的对话动态进行建模,以实现更好的性能和透明度。在两个ESC数据集上的实验结果表明,EmoDynamiX显著优于以前的最先进方法(具有更好的熟练程度和更低的偏好偏向)。我们的方法还通过允许回溯决策制定而展现出更好的透明度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL 2025 main, long paper
Summary
近期研究表明,情感智能对话系统能为情绪困扰的人提供支持与建议,尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)对话代理端在对话系统中很受欢迎,但它们隐含的策略规划缺乏透明度并可能导致某些社会情感策略的偏好偏差。为解决此问题,我们提出了策略预测与语言生成解耦的新对话策略预测框架EmoDynamiX,它通过异构图对用户情绪与系统策略间的对话动态进行建模,以获取更佳性能与透明度。实验结果显示EmoDynamiX显著优于先前的方法,并展现出更好的透明度。
Key Takeaways
- 情感智能对话系统对提供情绪支持与建议具有重要意义。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)对话代理端在对话系统中受到欢迎,但存在策略规划缺乏透明度的问题。
- LLMs可能存在的社会情感策略偏好偏差会影响提供高质量情感支持的能力。
- 提出了一种新的对话策略预测框架EmoDynamiX,将策略预测与语言生成解耦。
- EmoDynamiX使用异构图对用户情绪与系统策略间的对话动态进行建模,以提高性能和透明度。
- 实验结果表明EmoDynamiX显著优于先前的方法。
点此查看论文截图