⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
SELMA: A Speech-Enabled Language Model for Virtual Assistant Interactions
Authors:Dominik Wagner, Alexander Churchill, Siddharth Sigtia, Erik Marchi
In this work, we present and evaluate SELMA, a Speech-Enabled Language Model for virtual Assistant interactions that integrates audio and text as inputs to a Large Language Model (LLM). SELMA is designed to handle three primary and two auxiliary tasks related to interactions with virtual assistants simultaneously within a single end-to-end model. We employ low-rank adaptation modules for parameter-efficient training of both the audio encoder and the LLM. Additionally, we implement a feature pooling strategy enabling the system to recognize global patterns and improve accuracy on tasks less reliant on individual sequence elements. Experimental results on Voice Trigger (VT) detection, Device-Directed Speech Detection (DDSD), and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), demonstrate that our approach both simplifies the typical input processing pipeline of virtual assistants significantly and also improves performance compared to dedicated models for each individual task. SELMA yields relative Equal-Error Rate improvements of 64% on the VT detection task, and 22% on DDSD, while also achieving word error rates close to the baseline.
在这项工作中,我们介绍并评估了SELMA,这是一个用于虚拟助理交互的语音赋能语言模型,它将音频和文本作为输入集成到大型语言模型(LLM)中。SELMA被设计用于在一个端到端的模型中同时处理与虚拟助理交互相关的三个主要任务和两个辅助任务。我们采用低阶适应模块,实现音频编码器和大语言模型的参数高效训练。此外,我们实施了一种特征池策略,使系统能够识别全局模式,提高对不依赖个别序列元素的任务的准确性。在语音触发(VT)检测、定向设备语音检测(DDSD)和自动语音识别(ASR)方面的实验结果表明,我们的方法大大简化了虚拟助理的典型输入处理管道,与为每个单独任务设计的模型相比,还提高了性能。在VT检测任务上,SELMA的相对等错误率提高了64%,在DDSD上提高了22%,同时实现了接近基准值的词错误率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了SELMA,一个用于虚拟助理交互的语音驱动语言模型。它通过整合音频和文本输入到大型语言模型(LLM)中,可同时处理三项主要任务和两项辅助任务。使用低秩自适应模块实现音频编码器和LLM的参数有效训练。采用特征池策略提高系统对全局模式的识别能力,并在依赖单个序列元素较少的任务上提高准确性。实验结果表明,在语音触发检测、设备定向语音识别和自动语音识别任务上,与为每个单独任务设计的模型相比,此方法显著简化了虚拟助理的输入处理流程并提高了性能。SELMA在语音触发检测任务上的等价误差率相对提高了64%,在设备定向语音识别任务上提高了22%,同时字词错误率接近基线水平。
Key Takeaways
- SELMA是一个用于虚拟助理交互的语音驱动语言模型,整合音频和文本作为输入。
- SELMA设计用于同时处理三项主要任务和两项辅助任务。
- 采用低秩自适应模块实现参数高效训练,包括音频编码器和LLM。
- 特征池策略用于识别全局模式,提高在依赖单个序列元素较少的任务上的准确性。
- 实验结果显示,SELMA在语音触发检测、设备定向语音识别和自动语音识别任务上表现出优越性能。
- 与传统为每个任务单独设计的模型相比,SELMA简化了虚拟助理的输入处理流程。
点此查看论文截图

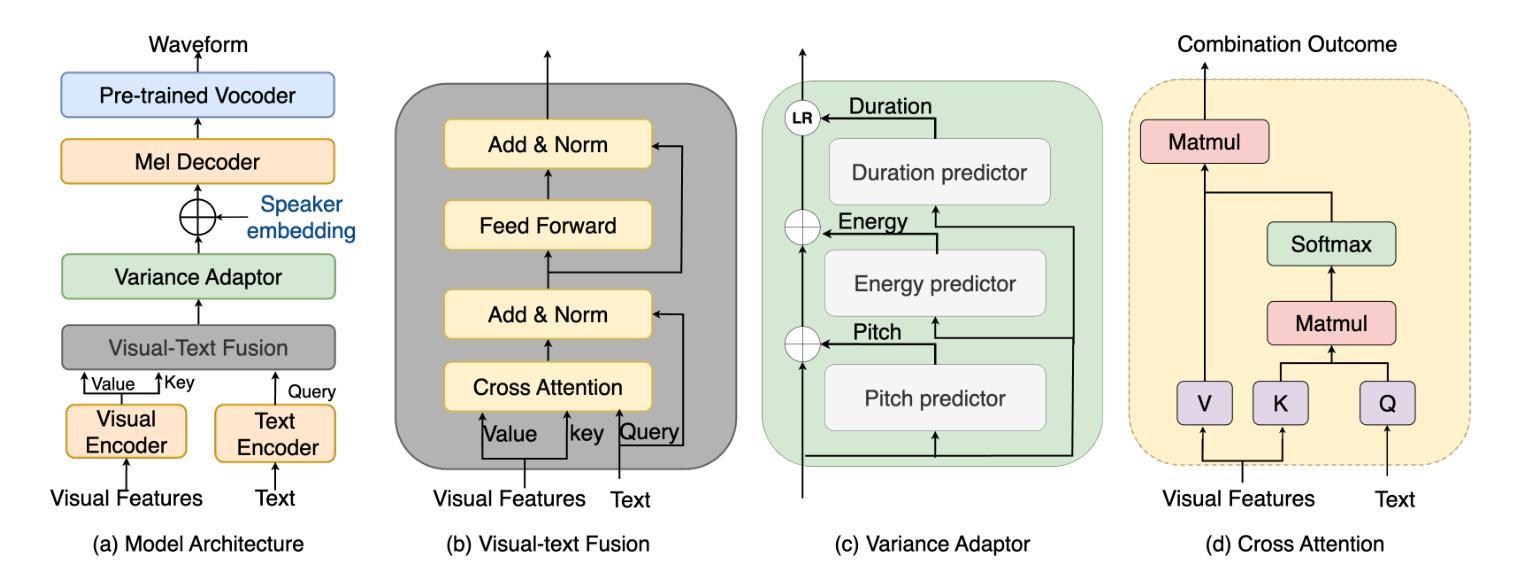
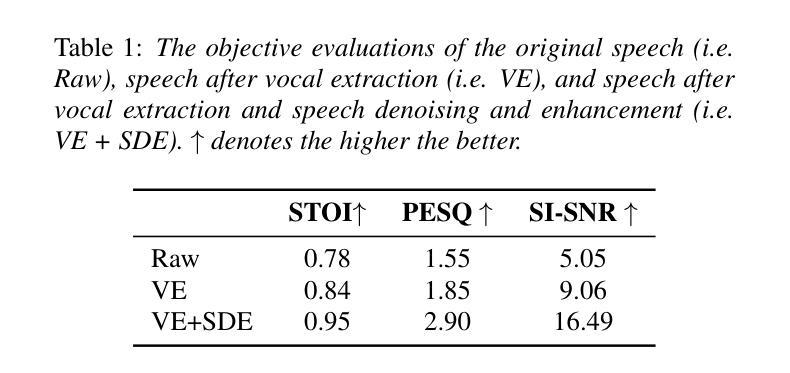
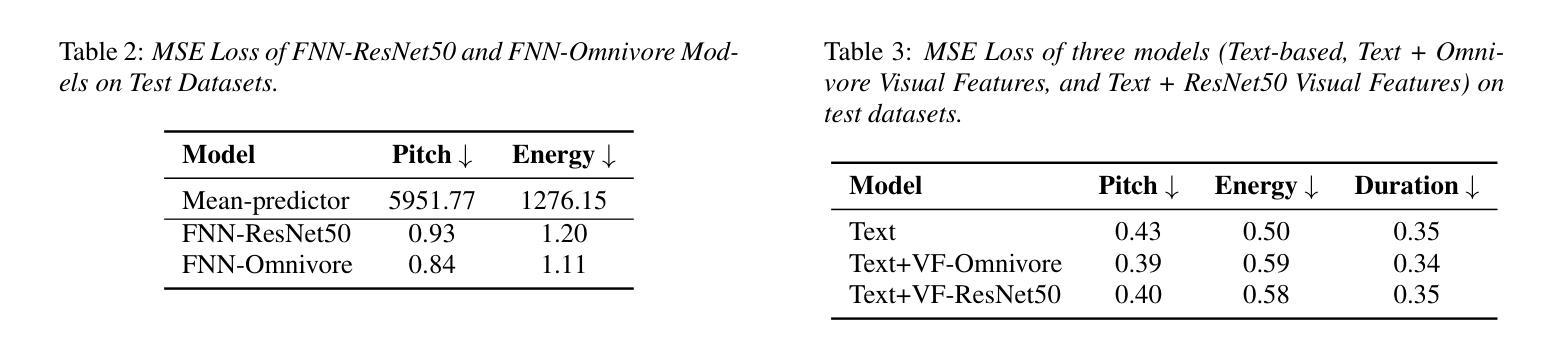
VisualSpeech: Enhance Prosody with Visual Context in TTS
Authors:Shumin Que, Anton Ragni
Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesis faces the inherent challenge of producing multiple speech outputs with varying prosody from a single text input. While previous research has addressed this by predicting prosodic information from both text and speech, additional contextual information, such as visual features, remains underutilized. This paper investigates the potential of integrating visual context to enhance prosody prediction. We propose a novel model, VisualSpeech, which incorporates both visual and textual information for improved prosody generation. Empirical results demonstrate that visual features provide valuable prosodic cues beyond the textual input, significantly enhancing the naturalness and accuracy of the synthesized speech. Audio samples are available at https://ariameetgit.github.io/VISUALSPEECH-SAMPLES/.
文本转语音(TTS)合成面临着一个固有挑战,即如何从单个文本输入生成具有不同韵律的多个语音输出。虽然之前的研究已经通过从文本和语音预测韵律信息来解决这个问题,但额外的上下文信息,如视觉特征,仍然被低估和忽略。本文探讨了整合视觉上下文以增强韵律预测的可能性。我们提出了一种新型模型VisualSpeech,该模型结合了视觉和文本信息,以改进韵律生成。经验结果表明,视觉特征提供了超越文本输入的宝贵韵律线索,显著增强了合成语音的自然度和准确性。音频样本可在https://ariameetgit.github.io/VISUALSPEECH-SAMPLES/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本文研究了将视觉上下文融入语音合成中的潜力,以增强语调预测。提出了一种新的模型VisualSpeech,该模型结合了视觉和文本信息,以改进语调生成。实验结果表明,视觉特征提供了文本输入之外的宝贵语调线索,显著增强了合成语音的自然度和准确性。
关键见解
- 文本转语音(TTS)合成面临从单一文本输入产生多种语音输出的固有挑战。
- 尽管先前的研究通过预测文本和语音的语调信息来解决这个问题,但视觉特征等额外上下文信息仍未得到充分利用。
- 本文探索了整合视觉上下文以增强语调预测的可能性。
- 提出了一个新的模型VisualSpeech,该模型结合了视觉和文本信息,以改进语调生成。
- 实证结果表明,视觉特征在提供语调线索方面具有重要价值,超越了文本输入。
- VisualSpeech模型能显著增强合成语音的自然度和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

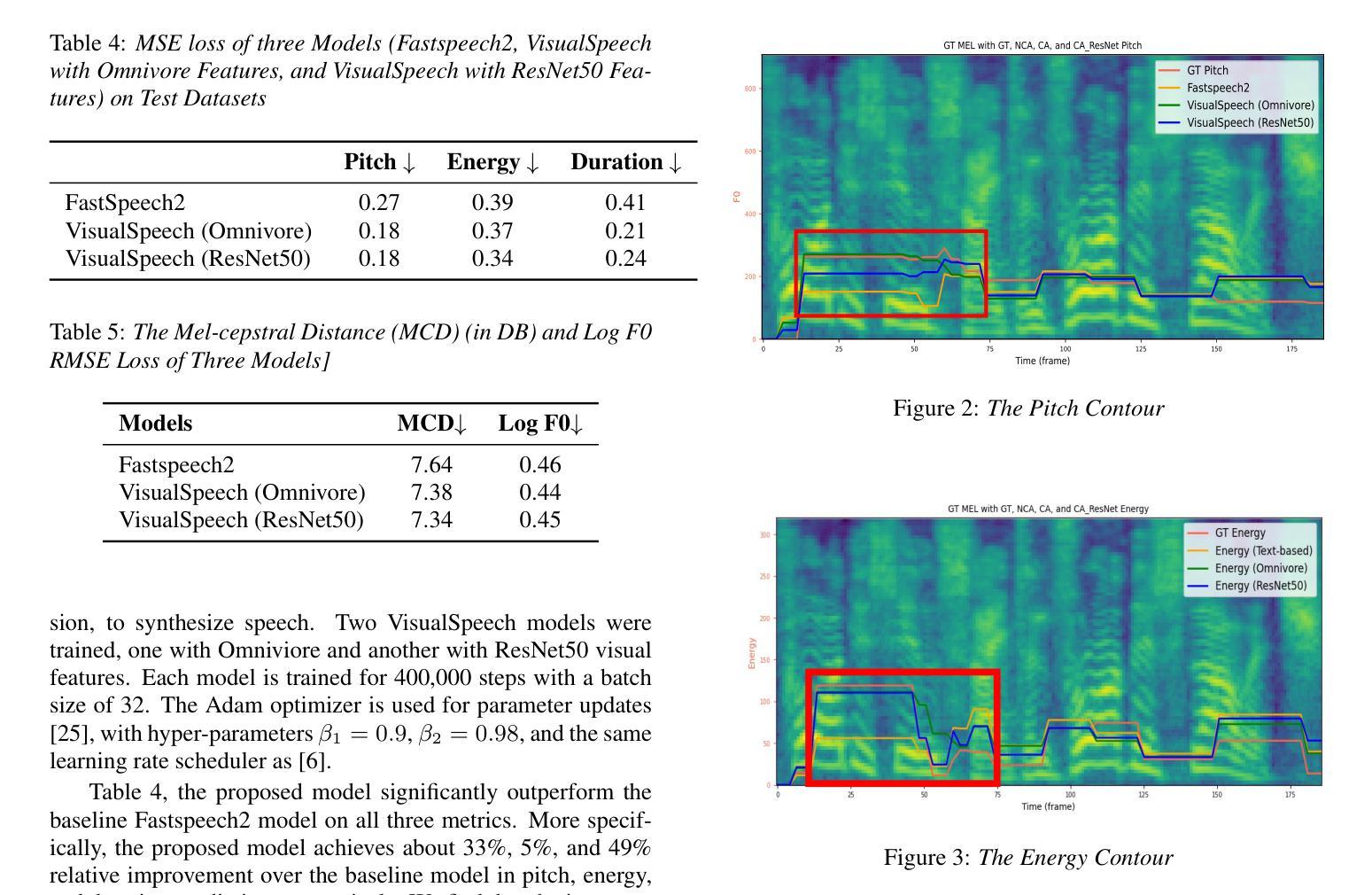
DyPCL: Dynamic Phoneme-level Contrastive Learning for Dysarthric Speech Recognition
Authors:Wonjun Lee, Solee Im, Heejin Do, Yunsu Kim, Jungseul Ok, Gary Geunbae Lee
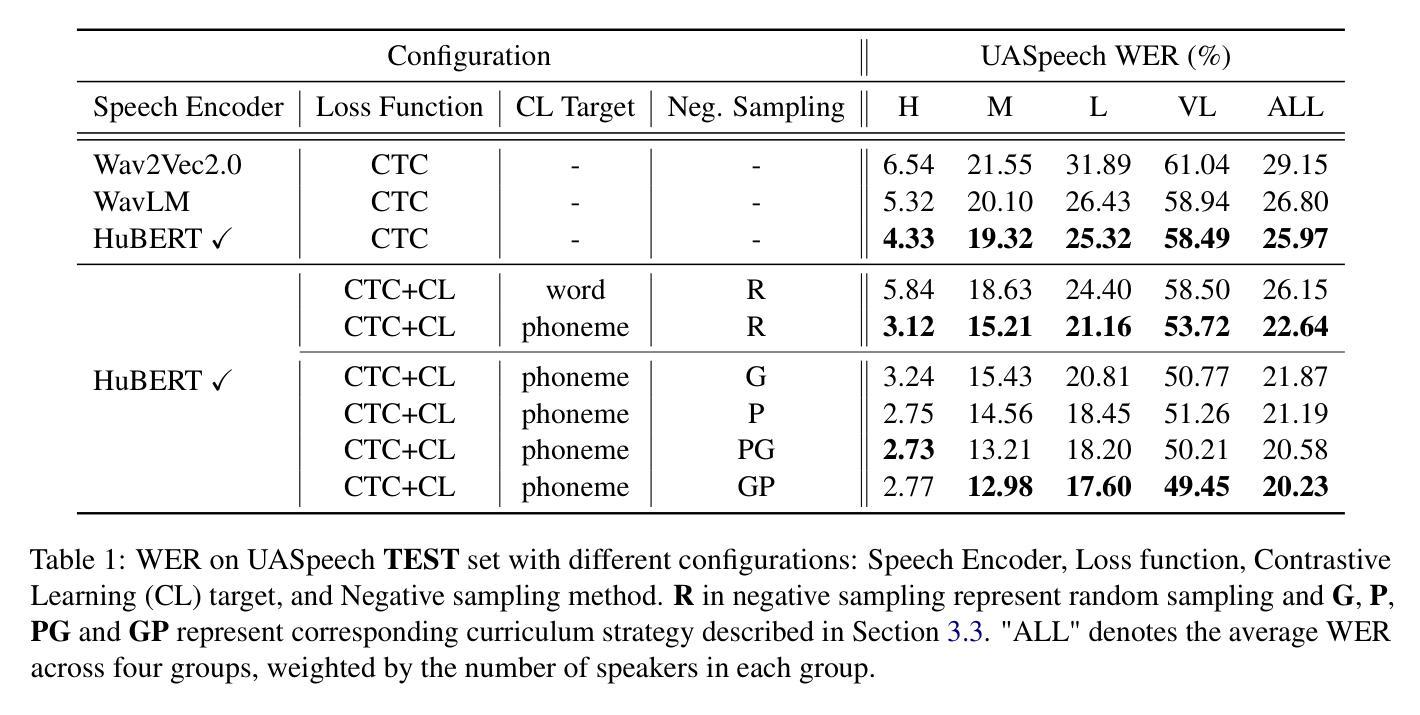
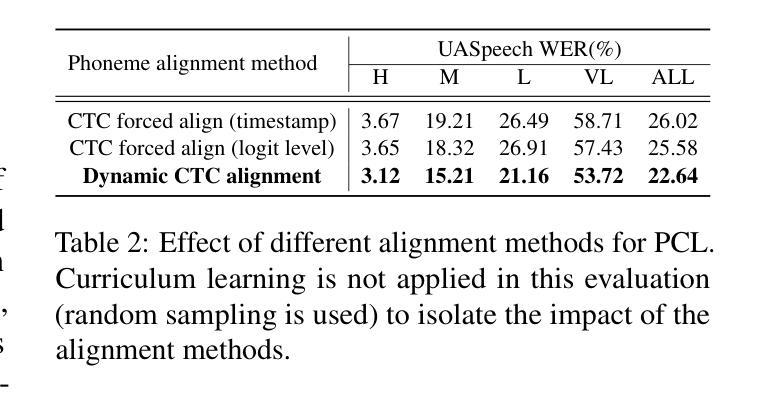
Dysarthric speech recognition often suffers from performance degradation due to the intrinsic diversity of dysarthric severity and extrinsic disparity from normal speech. To bridge these gaps, we propose a Dynamic Phoneme-level Contrastive Learning (DyPCL) method, which leads to obtaining invariant representations across diverse speakers. We decompose the speech utterance into phoneme segments for phoneme-level contrastive learning, leveraging dynamic connectionist temporal classification alignment. Unlike prior studies focusing on utterance-level embeddings, our granular learning allows discrimination of subtle parts of speech. In addition, we introduce dynamic curriculum learning, which progressively transitions from easy negative samples to difficult-to-distinguishable negative samples based on phonetic similarity of phoneme. Our approach to training by difficulty levels alleviates the inherent variability of speakers, better identifying challenging speeches. Evaluated on the UASpeech dataset, DyPCL outperforms baseline models, achieving an average 22.10% relative reduction in word error rate (WER) across the overall dysarthria group.
构音障碍语音识别常常因为构音障碍的固有多样性和与正常语音的外在差异而性能下降。为了弥补这些差距,我们提出了一种动态音素级对比学习(DyPCL)方法,该方法可以获得不同说话者的不变表示。我们将语音发音分解成音素片段进行音素级对比学习,利用动态连接时态分类对齐。与以往研究专注于句子级嵌入不同,我们的粒度学习可以区分语音的细微部分。此外,我们引入了动态课程学习,它根据音素的语音相似性,从容易区分的负样本逐渐过渡到难以区分的负样本。我们按难度级别进行培训的方法减轻了说话者的内在变化,更好地识别了具有挑战性的语音。在UASpeech数据集上评估,DyPCL优于基线模型,在整个构音障碍组中平均降低了22.10%的字错误率(WER)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025 main conference, 9pages, 1 page appendix
总结
本文提出一种动态音素级对比学习(DyPCL)方法,用于改善发音障碍语音识别性能。针对发音障碍多样性和与正常语音的差异性,DyPCL通过音素级对比学习获得跨不同说话者的不变表示。该方法采用动态连接时间分类对齐技术,将语音片段分解为音素片段进行学习。与传统的基于句子级别的嵌入方法不同,DyPCL的精细学习能够区分语音的细微部分。此外,还引入了动态课程学习,根据音素的语音相似性,从易于区分的负样本逐渐过渡到难以区分的负样本。该方法通过按难度级别进行培训,减轻了说话人的内在变化,更好地识别了具有挑战性的语音。在UASpeech数据集上的评估结果表明,DyPCL相较于基线模型表现出色,整体发音障碍组的平均词错误率(WER)降低了22.10%。
关键见解
- DyPCL方法旨在解决发音障碍语音识别的性能下降问题,面对发音障碍的多样性和与正常语音的差异。
- 通过音素级对比学习获得跨不同说话者的不变表示。
- 采用动态连接时间分类对齐技术分解语音片段进行更精细的学习。
- 引入动态课程学习,按语音相似性逐渐过渡学习难度。
- 按难度级别培训的方法减轻了说话人的内在变化,更好地识别具有挑战性的语音。
- 在UASpeech数据集上的评估显示,DyPCL相较于基线模型显著降低了词错误率(WER)。
- DyPCL方法实现了平均22.10%的相对减少词错误率。
点此查看论文截图

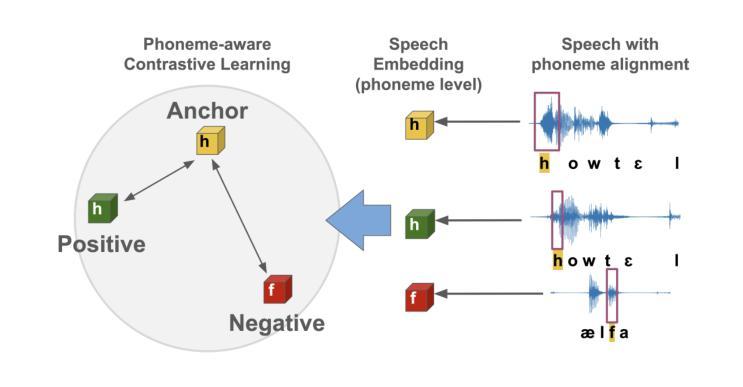
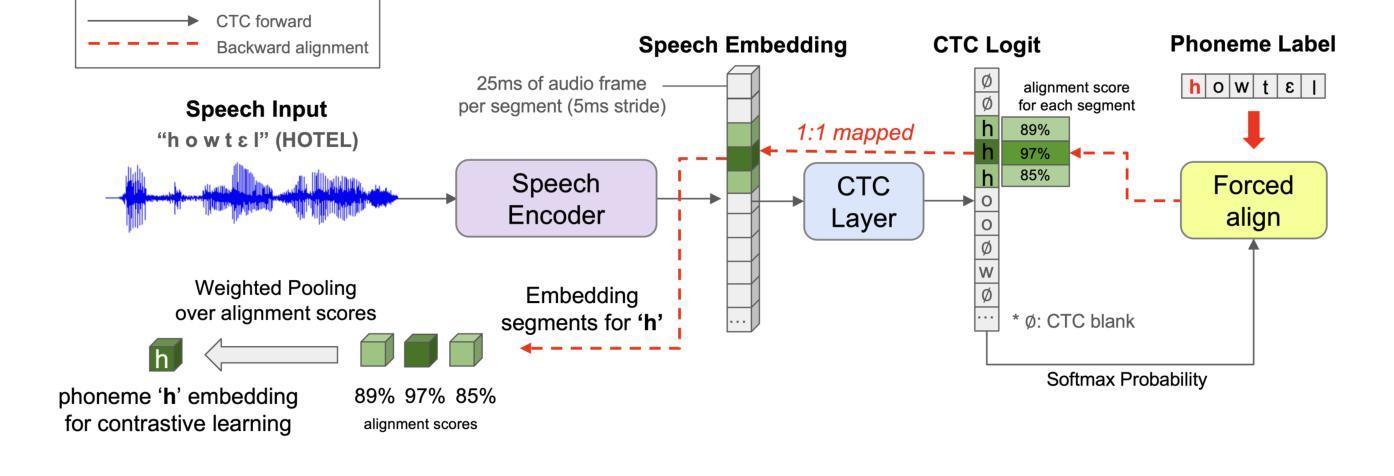
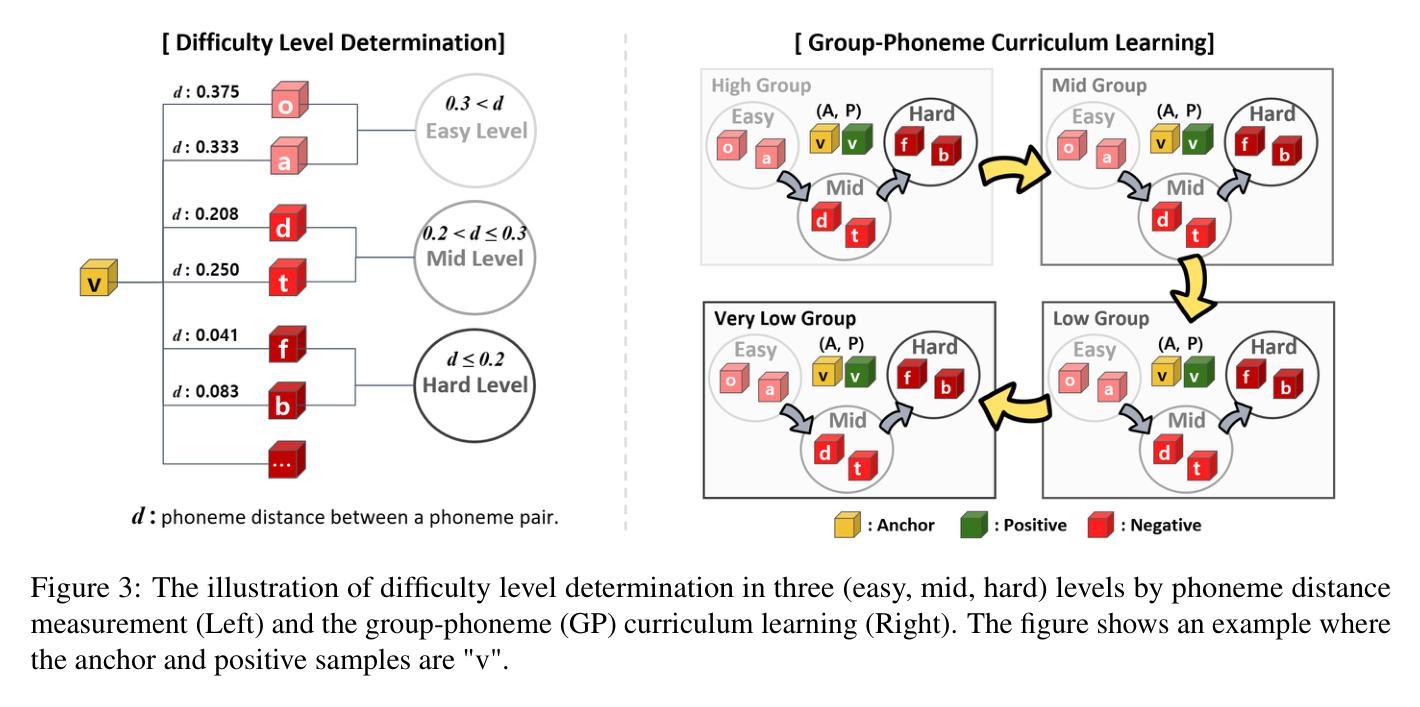
Image, Text, and Speech Data Augmentation using Multimodal LLMs for Deep Learning: A Survey
Authors:Ranjan Sapkota, Shaina Raza, Maged Shoman, Achyut Paudel, Manoj Karkee
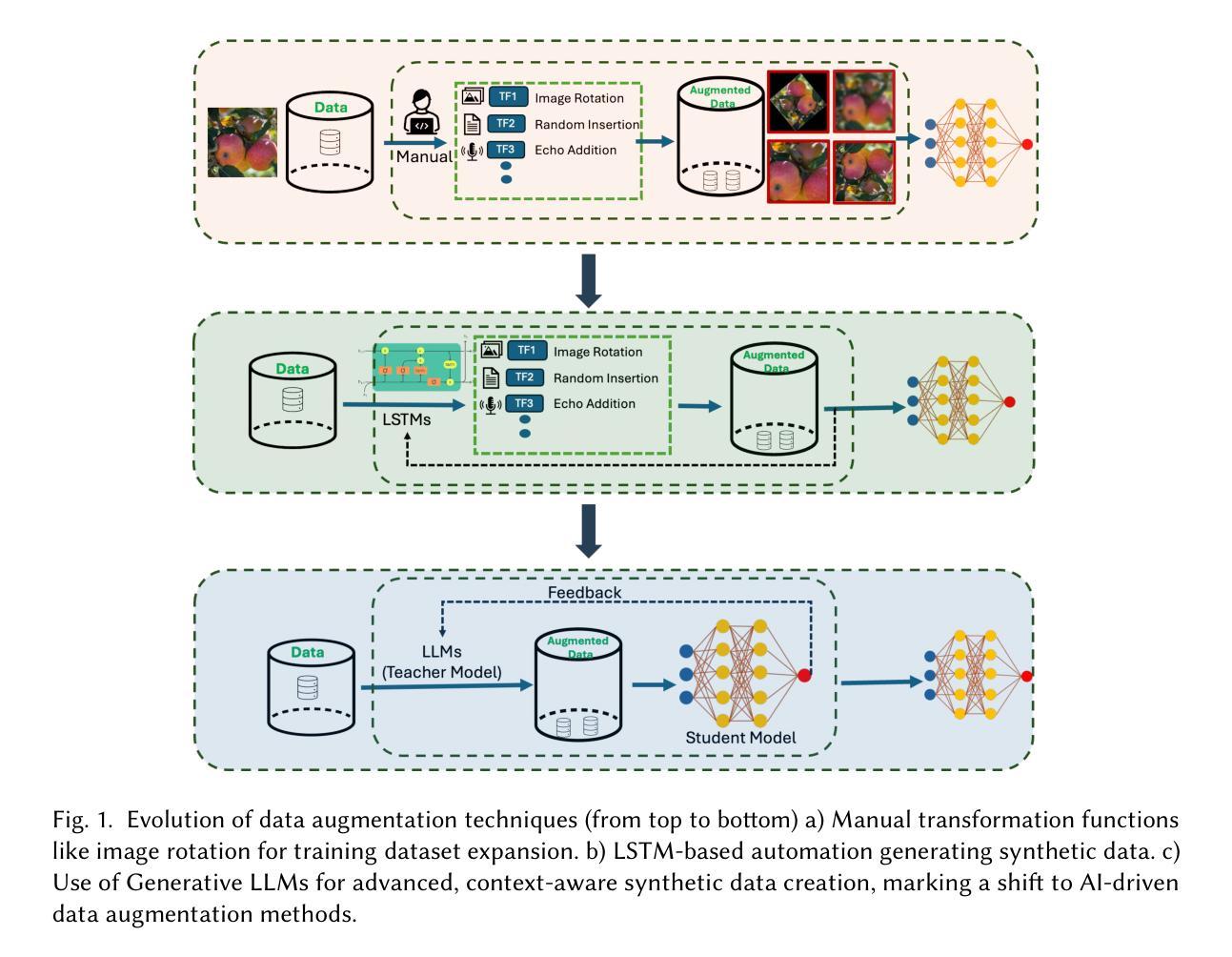
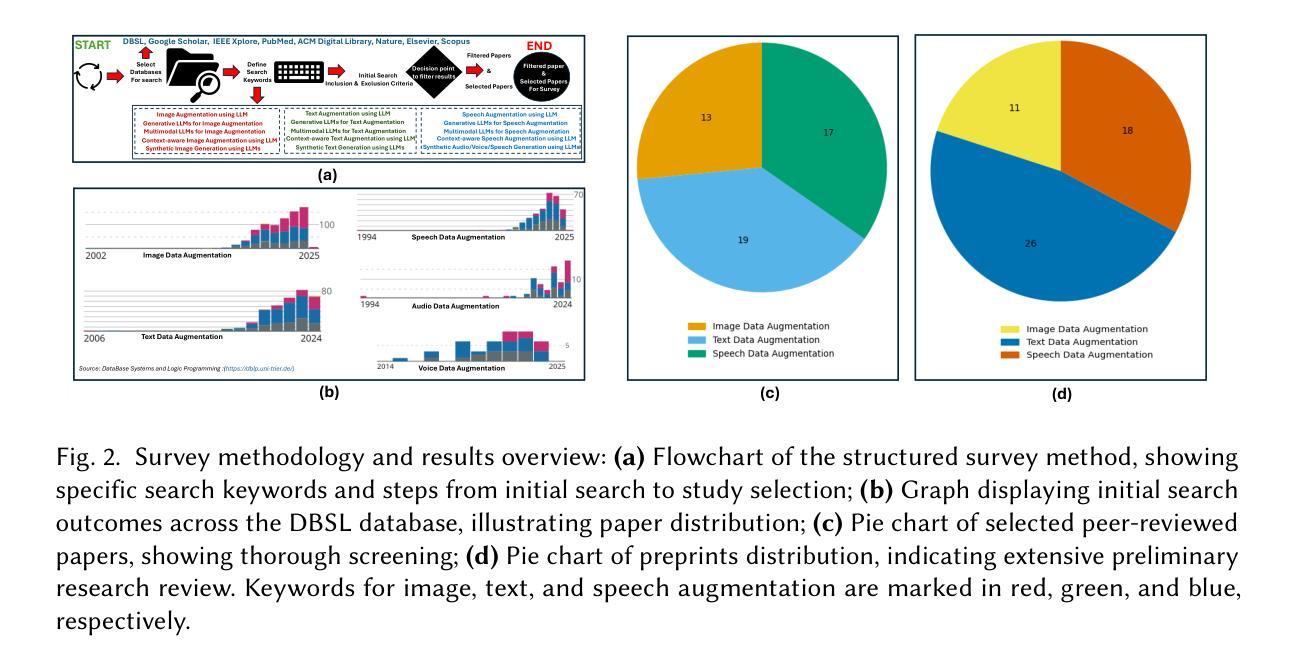
In the past five years, research has shifted from traditional Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) approaches to leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) , including multimodality, for data augmentation to enhance generalization, and combat overfitting in training deep convolutional neural networks. However, while existing surveys predominantly focus on ML and DL techniques or limited modalities (text or images), a gap remains in addressing the latest advancements and multi-modal applications of LLM-based methods. This survey fills that gap by exploring recent literature utilizing multimodal LLMs to augment image, text, and audio data, offering a comprehensive understanding of these processes. We outlined various methods employed in the LLM-based image, text and speech augmentation, and discussed the limitations identified in current approaches. Additionally, we identified potential solutions to these limitations from the literature to enhance the efficacy of data augmentation practices using multimodal LLMs. This survey serves as a foundation for future research, aiming to refine and expand the use of multimodal LLMs in enhancing dataset quality and diversity for deep learning applications. (Surveyed Paper GitHub Repo: https://github.com/WSUAgRobotics/data-aug-multi-modal-llm. Keywords: LLM data augmentation, LLM text data augmentation, LLM image data augmentation, LLM speech data augmentation, audio augmentation, voice augmentation, chatGPT for data augmentation, DeepSeek R1 text data augmentation, DeepSeek R1 image augmentation, Image Augmentation using LLM, Text Augmentation using LLM, LLM data augmentation for deep learning applications)
过去五年,研究已从传统的机器学习和深度学习方法转向利用大型语言模型(LLM),包括多模态,进行数据增强以提高泛化能力,并应对训练深度卷积神经网络时的过拟合问题。然而,尽管现有的调查主要集中在ML和DL技术或有限模式(文本或图像)上,但在解决基于LLM的方法的最新进展和多模态应用方面仍存在差距。本调查通过探索利用多模态LLM增强图像、文本和音频数据的最新文献来填补这一空白,为这些过程提供全面的理解。我们概述了基于LLM的图像、文本和语音增强所采用的各种方法,并讨论了当前方法中所识别的局限性。此外,我们从文献中确定了解决这些局限性的潜在解决方案,以提高使用多模态LLM的数据增强实践的有效性。本调查为未来研究奠定了基础,旨在完善和发展多模态LLM在深度学习应用中的使用和增强数据集质量和多样性的方法。(所调查论文GitHub仓库:https://github.com/WSUAgRobotics/data-aug-multi-modal-llm。关键词:LLM数据增强、LLM文本数据增强、LLM图像数据增强、LLM语音数据增强、音频增强、语音增强、ChatGPT用于数据增强、DeepSeek R1文本数据增强、DeepSeek R1图像增强、使用LLM的图像增强、使用LLM的文本增强、LLM数据增强在深度学习应用)
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
这篇调研论文填补了关于多模态大型语言模型(LLM)数据增强的研究空白。文章深入探讨了使用多模态LLM增强图像、文本和音频数据的最新文献,并概述了LLM在图像、文本和语音增强中的应用方法。此外,论文讨论了当前方法的局限性,并从文献中提出了针对这些局限性的潜在解决方案,以提高使用多模态LLM的数据增强实践效果。此调研为未来的研究奠定了基础,旨在完善并扩展多模态LLM在深度学习应用中的使用,以提高数据集的质量和多样性。
关键见解
- 调研论文概述了多模态大型语言模型(LLM)在数据增强方面的最新进展。
- 文章详细探讨了LLM在图像、文本和语音增强中的应用方法。
- 论文指出了现有LLM数据增强方法的局限性。
- 从文献中提出了针对这些局限性的潜在解决方案,以提高数据增强实践的效果。
- 调研强调了多模态LLM在提高数据集质量和多样性方面的作用。
- 文章提到的关键词包括LLM数据增强、音频增强、语音增强以及特定工具如ChatGPT用于数据增强等。
- 此调研为未来的研究提供了基础,旨在扩展和完善多模态LLM在深度学习领域的应用。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Event-based Delay Learning in Spiking Neural Networks
Authors:Balázs Mészáros, James C. Knight, Thomas Nowotny
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are attracting increased attention as a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional Artificial Neural Networks. Spiking neurons are stateful and intrinsically recurrent, making them well-suited for spatio-temporal tasks. However, this intrinsic memory is limited by synaptic and membrane time constants. A powerful additional mechanism are delays. In this paper, we propose a novel event-based training method for SNNs with delays, grounded in the EventProp formalism and enabling the calculation of exact gradients with respect to weights and delays. Our method supports multiple spikes per neuron and, to our best knowledge, is the first delay learning algorithm to be applied to recurrent SNNs. We evaluate our method on a simple sequence detection task, and the Yin-Yang, Spiking Heidelberg Digits and Spiking Speech Commands datasets, demonstrating that our algorithm can optimize delays from suboptimal initial conditions and enhance classification accuracy compared to architectures without delays. Finally, we show that our approach uses less than half the memory of the current state-of-the-art delay-learning method and is up to 26x faster.
脉冲神经网络(Spiking Neural Networks,简称SNNs)作为一种比传统人工神经网络更节能的替代方案,正越来越受到关注。脉冲神经元具有状态和内在复发的特性,使其非常适合时空任务。然而,这种内在的记忆受到突触和膜时间常数的限制。一种强大的附加机制是延迟。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于事件的新型脉冲神经网络训练方法,该方法以EventProp形式为基础,能够计算关于权重和延迟的精确梯度。我们的方法支持每个神经元的多个脉冲,并且据我们所知,是第一个应用于复发脉冲神经网络的延迟学习算法。我们在简单的序列检测任务以及阴阳、脉冲海德堡数字和脉冲语音命令数据集上评估了我们的方法,证明我们的算法可以从不佳的初始条件优化延迟并提高分类准确率,与没有延迟的架构相比具有优势。最后,我们证明我们的方法使用的内存不到当前最先进的延迟学习方法的一半,并且速度最快可提高26倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
脉冲神经网络(SNNs)作为更节能的传统人工神经网络替代品而备受关注。脉冲神经元具有状态和内在复发性,使其适合时空任务。然而,这种内在记忆受到突触和膜时间常数的限制。延迟是一种强大的附加机制。本文提出一种基于EventProp形式主义的带有延迟的SNNs的新型事件驱动训练方法,能够计算关于权重和延迟的确切梯度。我们的方法支持每个神经元的多个脉冲,据我们所知,是首个应用于递归SNNs的延迟学习算法。我们在简单的序列检测任务以及阴阳、脉冲海德堡数字和脉冲语音命令数据集上评估了我们的方法,证明我们的算法可以优化从次优初始条件开始的延迟,并提高分类精度,与没有延迟的架构相比。最后,我们证明我们的方法使用的内存不到当前最先进的延迟学习方法的一半,并且速度最快可达26倍。
Key Takeaways
- Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) 作为一种更节能的神经网络形式受到关注。
- 脉冲神经元具有状态和内在复发性,适合处理时空任务。
- 延迟是SNNs中强大的附加机制,用于优化性能。
- 提出了一种新型事件驱动训练方法,结合EventProp形式主义,可计算权重和延迟的确切梯度。
- 该方法支持多个脉冲,并首次应用于递归SNNs的延迟学习。
- 在序列检测任务及多个数据集上评估,证明算法能优化延迟并提升分类精度。
点此查看论文截图

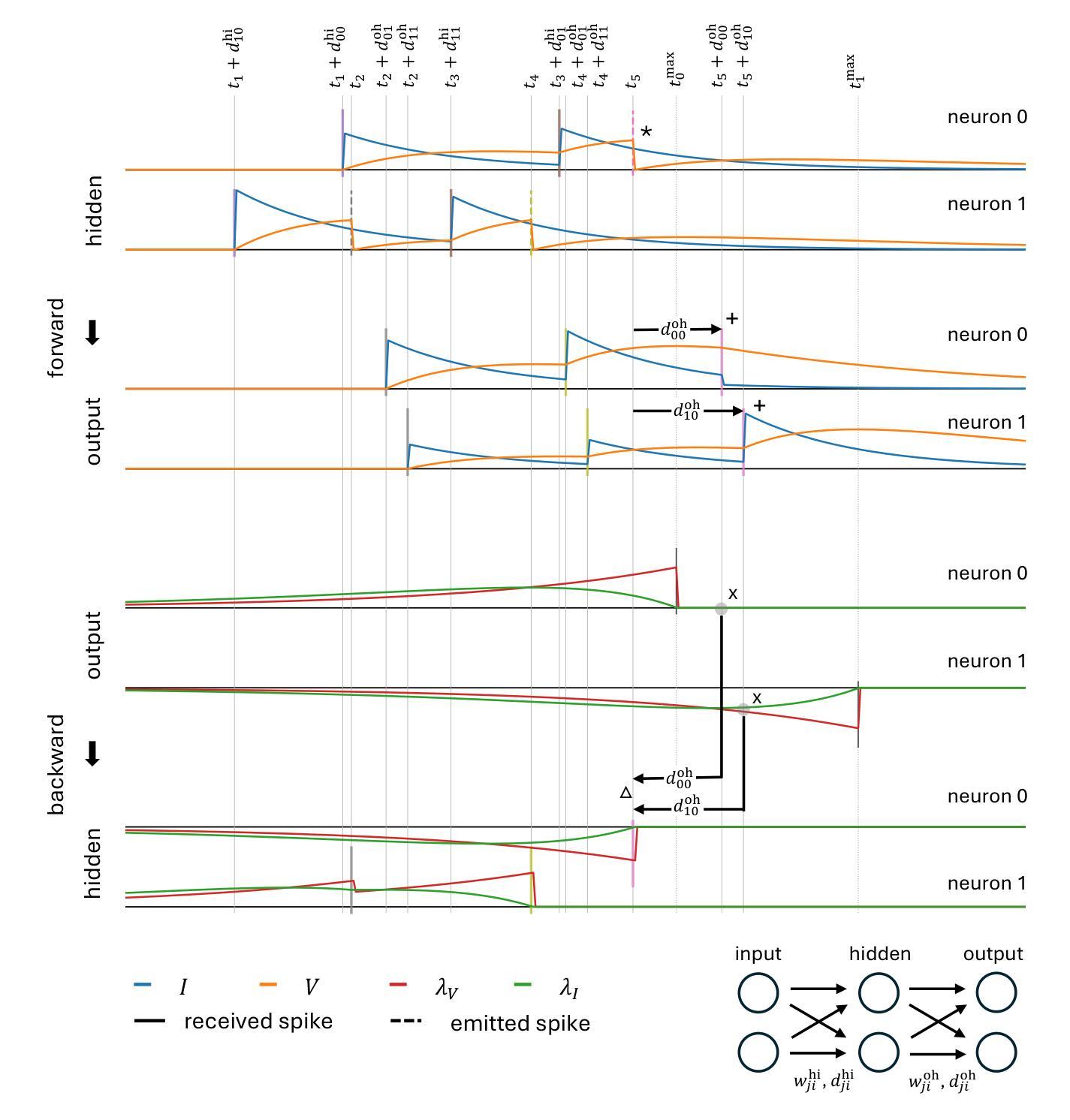
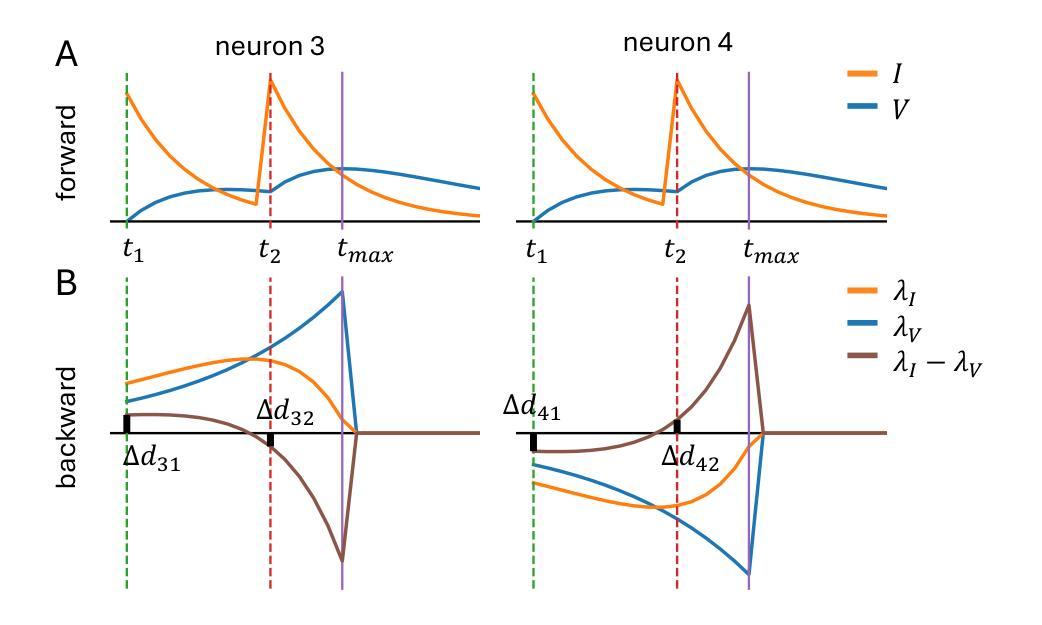
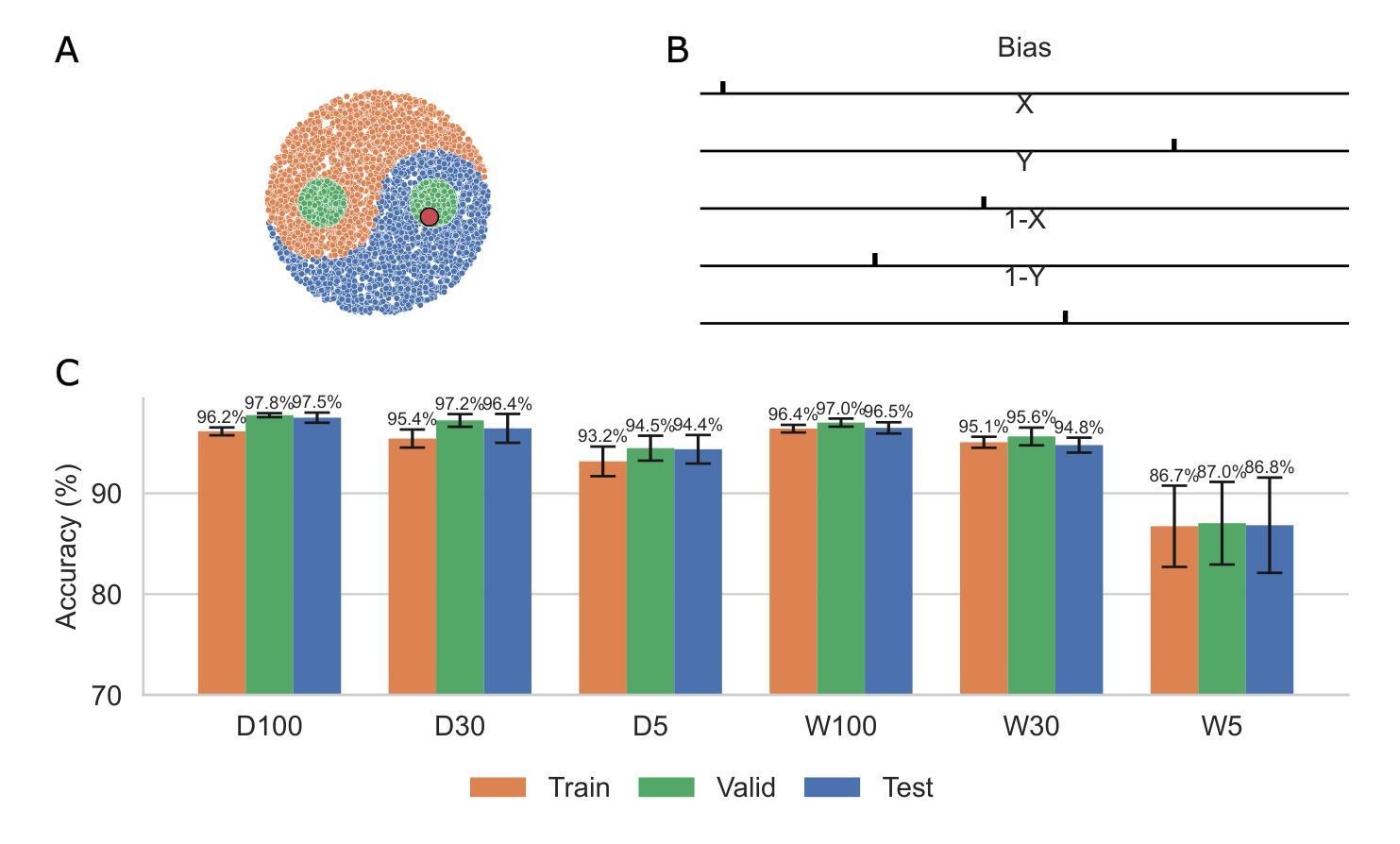
On Creating A Brain-To-Text Decoder
Authors:Zenon Lamprou, Yashar Moshfeghi
Brain decoding has emerged as a rapidly advancing and extensively utilized technique within neuroscience. This paper centers on the application of raw electroencephalogram (EEG) signals for decoding human brain activity, offering a more expedited and efficient methodology for enhancing our understanding of the human brain. The investigation specifically scrutinizes the efficacy of brain-computer interfaces (BCI) in deciphering neural signals associated with speech production, with particular emphasis on the impact of vocabulary size, electrode density, and training data on the framework’s performance. The study reveals the competitive word error rates (WERs) achievable on the Librispeech benchmark through pre-training on unlabelled data for speech processing. Furthermore, the study evaluates the efficacy of voice recognition under configurations with limited labeled data, surpassing previous state-of-the-art techniques while utilizing significantly fewer labels. Additionally, the research provides a comprehensive analysis of error patterns in voice recognition and the influence of model size and unlabelled training data. It underscores the significance of factors such as vocabulary size and electrode density in enhancing BCI performance, advocating for an increase in microelectrodes and refinement of language models.
脑解码作为神经科学领域的一种快速进步且广泛应用的技术已经崭露头角。本文重点研究原始脑电图(EEG)信号在解码人脑活动中的应用,为增强我们对人脑的理解提供了一种更快、更高效的方法。研究特别细致地审视了脑机接口(BCI)在解析与言语产生相关的神经信号方面的有效性,特别强调了词汇量、电极密度和训练数据对框架性能的影响。该研究通过在无标签数据上进行预训练,揭示了Librispeech基准测试上可实现的竞争词错误率(WERs)。此外,该研究在有限标记数据配置下对语音识别的有效性进行了评估,在利用明显更少的标签的情况下,超越了以前最先进的技术。此外,该研究还全面分析了语音识别中的错误模式以及模型大小和未标记训练数据的影响。它强调了增加词汇量和提高电极密度等要素在提高BCI性能中的重要性,提倡增加微电极数量和完善语言模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
脑解码是神经科学中发展迅速且广泛应用的技术。本文关注原始脑电图信号在解码人类脑活动中的应用,提供一种更快、更高效的方法,以提高对大脑的理解。研究重点探讨了脑机接口在解析与言语产生相关的神经信号方面的有效性,特别关注词汇量、电极密度和训练数据对系统性能的影响。研究还通过预训练未标记数据,揭示了Librispeech基准测试上可达到的竞争词错误率,并在有限标记数据配置下评估了语音识别的有效性,同时分析了语音识别的错误模式以及模型大小和未标记训练数据的影响。强调了增加微电极和改进语言模型的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 脑解码技术已成为神经科学中的核心方法,利用原始脑电图信号解码人类脑活动,提高我们对大脑的理解。
- 研究关注脑机接口在解析与言语产生相关的神经信号方面的有效性。
- 词汇量、电极密度和训练数据是影响脑机接口性能的关键因素。
- 通过预训练未标记数据,可以在Librispeech基准测试上实现较低的词错误率。
- 在有限标记数据配置下,研究提出的语音识别方法优于现有技术。
- 研究分析了语音识别的错误模式,并探讨了模型大小和未标记训练数据的影响。
点此查看论文截图

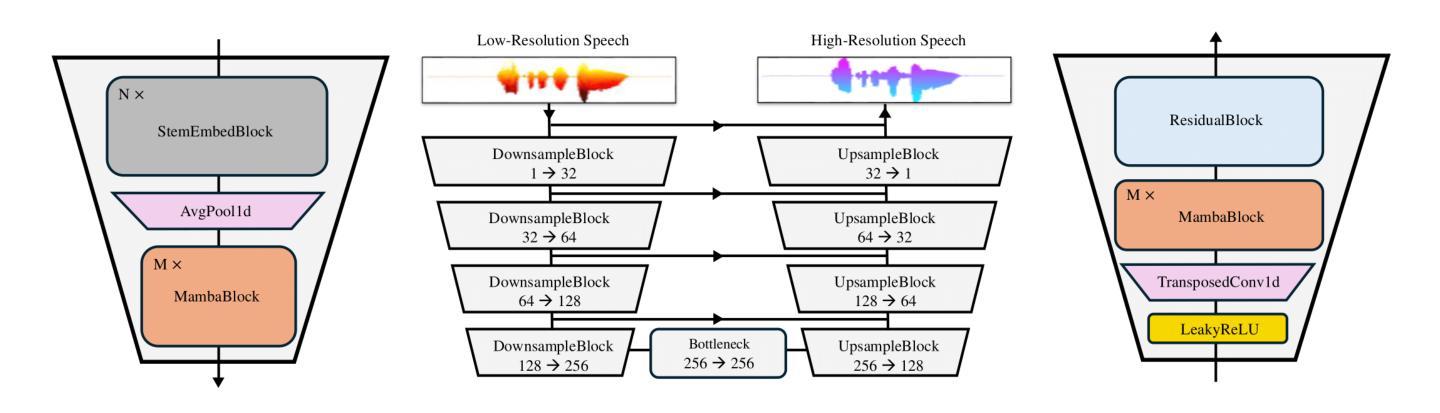
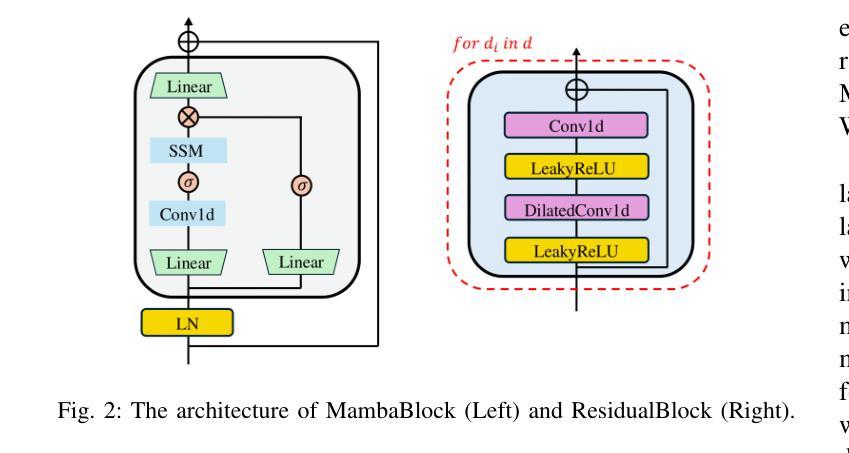
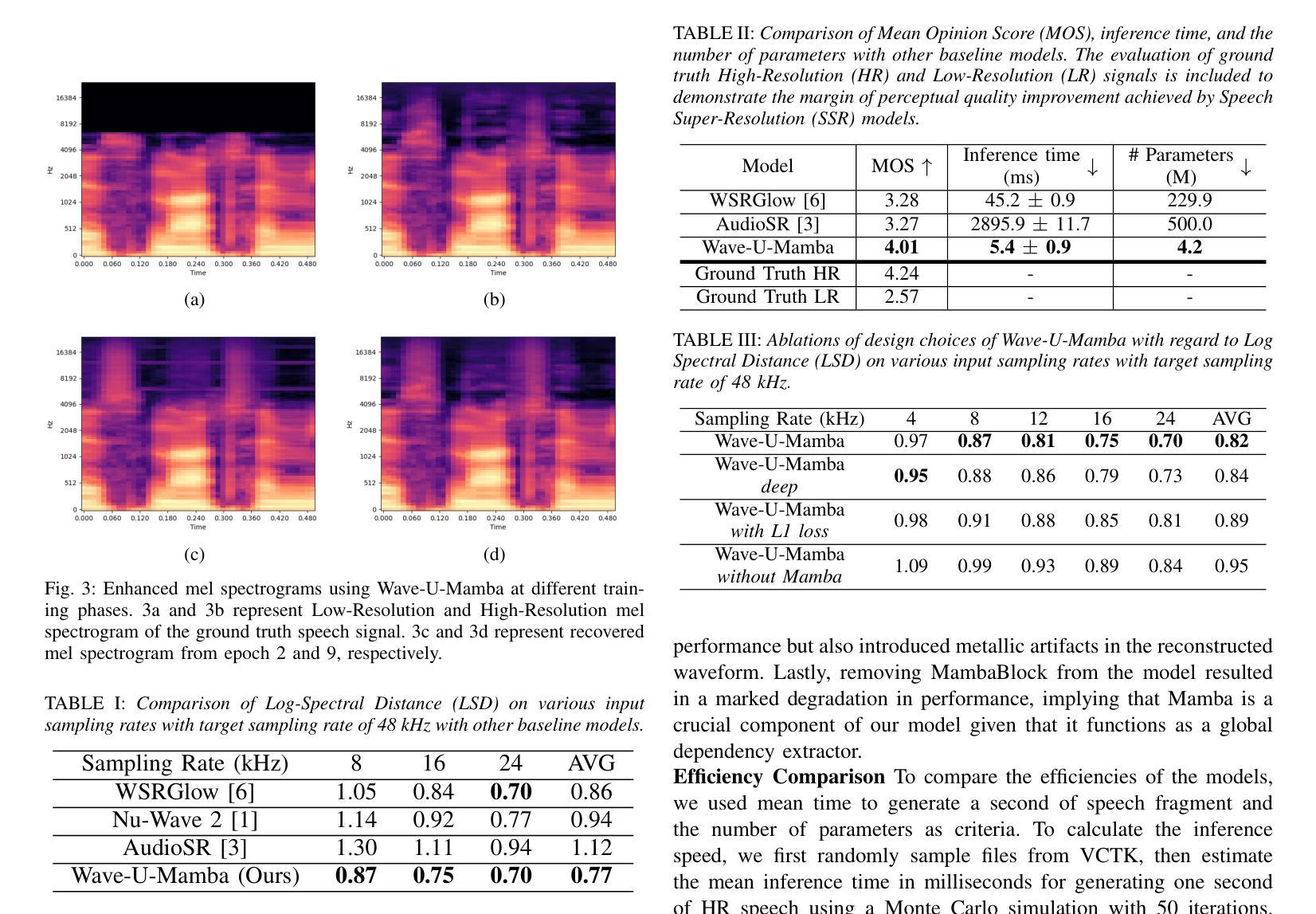
Wave-U-Mamba: An End-To-End Framework For High-Quality And Efficient Speech Super Resolution
Authors:Yongjoon Lee, Chanwoo Kim
Speech Super-Resolution (SSR) is a task of enhancing low-resolution speech signals by restoring missing high-frequency components. Conventional approaches typically reconstruct log-mel features, followed by a vocoder that generates high-resolution speech in the waveform domain. However, as mel features lack phase information, this can result in performance degradation during the reconstruction phase. Motivated by recent advances with Selective State Spaces Models (SSMs), we propose a method, referred to as Wave-U-Mamba that directly performs SSR in time domain. In our comparative study, including models such as WSRGlow, NU-Wave 2, and AudioSR, Wave-U-Mamba demonstrates superior performance, achieving the lowest Log-Spectral Distance (LSD) across various low-resolution sampling rates, ranging from 8 to 24 kHz. Additionally, subjective human evaluations, scored using Mean Opinion Score (MOS) reveal that our method produces SSR with natural and human-like quality. Furthermore, Wave-U-Mamba achieves these results while generating high-resolution speech over nine times faster than baseline models on a single A100 GPU, with parameter sizes less than 2% of those in the baseline models.
语音超分辨率(SSR)是通过恢复缺失的高频成分来提高低分辨率语音信号的任务。传统方法通常重建对数梅尔特征,然后通过声码器在波形域生成高分辨率语音。然而,由于梅尔特征缺乏相位信息,这可能导致重建阶段的性能下降。受最近选择性状态空间模型(SSM)进展的启发,我们提出了一种称为Wave-U-Mamba的方法,直接在时间域执行SSR。在我们的比较研究中,包括WSRGlow、NU-Wave 2和AudioSR等模型,Wave-U-Mamba展示了出色的性能,在各种低分辨率采样率(从8到24 kHz)下实现了最低的对数谱距离(LSD)。此外,使用平均意见得分(MOS)进行的主观人类评估表明,我们的方法产生的SSR具有自然和人性化质量。而且,Wave-U-Mamba在单个A100 GPU上生成高分辨率语音的速度是基线模型的9倍,参数大小不到基线模型的2%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了语音超分辨率(SSR)的任务,即通过对缺失的高频成分进行恢复来提高低分辨率语音信号的质量。文章提出了一种基于选择性状态空间模型(SSMs)的方法——Wave-U-Mamba,直接在时间域进行SSR。相较于其他模型,如WSRGlow、NU-Wave 2和AudioSR,Wave-U-Mamba在各项低分辨率采样率下的Log-Spectral Distance(LSD)指标表现更优,且生成的语音质量自然、逼真。同时,Wave-U-Mamba在单A100 GPU上的运行速度是基线模型的九倍,参数大小仅为基线模型的不到2%。
Key Takeaways
- 语音超分辨率(SSR)旨在提高低分辨率语音信号的质量,通过恢复缺失的高频成分来实现。
- 传统方法通常通过重建log-mel特征,然后利用vocoder生成高分辨率语音波形。
- log-mel特征缺乏相位信息,可能导致重建阶段性能下降。
- 基于选择性状态空间模型(SSMs)的Wave-U-Mamba方法直接在时间域进行SSR。
- 在各种低分辨率采样率下,Wave-U-Mamba的Log-Spectral Distance(LSD)表现优于其他模型。
- 人类主观评价显示,Wave-U-Mamba生成的语音质量自然、逼真。
点此查看论文截图

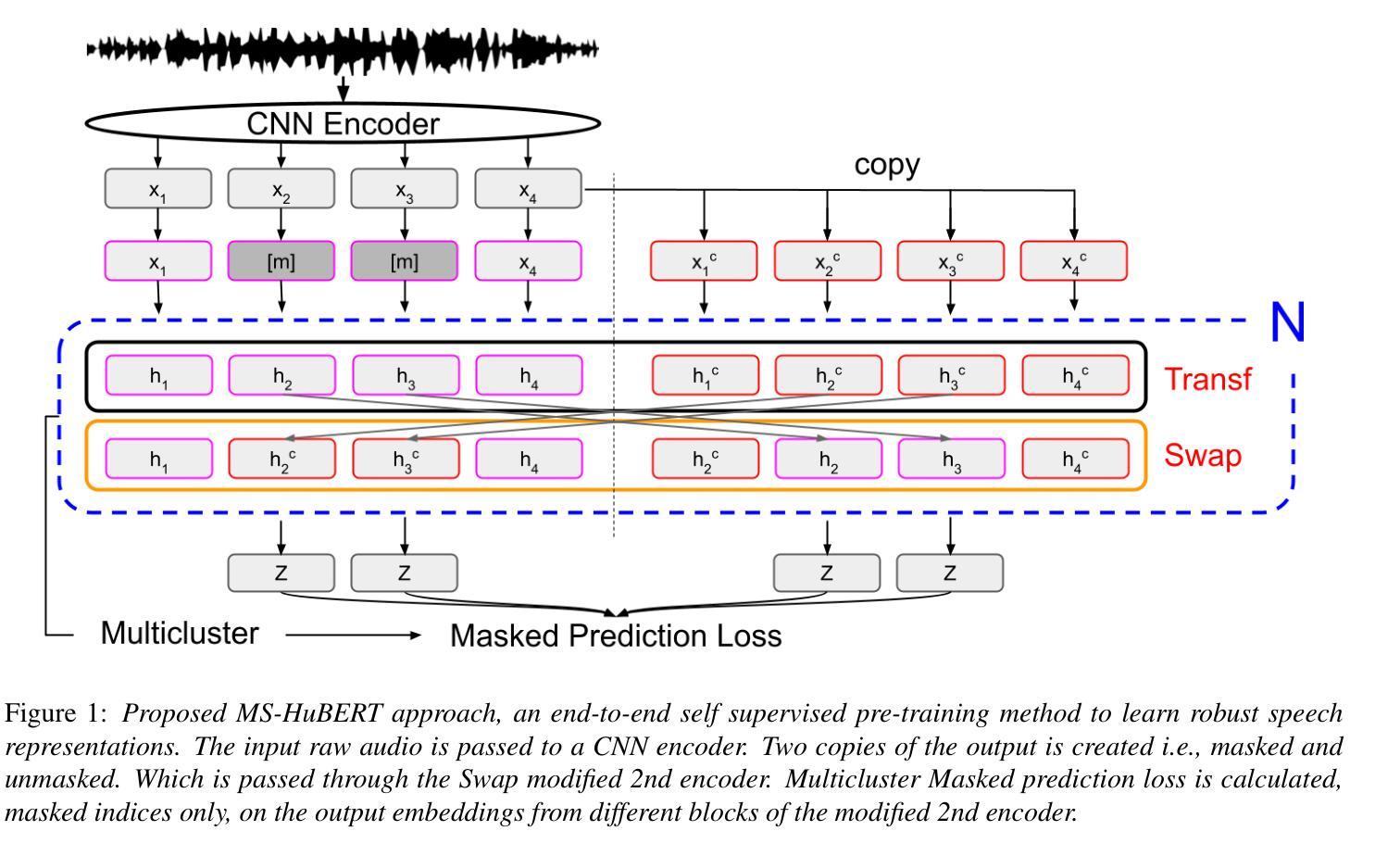
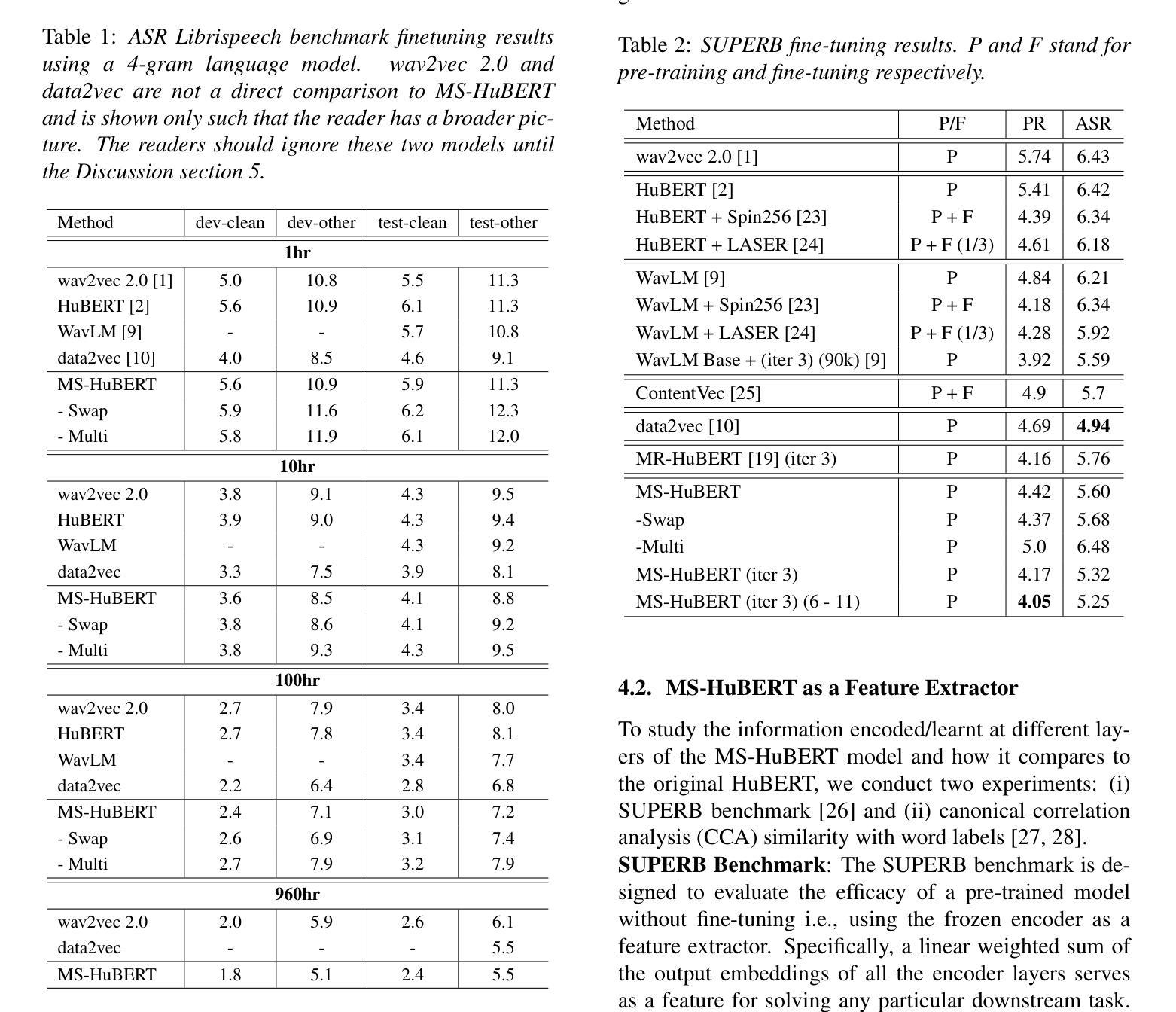
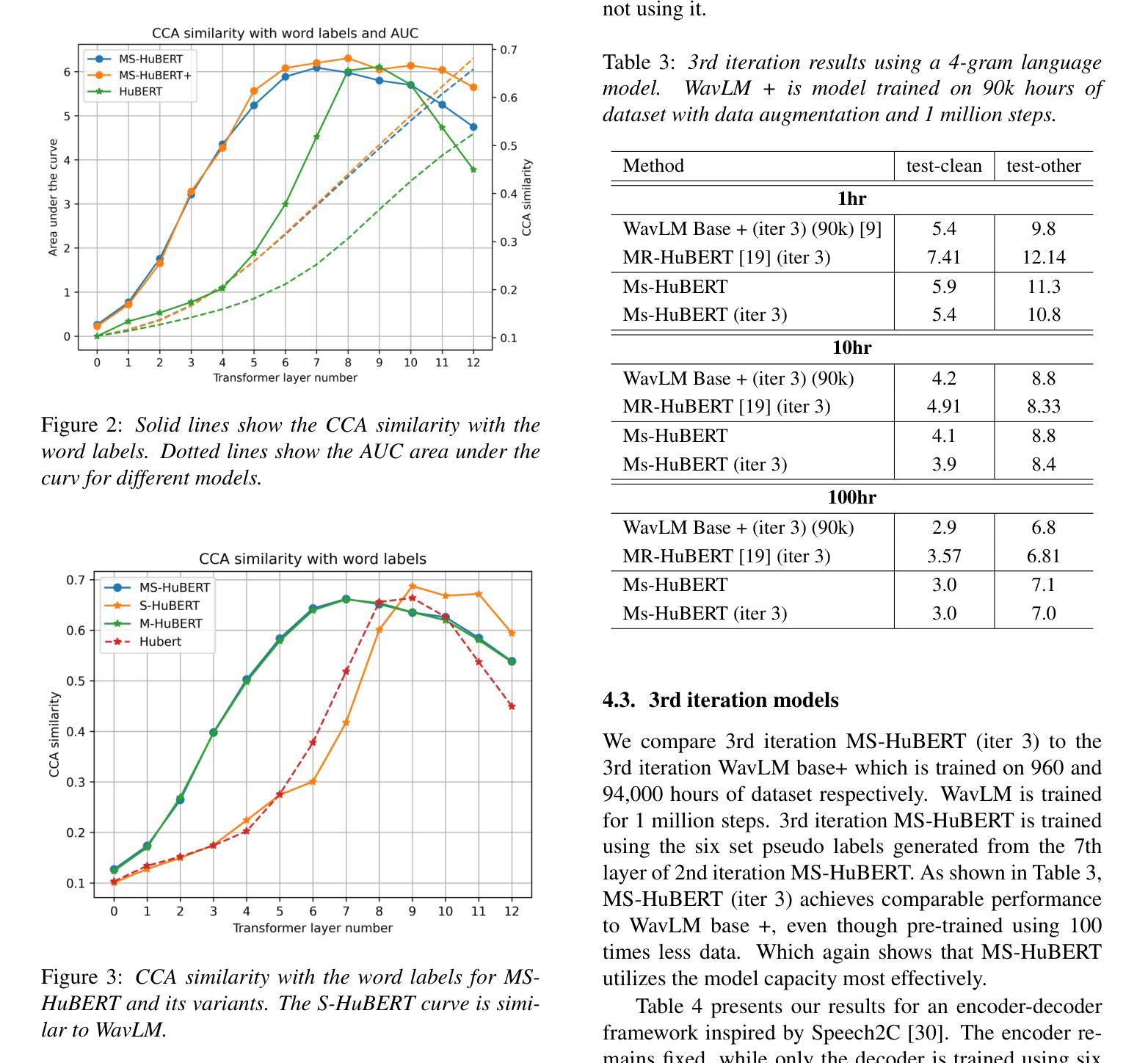
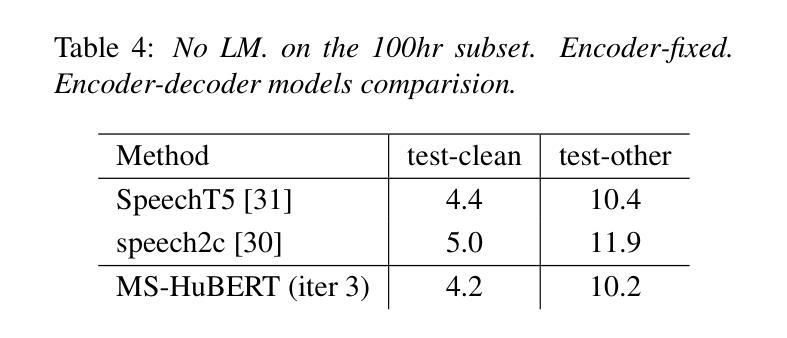
MS-HuBERT: Mitigating Pre-training and Inference Mismatch in Masked Language Modelling methods for learning Speech Representations
Authors:Hemant Yadav, Sunayana Sitaram, Rajiv Ratn Shah
In recent years, self-supervised pre-training methods have gained significant traction in learning high-level information from raw speech. Among these methods, HuBERT has demonstrated SOTA performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, HuBERT’s performance lags behind data2vec due to disparities in pre-training strategies. In this paper, we propose (i) a Swap method to address pre-training and inference mismatch observed in HuBERT and (ii) incorporates Multicluster masked prediction loss for more effective utilization of the models capacity. The resulting method is, MS-HuBERT, an end-to-end self-supervised pre-training method for learning robust speech representations. It beats vanilla HuBERT on the ASR Librispeech benchmark on average by a 5% margin when evaluated on different finetuning splits. Additionally, we demonstrate that the learned embeddings obtained during pre-training encode essential information for improving performance of content based tasks such as ASR.
近年来,自监督预训练方法在从原始语音中学习高级信息方面获得了很大的关注。在这些方法中,HuBERT在自动语音识别(ASR)方面表现出了卓越的性能。然而,由于预训练策略的差异,HuBERT的性能落后于data2vec。在本文中,我们提出了(i)一种Swap方法来解决HuBERT中观察到的预训练和推理不匹配的问题,(ii)并融入了多集群掩码预测损失,以更有效地利用模型容量。由此产生的方法为MS-HuBERT,是一种端到端的自监督预训练方法,用于学习稳健的语音表示。在平均意义上,当在不同微调分割上评估时,它在ASR Librispeech基准测试上的表现优于原版HuBERT,平均提高了5%的准确率。此外,我们证明了在预训练过程中获得的学习嵌入编码了对改进基于内容任务的性能至关重要的信息,例如自动语音识别等。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, submitted to interspeech2024
总结
近年来,自监督预训练方法已从原始语音中学习高级信息获得了显著进展。HuBERT等方法在自动语音识别(ASR)方面表现出卓越性能。然而,由于预训练策略的差异,HuBERT的性能落后于data2vec。本文提出了(i)解决HuBERT在预训练和推理过程中不匹配问题的Swap方法,以及(ii)结合多集群掩码预测损失,更有效地利用模型容量。由此产生的方法称为MS-HuBERT,是一种端到端的自监督预训练方法,用于学习稳健的语音表示。在ASR Librispeech基准测试中,与vanilla HuBERT相比,MS-HuBERT在微调的不同分割点上平均提高了5%的性能。此外,我们还证明,在预训练过程中获得的嵌入编码对于改进基于内容的任务(如ASR)的性能至关重要。
关键见解
- 自监督预训练方法已用于从原始语音中学习高级信息。
- HuBERT在自动语音识别(ASR)方面表现出卓越性能,但预训练策略的差异导致其在某些方面落后于data2vec。
- 本文提出了Swap方法来解决HuBERT在预训练和推理过程中的不匹配问题。
- 多集群掩码预测损失被引入以提高模型效率。
- MS-HuBERT是一种新的自监督预训练方法,旨在学习稳健的语音表示。
- MS-HuBERT在ASR Librispeech基准测试中优于原版HuBERT。
点此查看论文截图