⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-05 更新
ContextFormer: Redefining Efficiency in Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Mian Muhammad Naeem Abid, Nancy Mehta, Zongwei Wu, Fayaz Ali Dharejo, Radu Timofte
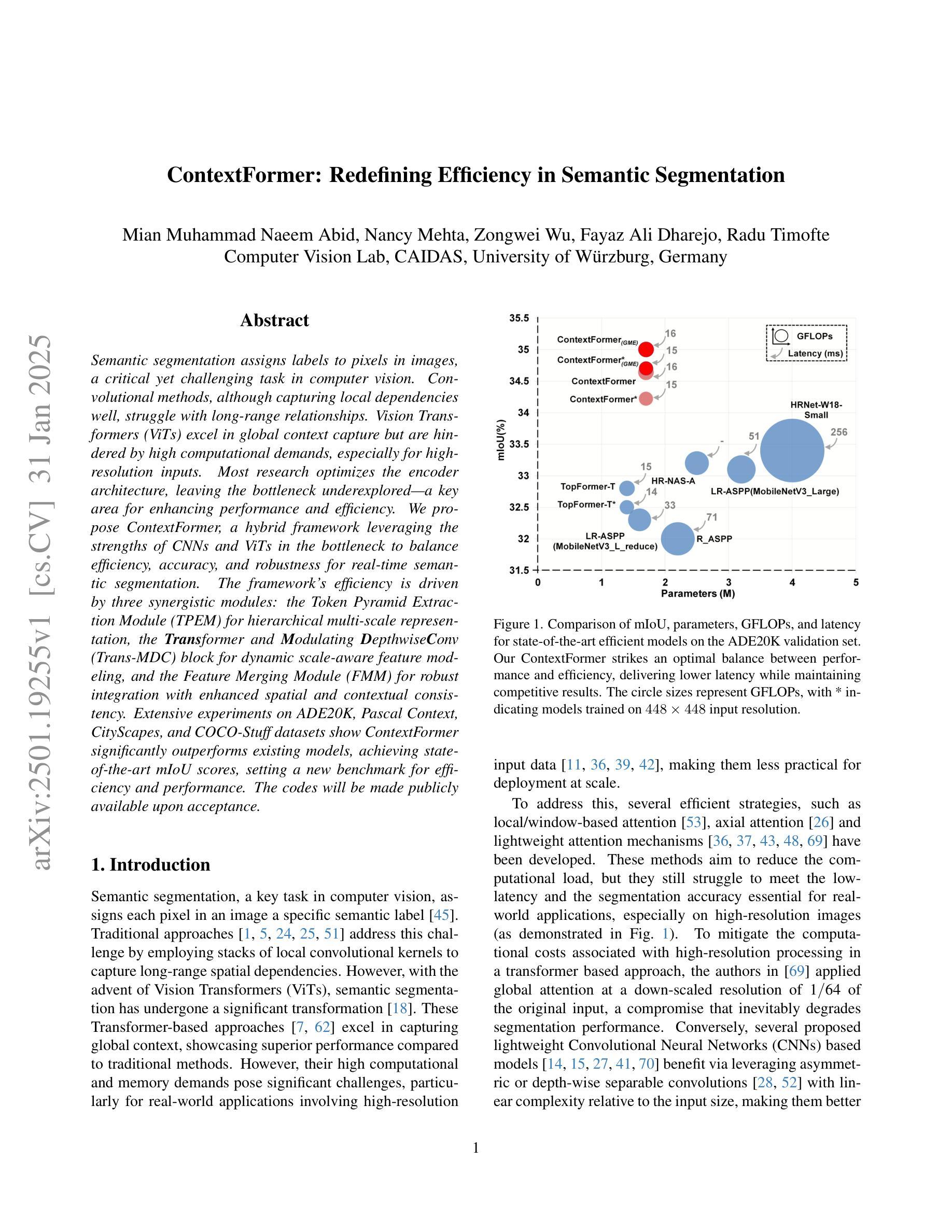
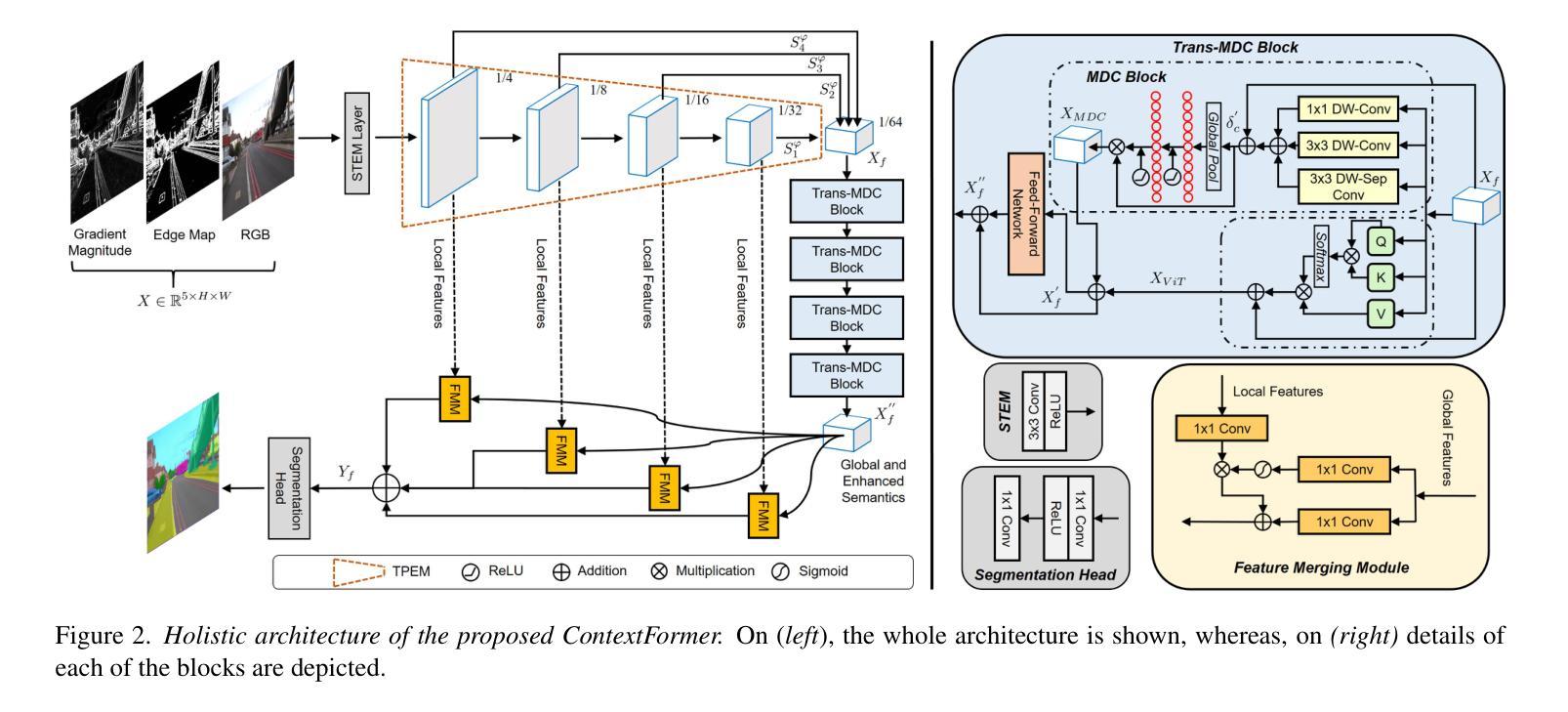
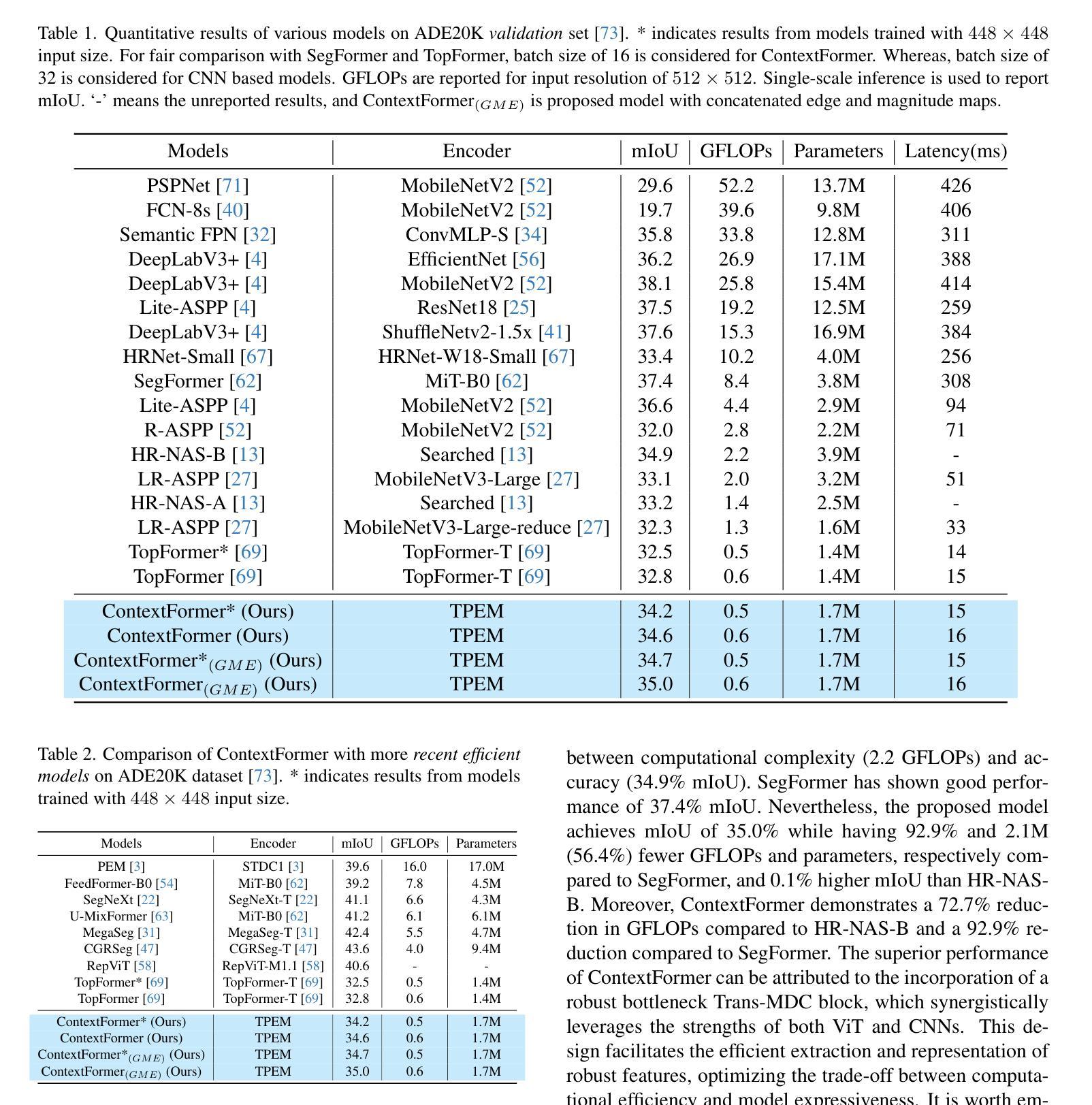
Semantic segmentation assigns labels to pixels in images, a critical yet challenging task in computer vision. Convolutional methods, although capturing local dependencies well, struggle with long-range relationships. Vision Transformers (ViTs) excel in global context capture but are hindered by high computational demands, especially for high-resolution inputs. Most research optimizes the encoder architecture, leaving the bottleneck underexplored - a key area for enhancing performance and efficiency. We propose ContextFormer, a hybrid framework leveraging the strengths of CNNs and ViTs in the bottleneck to balance efficiency, accuracy, and robustness for real-time semantic segmentation. The framework’s efficiency is driven by three synergistic modules: the Token Pyramid Extraction Module (TPEM) for hierarchical multi-scale representation, the Transformer and Modulating DepthwiseConv (Trans-MDC) block for dynamic scale-aware feature modeling, and the Feature Merging Module (FMM) for robust integration with enhanced spatial and contextual consistency. Extensive experiments on ADE20K, Pascal Context, CityScapes, and COCO-Stuff datasets show ContextFormer significantly outperforms existing models, achieving state-of-the-art mIoU scores, setting a new benchmark for efficiency and performance. The codes will be made publicly available.
语义分割是一项为图像中的像素分配标签的任务,这是计算机视觉中至关重要的挑战。卷积方法虽然能很好地捕捉局部依赖性,但在处理长距离关系方面却表现不佳。视觉转换器(ViTs)擅长捕获全局上下文,但计算需求较高,尤其是高分辨率输入时。大多数研究都在优化编码器架构,而瓶颈区域的关键作用却被忽视——这是提高性能和效率的关键领域。我们提出了ContextFormer,这是一个混合框架,利用CNN和ViT在瓶颈处的优势,在实时语义分割中平衡效率、准确性和稳健性。该框架的效率由三个协同模块驱动:用于分层多尺度表示的Token金字塔提取模块(TPEM)、用于动态尺度感知特征建模的Transformer和调制深度卷积(Trans-MDC)块,以及用于稳健集成的特征合并模块(FMM),具有增强的空间和时间一致性。在ADE20K、Pascal Context、CityScapes和COCO-Stuff数据集上的大量实验表明,ContextFormer显著优于现有模型,取得了最先进的mIoU分数,为效率和性能设定了新的基准。代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Vision Transformer在图像语义分割任务中面临计算量大、难以处理长距离关系等问题。本文提出ContextFormer框架,结合CNN和Vision Transformer的优点,以提高语义分割的效率、准确性和鲁棒性。该框架包括Token Pyramid Extraction Module(TPEM)、Transformer和Modulating DepthwiseConv(Trans-MDC)模块以及Feature Merging Module(FMM),可在多个数据集上实现最先进的mIoU得分,同时提高效率和性能。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer在处理图像语义分割任务时面临计算量大和长距离关系处理困难的问题。
- ContextFormer框架结合了CNN和Vision Transformer的优点,旨在提高语义分割的效率、准确性和鲁棒性。
- ContextFormer包含三个协同模块:Token Pyramid Extraction Module(TPEM)用于分层多尺度表示,Transformer和Modulating DepthwiseConv(Trans-MDC)模块用于动态尺度感知特征建模,以及Feature Merging Module(FMM)用于稳健集成,增强空间一致性。
- ContextFormer在多个数据集上实现了最先进的mIoU得分,表现出卓越的性能。
- ContextFormer框架将公开可用,为相关研究提供新的基准和参考。
- 该框架对于平衡效率和性能的研究具有关键意义,尤其是在实时语义分割应用中。
点此查看论文截图
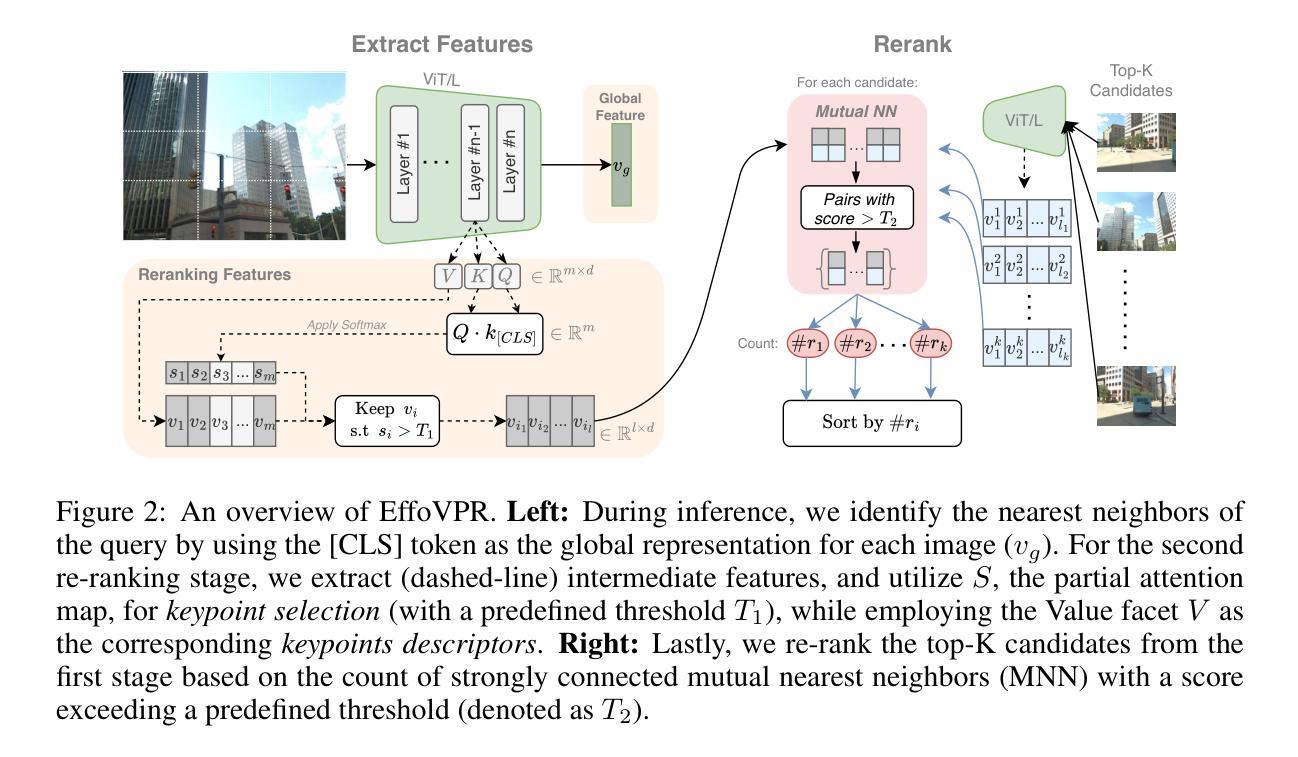
EffoVPR: Effective Foundation Model Utilization for Visual Place Recognition
Authors:Issar Tzachor, Boaz Lerner, Matan Levy, Michael Green, Tal Berkovitz Shalev, Gavriel Habib, Dvir Samuel, Noam Korngut Zailer, Or Shimshi, Nir Darshan, Rami Ben-Ari
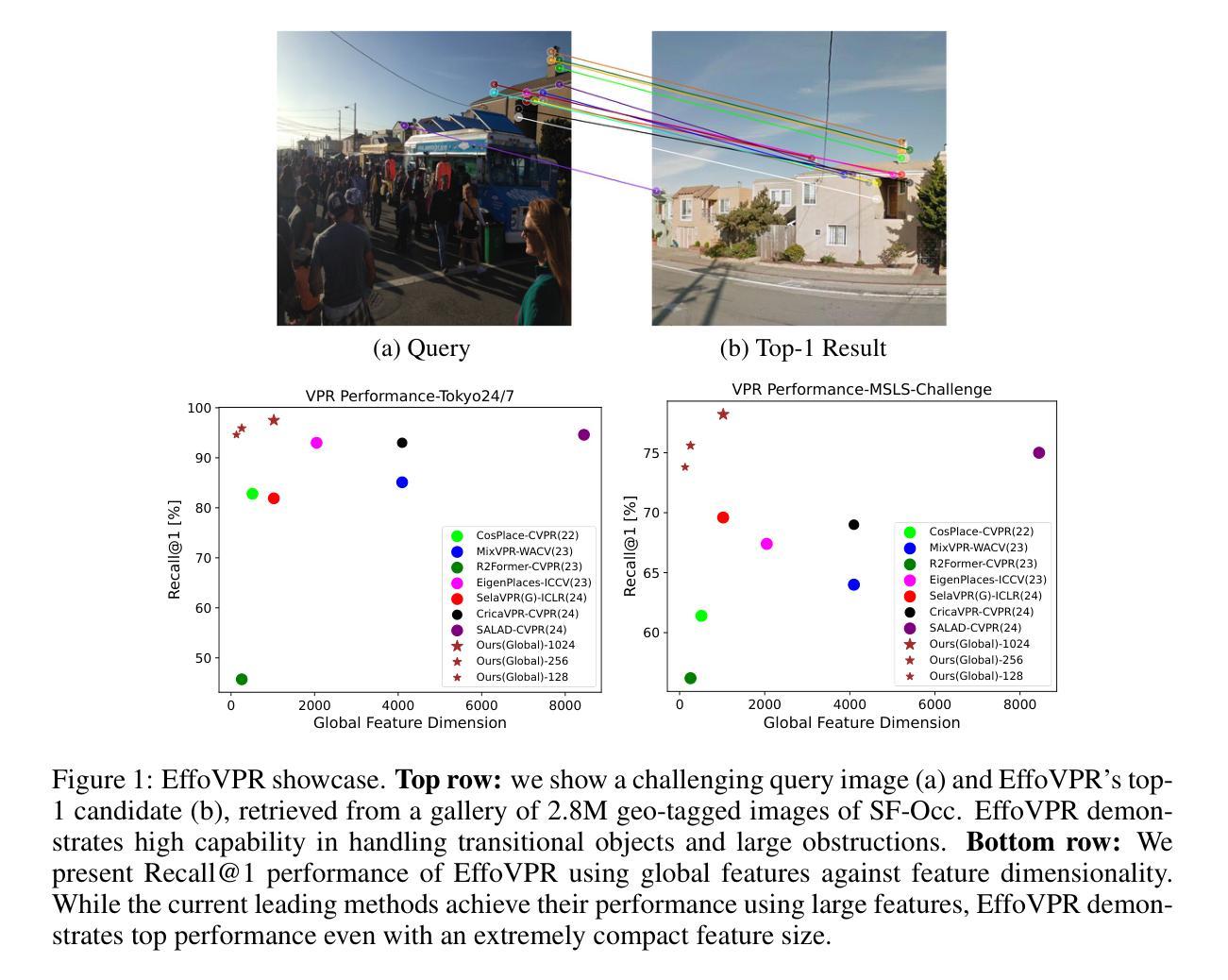
The task of Visual Place Recognition (VPR) is to predict the location of a query image from a database of geo-tagged images. Recent studies in VPR have highlighted the significant advantage of employing pre-trained foundation models like DINOv2 for the VPR task. However, these models are often deemed inadequate for VPR without further fine-tuning on VPR-specific data. In this paper, we present an effective approach to harness the potential of a foundation model for VPR. We show that features extracted from self-attention layers can act as a powerful re-ranker for VPR, even in a zero-shot setting. Our method not only outperforms previous zero-shot approaches but also introduces results competitive with several supervised methods. We then show that a single-stage approach utilizing internal ViT layers for pooling can produce global features that achieve state-of-the-art performance, with impressive feature compactness down to 128D. Moreover, integrating our local foundation features for re-ranking further widens this performance gap. Our method also demonstrates exceptional robustness and generalization, setting new state-of-the-art performance, while handling challenging conditions such as occlusion, day-night transitions, and seasonal variations.
视觉位置识别(VPR)的任务是从地理标记图像数据库中预测查询图像的位置。最近对VPR的研究强调了使用预训练的DINOv2等基础模型在VPR任务上的显著优势。然而,这些模型通常被认为在未经VPR特定数据进一步微调的情况下对VPR不足。在本文中,我们提出了一种有效利用基础模型潜力的方法来进行VPR。我们表明,从自注意力层提取的特征可以作为VPR的强大重新排序器,即使在零样本设置下也是如此。我们的方法不仅超越了以前的零样本方法,而且引入的结果与多种监督方法竞争。然后,我们展示了使用内部ViT层进行池化的单阶段方法能够产生全局特征,实现最新性能,令人印象深刻地降低到128D的特征紧凑性。此外,通过结合我们的局部基础特征进行重新排序,进一步扩大了这一性能差距。我们的方法还展示了出色的稳健性和泛化能力,在处理遮挡、昼夜交替和季节变化等挑战条件时达到了最新的性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
视觉定位识别(VPR)任务是从地理标签图像数据库中预测查询图像的位置。本研究利用预训练的DINOv2基础模型,展示了一种在VPR中有效利用基础模型潜力的方法。通过提取自注意力层的特征,即使在零样本设置下,也能对VPR进行强大的重新排序。该方法不仅优于之前的零样本方法,而且其结果与多种监督方法相竞争。此外,利用内部ViT层进行池化的单阶段方法能产生全球特征,实现最先进的性能,特征紧凑至128D。结合本地基础特征进行重新排序,进一步扩大了性能差距。该方法具有出色的鲁棒性和泛化能力,在应对遮挡、昼夜转换和季节变化等挑战条件时表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目标是解决视觉定位识别(VPR)任务,即从地理标签图像数据库中预测查询图像的位置。
- 研究采用预训练的DINOv2基础模型,并发现自注意力层的特征对于VPR任务具有很强的重新排序能力。
- 方法在零样本设置下表现出强大的性能,不仅优于之前的零样本方法,而且与一些监督方法相当。
- 利用ViT内部层进行池化的单阶段方法能产生紧凑的全球特征,实现最先进的性能。
- 结合本地基础特征进行重新排序进一步提升了性能。
- 该方法具有出色的鲁棒性和泛化能力,能在各种挑战条件下表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

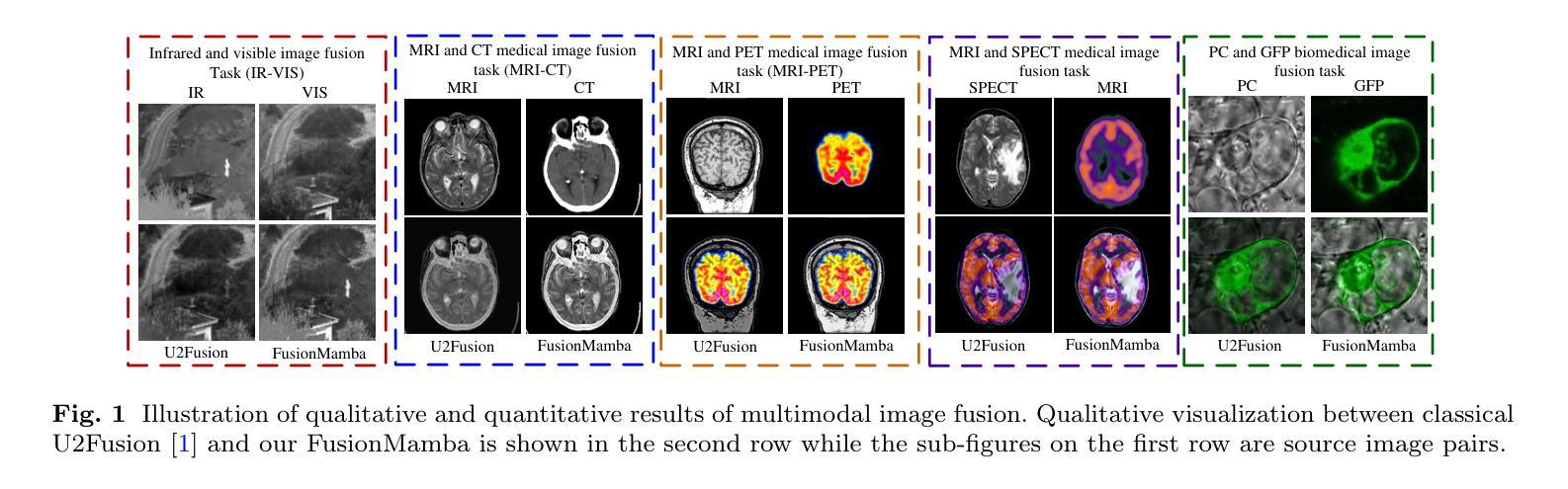
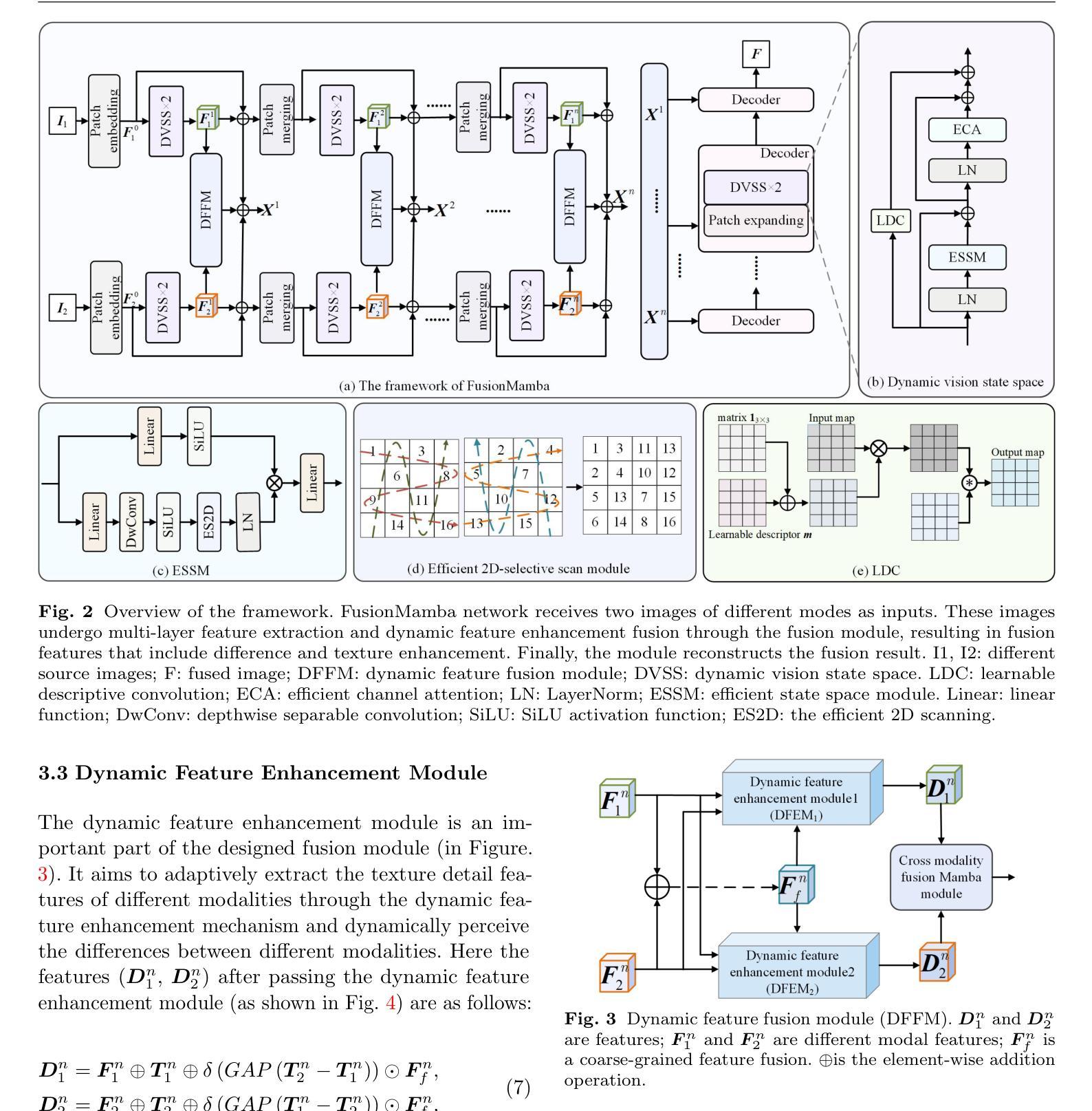
FusionMamba: Dynamic Feature Enhancement for Multimodal Image Fusion with Mamba
Authors:Xinyu Xie, Yawen Cui, Tao Tan, Xubin Zheng, Zitong Yu
Multimodal image fusion aims to integrate information from different imaging techniques to produce a comprehensive, detail-rich single image for downstream vision tasks. Existing methods based on local convolutional neural networks (CNNs) struggle to capture global features efficiently, while Transformer-based models are computationally expensive, although they excel at global modeling. Mamba addresses these limitations by leveraging selective structured state space models (S4) to effectively handle long-range dependencies while maintaining linear complexity. In this paper, we propose FusionMamba, a novel dynamic feature enhancement framework that aims to overcome the challenges faced by CNNs and Vision Transformers (ViTs) in computer vision tasks. The framework improves the visual state-space model Mamba by integrating dynamic convolution and channel attention mechanisms, which not only retains its powerful global feature modeling capability, but also greatly reduces redundancy and enhances the expressiveness of local features. In addition, we have developed a new module called the dynamic feature fusion module (DFFM). It combines the dynamic feature enhancement module (DFEM) for texture enhancement and disparity perception with the cross-modal fusion Mamba module (CMFM), which focuses on enhancing the inter-modal correlation while suppressing redundant information. Experiments show that FusionMamba achieves state-of-the-art performance in a variety of multimodal image fusion tasks as well as downstream experiments, demonstrating its broad applicability and superiority.
多模态图像融合旨在集成不同成像技术的信息,以生成用于下游视觉任务的全面、细节丰富的单一图像。基于局部卷积神经网络(CNN)的现有方法难以有效地捕获全局特征,而基于Transformer的模型虽然擅长全局建模,但计算成本较高。Mamba通过利用选择性结构化状态空间模型(S4)有效处理长距离依赖关系同时保持线性复杂性,解决了这些限制。在本文中,我们提出了FusionMamba,这是一种新型动态特征增强框架,旨在克服计算机视觉任务中CNN和视觉Transformer(ViT)所面临的挑战。该框架通过整合动态卷积和通道注意力机制,改进了视觉状态空间模型Mamba,这不仅保留了其强大的全局特征建模能力,而且大大减少了冗余性并增强了局部特征的表达能力。此外,我们开发了一个名为动态特征融合模块(DFFM)的新模块。它将用于纹理增强和视差感知的动态特征增强模块(DFEM)与专注于增强跨模态相关性同时抑制冗余信息的跨模态融合Mamba模块(CMFM)相结合。实验表明,FusionMamba在多种多模态图像融合任务和下游实验中实现了最先进的性能,证明了其广泛适用性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Visual Intelligence. Codes are at https://github.com/millieXie/FusionMamba
Summary
本文提出一种名为FusionMamba的动态特征增强框架,旨在克服卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs)在计算机视觉任务中的挑战。该框架通过集成动态卷积和通道注意力机制,改进了视觉状态空间模型Mamba,既保留了其强大的全局特征建模能力,又大大减少了冗余并增强了局部特征的表达能力。此外,还开发了一种新的动态特征融合模块(DFFM),包括用于纹理增强和视差感知的动态特征增强模块(DFEM)以及关注增强跨模态相关性和抑制冗余信息的跨模态融合Mamba模块(CMFM)。实验表明,FusionMamba在多种模态图像融合任务以及下游实验中取得了最先进的性能,证明了其广泛适用性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态图像融合旨在集成不同成像技术的信息以生成用于下游视觉任务的全面、细节丰富的单一图像。
- 现有基于局部卷积神经网络(CNNs)的方法难以有效地捕获全局特征,而基于Transformer的模型虽然擅长全局建模但计算成本较高。
- Mamba利用选择性结构化状态空间模型(S4)克服了这些限制,能够处理长距离依赖关系并保持线性复杂性。
- FusionMamba框架是一个动态特征增强框架,旨在解决CNN和Vision Transformer(ViT)在计算机视觉任务中的挑战。
- FusionMamba通过集成动态卷积和通道注意力机制改进了Mamba模型,既保留了全局特征建模能力,又增强了局部特征的表达能力。
- FusionMamba还包括一个名为DFFM的新模块,它结合了用于纹理增强和视差感知的DFEM以及专注于增强跨模态相关性和抑制冗余信息的CMFM模块。
点此查看论文截图

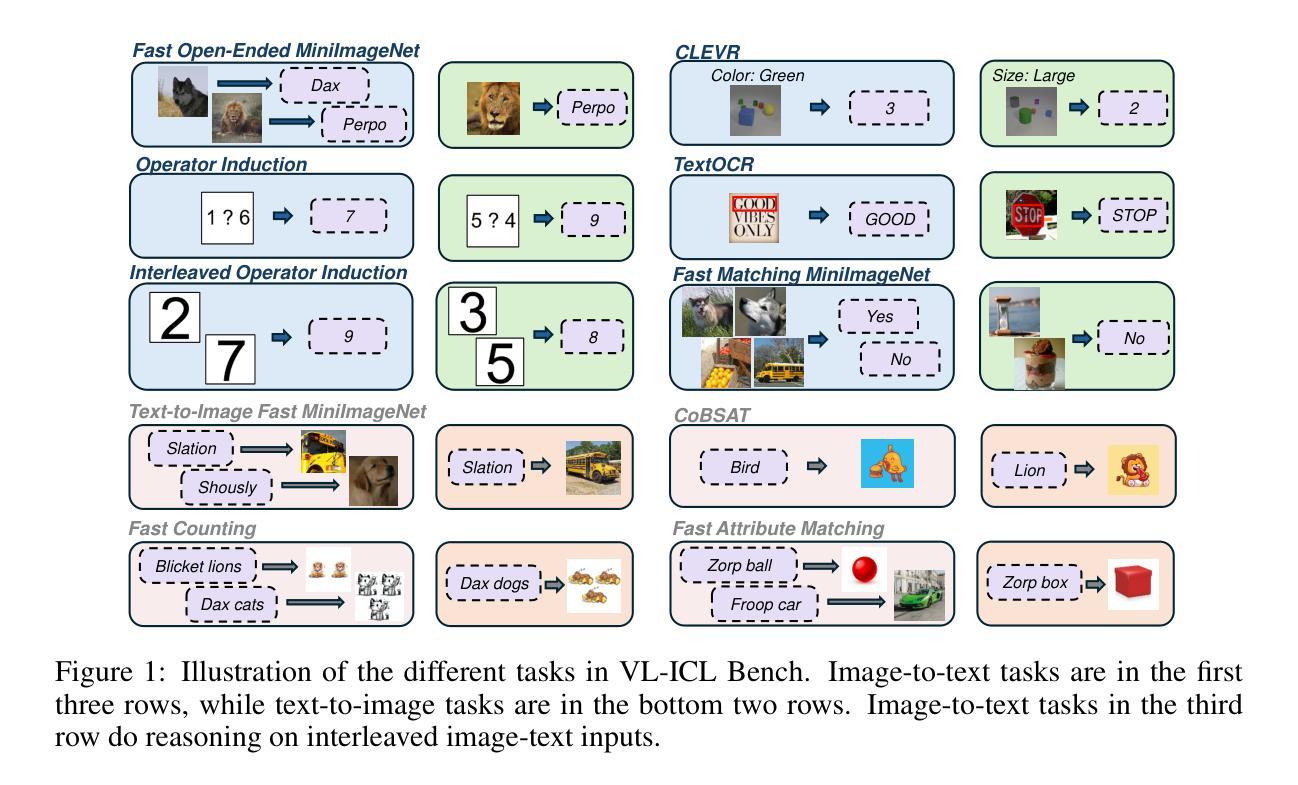
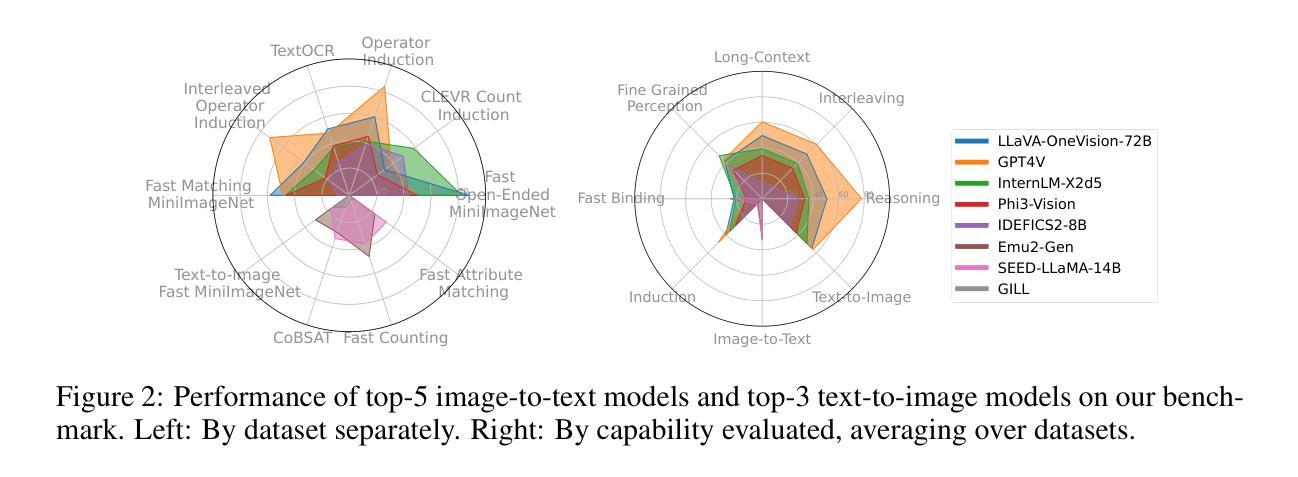
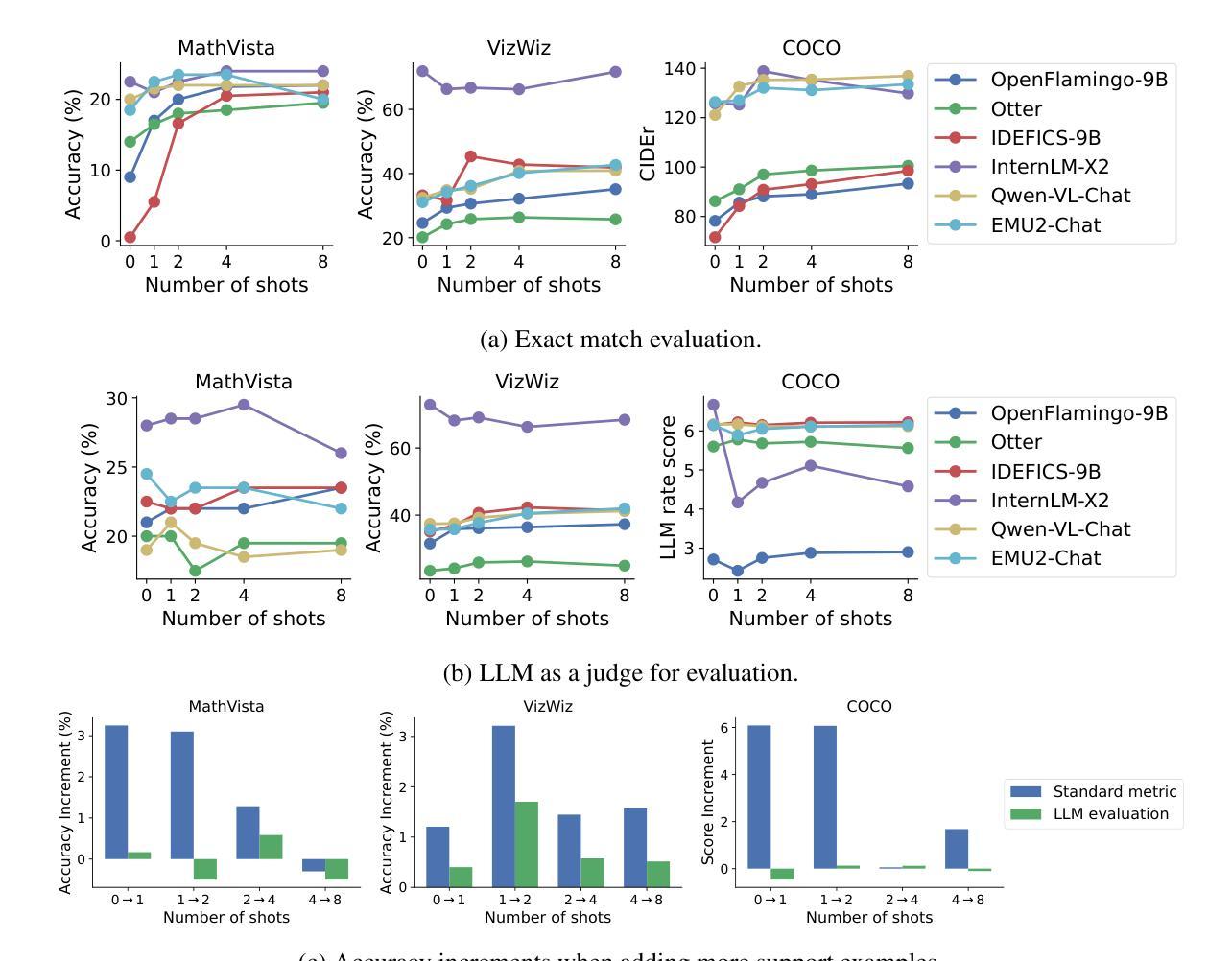
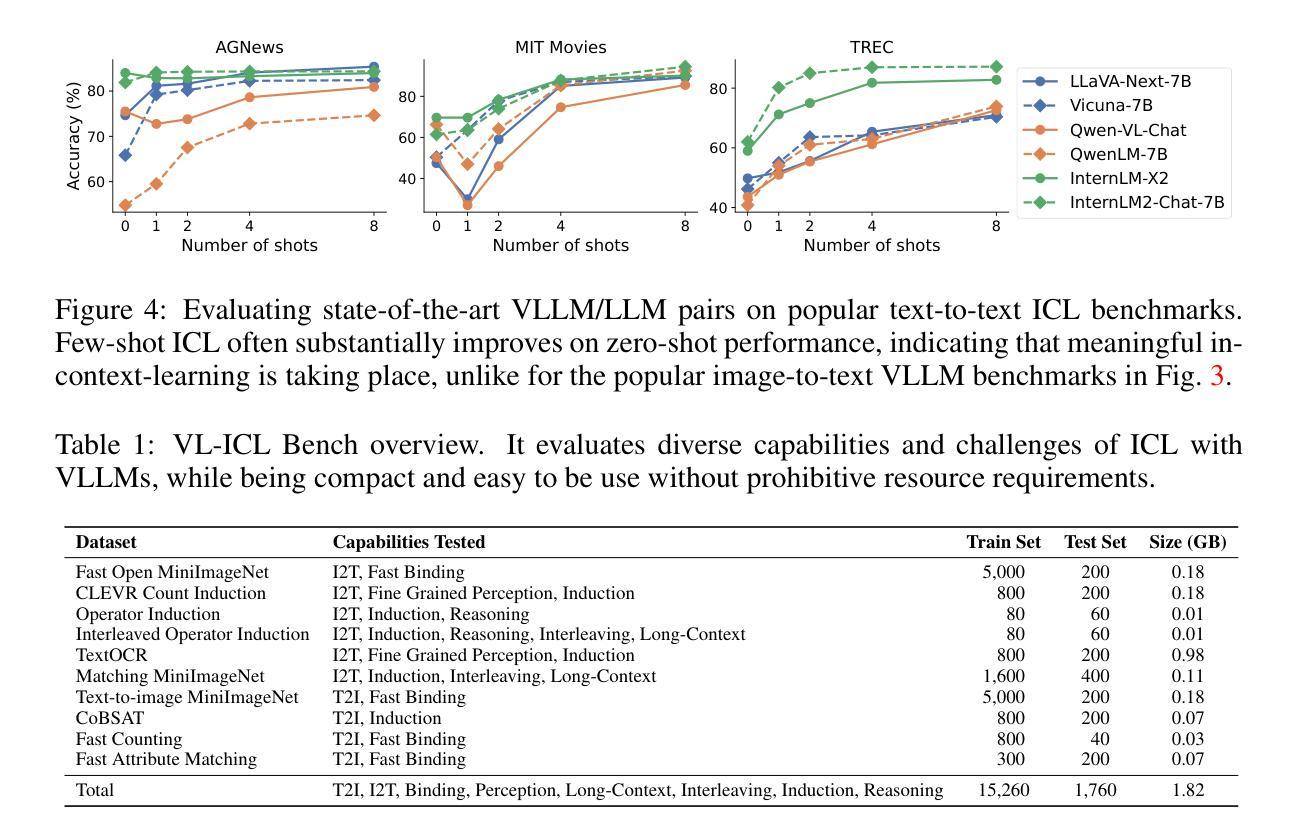
VL-ICL Bench: The Devil in the Details of Multimodal In-Context Learning
Authors:Yongshuo Zong, Ondrej Bohdal, Timothy Hospedales
Large language models (LLMs) famously exhibit emergent in-context learning (ICL) – the ability to rapidly adapt to new tasks using few-shot examples provided as a prompt, without updating the model’s weights. Built on top of LLMs, vision large language models (VLLMs) have advanced significantly in areas such as recognition, reasoning, and grounding. However, investigations into \emph{multimodal ICL} have predominantly focused on few-shot visual question answering (VQA), and image captioning, which we will show neither exploit the strengths of ICL, nor test its limitations. The broader capabilities and limitations of multimodal ICL remain under-explored. In this study, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark VL-ICL Bench for multimodal in-context learning, encompassing a broad spectrum of tasks that involve both images and text as inputs and outputs, and different types of challenges, from {perception to reasoning and long context length}. We evaluate the abilities of state-of-the-art VLLMs against this benchmark suite, revealing their diverse strengths and weaknesses, and showing that even the most advanced models, such as GPT-4, find the tasks challenging. By highlighting a range of new ICL tasks, and the associated strengths and limitations of existing models, we hope that our dataset will inspire future work on enhancing the in-context learning capabilities of VLLMs, as well as inspire new applications that leverage VLLM ICL. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ys-zong/VL-ICL.
大型语言模型(LLM)展现出一种称为情境学习(ICL)的能力——使用作为提示提供的少量示例快速适应新任务,而无需更新模型的权重。建立在大型语言模型之上,视觉大型语言模型(VLLM)在识别、推理和接地等领域取得了显著进展。然而,对多模态情境学习(Multimodal ICL)的研究主要集中在视觉问答和图像描述生成等少数任务上,我们将展示这些任务并没有充分利用情境学习的优势,也没有测试其局限性。多模态情境学习的更广泛能力和局限性尚未得到充分探索。本研究中,我们引入了全面的多模态情境学习基准测试VL-ICL Bench,涵盖一系列涉及图像和文本作为输入和输出的任务,包括从感知到推理和长上下文长度的不同类型挑战。我们在此基准测试套件上评估了最先进的VLLM的能力,揭示了它们的各种优势和劣势,并表明即使是最先进的模型,如GPT-4,也会发现这些任务具有挑战性。通过突出一系列新的情境学习任务以及现有模型的关联优势和局限性,我们希望我们的数据集将激发未来关于增强VLLM的情境学习能力的工作,并激发利用VLLM情境学习的新应用。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/ys-zong/VL-ICL上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
该文介绍了大型语言模型(LLMs)的上下文学习(ICL)能力,即利用少量样本提示快速适应新任务的能力。在此基础上,视觉大型语言模型(VLLMs)在识别、推理和定位等领域取得了显著进展。然而,对多模式ICL的研究主要集中在视觉问答和图像描述等方面,并未充分利用ICL的优势或测试其局限性。为了更全面地探索多模式ICL的潜力和限制,本文引入了一个全面的基准测试VL-ICL Bench,涵盖了涉及图像和文本作为输入和输出的广泛任务,以及从感知到推理和长文本语境的各种挑战。评估了最先进的VLLMs的能力,揭示其优势和劣势,并指出最先进的模型如GPT-4仍面临挑战。本文希望通过引入新的ICL任务和现有模型的优缺点,激发对增强VLLM的上下文学习能力的未来研究,并启发新的应用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)具备上下文学习能力(ICL),能利用少量样本快速适应新任务。
- 视觉大型语言模型(VLLMs)在识别、推理和定位等领域有显著改善。
- 多模式ICL的研究主要集中在视觉问答和图像描述,未充分探索其潜力和限制。
- 引入VL-ICL Bench基准测试,涵盖广泛的任务和挑战,以全面评估VLLMs的能力。
- 最先进的VLLMs在VL-ICL Bench上表现有优势和劣势。
- GPT-4等先进模型在多模式ICL任务上面临挑战。
点此查看论文截图

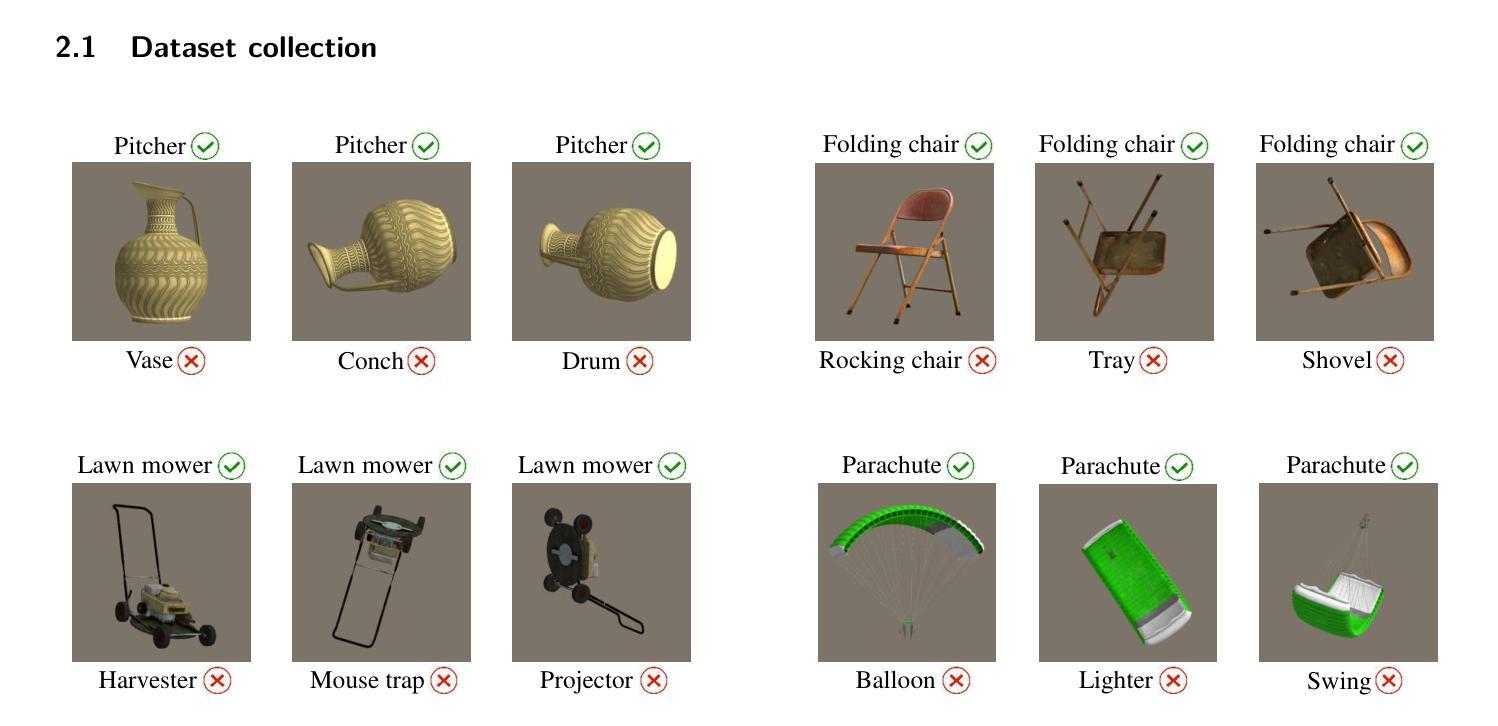
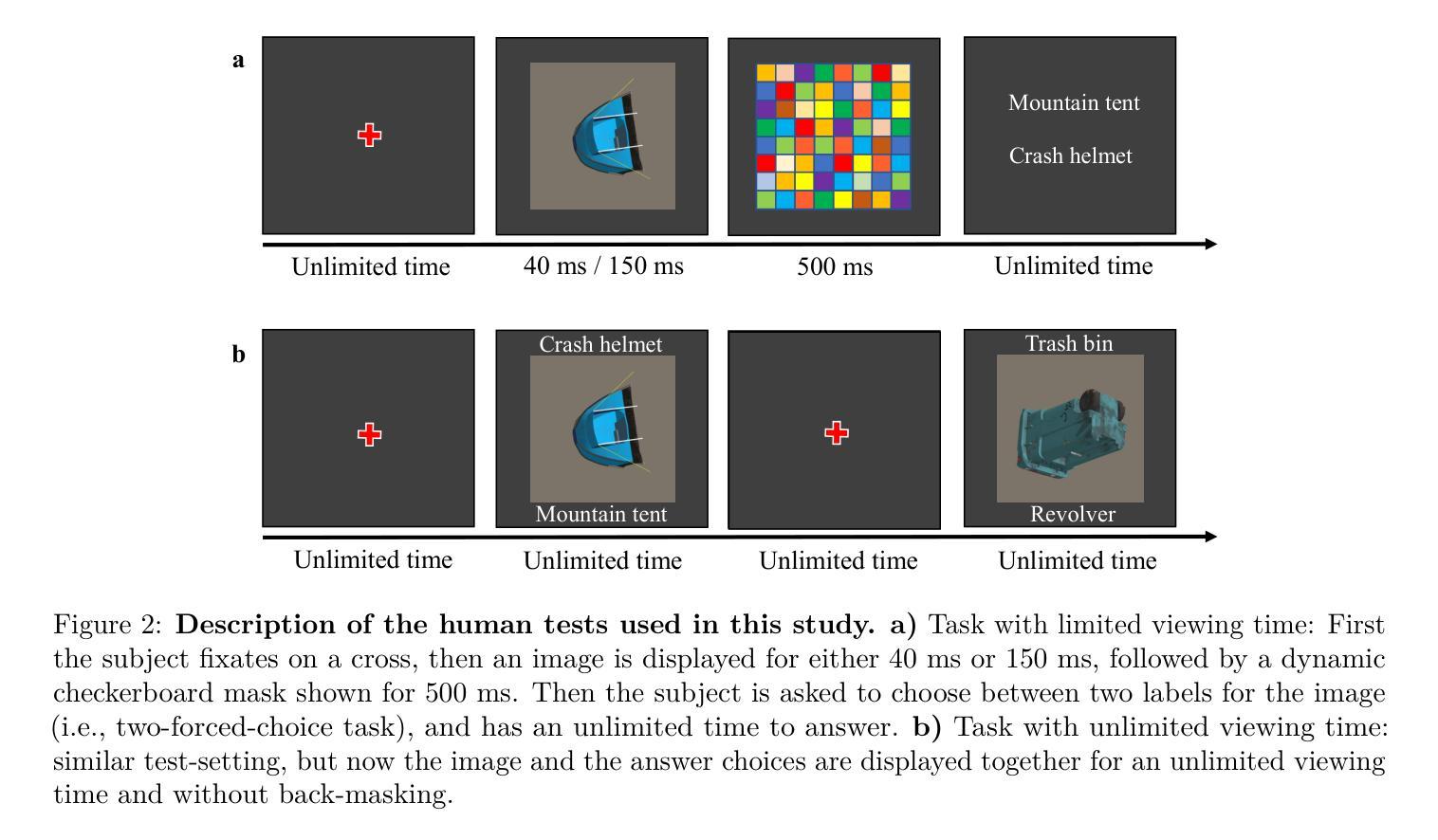
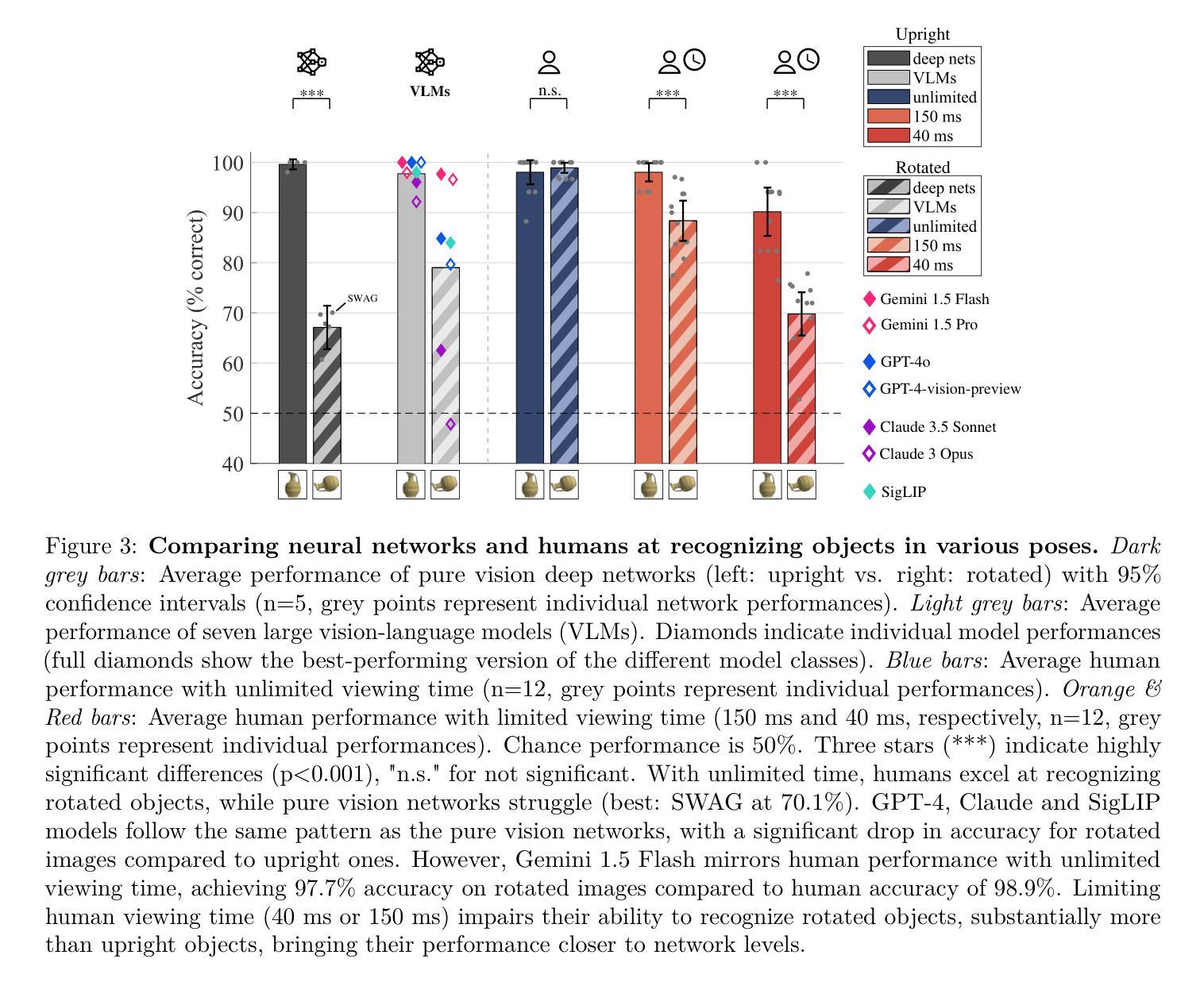
A comparison between humans and AI at recognizing objects in unusual poses
Authors:Netta Ollikka, Amro Abbas, Andrea Perin, Markku Kilpeläinen, Stéphane Deny
Deep learning is closing the gap with human vision on several object recognition benchmarks. Here we investigate this gap for challenging images where objects are seen in unusual poses. We find that humans excel at recognizing objects in such poses. In contrast, state-of-the-art deep networks for vision (EfficientNet, SWAG, ViT, SWIN, BEiT, ConvNext) and state-of-the-art large vision-language models (Claude 3.5, Gemini 1.5, GPT-4) are systematically brittle on unusual poses, with the exception of Gemini showing excellent robustness in that condition. As we limit image exposure time, human performance degrades to the level of deep networks, suggesting that additional mental processes (requiring additional time) are necessary to identify objects in unusual poses. An analysis of error patterns of humans vs. networks reveals that even time-limited humans are dissimilar to feed-forward deep networks. In conclusion, our comparison reveals that humans and deep networks rely on different mechanisms for recognizing objects in unusual poses. Understanding the nature of the mental processes taking place during extra viewing time may be key to reproduce the robustness of human vision in silico.
深度学习在多个物体识别基准测试上正在缩小与人类视觉的差距。在这里,我们研究这个差距针对具有挑战性的图像,这些图像中的物体呈现不寻常的姿势。我们发现人类在识别此类姿势中的物体方面表现出色。相比之下,最前沿的视觉深度网络(EfficientNet、SWAG、ViT、SWIN、Beit、ConvNext)以及最前沿的大型视觉语言模型(Claude 3.5、Gemini 1.5、GPT-4)在不寻常的姿势上表现出系统性脆弱,只有Gemini在该条件下表现出出色的稳健性。当我们限制图像曝光时间时,人类的表现会降至深度网络的水平,这表明识别不寻常姿势的物体需要额外的心理过程(需要额外的时间)。对人类与网络错误模式的分析表明,即使是时间受限的人类与一次性前馈深度网络也存在差异。总之,我们的比较表明,人类在识别不寻常姿势的物体时与深度网络依赖不同的机制。了解在额外观看时间内发生的心理过程的性质可能是模拟人类视觉稳健性的关键。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF version accepted at TMLR
Summary
本文探讨了深度学习在识别挑战图像方面的表现,尤其是物体在异常姿态下的识别能力。研究发现在这种情况下,人类视觉表现优秀,而当前最先进的深度网络和大型视觉语言模型在处理异常姿态物体时表现出脆弱性。人类识别物体可能涉及额外的心理过程,需要更多时间来识别物体。对比人类与网络的错误模式,发现即使时间受限的人类与深度网络表现不同。研究得出结论,人类和深度网络在识别异常姿态物体时依赖不同的机制。了解额外观看时间内发生的心理过程可能是模仿人类视觉稳健性的关键。
Key Takeaways
- 在异常姿态的挑战图像识别上,人类表现优于先进的深度网络和视觉语言模型。
- 目前顶尖的模型和算法在处理不寻常姿态的物体时显示出系统性脆弱性。
- 人类在识别物体时可能需要额外的心理过程来处理异常姿态,这表明了人类对这类情况的特殊性认知机制。
- 当限制图像曝光时间时,人类的表现会下降到与深度网络相当的水平,暗示了额外观看时间的必要性。
- 对比人类和网络的错误模式表明,即使面临时间限制,人类的表现也与深度网络存在显著差异。
- 人类和深度网络在识别物体时依赖不同的机制,特别是在处理异常姿态的物体时更为明显。
点此查看论文截图