⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-06 更新
AAD-DCE: An Aggregated Multimodal Attention Mechanism for Early and Late Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Prostate MRI Synthesis
Authors:Divya Bharti, Sriprabha Ramanarayanan, Sadhana S, Kishore Kumar M, Keerthi Ram, Harsh Agarwal, Ramesh Venkatesan, Mohanasankar Sivaprakasam
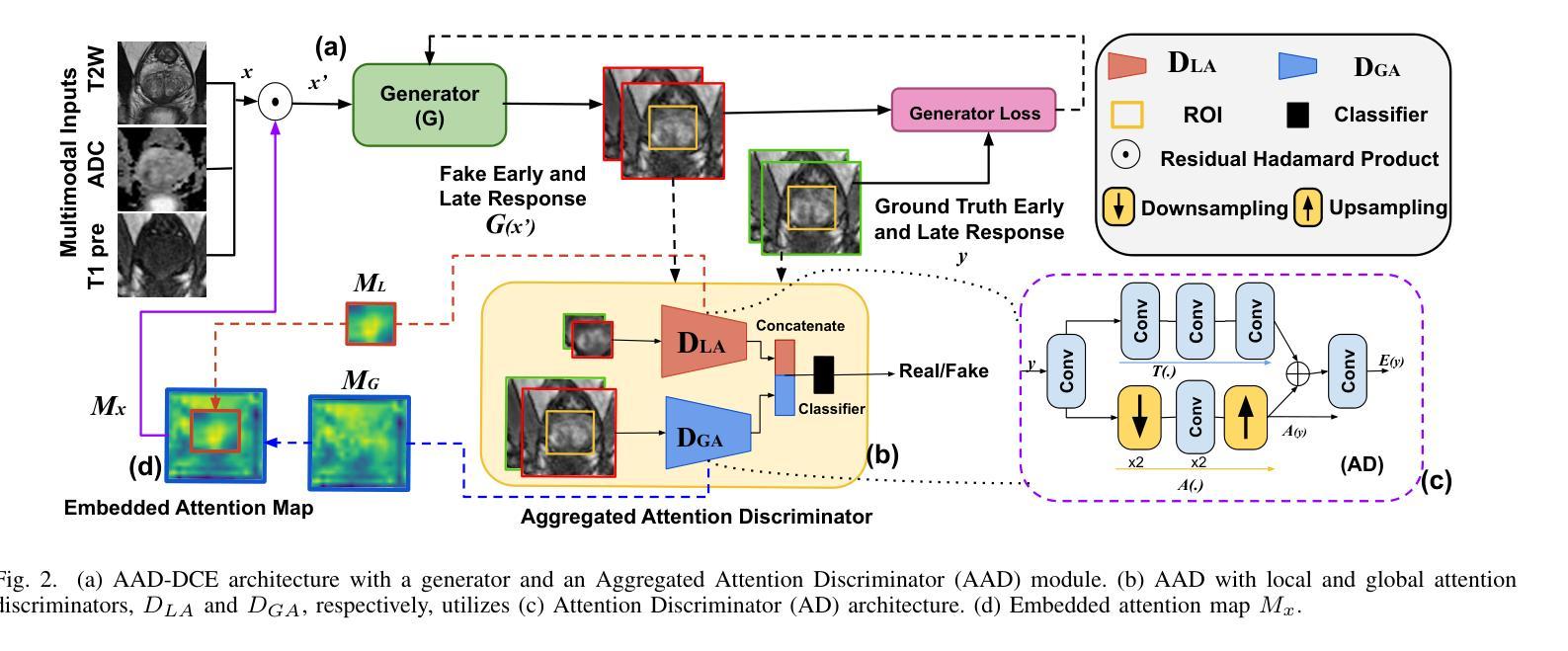
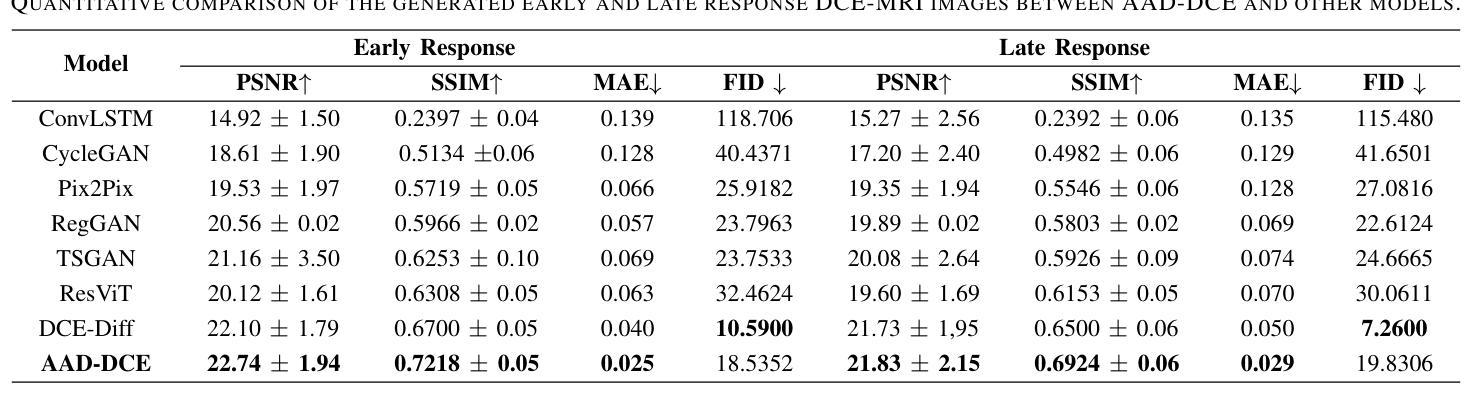
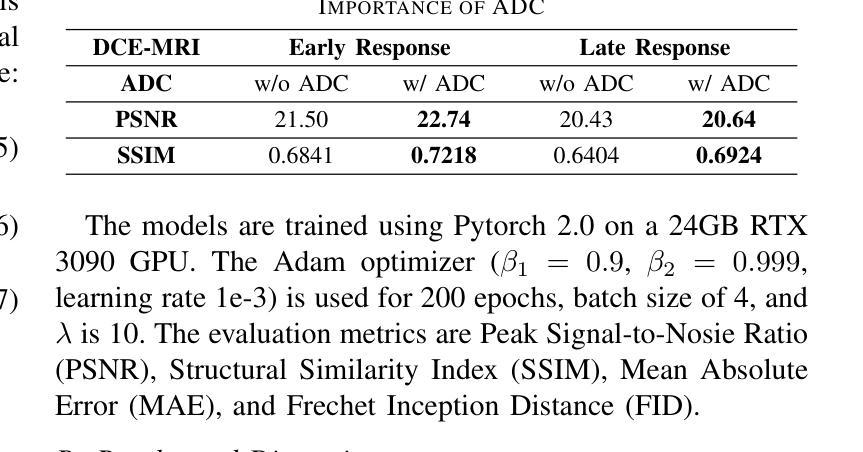
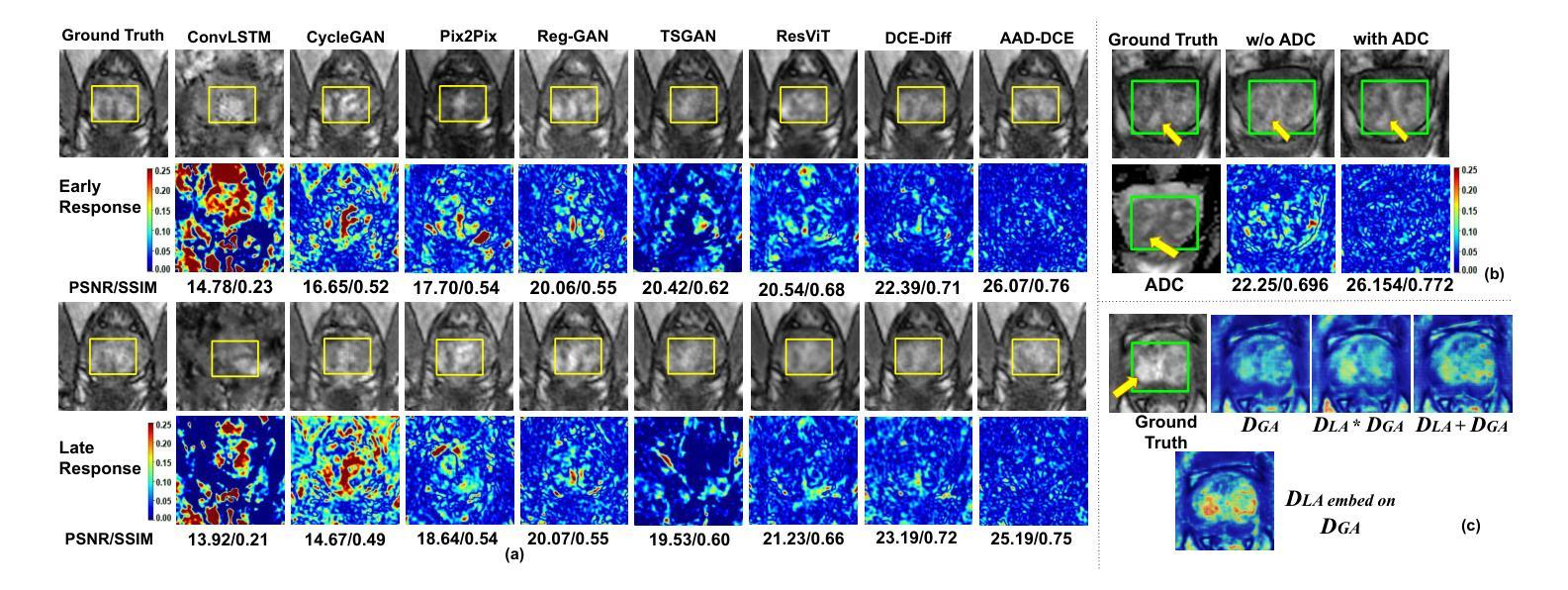
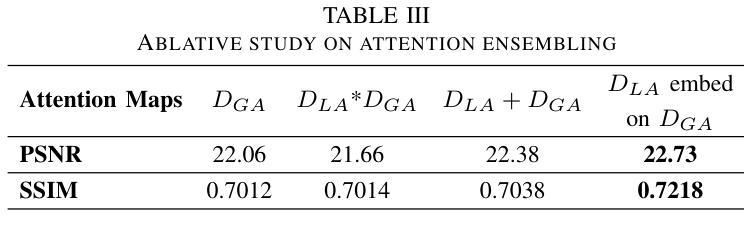
Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) is a medical imaging technique that plays a crucial role in the detailed visualization and identification of tissue perfusion in abnormal lesions and radiological suggestions for biopsy. However, DCE-MRI involves the administration of a Gadolinium based (Gad) contrast agent, which is associated with a risk of toxicity in the body. Previous deep learning approaches that synthesize DCE-MR images employ unimodal non-contrast or low-dose contrast MRI images lacking focus on the local perfusion information within the anatomy of interest. We propose AAD-DCE, a generative adversarial network (GAN) with an aggregated attention discriminator module consisting of global and local discriminators. The discriminators provide a spatial embedded attention map to drive the generator to synthesize early and late response DCE-MRI images. Our method employs multimodal inputs - T2 weighted (T2W), Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC), and T1 pre-contrast for image synthesis. Extensive comparative and ablation studies on the ProstateX dataset show that our model (i) is agnostic to various generator benchmarks and (ii) outperforms other DCE-MRI synthesis approaches with improvement margins of +0.64 dB PSNR, +0.0518 SSIM, -0.015 MAE for early response and +0.1 dB PSNR, +0.0424 SSIM, -0.021 MAE for late response, and (ii) emphasize the importance of attention ensembling. Our code is available at https://github.com/bhartidivya/AAD-DCE.
动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)是一种医学成像技术,在异常病变的血流灌注详细可视化以及针对活检的放射学建议中发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,DCE-MRI涉及使用基于钆(Gad)的造影剂,这带来了体内毒性风险。之前合成DCE-MR图像的深度学习方法主要采用非对比或低剂量对比MRI图像的单模态,缺乏关注解剖结构内局部灌注信息。我们提出了AAD-DCE,这是一种生成对抗网络(GAN),包含一个聚合注意力鉴别器模块,由全局和局部鉴别器组成。鉴别器提供空间嵌入注意力图,以驱动生成器合成早期和晚期响应DCE-MRI图像。我们的方法采用多模态输入,包括T2加权(T2W)、表观扩散系数(ADC)和T1预对比用于图像合成。在ProstateX数据集上的广泛比较和消融研究表明,我们的模型(i)对各种生成器基准测试表现稳定;(ii)在早期响应和晚期响应的PSNR、SSIM和MAE指标上分别提高了+0.64 dB、+0.0518和-0.015以及+0.1 dB、+0.0424和-0.021,相较于其他DCE-MRI合成方法表现更优异;(iii)强调了注意力集成的重要性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/bhartidivya/AAD-DCE获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
一种名为AAD-DCE的基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的技术,被用于合成动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)。该技术采用聚合注意力鉴别器模块,包含全局和局部鉴别器,并提供空间嵌入注意力图以指导生成器合成早期和晚期响应的DCE-MRI图像。采用多模态输入,如T2加权、表观扩散系数和T1预对比图像进行图像合成。在ProstateX数据集上的广泛比较和消融研究表明,该方法优于其他DCE-MRI合成方法。
Key Takeaways
- AAD-DCE是一种基于GAN的DCE-MRI图像合成技术。
- 该技术使用聚合注意力鉴别器模块,包含全局和局部鉴别器。
- 鉴别器提供空间嵌入注意力图,指导生成器合成早期和晚期响应的DCE-MRI图像。
- 该技术采用多模态输入,包括T2加权、ADC和T1预对比图像。
- 在ProstateX数据集上的研究结果显示,AAD-DCE在各种生成器指标上表现优异。
- AAD-DCE的合成图像在PSNR、SSIM和MAE等评价指标上优于其他DCE-MRI合成方法。
- 研究强调了注意力集成的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


Mosaic3D: Foundation Dataset and Model for Open-Vocabulary 3D Segmentation
Authors:Junha Lee, Chunghyun Park, Jaesung Choe, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang, Jan Kautz, Minsu Cho, Chris Choy
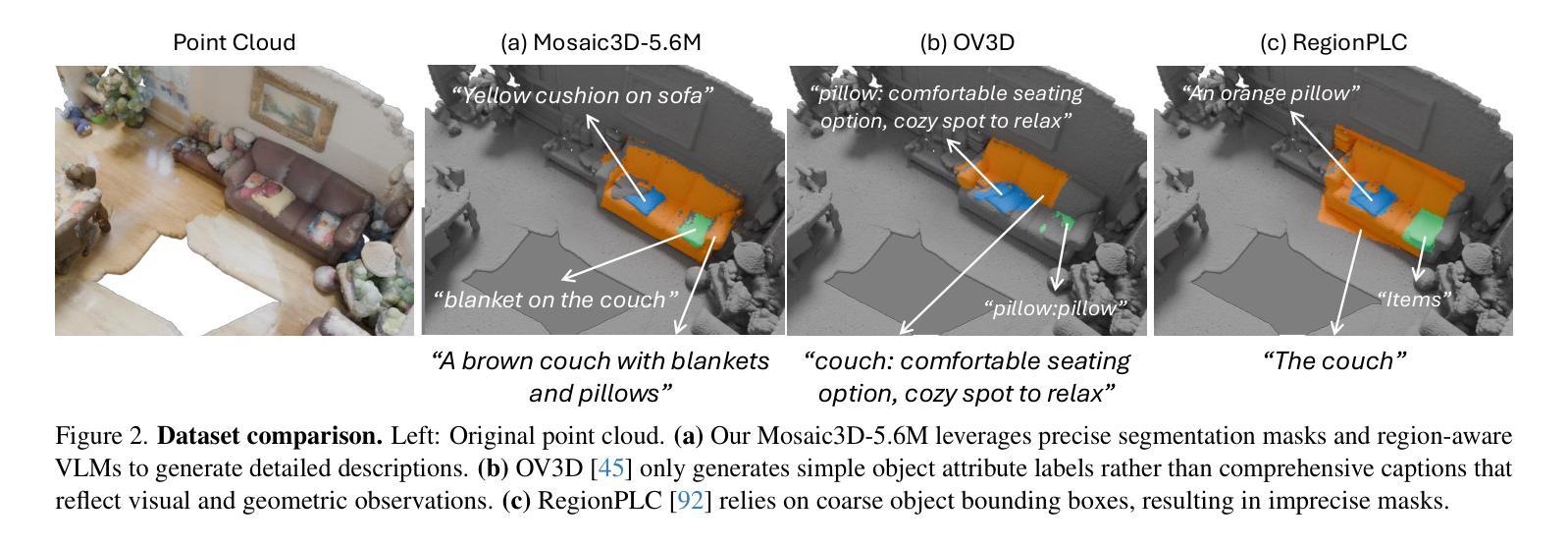
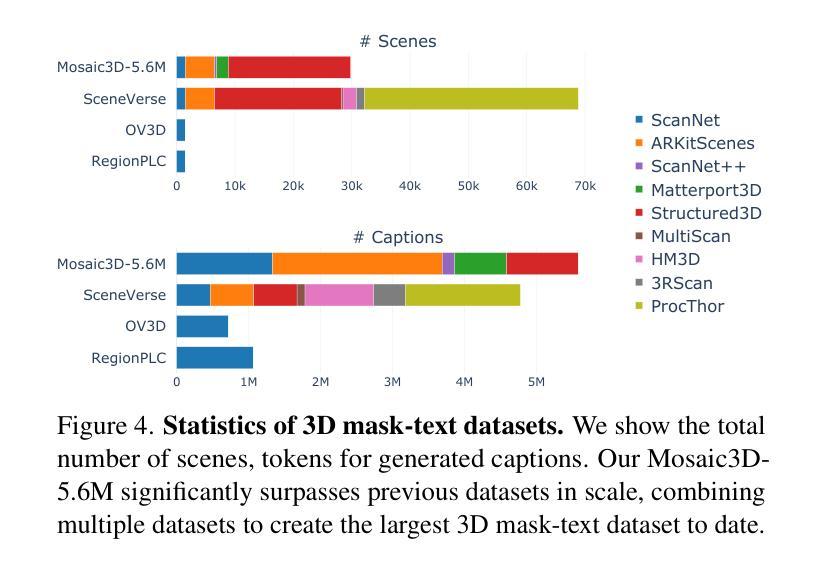
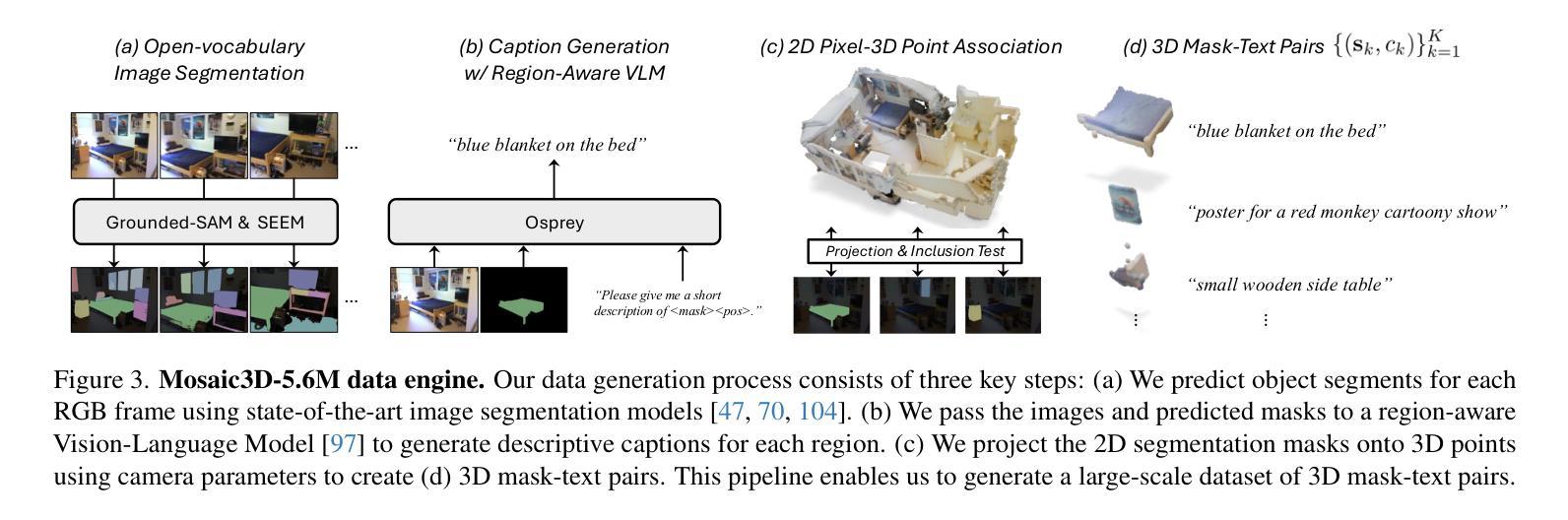
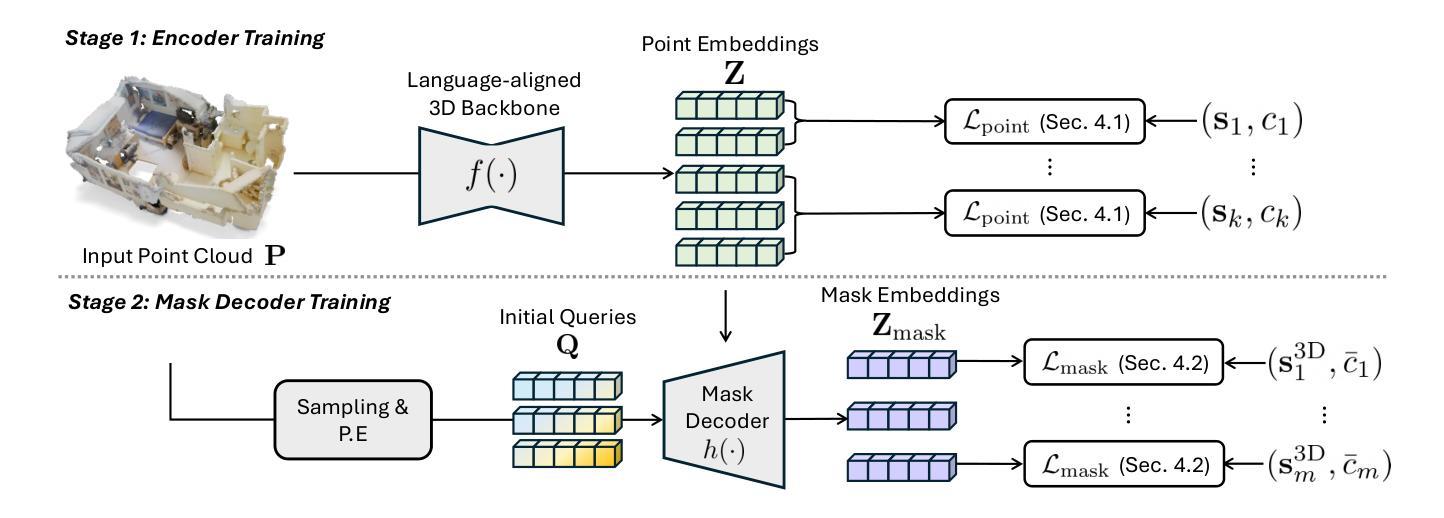
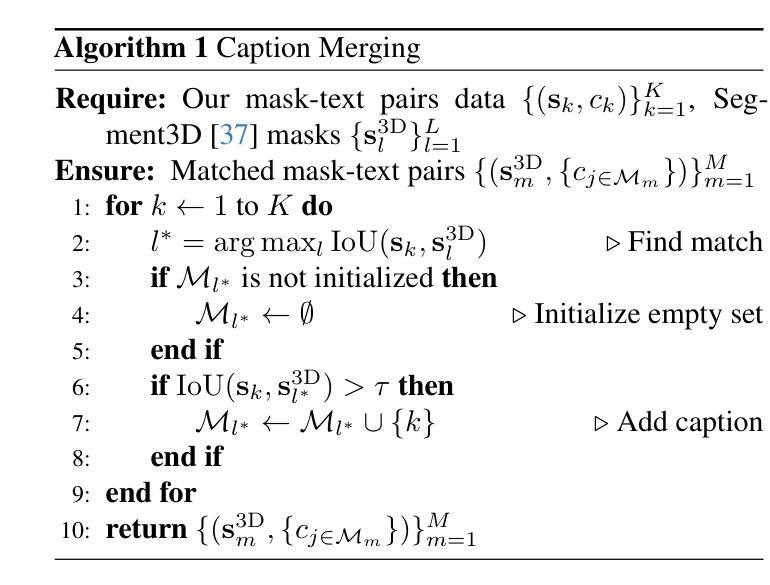
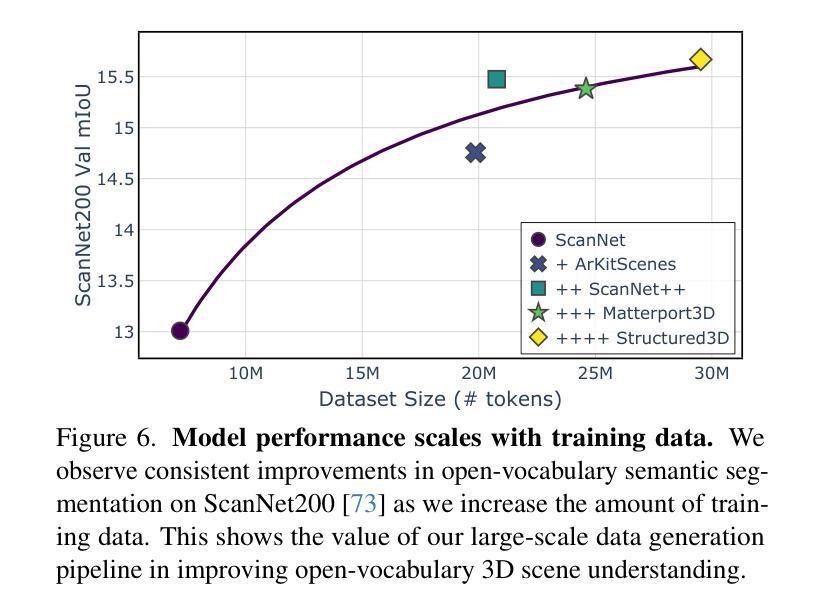
We tackle open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding by introducing a novel data generation pipeline and training framework. Our method addresses three critical requirements for effective training: precise 3D region segmentation, comprehensive textual descriptions, and sufficient dataset scale. By leveraging state-of-the-art open-vocabulary image segmentation models and region-aware Vision-Language Models, we develop an automatic pipeline that generates high-quality 3D mask-text pairs. Applying this pipeline to multiple 3D scene datasets, we create Mosaic3D-5.6M, a dataset of over 30K annotated scenes with 5.6M mask-text pairs, significantly larger than existing datasets. Building upon this data, we propose Mosaic3D, a foundation model combining a 3D encoder trained with contrastive learning and a lightweight mask decoder for open-vocabulary 3D semantic and instance segmentation. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on open-vocabulary 3D semantic and instance segmentation tasks including ScanNet200, Matterport3D, and ScanNet++, with ablation studies validating the effectiveness of our large-scale training data.
我们通过对新型数据生成流程和训练框架的引入,解决了开放式词汇表下的3D场景理解问题。我们的方法满足了有效训练的三项关键需求:精确的3D区域分割、全面的文本描述和足够规模的数据集。我们借助最先进的开放式词汇表图像分割模型和区域感知视觉语言模型,开发了一种自动流程,生成了高质量3D mask-text对。将此流程应用于多个3D场景数据集,我们创建了Mosaic3D-5.6M数据集,包含超过3万个注释场景和560万个mask-text对,显著大于现有数据集。在此基础上,我们提出了Mosaic3D模型,这是一个结合了通过对比学习训练的3D编码器和用于开放式词汇表的轻量级mask解码器的基础模型。我们的方法在开放式词汇表下的3D语义和实例分割任务上达到了最新结果,包括ScanNet200、Matterport3D和ScanNet++等任务,通过消融研究验证了大规模训练数据的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://nvlabs.github.io/Mosaic3D/
Summary
该研究解决了开放词汇表中的三维场景理解问题,通过引入新的数据生成流程和训练框架,满足了精确的三维区域分割、全面的文本描述和足够的数据集规模三个关键训练要求。研究团队使用先进的开放词汇图像分割模型和区域感知的视语言模型,开发出自动生成高质量三维掩膜-文本对的管道。该管道应用于多个三维场景数据集,创建了Mosaic3D-5.6M数据集,包含超过3万标注场景和560万掩膜-文本对,显著大于现有数据集。基于这些数据,研究团队提出了Mosaic3D模型,结合三维编码器对比学习和轻量级掩膜解码器进行开放词汇三维语义和实例分割。该模型在开放词汇的三维语义和实例分割任务上取得了最新结果。
Key Takeaways
- 引入新型数据生成流程和训练框架以解决开放词汇三维场景理解问题。
- 满足精确三维区域分割、全面文本描述和足够数据集规模三个关键训练要求。
- 利用先进图像分割模型和区域感知视语言模型,创建自动生成高质量三维掩膜-文本对的管道。
- 开发出大规模数据集Mosaic3D-5.6M,包含超过3万标注场景和560万掩膜-文本对。
- 提出Mosaic3D模型,结合三维编码器和轻量级掩膜解码器进行开放词汇三维语义和实例分割。
- Mosaic3D模型在多个开放词汇三维语义和实例分割任务上取得最新结果。
点此查看论文截图

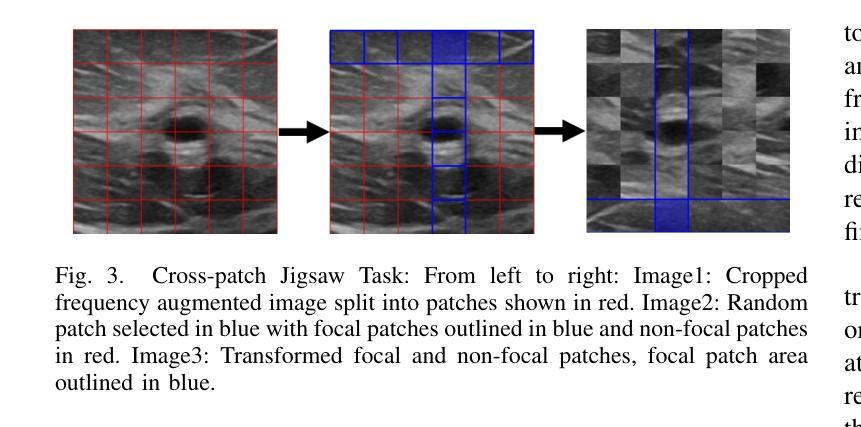
A Self-Supervised Framework for Improved Generalisability in Ultrasound B-mode Image Segmentation
Authors:Edward Ellis, Andrew Bulpitt, Nasim Parsa, Michael F Byrne, Sharib Ali
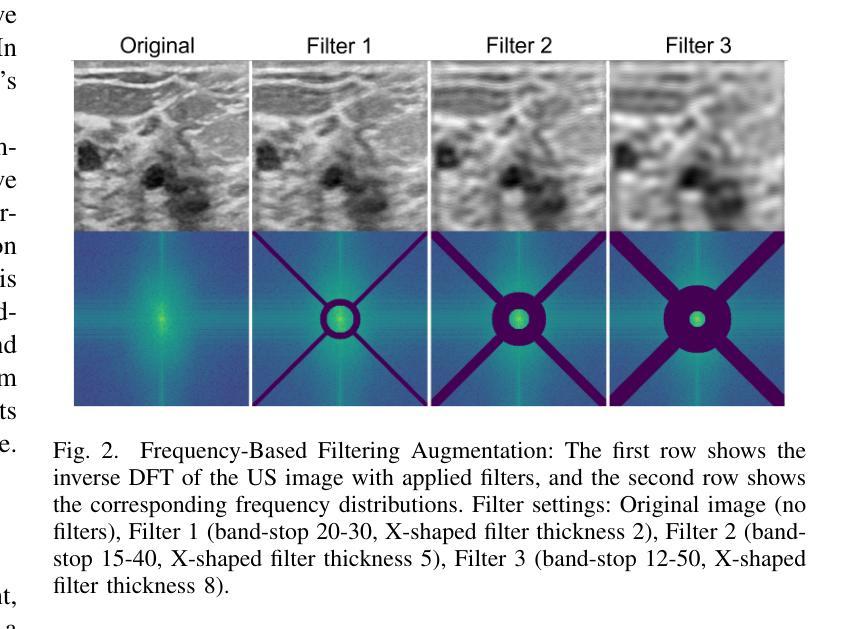
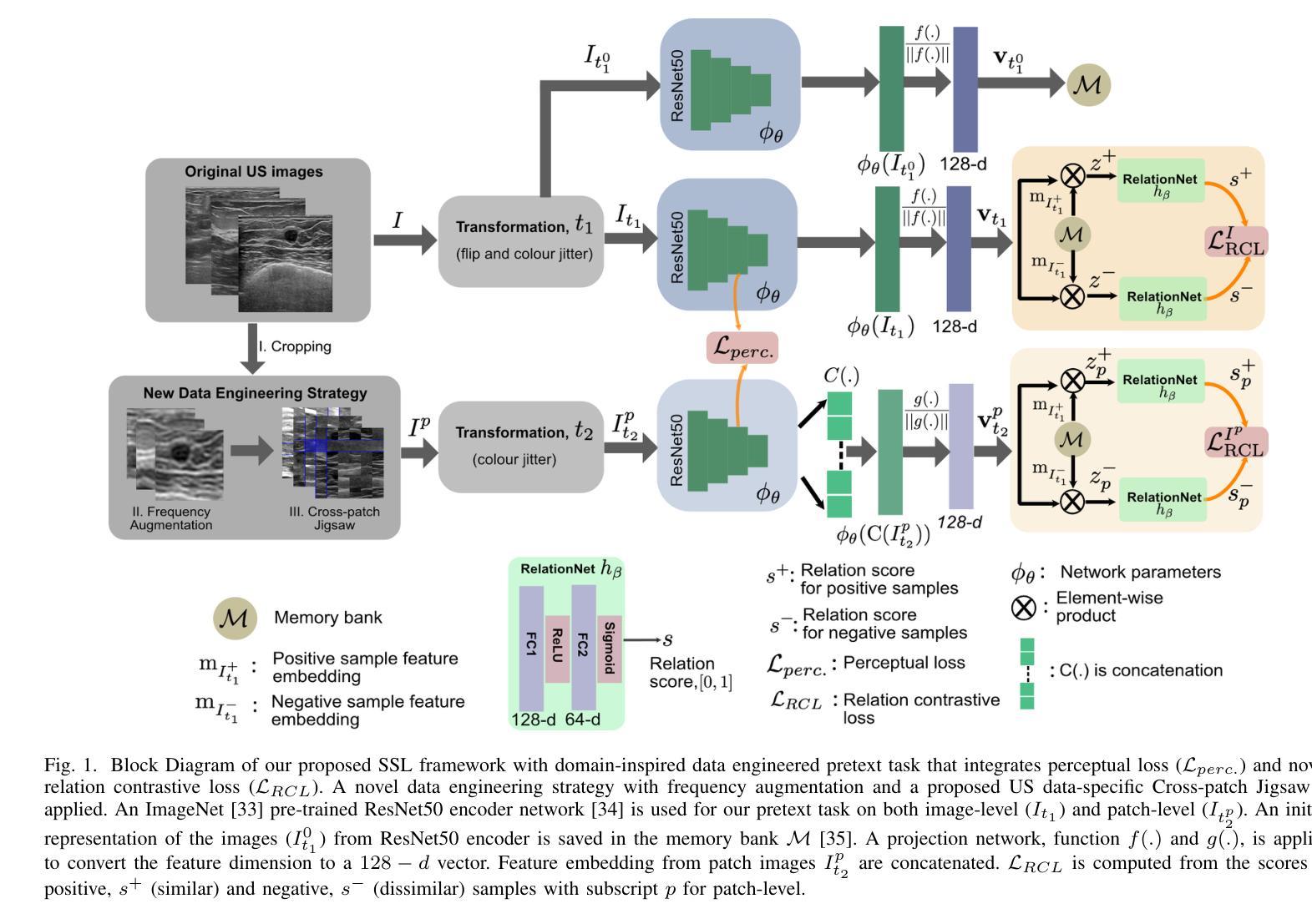
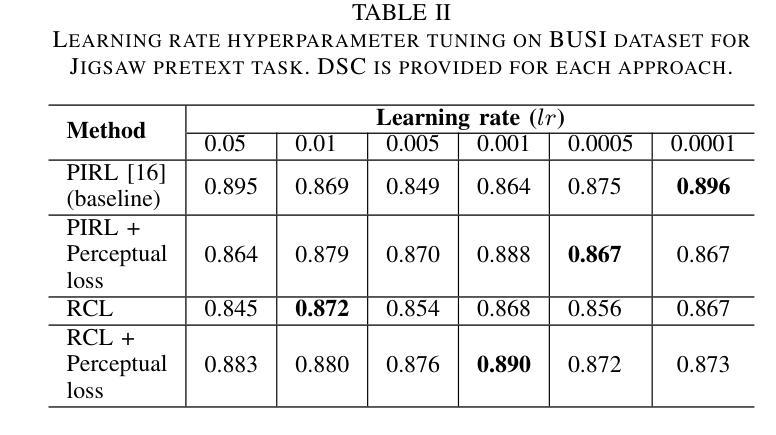
Ultrasound (US) imaging is clinically invaluable due to its noninvasive and safe nature. However, interpreting US images is challenging, requires significant expertise, and time, and is often prone to errors. Deep learning offers assistive solutions such as segmentation. Supervised methods rely on large, high-quality, and consistently labeled datasets, which are challenging to curate. Moreover, these methods tend to underperform on out-of-distribution data, limiting their clinical utility. Self-supervised learning (SSL) has emerged as a promising alternative, leveraging unlabeled data to enhance model performance and generalisability. We introduce a contrastive SSL approach tailored for B-mode US images, incorporating a novel Relation Contrastive Loss (RCL). RCL encourages learning of distinct features by differentiating positive and negative sample pairs through a learnable metric. Additionally, we propose spatial and frequency-based augmentation strategies for the representation learning on US images. Our approach significantly outperforms traditional supervised segmentation methods across three public breast US datasets, particularly in data-limited scenarios. Notable improvements on the Dice similarity metric include a 4% increase on 20% and 50% of the BUSI dataset, nearly 6% and 9% improvements on 20% and 50% of the BrEaST dataset, and 6.4% and 3.7% improvements on 20% and 50% of the UDIAT dataset, respectively. Furthermore, we demonstrate superior generalisability on the out-of-distribution UDIAT dataset with performance boosts of 20.6% and 13.6% compared to the supervised baseline using 20% and 50% of the BUSI and BrEaST training data, respectively. Our research highlights that domain-inspired SSL can improve US segmentation, especially under data-limited conditions.
超声(US)成像因其无创且安全的特点而在临床上具有巨大价值。然而,解读超声图像具有挑战性,需要专业知识和大量时间,并且容易出错。深度学习提供了辅助解决方案,如分割技术。监督学习方法依赖于大量高质量且持续标注的数据集,这些数据集难以整理。此外,这些方法在超出分布范围的数据上表现不佳,限制了它们在临床上的实用性。自监督学习(SSL)作为一种有前途的替代方法应运而生,它利用未标记的数据来提高模型的性能和通用性。我们针对B模式超声图像引入了一种对比自监督学习方法,并结合了一种新型的关系对比损失(RCL)。RCL通过可学习的指标来区分正负样本对,鼓励学习独特特征。此外,我们还提出了基于空间和频率的增强策略,用于超声图像上的表示学习。我们的方法在三个公共乳腺超声数据集上的表现远超传统的监督分割方法,特别是在数据有限的情况下。在迪氏相似度指标上的显著改进包括在BUSI数据集20%和50%的数据上分别提高了4%和近6%和近9%的改进;在BrEaST数据集上也有了相应的提高。此外,我们在分布外的UDIAT数据集上表现出了优越的泛化能力,与使用BUSI和BrEaST训练数据20%和50%的基线相比,性能分别提高了20.6%和13.6%。我们的研究强调了领域启发式的自监督学习能够改善超声分割技术,特别是在数据有限的情况下。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12
Summary
本文介绍了超声(US)成像的重要性及其解读的挑战性。深度学习中的自我监督学习(SSL)方法利用无标签数据提高模型性能和泛化能力,为解决这一问题提供了有效方案。研究团队提出了一种针对B模式超声图像的对比SSL方法,并引入了一种新的关系对比损失(RCL)。此方法在公开数据集上的表现优于传统的监督分割方法,尤其在数据有限的情况下改善明显。此外,该研究还展示了其在泛化能力上的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 超声(US)成像在临床中非常重要,但其图像解读具有挑战性。
- 深度学习中的自我监督学习(SSL)是解决这一挑战的有效方法之一。
- 研究团队提出了一种针对B模式超声图像的对比SSL方法,包括关系对比损失(RCL)和基于空间和频率的增强策略。
- 该方法在公开数据集上的表现优于传统监督分割方法,尤其在数据有限的情况下改善明显。
- 该方法在泛化能力上具有优势,尤其是在跨数据集的应用中表现良好。
点此查看论文截图


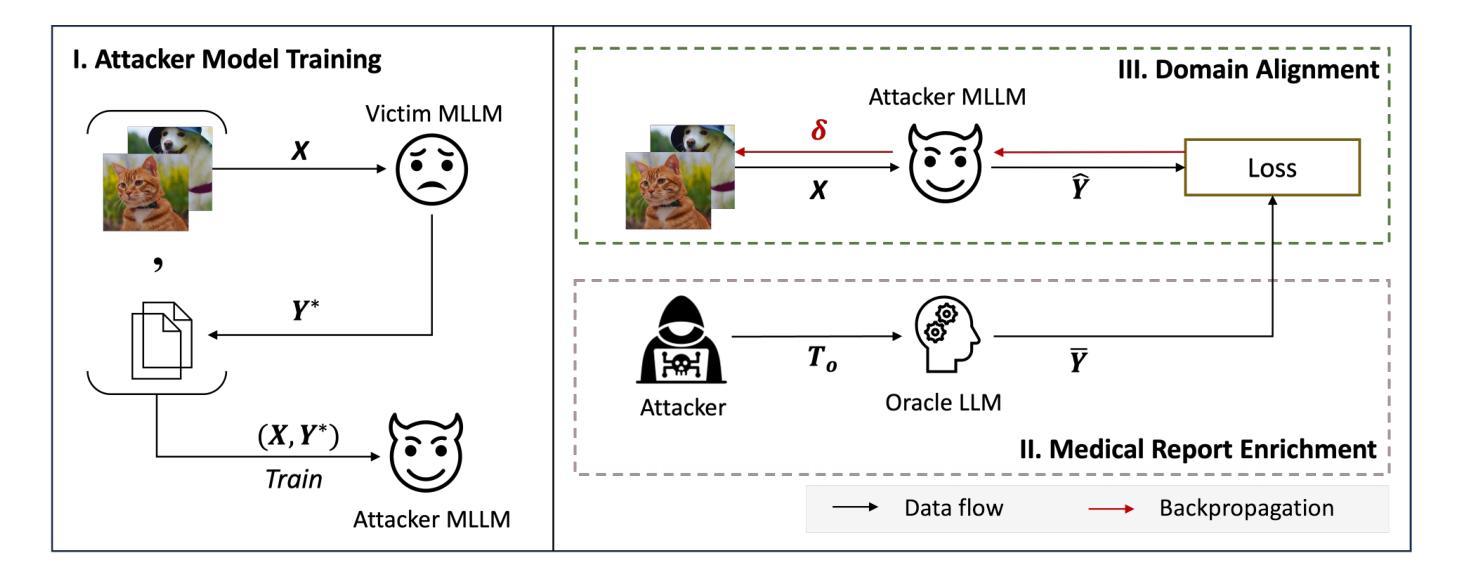
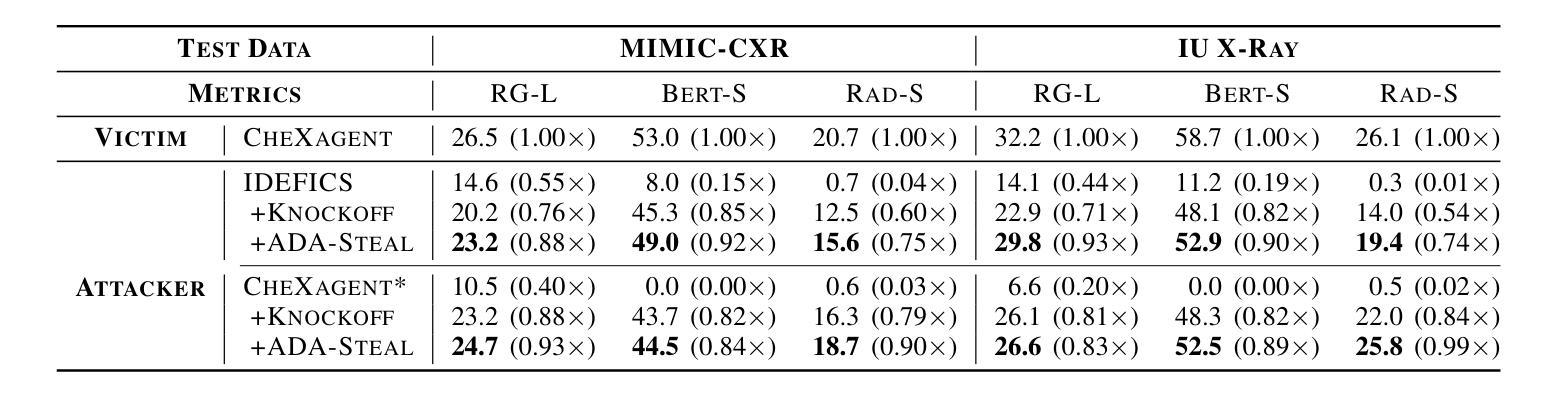
Medical Multimodal Model Stealing Attacks via Adversarial Domain Alignment
Authors:Yaling Shen, Zhixiong Zhuang, Kun Yuan, Maria-Irina Nicolae, Nassir Navab, Nicolas Padoy, Mario Fritz
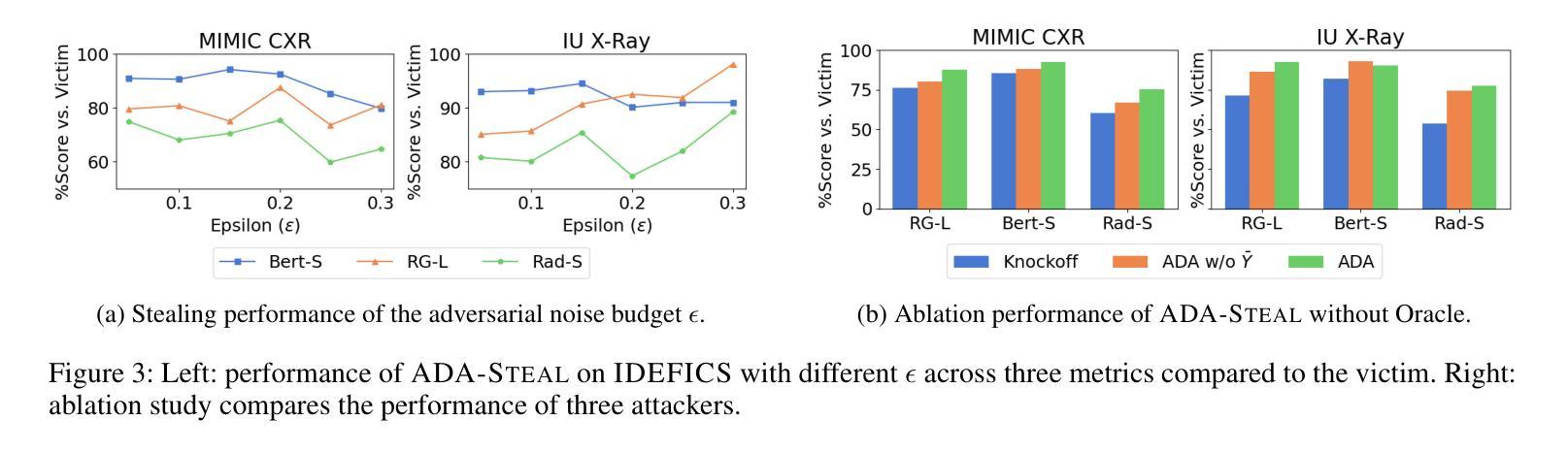
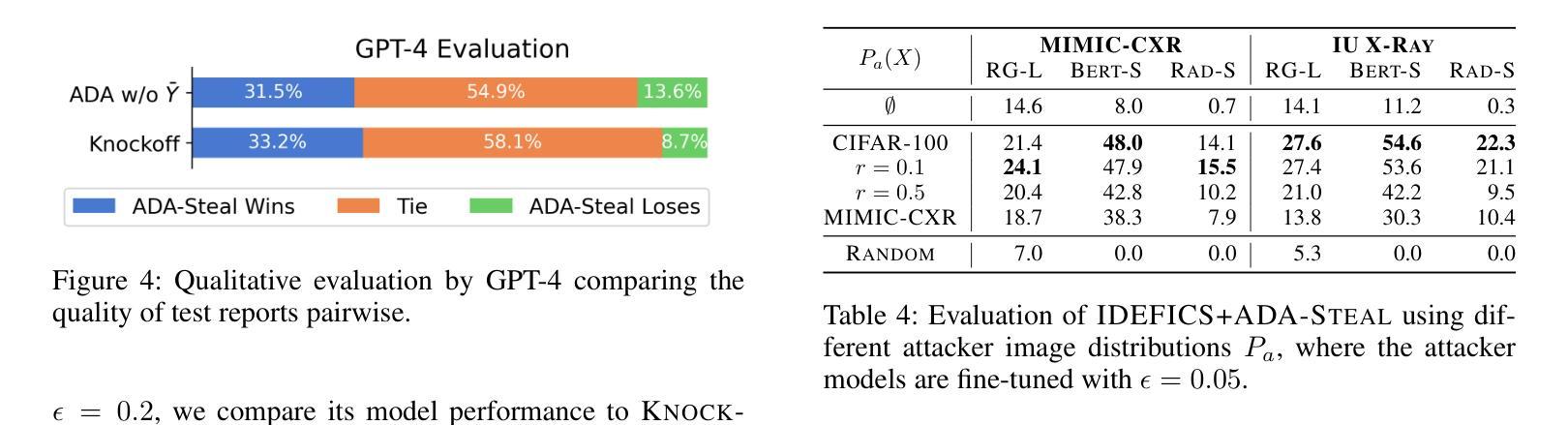
Medical multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are becoming an instrumental part of healthcare systems, assisting medical personnel with decision making and results analysis. Models for radiology report generation are able to interpret medical imagery, thus reducing the workload of radiologists. As medical data is scarce and protected by privacy regulations, medical MLLMs represent valuable intellectual property. However, these assets are potentially vulnerable to model stealing, where attackers aim to replicate their functionality via black-box access. So far, model stealing for the medical domain has focused on classification; however, existing attacks are not effective against MLLMs. In this paper, we introduce Adversarial Domain Alignment (ADA-STEAL), the first stealing attack against medical MLLMs. ADA-STEAL relies on natural images, which are public and widely available, as opposed to their medical counterparts. We show that data augmentation with adversarial noise is sufficient to overcome the data distribution gap between natural images and the domain-specific distribution of the victim MLLM. Experiments on the IU X-RAY and MIMIC-CXR radiology datasets demonstrate that Adversarial Domain Alignment enables attackers to steal the medical MLLM without any access to medical data.
医疗多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)正成为医疗保健系统的重要组成部分,协助医疗人员进行决策制定和结果分析。用于生成放射学报告的模型能够解释医学图像,从而减轻放射科医生的工作量。由于医疗数据稀缺且受隐私法规的保护,医疗MLLMs代表了宝贵的知识产权。然而,这些资产可能面临模型窃取的风险,攻击者通过黑箱访问试图复制其功能。迄今为止,医疗领域的模型窃取主要集中在分类领域,但现有的攻击对MLLMs并不有效。在本文中,我们介绍了针对医疗MLLMs的首个窃取攻击——对抗域对齐(ADA-STEAL)。ADA-STEAL依赖于公共且广泛可用的自然图像,而非医疗图像。我们表明,通过对抗性噪声进行数据增强足以克服自然图像和受害者MLLM领域特定分布之间的数据分布差距。在IU X射线以及MIMIC-CXR放射学数据集上的实验表明,对抗域对齐使攻击者无需访问医疗数据即可窃取医疗MLLM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI 2025
Summary
医疗多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医疗保健系统中发挥着重要作用,协助医疗人员进行决策和结果分析。针对放射学报告生成的模型能够解读医学图像,从而减轻放射科医生的工作量。由于医学数据稀缺且受隐私法规保护,医学MLLMs被视为宝贵的知识产权。然而,这些资产存在潜在的模型窃取风险,攻击者通过黑箱访问试图复制其功能。目前针对医学领域的模型窃取主要集中在分类方面,但现有攻击对MLLMs并不奏效。本文介绍了一种针对医学MLLMs的首个窃取攻击——对抗域对齐(ADA-STEAL)。ADA-STEAL依赖于公开且广泛可用的自然图像,而非医学图像。研究表明,通过数据增强添加对抗性噪声足以克服自然图像与受害者MLLM的特定领域分布之间的数据分布差距。在IU X光片和MIMIC-CXR放射学数据集上的实验表明,对抗域对齐使攻击者无需访问医学数据即可窃取医疗MLLM。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医疗保健系统中作用显著,辅助决策和结果分析。
- 医学MLLMs能够解读医学图像,减轻放射科医生工作负担。
- 医学数据稀缺性和隐私法规使医学MLLMs成为宝贵的知识产权。
- 医学MLLMs存在模型窃取风险,攻击者试图通过黑箱访问复制其功能。
- 目前针对医学领域的模型窃取主要集中在分类模型上,对MLLMs的攻击并不成功。
- 引入一种新的窃取攻击方法——对抗域对齐(ADA-STEAL),它利用公开的自然图像进行模型窃取。
点此查看论文截图

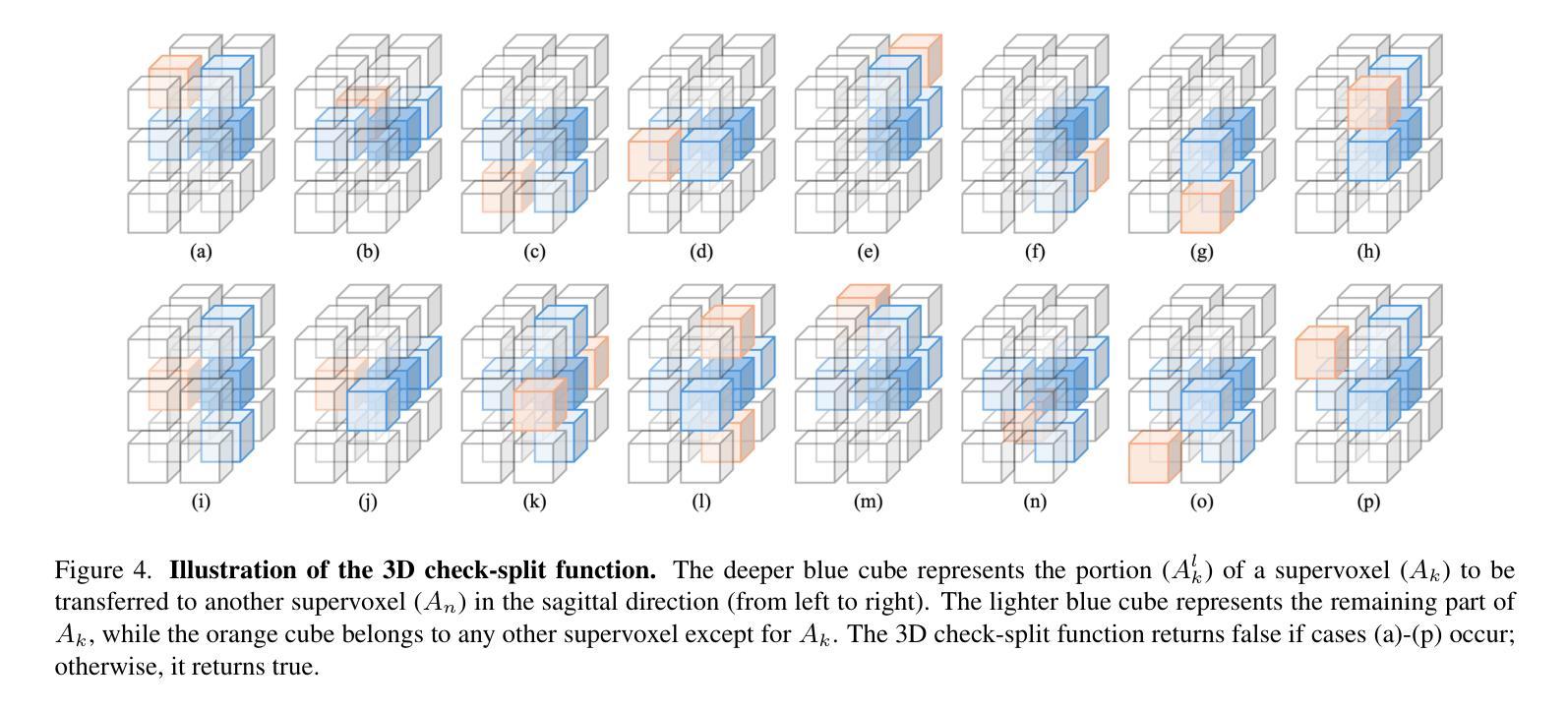
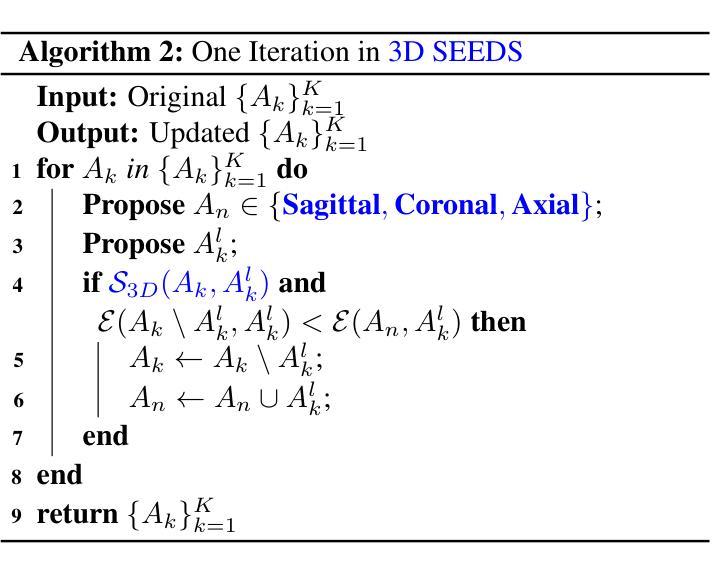
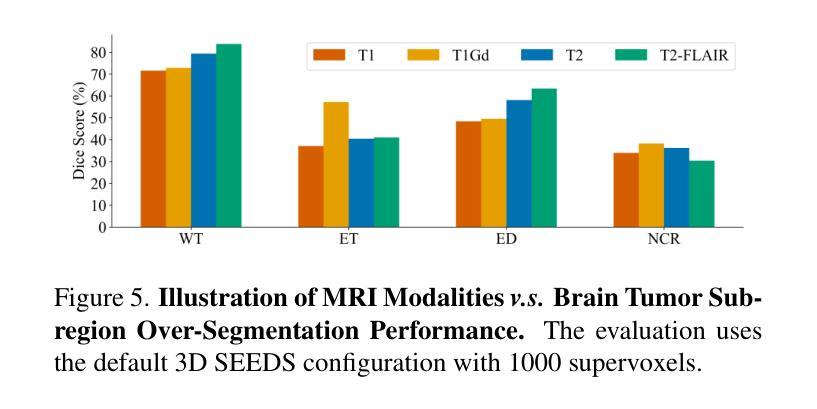
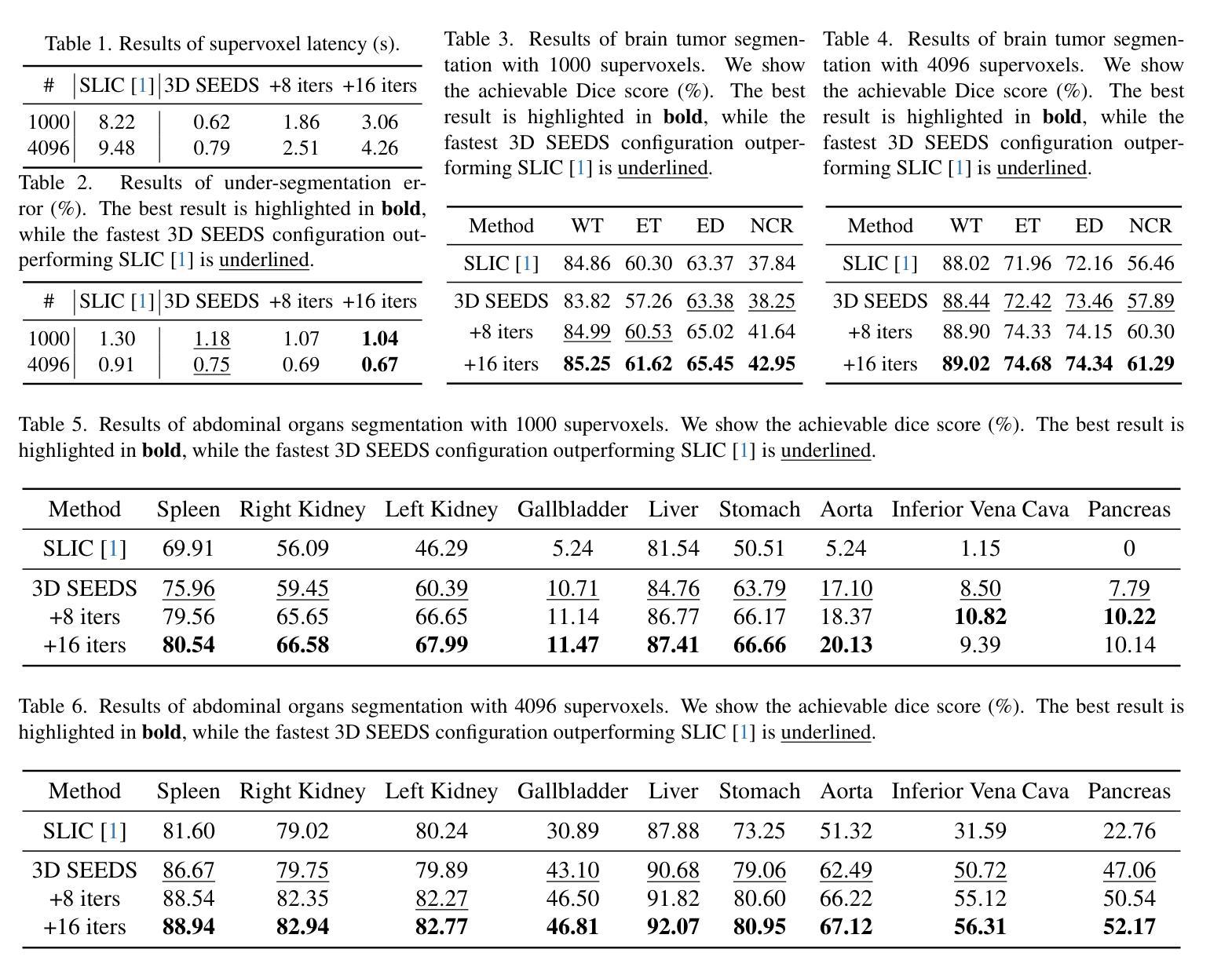
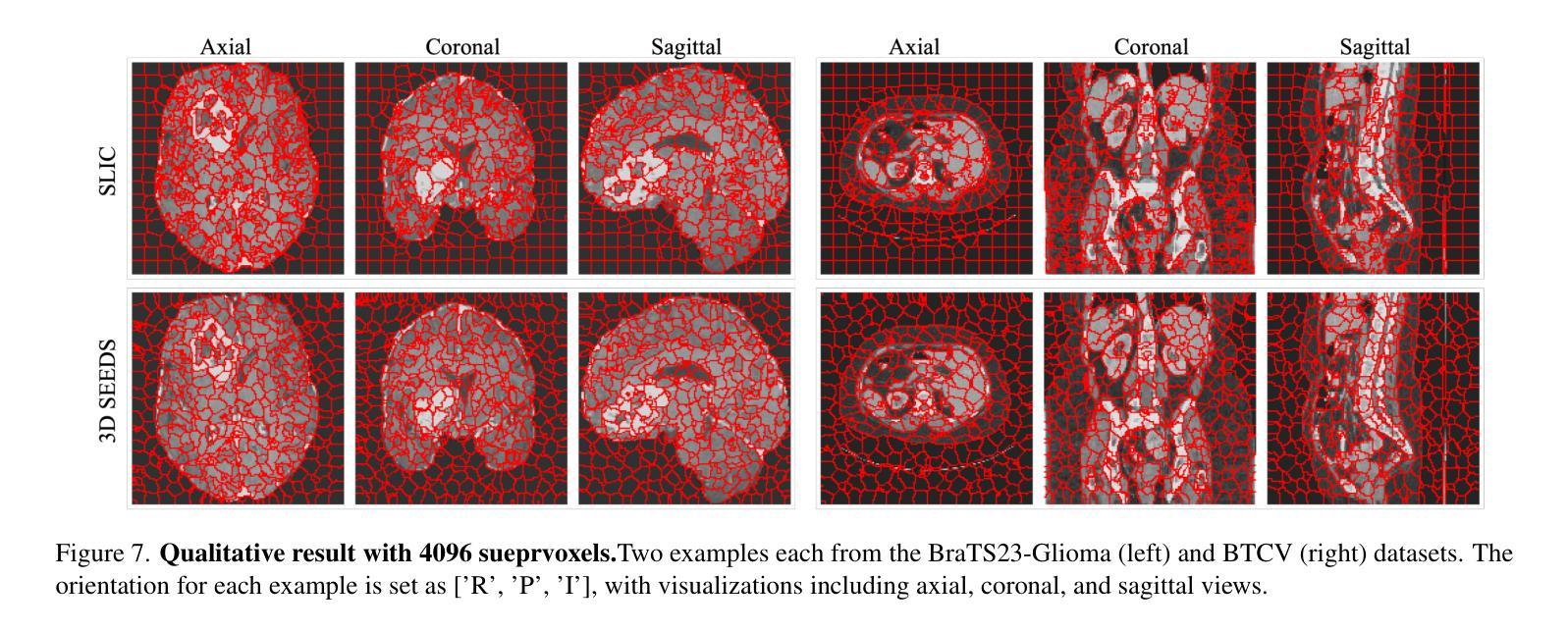
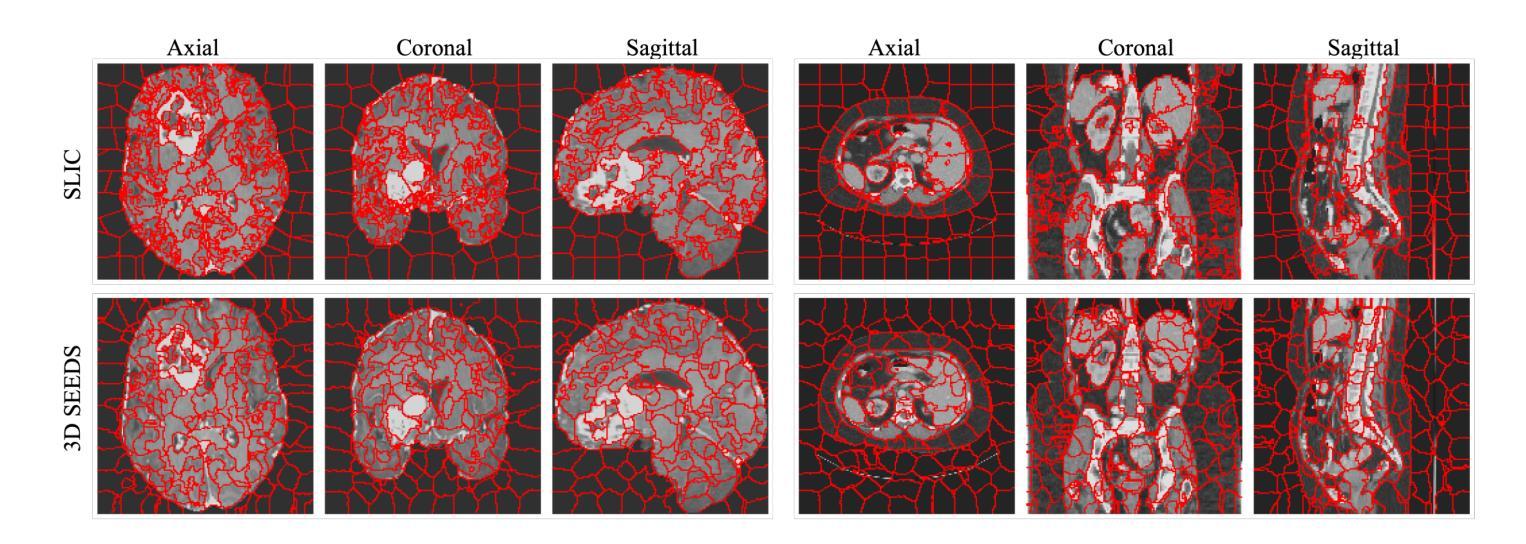
Extending SEEDS to a Supervoxel Algorithm for Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Chenhui Zhao, Yan Jiang, Todd C. Hollon
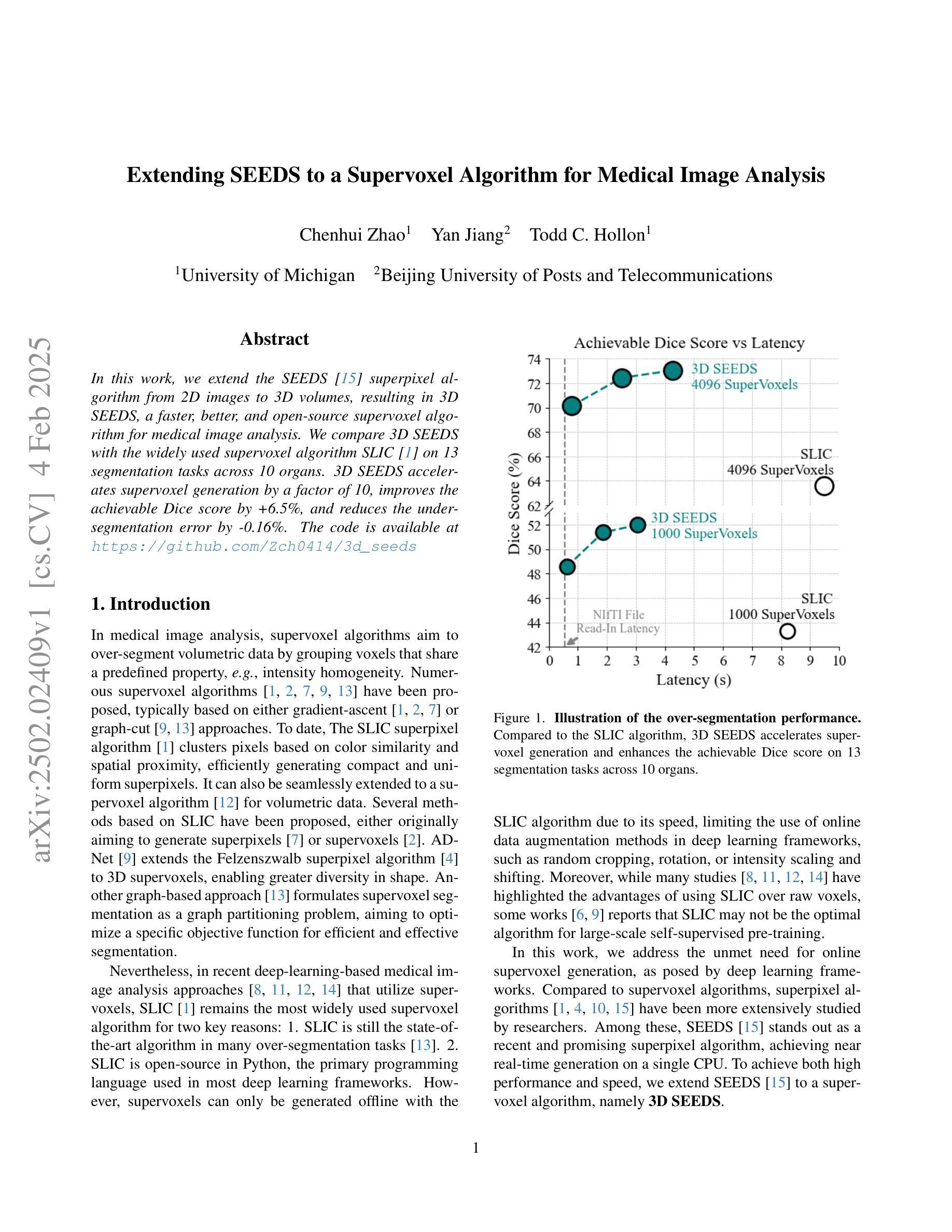
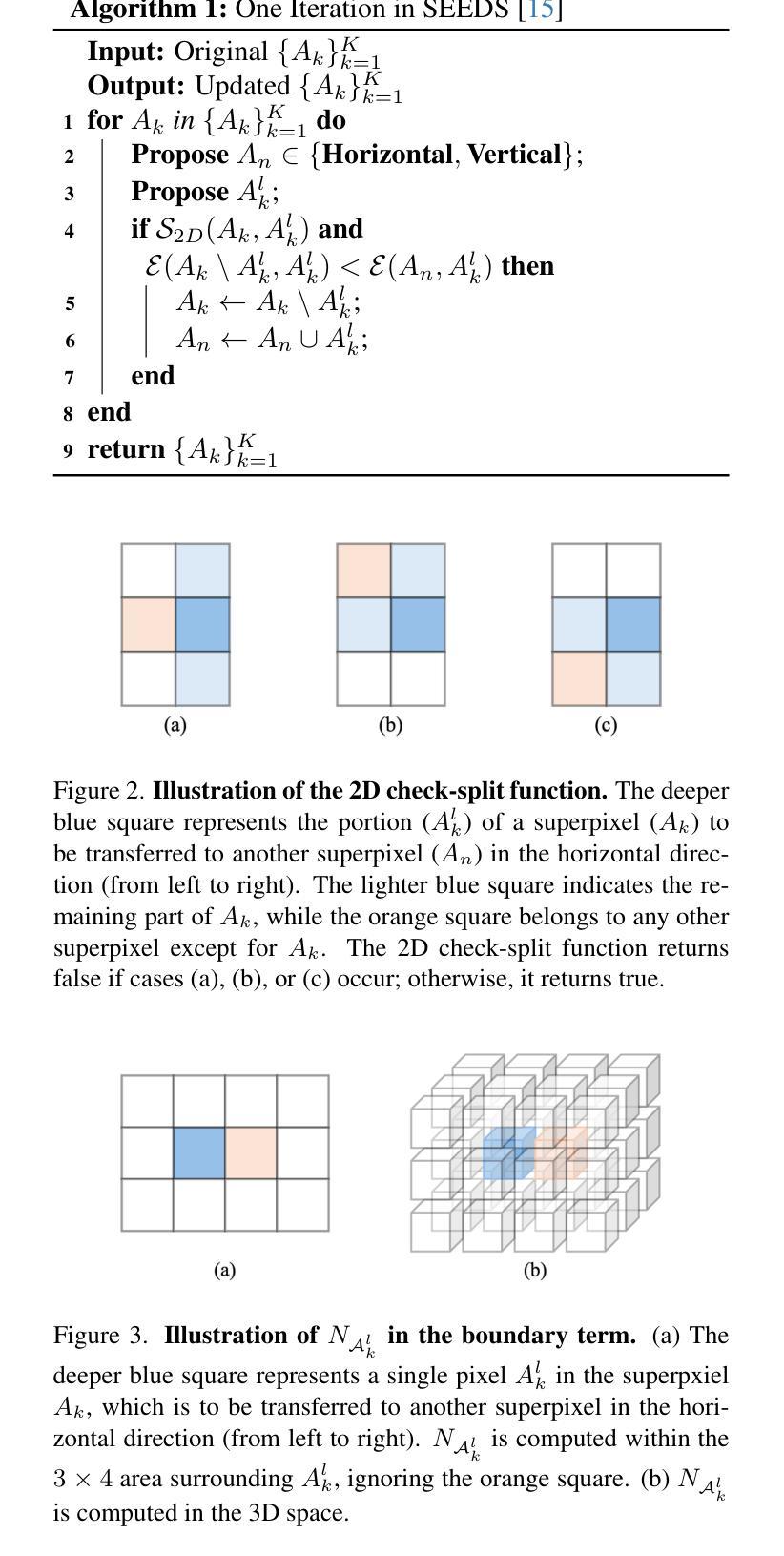
In this work, we extend the SEEDS superpixel algorithm from 2D images to 3D volumes, resulting in 3D SEEDS, a faster, better, and open-source supervoxel algorithm for medical image analysis. We compare 3D SEEDS with the widely used supervoxel algorithm SLIC on 13 segmentation tasks across 10 organs. 3D SEEDS accelerates supervoxel generation by a factor of 10, improves the achievable Dice score by +6.5%, and reduces the under-segmentation error by -0.16%. The code is available at https://github.com/Zch0414/3d_seeds
在这项工作中,我们将SEEDS超像素算法从2D图像扩展到3D体积,从而得到3D SEEDS,这是一个更快、更好、开源的用于医学图像分析的Supervoxel算法。我们在10个器官的13个分割任务上,将3D SEEDS与广泛使用的Supervoxel算法SLIC进行了比较。3D SEEDS将Supervoxel的生成速度提高了10倍,提高了Dice系数的得分+6.5%,并降低了欠分割误差-0.16%。代码可在https://github.com/Zch0414/3d_seeds上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tech report
Summary
本文扩展了SEEDS超像素算法,从2D图像到3D体积,提出了更快的、更好的、开源的用于医学图像分析的3D SEEDS超体素算法。在跨越10个器官的13个分割任务上,与广泛使用的SLIC超体素算法相比,3D SEEDS加速超体素生成速度提高10倍,提高了Dice评分,并降低了欠分割误差。代码已发布在https://github.com/Zch0414/3d_seeds。
Key Takeaways
- 本文成功将SEEDS超像素算法从2D图像扩展到3D体积,形成了新的超体素算法——3D SEEDS。
- 3D SEEDS在多个器官(共跨越十个)的多个分割任务(共13个)上与广泛使用的SLIC算法进行了比较。
- 相较于SLIC算法,3D SEEDS大大加速了超体素的生成速度,提高了效率。
- 相较于SLIC算法,使用3D SEEDS后Dice评分提高了约+6.5%。这表明了在医疗图像分析中可能提高的效果。
- 相较于SLIC算法,使用3D SEEDS后欠分割误差降低了约-0.16%,表明其在某些情况下能更好地处理复杂的图像分割任务。
- 代码已经开源,方便其他研究者使用和进一步开发。具体链接为:https://github.com/Zch0414/3d_seeds。这将加速算法的推广和实际应用。
点此查看论文截图
Deep Ensemble approach for Enhancing Brain Tumor Segmentation in Resource-Limited Settings
Authors:Jeremiah Fadugba, Isabel Lieberman, Olabode Ajayi, Mansour Osman, Solomon Oluwole Akinola, Tinashe Mustvangwa, Dong Zhang, Udunna C Anazondo, Raymond Confidence
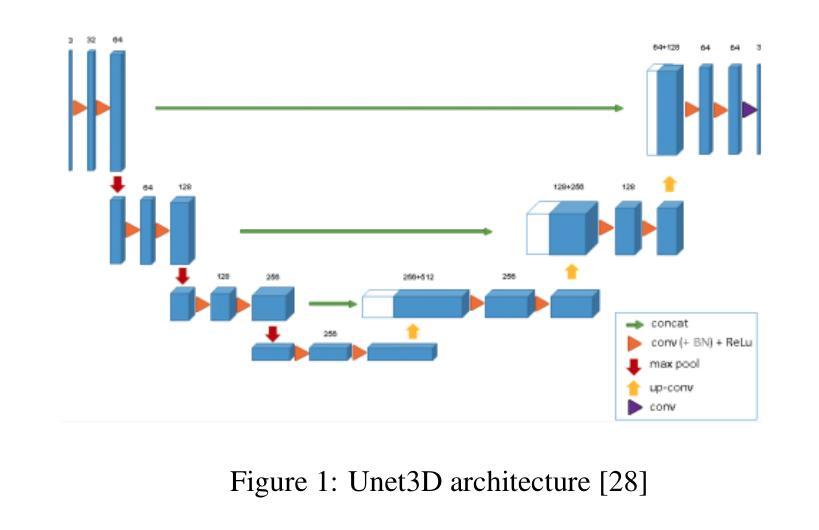
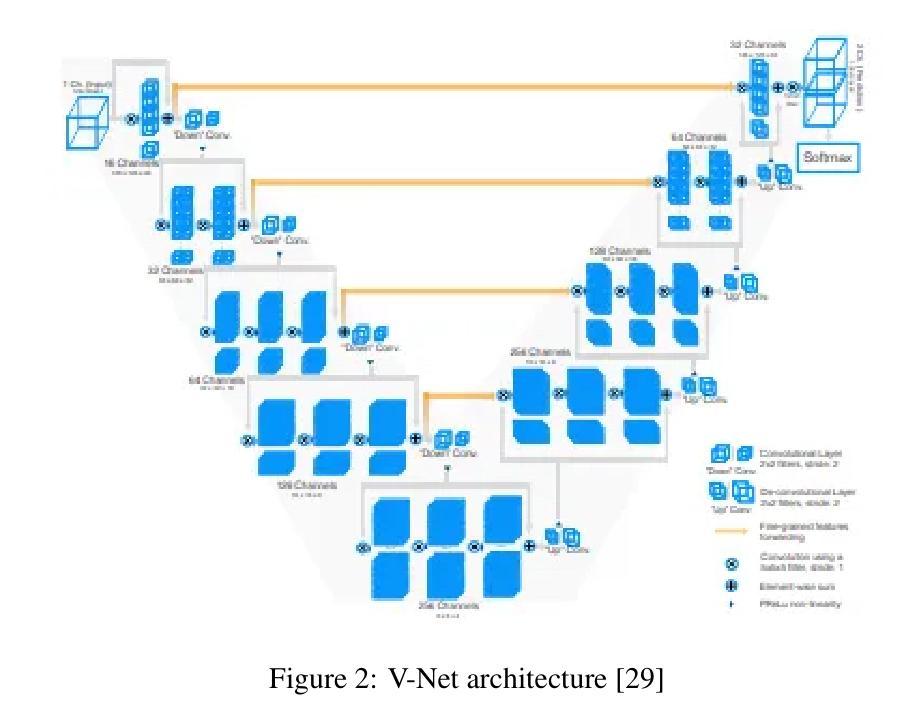
Segmentation of brain tumors is a critical step in treatment planning, yet manual segmentation is both time-consuming and subjective, relying heavily on the expertise of radiologists. In Sub-Saharan Africa, this challenge is magnified by overburdened medical systems and limited access to advanced imaging modalities and expert radiologists. Automating brain tumor segmentation using deep learning offers a promising solution. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), especially the U-Net architecture, have shown significant potential. However, a major challenge remains: achieving generalizability across different datasets. This study addresses this gap by developing a deep learning ensemble that integrates UNet3D, V-Net, and MSA-VNet models for the semantic segmentation of gliomas. By initially training on the BraTS-GLI dataset and fine-tuning with the BraTS-SSA dataset, we enhance model performance. Our ensemble approach significantly outperforms individual models, achieving DICE scores of 0.8358 for Tumor Core, 0.8521 for Whole Tumor, and 0.8167 for Enhancing Tumor. These results underscore the potential of ensemble methods in improving the accuracy and reliability of automated brain tumor segmentation, particularly in resource-limited settings.
脑部肿瘤的分割是治疗方案制定中的关键步骤,然而手动分割既耗时又存在主观性,并高度依赖于放射科专家的专业知识。在撒哈拉以南非洲地区,由于医疗系统负担过重以及先进的成像模式和专家级放射科医生资源有限,这一挑战进一步加剧。使用深度学习自动进行脑部肿瘤分割提供了一个有前景的解决方案。卷积神经网络(CNN)尤其是U-Net架构显示出了巨大的潜力。然而,仍然存在一个主要挑战:在不同数据集上实现泛化能力。本研究通过开发一个深度学习集成来解决这一差距,该集成结合了UNet3D、V-Net和MSA-VNet模型进行胶质瘤的语义分割。通过首先在BraTS-GLI数据集上进行训练,并在BraTS-SSA数据集上进行微调,我们提高了模型性能。我们的集成方法显著优于单个模型,肿瘤核心的DICE分数为0.8358,整个肿瘤的DICE分数为0.8521,增强肿瘤的DICE分数为0.8167。这些结果突显了集成方法在改进自动脑部肿瘤分割的准确性和可靠性方面的潜力,特别是在资源有限的环境中更是如此。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了使用深度学习技术自动化脑肿瘤分割的潜力,特别是在撒哈拉以南非洲地区面临挑战的情况下。该研究采用卷积神经网络(CNNs)的U-Net架构并结合UNet3D、V-Net和MSA-VNet模型,对胶质瘤进行语义分割。通过初始训练在BraTS-GLI数据集上,并使用BraTS-SSA数据集微调,提高了模型性能。该研究的结果表明,集成方法显著优于单个模型,肿瘤核心、整个肿瘤和增强肿瘤的DICE得分分别为0.8358、0.8521和0.8167。这突显了集成方法在改善自动化脑肿瘤分割的准确性和可靠性方面的潜力,尤其是在资源有限的环境中。
Key Takeaways
- 脑肿瘤的分割是治疗计划中的关键步骤,但手动分割耗时且主观,依赖于放射科专家的专业知识。
- 在撒哈拉以南非洲地区,由于医疗系统负担过重、先进的成像模式和专家放射科医生有限,这一挑战被放大。
- 深度学习自动脑肿瘤分割提供了解决方案。其中卷积神经网络(CNNs)特别是U-Net架构显示出巨大潜力。
- 集成多种模型(如UNet3D、V-Net和MSA-VNet)能够提高模型的性能,为语义分割提供更准确的预测。
- 通过在BraTS-GLI数据集上进行初始训练并使用BraTS-SSA数据集进行微调,增强了模型的性能。
- 集成方法显著优于单一模型,在肿瘤核心、整个肿瘤和增强肿瘤的DICE得分上表现出较高的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

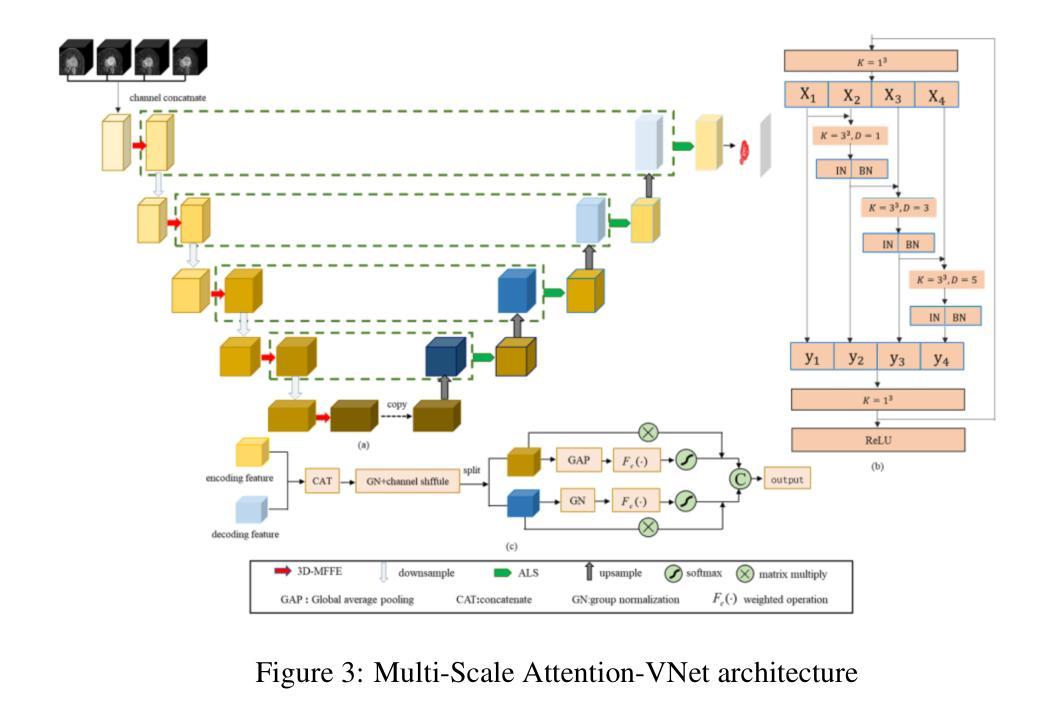
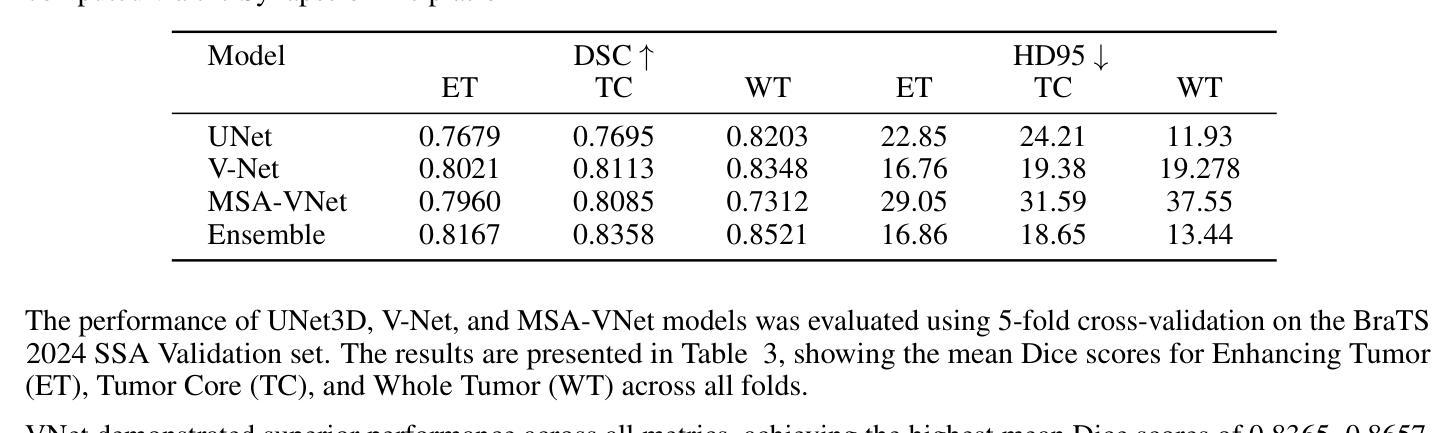
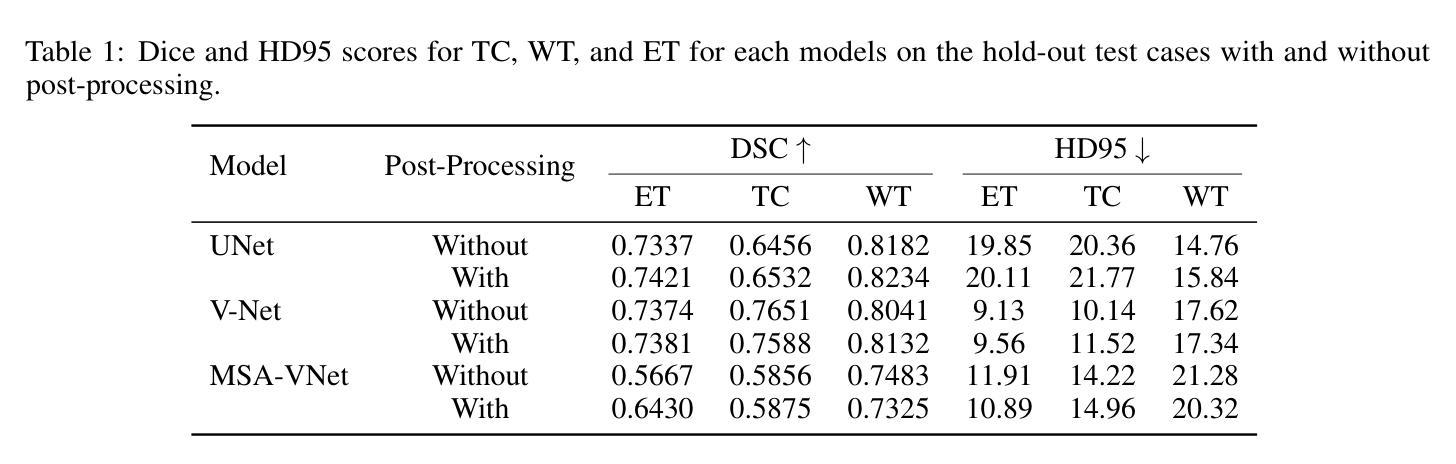
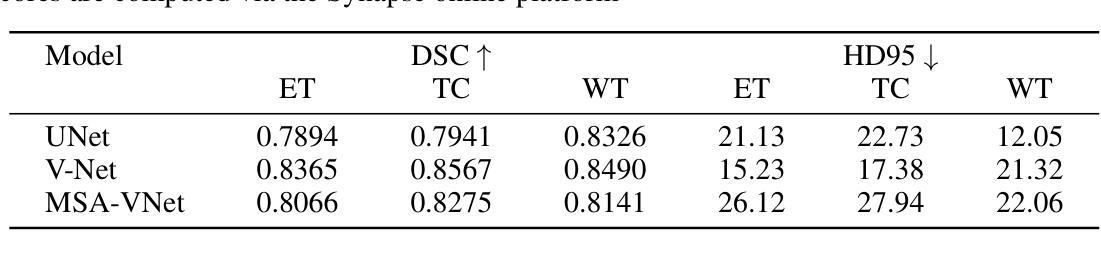
VerteNet – A Multi-Context Hybrid CNN Transformer for Accurate Vertebral Landmark Localization in Lateral Spine DXA Images
Authors:Zaid Ilyas, Arooba Maqsood, Afsah Saleem, Erchuan Zhang, David Suter, Parminder Raina, Jonathan M. Hodgson, John T. Schousboe, William D. Leslie, Joshua R. Lewis, Syed Zulqarnain Gilani
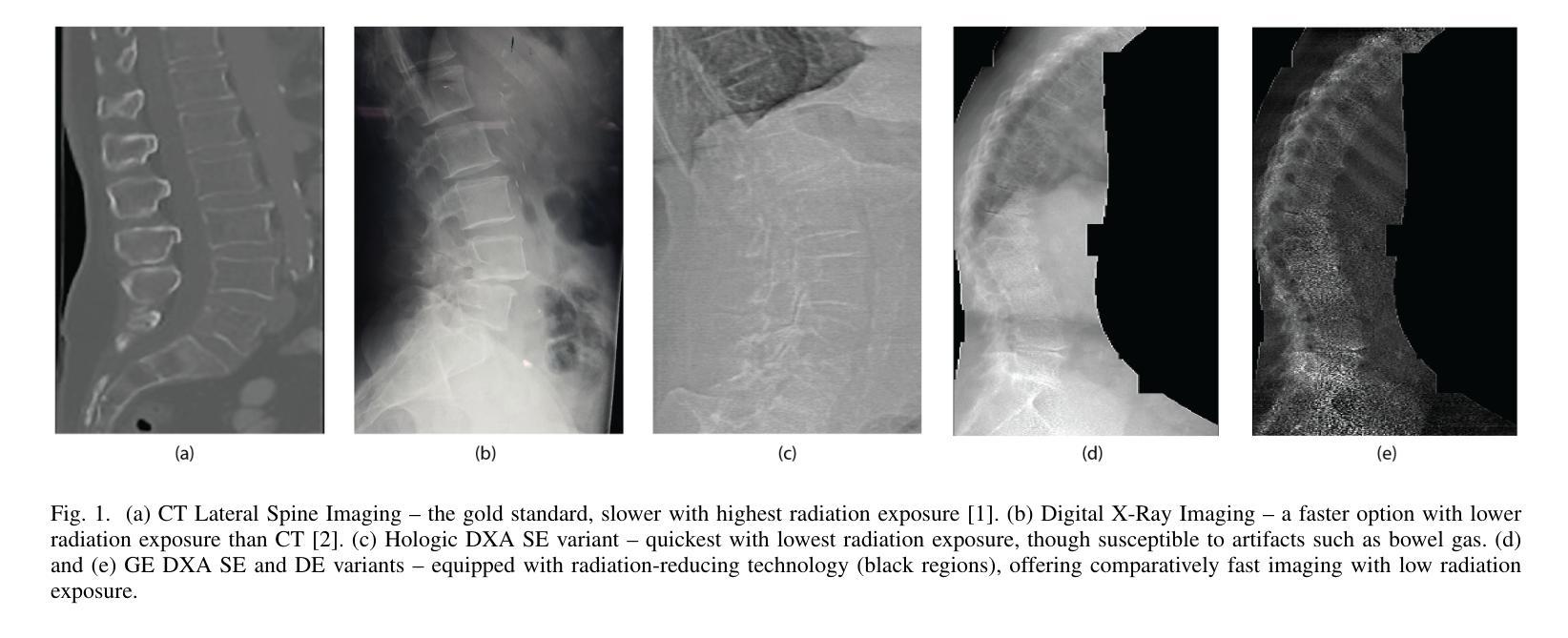
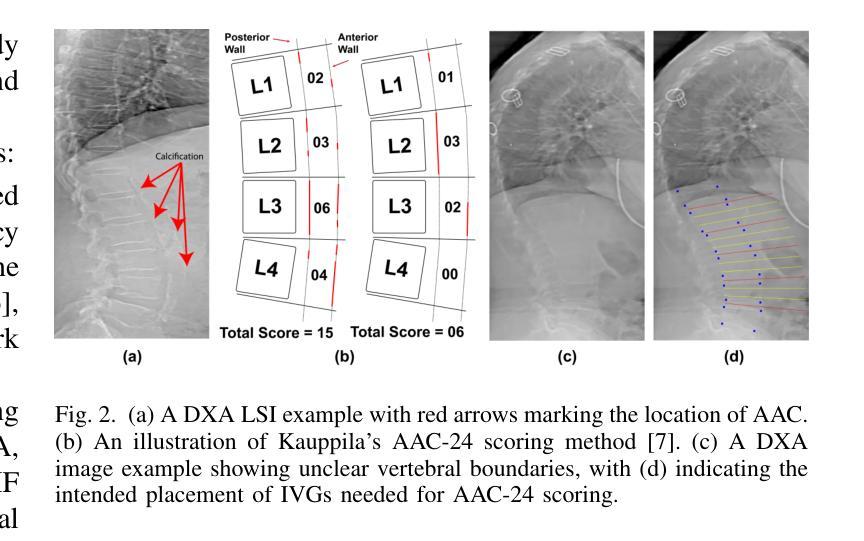
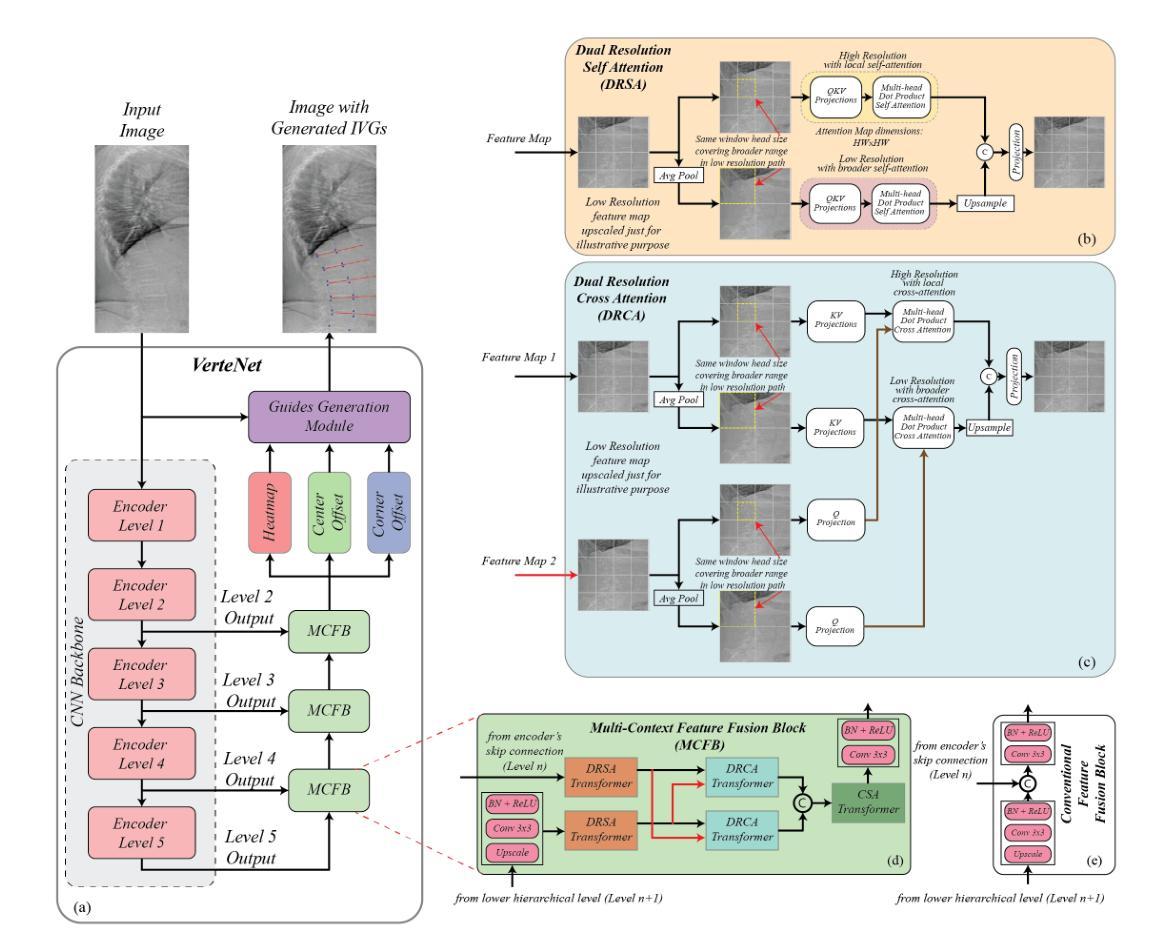
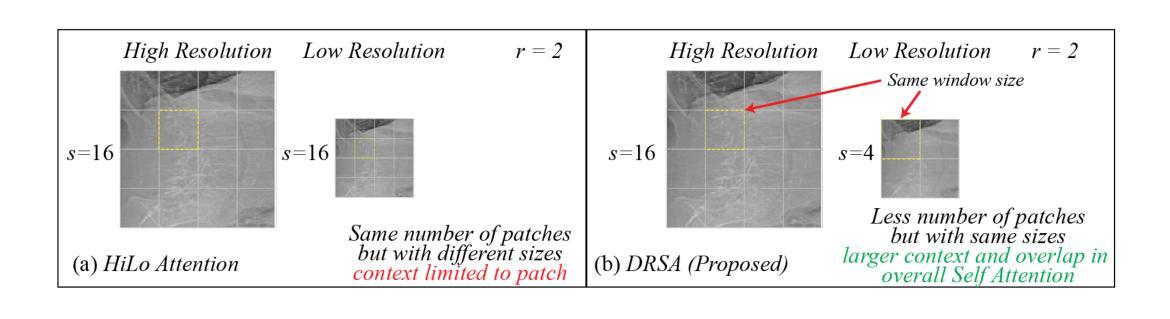
Lateral Spine Image (LSI) analysis is important for medical diagnosis, treatment planning, and detailed spinal health assessments. Although modalities like Computed Tomography and Digital X-ray Imaging are commonly used, Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) is often preferred due to lower radiation exposure, seamless capture, and cost-effectiveness. Accurate Vertebral Landmark Localization (VLL) on LSIs is important to detect spinal conditions like kyphosis and lordosis, as well as assessing Abdominal Aortic Calcification (AAC) using Inter-Vertebral Guides (IVGs). Nonetheless, few automated VLL methodologies have concentrated on DXA LSIs. We present VerteNet, a hybrid CNN-Transformer model featuring a novel dual-resolution attention mechanism in self and cross-attention domains, referred to as Dual Resolution Self-Attention (DRSA) and Dual Resolution Cross-Attention (DRCA). These mechanisms capture the diverse frequencies in DXA images by operating at two different feature map resolutions. Additionally, we design a Multi-Context Feature Fusion Block (MCFB) that efficiently integrates the features using DRSA and DRCA. We train VerteNet on 620 DXA LSIs from various machines and achieve superior results compared to existing methods. We also design an algorithm that utilizes VerteNet’s predictions in estimating the Region of Interest (ROI) to detect potential abdominal aorta cropping, where inadequate soft tissue hinders calcification assessment. Additionally, we present a small proof-of-concept study to show that IVGs generated from VLL information can improve inter-reader correlation in AAC scoring, addressing two key areas of disagreement in expert AAC-24 scoring: IVG placement and quality control for full abdominal aorta assessment. The code for this work can be found at https://github.com/zaidilyas89/VerteNet.
侧位脊柱图像(LSI)分析在医学诊断、治疗计划和详细的脊柱健康评估中具有重要意义。尽管计算机断层扫描和数字X射线成像等模式常用,但由于较低的辐射暴露、无缝捕获和成本效益,双能X射线吸收法(DXA)往往更受欢迎。在LSIs上进行准确的椎体地标定位(VLL)对于检测脊柱疾病如驼背和腰椎前凸很重要,同时还需使用椎间指南(IVGs)评估腹部主动脉钙化(AAC)。然而,很少有自动化VLL方法集中于DXA LSIs。我们提出了VerteNet,这是一个混合CNN-Transformer模型,具有一种新型的双分辨率注意力机制,在自我和交叉注意力域中被称为双分辨率自注意力(DRSA)和双分辨率交叉注意力(DRCA)。这些机制通过在两个不同的特征图分辨率上操作来捕捉DXA图像中的不同频率。此外,我们设计了一个多上下文特征融合块(MCFB),它有效地结合了使用DRSA和DRCA的特征。我们对来自各种机器的620个DXA LSI进行了VerteNet训练,并取得了比现有方法更好的结果。我们还设计了一种算法,利用VerteNet的预测来估计感兴趣区域(ROI),以检测潜在的腹部主动脉剪裁,其中软组织不足会妨碍钙化评估。此外,我们还进行了一项小型概念验证研究,以表明由VLL信息生成的IVG可以提高AAC评分的读者间相关性,解决专家AAC-24评分中的两个主要分歧领域:IVG放置和对整个腹部主动脉评估的质量控制。该工作的代码可在https://github.com/zaidilyas89/VerteNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages with 7 figures
Summary
医学图像中的侧位脊柱图像(LSI)分析对于医学诊断、治疗计划和详细的脊柱健康评估至关重要。虽然计算机断层扫描和数字X射线成像等模态是常用的,但由于较低的辐射暴露、无缝捕获和成本效益,双能X射线吸收法(DXA)常被优先选择。准确的椎体定位(VLL)对于检测脊柱疾病如驼背和脊柱侧凸以及评估腹部主动脉钙化(AAC)非常重要。本研究提出了一种混合CNN-Transformer模型VerteNet,具有新型的双分辨率注意力机制,用于DXA LSIs的VLL。该模型在多种机器上的620张DXA LSI图像上进行了训练,并取得了优越的结果。此外,还设计了一种利用VerteNet预测估计感兴趣区域(ROI)的算法,以检测因软组织不足导致的腹部主动脉裁剪问题。同时,本研究还展示了通过VLL信息生成的IVG可以提高AAC评分的读片间相关性。
Key Takeaways
1. Lateral Spine Image (LSI)分析在医学诊断、治疗计划和脊柱健康评估中具有重要作用。
2. 虽然存在多种成像方式,但Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA)因其低辐射暴露、无缝捕获和成本效益而常被采用。
3. 准确的椎体定位(VLL)对于诊断脊柱疾病和评估腹部主动脉钙化(AAC)至关重要。
4. 提出了一种混合CNN-Transformer模型VerteNet,具有双分辨率注意力机制用于DXA LSIs的VLL分析,取得了优越的结果。
5. VerteNet设计了一种算法用于估计感兴趣区域(ROI),以解决因软组织不足导致的腹部主动脉裁剪问题。
6. IVG的使用能提高AAC评分的读片间相关性,有助于解决专家评估中的两个问题:IVG放置和腹部主动脉全面评估的质量控制。
7. 该研究的代码已公开分享于GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

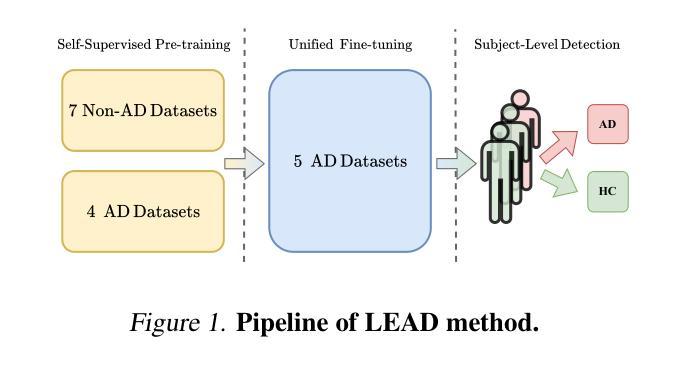
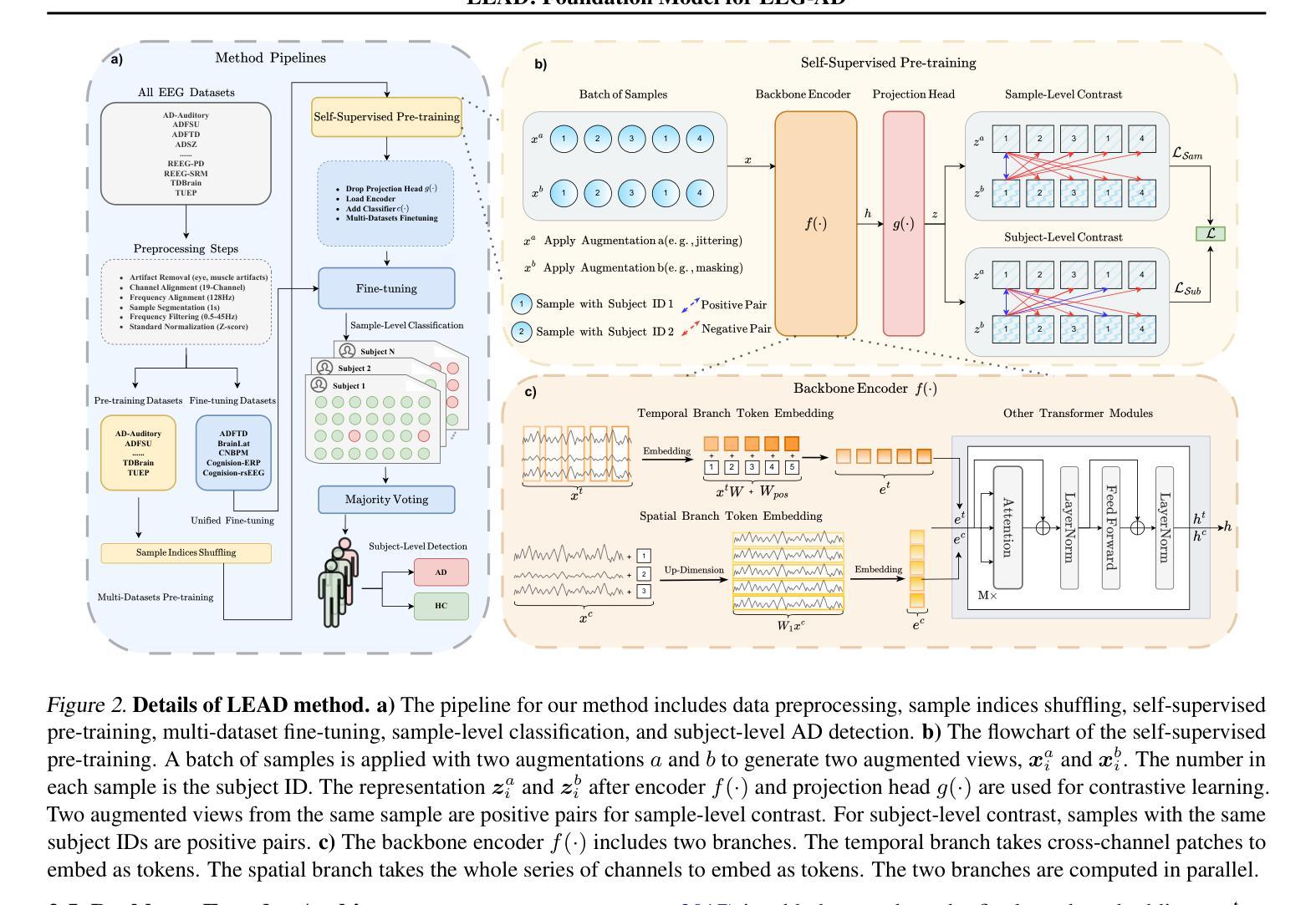
LEAD: Large Foundation Model for EEG-Based Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Authors:Yihe Wang, Nan Huang, Nadia Mammone, Marco Cecchi, Xiang Zhang
Electroencephalogram (EEG) provides a non-invasive, highly accessible, and cost-effective solution for Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) detection. However, existing methods, whether based on manual feature extraction or deep learning, face two major challenges: the lack of large-scale datasets for robust feature learning and evaluation, and poor detection performance due to inter-subject variations. To address these challenges, we curate an EEG-AD corpus containing 813 subjects, which forms the world’s largest EEG-AD dataset to the best of our knowledge. Using this unique dataset, we propose LEAD, the first large foundation model for EEG-based AD detection. Our method encompasses an entire pipeline, from data selection and preprocessing to self-supervised contrastive pretraining, fine-tuning, and key setups such as subject-independent evaluation and majority voting for subject-level detection. We pre-train the model on 11 EEG datasets and unified fine-tune it on 5 AD datasets. Our self-supervised pre-training design includes sample-level and subject-level contrasting to extract useful general EEG features. Fine-tuning is performed on 5 channel-aligned datasets together. The backbone encoder incorporates temporal and channel embeddings to capture features across both temporal and spatial dimensions. Our method demonstrates outstanding AD detection performance, achieving up to a 9.86% increase in F1 score at the sample-level and up to a 9.31% at the subject-level compared to state-of-the-art methods. The results of our model strongly confirm the effectiveness of contrastive pre-training and channel-aligned unified fine-tuning for addressing inter-subject variation. The source code is at https://github.com/DL4mHealth/LEAD.
脑电图(EEG)为阿尔茨海默病(AD)的检测提供了一种非侵入性、易于获取且成本效益高的解决方案。然而,现有方法,无论是基于手动特征提取还是深度学习,都面临两大挑战:缺乏用于稳健特征学习和评估的大规模数据集,以及因受试者间差异而导致的检测性能不佳。为了应对这些挑战,我们编纂了一个包含813名受试者的EEG-AD语料库,据我们所知,这是世界上最大的EEG-AD数据集。使用该独特数据集,我们提出了LEAD——首个用于基于EEG的AD检测的大型基础模型。我们的方法涵盖了从数据选择、预处理到自我监督对比预训练、微调以及主体级检测的独立评估和多投票等关键设置的整个流程。我们在11个EEG数据集上预训练模型,并在5个AD数据集上进行统一微调。我们的自我监督预训练设计包括样本级和受试者级的对比,以提取有用的通用EEG特征。微调是在5个通道对齐的数据集上一起进行的。主干编码器结合时间和通道嵌入,以捕获时间和空间两个维度的特征。我们的方法在AD检测方面表现出卓越的性能,与最先进的方法相比,样本级别的F1分数提高了9.86%,主体级别提高了9.31%。我们的模型结果强烈证明了对比预训练和通道对齐统一微调在解决受试者间差异方面的有效性。源代码位于https://github.com/DL4mHealth/LEAD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了利用脑电图(EEG)检测阿尔茨海默病(AD)的新方法。针对现有方法面临的挑战,如缺乏大规模数据集和主体间差异导致的检测性能不佳,本文构建了一个包含813名受试者的EEG-AD数据集,并基于此提出了首个用于EEG-AD检测的LEAD大型基础模型。通过样本级别和主体级别的对比进行自监督预训练,实现了出色的AD检测性能。与现有方法相比,F1得分最高可提高9.86%(样本级别)和9.31%(主体级别)。该模型可有效地处理主体间的差异,并具有潜力推动医学图像领域的发展。相关源代码已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
以下是关键观点的精简摘要:
- 该研究通过构建包含大量受试者的EEG-AD数据集解决了现有EEG检测AD方法的挑战。
- 提出LEAD模型,实现了EEG信号的全面处理流程,包括数据选择、预处理、自监督对比预训练等。
- 自监督预训练设计包含样本级别和主体级别的对比,有效提取通用EEG特征。
- 统一微调技术提高了模型在五个AD数据集上的性能。采用后端编码器实现时间嵌入和通道嵌入的融合处理,优化了时间、空间维度特征提取。
- LEAD模型在AD检测方面表现出卓越性能,与现有方法相比显著提高F1得分。
点此查看论文截图

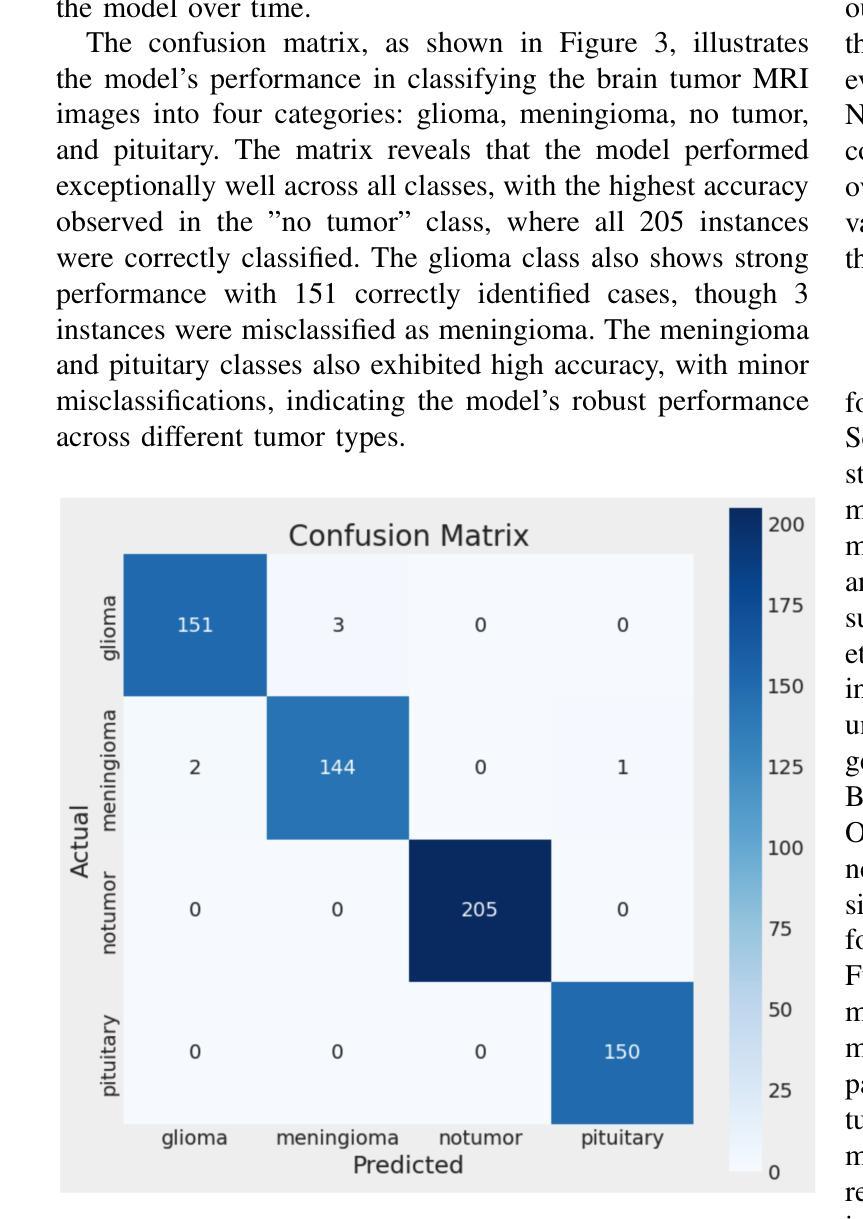
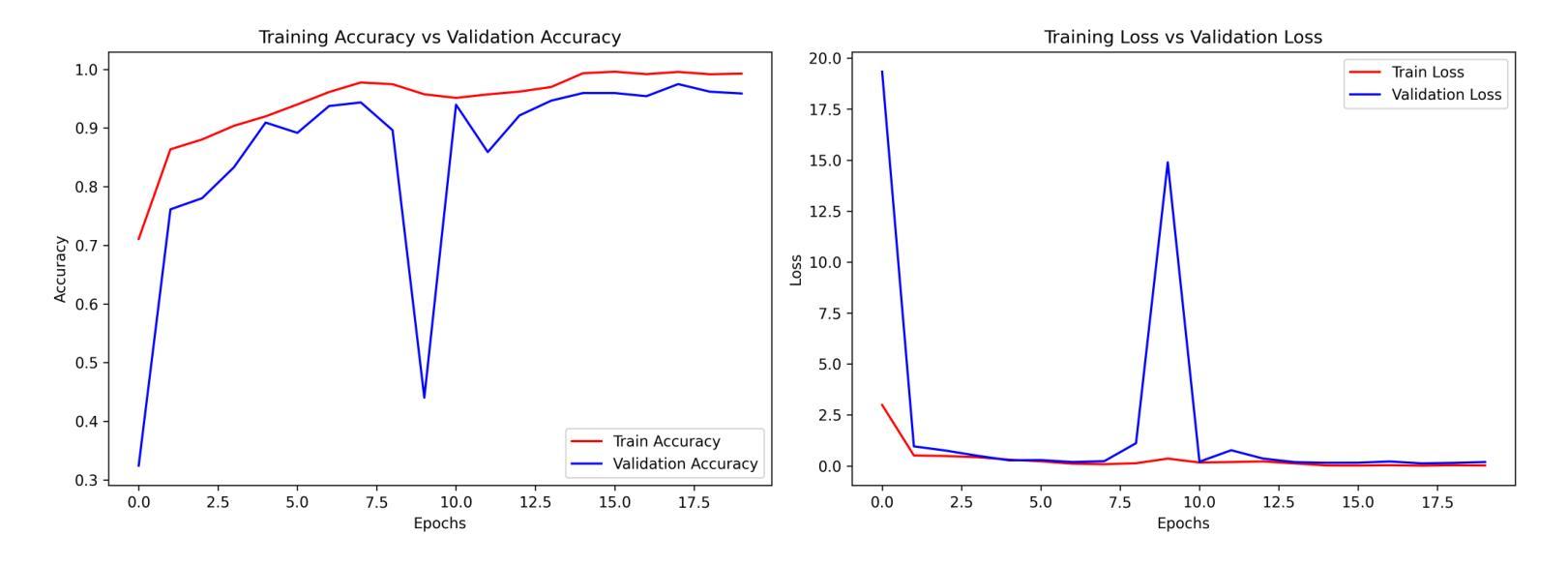
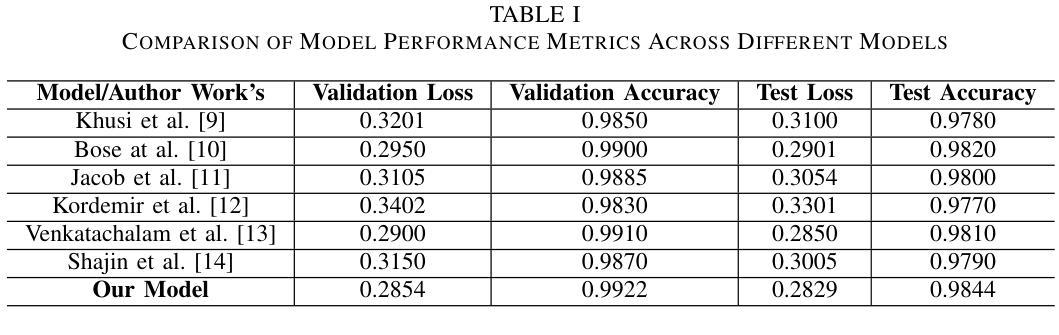
Efficient Brain Tumor Classification with Lightweight CNN Architecture: A Novel Approach
Authors:Priyam Ganguly, Akhilbaran Ghosh
Brain tumor classification using MRI images is critical in medical diagnostics, where early and accurate detection significantly impacts patient outcomes. While recent advancements in deep learning (DL), particularly CNNs, have shown promise, many models struggle with balancing accuracy and computational efficiency and often lack robustness across diverse datasets. To address these challenges, we propose a novel model architecture integrating separable convolutions and squeeze and excitation (SE) blocks, designed to enhance feature extraction while maintaining computational efficiency. Our model further incorporates batch normalization and dropout to prevent overfitting, ensuring stable and reliable performance. The proposed model is lightweight because it uses separable convolutions, which reduce the number of parameters, and incorporates global average pooling instead of fully connected layers to minimize computational complexity while maintaining high accuracy. Our model does better than other models by about 0.5% to 1.0% in accuracy and 1.5% to 2.5% in loss reduction, as shown by many experiments. It has a validation accuracy of 99.22% and a test accuracy of 98.44%. These results highlight the model’s ability to generalize effectively across different brain tumour types, offering a robust tools for clinical applications. Our work sets a new benchmark in the field, providing a foundation for future research in optimizing the accuracy and efficiency of DL models for medical image analysis.
使用MRI图像对脑肿瘤进行分类在医学诊断中至关重要,早期和准确的检测对患者的治疗效果具有重大影响。虽然最近深度学习(DL)的进展,特别是卷积神经网络(CNN)显示出良好的前景,但许多模型在平衡准确性和计算效率方面存在困难,并且在不同数据集之间缺乏稳健性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的模型架构,融合了可分离卷积和挤压激发(SE)块,旨在提高特征提取能力的同时保持计算效率。我们的模型还结合了批量归一化和丢弃法,以防止过拟合,确保稳定和可靠的性能。所提出模型的重量较轻,因为它使用了可分离卷积,减少了参数数量,并采用了全局平均池化而不是全连接层,以最小化计算复杂性同时保持高准确性。我们的模型在准确性上比其他模型高出约0.5%至1%,在损失减少方面高出约1.5%至2.5%,这些结果经过多次实验验证。它具有99.22%的验证准确率和98.44%的测试准确率。这些结果突显了该模型在不同脑肿瘤类型之间的有效泛化能力,为临床应用提供了稳健的工具。我们的工作为该领域设定了新的基准,为优化医学图像分析深度学习模型的准确性和效率提供了研究基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in FMLDS 2024
Summary
利用MRI图像进行脑肿瘤分类是医学诊断中的关键,早期准确检测对病人预后有重要影响。针对深度学习模型在平衡准确性和计算效率方面的挑战,我们提出了一种新型模型架构,集成可分卷积和挤压激发(SE)块,旨在增强特征提取的同时保持计算效率。模型还融入批量归一化和dropout以防止过拟合,确保稳定和可靠的性能。与现有模型相比,我们的模型在准确性上提高了约0.5%~1.0%,在损失减少上提高了约1.5%~2.5%。
Key Takeaways
- 脑肿瘤分类对医学诊断和患者预后至关重要。
- 深度学习,尤其是卷积神经网络(CNN),在医学图像分析中有广泛应用前景。
- 现有深度学习模型在平衡准确性和计算效率方面存在挑战。
- 提出的新型模型架构集成可分卷积和挤压激发(SE)块,以增强特征提取能力并保持计算效率。
- 模型采用批量归一化和dropout技术,防止过拟合,确保稳定和可靠性能。
- 与其他模型相比,该模型在准确性和损失减少方面表现更优。
点此查看论文截图

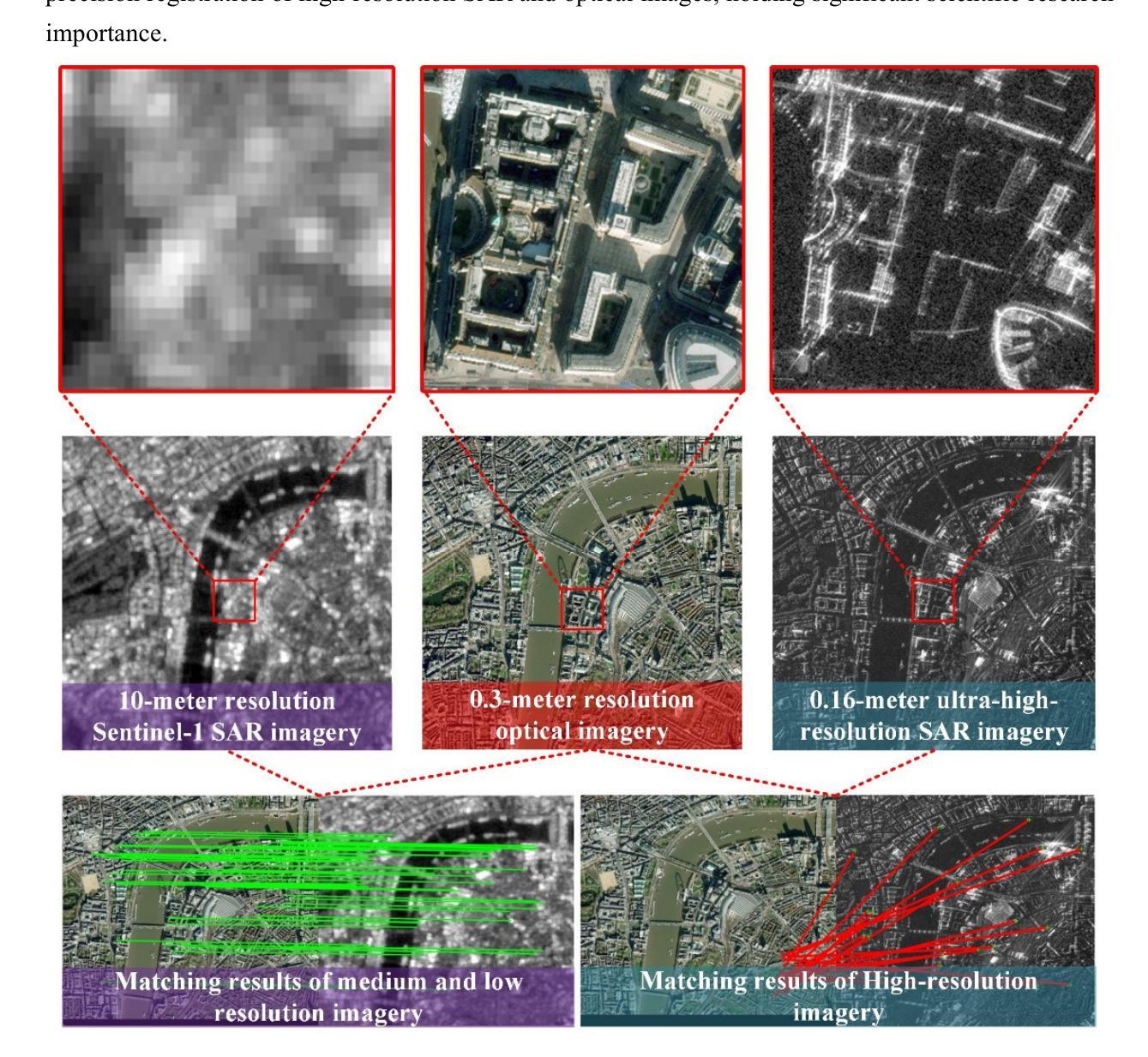
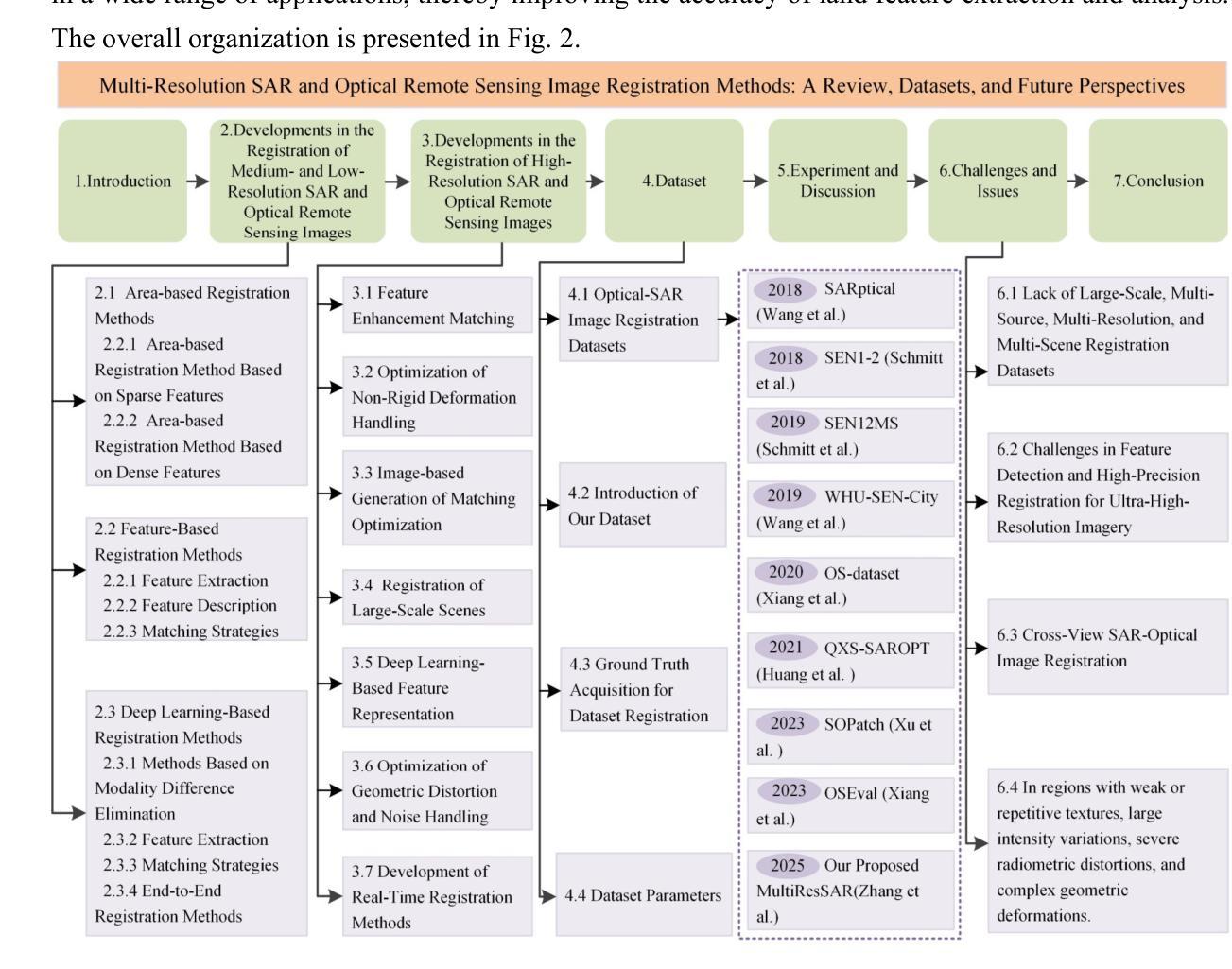
Multi-Resolution SAR and Optical Remote Sensing Image Registration Methods: A Review, Datasets, and Future Perspectives
Authors:Wenfei Zhang, Ruipeng Zhao, Yongxiang Yao, Yi Wan, Peihao Wu, Jiayuan Li, Yansheng Li, Yongjun Zhang
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical image registration is essential for remote sensing data fusion, with applications in military reconnaissance, environmental monitoring, and disaster management. However, challenges arise from differences in imaging mechanisms, geometric distortions, and radiometric properties between SAR and optical images. As image resolution increases, fine SAR textures become more significant, leading to alignment issues and 3D spatial discrepancies. Two major gaps exist: the lack of a publicly available multi-resolution, multi-scene registration dataset and the absence of systematic analysis of current methods. To address this, the MultiResSAR dataset was created, containing over 10k pairs of multi-source, multi-resolution, and multi-scene SAR and optical images. Sixteen state-of-the-art algorithms were tested. Results show no algorithm achieves 100% success, and performance decreases as resolution increases, with most failing on sub-meter data. XoFTR performs best among deep learning methods (40.58%), while RIFT performs best among traditional methods (66.51%). Future research should focus on noise suppression, 3D geometric fusion, cross-view transformation modeling, and deep learning optimization for robust registration of high-resolution SAR and optical images. The dataset is available at https://github.com/betterlll/Multi-Resolution-SAR-dataset-.
合成孔径雷达(SAR)和光学图像配准对于遥感数据融合至关重要,在军事侦察、环境监测和灾害管理等领域具有广泛的应用。然而,由于SAR和光学图像在成像机制、几何失真和辐射特性等方面的差异,带来了挑战。随着图像分辨率的提高,SAR的精细纹理变得更加重要,导致对齐问题和3D空间差异。目前存在两个主要空白:缺乏可公开访问的多分辨率、多场景配准数据集,以及缺乏对当前方法的系统分析。为了解决这一问题,创建了MultiResSAR数据集,包含超过1h千对多源、多分辨率、多场景的SAR和光学图像。对十六种最先进算法进行了测试。结果表明,没有算法能达到百分之百的成功率,随着分辨率的提高,性能下降,大多数算法在亚米级数据上失败。在深度学习方法中,XoFTR表现最佳(40.58%),而在传统方法中,RIFT表现最佳(66.51%)。未来的研究应专注于噪声抑制、3D几何融合、跨视图转换建模以及深度学习优化,以实现高分辨率SAR和光学图像的稳健配准。数据集可在https://github.com/betterlll/Multi-Resolution-SAR-dataset-上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 48 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了合成孔径雷达(SAR)和光学图像配准在遥感数据融合中的关键作用,以及其在军事侦察、环境监测和灾害管理中的应用。文章指出了SAR和光学图像之间的差异所带来的挑战,如成像机制、几何失真和辐射特性。为应对这些挑战,创建了MultiResSAR数据集,包含超过10k对的SAR和光学图像。测试了16种最新算法,结果显示没有算法达到100%的成功率,随着分辨率的提高,性能下降,特别是在亚米级数据上大多数算法失败。最好的深度学习方法是XoFTR(40.58%),而传统方法中RIFT表现最佳(66.51%)。未来研究应关注噪声抑制、3D几何融合、跨视图转换建模以及深度学习优化,以实现高分辨率SAR和光学图像的稳健配准。
Key Takeaways
- SAR和光学图像配准对于遥感数据融合至关重要,在军事侦察、环境监测和灾害管理中具有广泛应用。
- SAR和光学图像之间的差异导致配准挑战,如成像机制、几何失真和辐射特性。
- 缺少多分辨率、多场景注册数据集以及对当前方法的系统分析是现有的主要问题。
- 创建了MultiResSAR数据集,包含超过10k对的SAR和光学图像。
- 测试了16种最新算法,没有一种达到100%的成功率。
- 随着图像分辨率的提高,配准性能下降,特别是在亚米级数据上。
点此查看论文截图



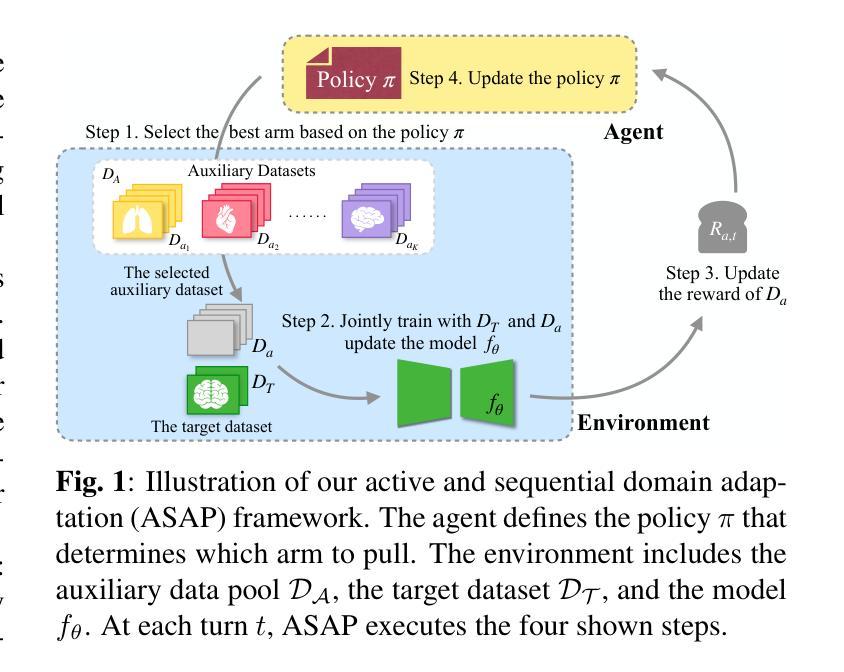
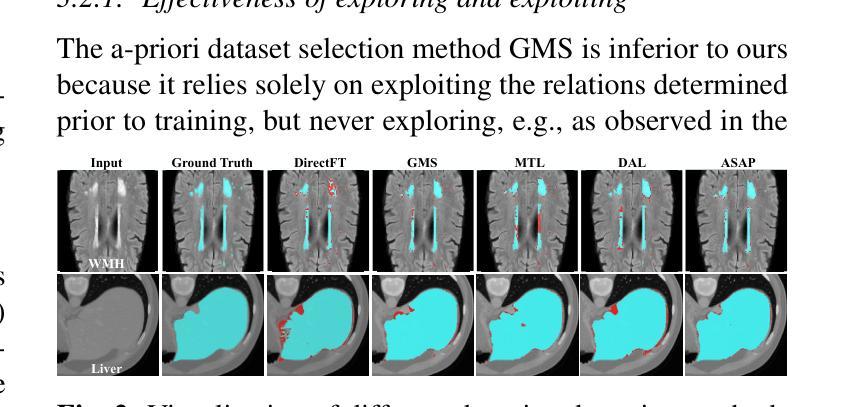
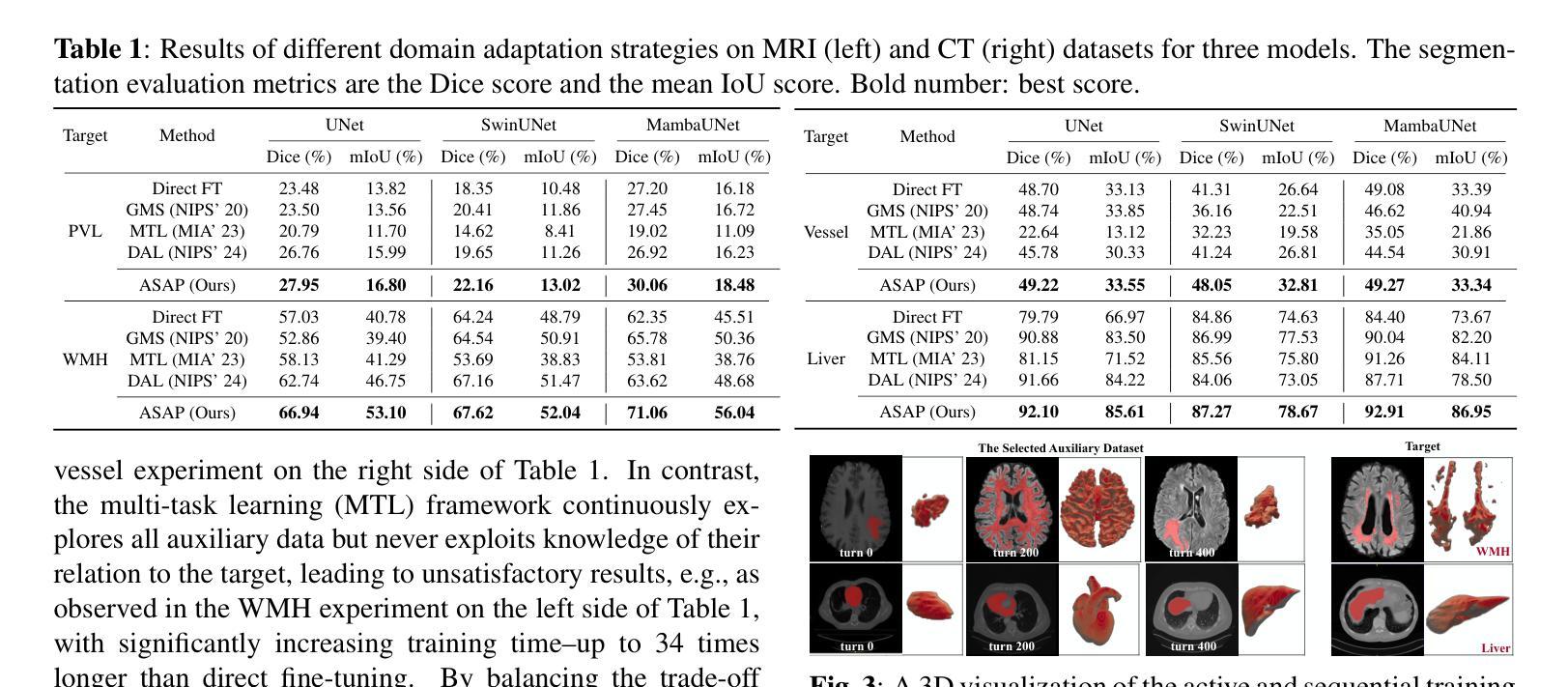
Adapting Foundation Models for Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation: Actively and Sequentially
Authors:Jingyun Yang, Guoqing Zhang, Jingge Wang, Yang Li
Recent advances in foundation models have brought promising results in computer vision, including medical image segmentation. Fine-tuning foundation models on specific low-resource medical tasks has become a standard practice. However, ensuring reliable and robust model adaptation when the target task has a large domain gap and few annotated samples remains a challenge. Previous few-shot domain adaptation (FSDA) methods seek to bridge the distribution gap between source and target domains by utilizing auxiliary data. The selection and scheduling of auxiliaries are often based on heuristics, which can easily cause negative transfer. In this work, we propose an Active and Sequential domain AdaPtation (ASAP) framework for dynamic auxiliary dataset selection in FSDA. We formulate FSDA as a multi-armed bandit problem and derive an efficient reward function to prioritize training on auxiliary datasets that align closely with the target task, through a single-round fine-tuning. Empirical validation on diverse medical segmentation datasets demonstrates that our method achieves favorable segmentation performance, significantly outperforming the state-of-the-art FSDA methods, achieving an average gain of 27.75% on MRI and 7.52% on CT datasets in Dice score. Code is available at the git repository: https://github.com/techicoco/ASAP.
最近的进展为基于模型的计算机视觉领域带来了有希望的结果,包括医学图像分割。对特定低资源医学任务进行微调基础模型已经成为一种标准做法。然而,当目标任务具有较大的领域差距和较少的标注样本时,确保可靠和稳健的模型适应仍然是一个挑战。之前的少样本域自适应(FSDA)方法试图通过利用辅助数据来缩小源域和目标域之间的分布差距。辅助数据的选择和调度通常基于启发式方法,这很容易导致负迁移。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于FSDA中动态辅助数据集选择的主动序贯域适应(ASAP)框架。我们将FSDA制定为多臂老虎机问题,并制定了有效的奖励函数,以优先训练与目标任务紧密相关的辅助数据集,通过一轮微调实现这一目标。在多样化的医学分割数据集上的经验验证表明,我们的方法实现了有利的分割性能,显著优于最新的FSDA方法,在MRI和CT数据集上的Dice得分平均提高了27.75%和7.52%。代码可在git仓库中找到:https://github.com/techicoco/ASAP。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要研究了基于计算机视觉的医疗图像分割任务中的域适应问题。针对具有大量域间隙和少量标注样本的目标任务,提出了一种新的主动序贯域适应(ASAP)框架进行动态辅助数据集选择。该方法通过制定多臂老虎机问题来动态选择辅助数据集,并通过单轮微调实现与目标任务紧密对齐的辅助训练,实现了较好的医学图像分割性能。该方法平均提升了MRI数据集的Dice分数达到27.75%,并提高了CT数据集的Dice分数达到7.52%。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对医疗图像分割任务的域适应问题。
- 提出了一种新的主动序贯域适应(ASAP)框架进行动态辅助数据集选择。
- 将问题建模为多臂老虎机问题,制定高效奖励函数选择与目标任务对齐的辅助数据集。
- 通过单轮微调实现了与目标任务紧密对齐的辅助训练。
- 在多样的医学分割数据集上进行了实证研究,验证了该方法的有效性。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法实现了较好的医学图像分割性能,平均提升了MRI数据集的Dice分数达到27.75%,并提高了CT数据集的Dice分数达到7.52%。
点此查看论文截图


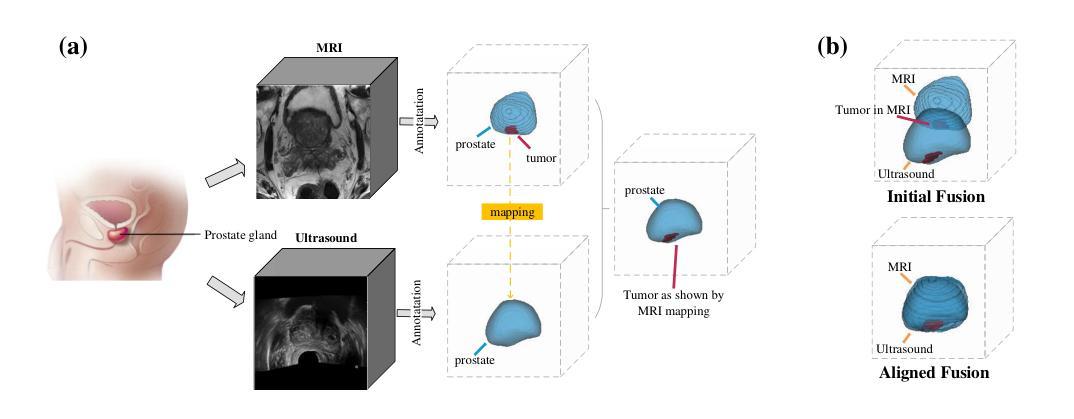
Registration-Enhanced Segmentation Method for Prostate Cancer in Ultrasound Images
Authors:Shengtian Sang, Hassan Jahanandish, Cynthia Xinran Li, Indrani Bhattachary, Jeong Hoon Lee, Lichun Zhang, Sulaiman Vesal, Pejman Ghanouni, Richard Fan, Geoffrey A. Sonn, Mirabela Rusu
Prostate cancer is a major cause of cancer-related deaths in men, where early detection greatly improves survival rates. Although MRI-TRUS fusion biopsy offers superior accuracy by combining MRI’s detailed visualization with TRUS’s real-time guidance, it is a complex and time-intensive procedure that relies heavily on manual annotations, leading to potential errors. To address these challenges, we propose a fully automatic MRI-TRUS fusion-based segmentation method that identifies prostate tumors directly in TRUS images without requiring manual annotations. Unlike traditional multimodal fusion approaches that rely on naive data concatenation, our method integrates a registration-segmentation framework to align and leverage spatial information between MRI and TRUS modalities. This alignment enhances segmentation accuracy and reduces reliance on manual effort. Our approach was validated on a dataset of 1,747 patients from Stanford Hospital, achieving an average Dice coefficient of 0.212, outperforming TRUS-only (0.117) and naive MRI-TRUS fusion (0.132) methods, with significant improvements (p $<$ 0.01). This framework demonstrates the potential for reducing the complexity of prostate cancer diagnosis and provides a flexible architecture applicable to other multimodal medical imaging tasks.
前列腺癌是男性癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,早期发现可以大大提高存活率。虽然MRI-TRUS融合活检通过结合MRI的详细可视化和TRUS的实时指导提供了更高的准确性,但它是一个复杂且耗时的程序,严重依赖于手动注释,从而导致潜在误差。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于全自动MRI-TRUS融合的分割方法,该方法可直接在TRUS图像中识别前列腺肿瘤,无需手动注释。与传统的多模态融合方法不同,这些方法依赖于幼稚的数据拼接,我们的方法整合了注册分割框架,以对齐和利用MRI和TRUS模态之间的空间信息。这种对齐提高了分割精度,并减少了对手动操作的依赖。我们的方法已在斯坦福医院的1747例患者数据集上进行了验证,平均Dice系数为0.212,优于仅使用TRUS(0.117)和简单MRI-TRUS融合(0.132)的方法,具有显著改进(p<0.01)。该框架展示了降低前列腺癌诊断复杂性的潜力,并提供了适用于其他多模态医学成像任务的灵活架构。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种全自动MRI-TRUS融合分割方法,用于直接识别TRUS图像中的前列腺肿瘤,无需手动注释。该方法通过注册分割框架实现对MRI和TRUS模态的空间信息对齐和利用,提高分割精度,减少对人工操作的依赖。在Stanford医院的患者数据集上进行验证,平均Dice系数为0.212,优于仅使用TRUS(0.117)和简单的MRI-TRUS融合方法(0.132),具有显著的改进(p < 0.01)。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究针对前列腺癌诊断中的挑战,提出了一种全自动MRI-TRUS融合分割方法。
- 该方法能够在TRUS图像中直接识别前列腺肿瘤,无需手动注释。
- 通过注册分割框架实现对MRI和TRUS模态的空间信息对齐和利用。
- 方法在Stanford医院的患者数据集上进行了验证,平均Dice系数为0.212。
- 与仅使用TRUS和简单的MRI-TRUS融合方法相比,该方法具有更高的分割精度。
- 该方法具有显著的改进效果(p < 0.01),为减少前列腺癌诊断的复杂性提供了潜力。
点此查看论文截图

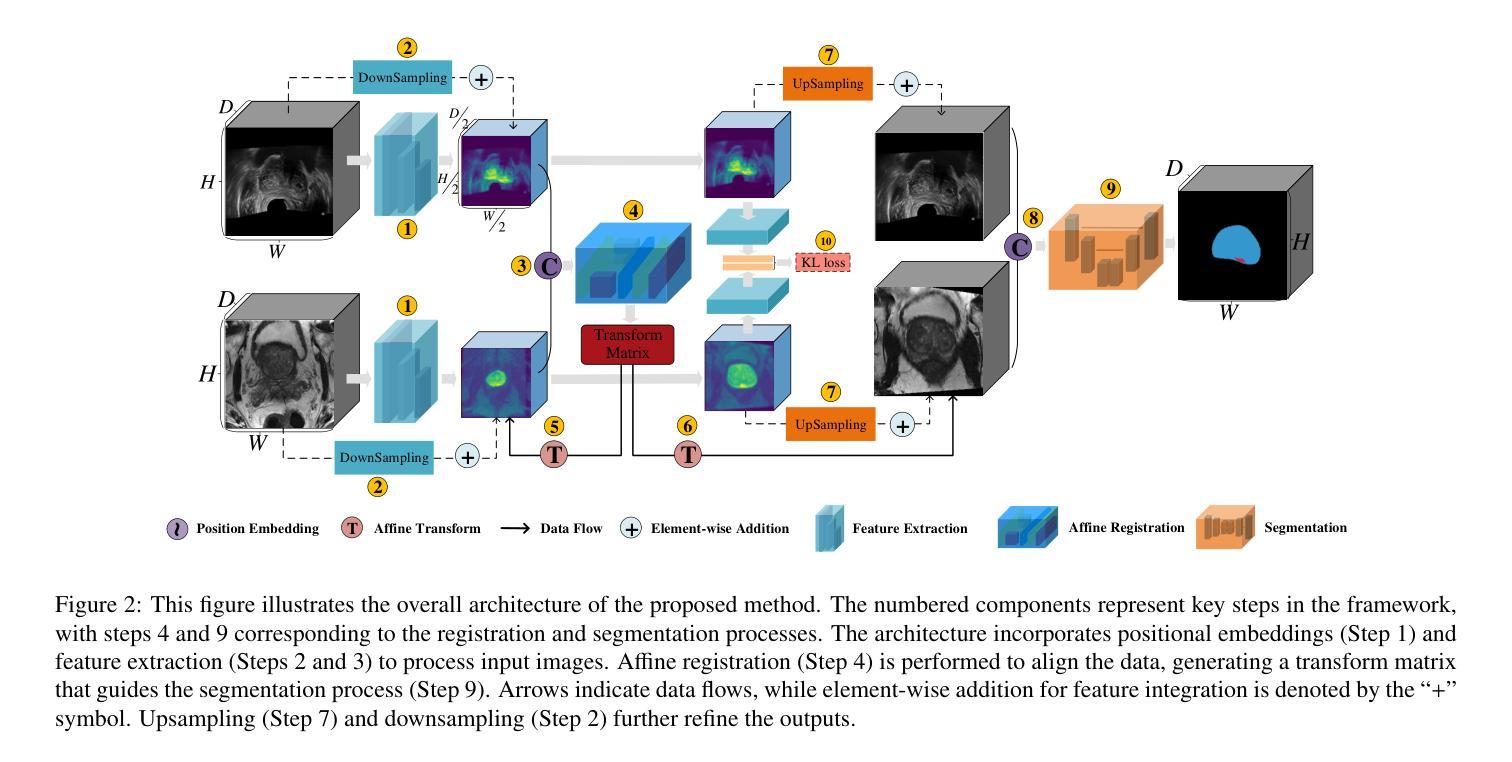
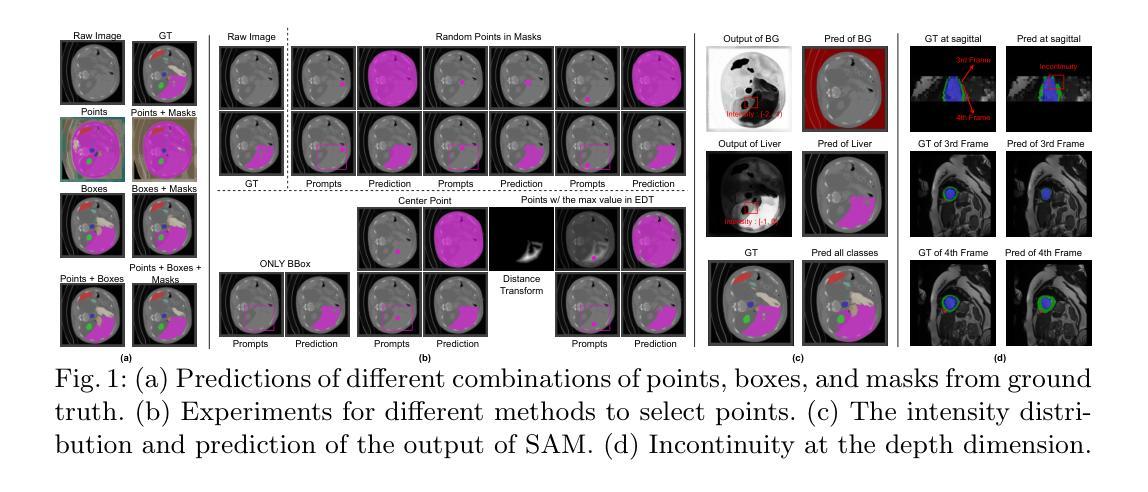
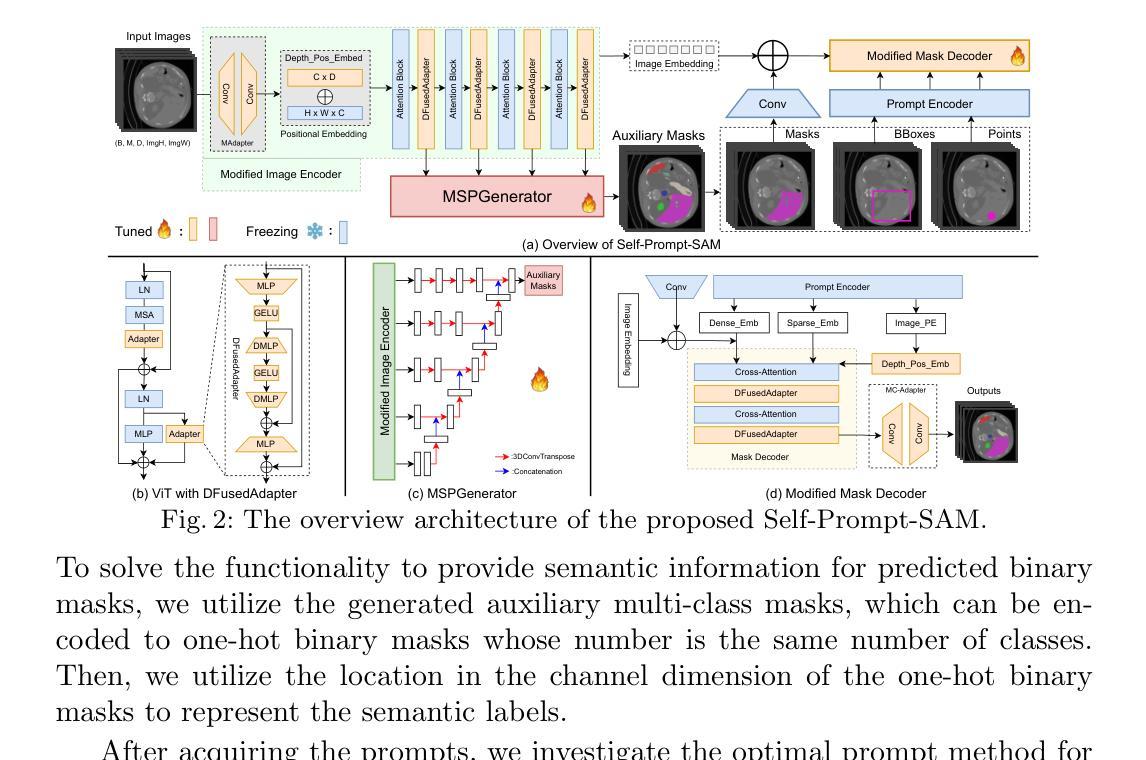
Self-Prompt SAM: Medical Image Segmentation via Automatic Prompt SAM Adaptation
Authors:Bin Xie, Hao Tang, Dawen Cai, Yan Yan, Gady Agam
Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated impressive zero-shot performance and brought a range of unexplored capabilities to natural image segmentation tasks. However, as a very important branch of image segmentation, the performance of SAM remains uncertain when applied to medical image segmentation due to the significant differences between natural images and medical images. Meanwhile, it is harsh to meet the SAM’s requirements of extra prompts provided, such as points or boxes to specify medical regions. In this paper, we propose a novel self-prompt SAM adaptation framework for medical image segmentation, named Self-Prompt-SAM. We design a multi-scale prompt generator combined with the image encoder in SAM to generate auxiliary masks. Then, we use the auxiliary masks to generate bounding boxes as box prompts and use Distance Transform to select the most central points as point prompts. Meanwhile, we design a 3D depth-fused adapter (DfusedAdapter) and inject the DFusedAdapter into each transformer in the image encoder and mask decoder to enable pre-trained 2D SAM models to extract 3D information and adapt to 3D medical images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and outperforms nnUNet by 2.3% on AMOS2022, 1.6% on ACDCand 0.5% on Synapse datasets.
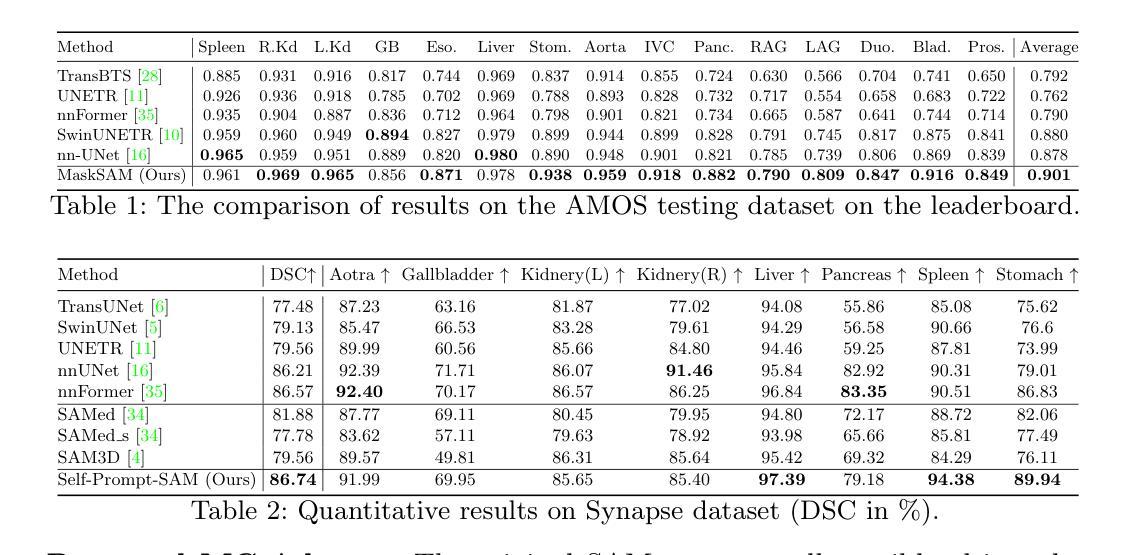
Segment Anything Model(SAM)已经展示了令人印象深刻的零样本性能,并为自然图像分割任务带来了一系列未探索的能力。然而,作为图像分割的一个重要分支,SAM在应用于医学图像分割时的表现仍然不确定,因为自然图像和医学图像之间存在显著差异。同时,满足SAM对额外提示的要求是很严格的,如用于指定医疗区域的点或框。在本文中,我们提出了一个用于医学图像分割的新型Self-Prompt-SAM自提示SAM适应框架。我们设计了一个多尺度提示生成器,结合SAM中的图像编码器生成辅助掩码。然后,我们使用辅助掩码生成边界框作为框提示,并使用距离变换选择最中心点作为点提示。同时,我们设计了一个3D深度融合适配器(DfusedAdapter),并将其注入图像编码器和掩码解码器中的每个转换器,使预训练的2D SAM模型能够提取3D信息并适应3D医学图像。大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的技术性能,在AMOS2022数据集上比nnUNet高出2.3%,在ACDC数据集上高出1.6%,在Synapse数据集上高出0.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAM模型在自然图像分割任务中展现出零样本性能,但其在医学图像分割中的应用性能尚不确定。本文提出一种名为Self-Prompt-SAM的新型自适应框架,通过设计多尺度提示生成器与SAM的图像编码器结合,生成辅助掩膜来产生边界框和点提示。同时,设计3D深度融合适配器(DfusedAdapter),注入图像编码器和掩膜解码器的每个转换器中,使预训练的2D SAM模型能够提取3D信息并适应3D医学图像。实验证明,该方法达到了最新技术水平并在多个数据集上超过了nnUNet。
Key Takeaways
- SAM模型在自然图像分割中表现出零样本性能。
- SAM在医学图像分割中的应用性能尚不确定。
- 提出了名为Self-Prompt-SAM的新型自适应框架用于医学图像分割。
- 设计了多尺度提示生成器以生成辅助掩膜,从而产生边界框和点提示。
- 使用了DfusedAdapter,使SAM模型能够适应3D医学图像。
- 该方法在多个数据集上的性能超过了nnUNet。
点此查看论文截图

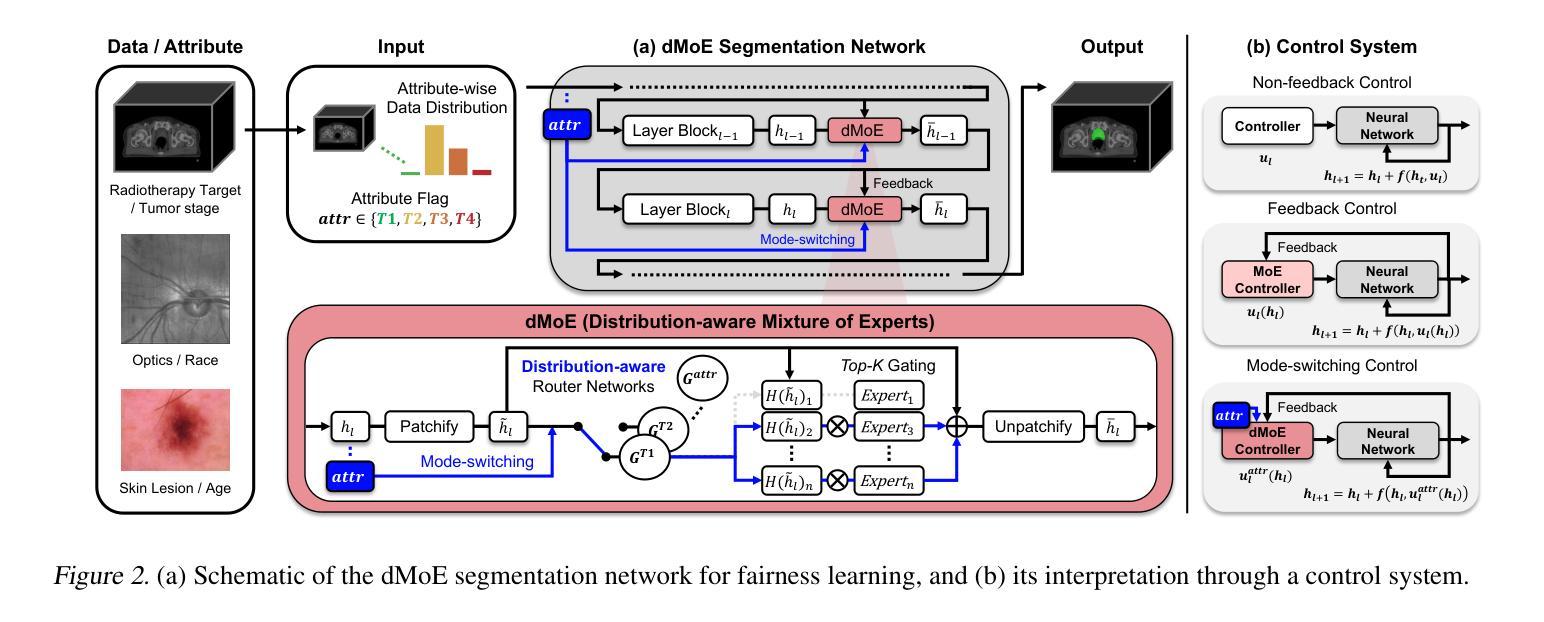
Distribution-aware Fairness Learning in Medical Image Segmentation From A Control-Theoretic Perspective
Authors:Yujin Oh, Pengfei Jin, Sangjoon Park, Sekeun Kim, Siyeop Yoon, Kyungsang Kim, Jin Sung Kim, Xiang Li, Quanzheng Li
Ensuring fairness in medical image segmentation is critical due to biases in imbalanced clinical data acquisition caused by demographic attributes (e.g., age, sex, race) and clinical factors (e.g., disease severity). To address these challenges, we introduce Distribution-aware Mixture of Experts (dMoE), inspired by optimal control theory. We provide a comprehensive analysis of its underlying mechanisms and clarify dMoE’s role in adapting to heterogeneous distributions in medical image segmentation. Furthermore, we integrate dMoE into multiple network architectures, demonstrating its broad applicability across diverse medical image analysis tasks. By incorporating demographic and clinical factors, dMoE achieves state-of-the-art performance on two 2D benchmark datasets and a 3D in-house dataset. Our results highlight the effectiveness of dMoE in mitigating biases from imbalanced distributions, offering a promising approach to bridging control theory and medical image segmentation within fairness learning paradigms. The source code will be made available.
确保医学图像分割的公平性是至关重要的,因为由于人口统计学属性(如年龄、性别、种族)和临床因素(如疾病严重程度)导致的不平衡临床数据采集中的偏见。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了受最优控制理论启发的“分布感知专家混合(dMoE)”方法。我们对dMoE的内在机制进行了综合分析,并明确了其在医学图像分割中适应异质分布的作用。此外,我们将dMoE集成到多种网络架构中,证明了其在不同医学图像分析任务中的广泛应用性。通过结合人口统计学和临床因素,dMoE在两个二维基准数据集和一个三维内部数据集中实现了最先进的性能。我们的结果突出了dMoE在缓解不平衡分布中的偏见方面的有效性,为在公平学习范式内将控制理论与医学图像分割之间架起桥梁提供了有前途的方法。源代码将提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 3 figures, 9 tables
Summary
本文强调了在医学图像分割中确保公平性的重要性,因为临床数据获取中的不平衡会导致由人口统计学属性(如年龄、性别、种族)和临床因素(如疾病严重程度)产生的偏见。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了基于最优控制理论的分布感知混合专家(dMoE)。本文对其内在机制进行了综合分析,并明确了dMoE在适应医学图像分割中的异质分布中的作用。此外,我们将dMoE集成到多种网络架构中,证明了其在不同医学图像分析任务中的广泛应用性。通过结合人口统计学和临床因素,dMoE在两个2D基准数据集和一个3D内部数据集中实现了最先进的性能。结果表明,dMoE在缓解由分布不平衡导致的偏见方面非常有效,为控制理论与医学图像分割在公平学习范式中的融合提供了有前途的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中存在由数据不平衡导致的偏见问题,这些问题可能源于人口统计学属性和临床因素。
- 为了解决这些问题,引入了分布感知混合专家(dMoE)方法,该方法受到最优控制理论的启发。
- dMoE能够综合处理医学图像分割中的异质分布问题。
- dMoE被成功集成到多种网络架构中,证明了其在不同医学图像分析任务中的广泛应用性。
- 通过结合人口统计学和临床因素,dMoE在多个数据集中实现了最先进的性能。
- dMoE在缓解由分布不平衡导致的偏见方面非常有效。
点此查看论文截图

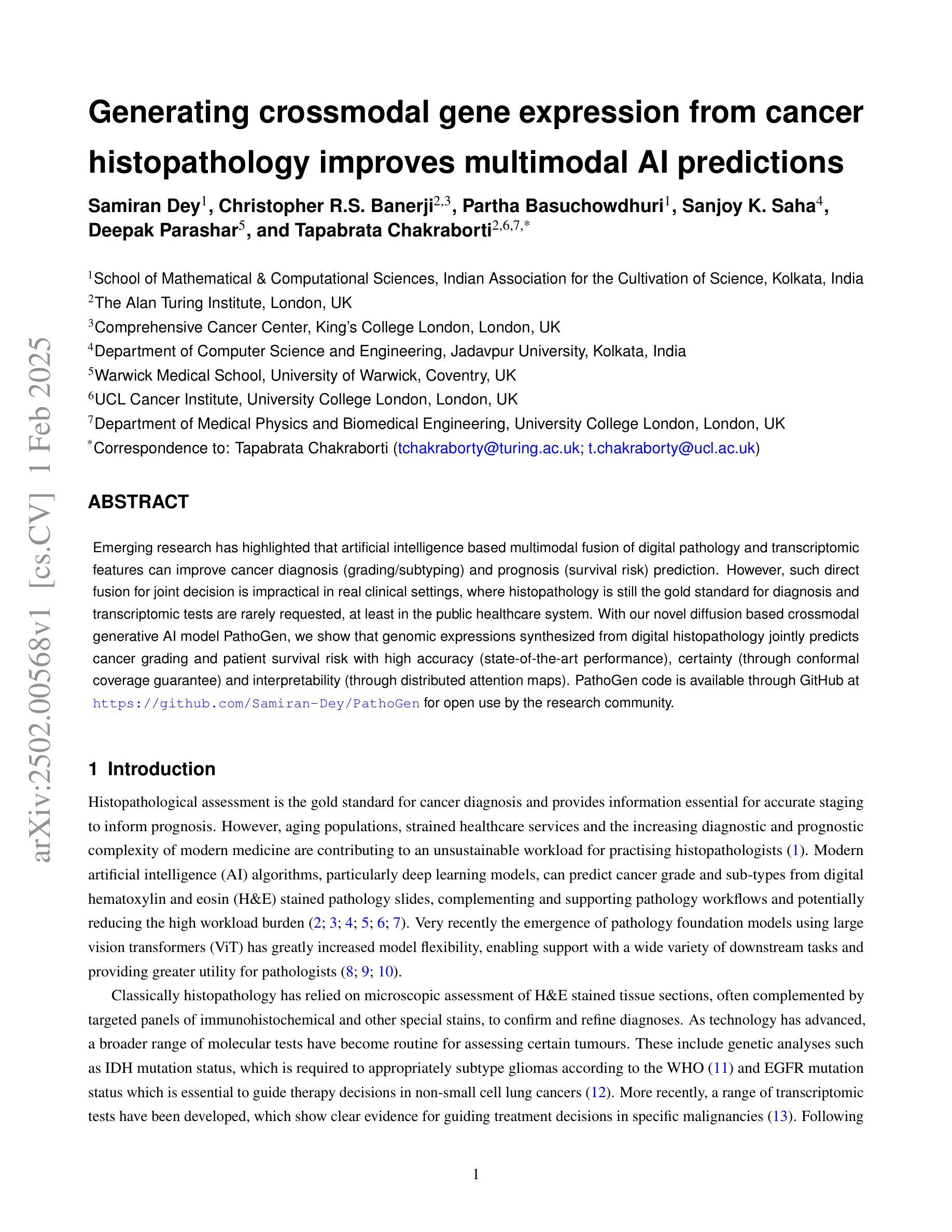
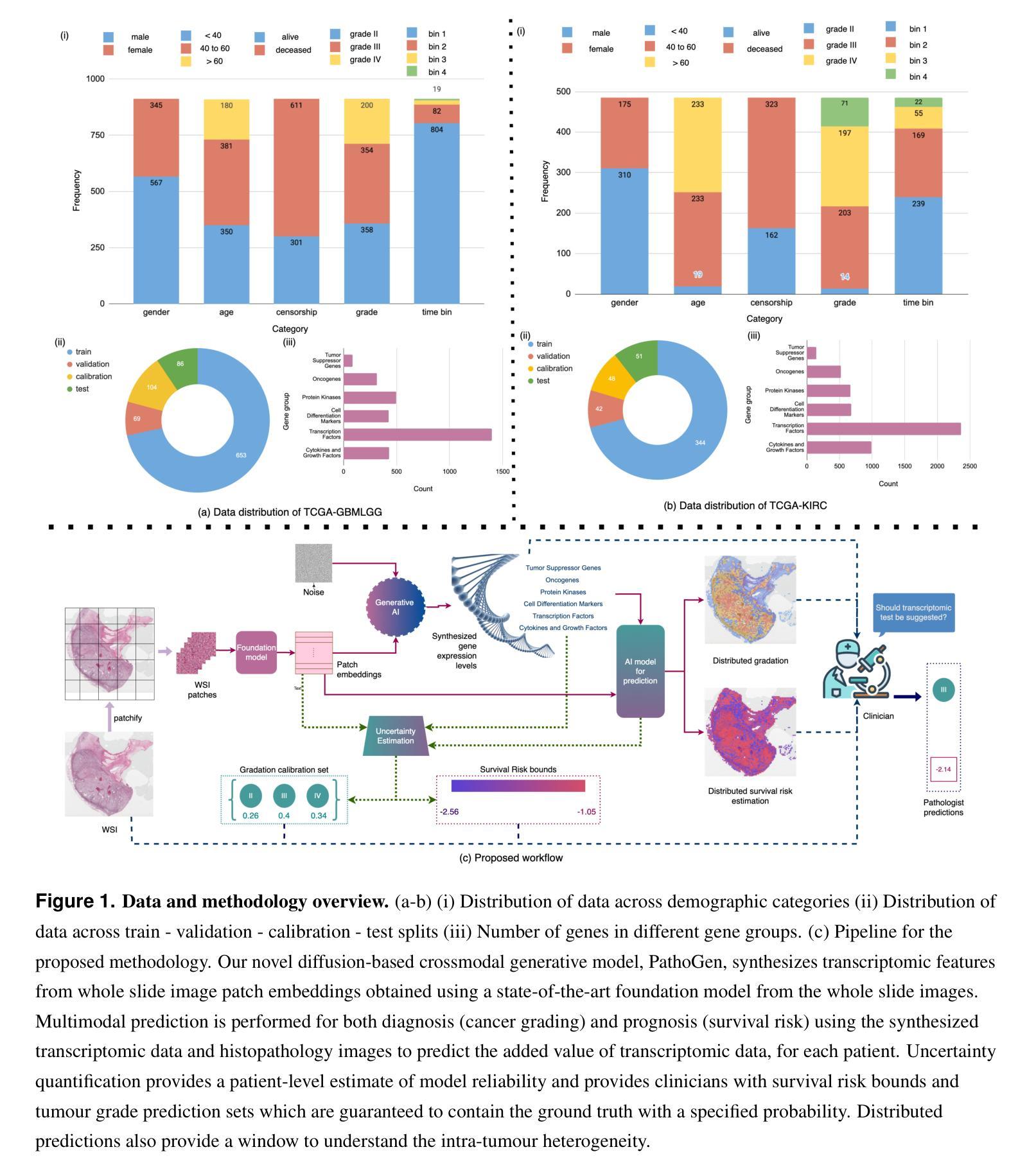
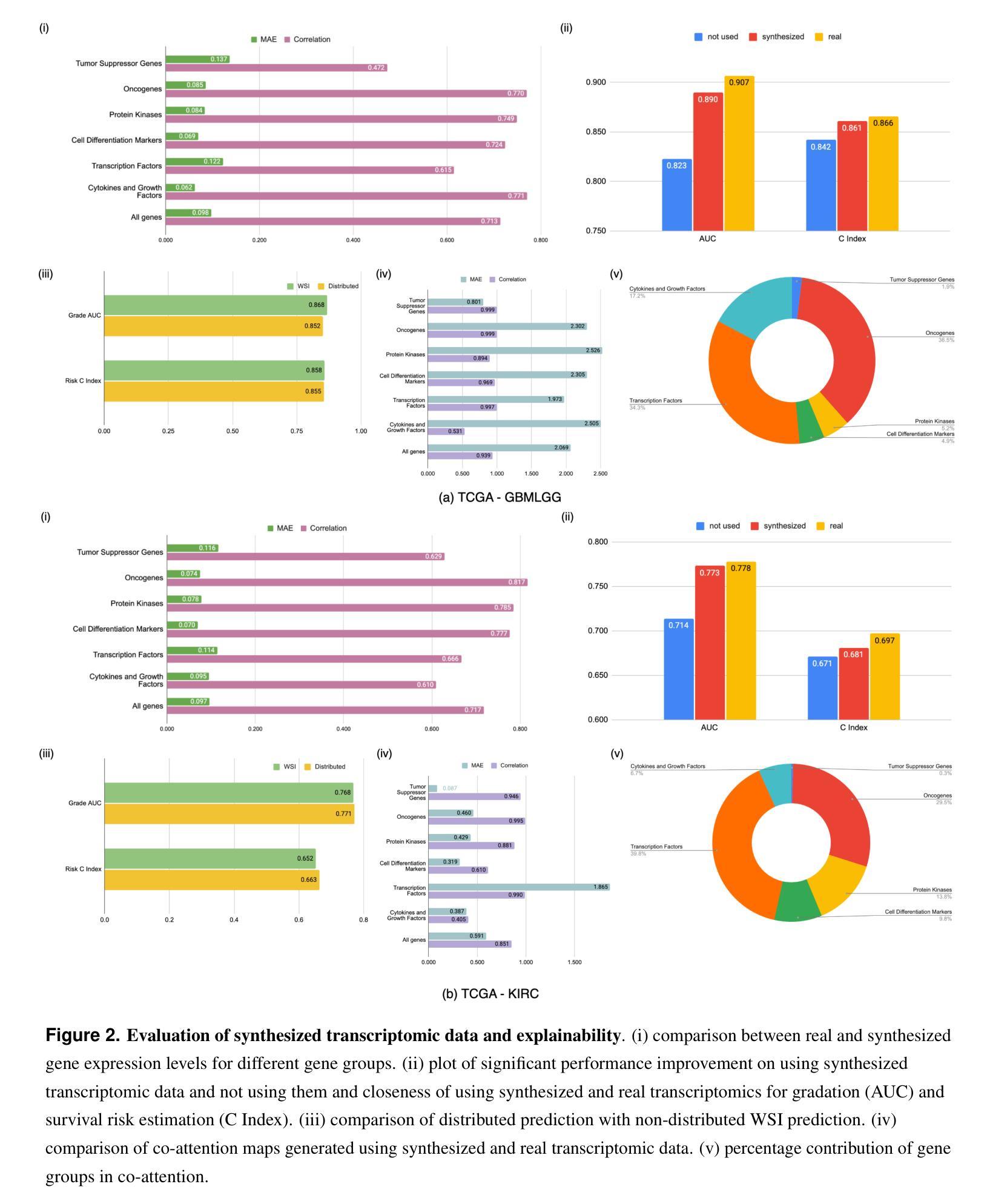
Generating crossmodal gene expression from cancer histopathology improves multimodal AI predictions
Authors:Samiran Dey, Christopher R. S. Banerji, Partha Basuchowdhuri, Sanjoy K. Saha, Deepak Parashar, Tapabrata Chakraborti
Emerging research has highlighted that artificial intelligence based multimodal fusion of digital pathology and transcriptomic features can improve cancer diagnosis (grading/subtyping) and prognosis (survival risk) prediction. However, such direct fusion for joint decision is impractical in real clinical settings, where histopathology is still the gold standard for diagnosis and transcriptomic tests are rarely requested, at least in the public healthcare system. With our novel diffusion based crossmodal generative AI model PathoGen, we show that genomic expressions synthesized from digital histopathology jointly predicts cancer grading and patient survival risk with high accuracy (state-of-the-art performance), certainty (through conformal coverage guarantee) and interpretability (through distributed attention maps). PathoGen code is available for open use by the research community through GitHub at https://github.com/Samiran-Dey/PathoGen.
最新的研究已经强调,基于人工智能的数字病理和转录组特征的多模式融合可以提高癌症诊断(分级/亚型)和预后(生存风险)预测的准确性。然而,在实际的临床环境中,这种直接融合进行联合决策并不实用。在公共医疗体系中,组织病理学仍然是诊断的金标准,转录组测试很少被要求。通过我们的新型基于扩散的跨模态生成人工智能模型PathoGen,我们证明了由数字病理学合成的基因表达能够联合预测癌症分级和患者生存风险,具有高精度(最先进的性能)、确定性(通过置信区间保证)和可解释性(通过分布式注意力图)。PathoGen代码可通过GitHub供研究界开放使用,网址为:https://github.com/Samiran-Dey/PathoGen。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新兴研究表明,基于人工智能的多模态融合数字病理与转录组特征能提高癌症诊断(分级/亚型)和预后(生存风险)预测的准确性。然而,在实际临床环境中直接融合进行联合决策并不现实。我们的新型扩散式跨模态生成式人工智能模型PathoGen,能够在数字病理中合成基因表达,以高精确度、高可解释性联合预测癌症分级和患者生存风险,达到业界领先水平。PathoGen代码已开源供研究社区使用,可通过GitHub访问。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在多模态融合数字病理和转录组特征方面展现出提高癌症诊断和治疗预测的准确性。
- 当前直接融合多模态数据在实际临床环境中的实用性有限。
- PathoGen模型能够在数字病理中合成基因表达,进行癌症分级和患者生存风险的预测。
- PathoGen模型具有高精度、高可解释性和高可靠性。
- 该模型达到了业界领先水平。
- PathoGen代码已开源,供研究社区使用。
点此查看论文截图
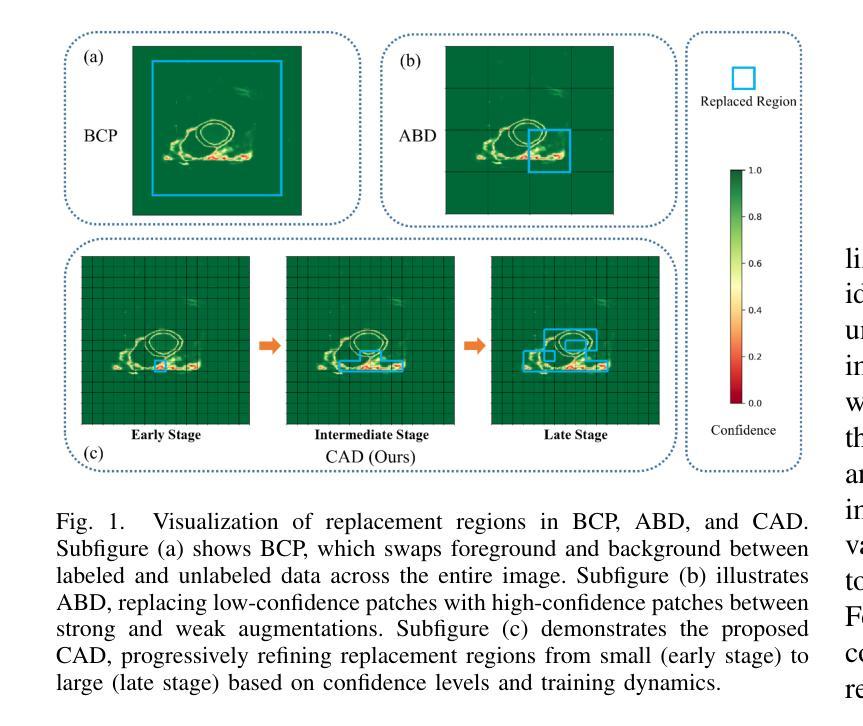
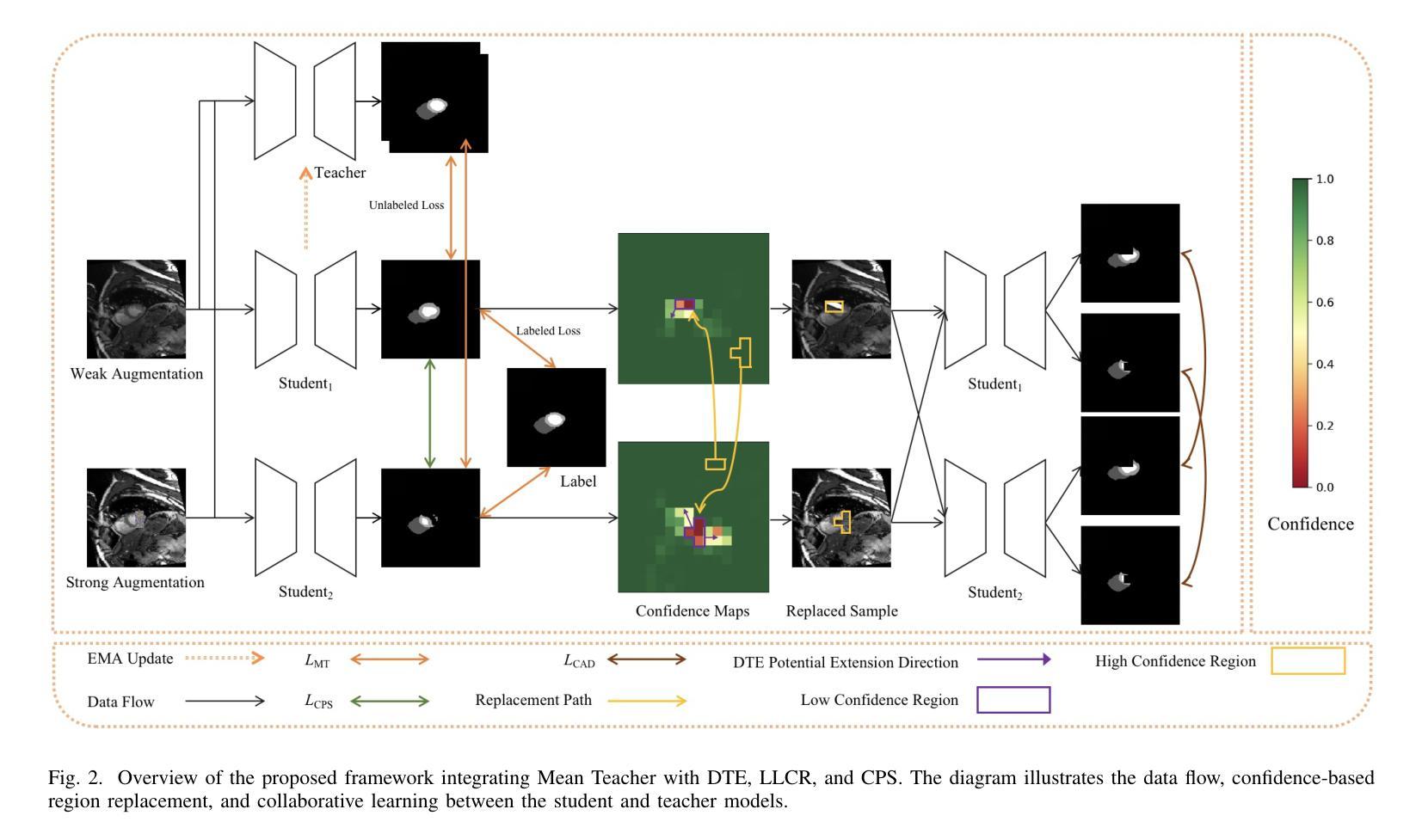
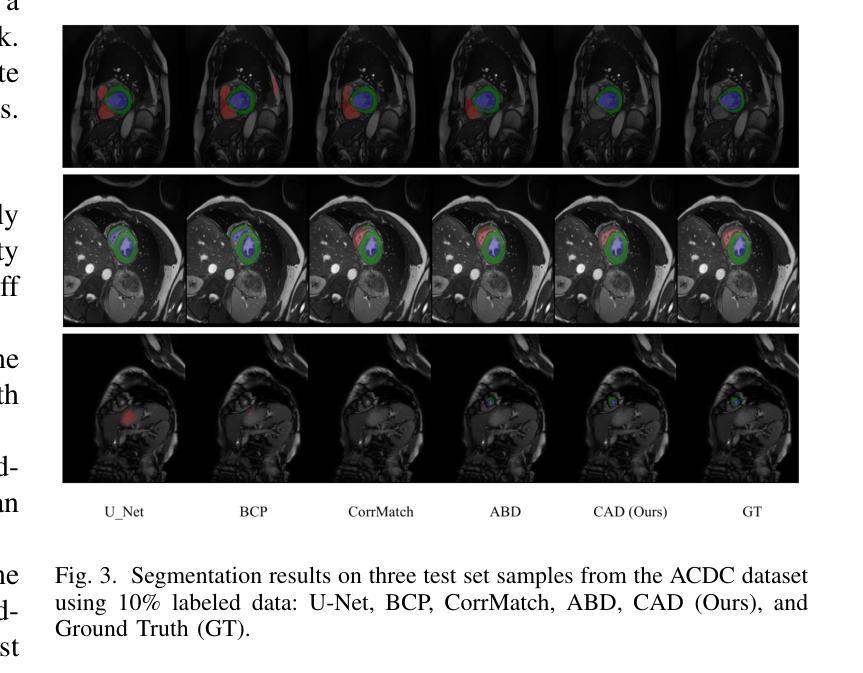
CAD: Confidence-Aware Adaptive Displacement for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Wenbo Xiao, Zhihao Xu, Guiping Liang, Yangjun Deng, Yi Xiao
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation aims to leverage minimal expert annotations, yet remains confronted by challenges in maintaining high-quality consistency learning. Excessive perturbations can degrade alignment and hinder precise decision boundaries, especially in regions with uncertain predictions. In this paper, we introduce Confidence-Aware Adaptive Displacement (CAD), a framework that selectively identifies and replaces the largest low-confidence regions with high-confidence patches. By dynamically adjusting both the maximum allowable replacement size and the confidence threshold throughout training, CAD progressively refines the segmentation quality without overwhelming the learning process. Experimental results on public medical datasets demonstrate that CAD effectively enhances segmentation quality, establishing new state-of-the-art accuracy in this field. The source code will be released after the paper is published.
半监督医学图像分割旨在利用最少的专家标注,但仍面临保持高质量一致性学习的挑战。过多的扰动可能会降低对齐精度,阻碍精确决策边界的形成,特别是在预测不确定的区域。在本文中,我们引入了信心感知自适应位移(CAD)框架,该框架能够有选择地识别和用高信心补丁替换最大的低信心区域。通过动态调整训练过程中允许的最大替换大小和置信阈值,CAD可以逐步提高分割质量,而不会使学习过程过于复杂。在公共医学数据集上的实验结果表明,CAD有效提高了分割质量,在此领域建立了新的最先进的精度。论文发布后将公布源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 3 figures, 4 tables
Summary
医学图像半监督分割旨在利用最少的专家标注,但仍面临保持高质量一致性学习的挑战。本文提出一种名为Confidence-Aware Adaptive Displacement(CAD)的框架,能够选择性识别并替换最大低置信度区域为高置信度补丁。通过动态调整最大允许替换大小和置信阈值,CAD在训练过程中逐步优化分割质量,而不会使学习过程过于复杂。在公共医学数据集上的实验结果表明,CAD能有效提高分割质量,在该领域建立新的最先进的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割旨在利用少量专家标注,但面临保持高质量一致性学习的挑战。
- 提出的Confidence-Aware Adaptive Displacement(CAD)框架能识别并替换低置信度区域。
- CAD通过动态调整最大允许替换大小和置信阈值,在训练过程中逐步优化分割质量。
- CAD在公共医学数据集上的实验表现优异,能有效提高分割质量。
- 该方法建立了新的最先进的准确性,特别是在处理具有不确定预测的区域时。
- CAD框架的应用有助于改善过度扰动导致的对齐问题,提高决策边界的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

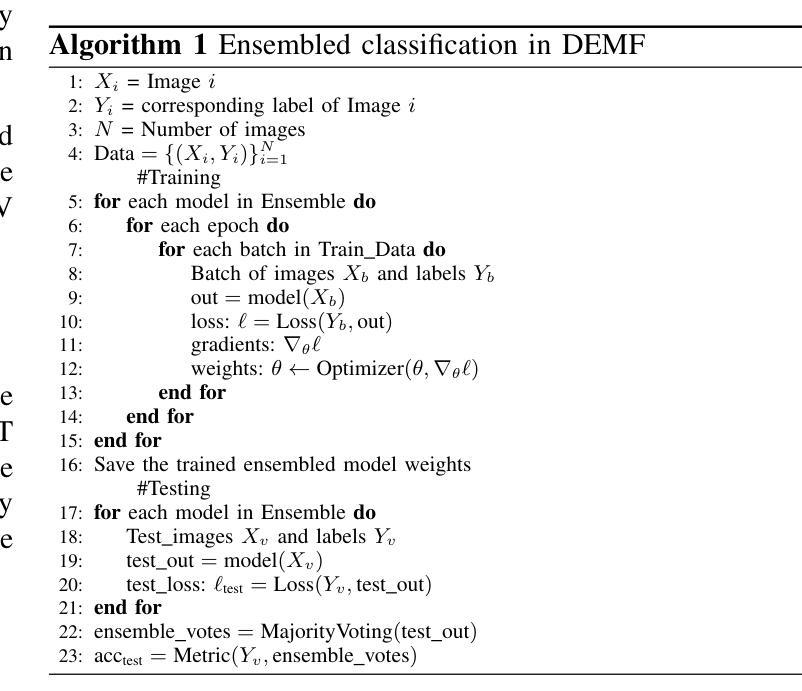
Deep Ensembling with Multimodal Image Fusion for Efficient Classification of Lung Cancer
Authors:Surochita Pal, Sushmita Mitra
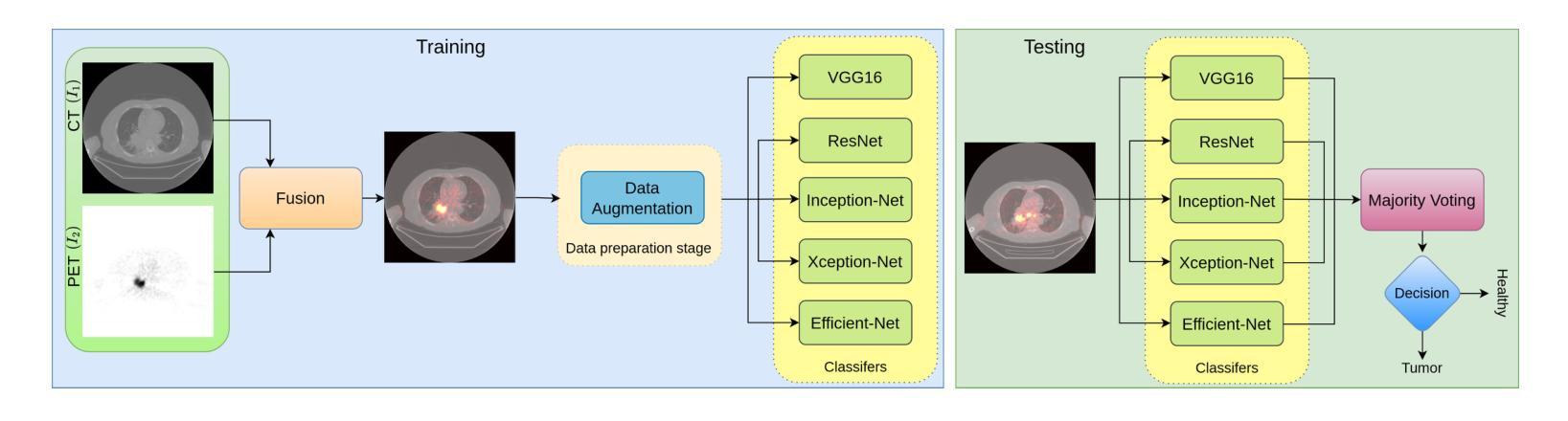
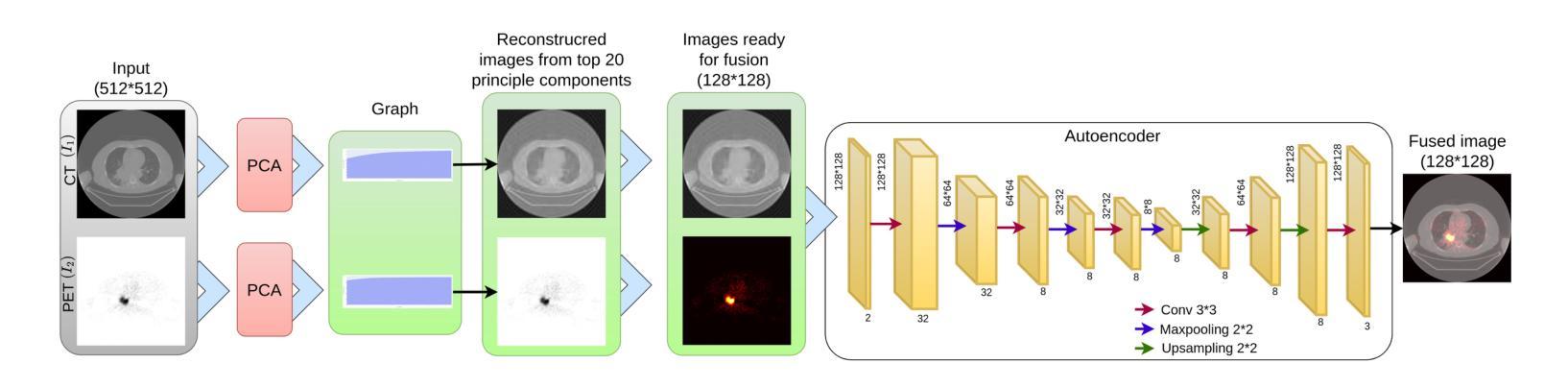
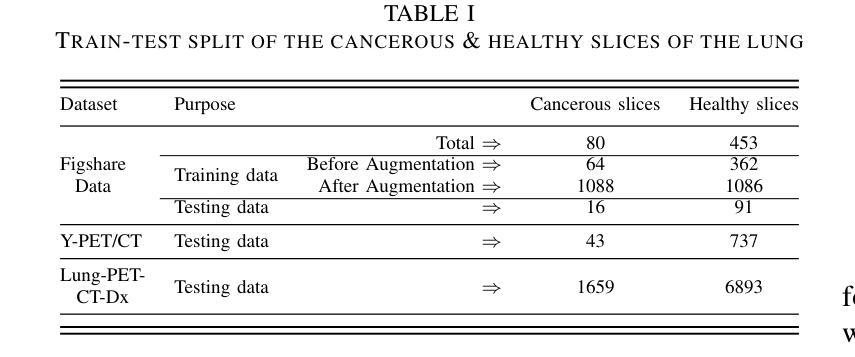
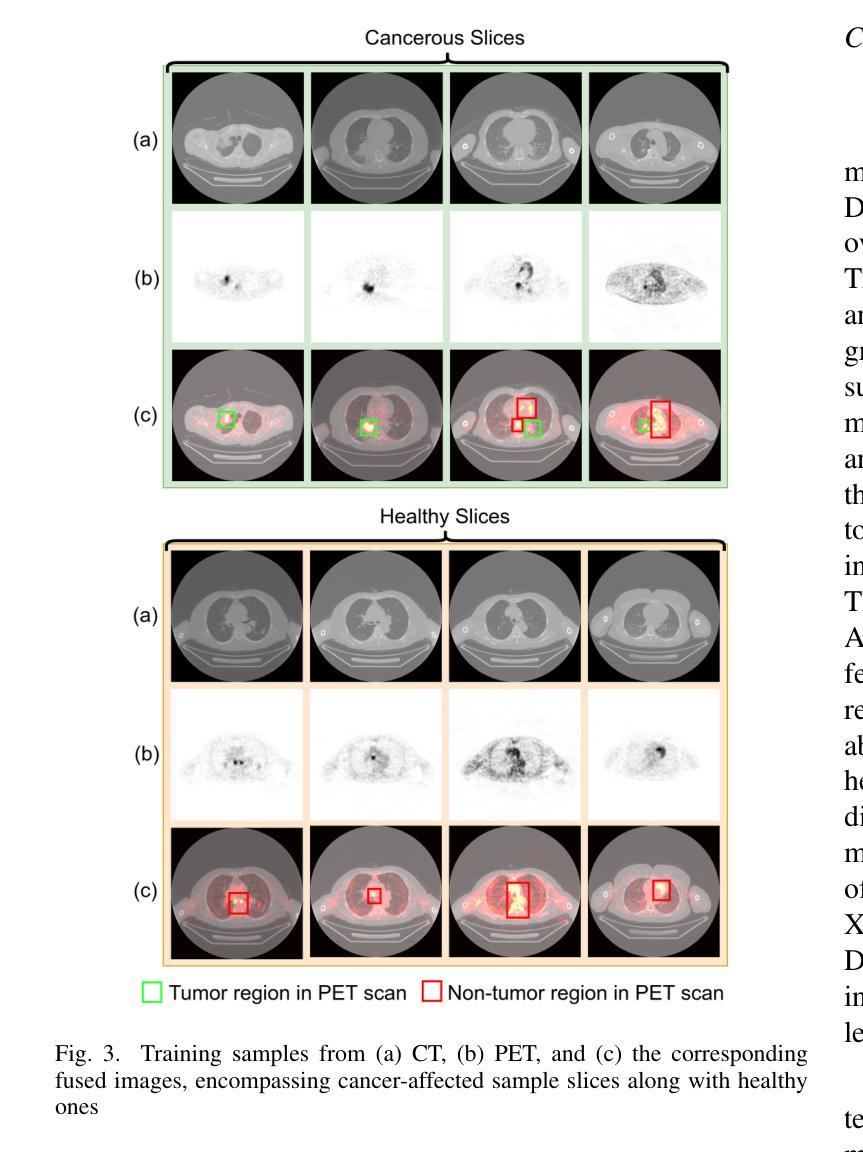
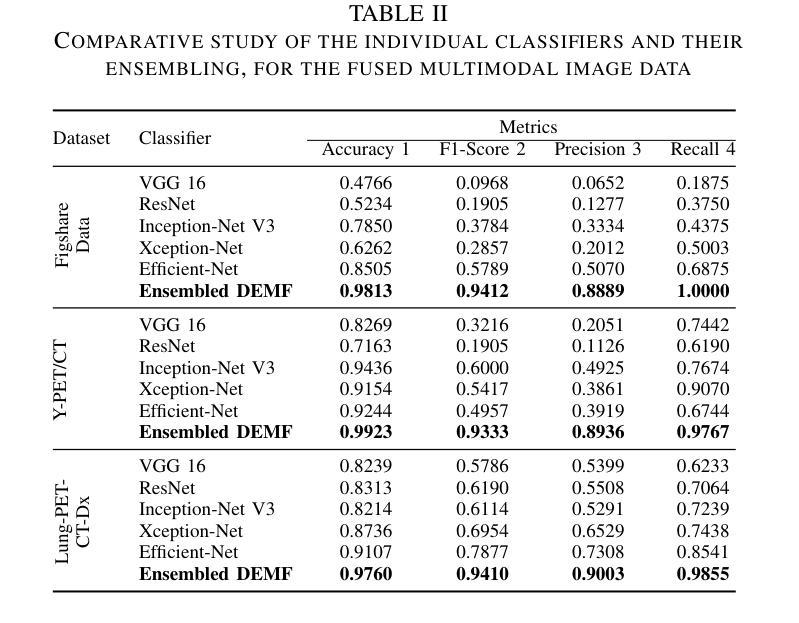
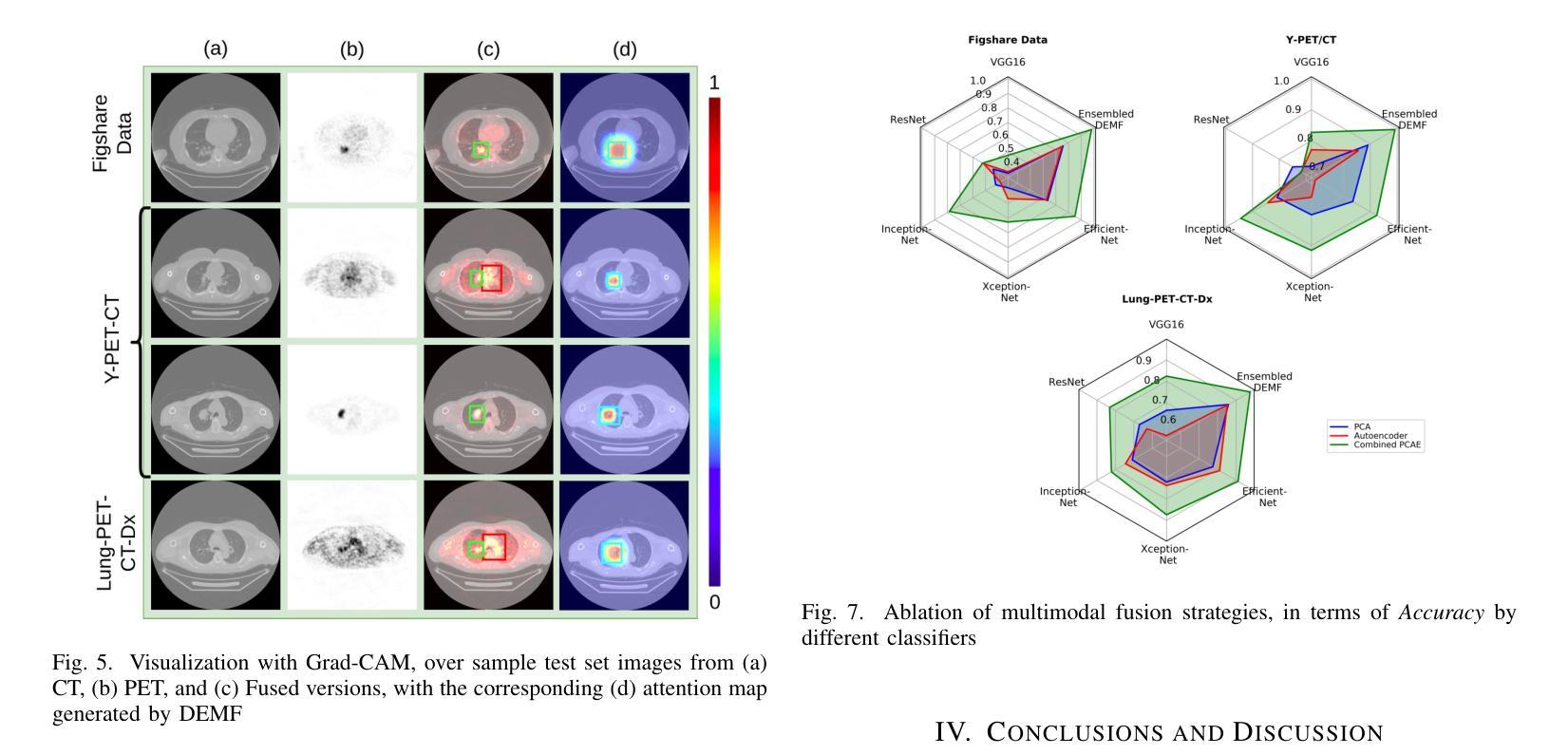
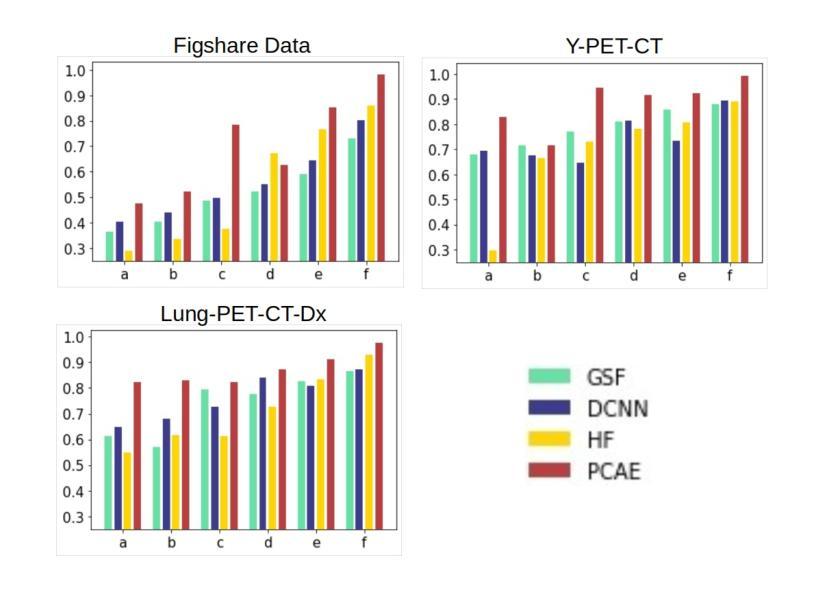
This study focuses on the classification of cancerous and healthy slices from multimodal lung images. The data used in the research comprises Computed Tomography (CT) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) images. The proposed strategy achieves the fusion of PET and CT images by utilizing Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and an Autoencoder. Subsequently, a new ensemble-based classifier developed, Deep Ensembled Multimodal Fusion (DEMF), employing majority voting to classify the sample images under examination. Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) employed to visualize the classification accuracy of cancer-affected images. Given the limited sample size, a random image augmentation strategy employed during the training phase. The DEMF network helps mitigate the challenges of scarce data in computer-aided medical image analysis. The proposed network compared with state-of-the-art networks across three publicly available datasets. The network outperforms others based on the metrics - Accuracy, F1-Score, Precision, and Recall. The investigation results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed network.
本研究关注多模态肺部图像中的癌变与正常切片的分类。研究中使用的数据包括计算机断层扫描(CT)和正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像。提出的策略通过利用主成分分析(PCA)和自动编码器实现PET和CT图像的融合。随后,开发了一种新的基于集成分类器的多模态融合集成网络(DEMF),采用多数投票方式对检查样本图像进行分类。采用梯度加权类激活映射(Grad-CAM)可视化癌症受影响图像的分类准确性。考虑到样本量有限,在训练阶段采用了随机图像增强策略。DEMF网络有助于缓解计算机辅助医学图像分析中数据稀缺的挑战。与三个公开数据集上的最先进的网络相比,所提出的网络在准确率、F1分数、精确率和召回率等指标上表现较好。调查结果突出了所提出网络的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用多模态肺部图像对癌变和正常切片进行分类。数据包括计算机断层扫描(CT)和正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像。通过主成分分析(PCA)和自编码器实现PET和CT图像的融合。开发了一种基于集成的新分类器——深度集成多模态融合(DEMF),采用投票多数制对检查样本图像进行分类。利用梯度加权类激活映射(Grad-CAM)可视化癌症受影响图像的分类准确性。鉴于样本量有限,训练阶段采用了随机图像增强策略。DEMF网络有助于解决计算机辅助医学图像分析中数据稀缺的挑战。在三个公开数据集上,该网络与最新网络进行了比较,在准确性、F1分数、精确度和召回率等指标上表现较好。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注多模态肺部图像(包括CT和PET图像)的癌变和正常切片分类。
- 研究通过PCA和自编码器实现了PET和CT图像的融合。
- 引入了一种新的基于集成的分类器DEMF,通过多数投票机制对图像进行分类。
- 使用Grad-CAM可视化癌症图像分类的准确性。
- 由于样本量有限,采用了随机图像增强策略以改善模型训练。
- DEMF网络在解决医学图像分析中数据稀缺问题方面表现出优势。
- 在多个公开数据集上,DEMF网络在分类性能上超过了其他网络。
点此查看论文截图

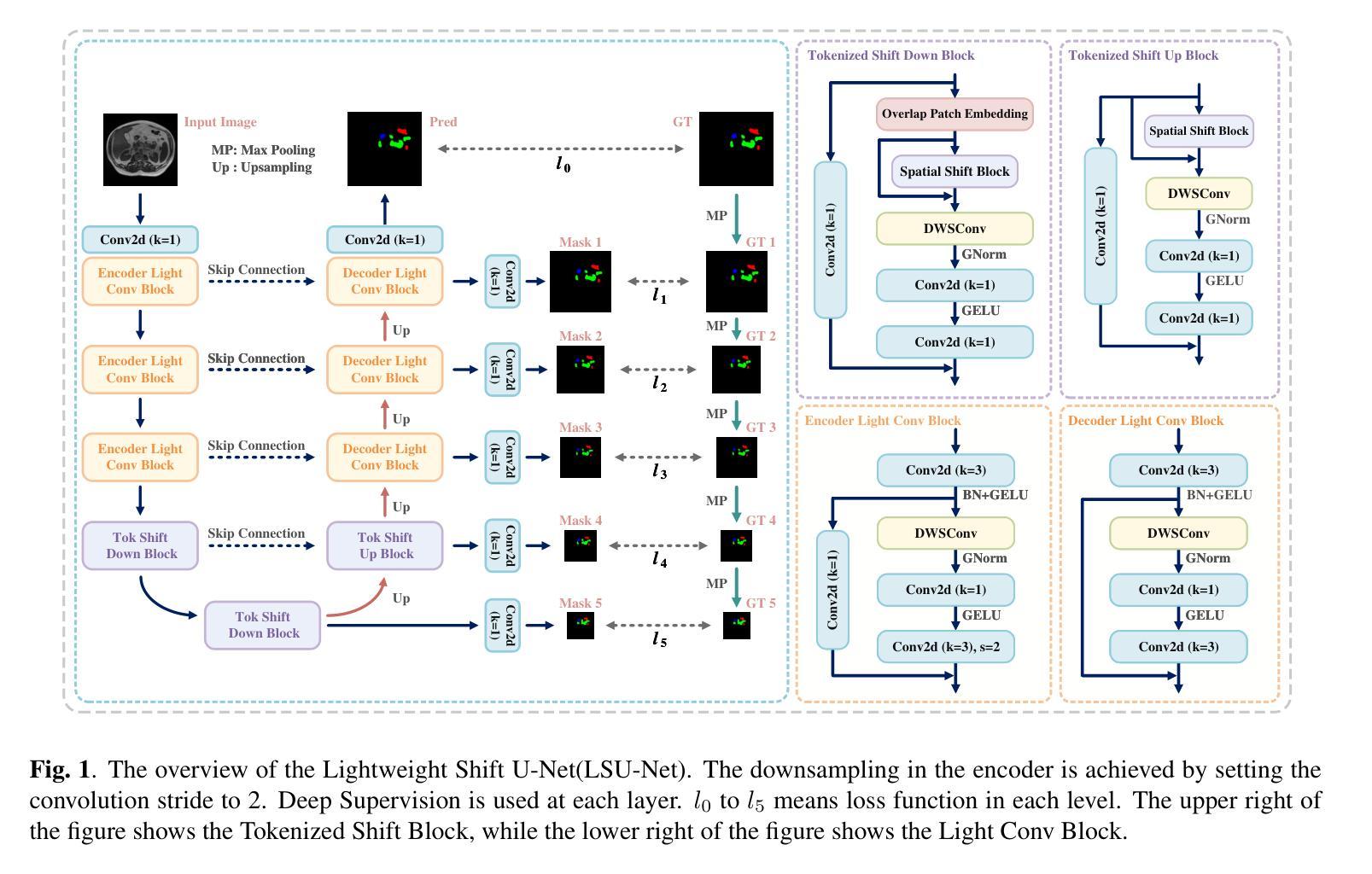
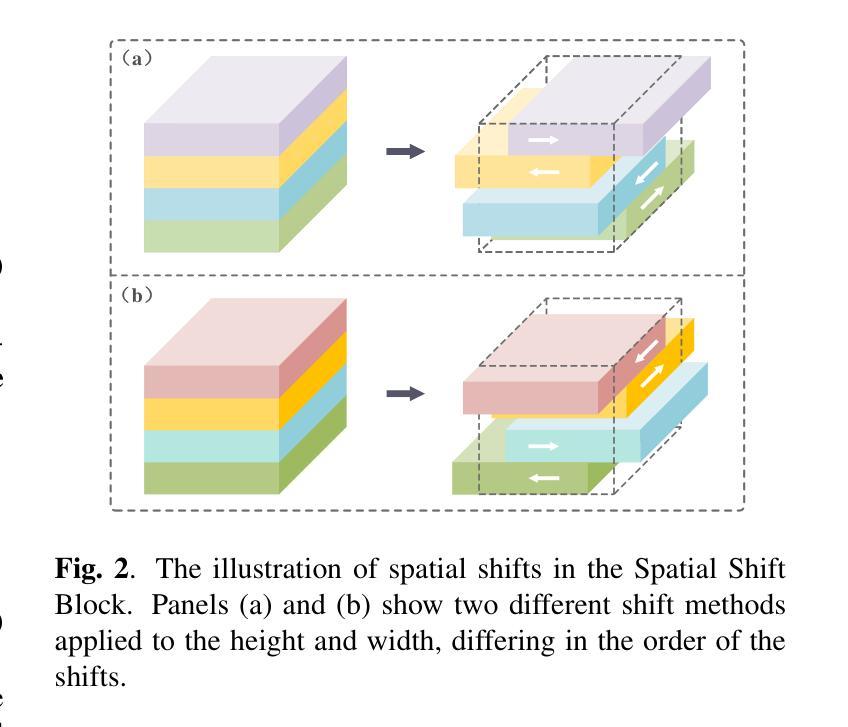
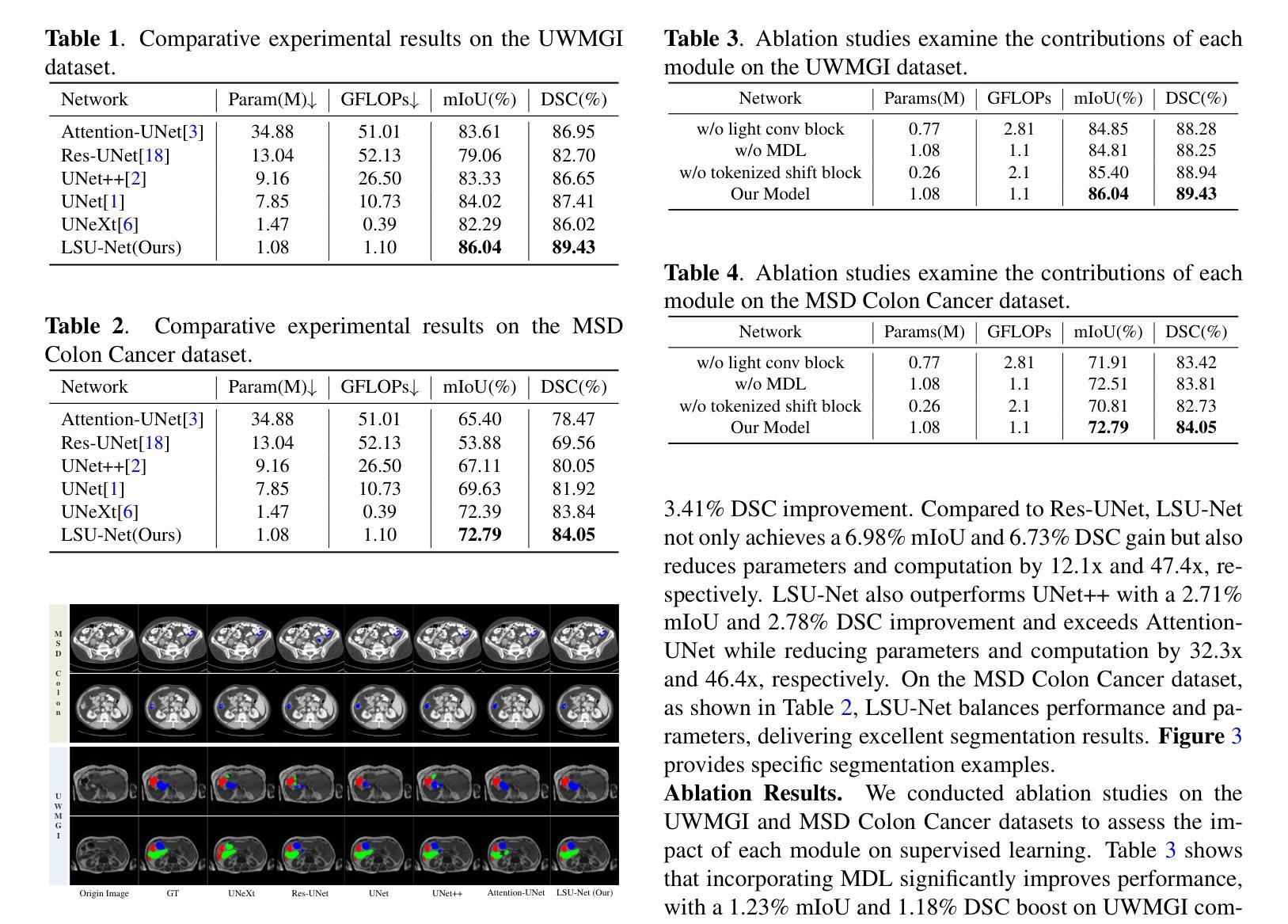
LSU-Net: Lightweight Automatic Organs Segmentation Network For Medical Images
Authors:Yujie Ding, Shenghua Teng, Zuoyong Li, Xiao Chen
UNet and its variants have widespread applications in medical image segmentation. However, the substantial number of parameters and computational complexity of these models make them less suitable for use in clinical settings with limited computational resources. To address this limitation, we propose a novel Lightweight Shift U-Net (LSU-Net). We integrate the Light Conv Block and the Tokenized Shift Block in a lightweight manner, combining them with a dynamic weight multi-loss design for efficient dynamic weight allocation. The Light Conv Block effectively captures features with a low parameter count by combining standard convolutions with depthwise separable convolutions. The Tokenized Shift Block optimizes feature representation by shifting and capturing deep features through a combination of the Spatial Shift Block and depthwise separable convolutions. Dynamic adjustment of the loss weights at each layer approaches the optimal solution and enhances training stability. We validated LSU-Net on the UWMGI and MSD Colon datasets, and experimental results demonstrate that LSU-Net outperforms most state-of-the-art segmentation architectures.
UNet及其变体在医学图像分割中有着广泛应用。然而,这些模型参数众多,计算复杂度较高,对于计算资源有限的临床环境来说不太适用。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种新型的轻量化移位U-Net(LSU-Net)。我们通过轻量级的方式集成了Light Conv Block和Tokenized Shift Block,并结合动态权重多损失设计,实现了有效的动态权重分配。Light Conv Block通过结合标准卷积和深度可分离卷积,以较低的参数数量有效地捕捉特征。Tokenized Shift Block通过优化空间移位块和深度可分离卷积的组合,实现了特征的移位和深层特征的捕捉,从而优化了特征表示。动态调整每层的损失权重接近最优解,提高了训练稳定性。我们在UWMGI和MSD结肠数据集上对LSU-Net进行了验证,实验结果表明LSU-Net在大多数最先进的分割架构中表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures, 4 tables. Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
针对医疗图像分割中UNet及其变体模型参数多、计算复杂度高的问题,提出了轻量级移位U-Net(LSU-Net)。通过集成轻量级卷积块和标记移位块,并结合动态权重多损失设计,实现高效动态权重分配。在UWMGI和MSD结肠数据集上的实验结果表明,LSU-Net优于大多数最先进的分割架构。
Key Takeaways
- UNet及其变体在医疗图像分割中有广泛应用,但存在参数多、计算复杂度高的问题。
- 为解决这一问题,提出了轻量级移位U-Net(LSU-Net)。
- LSU-Net集成了轻量级卷积块和标记移位块。
- 轻量级卷积块通过结合标准卷积和深度可分离卷积,实现低参数特征捕获。
- 标记移位块通过移位操作和优化特征表示,实现了深层特征的捕获。
- LSU-Net采用动态权重多损失设计,实现每层损失权重的动态调整,接近最优解,提高训练稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

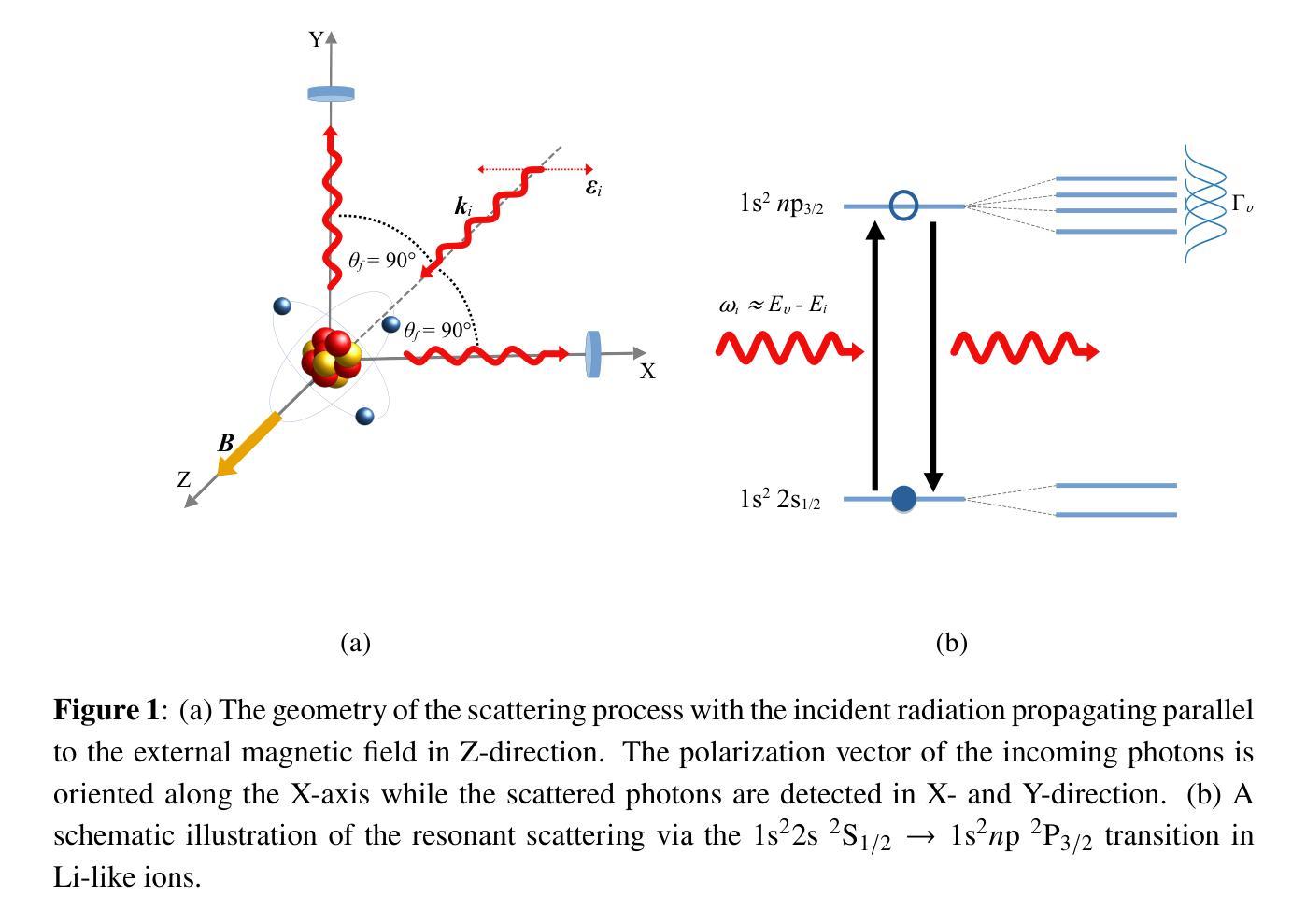
Hanle Effect for Lifetime Analysis: Li-like Ions
Authors:Jan Richter, Moto Togawa, José R. Crespo López-Urrutia, Andrey Surzhykov
Accurate lifetime measurements of excited states of highly charged ions (HCIs) are essential for advancing diagnostics in both laboratory and astrophysical plasmas, especially in the X-ray regime. The Hanle effect, which utilizes external magnetic fields to modify photon scattering patterns, provides a powerful technique for these measurements. Previously, this method has been successfully employed for He-like ions. Here, we present a theoretical study of the prospects of the Hanle effect for lifetime determinations of Li-like ions. Our results highlight the potential for plasma diagnostics and X-ray spectral analysis.
对高电荷离子(HCIs)激发态的精确寿命测量对于推进实验室和天文等离子体诊断至关重要,特别是在X射线领域。Hanle效应是一种利用外部磁场改变光子散射模式的强大技术,为这些测量提供了有力手段。以前,这种方法已成功应用于类氦离子。在这里,我们对类锂离子寿命确定的Hanle效应进行了理论研究。我们的结果突出了等离子体诊断和X射线光谱分析方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于外部磁场对光子散射模式的修改作用,汉勒效应为高度电离离子激发态寿命的精确测量提供了有力手段。本文理论研究了汉勒效应在Li类离子寿命测定中的应用前景,为等离子体诊断和X射线光谱分析提供了潜在可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 高度电离离子(HCIs)激发态的精确寿命测量对于推进实验室和天文等离子体诊断至关重要,特别是在X射线领域。
- 汉勒效应利用外部磁场修改光子散射模式,为这些测量提供了有力技术。
- 此方法已成功应用于类氦离子。
- 本文理论研究了汉勒效应在Li类离子寿命测定中的应用前景。
- 研究结果突出了汉勒效应在等离子体诊断和X射线光谱分析中的潜在应用价值。
- 此研究有望提高等离子体物理和光谱分析领域的准确性和理解。
点此查看论文截图

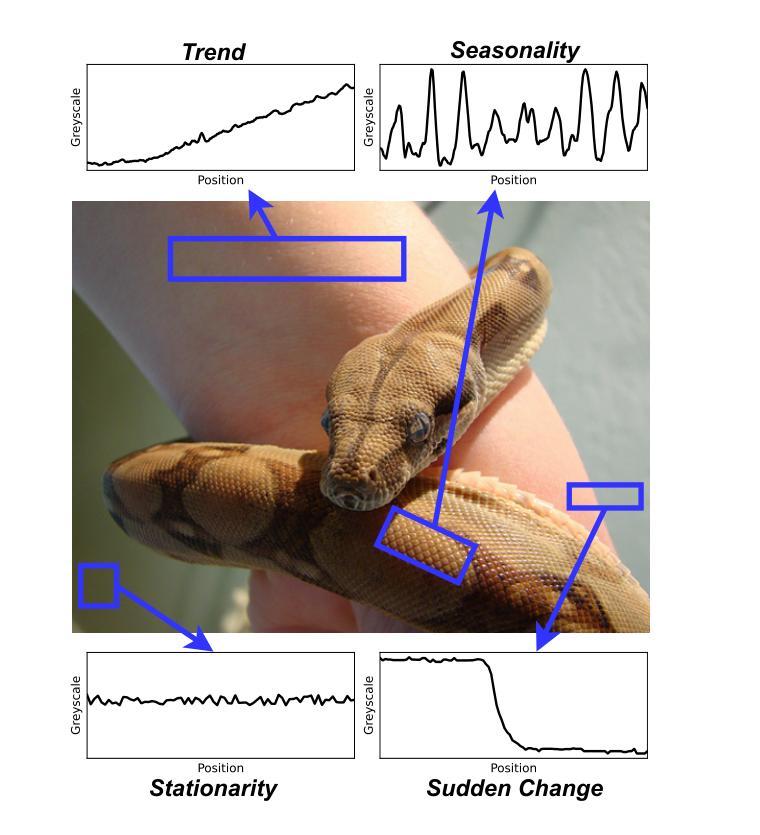
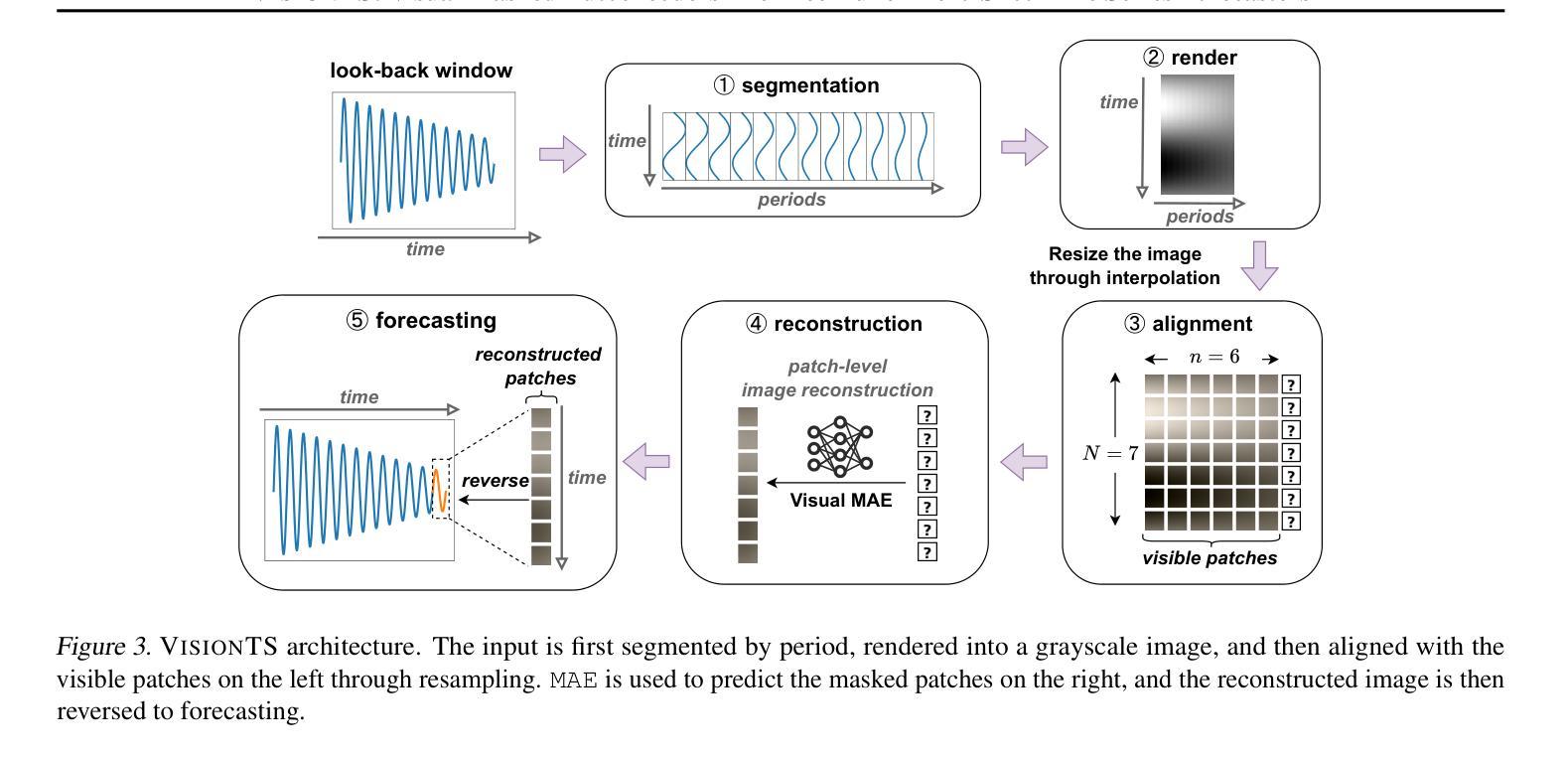
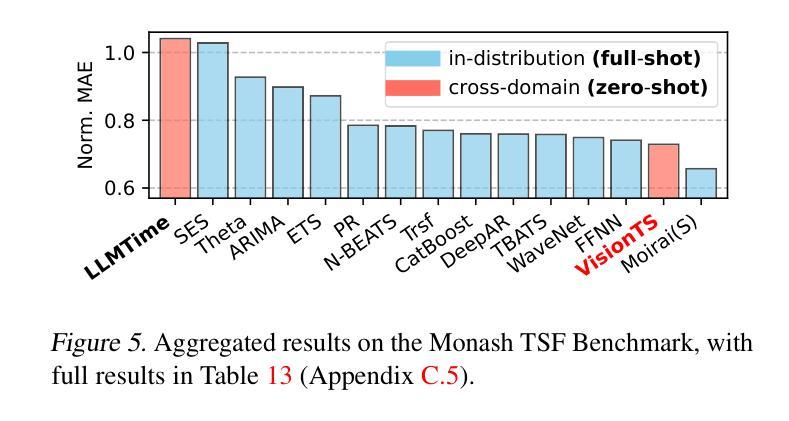
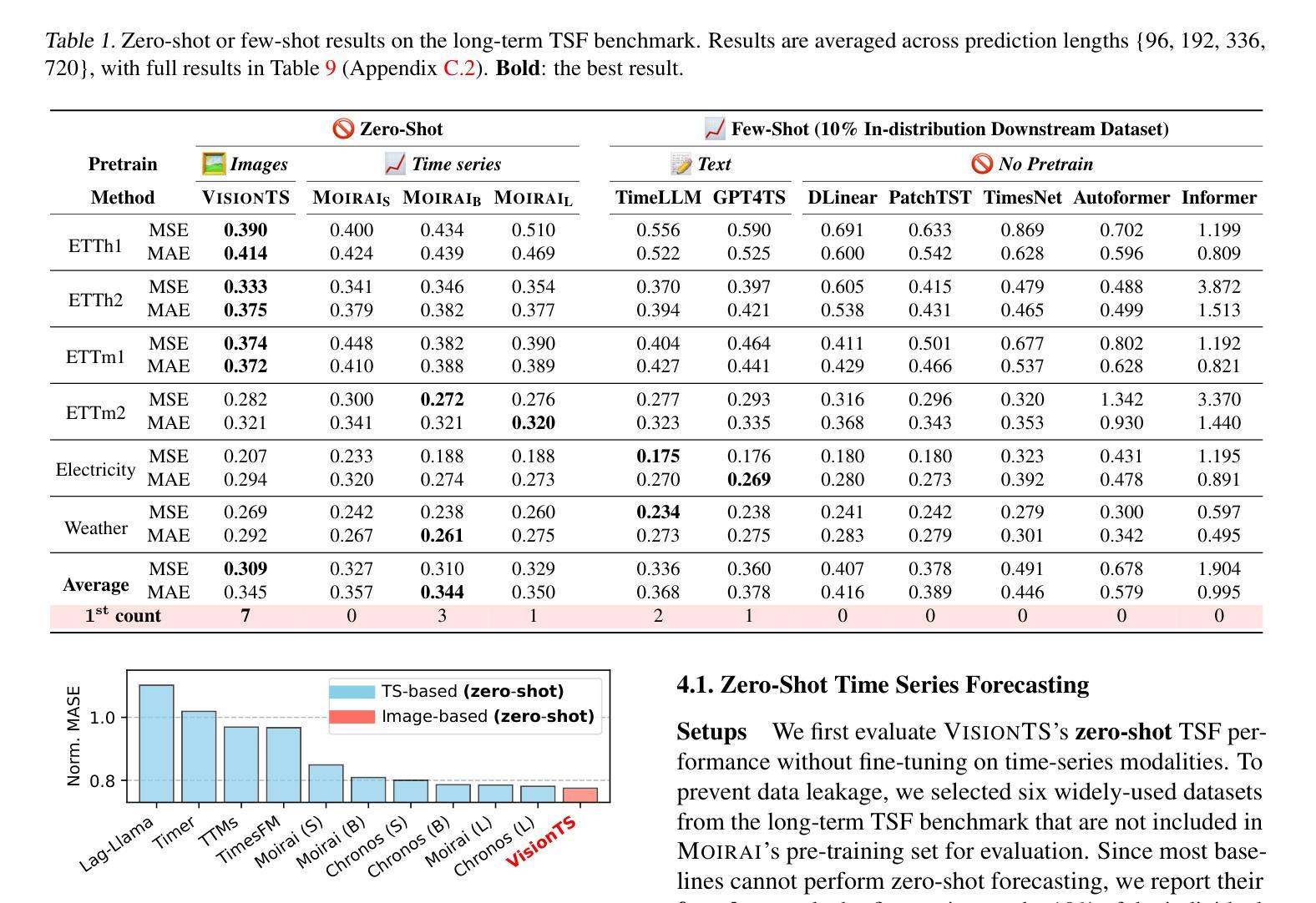
VisionTS: Visual Masked Autoencoders Are Free-Lunch Zero-Shot Time Series Forecasters
Authors:Mouxiang Chen, Lefei Shen, Zhuo Li, Xiaoyun Joy Wang, Jianling Sun, Chenghao Liu
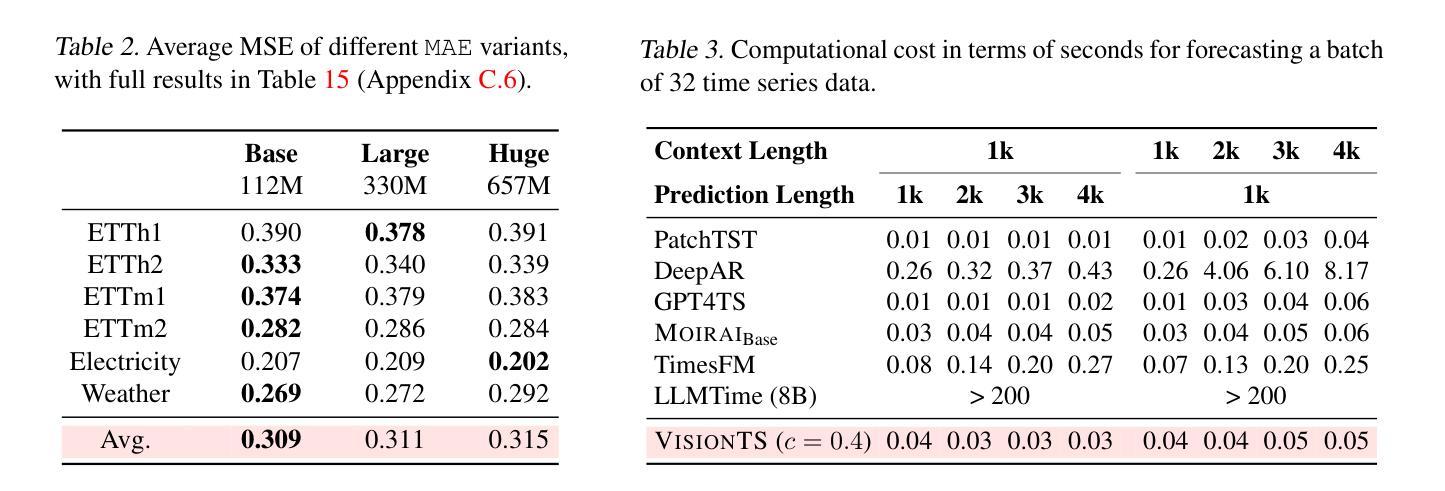
Foundation models have emerged as a promising approach in time series forecasting (TSF). Existing approaches either repurpose large language models (LLMs) or build large-scale time series datasets to develop TSF foundation models for universal forecasting. However, these methods face challenges due to the severe cross-domain gap or in-domain heterogeneity. This paper explores a new road to building a TSF foundation model from rich, high-quality natural images. Our key insight is that a visual masked autoencoder, pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset, can naturally be a numeric series forecaster. By reformulating TSF as an image reconstruction task, we bridge the gap between image pre-training and TSF downstream tasks. Surprisingly, without further adaptation in the time series domain, the proposed VisionTS could achieve better zero-shot forecast performance than existing TSF foundation models. With fine-tuning for one epoch, VisionTS could further improve the forecasting and achieve state-of-the-art performance in most cases. Extensive experiments reveal intrinsic similarities between images and real-world time series, suggesting that visual models may offer a “free lunch” for TSF and highlight the potential for future cross-modality research. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Keytoyze/VisionTS.
时间序列预测(TSF)中的基础模型已成为一种前景广阔的方法。现有的方法要么重新利用大型语言模型(LLM),要么构建大规模时间序列数据集,以开发用于通用预测的时间序列预测基础模型。然而,这些方法面临着跨域差距大或域内异质性的挑战。本文探索了一条新的构建时间序列预测基础模型的途径,即从丰富、高质量的自然图像中构建。我们的关键见解是,在ImageNet数据集上预训练的视觉掩码自动编码器可以自然地成为数值序列预测器。通过将时间序列预测重新构建为图像重建任务,我们弥合了图像预训练和下游时间序列预测任务之间的差距。令人惊讶的是,无需在时序领域进一步适应,我们提出的VisionTS可以在零样本预测方面实现优于现有时间序列预测基础模型的表现。经过一个周期的微调后,VisionTS可以进一步提高预测能力,并在大多数情况下达到最佳性能。大量实验揭示了图像和现实世界时间序列之间的内在相似性,这表明视觉模型可能为时间序列预测提供了“免费午餐”,并突显了未来跨模态研究的潜力。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/Keytoyze/VisionTS 上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v3: add GIFT-EVAL results
Summary
基于大规模图像预训练模型构建时间序列预测(TSF)基础模型是一种新兴且有前景的方法。本研究通过图像重建任务重新构建TSF,实现图像预训练与TSF下游任务之间的桥梁,无需进一步的时间序列域适应,即可实现零样本预测性能优于现有TSF基础模型。通过微调一个周期,该模型可以进一步提高预测性能,并在多数情况下达到领先水平。本研究揭示了图像与真实世界时间序列之间的内在相似性,显示出视觉模型对TSF的潜在贡献,并为未来的跨模态研究提供了启示。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种基于大规模图像预训练模型构建时间序列预测(TSF)基础模型的新方法。
- 通过图像重建任务重新构建TSF,实现了图像预训练与TSF下游任务之间的桥梁。
- 该模型无需进一步适应时间序列域,即可实现零样本预测性能优于现有TSF基础模型。
- 通过微调一个周期,该模型的预测性能可以进一步提高,并在多数情况下达到领先水平。
- 研究揭示了图像与真实世界时间序列之间的内在相似性。
- 视觉模型对TSF具有潜在贡献。
点此查看论文截图