⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-06 更新
LAYOUTDREAMER: Physics-guided Layout for Text-to-3D Compositional Scene Generation
Authors:Yang Zhou, Zongjin He, Qixuan Li, Chao Wang
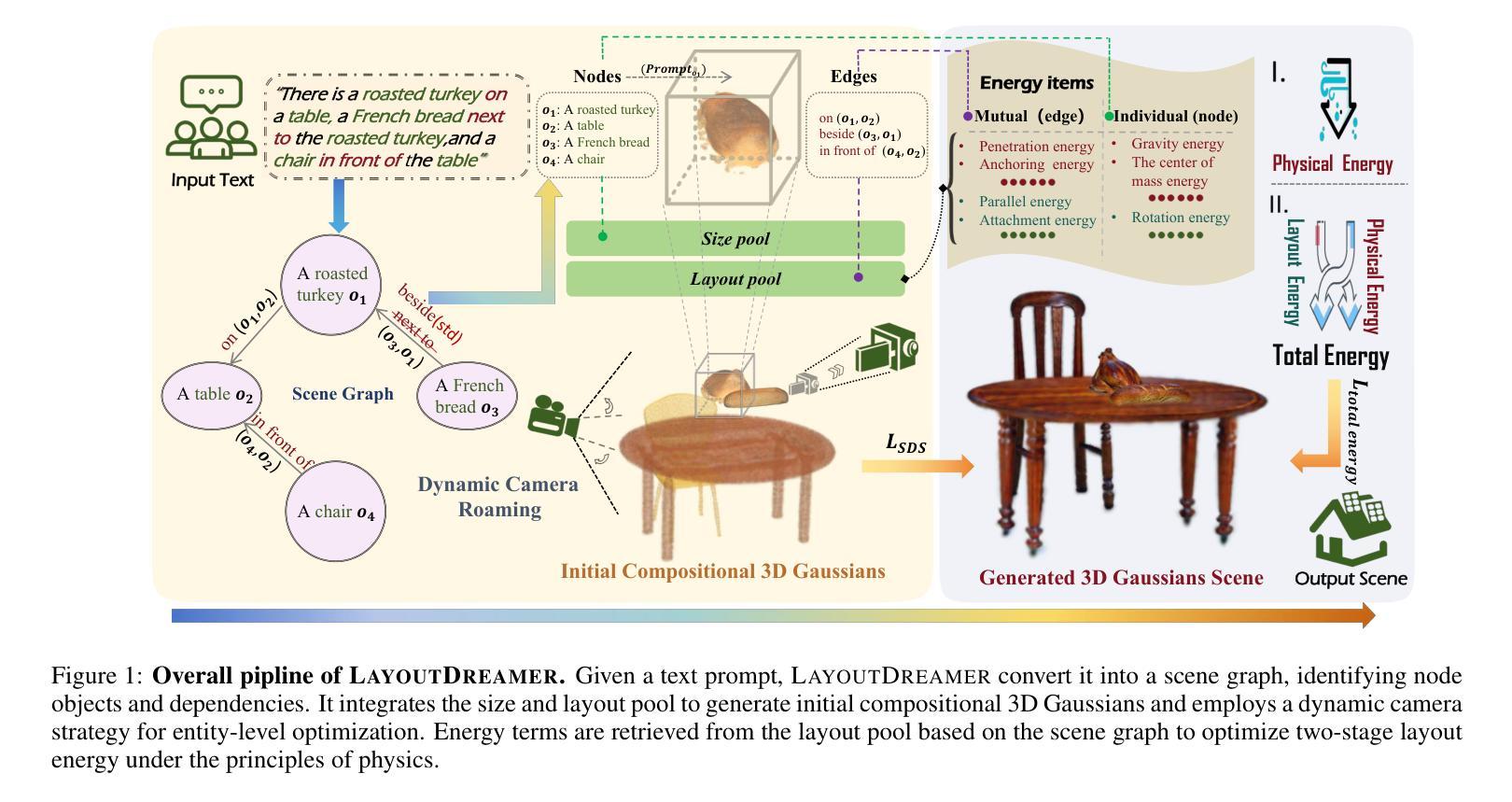
Recently, the field of text-guided 3D scene generation has garnered significant attention. High-quality generation that aligns with physical realism and high controllability is crucial for practical 3D scene applications. However, existing methods face fundamental limitations: (i) difficulty capturing complex relationships between multiple objects described in the text, (ii) inability to generate physically plausible scene layouts, and (iii) lack of controllability and extensibility in compositional scenes. In this paper, we introduce LayoutDreamer, a framework that leverages 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to facilitate high-quality, physically consistent compositional scene generation guided by text. Specifically, given a text prompt, we convert it into a directed scene graph and adaptively adjust the density and layout of the initial compositional 3D Gaussians. Subsequently, dynamic camera adjustments are made based on the training focal point to ensure entity-level generation quality. Finally, by extracting directed dependencies from the scene graph, we tailor physical and layout energy to ensure both realism and flexibility. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that LayoutDreamer outperforms other compositional scene generation quality and semantic alignment methods. Specifically, it achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in the multiple objects generation metric of T3Bench.
近期,文本引导的三维场景生成领域引起了广泛关注。生成高质量且符合物理现实和高可控性的三维场景对于实际应用至关重要。然而,现有方法面临根本性局限:(i)难以捕捉文本中描述的多个对象之间的复杂关系;(ii)无法生成物理上可行的场景布局;(iii)在组合场景中的可控性和扩展性不足。在本文中,我们介绍了LayoutDreamer框架,它利用三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)来促进由文本引导的高质量、物理一致性的组合场景生成。具体而言,给定文本提示,我们将其转换为有向场景图,并自适应地调整初始组合三维高斯分布的密度和布局。随后,基于训练焦点进行动态相机调整,以确保实体级生成质量。最后,我们通过从场景图中提取有向依赖关系,定制物理和布局能量,以确保现实性和灵活性。综合实验表明,LayoutDreamer在组合场景生成质量和语义对齐方面优于其他方法。特别是在T3Bench的多对象生成指标上取得了最新(SOTA)性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
文本引导的三维场景生成领域近期受到广泛关注。高质量且符合物理现实、高度可控的三维场景生成对实际应用至关重要。然而,现有方法存在根本性局限:一,难以捕捉文本描述的多个对象间的复杂关系;二,无法生成物理上合理的场景布局;三,场景组合的操控性和扩展性不足。本文介绍LayoutDreamer框架,利用三维高斯拼贴技术(3DGS),实现由文本引导的高质量、物理一致性强的组合场景生成。给定文本提示,将其转换为有向场景图,自适应调整初始组合三维高斯分布的密度和布局。基于训练焦点进行动态相机调整,确保实体级别的生成质量。通过提取场景图的有向依赖关系,定制物理和布局能量,确保真实性和灵活性。综合实验表明,LayoutDreamer在场景组合生成质量和语义对齐方面优于其他方法,特别是在T3Bench多对象生成指标上取得最佳性能。
关键见解
- 文本引导的三维场景生成受到关注,需要高质量、符合物理现实的生成技术。
- 现有方法存在捕捉复杂关系、生成合理场景布局以及操控性和扩展性的局限。
- LayoutDreamer框架利用三维高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)解决这些问题,实现高质量场景生成。
- LayoutDreamer将文本转换为有向场景图,自适应调整高斯分布,确保实体级别的生成质量。
- 动态相机调整基于训练焦点,进一步提高生成质量。
- 通过提取场景图的有向依赖关系,确保生成场景的物理一致性和灵活性。
- 综合实验显示,LayoutDreamer在多个指标上优于其他方法,特别是在T3Bench多对象生成上取得最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图


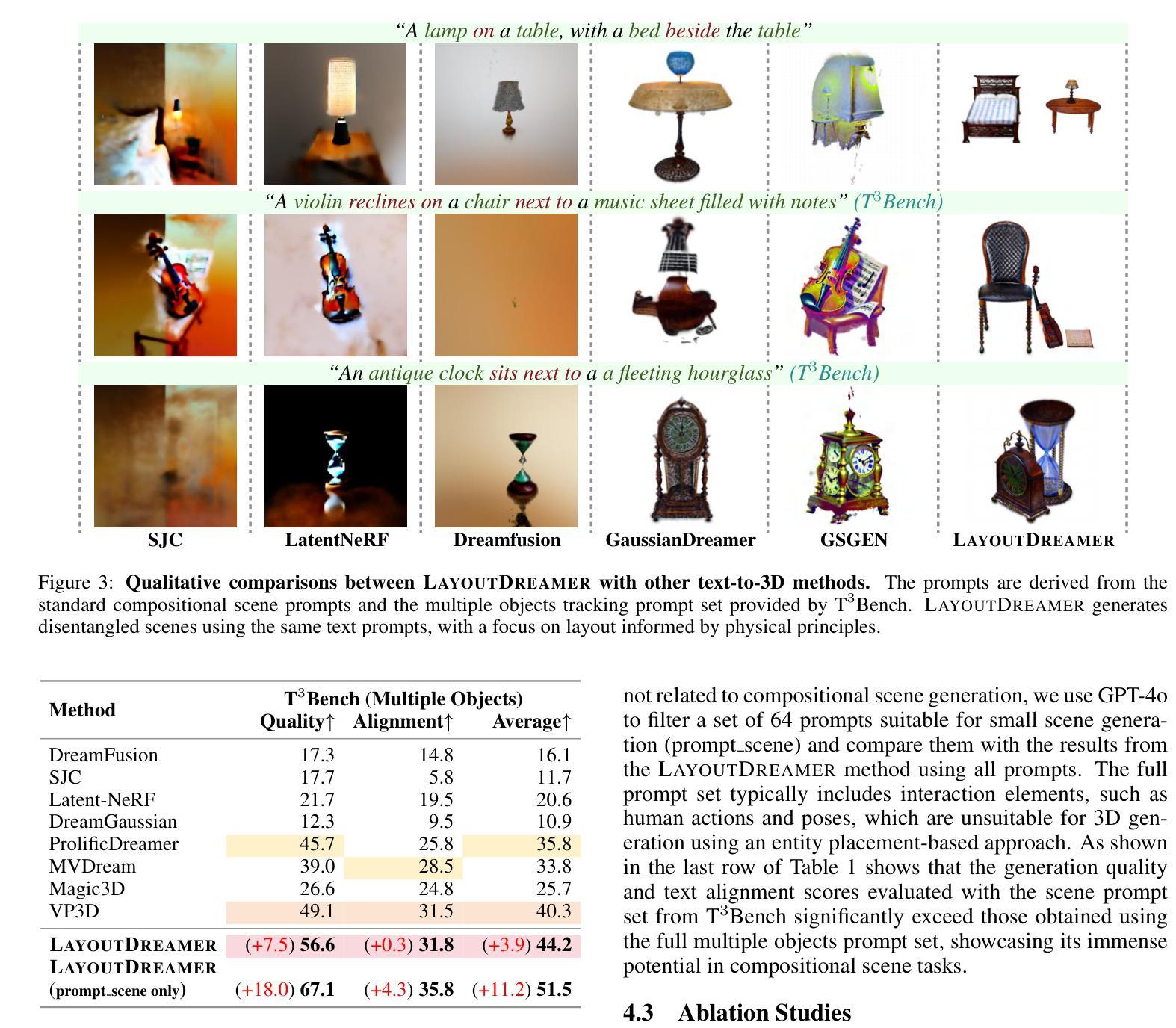
Scalable 3D Gaussian Splatting-Based RF Signal Spatial Propagation Modeling
Authors:Kang Yang, Gaofeng Dong, Sijie Ji, Wan Du, Mani Srivastava
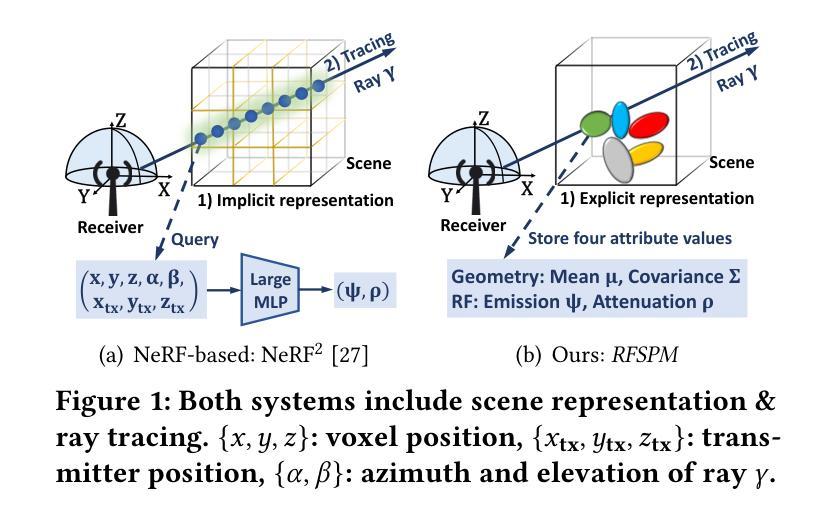
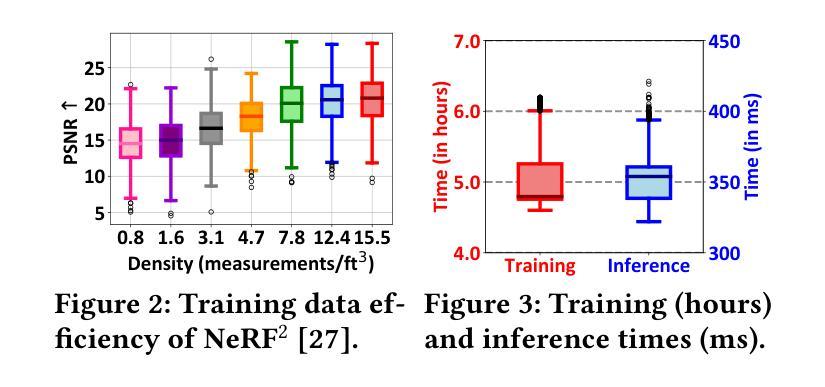
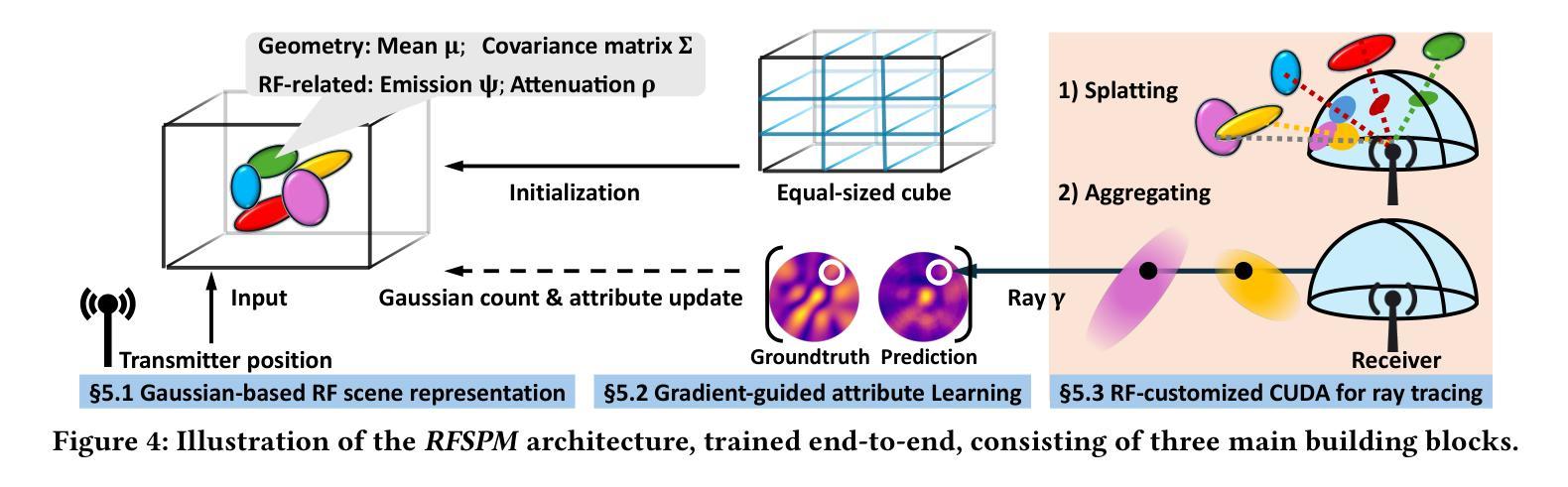
Effective network planning and sensing in wireless networks require resource-intensive site surveys for data collection. An alternative is Radio-Frequency (RF) signal spatial propagation modeling, which computes received signals given transceiver positions in a scene (e.g.s a conference room). We identify a fundamental trade-off between scalability and fidelity in the state-of-the-art method. To address this issue, we explore leveraging 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), an advanced technique for the image synthesis of 3D scenes in real-time from arbitrary camera poses. By integrating domain-specific insights, we design three components for adapting 3DGS to the RF domain, including Gaussian-based RF scene representation, gradient-guided RF attribute learning, and RF-customized CUDA for ray tracing. Building on them, we develop RFSPM, an end-to-end framework for scalable RF signal Spatial Propagation Modeling. We evaluate RFSPM in four field studies and two applications across RFID, BLE, LoRa, and 5G, covering diverse frequencies, antennas, signals, and scenes. The results show that RFSPM matches the fidelity of the state-of-the-art method while reducing data requirements, training GPU-hours, and inference latency by up to 9.8,$\times$, 18.6,$\times$, and 84.4,$\times$, respectively.
无线网络的网络规划和感知需要大量的现场调查进行数据采集。另一种方法是无线电频率(RF)信号空间传播建模,它通过场景中收发器的位置计算接收到的信号(例如会议室)。我们发现最先进的方法在可扩展性和保真度之间存在基本的权衡。为了解决这个问题,我们探索利用三维高斯混合法(Gaussian Splatting for Three-Dimensional Scene,简称 3DGS),这是一种用于从任意相机姿态对三维场景进行实时图像合成的先进技术。通过结合领域专业知识,我们设计了三个适应射频领域的组件,包括基于高斯分布的射频场景表示、梯度引导射频属性学习以及用于光线追踪的定制射频CUDA技术。基于这些技术,我们开发了一个用于可扩展射频信号空间传播建模的端到端框架——RFSPM。我们对四种场研究和两个应用于RFID、BLE、LoRa和5G等领域的项目进行了评估,涵盖不同频率、天线、信号和场景的应用环境。结果显示,RFSPM在最先进方法的保真度基础上有所突破,同时降低了数据需求,并减少训练GPU小时和推理延迟时间,最高分别达到了高达 9.8倍、18.6倍和 84.4倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
无线网络的网络规划和感知需要通过资源密集型的现场调查进行数据收集,也可以通过无线信号的空间传播建模来计算场景中的接收信号强度,例如会议室等场景。本文探讨了当前建模方法存在的可扩展性和保真度之间的权衡问题。为了解决这个问题,本文探索利用三维高斯涂敷技术(简称三维网格化渲染技术),这种用于三维场景图像合成的先进技术可以从任意相机姿态实现实时渲染。本文结合特定领域的见解,设计了三个适用于射频领域三维网格化渲染技术的组件,包括基于高斯函数的射频场景表示法、梯度引导的射频属性学习以及定制CUDA算法用于实现射线路径追踪等。最终建立了一套用于实现无线信号空间传播建模的端到端框架——RFSPM框架。通过在四个场地测试两个实际应用中的射频识别技术、蓝牙低功耗技术、LoRa技术以及第五代移动通信技术等场景下进行评估的结果显示,RFSPM框架能够在保持高度保真度的同时降低数据需求量、减少GPU训练时长以及推理延迟,其效果最高可达当前先进方法的约九成八倍(时间减少)、十八倍半(成本降低)以及近八十四倍半(延时降低)。通过有效使用该方法有望改进未来无线网络的规划方法和性能感知效果。总的来说,该框架是构建大规模无线通信网络的有效工具。它极大地减少了所需的资源和时间,提升了信号模拟和无线网络规划的效率与精度。为实现高质量的无线网络服务和个性化感知体验奠定了重要基础。此外,通过本框架收集的数据也可用于进一步研究和优化无线通信系统的性能。我们相信该框架将为无线通信领域带来重大突破和进展。
关键见解
一、文章探讨了无线网络的网络规划和感知的一种新方法是利用RF信号空间传播建模来计算场景中接收信号的强度。同时揭示了目前方法的局限性:可扩展性和保真度之间的权衡问题。
二、引入三维高斯涂敷技术(简称三维网格化渲染技术),用于解决此问题。将特定领域的见解应用于三个主要组件的设计以适应射频领域:高斯基础射频场景表示法、梯度引导射频属性学习以及定制CUDA算法用于射线路径追踪等。
点此查看论文截图

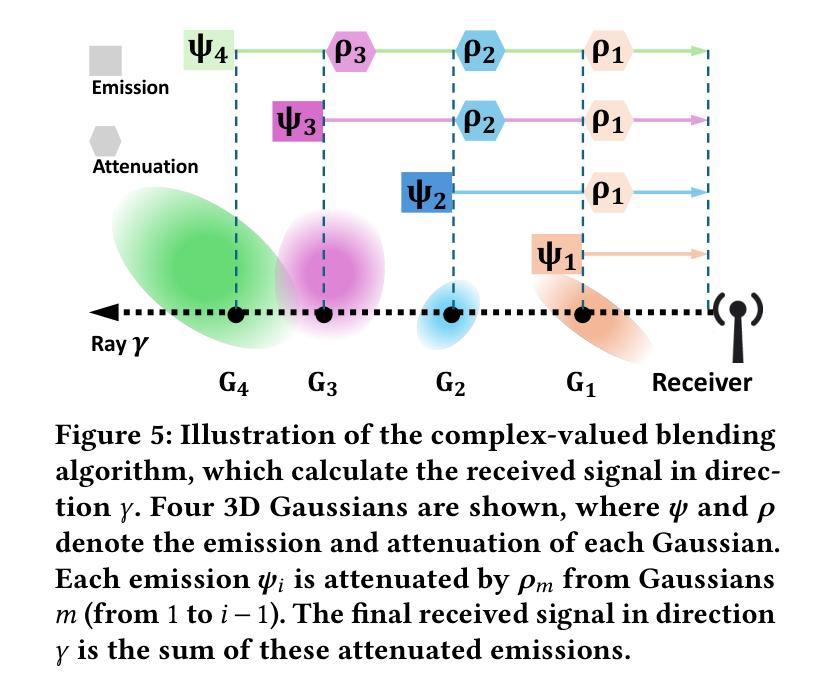
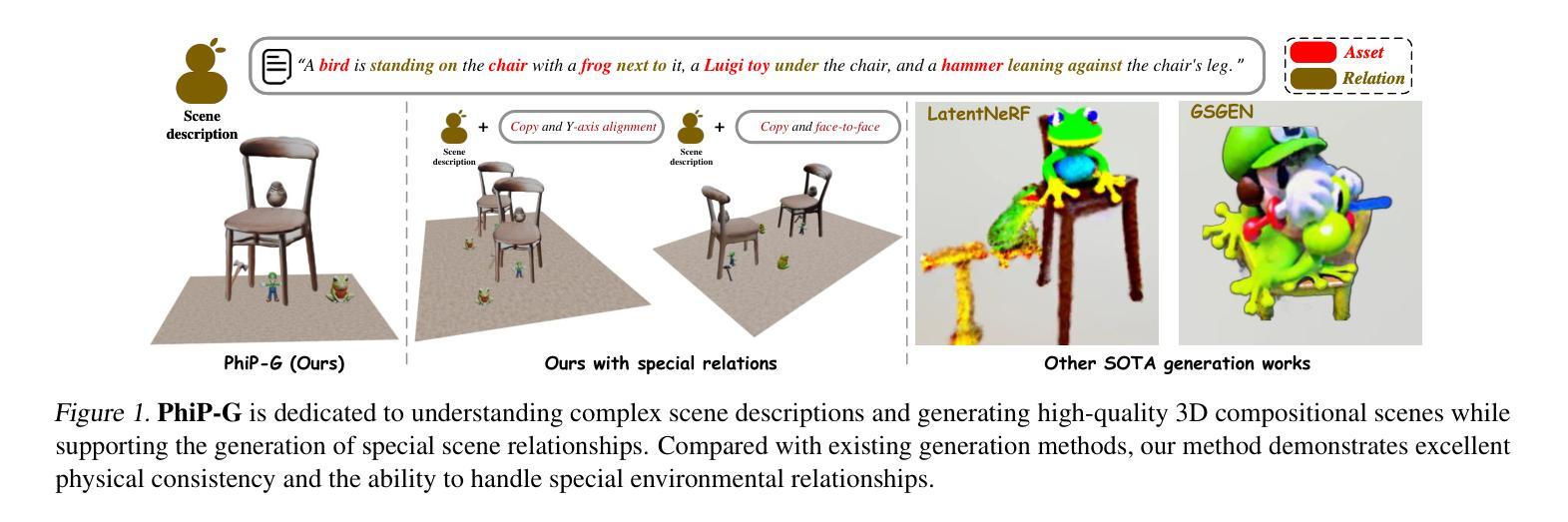
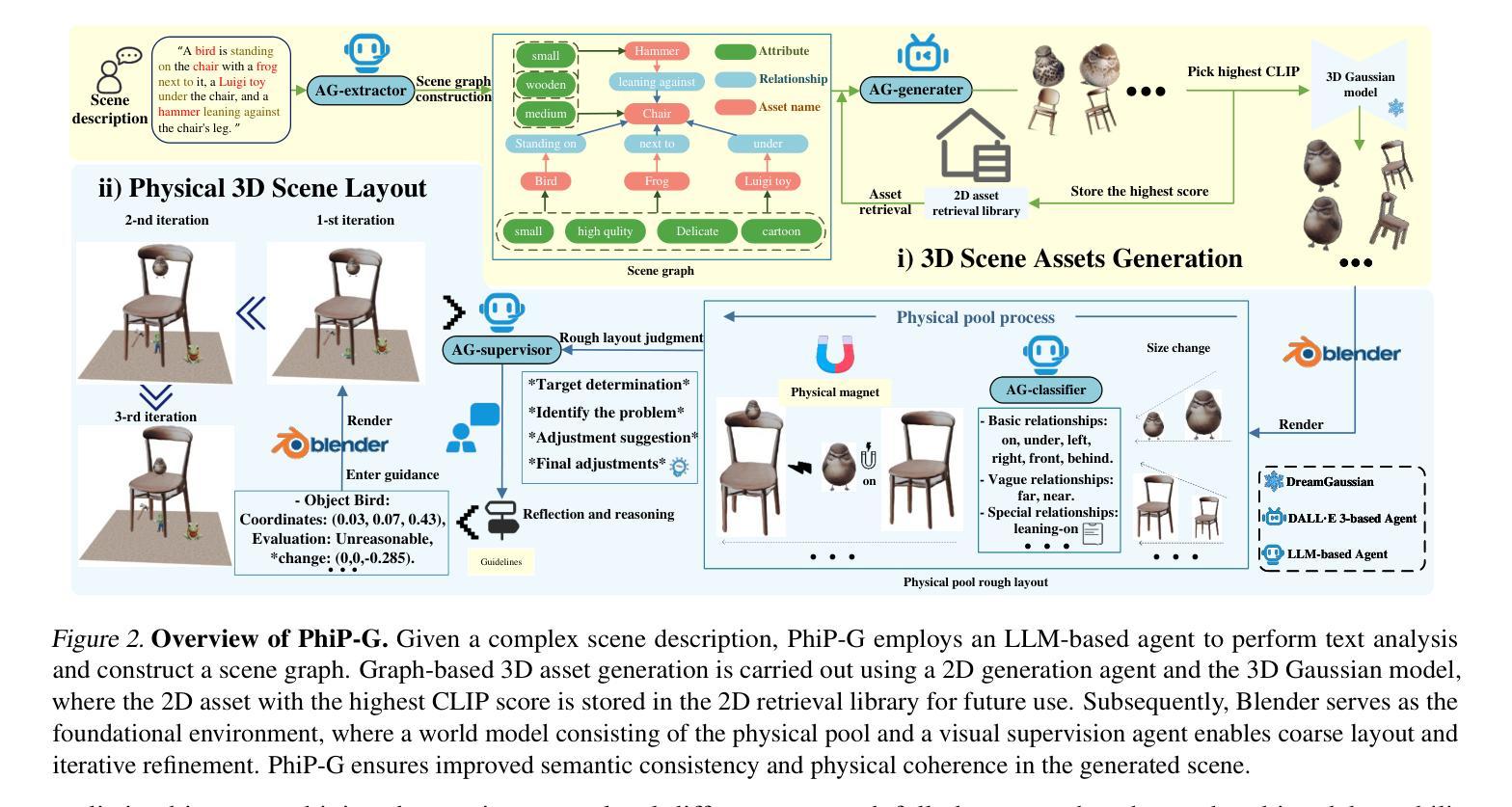
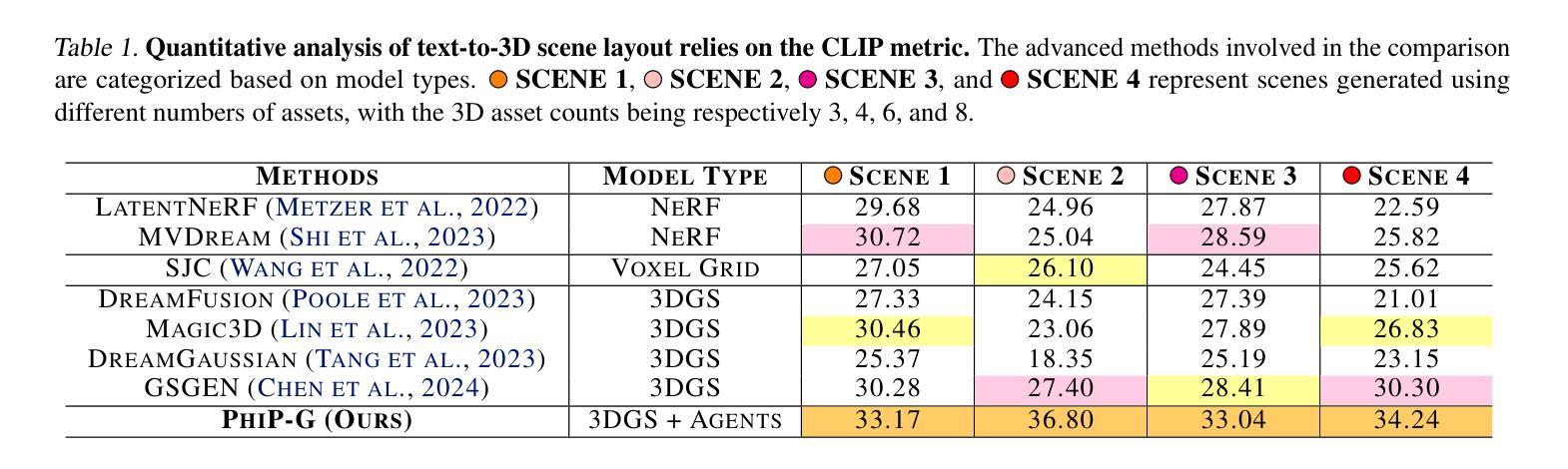
PhiP-G: Physics-Guided Text-to-3D Compositional Scene Generation
Authors:Qixuan Li, Chao Wang, Zongjin He, Yan Peng
Text-to-3D asset generation has achieved significant optimization under the supervision of 2D diffusion priors. However, when dealing with compositional scenes, existing methods encounter several challenges: 1). failure to ensure that composite scene layouts comply with physical laws; 2). difficulty in accurately capturing the assets and relationships described in complex scene descriptions; 3). limited autonomous asset generation capabilities among layout approaches leveraging large language models (LLMs). To avoid these compromises, we propose a novel framework for compositional scene generation, PhiP-G, which seamlessly integrates generation techniques with layout guidance based on a world model. Leveraging LLM-based agents, PhiP-G analyzes the complex scene description to generate a scene graph, and integrating a multimodal 2D generation agent and a 3D Gaussian generation method for targeted assets creation. For the stage of layout, PhiP-G employs a physical pool with adhesion capabilities and a visual supervision agent, forming a world model for layout prediction and planning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PhiP-G significantly enhances the generation quality and physical rationality of the compositional scenes. Notably, PhiP-G attains state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in CLIP scores, achieves parity with the leading methods in generation quality as measured by the T$^3$Bench, and improves efficiency by 24x.
文本到3D资产生成在二维扩散先验的监督下实现了显著优化。然而,在处理组合场景时,现有方法面临多个挑战:1.无法保证组合场景布局符合物理定律;2.难以准确捕捉复杂场景描述中的资产和关系;3.利用大型语言模型(LLM)的布局方法自主资产生成能力有限。为了避免这些妥协,我们提出了一种新型组合场景生成框架PhiP-G,它无缝集成了基于世界模型的布局指导生成技术。PhiP-G利用基于LLM的代理分析复杂场景描述来生成场景图,并集成多模式二维生成代理和3D高斯生成方法进行有针对性的资产创建。在布局阶段,PhiP-G采用具有粘附能力的物理池和视觉监督代理,形成布局预测和规划的世模型。大量实验表明,PhiP-G显著提高了组合场景的生成质量和物理合理性。值得注意的是,PhiP-G在CLIP评分上达到最新水平(SOTA),在T$^3$Bench衡量生成质量方面与领先方法持平,并提高了24倍的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages.8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了在二维扩散先验监督下,文本到三维资产生成已经实现了显著优化。然而,在处理组合场景时,现有方法面临多个挑战。为此,提出了一种新型组合场景生成框架PhiP-G,它无缝集成了基于世界模型的布局指导生成技术。PhiP-G利用基于LLM的代理分析复杂场景描述以生成场景图,并集成多模式二维生成代理和三维高斯生成方法进行有针对性的资产创建。在布局阶段,PhiP-G采用具有粘附能力的物理池和视觉监督代理,形成世界模型进行布局预测和规划。实验表明,PhiP-G显著提高了组合场景的生成质量和物理合理性,达到了CLIP评分中的最新技术水平,在T$^3$Bench中以卓越表现证明了生成质量方面的领先效率提升高达24倍。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到三维资产生成已经取得了在二维扩散先验监督下的显著优化进展。
- 组合场景生成面临确保遵守物理定律、准确捕捉复杂场景描述的资产及关系和自主资产生成能力有限的挑战。
- 提出了一种新型组合场景生成框架PhiP-G,结合了生成技术与基于世界模型的布局指导。
- PhiP-G通过LLM代理分析复杂场景描述生成场景图,并利用多模式二维生成和三维高斯生成方法创建资产。
- PhiP-G采用物理池和视觉监督代理进行布局预测和规划,确保场景的物理合理性。
- 实验显示,PhiP-G在提高生成质量和物理合理性的同时,达到了CLIP评分的最新技术水平,并在T$^3$Bench上表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

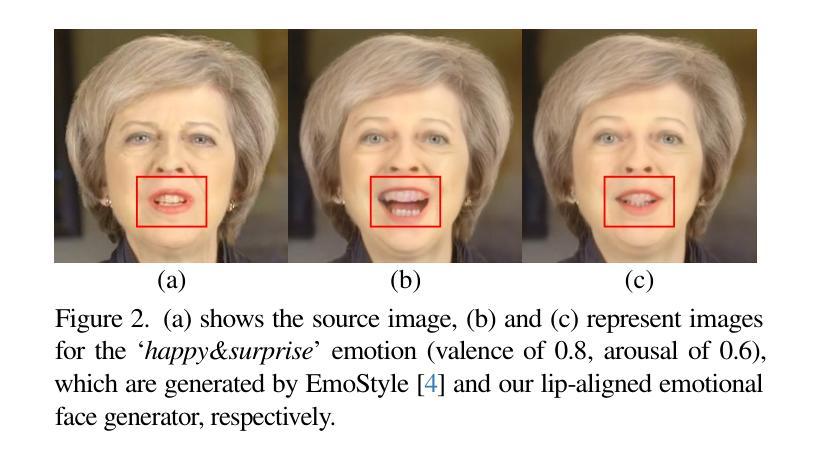
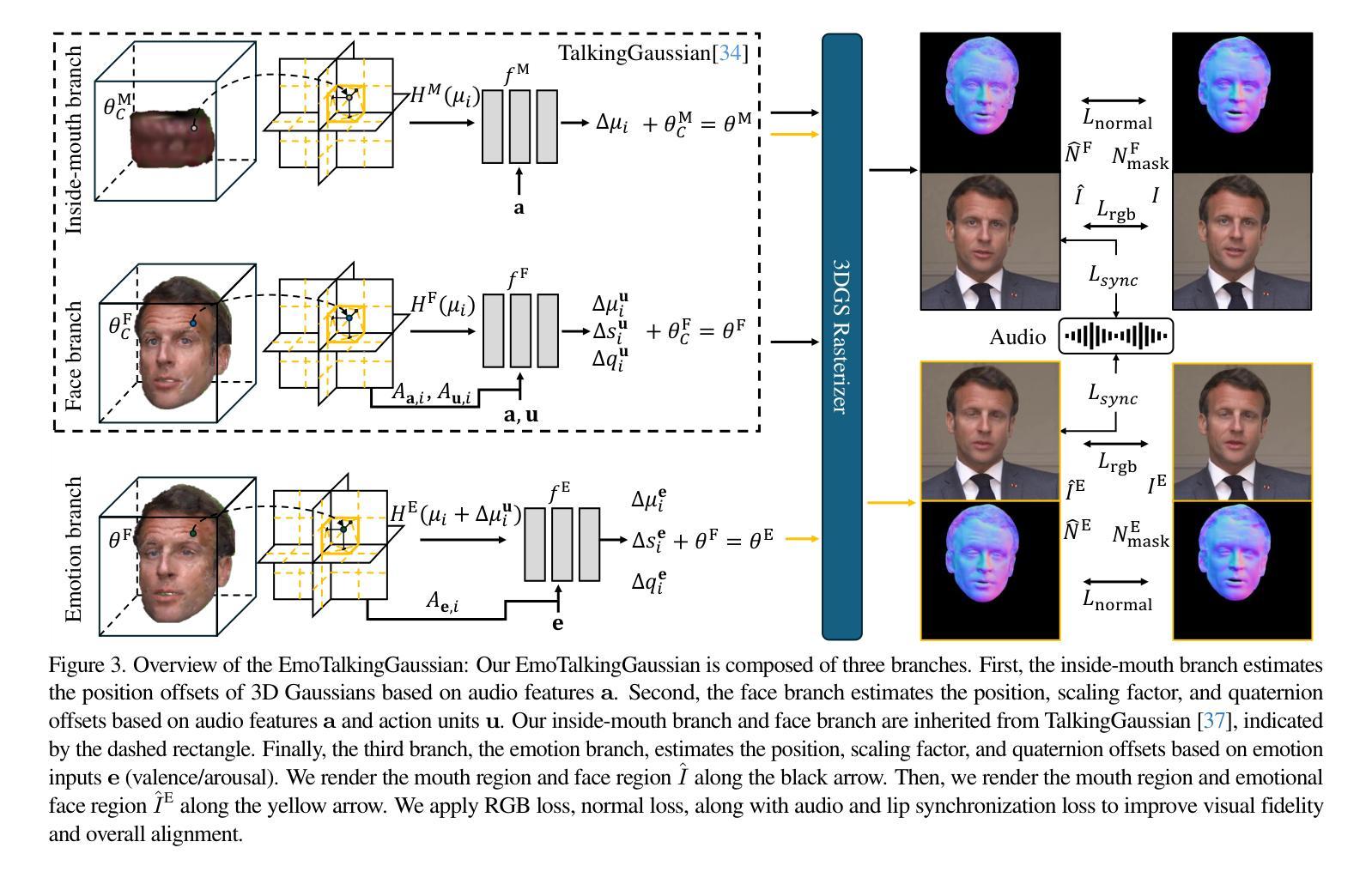
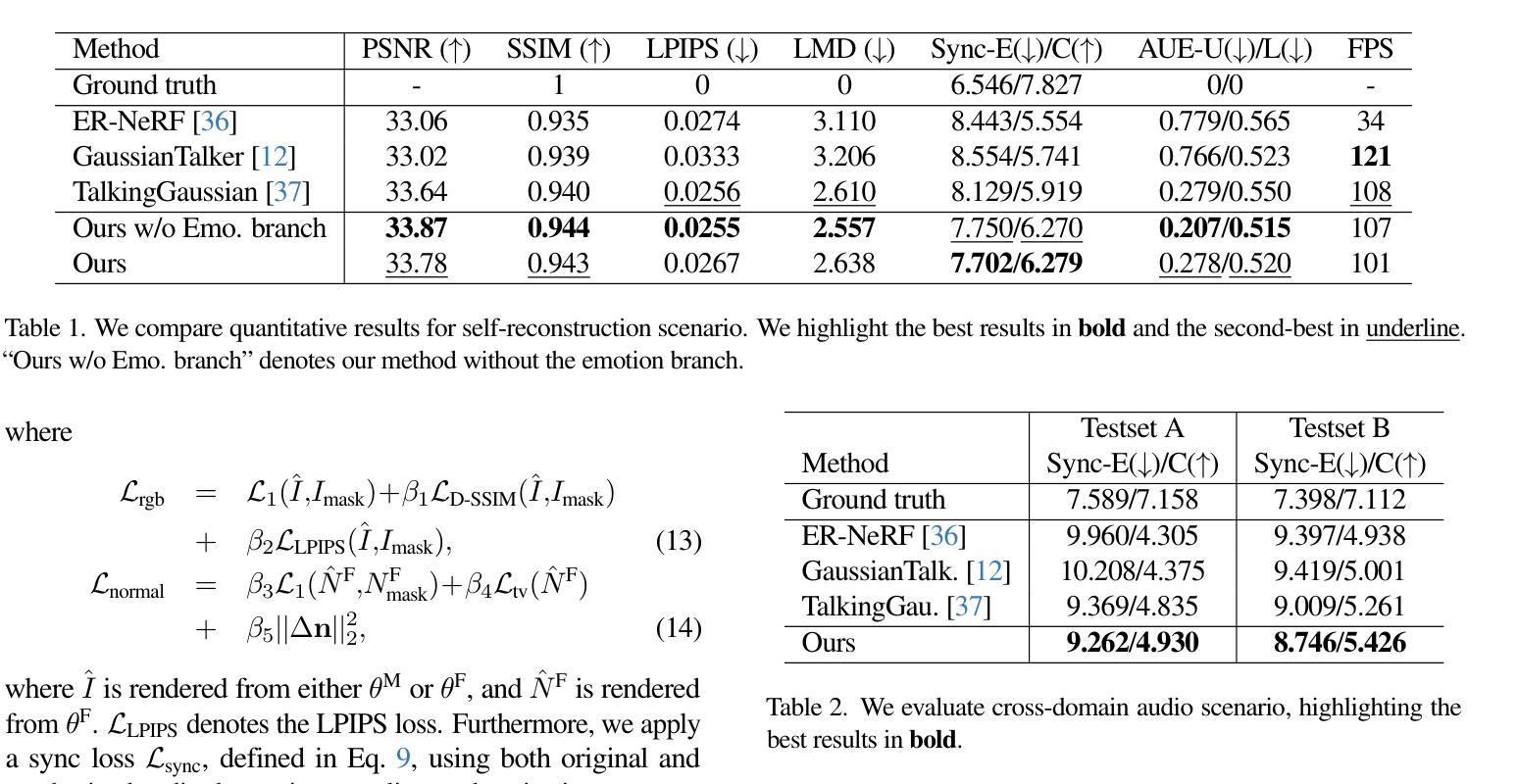
EmoTalkingGaussian: Continuous Emotion-conditioned Talking Head Synthesis
Authors:Junuk Cha, Seongro Yoon, Valeriya Strizhkova, Francois Bremond, Seungryul Baek
3D Gaussian splatting-based talking head synthesis has recently gained attention for its ability to render high-fidelity images with real-time inference speed. However, since it is typically trained on only a short video that lacks the diversity in facial emotions, the resultant talking heads struggle to represent a wide range of emotions. To address this issue, we propose a lip-aligned emotional face generator and leverage it to train our EmoTalkingGaussian model. It is able to manipulate facial emotions conditioned on continuous emotion values (i.e., valence and arousal); while retaining synchronization of lip movements with input audio. Additionally, to achieve the accurate lip synchronization for in-the-wild audio, we introduce a self-supervised learning method that leverages a text-to-speech network and a visual-audio synchronization network. We experiment our EmoTalkingGaussian on publicly available videos and have obtained better results than state-of-the-arts in terms of image quality (measured in PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS), emotion expression (measured in V-RMSE, A-RMSE, V-SA, A-SA, Emotion Accuracy), and lip synchronization (measured in LMD, Sync-E, Sync-C), respectively.
基于3D高斯展平的说话人头部合成技术近期因其能够实时渲染高保真图像而受到关注。然而,因为它通常只在缺乏面部表情多样性的短视频上进行训练,所以生成的说话人的头部在表达各种情绪时表现吃力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种唇形对齐的情感面部生成器,并利用它训练我们的EmoTalkingGaussian模型。该模型能够基于连续的情绪值(即效价和唤起)来操作面部表情;同时保留与输入音频的唇部运动同步。此外,为了实现野外音频的精确唇形同步,我们引入了一种自我监督学习方法,该方法利用文本到语音网络和视觉-音频同步网络。我们在公开视频上对EmoTalkingGaussian进行了实验,在图像质量(以PSNR、SSIM、LPIPS衡量)、情感表达(以V-RMSE、A-RMSE、V-SA、A-SA、情感准确率衡量)和唇形同步(以LMD、Sync-E、Sync-C衡量)等方面获得了比当前最佳水平更好的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages
Summary
本文介绍了基于3D高斯点云技术的说话人头部合成方法,针对现有技术缺乏情感多样性问题,提出了情感脸生成器,并结合情绪值操控面部表情。通过自监督学习方法实现唇音同步,提高在野音频的准确同步性,并在公开视频上测试得到优于现有技术的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯点云技术用于说话人头部合成,实现高保真图像和实时推理速度。
- 现有方法因训练视频缺乏情感多样性,导致生成的说话头无法表现广泛情绪。
- 提出了情感脸生成器EmoTalkingGaussian模型,可根据连续情绪值操控面部表情。
- 模型保留唇部动作与输入音频的同步性。
- 为实现在野音频的准确唇音同步,引入自监督学习方法。
- 结合文本转语音网络和视听同步网络实现自监督学习。
点此查看论文截图

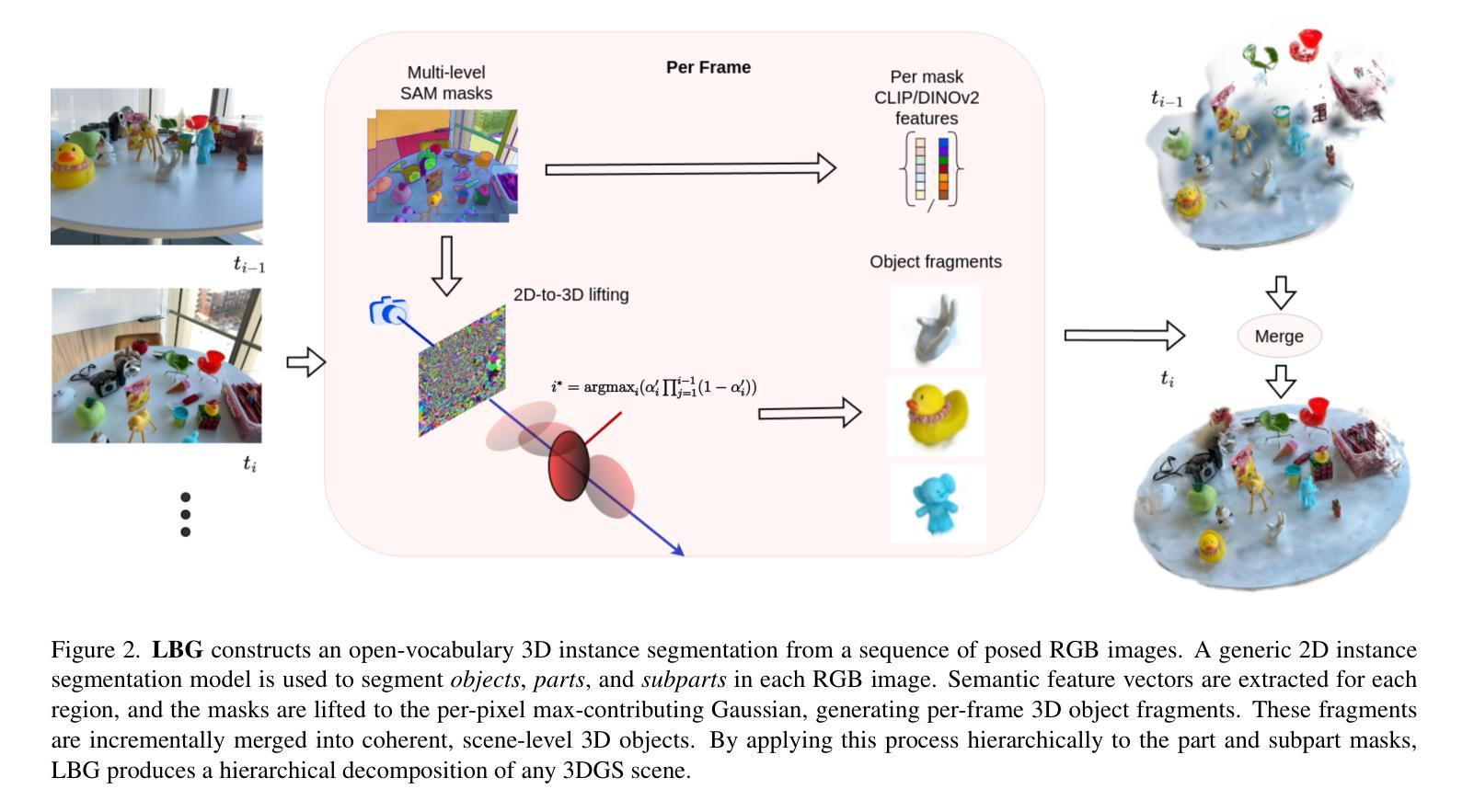
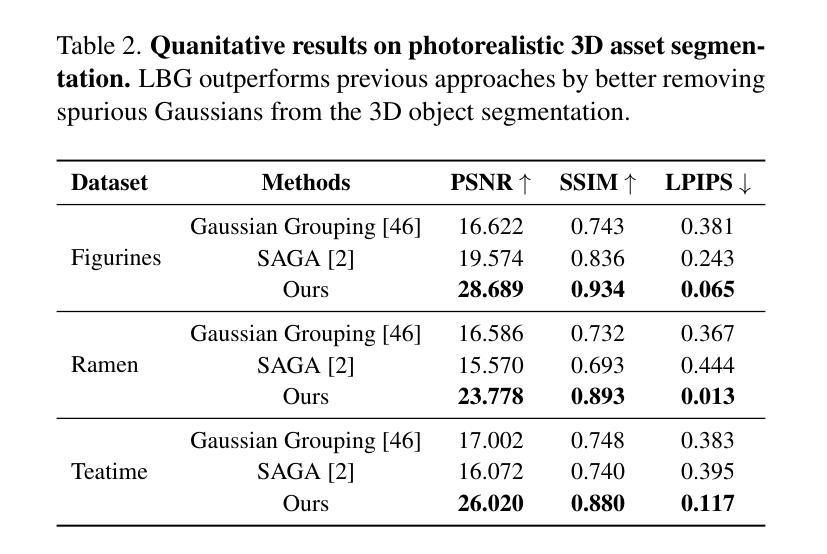
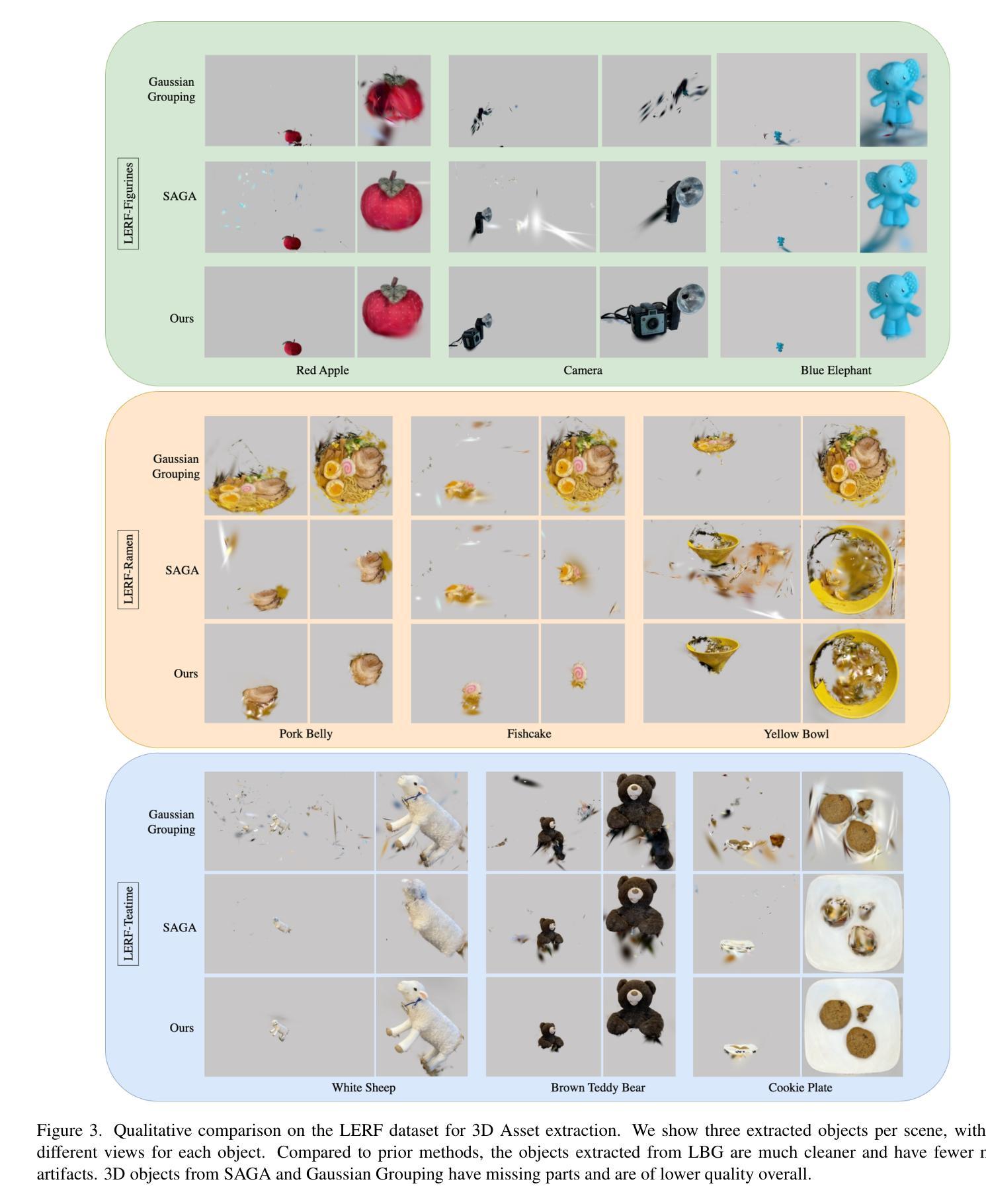
Lifting by Gaussians: A Simple, Fast and Flexible Method for 3D Instance Segmentation
Authors:Rohan Chacko, Nicolai Haeni, Eldar Khaliullin, Lin Sun, Douglas Lee
We introduce Lifting By Gaussians (LBG), a novel approach for open-world instance segmentation of 3D Gaussian Splatted Radiance Fields (3DGS). Recently, 3DGS Fields have emerged as a highly efficient and explicit alternative to Neural Field-based methods for high-quality Novel View Synthesis. Our 3D instance segmentation method directly lifts 2D segmentation masks from SAM (alternately FastSAM, etc.), together with features from CLIP and DINOv2, directly fusing them onto 3DGS (or similar Gaussian radiance fields such as 2DGS). Unlike previous approaches, LBG requires no per-scene training, allowing it to operate seamlessly on any existing 3DGS reconstruction. Our approach is not only an order of magnitude faster and simpler than existing approaches; it is also highly modular, enabling 3D semantic segmentation of existing 3DGS fields without requiring a specific parametrization of the 3D Gaussians. Furthermore, our technique achieves superior semantic segmentation for 2D semantic novel view synthesis and 3D asset extraction results while maintaining flexibility and efficiency. We further introduce a novel approach to evaluate individually segmented 3D assets from 3D radiance field segmentation methods.
我们介绍了通过高斯提升(LBG)这一新方法,实现了对三维高斯平铺辐射场(3DGS)的开放世界实例分割。最近,3DGS场作为基于神经场方法的高质量新型视图合成的高效显式替代方案而崭露头角。我们的三维实例分割方法直接从SAM(或FastSAM等)提取二维分割掩膜,并结合CLIP和DINOv2的特征,将它们直接融合到3DGS(或类似的二维高斯辐射场如二维高斯分割)中。与以前的方法不同,LBG无需针对每个场景进行训练,因此可以无缝地应用于任何现有的3DGS重建。我们的方法不仅比现有方法快得多、简单得多;而且高度模块化,能够在不需要对三维高斯进行特定参数化的条件下,实现现有3DGS场的三维语义分割。此外,我们的技术在进行二维语义新型视图合成和三维资产提取结果时,实现了出色的语义分割,同时保持了灵活性和效率。我们还介绍了一种新型方法,用于评估来自三维辐射场分割方法的单独分割的三维资产。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WACV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了通过高斯提升(LBG)方法,这是一种用于开放世界实例分割的3D高斯展开辐射场(3DGS)的新方法。它可以直接从SAM等提取的二维分割掩码中提升特征,将其融合到3DGS中,实现高效的实例分割。此方法无需对场景进行训练,具有模块化特性,能在不特定参数化三维高斯的情况下实现灵活的语义分割。同时,此方法可实现卓越的二三维语义分割结果。
Key Takeaways
- LBG是一种用于开放世界实例分割的3DGS新方法。
- 它利用二维分割掩码与特征进行提升并融合到三维高斯辐射场中。
- LBG方法无需场景训练,可以无缝地应用于任何现有的3DGS重建上。
- 该方法比现有方法更简单快捷,具有高度的模块化特性。
- LBG可实现灵活的三维语义分割,而无需特定高斯参数化。
- 该方法在二维语义新视角合成和三维资产提取方面取得了卓越的语义分割结果。
点此查看论文截图

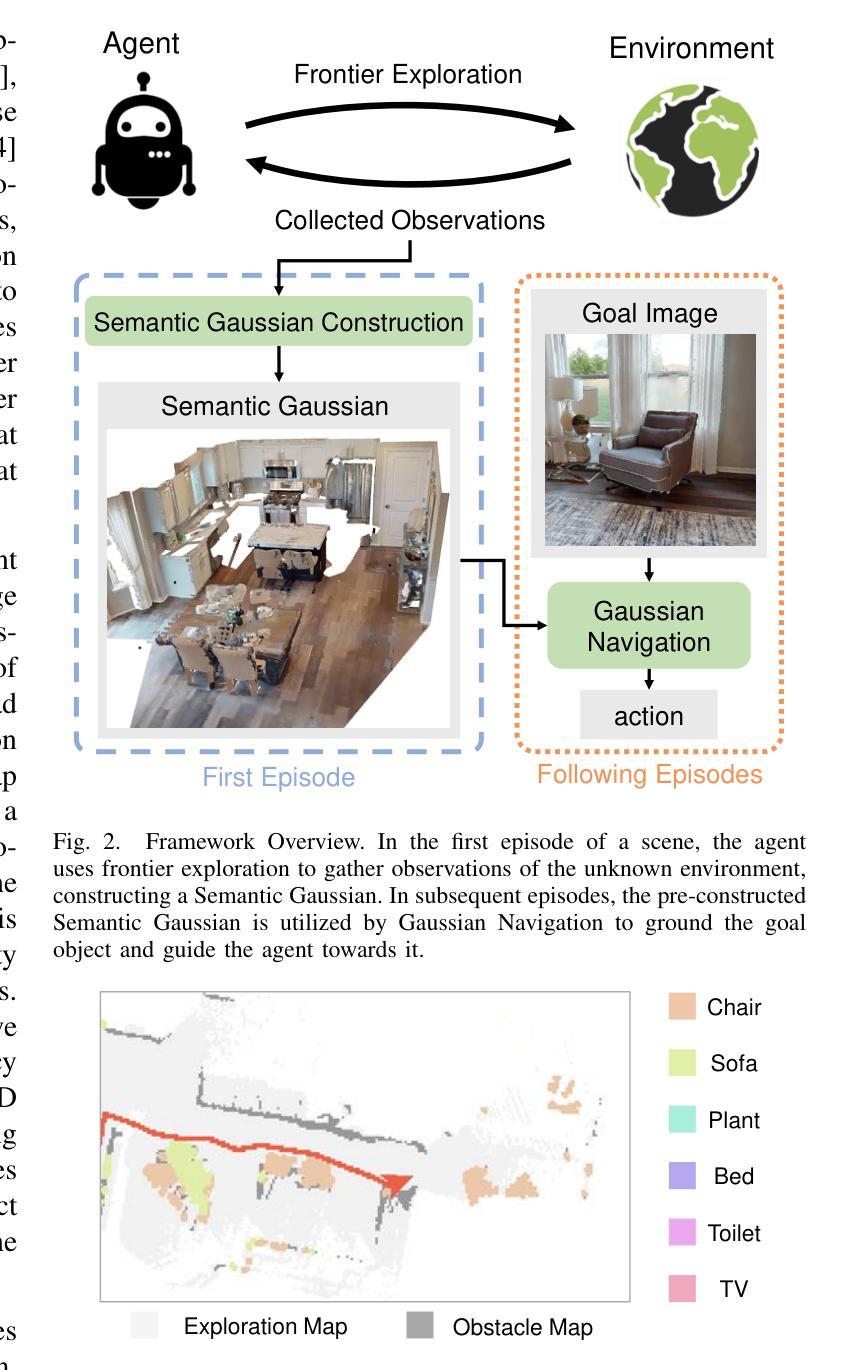
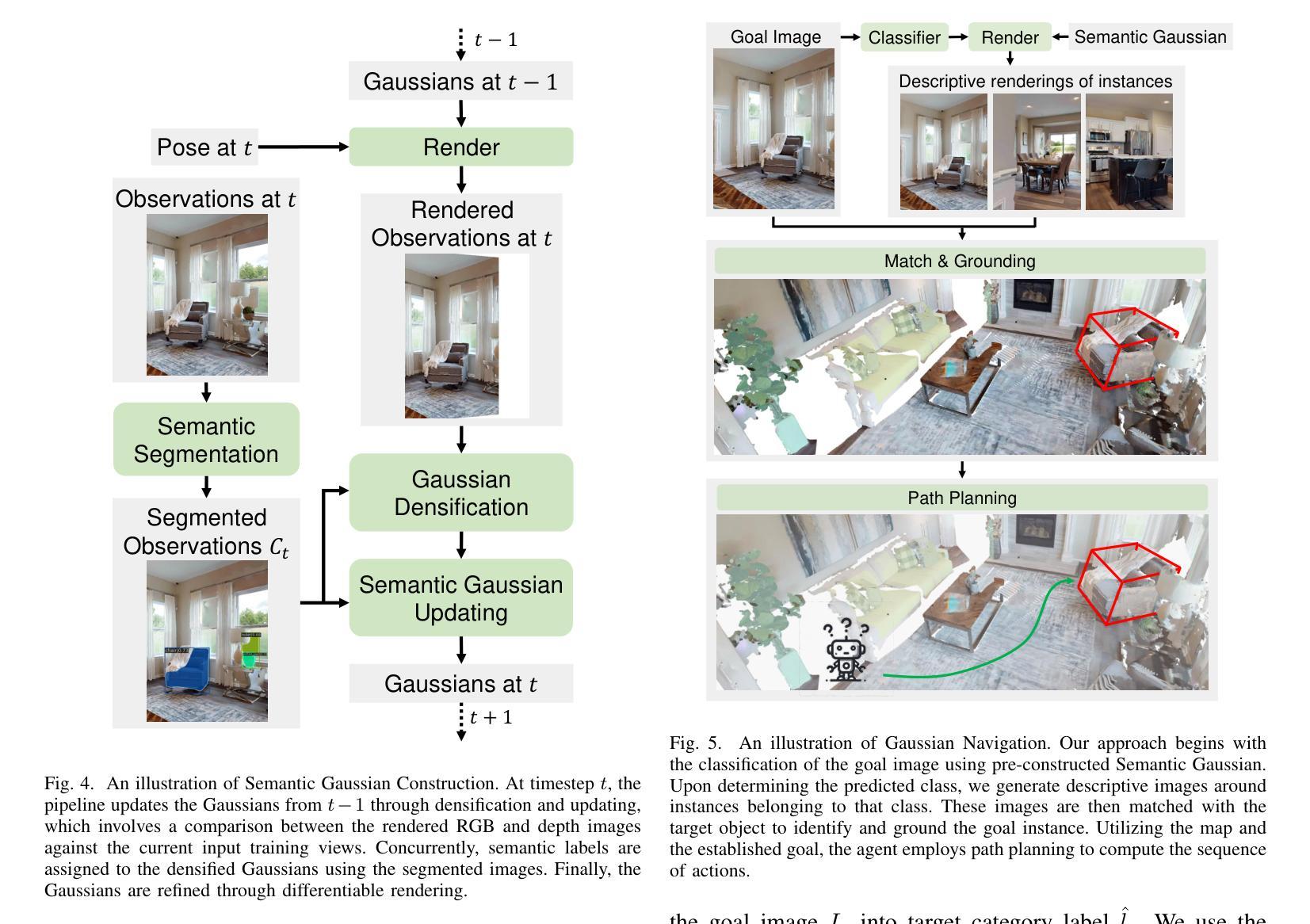
GaussNav: Gaussian Splatting for Visual Navigation
Authors:Xiaohan Lei, Min Wang, Wengang Zhou, Houqiang Li
In embodied vision, Instance ImageGoal Navigation (IIN) requires an agent to locate a specific object depicted in a goal image within an unexplored environment. The primary challenge of IIN arises from the need to recognize the target object across varying viewpoints while ignoring potential distractors. Existing map-based navigation methods typically use Bird’s Eye View (BEV) maps, which lack detailed texture representation of a scene. Consequently, while BEV maps are effective for semantic-level visual navigation, they are struggling for instance-level tasks. To this end, we propose a new framework for IIN, Gaussian Splatting for Visual Navigation (GaussNav), which constructs a novel map representation based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). The GaussNav framework enables the agent to memorize both the geometry and semantic information of the scene, as well as retain the textural features of objects. By matching renderings of similar objects with the target, the agent can accurately identify, ground, and navigate to the specified object. Our GaussNav framework demonstrates a significant performance improvement, with Success weighted by Path Length (SPL) increasing from 0.347 to 0.578 on the challenging Habitat-Matterport 3D (HM3D) dataset. The source code is publicly available at the link: https://github.com/XiaohanLei/GaussNav.
在实体视觉中,实例图像目标导航(IIN)要求智能体在一个未探索的环境中定位目标图像所描绘的特定对象。IIN的主要挑战在于需要在不同的视角中识别目标对象,同时忽略潜在的干扰物。现有的基于地图的导航方法通常使用鸟瞰图(BEV),但缺乏场景的详细纹理表示。因此,虽然BEV地图在语义级视觉导航中有效,但在实例级任务中却表现不佳。为此,我们针对IIN提出了一种新的框架,即高斯涂抹视觉导航(GaussNav),它基于三维高斯涂抹(3DGS)构建了一种新的地图表示。GaussNav框架使智能体能够记住场景中的几何和语义信息,同时保留对象的纹理特征。通过匹配与目标相似的对象的渲染,智能体可以准确识别、定位并导航到指定对象。我们的GaussNav框架在具有挑战性的Habitat-Matterport 3D(HM3D)数据集上实现了显著的性能提升,路径长度加权成功率(SPL)从0.347提高到0.578。源代码可在以下链接处公开获取:https://github.com/XiaohanLei/GaussNav。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF journal
Summary
该文介绍了一种针对实体视觉中的Instance ImageGoal Navigation(IIN)任务的新型框架——Gaussian Splatting for Visual Navigation(GaussNav)。该框架基于3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)构建了一种新的地图表示方法,使代理能够记住场景中的几何和语义信息,并保留对象的纹理特征。通过匹配相似对象的渲染与目标对象,代理可以准确识别、定位和导航到指定对象。在具有挑战性的Habitat-Matterport 3D(HM3D)数据集上,GaussNav框架的性能显著提高,成功路径长度(SPL)从0.347提高到0.578。
Key Takeaways
- Instance ImageGoal Navigation (IIN) 要求代理在未知环境中找到目标图像中描绘的特定对象。
- 主要挑战在于需要从不同的视角识别目标对象,同时忽略潜在的干扰物。
- 现有基于地图的导航方法通常使用缺乏场景纹理表示的鸟瞰图(BEV)。
- BEV地图在语义级视觉导航中有效,但在实例级任务中表现不佳。
- 提出了一个新的框架GaussNav,基于3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) 构建新型地图表示。
- GaussNav使代理能够记住场景的几何和语义信息,并保留对象的纹理特征。
点此查看论文截图