⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-06 更新
Calibrated Multi-Preference Optimization for Aligning Diffusion Models
Authors:Kyungmin Lee, Xiaohang Li, Qifei Wang, Junfeng He, Junjie Ke, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Irfan Essa, Jinwoo Shin, Feng Yang, Yinxiao Li
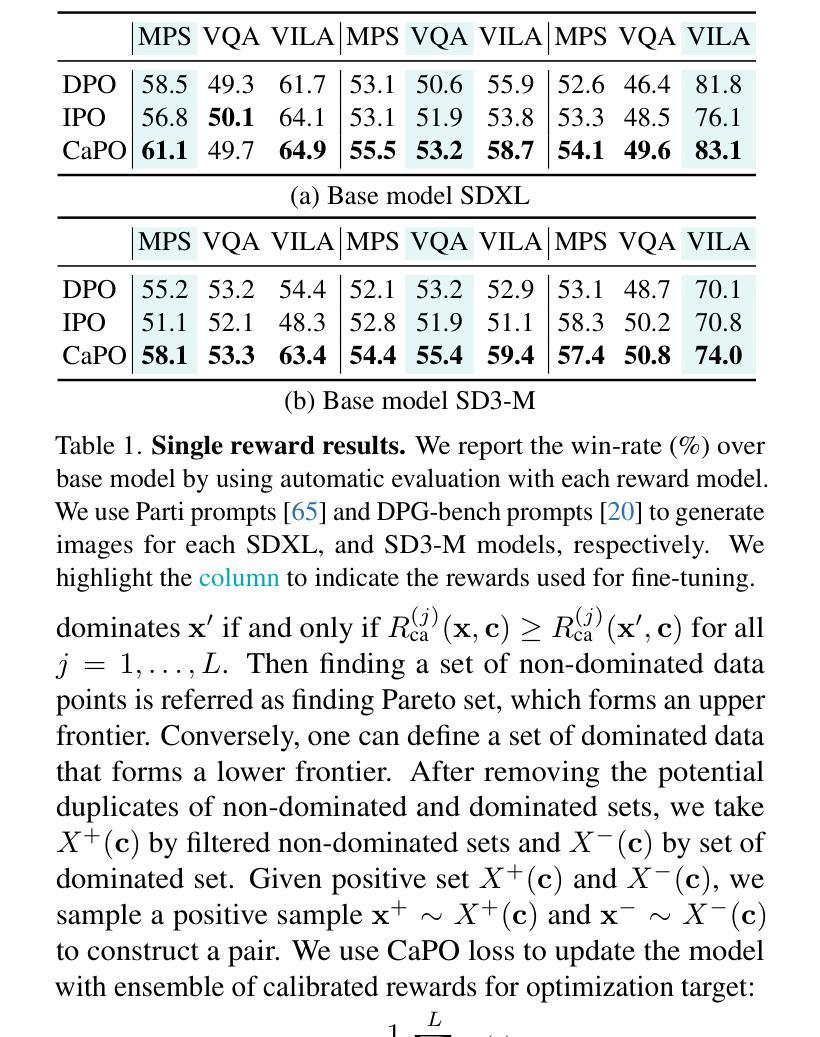
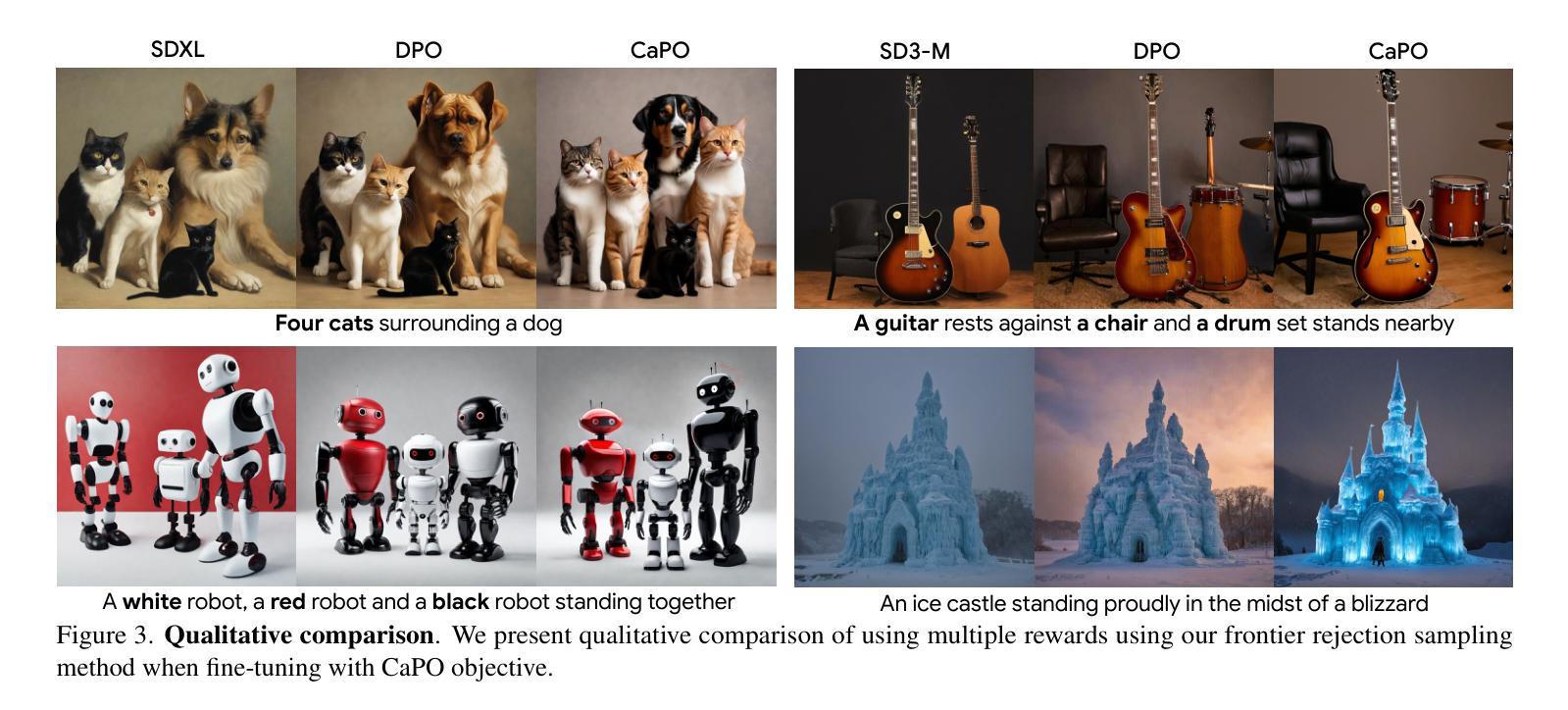
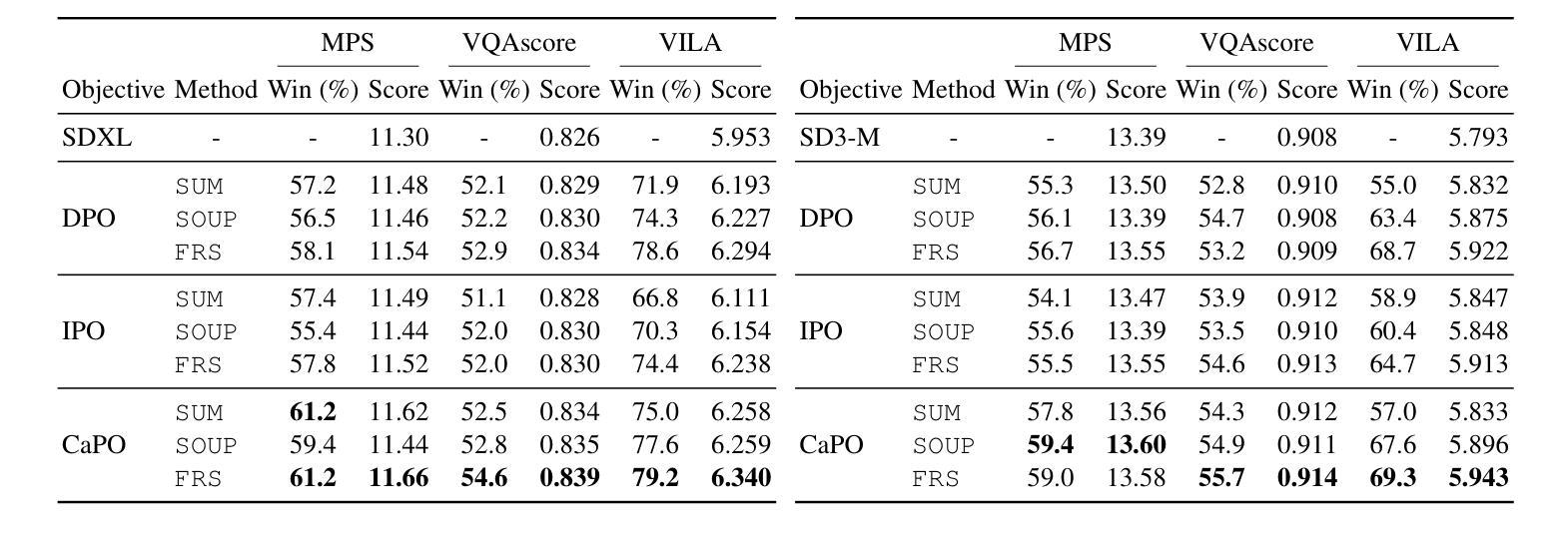
Aligning text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models with preference optimization is valuable for human-annotated datasets, but the heavy cost of manual data collection limits scalability. Using reward models offers an alternative, however, current preference optimization methods fall short in exploiting the rich information, as they only consider pairwise preference distribution. Furthermore, they lack generalization to multi-preference scenarios and struggle to handle inconsistencies between rewards. To address this, we present Calibrated Preference Optimization (CaPO), a novel method to align T2I diffusion models by incorporating the general preference from multiple reward models without human annotated data. The core of our approach involves a reward calibration method to approximate the general preference by computing the expected win-rate against the samples generated by the pretrained models. Additionally, we propose a frontier-based pair selection method that effectively manages the multi-preference distribution by selecting pairs from Pareto frontiers. Finally, we use regression loss to fine-tune diffusion models to match the difference between calibrated rewards of a selected pair. Experimental results show that CaPO consistently outperforms prior methods, such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), in both single and multi-reward settings validated by evaluation on T2I benchmarks, including GenEval and T2I-Compbench.
将文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型与偏好优化对齐对于人类注释数据集是有价值的,但手动数据收集的沉重成本限制了可扩展性。使用奖励模型提供了一种替代方案,然而,当前的偏好优化方法未能充分利用丰富信息,因为它们只考虑成对偏好分布。此外,它们缺乏在多种偏好场景下的通用性,并且难以处理奖励之间的一致性问题。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了校准偏好优化(CaPO)这一新方法,通过结合来自多个奖励模型的通用偏好,无需人类注释数据即可对齐T2I扩散模型。我们的方法的核心在于奖励校准方法,通过计算预训练模型生成的样本的预期胜率来近似通用偏好。此外,我们提出了一种基于前沿的配对选择方法,通过从帕累托前沿选择配对来有效地管理多偏好分布。最后,我们使用回归损失对扩散模型进行微调,以匹配选定配对的校准奖励之间的差异。实验结果表明,无论是在单一奖励还是多奖励设置下,CaPO在GenEval和T2I-Compbench等T2I基准测试上的表现均优于先前的方法,如直接偏好优化(DPO)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型与偏好优化的对齐对于人类注释数据集具有价值,但手动数据收集的昂贵成本限制了其可扩展性。使用奖励模型作为替代方案,但当前偏好优化方法未能充分利用丰富信息,仅考虑成对偏好分布。此外,它们缺乏在多种偏好场景下的通用性,并难以处理奖励间的不一致性。为解决这些问题,我们提出了校准偏好优化(CaPO)方法,通过结合多个奖励模型的通用偏好,无需人类注释数据即可对齐T2I扩散模型。核心在于奖励校准方法,通过计算预期胜率来近似通用偏好,对抗由预训练模型生成的样本。同时,我们提出了基于前沿的配对选择方法,通过选择帕累托前沿的配对来有效管理多偏好分布。最后,使用回归损失对扩散模型进行微调,以匹配选定配对的校准奖励差异。实验结果表明,CaPO在单奖励和多奖励设置下均优于Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)方法,并在GenEval和T2I-Compbench等T2I基准测试中得到了验证。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的偏好优化对于人类注释数据集至关重要,但手动数据收集成本高昂。
- 当前偏好优化方法仅考虑成对偏好分布,无法充分利用丰富信息。
- 现有方法缺乏在多种偏好场景下的通用性,难以处理奖励间的不一致性。
- 提出了校准偏好优化(CaPO)方法,结合多个奖励模型的通用偏好,无需人类注释数据即可对齐T2I扩散模型。
- CaPO通过奖励校准方法和基于前沿的配对选择方法来管理多偏好分布。
- CaPO使用回归损失微调扩散模型,以匹配选定配对的校准奖励差异。
点此查看论文截图



Privacy Attacks on Image AutoRegressive Models
Authors:Antoni Kowalczuk, Jan Dubiński, Franziska Boenisch, Adam Dziedzic
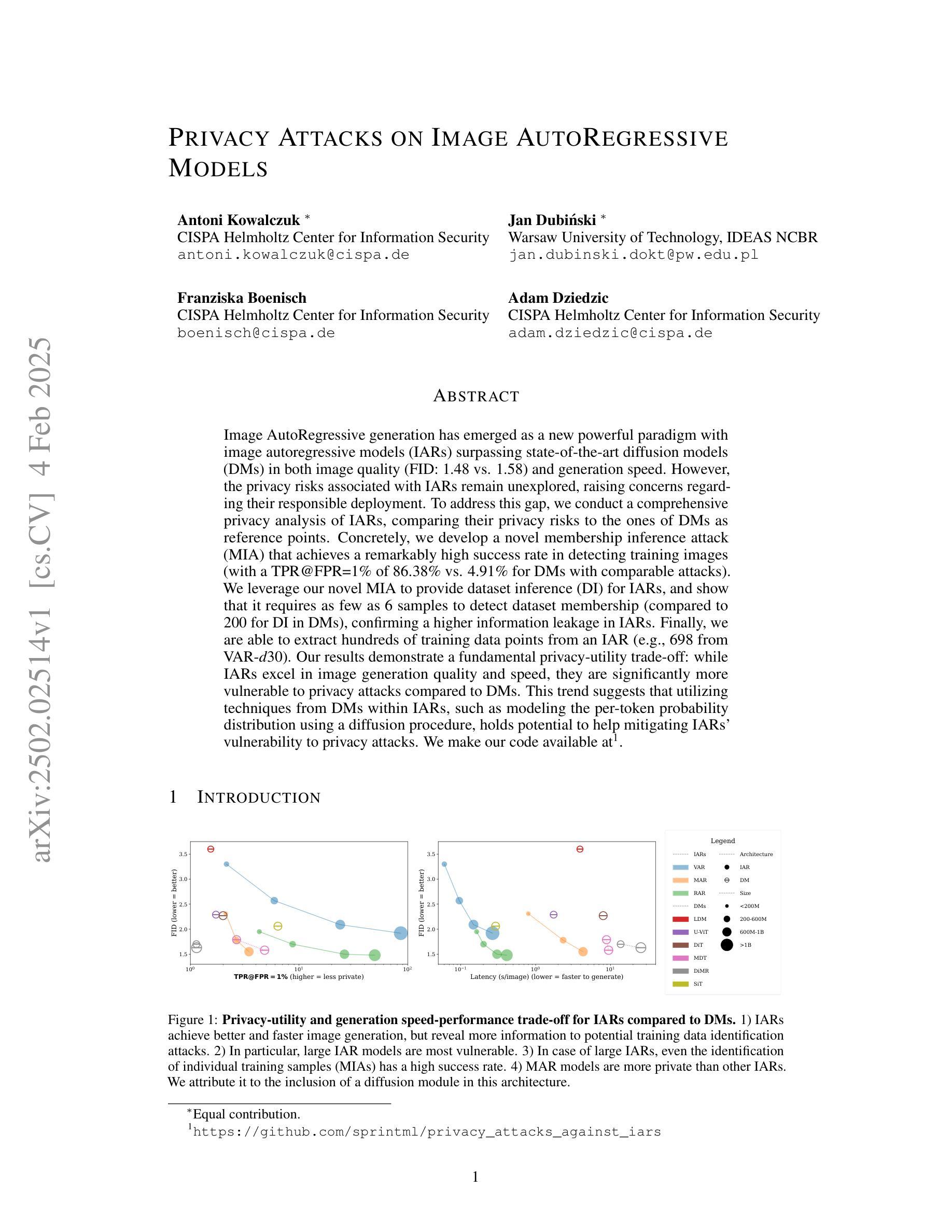
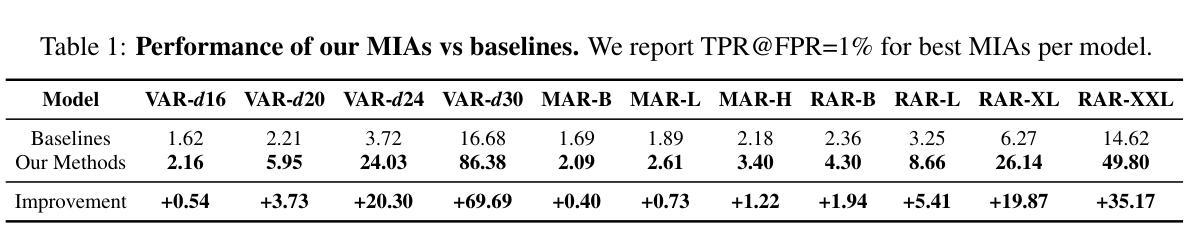
Image autoregressive (IAR) models have surpassed diffusion models (DMs) in both image quality (FID: 1.48 vs. 1.58) and generation speed. However, their privacy risks remain largely unexplored. To address this, we conduct a comprehensive privacy analysis comparing IARs to DMs. We develop a novel membership inference attack (MIA) that achieves a significantly higher success rate in detecting training images (TPR@FPR=1%: 86.38% for IARs vs. 4.91% for DMs). Using this MIA, we perform dataset inference (DI) and find that IARs require as few as six samples to detect dataset membership, compared to 200 for DMs, indicating higher information leakage. Additionally, we extract hundreds of training images from an IAR (e.g., 698 from VAR-d30). Our findings highlight a fundamental privacy-utility trade-off: while IARs excel in generation quality and speed, they are significantly more vulnerable to privacy attacks. This suggests that incorporating techniques from DMs, such as per-token probability modeling using diffusion, could help mitigate IARs’ privacy risks. Our code is available at https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars.
图像自回归(IAR)模型在图像质量(FID:1.48 vs 1.58)和生成速度方面都超越了扩散模型(DMs)。然而,它们的隐私风险尚未得到充分探索。为了解决这个问题,我们对IARs和DMs进行了全面的隐私分析比较。我们开发了一种新型的成员推理攻击(MIA),它在检测训练图像时成功率显著提高(TPR@FPR=1%:IARs为86.38%,DMs为4.91%)。使用这种MIA,我们执行数据集推理(DI),发现IARs仅需六个样本即可检测数据集成员身份,而DMs则需要200个样本,这表明信息泄露更高。此外,我们从IAR中提取了数百张训练图像(例如,从VAR-d30中提取了698张)。我们的研究结果凸显了隐私效用之间的基本权衡:虽然IAR在生成质量和速度方面表现出色,但它们更容易受到隐私攻击。这表明结合DMs的技术,如使用扩散的每令牌概率建模,可能有助于缓解IARs的隐私风险。我们的代码可在https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars
Summary
图像自回归(IAR)模型在图像质量和生成速度上超越了扩散模型(DM),但其隐私风险尚未得到充分探索。本研究对IAR和DM进行了全面的隐私分析,开发了一种新型成员推理攻击(MIA),在检测训练图像方面取得了较高的成功率。研究表明,IAR在数据集推理(DI)方面所需样本数量较少,且能从IAR中提取大量训练图像。研究指出,虽然IAR在生成质量和速度方面表现出色,但更易受到隐私攻击。结合扩散模型的某些技术可能有助于缓解IAR的隐私风险。
Key Takeaways
- IAR模型在图像质量和生成速度上超越了DM,但隐私风险尚未得到足够研究。
- 开发了一种新型的MIA,能够成功检测IAR中训练图像的成功率远高于DM。
- 在数据集推理方面,IAR所需样本数量较少,仅需六个样本即可检测数据集成员身份,而DM需要200个样本。
- IAR模型更容易泄露训练图像信息,可以从IAR中提取大量训练图像。
- IAR和DM之间存在隐私实用性的权衡:IAR在生成质量和速度方面表现出色,但隐私风险更高。
- 结合扩散模型的某些技术,如通过扩散进行每令牌概率建模,可能有助于缓解IAR的隐私风险。
点此查看论文截图
InterLCM: Low-Quality Images as Intermediate States of Latent Consistency Models for Effective Blind Face Restoration
Authors:Senmao Li, Kai Wang, Joost van de Weijer, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Chun-Le Guo, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng
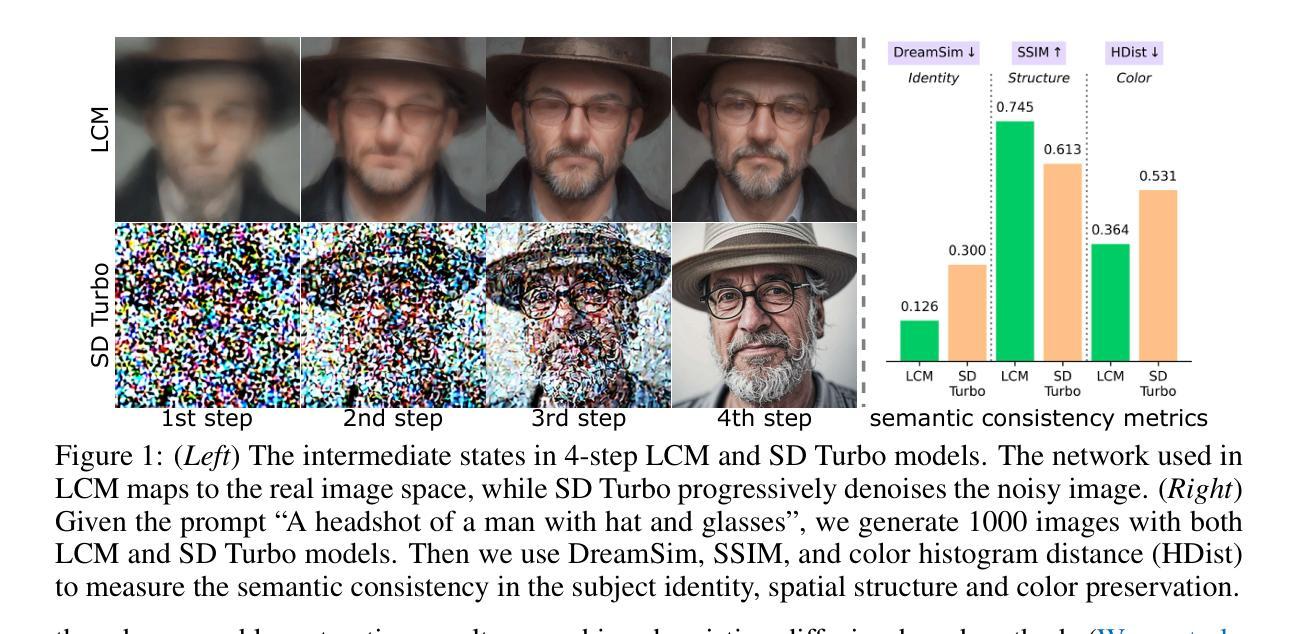
Diffusion priors have been used for blind face restoration (BFR) by fine-tuning diffusion models (DMs) on restoration datasets to recover low-quality images. However, the naive application of DMs presents several key limitations. (i) The diffusion prior has inferior semantic consistency (e.g., ID, structure and color.), increasing the difficulty of optimizing the BFR model; (ii) reliance on hundreds of denoising iterations, preventing the effective cooperation with perceptual losses, which is crucial for faithful restoration. Observing that the latent consistency model (LCM) learns consistency noise-to-data mappings on the ODE-trajectory and therefore shows more semantic consistency in the subject identity, structural information and color preservation, we propose InterLCM to leverage the LCM for its superior semantic consistency and efficiency to counter the above issues. Treating low-quality images as the intermediate state of LCM, InterLCM achieves a balance between fidelity and quality by starting from earlier LCM steps. LCM also allows the integration of perceptual loss during training, leading to improved restoration quality, particularly in real-world scenarios. To mitigate structural and semantic uncertainties, InterLCM incorporates a Visual Module to extract visual features and a Spatial Encoder to capture spatial details, enhancing the fidelity of restored images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InterLCM outperforms existing approaches in both synthetic and real-world datasets while also achieving faster inference speed.
扩散先验已被用于盲脸修复(BFR)中,通过对扩散模型(DMs)进行微调以恢复低质量图像。然而,扩散模型的直接应用存在几个关键局限性。(i)扩散先验的语义一致性较差(例如,身份、结构和颜色),增加了优化BFR模型的难度;(ii)依赖于数百次的去噪迭代,阻碍了与感知损失的协同工作,这对于忠实恢复至关重要。观察到潜在一致性模型(LCM)学习噪声到数据的一致性映射在ODE轨迹上,因此在对主体身份、结构信息和颜色保留方面显示出更高的语义一致性,我们提出InterLCM,利用LCM的优异语义一致性和效率来解决上述问题。将低质量图像视为LCM的中间状态,InterLCM通过从较早的LCM步骤开始,在保真度和质量之间取得平衡。LCM还允许在训练过程中整合感知损失,从而提高恢复质量,特别是在现实场景应用中。为了减轻结构和语义不确定性,InterLCM结合了视觉模块来提取视觉特征和一个空间编码器来捕捉空间细节,增强了恢复图像的保真度。大量实验表明,InterLCM在合成和真实世界数据集上均优于现有方法,同时实现了更快的推理速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR2025
Summary
本文介绍了扩散先验在盲脸修复(BFR)中的应用,通过对扩散模型(DMs)进行微调以恢复低质量图像。然而,直接使用DMs存在语义一致性差和需要大量去噪迭代等局限性。为此,提出了InterLCM方法,该方法结合了潜在一致性模型(LCM)的优势和效率,改善了语义一致性和优化速度。InterLCM通过将低质量图像视为LCM的中间状态,实现了保真度和质量之间的平衡。此外,它引入了视觉模块和空间编码器来缓解结构和语义不确定性,提高了修复图像的保真度。实验表明,InterLCM在合成和真实世界数据集上均优于现有方法,同时推理速度更快。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散先验被用于盲脸修复(BFR),通过微调扩散模型(DMs)来恢复低质量图像。
- 单纯应用DMs存在语义一致性差和需要大量去噪迭代的关键局限。
- InterLCM方法结合潜在一致性模型(LCM)的优势和效率,改善语义一致性和优化速度。
- InterLCM通过将低质量图像视为LCM的中间状态,实现保真度和质量间的平衡。
- InterLCM引入视觉模块和空间编码器,增强图像修复的保真度。
- InterLCM在合成和真实世界数据集上的表现均优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图




On the Guidance of Flow Matching
Authors:Ruiqi Feng, Tailin Wu, Chenglei Yu, Wenhao Deng, Peiyan Hu
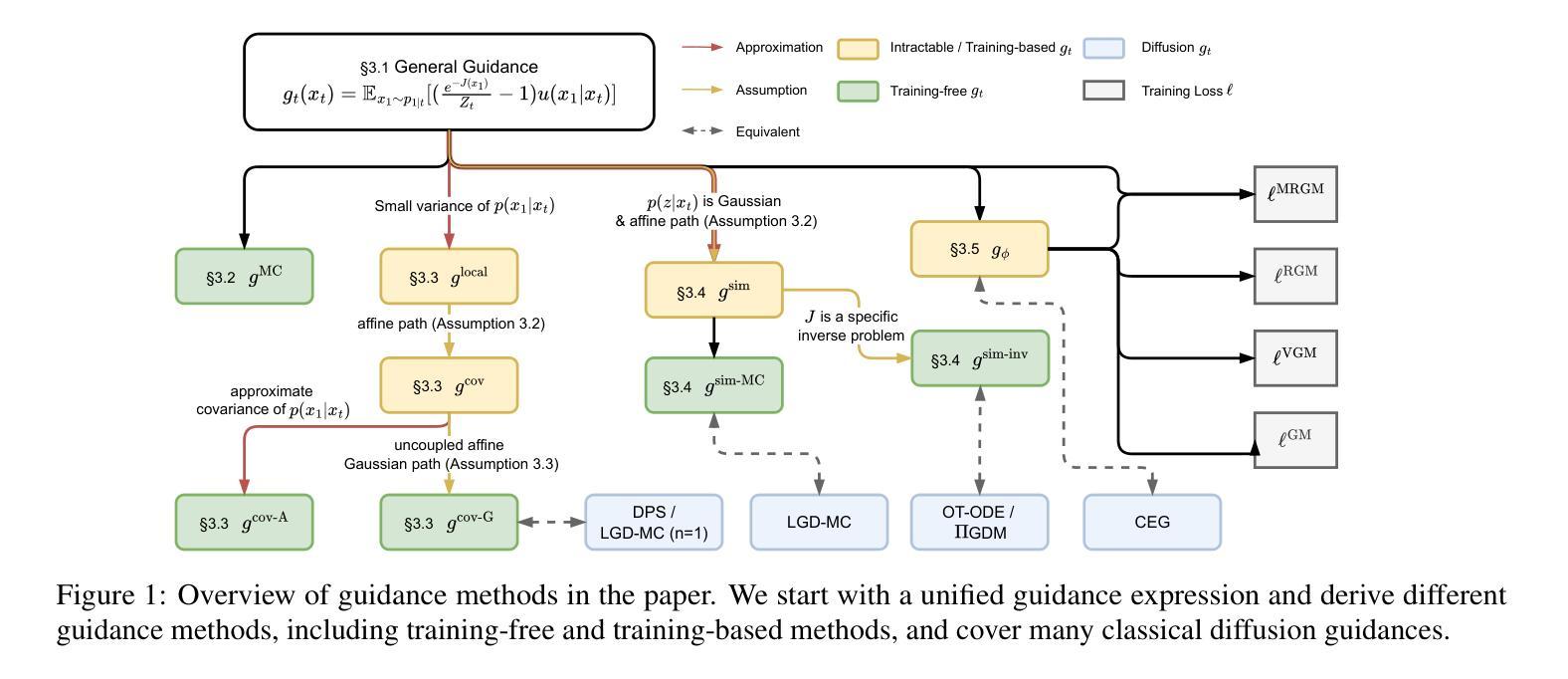
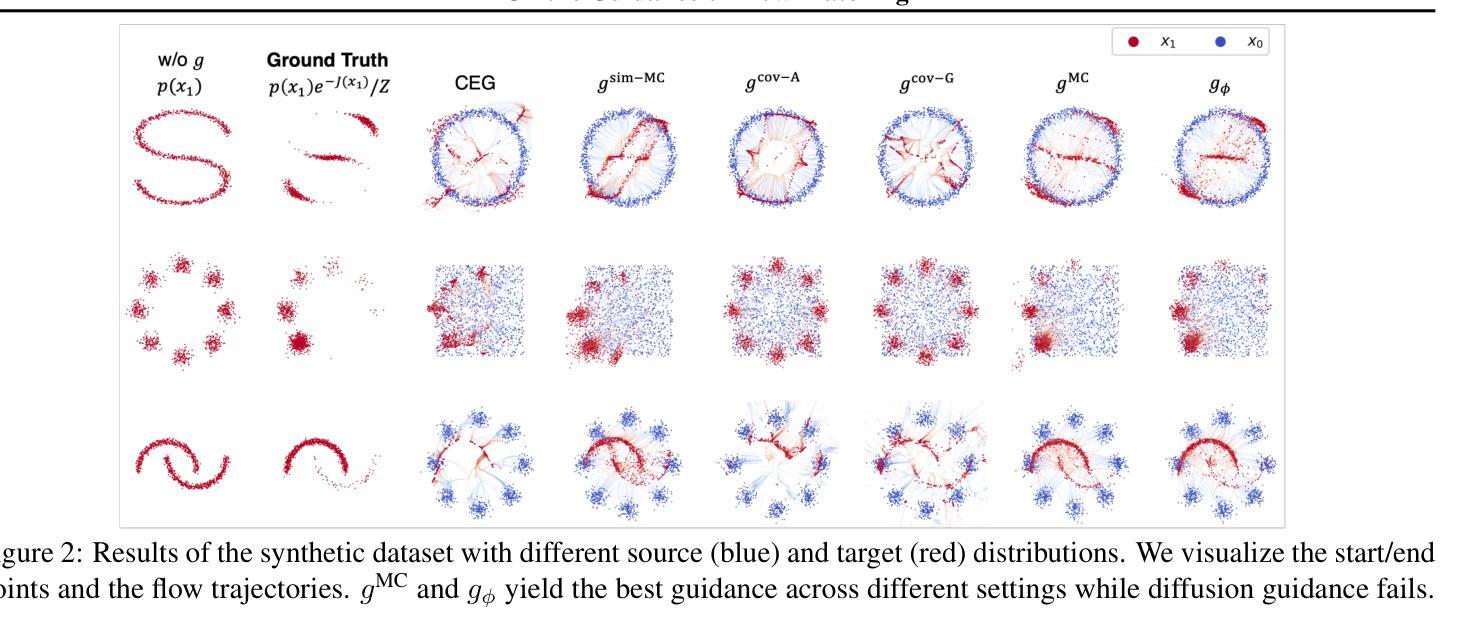
Flow matching has shown state-of-the-art performance in various generative tasks, ranging from image generation to decision-making, where guided generation is pivotal. However, the guidance of flow matching is more general than and thus substantially different from that of its predecessor, diffusion models. Therefore, the challenge in guidance for general flow matching remains largely underexplored. In this paper, we propose the first framework of general guidance for flow matching. From this framework, we derive a family of guidance techniques that can be applied to general flow matching. These include a new training-free asymptotically exact guidance, novel training losses for training-based guidance, and two classes of approximate guidance that cover classical gradient guidance methods as special cases. We theoretically investigate these different methods to give a practical guideline for choosing suitable methods in different scenarios. Experiments on synthetic datasets, image inverse problems, and offline reinforcement learning demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed guidance methods and verify the correctness of our flow matching guidance framework. Code to reproduce the experiments can be found at https://github.com/AI4Science-WestlakeU/flow_guidance.
流匹配在各种生成任务中表现出了卓越的性能,从图像生成到决策制定,其中引导生成是关键。然而,流匹配的指导更加通用,因此与其前身扩散模型有着本质的区别。因此,通用流匹配的指导挑战仍然被大大忽视。在本文中,我们提出了流匹配通用指导框架。基于此框架,我们开发了一系列可应用于通用流匹配的指导技术。这包括无需训练即可渐近精确指导的新技术、基于训练指导的新训练损失,以及涵盖经典梯度指导方法为特例的两类近似指导。我们从理论上探讨了这些方法,为不同场景选择适当的方法提供了实用指南。在合成数据集、图像反问题和离线强化学习上的实验证明了我们提出的指导方法的有效性,并验证了我们的流匹配指导框架的正确性。可在此找到重现实验的代码:https://github.com/AI4Science-WestlakeU/flow_guidance。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出了流匹配通用指导框架,解决了流匹配在生成任务中的指导问题。该框架涵盖了一系列指导技术,包括无训练渐进精确指导、新型训练损失训练指导以及涵盖经典梯度指导方法的两类近似指导。通过理论研究和实验验证,本文展示了该框架在不同场景下的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 流匹配在生成任务中展现出卓越性能,特别是在需要引导生成的任务中。
- 流匹配的指导与其前身扩散模型相比更为通用且有所差异。
- 提出首个流匹配通用指导框架,涵盖多种指导技术。
- 框架包括无训练渐进精确指导,新型训练损失训练指导以及涵盖经典梯度指导方法的两类近似指导。
- 对不同指导方法进行了理论研究,为不同场景选择合适方法提供了实践指南。
- 在合成数据集、图像反问题以及离线强化学习上的实验验证了所提指导方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

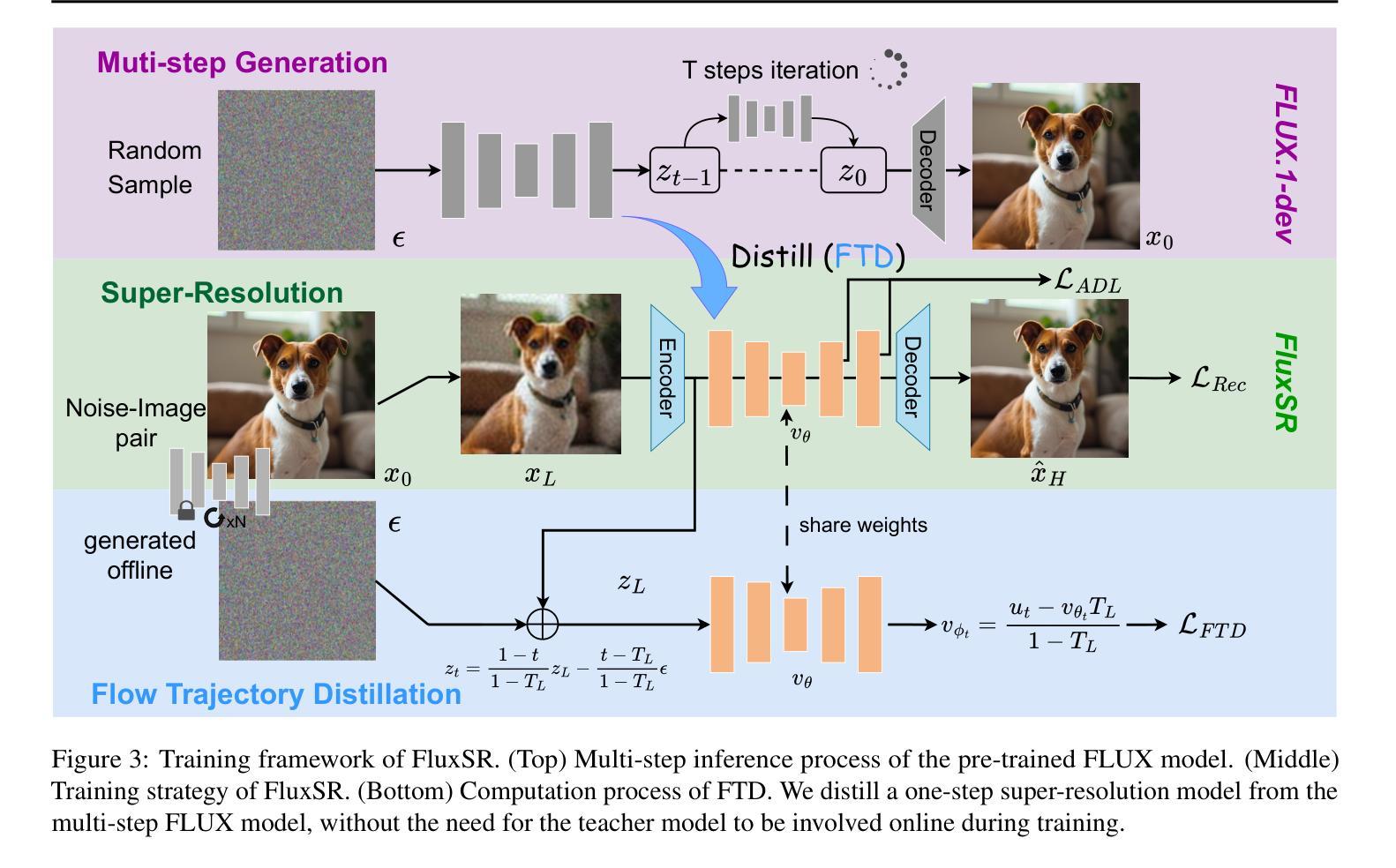
One Diffusion Step to Real-World Super-Resolution via Flow Trajectory Distillation
Authors:Jianze Li, Jiezhang Cao, Yong Guo, Wenbo Li, Yulun Zhang
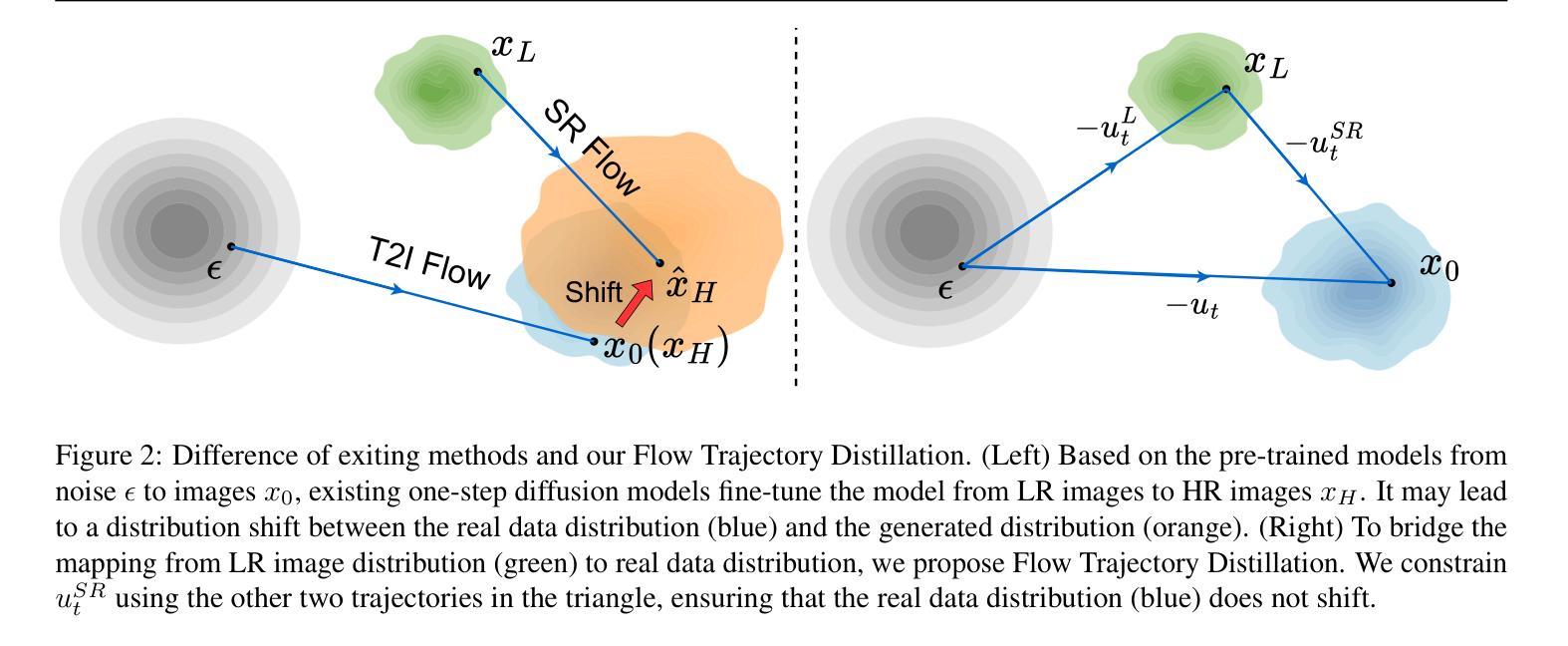
Diffusion models (DMs) have significantly advanced the development of real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR), but the computational cost of multi-step diffusion models limits their application. One-step diffusion models generate high-quality images in a one sampling step, greatly reducing computational overhead and inference latency. However, most existing one-step diffusion methods are constrained by the performance of the teacher model, where poor teacher performance results in image artifacts. To address this limitation, we propose FluxSR, a novel one-step diffusion Real-ISR technique based on flow matching models. We use the state-of-the-art diffusion model FLUX.1-dev as both the teacher model and the base model. First, we introduce Flow Trajectory Distillation (FTD) to distill a multi-step flow matching model into a one-step Real-ISR. Second, to improve image realism and address high-frequency artifact issues in generated images, we propose TV-LPIPS as a perceptual loss and introduce Attention Diversification Loss (ADL) as a regularization term to reduce token similarity in transformer, thereby eliminating high-frequency artifacts. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing one-step diffusion-based Real-ISR methods. The code and model will be released at https://github.com/JianzeLi-114/FluxSR.
扩散模型(DMs)显著推动了真实世界图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)的发展,但多步扩散模型的计算成本限制了其应用。一步扩散模型在一步采样过程中生成高质量图像,大大降低了计算开销和推理延迟。然而,大多数现有的一步扩散方法受到教师模型性能的制约,教师模型性能不佳会导致图像出现伪影。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了FluxSR,这是一种基于流匹配模型的新型一步扩散Real-ISR技术。我们使用最先进的扩散模型FLUX.1-dev作为教师模型和基础模型。首先,我们引入流轨迹蒸馏(FTD)技术,将多步流匹配模型转化为一步Real-ISR。其次,为了提高图像的真实性和解决生成图像中的高频伪影问题,我们提出将TV-LPIPS作为感知损失,并引入注意力多样化损失(ADL)作为正则化项,以减少transformer中的令牌相似性,从而消除高频伪影。综合实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的基于一步扩散的Real-ISR方法。代码和模型将在https://github.com/JianzeLi-114/FluxSR发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在真实图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)领域取得显著进展,但多步扩散模型计算成本高。本文提出一种基于流匹配模型的新型一步扩散Real-ISR技术FluxSR,通过引入Flow Trajectory Distillation(FTD)将多步流匹配模型转化为一步Real-ISR,并引入TV-LPIPS作为感知损失和注意力多样化损失(ADL)作为正则化项来减少变换器中的令牌相似性,消除高频伪影。实验表明,该方法优于现有的一步扩散Real-ISR方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在真实图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)方面取得进展。
- 多步扩散模型计算成本高,限制了其应用。
- FluxSR是一种新型一步扩散Real-ISR技术,基于流匹配模型。
- FluxSR通过Flow Trajectory Distillation(FTD)将多步流匹配模型转化为一步Real-ISR。
- 为提高图像真实性和解决生成图像的高频伪影问题,FluxSR引入TV-LPIPS作为感知损失。
- FluxSR提出Attention Diversification Loss(ADL)作为正则化项,以减少变换器中的令牌相似性。
点此查看论文截图


Fast Direct: Query-Efficient Online Black-box Guidance for Diffusion-model Target Generation
Authors:Kim Yong Tan, Yueming Lyu, Ivor Tsang, Yew-Soon Ong
Guided diffusion-model generation is a promising direction for customizing the generation process of a pre-trained diffusion-model to address the specific downstream tasks. Existing guided diffusion models either rely on training of the guidance model with pre-collected datasets or require the objective functions to be differentiable. However, for most real-world tasks, the offline datasets are often unavailable, and their objective functions are often not differentiable, such as image generation with human preferences, molecular generation for drug discovery, and material design. Thus, we need an \textbf{online} algorithm capable of collecting data during runtime and supporting a \textbf{black-box} objective function. Moreover, the \textbf{query efficiency} of the algorithm is also critical because the objective evaluation of the query is often expensive in the real-world scenarios. In this work, we propose a novel and simple algorithm, \textbf{Fast Direct}, for query-efficient online black-box target generation. Our Fast Direct builds a pseudo-target on the data manifold to update the noise sequence of the diffusion model with a universal direction, which is promising to perform query-efficient guided generation. Extensive experiments on twelve high-resolution ($\small {1024 \times 1024}$) image target generation tasks and six 3D-molecule target generation tasks show $\textbf{6}\times$ up to $\textbf{10}\times$ query efficiency improvement and $\textbf{11}\times$ up to $\textbf{44}\times$ query efficiency improvement, respectively. Our implementation is publicly available at: https://github.com/kimyong95/guide-stable-diffusion/tree/fast-direct
引导式扩散模型生成方向对于定制预训练的扩散模型的生成过程以解决特定的下游任务具有广阔前景。现有的引导式扩散模型要么依赖于使用预先收集的数据集对引导模型进行训练,要么需要目标函数可微。然而,对于大多数现实世界任务而言,离线数据集通常不可用,并且其目标函数通常不可微分,例如具有人类偏好的图像生成、用于药物发现的分子生成以及材料设计。因此,我们需要一种在线算法,该算法能够在运行时收集数据并支持黑箱目标函数。此外,算法的查询效率也至关重要,因为在现实场景中,目标查询的评估往往成本高昂。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新颖而简单的算法——Fast Direct,用于高效查询在线黑箱目标生成。我们的Fast Direct在数据流形上构建伪目标,以通用方向更新扩散模型的噪声序列,这在执行高效查询引导生成方面显示出巨大潜力。在十二个高分辨率($\small {1024 \times 1024}$)图像目标生成任务和六个3D分子目标生成任务上的广泛实验显示,查询效率提高了$\textbf{6}$倍至$\textbf{10}$倍,以及分别提高了$\textbf{11}$倍至$\textbf{44}$倍。我们的实现可在以下网址公开访问:https://github.com/kimyong95/guide-stable-diffusion/tree/fast-direct。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
引导扩散模型生成是定制预训练扩散模型的生成过程以应对特定下游任务的有前途的方向。现有引导扩散模型依赖于使用预先收集的数据集训练的指导模型,或者需要目标函数可微。然而,对于大多数现实世界任务,离线数据集通常不可用,且其目标函数通常不可微分,如基于人类偏好的图像生成、用于药物发现的分子生成和材料设计。因此,我们需要一种能够在运行时收集数据的在线算法,并支持黑箱目标函数。此外,算法的查询效率也至关重要,因为在现实场景中目标查询的评估往往很昂贵。本研究提出了一种新颖而简单的算法Fast Direct,用于查询高效的在线黑箱目标生成。我们的Fast Direct在数据流形上构建伪目标,以通用方向更新扩散模型的噪声序列,有望在查询高效的引导生成方面表现出色。在十二个高分辨率($1024 \times 1024$)图像目标生成任务和六个3D分子目标生成任务上的广泛实验显示,查询效率提高了6至10倍和11至44倍。我们的实现可在https://github.com/kimyong95/guide-stable-diffusion/tree/fast-direct公开访问。
关键见解
- 引导扩散模型生成是定制预训练扩散模型的有力方向,尤其适用于特定下游任务。
- 现有引导扩散模型依赖于离线数据集或可微目标函数,这在现实任务中往往不可用或不可微。
- 提出了一种新颖算法Fast Direct,支持在线黑箱目标生成,可在运行时收集数据。
- Fast Direct通过构建伪目标在数据流形上更新噪声序列,具有查询高效的潜力。
- 在图像和分子生成等任务上,Fast Direct显示出显著的查询效率改进。
- Fast Direct算法的实现已公开可用,方便公众访问和使用。
- 该方法具有潜力解决现实世界中目标查询评估昂贵的问题。
点此查看论文截图


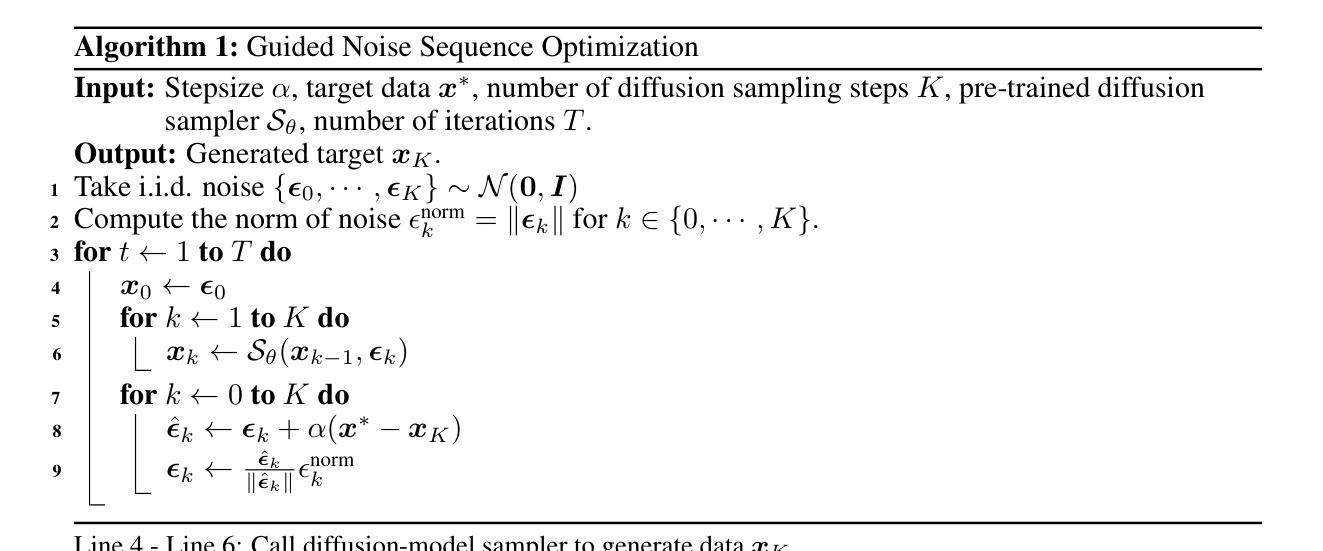
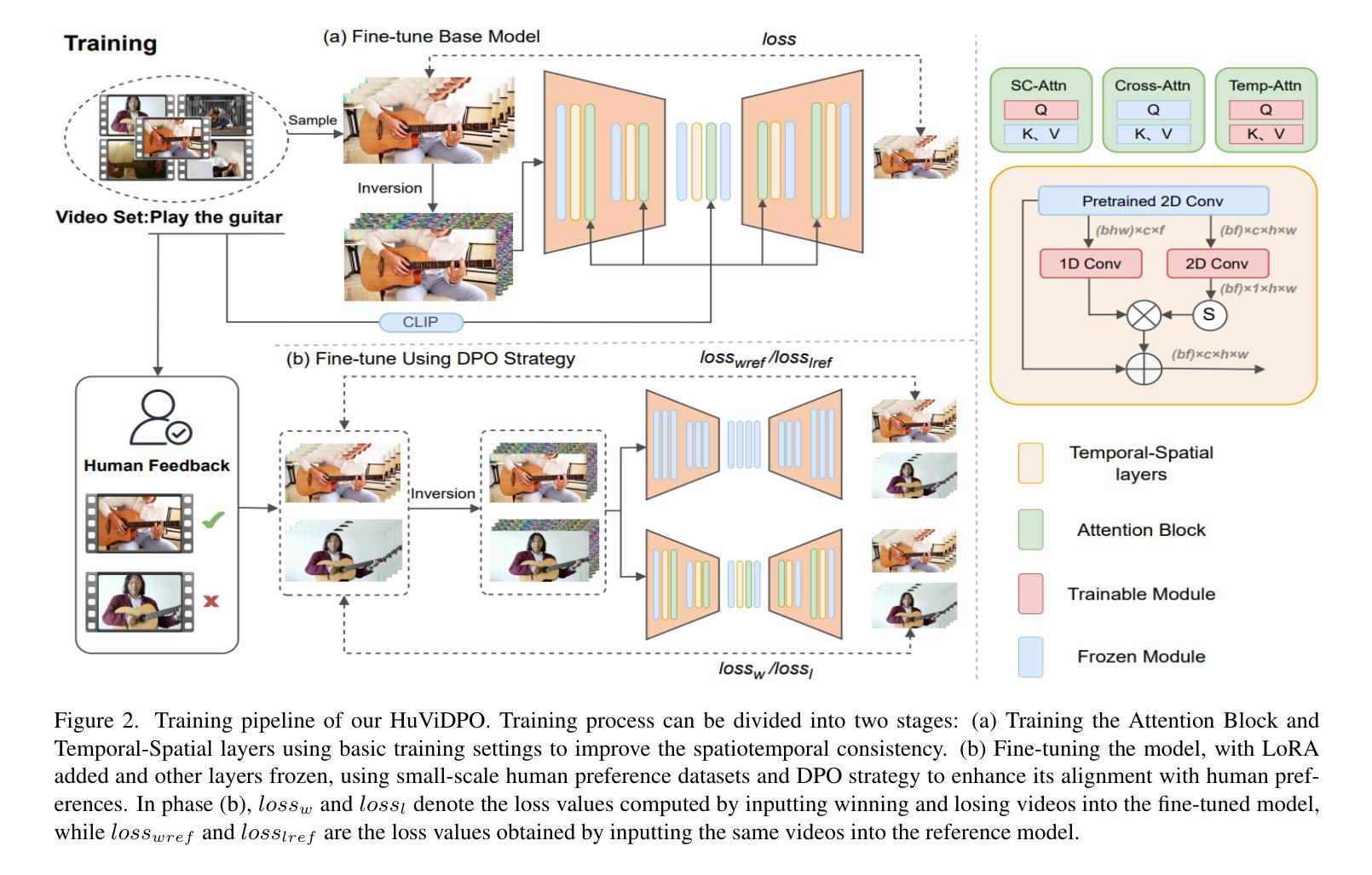
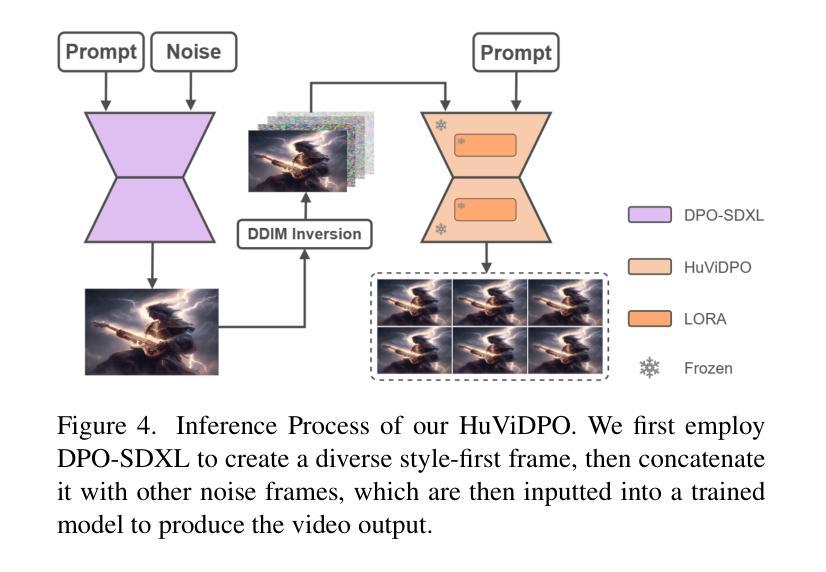
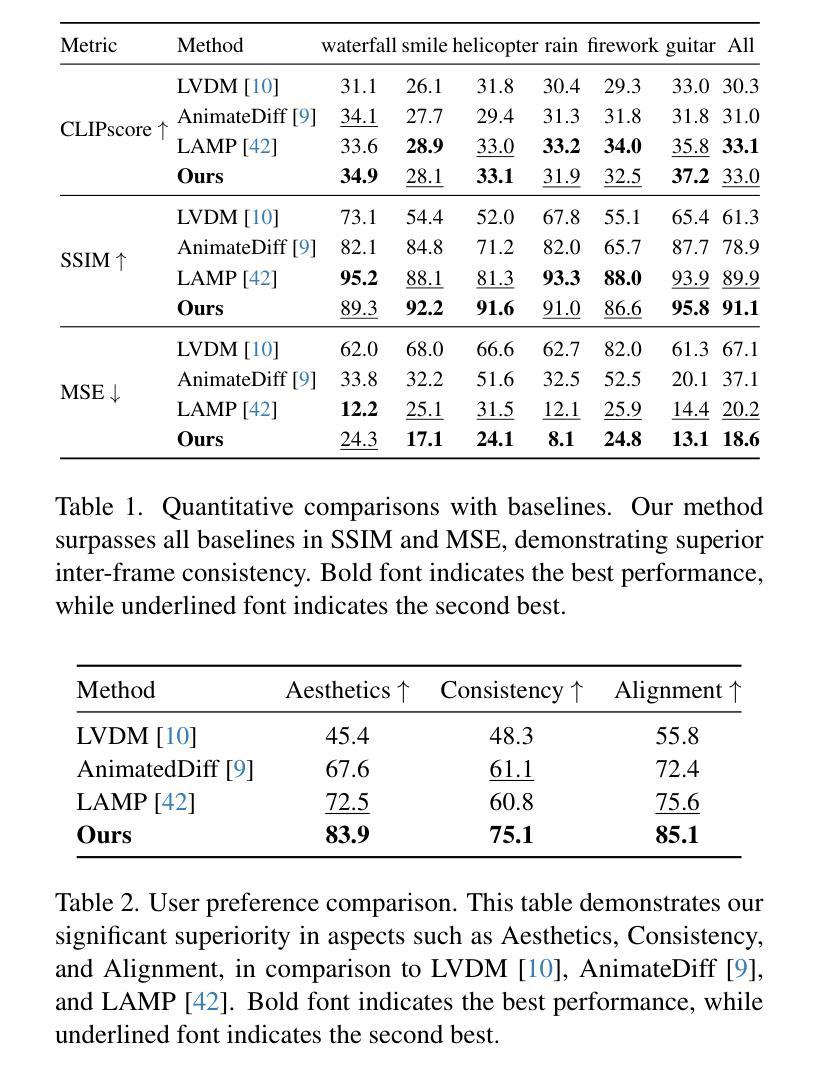
HuViDPO:Enhancing Video Generation through Direct Preference Optimization for Human-Centric Alignment
Authors:Lifan Jiang, Boxi Wu, Jiahui Zhang, Xiaotong Guan, Shuang Chen
With the rapid development of AIGC technology, significant progress has been made in diffusion model-based technologies for text-to-image (T2I) and text-to-video (T2V). In recent years, a few studies have introduced the strategy of Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) into T2I tasks, significantly enhancing human preferences in generated images. However, existing T2V generation methods lack a well-formed pipeline with exact loss function to guide the alignment of generated videos with human preferences using DPO strategies. Additionally, challenges such as the scarcity of paired video preference data hinder effective model training. At the same time, the lack of training datasets poses a risk of insufficient flexibility and poor video generation quality in the generated videos. Based on those problems, our work proposes three targeted solutions in sequence. 1) Our work is the first to introduce the DPO strategy into the T2V tasks. By deriving a carefully structured loss function, we utilize human feedback to align video generation with human preferences. We refer to this new method as HuViDPO. 2) Our work constructs small-scale human preference datasets for each action category and fine-tune this model, improving the aesthetic quality of the generated videos while reducing training costs. 3) We adopt a First-Frame-Conditioned strategy, leveraging the rich in formation from the first frame to guide the generation of subsequent frames, enhancing flexibility in video generation. At the same time, we employ a SparseCausal Attention mechanism to enhance the quality of the generated videos.More details and examples can be accessed on our website: https://tankowa.github.io/HuViDPO. github.io/.
随着AIGC技术的快速发展,基于扩散模型的文本到图像(T2I)和文本到视频(T2V)技术在近年来取得了显著进展。一些研究已将直接偏好优化(DPO)策略引入T2I任务,显著提高了生成图像的人类偏好。然而,现有的T2V生成方法缺乏完善的管道和精确的损失函数,无法使用DPO策略将生成视频与人类偏好对齐。此外,配对视频偏好数据的稀缺性给模型的有效训练带来了挑战。同时,训练数据集的缺乏可能导致生成视频的灵活性和质量不足。基于这些问题,我们的工作提出了三个有针对性的解决方案。1)我们的工作是首次将DPO策略引入T2V任务。通过精心构建的损失函数,我们利用人类反馈将视频生成与人类偏好对齐。我们将这种新方法称为HuViDPO。2)我们的工作为每个动作类别构建了小规模的人类偏好数据集,并对模型进行了微调,提高了生成视频的美学质量,同时降低了训练成本。3)我们采用First-Frame-Conditioned策略,利用第一帧的丰富信息来引导后续帧的生成,提高视频生成的灵活性。同时,我们采用SparseCausal Attention机制,以提高生成视频的质量。更多详情和示例请访问我们的网站:[https://tankowa.github.io/HuViDPO/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
随着AIGC技术的快速发展,文本转图像(T2I)和文本转视频(T2V)的扩散模型技术取得了显著进展。虽然Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)策略已应用于T2I任务并提升了生成图像的人类偏好,但在T2V生成方法中,应用DPO策略的管道尚未完善,缺乏精确的损失函数来指导生成视频与人类偏好的对齐。此外,缺乏配对视频偏好数据等挑战影响了模型的有效训练。针对这些问题,我们的工作提出了三项针对性解决方案。首先,我们首次将DPO策略引入T2V任务,通过构建精细结构的损失函数,利用人类反馈将视频生成与人类偏好对齐,我们称之为HuViDPO。其次,我们构建了每个动作类别的小规模人类偏好数据集进行微调,提高了生成视频的美学质量并降低了训练成本。最后,我们采用First-Frame-Conditioned策略,利用第一帧的丰富信息来指导后续帧的生成,增强了视频生成的灵活性。同时,我们采用了SparseCausal Attention机制来提升生成视频的质量。更多详情和示例可访问我们的网站:HuViDPO官网链接。
关键见解
- 首次将Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)策略引入文本转视频(T2V)任务,提出HuViDPO方法。
- 通过构建损失函数,利用人类反馈将视频生成与人类偏好对齐。
- 构建小规模人类偏好数据集进行模型微调,提高生成视频的美学质量并降低训练成本。
- 采用First-Frame-Conditioned策略,利用第一帧信息提升视频生成的灵活性和质量。
- 引入SparseCausal Attention机制,进一步增强生成视频的质量。
- 提供了网站链接,可获取更多关于HuViDPO的细节和示例。
点此查看论文截图


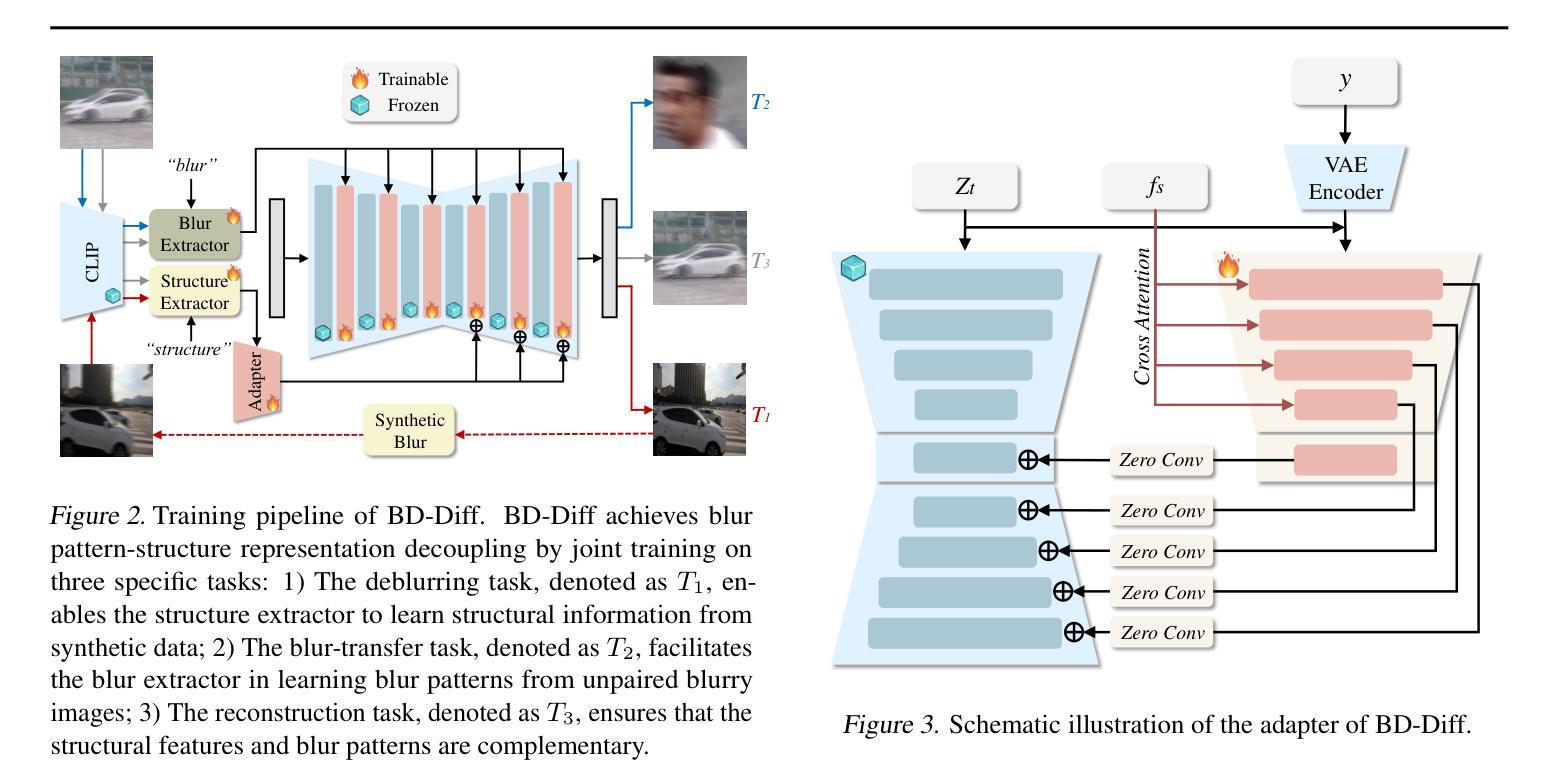
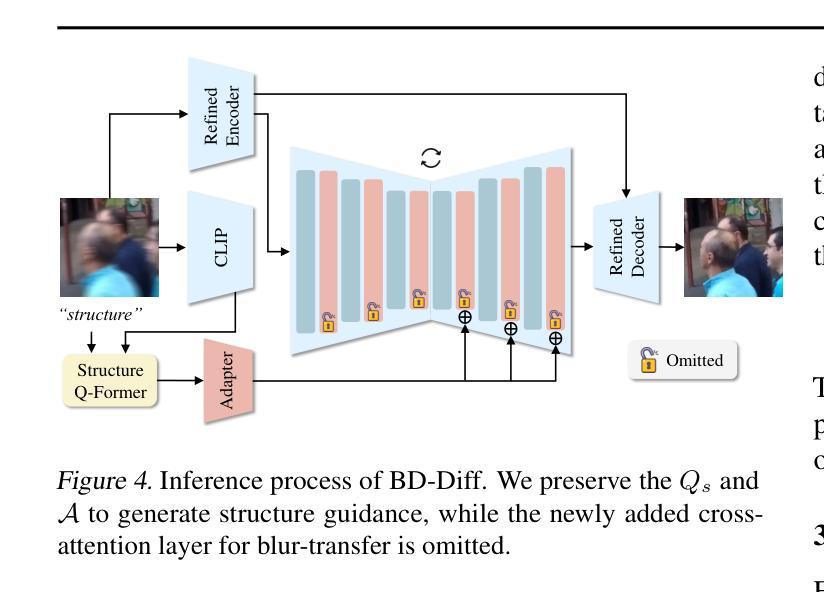
BD-Diff: Generative Diffusion Model for Image Deblurring on Unknown Domains with Blur-Decoupled Learning
Authors:Junhao Cheng, Wei-Ting Chen, Xi Lu, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Generative diffusion models trained on large-scale datasets have achieved remarkable progress in image synthesis. In favor of their ability to supplement missing details and generate aesthetically pleasing contents, recent works have applied them to image deblurring tasks via training an adapter on blurry-sharp image pairs to provide structural conditions for restoration. However, acquiring substantial amounts of realistic paired data is challenging and costly in real-world scenarios. On the other hand, relying solely on synthetic data often results in overfitting, leading to unsatisfactory performance when confronted with unseen blur patterns. To tackle this issue, we propose BD-Diff, a generative-diffusion-based model designed to enhance deblurring performance on unknown domains by decoupling structural features and blur patterns through joint training on three specially designed tasks. We employ two Q-Formers as structural representations and blur patterns extractors separately. The features extracted by them will be used for the supervised deblurring task on synthetic data and the unsupervised blur-transfer task by leveraging unpaired blurred images from the target domain simultaneously. Furthermore, we introduce a reconstruction task to make the structural features and blur patterns complementary. This blur-decoupled learning process enhances the generalization capabilities of BD-Diff when encountering unknown domain blur patterns. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that BD-Diff outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in blur removal and structural preservation in various challenging scenarios. The codes will be released in https://github.com/donahowe/BD-Diff
基于大规模数据集训练的生成扩散模型在图像合成方面取得了显著的进展。由于其能够补充缺失的细节并生成美观的内容,最近的研究将其应用于图像去模糊任务,通过训练适配器对模糊和清晰图像对进行训练,为恢复提供结构条件。然而,在现实世界场景中获取大量真实的配对数据具有挑战性和成本高昂。另一方面,仅依赖合成数据往往会导致过度拟合,在面对未知的模糊模式时,性能往往不尽如人意。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了BD-Diff,这是一个基于生成扩散的模型,通过联合训练三个专门设计的任务,旨在提高未知领域的去模糊性能。我们采用两个Q-Formers分别作为结构特征和模糊模式的表示和提取器。它们提取的特征将用于合成数据上的监督去模糊任务,并同时利用来自目标域的无配对模糊图像进行无监督的模糊转移任务。此外,我们引入了一个重建任务,使结构特征和模糊模式相互补充。这种去模糊解耦的学习过程提高了BD-Diff在遇到未知领域模糊模式时的泛化能力。在真实世界数据集上的实验表明,BD-Diff在多种具有挑战性的场景中,在模糊去除和结构保留方面超越了现有的先进方法。相关代码将发布在:https://github.com/donahowe/BD-Diff。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We propose BD-Diff to integrate generative diffusion model into unpaired deblurring tasks
Summary
基于大型数据集训练的生成扩散模型已在图像合成方面取得显著进展。为利用其在补充缺失细节和生成美观内容方面的能力,近期研究尝试将其应用于图像去模糊任务。然而,获取大量真实配对数据具有挑战性和成本高昂。为解决这个问题,本文提出BD-Diff模型,通过联合训练三个特别设计的任务,增强在未知域上的去模糊性能。该模型采用两个Q-Formers分别作为结构特征表示和模糊模式提取器。实验证明,BD-Diff在真实世界数据集上优于现有先进方法,在各种挑战场景下实现更好的去模糊和结构保留效果。
Key Takeaways
- 生成扩散模型在图像合成方面取得显著进展,可应用于图像去模糊任务。
- 获取真实配对数据具有挑战性和成本,单纯依赖合成数据可能导致过度拟合。
- BD-Diff模型通过联合训练三个特别设计的任务,旨在增强在未知域上的去模糊性能。
- BD-Diff模型采用两个Q-Formers分别提取结构特征和模糊模式。
- BD-Diff在真实世界数据集上实现优越的去模糊效果,优于现有方法。
- BD-Diff模型具有更好的结构保留效果,在各种挑战场景下表现突出。
点此查看论文截图

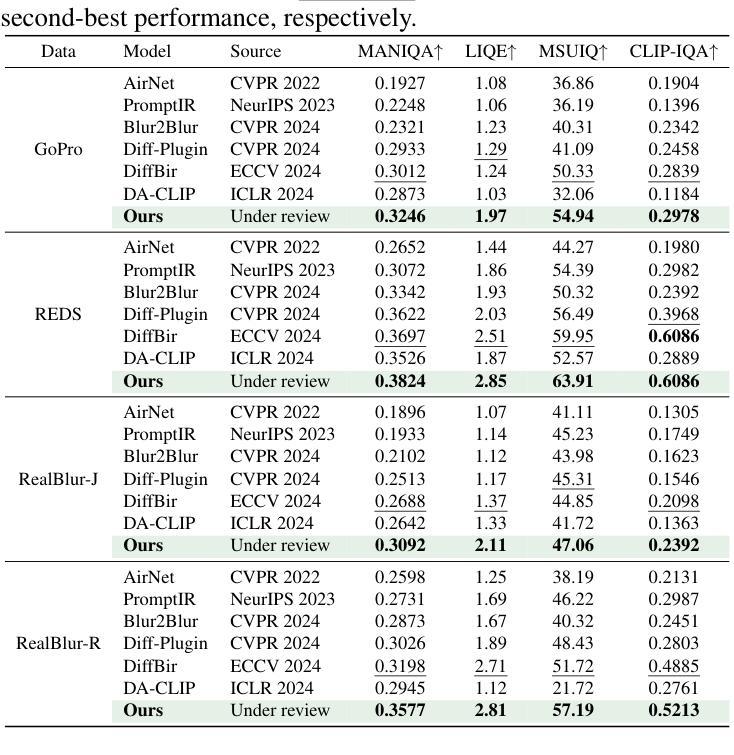

Improved Training Technique for Latent Consistency Models
Authors:Quan Dao, Khanh Doan, Di Liu, Trung Le, Dimitris Metaxas
Consistency models are a new family of generative models capable of producing high-quality samples in either a single step or multiple steps. Recently, consistency models have demonstrated impressive performance, achieving results on par with diffusion models in the pixel space. However, the success of scaling consistency training to large-scale datasets, particularly for text-to-image and video generation tasks, is determined by performance in the latent space. In this work, we analyze the statistical differences between pixel and latent spaces, discovering that latent data often contains highly impulsive outliers, which significantly degrade the performance of iCT in the latent space. To address this, we replace Pseudo-Huber losses with Cauchy losses, effectively mitigating the impact of outliers. Additionally, we introduce a diffusion loss at early timesteps and employ optimal transport (OT) coupling to further enhance performance. Lastly, we introduce the adaptive scaling-$c$ scheduler to manage the robust training process and adopt Non-scaling LayerNorm in the architecture to better capture the statistics of the features and reduce outlier impact. With these strategies, we successfully train latent consistency models capable of high-quality sampling with one or two steps, significantly narrowing the performance gap between latent consistency and diffusion models. The implementation is released here: https://github.com/quandao10/sLCT/
一致性模型是一种新型生成模型家族,能够在单步或多步中生成高质量样本。最近,一致性模型表现出了令人印象深刻的性能,在像素空间达到了与扩散模型相当的结果。然而,将一致性训练扩展到大规模数据集的成功,特别是在文本到图像和视频生成任务中,取决于其在潜在空间中的性能。
在这项工作中,我们分析了像素和潜在空间之间的统计差异,发现潜在数据经常包含高度冲动的异常值,这会显著降级潜在空间中的iCT性能。为了解决这一问题,我们用Cauchy损失替换了Pseudo-Huber损失,有效地减轻了异常值的影响。此外,我们在早期时间步长中引入了扩散损失,并采用最优传输(OT)耦合来进一步提高性能。最后,我们引入了自适应缩放-c调度器来管理稳健的训练过程,并在架构中采用非缩放LayerNorm,以更好地捕获特征的统计信息并减少异常值的影响。
通过这些策略,我们成功训练了能够在一步或两步内生成高质量样本的潜在一致性模型,显著缩小了潜在一致性与扩散模型之间的性能差距。相关实现已在此处发布:https://github.com/quandao10/sLCT/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR2025
摘要
一致性模型是新一代生成模型,能一步或多步生成高质量样本。近期,它在像素空间的表现已接近扩散模型。然而,在大规模数据集上,特别是在文本到图像和视频生成任务中,一致性模型在潜在空间的性能决定其成功。本研究分析了像素和潜在空间之间的统计差异,发现潜在数据常含有冲动异常值,会显著影响iCT在潜在空间的性能。为此,我们用Cauchy损失替代Pseudo-Huber损失,有效减轻异常值的影响。此外,我们在早期时间步长引入扩散损失,并采用最优传输耦合进一步增强性能。最后,我们引入自适应缩放-c调度器管理稳健训练过程,并在架构中采用非缩放LayerNorm,以更好地捕捉特征统计信息并减少异常值影响。这些策略使我们能训练出能在一步或两步内生成高质量样本的潜在一致性模型,显著缩小了其与扩散模型之间的性能差距。
关键见解
- 一致性模型是生成高质量样本的新模型,能在单步或多步中生成样本。
- 在大规模数据集上,一致性模型在潜在空间的性能对其成功至关重要。
- 潜在数据包含冲动异常值,这些异常值会显著影响iCT的性能。
- 使用Cauchy损失替代Pseudo-Huber损失以减轻异常值的影响。
- 在早期时间步长引入扩散损失和采用最优传输耦合增强性能。
- 引入自适应缩放-c调度器管理稳健训练过程。
- 在架构中使用非缩放LayerNorm,以捕捉特征统计信息并减少异常值影响。这些策略帮助缩小了潜在一致性模型和扩散模型之间的性能差距。
点此查看论文截图

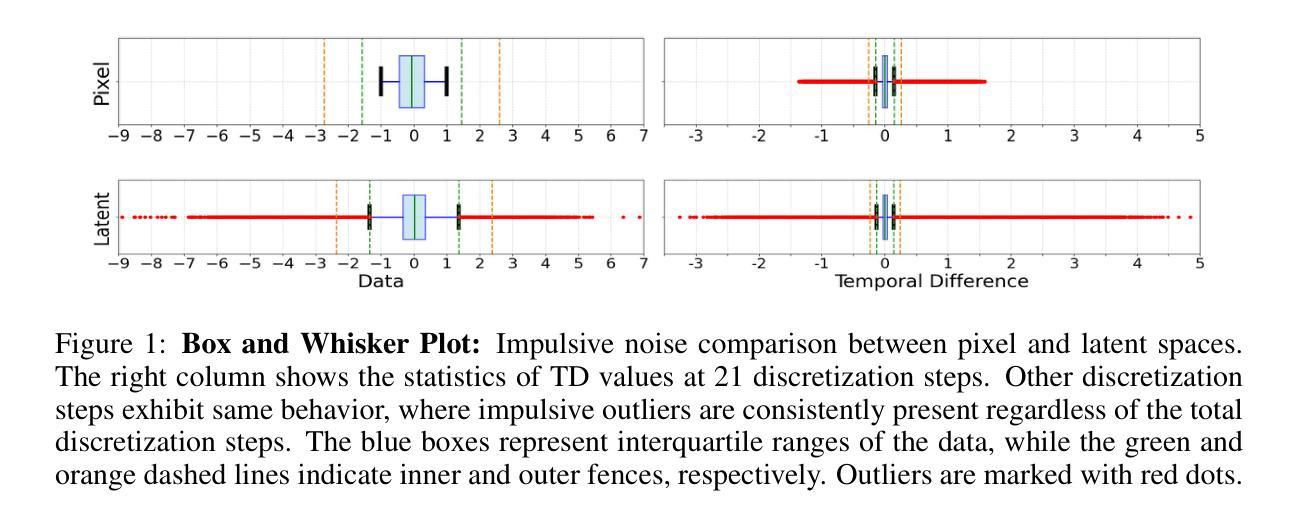
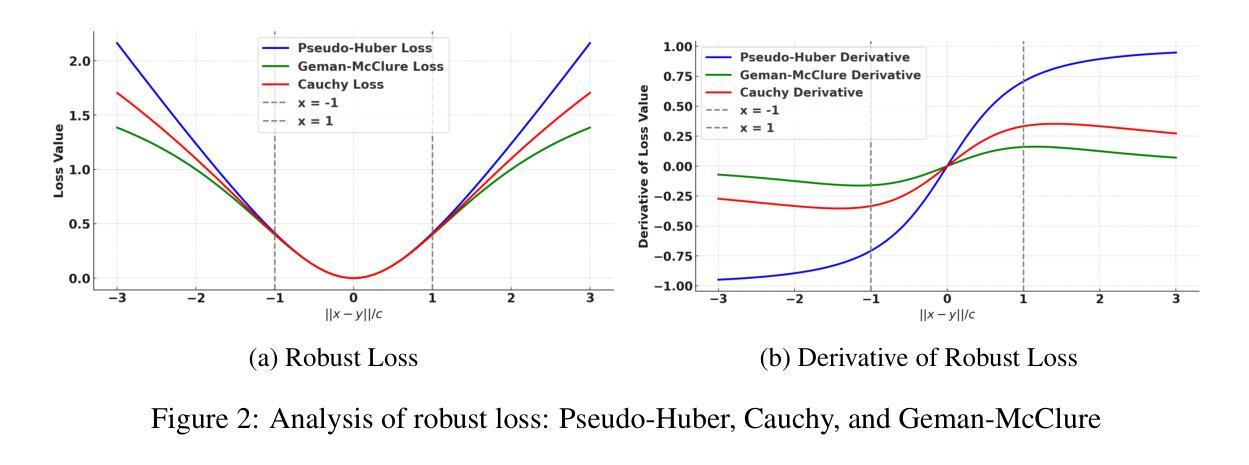
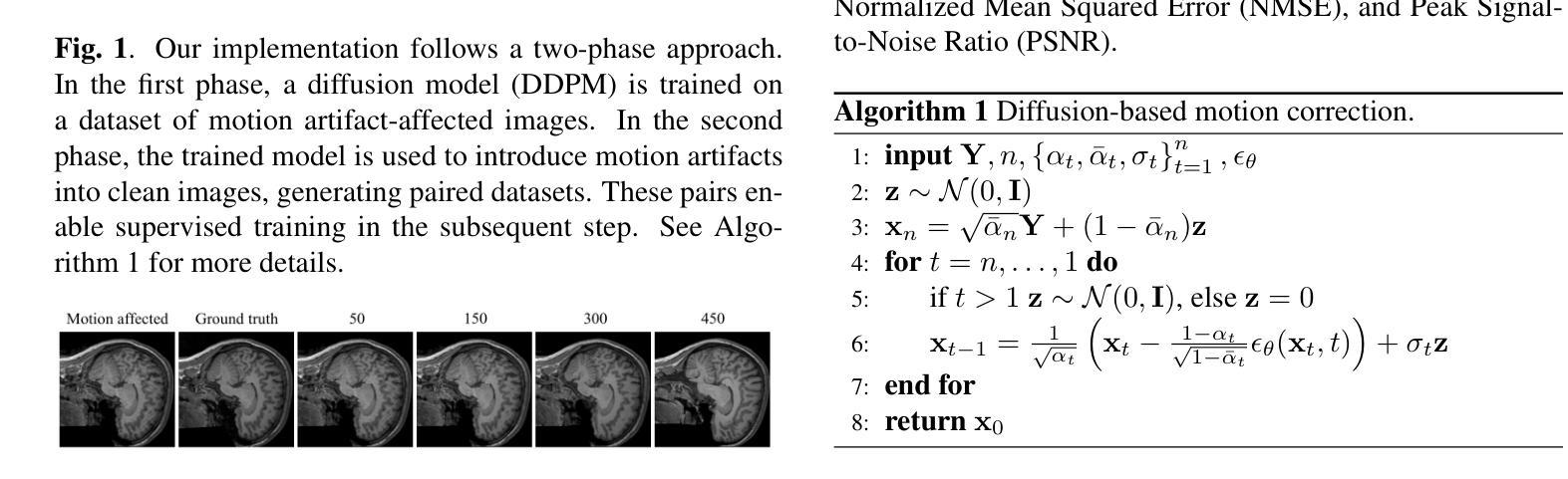
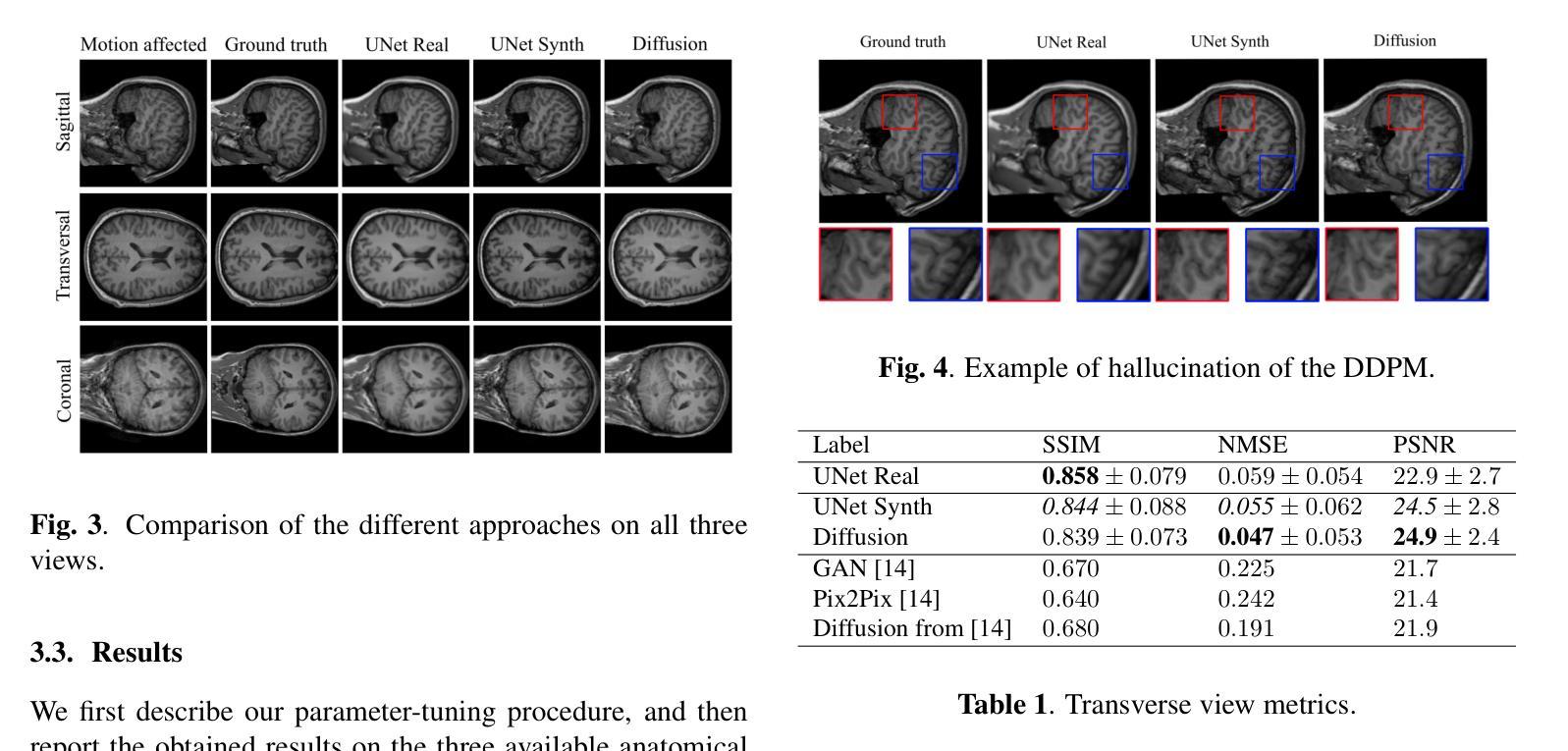
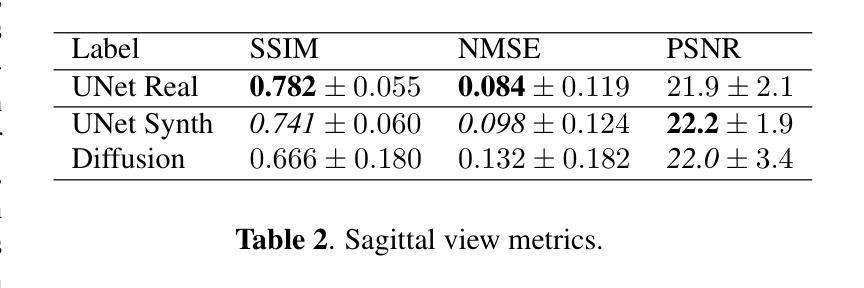
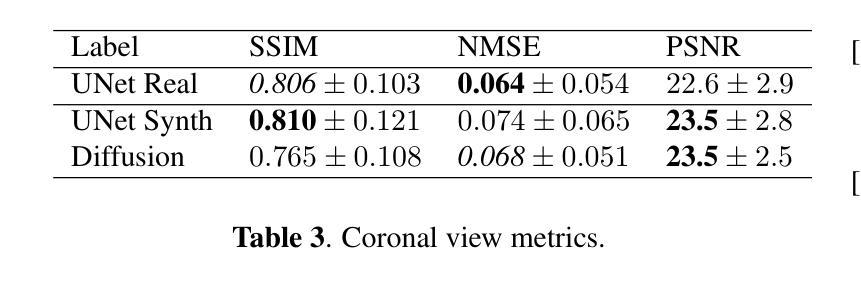
Assessing the use of Diffusion models for motion artifact correction in brain MRI
Authors:Paolo Angella, Vito Paolo Pastore, Matteo Santacesaria
Magnetic Resonance Imaging generally requires long exposure times, while being sensitive to patient motion, resulting in artifacts in the acquired images, which may hinder their diagnostic relevance. Despite research efforts to decrease the acquisition time, and designing efficient acquisition sequences, motion artifacts are still a persistent problem, pushing toward the need for the development of automatic motion artifact correction techniques. Recently, diffusion models have been proposed as a solution for the task at hand. While diffusion models can produce high-quality reconstructions, they are also susceptible to hallucination, which poses risks in diagnostic applications. In this study, we critically evaluate the use of diffusion models for correcting motion artifacts in 2D brain MRI scans. Using a popular benchmark dataset, we compare a diffusion model-based approach with state-of-the-art methods consisting of Unets trained in a supervised fashion on motion-affected images to reconstruct ground truth motion-free images. Our findings reveal mixed results: diffusion models can produce accurate predictions or generate harmful hallucinations in this context, depending on data heterogeneity and the acquisition planes considered as input.
磁共振成像通常需要长时间的曝光,同时对患者动作敏感,导致采集的图像出现伪影,可能会降低其诊断价值。尽管已付出努力减少采集时间并设计有效的采集序列,但运动伪影仍是一个持续存在的问题,推动了对开发自动运动伪影校正技术的需求。最近,扩散模型已被提议作为解决手头任务的一种解决方案。虽然扩散模型可以产生高质量的重建,但它们也容易出现幻觉,这在诊断应用中构成风险。在这项研究中,我们全面评估了使用扩散模型校正二维脑部MRI扫描中的运动伪影的使用情况。我们使用流行的大型数据集,将基于扩散模型的方法与最先进的Unets方法进行对比,Unets方法在有运动影响图像的监督训练下重建出真实无运动图像。我们的研究结果喜忧参半:扩散模型可以根据数据异质性和输入的采集平面产生准确的预测或产生有害的幻觉。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE International Symposium for Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025
Summary
扩散模型在纠正二维脑核磁共振扫描中的运动伪影方面具有潜力,但存在产生幻觉的风险。本研究采用基准数据集对比扩散模型与当前先进方法,结果显示混合结果,取决于数据异质性和输入采集平面。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型可用于纠正MRI中的运动伪影。
- 扩散模型能生成高质量重建,但也存在产生幻觉的风险。
- 研究采用基准数据集对扩散模型与当前先进方法进行了比较。
- 数据异质性和输入采集平面会影响扩散模型的预测结果。
- 扩散模型在某些情况下可能产生准确预测,而在其他情况下可能生成有害的幻觉。
- 需要进一步研究和改进扩散模型,以提高其在MRI运动伪影纠正中的性能和稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

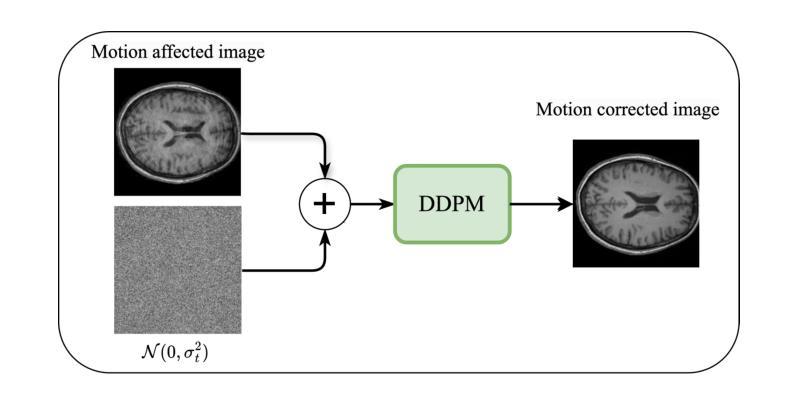
Human Body Restoration with One-Step Diffusion Model and A New Benchmark
Authors:Jue Gong, Jingkai Wang, Zheng Chen, Xing Liu, Hong Gu, Yulun Zhang, Xiaokang Yang
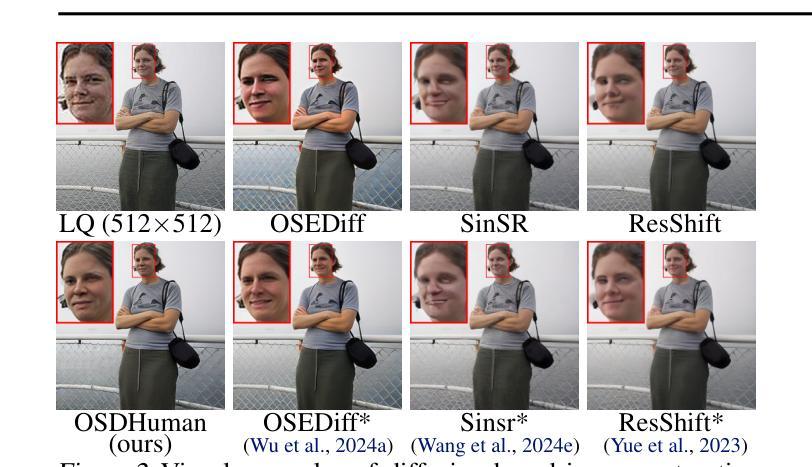
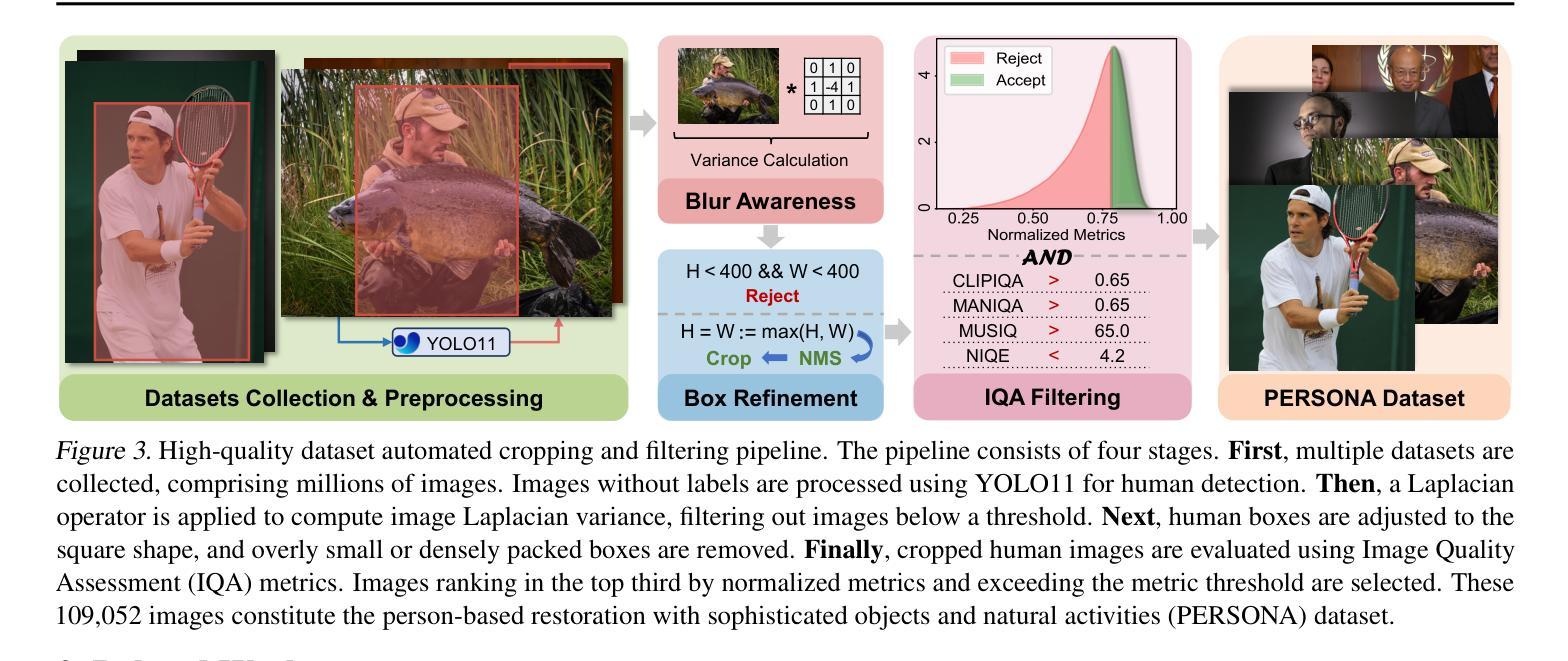
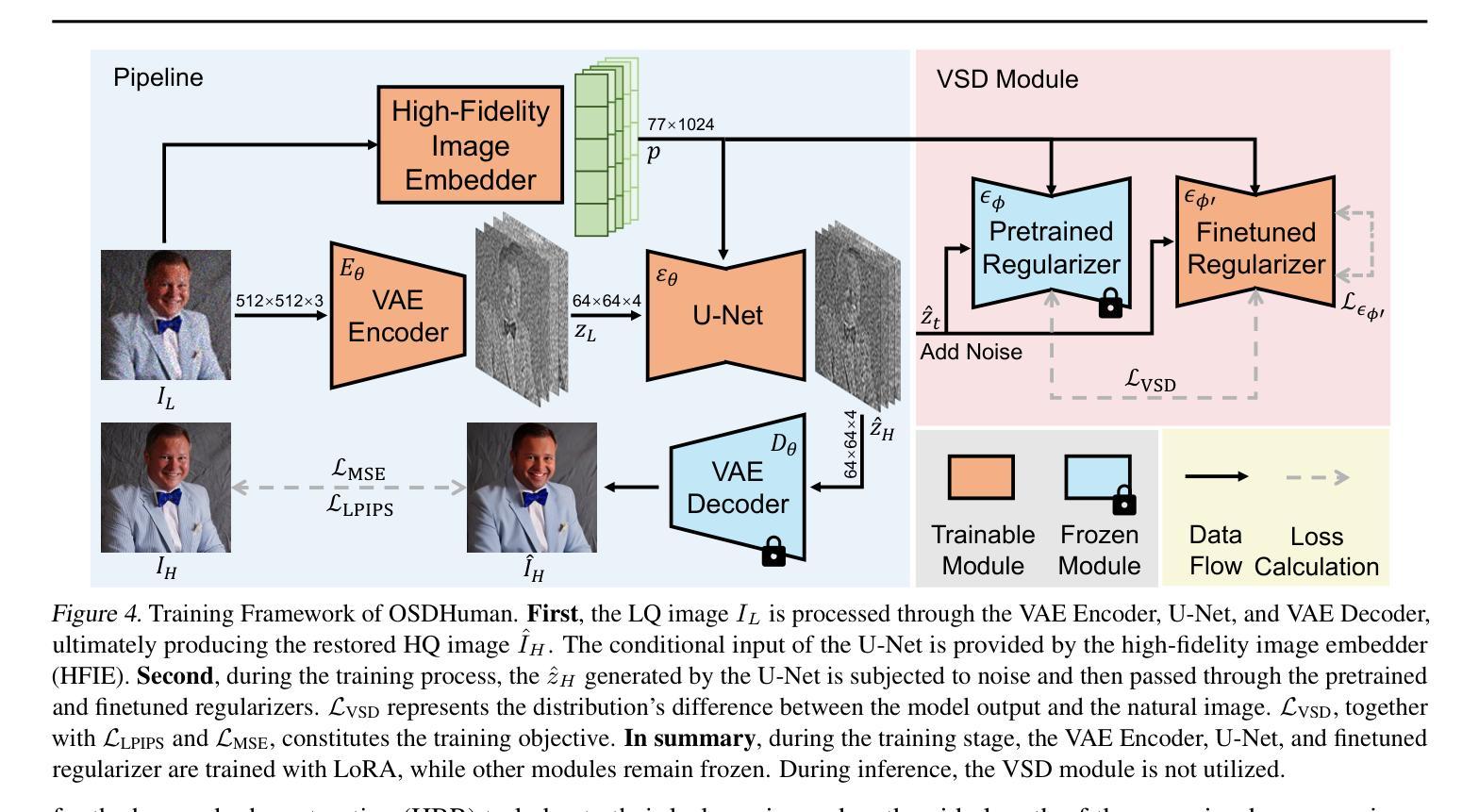
Human body restoration, as a specific application of image restoration, is widely applied in practice and plays a vital role across diverse fields. However, thorough research remains difficult, particularly due to the lack of benchmark datasets. In this study, we propose a high-quality dataset automated cropping and filtering (HQ-ACF) pipeline. This pipeline leverages existing object detection datasets and other unlabeled images to automatically crop and filter high-quality human images. Using this pipeline, we constructed a person-based restoration with sophisticated objects and natural activities (\emph{PERSONA}) dataset, which includes training, validation, and test sets. The dataset significantly surpasses other human-related datasets in both quality and content richness. Finally, we propose \emph{OSDHuman}, a novel one-step diffusion model for human body restoration. Specifically, we propose a high-fidelity image embedder (HFIE) as the prompt generator to better guide the model with low-quality human image information, effectively avoiding misleading prompts. Experimental results show that OSDHuman outperforms existing methods in both visual quality and quantitative metrics. The dataset and code will at https://github.com/gobunu/OSDHuman.
人体修复作为图像修复的一种特定应用,在实践中得到广泛应用,并在各个领域发挥着重要作用。然而,由于其难度较高,尤其是缺乏基准数据集,相关研究仍然困难重重。在本研究中,我们提出了一种高质量数据集自动裁剪和过滤(HQ-ACF)管道。该管道利用现有的目标检测数据集和其他未标记的图像,自动裁剪和过滤高质量的人体图像。使用该管道,我们构建了一个基于人的修复与复杂目标和自然活动(PERSONA)数据集,包括训练集、验证集和测试集。该数据集在质量和内容丰富程度上都大大超过了其他与人体相关的数据集。最后,我们提出了一种用于人体修复的新型一步扩散模型OSDHuman。具体来说,我们提出了一种高保真图像嵌入器(HFIE)作为提示生成器,以更好地利用低质量人体图像信息来指导模型,有效避免误导性提示。实验结果表明,OSDHuman在视觉质量和定量指标上均优于现有方法。数据集和代码将在https://github.com/gobunu/OSDHuman公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 9 figures. The code and model will be available at https://github.com/gobunu/OSDHuman
Summary
该研究针对人体恢复图像修复的一个具体应用,提出一个高质量数据集自动化裁剪和过滤(HQ-ACF)管道,利用现有目标检测数据集和其他未标记图像自动裁剪和过滤高质量的人体图像。基于此管道,构建了包含训练、验证和测试集的人员恢复与复杂物体和自然活动(PERSONA)数据集。此外,提出了一种新型一步扩散模型OSDHuman用于人体恢复,并提出高保真图像嵌入器(HFIE)作为提示生成器,更好地引导模型利用低质量人体图像信息,避免误导提示。实验结果表明,OSDHuman在视觉质量和定量指标上均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 人体恢复作为图像修复的一个特定应用,在实践中得到广泛应用,并在多个领域中发挥重要作用。
- 缺乏基准数据集使深入研究变得困难。
- 提出一个高质量数据集自动化裁剪和过滤(HQ-ACF)管道,用于自动裁剪和过滤高质量的人体图像。
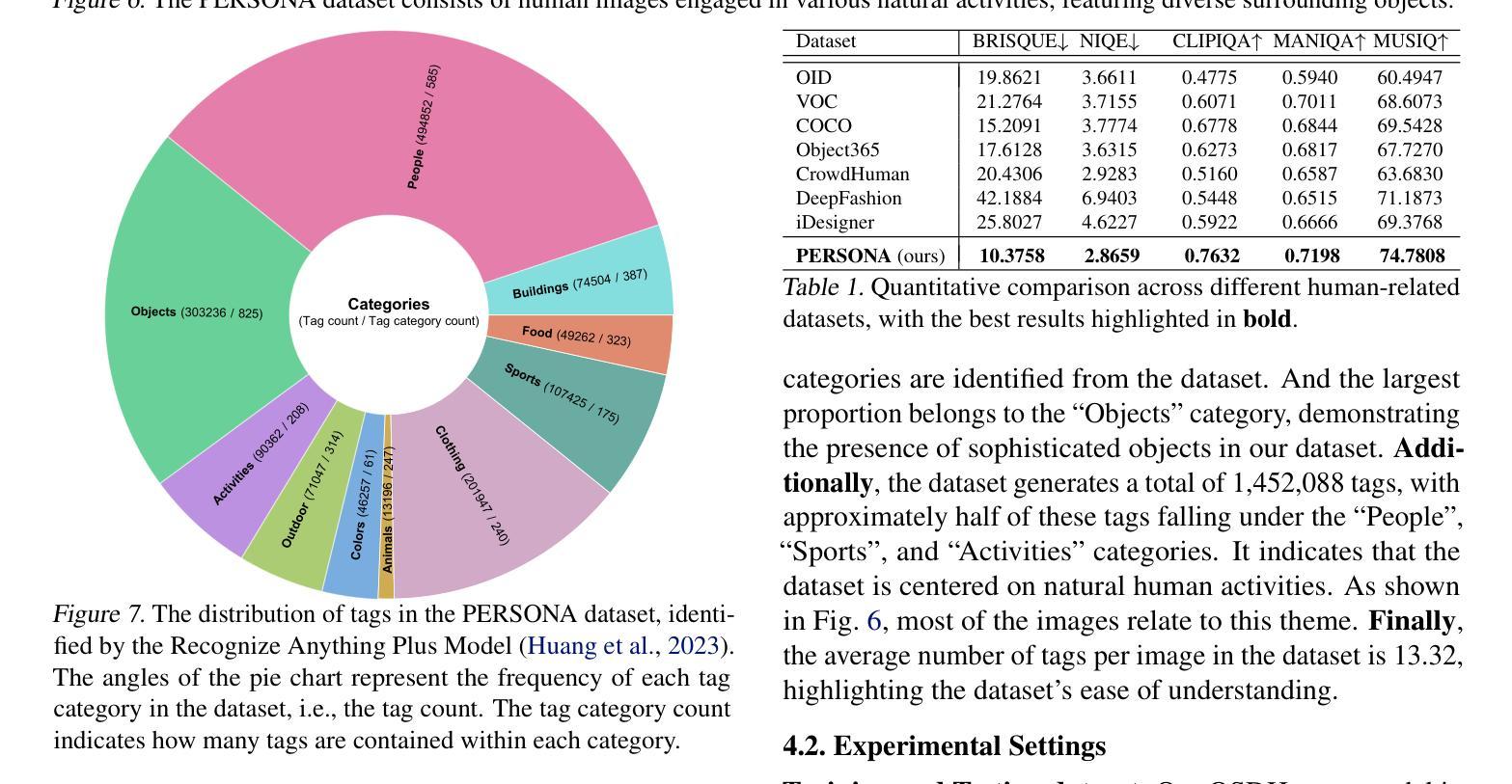
- 构建了一个包括训练、验证和测试集的人员恢复与复杂物体和自然活动(PERSONA)数据集。
- 提出了一种新型一步扩散模型OSDHuman用于人体恢复。
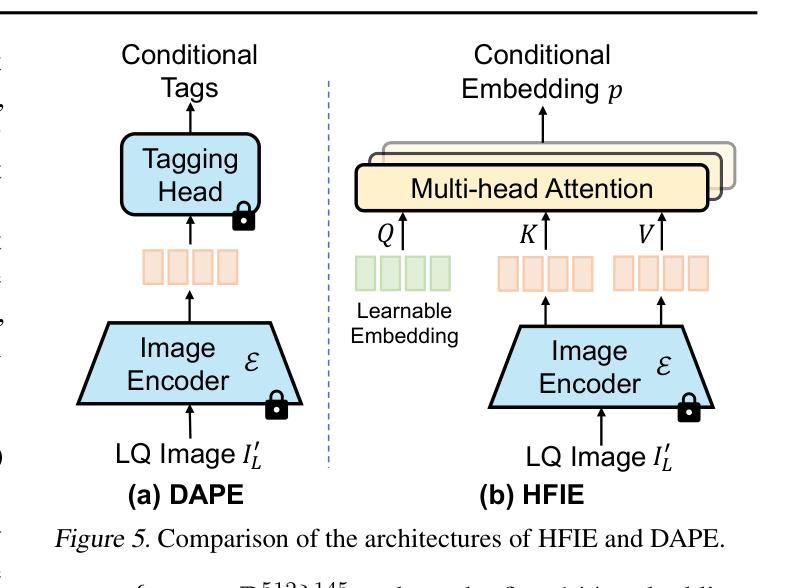
- 高保真图像嵌入器(HFIE)作为提示生成器,更好地引导模型利用低质量人体图像信息。
点此查看论文截图


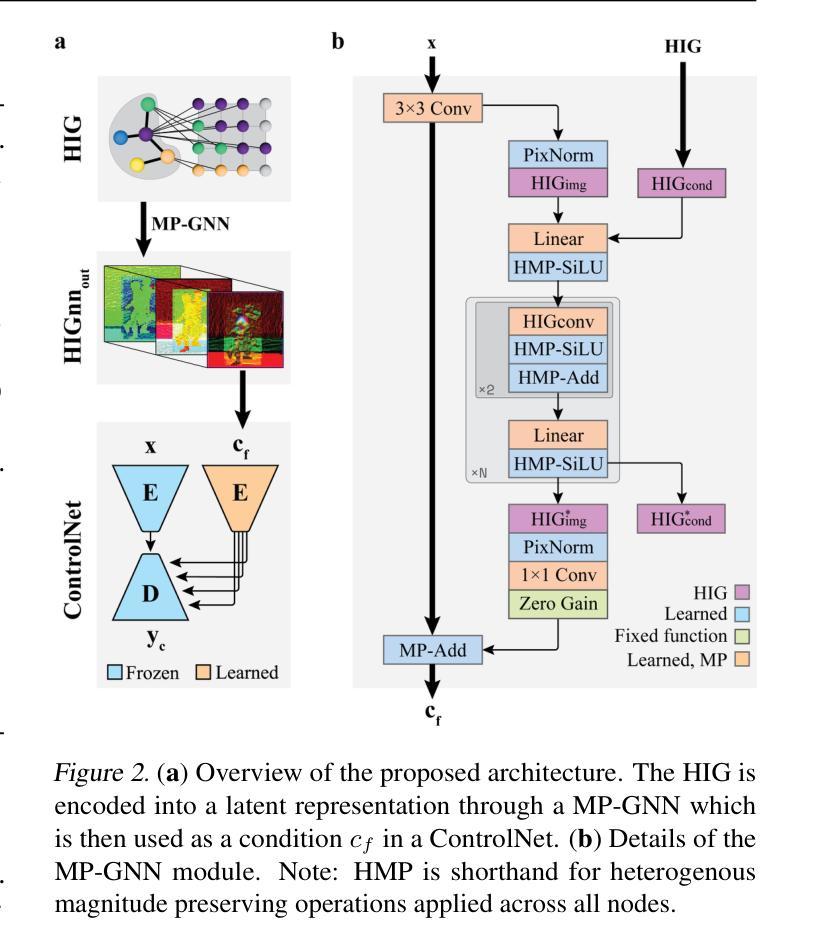
Heterogeneous Image GNN: Graph-Conditioned Diffusion for Image Synthesis
Authors:Rupert Menneer, Christos Margadji, Sebastian W. Pattinson
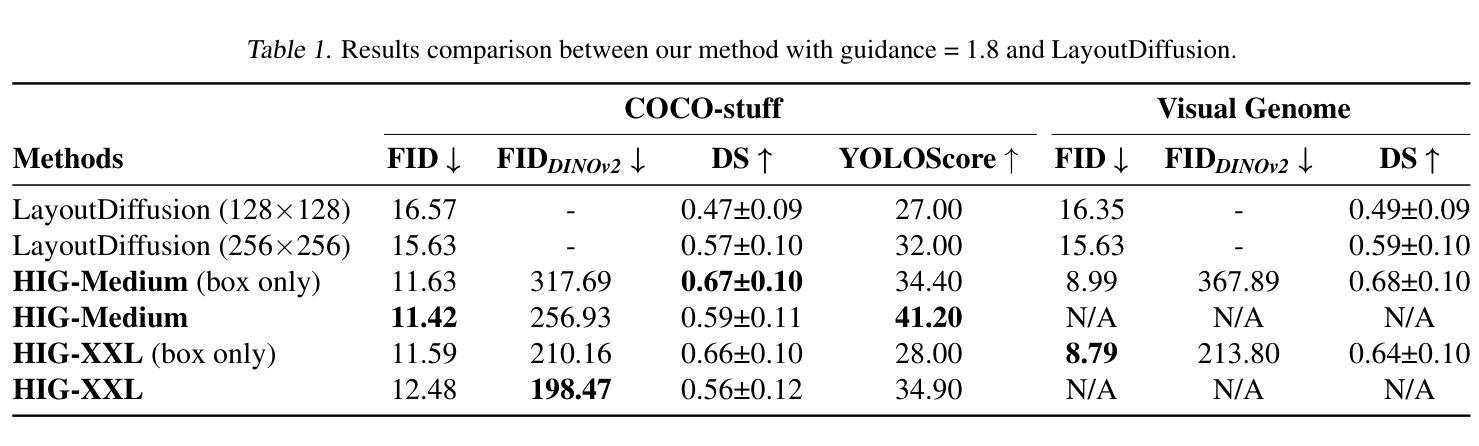
We introduce a novel method for conditioning diffusion-based image synthesis models with heterogeneous graph data. Existing approaches typically incorporate conditioning variables directly into model architectures, either through cross-attention layers that attend to text latents or image concatenation that spatially restrict generation. However, these methods struggle to handle complex scenarios involving diverse, relational conditioning variables, which are more naturally represented as unstructured graphs. This paper presents Heterogeneous Image Graphs (HIG), a novel representation that models conditioning variables and target images as two interconnected graphs, enabling efficient handling of variable-length conditioning inputs and their relationships. We also propose a magnitude-preserving GNN that integrates the HIG into the existing EDM2 diffusion model using a ControlNet approach. Our approach improves upon the SOTA on a variety of conditioning inputs for the COCO-stuff and Visual Genome datasets, and showcases the ability to condition on graph attributes and relationships represented by edges in the HIG.
我们介绍了一种基于异质图数据对扩散图像合成模型进行条件控制的新方法。现有方法通常直接将条件变量纳入模型架构中,无论是通过关注文本潜在特征的交叉注意力层,还是通过空间限制生成的图像拼接。然而,这些方法在处理涉及多样化、关系型条件变量的复杂场景时面临困难,这些场景更自然地表现为无结构的图形。本文提出了异质图像图(HIG)这一新表示方法,它将条件变量和目标图像建模为两个相互连接的图,能够高效处理可变长度的条件输入及其关系。我们还提出了一种幅度保持图神经网络(GNN),采用ControlNet方法将HIG集成到现有的EDM2扩散模型中。我们的方法在COCO-stuff和Visual Genome数据集的各种条件输入上改进了最新技术水平,并展示了在HIG中根据图形属性和边缘表示的关系进行条件设置的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种将扩散图像合成模型与异质图数据进行条件化结合的新方法。现有方法通常直接将条件变量纳入模型架构中,通过关注文本潜在变量或图像拼接来限制生成过程。然而,这些方法在处理涉及多样化和关系性条件变量的复杂场景时遇到困难,这些场景更适合用无结构的图来表示。本文提出了异质图像图(HIG)这一新表示法,将条件变量和目标图像建模为两个相互连接的图,能够高效处理可变长度的条件输入及其关系。此外,我们还提出了一种幅度保持图神经网络(GNN),采用ControlNet方法将HIG集成到现有的EDM2扩散模型中。我们的方法在COCO-stuff和Visual Genome数据集上的多种条件输入上超越了现有最佳水平,并展示了在HIG中由边缘表示的图形属性和关系进行条件设置的能力。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新的方法,使用异质图像图(HIG)对扩散图像合成模型进行条件化,以处理复杂和多样化的条件变量。
- HIG建模将条件变量和目标图像表示为相互连接的图,能够处理可变长度的条件输入及其关系。
- 幅度保持图神经网络(GNN)被用来集成HIG到现有的扩散模型中。
- 该方法在多个数据集上超越了现有最佳水平,包括COCO-stuff和Visual Genome。
- 展示了在HIG中利用图形属性和关系进行条件设置的能力,这是以前方法难以处理的。
- 这种新方法为处理涉及复杂和多样化条件变量的图像生成任务提供了新的视角和工具。
- 通过整合异质图数据和扩散模型,提高了图像生成的灵活性和质量。
点此查看论文截图

Compressed Image Generation with Denoising Diffusion Codebook Models
Authors:Guy Ohayon, Hila Manor, Tomer Michaeli, Michael Elad
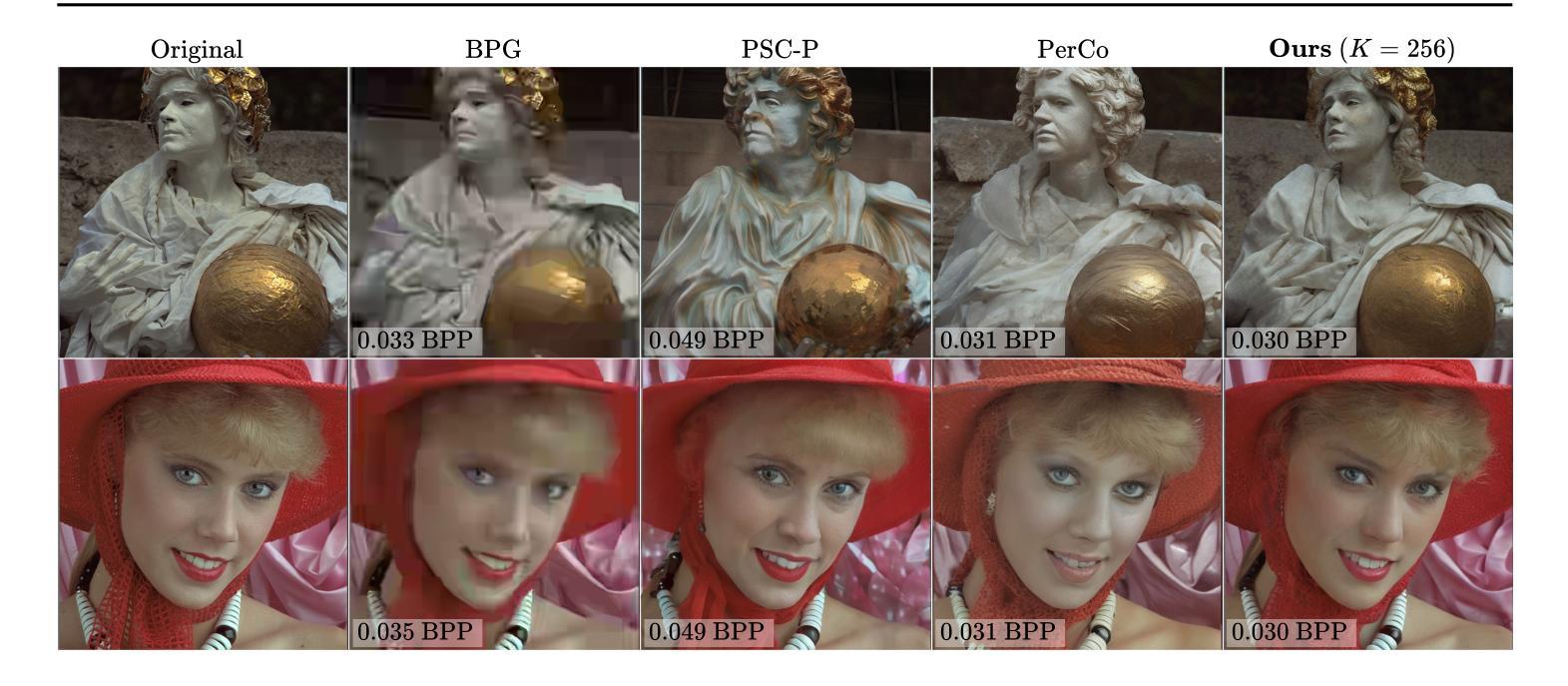
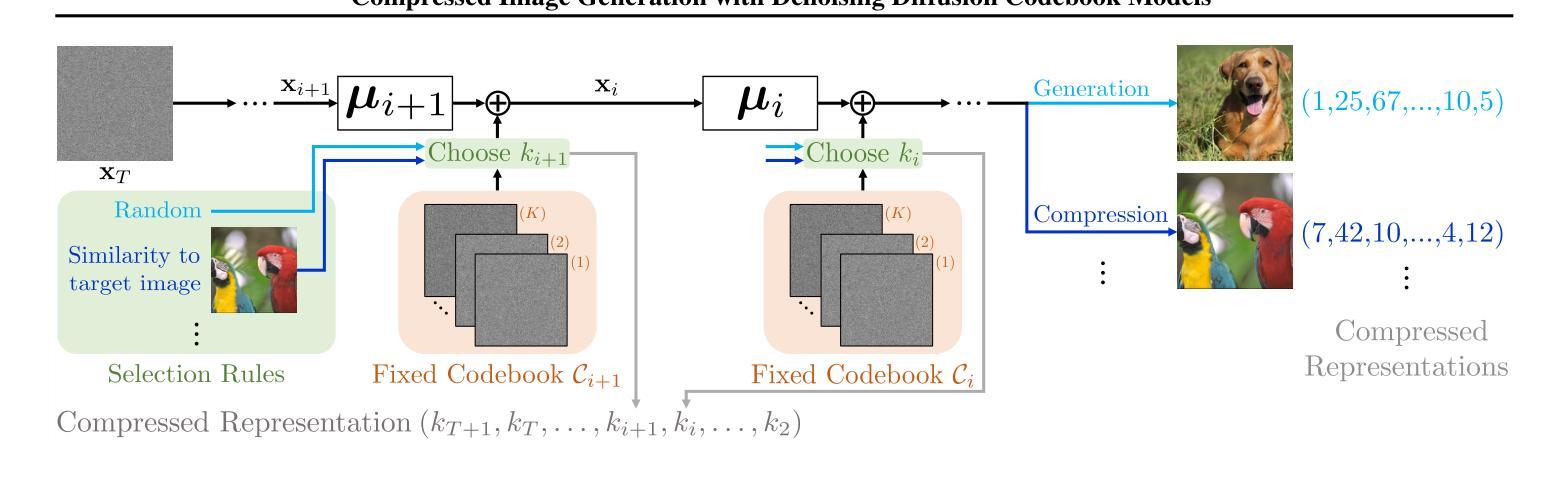
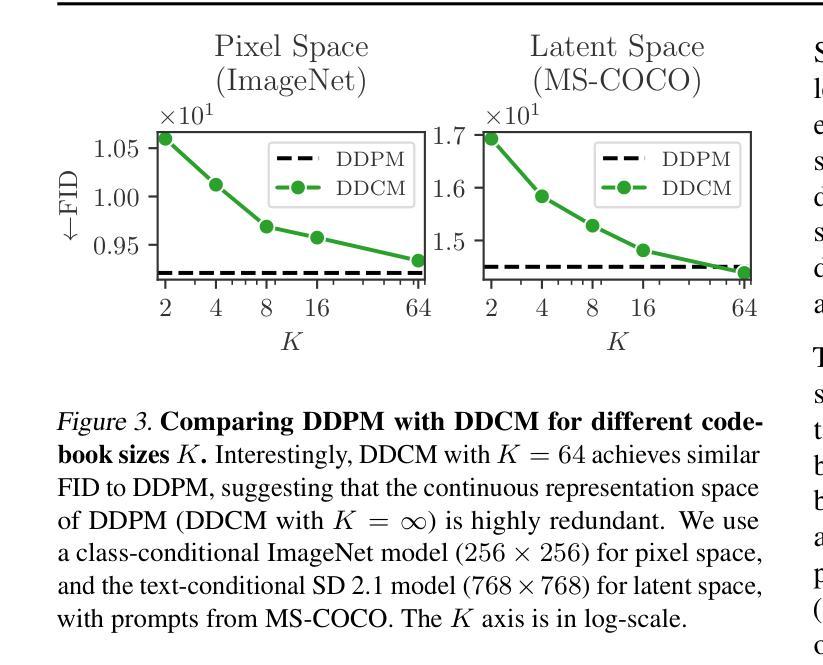
We present a novel generative approach based on Denoising Diffusion Models (DDMs), which produces high-quality image samples along with their losslessly compressed bit-stream representations. This is obtained by replacing the standard Gaussian noise sampling in the reverse diffusion with a selection of noise samples from pre-defined codebooks of fixed iid Gaussian vectors. Surprisingly, we find that our method, termed Denoising Diffusion Codebook Model (DDCM), retains sample quality and diversity of standard DDMs, even for extremely small codebooks. We leverage DDCM and pick the noises from the codebooks that best match a given image, converting our generative model into a highly effective lossy image codec achieving state-of-the-art perceptual image compression results. More generally, by setting other noise selections rules, we extend our compression method to any conditional image generation task (e.g., image restoration), where the generated images are produced jointly with their condensed bit-stream representations. Our work is accompanied by a mathematical interpretation of the proposed compressed conditional generation schemes, establishing a connection with score-based approximations of posterior samplers for the tasks considered.
我们提出了一种基于去噪扩散模型(DDMs)的新型生成方法,该方法能够生成高质量的图像样本及其无损压缩的位流表示形式。这是通过将反向扩散中的标准高斯噪声采样替换为从预定义的固定独立同分布高斯向量的代码库中选择的噪声样本而获得的。令人惊讶的是,我们发现我们的方法,即去噪扩散代码本模型(DDCM),即使在极小的代码本中,也能保持标准DDM的样本质量和多样性。我们利用DDCM,从代码库中挑选与给定图像最匹配的噪声,将我们的生成模型转化为一种高效的有损图像编码,实现了先进的感知图像压缩结果。更一般地说,通过设置其他噪声选择规则,我们将我们的压缩方法扩展到任何条件图像生成任务(例如图像修复),其中生成的图像与其压缩的位流表示形式联合生成。我们的工作还提供了对所提出的压缩条件生成方案的数学解释,与所考虑任务的基于分数的后采样器的近似建立了联系。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code and demo are available at https://ddcm-2025.github.io/
Summary
基于去噪扩散模型(DDM),我们提出了一种新的生成方法,该方法可以生成高质量图像样本及其无损压缩比特流表示。通过用预定义的固定独立同分布高斯向量的代码本中的噪声样本替换反向扩散中的标准高斯噪声样本,我们实现了称为去噪扩散代码本模型(DDCM)的方法。令人惊讶的是,即使对于极小的代码本,DDCM也能保持标准DDM的样本质量和多样性。我们利用DDCM,从代码本中选择与给定图像最佳匹配的噪声,将我们的生成模型转化为一种高效的有损图像编码,实现了最先进的感知图像压缩结果。更一般地说,通过设置其他噪声选择规则,我们将压缩方法扩展到任何条件图像生成任务(例如图像恢复),其中生成的图像与其浓缩的比特流表示一起产生。我们的工作还提供了对所提出的压缩条件生成方案进行数学解释,与所考虑任务的基于分数的后验采样器建立了联系。
Key Takeaways
- 基于Denoising Diffusion Models(DDM)提出一种新的生成方法,能够生成高质量图像样本及其无损压缩表示。
- 引入Denoising Diffusion Codebook Model(DDCM),在极小的代码本下仍能保持样本质量和多样性。
- 利用DDCM将生成模型转化为高效的有损图像编码,实现先进感知图像压缩结果。
- 压缩方法可扩展到任何条件图像生成任务,如图像恢复。
- 所提出的方法具有数学解释,与基于分数的后验采样器建立联系。
- DDCM通过选择最佳匹配给定图像的噪声,实现了图像生成与压缩的联合过程。
点此查看论文截图



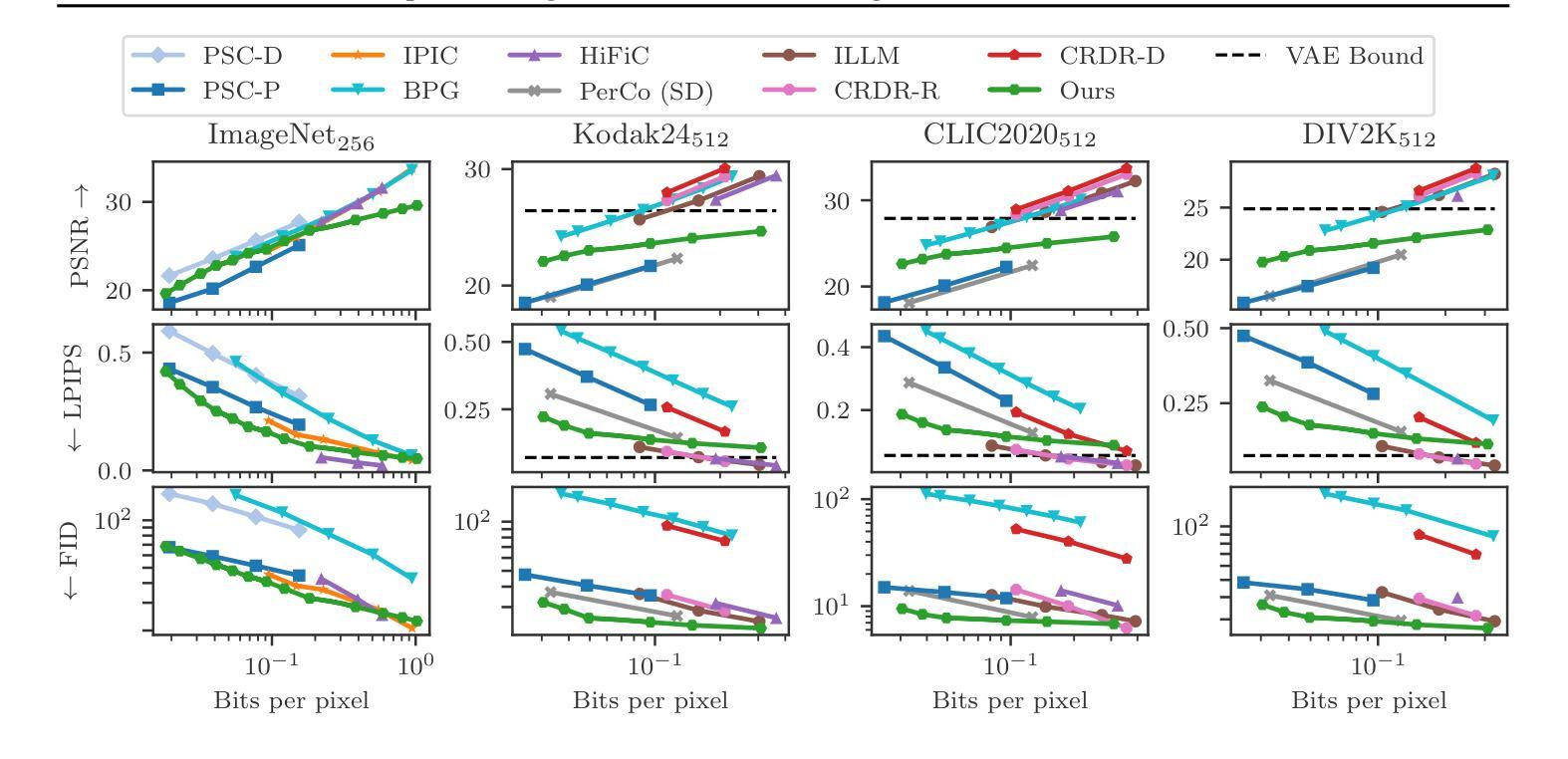
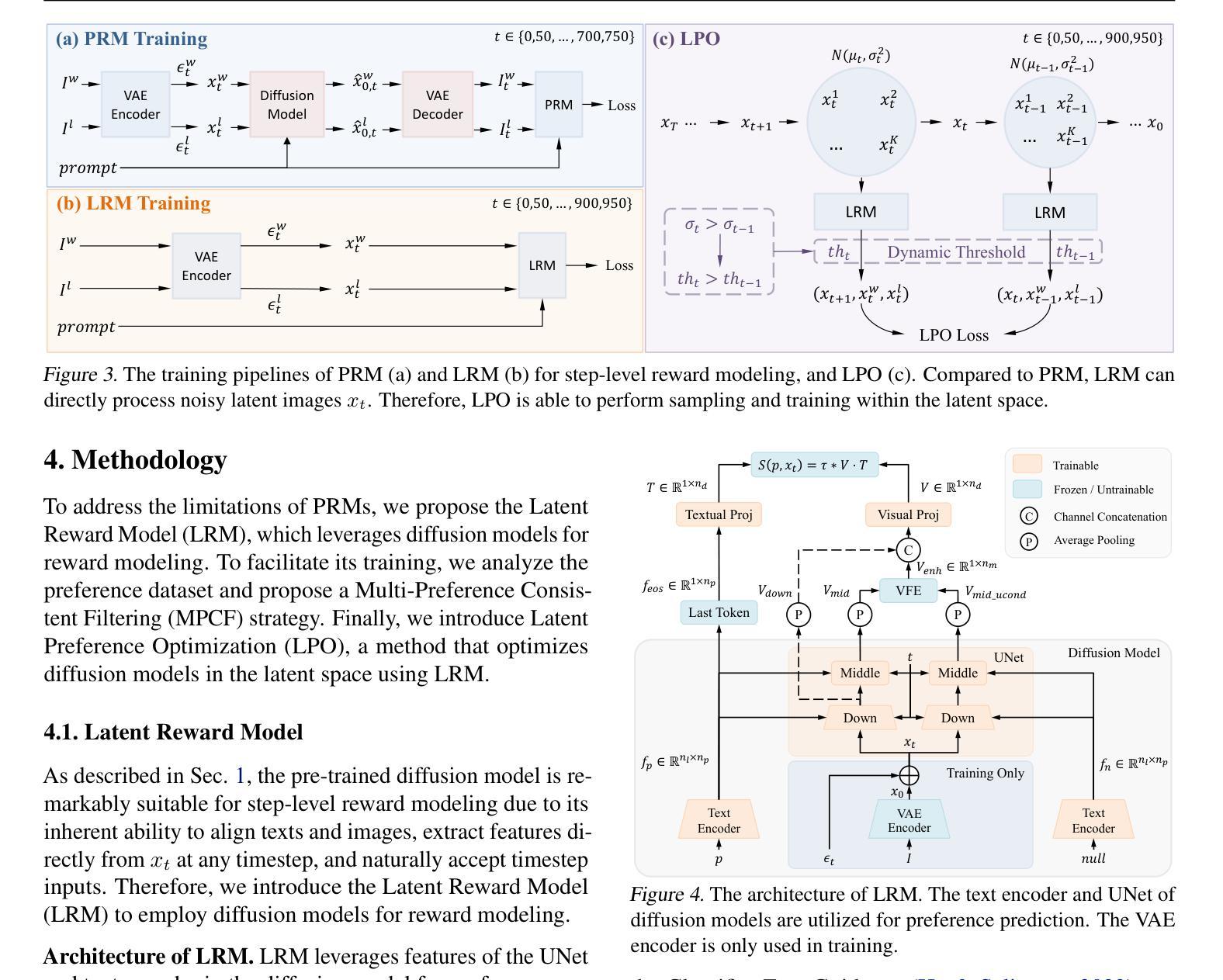
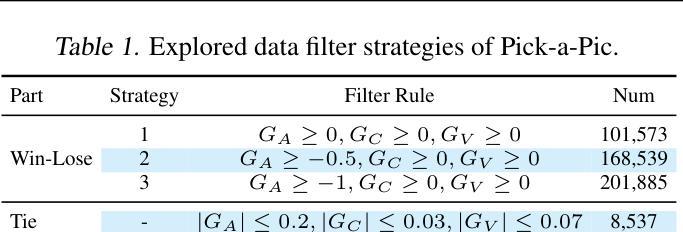
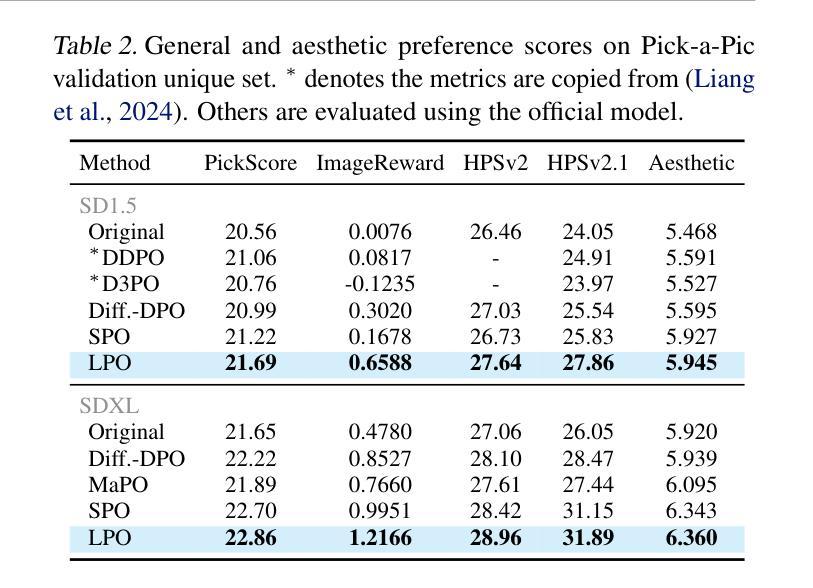
Diffusion Model as a Noise-Aware Latent Reward Model for Step-Level Preference Optimization
Authors:Tao Zhang, Cheng Da, Kun Ding, Kun Jin, Yan Li, Tingting Gao, Di Zhang, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan
Preference optimization for diffusion models aims to align them with human preferences for images. Previous methods typically leverage Vision-Language Models (VLMs) as pixel-level reward models to approximate human preferences. However, when used for step-level preference optimization, these models face challenges in handling noisy images of different timesteps and require complex transformations into pixel space. In this work, we demonstrate that diffusion models are inherently well-suited for step-level reward modeling in the latent space, as they can naturally extract features from noisy latent images. Accordingly, we propose the Latent Reward Model (LRM), which repurposes components of diffusion models to predict preferences of latent images at various timesteps. Building on LRM, we introduce Latent Preference Optimization (LPO), a method designed for step-level preference optimization directly in the latent space. Experimental results indicate that LPO not only significantly enhances performance in aligning diffusion models with general, aesthetic, and text-image alignment preferences, but also achieves 2.5-28$\times$ training speedup compared to existing preference optimization methods. Our code will be available at https://github.com/casiatao/LPO.
扩散模型的偏好优化旨在使图像与人类偏好相一致。之前的方法通常利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)作为像素级奖励模型来近似人类偏好。然而,当用于步骤级偏好优化时,这些模型在处理不同时间步长的噪声图像时面临挑战,并需要将复杂转换应用于像素空间。在这项工作中,我们证明了扩散模型天然适合在潜在空间中进行步骤级奖励建模,因为它们可以从噪声潜在图像中自然提取特征。因此,我们提出了潜在奖励模型(LRM),该模型重新利用扩散模型的组件来预测不同时间步长的潜在图像的偏好。基于LRM,我们引入了潜在偏好优化(LPO),这是一种专为潜在空间中的步骤级偏好优化设计的算法。实验结果表明,LPO不仅显著提高了扩散模型与一般偏好、美学偏好和文本图像对齐偏好的对齐性能,而且与现有的偏好优化方法相比实现了2.5-28倍的训练速度提升。我们的代码将在https://github.com/casiatao/LPO上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 14 tables, 15 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为Latent Reward Model(LRM)的方法,利用扩散模型的固有特性在潜在空间进行步骤级别的奖励建模,从而预测不同时间步长潜在图像的偏好。在此基础上,进一步引入了Latent Preference Optimization(LPO)方法,直接在潜在空间进行步骤级别的偏好优化。实验结果表明,LPO不仅显著提高了扩散模型与通用、美学和文本-图像对齐偏好的对齐性能,而且与现有偏好优化方法相比,实现了2.5-28倍的训练速度提升。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在潜在空间进行步骤级别的奖励建模具有天然优势,能够提取噪声潜在图像的特征。
- 提出Latent Reward Model(LRM)方法,利用扩散模型的组件预测不同时间步长潜在图像的偏好。
- 基于LRM,引入Latent Preference Optimization(LPO)方法,直接在潜在空间进行步骤级别的偏好优化。
- LPO不仅能显著提高扩散模型与各种偏好的对齐性能,而且实现了显著的训练速度提升。
- LPO方法适用于通用、美学和文本-图像对齐等多种偏好场景。
- 该研究解决了使用Vision-Language Models(VLMs)在处理不同时间步长噪声图像时的复杂转换问题。
点此查看论文截图



Diffusion Transformer Captures Spatial-Temporal Dependencies: A Theory for Gaussian Process Data
Authors:Hengyu Fu, Zehao Dou, Jiawei Guo, Mengdi Wang, Minshuo Chen
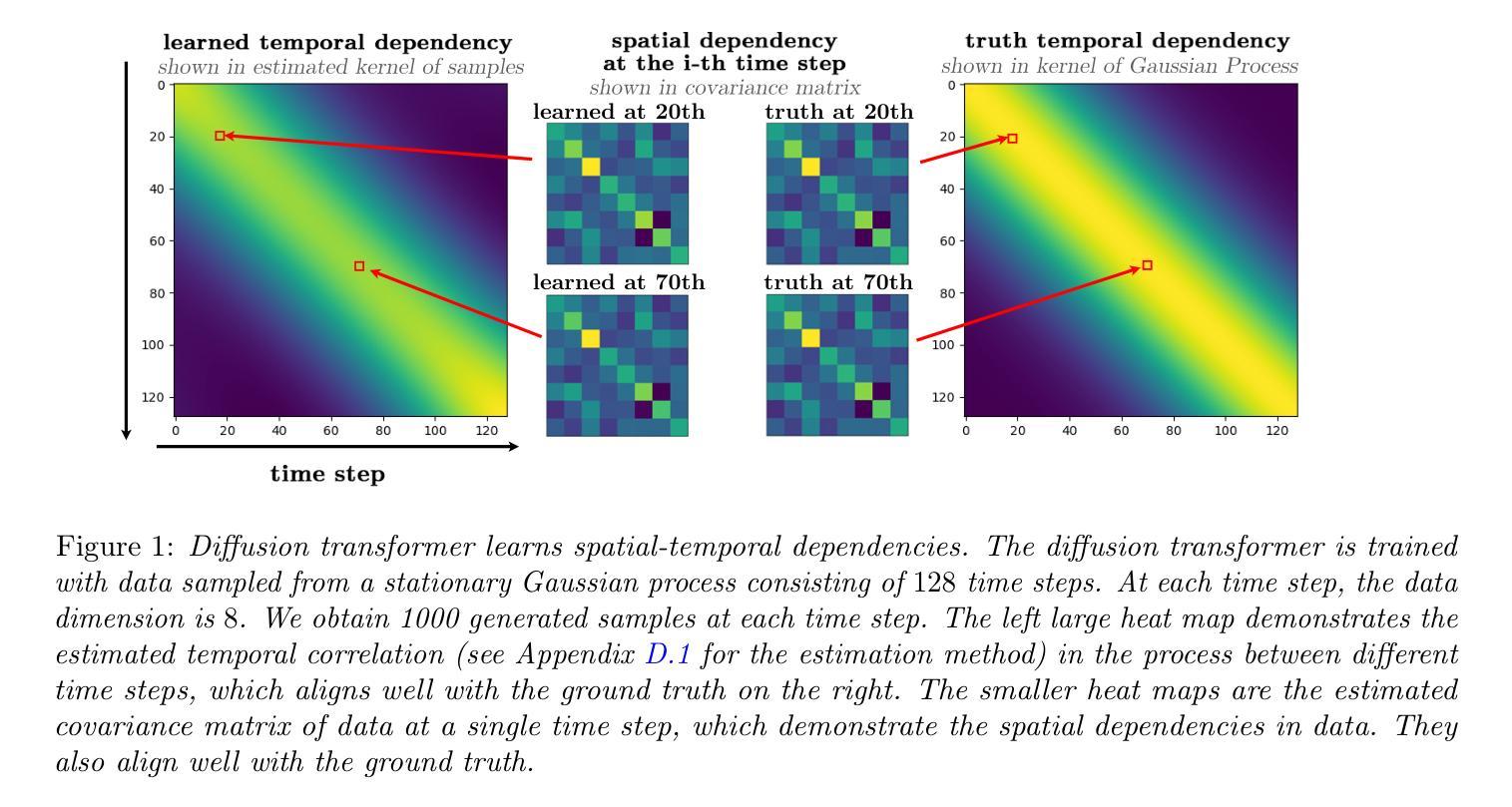
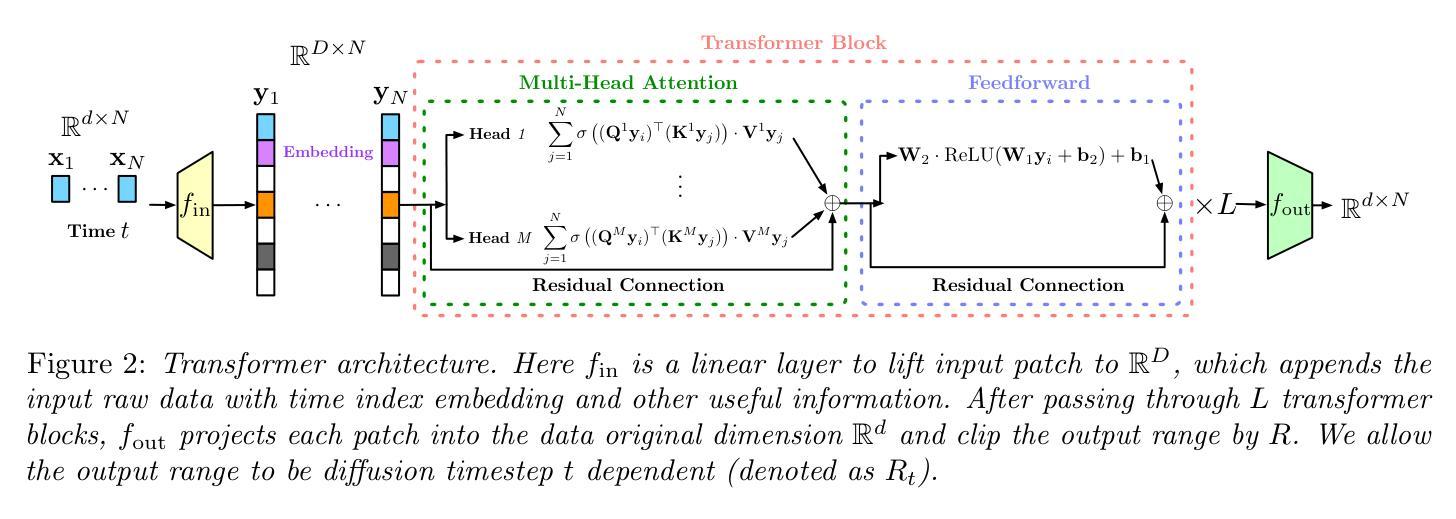
Diffusion Transformer, the backbone of Sora for video generation, successfully scales the capacity of diffusion models, pioneering new avenues for high-fidelity sequential data generation. Unlike static data such as images, sequential data consists of consecutive data frames indexed by time, exhibiting rich spatial and temporal dependencies. These dependencies represent the underlying dynamic model and are critical to validate the generated data. In this paper, we make the first theoretical step towards bridging diffusion transformers for capturing spatial-temporal dependencies. Specifically, we establish score approximation and distribution estimation guarantees of diffusion transformers for learning Gaussian process data with covariance functions of various decay patterns. We highlight how the spatial-temporal dependencies are captured and affect learning efficiency. Our study proposes a novel transformer approximation theory, where the transformer acts to unroll an algorithm. We support our theoretical results by numerical experiments, providing strong evidence that spatial-temporal dependencies are captured within attention layers, aligning with our approximation theory.
扩散模型的核心——Diffusion Transformer,为视频生成提供了强大的支撑,成功扩大了扩散模型的容量,为高质量序列数据生成开辟了新途径。不同于静态数据(如图像),序列数据由时间索引的连续数据帧组成,具有丰富的空间和时间依赖性。这些依赖关系代表了基础动态模型,对验证生成的数据至关重要。在本文中,我们朝着将扩散模型应用于捕捉时空依赖性的方向迈出了理论上的第一步。具体来说,我们为学习具有各种衰减模式的协方差函数的高斯过程数据建立扩散模型的得分近似和分布估计保证。我们强调了时空依赖性是如何被捕获并影响学习效率的。我们的研究提出了一种新的转换器近似理论,其中转换器起到展开算法的作用。我们通过数值实验支持我们的理论结果,提供强有力的证据表明时空依赖性被注意力层捕获,这与我们的近似理论相符。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 56 pages, 13 figures
Summary
扩散Transformer作为Sora视频生成的核心,成功扩展了扩散模型的容量,为高质量序列数据生成开辟了新途径。与静态数据(如图像)不同,序列数据由时间索引的连续数据帧组成,表现出丰富的空间和时间依赖性。本文首次从理论上探讨了扩散Transformer在捕捉时空依赖性方面的应用。我们建立了扩散Transformer对具有各种衰减模式的高斯过程数据进行评分逼近和分布估计的保证。本文强调了时空依赖性如何影响学习效率和捕捉方式,并提出了新的Transformer逼近理论,其中Transformer扮演展开算法的角色。数值实验支持我们的理论结果,提供有力证据表明时空依赖性被捕获在注意力层中,与我们的逼近理论相符。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散Transformer成功扩展了扩散模型的容量,为高质量序列数据生成提供了新途径。
- 序列数据具有时空依赖性,这是生成数据验证的关键。
- 本文首次从理论上探讨了扩散Transformer在捕捉时空依赖性方面的应用。
- 建立了扩散Transformer对具有不同衰减模式的高斯过程数据的评分逼近和分布估计的保证。
- 扩散Transformer能够捕捉和学习时空依赖性,这影响了学习效率和模型性能。
- 提出新的Transformer逼近理论,其中Transformer扮演算法展开的角色。
点此查看论文截图