⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-07 更新
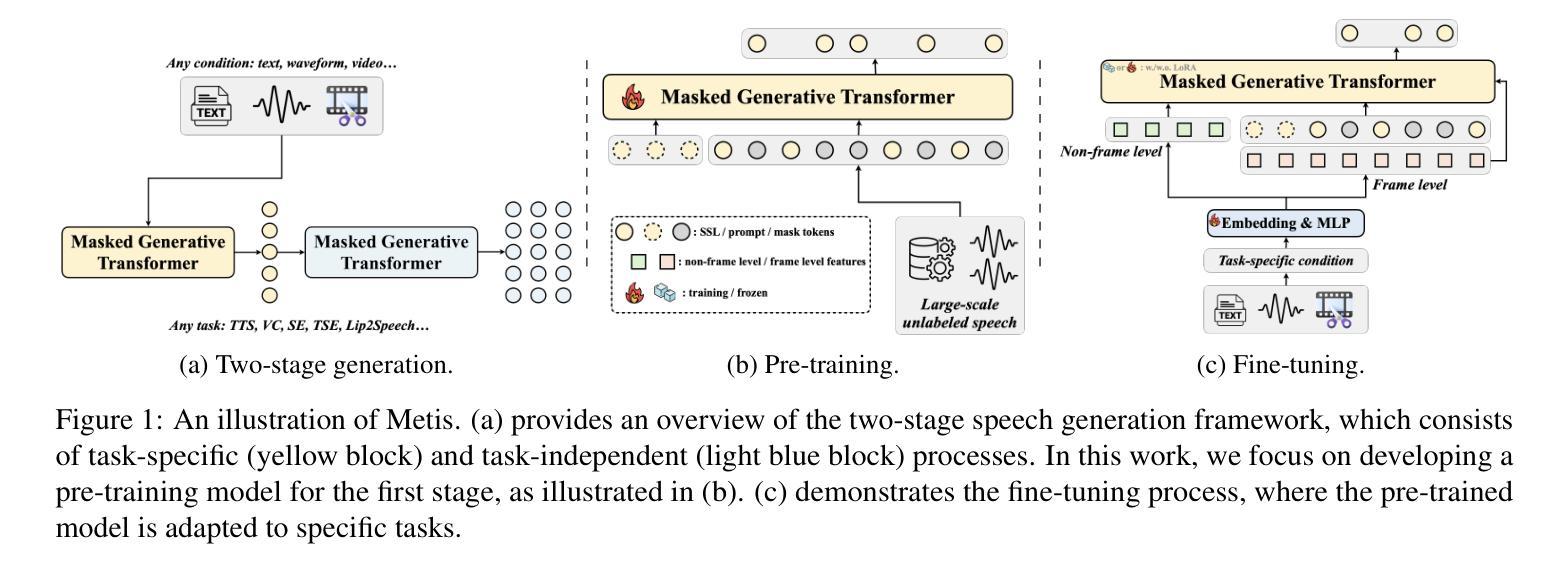
RadVLM: A Multitask Conversational Vision-Language Model for Radiology
Authors:Nicolas Deperrois, Hidetoshi Matsuo, Samuel Ruipérez-Campillo, Moritz Vandenhirtz, Sonia Laguna, Alain Ryser, Koji Fujimoto, Mizuho Nishio, Thomas M. Sutter, Julia E. Vogt, Jonas Kluckert, Thomas Frauenfelder, Christian Blüthgen, Farhad Nooralahzadeh, Michael Krauthammer
The widespread use of chest X-rays (CXRs), coupled with a shortage of radiologists, has driven growing interest in automated CXR analysis and AI-assisted reporting. While existing vision-language models (VLMs) show promise in specific tasks such as report generation or abnormality detection, they often lack support for interactive diagnostic capabilities. In this work we present RadVLM, a compact, multitask conversational foundation model designed for CXR interpretation. To this end, we curate a large-scale instruction dataset comprising over 1 million image-instruction pairs containing both single-turn tasks – such as report generation, abnormality classification, and visual grounding – and multi-turn, multi-task conversational interactions. After fine-tuning RadVLM on this instruction dataset, we evaluate it across different tasks along with re-implemented baseline VLMs. Our results show that RadVLM achieves state-of-the-art performance in conversational capabilities and visual grounding while remaining competitive in other radiology tasks. Ablation studies further highlight the benefit of joint training across multiple tasks, particularly for scenarios with limited annotated data. Together, these findings highlight the potential of RadVLM as a clinically relevant AI assistant, providing structured CXR interpretation and conversational capabilities to support more effective and accessible diagnostic workflows.
胸部X射线(CXR)的广泛应用以及放射科医生的短缺,推动了自动CXR分析和AI辅助报告功能的不断增长需求。虽然现有的视觉语言模型(VLM)在报告生成或异常检测等特定任务上展现出潜力,但它们往往缺乏支持交互式诊断的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了RadVLM,这是一个紧凑的多任务对话基础模型,专为CXR解释设计。为此,我们整理了一个大规模指令数据集,包含超过100万张图像和指令对,其中包括单回合任务,如报告生成、异常分类和视觉定位,以及多回合、多任务对话交互。通过对RadVLM进行微调后在此指令数据集上进行评估,以及重新实现基线VLMs的不同任务。我们的结果表明,RadVLM在对话能力和视觉定位方面达到了最新技术水平,同时在其他放射学任务中保持竞争力。消融研究进一步强调了联合训练多个任务的优势,特别是在有限标注数据的情况下。这些发现共同突出了RadVLM作为临床相关的AI助理的潜力,提供结构化CXR解释和对话能力,以支持更有效和可访问的诊断工作流程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 15 figures
Summary
本文介绍了由于胸部X射线(CXR)的广泛应用和放射科医生短缺,对自动化CXR分析和AI辅助报告的需求不断增长。尽管现有的视觉语言模型(VLM)在报告生成或异常检测等特定任务上显示出潜力,但它们往往缺乏交互式诊断功能。为此,本文提出了一种紧凑、多任务对话基础模型RadVLM,用于CXR解读。为此目的,我们创建了一个大规模指令数据集,包含超过1百万个图像指令对,包括报告生成、异常分类和视觉定位等单任务以及多任务多轮对话交互。经过在此指令数据集上微调后,RadVLM在不同任务上的表现优于重新实现的基线VLM。结果证明RadVLM在对话能力和视觉定位方面达到最新水平,同时在其他放射学任务中保持竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 胸部X射线(CXR)的广泛应用和放射科医生短缺,导致对自动化CXR分析和AI辅助报告的需求增长。
- 现有视觉语言模型(VLM)在特定任务上表现良好,但缺乏交互式诊断功能。
- RadVLM是一个紧凑、多任务对话基础模型,用于CXR解读。
- 创建一个大规模指令数据集,包含图像指令对,涵盖单任务和多任务对话交互。
- RadVLM在不同任务上的表现优于基线VLM,具有先进的多任务处理能力。
- RadVLM在对话能力和视觉定位方面表现出色,并可能成为临床相关的AI助手。
点此查看论文截图


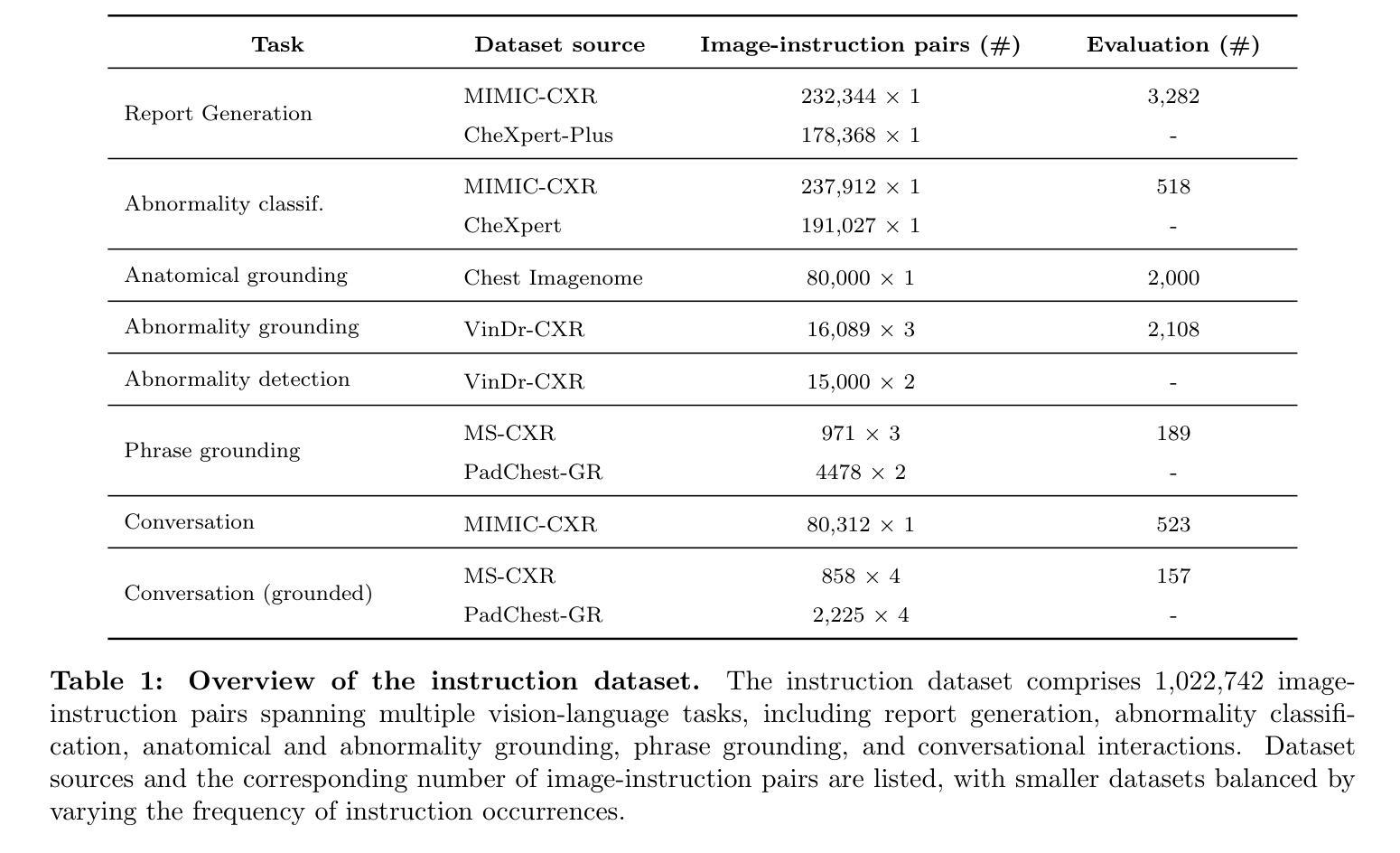

MAP Image Recovery with Guarantees using Locally Convex Multi-Scale Energy (LC-MUSE) Model
Authors:Jyothi Rikhab Chand, Mathews Jacob
We propose a multi-scale deep energy model that is strongly convex in the local neighbourhood around the data manifold to represent its probability density, with application in inverse problems. In particular, we represent the negative log-prior as a multi-scale energy model parameterized by a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). We restrict the gradient of the CNN to be locally monotone, which constrains the model as a Locally Convex Multi-Scale Energy (LC-MuSE). We use the learned energy model in image-based inverse problems, where the formulation offers several desirable properties: i) uniqueness of the solution, ii) convergence guarantees to a minimum of the inverse problem, and iii) robustness to input perturbations. In the context of parallel Magnetic Resonance (MR) image reconstruction, we show that the proposed method performs better than the state-of-the-art convex regularizers, while the performance is comparable to plug-and-play regularizers and end-to-end trained methods.
我们提出了一种多尺度深度能量模型,该模型在数据流形附近的局部邻域内强烈凸,用于表示其概率密度,并应用于反问题。具体来说,我们将负对数先验表示为一个多尺度能量模型,该模型由卷积神经网络(CNN)参数化。我们将CNN的梯度限制为局部单调,从而将模型约束为局部凸多尺度能量(LC-MuSE)。我们在基于图像的反问题中使用学到的能量模型,其公式具有几个理想的特性:i)解的唯一性,ii)对反问题的最小收敛保证,以及iii)对输入扰动的鲁棒性。在并行磁共振(MR)图像重建的上下文中,我们证明了所提出的方法优于最新的凸正则化器,同时其性能与即插即用正则化器和端到端训练的方法相当。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一种多尺度深度能量模型,通过卷积神经网络(CNN)参数化表示负对数先验作为多尺度能量模型,并限制CNN的梯度在局部单调,将其约束为局部凸多尺度能量(LC-MuSE)。该模型应用于图像逆问题,具有唯一解、向逆问题最小值的收敛保证以及对输入扰动的鲁棒性。在并行磁共振(MR)图像重建的上下文中,该方法优于最先进的凸正则化方法,性能与即插即用正则化方法和端到端训练方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种多尺度深度能量模型,用于表示概率密度,并应用于逆问题。
- 将负对数先验表示为多尺度能量模型,通过卷积神经网络进行参数化。
- 模型的梯度在局部被限制为单调,形成局部凸多尺度能量(LC-MuSE)。
- 该模型在图像逆问题中表现出优良性能,具有唯一解、收敛保证和对输入扰动的鲁棒性。
- 在并行磁共振图像重建中,该方法优于许多先进的凸正则化方法。
- 该方法的性能与即插即用正则化方法和端到端训练方法相当。
点此查看论文截图

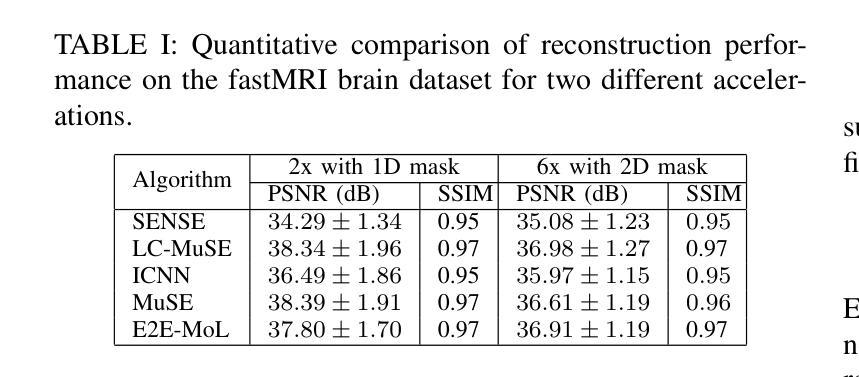
A Unified Framework for Semi-Supervised Image Segmentation and Registration
Authors:Ruizhe Li, Grazziela Figueredo, Dorothee Auer, Rob Dineen, Paul Morgan, Xin Chen
Semi-supervised learning, which leverages both annotated and unannotated data, is an efficient approach for medical image segmentation, where obtaining annotations for the whole dataset is time-consuming and costly. Traditional semi-supervised methods primarily focus on extracting features and learning data distributions from unannotated data to enhance model training. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach incorporating an image registration model to generate pseudo-labels for the unannotated data, producing more geometrically correct pseudo-labels to improve the model training. Our method was evaluated on a 2D brain data set, showing excellent performance even using only 1% of the annotated data. The results show that our approach outperforms conventional semi-supervised segmentation methods (e.g. teacher-student model), particularly in a low percentage of annotation scenario. GitHub: https://github.com/ruizhe-l/UniSegReg.
半监督学习结合了标注数据和非标注数据,是医学图像分割的一种高效方法。在医学图像分割中,对整个数据集进行标注是非常耗时和昂贵的。传统的半监督方法主要关注从非标注数据中提取特征和学习数据分布,以提高模型训练的效果。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,结合图像配准模型生成非标注数据的伪标签,生成更几何正确的伪标签,以提高模型训练的效果。我们的方法在2D脑数据集上进行了评估,即使在仅使用1%的标注数据的情况下也表现出卓越的性能。结果表明,我们的方法优于传统的半监督分割方法(如师徒模型),特别是在标注比例较低的情况下。GitHub地址:链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025
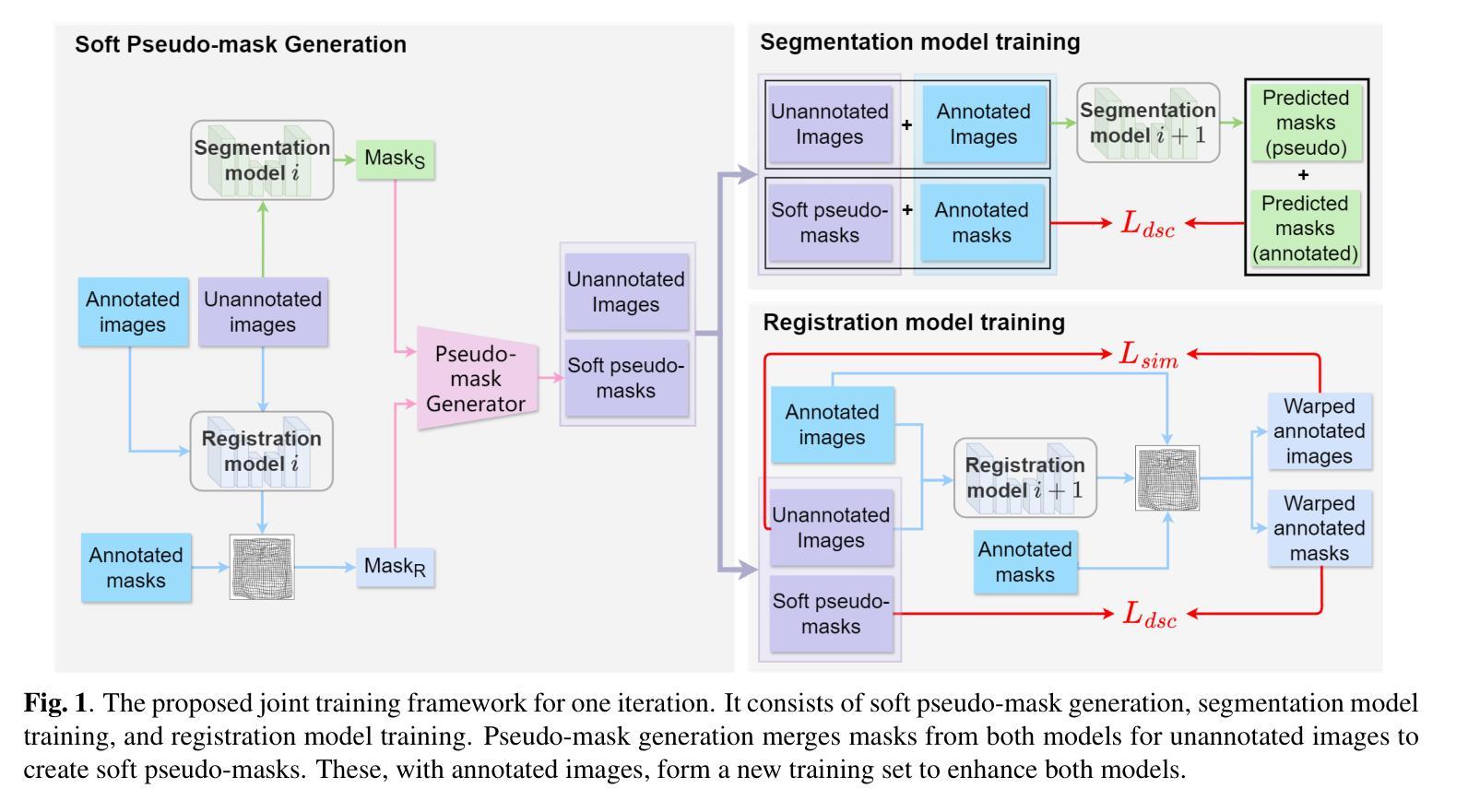
总结
本文提出了一种利用图像注册模型生成未标注数据的伪标签的新方法,以改善模型训练,并在低标注场景中表现出卓越性能。该方法在二维脑数据集上评估,仅使用1%的标注数据即可实现良好表现。相较于传统的半监督分割方法,如师徒模型等,该方法更为出色。可以通过GitHub访问详细信息和代码:https://github.com/ruizhe-l/UniSegReg。
关键收获点
利用半监督学习(利用标注和未标注数据)提高医学图像分割效率。这是因为标注整个数据集的时间成本高且成本高昂。传统方法主要集中在从未标注数据中提取特征和进行数据分布学习以提高模型训练。本研究采用一种新方法结合图像注册模型。
利用图像注册模型生成伪标签的技术以改进模型训练,这种方式相较于传统半监督分割方法能更好地使用未标注数据的信息。这为提升模型的精度提供了新的可能。而且其优势在于即使在仅使用极少标注数据的情况下也依然有良好的表现。同时它还带来了另一个好处:无需在昂贵的硬件设备或训练过程中投入大量资源,就可以提高模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Tell2Reg: Establishing spatial correspondence between images by the same language prompts
Authors:Wen Yan, Qianye Yang, Shiqi Huang, Yipei Wang, Shonit Punwani, Mark Emberton, Vasilis Stavrinides, Yipeng Hu, Dean Barratt
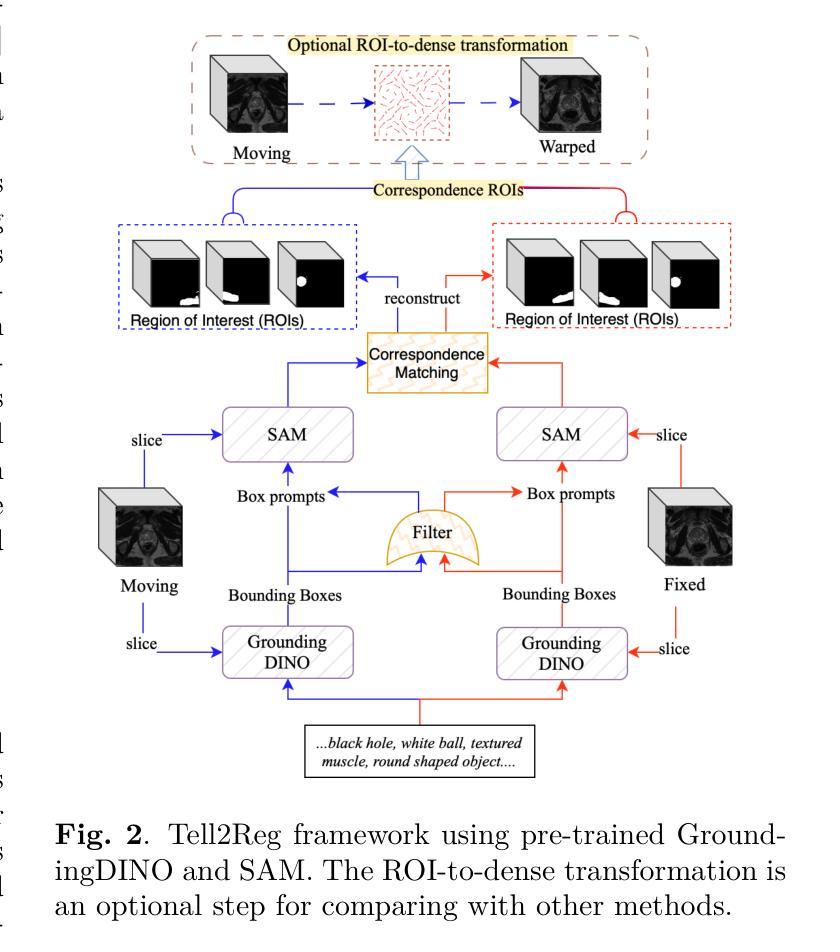
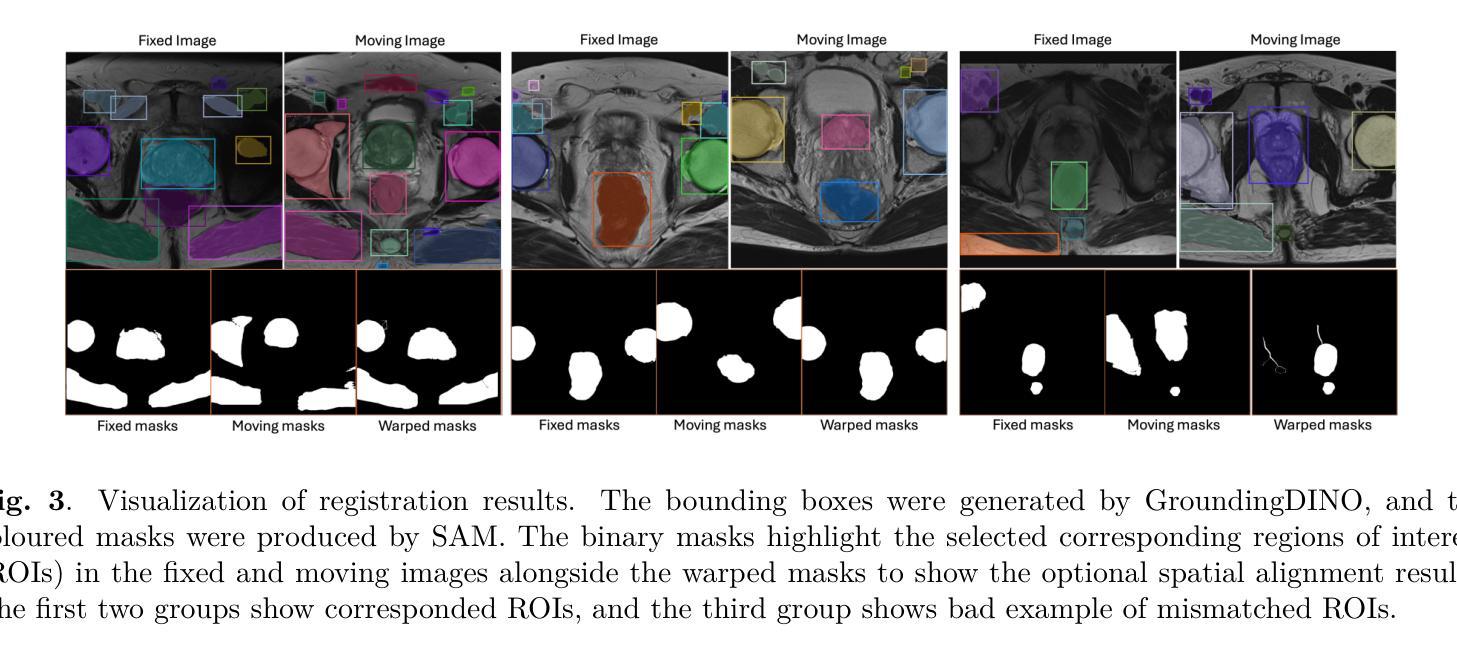
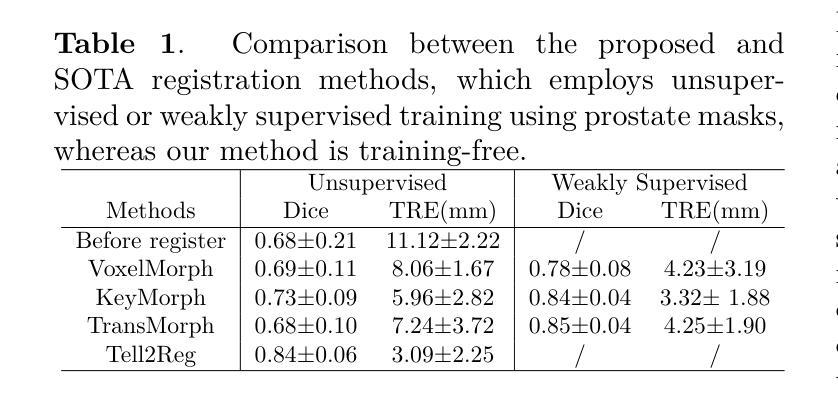
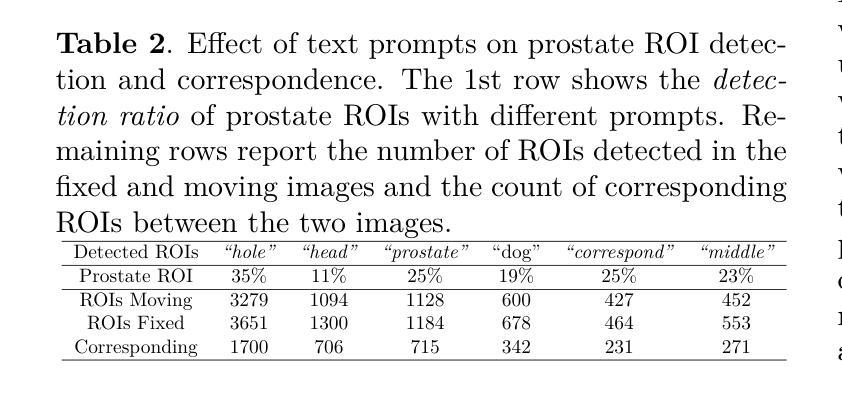
Spatial correspondence can be represented by pairs of segmented regions, such that the image registration networks aim to segment corresponding regions rather than predicting displacement fields or transformation parameters. In this work, we show that such a corresponding region pair can be predicted by the same language prompt on two different images using the pre-trained large multimodal models based on GroundingDINO and SAM. This enables a fully automated and training-free registration algorithm, potentially generalisable to a wide range of image registration tasks. In this paper, we present experimental results using one of the challenging tasks, registering inter-subject prostate MR images, which involves both highly variable intensity and morphology between patients. Tell2Reg is training-free, eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming data curation and labelling that was previously required for this registration task. This approach outperforms unsupervised learning-based registration methods tested, and has a performance comparable to weakly-supervised methods. Additional qualitative results are also presented to suggest that, for the first time, there is a potential correlation between language semantics and spatial correspondence, including the spatial invariance in language-prompted regions and the difference in language prompts between the obtained local and global correspondences. Code is available at https://github.com/yanwenCi/Tell2Reg.git.
空间对应关系可以通过成对的分割区域来表示,图像注册网络的目标是分割对应区域,而不是预测位移场或转换参数。在这项工作中,我们展示了通过基于GroundingDINO和SAM的预训练多模式模型,使用同一语言提示预测两个不同图像上的对应区域对。这实现了全自动、无需训练的图象注册算法,可广泛应用于各种图像注册任务。在本文中,我们展示了使用挑战性任务之一——跨受试者前列腺MR图像注册的实验结果,该任务涉及患者之间强度和形态的很大变化。Tell2Reg无需训练,消除了以前对此注册任务所需的高成本和时间密集的数据整理和标记的需求。该方法优于经过测试的无监督学习基础的注册方法,其性能与弱监督方法相当。此外,还提供了额外的定性结果,建议首次发现语言语义与空间对应关系之间存在潜在关联,包括语言提示区域的空简不变性以及获得局部和全局对应关系之间语言提示的差异。代码可通过https://github.com/yanwenCi/Tell2Reg.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures, conference paper
Summary
本文提出一种全新的图像注册方法,通过预训练的跨模态模型,利用相同的语言提示预测两个不同图像中的对应区域对,实现全自动且无需训练的图象注册算法。该方法适用于多种图像注册任务,并在病人间前列腺MR图像注册这一具有挑战性的任务上表现出优越性能。此方法无需耗时耗力的数据整理和标注,性能与弱监督方法相当。研究发现语言语义与空间对应之间可能存在潜在关联。
Key Takeaways
- 图像注册网络通过预测对应区域对表示空间对应关系,而非预测位移场或转换参数。
- 同一语言提示可用于预测两个不同图像中的对应区域对。
- 使用预训练的跨模态模型,基于GroundingDINO和SAM,实现无需训练的图象注册算法。
- 该方法适用于多种图像注册任务,并在前列腺MR图像注册这一具有挑战性的任务上表现优越。
- 该方法消除了对昂贵和耗时的数据整理和标注的需求。
- 此方法性能与弱监督方法相当。
点此查看论文截图


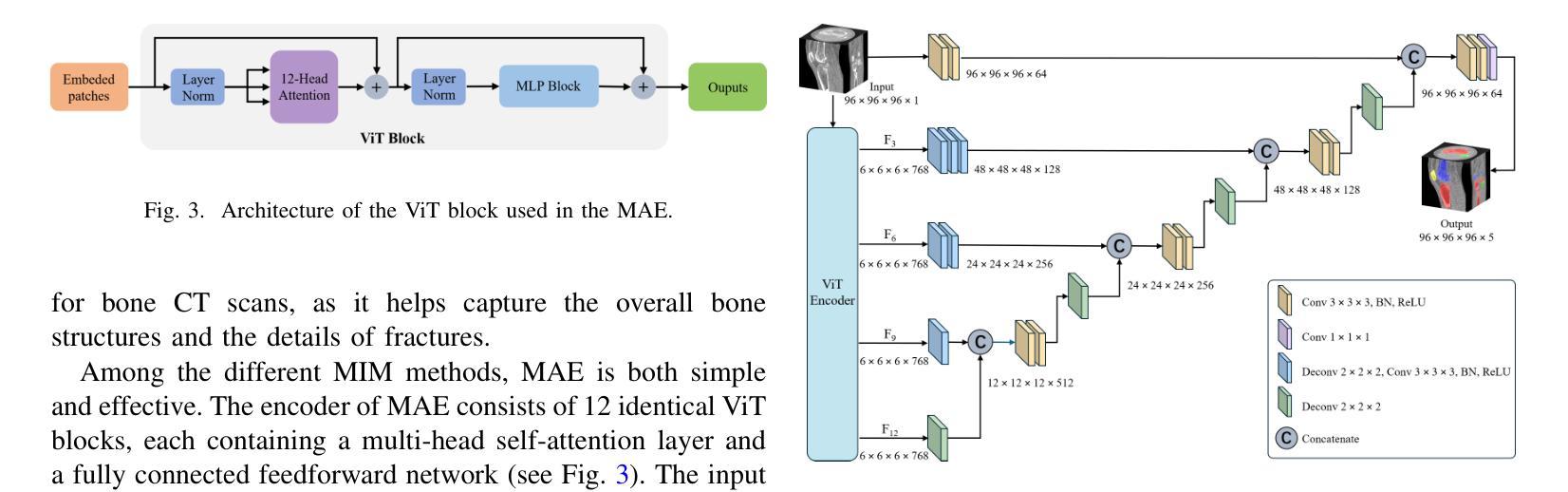
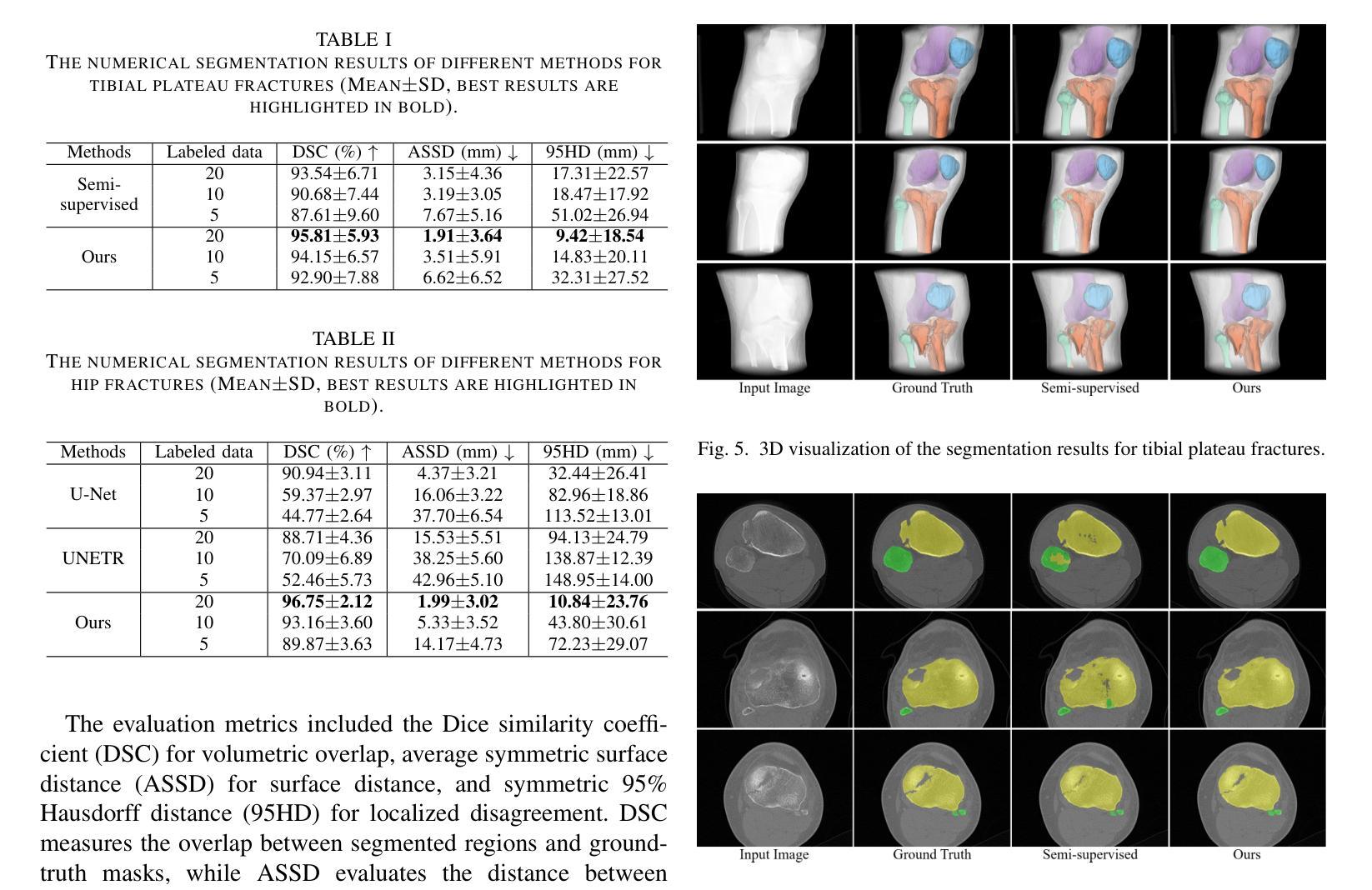
Learning Generalizable Features for Tibial Plateau Fracture Segmentation Using Masked Autoencoder and Limited Annotations
Authors:Peiyan Yue, Die Cai, Chu Guo, Mengxing Liu, Jun Xia, Yi Wang
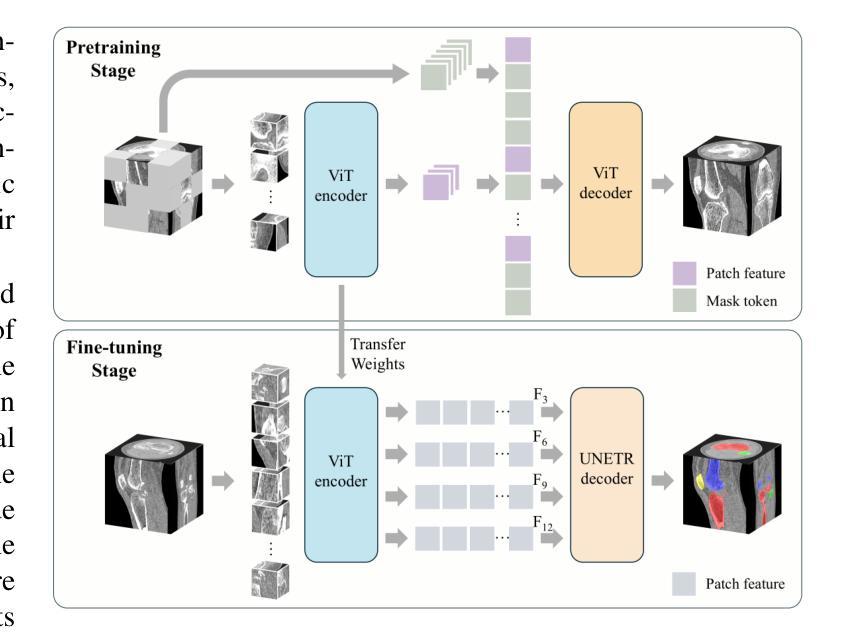
Accurate automated segmentation of tibial plateau fractures (TPF) from computed tomography (CT) requires large amounts of annotated data to train deep learning models, but obtaining such annotations presents unique challenges. The process demands expert knowledge to identify diverse fracture patterns, assess severity, and account for individual anatomical variations, making the annotation process highly time-consuming and expensive. Although semi-supervised learning methods can utilize unlabeled data, existing approaches often struggle with the complexity and variability of fracture morphologies, as well as limited generalizability across datasets. To tackle these issues, we propose an effective training strategy based on masked autoencoder (MAE) for the accurate TPF segmentation in CT. Our method leverages MAE pretraining to capture global skeletal structures and fine-grained fracture details from unlabeled data, followed by fine-tuning with a small set of labeled data. This strategy reduces the dependence on extensive annotations while enhancing the model’s ability to learn generalizable and transferable features. The proposed method is evaluated on an in-house dataset containing 180 CT scans with TPF. Experimental results demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms semi-supervised methods, achieving an average Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 95.81%, average symmetric surface distance (ASSD) of 1.91mm, and Hausdorff distance (95HD) of 9.42mm with only 20 annotated cases. Moreover, our method exhibits strong transferability when applying to another public pelvic CT dataset with hip fractures, highlighting its potential for broader applications in fracture segmentation tasks.
对胫骨平台骨折(TPF)进行准确的自动分割,需要从计算机断层扫描(CT)图像中识别出大量的标注数据来训练深度学习模型。然而,获取这些标注数据面临诸多挑战。这一过程需要专业知识来识别多种骨折模式、评估严重程度,并考虑个体解剖结构差异,这使得标注过程非常耗时且成本高昂。虽然半监督学习方法可以利用未标注数据,但现有方法往往难以应对骨折形态的复杂性和差异性,以及数据集之间有限的通用性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于掩码自编码器(MAE)的有效训练策略,用于CT图像中TPF的准确分割。我们的方法利用MAE进行预训练,从未标注数据中捕获全局骨骼结构和精细的骨折细节,然后使用少量标注数据进行微调。此策略减少了对大量标注的依赖,同时提高了模型学习通用和可迁移特征的能力。该方法在包含180例TPF的CT扫描内部数据集上进行了评估。实验结果表明,该方法在仅使用20个标注病例的情况下,平均Dice相似系数(DSC)达到95.81%,平均对称表面距离(ASSD)为1.91毫米,Hausdorff距离(95HD)为9.42毫米,性能持续优于半监督方法。此外,我们的方法在处理另一公共骨盆CT数据集(包含髋关节骨折)时表现出强大的可迁移性,突显其在骨折分割任务中更广泛应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文提出一种基于掩码自编码器(MAE)的有效训练策略,用于准确地对CT中的胫骨平台骨折(TPF)进行自动分割。该方法利用MAE的预训练功能,从非标记数据中捕获全局骨骼结构和精细骨折细节,然后用少量标记数据进行微调。这种策略减少了大量注释的依赖,提高了模型学习通用和可转移特征的能力。实验结果表明,该方法在内部数据集上的表现优于半监督方法,并在另一个公共骨盆CT数据集上也表现出强大的可转移性。
Key Takeaways
- 准确自动分割胫骨平台骨折对于治疗计划和预后评估至关重要。
- 获取标注数据是该领域的一大挑战,因为需要专业知识来识别多样的骨折模式、评估严重程度以及考虑个体解剖结构差异。
- 半监督学习方法虽可利用未标记数据,但现有方法难以处理骨折形态的复杂性和可变性,且在跨数据集方面的通用性有限。
- 提出的基于掩码自编码器(MAE)的训练策略能够利用未标记数据捕捉全局骨骼结构和精细骨折细节,并通过微调少量标记数据进行优化。
- 该策略减少了大量注释的依赖,提高了模型的泛化能力和特征迁移能力。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在内部数据集上表现优异,与半监督方法相比具有更高的Dice相似系数、更低的对称表面距离和Hausdorff距离。
点此查看论文截图

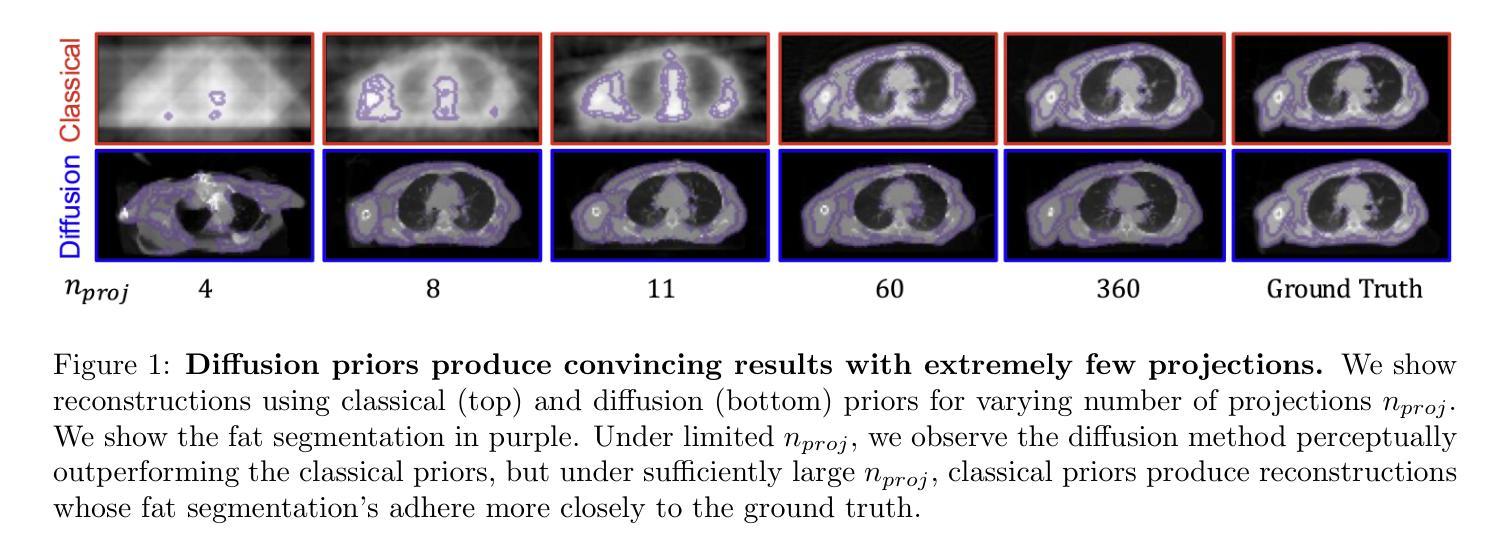
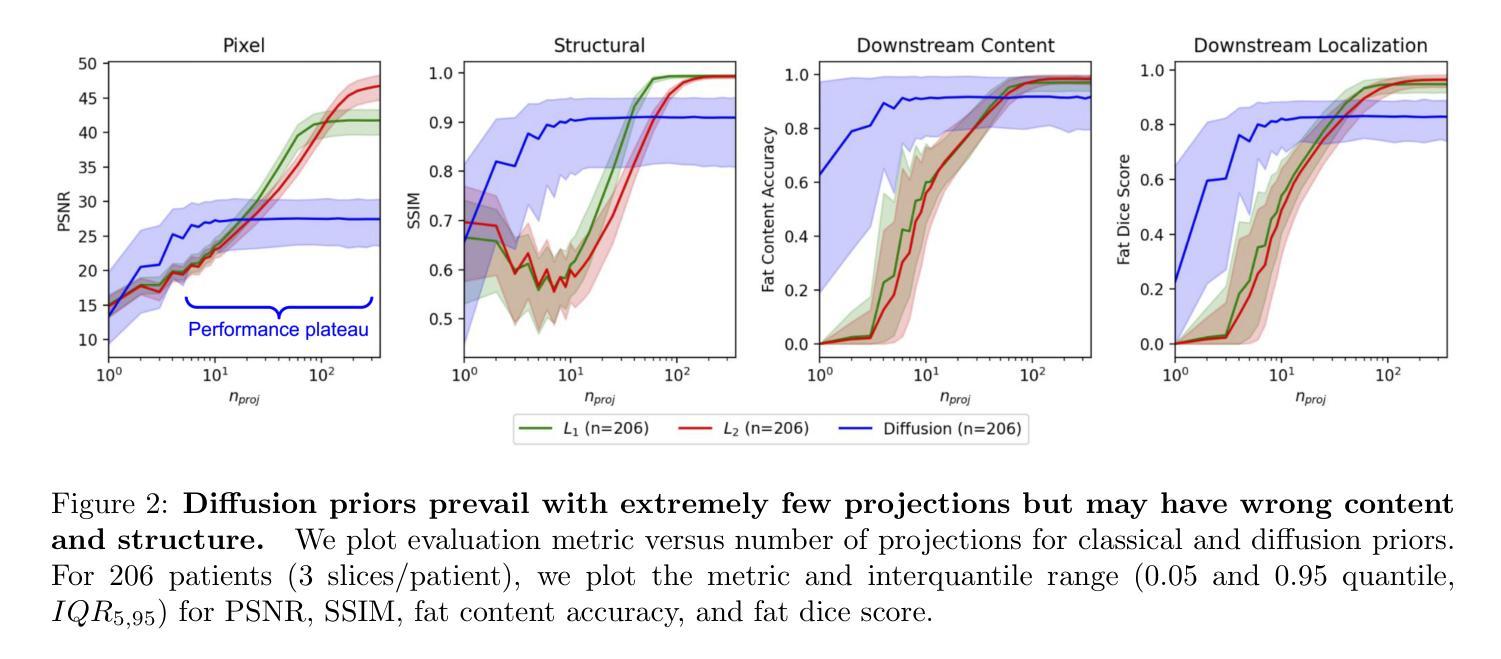
When are Diffusion Priors Helpful in Sparse Reconstruction? A Study with Sparse-view CT
Authors:Matt Y. Cheung, Sophia Zorek, Tucker J. Netherton, Laurence E. Court, Sadeer Al-Kindi, Ashok Veeraraghavan, Guha Balakrishnan
Diffusion models demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on image generation, and are gaining traction for sparse medical image reconstruction tasks. However, compared to classical reconstruction algorithms relying on simple analytical priors, diffusion models have the dangerous property of producing realistic looking results \emph{even when incorrect}, particularly with few observations. We investigate the utility of diffusion models as priors for image reconstruction by varying the number of observations and comparing their performance to classical priors (sparse and Tikhonov regularization) using pixel-based, structural, and downstream metrics. We make comparisons on low-dose chest wall computed tomography (CT) for fat mass quantification. First, we find that classical priors are superior to diffusion priors when the number of projections is ``sufficient’’. Second, we find that diffusion priors can capture a large amount of detail with very few observations, significantly outperforming classical priors. However, they fall short of capturing all details, even with many observations. Finally, we find that the performance of diffusion priors plateau after extremely few ($\approx$10-15) projections. Ultimately, our work highlights potential issues with diffusion-based sparse reconstruction and underscores the importance of further investigation, particularly in high-stakes clinical settings.
扩散模型在图像生成方面表现出最先进的技术性能,并且正逐渐应用于稀疏医学图像重建任务。然而,与依赖于简单分析先验知识的传统重建算法相比,扩散模型具有一个危险的特性,即即使结果不正确,也能产生逼真的图像,特别是在观测数据较少的情况下。我们通过改变观测数据的数量,研究扩散模型作为图像重建先验知识的实用性,并利用像素级、结构级和下游指标与经典先验知识(稀疏和Tikhonov正则化)进行比较。我们对低剂量胸部壁计算机断层扫描(CT)进行脂肪质量定量比较。首先,我们发现当投影数量“足够”时,经典先验知识优于扩散先验知识。其次,我们发现扩散先验知识能够在很少的观测数据下捕捉到大量细节,显著优于经典先验知识。然而,即使在很多观测数据的情况下,它们也无法捕捉到所有细节。最后,我们发现扩散先验知识的性能在极少的(约10-15个)投影后达到平稳。总的来说,我们的工作突出了扩散模型在稀疏重建中的潜在问题,并强调了进一步调查的重要性,特别是在高风险的临床环境中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE ISBI 2025, 5 pages, 2 figures, 1 table
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成方面表现出卓越的性能,并在稀疏医学图像重建任务中获得关注。本文探讨了扩散模型作为图像重建先验的效用,通过改变观测数量,与经典先验(稀疏和Tikhonov正则化)进行比较,并在低剂量胸腔计算机断层扫描(CT)中进行脂肪质量量化的评估。研究发现,在观测数量充足时,经典先验优于扩散先验;扩散先验在观测数量极少时即可捕捉大量细节,显著优于经典先验,但在捕捉所有细节方面仍有不足;此外,扩散先验在极少投影后的性能趋于稳定。本文强调了扩散模型在稀疏重建中的潜在问题,并强调了在高风险临床环境中进一步调查的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成领域表现卓越,并在医学图像重建中获得关注。
- 相比经典先验,扩散模型在观测数量极少时仍能捕捉大量细节。
- 在充足观测下,经典先验表现优于扩散先验。
- 扩散模型在捕捉所有细节方面存在不足。
- 扩散先验的性能在极少投影后趋于稳定。
- 扩散模型在稀疏重建中存在潜在问题,需要进一步调查。
点此查看论文截图

Adaptive Voxel-Weighted Loss Using L1 Norms in Deep Neural Networks for Detection and Segmentation of Prostate Cancer Lesions in PET/CT Images
Authors:Obed Korshie Dzikunu, Shadab Ahamed, Amirhossein Toosi, Xiaoxiao Li, Arman Rahmim
This study proposes a new loss function for deep neural networks, L1-weighted Dice Focal Loss (L1DFL), that leverages L1 norms for adaptive weighting of voxels based on their classification difficulty, towards automated detection and segmentation of metastatic prostate cancer lesions in PET/CT scans. We obtained 380 PSMA [18-F] DCFPyL PET/CT scans of patients diagnosed with biochemical recurrence metastatic prostate cancer. We trained two 3D convolutional neural networks, Attention U-Net and SegResNet, and concatenated the PET and CT volumes channel-wise as input. The performance of our custom loss function was evaluated against the Dice and Dice Focal Loss functions. For clinical significance, we considered a detected region of interest (ROI) as a true positive if at least the voxel with the maximum standardized uptake value falls within the ROI. We assessed the models’ performance based on the number of lesions in an image, tumour volume, activity, and extent of spread. The L1DFL outperformed the comparative loss functions by at least 13% on the test set. In addition, the F1 scores of the Dice Loss and the Dice Focal Loss were lower than that of L1DFL by at least 6% and 34%, respectively. The Dice Focal Loss yielded more false positives, whereas the Dice Loss was more sensitive to smaller volumes and struggled to segment larger lesions accurately. They also exhibited network-specific variations and yielded declines in segmentation accuracy with increased tumour spread. Our results demonstrate the potential of L1DFL to yield robust segmentation of metastatic prostate cancer lesions in PSMA PET/CT images. The results further highlight potential complexities arising from the variations in lesion characteristics that may influence automated prostate cancer tumour detection and segmentation. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/ObedDzik/pca_segment.git.
本研究针对深度神经网络提出了一种新的损失函数,即L1加权Dice Focal Loss(L1DFL)。它利用L1范数根据分类难度对体素进行自适应加权,旨在实现PET/CT扫描中转移性前列腺癌病变的自动检测和分割。我们获得了380例被诊断为生化复发转移性前列腺癌患者的PSMA [18-F] DCFPyL PET/CT扫描。我们训练了两个3D卷积神经网络,即Attention U-Net和SegResNet,并将PET和CT体积按通道合并作为输入。我们的自定义损失函数的性能与Dice和Dice Focal Loss函数进行了评估。对于临床意义,如果最大标准化摄取值的体素位于感兴趣区域内,则我们将其视为真正的阳性区域。我们根据图像中的病变数量、肿瘤体积、活动性以及扩散程度评估了模型性能。在测试集上,L1DFL至少比对比损失函数高出13%的性能。此外,Dice Loss和Dice Focal Loss的F1分数至少比L1DFL低6%和34%。Dice Focal Loss产生了更多的假阳性,而Dice Loss对较小的体积更敏感,并且在分割较大的病变时准确性较差。它们还表现出网络特定的变化,并随着肿瘤扩散的增加而导致分割精度下降。我们的结果证明了L1DFL在PSMA PET/CT图像中稳健分割转移性前列腺癌病变的潜力。结果还进一步强调了由于病变特征的差异所产生的潜在复杂性,这可能会影响自动化前列腺癌肿瘤检测和分割。代码公开在:https://github.com/ObedDzik/pca_segment.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 7 figures, 1 table
摘要
该研究提出了一种新的深度学习损失函数,名为L1范数加权的Dice Focal Loss(L1DFL),用于自适应加权分类难度的体素。此函数应用于PET/CT扫描中转移性前列腺癌病变的自动检测和分割。研究使用了380例PSMA [18-F] DCFPyL PET/CT扫描的病患数据,并训练了两种3D卷积神经网络(Attention U-Net和SegResNet)。该研究将PET和CT体积按通道方式结合作为输入,并评估了自定义损失函数与Dice和Dice Focal损失函数的性能。在临床意义方面,如果最大标准化摄取值的体素位于感兴趣区域内,则将其视为真正的阳性。根据图像中的病变数量、肿瘤体积、活动性和扩散程度评估模型性能。L1DFL在测试集上的表现至少比对比损失函数高出13%。此外,Dice Loss和Dice Focal Loss的F1分数至少比L1DFL低6%和34%。Dice Focal Loss产生更多的假阳性,而Dice Loss对较小的体积更敏感,并且难以准确分割较大的病变。他们的网络特定变化随着肿瘤扩散的增加,分割精度下降。研究结果展示了L1DFL在PSMA PET/CT图像中稳健分割转移性前列腺癌病变的潜力,并突出了病变特征变化对自动前列腺癌肿瘤检测和分割的影响。相关代码已公开于:https://github.com/ObedDzik/pca_segment.git。
要点归纳
- 研究提出了一种新的损失函数L1DFL,用于深度神经网络,特别关注于自适应加权体素在转移性前列腺癌病变检测与分割中的应用。
- 通过使用PSMA [18-F] DCFPyL PET/CT扫描数据,训练了两种3D卷积神经网络模型。
- L1DFL在测试集上的性能优于传统的Dice Loss和Dice Focal Loss,至少高出13%。
- Dice Focal Loss产生较多假阳性,而Dice Loss对小体积更敏感,对大型病变的分割准确性较差。
- 随着肿瘤扩散的增加,所有损失函数都表现出网络特定的变化及分割精度的下降。
- L1DFL具有在PSMA PET/CT图像中稳健分割转移性前列腺癌病变的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

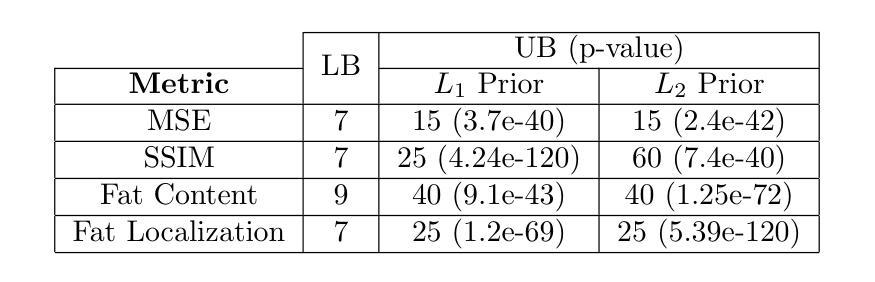
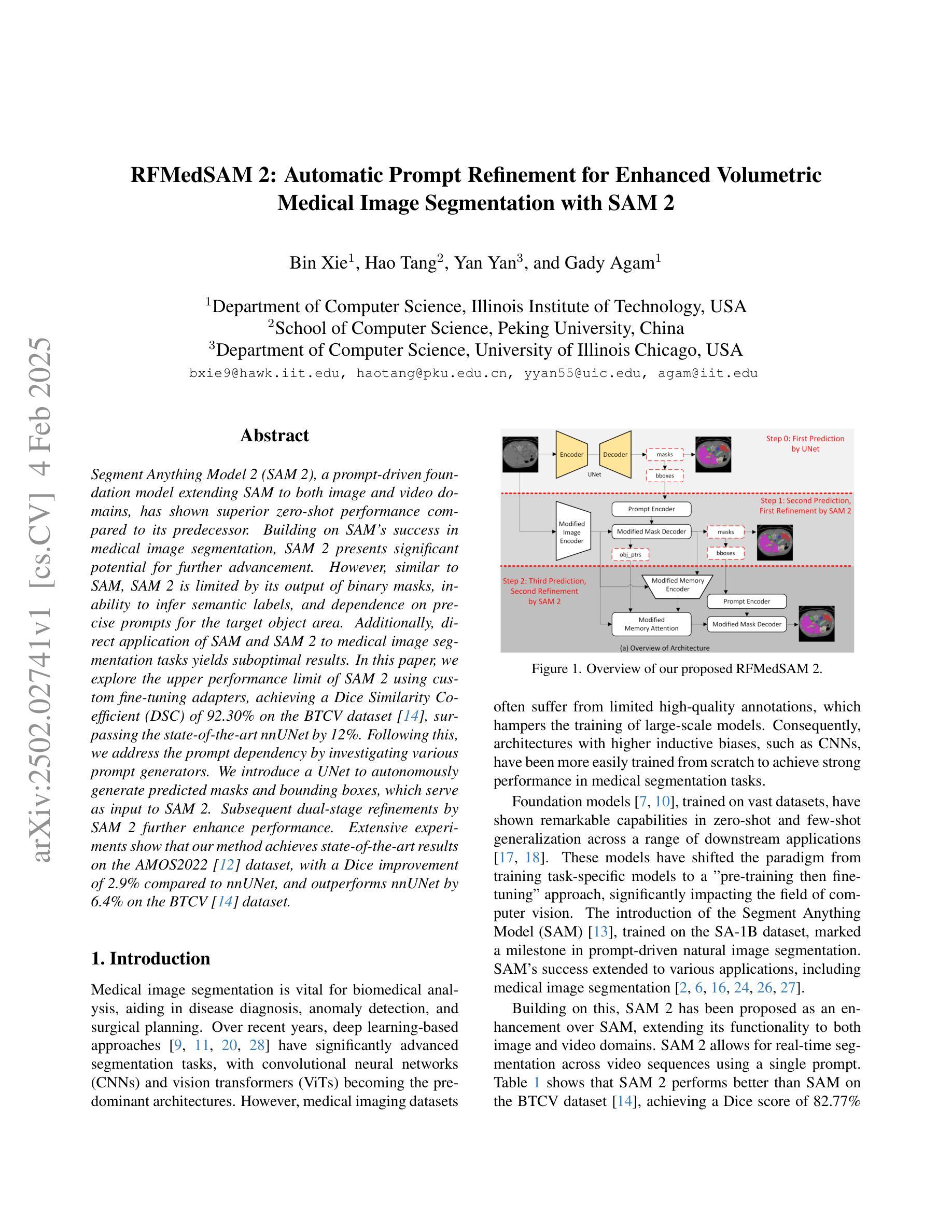
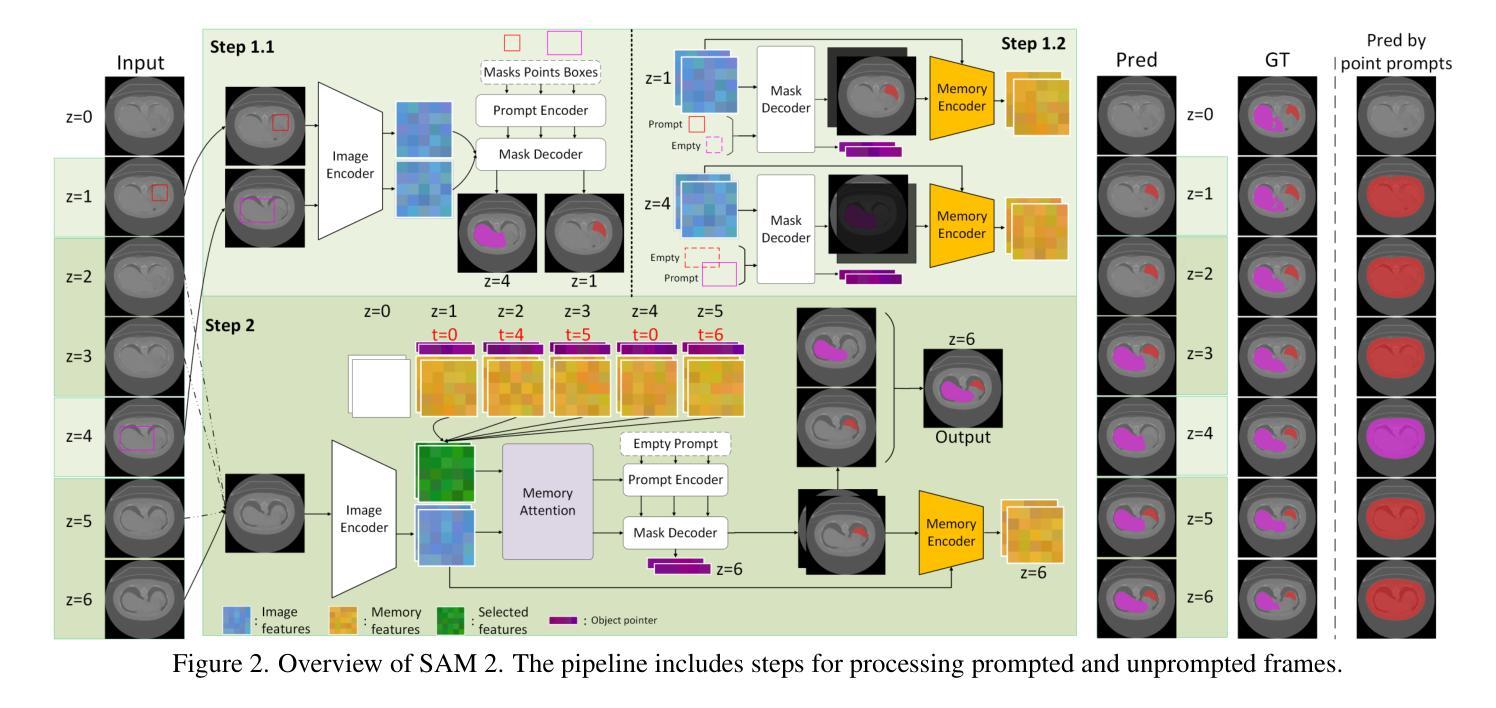
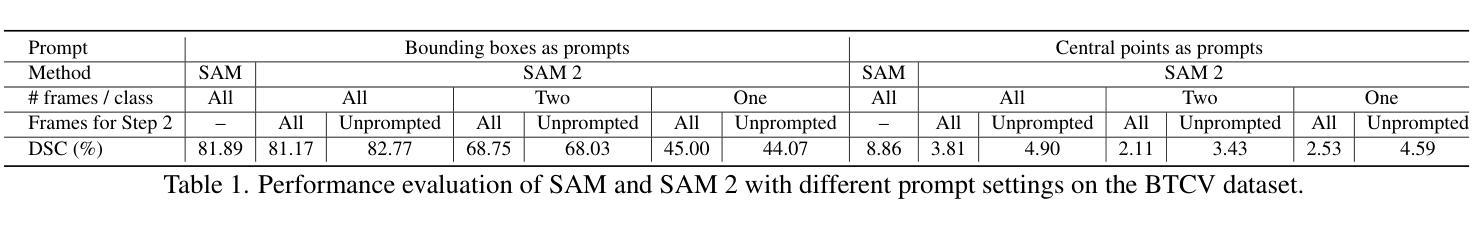
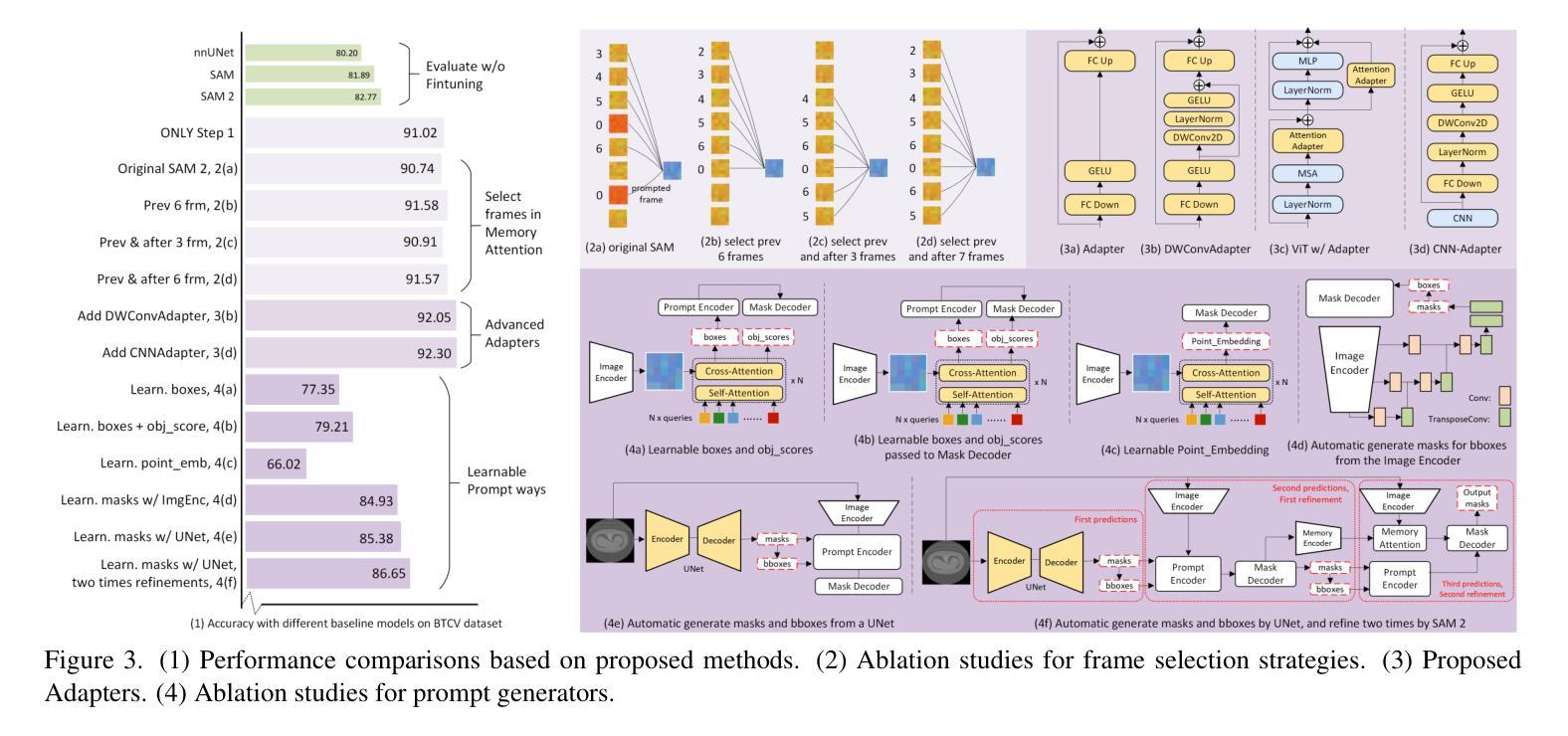
RFMedSAM 2: Automatic Prompt Refinement for Enhanced Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation with SAM 2
Authors:Bin Xie, Hao Tang, Yan Yan, Gady Agam
Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2), a prompt-driven foundation model extending SAM to both image and video domains, has shown superior zero-shot performance compared to its predecessor. Building on SAM’s success in medical image segmentation, SAM 2 presents significant potential for further advancement. However, similar to SAM, SAM 2 is limited by its output of binary masks, inability to infer semantic labels, and dependence on precise prompts for the target object area. Additionally, direct application of SAM and SAM 2 to medical image segmentation tasks yields suboptimal results. In this paper, we explore the upper performance limit of SAM 2 using custom fine-tuning adapters, achieving a Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 92.30% on the BTCV dataset, surpassing the state-of-the-art nnUNet by 12%. Following this, we address the prompt dependency by investigating various prompt generators. We introduce a UNet to autonomously generate predicted masks and bounding boxes, which serve as input to SAM 2. Subsequent dual-stage refinements by SAM 2 further enhance performance. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results on the AMOS2022 dataset, with a Dice improvement of 2.9% compared to nnUNet, and outperforms nnUNet by 6.4% on the BTCV dataset.
Segment Anything Model 2(SAM 2)是一个提示驱动的基础模型,它将SAM扩展到图像和视频领域,并显示出比其前身更出色的零样本性能。建立在SAM成功进行医学图像分割的基础上,SAM 2呈现出巨大的发展潜力。然而,与SAM类似,SAM 2受限于其输出二进制蒙版、无法推断语义标签以及对目标对象区域精确提示的依赖。此外,直接将SAM和SAM 2应用于医学图像分割任务会产生不理想的结果。在本文中,我们通过使用自定义微调适配器探索了SAM 2的性能上限,在BTCV数据集上实现了92.30%的Dice相似系数(DSC),超过了现存的nnUNet模型,提高了12%。之后,我们通过研究各种提示生成器来解决提示依赖问题。我们引入了一个UNet来自主生成预测蒙版和边界框,作为SAM 2的输入。随后,SAM 2的两阶段精细化进一步提高了性能。大量实验表明,我们的方法在AMOS2022数据集上达到了最新水平,与nnUNet相比,Dice系数提高了2.9%,在BTCV数据集上超过了nnUNet 6.4%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAM 2模型在图像和视频领域表现出卓越的无训练性能,特别是在医学图像分割上具有巨大潜力。本文通过自定义微调适配器和自主生成的提示掩膜和边界框,提高了SAM 2的性能,实现了在BTCV数据集上的DSC达到92.3%,并超越了最新方法的性能。通过双阶段精细调整,该方法在AMOS2022数据集上取得了最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- SAM 2模型扩展了SAM模型在图像和视频领域的应用,展现出卓越的无训练性能。
- SAM 2在医学图像分割上具有巨大潜力,但受限于输出为二进制掩码、无法推断语义标签以及依赖精确的目标对象区域提示。
- 通过自定义的微调适配器,SAM 2的性能得到了提升,实现了在BTCV数据集上的DSC高达92.3%,超越了nnUNet的方法。
- 引入UNet自主生成预测掩码和边界框,作为SAM 2的输入,解决了对提示的依赖问题。
- 通过SAM 2的双阶段精细调整,进一步提高了性能。
- 在AMOS2022数据集上,该方法实现了最佳结果,相较于nnUNet,Dice系数提高了2.9%。
点此查看论文截图
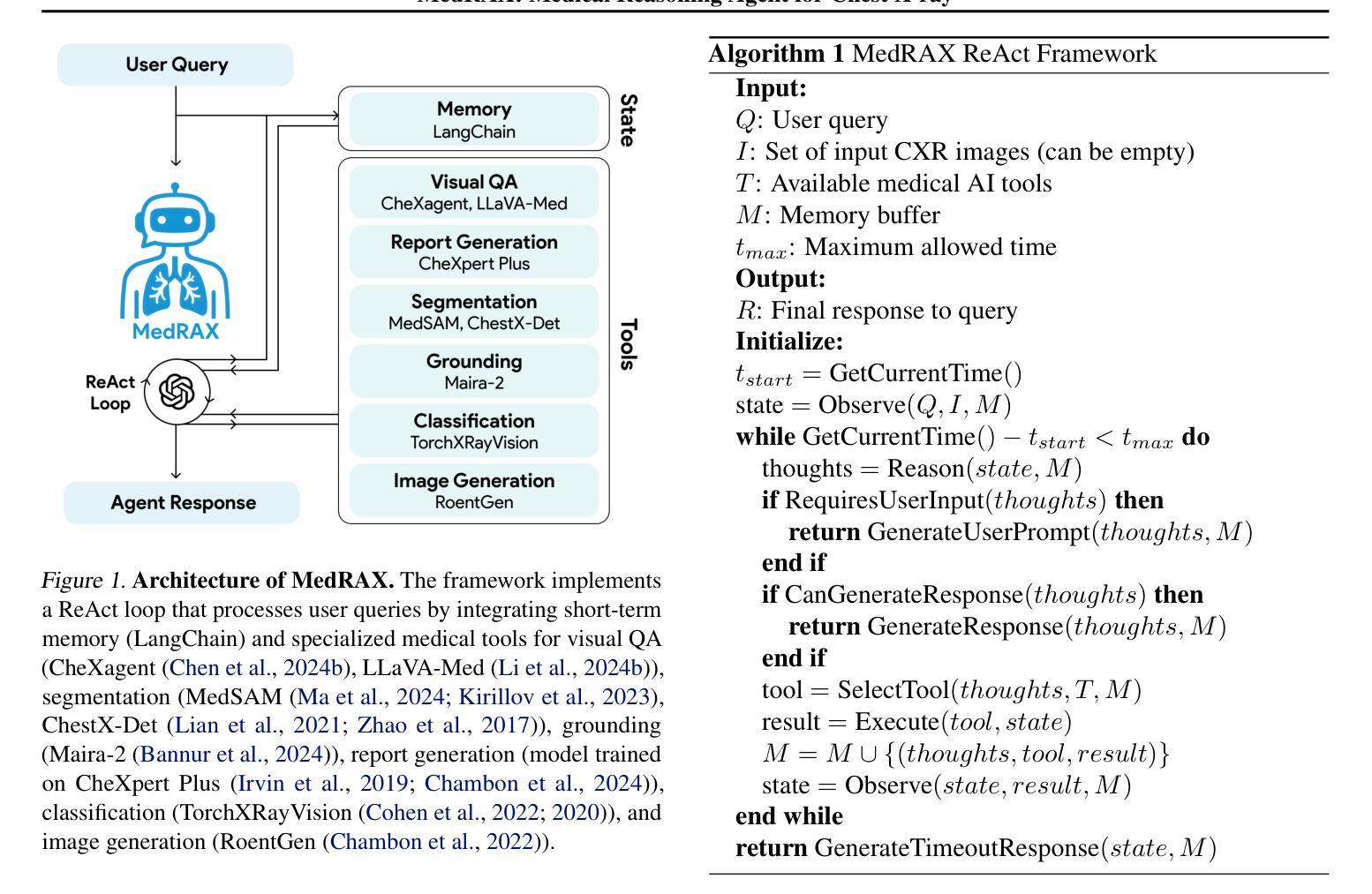
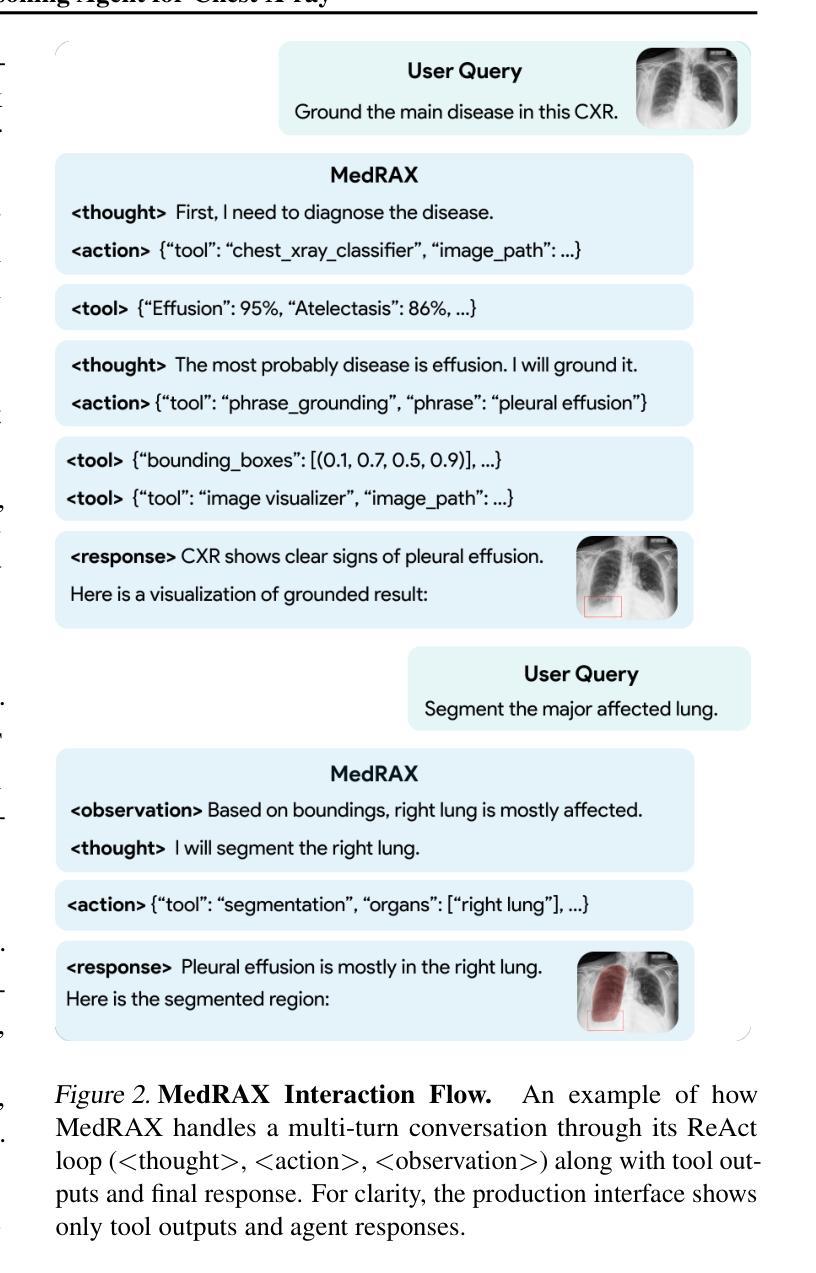
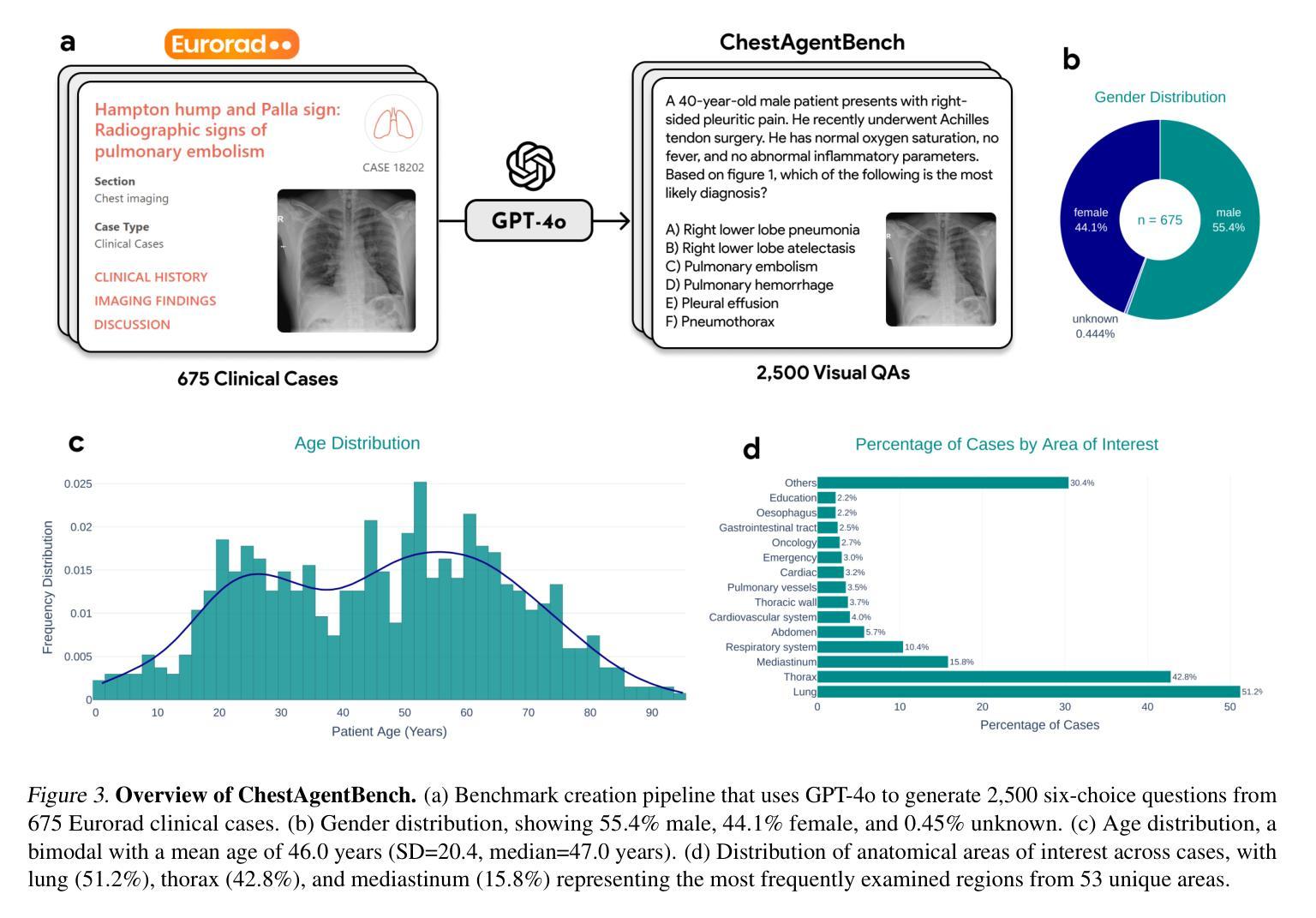
MedRAX: Medical Reasoning Agent for Chest X-ray
Authors:Adibvafa Fallahpour, Jun Ma, Alif Munim, Hongwei Lyu, Bo Wang
Chest X-rays (CXRs) play an integral role in driving critical decisions in disease management and patient care. While recent innovations have led to specialized models for various CXR interpretation tasks, these solutions often operate in isolation, limiting their practical utility in clinical practice. We present MedRAX, the first versatile AI agent that seamlessly integrates state-of-the-art CXR analysis tools and multimodal large language models into a unified framework. MedRAX dynamically leverages these models to address complex medical queries without requiring additional training. To rigorously evaluate its capabilities, we introduce ChestAgentBench, a comprehensive benchmark containing 2,500 complex medical queries across 7 diverse categories. Our experiments demonstrate that MedRAX achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to both open-source and proprietary models, representing a significant step toward the practical deployment of automated CXR interpretation systems. Data and code have been publicly available at https://github.com/bowang-lab/MedRAX
胸部X射线(CXRs)在疾病管理和患者护理的关键决策中扮演着不可或缺的角色。虽然最近的创新已经导致各种CXR解释任务的专用模型的出现,但这些解决方案通常独立运行,限制了它们在临床实践中的实用效用。我们推出了MedRAX,这是第一个通用的人工智能代理,它将最先进的CXR分析工具和多模态大型语言模型无缝集成到一个统一框架中。MedRAX动态利用这些模型来解决复杂的医疗查询,无需额外的训练。为了严格评估其能力,我们引入了ChestAgentBench,这是一个包含2500个复杂医疗查询的综合性基准测试,涵盖7个不同的类别。我们的实验表明,与开源和专有模型相比,MedRAX实现了最先进的性能,这代表了在实际部署自动化CXR解释系统方面取得了重要的一步。数据和代码已公开可用:https://github.com/bowang-lab/MedRAX。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文主要介绍了MedRAX系统及其在医学领域的应用价值。作为首个整合了先进计算机化X光影像分析工具和多模态大型语言模型的智能体,MedRAX能够动态利用这些模型解决复杂的医学问题,无需额外的训练。同时,文章还介绍了用于评估其性能的ChestAgentBench基准测试平台,展示了MedRAX相较于其他开源和专有模型在性能上的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- MedRAX是一个集成了先进CXR分析工具和多种语言模型的智能体,能够解决复杂的医学问题。
- MedRAX无需额外训练即可动态利用多种模型进行诊断。
- MedRAX通过ChestAgentBench基准测试平台进行了评估,表现出卓越的性能。
- MedRAX实现了相较于其他开源和专有模型在CXR解读领域的最佳性能。
- MedRAX系统的数据代码已公开,便于共享和进一步开发。
点此查看论文截图

Graph Structure Learning for Tumor Microenvironment with Cell Type Annotation from non-spatial scRNA-seq data
Authors:Yu-An Huang, Yue-Chao Li, Hai-Ru You, Jie Pan, Xiyue Cao, Xinyuan Li, Zhi-An Huang, Zhu-Hong You
The exploration of cellular heterogeneity within the tumor microenvironment (TME) via single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is essential for understanding cancer progression and response to therapy. Current scRNA-seq approaches, however, lack spatial context and rely on incomplete datasets of ligand-receptor interactions (LRIs), limiting accurate cell type annotation and cell-cell communication (CCC) inference. This study addresses these challenges using a novel graph neural network (GNN) model that enhances cell type prediction and cell interaction analysis. Our study utilized a dataset consisting of 49,020 cells from 19 patients across three cancer types: Leukemia, Breast Invasive Carcinoma, and Colorectal Cancer. The proposed scGSL model demonstrated robust performance, achieving an average accuracy of 84.83%, precision of 86.23%, recall of 81.51%, and an F1 score of 80.92% across all datasets. These metrics represent a significant enhancement over existing methods, which typically exhibit lower performance metrics. Additionally, by reviewing existing literature on gene interactions within the TME, the scGSL model proves to robustly identify biologically meaningful gene interactions in an unsupervised manner, validated by significant expression differences in key gene pairs across various cancers. The source code and data used in this paper can be found in https://github.com/LiYuechao1998/scGSL.
通过单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)探索肿瘤微环境(TME)中的细胞异质性对于理解癌症进展和治疗效果至关重要。然而,当前的scRNA-seq方法缺乏空间背景,依赖于不完全的配体-受体相互作用(LRI)数据集,限制了准确的细胞类型注释和细胞间通信(CCC)推断。本研究使用新型图神经网络(GNN)模型来解决这些挑战,该模型可提高细胞类型预测和细胞相互作用分析。我们的研究使用了包含来自三种癌症类型(白血病、侵袭性乳腺癌和结肠癌)的19名患者的49,020个细胞的数据库。所提出的scGSL模型表现出稳健的性能,在所有数据集上的平均准确度为84.83%,精确度为86.23%,召回率为81.51%,F1分数为80.92%。这些指标相较于现有方法有了显著的提升,通常现有方法的性能指标较低。此外,通过对肿瘤微环境中基因相互作用的现有文献进行回顾,scGSL模型能够稳健地识别出生物学上有意义的基因相互作用,这是以无监督的方式进行的,并通过各种癌症中关键基因对表达差异的显著性得到了验证。本文使用的源代码和数据可在https://github.com/LiYuechao1998/scGSL 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 6 figures
摘要
基于单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)技术,探索肿瘤微环境(TME)中的细胞异质性对于理解癌症进展和治疗反应至关重要。本研究使用新型图神经网络(GNN)模型应对现有scRNA-seq方法缺乏空间上下文和不完全的配体-受体相互作用数据集的问题,提升了细胞类型预测和细胞交互分析的能力。研究使用包含来自白血病、乳腺浸润性癌和结直肠癌的19名患者共49,020个细胞的数据库,所提scGSL模型展现出稳健性能,平均准确率达到了84.83%,精度为86.23%,召回率为81.51%,F1分数为80.92%,相较于现有方法性能有所提升。此外,通过对肿瘤微环境中基因交互的现有文献进行回顾,scGSL模型能够稳健地识别出生物学上重要的基因交互,且在多种癌症中关键基因对的表达差异显著。相关研究代码和数据可在https://github.com/LiYuechao1998/scGSL找到。
要点
- 使用单细胞RNA测序技术探索肿瘤微环境中的细胞异质性对理解癌症进展和治疗反应至关重要。
- 当前scRNA-seq方法存在空间上下文缺失和配体-受体互动数据集不完全的问题。
- 本研究使用新型图神经网络模型scGSL,提升了细胞类型预测和细胞交互分析的准确性。
- scGSL模型在多种癌症细胞数据集中展现出稳健性能,准确率等指标优于现有方法。
- scGSL模型能够识别生物学上重要的基因交互,且在多种癌症中关键基因对表达差异显著。
- 所提模型在识别细胞类型和提升细胞交互分析方面具有重要的医学研究和治疗应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

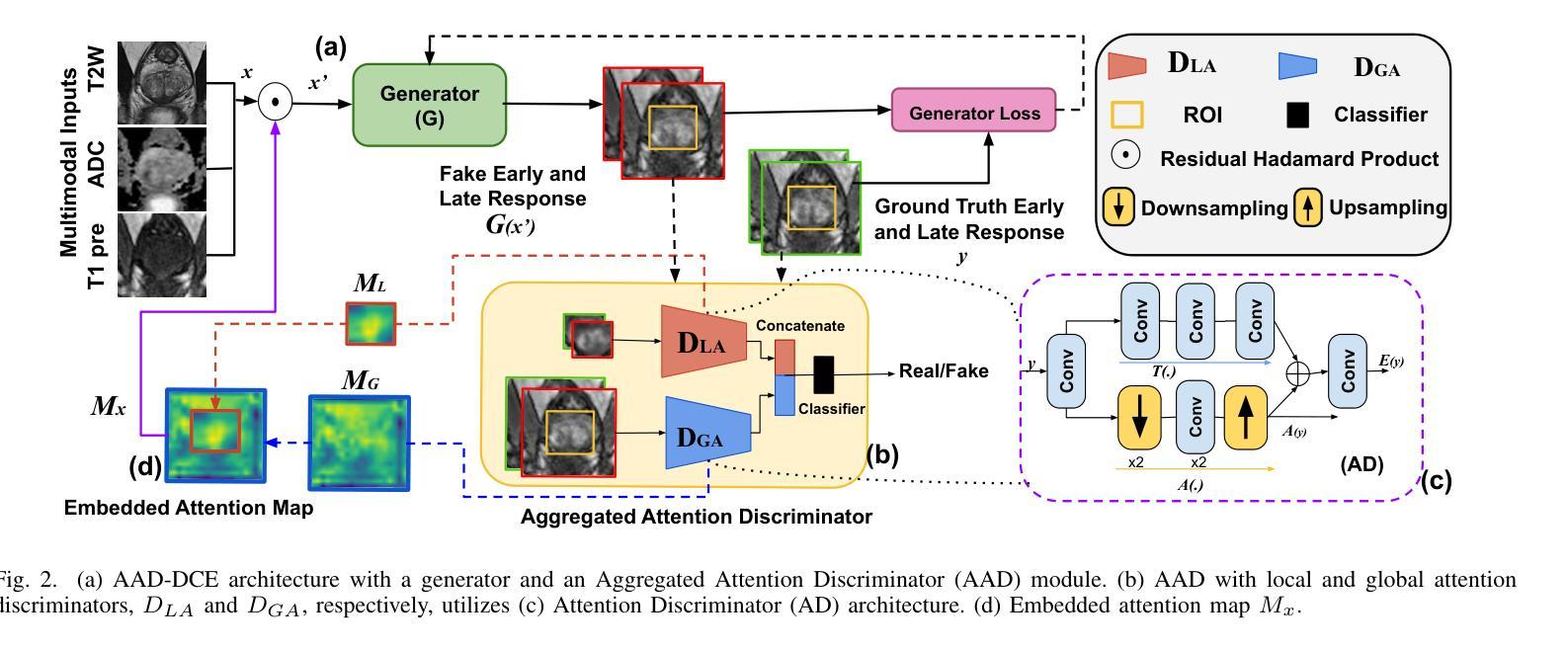
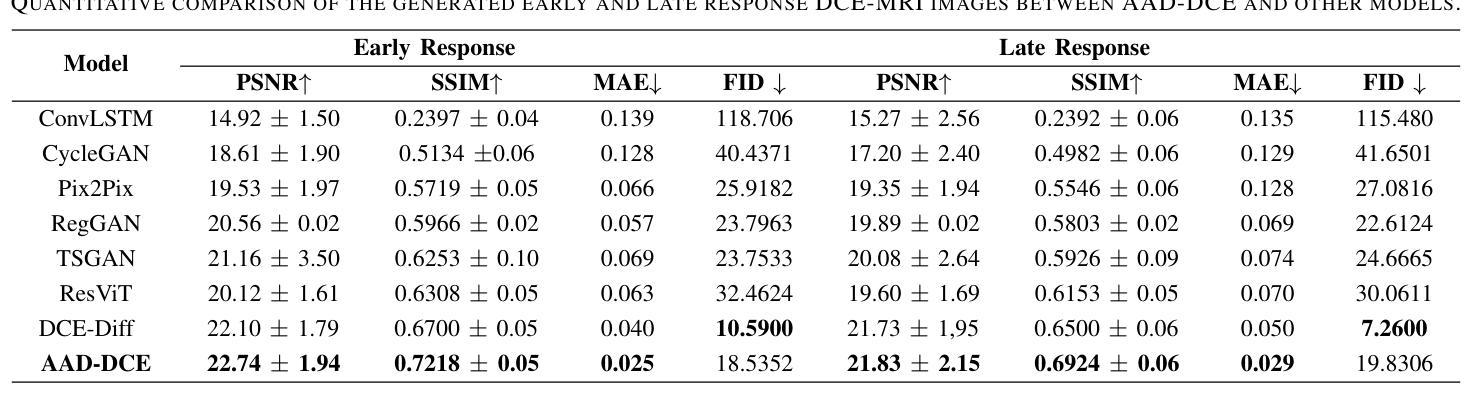
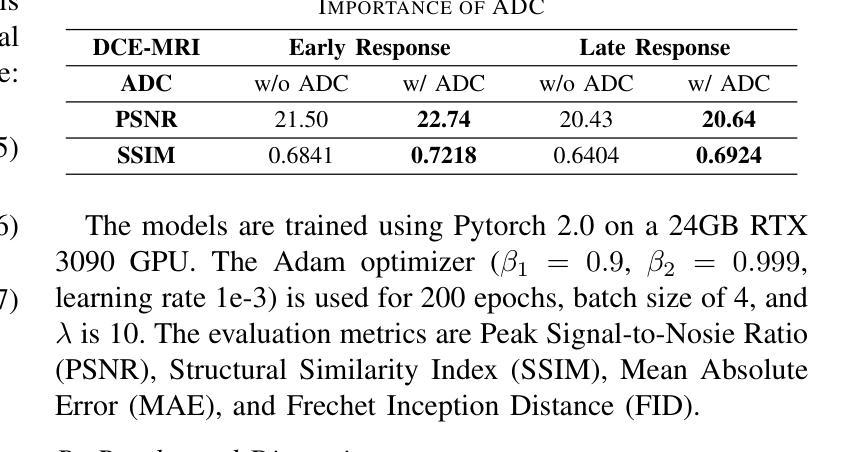
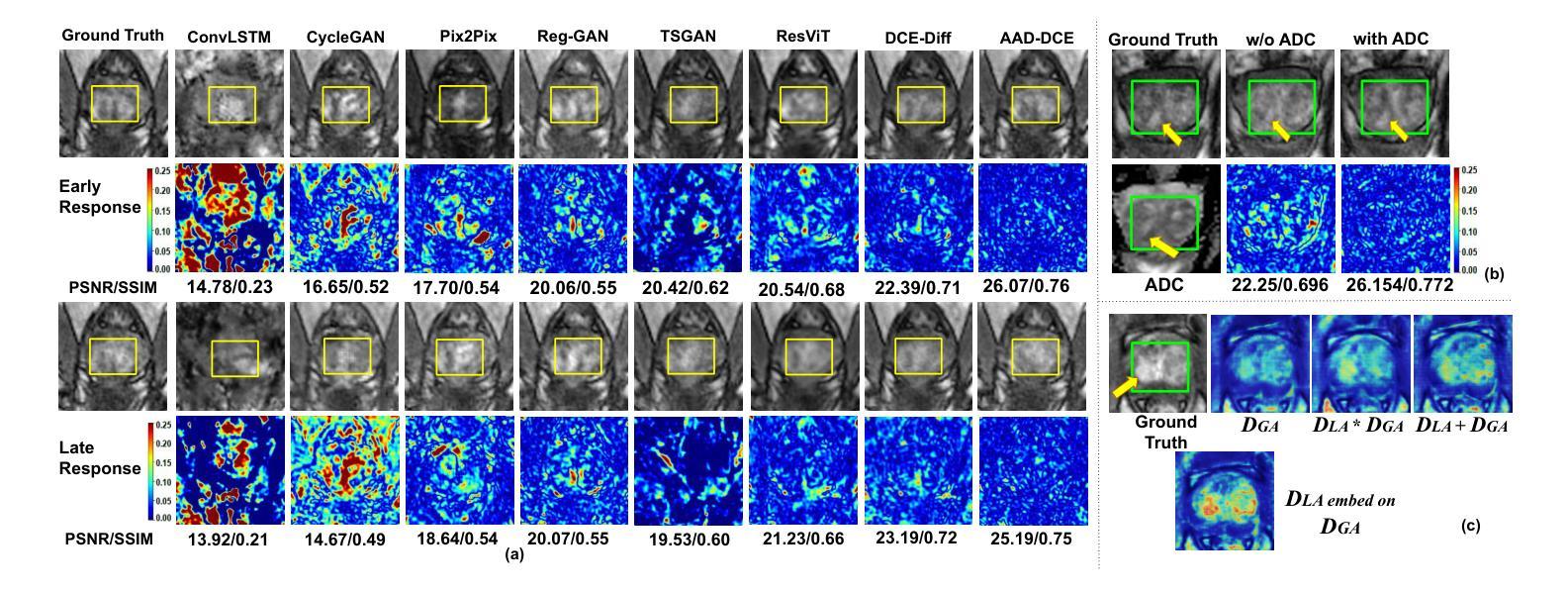
AAD-DCE: An Aggregated Multimodal Attention Mechanism for Early and Late Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Prostate MRI Synthesis
Authors:Divya Bharti, Sriprabha Ramanarayanan, Sadhana S, Kishore Kumar M, Keerthi Ram, Harsh Agarwal, Ramesh Venkatesan, Mohanasankar Sivaprakasam
Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) is a medical imaging technique that plays a crucial role in the detailed visualization and identification of tissue perfusion in abnormal lesions and radiological suggestions for biopsy. However, DCE-MRI involves the administration of a Gadolinium based (Gad) contrast agent, which is associated with a risk of toxicity in the body. Previous deep learning approaches that synthesize DCE-MR images employ unimodal non-contrast or low-dose contrast MRI images lacking focus on the local perfusion information within the anatomy of interest. We propose AAD-DCE, a generative adversarial network (GAN) with an aggregated attention discriminator module consisting of global and local discriminators. The discriminators provide a spatial embedded attention map to drive the generator to synthesize early and late response DCE-MRI images. Our method employs multimodal inputs - T2 weighted (T2W), Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC), and T1 pre-contrast for image synthesis. Extensive comparative and ablation studies on the ProstateX dataset show that our model (i) is agnostic to various generator benchmarks and (ii) outperforms other DCE-MRI synthesis approaches with improvement margins of +0.64 dB PSNR, +0.0518 SSIM, -0.015 MAE for early response and +0.1 dB PSNR, +0.0424 SSIM, -0.021 MAE for late response, and (ii) emphasize the importance of attention ensembling. Our code is available at https://github.com/bhartidivya/AAD-DCE.
动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)是一种医学成像技术,在异常病变的血流灌注详细可视化以及针对活检的放射学建议中发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,DCE-MRI涉及使用基于钆(Gad)的造影剂,这可能与体内毒性风险相关。以前合成DCE-MR图像的深度学习方法采用非对比或低剂量对比MRI图像作为单模态输入,缺乏关注解剖结构内的局部灌注信息。我们提出了AAD-DCE,这是一种生成对抗网络(GAN),包含一个聚合注意力判别器模块,它由全局和局部判别器组成。判别器提供空间嵌入注意力图,以驱动生成器合成早期和晚期响应DCE-MRI图像。我们的方法采用多模态输入,包括T2加权(T2W)、表观扩散系数(ADC)和T1预对比用于图像合成。在ProstateX数据集上的广泛比较和消融研究表明,我们的模型(i)对各种生成器指标表现中立;(ii)与其他DCE-MRI合成方法相比表现出优越性,早期响应的PSNR提高0.64dB、SSIM提高0.0518、MAE降低0.015,晚期响应的PSNR提高0.1dB、SSIM提高0.0424、MAE降低0.021;(iii)强调了注意力集成的重要性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/bhartidivya/AAD-DCE上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本研究采用生成对抗网络(GAN)技术,提出一种名为AAD-DCE的DCE-MRI图像合成方法。该方法利用聚集注意力鉴别器模块,结合全局和局部鉴别器,提供空间嵌入注意力图,驱动生成器合成早期和晚期响应的DCE-MRI图像。使用多模态输入(T2加权、表观扩散系数和T1预对比图像)进行图像合成,并在ProstateX数据集上进行广泛对比和消融研究,证明该方法性能优越。
Key Takeaways
- DCE-MRI在异常病变组织灌注的详细可视化和识别中起关键作用,但使用基于钆的对比剂存在毒性风险。
- 以往的深度学习方法在合成DCE-MRI图像时,主要依赖非对比或低剂量对比MRI图像,忽略了局部灌注信息。
- 本研究提出一种名为AAD-DCE的GAN方法,使用聚集注意力鉴别器模块,包含全局和局部鉴别器。
- 鉴别器提供空间嵌入注意力图,指导生成器合成早期和晚期响应的DCE-MRI图像。
- AAD-DCE方法采用多模态输入(T2加权、ADC和T1预对比图像)进行图像合成。
- 在ProstateX数据集上的研究表明,AAD-DCE方法在各种生成器指标上表现不敏感,并优于其他DCE-MRI合成方法。
点此查看论文截图


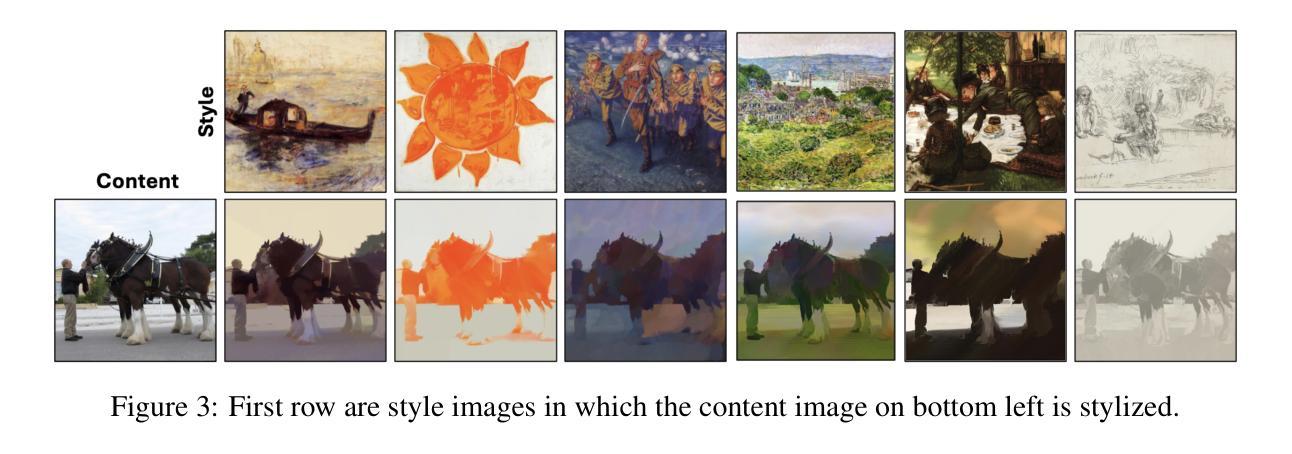
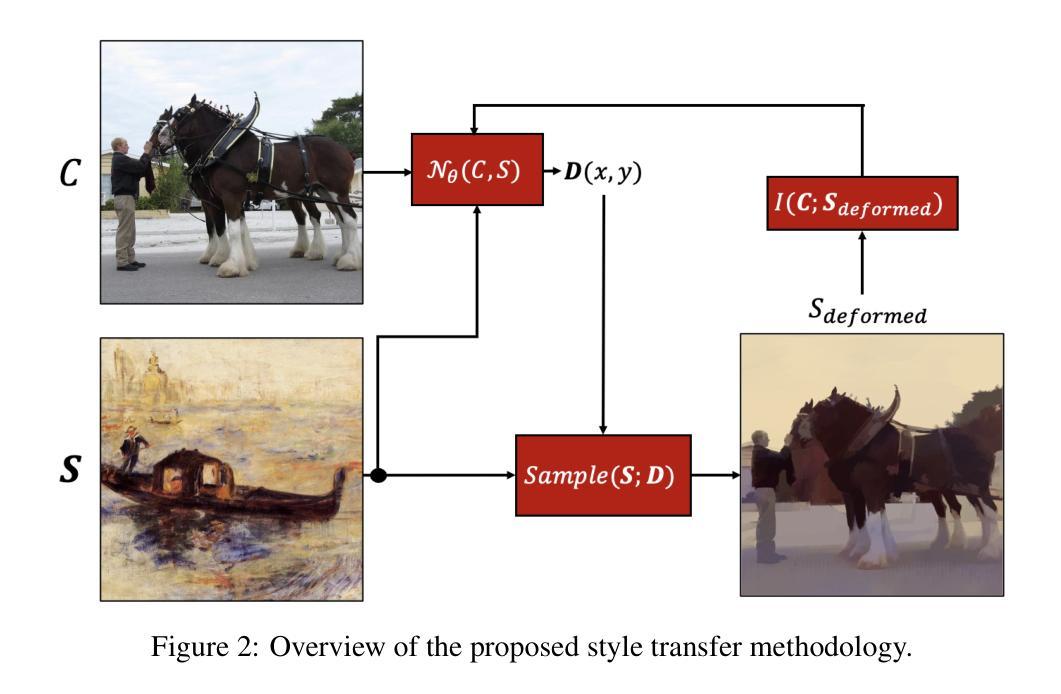
PixelShuffler: A Simple Image Translation Through Pixel Rearrangement
Authors:Omar Zamzam
Image-to-image translation is a topic in computer vision that has a vast range of use cases ranging from medical image translation, such as converting MRI scans to CT scans or to other MRI contrasts, to image colorization, super-resolution, domain adaptation, and generating photorealistic images from sketches or semantic maps. Image style transfer is also a widely researched application of image-to-image translation, where the goal is to synthesize an image that combines the content of one image with the style of another. Existing state-of-the-art methods often rely on complex neural networks, including diffusion models and language models, to achieve high-quality style transfer, but these methods can be computationally expensive and intricate to implement. In this paper, we propose a novel pixel shuffle method that addresses the image-to-image translation problem generally with a specific demonstrative application in style transfer. The proposed method approaches style transfer by shuffling the pixels of the style image such that the mutual information between the shuffled image and the content image is maximized. This approach inherently preserves the colors of the style image while ensuring that the structural details of the content image are retained in the stylized output. We demonstrate that this simple and straightforward method produces results that are comparable to state-of-the-art techniques, as measured by the Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) loss for content preservation and the Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) score for style similarity. Our experiments validate that the proposed pixel shuffle method achieves competitive performance with significantly reduced complexity, offering a promising alternative for efficient image style transfer, as well as a promise in usability of the method in general image-to-image translation tasks.
图像到图像的转换是计算机视觉中的一个主题,具有广泛的用例,从医学图像转换(例如将MRI扫描转换为CT扫描或其他MRI对比剂)到图像彩色化、超分辨率、域适应以及从草图或语义地图生成逼真的图像。图像风格迁移也是图像到图像转换的一个广泛研究的应用,其目标是将一个图像的内容与另一个图像的风格结合起来合成一个新的图像。现有的先进方法通常依赖于复杂的神经网络,包括扩散模型和语言模型,来实现高质量的风格迁移,但这些方法计算量大且实施复杂。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的像素重排方法,该方法一般可以解决图像到图像的转换问题,并在风格迁移中有特定的演示应用。所提出的方法通过重排风格图像的像素,使重排图像与内容图像之间的互信息最大化来实现风格迁移。这种方法本质上保留了风格图像的颜色,同时确保内容图像的结构细节保留在风格化的输出中。我们证明,这种简单直接的方法产生的结果与先进技术的结果相当,通过Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS)损失来衡量内容保留情况,以及Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)分数来衡量风格相似性。我们的实验验证了所提出的像素重排方法在显著降低复杂度的同时,实现了具有竞争力的性能,为高效的图像风格迁移提供了一个有前途的替代方案,同时也为该方法在一般的图像到图像转换任务中的可用性提供了承诺。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的像素级图像翻译方法,以图像风格转移为具体应用场景。该方法通过重新排列风格图像的像素,使重新排列后的图像与内容图像之间的互信息最大化,从而在保持风格图像颜色的同时保留内容图像的细节信息。该方法与现有的复杂神经网络相比,在复杂性和效果上具有竞争优势,尤其是在风格迁移方面尤为显著。有望成为图像风格转移的一种有效选择,且在更广泛的图像到图像翻译任务中亦有广泛应用前景。
Key Takeaways:
点此查看论文截图


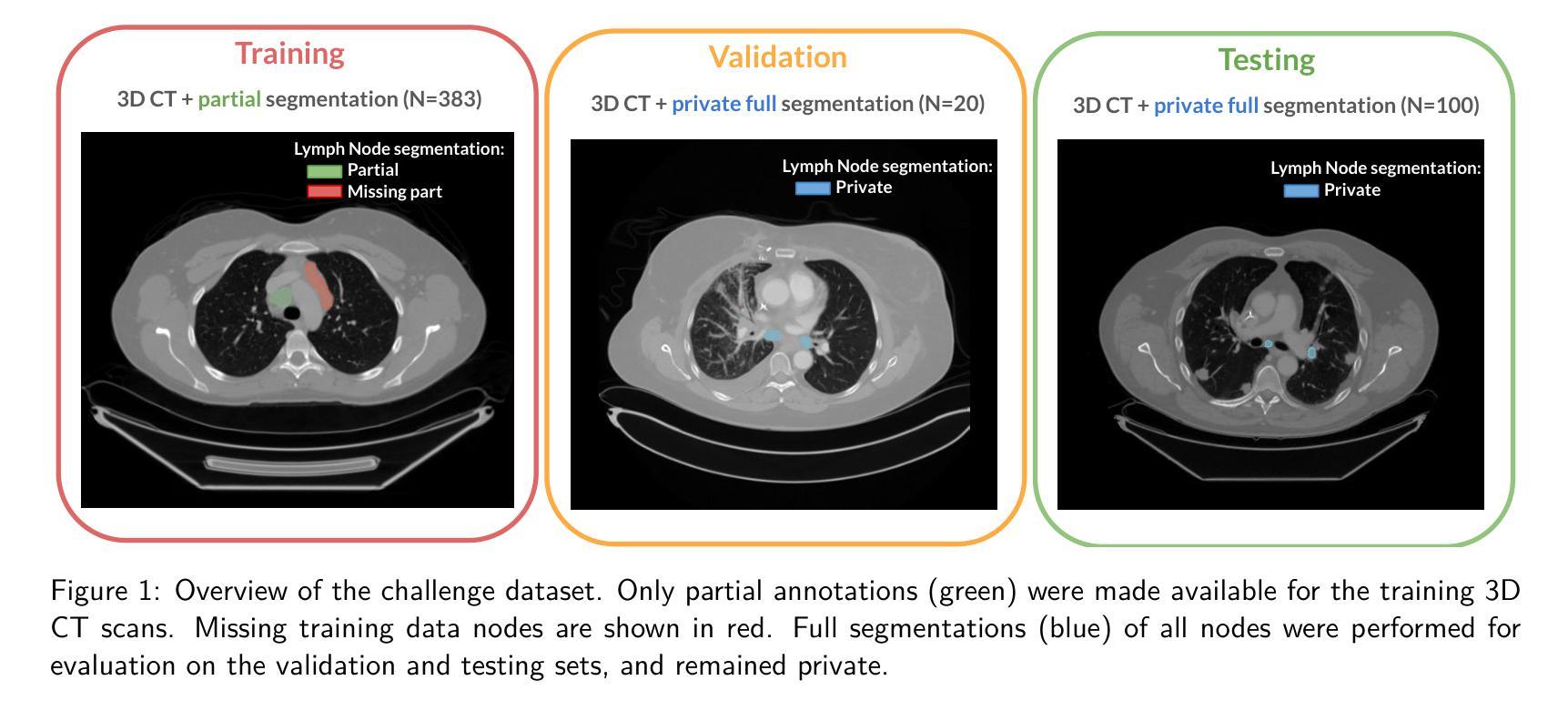
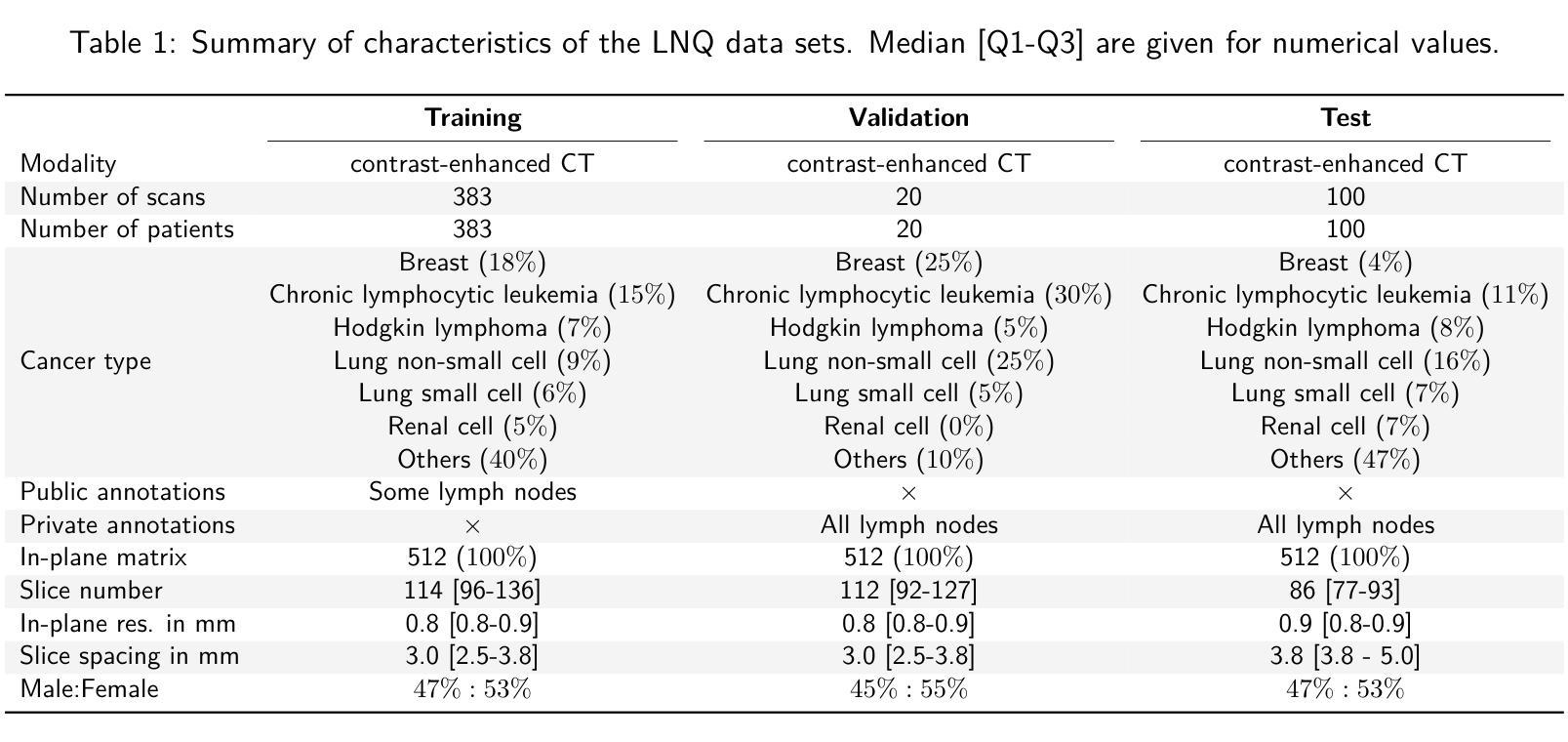
LNQ 2023 challenge: Benchmark of weakly-supervised techniques for mediastinal lymph node quantification
Authors:Reuben Dorent, Roya Khajavi, Tagwa Idris, Erik Ziegler, Bhanusupriya Somarouthu, Heather Jacene, Ann LaCasce, Jonathan Deissler, Jan Ehrhardt, Sofija Engelson, Stefan M. Fischer, Yun Gu, Heinz Handels, Satoshi Kasai, Satoshi Kondo, Klaus Maier-Hein, Julia A. Schnabel, Guotai Wang, Litingyu Wang, Tassilo Wald, Guang-Zhong Yang, Hanxiao Zhang, Minghui Zhang, Steve Pieper, Gordon Harris, Ron Kikinis, Tina Kapur
Accurate assessment of lymph node size in 3D CT scans is crucial for cancer staging, therapeutic management, and monitoring treatment response. Existing state-of-the-art segmentation frameworks in medical imaging often rely on fully annotated datasets. However, for lymph node segmentation, these datasets are typically small due to the extensive time and expertise required to annotate the numerous lymph nodes in 3D CT scans. Weakly-supervised learning, which leverages incomplete or noisy annotations, has recently gained interest in the medical imaging community as a potential solution. Despite the variety of weakly-supervised techniques proposed, most have been validated only on private datasets or small publicly available datasets. To address this limitation, the Mediastinal Lymph Node Quantification (LNQ) challenge was organized in conjunction with the 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2023). This challenge aimed to advance weakly-supervised segmentation methods by providing a new, partially annotated dataset and a robust evaluation framework. A total of 16 teams from 5 countries submitted predictions to the validation leaderboard, and 6 teams from 3 countries participated in the evaluation phase. The results highlighted both the potential and the current limitations of weakly-supervised approaches. On one hand, weakly-supervised approaches obtained relatively good performance with a median Dice score of $61.0%$. On the other hand, top-ranked teams, with a median Dice score exceeding $70%$, boosted their performance by leveraging smaller but fully annotated datasets to combine weak supervision and full supervision. This highlights both the promise of weakly-supervised methods and the ongoing need for high-quality, fully annotated data to achieve higher segmentation performance.
对3D CT扫描中的淋巴结大小进行准确评估对于癌症分期、治疗管理以及监测治疗反应至关重要。医学成像领域最先进的分割框架通常依赖于完全注释的数据集。然而,对于淋巴结分割,这些数据集通常很小,因为对3D CT扫描中的大量淋巴结进行注释需要花费大量时间和专业知识。最近,弱监督学习引起了医学成像社区的广泛关注,它利用不完整或嘈杂的注释作为潜在解决方案。尽管已经提出了多种弱监督技术,但大多数技术仅在私有数据集或小型公开数据集上得到了验证。为了解决这一局限性,纵隔淋巴结量化(LNQ)挑战赛与第26届医学图像计算和计算机辅助干预国际会议(MICCAI 2023)联合举办。该挑战赛旨在通过提供新的部分注释数据集和稳健的评估框架,推动弱监督分割方法的发展。总共有来自5个国家的16个团队提交了验证排行榜的预测,有来自3个国家的6个团队参加了评估阶段。结果既突出了弱监督方法的潜力,也指出了其当前局限性。一方面,弱监督方法取得了相对较好的性能,中位数Dice得分为61.0%。另一方面,排名靠前的团队的中位数Dice得分超过70%,他们通过结合弱监督和全监督、利用较小但完全注释的数据集来提升性能。这既突显了弱监督方法的潜力,也表明为了实现更高的分割性能,仍需要高质量、完全注释的数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to MELBA; Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2025:001
Summary
本文介绍了淋巴节点在三维CT扫描中的精确评估对癌症分期、治疗管理以及监测治疗效果的重要性。现有先进的医学成像分割框架通常依赖于完全标注的数据集,但淋巴节点分割数据集通常较小,因为对三维CT扫描中的多个淋巴节点进行标注需要耗费大量时间和专业知识。最近,医学成像社区对利用不完全或嘈杂标注的弱监督学习产生了兴趣,作为一种可能的解决方案。尽管提出了多种弱监督技术,但大多数技术仅在私有数据集或小型公开数据集上得到验证。为解决这一局限性,媒体旁淋巴结量化(LNQ)挑战与第26届医学图像计算和计算机辅助干预国际会议(MICCAI 2023)结合举办。该挑战旨在通过提供新的部分标注数据集和稳健的评估框架,推动弱监督分割方法的发展。结果显示弱监督方法的潜力和当前局限性。一方面,弱监督方法取得了相对较好的性能,中位Dice系数为61.0%。另一方面,排名靠前的团队通过结合弱监督和全监督的小规模完全标注数据集,取得了超过70%的中位Dice系数,这突显了弱监督方法的潜力以及实现更高分割性能对高质量完全标注数据的需求。
Key Takeaways
- 淋巴节点在三维CT扫描中的精确评估对癌症治疗至关重要。
- 现有医学成像分割框架通常依赖完全标注的数据集,但淋巴节点分割数据集因标注难度大而较小。
- 弱监督学习已成为解决这一问题的潜在方法。
- LNQ挑战提供了新的部分标注数据集和评估框架,推动弱监督分割方法的发展。
- 弱监督方法取得较好性能,中位Dice系数达到61.0%。
- 高性能团队结合弱监督和全监督方法,利用小规模完全标注数据集提升性能。
点此查看论文截图

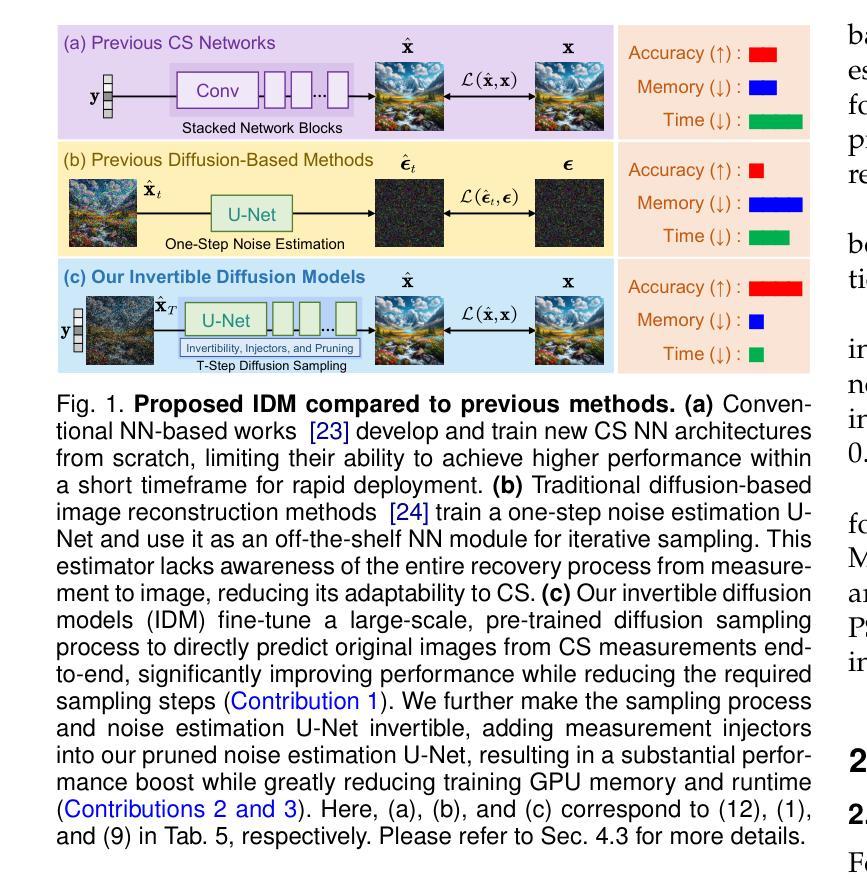
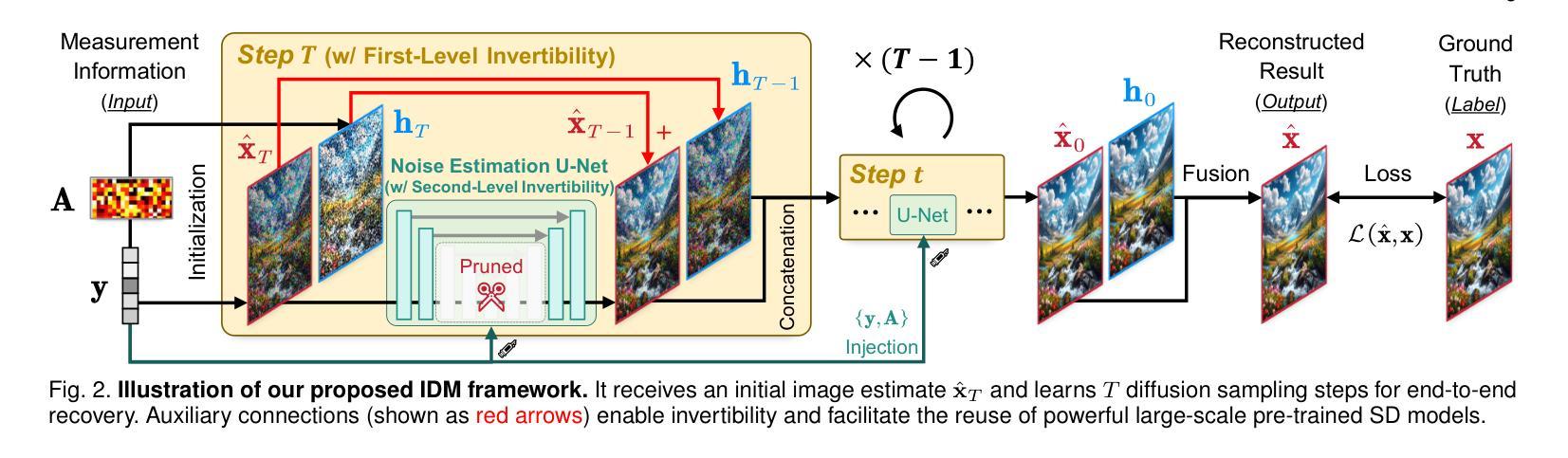
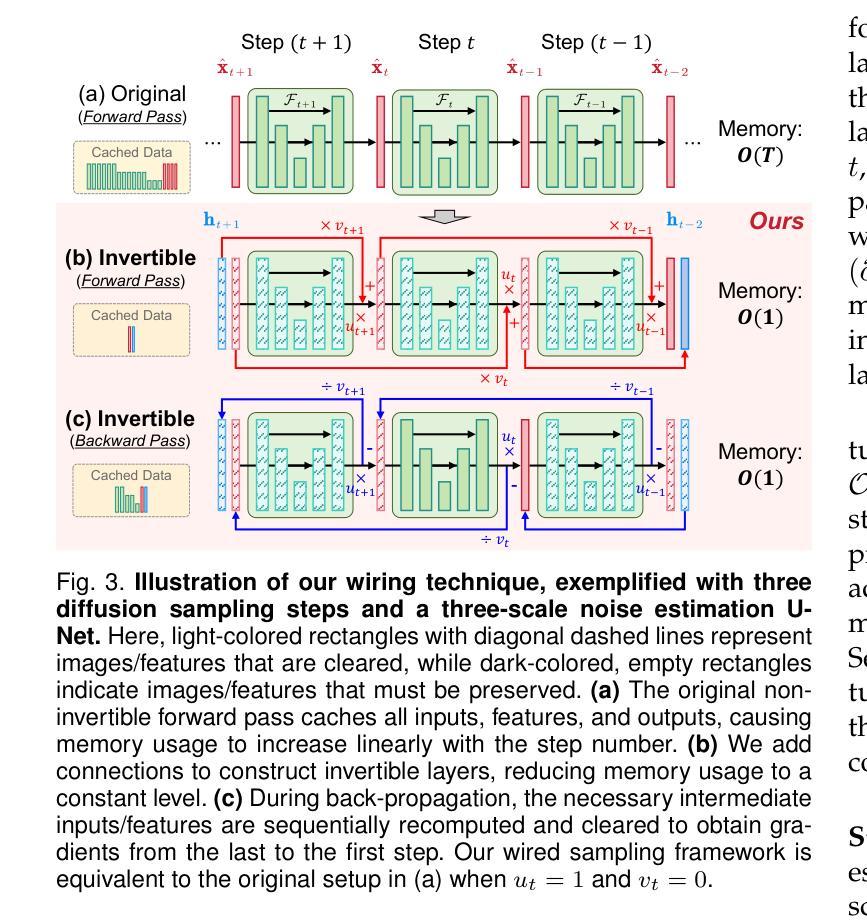
Invertible Diffusion Models for Compressed Sensing
Authors:Bin Chen, Zhenyu Zhang, Weiqi Li, Chen Zhao, Jiwen Yu, Shijie Zhao, Jie Chen, Jian Zhang
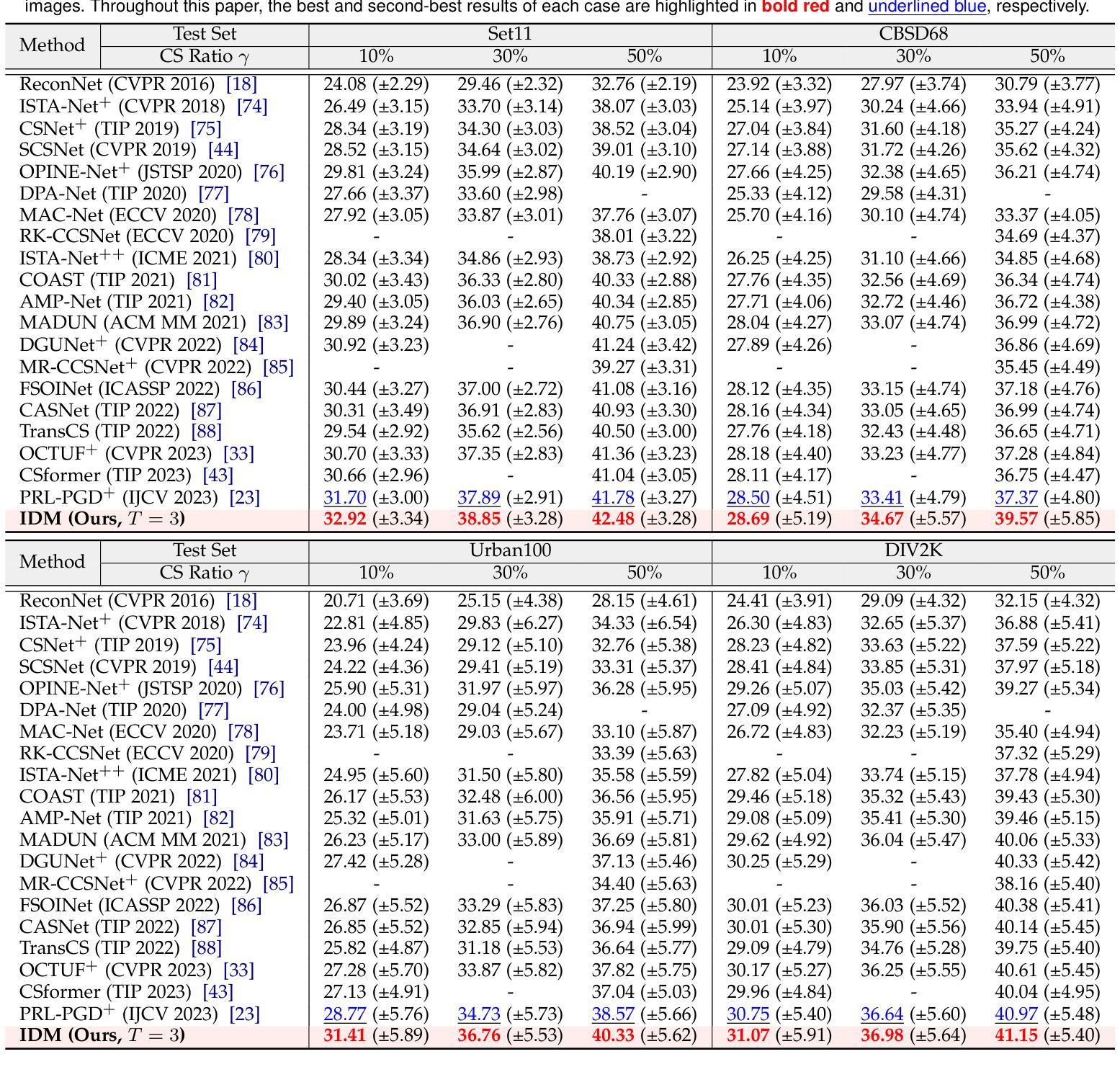
While deep neural networks (NN) significantly advance image compressed sensing (CS) by improving reconstruction quality, the necessity of training current CS NNs from scratch constrains their effectiveness and hampers rapid deployment. Although recent methods utilize pre-trained diffusion models for image reconstruction, they struggle with slow inference and restricted adaptability to CS. To tackle these challenges, this paper proposes Invertible Diffusion Models (IDM), a novel efficient, end-to-end diffusion-based CS method. IDM repurposes a large-scale diffusion sampling process as a reconstruction model, and fine-tunes it end-to-end to recover original images directly from CS measurements, moving beyond the traditional paradigm of one-step noise estimation learning. To enable such memory-intensive end-to-end fine-tuning, we propose a novel two-level invertible design to transform both (1) multi-step sampling process and (2) noise estimation U-Net in each step into invertible networks. As a result, most intermediate features are cleared during training to reduce up to 93.8% GPU memory. In addition, we develop a set of lightweight modules to inject measurements into noise estimator to further facilitate reconstruction. Experiments demonstrate that IDM outperforms existing state-of-the-art CS networks by up to 2.64dB in PSNR. Compared to the recent diffusion-based approach DDNM, our IDM achieves up to 10.09dB PSNR gain and 14.54 times faster inference. Code is available at https://github.com/Guaishou74851/IDM.
虽然深度神经网络(NN)通过提高重建质量来显著推进图像压缩感知(CS)的发展,但当前需要从零开始训练CS神经网络的需求制约了其有效性并阻碍了快速部署。尽管最近的方法利用预训练的扩散模型进行图像重建,但它们面临推理速度慢以及对CS适应性有限的问题。为了应对这些挑战,本文提出了可逆扩散模型(IDM),这是一种基于扩散的新型高效端到端CS方法。IDM将大规模的扩散采样过程重新用作重建模型,并对其进行端到端微调,直接从CS测量中恢复原始图像,超越了传统的一步噪声估计学习范式。为了实现这种内存密集型的端到端微调,我们提出了一种新型的两级可逆设计,将(1)多步采样过程和(2)每一步中的噪声估计U-Net转换为可逆网络。因此,在训练过程中清除了大多数中间特征,以减少高达93.8%的GPU内存。此外,我们开发了一系列轻量级模块,将测量值注入噪声估计器,以进一步促进重建。实验表明,IDM在PSNR上比现有的最先进的CS网络高出高达2.64dB。与最近的基于扩散的方法DDNM相比,我们的IDM在PSNR上实现了高达10.09dB的增益,推理速度提高了14.54倍。代码可在https://github.com/Guaishou74851/IDM上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)
Summary
该论文针对图像压缩感知(CS)提出了一种新型高效的端到端扩散模型——可逆扩散模型(IDM)。通过对大规模扩散采样过程进行重构模型的重构和利用端对端微调,直接对原始图像进行恢复,打破了传统噪声估计学习的一步处理范式。采用可逆设计实现了内存密集型的端到端微调,减少了GPU内存使用。实验表明,IDM在峰值信噪比(PSNR)上优于现有最先进的CS网络,相比最新的扩散模型DDNM有更高的性能提升速度。代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了新型图像压缩感知技术可逆扩散模型(IDM)。
- IDM使用预训练的扩散模型进行图像重建,解决了现有方法推理速度慢和适应性差的问题。
- 采用可逆设计实现了内存密集型的端到端微调,显著减少了GPU内存使用。
- 实验结果显示,IDM在峰值信噪比(PSNR)上优于其他CS网络,性能提升显著。
- 与现有的扩散模型DDNM相比,IDM实现了更高的性能提升和更快的推理速度。
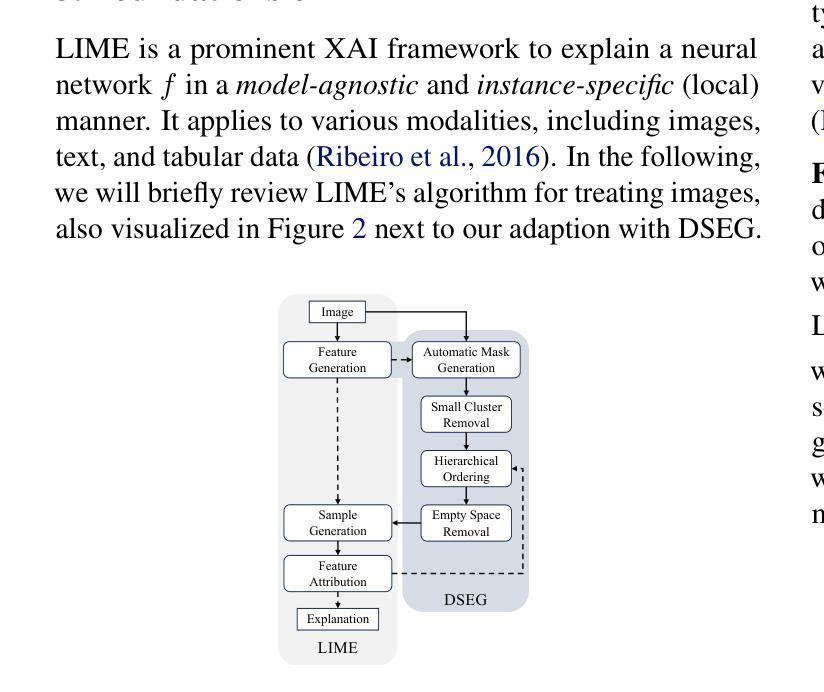
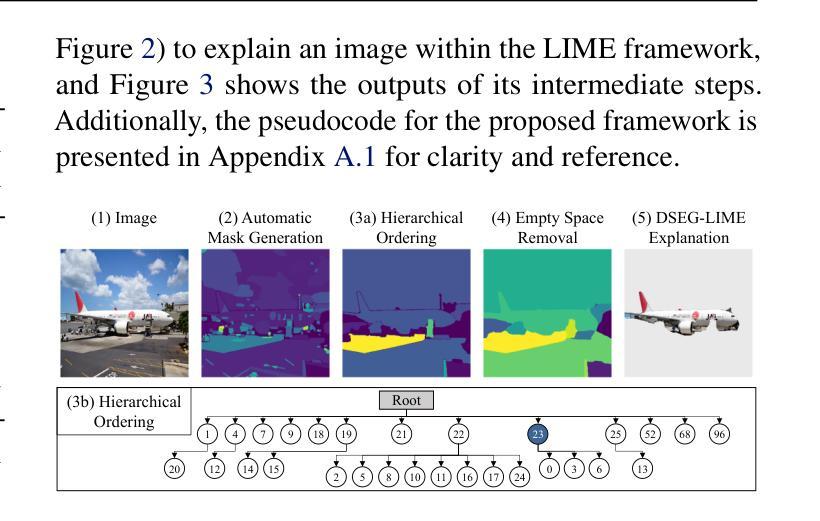
点此查看论文截图

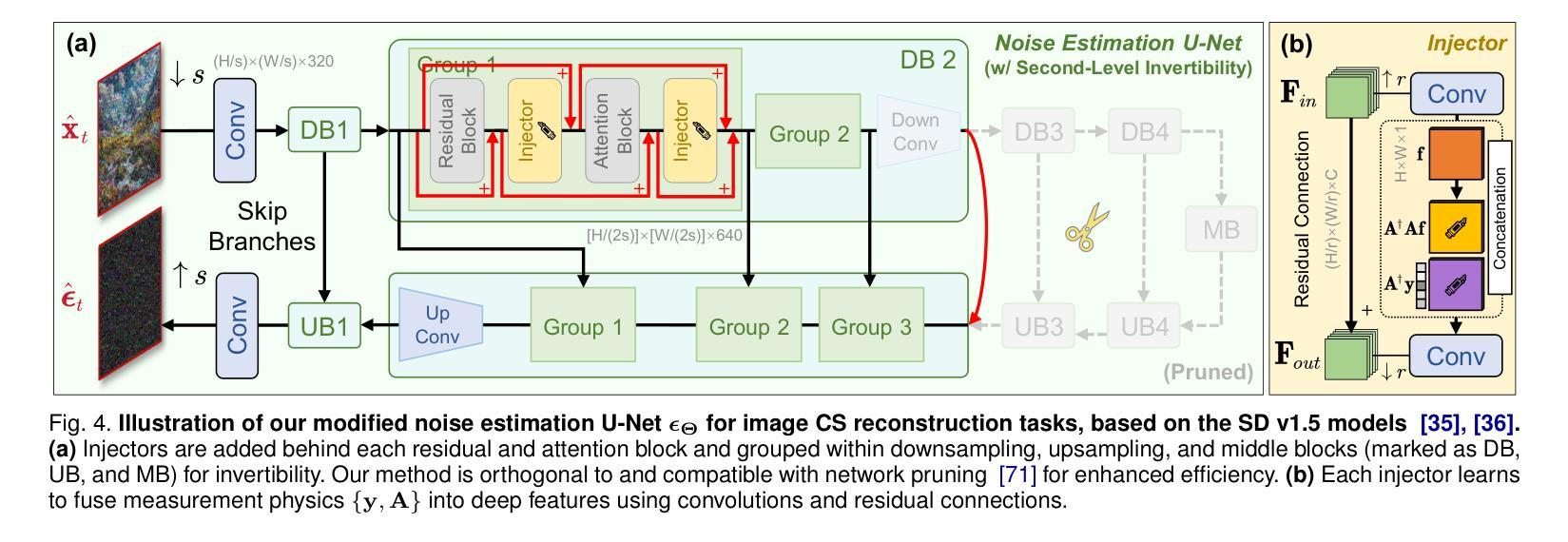
Beyond Pixels: Enhancing LIME with Hierarchical Features and Segmentation Foundation Models
Authors:Patrick Knab, Sascha Marton, Christian Bartelt
LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) is a popular XAI framework for unraveling decision-making processes in vision machine-learning models. The technique utilizes image segmentation methods to identify fixed regions for calculating feature importance scores as explanations. Therefore, poor segmentation can weaken the explanation and reduce the importance of segments, ultimately affecting the overall clarity of interpretation. To address these challenges, we introduce the DSEG-LIME (Data-Driven Segmentation LIME) framework, featuring: i) a data-driven segmentation for human-recognized feature generation by foundation model integration, and ii) a user-steered granularity in the hierarchical segmentation procedure through composition. Our findings demonstrate that DSEG outperforms on several XAI metrics on pre-trained ImageNet models and improves the alignment of explanations with human-recognized concepts. The code is available under: https://github. com/patrick-knab/DSEG-LIME
LIME(本地可解释模型无关解释)是一个流行的XAI框架,用于揭示视觉机器学习模型中的决策制定过程。该技术利用图像分割方法来识别固定区域,以计算特征重要性分数作为解释。因此,分割不佳可能会削弱解释,降低片段的重要性,最终影响整体解释的清晰度。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了DSEG-LIME(数据驱动分割LIME)框架,其特点包括:i)通过基础模型集成进行数据驱动分割,以产生人类识别的特征;ii)通过组合实现层次分割过程中的用户导向粒度。我们的研究结果表明,DSEG在预训练的ImageNet模型上的多个XAI指标上表现优于其他方法,并提高了与人类识别概念的解释对齐。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/patrick-knab/DSEG-LIME
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
LIME框架在揭示机器视觉模型决策过程中存在局限性,尤其在图像分割方面。为解决此问题,引入DSEG-LIME框架,通过集成基础模型实现数据驱动分割,并允许用户调整层次分割过程的粒度。研究表明,DSEG在多个可解释性指标上表现优异,提高了对预训练ImageNet模型的解释与人类认知概念的契合度。
关键见解
- LIME是流行的XAI框架,用于揭示机器学习模型的决策过程,尤其在图像领域。
- LIME利用图像分割方法识别固定区域来计算特征重要性分数作为解释。
- 较差的分割会削弱解释并降低段的重要性,影响整体解释清晰度。
- DSEG-LIME框架被引入以解决这些问题,通过数据驱动分割生成人类识别特征,并允许用户调整层次分割过程的粒度。
- DSEG在多个可解释性指标上表现优于传统LIME。
- DSEG提高了对预训练模型的解释与人类认知概念的契合度。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Full Automation of Geometry Extraction for Biomechanical Analysis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm; Neural Network-Based versus Classical Methodologies
Authors:Farah Alkhatib, Mostafa Jamshidian, Donatien Le Liepvre, Florian Bernard, Ludovic Minvielle, Antoine Fondanèche, Elke R. Gizewski, Eva Gassner, Alexander Loizides, Maximilian Lutz, Florian Enzmann, Hozan Mufty, Inge Fourneau, Adam Wittek, Karol Miller
Background: For the clinical adoption of stress-based rupture risk estimation in abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs), a fully automated pipeline, from clinical imaging to biomechanical stress computation, is essential. To this end, we investigated the impact of AI-based image segmentation methods on stress computation results in the walls of AAAs. We compared wall stress distributions and magnitudes calculated from geometry models obtained from classical semi-automated segmentation versus automated neural network-based segmentation. Method: 16 different AAA contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) images were semi-automatically segmented by an analyst, taking between 15 and 40 minutes of human effort per patient, depending on image quality. The same images were automatically segmented using PRAEVAorta2 commercial software by NUREA (https://www.nurea-soft.com/), developed based on artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, and automatically post-processed with an in-house MATLAB code, requiring only 1-2 minutes of computer time per patient. Aneurysm wall stress calculations were automatically performed using the BioPARR software (https://bioparr.mech.uwa.edu.au/). Results: Compared to the classical semi-automated segmentation, the automatic neural network-based segmentation leads to equivalent stress distributions, and slightly higher peak and 99th percentile maximum principal stress values. However, our statistical analysis indicated that the differences in AAA wall stress obtained using the two segmentation methods are not statistically significant and fall well within the typical range of inter-analyst and intra-analyst variability. Conclusions: Our findings are a steppingstone toward a fully automated pipeline for biomechanical analysis of AAAs, starting with CT scans and concluding with wall stress assessment.
背景:为了在腹部主动脉瘤(AAA)的临床治疗中采用基于应力的破裂风险评估,开发一个从临床成像到生物力学应力计算的全自动化流程至关重要。为此,我们研究了基于人工智能的图像分割方法对AAA壁应力计算结果的影响。我们比较了经典半自动分割和基于自动化神经网络分割所得到的几何模型计算的壁应力分布和大小。
方法:对16例不同AAA患者的增强计算机断层扫描(CT)图像进行半自动分析,分析员根据图像质量需要花费15至40分钟的时间处理每位患者。使用NUREA开发的PRAEVAorta2商业软件(https://www.nurea-soft.com/)对相同图像进行基于人工智能算法的自动分割,并使用内部MATLAB代码进行自动后处理,每位患者仅需花费1\~2分钟的计算机处理时间。动脉瘤壁应力计算自动通过BioPARR软件(https://bioparr.mech.uwa.edu.au/)进行。
结果:与经典半自动分割相比,基于自动神经网络的分割导致应力分布相当,峰值和99th百分位最大主应力值略高。然而,我们的统计分析表明,使用这两种分割方法获得的AAA壁应力之间的差异在统计学上并不显著,并且远远低于分析员间和分析员内部的变异性典型范围。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 43 pages, 11 figures
Summary
基于临床影像数据的腹部主动脉瘤(AAA)破裂风险评估在临床应用过程中需要全自动化处理流程。本文研究了基于人工智能的图像分割技术对AAA壁应力计算的影响,并与传统半自动分割方法进行了对比。结果显示,自动神经网络分割方法与传统半自动分割方法得到的应力分布相当,峰值和99th百分位最大主应力值略高,但二者在统计学上没有显著差异,并落在分析师间和分析师内部的变异范围内。这为进一步开发全自动的AAA生物力学分析流程奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 临床采用基于应力方法的腹部主动脉瘤(AAA)破裂风险评估需要全自动处理流程。
- 对比了基于人工智能的图像分割方法和传统半自动分割方法在AAA壁应力计算中的应用。
- 自动神经网络分割得到的应力分布与传统方法相当,峰值和特定百分位应力值略高。
- 两种分割方法在统计学上没有显著差异,并处于分析师间的变异范围内。
点此查看论文截图

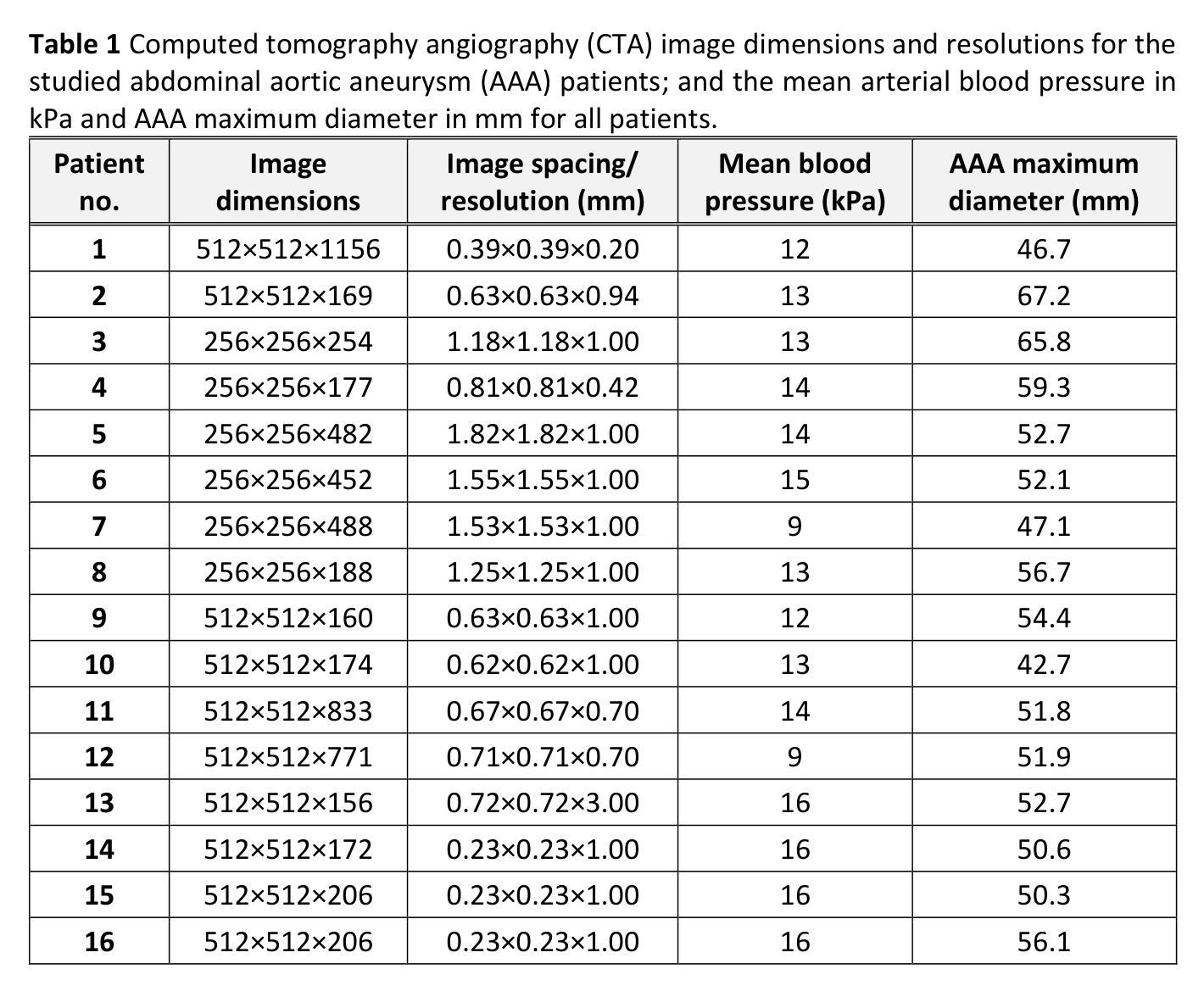
One Model to Rule them All: Towards Universal Segmentation for Medical Images with Text Prompts
Authors:Ziheng Zhao, Yao Zhang, Chaoyi Wu, Xiaoman Zhang, Ya Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, Weidi Xie
In this study, we aim to build up a model that can Segment Anything in radiology scans, driven by medical terminologies as Text prompts, termed as SAT. Our main contributions are three folds: (i) for dataset construction, we construct the first multi-modal knowledge tree on human anatomy, including 6502 anatomical terminologies; Then, we build up the largest and most comprehensive segmentation dataset for training, by collecting over 22K 3D medical image scans from72 segmentation datasets, across 497 classes, with careful standardization on both image scans and label space; (ii) for architecture design, we propose to inject medical knowledge into a text encoder via contrastive learning, and then formulate a universal segmentation model, that can be prompted by feeding in medical terminologies in text form; (iii) As a result, we have trained SAT-Nano (110M parameters) and SAT-Pro (447M parameters), demonstrating superior or comparable performance to 72 specialist models, i.e., nnU-Nets, U-Mamba or SwinUNETR, trained on each dataset/subsets. We validate SAT as a foundational segmentation model, with better generalization on external (cross-center) datasets, and can be further improved on specific tasks after fine-tuning adaptation. Comparing with state-of-the-art interactive segmentation model MedSAM, SAT demonstrate superior performance, scalability and robustness. We further compare SAT with BiomedParse, and observe SAT is significantly superior in both internal and external evaluation. Through extensive ablation study, we validate the benefit of domain knowledge on universal segmentation, especially on tail categories. As a use case, we demonstrate that SAT can act as a powerful out-of-the-box agent for large language models, enabling visual grounding in versatile application scenarios. All the data, codes, and models in this work have been released.
在这项研究中,我们的目标是建立一个模型,该模型能够在放射学扫描中分割任何东西,以医学术语作为文本提示进行驱动,称为SAT。我们的主要贡献分为三个部分:(i)对于数据集构建,我们构建了第一棵关于人体解剖学的多模态知识树,包含6502个解剖学术语;然后,我们通过收集来自72个分割数据集的超过2.2万份3D医学图像扫描数据,构建了用于训练的最大且最全面的分割数据集,涵盖497类,并对图像扫描和标签空间进行了严谨的标准化;(ii)在架构设计方面,我们提出通过对比学习将医学知识注入文本编码器,然后制定一个通用分割模型,该模型可以通过输入医学术语的文本形式进行提示;(iii)因此,我们训练了SAT-Nano(1.1亿参数)和SAT-Pro(4.47亿参数),其性能优于或与在每个数据集/子集上训练的72个专家模型(即nnU-Net、U-Mamba或SwinUNETR)相比具有竞争力。我们验证了SAT作为一个基础分割模型,在外部数据集上具有更好的泛化能力,并且在特定任务上进行微调适应后可以进一步改进。与最先进的交互式分割模型MedSAM相比,SAT在性能、可扩展性和稳健性方面表现出优势。我们将SAT与BiomedParse进行了比较,发现SAT在内部和外部评估中都显著优越。通过广泛的消融研究,我们验证了领域知识对通用分割(特别是在尾部类别中)的益处。作为一个用例,我们展示了SAT可以作为大型语言模型的有力工具,在多种应用场景中实现视觉定位。本工作中的所有数据、代码和模型均已发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 69 pages
Summary
本研究旨在建立一个模型,该模型能够在放射扫描中实现任意分割,以医学术语作为文本提示进行驱动,被称为SAT。主要贡献包括:一、在数据集构建方面,构建了首个人体解剖学的多模态知识树,包含6502个解剖学术语;并通过收集超过22K个三维医学图像扫描和标准化图像扫描和标签空间,建立了最大的综合分割数据集;二、在架构设计方面,提出通过对比学习将医学知识注入文本编码器,并制定通用分割模型,可通过输入医学术语进行提示;三、训练了SAT-Nano(1.1亿参数)和SAT-Pro(4.47亿参数),相较于在每个数据集/子集上训练的nnU-Net、U-Mamba或SwinUNETR等72种专业模型表现出优越或相当的性能。验证了SAT作为基础分割模型的优越性,在外部数据集上具有更好的泛化能力,并在特定任务上经过微调后能够进一步提高性能。相较于先进的交互式分割模型MedSAM,SAT展现出性能、可扩展性和稳健性的优势。通过与BiomedParse的比较,证明了SAT在内部和外部评估中的显著优势。通过广泛的消融研究,验证了领域知识对通用分割的益处,尤其是针对尾部类别。作为一个应用场景,展示了SAT可以作为大型语言模型的强大外盒代理,在多种应用场景中实现视觉定位。
Key Takeaways
- 建立了一个名为SAT的模型,可在放射扫描中实现任意分割,以医学术语作为文本提示进行驱动。
- 构建了首个人体解剖学的多模态知识树和最大的综合医学图像分割数据集。
- 通过对比学习将医学知识注入文本编码器,提出通用分割模型。
- 训练了SAT-Nano和SAT-Pro两种模型,表现出优越或相当的性能。
- SAT具有良好的泛化能力,并在特定任务上经过微调后可进一步提高性能。
- SAT相较于其他先进模型展现出性能、可扩展性和稳健性的优势。
点此查看论文截图

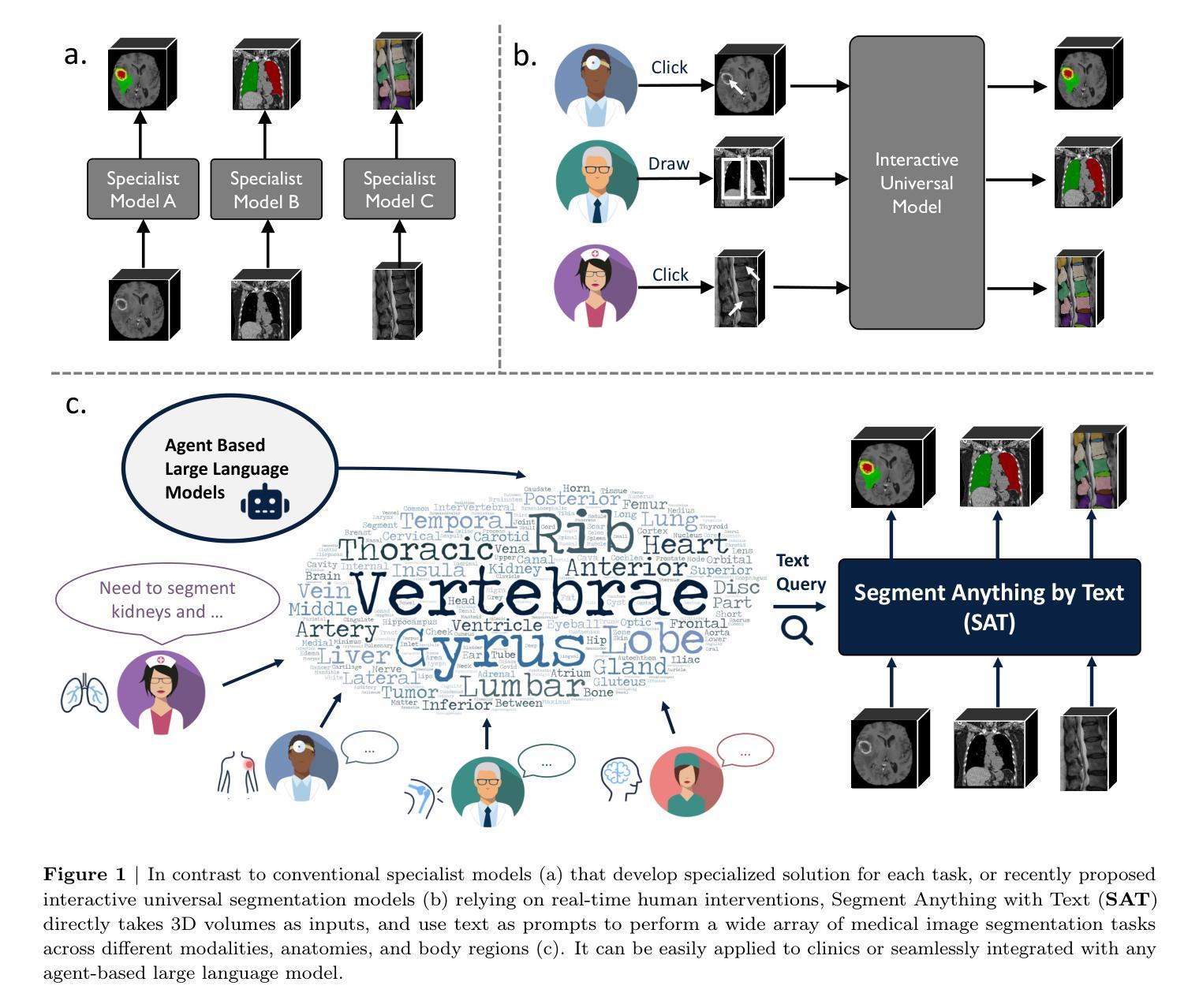
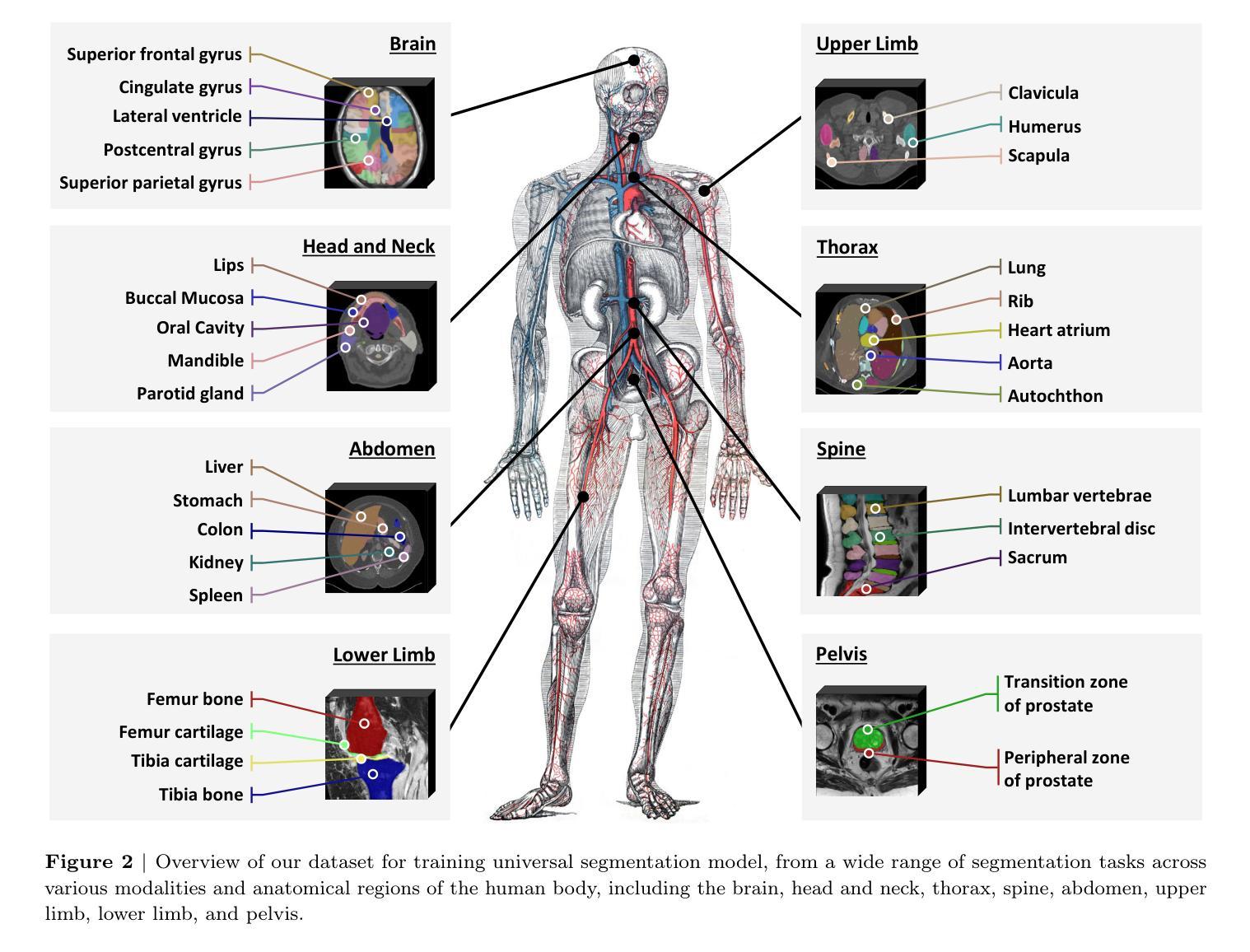
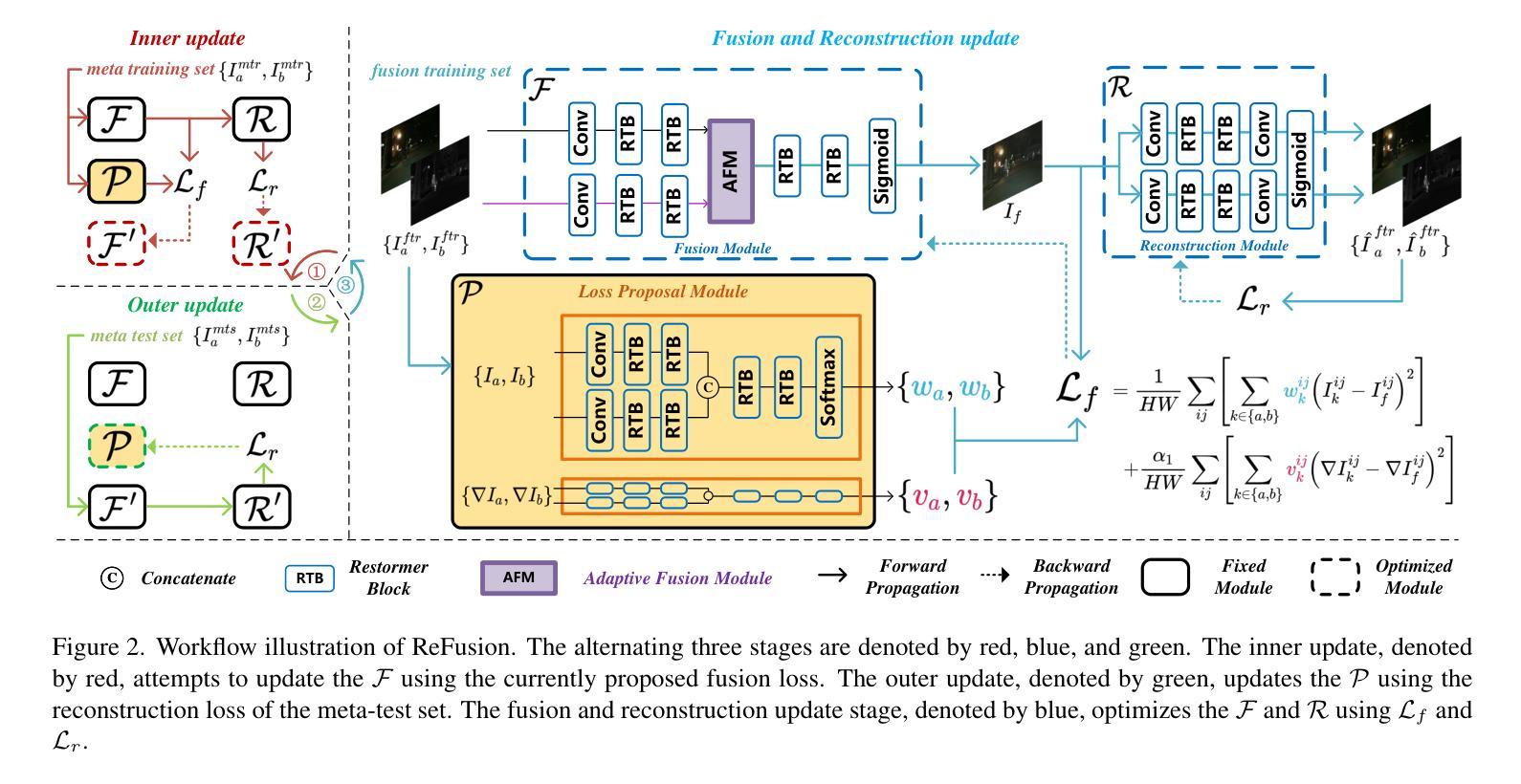
ReFusion: Learning Image Fusion from Reconstruction with Learnable Loss via Meta-Learning
Authors:Haowen Bai, Zixiang Zhao, Jiangshe Zhang, Yichen Wu, Lilun Deng, Yukun Cui, Shuang Xu, Baisong Jiang
Image fusion aims to combine information from multiple source images into a single one with more comprehensive informational content. Deep learning-based image fusion algorithms face significant challenges, including the lack of a definitive ground truth and the corresponding distance measurement. Additionally, current manually defined loss functions limit the model’s flexibility and generalizability for various fusion tasks. To address these limitations, we propose ReFusion, a unified meta-learning based image fusion framework that dynamically optimizes the fusion loss for various tasks through source image reconstruction. Compared to existing methods, ReFusion employs a parameterized loss function, that allows the training framework to be dynamically adapted according to the specific fusion scenario and task. ReFusion consists of three key components: a fusion module, a source reconstruction module, and a loss proposal module. We employ a meta-learning strategy to train the loss proposal module using the reconstruction loss. This strategy forces the fused image to be more conducive to reconstruct source images, allowing the loss proposal module to generate a adaptive fusion loss that preserves the optimal information from the source images. The update of the fusion module relies on the learnable fusion loss proposed by the loss proposal module. The three modules update alternately, enhancing each other to optimize the fusion loss for different tasks and consistently achieve satisfactory results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ReFusion is capable of adapting to various tasks, including infrared-visible, medical, multi-focus, and multi-exposure image fusion.
图像融合旨在将来自多个源图像的信息合并到一个单一图像中,以获取更全面的信息内容。基于深度学习的图像融合算法面临重大挑战,包括缺乏明确的真实标签和相应的距离度量。此外,当前手动定义的损失函数限制了模型对各种融合任务的灵活性和通用性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了ReFusion,一个统一的基于元学习的图像融合框架,它通过源图像重建动态优化融合损失。与现有方法相比,ReFusion采用参数化损失函数,允许训练框架根据特定的融合场景和任务进行动态适应。ReFusion由三个关键组件组成:融合模块、源重建模块和损失提案模块。我们采用元学习策略来训练损失提案模块,使用重建损失。这一策略强制融合图像更有助于重建源图像,使损失提案模块能够生成自适应融合损失,保留源图像中的最佳信息。融合模块的更新依赖于由损失提案模块提出的可学习融合损失。这三个模块交替更新,相互增强,针对各种任务优化融合损失,并始终取得令人满意的结果。大量实验表明,ReFusion能够适应各种任务,包括红外可见光、医疗、多焦点和多曝光图像融合。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This article is published in International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 2024
Summary
基于深度学习和元学习的图像融合框架ReFusion,通过源图像重建动态优化融合损失,适用于多种融合任务,提高模型的灵活性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像融合旨在将多个源图像的信息合并到一个更全面的单一图像中。
- 深度学习在图像融合中面临缺乏明确的地面真实和相应的距离测量的挑战。
- ReFusion是一个基于元学习的图像融合框架,通过源图像重建动态优化融合损失。
- ReFusion采用参数化的损失函数,根据特定的融合情景和任务动态调整训练框架。
- ReFusion包含三个关键组件:融合模块、源重建模块和损失提案模块。
- 采用元学习策略训练损失提案模块,使用重建损失迫使融合图像更有助于重建源图像。
点此查看论文截图


SelfFed: Self-Supervised Federated Learning for Data Heterogeneity and Label Scarcity in Medical Images
Authors:Sunder Ali Khowaja, Kapal Dev, Syed Muhammad Anwar, Marius George Linguraru
Self-supervised learning in the federated learning paradigm has been gaining a lot of interest both in industry and research due to the collaborative learning capability on unlabeled yet isolated data. However, self-supervised based federated learning strategies suffer from performance degradation due to label scarcity and diverse data distributions, i.e., data heterogeneity. In this paper, we propose the SelfFed framework for medical images to overcome data heterogeneity and label scarcity issues. The first phase of the SelfFed framework helps to overcome the data heterogeneity issue by leveraging the pre-training paradigm that performs augmentative modeling using Swin Transformer-based encoder in a decentralized manner. The label scarcity issue is addressed by fine-tuning paradigm that introduces a contrastive network and a novel aggregation strategy. We perform our experimental analysis on publicly available medical imaging datasets to show that SelfFed performs better when compared to existing baselines and works. Our method achieves a maximum improvement of 8.8% and 4.1% on Retina and COVID-FL datasets on non-IID datasets. Further, our proposed method outperforms existing baselines even when trained on a few (10%) labeled instances.
在联邦学习范式中,自监督学习因其在无标签但孤立数据上的协作学习能力而受到业界和研究人员的广泛关注。然而,基于自监督的联邦学习策略由于标签稀缺和多样化的数据分布(即数据异质性)而面临性能下降的问题。在本文中,我们提出了针对医学图像的SelfFed框架,以解决数据异质性和标签稀缺问题。SelfFed框架的第一阶段通过利用预训练范式,以分布式方式使用基于Swin Transformer的编码器进行增强建模,有助于克服数据异质性问题。通过微调范式引入对比网络和一种新的聚合策略来解决标签稀缺问题。我们在公开可用的医学成像数据集上进行实验分析,以证明SelfFed与现有基准相比表现更好。我们的方法在Retina和COVID-FL数据集上的非IID数据集上分别实现了最高达8.8%和4.1%的改进。此外,即使在少数(10%)标记实例上进行训练,我们提出的方法也优于现有基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 10 figures, 2 tables
Summary
医学图像领域中的联邦学习面临数据异质性和标签稀缺的问题。本文提出的SelfFed框架通过预训练阶段利用基于Swin Transformer的编码器进行增强建模,解决数据异质性,并通过微调阶段引入对比网络和新型聚合策略应对标签稀缺问题。实验表明,SelfFed相较于现有基线在非IID数据集上最大提升达8.8%和4.1%,在仅使用少量(10%)标记实例的情况下依然优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习中的自监督学习面临数据异质性和标签稀缺的挑战。
- SelfFed框架利用预训练阶段解决数据异质性,通过基于Swin Transformer的编码器进行增强建模。
- SelfFed通过微调阶段引入对比网络和新型聚合策略来应对标签稀缺问题。
- 在公开医学成像数据集上的实验表明,SelfFed相较于现有方法表现更优。
- SelfFed在非IID数据集上的性能提升显著,最大提升达8.8%和4.1%。
- SelfFed在仅使用少量标记实例的情况下仍能保持优于基线方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图