⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-07 更新
Secure & Personalized Music-to-Video Generation via CHARCHA
Authors:Mehul Agarwal, Gauri Agarwal, Santiago Benoit, Andrew Lippman, Jean Oh
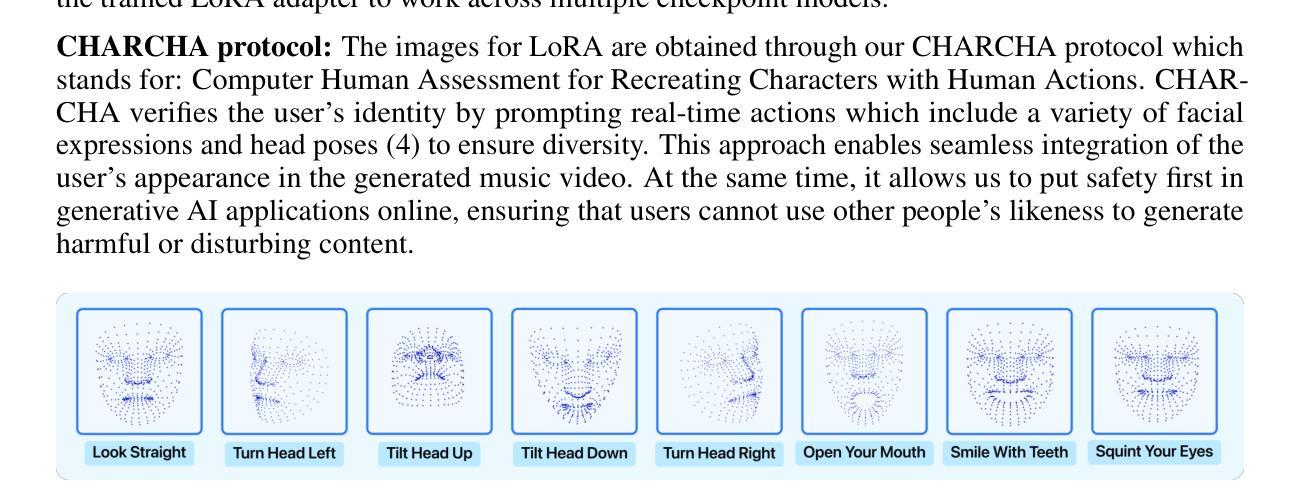
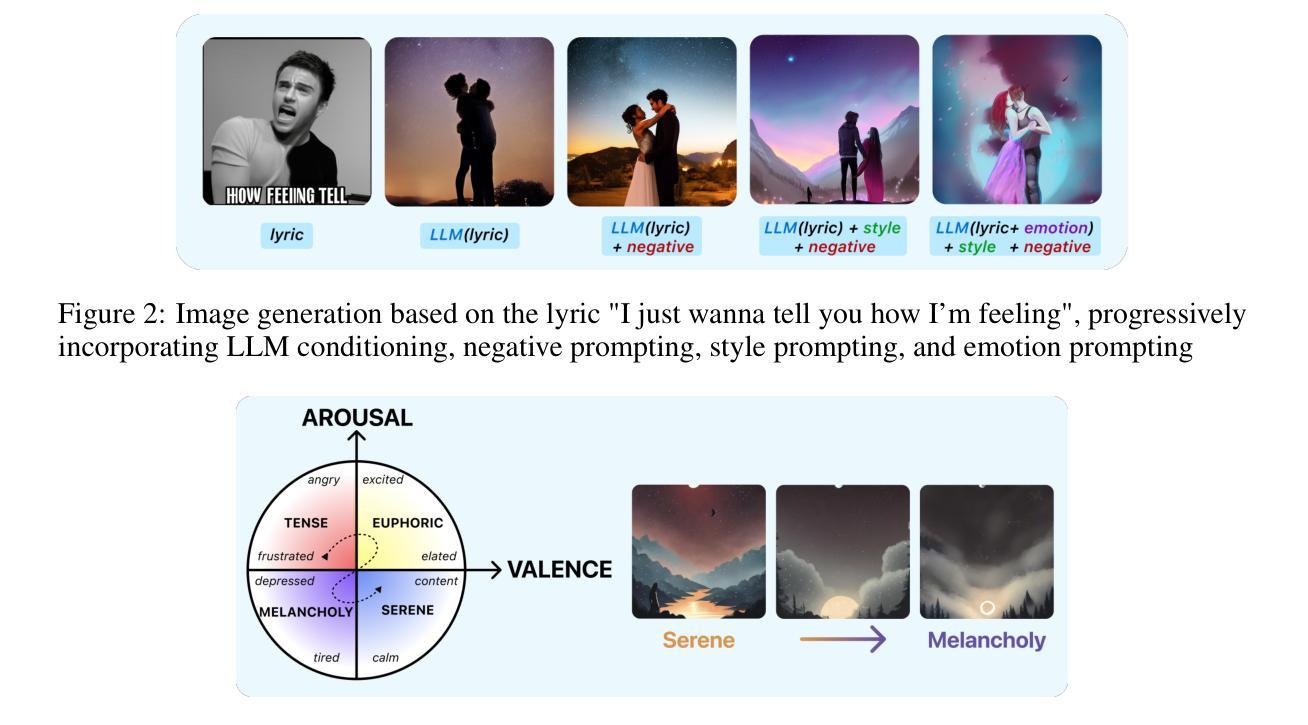
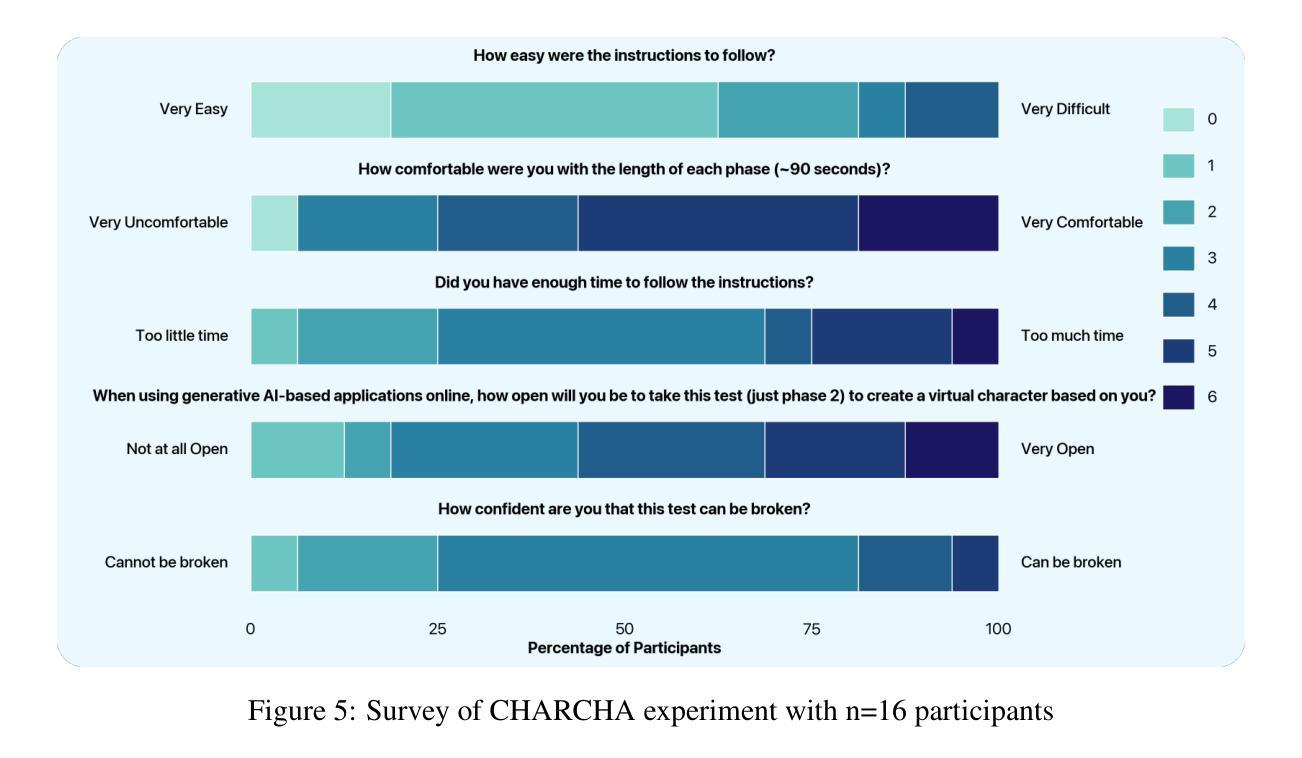
Music is a deeply personal experience and our aim is to enhance this with a fully-automated pipeline for personalized music video generation. Our work allows listeners to not just be consumers but co-creators in the music video generation process by creating personalized, consistent and context-driven visuals based on lyrics, rhythm and emotion in the music. The pipeline combines multimodal translation and generation techniques and utilizes low-rank adaptation on listeners’ images to create immersive music videos that reflect both the music and the individual. To ensure the ethical use of users’ identity, we also introduce CHARCHA (patent pending), a facial identity verification protocol that protects people against unauthorized use of their face while at the same time collecting authorized images from users for personalizing their videos. This paper thus provides a secure and innovative framework for creating deeply personalized music videos.
音乐是一种非常个人的体验,我们的目标是通过全自动化的个性化音乐视频生成管道来增强这种体验。我们的工作不仅允许听众成为消费者,而且成为音乐视频生成过程的共同创作者,通过基于歌词、节奏和音乐情感的个性化、一致性和情境驱动的视觉创作。该管道结合了多模式翻译和生成技术,利用听众图像的低位适应技术,以创建沉浸式音乐视频,这些视频既反映音乐又反映个人特点。为确保用户身份使用的道德性,我们还引入了CHARCHA(专利申请中),这是一种面部身份认证协议,可保护人们免受其面部未经授权的使用,同时从用户那里收集授权图像,以个性化他们的视频。因此,本文提供了一个安全、创新的框架,用于创建深度个性化的音乐视频。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024 Creative AI Track
Summary
音乐是一种深具个性化的体验,我们的目标是通过全自动化的个性化音乐视频生成管道来增强这一体验。我们的工作让听众不仅是消费者,而且是音乐视频生成过程的共同创作者,通过基于歌词、节奏和音乐的情感创造个性化、一致且基于上下文视觉效果的个性化音乐视频。该管道结合了多模式翻译和生成技术,并利用听众图像的低位适应技术来创建沉浸式音乐视频,这些视频既能反映音乐也能反映个性。为确保用户身份使用的道德性,我们还引入了面部身份认证协议CHARCHA(专利申请中),既保护人们免受其面部未经授权的滥用,同时从用户收集授权图像用于个性化视频制作。这篇论文因此提供了一个安全创新的框架来创作深度个性化的音乐视频。
Key Takeaways
- 论文旨在通过全自动化的管道增强个性化音乐体验。
- 允许听众参与音乐视频的生成过程,创造个性化的视觉效果。
- 管道结合了多模式翻译和生成技术。
- 利用低位适应技术使用听众图像创建沉浸式音乐视频。
- 音乐视频生成需反映音乐与听众的个性。
- 引入面部身份认证协议CHARCHA,保护用户身份不受未经授权的滥用。
点此查看论文截图

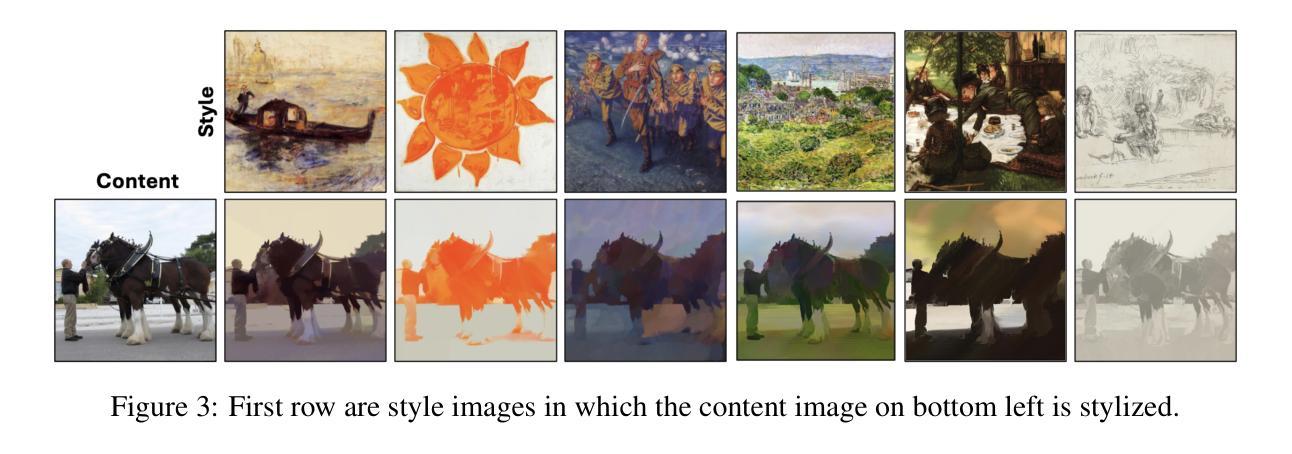
PixelShuffler: A Simple Image Translation Through Pixel Rearrangement
Authors:Omar Zamzam
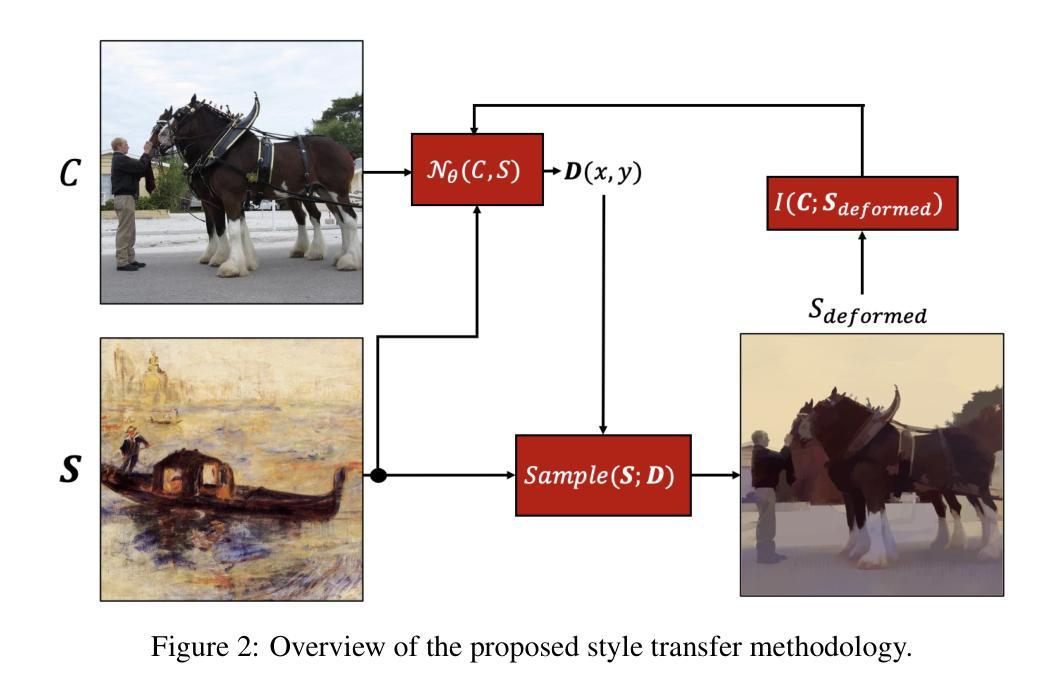
Image-to-image translation is a topic in computer vision that has a vast range of use cases ranging from medical image translation, such as converting MRI scans to CT scans or to other MRI contrasts, to image colorization, super-resolution, domain adaptation, and generating photorealistic images from sketches or semantic maps. Image style transfer is also a widely researched application of image-to-image translation, where the goal is to synthesize an image that combines the content of one image with the style of another. Existing state-of-the-art methods often rely on complex neural networks, including diffusion models and language models, to achieve high-quality style transfer, but these methods can be computationally expensive and intricate to implement. In this paper, we propose a novel pixel shuffle method that addresses the image-to-image translation problem generally with a specific demonstrative application in style transfer. The proposed method approaches style transfer by shuffling the pixels of the style image such that the mutual information between the shuffled image and the content image is maximized. This approach inherently preserves the colors of the style image while ensuring that the structural details of the content image are retained in the stylized output. We demonstrate that this simple and straightforward method produces results that are comparable to state-of-the-art techniques, as measured by the Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) loss for content preservation and the Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) score for style similarity. Our experiments validate that the proposed pixel shuffle method achieves competitive performance with significantly reduced complexity, offering a promising alternative for efficient image style transfer, as well as a promise in usability of the method in general image-to-image translation tasks.
图像到图像的翻译是计算机视觉中的一个话题,具有广泛的用例,从医学图像翻译(例如将MRI扫描转换为CT扫描或其他MRI对比剂)到图像彩色化、超分辨率、域适应以及从草图或语义地图生成逼真的图像等。图像风格迁移也是图像到图像翻译的一个广泛应用,其目标是将一个图像的内容与另一个图像的风格结合起来合成一个新的图像。现有的先进方法通常依赖于复杂的神经网络(包括扩散模型和语言模型)来实现高质量的样式转移,但这些方法计算量大且实施复杂。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的像素级混合方法来解决图像到图像的翻译问题,并通过风格迁移这一具体的应用进行了展示。该方法通过混合风格图像的像素来进行风格迁移,使得混合图像和内容图像之间的互信息最大化。这种方法本质上保留了风格图像的颜色,同时确保内容图像的结构细节保留在风格化的输出中。我们通过实验证明,这种简单直接的方法产生的结果与先进技术相比具有竞争力,通过内容保留的LPIPS损失和风格相似度的FID分数来衡量。我们的实验验证了所提的像素级混合方法取得了有竞争力的性能表现,大大降低了复杂度,为提高图像风格转移的效率提供了有前景的替代方案,同时也为该方法的通用图像到图像翻译任务的可使用性提供了前景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的像素重排方法,用于图像到图像的翻译问题,特别是在风格转换方面的应用。该方法通过重排风格图像的像素,使重排图像与内容图像之间的互信息最大化,从而实现风格转换。此方法既保留了风格图像的颜色,又确保了内容图像的结构细节在风格化输出中得到保留。实验证明,该方法与先进技术相比具有竞争力,复杂度显著降低,为高效的图像风格转换提供了一个有前途的替代方案,并且在一般的图像到图像翻译任务中具有可用性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像到图像翻译具有广泛的应用领域,包括医学图像翻译、图像色彩化、超分辨率、域适应以及从草图或语义地图生成逼真的图像等。
- 现有先进技术通常依赖复杂的神经网络,如扩散模型和语言模型,来实现高质量的风格转换,但计算成本高昂且实施复杂。
- 本文提出了一种新型的像素重排方法,专门解决图像到图像翻译问题,并在风格转换中进行了具体展示。
- 该方法通过重排风格图像的像素,最大化重排图像与内容图像之间的互信息来实现风格转换。
- 方法既保留了风格图像的颜色,又确保了内容图像的结构细节在风格化输出中得到保留。
- 实验证明,该方法与先进技术相比具有竞争力,并且复杂度显著降低。
点此查看论文截图


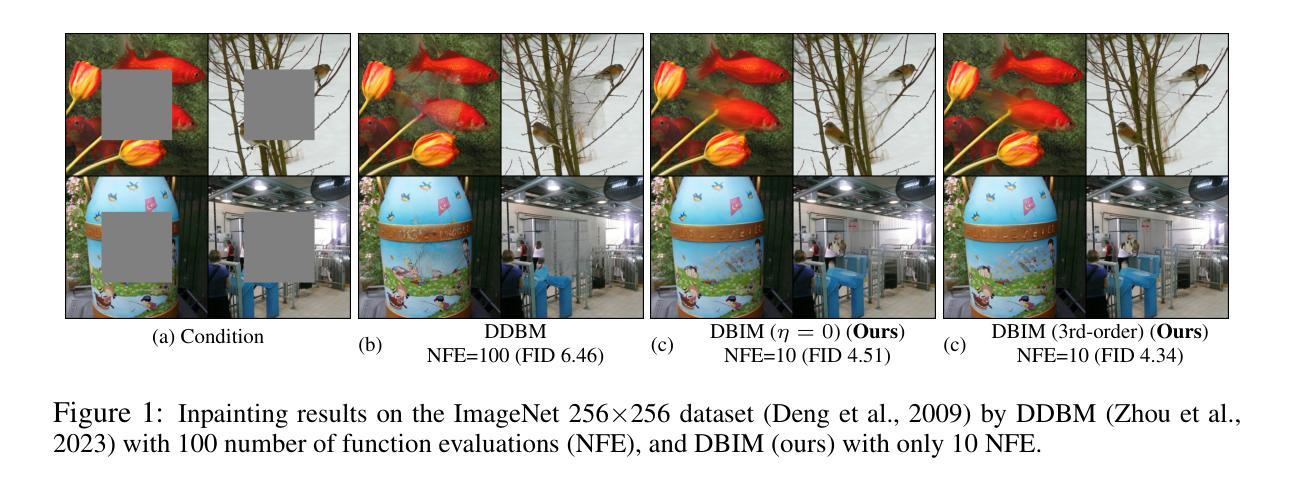
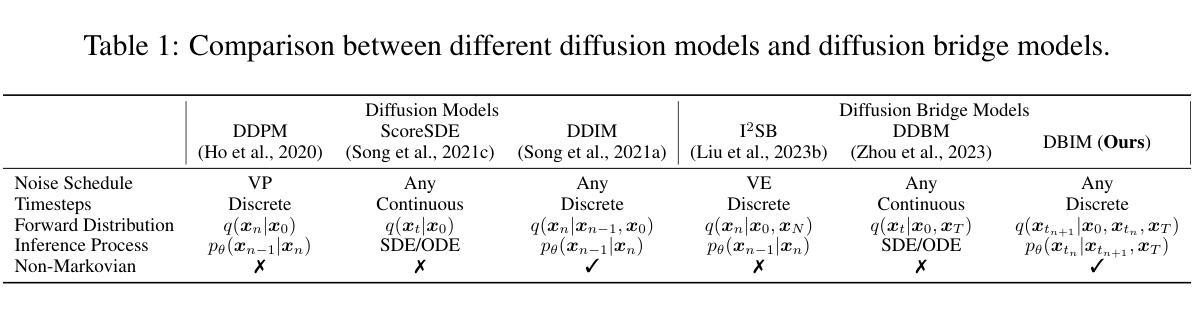
Diffusion Bridge Implicit Models
Authors:Kaiwen Zheng, Guande He, Jianfei Chen, Fan Bao, Jun Zhu
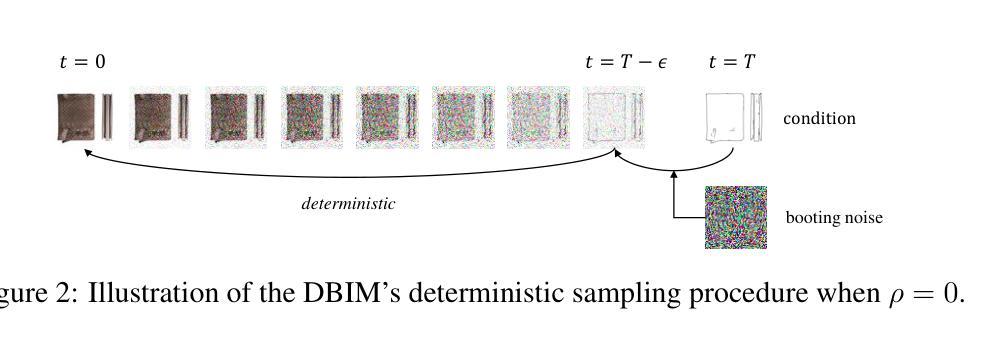
Denoising diffusion bridge models (DDBMs) are a powerful variant of diffusion models for interpolating between two arbitrary paired distributions given as endpoints. Despite their promising performance in tasks like image translation, DDBMs require a computationally intensive sampling process that involves the simulation of a (stochastic) differential equation through hundreds of network evaluations. In this work, we take the first step in fast sampling of DDBMs without extra training, motivated by the well-established recipes in diffusion models. We generalize DDBMs via a class of non-Markovian diffusion bridges defined on the discretized timesteps concerning sampling, which share the same marginal distributions and training objectives, give rise to generative processes ranging from stochastic to deterministic, and result in diffusion bridge implicit models (DBIMs). DBIMs are not only up to 25$\times$ faster than the vanilla sampler of DDBMs but also induce a novel, simple, and insightful form of ordinary differential equation (ODE) which inspires high-order numerical solvers. Moreover, DBIMs maintain the generation diversity in a distinguished way, by using a booting noise in the initial sampling step, which enables faithful encoding, reconstruction, and semantic interpolation in image translation tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/thu-ml/DiffusionBridge.
降噪扩散桥梁模型(DDBMs)是在给定两个任意配对分布作为端点时,用于两者之间插值的扩散模型的一种强大变体。尽管它们在图像翻译等任务中的表现很有希望,但DDBMs需要一个计算密集型的采样过程,这需要通过数百次网络评估来模拟(随机)微分方程。在这项工作中,我们采取了无需额外训练即可快速采样DDBMs的第一步,这得益于扩散模型中成熟的配方。我们通过定义关于采样的离散时间步长上的一类非马尔可夫扩散桥梁来推广DDBMs,它们具有相同的边缘分布和训练目标,产生从随机到确定性的生成过程,并形成扩散桥梁隐模型(DBIMs)。DBIMs不仅比DDBMs的原生采样器快达25倍,还引发了一种新型、简单、有洞察力的常微分方程(ODE),这激发了高阶数值求解器的灵感。此外,DBIM以独特的方式保持了生成的多样性,通过在初始采样步骤中使用引导噪声,这使其在图像翻译任务中实现了忠实的编码、重建和语义插值。代码可从https://github.com/thu-ml/DiffusionBridge获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR 2025
Summary
DDBMs(去噪扩散桥梁模型)是一种强大的扩散模型变体,可在两个任意配对分布之间插值。尽管它们在图像翻译等任务中表现出色,但DDBMs需要计算密集型的采样过程,涉及数百次网络评估的(随机)微分方程模拟。本研究首次尝试对DDBMs进行快速采样,无需额外训练,受到扩散模型的成熟配方的启发。通过定义一类关于采样的离散时间步长的非马尔可夫扩散桥梁,我们推广了DDBMs,形成了扩散桥梁隐模型(DBIMs)。DBIMs不仅高达原DDBMs采样速度的25倍,还产生了一种新颖、简单、有洞察力的常微分方程(ODE),激发了对高阶数值解算器的思考。此外,DBIMs以独特的方式保持了生成多样性,通过在初始采样步骤中使用引导噪声,实现在图像翻译任务中的忠实编码、重建和语义插值。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- DDBMs是一种强大的扩散模型变体,可在两个任意配对分布之间插值。
- DDBMs的采样过程计算密集,涉及大量网络评估和微分方程模拟。
- 本研究通过非马尔可夫扩散桥梁模型推广了DDBMs,形成了更快的DBIMs采样方法。
- DBIMs不仅提高了采样速度,还提供了新的ODE形式,有助于高阶数值解算器的开发。
- DBIMs通过初始采样步骤中的引导噪声,实现了生成多样性的独特维护。
- DBIMs在图像翻译任务中展现出忠实编码、重建和语义插值的能力。
点此查看论文截图