⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-07 更新
SiLVR: Scalable Lidar-Visual Radiance Field Reconstruction with Uncertainty Quantification
Authors:Yifu Tao, Maurice Fallon
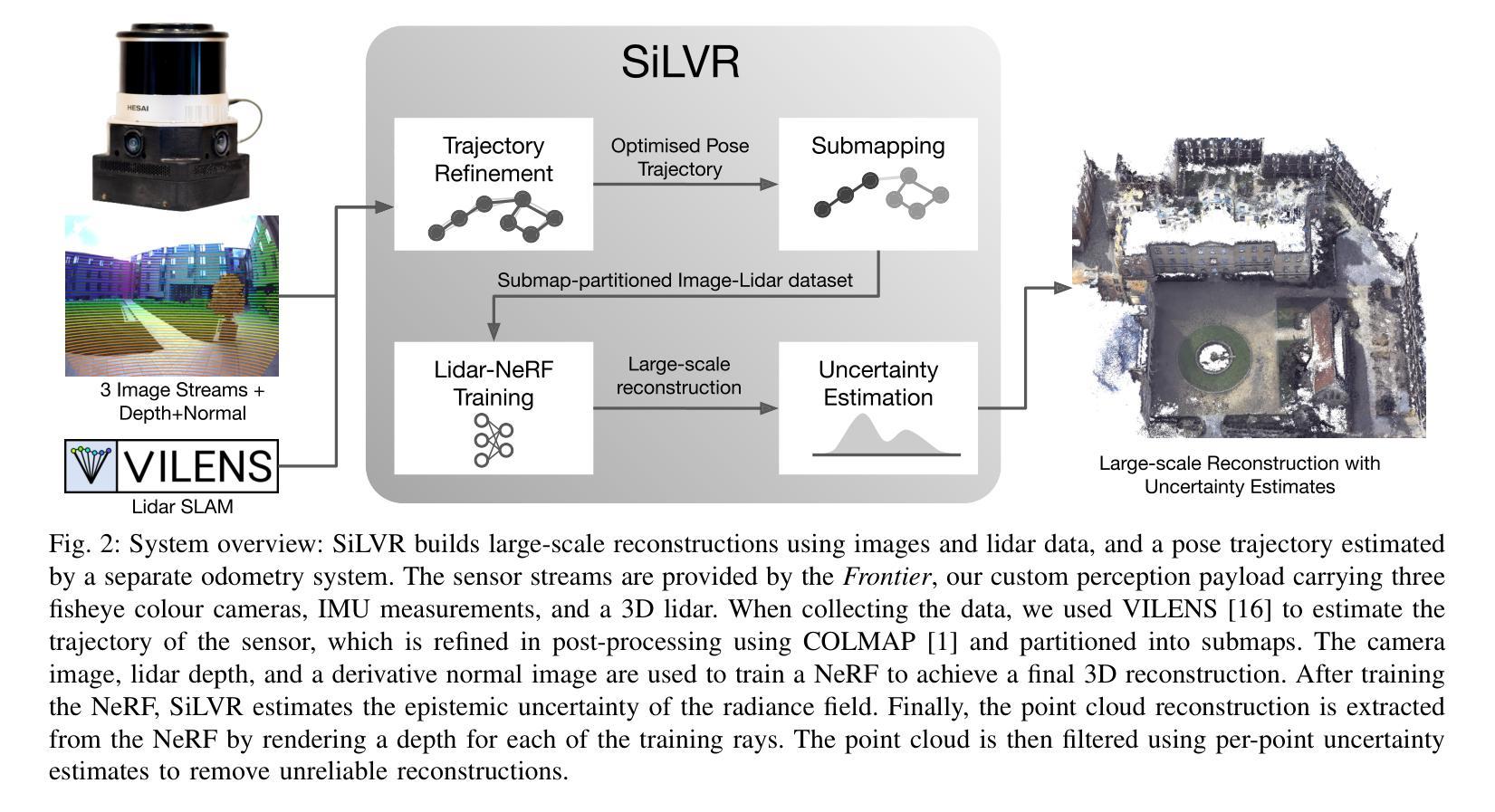
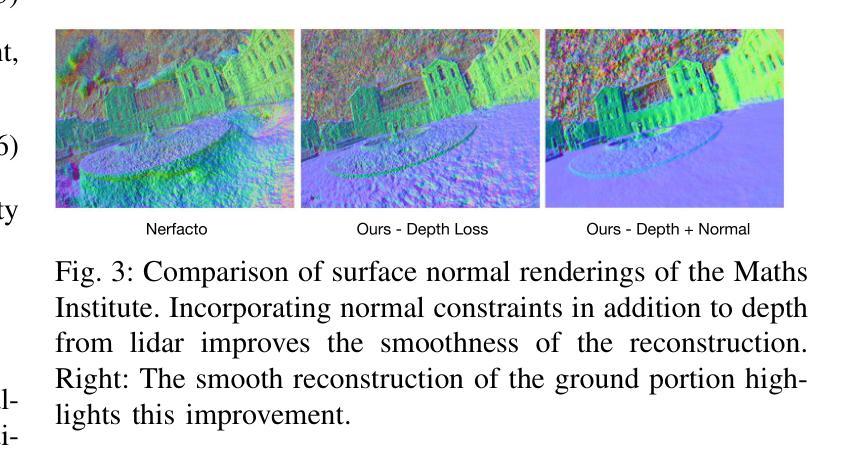
We present a neural radiance field (NeRF) based large-scale reconstruction system that fuses lidar and vision data to generate high-quality reconstructions that are geometrically accurate and capture photorealistic texture. Our system adopts the state-of-the-art NeRF representation to additionally incorporate lidar. Adding lidar data adds strong geometric constraints on the depth and surface normals, which is particularly useful when modelling uniform texture surfaces which contain ambiguous visual reconstruction cues. Furthermore, we estimate the epistemic uncertainty of the reconstruction as the spatial variance of each point location in the radiance field given the sensor observations from camera and lidar. This enables the identification of areas that are reliably reconstructed by each sensor modality, allowing the map to be filtered according to the estimated uncertainty. Our system can also exploit the trajectory produced by a real-time pose-graph lidar SLAM system during online mapping to bootstrap a (post-processed) Structure-from-Motion (SfM) reconstruction procedure reducing SfM training time by up to 70%. It also helps to properly constrain the overall metric scale which is essential for the lidar depth loss. The globally-consistent trajectory can then be divided into submaps using Spectral Clustering to group sets of co-visible images together. This submapping approach is more suitable for visual reconstruction than distance-based partitioning. Each submap is filtered according to point-wise uncertainty estimates and merged to obtain the final large-scale 3D reconstruction. We demonstrate the reconstruction system using a multi-camera, lidar sensor suite in experiments involving both robot-mounted and handheld scanning. Our test datasets cover a total area of more than 20,000 square metres, including multiple university buildings and an aerial survey of a multi-storey.
我们提出了一种基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的大规模重建系统,该系统融合了激光雷达和视觉数据,生成了高质量的三维重建模型,具有几何准确性,并捕捉了逼真的纹理。我们的系统采用了最先进的NeRF表示法,并额外融入了激光雷达数据。加入激光雷达数据为深度和表面法线增加了强大的几何约束,这在建模具有模糊视觉重建线索的均匀纹理表面时特别有用。此外,我们根据来自相机和激光雷达的传感器观测结果,估计重建的认知不确定性作为辐射场中每个点位置的空间方差。这能够识别出每个传感器模态可靠重建的区域,并根据估计的不确定性对地图进行过滤。我们的系统还能在线映射期间利用实时姿态图激光雷达SLAM系统产生的轨迹来引导运动恢复结构(SfM)重建过程(经过后处理),将SfM训练时间减少高达70%。这还有助于正确约束整体度量尺度,这对激光雷达深度损失至关重要。全球一致的轨迹可以使用谱聚类方法划分为子图,将共视图像组合在一起。这种子图方法比基于距离的分区更适合于视觉重建。每个子图根据点级不确定性估计进行过滤,然后合并以获得最终的大规模三维重建。我们通过使用多相机和激光雷达传感器组合的实验,展示了该重建系统在机器人和手持扫描中的应用。我们的测试数据集覆盖总面积超过20,000平方米,包括多个大学建筑和多层楼的空中调查。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF webpage: https://dynamic.robots.ox.ac.uk/projects/silvr/
摘要
本研究提出了基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的大规模重建系统,该系统融合了激光雷达和视觉数据,可生成高质量的三维重建模型,具有几何准确性并捕捉逼真的纹理。本系统采用最先进的NeRF表示法,并融入了激光雷达数据,增强了深度及表面法线的几何约束,尤其擅长对具有模糊视觉重建线索的均匀纹理表面进行建模。此外,本系统还估计了重建的可知论不确定性,表现为给定传感器观测值下辐射场中每个点的空间方差。这有助于识别各传感器模态可靠重建的区域,并根据估计的不确定性过滤地图。本系统还能利用实时姿态图激光雷达SLAM系统产生的轨迹,在线进行地图构建,引导结构从运动(SfM)重建过程的后处理阶段,将SfM训练时间缩短高达70%,并有助于正确约束整体度量尺度,这对激光雷达深度损失至关重要。全局一致的轨迹可通过谱聚类划分为子图,将共视图集合分组在一起。这种子图方法更适合于视觉重建,而不是基于距离的分隔方法。根据点的不确定性估计过滤每个子图并进行合并,以获得最终的大规模三维重建。我们通过使用多相机、激光雷达传感器组合进行实验,展示了在机器人和手持扫描中的重建系统。测试数据集覆盖超过2万平米的区域,包括多个大学建筑和多层楼的空中调查。
关键见解
- 提出基于NeRF的大规模重建系统,融合激光雷达和视觉数据生成高质量三维模型。
- 利用NeRF表示法融入激光雷达数据,增强深度与表面法线的几何约束。
- 估计重建的可知论不确定性,用于识别各传感器模态可靠重建的区域并过滤地图。
- 利用实时姿态图激光雷达SLAM系统的轨迹引导SfM重建过程,减少训练时间并提高约束准确性。
- 通过谱聚类将全局轨迹划分为子图,更适合于视觉重建。
- 根据点的不确定性估计过滤和合并子图以完成最终的大规模三维重建。
点此查看论文截图

GS-LiDAR: Generating Realistic LiDAR Point Clouds with Panoramic Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Junzhe Jiang, Chun Gu, Yurui Chen, Li Zhang
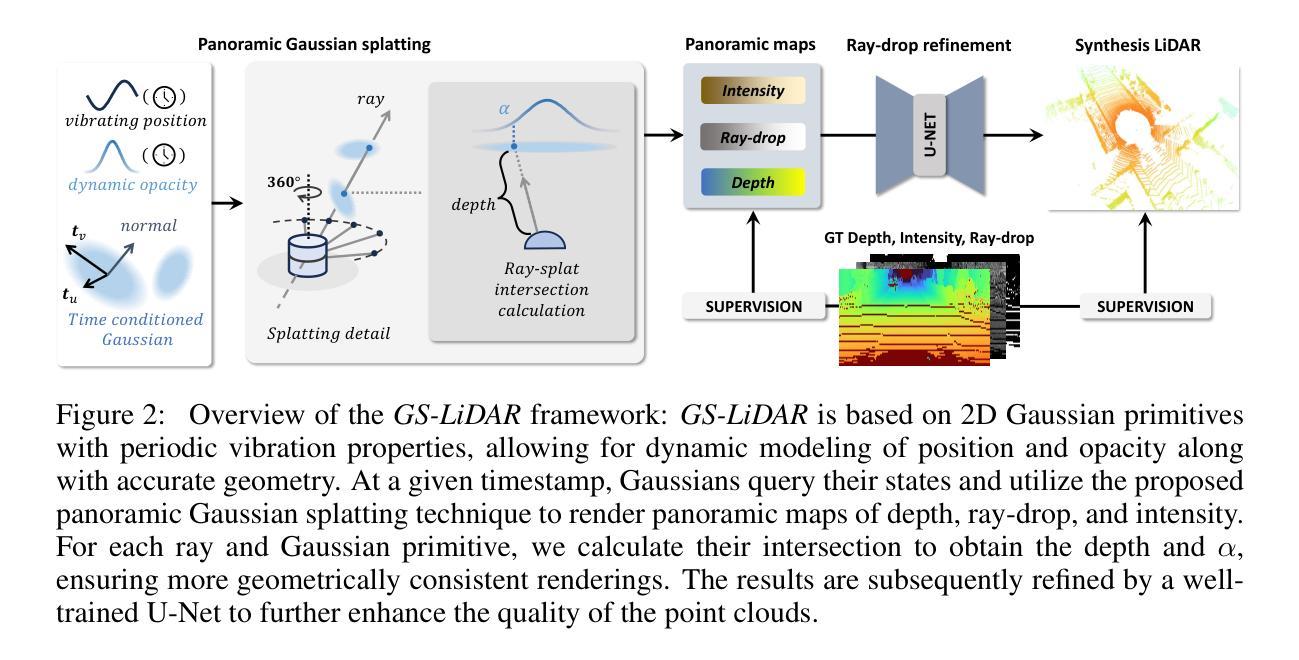
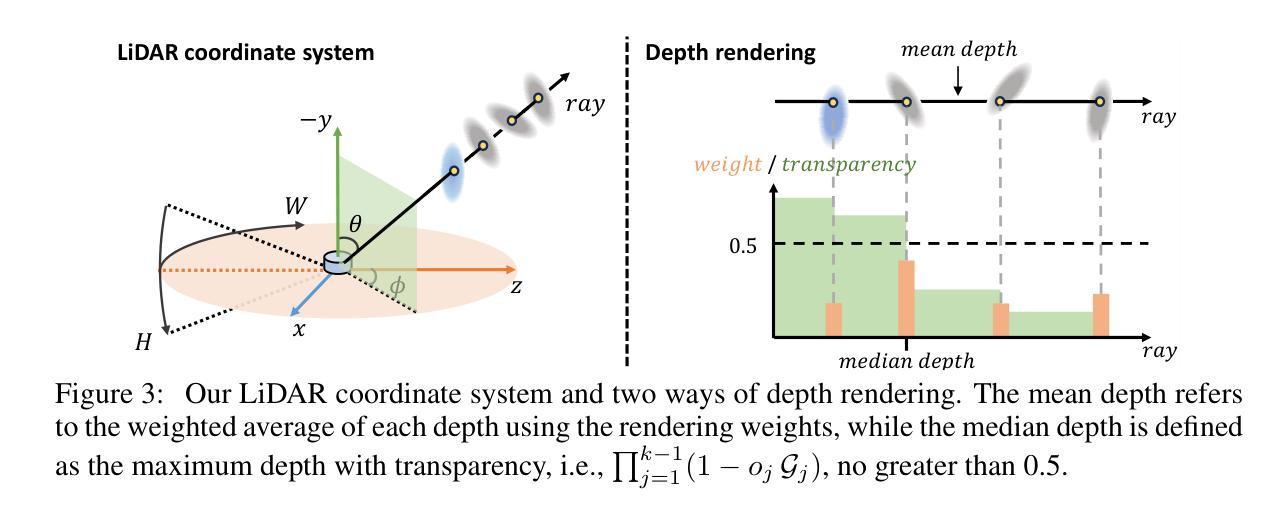
LiDAR novel view synthesis (NVS) has emerged as a novel task within LiDAR simulation, offering valuable simulated point cloud data from novel viewpoints to aid in autonomous driving systems. However, existing LiDAR NVS methods typically rely on neural radiance fields (NeRF) as their 3D representation, which incurs significant computational costs in both training and rendering. Moreover, NeRF and its variants are designed for symmetrical scenes, making them ill-suited for driving scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose GS-LiDAR, a novel framework for generating realistic LiDAR point clouds with panoramic Gaussian splatting. Our approach employs 2D Gaussian primitives with periodic vibration properties, allowing for precise geometric reconstruction of both static and dynamic elements in driving scenarios. We further introduce a novel panoramic rendering technique with explicit ray-splat intersection, guided by panoramic LiDAR supervision. By incorporating intensity and ray-drop spherical harmonic (SH) coefficients into the Gaussian primitives, we enhance the realism of the rendered point clouds. Extensive experiments on KITTI-360 and nuScenes demonstrate the superiority of our method in terms of quantitative metrics, visual quality, as well as training and rendering efficiency.
激光雷达视点合成(NVS)作为激光雷达模拟领域的一项新任务应运而生,其从新型视点提供有价值的模拟点云数据,以辅助自动驾驶系统。然而,现有的激光雷达NVS方法通常依赖于神经辐射场(NeRF)作为其三维表示,这在训练和渲染过程中都会带来相当大的计算成本。此外,NeRF及其变体是为对称场景设计的,使得它们不适合驾驶场景。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了GS-激光雷达,这是一个利用全景高斯涂抹技术生成真实激光雷达点云数据的新框架。我们的方法采用具有周期性振动特性的二维高斯基元,能够精确重建驾驶场景中静态和动态元素的几何结构。我们进一步引入了一种新型的全景渲染技术,具有明确的射线-涂抹交点,由全景激光雷达监督指导。我们将强度和射线降维球面谐波系数纳入高斯基元中,增强了渲染点云的真实性。在KITTI-360和nuScenes上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在定量指标、视觉质量以及训练和渲染效率方面都表现出优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于LiDAR全景模拟的驾驶场景合成方法
Key Takeaways
- 提出GS-LiDAR框架用于生成真实的LiDAR点云数据。
- 使用具有周期性振动属性的2D高斯基本单元实现精确的几何重建。
- 采用全景渲染技术,通过明确的射线-平面交点,以全景LiDAR监督指导。
- 结合强度和射线下降球面谐波系数增强点云的真实性。
- 在KITTI-360和nuScenes等数据集上的实验证明了该方法在定量指标、视觉质量以及训练和渲染效率上的优越性。
- 此方法能够处理静态和动态元素的驾驶场景合成。
点此查看论文截图

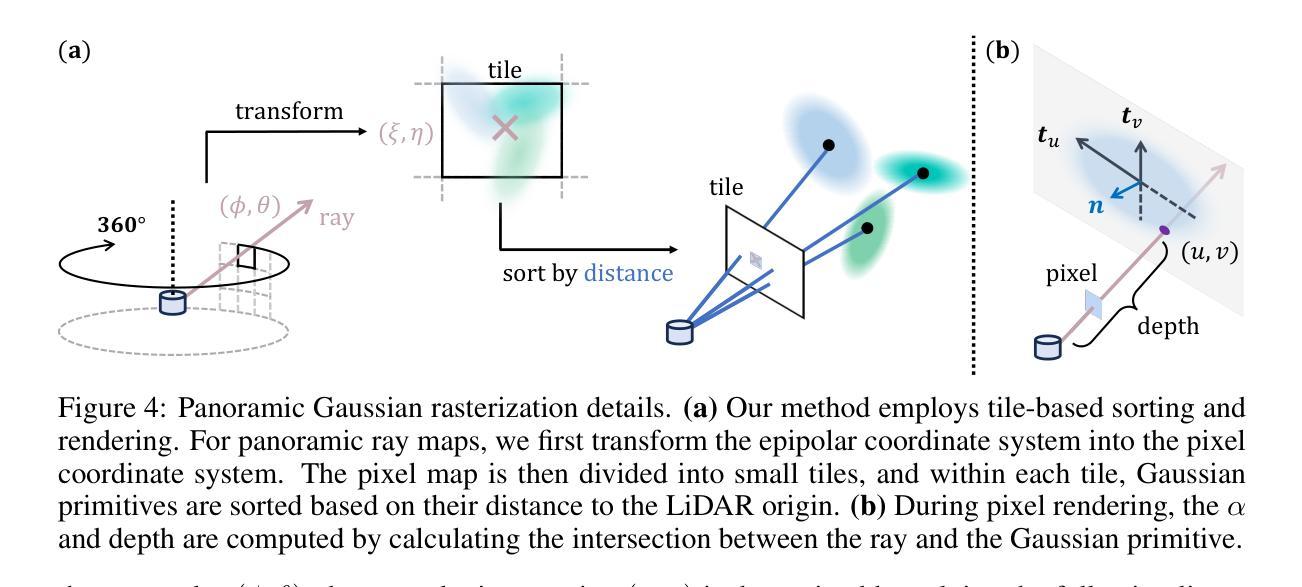
GS-CPR: Efficient Camera Pose Refinement via 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Changkun Liu, Shuai Chen, Yash Bhalgat, Siyan Hu, Ming Cheng, Zirui Wang, Victor Adrian Prisacariu, Tristan Braud
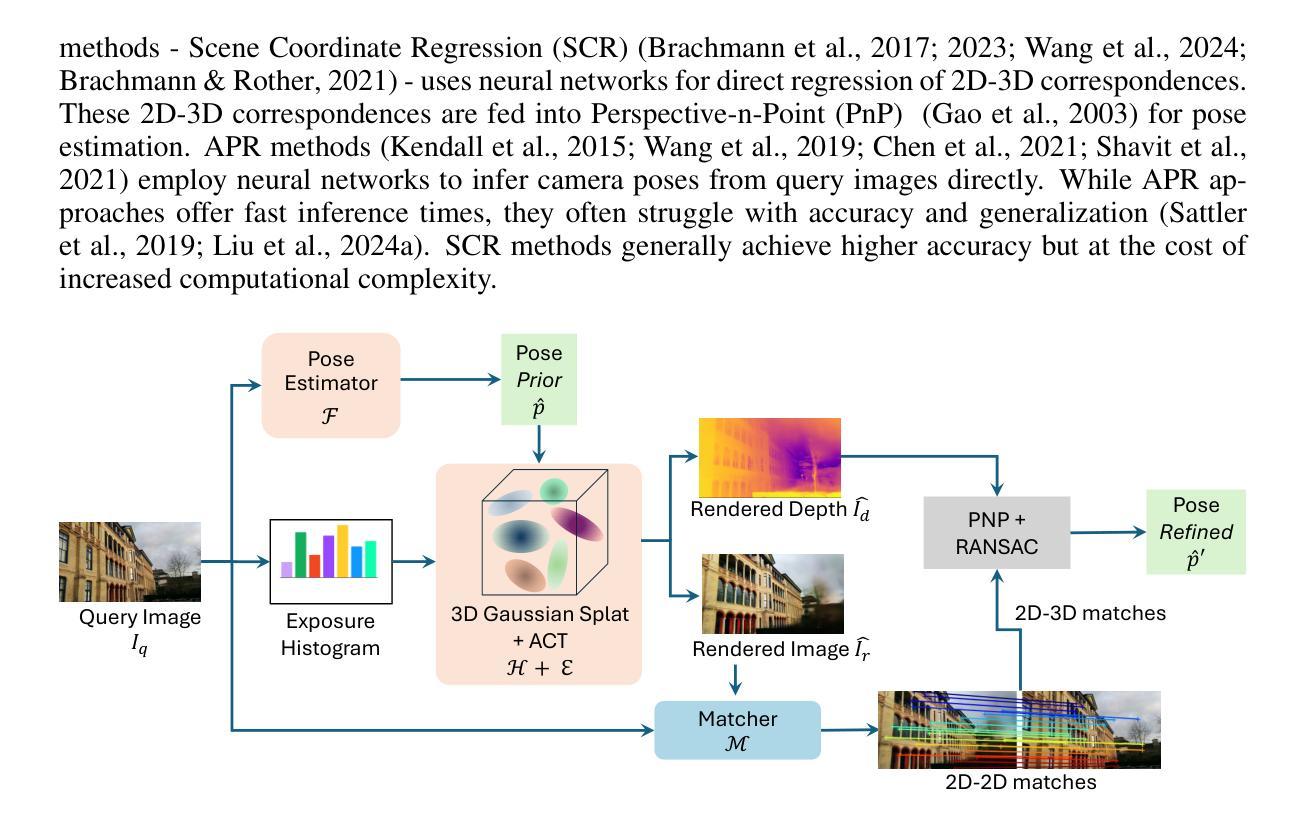
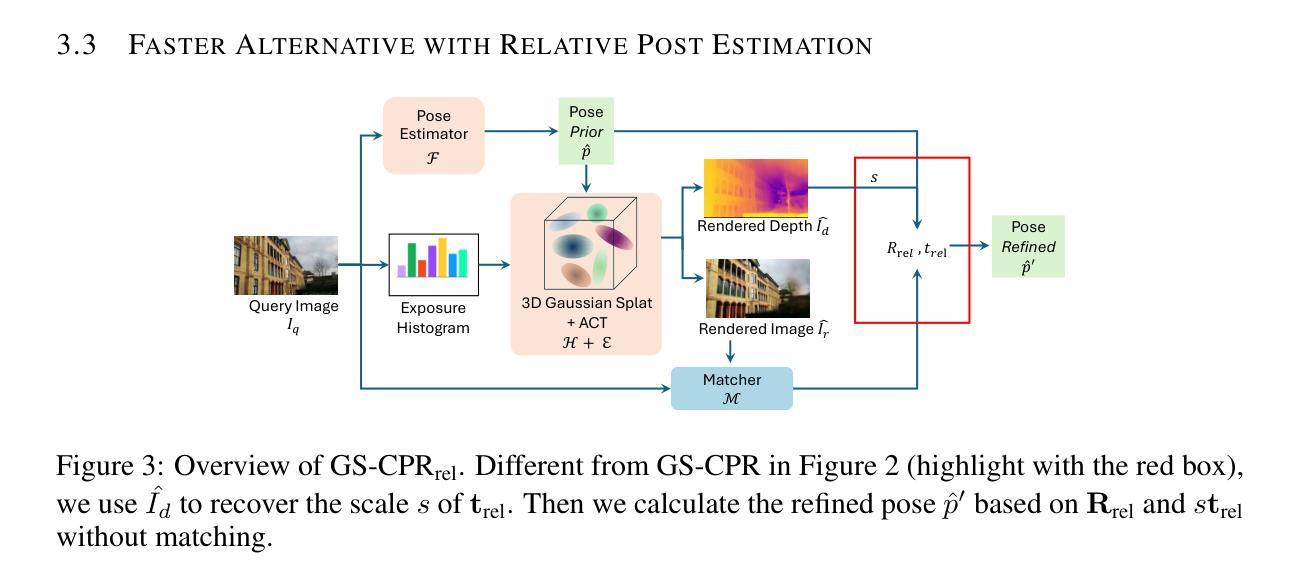
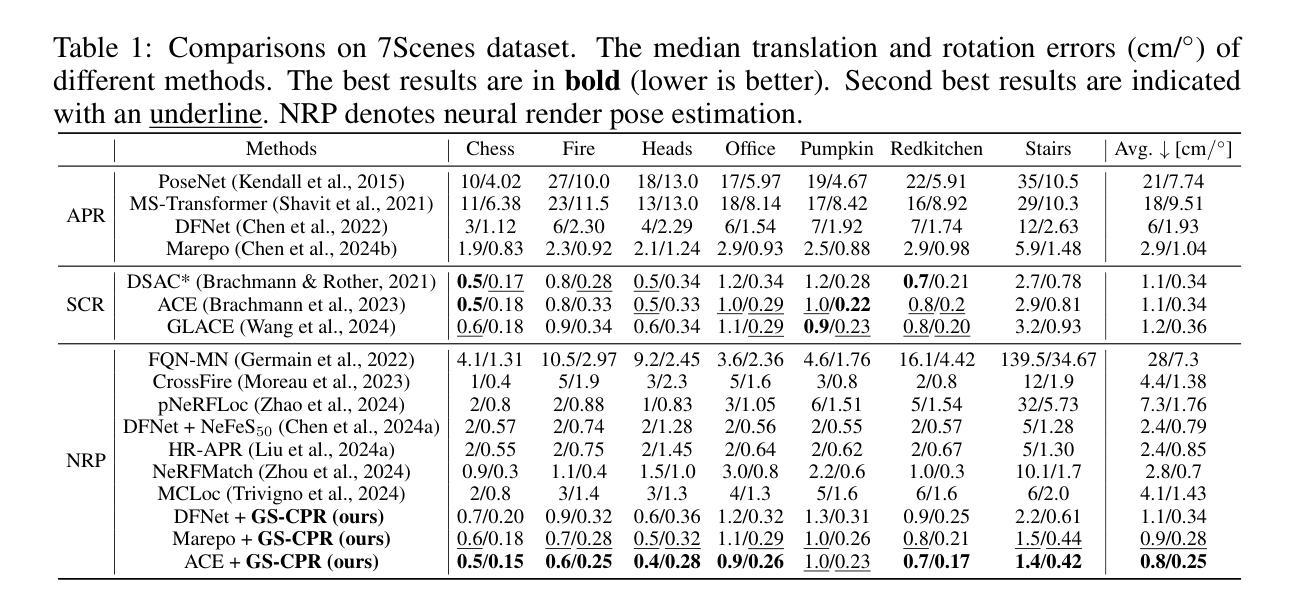
We leverage 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) as a scene representation and propose a novel test-time camera pose refinement (CPR) framework, GS-CPR. This framework enhances the localization accuracy of state-of-the-art absolute pose regression and scene coordinate regression methods. The 3DGS model renders high-quality synthetic images and depth maps to facilitate the establishment of 2D-3D correspondences. GS-CPR obviates the need for training feature extractors or descriptors by operating directly on RGB images, utilizing the 3D foundation model, MASt3R, for precise 2D matching. To improve the robustness of our model in challenging outdoor environments, we incorporate an exposure-adaptive module within the 3DGS framework. Consequently, GS-CPR enables efficient one-shot pose refinement given a single RGB query and a coarse initial pose estimation. Our proposed approach surpasses leading NeRF-based optimization methods in both accuracy and runtime across indoor and outdoor visual localization benchmarks, achieving new state-of-the-art accuracy on two indoor datasets. The project page is available at https://gsloc.active.vision.
我们利用三维高斯展布(3DGS)作为场景表示,并提出了一种新型测试时相机姿态优化(CPR)框架,即GS-CPR。该框架提高了最先进的绝对姿态回归和场景坐标回归方法的定位精度。3DGS模型渲染高质量合成图像和深度图,以促进2D-3D对应关系的建立。GS-CPR直接在RGB图像上操作,无需训练特征提取器或描述符,利用三维基础模型MASt3R进行精确2D匹配。为了提高我们的模型在具有挑战性的户外环境中的稳健性,我们在3DGS框架中引入了一个曝光自适应模块。因此,GS-CPR能够在给定单个RGB查询和粗略的初始姿态估计的情况下,实现高效的一次性姿态优化。我们提出的方法在室内外视觉定位基准测试上超越了领先的基于NeRF的优化方法,在两项室内数据集上达到了新的最先进的精度。项目页面可通过https://gsloc.active.vision访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR2025. During the ICLR review process, we changed the name of our framework from GSLoc to GS-CPR (Camera Pose Refinement) according to the comments of reviewers. The project page is available at https://gsloc.active.vision
Summary
本文利用3D高斯绘制技术作为场景表达,并提了一种名为GS-CPR的新测试时相机姿态优化框架。它提升了现有的绝对姿态回归和场景坐标回归方法的定位精度。该框架通过在渲染的高质量合成图像和深度图上建立二维到三维对应关系来建立图像信息与三维场景的关联。GS-CPR无需训练特征提取器或描述符,可直接在RGB图像上操作,并利用三维基础模型MASt3R进行精确二维匹配。通过引入曝光自适应模块,GS-CPR模型在复杂户外环境下的稳健性得到了提升。GS-CPR可实现一次高效的姿态优化,只需一个RGB查询图像和一个粗略的初始姿态估计。该方法在室内外视觉定位基准测试中超越了领先的NeRF优化方法,在两项室内数据集上达到了新的最高精度。
Key Takeaways
- 利用3D高斯绘制技术(3DGS)作为场景表达,建立图像信息与三维场景的关联。
- 提出名为GS-CPR的新型测试时相机姿态优化框架,提升定位精度。
- 通过渲染高质量合成图像和深度图,实现精确的二维到三维对应关系。
- GS-CPR无需训练特征提取器或描述符,直接在RGB图像上操作。
- 利用三维基础模型MASt3R进行精确二维匹配,提高模型性能。
- 通过引入曝光自适应模块增强模型在复杂户外环境的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

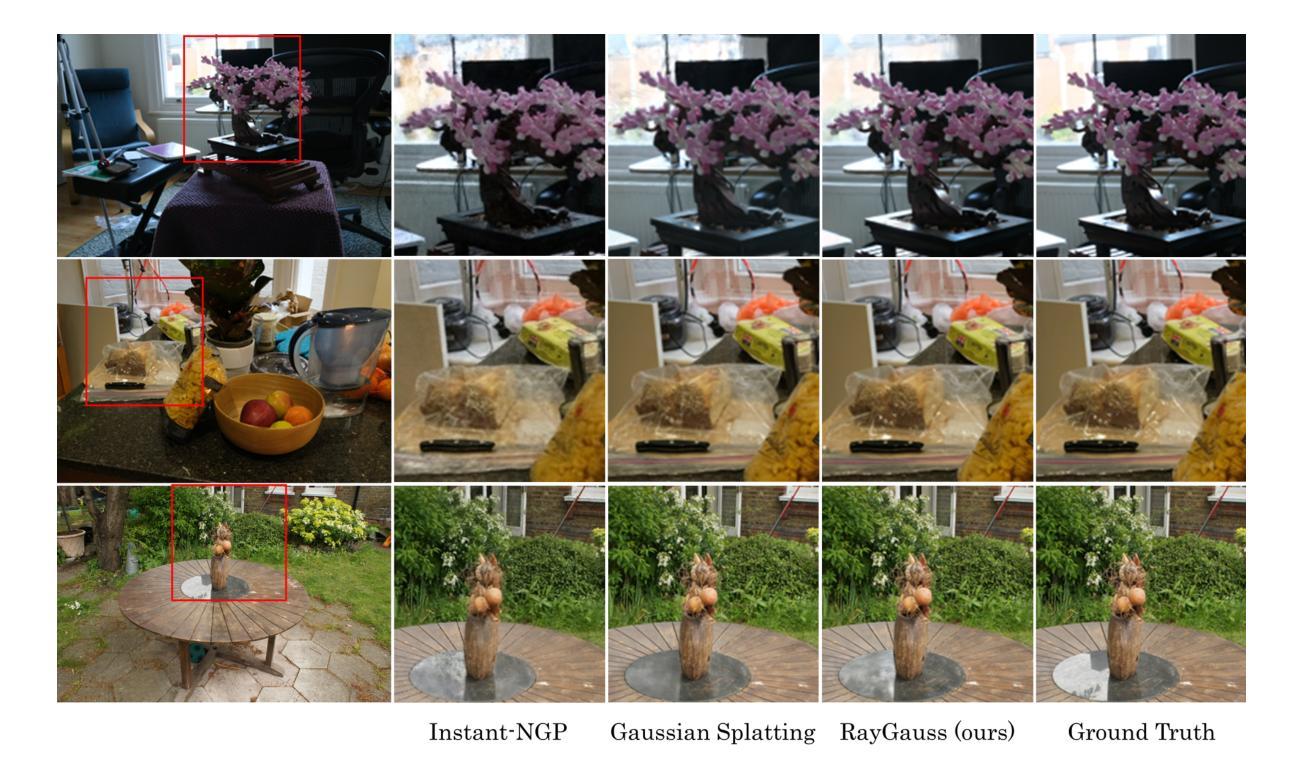
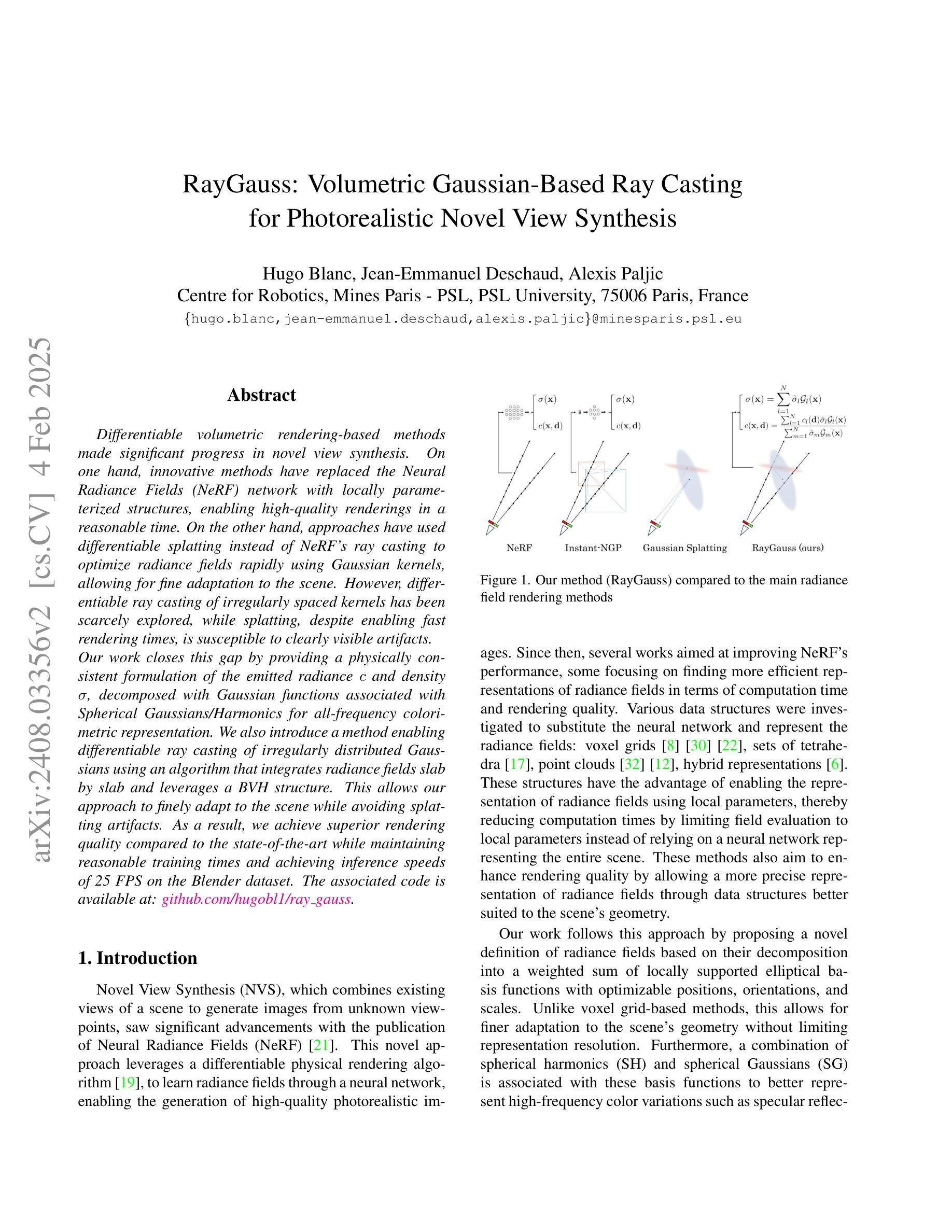
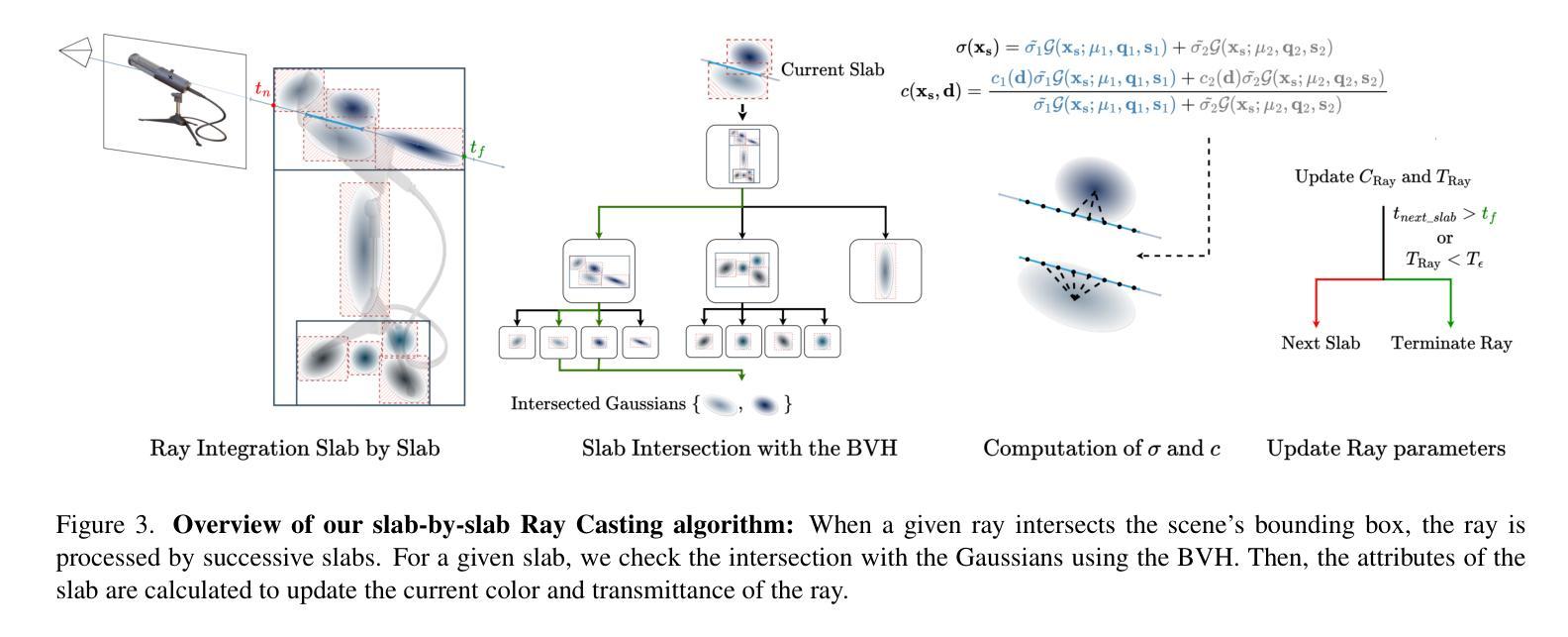
RayGauss: Volumetric Gaussian-Based Ray Casting for Photorealistic Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Hugo Blanc, Jean-Emmanuel Deschaud, Alexis Paljic
Differentiable volumetric rendering-based methods made significant progress in novel view synthesis. On one hand, innovative methods have replaced the Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) network with locally parameterized structures, enabling high-quality renderings in a reasonable time. On the other hand, approaches have used differentiable splatting instead of NeRF’s ray casting to optimize radiance fields rapidly using Gaussian kernels, allowing for fine adaptation to the scene. However, differentiable ray casting of irregularly spaced kernels has been scarcely explored, while splatting, despite enabling fast rendering times, is susceptible to clearly visible artifacts. Our work closes this gap by providing a physically consistent formulation of the emitted radiance c and density {\sigma}, decomposed with Gaussian functions associated with Spherical Gaussians/Harmonics for all-frequency colorimetric representation. We also introduce a method enabling differentiable ray casting of irregularly distributed Gaussians using an algorithm that integrates radiance fields slab by slab and leverages a BVH structure. This allows our approach to finely adapt to the scene while avoiding splatting artifacts. As a result, we achieve superior rendering quality compared to the state-of-the-art while maintaining reasonable training times and achieving inference speeds of 25 FPS on the Blender dataset. Project page with videos and code: https://raygauss.github.io/
基于可微分体积渲染的方法在新型视图合成方面取得了显著进展。一方面,创新方法用局部参数化结构替换了神经辐射场(NeRF)网络,能够在合理的时间内实现高质量渲染。另一方面,一些方法使用可微分的涂抹技术,而非NeRF的射线投射,利用高斯核优化辐射场,实现对场景的精细适应。然而,不规则间隔核的可微分射线投射几乎未被探索,而涂抹技术尽管能够实现快速的渲染时间,但容易产生明显的伪影。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page with videos and code: https://raygauss.github.io/
Summary
NeRF技术取得显著进展,对于新型视角合成领域尤为重要。最新方法采用可微分的体积渲染技术,通过替换NeRF网络为局部参数化结构或使用可微分的摊开技术替代射线投射法,优化了辐射场并提高了渲染质量。本研究填补了不规则间距核的可微分射线投射技术的空白,并引入了一种新方法,通过分层集成辐射场并使用BVH结构进行射线投射,避免了摊开技术的明显缺陷。因此,本研究在保持合理训练时间的同时,实现了较高的渲染质量,并在Blender数据集上达到了每秒25帧的推理速度。
Key Takeaways
- 可微分的体积渲染技术在新型视角合成领域取得了显著进展。
- NeRF技术被局部参数化结构替换,实现了合理时间内的高质量渲染。
- 可微分摊开技术被用于优化辐射场,但也存在明显的缺点。
- 研究填补了不规则间距核的可微分射线投射技术的空白。
- 通过分层集成辐射场并使用BVH结构进行射线投射,避免了摊开技术的缺陷。
- 研究实现了高质量的渲染,同时保持了合理的训练时间和推理速度。
点此查看论文截图