⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-07 更新
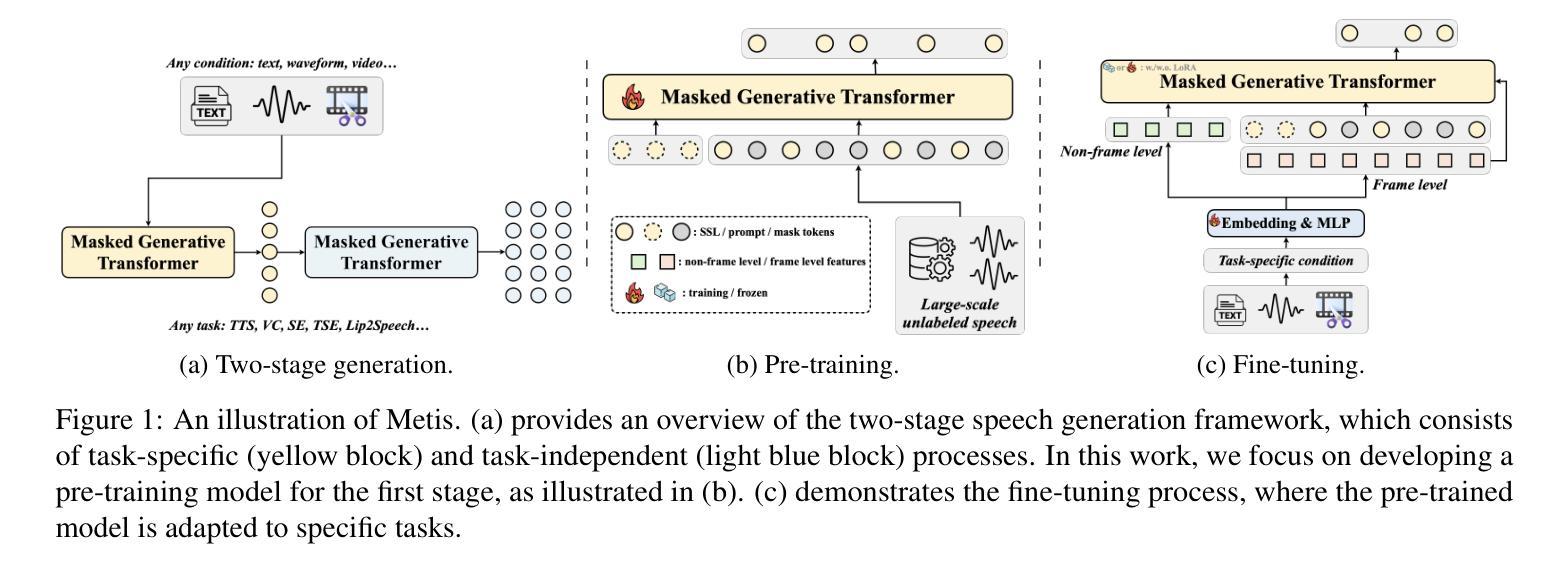
Metis: A Foundation Speech Generation Model with Masked Generative Pre-training
Authors:Yuancheng Wang, Jiachen Zheng, Junan Zhang, Xueyao Zhang, Huan Liao, Zhizheng Wu
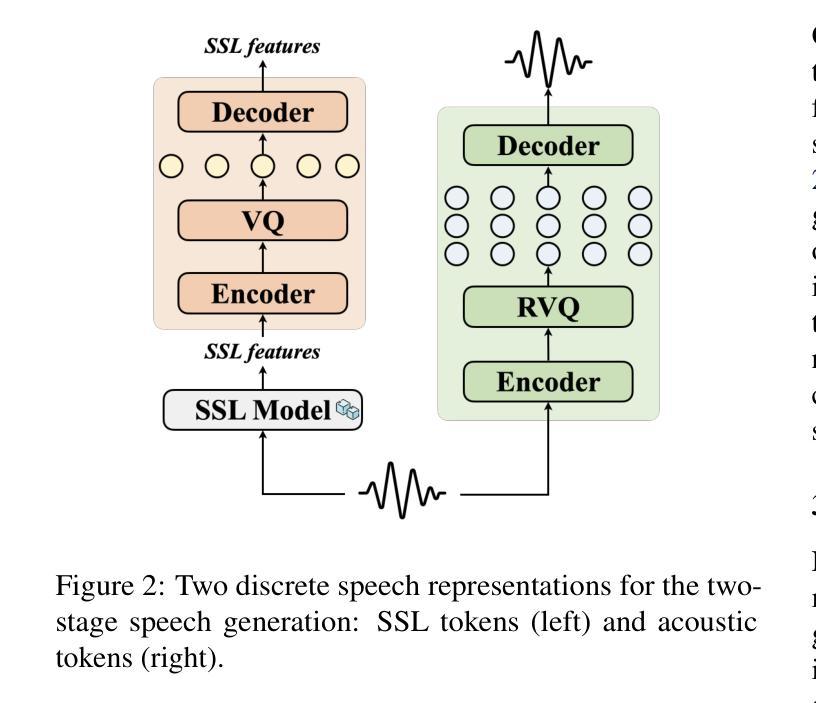
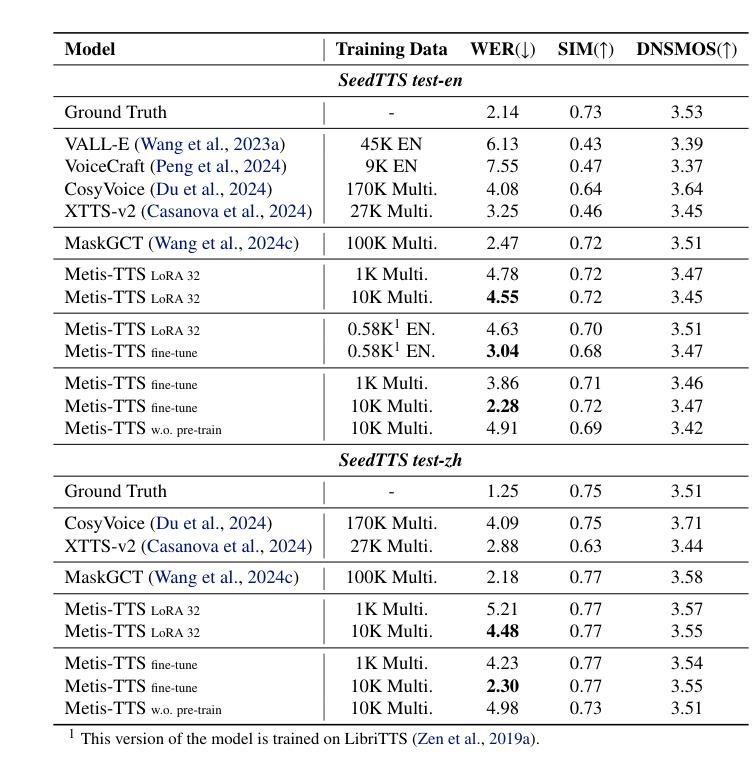
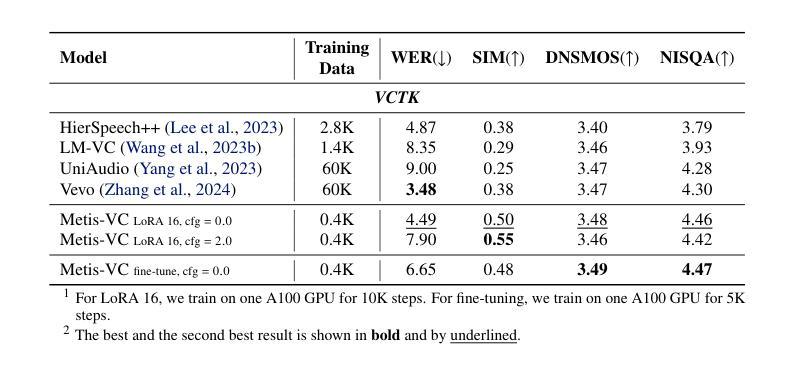
We introduce Metis, a foundation model for unified speech generation. Unlike previous task-specific or multi-task models, Metis follows a pre-training and fine-tuning paradigm. It is pre-trained on large-scale unlabeled speech data using masked generative modeling and then fine-tuned to adapt to diverse speech generation tasks. Specifically, 1) Metis utilizes two discrete speech representations: SSL tokens derived from speech self-supervised learning (SSL) features, and acoustic tokens directly quantized from waveforms. 2) Metis performs masked generative pre-training on SSL tokens, utilizing 300K hours of diverse speech data, without any additional condition. 3) Through fine-tuning with task-specific conditions, Metis achieves efficient adaptation to various speech generation tasks while supporting multimodal input, even when using limited data and trainable parameters. Experiments demonstrate that Metis can serve as a foundation model for unified speech generation: Metis outperforms state-of-the-art task-specific or multi-task systems across five speech generation tasks, including zero-shot text-to-speech, voice conversion, target speaker extraction, speech enhancement, and lip-to-speech, even with fewer than 20M trainable parameters or 300 times less training data. Audio samples are are available at https://metis-demo.github.io/.
我们介绍了Metis,这是一个统一的语音生成基础模型。不同于之前的任务特定或多任务模型,Metis遵循预训练和调整的范式。它使用遮罩生成建模在大规模无标签语音数据上进行预训练,然后微调以适应各种语音生成任务。具体来说,1)Metis利用两种离散语音表示:从语音自监督学习(SSL)特征派生的SSL令牌和直接从波形量化的声学令牌。2)Metis在SSL令牌上进行遮罩生成预训练,利用30万小时的多样语音数据,无需任何额外条件。3)通过特定任务的调整,Metis可以在使用有限的数据和可训练参数的情况下,有效地适应各种语音生成任务,同时支持多模式输入。实验表明,Metis可以作为统一的语音生成基础模型:即使在少于20M的可训练参数或仅使用300倍的训练数据的情况下,Metis在五个语音生成任务上的表现也超过了最先进的特定任务或多任务系统,包括零样本文本到语音、语音转换、目标说话人提取、语音增强和唇到语音。音频样本可在https://metis-demo.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
Metis是一个统一的语音生成基础模型,采用预训练和微调的模式。它利用大规模无标签语音数据进行预训练,采用掩码生成建模,并可以适应多种语音生成任务。Metis使用两种离散语音表示:SSL令牌和直接从波形量化的声学令牌。实验表明,Metis在五个语音生成任务上的表现优于最新的任务特定或多任务系统,包括零样本文本到语音、语音转换、目标说话人提取、语音增强和唇到语音等。
Key Takeaways:
- Metis是一个统一的语音生成基础模型,有别于之前的任务特定或多任务模型。
- Metis采用了预训练和微调的模式,可以更好地适应多种语音生成任务。
- Metis利用大规模无标签语音数据进行预训练,并采用掩码生成建模。
- Metis使用两种离散语音表示:SSL令牌和直接从波形量化的声学令牌。
- Metis可以在有限的数据和参数条件下,实现高效的适应各种语音生成任务,并支持多模态输入。
- 实验表明,Metis在多个语音生成任务上的表现优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图

GenSE: Generative Speech Enhancement via Language Models using Hierarchical Modeling
Authors:Jixun Yao, Hexin Liu, Chen Chen, Yuchen Hu, EngSiong Chng, Lei Xie
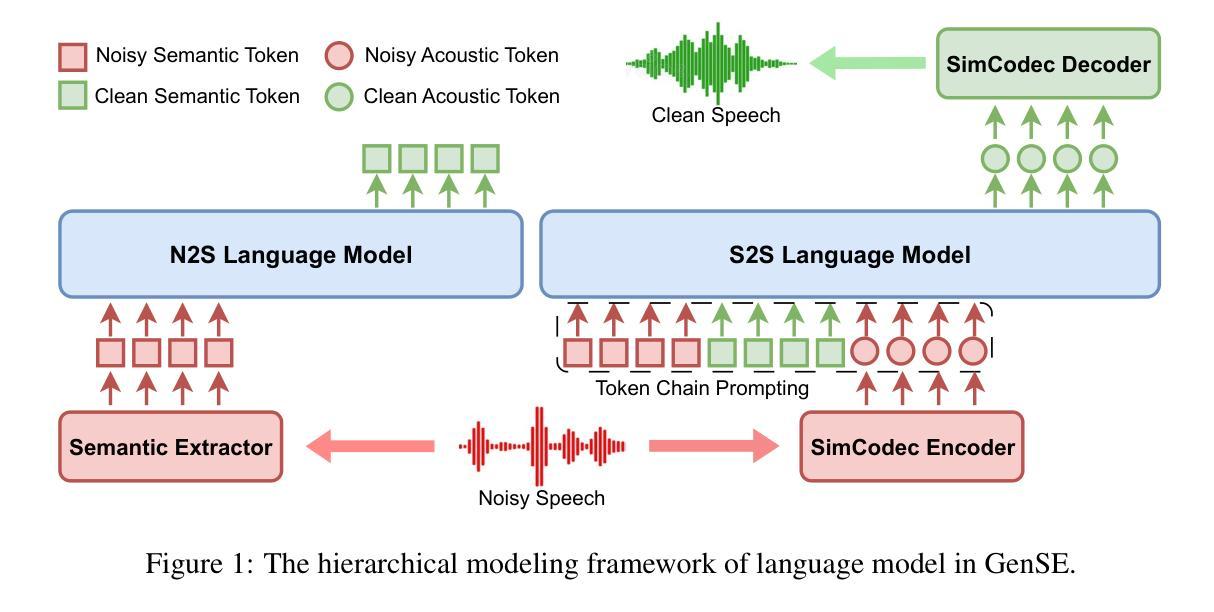
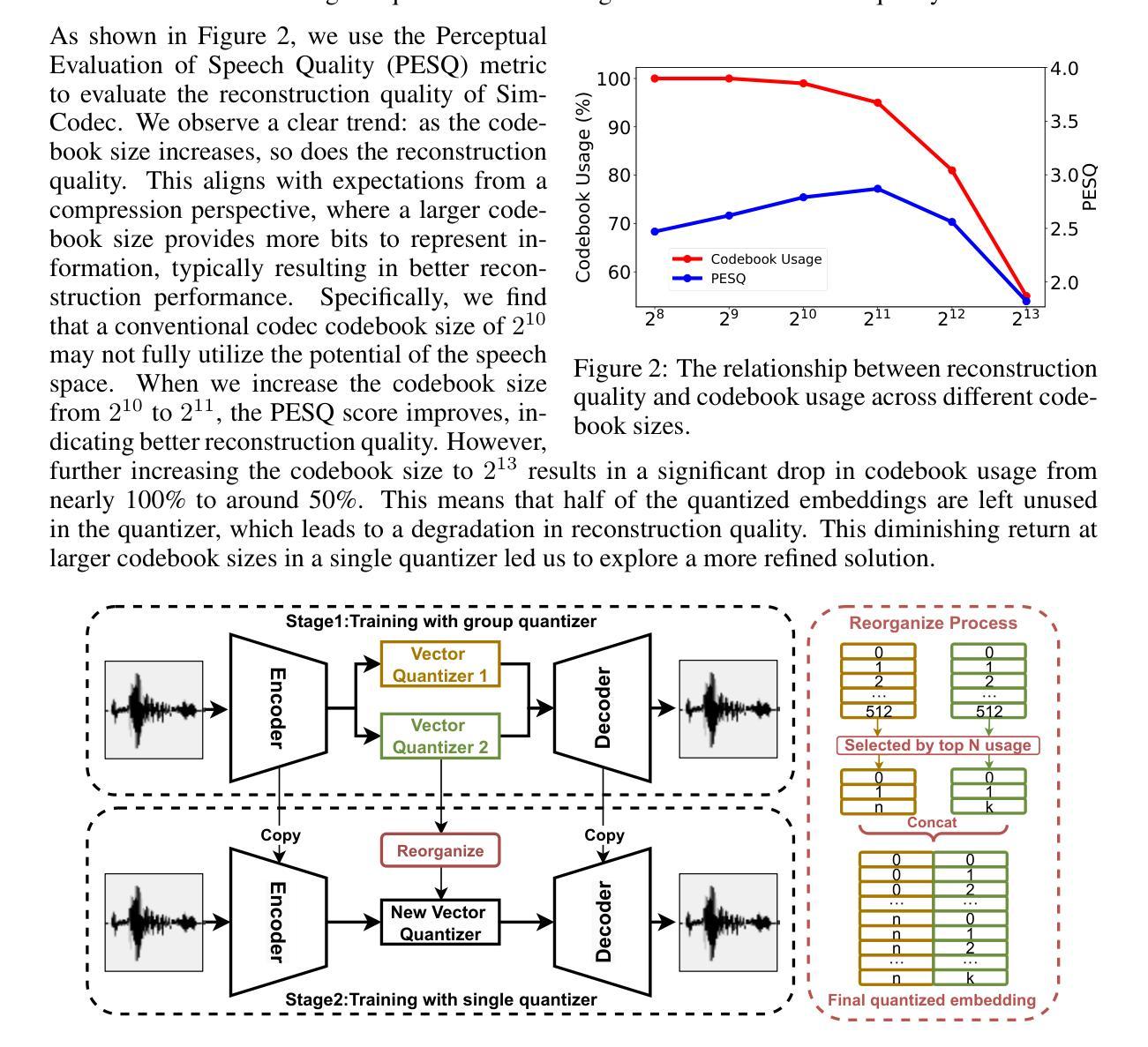
Semantic information refers to the meaning conveyed through words, phrases, and contextual relationships within a given linguistic structure. Humans can leverage semantic information, such as familiar linguistic patterns and contextual cues, to reconstruct incomplete or masked speech signals in noisy environments. However, existing speech enhancement (SE) approaches often overlook the rich semantic information embedded in speech, which is crucial for improving intelligibility, speaker consistency, and overall quality of enhanced speech signals. To enrich the SE model with semantic information, we employ language models as an efficient semantic learner and propose a comprehensive framework tailored for language model-based speech enhancement, called \textit{GenSE}. Specifically, we approach SE as a conditional language modeling task rather than a continuous signal regression problem defined in existing works. This is achieved by tokenizing speech signals into semantic tokens using a pre-trained self-supervised model and into acoustic tokens using a custom-designed single-quantizer neural codec model. To improve the stability of language model predictions, we propose a hierarchical modeling method that decouples the generation of clean semantic tokens and clean acoustic tokens into two distinct stages. Moreover, we introduce a token chain prompting mechanism during the acoustic token generation stage to ensure timbre consistency throughout the speech enhancement process. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art SE systems in terms of speech quality and generalization capability.
语义信息是指通过给定语言结构中的单词、短语和上下文关系所传达的意义。人类可以利用语义信息,如熟悉的语言模式和上下文线索,来重建嘈杂环境中的不完整或遮蔽的语音信号。然而,现有的语音增强(SE)方法往往忽视了嵌入在语音中的丰富语义信息,这对于提高语音的清晰度、说话人的连贯性和增强语音信号的整体质量至关重要。为了丰富SE模型的语义信息,我们采用语言模型作为有效的语义学习者,并针对基于语言模型的语音增强提出了一个全面的框架,称为GenSE。具体来说,我们将语音增强视为条件语言建模任务,而不是现有工作中定义的连续信号回归问题。这是通过预训练的自我监督模型将语音信号标记为语义标记和自定义的单量化神经网络编码模型标记为声学标记来实现的。为了提高语言模型预测的稳定性,我们提出了一种分层建模方法,将干净语义标记和干净声学标记的产生分为两个阶段。此外,在声学标记生成阶段引入了一种标记链提示机制,以确保在语音增强过程中音色保持一致。在基准数据集上的实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在语音质量和泛化能力方面优于最先进的SE系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary:
语义信息通过词语、短语和语境关系在给定语言结构中传达意义。人类可以利用语义信息,如熟悉的语言模式和语境线索,来重建嘈杂环境中的不完整或遮蔽的语音信号。现有的语音增强方法常常忽视语音中嵌入的丰富语义信息,这对于提高语音清晰度、说话者一致性和增强语音信号的整体质量至关重要。为了丰富语音增强模型中的语义信息,我们采用语言模型作为有效的语义学习者,并提出了一种针对语言模型为基础的语音增强定制框架,称为GenSE。通过将语音信号标记为语义标记和声音标记,并将其视为条件语言建模任务,我们的方法改进了现有工作中的连续信号回归问题。实验结果表明,与最先进的语音增强系统相比,我们的方法在提高语音质量和泛化能力方面表现出优势。
Key Takeaways:
- 语义信息对于在嘈杂环境中重建不完整或遮蔽的语音信号至关重要。
- 现有语音增强方法忽略了语义信息的重要性。
- 提出了一种新的基于语言模型的语音增强框架GenSE。
- 将语音增强视为条件语言建模任务,而非连续信号回归问题。
- 通过将语音信号标记为语义标记和声音标记来处理语音信号。
- 采用层次建模方法,将干净语义标记和干净声音标记的生成分为两个阶段,以提高语言模型预测的稳定性。
- 引入令牌链提示机制,确保在语音增强过程中音色一致性。
点此查看论文截图

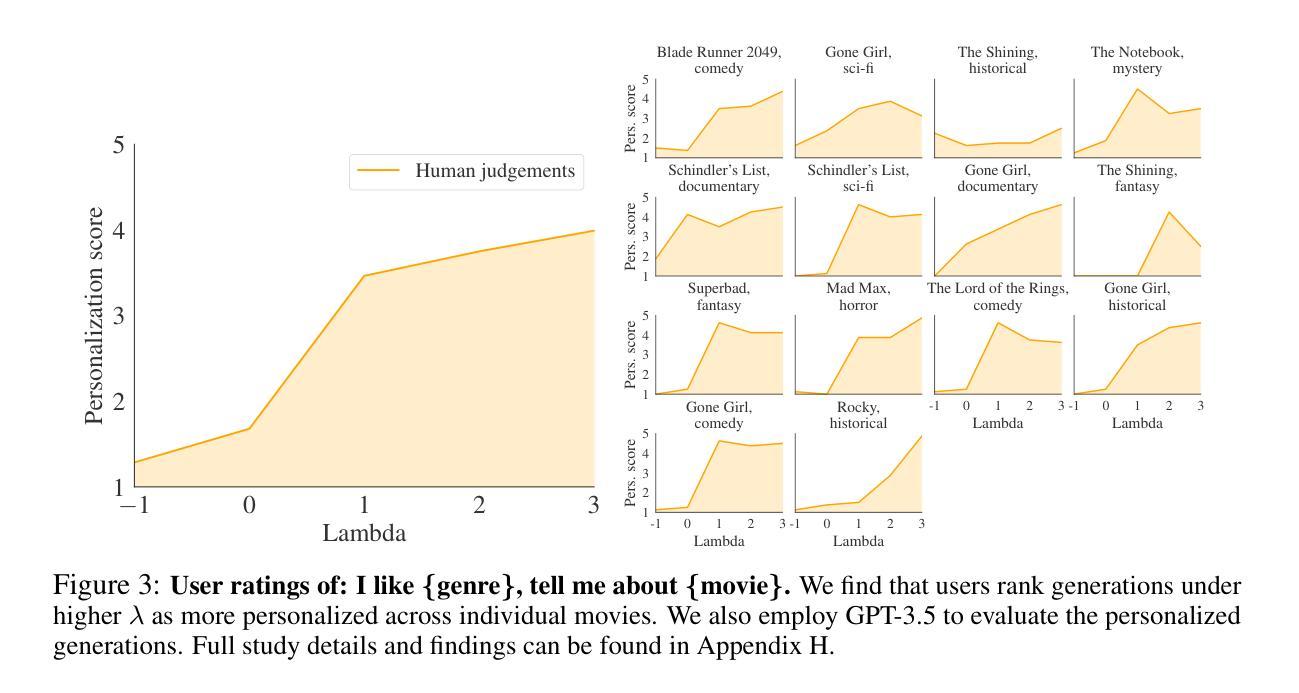
CoS: Enhancing Personalization and Mitigating Bias with Context Steering
Authors:Jerry Zhi-Yang He, Sashrika Pandey, Mariah L. Schrum, Anca Dragan
When querying a large language model (LLM), the context, i.e. personal, demographic, and cultural information specific to an end-user, can significantly shape the response of the LLM. For example, asking the model to explain Newton’s second law with the context “I am a toddler” yields a different answer compared to the context “I am a physics professor.” Proper usage of the context enables the LLM to generate personalized responses, whereas inappropriate contextual influence can lead to stereotypical and potentially harmful generations (e.g. associating “female” with “housekeeper”). In practice, striking the right balance when leveraging context is a nuanced and challenging problem that is often situation-dependent. One common approach to address this challenge is to fine-tune LLMs on contextually appropriate responses. However, this approach is expensive, time-consuming, and not controllable for end-users in different situations. In this work, we propose Context Steering (CoS) - a simple training-free method that can be easily applied to autoregressive LLMs at inference time. By measuring the contextual influence in terms of token prediction likelihood and modulating it, our method enables practitioners to determine the appropriate level of contextual influence based on their specific use case and end-user base. We showcase a variety of applications of CoS including amplifying the contextual influence to achieve better personalization and mitigating unwanted influence for reducing model bias. In addition, we show that we can combine CoS with Bayesian Inference to quantify the extent of hate speech on the internet. We demonstrate the effectiveness of CoS on state-of-the-art LLMs and benchmarks.
在查询大型语言模型(LLM)时,上下文,即针对最终用户的个人、人口统计和文化信息,可以显著地塑造LLM的响应。例如,要求模型以“我是一个学步儿童”的上下文来解释牛顿的第二定律,与以“我是一名物理教授”的上下文得到的答案不同。正确地使用上下文使LLM能够生成个性化的响应,而不当的上下文影响可能导致刻板印象和潜在的有害生成(例如,将“女性”与“家庭主妇”联系在一起)。在实践中,在利用上下文时找到正确的平衡是一个微妙而具有挑战性的问题,通常需要根据具体情况而定。一种解决此挑战的常见方法是微调LLM以产生适当的上下文响应。然而,这种方法既昂贵又耗时,对于不同情境下的最终用户来说并不可控。在这项工作中,我们提出了Context Steering(CoS)——一种无需训练的简单方法,可以轻松应用于推断时的大型语言模型。通过测量上下文影响的token预测概率并进行调节,我们的方法使从业者能够根据他们的特定用例和最终用户基础来确定适当的上下文影响水平。我们展示了CoS的各种应用,包括增强上下文影响以实现更好的个性化和缓解不必要的影响以减少模型偏见。此外,我们展示了我们可以将CoS与贝叶斯推理相结合,以量化网络上仇恨言论的程度。我们在先进的大型语言模型和基准测试上展示了CoS的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在大规模语言模型(LLM)查询中,上下文信息(如个人、人口统计和文化信息)对模型的响应具有显著影响。适当地使用上下文可实现个性化响应,而不当的上下文影响可能导致刻板印象和潜在有害生成。本文提出了一种简单、无需训练的方法——Context Steering(CoS),可在推理时间轻松应用于自动回归LLM。通过测量上下文影响的令牌预测概率并进行调整,CoS使从业者能够根据特定用例和最终用户基础确定适当的上下文影响程度。本文展示了CoS在各种应用中的效果,包括增强上下文影响以实现更好的个性化和减少不良影响以减轻模型偏见。此外,我们还展示了可以将CoS与贝叶斯推理相结合,以量化互联网上的仇恨言论程度。在先进的LLM和基准测试中,我们证明了CoS的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 上下文信息在大规模语言模型(LLM)查询中起着重要作用,能够显著影响模型的响应。
- 适当的上下文使用可实现个性化响应,但不当的上下文可能导致刻板印象和潜在有害生成。
- Context Steering(CoS)是一种简单、无需训练的推理时间方法,可轻松应用于自动回归LLM。
- CoS通过测量和调整上下文影响的令牌预测概率,使从业者能够根据特定情境和最终用户确定适当的上下文影响程度。
- CoS在多种应用中表现出效果,包括增强上下文影响以实现个性化,减少不良影响以减轻模型偏见。
- CoS可与贝叶斯推理相结合,以量化互联网上的仇恨言论程度。
点此查看论文截图