⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-08 更新
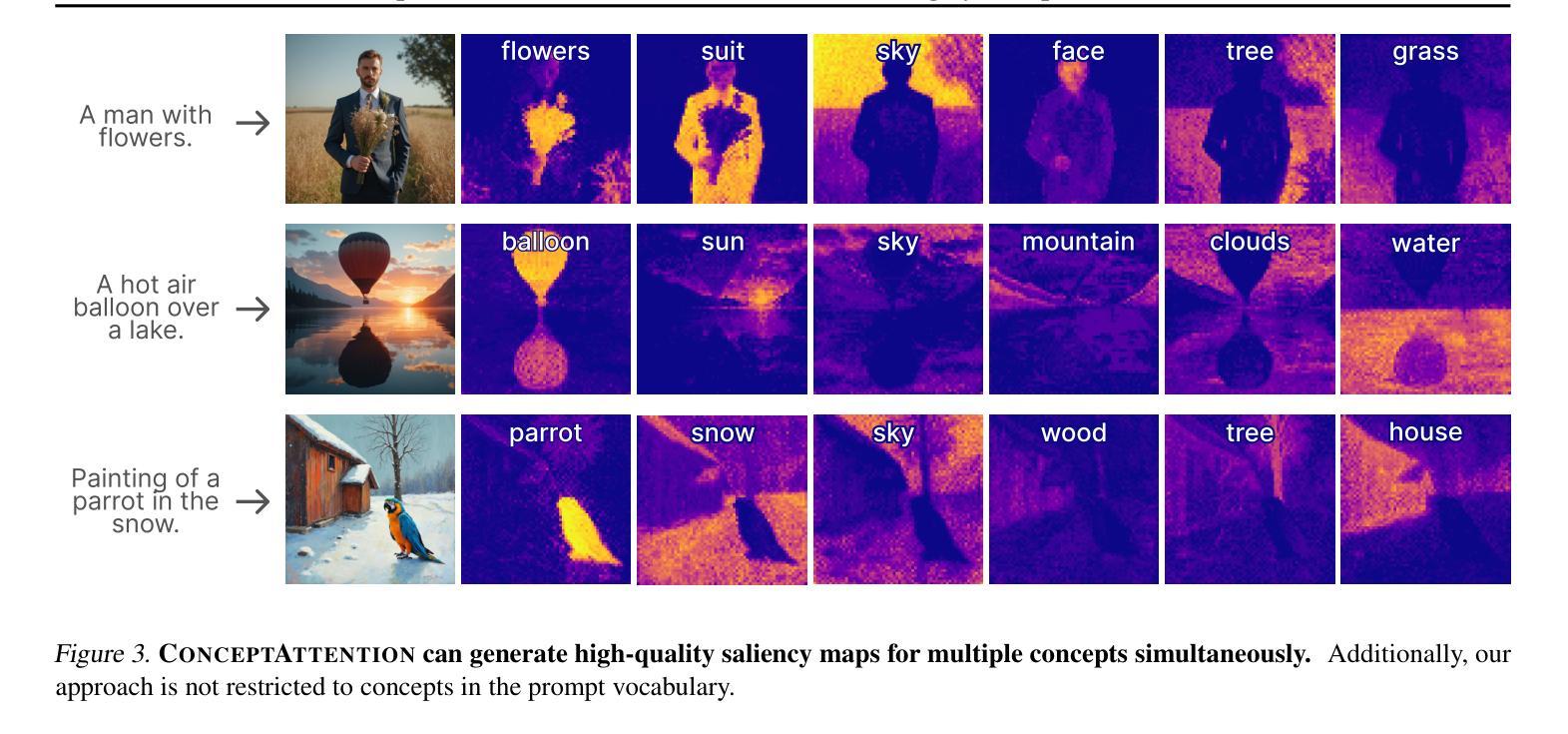
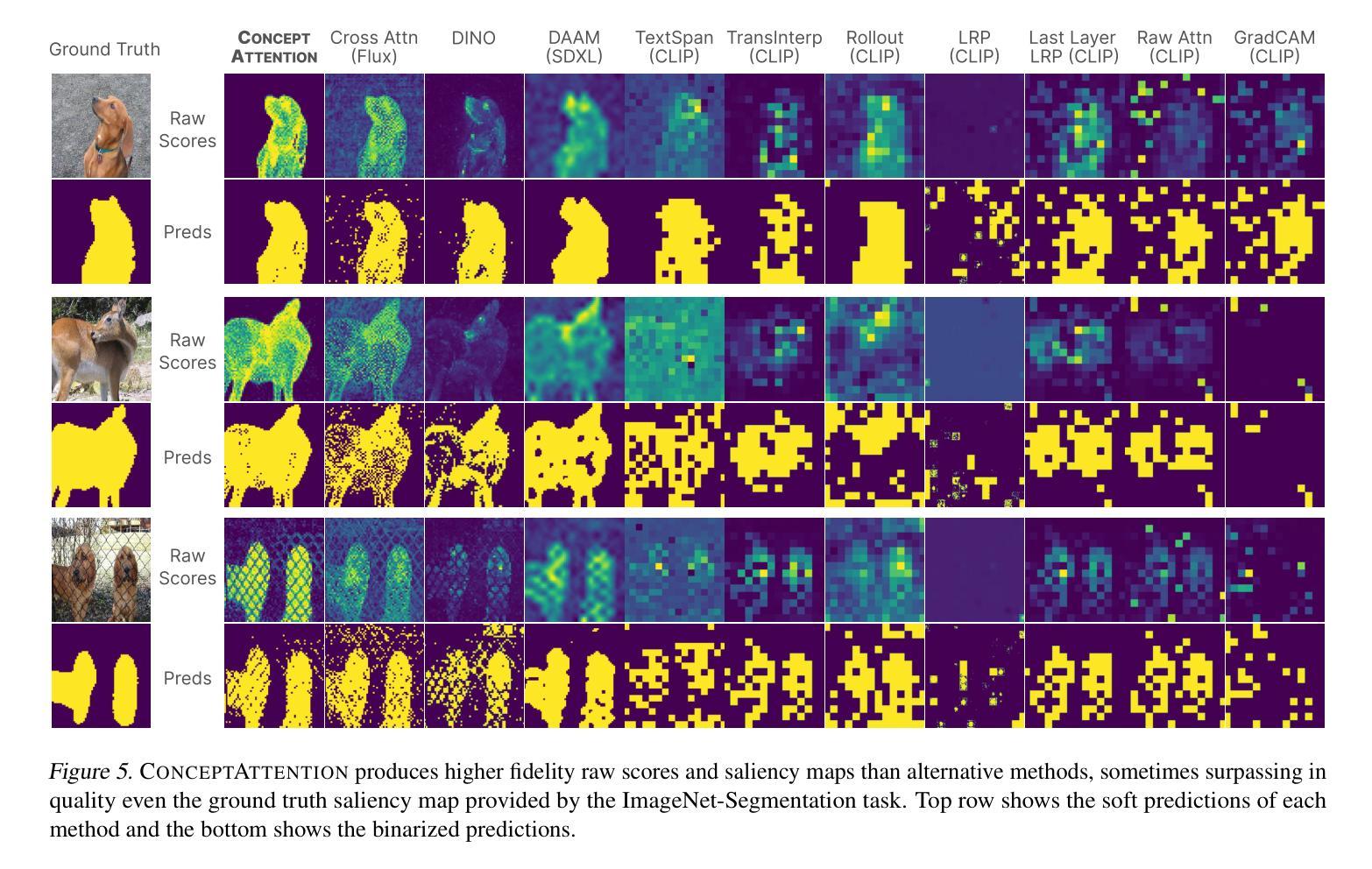
ConceptAttention: Diffusion Transformers Learn Highly Interpretable Features
Authors:Alec Helbling, Tuna Han Salih Meral, Ben Hoover, Pinar Yanardag, Duen Horng Chau
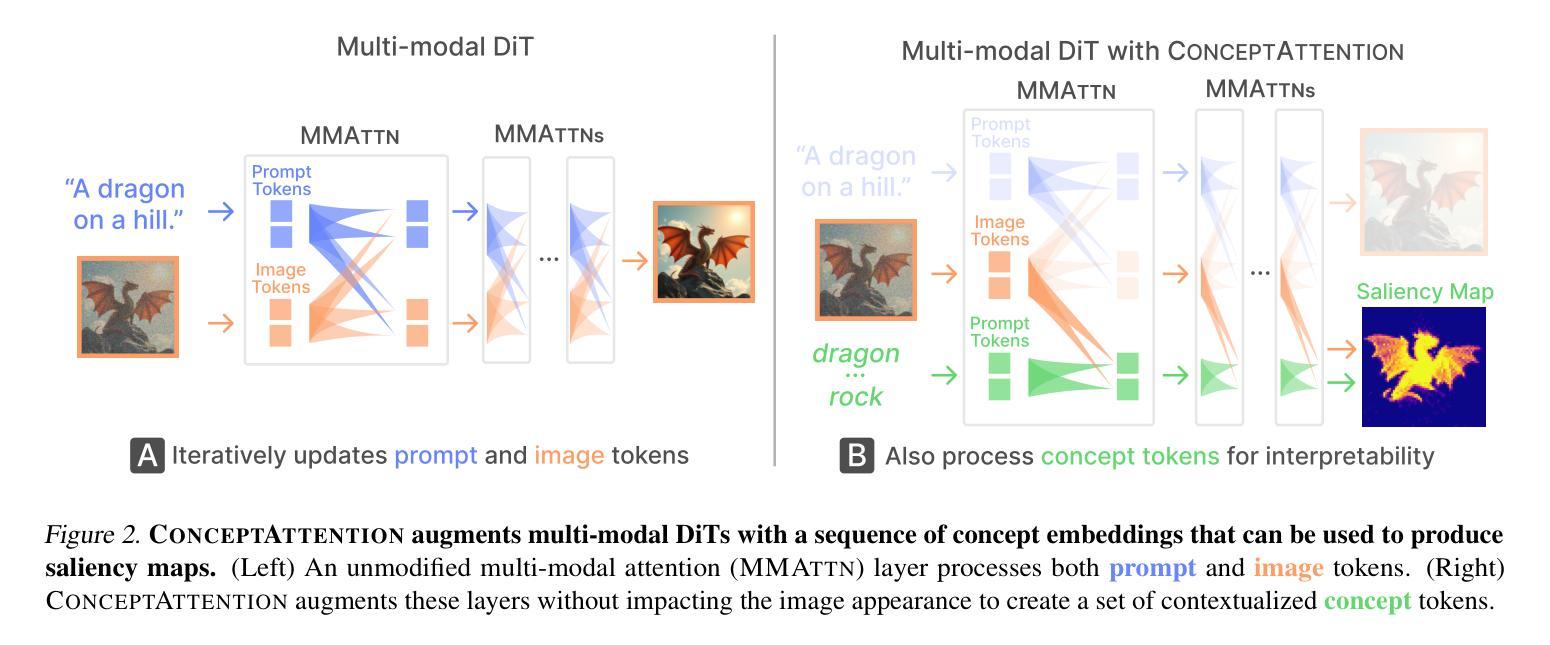
Do the rich representations of multi-modal diffusion transformers (DiTs) exhibit unique properties that enhance their interpretability? We introduce ConceptAttention, a novel method that leverages the expressive power of DiT attention layers to generate high-quality saliency maps that precisely locate textual concepts within images. Without requiring additional training, ConceptAttention repurposes the parameters of DiT attention layers to produce highly contextualized concept embeddings, contributing the major discovery that performing linear projections in the output space of DiT attention layers yields significantly sharper saliency maps compared to commonly used cross-attention mechanisms. Remarkably, ConceptAttention even achieves state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot image segmentation benchmarks, outperforming 11 other zero-shot interpretability methods on the ImageNet-Segmentation dataset and on a single-class subset of PascalVOC. Our work contributes the first evidence that the representations of multi-modal DiT models like Flux are highly transferable to vision tasks like segmentation, even outperforming multi-modal foundation models like CLIP.
多模态扩散转换器(DiTs)的丰富表示是否具有独特的属性,可以增强其可解释性?我们引入了一种名为ConceptAttention的新方法,它利用DiT注意力层的表达能力来生成精确定位图像中文本概念的高质量显著性图。ConceptAttention不需要额外的训练,它能够重新利用DiT注意力层的参数来产生高度上下文化的概念嵌入,主要发现是在DiT注意力层的输出空间进行线性投影,与常用的交叉注意力机制相比,能够产生更为清晰的显著性图。值得注意的是,ConceptAttention甚至在零样本图像分割基准测试上实现了最先进的性能,在ImageNet-Segmentation数据集以及PascalVOC的单类子集上超越了其他11种零样本可解释性方法。我们的工作首次证明,多模态DiT模型(如Flux)的表示高度可转移到分割等视觉任务上,甚至超越了多模态基础模型(如CLIP)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为ConceptAttention的新方法,利用多模态扩散变压器(DiT)的表达能力生成高质量的显著性地图,无需额外训练即可精确定位图像中的文本概念。研究发现,在DiT注意力层的输出空间进行线性投影,能产生比其他常用交叉注意力机制更清晰锐利的显著性地图。此外,ConceptAttention在零样本图像分割基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,在ImageNet-Segmentation数据集和PascalVOC的单类子集上超越了其他11种零样本解释方法。本文首次证明多模态DiT模型(如Flux)的表征高度适用于分割等视觉任务,甚至超越了多模态基础模型如CLIP。
Key Takeaways
- ConceptAttention利用DiT注意力层的丰富表示生成精确的定位图像中文本概念的显著性地图。
- 通过在DiT注意力层的输出空间进行线性投影,产生更清晰锐利的显著性地图。
- ConceptAttention在零样本图像分割方面表现出卓越性能,优于其他方法。
- ConceptAttention在ImageNet-Segmentation和PascalVOC数据集上实现了先进的结果。
- 多模态DiT模型的表征(如Flux)高度适用于视觉任务,如分割。
- ConceptAttention方法无需额外的训练。
点此查看论文截图


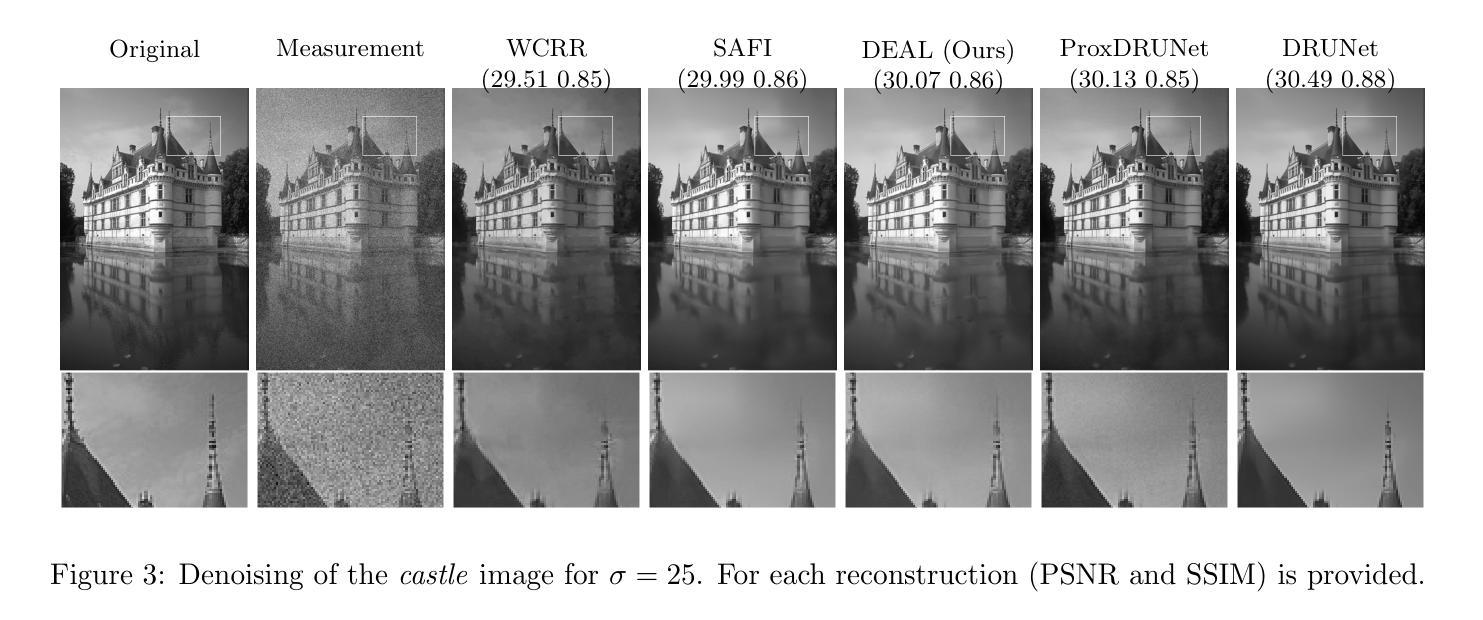
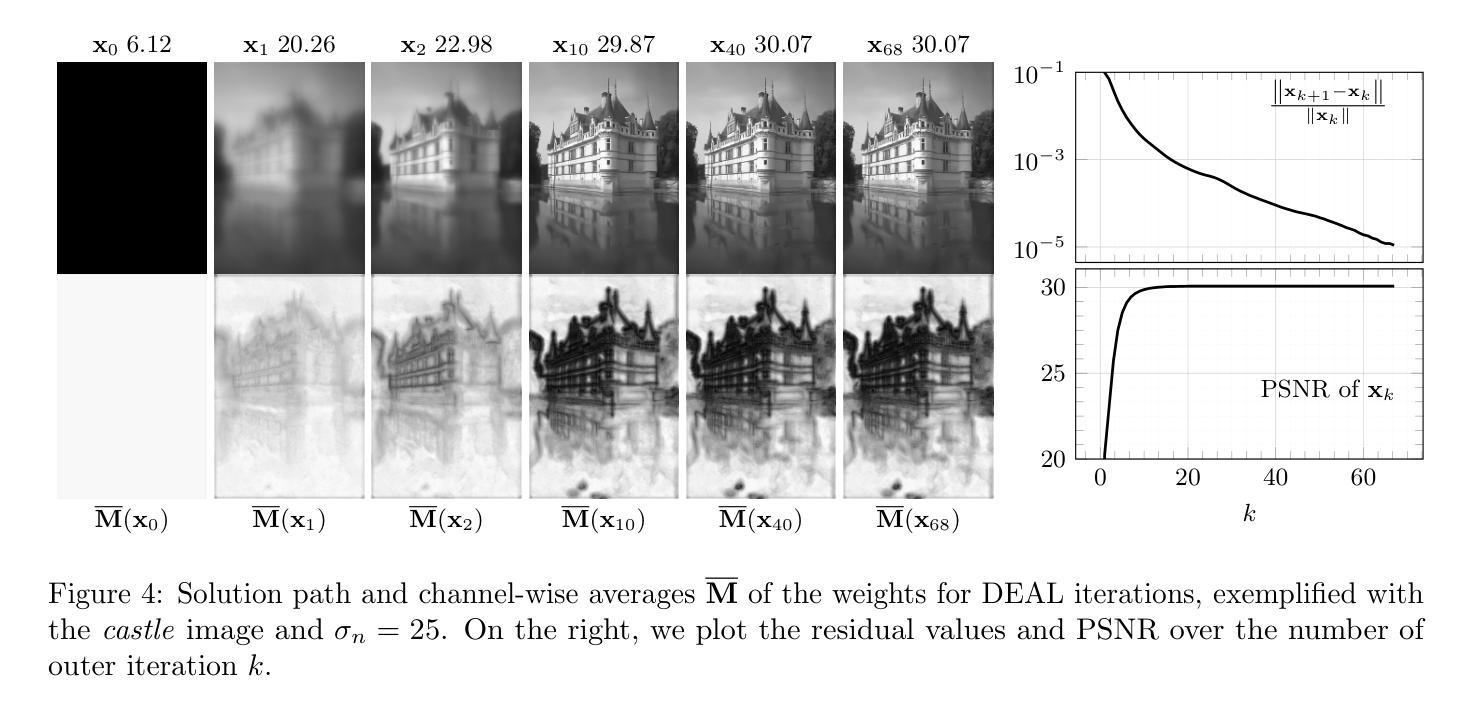
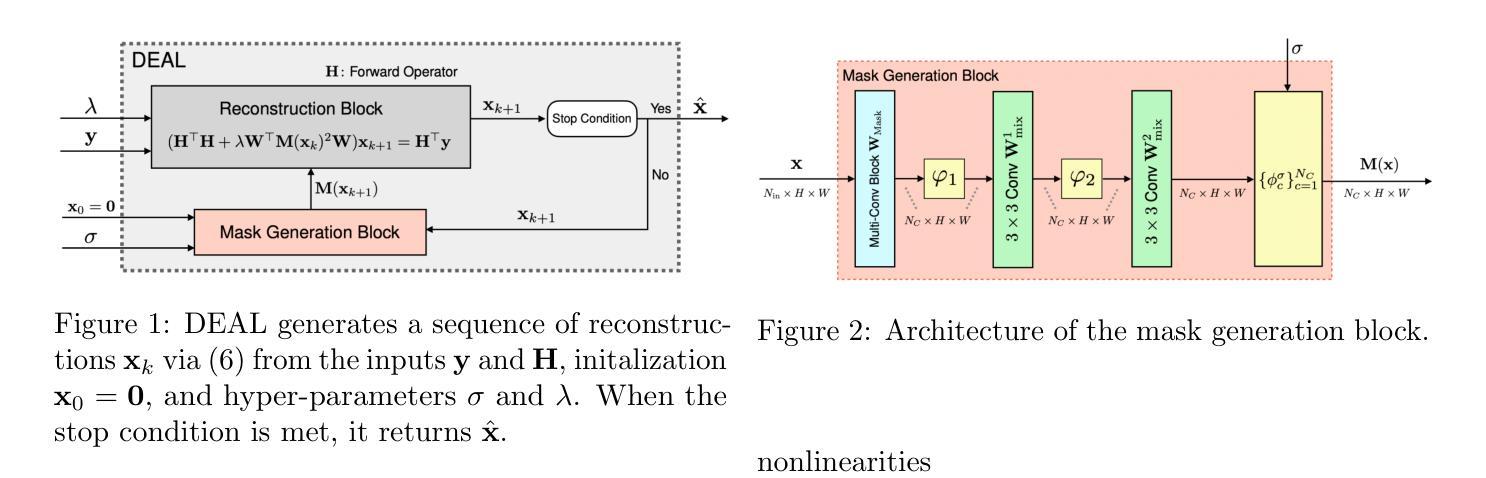
DEALing with Image Reconstruction: Deep Attentive Least Squares
Authors:Mehrsa Pourya, Erich Kobler, Michael Unser, Sebastian Neumayer
State-of-the-art image reconstruction often relies on complex, highly parameterized deep architectures. We propose an alternative: a data-driven reconstruction method inspired by the classic Tikhonov regularization. Our approach iteratively refines intermediate reconstructions by solving a sequence of quadratic problems. These updates have two key components: (i) learned filters to extract salient image features, and (ii) an attention mechanism that locally adjusts the penalty of filter responses. Our method achieves performance on par with leading plug-and-play and learned regularizer approaches while offering interpretability, robustness, and convergent behavior. In effect, we bridge traditional regularization and deep learning with a principled reconstruction approach.
当前先进的图像重建大多依赖于复杂、高度参数化的深度架构。我们提出了一种替代方法:受经典Tikhonov正则化启发的数据驱动重建方法。我们的方法通过解决一系列二次问题来迭代优化中间重建。这些更新包括两个关键组成部分:(i)学习滤波器以提取图像的关键特征;(ii)一种注意机制,可局部调整滤波器响应的惩罚力度。我们的方法与领先的即插即用和学习的正则化方法性能相当,同时提供了可解释性、稳健性和收敛行为。实质上,我们通过一种有原则的重建方法,架起了传统正则化和深度学习之间的桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于数据驱动、受Tikhonov正则化启发的图像重建方法。该方法通过求解一系列二次问题来迭代优化中间重建结果,包括两个关键组成部分:学习滤波器以提取图像特征以及注意力机制,可局部调整滤波器的响应惩罚。该方法实现了与即插即用和学习的正则化方法相当的性能,同时具备可解释性、鲁棒性和收敛性。本文在传统正则化与深度学习之间架起了一座有原则的重建桥梁。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种数据驱动的图像重建方法,受到Tikhonov正则化的启发。
- 方法通过迭代优化中间重建结果,求解一系列二次问题。
- 包括两个关键组成部分:学习滤波器提取图像特征和使用注意力机制局部调整滤波器的响应惩罚。
- 该方法实现了与现有主流方法相当的性能。
- 该方法具备可解释性、鲁棒性和收敛性。
- 本文结合了传统正则化技术和深度学习,为图像重建提供了一种有原则的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图




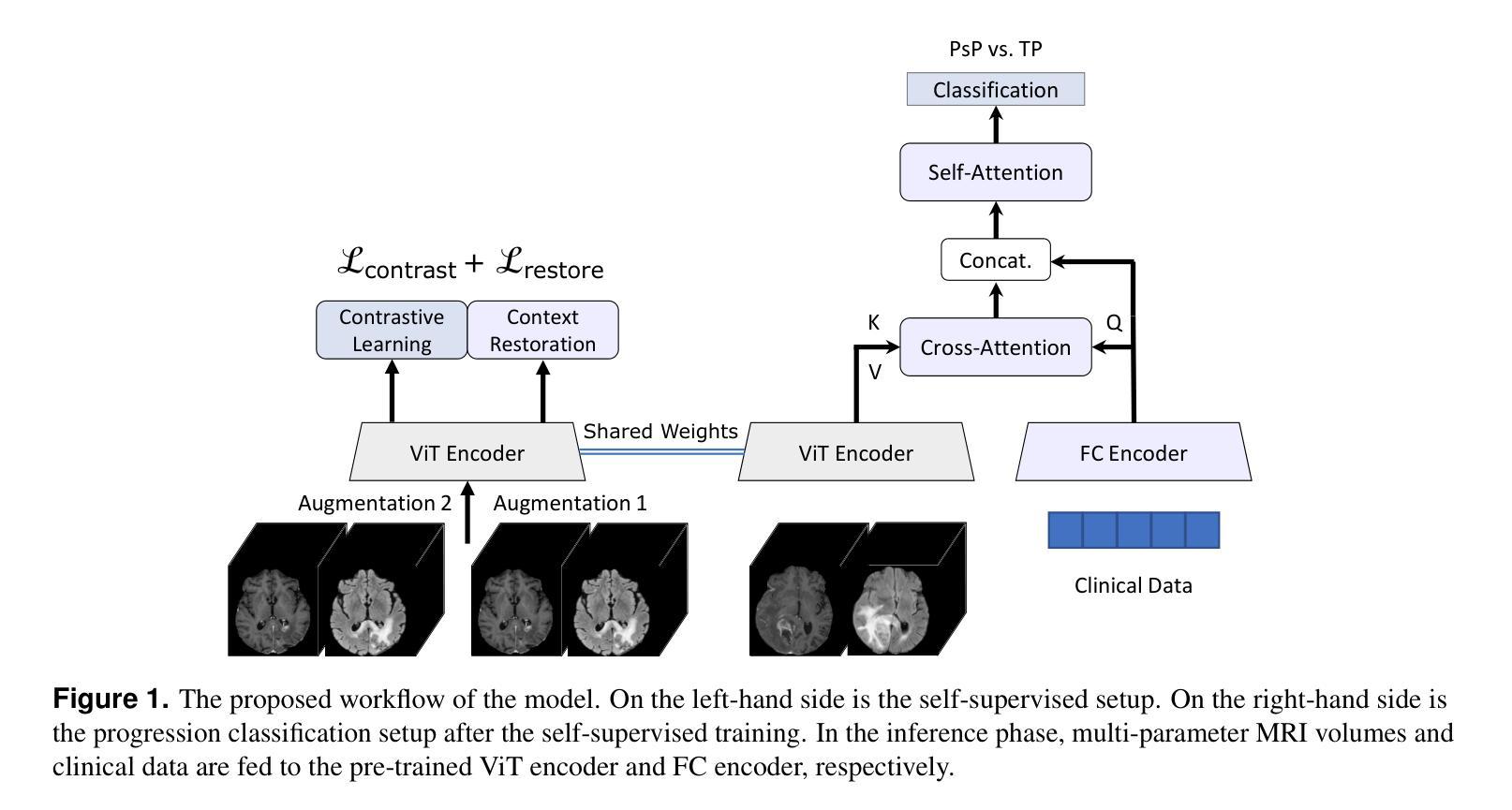
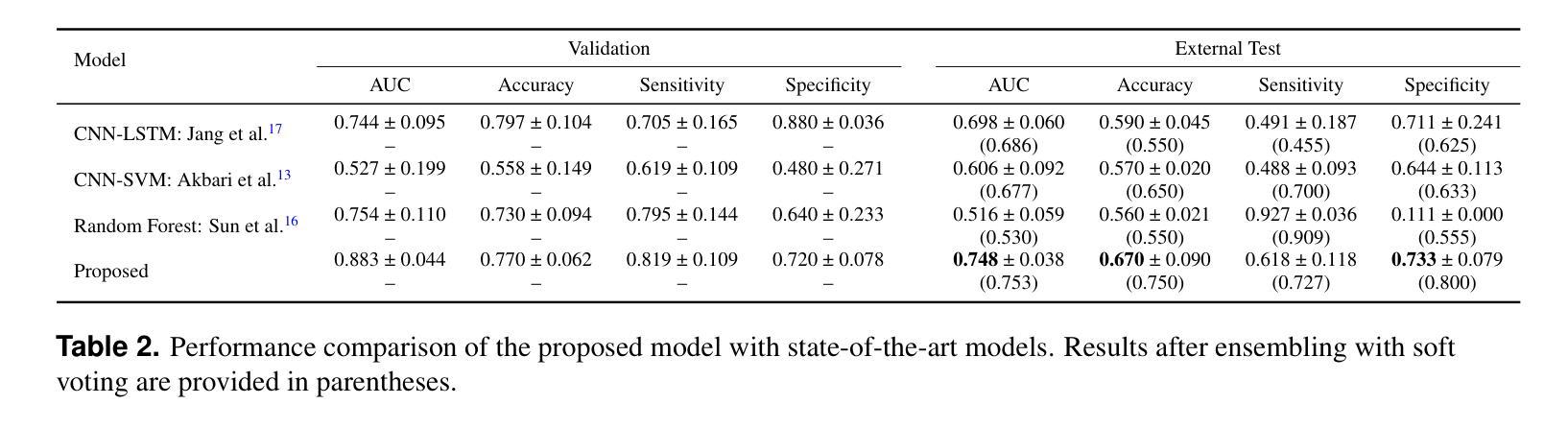
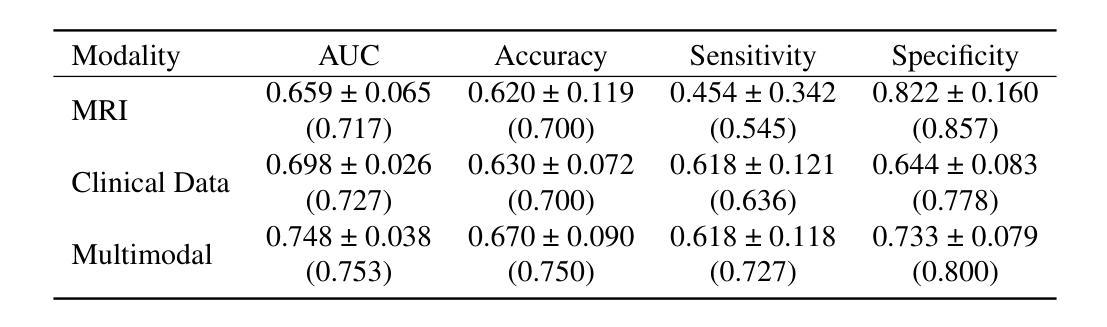
A Self-supervised Multimodal Deep Learning Approach to Differentiate Post-radiotherapy Progression from Pseudoprogression in Glioblastoma
Authors:Ahmed Gomaa, Yixing Huang, Pluvio Stephan, Katharina Breininger, Benjamin Frey, Arnd Dörfler, Oliver Schnell, Daniel Delev, Roland Coras, Charlotte Schmitter, Jenny Stritzelberger, Sabine Semrau, Andreas Maier, Siming Bayer, Stephan Schönecker, Dieter H Heiland, Peter Hau, Udo S. Gaipl, Christoph Bert, Rainer Fietkau, Manuel A. Schmidt, Florian Putz
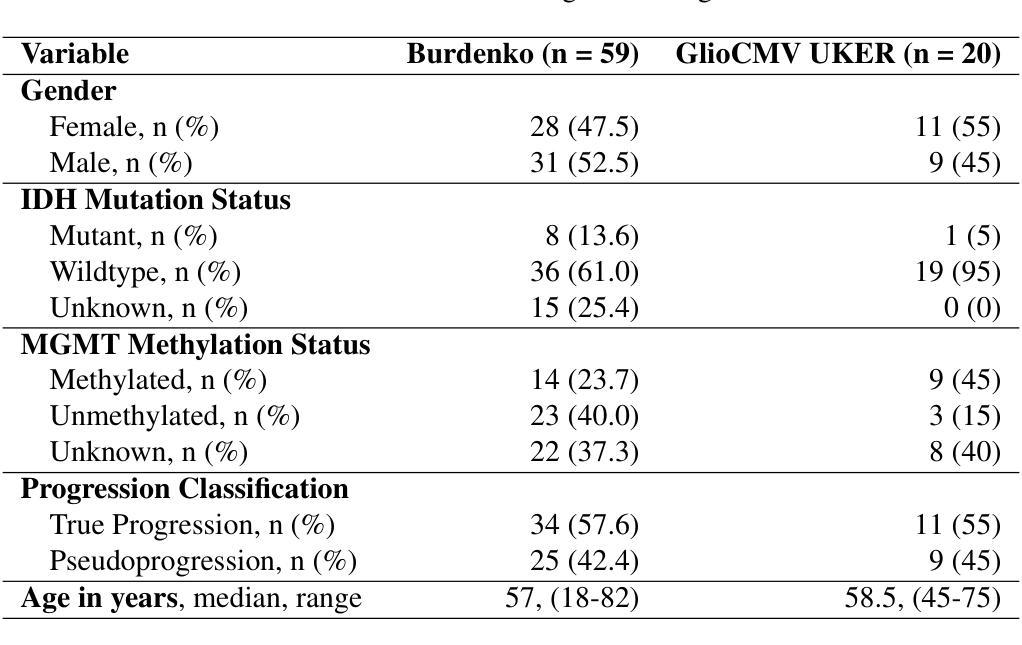
Accurate differentiation of pseudoprogression (PsP) from True Progression (TP) following radiotherapy (RT) in glioblastoma (GBM) patients is crucial for optimal treatment planning. However, this task remains challenging due to the overlapping imaging characteristics of PsP and TP. This study therefore proposes a multimodal deep-learning approach utilizing complementary information from routine anatomical MR images, clinical parameters, and RT treatment planning information for improved predictive accuracy. The approach utilizes a self-supervised Vision Transformer (ViT) to encode multi-sequence MR brain volumes to effectively capture both global and local context from the high dimensional input. The encoder is trained in a self-supervised upstream task on unlabeled glioma MRI datasets from the open BraTS2021, UPenn-GBM, and UCSF-PDGM datasets to generate compact, clinically relevant representations from FLAIR and T1 post-contrast sequences. These encoded MR inputs are then integrated with clinical data and RT treatment planning information through guided cross-modal attention, improving progression classification accuracy. This work was developed using two datasets from different centers: the Burdenko Glioblastoma Progression Dataset (n = 59) for training and validation, and the GlioCMV progression dataset from the University Hospital Erlangen (UKER) (n = 20) for testing. The proposed method achieved an AUC of 75.3%, outperforming the current state-of-the-art data-driven approaches. Importantly, the proposed approach relies on readily available anatomical MRI sequences, clinical data, and RT treatment planning information, enhancing its clinical feasibility. The proposed approach addresses the challenge of limited data availability for PsP and TP differentiation and could allow for improved clinical decision-making and optimized treatment plans for GBM patients.
在胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)患者中,放射治疗(RT)后的假性进展(PsP)与真实进展(TP)的准确区分对于制定最佳治疗方案至关重要。然而,由于PsP和TP的成像特征重叠,这项任务仍然具有挑战性。因此,本研究提出了一种多模态深度学习的方法,该方法利用常规解剖MRI图像、临床参数和RT治疗计划信息的互补信息,以提高预测准确性。该方法使用自监督的Vision Transformer(ViT)对多序列MR脑体积进行编码,以有效地捕获高维输入的全局和局部上下文。编码器在自监督的上游任务上接受训练,在开放的BraTS2021、UPenn-GBM和UCSF-PDGM数据集的无标签胶质母细胞瘤MRI数据集上生成紧凑且临床相关的表示,这些表示来自FLAIR和T1增强序列。然后,这些编码的MR输入与临床数据和RT治疗计划信息通过引导跨模态注意力进行整合,提高了进展分类的准确性。这项工作使用了来自两个不同中心的两个数据集:Burdenko胶质母细胞瘤进展数据集(n=5.0用于训练和验证),以及来自埃朗根大学医院(UKER)的GlioCMV进展数据集(n=20用于测试)。所提出的方法达到了75.3%的AUC,优于当前最先进的基于数据的方法。重要的是,所提出的方法依赖于可获得的解剖MRI序列、临床数据和RT治疗计划信息,增强了其临床可行性。所提出的方法解决了PsP和TP区分中数据可用性有限的挑战,并可能有助于改进胶质母细胞瘤患者的临床决策和优化的治疗方案。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
放疗后鉴别假性进展(PsP)与真实进展(TP)在胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)患者中的准确区分对于优化治疗方案至关重要。然而,由于PsP和TP的成像特征重叠,这一任务仍然具有挑战性。因此,本研究提出了一种多模态深度学习方法,该方法利用常规解剖MR图像、临床参数和RT治疗计划信息的互补信息,以提高预测准确性。该方法使用自监督的Vision Transformer(ViT)对多序列MR脑容积进行编码,以有效地捕获高维输入的全局和局部上下文。编码器在未经标记的胶质母细胞瘤MRI数据集(来自BraTS2021、UPenn-GBM和UCSF-PDGM数据集)上进行自监督上游任务训练,从FLAIR和T1增强序列生成紧凑、临床相关的表示。这些编码的MR输入然后与临床数据和RT治疗计划信息通过引导跨模态注意力进行整合,提高了进展分类的准确性。该研究使用了来自不同中心的两个数据集:Burdenko胶质母细胞瘤进展数据集(n=59)用于训练和验证,以及来自Erlangen大学医院(UKER)的GlioCMV进展数据集(n=20)用于测试。所提出的方法达到了75.3%的AUC,优于当前最先进的数据驱动方法。重要的是,该方法依赖于可获得的解剖MRI序列、临床数据和RT治疗计划信息,增强了其临床可行性。所提出的方法解决了PsP和TP鉴别中数据有限性的挑战,并可能有助于改进GBM患者的临床决策和优化治疗方案。
关键见解
- 区分胶质母细胞瘤患者放疗后的假性进展和真实进展对优化治疗方案至关重要。
- 当前鉴别任务面临挑战,因为假性进展和真实进展的成像特征重叠。
- 提出了一种多模态深度学习方法,结合常规解剖MR图像、临床参数和RT治疗计划信息,以提高预测准确性。
- 使用自监督的Vision Transformer(ViT)对多序列MR脑体积进行编码,捕捉全局和局部上下文。
- 方法在多个数据集上进行了训练和验证,包括Burdenko和GlioCMV数据集。
- 所提出的方法达到了75.3%的AUC,优于当前最先进的数据驱动方法。
点此查看论文截图

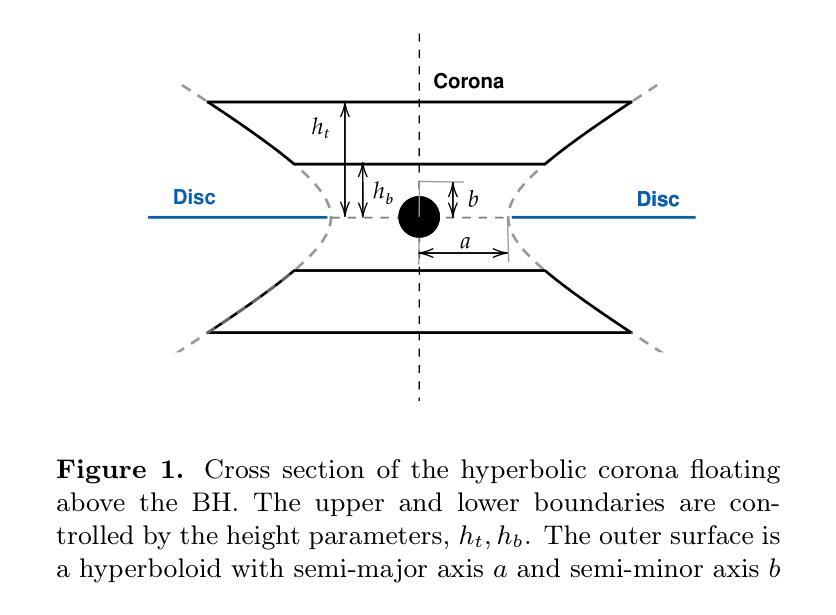
Modeling fast X-ray variability around an accreting black hole
Authors:Yejing Zhan, Bei You, Adam Ingram, Wenkang Jiang, Fayin Wang
X-ray inter-band time lags are observed during the outbursts of black hole X-ray binaries (BHXRBs). Timing analysis of fast variability in low Fourier frequency bands shows that high-energy photons lag behind low-energy photons, a phenomenon referred to as hard lag. Conversely, in high Fourier frequency bands, low-energy photons lag behind high-energy photons, known as soft lag. This frequency-dependent lag spectrum suggests that the lags arise from different physical processes. Notably, a trend has been observed wherein the lags shift towards shorter timescales during the rising hard state, indicating an evolution in the inner accretion flow. In this study, we simulate these inter-band lags by conducting Monte Carlo simulations of the rapid variability within the geometry of a jet base corona. We consider both inward propagating accretion rate fluctuations and reverberation (light crossing) delays in our simulations. We successfully reproduce both low-frequency hard lags and high-frequency soft lags in a self-consistent manner. We replicate the observed evolution of the frequency-dependent lag spectra by varying the geometrical scale of the corona and the viscous frequency of the disc. Finally, we discuss the potential of a spherical corona and emphasize that polarization observations from the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) and the enhanced X-ray Timing and Polarimetry mission (eXTP) will be crucial for distinguishing the corona’s geometry in future studies.
在黑洞X射线双星(BHXRBs)的爆发期间,观察到X射线波段之间的时间延迟。对低傅里叶频段快速变化的时序分析表明,高能光子落后于低能光子,这种现象被称为硬延迟。相反,在高傅里叶频段,低能光子落后于高能光子,被称为软延迟。这种与频率相关的延迟谱表明延迟来自于不同的物理过程。值得注意的是,已经观察到一种趋势,即延迟向较短的时间尺度转变,这在硬态上升期间表明内吸积流的演变。在本研究中,我们通过模拟喷流基冕几何结构内快速变化的蒙特卡罗模拟来研究这些波段间的延迟。我们在模拟中考虑了向内传播的吸积率波动和回声(光速穿越)延迟。我们成功地以一致的方式再现了低频硬延迟和高频软延迟。我们通过改变冕的几何尺度和盘的粘性频率来复制观察到的频率依赖延迟谱的演化。最后,我们讨论了球形冕的潜力,并强调成像X射线偏振仪(IXPE)和增强型X射线定时偏振任务(eXTP)的偏振观测对于未来研究中区分冕的几何形状将至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 9 figures, submitted to ApJ
Summary
本文探讨了黑洞X射线双星(BHXRBs)爆发期间的X射线跨波段时间延迟现象。研究通过对快速变异的时序分析发现,低能量光子在高能量光子之前到达,称为硬滞后现象;而在高傅立叶频率波段,则是高能量光子先于低能量光子到达,称为软滞后现象。通过蒙特卡洛模拟,成功再现了这种跨波段滞后现象,并讨论了球状冕的潜在可能性。未来研究中,成像X射线偏振探测器(IXPE)和增强型X射线定时偏振任务(eXTP)的偏振观测对于鉴别冕的几何形态至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 黑洞X射线双星(BHXRBs)爆发期间观察到X射线的跨波段时间延迟现象。
- 跨波段时间延迟表现出频率依赖性,反映不同的物理过程。
- 蒙特卡洛模拟成功再现了硬滞后和软滞后现象。
- 硬态上升期间的时间延迟向更短时间尺度转变,表明内吸积流的演化。
- 通过改变冕的几何尺度和磁盘的粘性频率,模拟了频率依赖的滞后光谱演化。
- 球状冕的潜在可能性被讨论。
点此查看论文截图

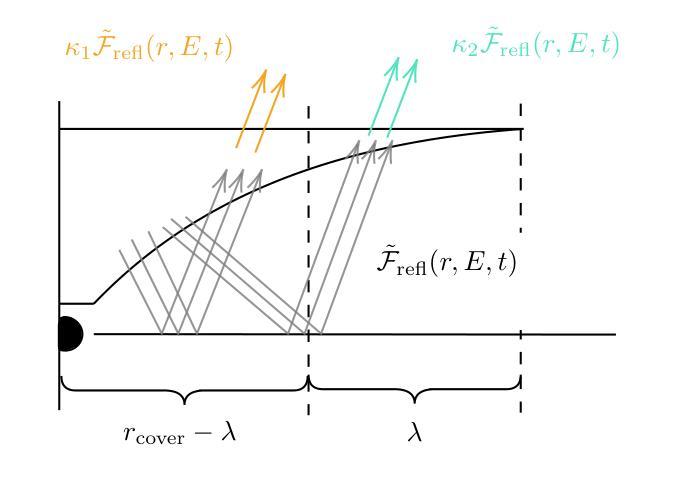
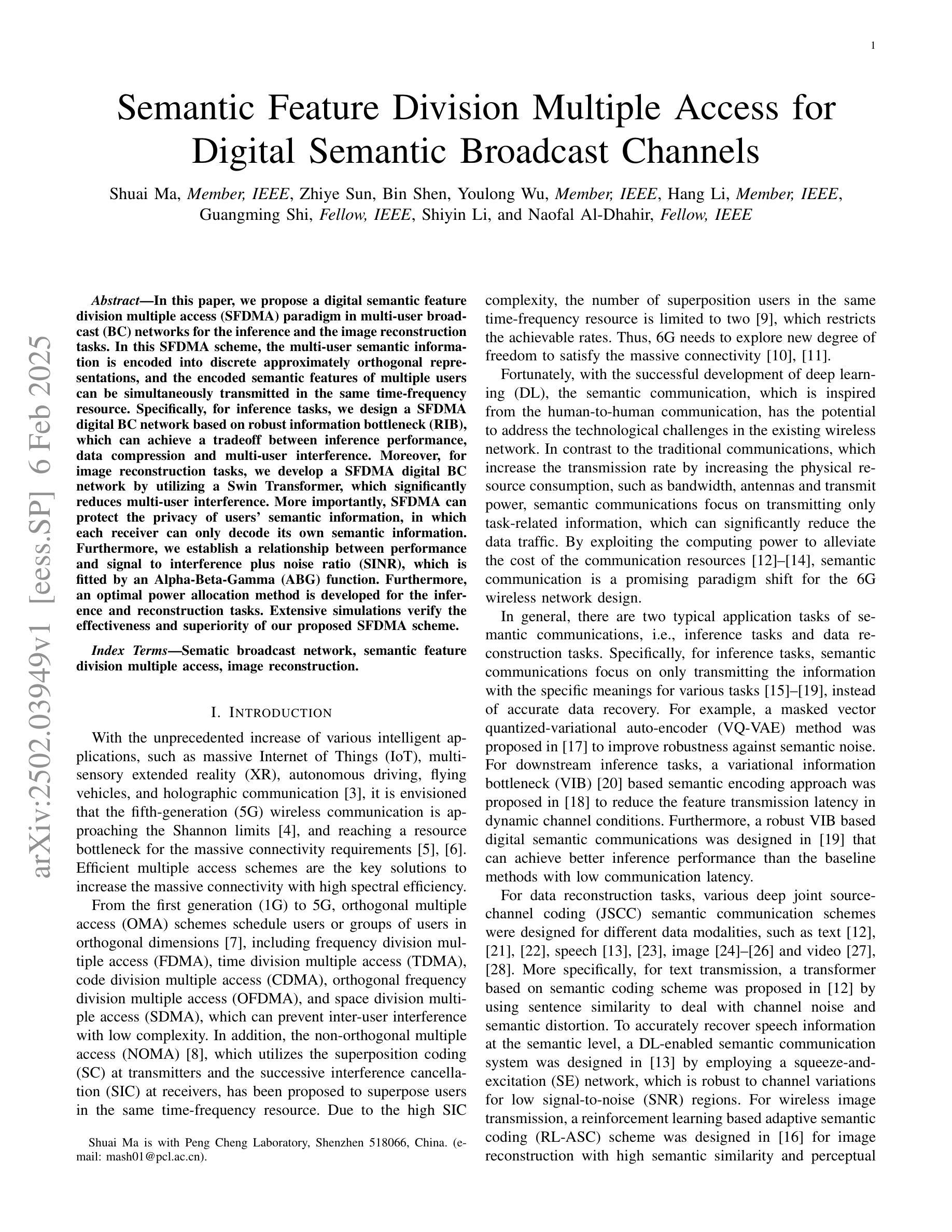
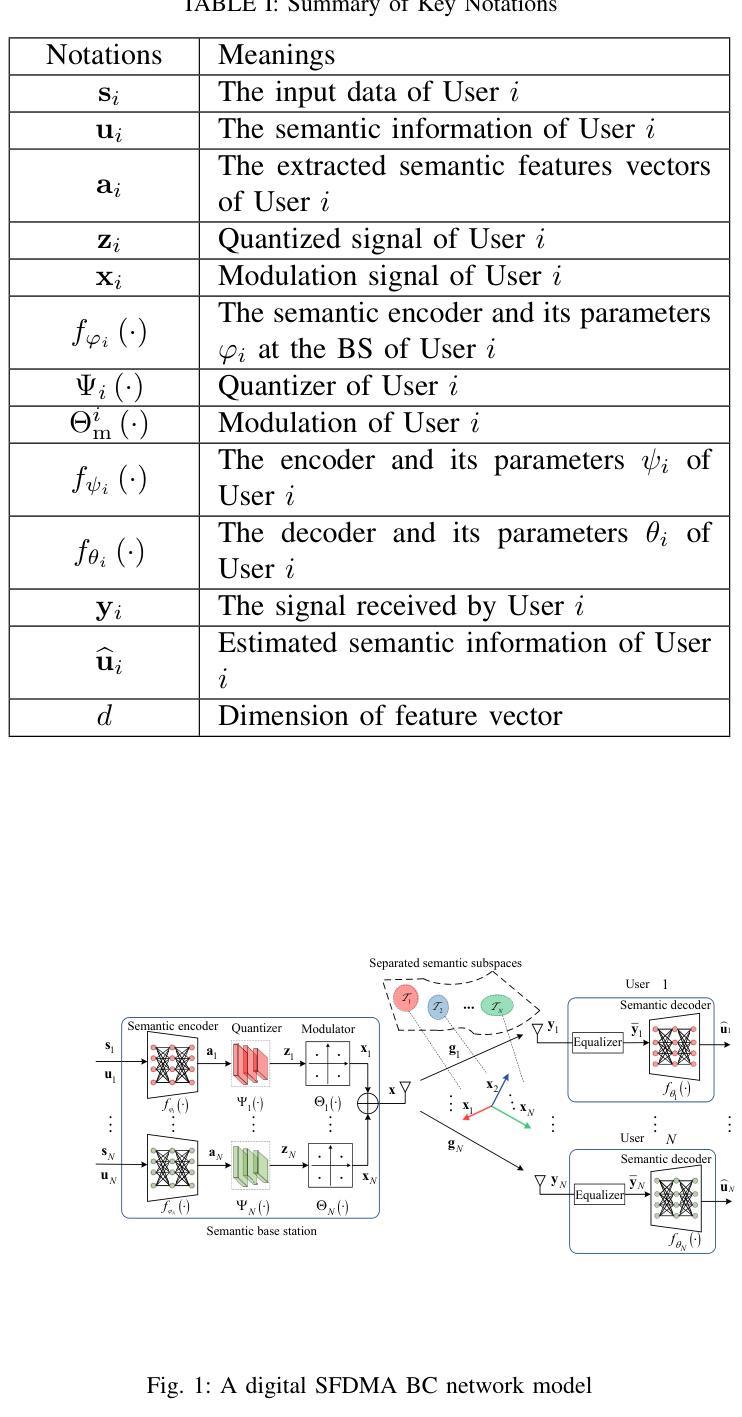
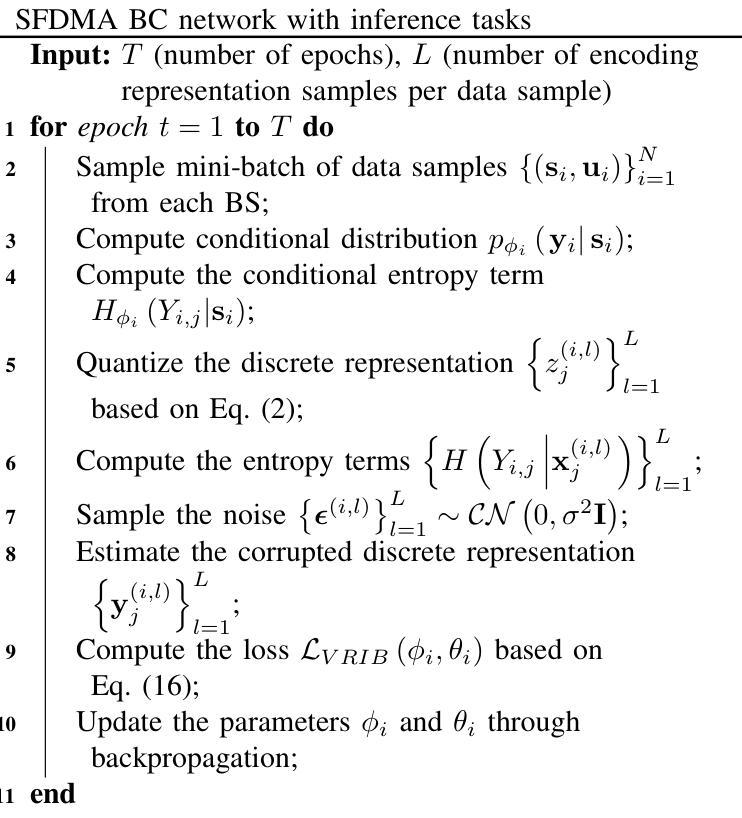
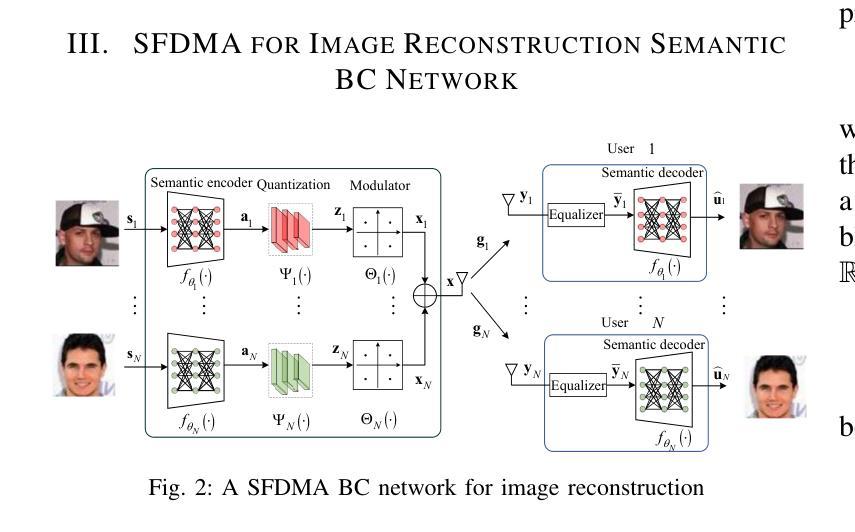
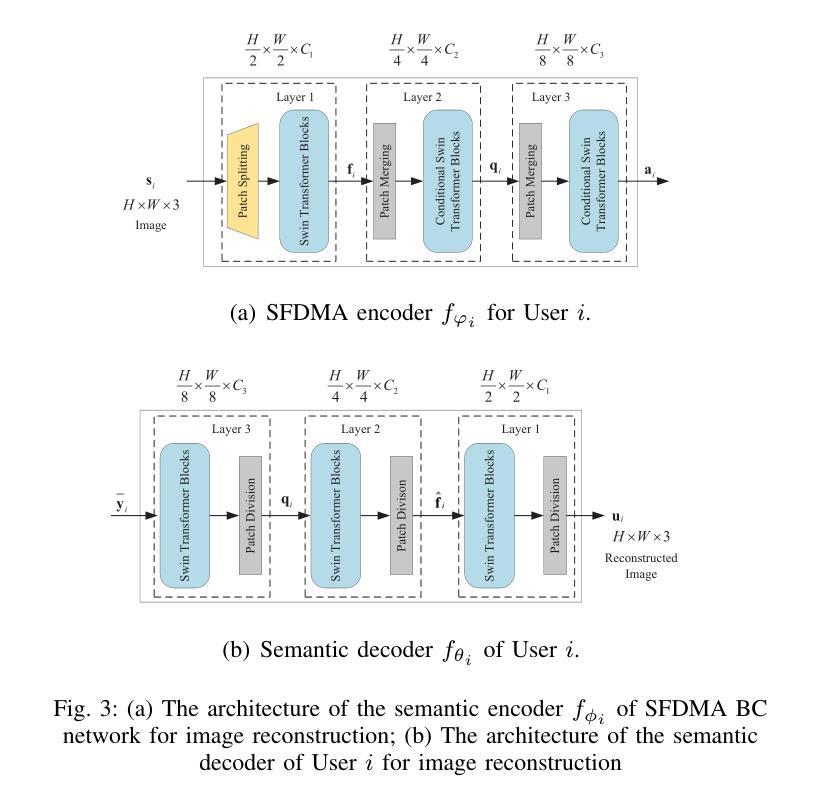
Semantic Feature Division Multiple Access for Digital Semantic Broadcast Channels
Authors:Shuai Ma, Zhiye Sun, Bin Shen, Youlong Wu, Hang Li, Guangming Shi, Shiyin Li, Naofal Al-Dhahir
In this paper, we propose a digital semantic feature division multiple access (SFDMA) paradigm in multi-user broadcast (BC) networks for the inference and the image reconstruction tasks. In this SFDMA scheme, the multi-user semantic information is encoded into discrete approximately orthogonal representations, and the encoded semantic features of multiple users can be simultaneously transmitted in the same time-frequency resource. Specifically, for inference tasks, we design a SFDMA digital BC network based on robust information bottleneck (RIB), which can achieve a tradeoff between inference performance, data compression and multi-user interference. Moreover, for image reconstruction tasks, we develop a SFDMA digital BC network by utilizing a Swin Transformer, which significantly reduces multi-user interference. More importantly, SFDMA can protect the privacy of users’ semantic information, in which each receiver can only decode its own semantic information. Furthermore, we establish a relationship between performance and signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR), which is fitted by an Alpha-Beta-Gamma (ABG) function. Furthermore, an optimal power allocation method is developed for the inference and reconstruction tasks. Extensive simulations verify the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed SFDMA scheme.
本文提出了一种多用户广播(BC)网络中用于推理和图像重建任务的数字语义特征划分多址接入(SFDMA)范式。在SFDMA方案中,多用户语义信息被编码成离散近似正交表示,多个用户的编码语义特征可以在同一时间-频率资源中同时传输。具体来说,对于推理任务,我们设计了一种基于稳健信息瓶颈(RIB)的SFDMA数字BC网络,可以在推理性能、数据压缩和多用户干扰之间取得平衡。此外,对于图像重建任务,我们利用Swin Transformer开发了一种SFDMA数字BC网络,这显著降低了多用户干扰。更重要的是,SFDMA可以保护用户语义信息的隐私,其中每个接收器只能解码其自己的语义信息。此外,我们建立了性能与信干噪比(SINR)之间的关系,通过Alpha-Beta-Gamma(ABG)函数进行拟合。此外,还针对推理和重建任务开发了一种最优功率分配方法。大量仿真验证了所提SFDMA方案的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 13 figures
Summary
医学图像领域提出了一种数字语义特征分割多址访问(SFDMA)范式,用于多用户广播网络的推断和图像重建任务。此方案可将多用户语义信息编码成离散近似正交表示,并在同一时间-频率资源中同时传输编码的语义特征。设计用于推断任务的SFDMA数字广播网络可实现推断性能、数据压缩和多用户干扰之间的权衡;用于图像重建任务的网络则采用Swin Transformer,显著降低多用户干扰。此外,SFDMA可保护用户语义信息的隐私,且性能与信干噪比(SINR)之间存在关联,由Alpha-Beta-Gamma(ABG)函数拟合。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了数字语义特征分割多址访问(SFDMA)范式,适用于多用户广播网络。
- SFDMA将多用户语义信息编码成离散近似正交表示,实现同时传输。
- 针对推断任务,设计基于稳健信息瓶颈(RIB)的SFDMA数字广播网络。
- 采用Swin Transformer构建用于图像重建任务的SFDMA数字广播网络。
- SFDMA能够保护用户语义信息的隐私。
- 性能与信干噪比(SINR)之间存在关联,由Alpha-Beta-Gamma(ABG)函数描述。
点此查看论文截图
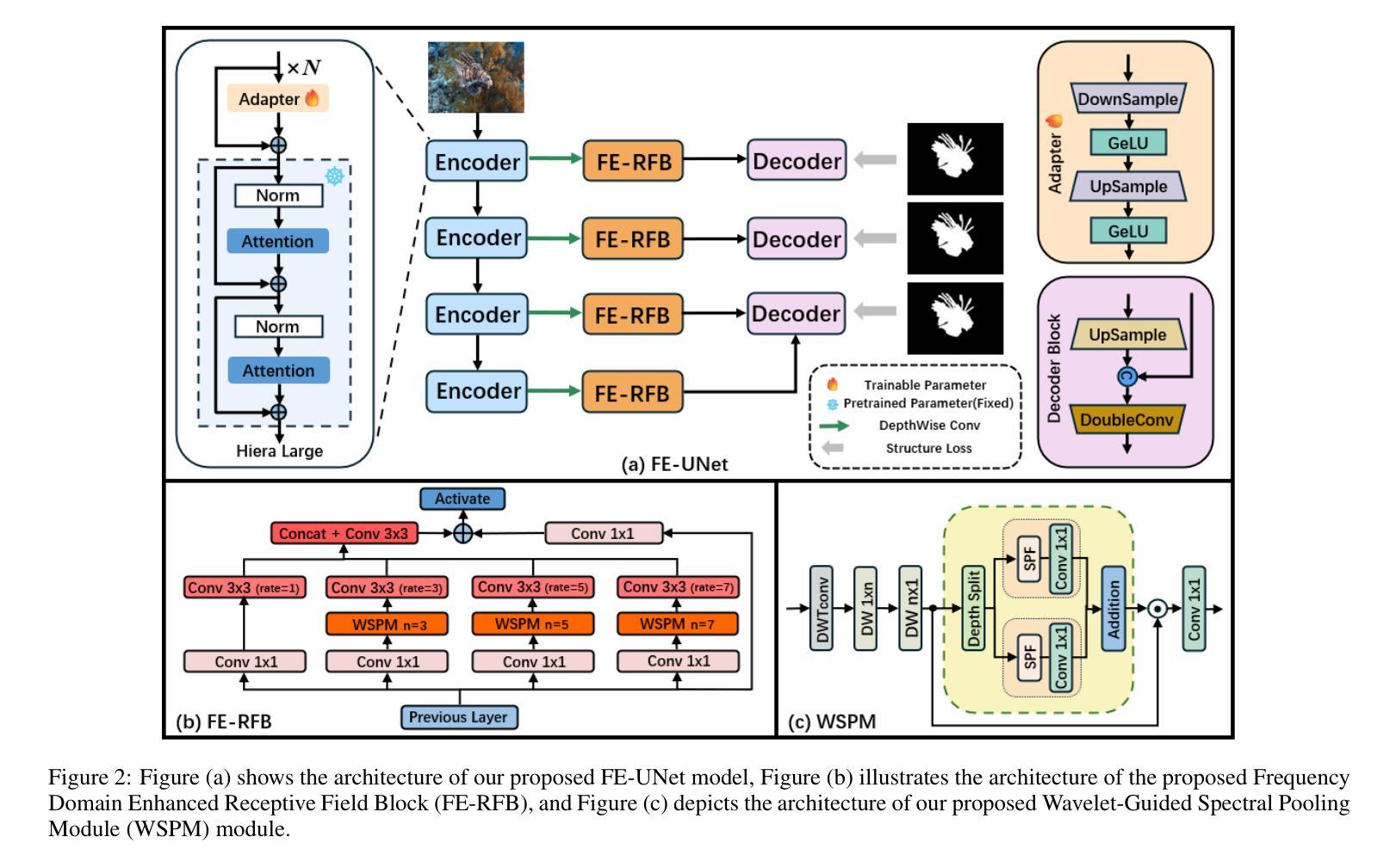
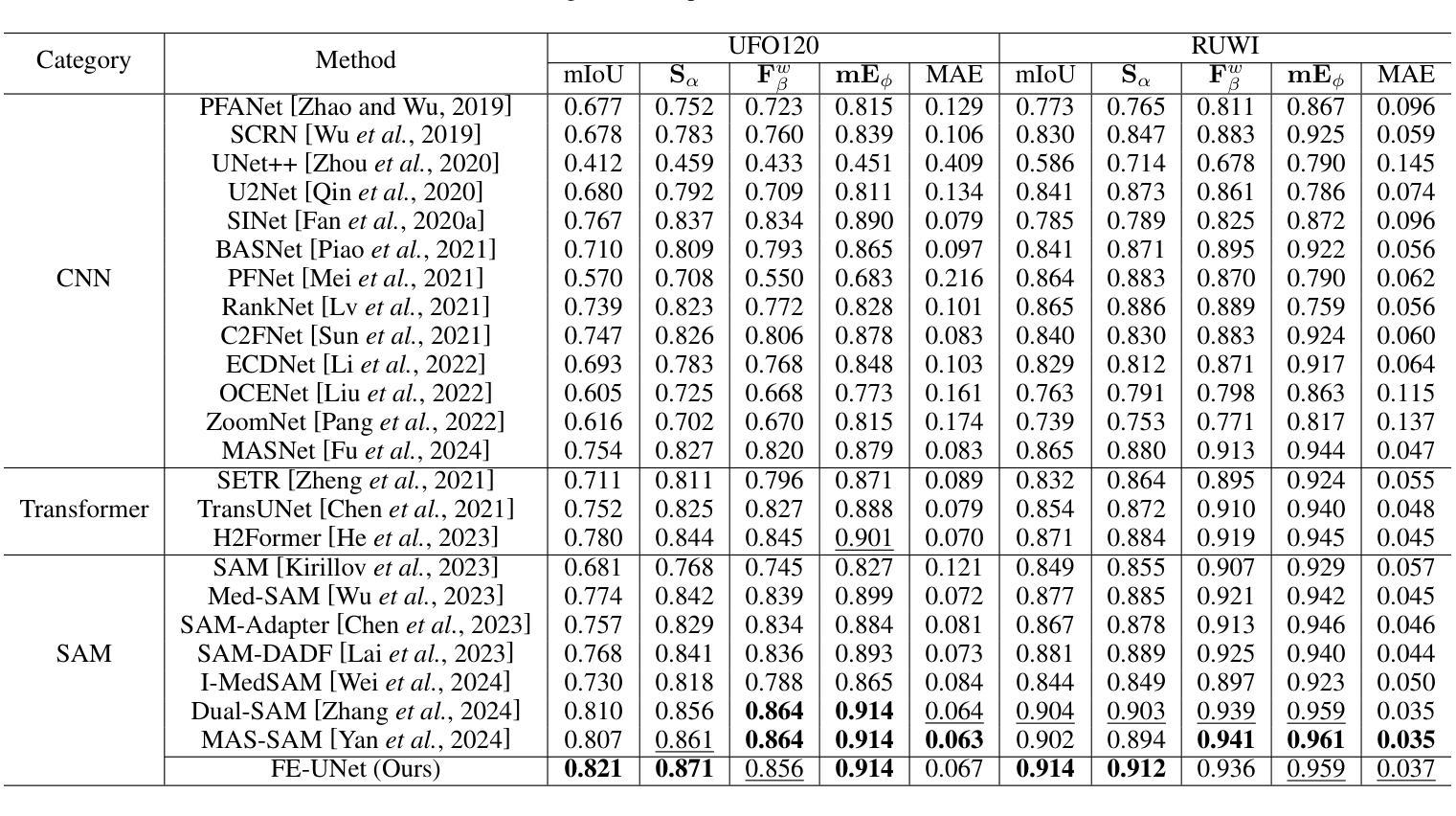
FE-UNet: Frequency Domain Enhanced U-Net with Segment Anything Capability for Versatile Image Segmentation
Authors:Guohao Huo, Ruiting Dai, Ling Shao, Hao Tang
Image segmentation is a critical task in visual understanding. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are predisposed to capture high-frequency features in images, while Transformers exhibit a contrasting focus on low-frequency features. In this paper, we experimentally quantify the contrast sensitivity function of CNNs and compare it with that of the human visual system, informed by the seminal experiments of Mannos and Sakrison. Leveraging these insights, we propose the Wavelet-Guided Spectral Pooling Module (WSPM) to enhance and balance image features across the frequency domain. To further emulate the human visual system, we introduce the Frequency Domain Enhanced Receptive Field Block (FE-RFB), which integrates WSPM to extract enriched features from the frequency domain. Building on these innovations, we develop FE-UNet, a model that utilizes SAM2 as its backbone and incorporates Hiera-Large as a pre-trained block, designed to enhance generalization capabilities while ensuring high segmentation accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that FE-UNet achieves state-of-the-art performance in diverse tasks, including marine animal and polyp segmentation, underscoring its versatility and effectiveness.
图像分割是视觉理解中的一项关键任务。卷积神经网络(CNNs)倾向于捕捉图像中的高频特征,而Transformer则更关注低频特征。在本文中,我们通过实验量化CNNs的对比敏感度函数,并将其与人类视觉系统进行比较,这得益于Mannos和Sakrison的经典实验。借助这些见解,我们提出了小波引导谱池模块(WSPM),以增强和平衡频率域中的图像特征。为了更进一步模拟人类视觉系统,我们引入了频率域增强感受野块(FE-RFB),该模块结合了WSPM,可从频率域中提取丰富的特征。基于这些创新,我们开发了FE-UNet模型,该模型以SAM2作为骨干网,并融入了Hiera-Large预训练块,旨在增强模型的通用化能力,同时确保高分割精度。实验结果表明,FE-UNet在不同任务中均达到了最先进的性能,包括海洋动物和息肉分割,凸显了其多样性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了图像分割中的卷积神经网络(CNN)与人类视觉系统的对比。通过借鉴Mannos和Sakrison的经典实验,对CNN的对比敏感度函数进行了量化分析。在此基础上,提出了基于小波引导谱池化模块(WSPM)和频率域增强感受野块(FE-RFB)的方法,用于提高和平衡图像在不同频率域的特征提取能力,并模拟人类视觉系统。最后,开发了一种名为FE-UNet的模型,该模型以SAM2为骨干,结合预先训练的Hiera-Large块,旨在提高泛化能力和分割精度。实验结果表明,FE-UNet在包括海洋生物和息肉分割等多项任务中达到了领先水平,显示了其灵活性和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割中卷积神经网络(CNN)与人类视觉系统的对比研究。
- 通过对CNN的对比敏感度函数进行量化分析,借鉴了Mannos和Sakrison的经典实验。
- 引入小波引导谱池化模块(WSPM)以增强和平衡图像在不同频率域的特征。
- 提出频率域增强感受野块(FE-RFB)以模拟人类视觉系统。
- 开发FE-UNet模型,结合SAM2骨干和Hiera-Large预训练块,旨在提高泛化能力和分割精度。
- FE-UNet在多项任务中达到领先水平,包括海洋生物和息肉分割等。
点此查看论文截图


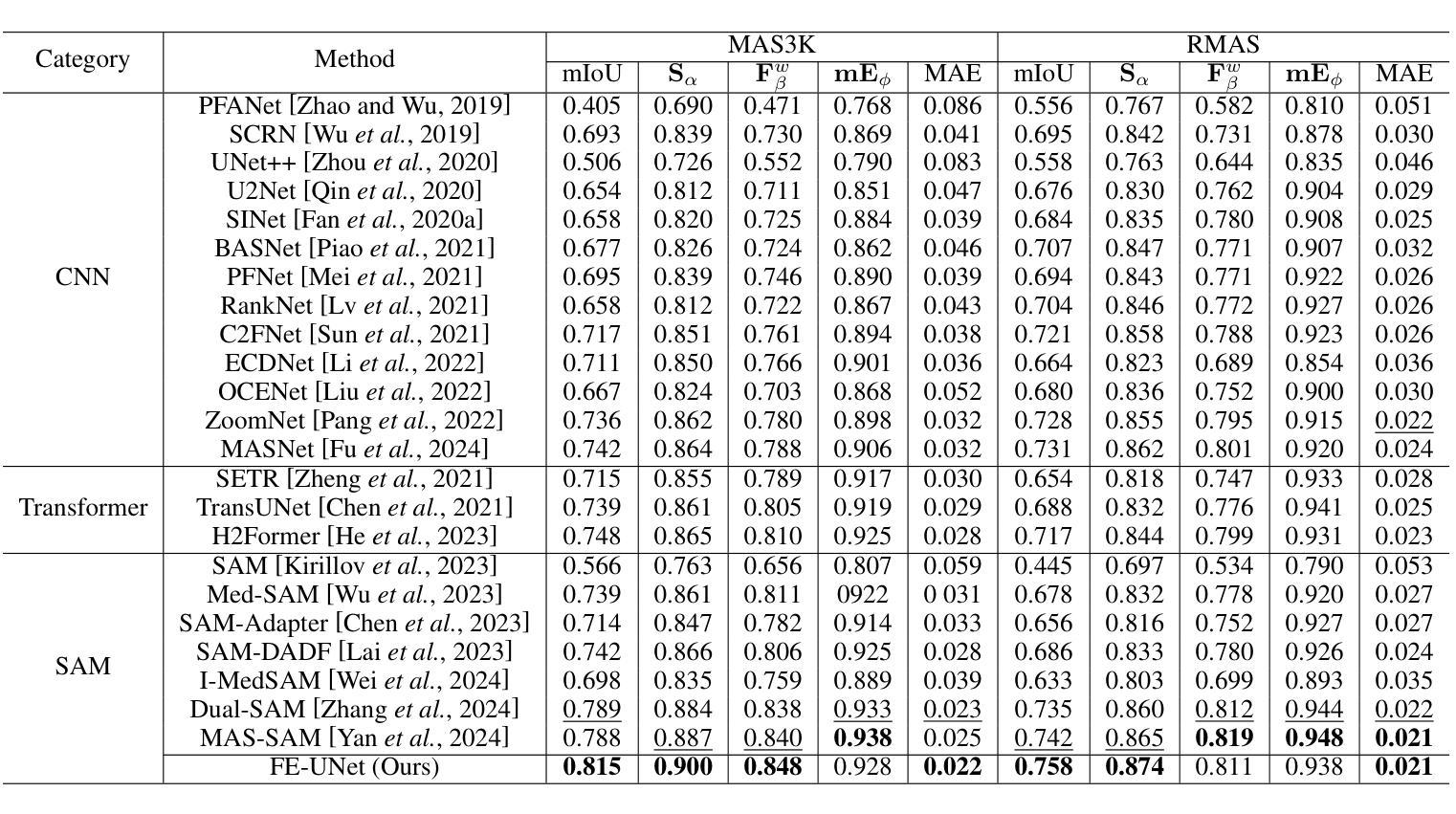
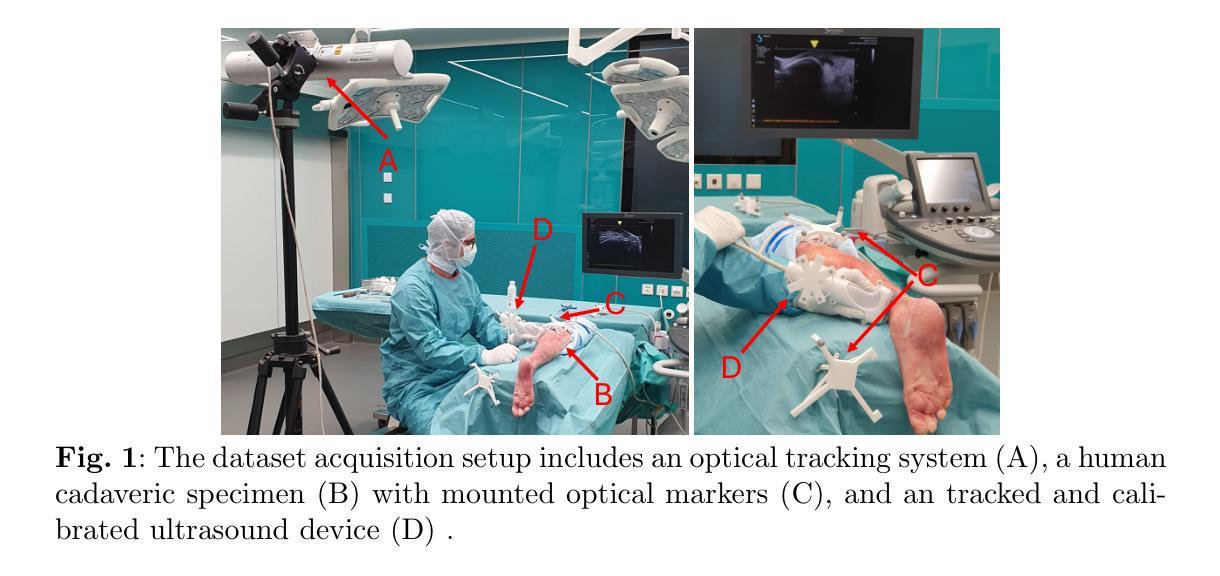
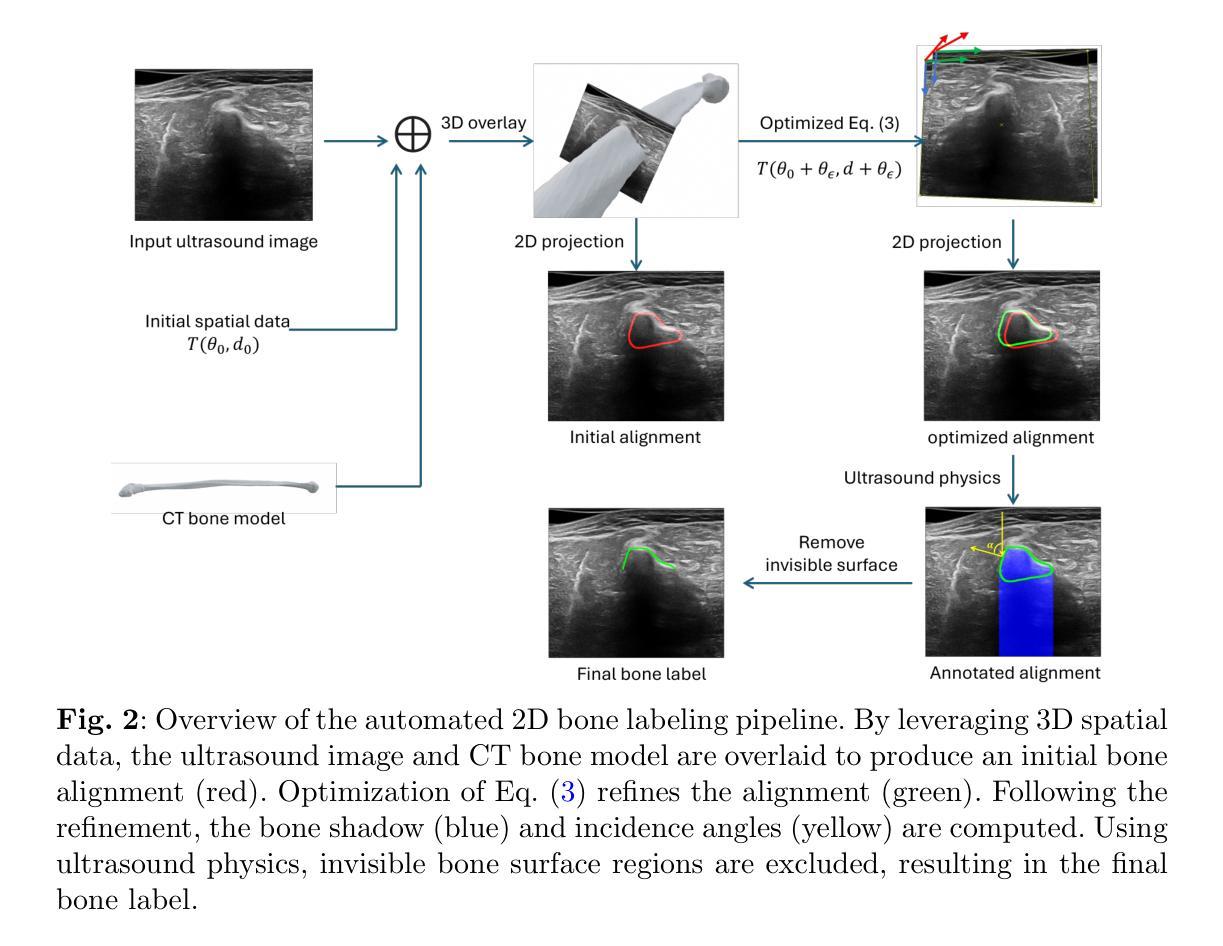
UltraBones100k: An Ultrasound Image Dataset with CT-Derived Labels for Lower Extremity Long Bone Surface Segmentation
Authors:Luohong Wu, Nicola A. Cavalcanti, Matthias Seibold, Giuseppe Loggia, Lisa Reissner, Jonas Hein, Silvan Beeler, Arnd Viehöfer, Stephan Wirth, Lilian Calvet, Philipp Fürnstahl
Ultrasound-based bone surface segmentation is crucial in computer-assisted orthopedic surgery. However, ultrasound images have limitations, including a low signal-to-noise ratio, and acoustic shadowing, which make interpretation difficult. Existing deep learning models for bone segmentation rely primarily on costly manual labeling by experts, limiting dataset size and model generalizability. Additionally, the complexity of ultrasound physics and acoustic shadow makes the images difficult for humans to interpret, leading to incomplete labels in anechoic regions and limiting model performance. To advance ultrasound bone segmentation and establish effective model benchmarks, larger and higher-quality datasets are needed. We propose a methodology for collecting ex-vivo ultrasound datasets with automatically generated bone labels, including anechoic regions. The proposed labels are derived by accurately superimposing tracked bone CT models onto the tracked ultrasound images. These initial labels are refined to account for ultrasound physics. A clinical evaluation is conducted by an expert physician specialized on orthopedic sonography to assess the quality of the generated bone labels. A neural network for bone segmentation is trained on the collected dataset and its predictions are compared to expert manual labels, evaluating accuracy, completeness, and F1-score. We collected the largest known dataset of 100k ultrasound images of human lower limbs with bone labels, called UltraBones100k. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test with Bonferroni correction confirmed that the bone alignment after our method significantly improved the quality of bone labeling (p < 0.001). The model trained on UltraBones100k consistently outperforms manual labeling in all metrics, particularly in low-intensity regions (320% improvement in completeness at a distance threshold of 0.5 mm).
基于超声的骨骼表面分割在计算机辅助骨科手术中至关重要。然而,超声图像存在信号噪声比低和声影等局限性,使得解读困难。现有的骨骼分割深度学习模型主要依赖于专家昂贵的手动标注,这限制了数据集的大小和模型的泛化能力。此外,超声物理和声影的复杂性使得图像对人类来说难以解读,导致无声区域的标签不完整,并限制了模型性能。为了推进超声骨分割并建立有效的模型基准,需要更大、更高质量的数据集。我们提出了一种收集离体超声数据集的方法,该方法可自动生成骨骼标签,包括无声区域。这些标签是通过将跟踪的骨骼CT模型准确叠加到跟踪的超声图像上而得出的。这些初始标签经过改进,以考虑超声物理。由专攻骨科超声的专家医生进行临床评估,以评估生成的骨骼标签的质量。在收集的数据集上训练骨骼分割的神经网络,并将其预测结果与专家手动标签进行比较,评估准确性、完整性和F1分数。我们收集了已知最大规模的下肢骨骼标签超声图像数据集,称为UltraBones100k数据集。采用威尔科克森符号秩检验进行Bonferroni校正后证实,我们的方法显著提高了骨骼标记的质量(p < 0.001)。在UltraBones100k数据集上训练的模型在所有指标上都优于手动标注,特别是在低强度区域(在距离阈值为0.5毫米的情况下,完整性提高了320%)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了基于超声的骨骼表面分割在计算机辅助骨科手术中的重要性及其面临的挑战。为解决现有深度学习模型对专家手动标注的依赖问题,提出了一种结合CT模型和超声图像自动生成骨骼标签的方法,并建立了包含十万张人类下肢超声图像的最大的骨骼标签数据集UltraBones100k。实验结果显示,该方法显著提高了骨骼标注的质量,并且基于该数据集的模型在所有评价指标上均优于手动标注,特别是在低强度区域的性能有大幅提升。
Key Takeaways
- 超声骨表面分割在计算机辅助骨科手术中很重要,但存在信号噪声比低和声影等挑战。
- 现有深度学习模型对专家手动标注的依赖限制了数据集大小和模型泛化能力。
- 提出了一种结合CT模型和超声图像自动生成骨骼标签的方法。
- 成功建立了包含十万张人类下肢超声图像的最大的骨骼标签数据集UltraBones100k。
- 临床评估显示生成的骨骼标签质量高。
- 基于UltraBones100k数据集的模型在所有评价指标上均优于手动标注。
点此查看论文截图

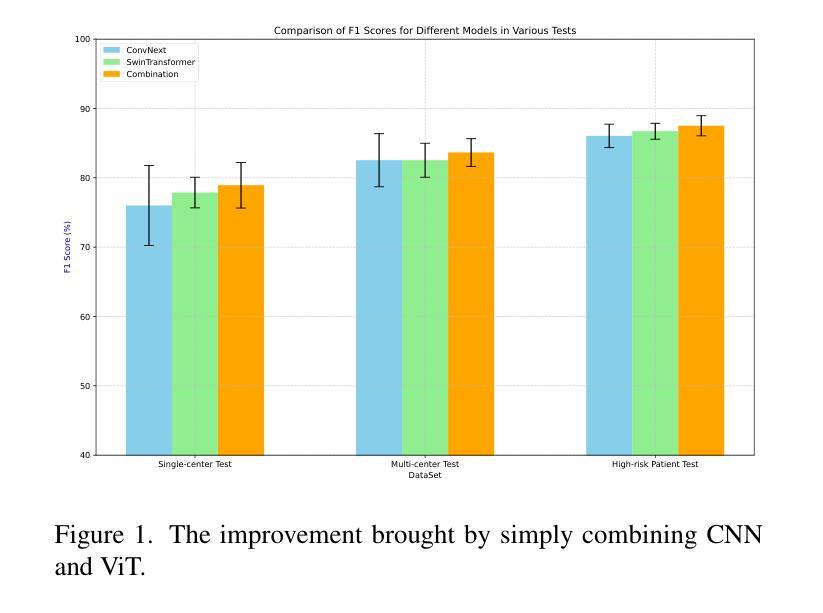
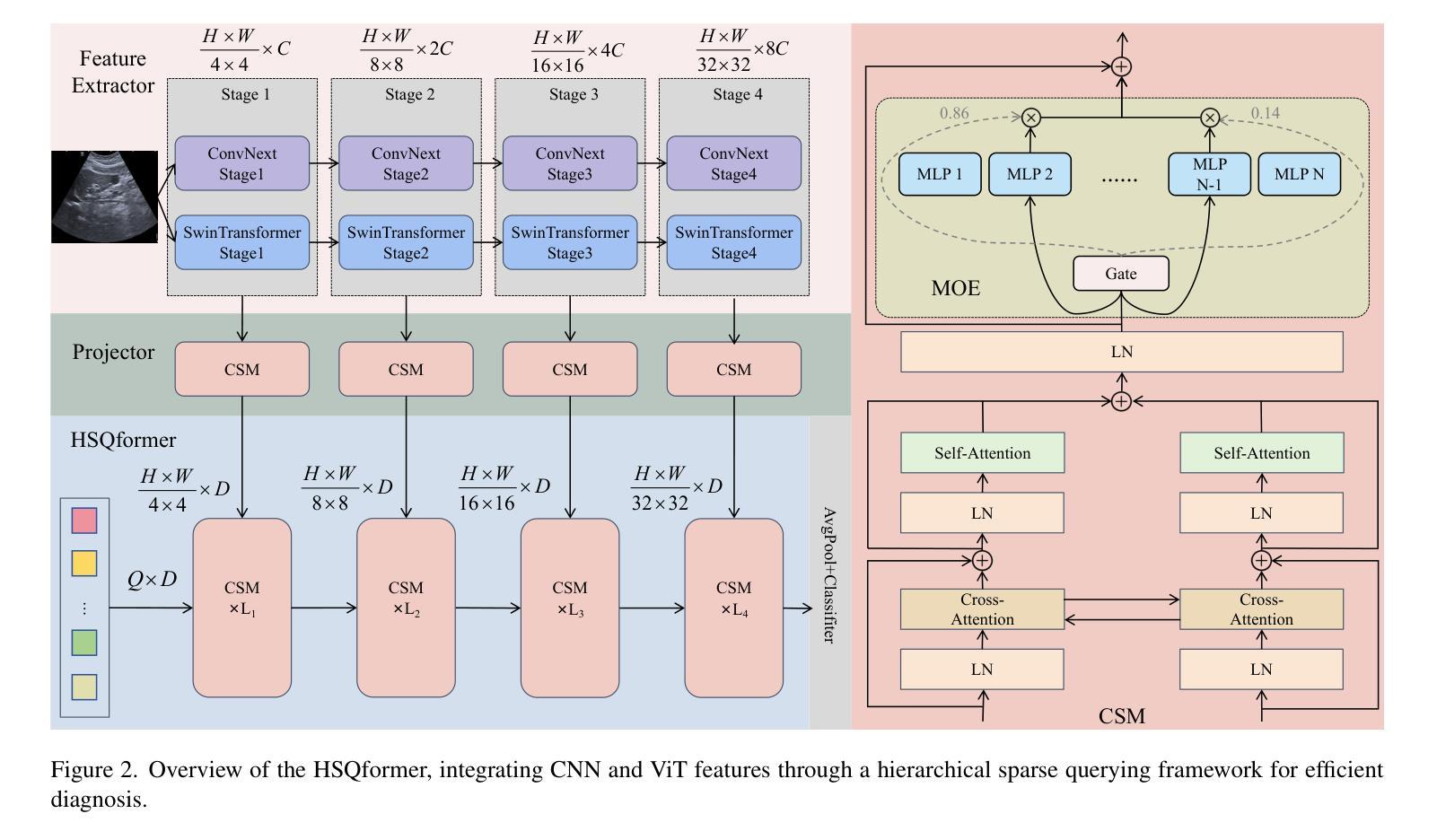
A Retrospective Systematic Study on Hierarchical Sparse Query Transformer-assisted Ultrasound Screening for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Authors:Chaoyin She, Ruifang Lu, Danni He, Jiayi Lv, Yadan Lin, Meiqing Cheng, Hui Huang, Lida Chen, Wei Wang, Qinghua Huang
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks as the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with early detection being crucial for improving patient survival rates. However, early screening for HCC using ultrasound suffers from insufficient sensitivity and is highly dependent on the expertise of radiologists for interpretation. Leveraging the latest advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging, this study proposes an innovative Hierarchical Sparse Query Transformer (HSQformer) model that combines the strengths of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) to enhance the accuracy of HCC diagnosis in ultrasound screening. The HSQformer leverages sparse latent space representations to capture hierarchical details at various granularities without the need for complex adjustments, and adopts a modular, plug-and-play design philosophy, ensuring the model’s versatility and ease of use. The HSQformer’s performance was rigorously tested across three distinct clinical scenarios: single-center, multi-center, and high-risk patient testing. In each of these settings, it consistently outperformed existing state-of-the-art models, such as ConvNext and SwinTransformer. Notably, the HSQformer even matched the diagnostic capabilities of senior radiologists and comprehensively surpassed those of junior radiologists. The experimental results from this study strongly demonstrate the effectiveness and clinical potential of AI-assisted tools in HCC screening. The full code is available at https://github.com/Asunatan/HSQformer.
肝细胞癌(HCC)是全球癌症相关死亡率的第三大主要原因,早期发现对于提高患者存活率至关重要。然而,使用超声进行HCC的早期筛查敏感性不足,并且高度依赖于放射科医生的解释专长。本研究利用医疗影像人工智能(AI)的最新进展,提出了一种创新的分层稀疏查询转换器(HSQformer)模型。该模型结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)的优点,提高了超声筛查中HCC诊断的准确性。HSQformer利用稀疏潜在空间表示来捕获各种粒度下的层次细节,而无需进行复杂调整,并采用了模块化、即插即用的设计哲学,确保模型的通用性和易用性。HSQformer的性能在三种不同的临床场景:单中心、多中心和高危患者测试中都经过了严格测试。在这些场景中,它始终超越了现有的最先进的模型,如ConvNext和SwinTransformer。值得注意的是,HSQformer甚至达到了资深放射科医生的诊断水平,并全面超越了初级放射科医生的表现。本研究的实验结果强烈证明了AI辅助工具在HCC筛查中的有效性和临床潜力。完整的代码可在https://github.com/Asunatan/HSQformer上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用人工智能(AI)技术,结合卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)的优势,开发出一种名为HSQformer的新型模型,用于提高肝癌(HCC)超声筛查诊断的准确性。HSQformer采用分层稀疏查询转换器,无需复杂调整即可捕捉不同粒度的层次细节,并具备模块化、即插即用的设计哲学,确保模型的通用性和易用性。在不同临床场景下的测试中,HSQformer表现出卓越的性能,甚至与资深放射科医生的诊断能力相匹配并超越了初级放射科医生。
Key Takeaways
- HCC是世界范围内第三大致癌死因,早期检测对改善患者生存率至关重要。
- 现有超声筛查方法存在灵敏度不足和依赖放射科医生解读的问题。
- 研究提出了一种名为HSQformer的新型模型,结合了CNN和ViT的优点,旨在提高HCC诊断的准确性。
- HSQformer采用分层稀疏查询转换器,能够捕捉不同粒度的层次细节,且模型设计模块化,易于使用。
- HSQformer在不同临床场景下的测试中表现优异,超越了现有先进模型,如ConvNext和SwinTransformer。
- HSQformer的诊断能力与资深放射科医生相匹配,并全面超越了初级放射科医生。
点此查看论文截图

Identifying Compton-thick AGNs in the COSMOS. I. Among X-ray AGNs with Low Photon Counts
Authors:Xiaotong Guo, Qiusheng Gu, Guanwen Fang, Yongyun Chen, Nan Ding, Xiaoling Yu, Hongtao Wang
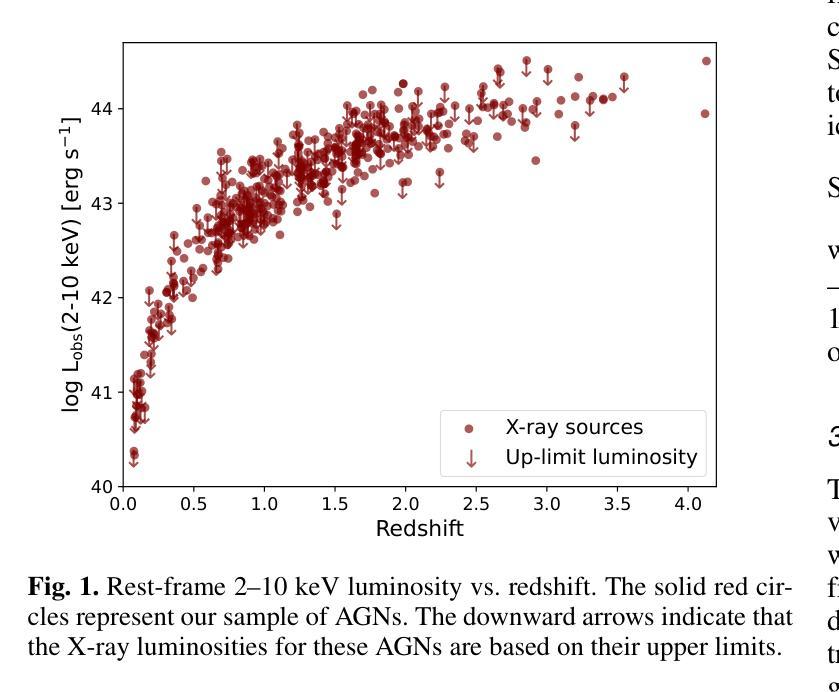
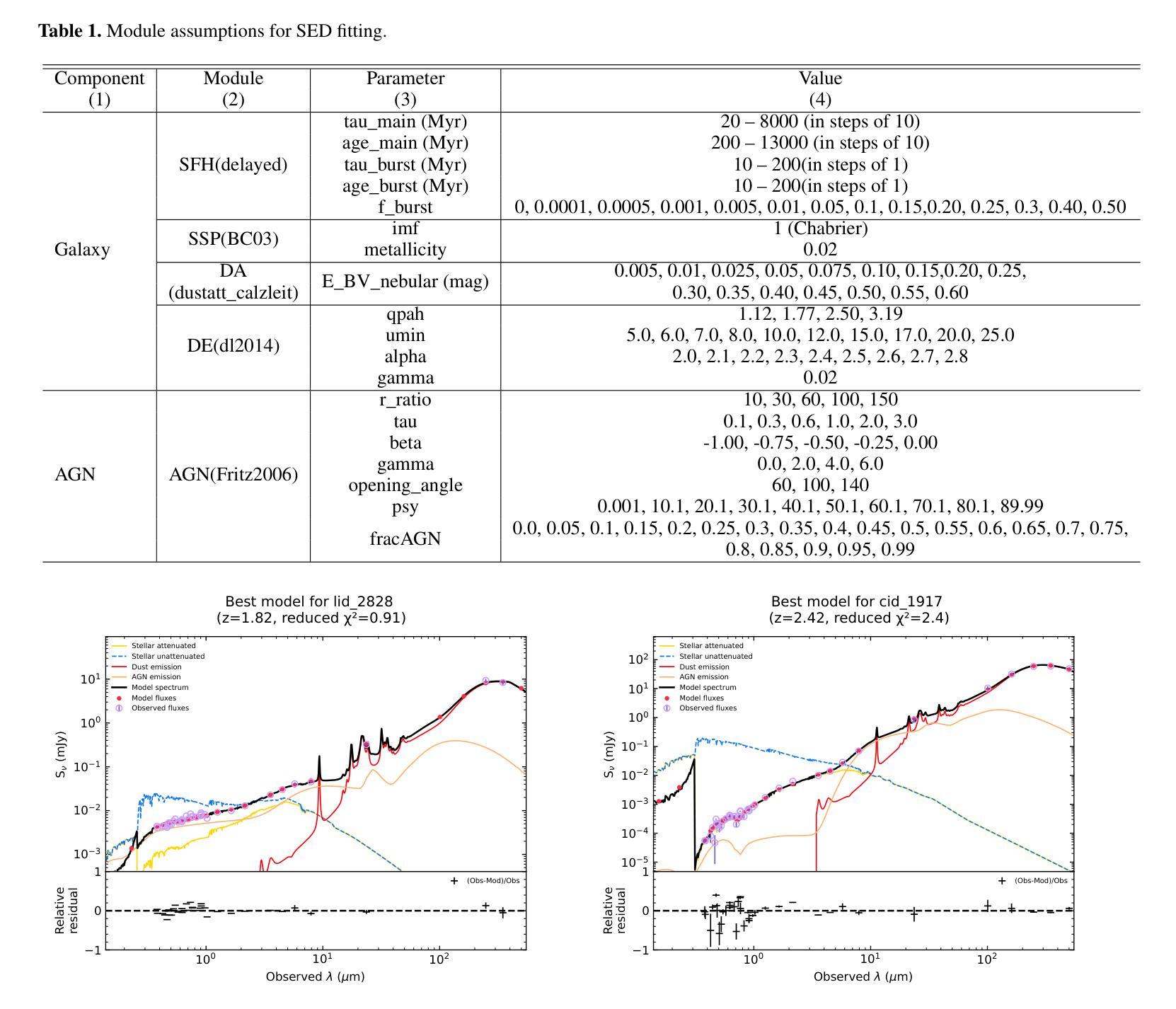
Compton-thick active galactic nuclei (CT-AGNs), characterized by a significant absorption with column densities of $\mathrm{N_H}\geqslant 1.5\times 10^{24} \ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$, emit feeble X-ray radiation and are even undetectable by X-ray instruments, making them difficult to identify. X-ray radiation from AGNs is the predominant source of the cosmic X-ray background (CXB). Based on AGN synthesis models for the CXB, the fraction of CT-AGNs should constitute a substantial portion of AGN population, approximately 30% or more. The fraction of CT-AGNs discovered in the Cosmological Evolution Survey (COSMOS) is significantly lower than this value. This means that many CT-AGNs may be hidden in AGNs that exhibit low photon counts or that have not been detected by X-ray instruments. This work focuses on identifying CT-AGNs hidden in AGNs with low photon counts. Firstly, we selected 440 AGNs with abundant multiwavelength data as our sample. Secondly, we analyzed multiwavelength data, extracting crucial physical parameters required for the CT-AGN diagnosis. Finally, we used multiwavelength approaches to identify CT-AGNs. We have successfully identified 18 CT-AGNs in our sample. Among the CT-AGNs, four AGNs show discrepant results across different diagnostic methods. We discuss the potential reasons behind these diagnostic discrepancies. We explore the impact of estimating [OIII]$\lambda5007$ luminosities based on [OII]$\lambda3727$ luminosities for the CT-AGN diagnosis. We have also found that the properties of host galaxies for CT-AGNs and non-CT-AGNs do not show significant discrepancies.
康普顿厚活动星系核(CT-AGNs),以其显著吸收为特征,其柱密度达到NH≥1.5×10^24 cm^-2,发出微弱的X射线辐射,甚至无法被X射线仪器探测到,因此难以识别。来自AGNs的X射线辐射是宇宙X射线背景(CXB)的主要来源。基于CXB的AGNs合成模型,CT-AGNs应占AGNs相当大的比例,约为30%或更多。然而,在宇宙演化调查(COSMOS)中发现的CT-AGNs比例明显低于这一数值。这意味着许多CT-AGNs可能隐藏在光子计数较低的AGNs中,或者尚未被X射线仪器探测到。本工作着重于识别隐藏在光子计数较低的AGNs中的CT-AGNs。首先,我们选择了440个具有丰富多波长数据的AGNs作为样本。其次,我们分析了多波长数据,提取了进行CT-AGN诊断所需的关键物理参数。最后,我们采用了多波长方法来识别CT-AGNs。在我们的样本中,已成功识别出18个CT-AGNs。其中,有4个AGNs在不同诊断方法的结果之间存在差异。我们讨论了这些诊断差异背后的潜在原因。我们探讨了基于[O II]λ3727亮度估计[O III]λ5007亮度对CT-AGN诊断的影响。我们还发现,CT-AGNs和非CT-AGNs的主宿星系性质没有显著差别。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 7 figures, 4 tables. Accepted in Astronomy & Astrophysics
Summary
文中探讨了Compton厚活跃星系核(CT-AGNs)的特性,其特点是存在显著吸收,导致X射线辐射微弱甚至无法被X射线仪器探测到。基于CXB的AGNs合成模型推测,CT-AGNs在AGNs中应占相当大的比例(约30%或以上)。然而,在宇宙演化调查(COSMOS)中发现的CT-AGNs比例远低于此,表明许多CT-AGNs可能隐藏在低光子计数或未被X射线仪器探测到的AGNs中。本研究专注于识别隐藏在低光子计数AGNs中的CT-AGNs,成功识别出其中的18个CT-AGNs,并对其中存在的诊断差异及其原因进行了探讨。此外,还对基于[O II]λ3727亮度估算的CT-AGNs诊断进行了探索,发现CT-AGNs与非CT-AGNs的宿主星系特性无显著差异。
Key Takeaways
- CT-AGNs具有显著吸收特性,导致X射线辐射微弱或无法被探测。
- 基于CXB的AGNs合成模型推测CT-AGNs应占相当大的比例。
- COSMOS调查中发现的CT-AGNs比例远低于预测值,暗示许多CT-AGNs可能被忽视。
- 研究成功识别出隐藏在低光子计数AGNs中的18个CT-AGNs。
- 部分CT-AGNs在不同诊断方法中存在结果差异,讨论了这些差异的原因。
- 研究探索了基于[O II]λ3727亮度估算的CT-AGNs诊断方法。
点此查看论文截图

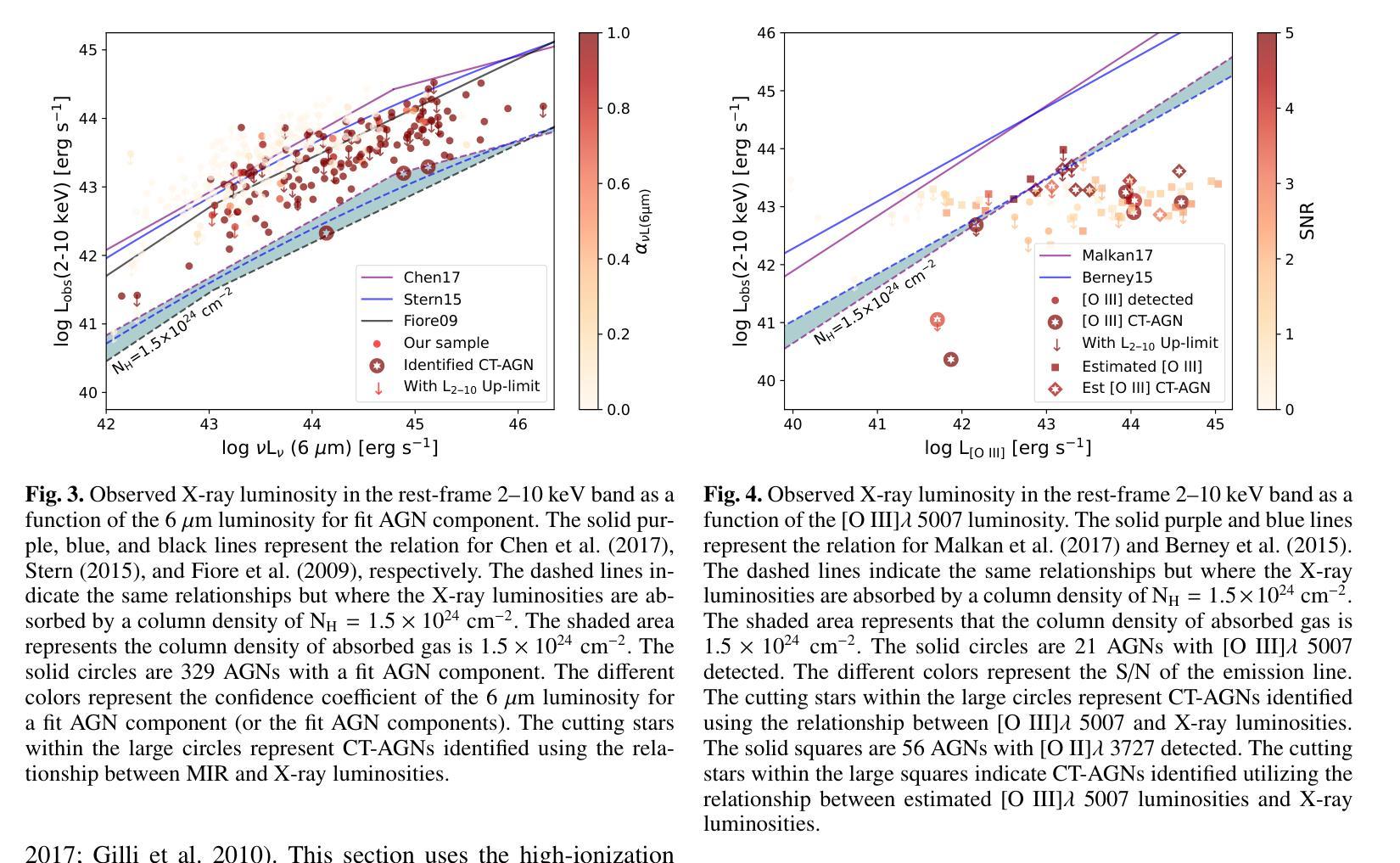
Conditional Diffusion Models are Medical Image Classifiers that Provide Explainability and Uncertainty for Free
Authors:Gian Mario Favero, Parham Saremi, Emily Kaczmarek, Brennan Nichyporuk, Tal Arbel
Discriminative classifiers have become a foundational tool in deep learning for medical imaging, excelling at learning separable features of complex data distributions. However, these models often need careful design, augmentation, and training techniques to ensure safe and reliable deployment. Recently, diffusion models have become synonymous with generative modeling in 2D. These models showcase robustness across a range of tasks including natural image classification, where classification is performed by comparing reconstruction errors across images generated for each possible conditioning input. This work presents the first exploration of the potential of class conditional diffusion models for 2D medical image classification. First, we develop a novel majority voting scheme shown to improve the performance of medical diffusion classifiers. Next, extensive experiments on the CheXpert and ISIC Melanoma skin cancer datasets demonstrate that foundation and trained-from-scratch diffusion models achieve competitive performance against SOTA discriminative classifiers without the need for explicit supervision. In addition, we show that diffusion classifiers are intrinsically explainable, and can be used to quantify the uncertainty of their predictions, increasing their trustworthiness and reliability in safety-critical, clinical contexts. Further information is available on our project page: https://faverogian.github.io/med-diffusion-classifier.github.io/
判别分类器已成为医学成像深度学习中的基础工具,擅长学习复杂数据分布的可分特征。然而,为了确保安全和可靠的部署,这些模型通常需要精心设计、增强和训练技术。最近,扩散模型已成为二维生成建模的同义词。这些模型展示了在各种任务中的稳健性,包括自然图像分类,其中分类是通过比较为每种可能的条件输入生成的图像的重构误差来完成的。这项工作首次探索了类条件扩散模型在二维医学图像分类中的潜力。首先,我们开发了一种新型多数投票方案,该方案被证明可以提高医学扩散分类器的性能。其次,在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的大量实验表明,基础扩散模型和从头训练的扩散模型能够达到与最新判别分类器相竞争的性能,而无需显式监督。此外,我们还表明,扩散分类器本质上是可解释的,可用于量化其预测的的不确定性,这在安全关键的临床环境中增加了其可信度和可靠性。更多信息请参见我们的项目页面:链接地址。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了类条件扩散模型在二维医学图像分类中的潜力,提出一种新型多数投票方案,并在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上进行实验验证。结果显示,扩散模型性能具有竞争力,无需显式监督即可达到最先进判别分类器的水平。此外,扩散分类器具有内在的可解释性,并可量化预测的不确定性,提高其在安全关键的医疗环境中的可信度和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在二维医学图像分类中具有潜力。
- 提出了一种新型多数投票方案,提高了医学扩散分类器的性能。
- 在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的实验验证了扩散模型的竞争力。
- 扩散模型性能与最先进判别分类器相当,无需显式监督。
- 扩散分类器具有内在的可解释性。
- 扩散分类器可以量化预测的不确定性。
点此查看论文截图

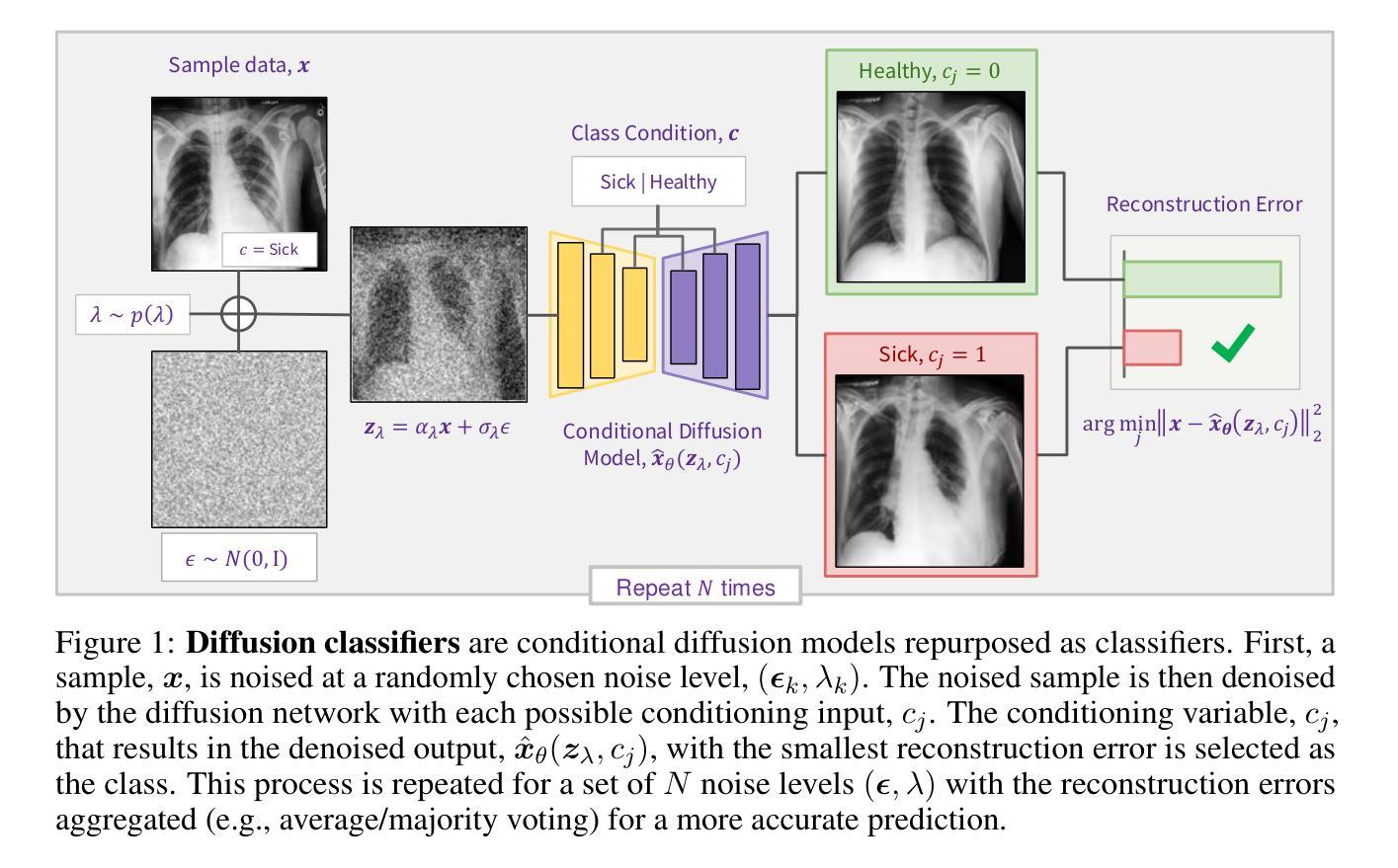
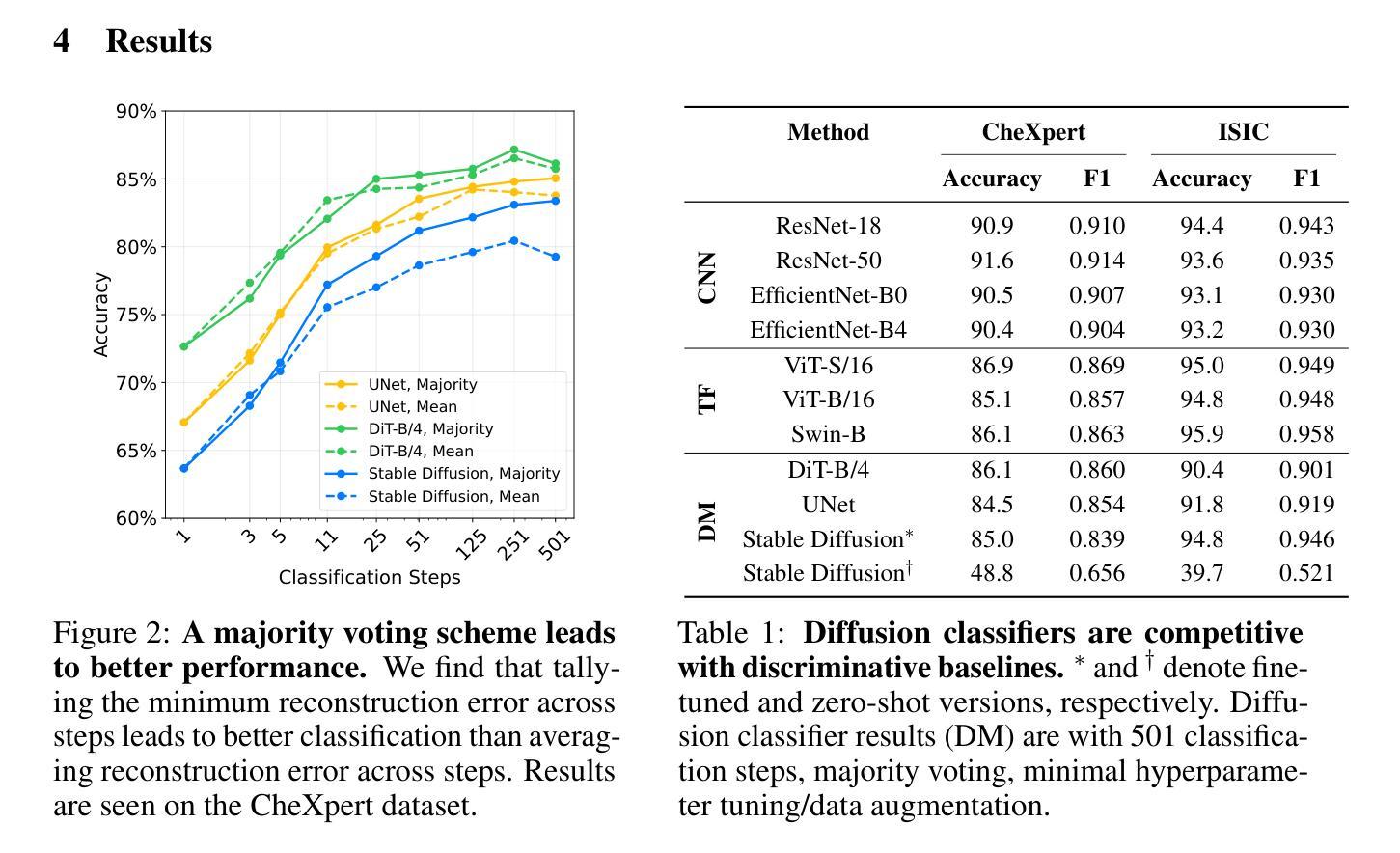
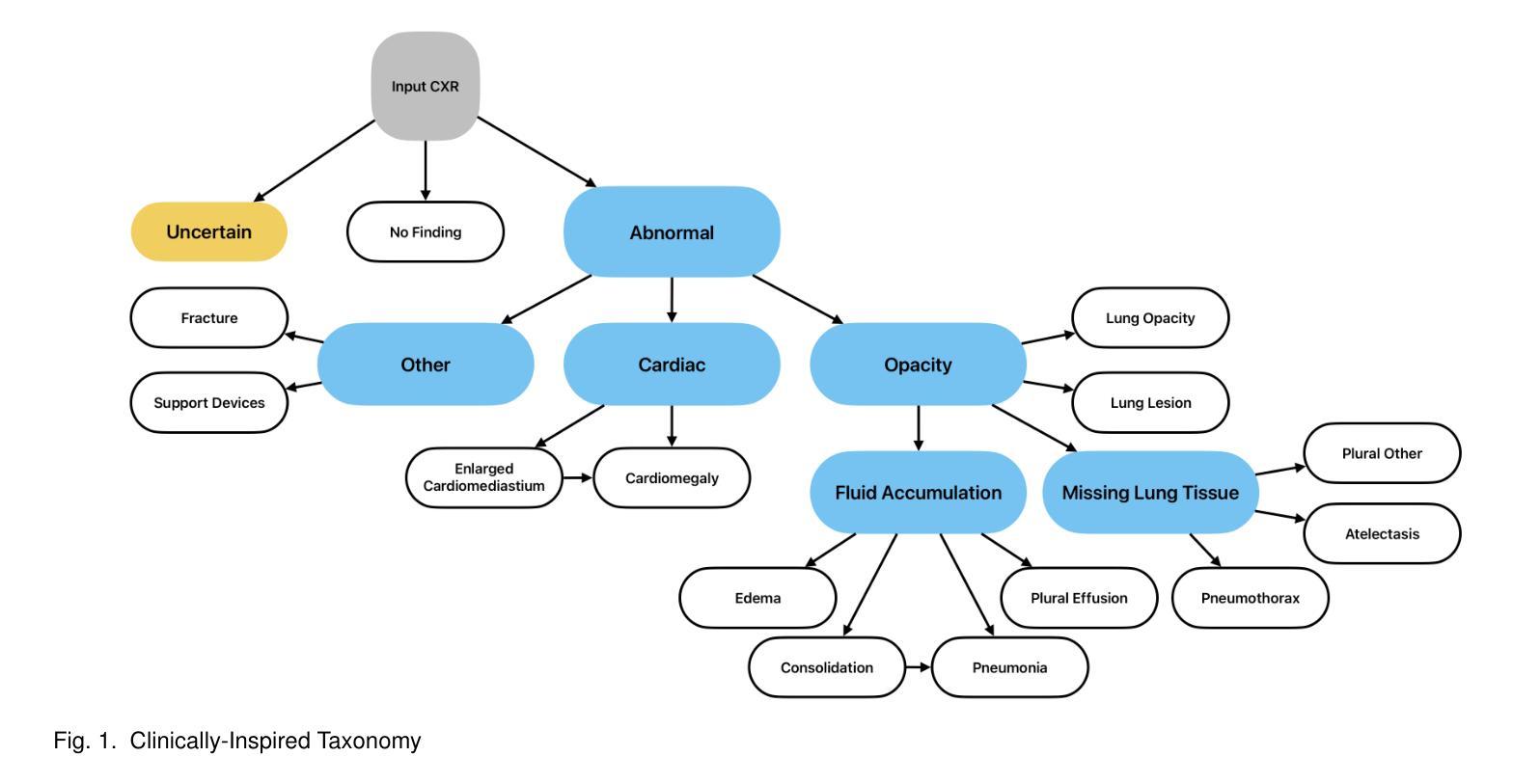
Clinically-Inspired Hierarchical Multi-Label Classification of Chest X-rays with a Penalty-Based Loss Function
Authors:Mehrdad Asadi, Komi Sodoké, Ian J. Gerard, Marta Kersten-Oertel
In this work, we present a novel approach to multi-label chest X-ray (CXR) image classification that enhances clinical interpretability while maintaining a streamlined, single-model, single-run training pipeline. Leveraging the CheXpert dataset and VisualCheXbert-derived labels, we incorporate hierarchical label groupings to capture clinically meaningful relationships between diagnoses. To achieve this, we designed a custom hierarchical binary cross-entropy (HBCE) loss function that enforces label dependencies using either fixed or data-driven penalty types. Our model achieved a mean area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.903 on the test set. Additionally, we provide visual explanations and uncertainty estimations to further enhance model interpretability. All code, model configurations, and experiment details are made available.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的多标签胸部X射线(CXR)图像分类方法,这种方法提高了临床解释性,同时保持了一个精简的单模型、单运行训练流程。我们利用CheXpert数据集和VisualCheXbert衍生的标签,融入层次标签分组,以捕获诊断之间临床上有意义的关系。为此,我们设计了一个自定义的层次二元交叉熵(HBCE)损失函数,该函数通过固定或数据驱动型的惩罚类型来强制执行标签依赖性。我们的模型在测试集上取得了平均受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUROC)为0.903的成绩。此外,我们还提供了视觉解释和不确定性估计,以进一步增强模型的可解释性。所有代码、模型配置和实验细节均已公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages with 3 figures, for associated implementation see https://github.com/the-mercury/CIHMLC
Summary
本文提出了一种新的多标签胸部X射线(CXR)图像分类方法,该方法在提高临床可解释性的同时,保持了一个简洁的单模型、单运行训练流程。通过利用CheXpert数据集和VisualCheXbert衍生的标签,融入层次标签分组,以捕捉诊断之间的临床有意义的关系。为此,设计了一种自定义的层次二进制交叉熵(HBCE)损失函数,通过固定或数据驱动型的惩罚类型来实施标签依赖性。该模型在测试集上取得了平均受试者工作特征曲线下的面积(AUROC)为0.903的成绩。此外,还提供了视觉解释和不确定性估计,以进一步提高模型的可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了针对多标签胸部X射线图像分类的新方法,兼顾临床可解释性和简洁的训练流程。
- 利用CheXpert数据集和VisualCheXbert衍生的标签,融入层次标签分组。
- 自定义了层次二进制交叉熵(HBCE)损失函数,实施标签依赖性。
- 模型在测试集上取得了较高的平均受试者工作特征曲线下的面积(AUROC)为0.903。
- 提供视觉解释和不确定性估计,增强模型可解释性。
- 代码、模型配置和实验细节全部公开可用。
点此查看论文截图
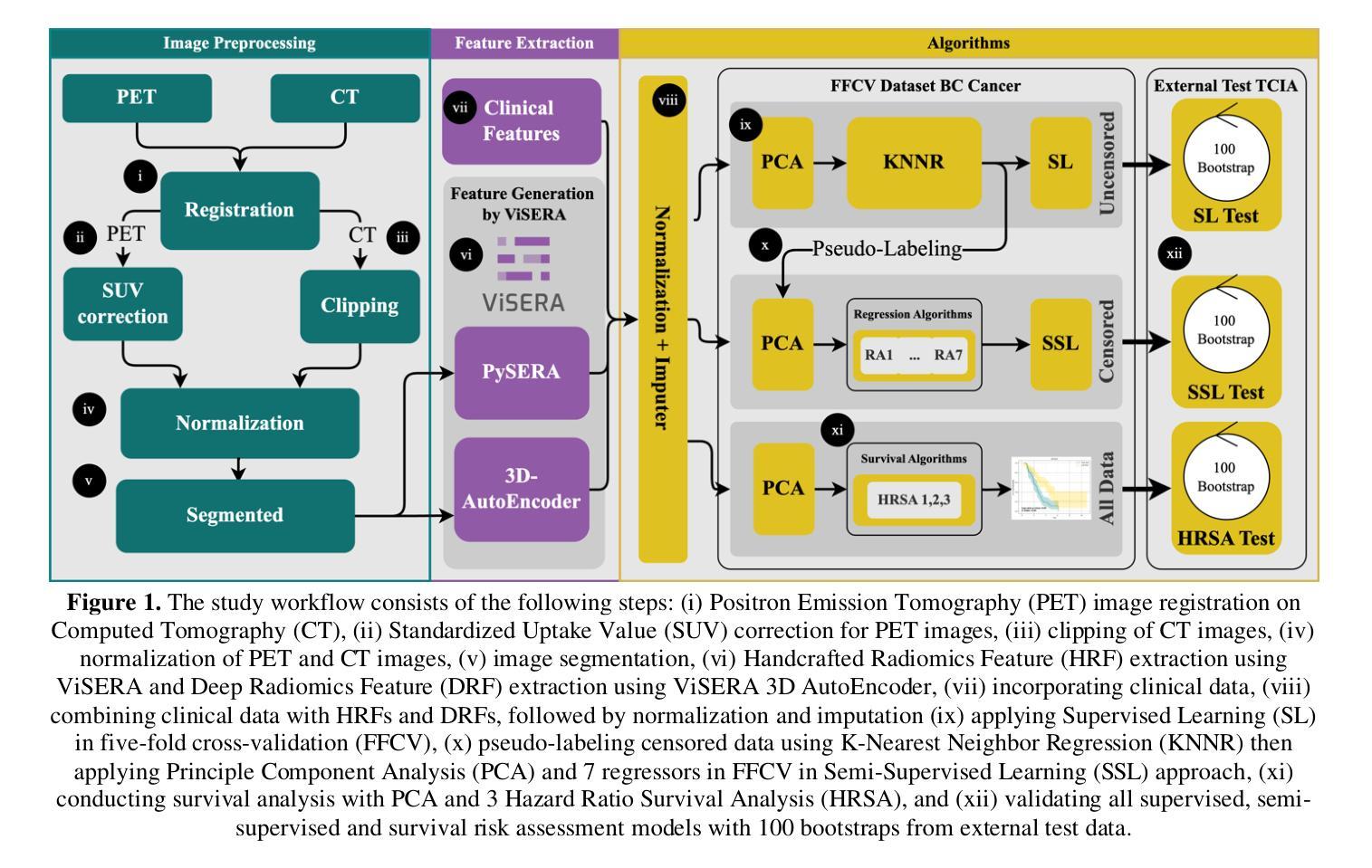
Censor-Aware Semi-Supervised Survival Time Prediction in Lung Cancer Using Clinical and Radiomics Features
Authors:Arman Groji, Ali Fathi Jouzdani, Nima Sanati, Amir Mahmoud Ahmadzadeh, Ren Yuan, Arman Rahmim, Mohammad R. Salmanpour
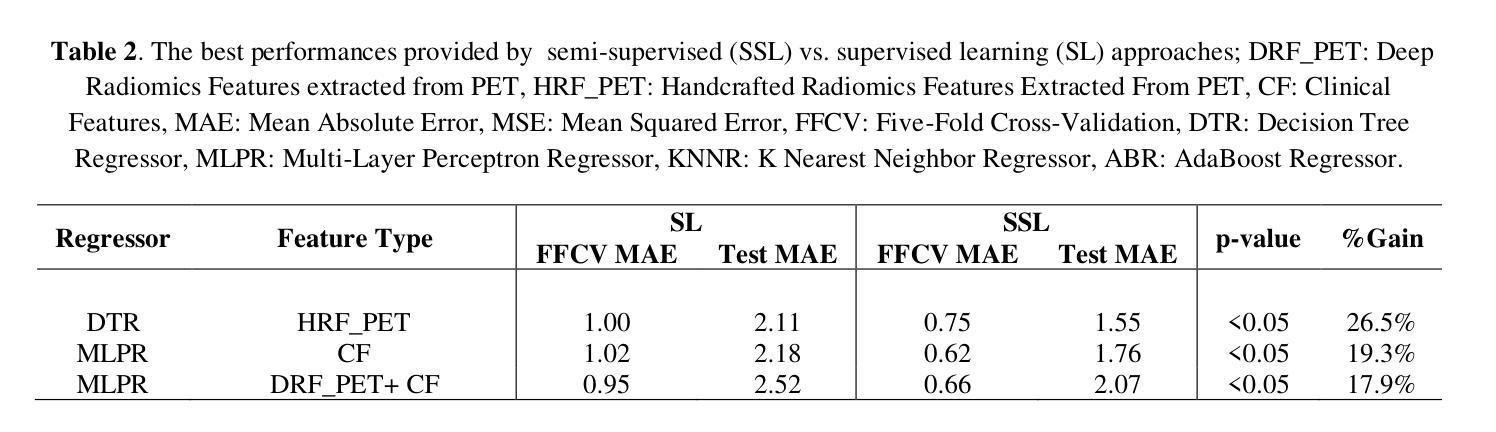
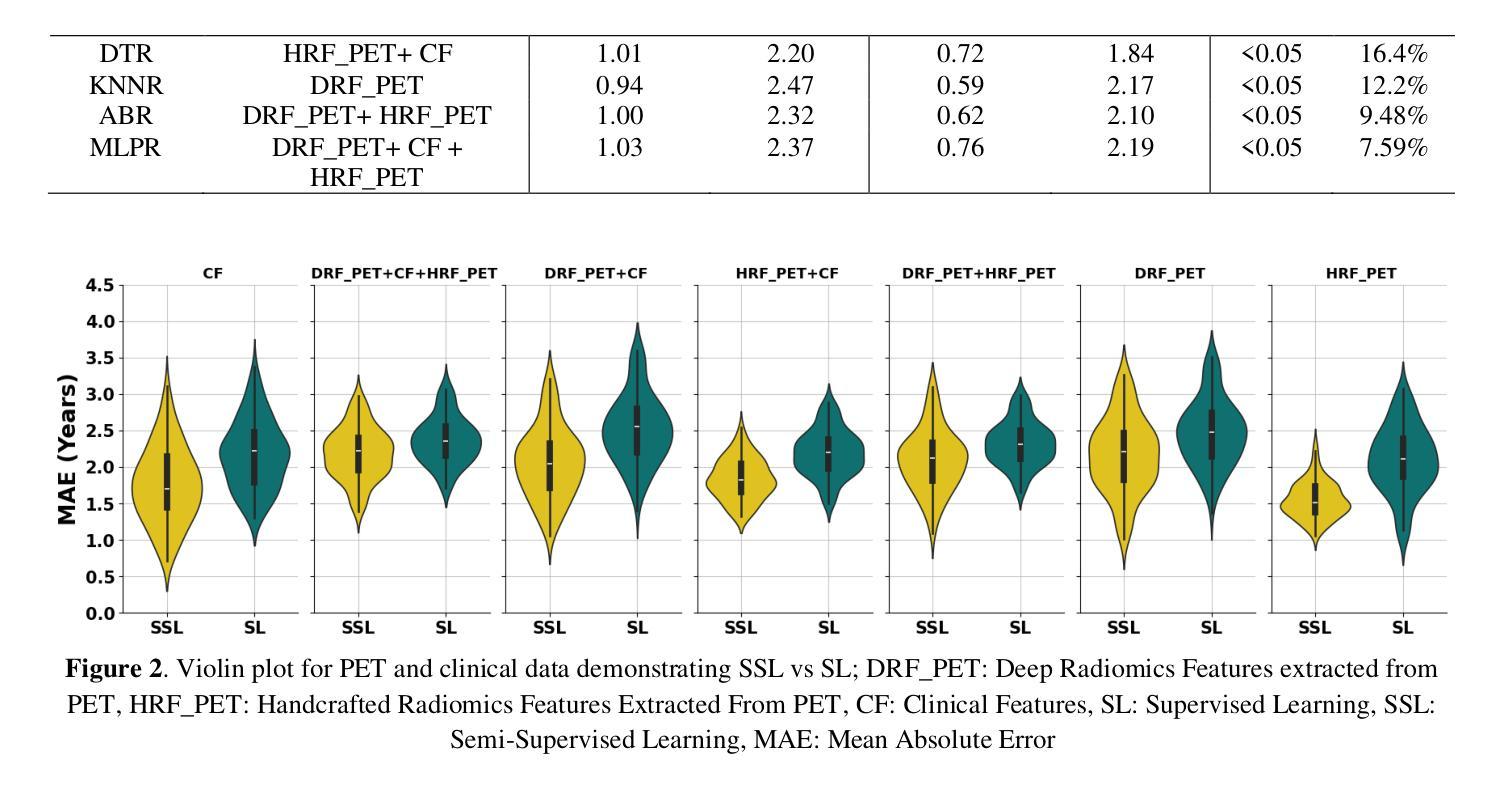
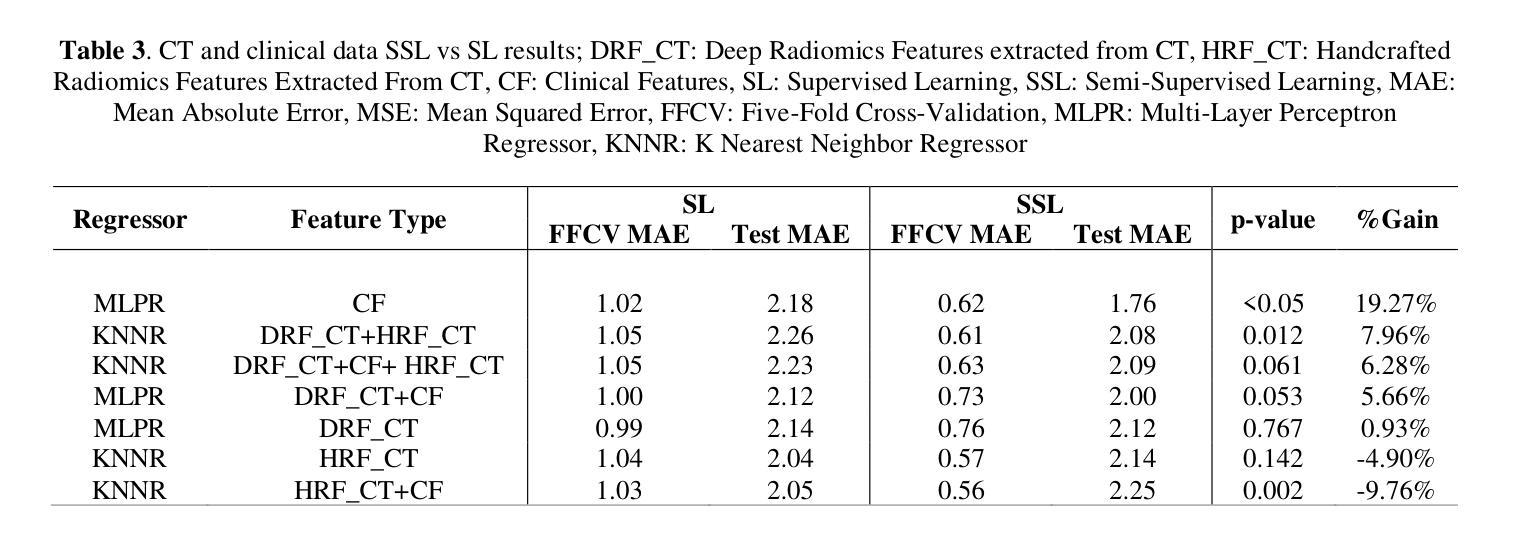
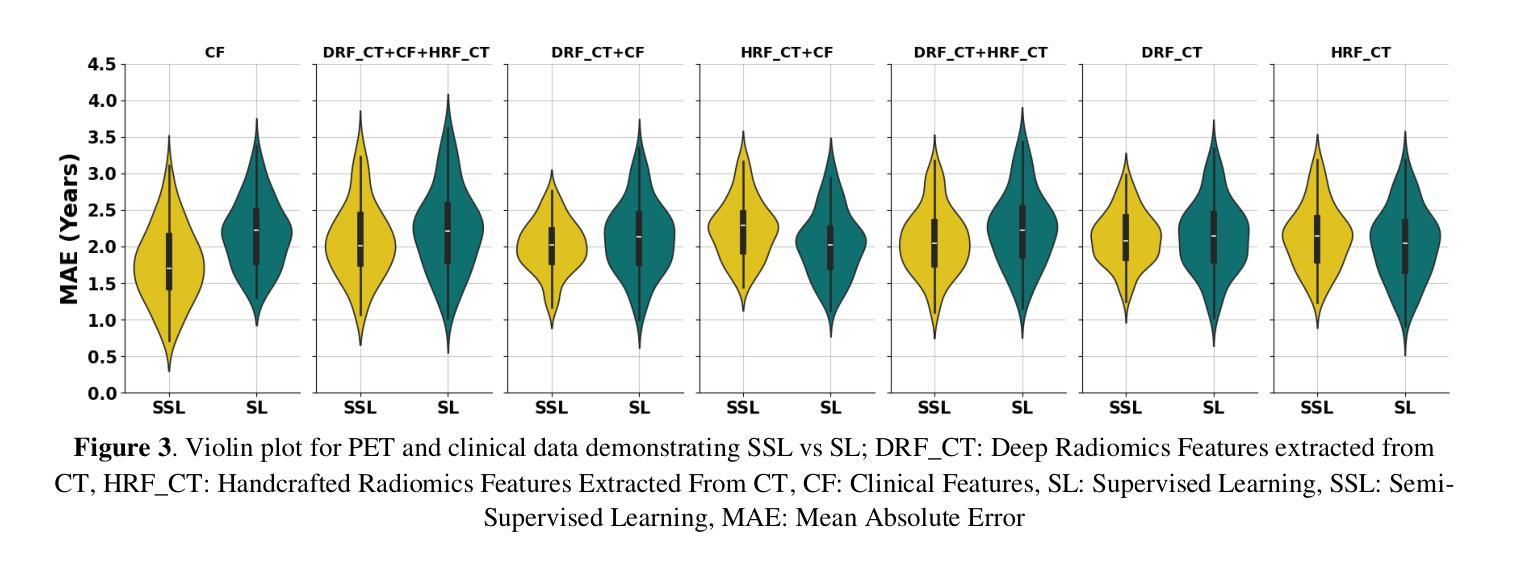
Objectives: Lung cancer poses a significant global health challenge, necessitating improved prognostic methods for personalized treatment. This study introduces a censor-aware semi-supervised learning (SSL) framework that integrates clinical and imaging data, addressing biases in traditional models handling censored data. Methods: We analyzed clinical, PET and CT data from 199 lung cancer patients from public and local data respositories, focusing on overall survival (OS) time as the primary outcome. Handcrafted (HRF) and Deep Radiomics features (DRF) were extracted after preprocessing using ViSERA software and were combined with clinical features (CF). Feature dimensions were optimized using Principal Component Analysis (PCA), followed by the application of supervised learning (SL) and SSL. SSL incorporated pseudo-labeling of censored data to improve performance. Seven regressors and three hazard ratio survival analysis (HRSA) algorithms were optimized using five-fold cross-validation, grid search and external test bootstrapping. Results: For PET HRFs, SSL reduced the mean absolute error (MAE) by 26.5%, achieving 1.55 years with PCA+decision tree regression, compared to SL’s 2.11 years with PCA+KNNR (p<0.05). Combining HRFs (CT_HRF) and DRFs from CT images using SSL+PCA+KNNR achieved an MAE of 2.08 years, outperforming SL’s 2.26 years by 7.96% (p<0.05). In HRSA, CT_HRF applied to PCA+Component Wise Gradient Boosting Survival Analysis achieved an external c-index of 0.65, effectively differentiating high- and low-risk groups. Conclusions: We demonstrated that the SSL strategy significantly outperforms SL across PET, CT, and CF. As such, censor-aware SSL applied to HRFs from PET images significantly improved survival prediction performance by 26.5% compared to the SL approach.
目标:肺癌给全球健康带来了巨大挑战,需要改进预测方法以实现个性化治疗。本研究介绍了一种有审查意识的半监督学习(SSL)框架,该框架融合了临床和成像数据,解决了传统模型在处理审查数据时的偏见问题。
方法:我们分析了来自公共和本地数据仓库的199名肺癌患者的临床、PET和CT数据,以总生存期(OS)时间为主要结果。使用ViSERA软件预处理后提取了手工特征(HRF)和深度放射学特征(DRF),并与临床特征(CF)相结合。使用主成分分析(PCA)优化特征维度,然后应用监督学习(SL)和SSL。SSL结合了审查数据的伪标签以提高性能。使用五折交叉验证、网格搜索和外部测试bootstrap方法优化了7个回归器和3种风险比率生存分析(HRSA)算法。
结果:对于PET的HRFs,SSL将平均绝对误差(MAE)降低了26.5%,使用PCA+决策树回归达到了1.55年,而SL+PCA+KNNR为2.11年(p<0.05)。使用SSL+PCA+KNNR结合来自CT图像的HRF和DRF,MAE为2.08年,优于SL的2.26年,提高了7.96%(p<0.05)。在HRSA中,将CT_HRF应用于PCA+组件智慧梯度提升生存分析达到了外部c指数为0.65,有效地区分了高、低风险组。
结论:我们证明SSL策略在PET、CT和CF方面显著优于SL。因此,与SL方法相比,应用于PET图像HRFs的有审查意识的SSL将生存预测性能提高了26.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 Figures and 4 Tables
Summary:本研究旨在应对肺癌预后预测方法的挑战,提出一种融合临床与成像数据的半监督学习框架,以解决传统模型中处理截断数据时的偏见问题。研究通过集成影像与临床数据,优化了特征维度与算法模型,提高了生存预测性能。结果表明,半监督学习方法显著优于传统监督学习方法,特别是在处理PET影像的HRFs时,预测误差降低了26.5%。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究旨在改善肺癌的个性化治疗预后方法,引入半监督学习框架整合临床与成像数据。
- 研究处理了传统模型在处理截断数据时的偏见问题。
- 通过使用ViSERA软件提取特征,并结合主成分分析(PCA)优化特征维度。
- 研究比较了监督学习与半监督学习方法在肺癌预后预测中的性能。
- 半监督学习方法在PET影像的HRFs处理中显著提高了生存预测准确性,误差降低了26.5%。
- 结合CT影像的HRFs与DRFs使用半监督学习方法也表现出更好的预测性能。
点此查看论文截图

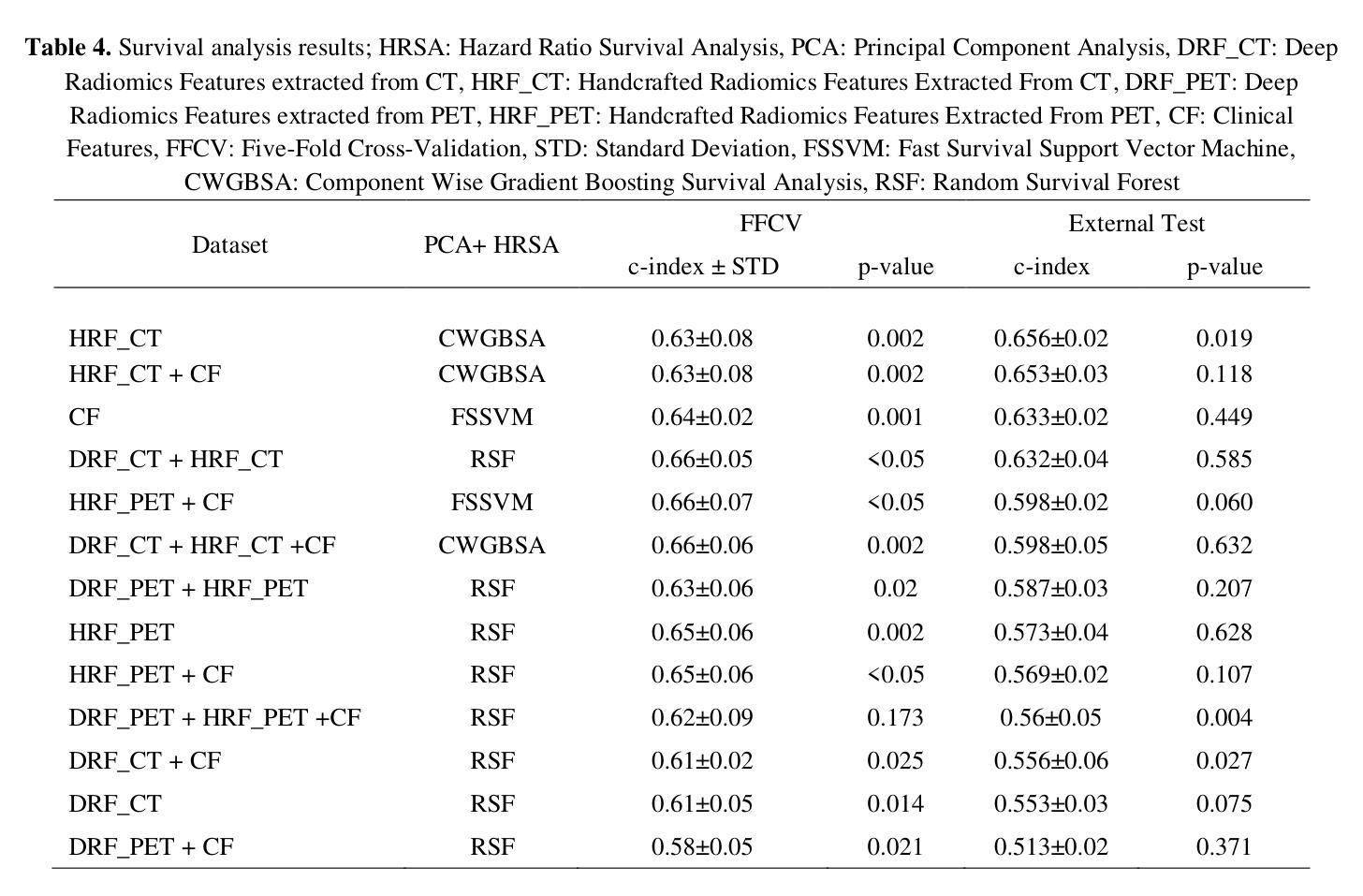
Moner: Motion Correction in Undersampled Radial MRI with Unsupervised Neural Representation
Authors:Qing Wu, Chenhe Du, Xuanyu Tian, Jingyi Yu, Yuyao Zhang, Hongjiang Wei
Motion correction (MoCo) in radial MRI is a challenging problem due to the unpredictability of subject’s motion. Current state-of-the-art (SOTA) MoCo algorithms often use extensive high-quality MR images to pre-train neural networks, obtaining excellent reconstructions. However, the need for large-scale datasets significantly increases costs and limits model generalization. In this work, we propose Moner, an unsupervised MoCo method that jointly solves artifact-free MR images and accurate motion from undersampled, rigid motion-corrupted k-space data, without requiring training data. Our core idea is to leverage the continuous prior of implicit neural representation (INR) to constrain this ill-posed inverse problem, enabling ideal solutions. Specifically, we incorporate a quasi-static motion model into the INR, granting its ability to correct subject’s motion. To stabilize model optimization, we reformulate radial MRI as a back-projection problem using the Fourier-slice theorem. Additionally, we propose a novel coarse-to-fine hash encoding strategy, significantly enhancing MoCo accuracy. Experiments on multiple MRI datasets show our Moner achieves performance comparable to SOTA MoCo techniques on in-domain data, while demonstrating significant improvements on out-of-domain data. The code is available at: https://github.com/iwuqing/Moner
磁共振成像中的运动校正(MoCo)是一个具有挑战性的任务,因为受试者运动具有不可预测性。目前最先进的MoCo算法通常使用大量高质量的MR图像来预先训练神经网络,从而获得出色的重建效果。然而,对大规模数据集的需求显著增加了成本并限制了模型的泛化能力。在本文中,我们提出了Moner,这是一种无需监督的MoCo方法,可以联合解决无伪影MR图像和从欠采样的刚性运动损坏的k空间数据中准确运动的问题,而无需训练数据。我们的核心思想是利用隐式神经表示(INR)的连续先验知识来约束这个不适定的反问题,以实现理想的解决方案。具体来说,我们将准静态运动模型纳入INR中,使其具备纠正受试者运动的能力。为了稳定模型优化,我们利用傅里叶切片定理将径向MRI重新表述为反向投影问题。此外,我们还提出了一种新颖的由粗到细的哈希编码策略,显著提高了MoCo的准确性。在多个MRI数据集上的实验表明,我们的Moner在领域内数据上的性能与最先进的MoCo技术相当,而在跨领域数据上则表现出显著改进。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/iwuqing/Moner
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Moner的无监督运动校正(MoCo)方法,用于解决MRI中的运动问题。该方法无需训练数据,可直接从欠采样的、受刚性运动影响的k空间数据中恢复无伪影的MR图像和精确运动。其核心思想是利用隐式神经表示(INR)的连续先验来约束这个不适定的逆问题,从而实现理想解。Moner在多个MRI数据集上的实验表明,其性能与最新MoCo技术相当,并在跨域数据上表现出显著改善。
Key Takeaways
- Moner是一种无监督的MoCo方法,无需训练数据。
- Moner能够从欠采样的、受刚性运动影响的k空间数据中恢复无伪影的MR图像和精确运动。
- 该方法利用隐式神经表示(INR)的连续先验来约束不适定的逆问题。
- Moner将径向MRI重新表述为反向投影问题,运用傅立叶切片定理。
- 提出了一种新颖的由粗到细的哈希编码策略,显著提高了MoCo的准确性。
- 在多个MRI数据集上的实验表明,Moner性能与最新MoCo技术相当,并在跨域数据上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

Uncertainty-Aware Liquid State Modeling from Experimental Scattering Measurements
Authors:Brennon L. Shanks
This dissertation is founded on the central notion that structural correlations in dense fluids, such as dense gases, liquids, and glasses, are directly related to fundamental interatomic forces. This relationship was identified early in the development of statistical theories of fluids through the mathematical formulations of Gibbs in the 1910s. However, it took nearly 80 years before practical implementations of structure-based theories became widely used for interpreting and understanding the atomic structures of fluids from experimental X-ray and neutron scattering data. The breakthrough in successfully applying structure-potential relations is largely attributed to the advancements in molecular mechanics simulations and the enhancement of computational resources. Despite advancements in understanding the relationship between structure and interatomic forces, a significant gap remains. Current techniques for interpreting experimental scattering measurements are widely used, yet there is little evidence that they yield physically accurate predictions for interatomic forces. In fact, it is generally assumed that these methods produce interatomic forces that poorly model the atomistic and thermodynamic behavior of fluids, rendering them unreliable and non-transferable. This thesis aims to address these limitations by refining the statistical theory, computational methods, and philosophical approach to structure-based analyses, thereby developing more robust and accurate techniques for characterizing structure-potential relationships.
本论文的核心观点是,密集流体(如致密气体、液体和玻璃)中的结构关联与基本原子间力有着直接联系。这种关系在流体统计理论发展的早期就被识别出来,吉布斯在20世纪提出了相关的数学公式。然而,在实际应用中,基于结构的理论被广泛用于解释和理解从实验X射线和中子散射数据得出的流体原子结构却耗费了近80年的时间。成功应用结构电位关系的突破在很大程度上归因于分子力学模拟的进步和计算资源的增强。尽管在理解结构与原子间力的关系方面取得了进展,但仍存在重大差距。目前用于解释实验散射测量的技术被广泛使用,但有证据表明它们对原子间力的预测并不准确。事实上,通常认为这些方法产生的原子间力模型不能很好地模拟流体的原子和热力学行为,使其不可靠且不可转移。本论文旨在通过改进统计理论、计算方法和基于结构的分析哲学方法,解决这些局限,从而开发更稳健和准确的技术来表征结构电位关系。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Doctoral thesis
Summary
这篇论文聚焦于密集流体(如致密气体、液体和玻璃)的结构关联与基本原子间力之间的直接关系。它回顾了早期统计流体理论的发展,特别是吉布斯在20世纪初的数学表述,指出两者之间的紧密联系。虽然利用结构基础理论的实践实现了在近八十年的突破,且在实验性X射线和中子散射数据的基础上成功应用结构势能关系,但仍然存在显著差距。当前用于解释实验散射测量的技术被广泛使用,但缺乏物理准确预测原子间力的证据。论文旨在通过改进统计理论、计算方法和哲学方法来解决这些局限性,开发更稳健和准确的结构势能关系表征技术。
Key Takeaways
- 此论文认为密集流体的结构关联与基本原子间力存在紧密联系。这一理念始于早期的统计流体理论发展。
- 结构基础理论的应用实践经历了近八十年的突破期,得益于分子力学模拟的进步和计算资源的提升。
- 成功应用结构势能关系的进步为理解和解释流体的原子结构提供了新的方法。
- 尽管取得了进展,但现有解释实验散射测量的技术在预测原子间力方面存在显著差距,这些方法往往不能准确模拟流体的原子和热力学行为。
- 当前技术中的方法被认为可靠性低且缺乏可转移性,对于实际应用的预测存在挑战。
- 论文旨在通过改进统计理论、计算方法和哲学方法来缩小差距,提高结构势能关系表征技术的准确性和稳健性。这将有助于更准确理解流体行为的内部机制。
点此查看论文截图

Fact-Aware Multimodal Retrieval Augmentation for Accurate Medical Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Liwen Sun, James Zhao, Megan Han, Chenyan Xiong
Multimodal foundation models hold significant potential for automating radiology report generation, thereby assisting clinicians in diagnosing cardiac diseases. However, generated reports often suffer from serious factual inaccuracy. In this paper, we introduce a fact-aware multimodal retrieval-augmented pipeline in generating accurate radiology reports (FactMM-RAG). We first leverage RadGraph to mine factual report pairs, then integrate factual knowledge to train a universal multimodal retriever. Given a radiology image, our retriever can identify high-quality reference reports to augment multimodal foundation models, thus enhancing the factual completeness and correctness of report generation. Experiments on two benchmark datasets show that our multimodal retriever outperforms state-of-the-art retrievers on both language generation and radiology-specific metrics, up to 6.5% and 2% score in F1CheXbert and F1RadGraph. Further analysis indicates that employing our factually-informed training strategy imposes an effective supervision signal, without relying on explicit diagnostic label guidance, and successfully propagates fact-aware capabilities from the multimodal retriever to the multimodal foundation model in radiology report generation.
多模态基础模型在自动放射学报告生成方面拥有巨大的潜力,从而帮助临床医生诊断心脏疾病。然而,生成的报告常常存在严重的事实不准确问题。在本文中,我们介绍了一种用于生成准确放射学报告的基于事实感知的多模态检索增强管道(FactMM-RAG)。我们首先利用RadGraph挖掘事实报告对,然后整合事实知识来训练一个通用的多模态检索器。给定一张放射学图像,我们的检索器可以识别高质量的参考报告,以增强多模态基础模型,从而提高报告生成的事实完整性和正确性。在两个基准数据集上的实验表明,我们的多模态检索器在语言生成和放射学特定指标上的表现均优于最新检索器,在F1CheXbert和F1RadGraph上的得分分别高达6.5%和2%。进一步的分析表明,采用我们的事实感知训练策略,在不依赖明确的诊断标签指导的情况下,成功地将多模态检索器的事实感知能力传播到多模态基础模型中,从而有效地监督了放射学报告的生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025 main
Summary
本文介绍了基于事实感知的多模态检索增强管道(FactMM-RAG),用于生成准确的放射学报告。该研究利用RadGraph挖掘事实报告对,并集成事实知识训练通用多模态检索器。给定放射学图像,该检索器可识别高质量参考报告,增强多模态基础模型的性能,从而提高报告生成的事实完整性和准确性。实验表明,该多模态检索器在语言生成和放射学特定指标上均优于最新检索器,最高可提高F1CheXbert和F1RadGraph的分数分别达6.5%和2%。进一步分析表明,采用基于事实的训练策略提供了有效的监督信号,无需依赖明确的诊断标签指导,并成功将从多模态检索器中获取的事实感知能力传播到多模态基础模型中用于放射学报告生成。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态基础模型在自动化放射学报告生成方面具有巨大潜力,有助于临床医生诊断心脏病。
- 生成的报告常常存在事实准确性问题。
- 引入了一种基于事实感知的多模态检索增强管道(FactMM-RAG)以提高报告准确性。
- 使用RadGraph挖掘事实报告对,并集成事实知识训练多模态检索器。
- 多模态检索器可识别高质量参考报告,增强模型性能。
- 实验表明,该多模态检索器在语言生成和放射学特定指标上均表现出优异性能。
点此查看论文截图


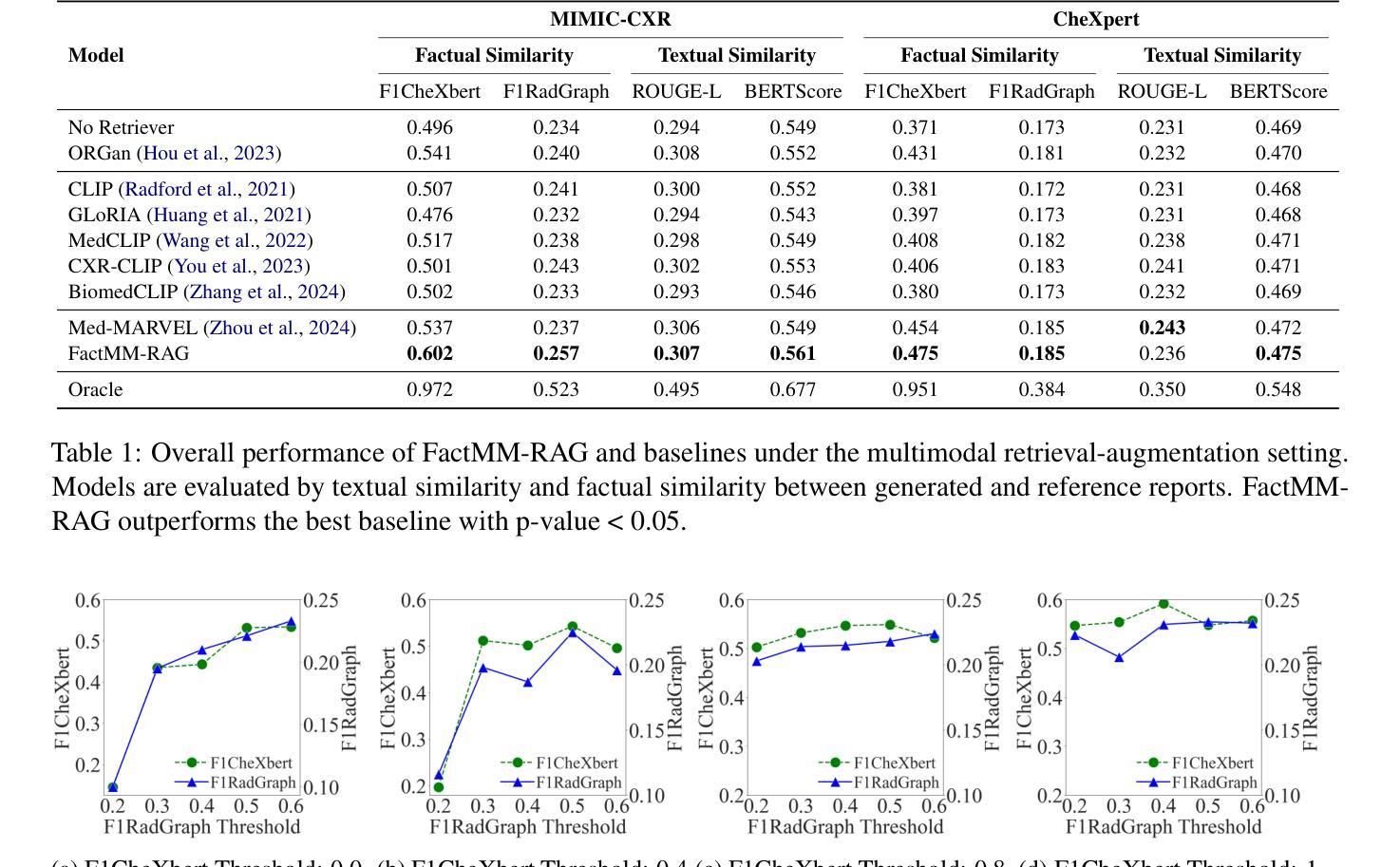
A study of why we need to reassess full reference image quality assessment with medical images
Authors:Anna Breger, Ander Biguri, Malena Sabaté Landman, Ian Selby, Nicole Amberg, Elisabeth Brunner, Janek Gröhl, Sepideh Hatamikia, Clemens Karner, Lipeng Ning, Sören Dittmer, Michael Roberts, AIX-COVNET Collaboration, Carola-Bibiane Schönlieb
Image quality assessment (IQA) is indispensable in clinical practice to ensure high standards, as well as in the development stage of machine learning algorithms that operate on medical images. The popular full reference (FR) IQA measures PSNR and SSIM are known and tested for working successfully in many natural imaging tasks, but discrepancies in medical scenarios have been reported in the literature, highlighting the gap between development and actual clinical application. Such inconsistencies are not surprising, as medical images have very different properties than natural images, and PSNR and SSIM have neither been targeted nor properly tested for medical images. This may cause unforeseen problems in clinical applications due to wrong judgment of novel methods. This paper provides a structured and comprehensive overview of examples where PSNR and SSIM prove to be unsuitable for the assessment of novel algorithms using different kinds of medical images, including real-world MRI, CT, OCT, X-Ray, digital pathology and photoacoustic imaging data. Therefore, improvement is urgently needed in particular in this era of AI to increase reliability and explainability in machine learning for medical imaging and beyond. Lastly, we will provide ideas for future research as well as suggesting guidelines for the usage of FR-IQA measures applied to medical images.
图像质量评估(IQA)在临床实践中是不可或缺的,以确保高标准,以及在医学图像操作的机器学习算法的开发阶段也是不可或缺的。流行的全参考(FR)IQA措施PSNR和SSIM在众多的自然成像任务中得到了很好的应用,但在医学场景中报道了文献中的差异,突出了开发与实际应用之间的差距。这种不一致性并不奇怪,因为医学图像具有与自然图像非常不同的属性,并且PSNR和SSIM既没有被定位也没有针对医学图像进行适当的测试。这可能导致新型方法判断错误,从而在临床应用中造成意想不到的问题。本文对PSNR和SSIM在不使用不同医学图像的全新算法评估中表现不佳的案例进行了结构和全面的概述,这些医学图像包括现实世界的MRI、CT、OCT、X射线、数字病理和光声成像数据。因此,特别是在人工智能时代,迫切需要在提高机器学习在医学成像等领域的可靠性和可解释性方面进行改进。最后,我们将为未来的研究提供思路,并为应用于医学图像的全参考IQA措施的使用提供指导建议。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了图像质量评估(IQA)在医疗图像领域的挑战和局限性。虽然PSNR和SSIM等全参考(FR)IQA方法在自然成像任务中表现良好,但在医学场景中却存在不一致性。本文提供了在不同医学图像类型中使用PSNR和SSIM评估新方法时可能出现的问题的例子,强调需要改进以增强AI时代的可靠性和可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 在临床实践和医学影像的机器学习算法开发阶段中,图像质量评估(IQA)至关重要。
- 全参考(FR)IQA中的PSNR和SSIM在自然成像任务中表现良好,但在医学图像中却存在差距和不一致性。
- 医学图像具有与自然图像不同的特性,使得PSNR和SSIM可能不适合用于医学图像的评估。
- 在临床应用中,错误的判断新方法可能导致未预见的问题。
- 文章提供了在不同医学图像类型中使用PSNR和SSIM评估算法时可能出现问题的例子。
- 在AI时代,需要提高在医学图像领域中的可靠性和可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

Photoevaporation from Inner Protoplanetary Disks Confronted with Observations
Authors:Yiren Lin, Lile Wang, Min Fang, Ahmad Nemer, Jeremy Goodman
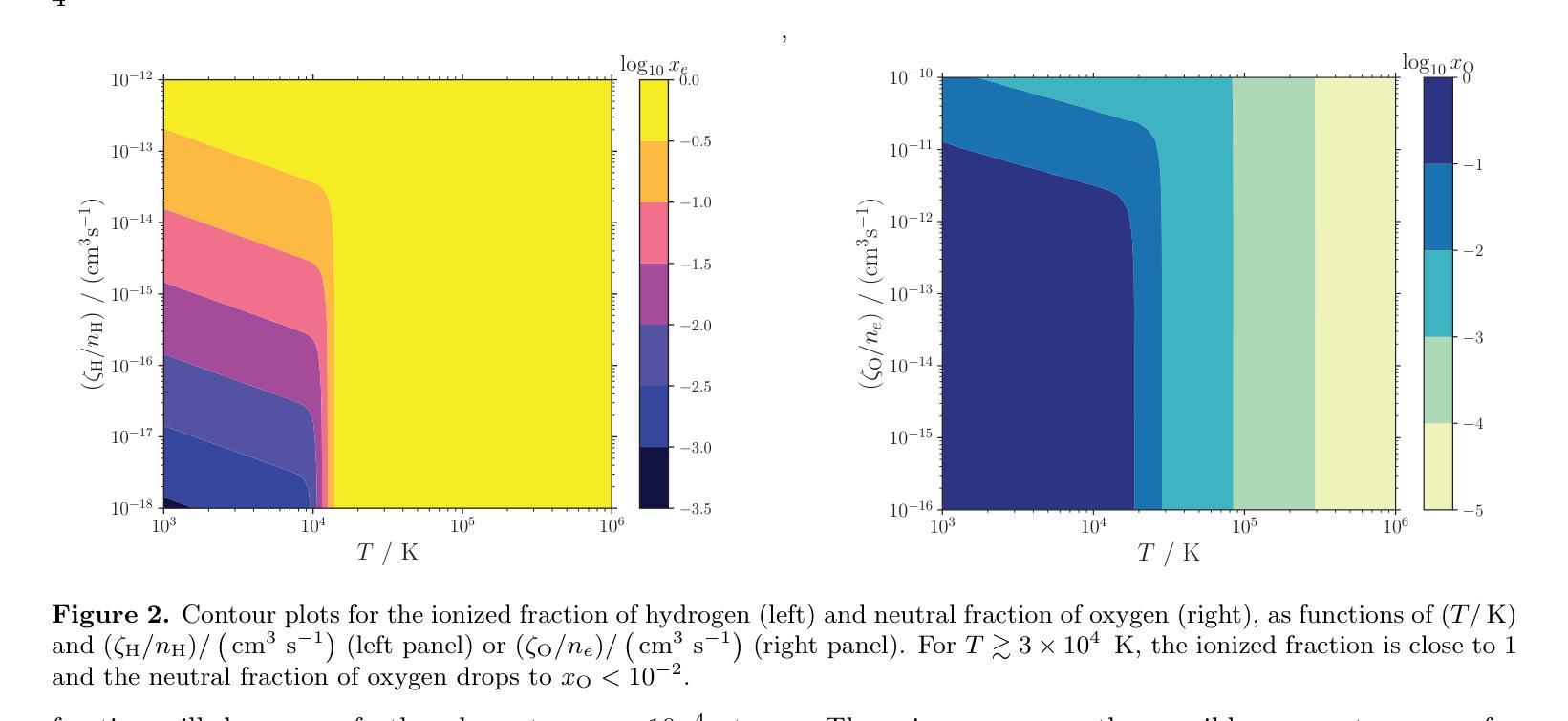
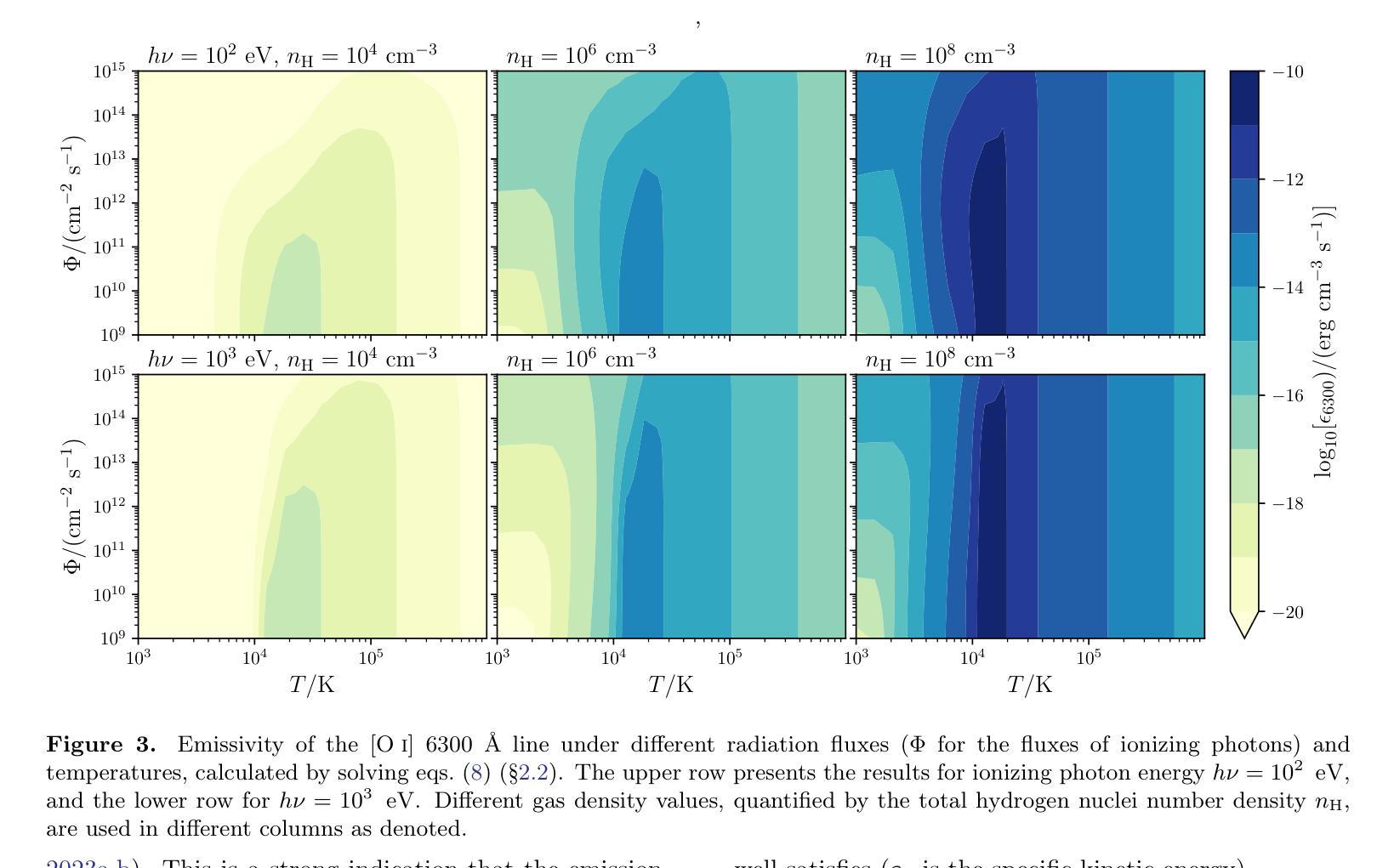
The decades-long explorations on the dispersal of protoplanetary disks involve many debates about photoevaporation versus magnetized wind launching mechanisms. This letter argues that the observed winds originating from the inner disk ($R\lesssim 0.3$ AU) cannot be explained by the photoevaporative mechanism. Energy conservation requires the presumed photoevaporative winds to be heated to $\gtrsim 10^5$ K when launched from inner disks. However, due to efficient thermal accommodation with dust grains and cooling processes at high densities, X-ray irradiation at energies above 1 keV cannot efficiently launch winds in the first place because of its high penetration. Some studies claiming X-ray wind launching have oversimplified the thermochemical couplings. Furthermore, heating the gas to escape velocity will over-ionize it, suppressing the species responsible for observed forbidden lines (e.g., [OI] 6300 $\r{A}$ ). Confirmed by semi-analytic integrations of thermochemical fluid structures, such high ionizations contradict the observed emission of neutral and singly-ionized atoms from the winds originating from the inner disks.
对于原行星盘扩散几十年的探索中,涉及到了许多关于光蒸发和磁化风发射机制之间的争论。这篇论文认为,从内盘(R≤0.3AU)观测到的风无法用光蒸发机制来解释。能量守恒要求从内盘发射的光蒸发风在被发射时需要加热到≥10^5K。然而,由于与尘埃颗粒的高效热适应和在高密度下的冷却过程,X射线辐射在高于1keV的能量下无法有效地发射风,因为它的穿透性很强。一些声称X射线风发射的研究过于简化了热化学耦合。此外,将气体加热到逃逸速度会使其过度电离,从而抑制了观测到的禁戒线(例如,[OI] 6300Å)所负责的物种。通过热化学流体结构的半解析积分证实,这种高电离与来自内盘的风中性和单电离原子的观测发射相矛盾。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 6 figures, accepted for publication by the ApJ
Summary
这篇文章探讨了原行星盘扩散几十年的探索历程,其中关于光蒸发和磁化风发射机制的争议不断。作者认为从内盘(R≤0.3 AU)观测到的风无法用光蒸发机制解释。能量守恒要求假设的光蒸发风从内盘发射时需要加热到≥10^5 K。但由于与尘埃颗粒的热适应和高密度下的冷却过程,X射线辐射无法有效发射风。一些声称X射线风发射的研究过于简化了热化学耦合。此外,将气体加热到逃逸速度会过度电离它,抑制了观测到的禁戒线(如OI 6300 A)对应的物种。通过半解析积分热化学流体结构证实,高电离与来自内盘的风中观测到的中性及单电离原子发射相矛盾。
Key Takeaways
- 文章讨论了原行星盘扩散过程中关于光蒸发和磁化风发射机制的争议。
- 从内盘观测到的风无法用光蒸发机制解释,因为这需要气体被加热到过高的温度。
- X射线辐射无法有效发射风,因为其与尘埃颗粒的热适应以及高密度下的冷却过程。
- 一些关于X射线风发射的研究过于简化了热化学耦合。
- 加热气体到逃逸速度会过度电离它,抑制了某些观测到的物种的禁戒线。
- 通过半解析积分热化学流体结构证实,高电离与来自内盘的风的观测结果相矛盾。
点此查看论文截图