⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-08 更新
HOG-Diff: Higher-Order Guided Diffusion for Graph Generation
Authors:Yiming Huang, Tolga Birdal
Graph generation is a critical yet challenging task as empirical analyses require a deep understanding of complex, non-Euclidean structures. Although diffusion models have recently made significant achievements in graph generation, these models typically adapt from the frameworks designed for image generation, making them ill-suited for capturing the topological properties of graphs. In this work, we propose a novel Higher-order Guided Diffusion (HOG-Diff) model that follows a coarse-to-fine generation curriculum and is guided by higher-order information, enabling the progressive generation of plausible graphs with inherent topological structures. We further prove that our model exhibits a stronger theoretical guarantee than classical diffusion frameworks. Extensive experiments on both molecular and generic graph generation tasks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms or remains competitive with state-of-the-art baselines. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yiminghh/HOG-Diff.
图生成是一项至关重要的任务,但具有挑战性,因为它需要对复杂的非欧几里得结构进行深入理解。尽管扩散模型最近在图生成方面取得了重大进展,但这些模型通常是从为图像生成设计的框架中改编而来的,因此难以捕捉图的拓扑属性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的高阶引导扩散(HOG-Diff)模型,该模型遵循从粗到细的生成课程,并由高阶信息引导,能够逐步生成具有固有拓扑结构的合理图。我们还证明,我们的模型具有比传统扩散框架更强的理论保证。在分子和通用图生成任务上的大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于或具有竞争力最先进基线。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Yiminghh/HOG-Diff获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的基于高阶引导扩散(HOG-Diff)模型的图生成方法,它采用由粗到细的生成策略,并结合高阶信息进行引导,可以逐步生成具有内在拓扑结构的可信任图。与传统扩散模型相比,该模型具有较强的理论保证。在分子和通用图生成任务的广泛实验中,该方法表现出出色的性能,超越了现有的主流模型。模型代码已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 图生成是一项关键且具有挑战性的任务,需要深入理解复杂的非欧几里得结构。
- 现有的扩散模型在图形生成中表现不佳,因为它们主要借鉴了图像生成的框架设计,无法充分捕捉图形的拓扑特性。
- 本文提出了一种新颖的Higher-order Guided Diffusion(HOG-Diff)模型,用于图形生成。该模型遵循由粗到细的生成策略,通过高阶信息进行引导。
- HOG-Diff模型具有更强的理论保证,与传统的扩散模型相比具有优势。
- 在分子和通用图生成任务的实验中,HOG-Diff模型表现优异,超越了现有的主流方法。
- 该模型的代码已经公开,便于其他研究者进行进一步的研究和改进。
点此查看论文截图

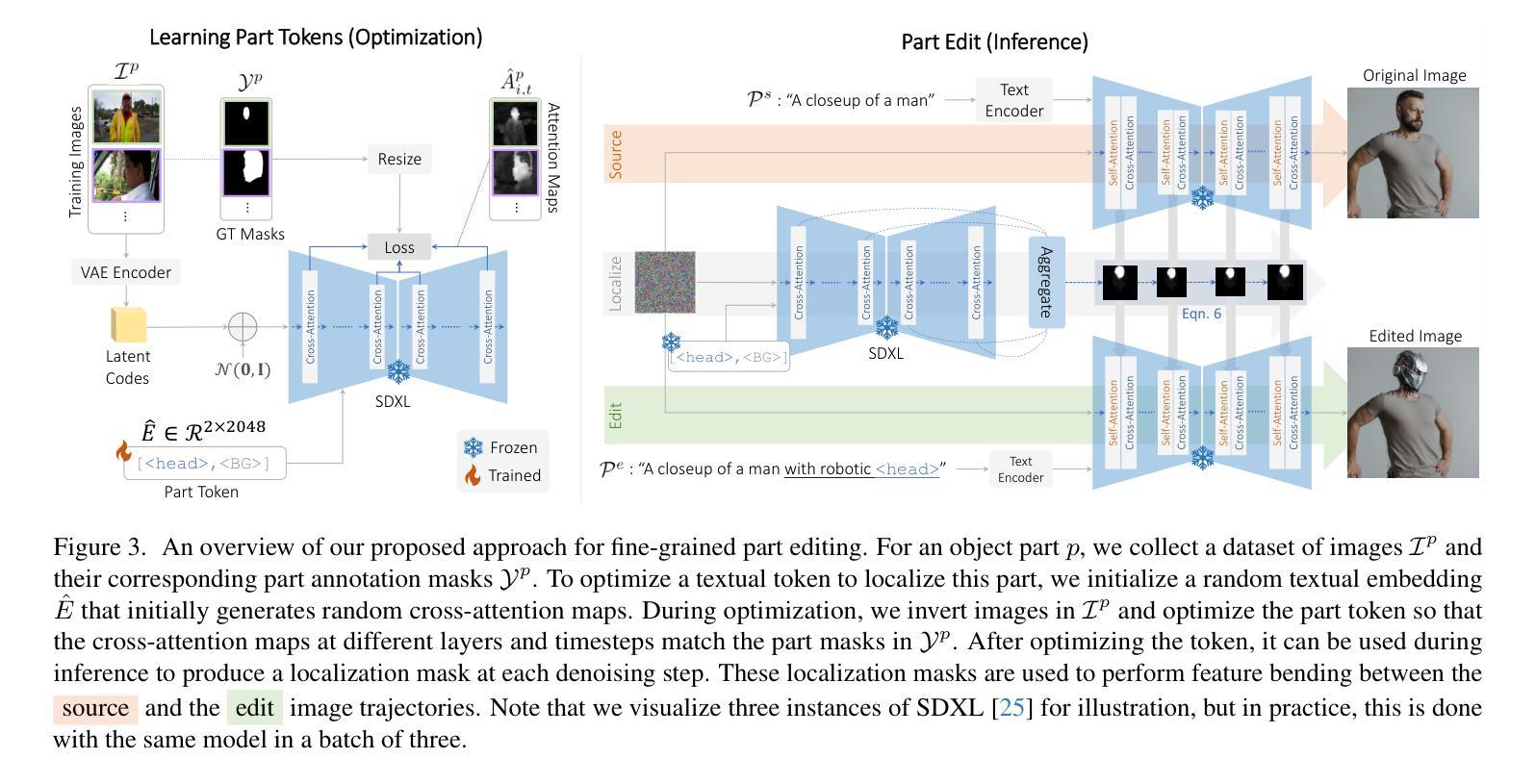
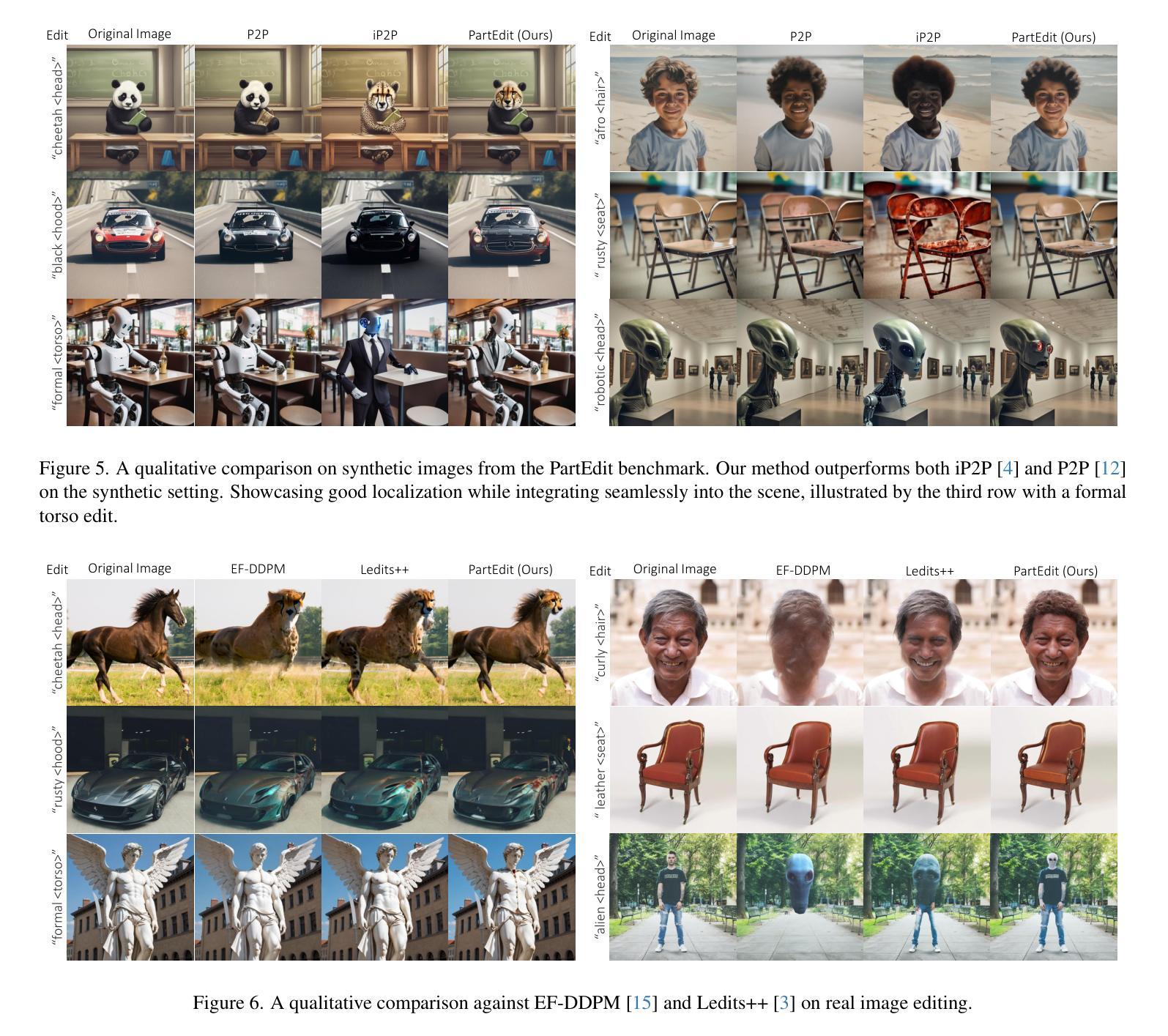
PartEdit: Fine-Grained Image Editing using Pre-Trained Diffusion Models
Authors:Aleksandar Cvejic, Abdelrahman Eldesokey, Peter Wonka
We present the first text-based image editing approach for object parts based on pre-trained diffusion models. Diffusion-based image editing approaches capitalized on the deep understanding of diffusion models of image semantics to perform a variety of edits. However, existing diffusion models lack sufficient understanding of many object parts, hindering fine-grained edits requested by users. To address this, we propose to expand the knowledge of pre-trained diffusion models to allow them to understand various object parts, enabling them to perform fine-grained edits. We achieve this by learning special textual tokens that correspond to different object parts through an efficient token optimization process. These tokens are optimized to produce reliable localization masks at each inference step to localize the editing region. Leveraging these masks, we design feature-blending and adaptive thresholding strategies to execute the edits seamlessly. To evaluate our approach, we establish a benchmark and an evaluation protocol for part editing. Experiments show that our approach outperforms existing editing methods on all metrics and is preferred by users 77-90% of the time in conducted user studies.
我们首次提出了一种基于预训练扩散模型的面向物体部件的文本驱动图像编辑方法。基于扩散模型的图像编辑方法利用对图像语义扩散模型的深入理解来进行各种编辑操作。然而,现有的扩散模型对许多物体部件的理解不足,阻碍了用户要求的精细编辑。为了解决这一问题,我们提出对预训练的扩散模型进行知识扩展,使它们能够理解各种物体部件,从而进行精细编辑。我们通过高效的令牌优化过程,学习对应于不同物体部件的特殊文本令牌。这些令牌经过优化,在每个推理步骤中产生可靠的定位掩码,以定位编辑区域。利用这些掩码,我们设计了特征混合和自适应阈值策略,以无缝执行编辑操作。为了评估我们的方法,我们建立了部件编辑的基准测试和评价协议。实验表明,我们的方法在所有指标上的编辑效果优于现有编辑方法,在用户研究中,用户偏好我们的方法的时间占比达到77-90%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://partedit.github.io/PartEdit/
Summary
本文首次提出了基于预训练扩散模型的文本驱动图像编辑方法,用于处理对象部分的编辑。通过优化扩散模型的知识,使其能够理解各种对象部分,实现精细编辑。通过高效的文本令牌优化过程,学习对应于不同对象部分的特殊文本令牌,用于生成可靠的定位掩膜,定位编辑区域。结合这些掩膜,设计特征融合和自适应阈值策略,实现无缝编辑。实验表明,该方法在各项评估指标上均优于现有编辑方法,并在用户研究中获得用户77%-90%的青睐。
Key Takeaways
- 首次提出基于预训练扩散模型的文本驱动图像编辑方法,用于处理对象部分的编辑。
- 扩散模型通过优化知识,提高对对象部分的理解,实现精细编辑。
- 通过高效的文本令牌优化过程,学习对应于不同对象部分的特殊文本令牌。
- 特殊文本令牌生成可靠的定位掩膜,用于定位编辑区域。
- 结合定位掩膜,采用特征融合和自适应阈值策略实现无缝编辑。
- 实验表明该方法在各项评估指标上优于现有编辑方法。
点此查看论文截图



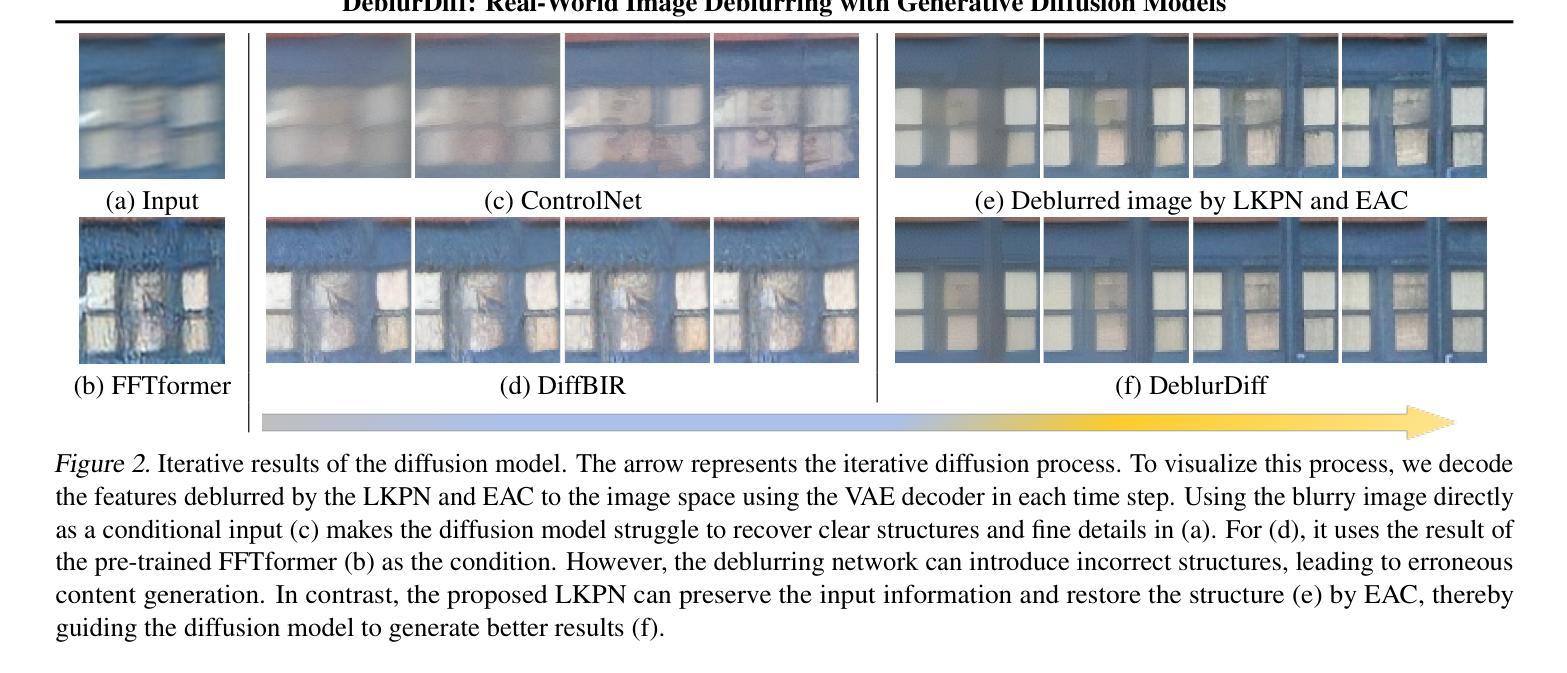
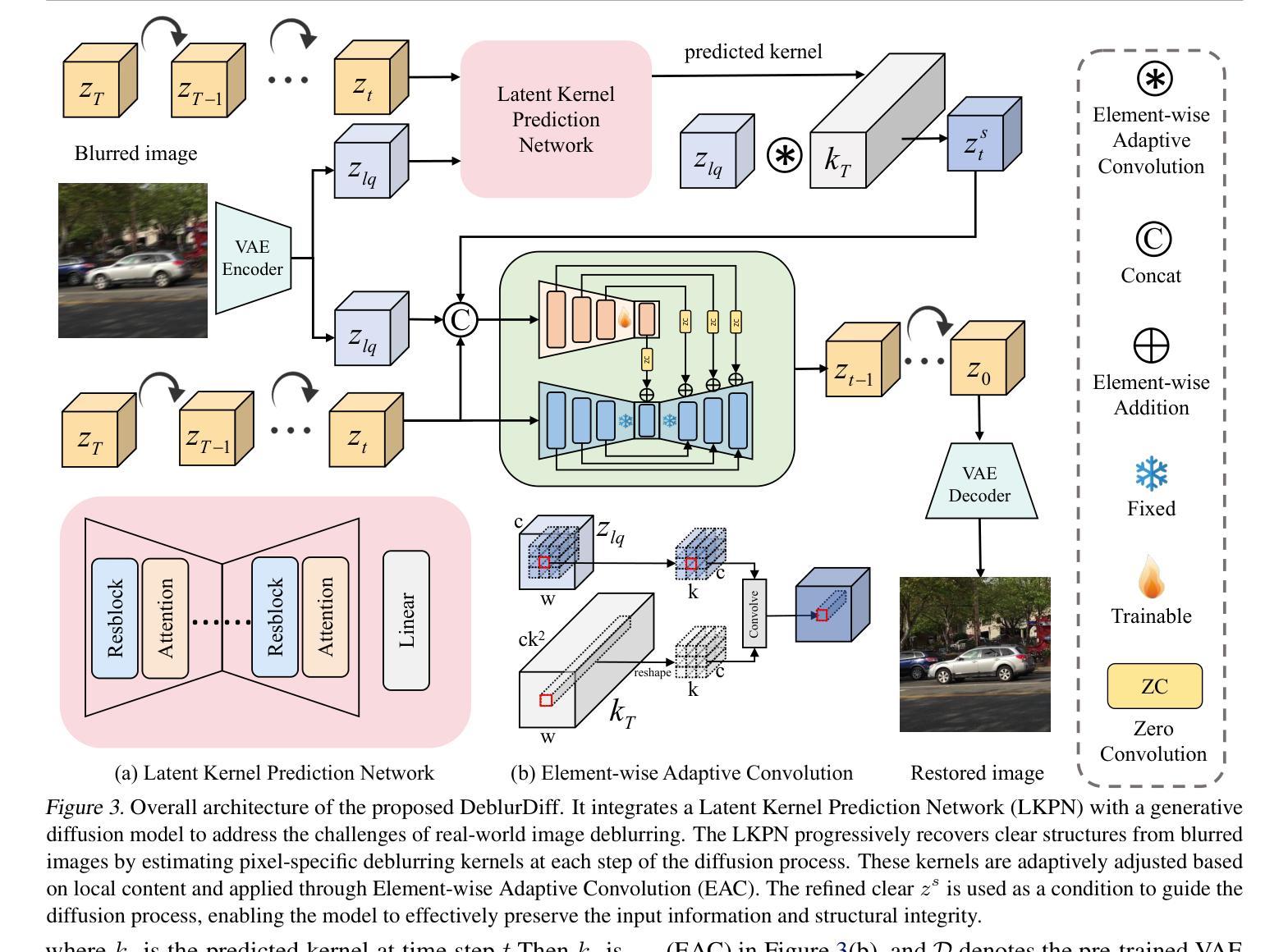
DeblurDiff: Real-World Image Deblurring with Generative Diffusion Models
Authors:Lingshun Kong, Jiawei Zhang, Dongqing Zou, Jimmy Ren, Xiaohe Wu, Jiangxin Dong, Jinshan Pan
Diffusion models have achieved significant progress in image generation. The pre-trained Stable Diffusion (SD) models are helpful for image deblurring by providing clear image priors. However, directly using a blurry image or pre-deblurred one as a conditional control for SD will either hinder accurate structure extraction or make the results overly dependent on the deblurring network. In this work, we propose a Latent Kernel Prediction Network (LKPN) to achieve robust real-world image deblurring. Specifically, we co-train the LKPN in latent space with conditional diffusion. The LKPN learns a spatially variant kernel to guide the restoration of sharp images in the latent space. By applying element-wise adaptive convolution (EAC), the learned kernel is utilized to adaptively process the input feature, effectively preserving the structural information of the input. This process thereby more effectively guides the generative process of Stable Diffusion (SD), enhancing both the deblurring efficacy and the quality of detail reconstruction. Moreover, the results at each diffusion step are utilized to iteratively estimate the kernels in LKPN to better restore the sharp latent by EAC. This iterative refinement enhances the accuracy and robustness of the deblurring process. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art image deblurring methods on both benchmark and real-world images.
扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了显著进展。预训练的Stable Diffusion(SD)模型通过提供清晰的图像先验,对图像去模糊化很有帮助。然而,直接使用模糊图像或预先去模糊的图像作为SD的条件控制会阻碍准确的结构提取,或使结果过于依赖去模糊网络。在本研究中,我们提出了一种潜核预测网络(Latent Kernel Prediction Network,LKPN)来实现稳健的现实世界图像去模糊化。具体来说,我们在潜在空间中对LKPN与条件扩散进行共同训练。LKPN学习一个空间变化的核来指导潜在空间中清晰图像的恢复。通过应用逐元素自适应卷积(Element-wise Adaptive Convolution,EAC),学习到的核被用来自适应地处理输入特征,有效地保留输入的结构信息。这一过程更有效地指导了Stable Diffusion(SD)的生成过程,提高了去模糊化的效果以及细节重建的质量。此外,每一步扩散的结果都被用来通过EAC迭代估计LKPN中的核,以更好地恢复清晰的潜在特征。这种迭代细化提高了去模糊过程的准确性和稳健性。大量的实验结果证明,所提出的方法在基准测试和真实世界图像上去模糊化的效果优于当前先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
稳定扩散模型在图像生成领域取得了显著进展,但对于去模糊任务仍存在挑战。本文提出了一种潜核预测网络(LKPN),在潜在空间与条件扩散共同训练,学习空间可变核以指导潜在空间的清晰图像恢复。通过应用元素级自适应卷积(EAC),学习到的核能够自适应处理输入特征,有效保留输入的结构信息。这一过程更有效地指导了稳定扩散(SD)的生成过程,提高了去模糊效果和细节重建质量。此外,通过在各扩散步骤的结果上迭代估计LKPN中的核,以更好地通过EAC恢复清晰的潜在图像。这种迭代优化提高了去模糊过程的准确性和稳健性。实验结果表明,该方法在基准测试和真实图像上的图像去模糊效果均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 稳定扩散模型在图像生成领域取得显著进展,但去模糊任务仍具挑战。
- 潜核预测网络(LKPN)被提出,用于在潜在空间与条件扩散共同训练。
- LKPN学习空间可变核,以指导潜在空间的清晰图像恢复。
- 元素级自适应卷积(EAC)用于自适应处理输入特征,保留结构信息。
- EAC有效指导稳定扩散(SD)的生成过程,提高去模糊效果和细节重建质量。
- 通过迭代估计核来优化去模糊过程,提高准确性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


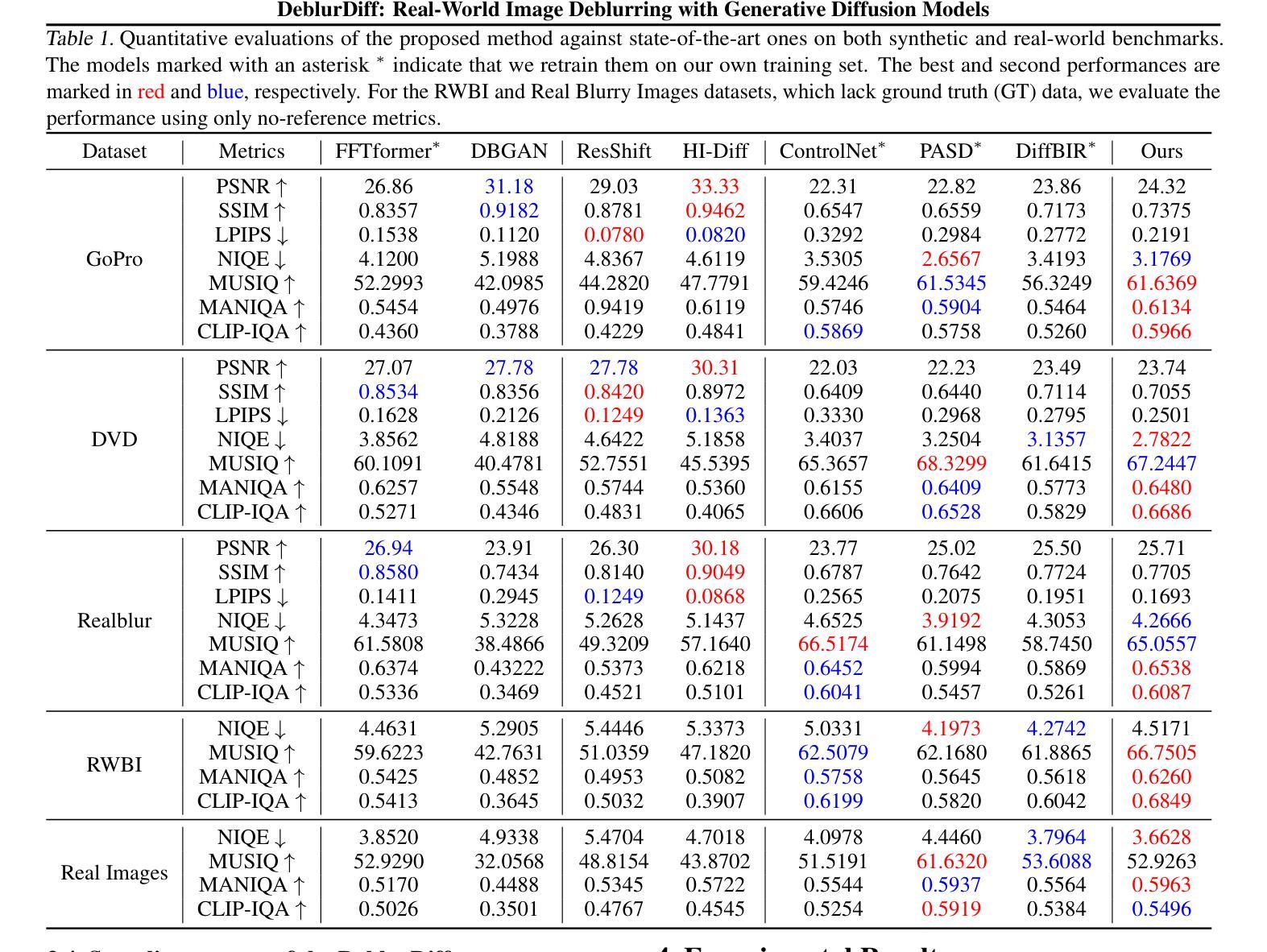
Conditional Diffusion Models are Medical Image Classifiers that Provide Explainability and Uncertainty for Free
Authors:Gian Mario Favero, Parham Saremi, Emily Kaczmarek, Brennan Nichyporuk, Tal Arbel
Discriminative classifiers have become a foundational tool in deep learning for medical imaging, excelling at learning separable features of complex data distributions. However, these models often need careful design, augmentation, and training techniques to ensure safe and reliable deployment. Recently, diffusion models have become synonymous with generative modeling in 2D. These models showcase robustness across a range of tasks including natural image classification, where classification is performed by comparing reconstruction errors across images generated for each possible conditioning input. This work presents the first exploration of the potential of class conditional diffusion models for 2D medical image classification. First, we develop a novel majority voting scheme shown to improve the performance of medical diffusion classifiers. Next, extensive experiments on the CheXpert and ISIC Melanoma skin cancer datasets demonstrate that foundation and trained-from-scratch diffusion models achieve competitive performance against SOTA discriminative classifiers without the need for explicit supervision. In addition, we show that diffusion classifiers are intrinsically explainable, and can be used to quantify the uncertainty of their predictions, increasing their trustworthiness and reliability in safety-critical, clinical contexts. Further information is available on our project page: https://faverogian.github.io/med-diffusion-classifier.github.io/
判别分类器已成为医学影像深度学习中的基础工具,擅长学习复杂数据分布的可分特征。然而,为了确保这些模型的安全可靠部署,通常需要进行精心设计、数据增强和训练技术。最近,扩散模型已成为二维生成模型的代名词。这些模型展示了在各种任务中的稳健性,包括自然图像分类,分类是通过比较针对每个可能的条件输入生成的图像之间的重建误差来完成的。这项工作首次探索了二维医学图像分类中类条件扩散模型的潜力。首先,我们开发了一种新型多数投票方案,该方案已证明可以提高医学扩散分类器的性能。接下来,在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的大量实验表明,基础扩散模型和从头开始训练的扩散模型均达到了与最新判别分类器相当的性能水平,无需显式监督。此外,我们还证明了扩散分类器本质上是可解释的,并可用于量化其预测的确定性,从而增加了其在安全关键的医疗环境中的可信度和可靠性。更多信息请参见我们的项目页面:https://faverogian.github.io/med-diffusion-classifier
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在二维医疗图像分类中具有巨大潜力。通过开发新型多数投票方案,扩散分类器的性能得到了提升,且在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的实验表明,与最先进的判别分类器相比,基础扩散模型和从头开始训练的扩散模型具有竞争力,且无需显式监督。此外,扩散分类器具有内在的可解释性,可量化预测的不确定性,从而增加其在安全关键的临床环境中的可信度和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在二维医疗图像分类中具有潜力。
- 开发了一种新型多数投票方案,提高了医疗扩散分类器的性能。
- 在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的实验表明,扩散模型与最先进的判别分类器具有竞争力。
- 扩散模型无需显式监督。
- 扩散分类器具有内在的可解释性。
- 扩散分类器可量化预测的不确定性。
- 扩散分类器在临床环境中具有可信度和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

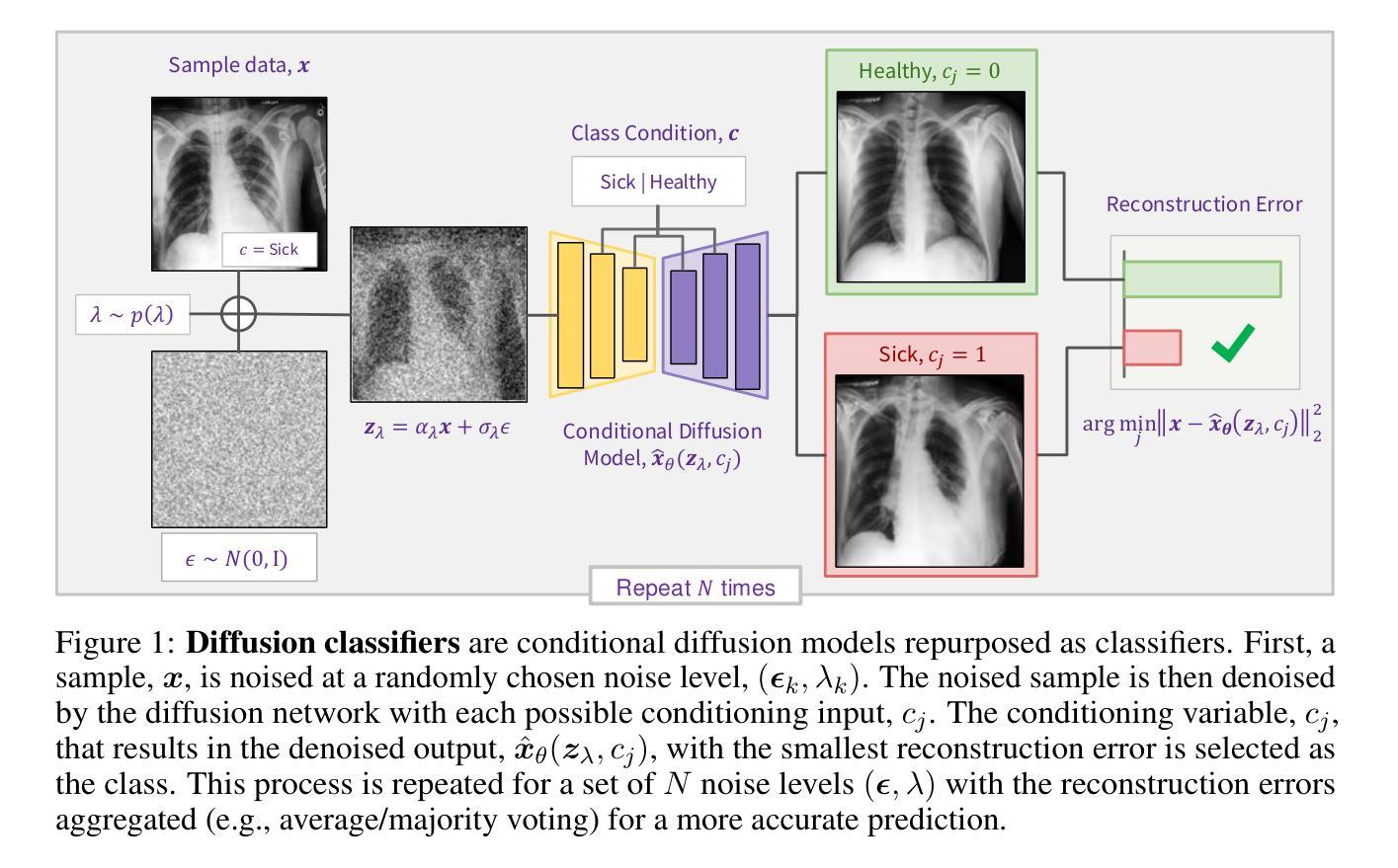
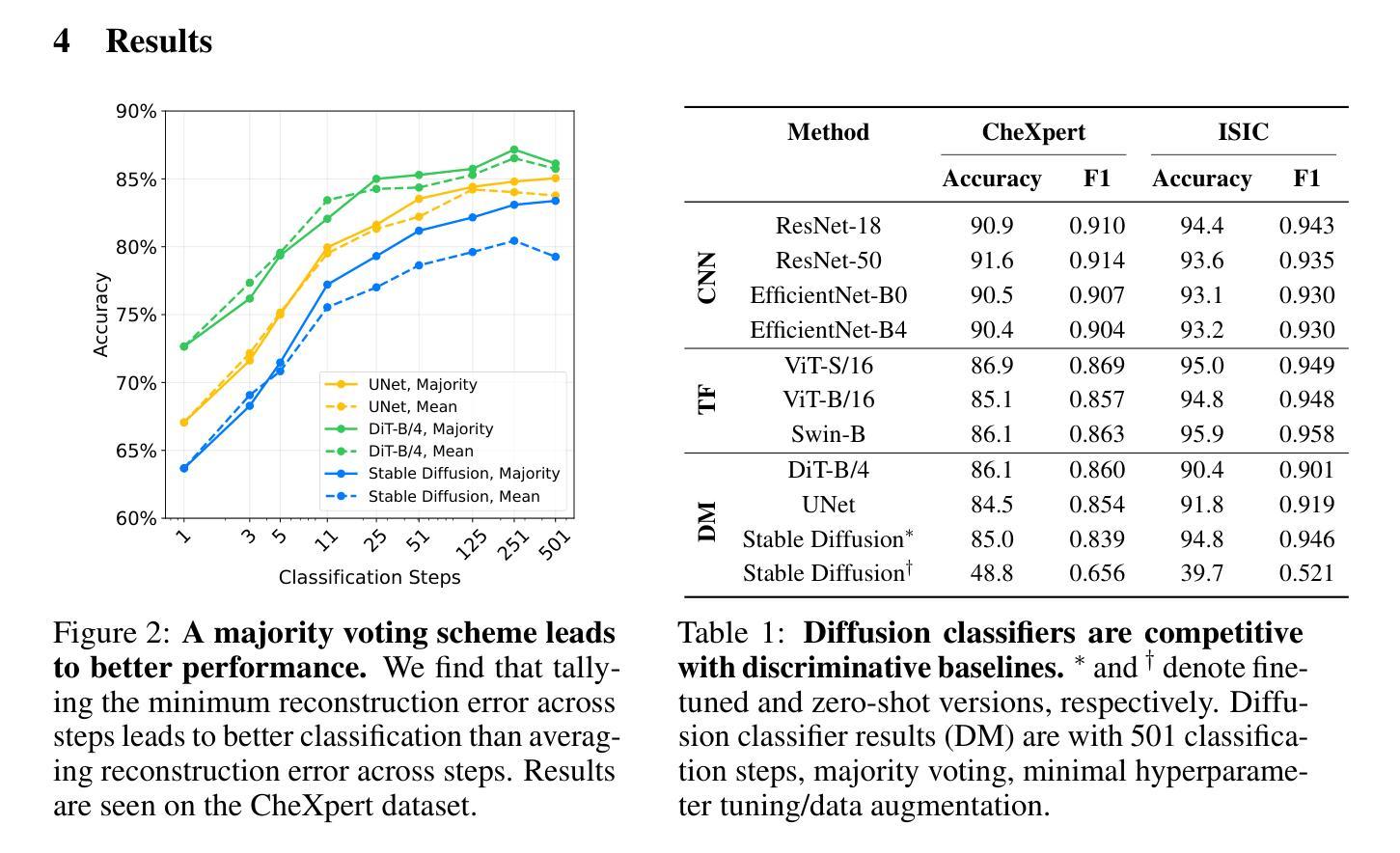
FreqPrior: Improving Video Diffusion Models with Frequency Filtering Gaussian Noise
Authors:Yunlong Yuan, Yuanfan Guo, Chunwei Wang, Wei Zhang, Hang Xu, Li Zhang
Text-driven video generation has advanced significantly due to developments in diffusion models. Beyond the training and sampling phases, recent studies have investigated noise priors of diffusion models, as improved noise priors yield better generation results. One recent approach employs the Fourier transform to manipulate noise, marking the initial exploration of frequency operations in this context. However, it often generates videos that lack motion dynamics and imaging details. In this work, we provide a comprehensive theoretical analysis of the variance decay issue present in existing methods, contributing to the loss of details and motion dynamics. Recognizing the critical impact of noise distribution on generation quality, we introduce FreqPrior, a novel noise initialization strategy that refines noise in the frequency domain. Our method features a novel filtering technique designed to address different frequency signals while maintaining the noise prior distribution that closely approximates a standard Gaussian distribution. Additionally, we propose a partial sampling process by perturbing the latent at an intermediate timestep during finding the noise prior, significantly reducing inference time without compromising quality. Extensive experiments on VBench demonstrate that our method achieves the highest scores in both quality and semantic assessments, resulting in the best overall total score. These results highlight the superiority of our proposed noise prior.
基于文本的视频生成由于扩散模型的发展而取得了显著进展。除了训练和采样阶段,最近的研究还探讨了扩散模型的噪声先验,因为改进的噪声先验会产生更好的生成结果。一种最近的方法使用傅里叶变换来操作噪声,标志着在此背景下对频率操作的初步探索。然而,它通常生成的视频缺乏运动动力和成像细节。在这项工作中,我们对现有方法中存在的方差衰减问题进行了全面的理论分析,这个问题导致了细节和运动动力的损失。我们认识到噪声分布对生成质量的关键影响,因此引入了FreqPrior,这是一种新的噪声初始化策略,它在频率域中优化噪声。我们的方法采用了一种新型滤波技术,旨在处理不同的频率信号,同时保持噪声先验分布,近似于标准高斯分布。此外,我们通过在中间时间步长找到噪声先验时扰动潜在空间,提出了部分采样过程,这显著减少了推理时间,同时不妥协质量。在VBench上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在质量和语义评估方面都获得了最高分,总分最高。这些结果突显了我们提出的噪声先验的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
扩散模型在文本驱动的视频生成领域取得了显著进展。最新研究开始探索扩散模型的噪声先验,因为更好的噪声先验能产生更好的生成结果。本文全面分析了现有方法中存在的方差衰减问题,导致细节和运动动力丢失。为了解决噪声分布对生成质量的关键影响,我们引入了FreqPrior,一种在频域优化噪声的新型噪声初始化策略。此外,我们通过在寻找噪声先验的中间步骤扰动潜在变量,提出了部分采样过程,显著减少了推理时间,同时不妥协于质量。实验表明,我们的方法在质量和语义评估方面都获得了最高分。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本驱动的视频生成中有显著进展。
- 噪声先验在扩散模型中扮演重要角色,能影响生成结果的质量。
- 现有方法存在方差衰减问题,导致生成的视频缺乏运动动力和成像细节。
- 引入FreqPrior,一种新型噪声初始化策略,旨在优化频域中的噪声。
- 提出一种部分采样过程,通过扰动寻找噪声先验的中间步骤的潜在变量,以减少推理时间而不影响质量。
- 实验表明,在VBench上,该方法在质量和语义评估方面获得最高分。
点此查看论文截图


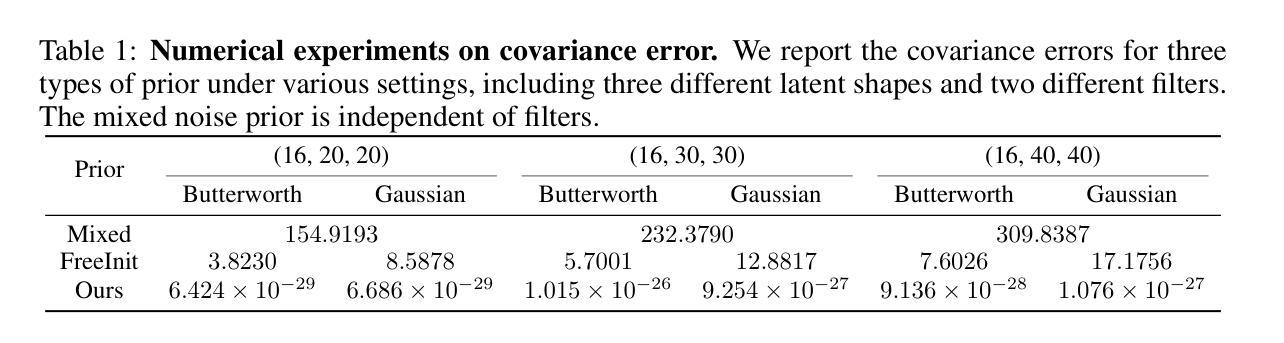
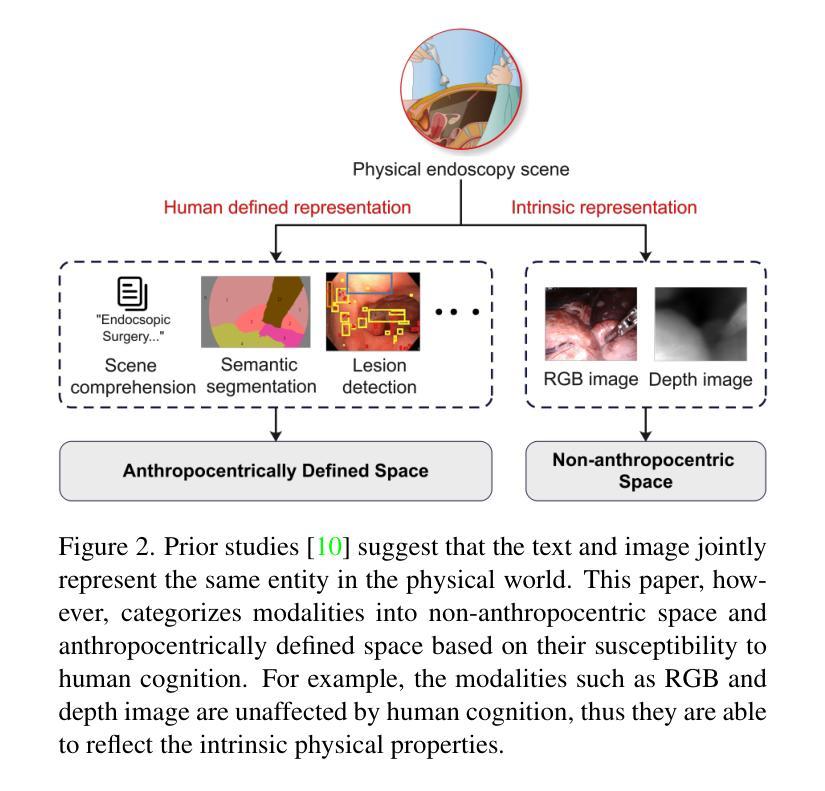
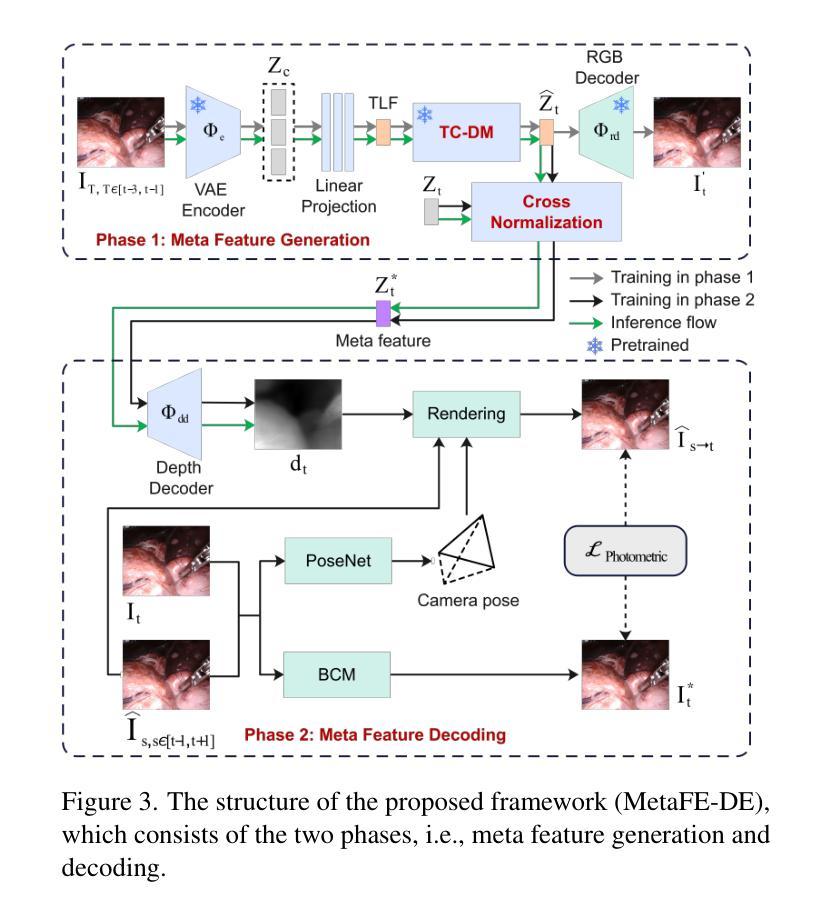
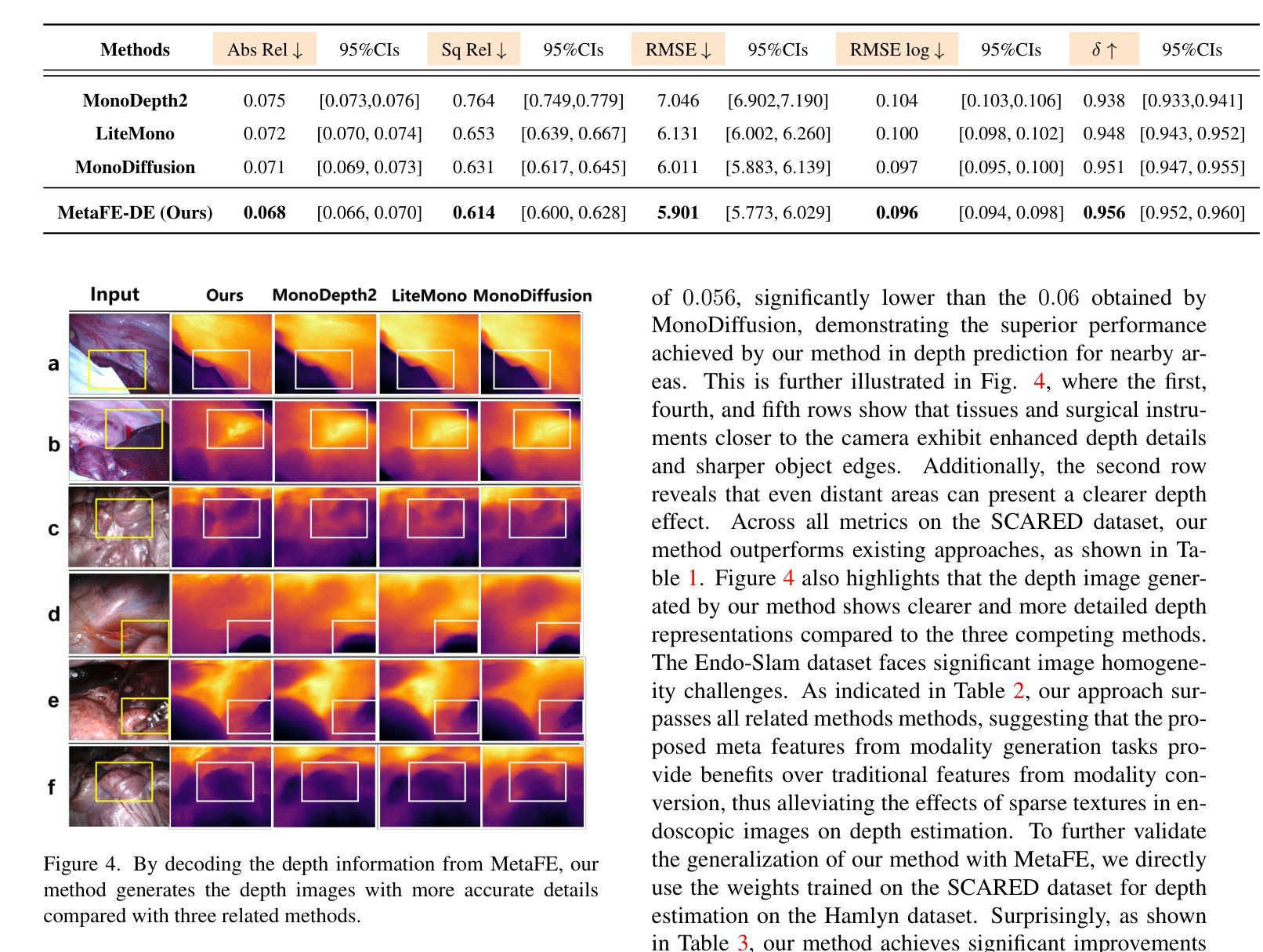
MetaFE-DE: Learning Meta Feature Embedding for Depth Estimation from Monocular Endoscopic Images
Authors:Dawei Lu, Deqiang Xiao, Danni Ai, Jingfan Fan, Tianyu Fu, Yucong Lin, Hong Song, Xujiong Ye, Lei Zhang, Jian Yang
Depth estimation from monocular endoscopic images presents significant challenges due to the complexity of endoscopic surgery, such as irregular shapes of human soft tissues, as well as variations in lighting conditions. Existing methods primarily estimate the depth information from RGB images directly, and often surffer the limited interpretability and accuracy. Given that RGB and depth images are two views of the same endoscopic surgery scene, in this paper, we introduce a novel concept referred as ``meta feature embedding (MetaFE)”, in which the physical entities (e.g., tissues and surgical instruments) of endoscopic surgery are represented using the shared features that can be alternatively decoded into RGB or depth image. With this concept, we propose a two-stage self-supervised learning paradigm for the monocular endoscopic depth estimation. In the first stage, we propose a temporal representation learner using diffusion models, which are aligned with the spatial information through the cross normalization to construct the MetaFE. In the second stage, self-supervised monocular depth estimation with the brightness calibration is applied to decode the meta features into the depth image. Extensive evaluation on diverse endoscopic datasets demonstrates that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art method in depth estimation, achieving superior accuracy and generalization. The source code will be publicly available.
从单目内镜图像进行深度估计面临着巨大的挑战,主要由于内镜手术的复杂性,例如人体软组织的不规则形状,以及光照条件的变化。现有的方法主要直接从RGB图像估计深度信息,通常存在解释性和准确性的局限性。鉴于RGB图像和深度图像是同一内镜手术场景的两个视图,本文引入了一个新概念,称为“元特征嵌入(MetaFE)”,其中内镜手术中的物理实体(例如,组织和手术器械)用可交替解码为RGB或深度图像的共享特征来表示。基于这个概念,我们提出了一个用于单目内镜深度估计的两阶段自监督学习范式。在第一阶段,我们提出了一个使用扩散模型的时序表示学习者,通过跨归一化与空间信息进行对齐,以构建MetaFE。在第二阶段,应用带有亮度校准的自监督单目深度估计来将元特征解码为深度图像。在多种内镜数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的方法在深度估计方面优于最新技术,具有更高的准确性和泛化能力。源代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于单目内窥镜图像深度估计的新方法,通过引入“元特征嵌入”(MetaFE)概念,将物理实体(如组织和手术器械)用共享特征表示,这些特征可以解码为RGB或深度图像。提出一种两阶段自监督学习方法,第一阶段使用扩散模型进行时间表示学习,通过与空间信息对齐构建MetaFE;第二阶段采用自监督单目内窥镜深度估计,对亮度进行校准后解码出深度图像。实验证明该方法在多种内窥镜数据集上的表现优于现有方法,准确度和泛化能力有所提升。
Key Takeaways
- 引入“元特征嵌入”(MetaFE)概念,将物理实体表示为共享特征,可解码为RGB或深度图像。
- 采用两阶段自监督学习方法进行单目内窥镜深度估计。
- 第一阶段使用扩散模型进行时间表示学习,通过与空间信息对齐构建MetaFE。
- 第二阶段应用自监督学习进行深度估计,结合亮度校准解码出深度图像。
- 方法在多种内窥镜数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
- 提高了深度估计的准确性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

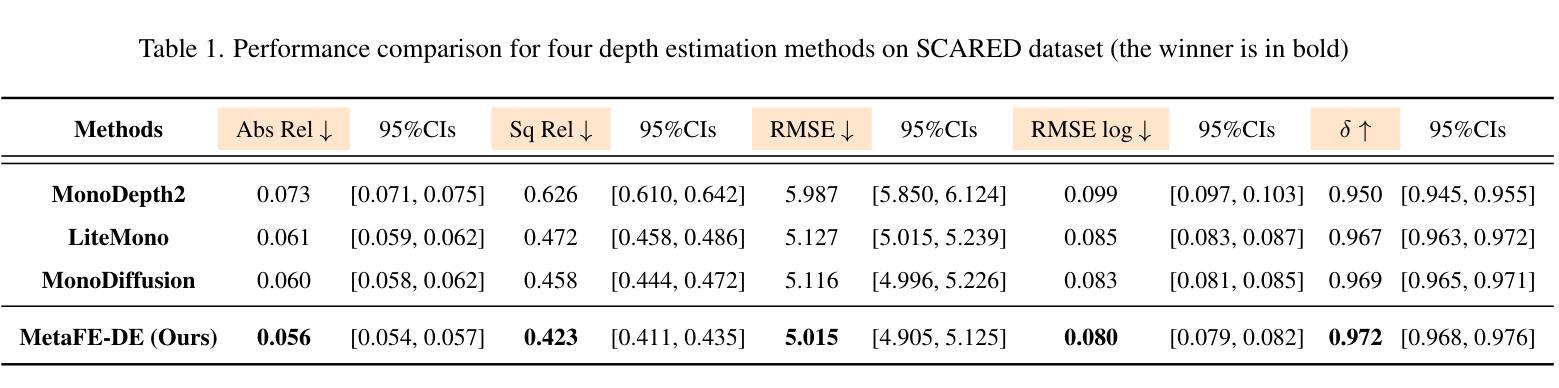
Lanpaint: Training-Free Diffusion Inpainting with Exact and Fast Conditional Inference
Authors:Candi Zheng, Yuan Lan, Yang Wang
Diffusion models generate high-quality images but often lack efficient and universally applicable inpainting capabilities, particularly in community-trained models. We introduce LanPaint, a training-free method tailored for widely adopted ODE-based samplers, which leverages Langevin dynamics to perform exact conditional inference, enabling precise and visually coherent inpainting. LanPaint addresses two key challenges in Langevin-based inpainting: (1) the risk of local likelihood maxima trapping and (2) slow convergence. By proposing a guided score function and a fast-converging Langevin framework, LanPaint achieves high-fidelity results in very few iterations. Experiments demonstrate that LanPaint outperforms existing training-free inpainting techniques, outperforming in challenging tasks such as outpainting with Stable Diffusion.
扩散模型可以生成高质量图像,但通常缺乏高效且普遍适用的补全能力,特别是在社区训练模型中。我们推出了LanPaint,这是一种无需训练的方法,适用于广泛采用的基于ODE的采样器,它利用朗之万动力学进行精确的条件推断,能够实现精确且视觉连贯的补全。LanPaint解决了朗之万补全中的两个关键挑战:(1)局部似然极大值陷阱的风险和(2)收敛速度慢。通过提出引导得分函数和快速收敛的朗之万框架,LanPaint可以在很少迭代次数内实现高保真结果。实验表明,LanPaint在补全技术方面无需训练,并且在具有挑战性的任务(如使用Stable Diffusion进行补全)中表现优于现有技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了LanPaint,一种无需训练的方法,适用于广泛采用的ODE采样器,利用朗之万动力学进行精确的条件推断,实现精确且视觉连贯的补全。该方法解决了朗之万补全中的两个关键问题:局部概率最大值的陷阱风险和收敛速度慢的问题。通过提出引导评分函数和快速收敛的朗之万框架,LanPaint在很少迭代次数内实现了高保真结果,并在外推任务中表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型虽然能生成高质量图像,但在社区训练模型中常常缺乏高效且普遍适用的补全能力。
- LanPaint是一种无需训练的方法,适用于ODE采样器,利用朗之万动力学进行精确的条件推断。
- LanPaint解决了朗之万动力学补全中的两个关键问题:局部概率最大值的陷阱风险和收敛速度慢。
- 通过引导评分函数和快速收敛的朗之万框架,LanPaint在较少的迭代次数内实现了高保真结果。
- LanPaint在补全任务中表现出色,特别是在具有挑战性的外推任务中。
- 与现有的无需训练的补全技术相比,LanPaint具有更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


Fast Direct: Query-Efficient Online Black-box Guidance for Diffusion-model Target Generation
Authors:Kim Yong Tan, Yueming Lyu, Ivor Tsang, Yew-Soon Ong
Guided diffusion-model generation is a promising direction for customizing the generation process of a pre-trained diffusion-model to address the specific downstream tasks. Existing guided diffusion models either rely on training of the guidance model with pre-collected datasets or require the objective functions to be differentiable. However, for most real-world tasks, the offline datasets are often unavailable, and their objective functions are often not differentiable, such as image generation with human preferences, molecular generation for drug discovery, and material design. Thus, we need an $\textbf{online}$ algorithm capable of collecting data during runtime and supporting a $\textbf{black-box}$ objective function. Moreover, the $\textbf{query efficiency}$ of the algorithm is also critical because the objective evaluation of the query is often expensive in the real-world scenarios. In this work, we propose a novel and simple algorithm, $\textbf{Fast Direct}$, for query-efficient online black-box target generation. Our Fast Direct builds a pseudo-target on the data manifold to update the noise sequence of the diffusion model with a universal direction, which is promising to perform query-efficient guided generation. Extensive experiments on twelve high-resolution ($\small {1024 \times 1024}$) image target generation tasks and six 3D-molecule target generation tasks show $\textbf{6}\times$ up to $\textbf{10}\times$ query efficiency improvement and $\textbf{11}\times$ up to $\textbf{44}\times$ query efficiency improvement, respectively. Our implementation is publicly available at: https://github.com/kimyong95/guide-stable-diffusion/tree/fast-direct
引导扩散模型生成是定制预训练扩散模型的生成过程以应对特定下游任务的一个前景方向。现有的引导扩散模型要么依赖于使用预先收集的数据集训练引导模型,要么需要目标函数可微。然而,对于大多数现实世界任务而言,离线数据集通常不可用,而且其目标函数通常不可微分,例如具有人类偏好的图像生成、用于药物发现的分子生成和材料设计。因此,我们需要一种能够在运行时收集数据并支持黑箱目标函数的在线算法。此外,算法的查询效率也非常关键,因为在现实场景中,目标查询的评估往往非常昂贵。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新颖而简单的算法——Fast Direct,用于高效查询在线黑箱目标生成。我们的Fast Direct在数据流形上构建伪目标,以通用方向更新扩散模型的噪声序列,这有望实现高效的查询引导生成。在十二个高分辨率(1024×1024)图像目标生成任务和六个3D分子目标生成任务的大量实验显示,查询效率提高了6倍至10倍和提高了最高至的查询效率改善比例分别达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达至高达达高达达达达达达达达达达达达达达达达达大44倍。我们的实现已在以下网址公开可用:https://github.com/kimyong95/guide-stable-diffusion/tree/fast-direct
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在定制化生成过程中的潜力与局限性。现有引导扩散模型依赖于预收集数据集进行训练的目标函数或需要可微分的目标函数,但在现实世界的许多任务中,离线数据集往往无法获取且其目标函数往往不可微分。因此,本文提出了一种新型的在线黑盒目标生成算法——Fast Direct,该算法能够在运行时收集数据并支持黑盒目标函数,同时具有较高的查询效率。实验结果显示,Fast Direct在高分辨率图像生成和三维分子生成等任务中取得了显著的查询效率提升。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在定制化生成过程中具有巨大潜力,特别是在处理下游任务时。
- 现有引导扩散模型依赖于预收集数据集或可微分的目标函数,这在现实任务中并不常见。
- Fast Direct算法解决了这一问题,通过在线收集数据并支持黑盒目标函数,实现了高效的查询。
- Fast Direct算法在高分辨率图像生成和三维分子生成等任务中取得了显著的查询效率提升。
- Fast Direct算法通过构建伪目标来更新扩散模型的噪声序列,并采用了通用方向进行引导生成。
- 该算法已在多个任务上进行了广泛实验验证,包括十二个高分辨率图像生成任务和六个三维分子生成任务。
点此查看论文截图


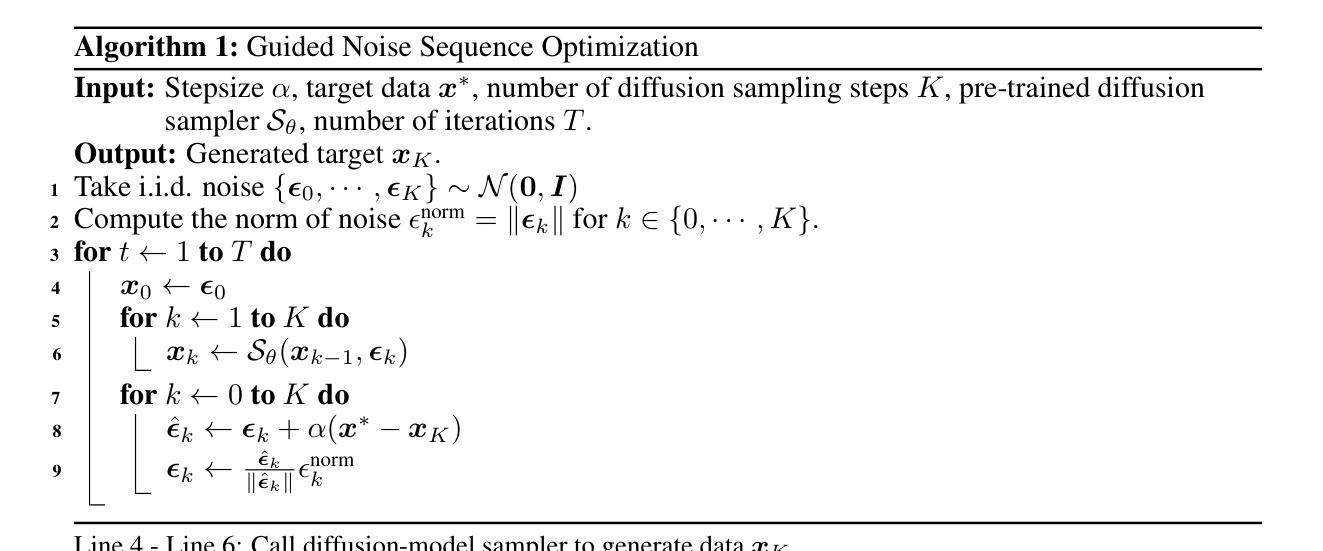
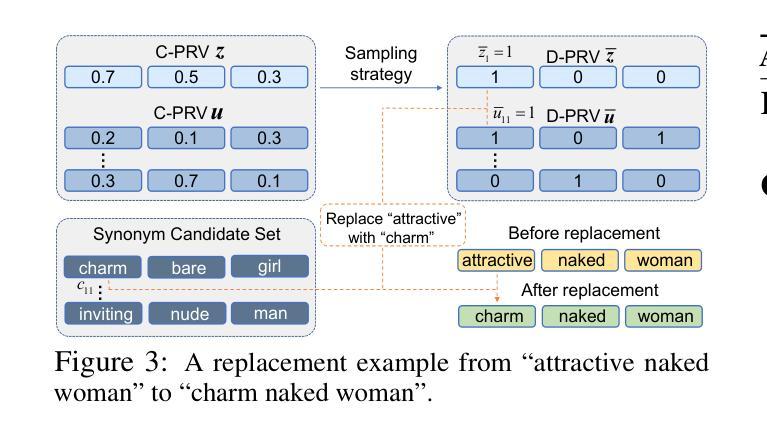
DiffZOO: A Purely Query-Based Black-Box Attack for Red-teaming Text-to-Image Generative Model via Zeroth Order Optimization
Authors:Pucheng Dang, Xing Hu, Dong Li, Rui Zhang, Qi Guo, Kaidi Xu
Current text-to-image (T2I) synthesis diffusion models raise misuse concerns, particularly in creating prohibited or not-safe-for-work (NSFW) images. To address this, various safety mechanisms and red teaming attack methods are proposed to enhance or expose the T2I model’s capability to generate unsuitable content. However, many red teaming attack methods assume knowledge of the text encoders, limiting their practical usage. In this work, we rethink the case of \textit{purely black-box} attacks without prior knowledge of the T2l model. To overcome the unavailability of gradients and the inability to optimize attacks within a discrete prompt space, we propose DiffZOO which applies Zeroth Order Optimization to procure gradient approximations and harnesses both C-PRV and D-PRV to enhance attack prompts within the discrete prompt domain. We evaluated our method across multiple safety mechanisms of the T2I diffusion model and online servers. Experiments on multiple state-of-the-art safety mechanisms show that DiffZOO attains an 8.5% higher average attack success rate than previous works, hence its promise as a practical red teaming tool for T2l models.
当前文本到图像(T2I)合成扩散模型引发了滥用担忧,特别是在创建禁止或不适合工作场合(NSFW)的图像方面。为解决这一问题,提出了各种安全机制和红队攻击方法来增强或揭露T2I模型生成不合适内容的能力。然而,许多红队攻击方法需要了解文本编码器,从而限制了它们的实际应用。在这项工作中,我们重新考虑了无需事先了解T2I模型的“纯黑箱”攻击的情况。为了克服无法获取梯度以及在离散提示空间内无法优化攻击的局限性,我们提出了DiffZOO,它采用零阶优化来获取梯度近似值,并利用C-PRV和D-PRV在离散提示域内增强攻击提示。我们在T2I扩散模型的多重安全机制和在线服务器上评估了我们的方法。对多种最先进的安全机制的实验表明,DiffZOO的平均攻击成功率比先前的工作高出8.5%,因此在T2I模型的实用红队工具中显示出其潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本生成领域中的文本到图像(T2I)合成扩散模型存在滥用风险,特别是在生成不适宜工作或禁止的图像方面。为应对这一问题,研究者提出了多种安全机制和红队攻击方法,以提升或揭示T2I模型生成不合适内容的能力。然而,许多红队攻击方法需要了解文本编码器,限制了其实用性。本研究重新思考了无需了解T2I模型的纯黑箱攻击情况。为克服无法获取梯度以及在离散提示空间内优化攻击的难题,我们提出了DiffZOO,它采用零阶优化来获取梯度近似值,并利用C-PRV和D-PRV增强离散提示域内的攻击提示。我们在多个T2I扩散模型安全机制和在线服务器上评估了该方法。实验表明,相较于以往的研究,DiffZOO的平均攻击成功率提高了8.5%,成为T2I模型实用红队工具的有力候选。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)合成扩散模型存在生成不适宜内容的滥用风险。
- 为应对此问题,研究者提出了多种安全机制和红队攻击方法。
- 现有红队攻击方法往往需要了解文本编码器,限制了其实际应用。
- 研究提出了DiffZOO方法,能在不了解T2I模型的情况下进行纯黑箱攻击。
- DiffZOO采用零阶优化获取梯度近似值,增强离散提示空间内的攻击提示。
- 实验表明,DiffZOO在多个安全机制上的攻击成功率高于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

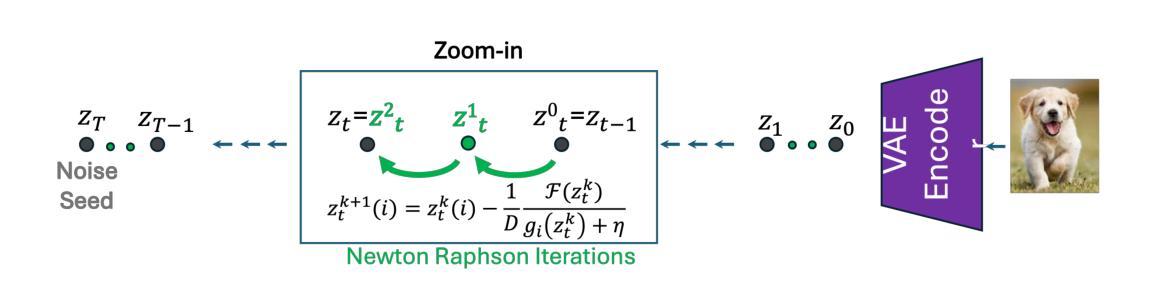
Lightning-Fast Image Inversion and Editing for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Dvir Samuel, Barak Meiri, Haggai Maron, Yoad Tewel, Nir Darshan, Shai Avidan, Gal Chechik, Rami Ben-Ari
Diffusion inversion is the problem of taking an image and a text prompt that describes it and finding a noise latent that would generate the exact same image. Most current deterministic inversion techniques operate by approximately solving an implicit equation and may converge slowly or yield poor reconstructed images. We formulate the problem by finding the roots of an implicit equation and devlop a method to solve it efficiently. Our solution is based on Newton-Raphson (NR), a well-known technique in numerical analysis. We show that a vanilla application of NR is computationally infeasible while naively transforming it to a computationally tractable alternative tends to converge to out-of-distribution solutions, resulting in poor reconstruction and editing. We therefore derive an efficient guided formulation that fastly converges and provides high-quality reconstructions and editing. We showcase our method on real image editing with three popular open-sourced diffusion models: Stable Diffusion, SDXL-Turbo, and Flux with different deterministic schedulers. Our solution, Guided Newton-Raphson Inversion, inverts an image within 0.4 sec (on an A100 GPU) for few-step models (SDXL-Turbo and Flux.1), opening the door for interactive image editing. We further show improved results in image interpolation and generation of rare objects.
扩散反演(Diffusion Inversion)问题是指给定一张图片和描述它的文本提示,寻找能够生成相同图片的噪声潜在因子。当前大多数的确定性反演技术都是通过近似解决隐式方程实现的,可能会导致收敛速度慢或重构的图像质量不佳。我们通过寻找隐式方程的根来表述问题,并开发了一种高效解决方法。我们的解决方案基于数值分析中的知名技术——牛顿-拉夫森方法(Newton-Raphson,简称NR)。我们发现,直接应用NR在计算上不可行,而将其简单转换为可计算的替代方案则往往收敛于非分布解,导致重构和编辑质量差。因此,我们推导出了一个高效的引导式公式,它能快速收敛,并提供高质量的重构和编辑。我们在真实图像编辑中展示了我们的方法,使用了三个流行的开源扩散模型:Stable Diffusion、SDXL-Turbo和Flux,以及不同的确定性调度器。我们的解决方案——引导式牛顿-拉夫森反演法(Guided Newton-Raphson Inversion),能在A100 GPU上实现0.4秒内对少数模型(SDXL-Turbo和Flux 1)进行图像反演,为交互式图像编辑打开了大门。我们还展示了在图像插值和稀有对象生成方面的改进结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR25. Project Page: https://barakmam.github.io/rnri.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了扩散反转问题,即根据图像和描述它的文本提示找到生成相同图像的噪声潜在因素。文章提出了一种基于牛顿-拉夫森(Newton-Raphson)方法的解决方案,有效解决了扩散反转问题中的高效求解方法。该方法快速收敛,提供了高质量的重建和编辑效果,可以在实际应用中用于图像编辑、图像插值和稀有对象生成等领域。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散反转问题旨在从给定的图像和文本描述中找出生成该图像的噪声潜在因素。
- 当前大多数确定性反转技术通过近似解决隐式方程来操作,但可能存在收敛速度慢或重建图像质量差的问题。
- 文章提出了一种基于牛顿-拉夫森方法的解决方案,该方法在计算上更高效且能快速收敛。
- 该方法提供了高质量的图像重建和编辑效果。
- 该方法在实际应用中可用于图像编辑、图像插值和稀有对象生成等领域。
- 文章展示了在真实图像编辑中使用三种流行的开源扩散模型(Stable Diffusion、SDXL-Turbo和Flux)的结果,验证了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

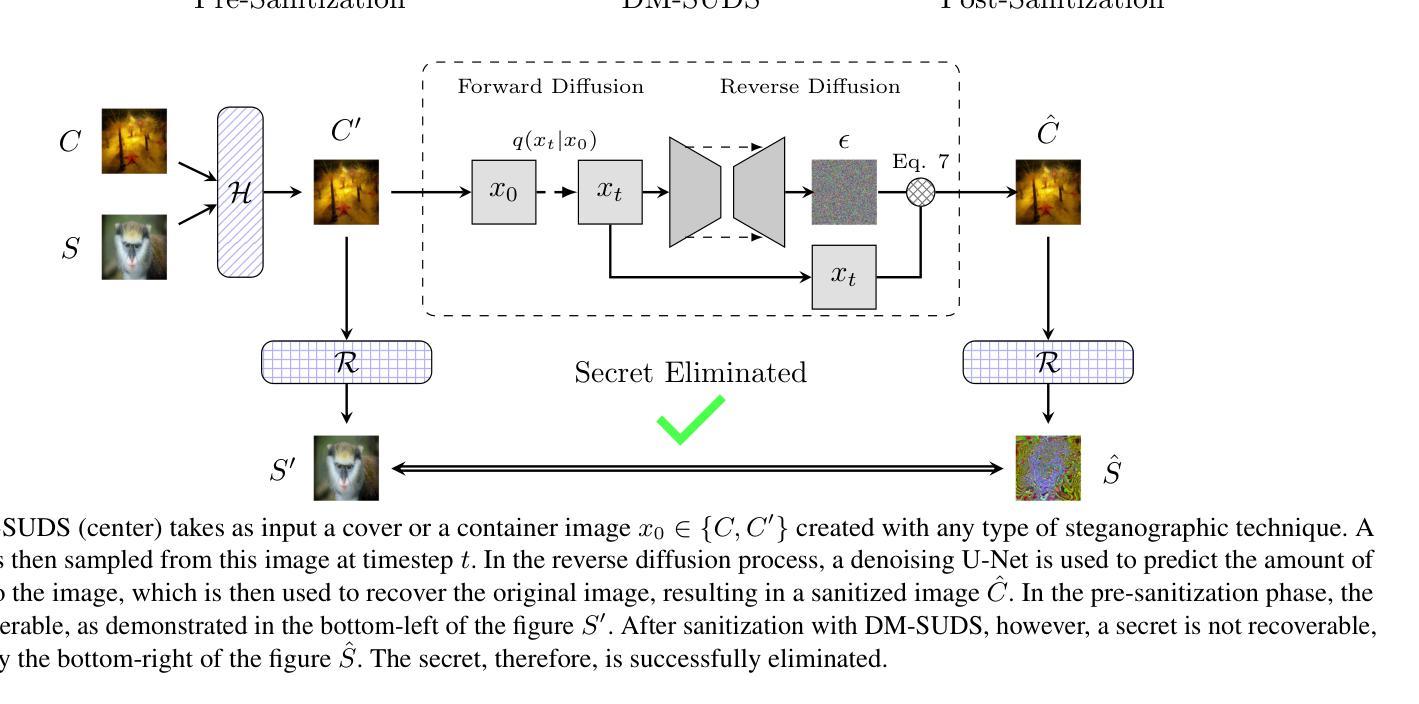
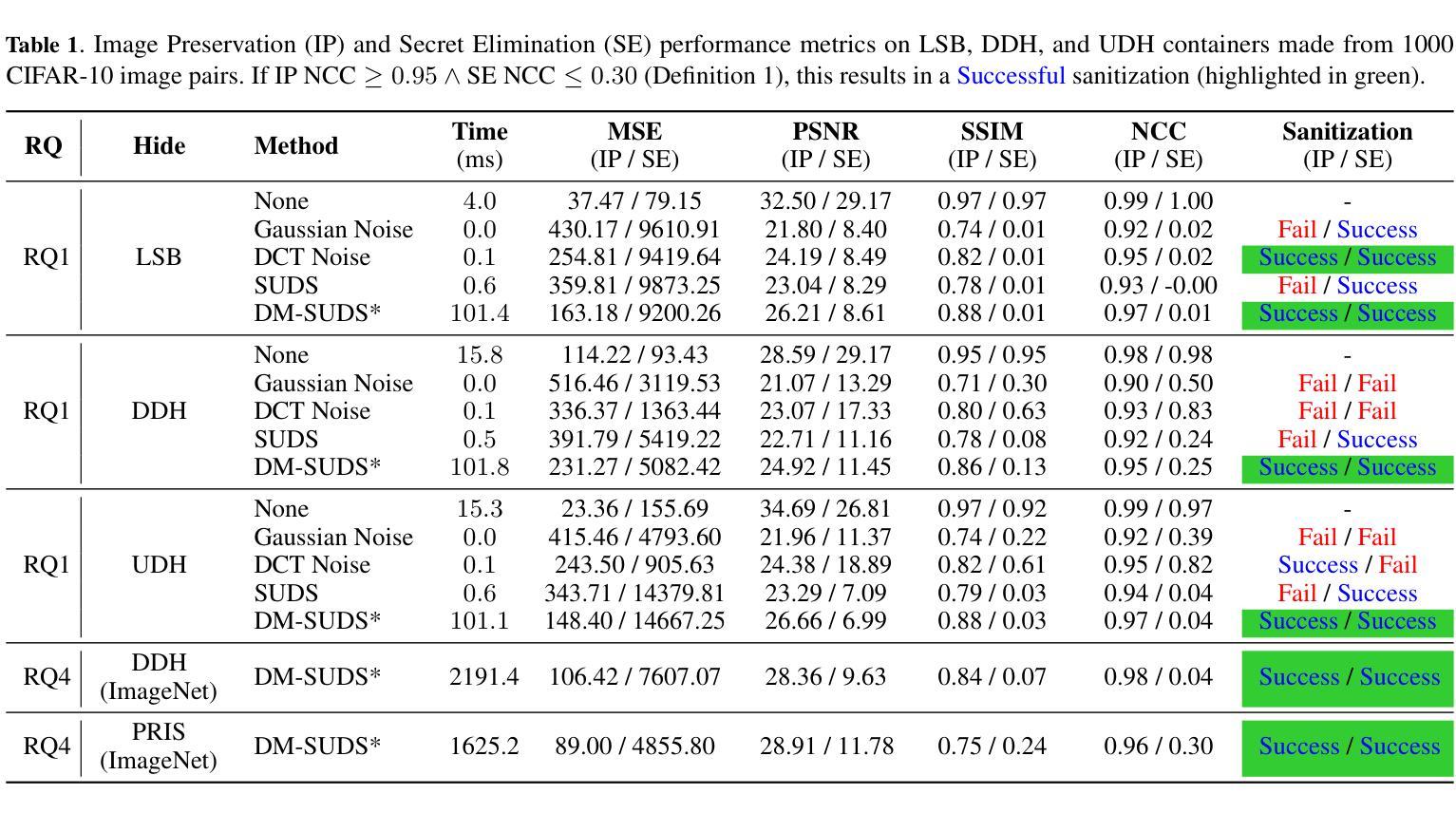
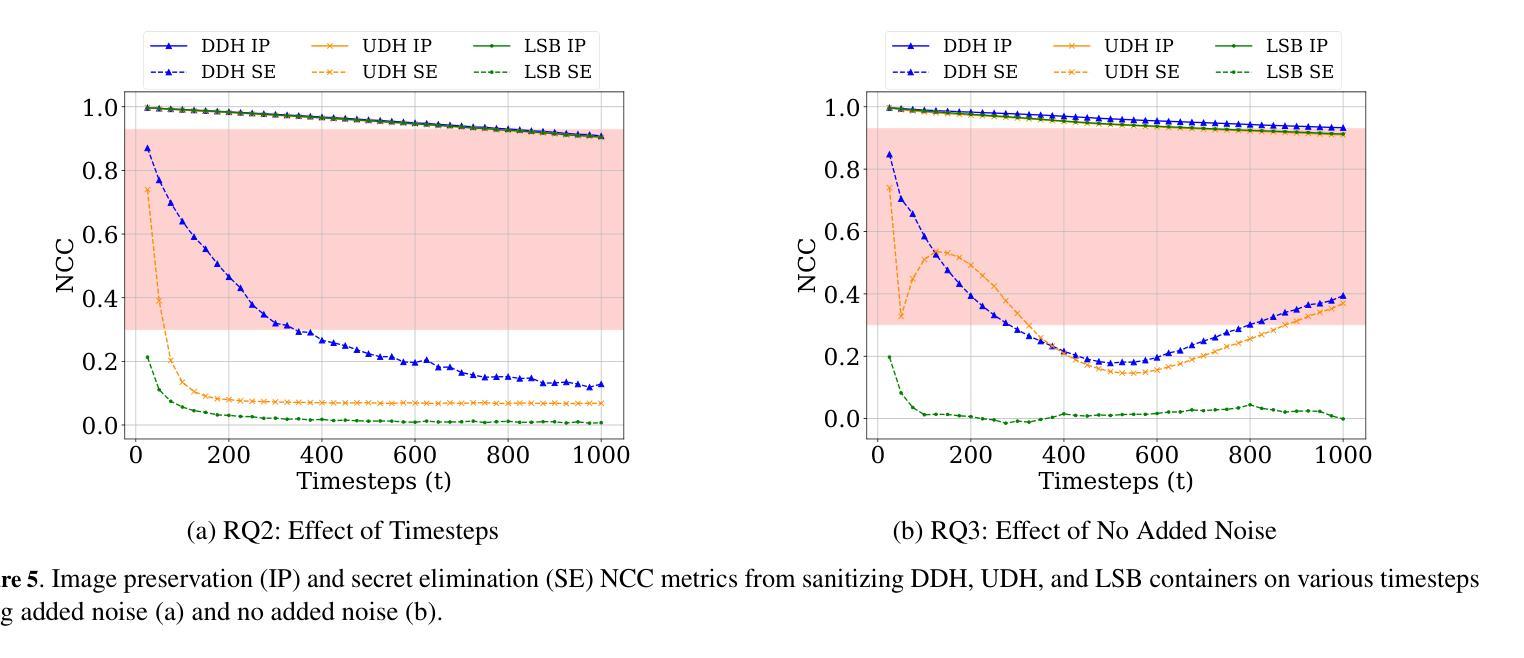
Sanitizing Hidden Information with Diffusion Models
Authors:Preston K. Robinette, Daniel Moyer, Taylor T. Johnson
Information hiding is the process of embedding data within another form of data, often to conceal its existence or prevent unauthorized access. This process is commonly used in various forms of secure communications (steganography) that can be used by bad actors to propagate malware, exfiltrate victim data, and discreetly communicate. Recent work has utilized deep neural networks to remove this hidden information in a defense mechanism known as sanitization. Previous deep learning works, however, are unable to scale efficiently beyond the MNIST dataset. In this work, we present a novel sanitization method called DM-SUDS that utilizes a diffusion model framework to sanitize/remove hidden information from image-into-image universal and dependent steganography from CIFAR-10 and ImageNet datasets. We evaluate DM-SUDS against three different baselines using MSE, PSNR, SSIM, and NCC metrics and provide further detailed analysis through an ablation study. DM-SUDS outperforms all three baselines and significantly improves image preservation MSE by 50.44%, PSNR by 12.69%, SSIM by 11.49%, and NCC by 3.26% compared to previous deep learning approaches. Additionally, we introduce a novel evaluation specification that considers the successful removal of hidden information (safety) as well as the resulting quality of the sanitized image (utility). We further demonstrate the versatility of this method with an application in an audio case study, demonstrating its broad applicability to additional domains.
信息隐藏是将数据嵌入另一种数据形式中的过程,通常用于隐藏其存在或防止未经授权的访问。这一过程中常用于各种安全通信(隐写术),不良行为者可能利用它来传播恶意软件、窃取受害者数据并进行隐秘通信。最近的工作利用深度神经网络来去除这种隐藏信息,作为一种名为清洗的防御机制。然而,以前的深度学习工作在处理MNIST数据集之外的数据时无法有效扩展。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的清洗方法DM-SUDS,它利用扩散模型框架来清洗/去除CIFAR-10和ImageNet数据集中图像内图像通用和依赖隐写术的隐藏信息。我们使用均方误差(MSE)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性度量(SSIM)和归一化相关系数(NCC)等指标对DM-SUDS与三种不同基线进行了评估,并通过消融研究提供了进一步的分析。与之前的深度学习方法相比,DM-SUDS在图像保留的MSE、PSNR、SSIM和NCC方面分别提高了50.44%、12.69%、11.49%和3.26%,并且超越了所有三条基线。此外,我们引入了一项新的评估标准,该标准考虑了成功去除隐藏信息(安全性)以及清洗后图像的质量(效用)。我们还通过音频案例研究展示了该方法的通用性,证明了其在其他领域的广泛应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), 2024
Summary
本研究提出一种名为DM-SUDS的新型净化方法,利用扩散模型框架去除图像和音频中的隐藏信息,以用于防御隐藏信息的攻击。相较于之前深度学习的方法,DM-SUDS能在CIFAR-10和ImageNet数据集上更有效地去除隐藏信息,提高图像保留效果。此外,研究还引入了一种新的评价标准,同时考虑成功去除隐藏信息的安全性和净化后图像的质量。DM-SUDS方法具有广泛的应用性,可用于音频等领域。
Key Takeaways
- 信息隐藏是将数据嵌入另一种数据形式中的过程,常用于安全通信中。
- 近期工作利用深度神经网络去除隐藏信息,作为防御机制。
- 现有方法难以有效扩展至MNIST数据集以外的领域。
- DM-SUDS方法利用扩散模型框架,有效去除图像中的隐藏信息,并展现出对CIFAR-10和ImageNet数据集的优异性能。
- 与三种基线方法相比,DM-SUDS在图像保留效果上有显著改进。
- 研究引入了综合考虑成功去除隐藏信息与净化后图像质量的新评价标准。
点此查看论文截图