⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-08 更新
Ola: Pushing the Frontiers of Omni-Modal Language Model with Progressive Modality Alignment
Authors:Zuyan Liu, Yuhao Dong, Jiahui Wang, Ziwei Liu, Winston Hu, Jiwen Lu, Yongming Rao
Recent advances in large language models, particularly following GPT-4o, have sparked increasing interest in developing omni-modal models capable of understanding more modalities. While some open-source alternatives have emerged, there is still a notable lag behind specialized single-modality models in performance. In this paper, we present Ola, an Omni-modal language model that achieves competitive performance across image, video, and audio understanding compared to specialized counterparts. The core design of Ola lies in its progressive modality alignment strategy that extends the supporting modality of the language model progressively. Our training pipeline begins with the most distinct modalities: image and text, then gradually expands the skill sets of the model using speech data that connects language and audio knowledge, and video data that connects all modalities. The progressive learning pipeline also enables us to maintain a relatively small size of the cross-modal alignment data, making developing omni-modal from existing vision-language models easy and less costly. Moreover, to unlock an advanced interactive experience like GPT-4o, we further design a sentence-wise decoding solution for streaming speech generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Ola surpasses existing open omni-modal LLMs across all modalities while achieving highly competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art specialized models of similar sizes. We aim to make Ola a fully open omni-modal understanding solution to advance future research in this emerging field. Model weights, code, and data are open-sourced at https://github.com/Ola-Omni/Ola.
最近大型语言模型的进步,尤其是GPT-4o之后,引发了人们对开发能够理解更多模态的通用模型的浓厚兴趣。虽然已经出现了一些开源的替代方案,但在性能上仍然明显落后于专业的单模态模型。在本文中,我们介绍了Ola,一种通用模态语言模型,在图像、视频和音频理解方面与专用模型相比具有竞争力。Ola的核心设计在于其渐进的模态对齐策略,该策略逐步扩展语言模型的支持模态。我们的训练管道始于最独特的模态:图像和文本,然后使用连接语言和音频知识的语音数据以及连接所有模态的视频数据,逐步扩展模型技能集。渐进式学习管道还使我们能够保持相对较小的跨模态对齐数据集规模,从而轻松低成本地从现有的视觉语言模型开发通用模态。此外,为了解锁像GPT-4o这样的高级交互体验,我们进一步设计了一种基于句子的解码解决方案,用于流式语音生成。大量实验表明,Ola在所有模态上都超越了现有的开源通用多模态大型语言模型,同时在类似规模的专业模型中取得了高度竞争力的性能。我们的目标是使Ola成为一个完全开源的通用多模态解决方案,以推动这一新兴领域未来的研究。模型权重、代码和数据已在https://github.com/Ola-Omni/Ola开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期大型语言模型的进步,尤其是GPT-4o之后,激发了开发能够理解和处理更多模态的通用多模态模型的兴趣。本文介绍了一款名为Ola的通用多模态语言模型,该模型在图像、视频和音频理解方面表现出与专项单模态模型相当的竞争力。Ola的核心设计在于其渐进式模态对齐策略,该策略逐步扩展语言模型的支持模态。其训练流程从最具特色的模态(图像和文本)开始,然后通过连接语言和音频知识的语音数据以及连接所有模态的视频数据,逐步扩展模型技能集。这种渐进式学习流程还使得跨模态对齐数据集的规模相对较小,使得从现有视觉语言模型出发开发通用多模态模型变得更加容易和成本更低。此外,Ola还设计了一种句子级的解码解决方案,用于流式语音生成,解锁了类似GPT-4o的高级交互体验。实验表明,Ola在所有模态上超越了现有的开源通用多模态大型语言模型,同时在类似规模的专业模型中表现出高度竞争力。我们的目标是使Ola成为完全开源的通用多模态理解解决方案,以推动这一新兴领域的发展。
Key Takeaways
- Ola是一款通用多模态语言模型,能够在图像、视频和音频理解方面表现出与专项单模态模型相当的竞争力。
- Ola的核心设计在于其渐进式模态对齐策略,通过逐步扩展语言模型的支持模态来实现多模态理解。
- Ola的训练流程从图像和文本开始,然后逐步引入语音和视频数据,以扩展模型的能力。
- 渐进式学习流程使得跨模态对齐数据集的规模相对较小,降低了开发成本。
- Ola设计了一种句子级的解码解决方案,用于流式语音生成,增强了模型的交互性。
- Ola在所有模态上的表现超越了现有的开源通用多模态大型语言模型。
点此查看论文截图

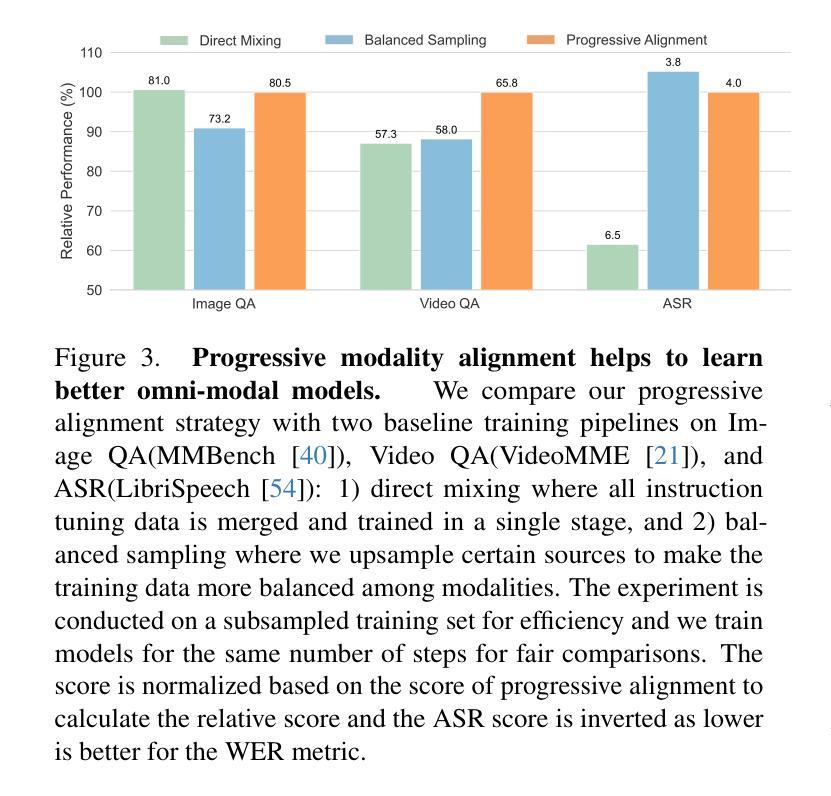

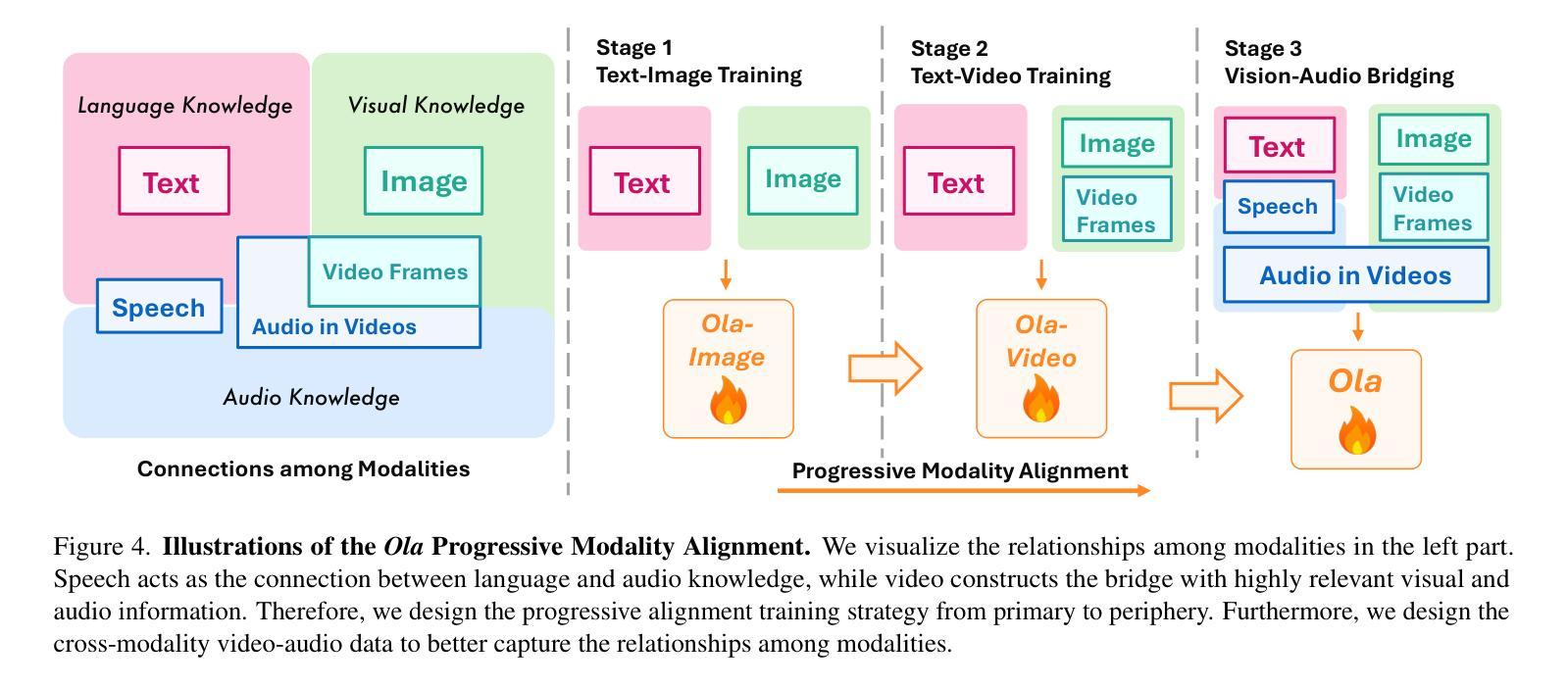
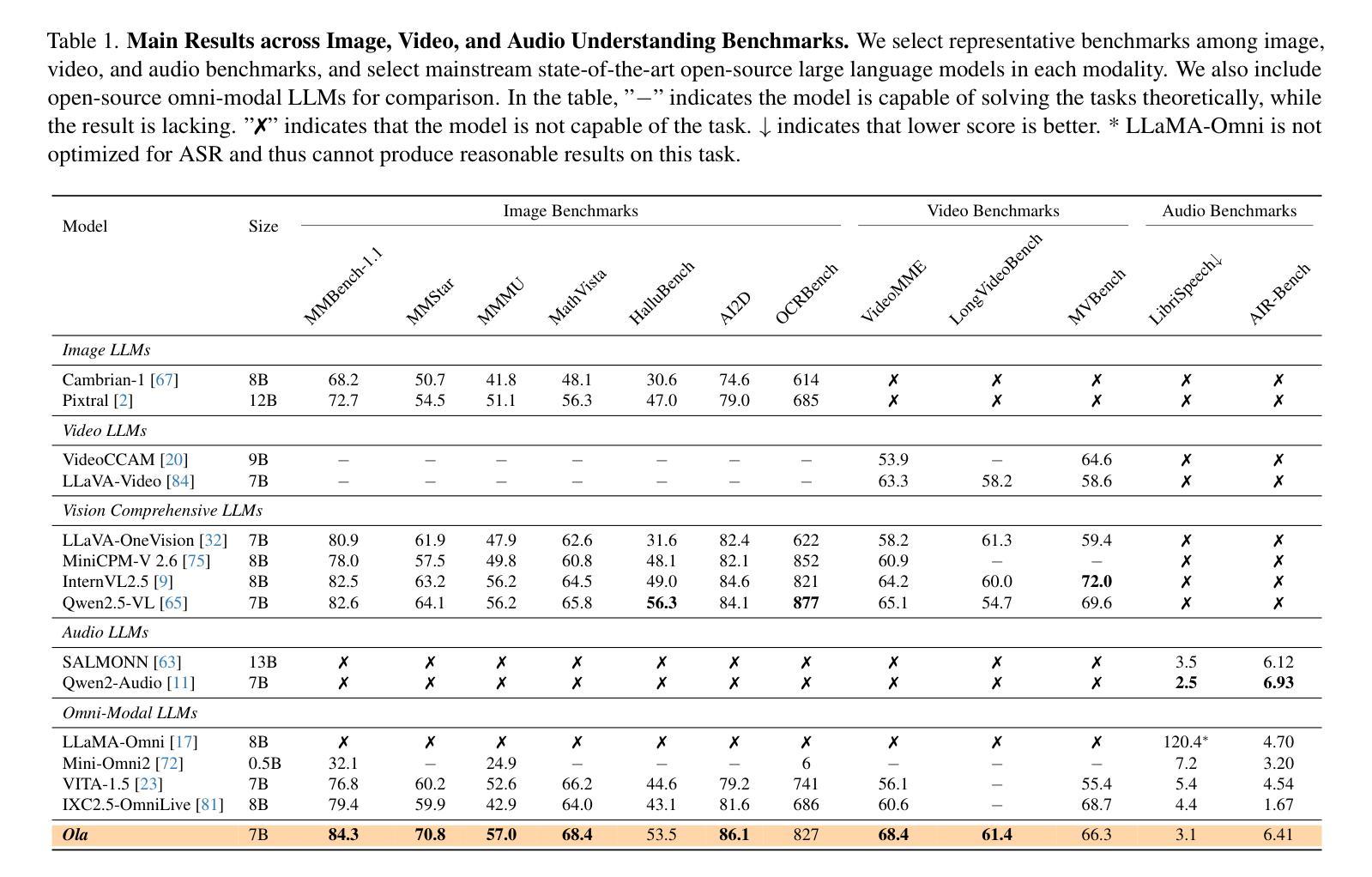
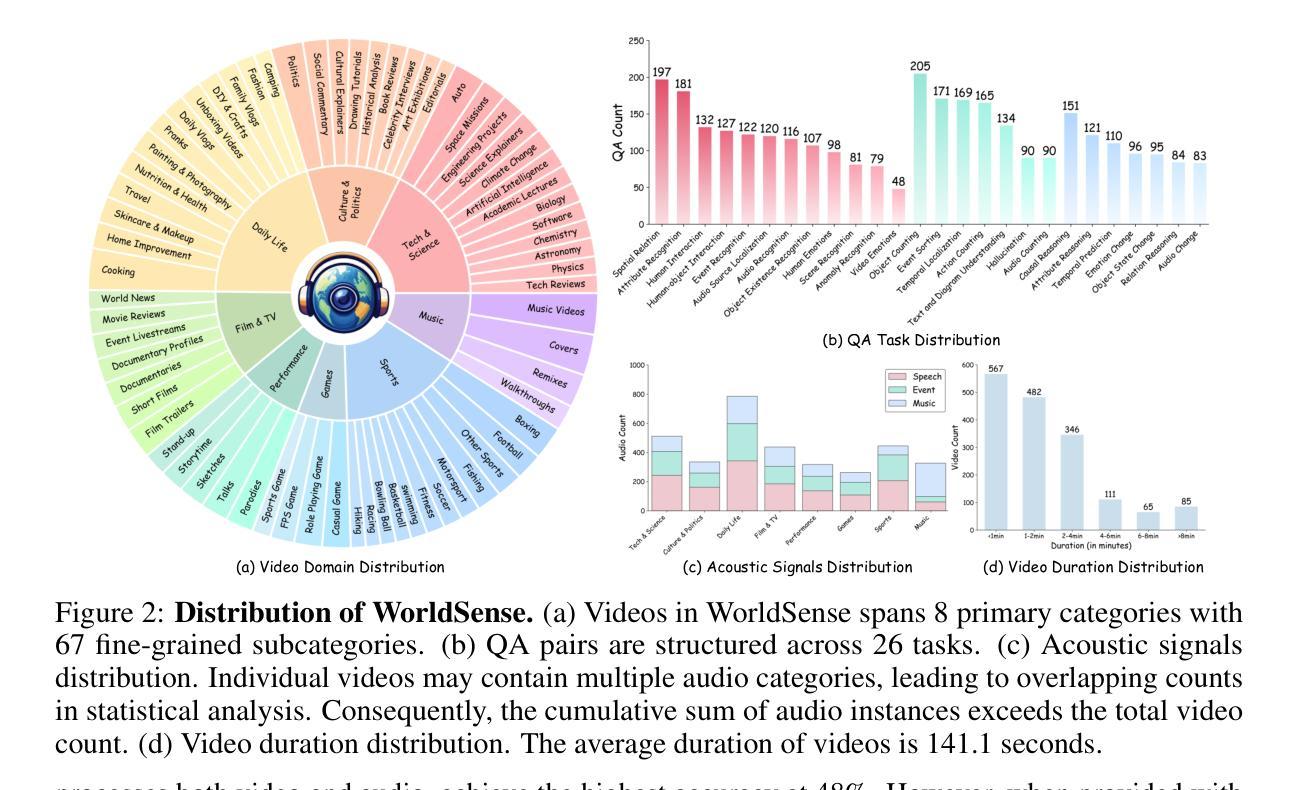
WorldSense: Evaluating Real-world Omnimodal Understanding for Multimodal LLMs
Authors:Jack Hong, Shilin Yan, Jiayin Cai, Xiaolong Jiang, Yao Hu, Weidi Xie
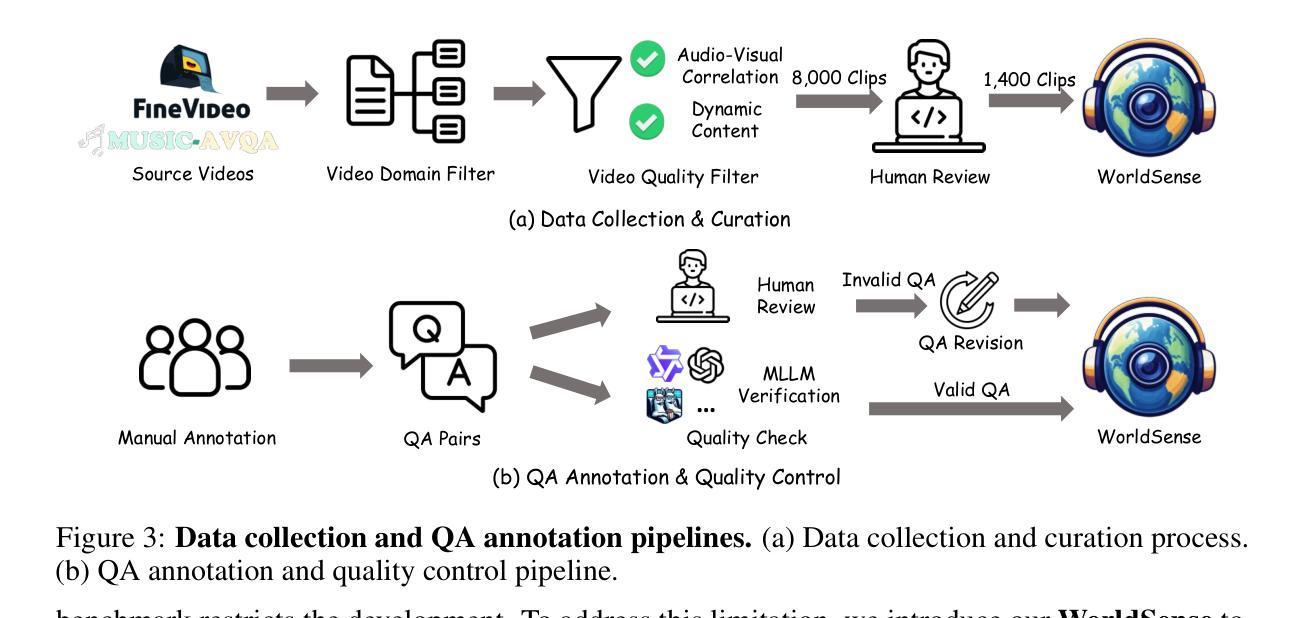
In this paper, we introduce WorldSense, the first benchmark to assess the multi-modal video understanding, that simultaneously encompasses visual, audio, and text inputs. In contrast to existing benchmarks, our WorldSense has several features: (i) collaboration of omni-modality, we design the evaluation tasks to feature a strong coupling of audio and video, requiring models to effectively utilize the synergistic perception of omni-modality; (ii) diversity of videos and tasks, WorldSense encompasses a diverse collection of 1,662 audio-visual synchronised videos, systematically categorized into 8 primary domains and 67 fine-grained subcategories to cover the broad scenarios, and 3,172 multi-choice QA pairs across 26 distinct tasks to enable the comprehensive evaluation; (iii) high-quality annotations, all the QA pairs are manually labeled by 80 expert annotators with multiple rounds of correction to ensure quality. Based on our WorldSense, we extensively evaluate various state-of-the-art models. The experimental results indicate that existing models face significant challenges in understanding real-world scenarios (48.0% best accuracy). We hope our WorldSense can provide a platform for evaluating the ability in constructing and understanding coherent contexts from omni-modality.
在本文中,我们介绍了WorldSense,这是第一个评估多模式视频理解的基准测试,它同时涵盖了视觉、音频和文本输入。与现有基准测试相比,我们的WorldSense具有几个特点:(i)全模式协作,我们设计的评估任务旨在突出音频和视频的强烈耦合,要求模型有效利用全模式的协同感知;(ii)视频和任务多样性,WorldSense涵盖了多样化的1662个音视频同步视频,系统地分为8个主要领域和67个精细子类别,以涵盖广泛的场景,以及26个不同任务的3172个多项选择问答对,以实现全面评估;(iii)高质量注释,所有问答对均由80名专业注释员手动标注,经过多轮校正以确保质量。基于我们的WorldSense,我们对各种最新模型进行了广泛评估。实验结果表明,现有模型在理解真实场景方面面临重大挑战(最佳精度为48.0%)。我们希望WorldSense能为评估从全模式构建和理解连贯上下文的能力提供一个平台。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了WorldSense,首个评估多模态视频理解能力的基准测试平台。该平台融合了视觉、听觉和文本输入,具有多模态协作、视频任务多样以及高质量注释等特点。通过对现有模型的广泛评估,发现现有模型在理解真实场景方面存在挑战。WorldSense有望为评估多模态构建和理解连贯上下文的能力提供平台。
Key Takeaways:
- WorldSense是首个评估多模态视频理解的基准测试平台,融合了视觉、听觉和文本输入。
- 平台设计评价任务,强调音频和视频的强耦合,要求模型有效利用多模态的协同感知。
- WorldSense包含1662个音视频同步视频和3172个多选择题对,覆盖26个不同任务,具有视频和任务的多样性。
- 所有问题对都是经过80名专家标注者手动标注,并经过多轮修正,保证了高质量注释。
- 现有模型在理解真实场景方面存在挑战,最佳准确率仅为48.0%。
- WorldSense可以为评估构建和理解多模态连贯上下文的能力提供平台。
点此查看论文截图




ChamaleonLLM: Batch-Aware Dynamic Low-Rank Adaptation via Inference-Time Clusters
Authors:Kamer Ali Yuksel, Hassan Sawaf
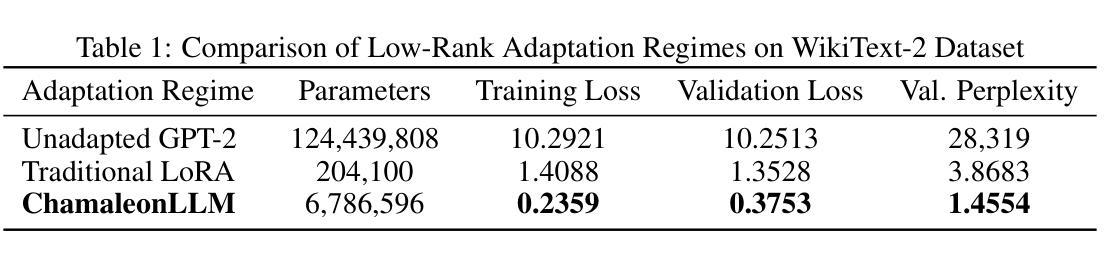
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable performance across diverse tasks. However, these models are typically deployed with fixed weights, which limits their ability to adapt dynamically to the variability inherent in real-world data during inference. This paper introduces ChamaleonLLM, a novel framework that enables inference-time adaptation of LLMs by leveraging batch-aware clustering and on-the-fly generation of low-rank updates. Unlike traditional fine-tuning approaches such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) or methods that rely on a fixed set of pre-learned uniforms (changeable masks), our method dynamically generates adaptive modifications to the decoder weights based on the aggregated statistics of clustered batches. By intelligently grouping similar inputs and computing context-aware low-rank updates via a hyper-network, ChamaleonLLM achieves significant performance gains, outperforming conventional LoRA methods while eliminating the overhead of maintaining multiple expert models. Our experiments highlight the potential of our approach to serve as a versatile and highly adaptive solution for language model inference. ChamaleonLLM is open-sourced to ensure the reproducibility of our experiments: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ChamaleonLLM/
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展在多种任务中表现出了显著的性能。然而,这些模型通常使用固定的权重进行部署,这限制了它们在推理过程中适应现实世界数据固有可变性的能力。本文介绍了ChamaleonLLM,这是一个利用批处理感知聚类和即时生成低秩更新来实现LLM推理时间自适应的新型框架。与传统的微调方法,如低秩适应(LoRA)或依赖于预学习统一集(可更改的掩码)的方法不同,我们的方法根据聚类批次的聚合统计动态生成对解码器权重的自适应修改。通过智能地分组相似输入并通过超网络计算上下文感知的低秩更新,ChamaleonLLM实现了显著的性能提升,不仅超越了传统的LoRA方法,而且消除了维护多个专家模型的开销。我们的实验突显了我们方法作为语言模型推理的通用和高度自适应解决方案的潜力。ChamaleonLLM已开源,以确保我们实验的可重复性:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ChamaleonLLM/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进步在各种任务中表现出卓越性能。然而,这些模型通常在推理时具有固定的权重,无法动态适应现实数据中的变化。本文提出ChamaleonLLM框架,通过批量感知聚类和即时生成低秩更新,实现LLM的推理时间适应。相较于传统的微调方法如LoRA或依赖于预学习统一(可更换蒙版)的方法,我们的方法能够根据聚类批次的聚合统计动态生成解码器权重的自适应修改。ChamaleonLLM通过智能分组相似输入并通过超网络计算上下文感知的低秩更新,实现了显著的性能提升,不仅超越了传统的LoRA方法,而且消除了维护多个专家模型的开销。我们的实验展示了该方法的通用性和高度适应性,可作为语言模型推理的实用解决方案。ChamaleonLLM已开源,确保实验的可重复性。
Key Takeaways:
- ChamaleonLLM框架实现了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理时间适应。
- 该框架通过批量感知聚类和低秩更新,提升了LLM的性能。
- ChamaleonLLM能动态生成解码器权重的自适应修改,基于聚类批次的聚合统计。
- 该方法与传统的微调方法如LoRA有所区别,并超越了预学习统一(可更换蒙版)的方法。
- ChamaleonLLM通过智能分组相似输入和计算上下文感知的低秩更新,实现了显著的性能提升。
- ChamaleonLLM方法具有高度的通用性和适应性,可以适应不同的语言模型推理需求。
点此查看论文截图

ScoreFlow: Mastering LLM Agent Workflows via Score-based Preference Optimization
Authors:Yinjie Wang, Ling Yang, Guohao Li, Mengdi Wang, Bryon Aragam
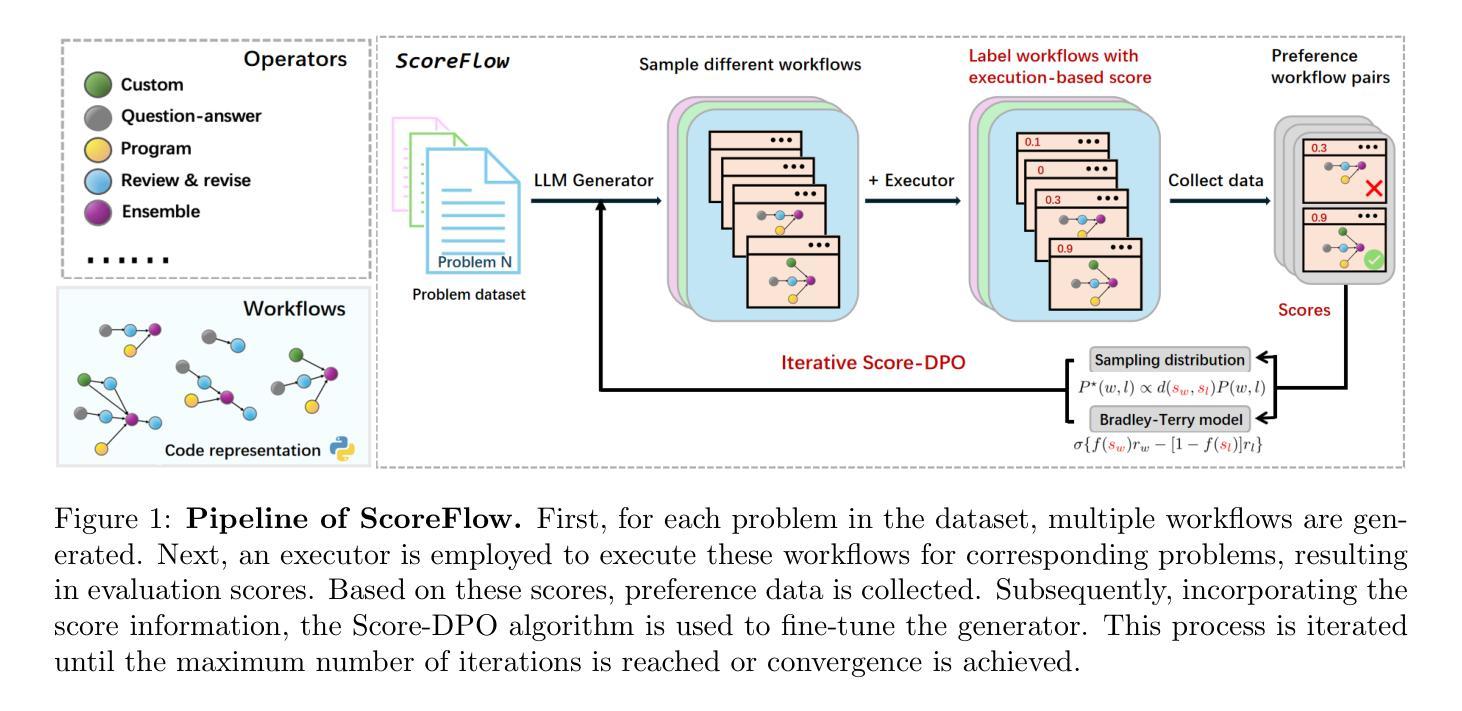
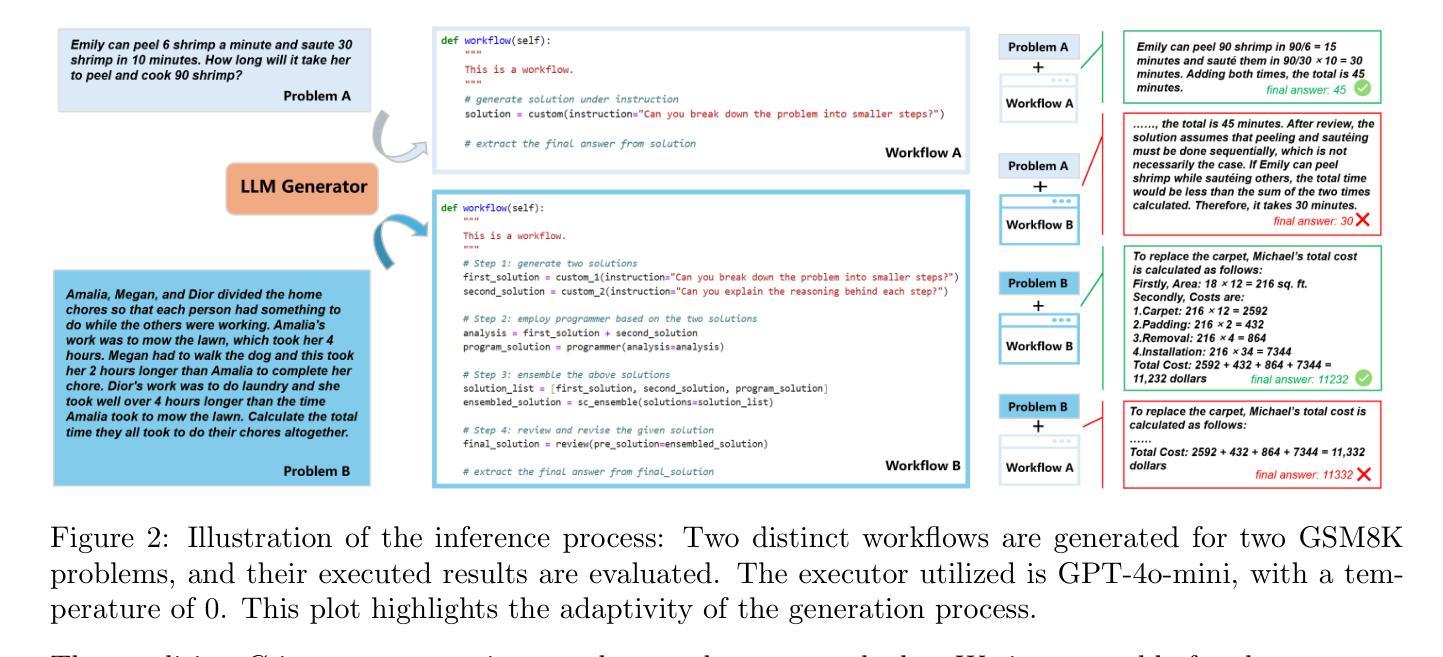
Recent research has leveraged large language model multi-agent systems for complex problem-solving while trying to reduce the manual effort required to build them, driving the development of automated agent workflow optimization methods. However, existing methods remain inflexible due to representational limitations, a lack of adaptability, and poor scalability when relying on discrete optimization techniques. We address these challenges with ScoreFlow, a simple yet high-performance framework that leverages efficient gradient-based optimization in a continuous space. ScoreFlow incorporates Score-DPO, a novel variant of the direct preference optimization method that accounts for quantitative feedback. Across six benchmarks spanning question answering, coding, and mathematical reasoning, ScoreFlow achieves an 8.2% improvement over existing baselines. Moreover, it empowers smaller models to outperform larger ones with lower inference costs. Project: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/ScoreFlow
最近的研究利用大型语言模型多智能体系统来解决复杂问题,同时努力减少构建它们所需的人工努力,推动自动智能体工作流程优化方法的发展。然而,由于表征的局限性、缺乏适应性和在依赖离散优化技术时的糟糕可扩展性,现有方法仍然不够灵活。我们针对这些挑战,推出了ScoreFlow框架,这是一个简单而高性能的框架,利用连续空间中的高效基于梯度的优化。ScoreFlow结合了Score-DPO,这是一种考虑定量反馈的直接偏好优化方法的新变种。在涵盖问答、编码和数学推理的六个基准测试中,ScoreFlow相较于现有基准测试实现了8.2%的改进。此外,它还能使小型模型在推理成本较低的情况下超越大型模型。项目地址:https://github.com/Gen-Verse/ScoreFlow
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/ScoreFlow
Summary
大型语言模型多智能体系统用于复杂问题求解,减少人工构建工作量。现有自动化智能体工作流程优化方法因表达局限、缺乏适应性和离散优化技术导致的可扩展性差而显得不够灵活。ScoreFlow框架采用连续空间中的高效梯度优化,解决这些问题。ScoreFlow包含Score-DPO,一种考虑定量反馈的直接偏好优化方法的新变种。在涵盖问答、编码和数学推理的六个基准测试中,ScoreFlow较现有基线提高了8.2%。此外,它使小型模型能以较低的推理成本超越大型模型。项目网址:GitHub地址。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型多智能体系统被用于解决复杂问题,目标是减少构建时的手动工作量。
- 当前自动化智能体工作流程优化方法存在表达局限、缺乏适应性和在离散优化技术中可扩展性差的问题。
- ScoreFlow框架采用连续空间中的高效梯度优化来解决上述问题。
- ScoreFlow包含Score-DPO,这是一种考虑定量反馈的直接偏好优化方法的新变种。
- 在多个基准测试中,ScoreFlow较现有方法提高了8.2%的性能。
- ScoreFlow使小型模型能够在较低推理成本下表现出超越大型模型的能力。
点此查看论文截图

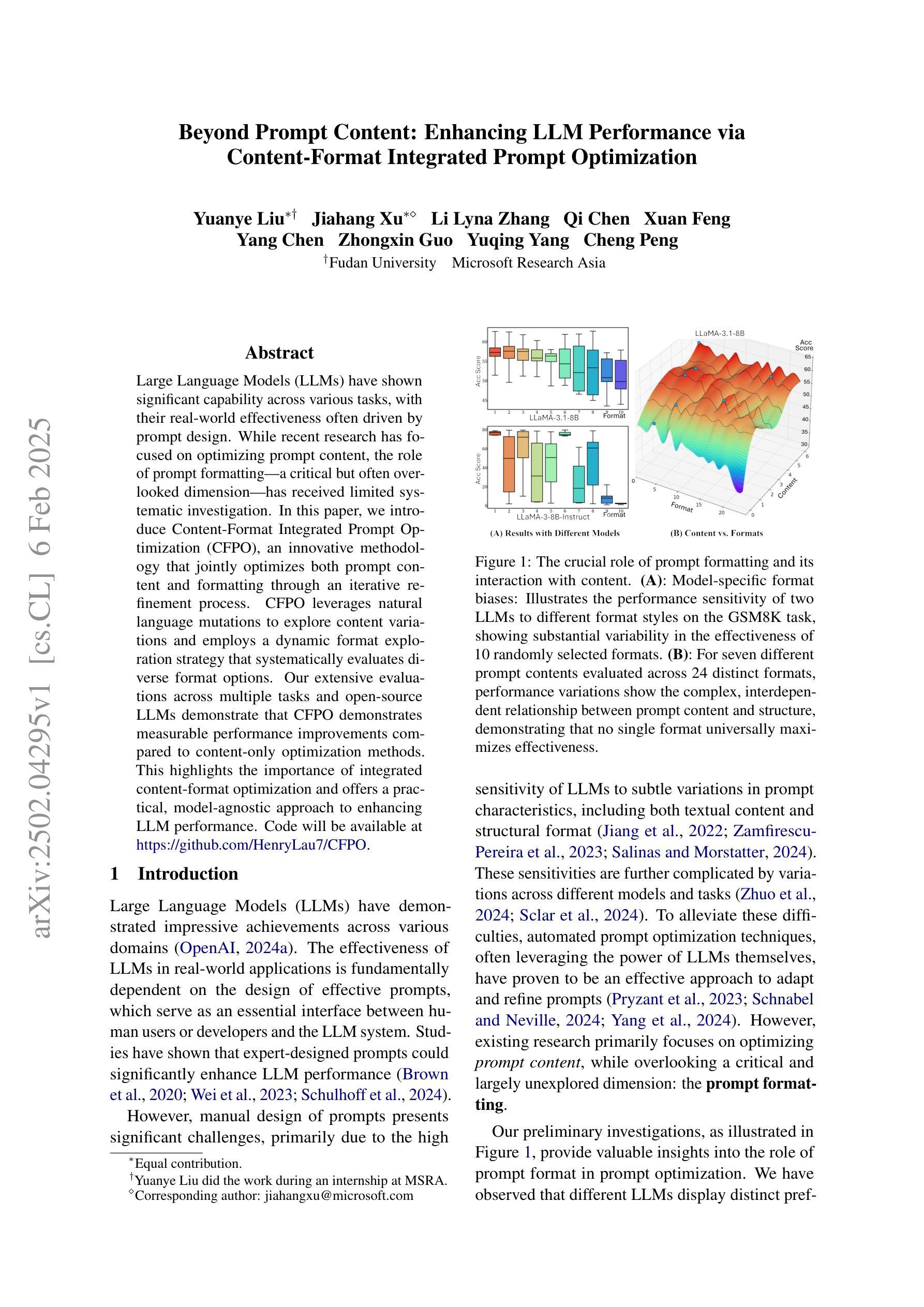
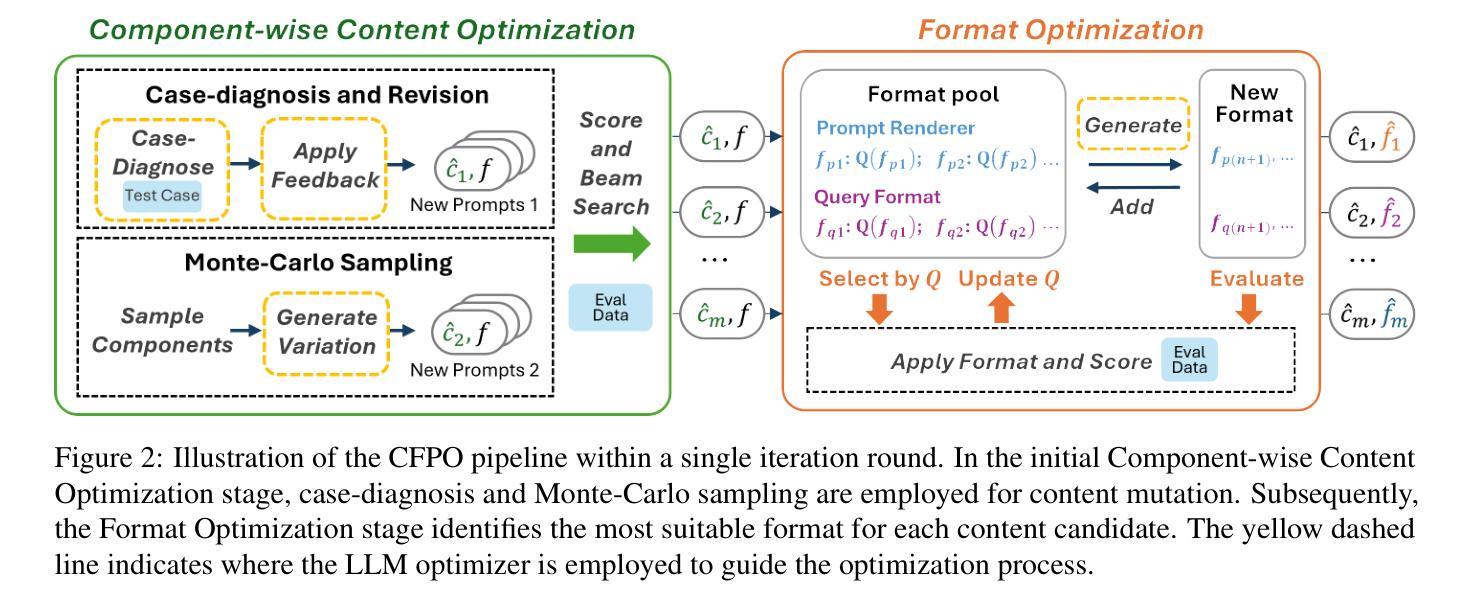
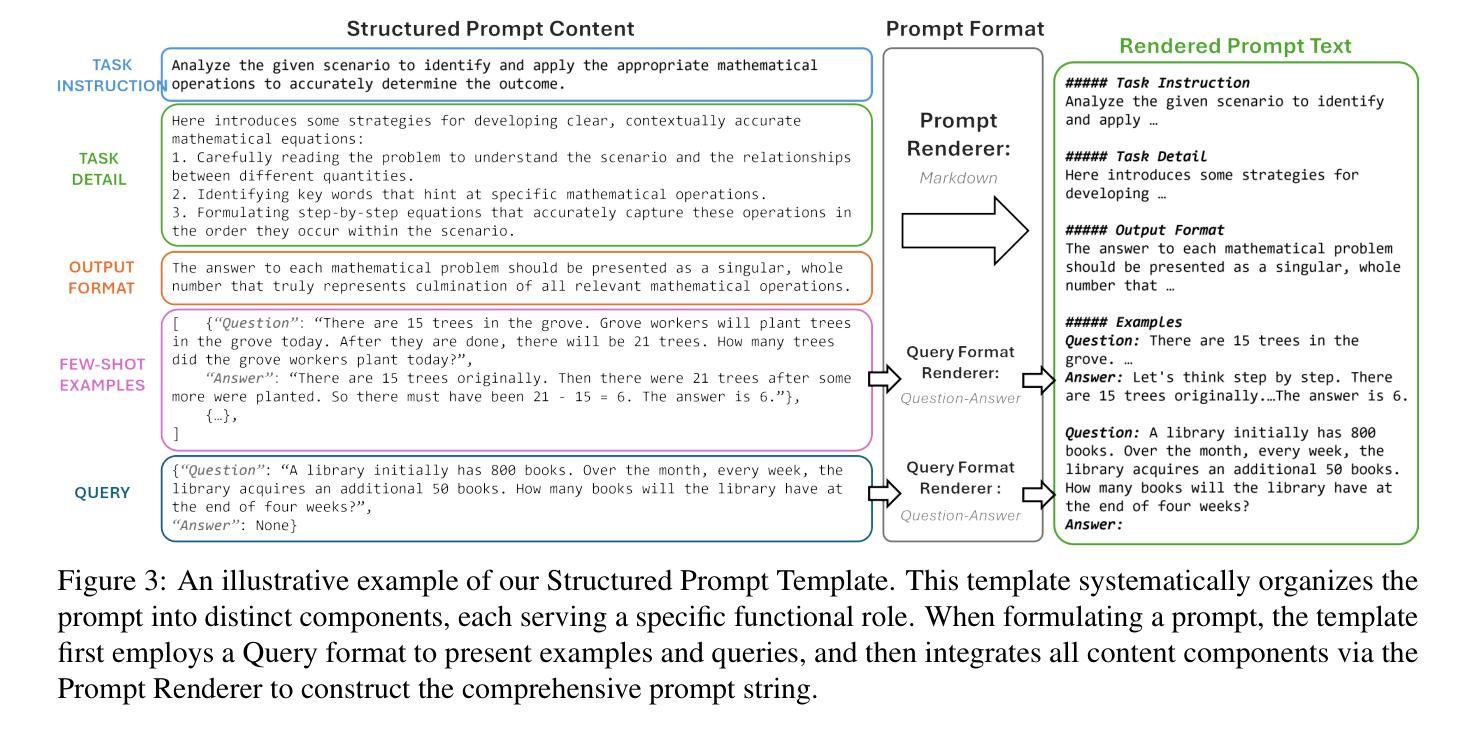
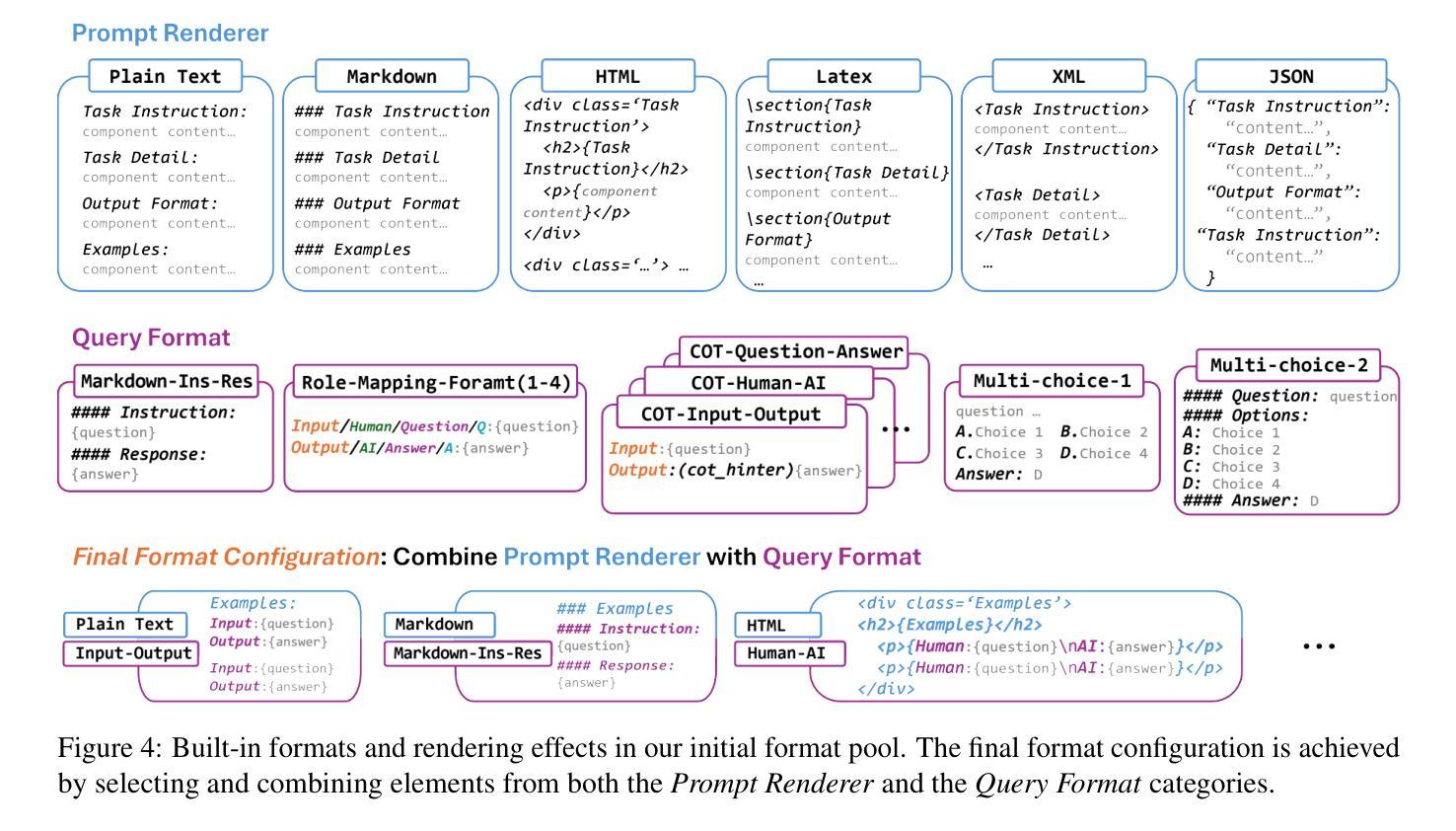
Beyond Prompt Content: Enhancing LLM Performance via Content-Format Integrated Prompt Optimization
Authors:Yuanye Liu, Jiahang Xu, Li Lyna Zhang, Qi Chen, Xuan Feng, Yang Chen, Zhongxin Guo, Yuqing Yang, Cheng Peng
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant capability across various tasks, with their real-world effectiveness often driven by prompt design. While recent research has focused on optimizing prompt content, the role of prompt formatting, a critical but often overlooked dimension, has received limited systematic investigation. In this paper, we introduce Content-Format Integrated Prompt Optimization (CFPO), an innovative methodology that jointly optimizes both prompt content and formatting through an iterative refinement process. CFPO leverages natural language mutations to explore content variations and employs a dynamic format exploration strategy that systematically evaluates diverse format options. Our extensive evaluations across multiple tasks and open-source LLMs demonstrate that CFPO demonstrates measurable performance improvements compared to content-only optimization methods. This highlights the importance of integrated content-format optimization and offers a practical, model-agnostic approach to enhancing LLM performance. Code will be available at https://github.com/HenryLau7/CFPO.
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中展现出显著的能力,其现实世界的有效性通常受到提示设计的驱动。虽然最近的研究侧重于优化提示内容,但提示格式的作用作为一个关键但常被忽视的维度,只得到了有限的系统研究。在本文中,我们介绍了内容格式集成提示优化(CFPO),这是一种通过迭代细化过程联合优化提示内容和格式的创新方法。CFPO利用自然语言变异来探索内容变化,并采用动态格式探索策略来系统评估不同的格式选项。我们在多个任务和开源LLM上的广泛评估表明,与仅优化内容的方法相比,CFPO显示出可衡量的性能改进。这强调了集成内容格式优化的重要性,并提供了一种提高LLM性能的实用、模型无关的方法。代码将在https://github.com/HenryLau7/CFPO中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
LLM在多种任务中展现出显著的能力,其实际效果往往依赖于提示设计。尽管最近有研究优化了提示内容,但提示格式这一重要但常被忽视的方面并未得到充分系统的研究。本文介绍了内容格式集成提示优化(CFPO)这一创新方法,它通过迭代过程共同优化提示内容和格式。CFPO利用自然语言变异来探索内容变化,并采用动态格式探索策略来系统地评估各种格式选项。在多个任务和开源LLM上的广泛评估表明,与仅优化内容的方法相比,CFPO在性能上取得了可衡量的改进。这强调了集成内容格式优化的重要性,并提供了一种提高LLM性能的实用且模型无关的方法。
要点
- LLM的实际效果取决于提示设计,包括提示内容和格式。
- 内容格式集成提示优化(CFPO)是一种同时优化提示内容和格式的方法。
- CFPO通过自然语言变异和动态格式探索策略进行工作。
- 广泛的评估表明,CFPO在多个任务和开源LLM上实现了比仅优化内容更好的性能。
- CFPO的重要性在于集成了内容格式的优化。
- CFPO提供了一种提高LLM性能的实用且模型无关的方法。
点此查看论文截图

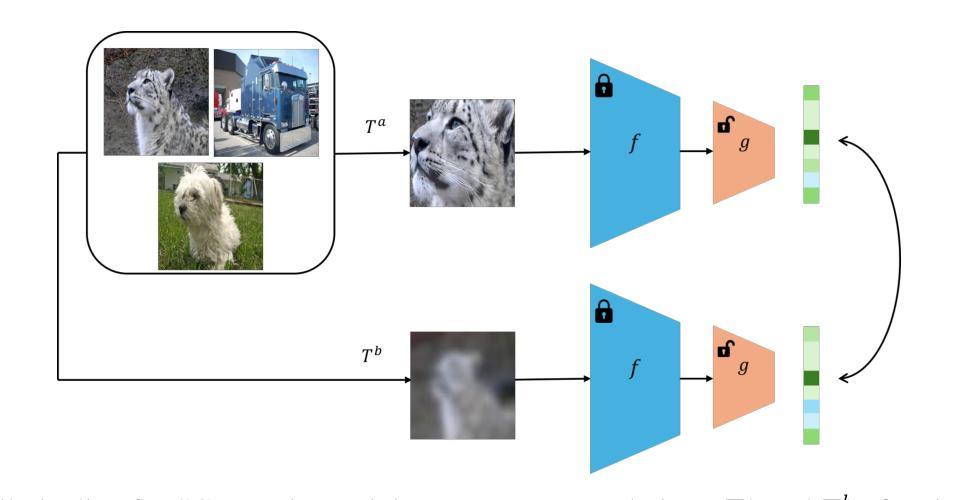
Keep It Light! Simplifying Image Clustering Via Text-Free Adapters
Authors:Yicen Li, Haitz Sáez de Ocáriz Borde, Anastasis Kratsios, Paul D. McNicholas
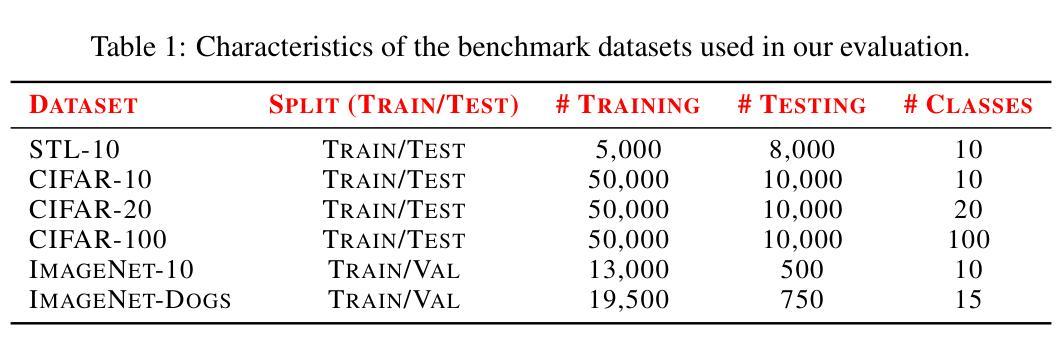
Many competitive clustering pipelines have a multi-modal design, leveraging large language models (LLMs) or other text encoders, and text-image pairs, which are often unavailable in real-world downstream applications. Additionally, such frameworks are generally complicated to train and require substantial computational resources, making widespread adoption challenging. In this work, we show that in deep clustering, competitive performance with more complex state-of-the-art methods can be achieved using a text-free and highly simplified training pipeline. In particular, our approach, Simple Clustering via Pre-trained models (SCP), trains only a small cluster head while leveraging pre-trained vision model feature representations and positive data pairs. Experiments on benchmark datasets including CIFAR-10, CIFAR-20, CIFAR-100, STL-10, ImageNet-10, and ImageNet-Dogs, demonstrate that SCP achieves highly competitive performance. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical result explaining why, at least under ideal conditions, additional text-based embeddings may not be necessary to achieve strong clustering performance in vision.
许多具有竞争力的聚类流程具有多模态设计,利用大型语言模型(LLM)或其他文本编码器以及文本图像对,但在现实世界的下游应用中往往无法获得这些资源。此外,此类框架通常训练复杂且需要大量的计算资源,使得难以广泛应用。在这项工作中,我们展示了在深度聚类中,使用无文本和高度简化的训练流程即可实现与更复杂的最先进方法相当的性能。特别是我们的方法——通过预训练模型进行简单聚类(SCP),只训练一个小型的聚类头,并利用预训练的视觉模型特征表示和正数据对。在包括CIFAR-10、CIFAR-20、CIFAR-100、STL-10、ImageNet-10和ImageNet-Dogs等基准数据集上的实验表明,SCP实现了高度竞争的性能。此外,我们还从理论上给出了结果,解释了至少在理想条件下,为了实现视觉聚类的强大性能,为何可能不需要额外的文本嵌入。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于预训练模型的简化聚类方法(SCP),该方法无需使用文本和多模态数据,仅通过训练小型集群头,利用预训练的视觉模型特征表示和正数据对即可实现与复杂的最先进方法相当的竞争性能。实验结果表明,该方法在包括CIFAR-10、CIFAR-20、CIFAR-100、STL-10、ImageNet-10和ImageNet-Dogs等多个基准数据集上取得了高度竞争的性能。此外,本文还提供了理论结果,解释了至少在理想条件下,实现视觉强聚类性能时,不必使用额外的文本嵌入。
Key Takeaways
- 简化聚类方法(SCP)无需使用文本和多模态数据,仅通过训练小型集群头即可实现高度竞争的性能。
- SCP方法利用预训练的视觉模型特征表示和正数据对进行训练。
- 实验结果表明,SCP在多个基准数据集上实现了与复杂的最先进方法相当的竞争性能。
- 本文提供了一种理论解释,说明在理想条件下,实现视觉强聚类性能时,不必依赖额外的文本嵌入。
- SCP方法简化了多模态设计的复杂性,并降低了计算资源需求,有助于更广泛的采用。
- SCP方法为深度聚类提供了一种新的、高效的训练策略。
点此查看论文截图

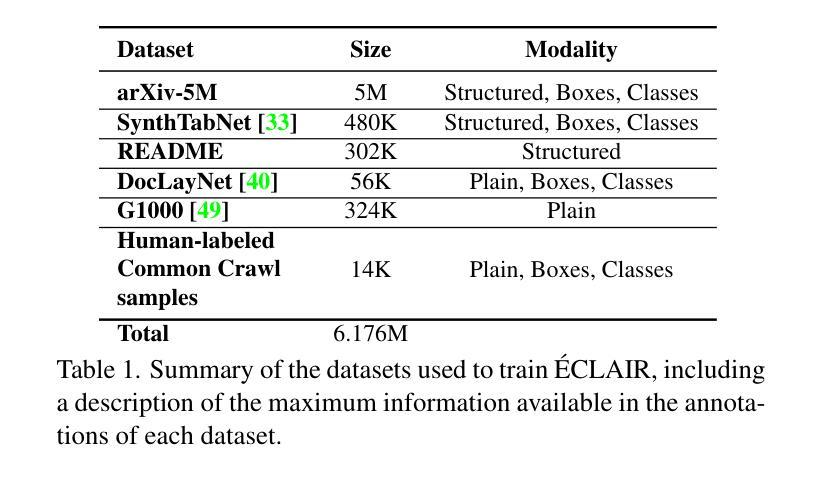
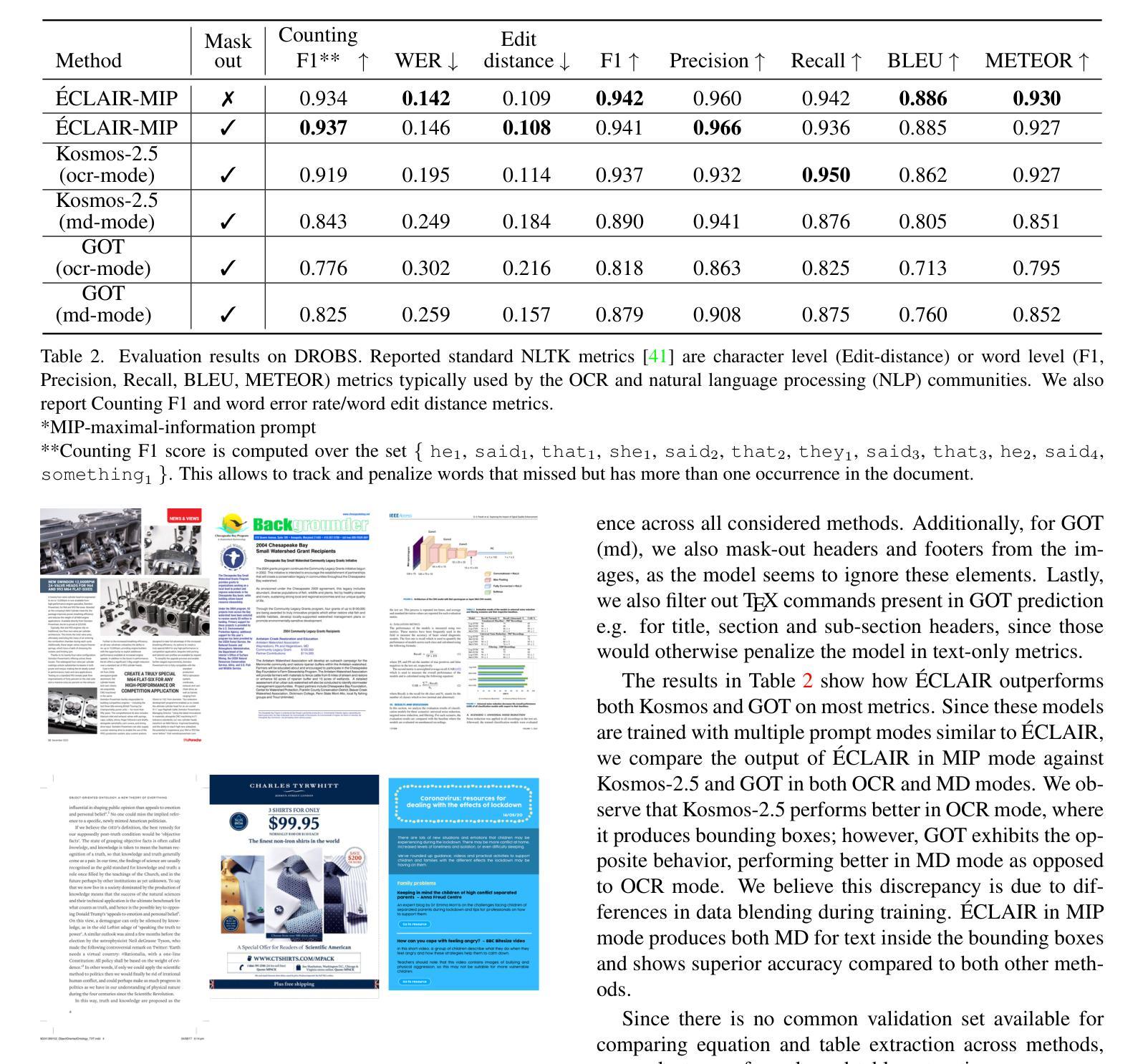
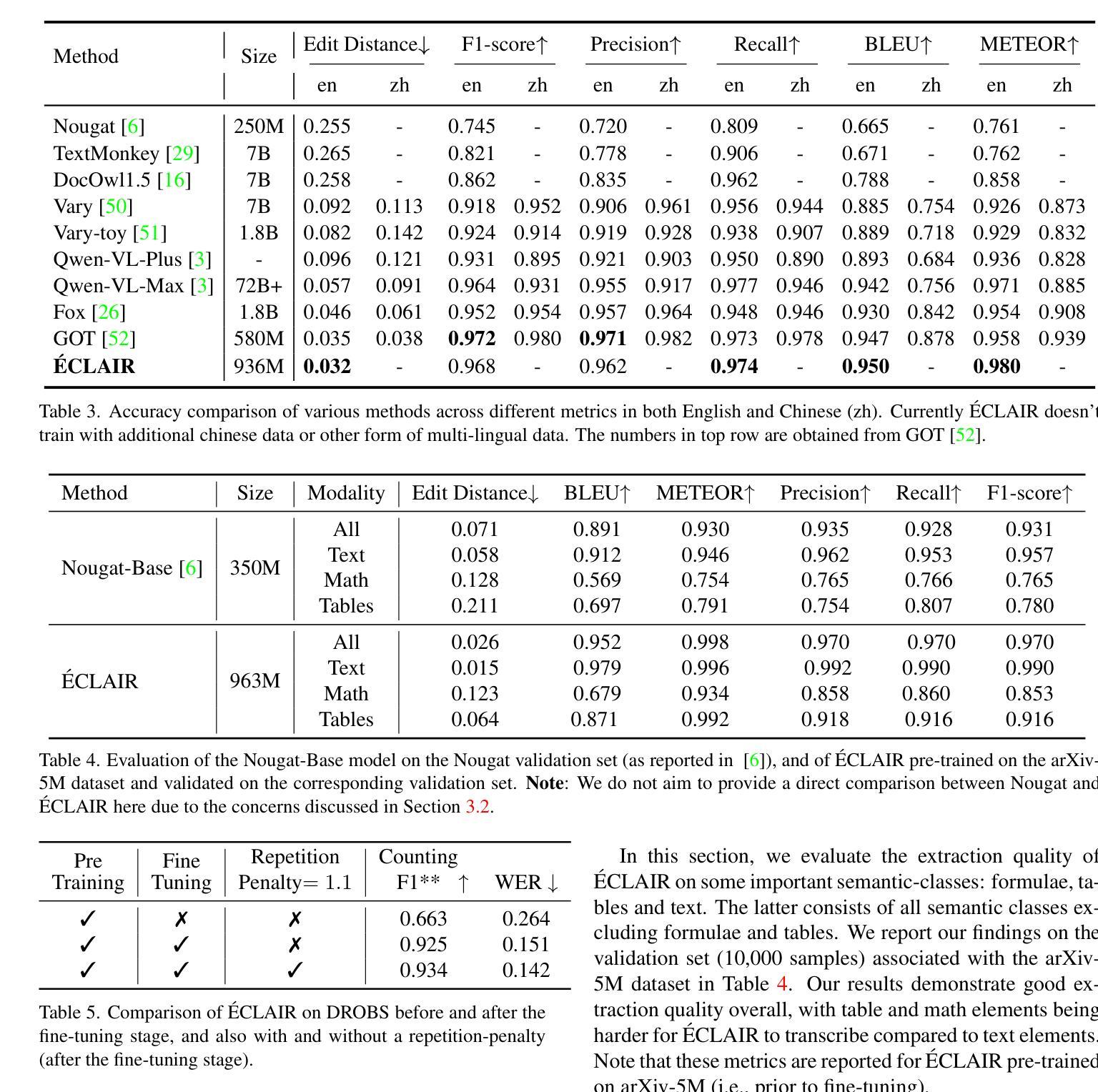
Éclair – Extracting Content and Layout with Integrated Reading Order for Documents
Authors:Ilia Karmanov, Amala Sanjay Deshmukh, Lukas Voegtle, Philipp Fischer, Kateryna Chumachenko, Timo Roman, Jarno Seppänen, Jupinder Parmar, Joseph Jennings, Andrew Tao, Karan Sapra
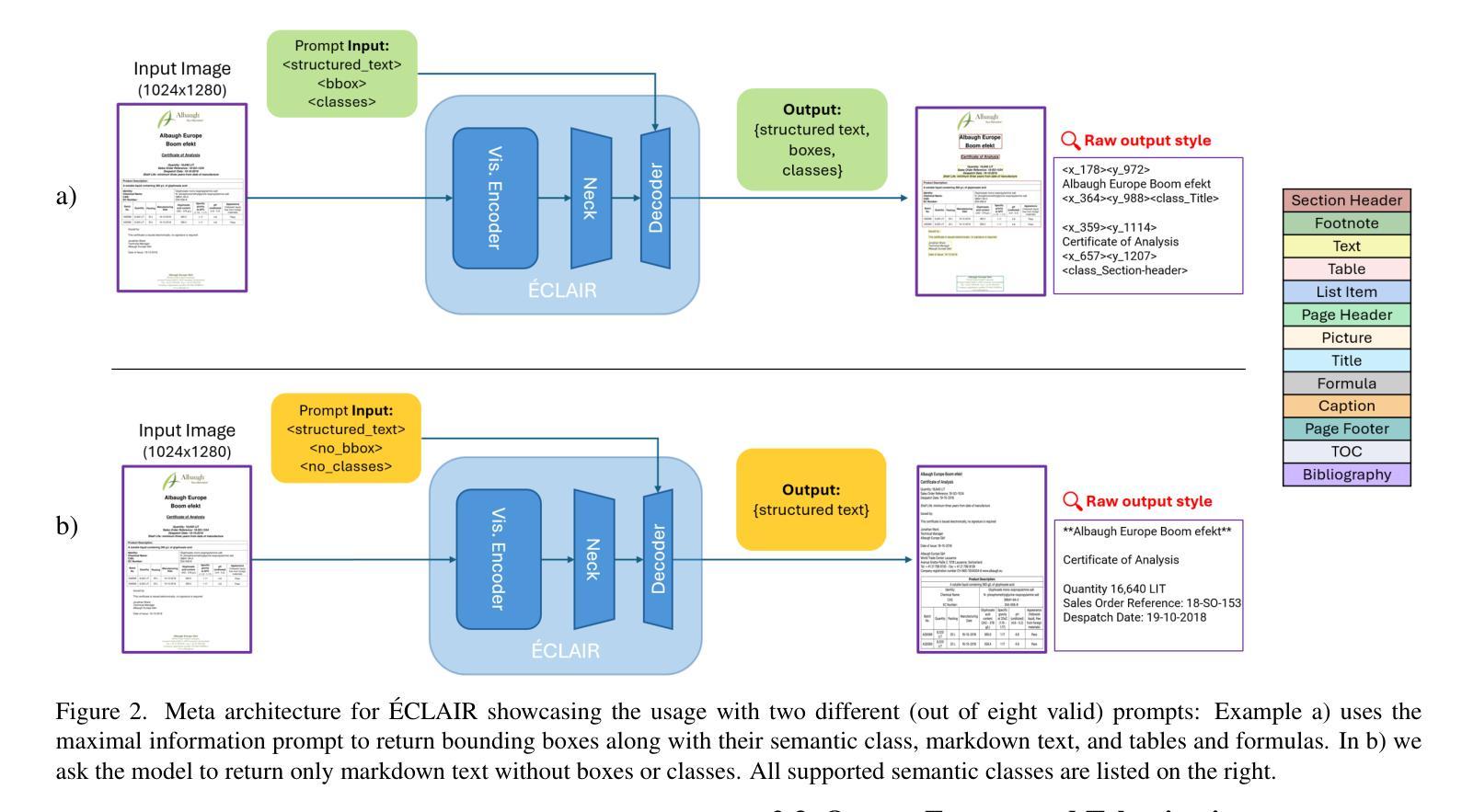
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology is widely used to extract text from images of documents, facilitating efficient digitization and data retrieval. However, merely extracting text is insufficient when dealing with complex documents. Fully comprehending such documents requires an understanding of their structure – including formatting, formulas, tables, and the reading order of multiple blocks and columns across multiple pages – as well as semantic information for detecting elements like footnotes and image captions. This comprehensive understanding is crucial for downstream tasks such as retrieval, document question answering, and data curation for training Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision Language Models (VLMs). To address this, we introduce 'Eclair, a general-purpose text-extraction tool specifically designed to process a wide range of document types. Given an image, 'Eclair is able to extract formatted text in reading order, along with bounding boxes and their corresponding semantic classes. To thoroughly evaluate these novel capabilities, we introduce our diverse human-annotated benchmark for document-level OCR and semantic classification. 'Eclair achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on this benchmark, outperforming other methods across key metrics. Additionally, we evaluate 'Eclair on established benchmarks, demonstrating its versatility and strength across several evaluation standards.
光学字符识别(OCR)技术广泛应用于从文档图像中提取文本,促进了高效的数字化和检索。然而,在处理复杂文档时,仅仅提取文本是不够的。要完全理解这些文档,需要了解它们的结构,包括格式、公式、表格以及跨多页的多个块和列的文本阅读顺序等,还需要检测脚注和图像标题等元素的语义信息。这种全面的理解对于下游任务至关重要,如检索、文档问答以及训练大型语言模型(LLM)和视觉语言模型(VLM)的数据整理等。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了名为”Eclair”的通用文本提取工具,它专门设计用于处理各种类型的文档。给定一张图像,”Eclair”能够按阅读顺序提取格式化文本,并提供边界框及其相应的语义类别。为了全面评估这些新颖的功能,我们引入了多样化的人工注释基准测试集,用于文档级别的OCR和语义分类。”Eclair”在这个基准测试集上达到了最先进的精度水平,在关键指标上优于其他方法。此外,我们在其他基准测试集上对”Eclair”进行了评估,证明了它在多个评估标准下的通用性和优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
光学字符识别(OCR)技术广泛应用于从文档图像中提取文本,促进数字化和检索效率的提升。但单纯提取文本对于复杂文档是不够的。全面理解文档需要理解其结构,包括格式、公式、表格以及跨多页的多个块和列的阅读顺序等,并检测脚注和图像标题等元素也需要语义信息。这种全面的理解对于下游任务至关重要,如检索、文档问答和训练大型语言模型(LLM)和视觉语言模型(VLM)的数据整理等。为解决此问题,我们引入了通用文本提取工具Eclair,专为处理各种文档类型而设计。给定一张图片,Eclair能够以阅读顺序提取格式化的文本,并带有边界框和相应的语义类别。为了全面评估这些新功能,我们引入了多样化的人标注文档级OCR和语义分类基准测试。Eclair在此基准测试中达到了最先进的准确性,并在关键指标上优于其他方法。此外,我们在既定的基准测试上对Eclair进行了评估,证明了其在多个评估标准下的通用性和实力。
Key Takeaways
- OCR技术广泛应用于从文档图像中提取文本,但仅提取文本不足以理解复杂文档的结构和语义信息。
- Eclair是一种通用文本提取工具,旨在处理各种类型的文档。
- Eclair能够从图像中提取格式化的文本并以阅读顺序呈现。
- Eclair能够识别文档的语义信息,如脚注和图像标题等。
- Eclair在多样化的文档级OCR和语义分类基准测试中表现出卓越的性能。
- Eclair在关键指标上优于其他OCR技术。
点此查看论文截图


“Short-length” Adversarial Training Helps LLMs Defend “Long-length” Jailbreak Attacks: Theoretical and Empirical Evidence
Authors:Shaopeng Fu, Liang Ding, Di Wang
Jailbreak attacks against large language models (LLMs) aim to induce harmful behaviors in LLMs through carefully crafted adversarial prompts. To mitigate attacks, one way is to perform adversarial training (AT)-based alignment, i.e., training LLMs on some of the most adversarial prompts to help them learn how to behave safely under attacks. During AT, the length of adversarial prompts plays a critical role in the robustness of aligned LLMs. This paper focuses on adversarial suffix jailbreak attacks and unveils that to defend against a jailbreak attack with an adversarial suffix of length $\Theta(M)$, it is enough to align LLMs on prompts with adversarial suffixes of length $\Theta(\sqrt{M})$. Theoretically, we analyze the adversarial in-context learning of linear transformers on linear regression tasks and prove a robust generalization bound for trained transformers. The bound depends on the term $\Theta(\sqrt{M_{\text{test}}}/M_{\text{train}})$, where $M_{\text{train}}$ and $M_{\text{test}}$ are the number of adversarially perturbed in-context samples during training and testing. Empirically, we conduct AT on popular open-source LLMs and evaluate their robustness against jailbreak attacks of different adversarial suffix lengths. Results confirm a positive correlation between the attack success rate and the ratio of the square root of the adversarial suffix during jailbreaking to the length during AT. Our findings show that it is practical to defend “long-length” jailbreak attacks via efficient “short-length” AT. The code is available at https://github.com/fshp971/adv-icl.
针对大型语言模型(LLM)的越狱攻击旨在通过精心设计的对抗性提示来诱导LLM产生有害行为。为了缓解攻击,一种方法是进行基于对抗性训练(AT)的对齐,即训练LLM对一些最具对抗性的提示,以帮助他们学习如何在攻击下安全地行为。在AT期间,对抗性提示的长度对于对齐LLM的稳健性起着至关重要的作用。本文专注于对抗性后缀越狱攻击,并揭示为了防御具有长度为Θ(M)的对抗性后缀的越狱攻击,只需在对提示进行对齐时,使用长度为Θ(√M)的对抗性后缀就足够了。从理论上讲,我们分析了线性回归任务中线性变换器的对抗性上下文学习,并为训练过的变换器证明了稳健的泛化界限。界限取决于项Θ(√M测试/M训练),其中M训练 和 M测试 是训练和测试期间的对抗性扰动上下文样本的数量。从经验上讲,我们对流行的开源LLM进行了AT,并评估了它们对抗不同对抗性后缀长度的越狱攻击的稳健性。结果证实,越狱攻击的成功率与越狱时的对抗性后缀长度平方根与AT期间长度的比率之间存在正相关。我们的研究结果表明,通过有效的“短长度”AT来防御“长长度”越狱攻击是切实可行的。代码可用在:https://github.com/fshp971/adv-icl。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
针对大型语言模型(LLM)的Jailbreak攻击通过精心设计的对抗性提示来诱导LLM产生有害行为。为了缓解攻击,一种方法是进行基于对抗训练(AT)的对齐。本文专注于对抗性后缀Jailbreak攻击,并揭示了对抗后缀的长度在防御Jailbreak攻击中的重要性。理论上,本文分析了线性回归任务中线性变压器的对抗性上下文学习,并为训练过的变压器证明了稳健的泛化边界。实证方面,我们对流行的开源LLM进行了AT,并评估了它们对抗不同对抗性后缀长度的Jailbreak攻击的稳健性。结果证实,攻击成功率与对抗训练期间使用的对抗性后缀长度的平方根之间存在正相关关系。我们的研究结果表明,通过高效的“短长度”AT来防御“长长度”的Jailbreak攻击是切实可行的。
Key Takeaways:
- Jailbreak攻击旨在通过精心设计的对抗性提示诱导LLM产生有害行为。
- 对抗训练(AT)是一种缓解Jailbreak攻击的方法。
- 对抗性后缀的长度在防御Jailbreak攻击中起着关键作用。
- 理论上,本文分析了线性回归任务中线性变压器的对抗性上下文学习。
- 实证研究表明,攻击成功率与对抗训练期间使用的对抗性后缀长度的平方根之间存在正相关关系。
- 通过高效的“短长度”AT来防御“长长度”的Jailbreak攻击是可行的。
点此查看论文截图

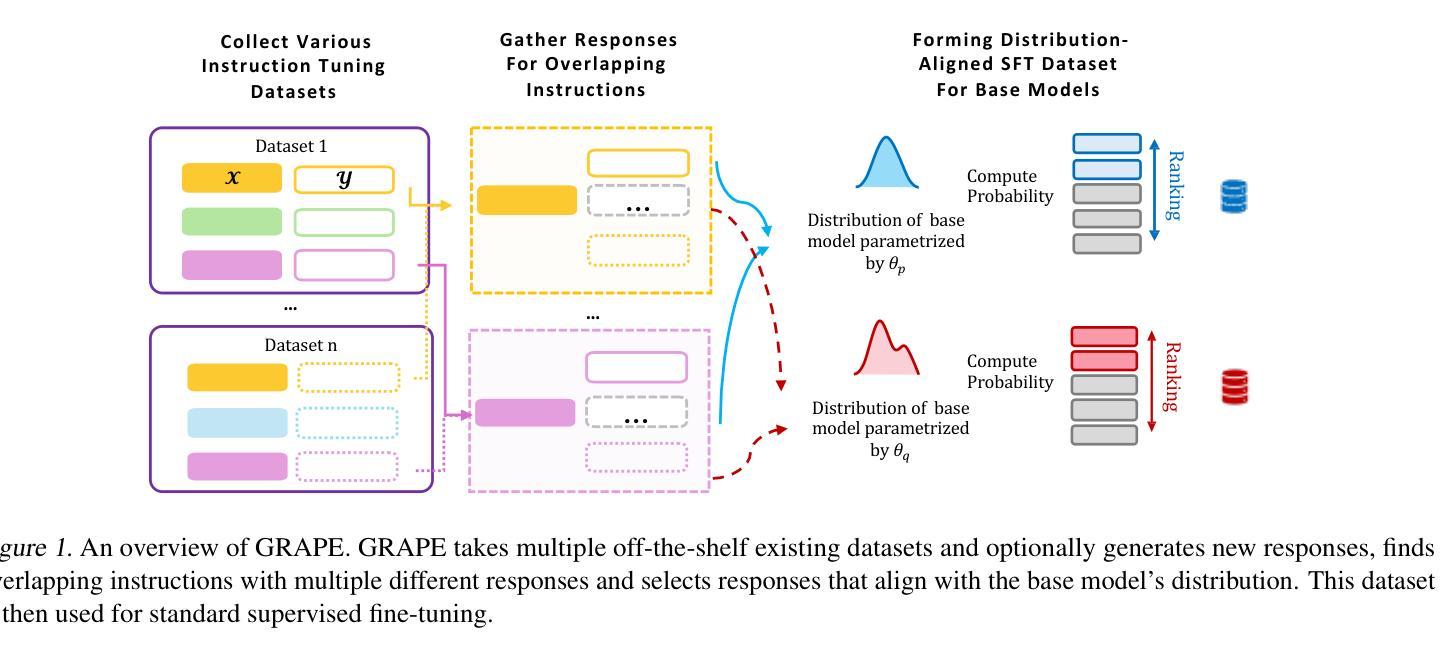
The Best Instruction-Tuning Data are Those That Fit
Authors:Dylan Zhang, Qirun Dai, Hao Peng
High-quality supervised fine-tuning (SFT) data are crucial for eliciting strong capabilities from pretrained large language models (LLMs). Typically, instructions are paired with multiple responses sampled from other LLMs, which are often out of the distribution of the target model to be fine-tuned. This, at scale, can lead to diminishing returns and even hurt the models’ performance and robustness. We propose GRAPE, a novel SFT framework that accounts for the unique characteristics of the target model. For each instruction, it gathers responses from various LLMs and selects the one with the highest probability measured by the target model, indicating that it aligns most closely with the target model’s pretrained distribution; it then proceeds with standard SFT training. We first evaluate GRAPE with a controlled experiment, where we sample various solutions for each question in UltraInteract from multiple models and fine-tune commonly used LMs like LLaMA3.1-8B, Mistral-7B, and Qwen2.5-7B on GRAPE-selected data. GRAPE significantly outperforms strong baselines, including distilling from the strongest model with an absolute gain of up to 13.8%, averaged across benchmarks, and training on 3x more data with a maximum performance improvement of 17.3%. GRAPE’s strong performance generalizes to realistic settings. We experiment with the post-training data used for Tulu3 and Olmo-2. GRAPE outperforms strong baselines trained on 4.5 times more data by 6.1% and a state-of-the-art data selection approach by 3% on average performance. Remarkably, using 1/3 of the data and half the number of epochs, GRAPE enables LLaMA3.1-8B to surpass the performance of Tulu3-SFT by 3.5%.
高质量监督微调(SFT)数据对于激发预训练大型语言模型(LLM)的强大能力至关重要。通常,指令会与从其他LLM采样的多个响应配对,这些响应往往超出了要微调的目标模型的分布。这在大规模情况下可能会导致收益递减,甚至会损害模型的性能和鲁棒性。我们提出了一个新型SFT框架GRAPE,它考虑了目标模型的独特特性。对于每个指令,它从各种LLM中收集响应,并选择目标模型测量概率最高的一个,这表明它与目标模型的预训练分布最密切对齐;然后它继续进行标准SFT训练。我们首先通过控制实验评估GRAPE,在该实验中,我们从多个模型中对UltraInteract中的每个问题采样各种解决方案,并使用GRAPE选定的数据对常用的LM(如LLaMA3.1-8B、Mistral-7B和Qwen2.5-7B)进行微调。GRAPE显著优于强大的基准模型,包括从最强模型蒸馏的绝对增益高达13.8%,平均跨基准测试,以及在比现有最佳方法多三倍的数据上进行训练,性能最高提高了17.3%。GRAPE的强大性能可推广到现实场景。我们对用于Tulu3和Olmo-2的后期训练数据进行了实验。GRAPE在比现有最佳方法多4.5倍的数据上训练的基线模型上高出6.1%,并且在平均性能上比最先进的数据选择方法高出3%。值得注意的是,使用三分之一的数据和减少一半的训练周期,GRAPE使LLaMA3.1-8B的性能超过了Tulu3-SFT的3.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)进行高质量监督精细调整(SFT)数据对于激发模型的强大能力至关重要。通常,指令与其他LLM生成的多个响应配对,这些响应往往超出目标模型的分布范围,大规模情况下可能导致收益递减甚至损害模型性能和稳健性。我们提出一种新型SFT框架GRAPE,它考虑了目标模型的独特特性。对于每个指令,它从各种LLM中收集响应,并选择目标模型测量的概率最高的一个,表明它与目标模型的预训练分布最接近;然后进行标准SFT训练。GRAPE在控制实验中的表现显著优于强大的基线,在通用模型如LLaMA3.1-8B、Mistral-7B和Qwen2.5-7B上进行GRAPE选定的数据微调。GRAPE的平均性能提高幅度高达13.8%,并且在现实环境中也具有强大的性能表现。在与Tulu3和Olmo-2的后期训练数据实验中,GRAPE表现出色,平均性能优于使用更多数据的强基线6.1%,并优于最新数据选择方法平均性能3%。值得注意的是,使用三分之一的数据和一半的训练周期,GRAPE使LLaMA3.1-8B的性能超过了Tulu3-SFT的3.5%。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量的监督精细调整(SFT)数据对于预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)至关重要。
- 传统的SFT方法可能在大规模应用时导致收益递减和模型性能下降。
- GRAPE框架考虑目标模型的独特特性,通过选择与目标模型预训练分布最接近的响应来进行SFT。
- GRAPE在控制实验中显著优于其他方法,平均性能提升高达13.8%。
- GRAPE在现实环境和不同数据集上的实验表现出强大的泛化能力。
- 与使用更多数据和更长时间训练的其他方法相比,GRAPE使用更少的数据和训练周期实现了更高的性能。
点此查看论文截图

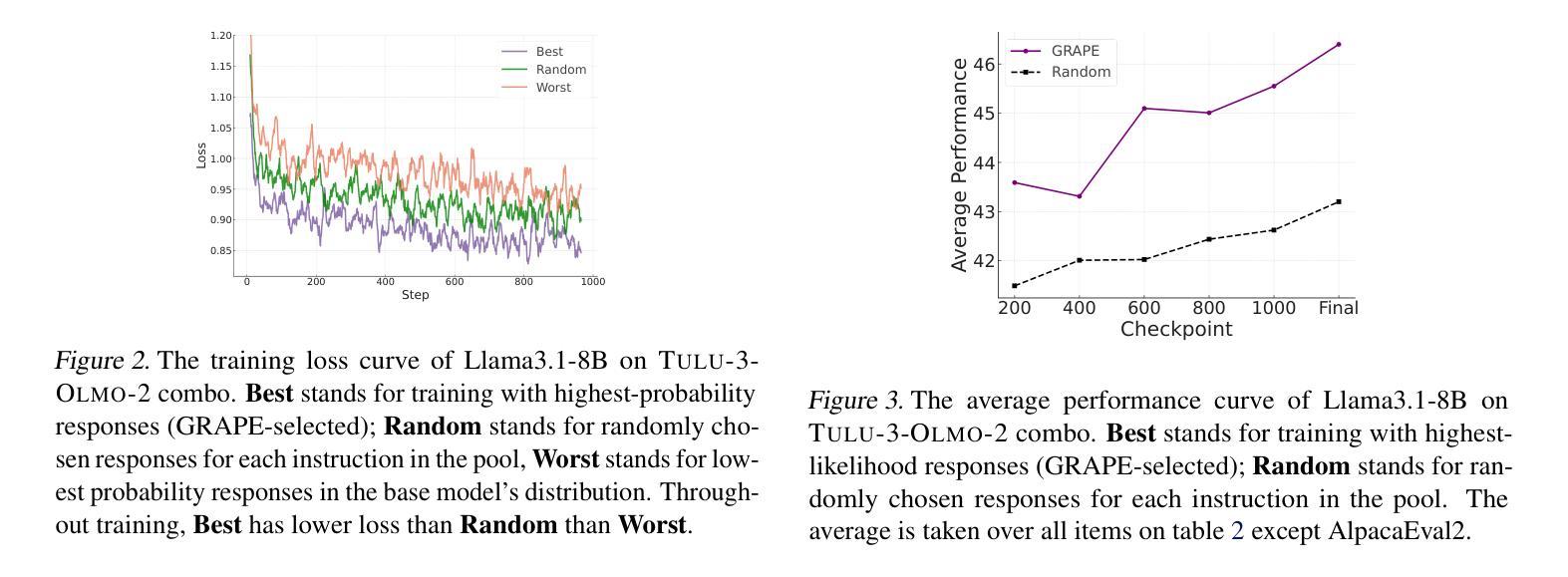
PixFoundation: Are We Heading in the Right Direction with Pixel-level Vision Foundation Models?
Authors:Mennatullah Siam
Multiple works have emerged to push the boundaries on multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) towards pixel-level understanding. Such approaches have shown strong performance on benchmarks for referring expression segmentation and grounded conversation generation. The current trend in pixel-level MLLMs is to train with pixel-level grounding supervision on large-scale labelled data. However, we show that such MLLMs when evaluated on recent challenging vision centric benchmarks, exhibit a weak ability in visual question answering. Surprisingly, some of these methods even downgrade the grounding ability of MLLMs that were never trained with such supervision. In this work, we propose two novel challenging benchmarks and show that MLLMs without pixel-level grounding supervision can outperform the state of the art in such tasks when evaluating both the pixel-level grounding and visual question answering. We propose simple baselines to extract the grounding information that can be plugged into any MLLM, which we call as PixFoundation. More importantly, we study the research question of ``When does grounding emerge in MLLMs that are not trained with pixel-level grounding supervision?’’ We show that grounding can coincide with object parts or location/appearance information. Code repository is at https://github.com/MSiam/PixFoundation/.
近年来,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的边界推动作品不断出现,它们朝着像素级理解的方向发展。这类方法在引用表达式分割和基于场景对话生成等基准测试中表现出强大的性能。目前像素级MLLMs的趋势是在大规模标记数据上进行像素级地面监督训练。然而,我们在最近的以视觉为中心的基准测试中评估这些MLLMs时,发现它们在视觉问答方面的能力较弱。令人惊讶的是,一些方法甚至降低了从未接受过此类监督的MLLMs的接地能力。在本文中,我们提出了两个新的具有挑战性的基准测试,并证明在没有像素级地面监督的MLLMs可以在评估像素级接地和视觉问答时超越现有技术。我们提出了一个简单的基线,可以提取接地信息,并将其插入任何MLLM中,我们称之为PixFoundation。更重要的是,我们研究了研究问题:“在没有进行像素级地面监督的情况下,MLLMs中的接地何时出现?”我们表明,接地可以与对象部分或位置/外观信息相符。代码仓库位于https://github.com/MSiam/PixFoundation/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
本文探讨多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在像素级理解方面的最新进展,并提出两个新的挑战性的基准测试。研究表明,即使在未接受像素级监督训练的MLLMs,在像素级理解和视觉问答任务上也能超越现有技术。同时,本文探讨了“未接受像素级监督训练的MLLMs中,何时会出现接地现象?”这一问题,并发现接地可以与对象部分或位置/外观信息相结合。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)正在向像素级理解推进,展示出在引用表达式分割和基于地面的对话生成方面的强大性能。
- 当前的趋势是使用像素级地面监督在大规模标记数据上进行训练。
- 在具有挑战性的视觉基准测试中,一些MLLMs在视觉问答能力方面表现较弱,甚至降级了从未接受过此类监督训练的MLLMs的地面能力。
- 提出两个新的基准测试,未接受像素级地面监督的MLLMs在这些任务上的表现超越了现有技术。
- 提出了一个简单的基线来提取地面信息,可以将其插入任何MLLM中,称为PixFoundation。
- 研究了“未接受像素级监督训练的MLLMs中,何时出现接地现象?”这一问题,并发现接地与对象部分或位置/外观信息有关。
点此查看论文截图


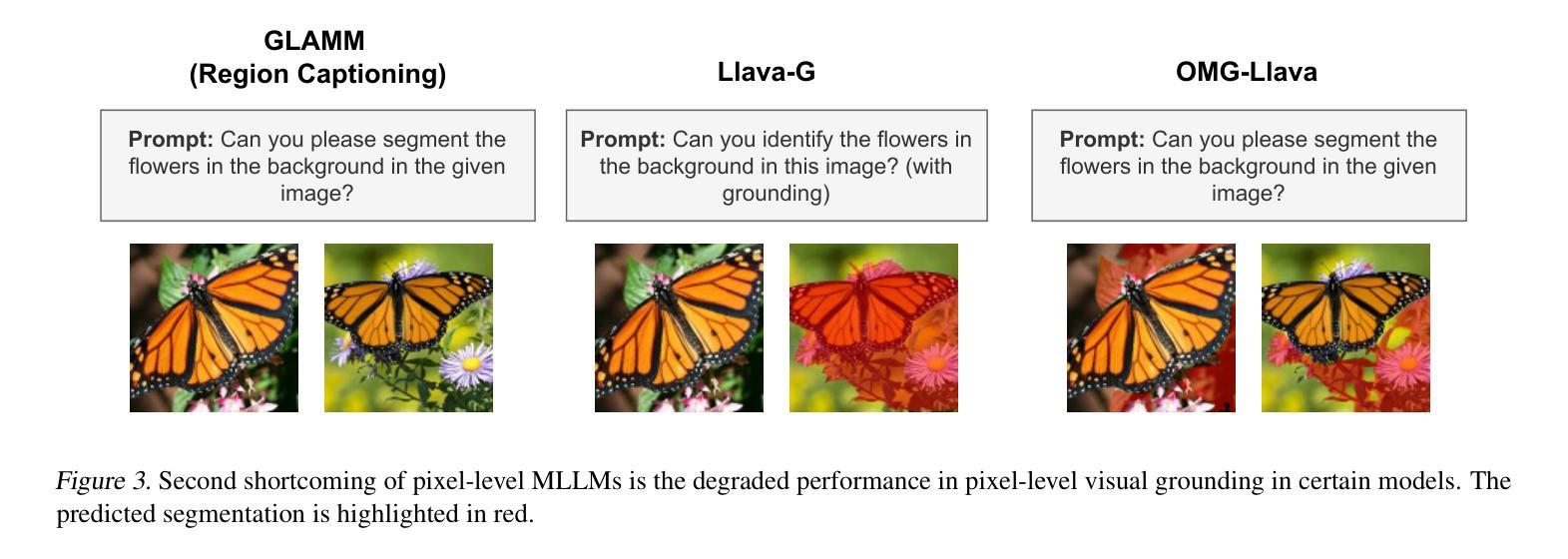


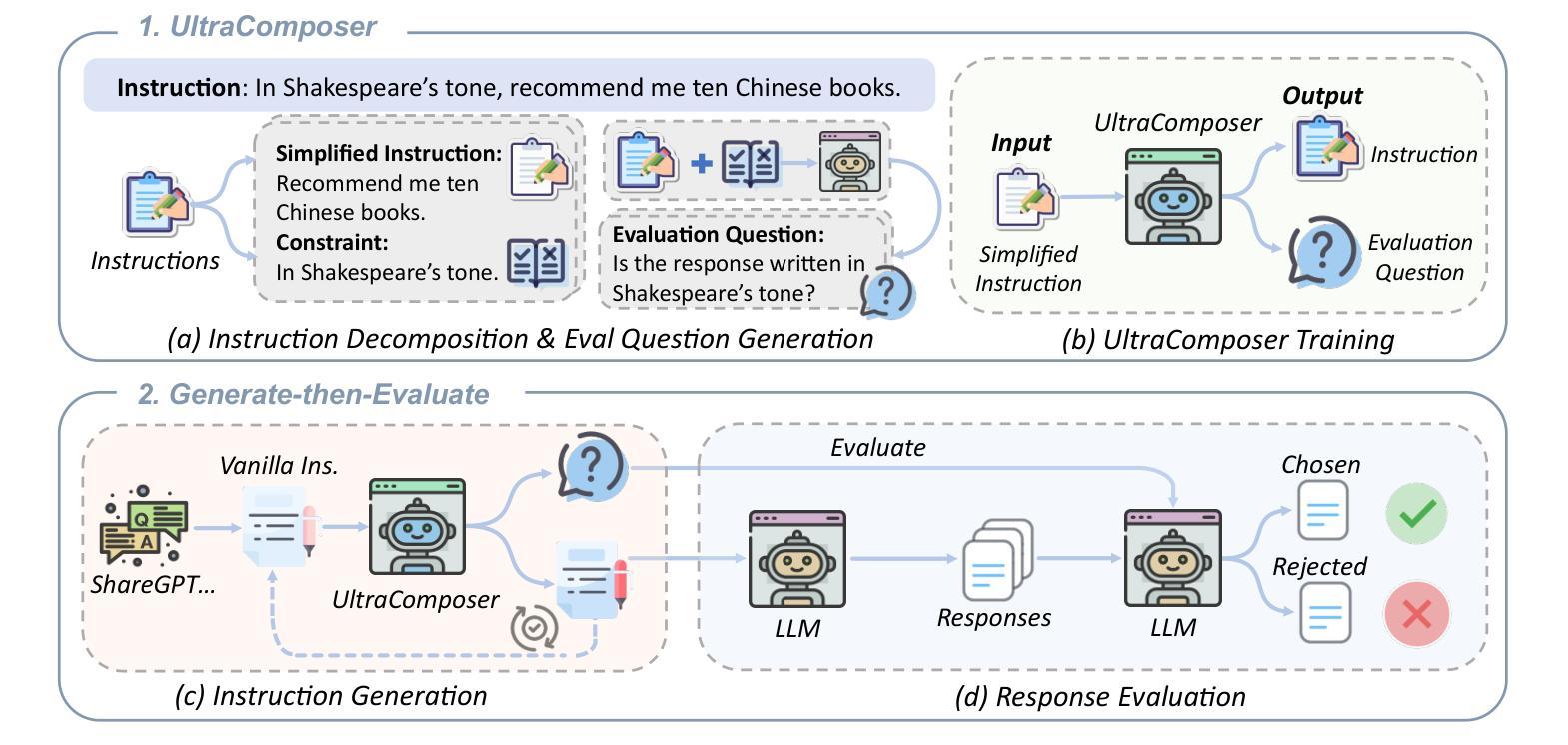
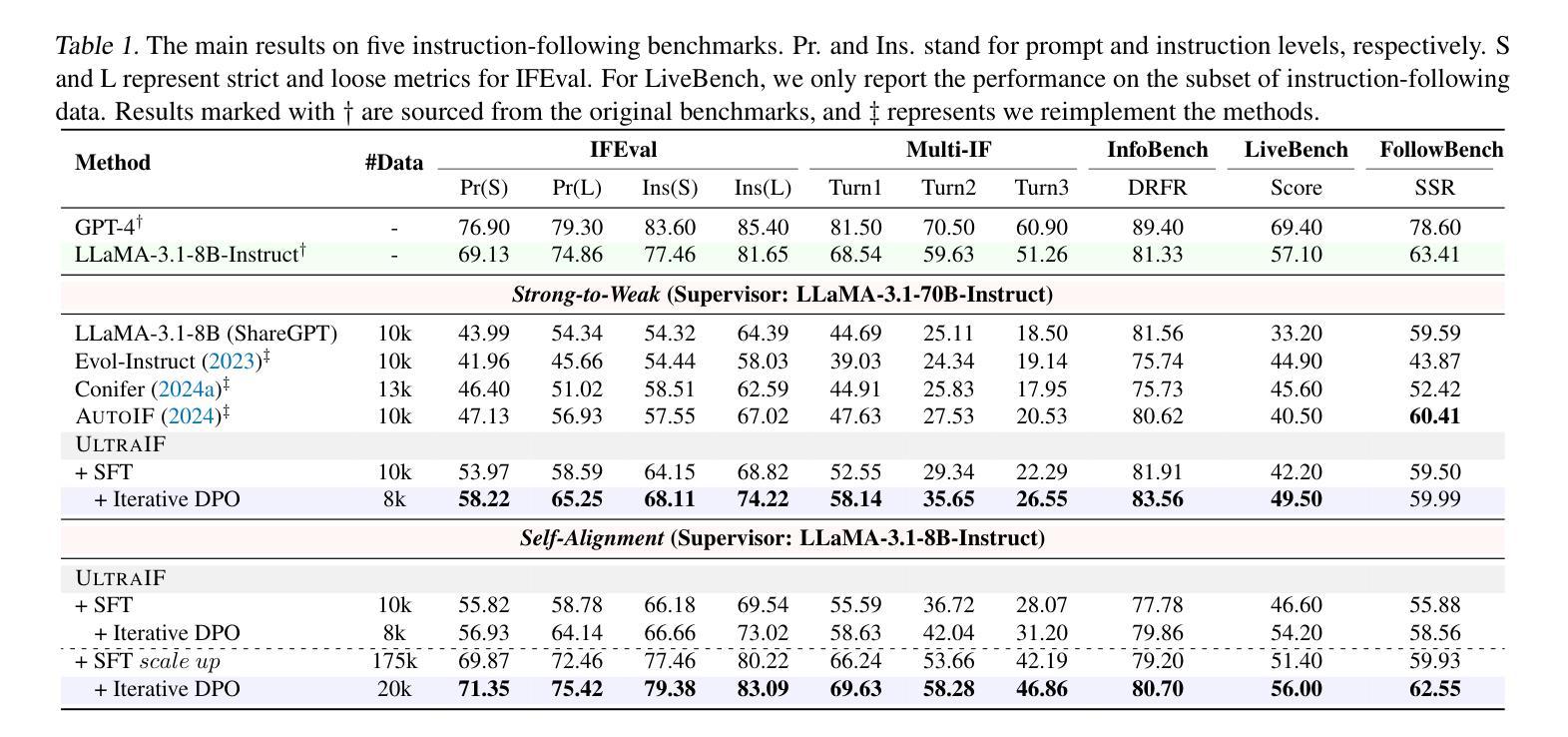
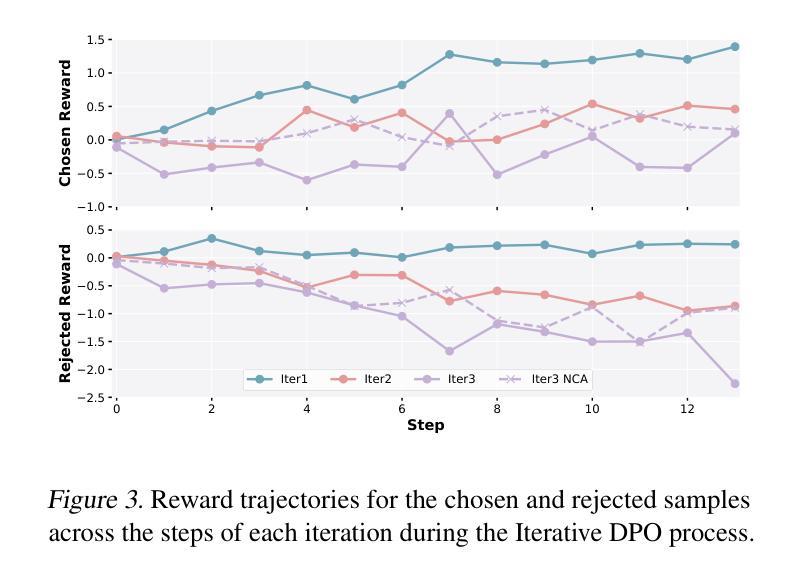
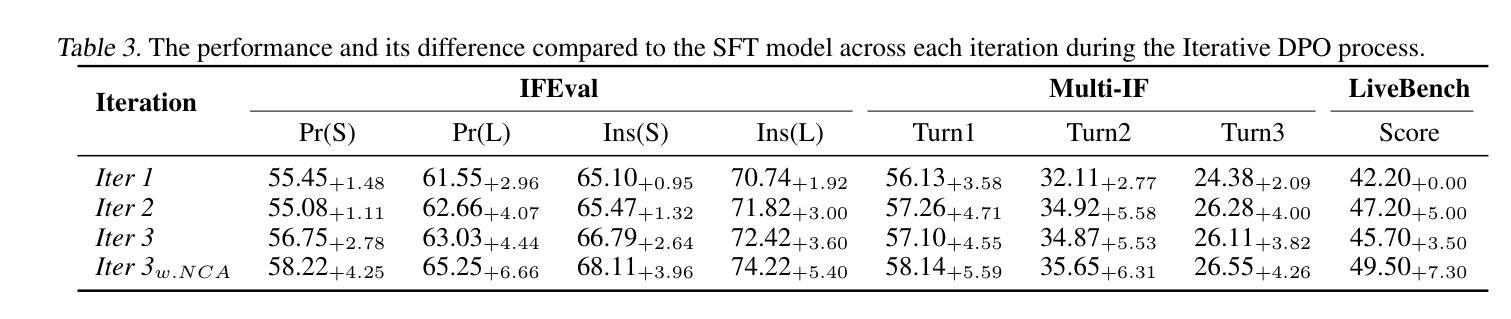
UltraIF: Advancing Instruction Following from the Wild
Authors:Kaikai An, Li Sheng, Ganqu Cui, Shuzheng Si, Ning Ding, Yu Cheng, Baobao Chang
Instruction-following made modern large language models (LLMs) helpful assistants. However, the key to taming LLMs on complex instructions remains mysterious, for that there are huge gaps between models trained by open-source community and those trained by leading companies. To bridge the gap, we propose a simple and scalable approach UltraIF for building LLMs that can follow complex instructions with open-source data. UltraIF first decomposes real-world user prompts into simpler queries, constraints, and corresponding evaluation questions for the constraints. Then, we train an UltraComposer to compose constraint-associated prompts with evaluation questions. This prompt composer allows us to synthesize complicated instructions as well as filter responses with evaluation questions. In our experiment, for the first time, we successfully align LLaMA-3.1-8B-Base to catch up with its instruct version on 5 instruction-following benchmarks without any benchmark information, using only 8B model as response generator and evaluator. The aligned model also achieved competitive scores on other benchmarks. Moreover, we also show that UltraIF could further improve LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct through self-alignment, motivating broader use cases for the method. Our code will be available at https://github.com/kkk-an/UltraIF.
指令遵循使现代大型语言模型(LLM)成为有用的助手。然而,在复杂指令上驾驭LLM的关键仍然神秘莫测,因为由开源社区训练模型和由领先公司训练模型之间存在巨大差距。为了缩小这一差距,我们提出了一种简单且可扩展的方法UltraIF,用于构建能够遵循复杂指令的LLM,并使用开源数据。UltraIF首先会将现实世界中的用户提示分解为更简单的查询、约束和相应的评估问题。然后,我们训练一个UltraComposer,将约束相关的提示与评估问题组合在一起。这个提示作曲家使我们能够合成复杂的指令,并使用评估问题过滤响应。在我们的实验中,我们成功地使用仅8B模型作为响应生成器和评估器,首次实现了LLaMA-3.1-8B-Base与指令版本在五个指令遵循基准测试上的对齐,且不使用任何基准测试信息。对齐模型在其他基准测试中也取得了有竞争力的分数。此外,我们还展示了UltraIF可以通过自我对齐进一步改进LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct,这为该方法的应用提供了更广泛的可能性。我们的代码将在https://github.com/kkk-an/UltraIF上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要介绍了一种新的方法UltraIF,用于构建大型语言模型(LLM),使其能够遵循复杂的指令并利用开源数据。UltraIF通过将现实世界用户指令分解为简单查询、约束和相应的评估问题来缩小模型之间的差距,并训练一个UltraComposer来组合约束相关的提示和评估问题。实验表明,该方法成功地将LLaMA-3.1-8B-Base与指令版本对齐,在五个指令遵循基准测试上表现优异,仅使用8B模型作为响应生成器和评估器。此外,UltraIF还可以通过自我对齐进一步优化LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct,为更广泛的应用场景提供动力。
Key Takeaways
- UltraIF是一种构建大型语言模型(LLM)的方法,旨在使模型能够遵循复杂的指令。
- UltraIF通过分解用户指令,将现实世界中的复杂指令转化为简单查询、约束和评估问题。
- UltraIF训练了一个提示组合器(UltraComposer)来组合约束相关的提示和评估问题,从而合成复杂指令并过滤响应。
- 实验表明,UltraIF成功地将LLaMA-3.1-8B-Base模型与指令版本对齐,在多个指令遵循基准测试上表现优异。
- UltraIF仅使用8B模型作为响应生成器和评估器,实现了与其他基准测试的竞争性能。
- UltraIF能够进一步优化LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct模型,通过自我对齐提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

Llasa: Scaling Train-Time and Inference-Time Compute for Llama-based Speech Synthesis
Authors:Zhen Ye, Xinfa Zhu, Chi-Min Chan, Xinsheng Wang, Xu Tan, Jiahe Lei, Yi Peng, Haohe Liu, Yizhu Jin, Zheqi DAI, Hongzhan Lin, Jianyi Chen, Xingjian Du, Liumeng Xue, Yunlin Chen, Zhifei Li, Lei Xie, Qiuqiang Kong, Yike Guo, Wei Xue
Recent advances in text-based large language models (LLMs), particularly in the GPT series and the o1 model, have demonstrated the effectiveness of scaling both training-time and inference-time compute. However, current state-of-the-art TTS systems leveraging LLMs are often multi-stage, requiring separate models (e.g., diffusion models after LLM), complicating the decision of whether to scale a particular model during training or testing. This work makes the following contributions: First, we explore the scaling of train-time and inference-time compute for speech synthesis. Second, we propose a simple framework Llasa for speech synthesis that employs a single-layer vector quantizer (VQ) codec and a single Transformer architecture to fully align with standard LLMs such as Llama. Our experiments reveal that scaling train-time compute for Llasa consistently improves the naturalness of synthesized speech and enables the generation of more complex and accurate prosody patterns. Furthermore, from the perspective of scaling inference-time compute, we employ speech understanding models as verifiers during the search, finding that scaling inference-time compute shifts the sampling modes toward the preferences of specific verifiers, thereby improving emotional expressiveness, timbre consistency, and content accuracy. In addition, we released the checkpoint and training code for our TTS model (1B, 3B, 8B) and codec model publicly available.
最近文本大型语言模型(LLM)的进步,尤其是GPT系列和O1模型,展示了在训练时间和推理时间计算上的扩展效果。然而,当前先进TTS系统利用LLM通常是多阶段的,需要单独模型(例如LLM之后的扩散模型),这增加了在训练或测试期间扩展特定模型的决策复杂性。本研究做出了以下贡献:首先,我们探索了语音合成的训练时间和推理时间计算的扩展。其次,我们提出了一个用于语音合成的简单框架Llasa,它采用单层向量量化(VQ)编解码器和单一Transformer架构,与标准LLM(如Llama)完全对齐。我们的实验表明,扩大Llasa的训练时间计算持续提高了合成语音的自然度,并能够生成更复杂和准确的语调模式。此外,从扩大推理时间计算的角度来看,我们在搜索过程中采用了语音理解模型作为验证器,发现扩大推理时间计算会使采样模式转向特定验证器的偏好,从而提高情感表现力、音色一致性和内容准确性。另外,我们公开发布了TTS模型(1B、3B、8B)和编解码器模型的检查点和训练代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了基于文本的大型语言模型(LLMs)在语音合成中的应用。文章介绍了LLMs在训练时间和推理时间计算扩展方面的进展,并提出了一种名为Llasa的简单语音合成框架。该框架使用单层向量量化编码器和单一的Transformer架构与标准LLMs对齐。研究表明,增加训练时间计算可以提高合成语音的自然度并生成更复杂的韵律模式。同时,在推理时间计算方面,采用语音理解模型作为验证器可以改善采样模式,提高情感表达、音色一致性和内容准确性。此外,作者公开了TTS模型(1B、3B、8B)和编码模型的检查点和训练代码。
Key Takeaways
- 文章探讨了LLMs在语音合成中的应用及其训练时间和推理时间计算的扩展效果。
- 提出了一种名为Llasa的语音合成框架,该框架使用单层向量量化编码器和单一的Transformer架构。
- 增加训练时间计算可以提高合成语音的自然度和生成更复杂的韵律模式。
- 采用语音理解模型作为验证器可以改善采样模式,提高情感表达、音色一致性和内容准确性。
- 文章介绍了作者在推理时间计算方面的研究结果,指出其可影响采样模式以符合特定验证器的偏好。
- 作者公开了TTS模型和编码模型的检查点和训练代码,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

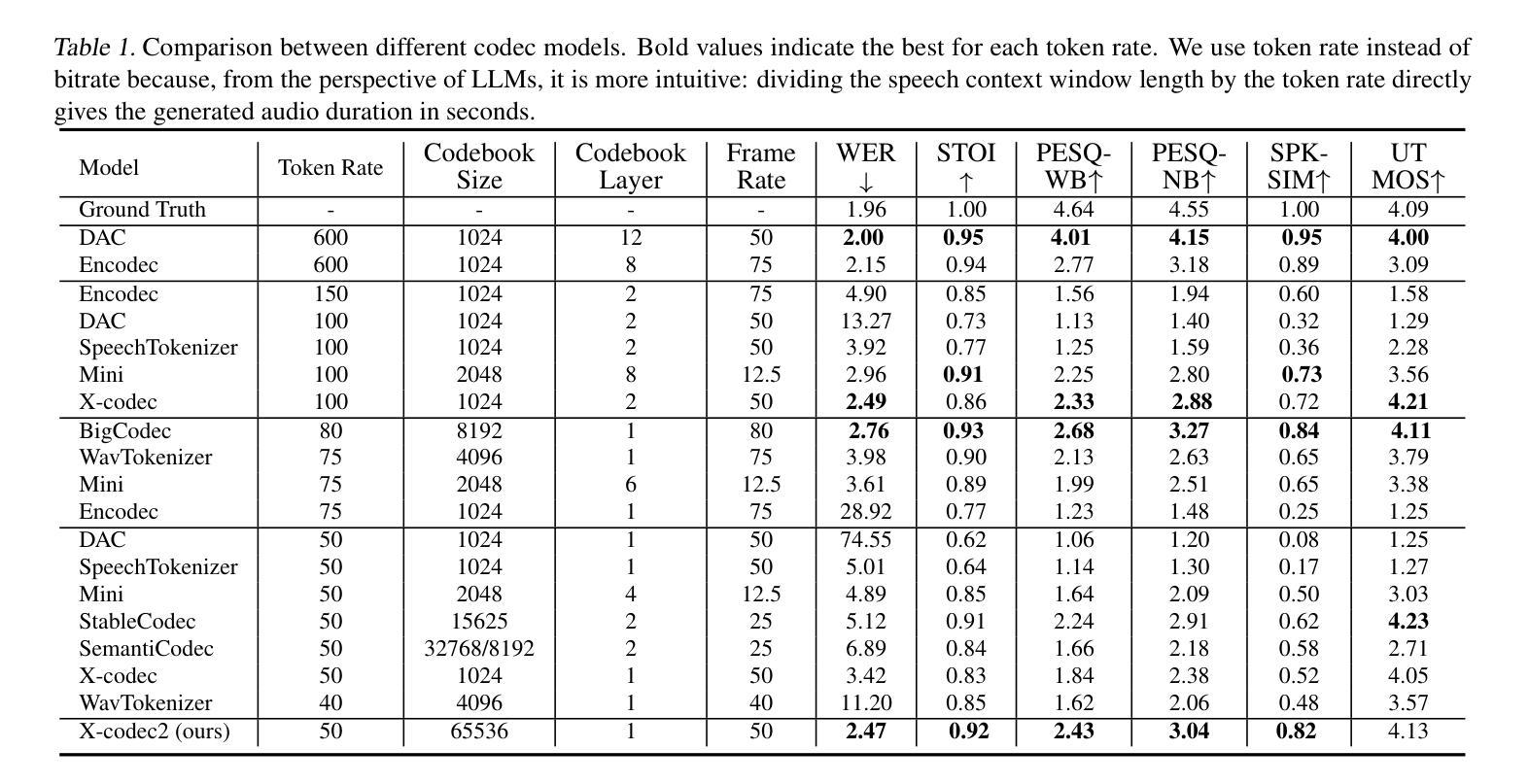
DiTAR: Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling for Speech Generation
Authors:Dongya Jia, Zhuo Chen, Jiawei Chen, Chenpeng Du, Jian Wu, Jian Cong, Xiaobin Zhuang, Chumin Li, Zhen Wei, Yuping Wang, Yuxuan Wang
Several recent studies have attempted to autoregressively generate continuous speech representations without discrete speech tokens by combining diffusion and autoregressive models, yet they often face challenges with excessive computational loads or suboptimal outcomes. In this work, we propose Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling (DiTAR), a patch-based autoregressive framework combining a language model with a diffusion transformer. This approach significantly enhances the efficacy of autoregressive models for continuous tokens and reduces computational demands. DiTAR utilizes a divide-and-conquer strategy for patch generation, where the language model processes aggregated patch embeddings and the diffusion transformer subsequently generates the next patch based on the output of the language model. For inference, we propose defining temperature as the time point of introducing noise during the reverse diffusion ODE to balance diversity and determinism. We also show in the extensive scaling analysis that DiTAR has superb scalability. In zero-shot speech generation, DiTAR achieves state-of-the-art performance in robustness, speaker similarity, and naturalness.
近期有几项研究尝试结合扩散模型和自回归模型,在无离散语音标记的情况下生成连续的语音表示。然而,这些方法常常面临计算负载过大或结果不理想等挑战。在本研究中,我们提出了扩散转换器自回归建模(DiTAR),这是一种结合语言模型和扩散转换器的基于补丁的自回归框架。该方法显著提高了自回归模型对连续标记的有效性,并降低了计算需求。DiTAR采用分而治之的策略进行补丁生成,其中语言模型处理聚合的补丁嵌入,然后扩散转换器根据语言模型的输出生成下一个补丁。对于推理,我们提议将温度定义为在反向扩散ODE过程中引入噪声的时间点,以平衡多样性和确定性。在广泛的规模分析中,我们还表明DiTAR具有出色的可扩展性。在零样本语音生成中,DiTAR在稳健性、说话人相似性和自然性方面达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出了Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling(DiTAR)方法,该方法结合了语言模型和扩散变压器,采用基于补丁的自动回归框架,有效提高了连续标记的自动回归模型的效率并降低了计算需求。DiTAR使用分而治之的策略进行补丁生成,通过语言模型处理聚合的补丁嵌入,然后扩散变压器基于语言模型的输出生成下一个补丁。在推理过程中,通过定义温度来平衡多样性和确定性,温度是在反向扩散ODE中引入噪声的时间点。DiTAR在零样本语音生成方面取得了出色的性能,在健壮性、说话人相似性和自然性方面达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- DiTAR结合了语言模型和扩散变压器,提出了基于补丁的自动回归框架。
- 该方法旨在提高连续标记的自动回归模型的效率并降低计算需求。
- DiTAR使用分而治之的策略进行补丁生成,通过语言模型处理补丁嵌入。
- 扩散变压器基于语言模型的输出生成下一个补丁。
- 通过定义温度来平衡推理过程中的多样性和确定性。
- DiTAR在零样本语音生成方面取得了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图


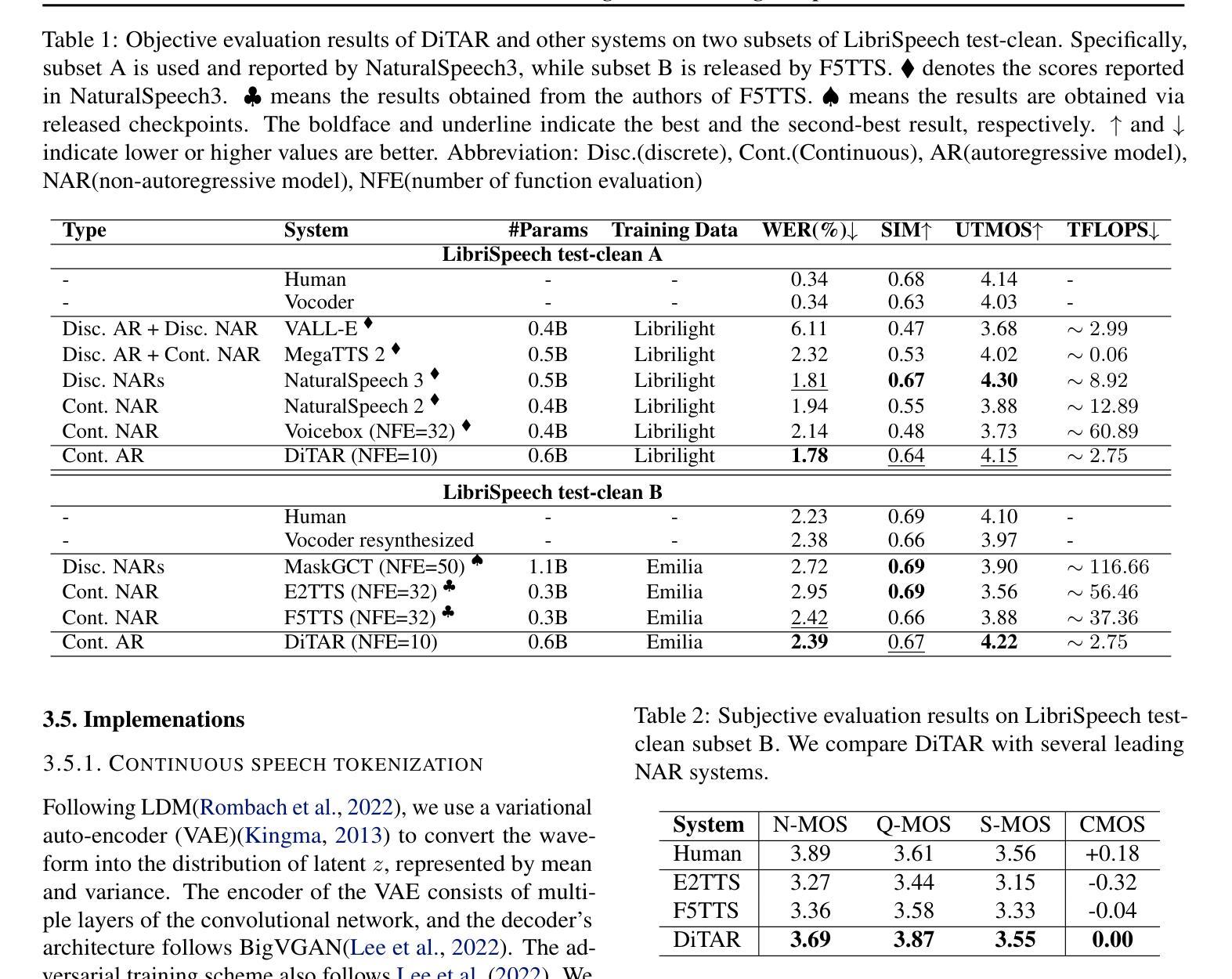
Transformers Boost the Performance of Decision Trees on Tabular Data across Sample Sizes
Authors:Mayuka Jayawardhana, Renbo, Samuel Dooley, Valeriia Cherepanova, Andrew Gordon Wilson, Frank Hutter, Colin White, Tom Goldstein, Micah Goldblum
Large language models (LLMs) perform remarkably well on tabular datasets in zero- and few-shot settings, since they can extract meaning from natural language column headers that describe features and labels. Similarly, TabPFN, a recent non-LLM transformer pretrained on numerous tables for in-context learning, has demonstrated excellent performance for dataset sizes up to a thousand samples. In contrast, gradient-boosted decision trees (GBDTs) are typically trained from scratch on each dataset without benefiting from pretraining data and must learn the relationships between columns from their entries alone since they lack natural language understanding. LLMs and TabPFN excel on small tabular datasets where a strong prior is essential, yet they are not competitive with GBDTs on medium or large datasets, since their context lengths are limited. In this paper, we propose a simple and lightweight approach for fusing large language models and TabPFN with gradient-boosted decision trees, which allows scalable GBDTs to benefit from the natural language capabilities and pretraining of transformers. We name our fusion methods LLM-Boost and PFN-Boost, respectively. While matching or surpassing the performance of the transformer at sufficiently small dataset sizes and GBDTs at sufficiently large sizes, LLM-Boost and PFN-Boost outperform both standalone components on a wide range of dataset sizes in between. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance against numerous baselines and ensembling algorithms. We find that PFN-Boost achieves the best average performance among all methods we test for all but very small dataset sizes. We release our code at http://github.com/MayukaJ/LLM-Boost .
大型语言模型(LLMs)在零样本和少样本设置下的表格数据集上表现非常出色,因为它们可以从描述特征和标签的自然语言列标题中提取意义。与此类似,TabPFN是一个最近的非LLM转换器,它在众多表格上进行预训练,用于上下文学习,并已显示出在多达一千个样本的数据集上的出色表现。相比之下,梯度提升决策树(GBDTs)通常是在每个数据集上从头开始训练的,无法受益于预训练数据,并且它们只能单独从条目中学习列之间的关系,因为它们缺乏自然语言理解。LLMs和TabPFN在小型表格数据集中表现出色,其中强大的先验知识至关重要,但在中等或大型数据集上,它们与GBDTs相比并不具备竞争力,因为它们的上下文长度是有限的。在本文中,我们提出了一种简单而轻量级的融合大型语言模型和TabPFN与梯度提升决策树的方法,这使得可扩展的GBDTs受益于转换器的自然语言能力和预训练。我们将我们的融合方法分别命名为LLM-Boost和PFN-Boost。虽然在小数据集上LLM-Boost和PFN-Boost的性能与转换器相匹配或超越,并且在足够大的数据集上超越GBDTs的性能,但它们在一系列中等数据集上的表现均超过了两种独立组件。我们与众多基准线和集成算法相比,展示了最先进的表现。我们发现除了非常小的数据集外,在所有测试的数据集大小中,PFN-Boost的平均性能表现最佳。我们在http://github.com/MayukaJ/LLM-Boost发布了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures
Summary
LLMs与TabPFN在小型表格数据集上表现优异,得益于它们对自然语言列标题的理解和预训练的优势。然而,在中等或大型数据集上,它们不如梯度增强决策树(GBDTs)。本研究提出了一种简单轻量级的融合方法,将大型语言模型与TabPFN与梯度增强决策树相结合,使GBDTs受益于transformers的自然语言能力和预训练。融合方法LLM-Boost和PFN-Boost在多种数据集大小上表现出超越单一组件的性能,其中PFN-Boost在除极小数据集外的所有测试方法中平均性能最佳。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs和TabPFN在小型表格数据集上表现优秀,因为它们能利用自然语言列标题的意义和预训练的优势。
- 梯度增强决策树(GBDTs)通常在每个数据集上进行训练,不依赖预训练数据,但它们在理解列关系方面依赖数据条目。
- LLMs和TabPFN在中等或大型数据集上的表现有限,主要因为它们处理上下文的能力有限。
- 研究提出了一种融合LLMs和TabPFN与梯度增强决策树的简单轻量级方法,名为LLM-Boost和PFN-Boost。
- LLM-Boost和PFN-Boost在各种数据集大小上的性能超越了单一的LLMs、TabPFN和GBDTs。
- PFN-Boost在除极小数据集外的所有测试方法中平均性能最佳。
- 研究代码已公开在http://github.com/MayukaJ/LLM-Boost。
点此查看论文截图

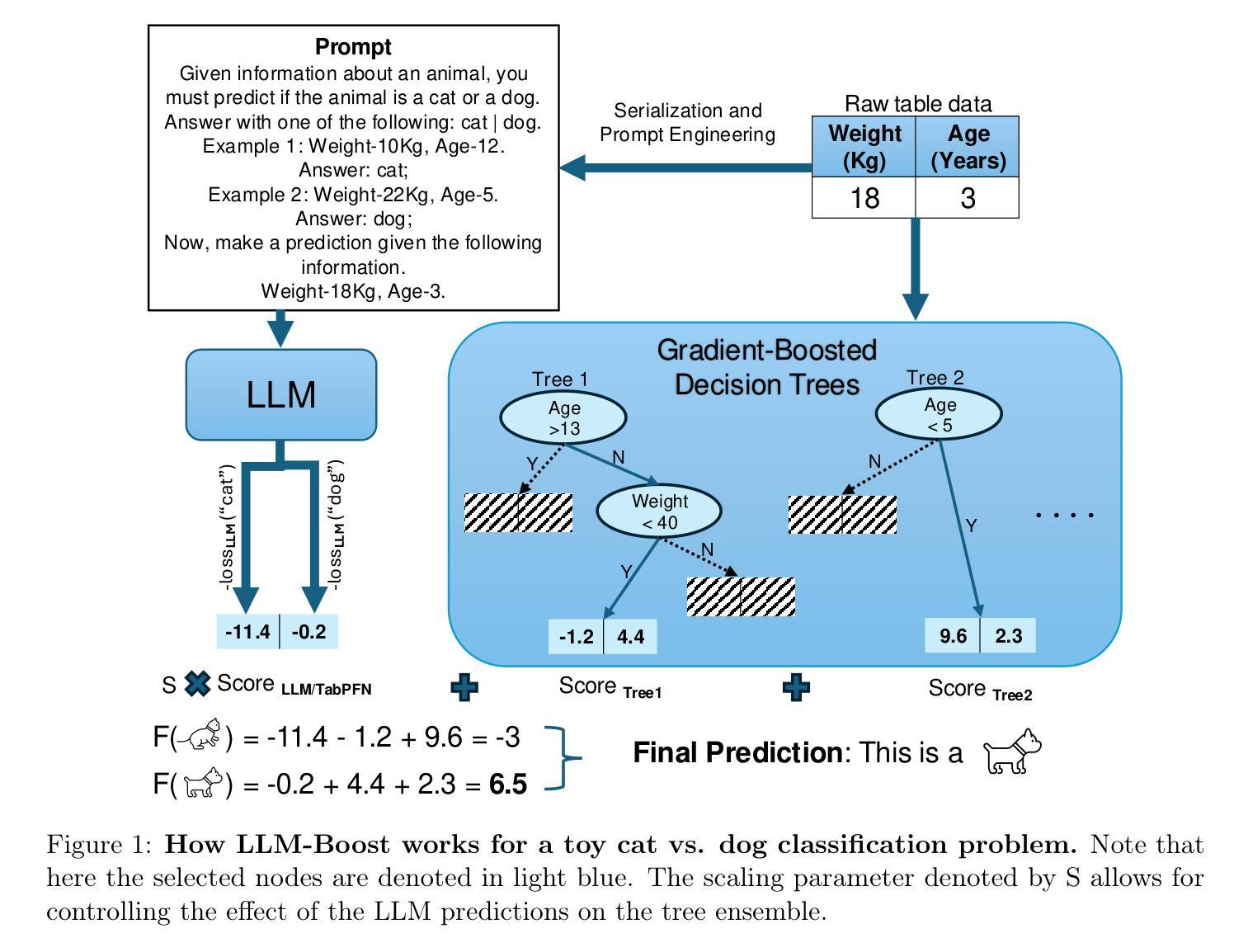
Relaxed Recursive Transformers: Effective Parameter Sharing with Layer-wise LoRA
Authors:Sangmin Bae, Adam Fisch, Hrayr Harutyunyan, Ziwei Ji, Seungyeon Kim, Tal Schuster
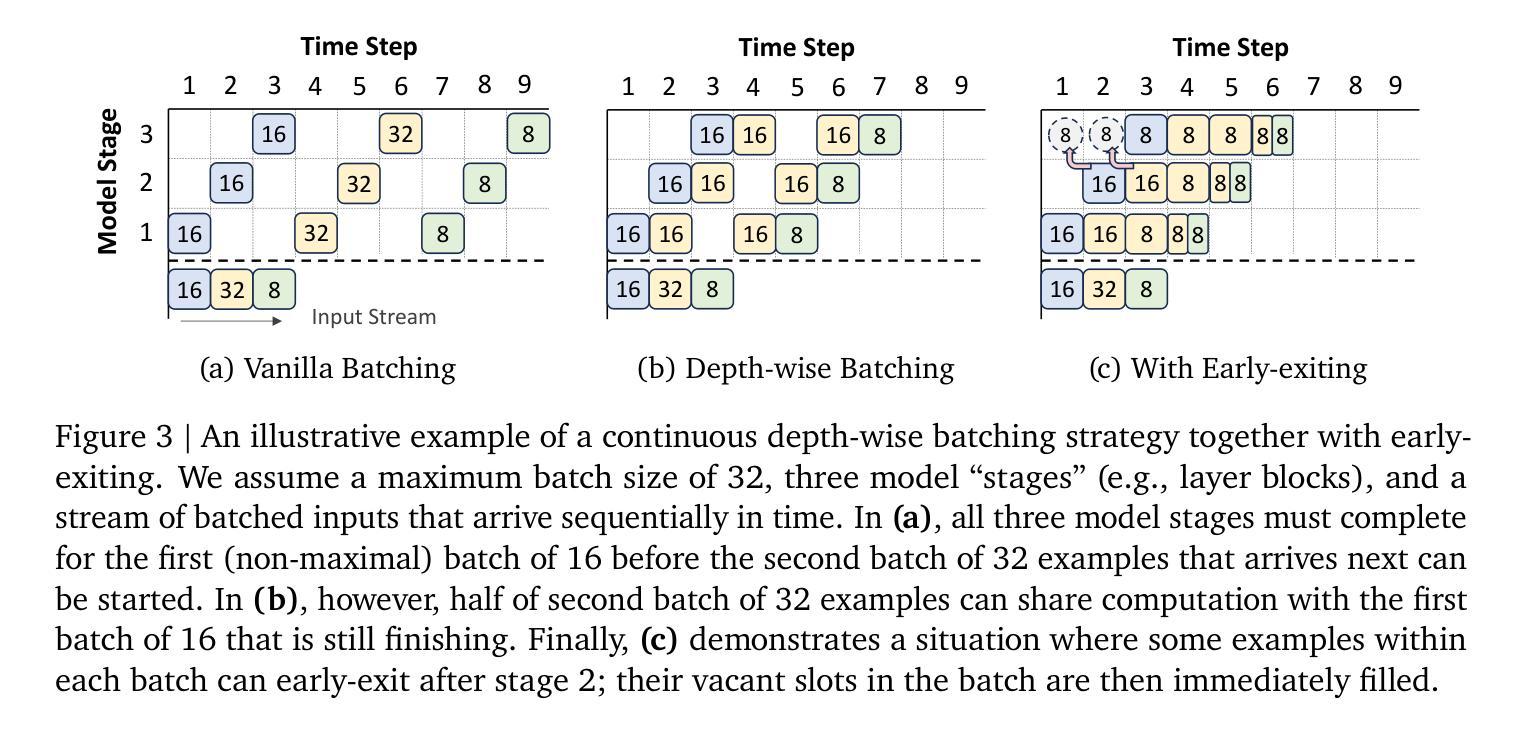
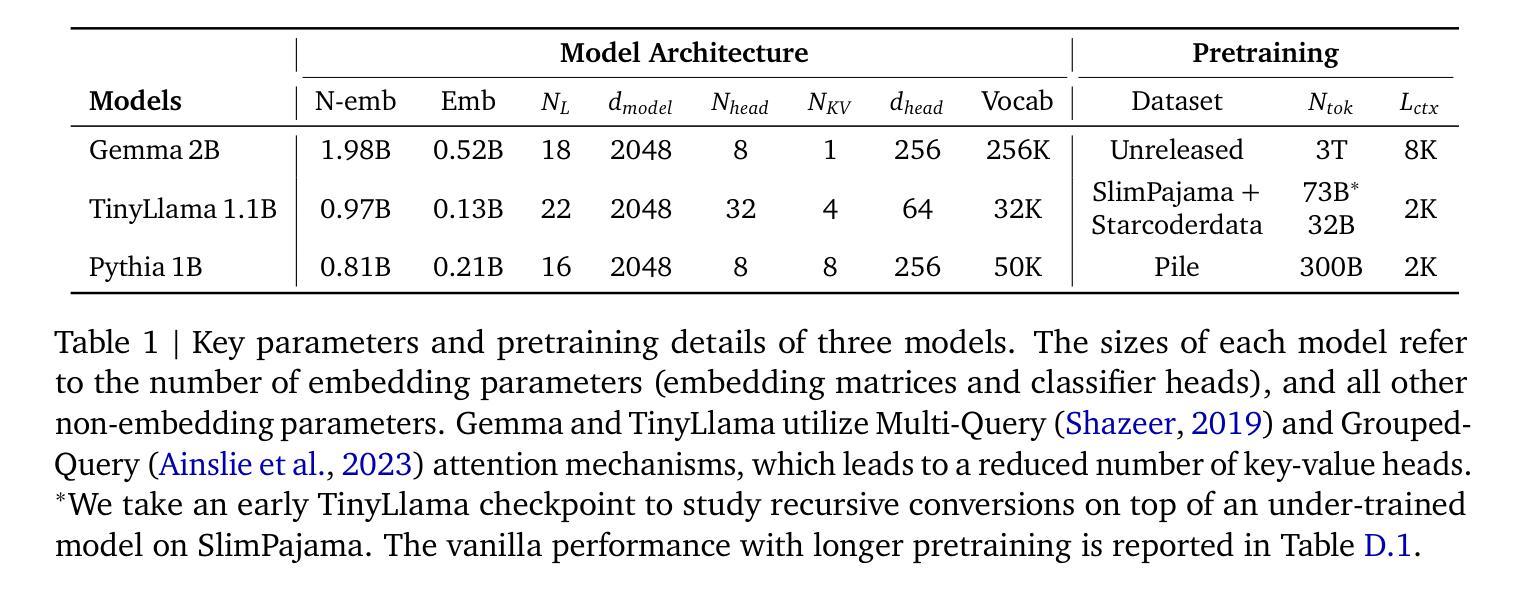
Large language models (LLMs) are expensive to deploy. Parameter sharing offers a possible path towards reducing their size and cost, but its effectiveness in modern LLMs remains fairly limited. In this work, we revisit “layer tying” as form of parameter sharing in Transformers, and introduce novel methods for converting existing LLMs into smaller “Recursive Transformers” that share parameters across layers, with minimal loss of performance. Here, our Recursive Transformers are efficiently initialized from standard pretrained Transformers, but only use a single block of unique layers that is then repeated multiple times in a loop. We further improve performance by introducing Relaxed Recursive Transformers that add flexibility to the layer tying constraint via depth-wise low-rank adaptation (LoRA) modules, yet still preserve the compactness of the overall model. We show that our recursive models (e.g., recursive Gemma 1B) outperform both similar-sized vanilla pretrained models (such as TinyLlama 1.1B and Pythia 1B) and knowledge distillation baselines – and can even recover most of the performance of the original “full-size” model (e.g., Gemma 2B with no shared parameters). Finally, we propose Continuous Depth-wise Batching, a promising new inference paradigm enabled by the Recursive Transformer when paired with early exiting. In a theoretical analysis, we show that this has the potential to lead to significant (2-3x) gains in inference throughput.
大型语言模型(LLM)的部署成本很高。参数共享为实现降低其规模和成本提供了可能的路径,但在现代LLM中的效果仍然相当有限。在这项工作中,我们重新访问了Transformer中的“层绑定”作为参数共享的一种形式,并介绍了将现有LLM转换为较小的“递归Transformer”的新方法,这些递归Transformer在层之间共享参数,同时性能损失最小。在这里,我们的递归Transformer是从标准预训练Transformer有效初始化的,但只使用一个唯一的块层,然后在循环中多次重复。通过引入具有深度方向低秩适应(LoRA)模块的灵活递归Transformer,我们进一步提高了性能,仍然保持了整体模型的紧凑性。我们表明,我们的递归模型(例如递归Gemma 1B)优于类似大小的普通预训练模型(如TinyLlama 1.1B和Pythia 1B)和知识蒸馏基线——甚至可以恢复原始“全尺寸”模型的大部分性能(例如,无共享参数的Gemma 2B)。最后,我们提出了连续深度方向批处理,这是由递归Transformer与早期退出相结合而实现的一种有前途的新推理范式。在理论分析中,我们证明了这有可能导致推理吞吐量实现显著(2-3倍)的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025; 47 pages, 17 figures, 17 tables
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)部署成本高昂,参数共享成为降低其规模与成本的可能途径之一,但在现代LLM中的效果有限。本研究重新审视Transformer中的“层绑定”作为参数共享方式,并引入新方法将现有LLM转换为更小的“递归Transformer”,在性能损失最小的情况下实现跨层参数共享。递归Transformer从标准预训练Transformer高效初始化,仅使用一个独特层块,在循环中多次重复。通过引入灵活的“松弛递归Transformer”和深度低秩适应(LoRA)模块,我们提高了性能,同时保持了模型的紧凑性。研究显示,我们的递归模型(如递归Gemma 1B)在类似大小的预训练模型(如TinyLlama 1.1B和Pythia 1B)和知识蒸馏基准测试中都表现出优势,甚至可以恢复大部分原“全尺寸”模型(如没有共享参数的Gemma 2B)的性能。此外,我们提出了由递归Transformer与早期退出相结合实现的“连续深度分批处理”这一有前景的新推理范式,并在理论分析中显示其有潜力实现推理吞吐量的显著(2-3倍)提升。
Key Takeaways
- 研究人员提出了一种新的方法,通过层绑定(参数共享)来减小大型语言模型(LLM)的规模并降低成本。
- 通过引入递归Transformer模型,实现了在性能损失最小化情况下的跨层参数共享。
- 递归Transformer能够从标准预训练Transformer模型中高效初始化,并只使用一个独特层块进行多次重复。
- 引入了灵活的松弛递归Transformer,通过深度低秩适应(LoRA)模块提高性能,同时保持模型紧凑。
- 递归模型在类似大小的预训练模型和知识蒸馏基准测试中表现出优势。
- 递归模型能够恢复大部分全尺寸模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图


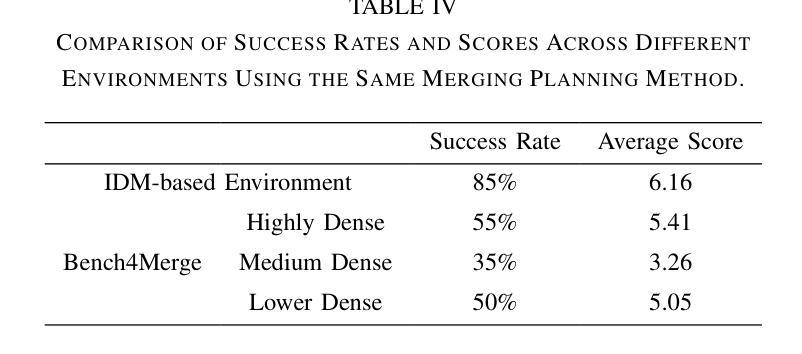
Bench4Merge: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Merging in Realistic Dense Traffic with Micro-Interactive Vehicles
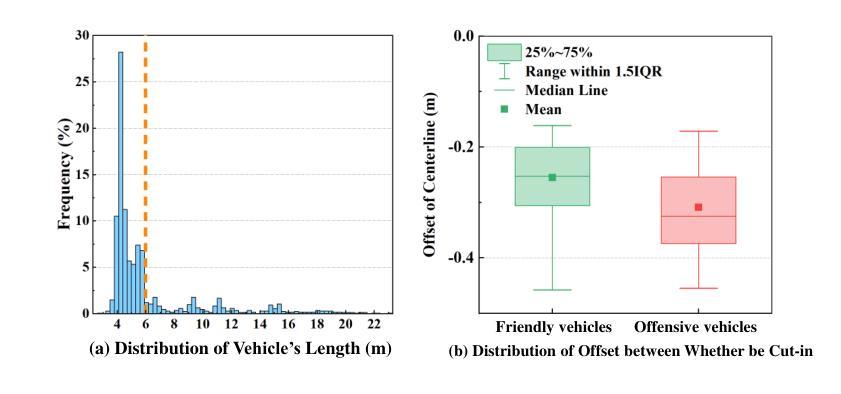
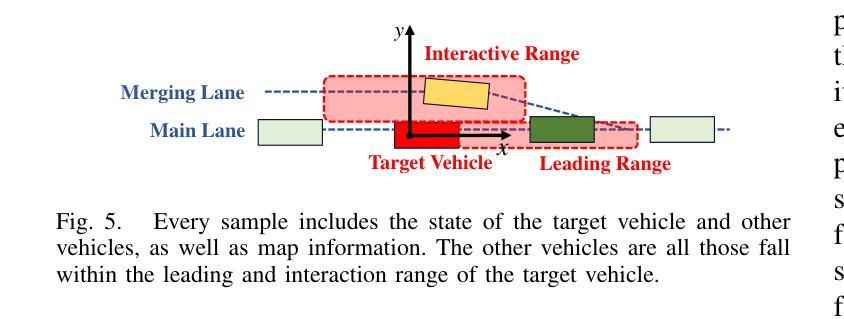
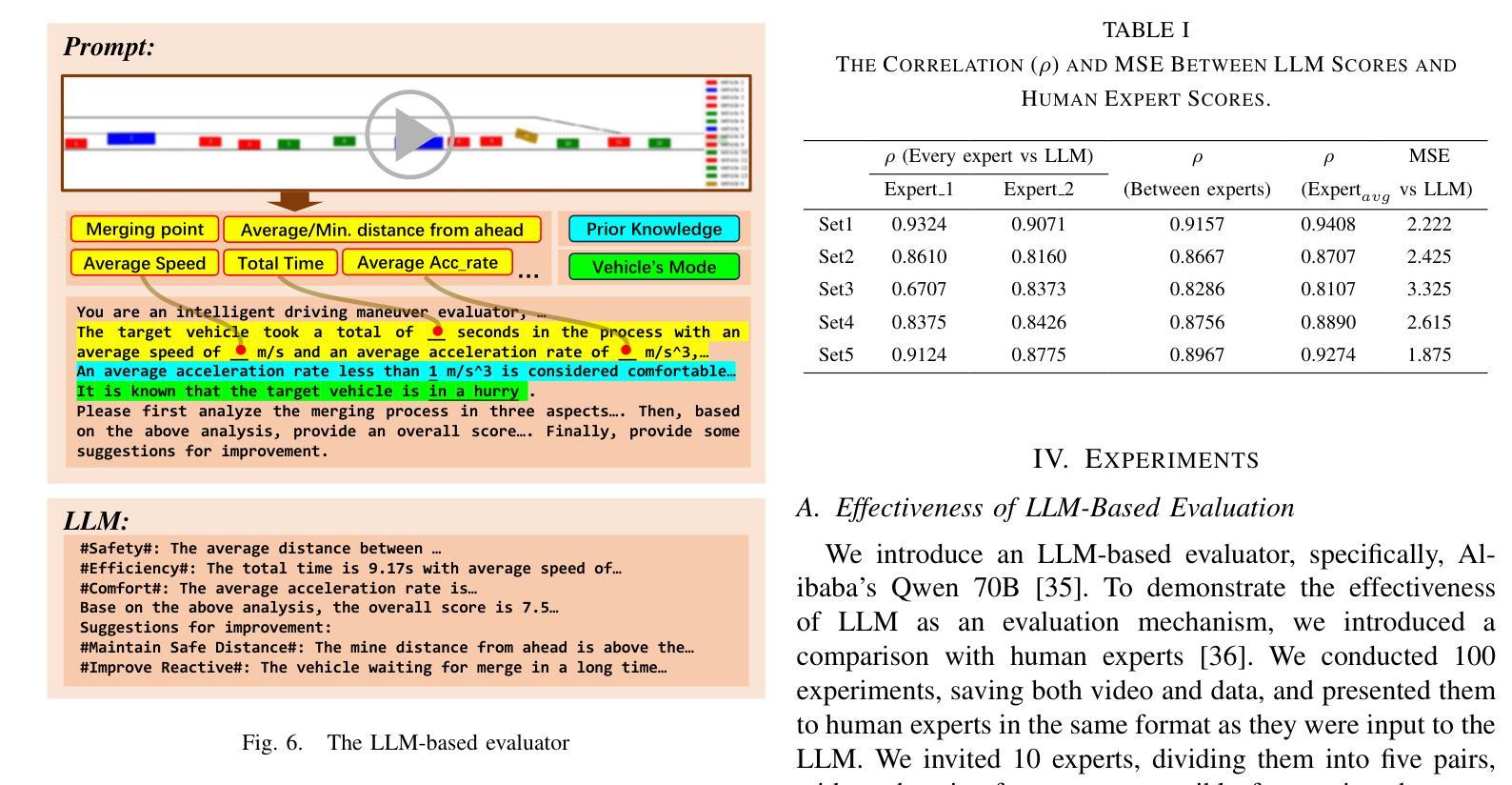
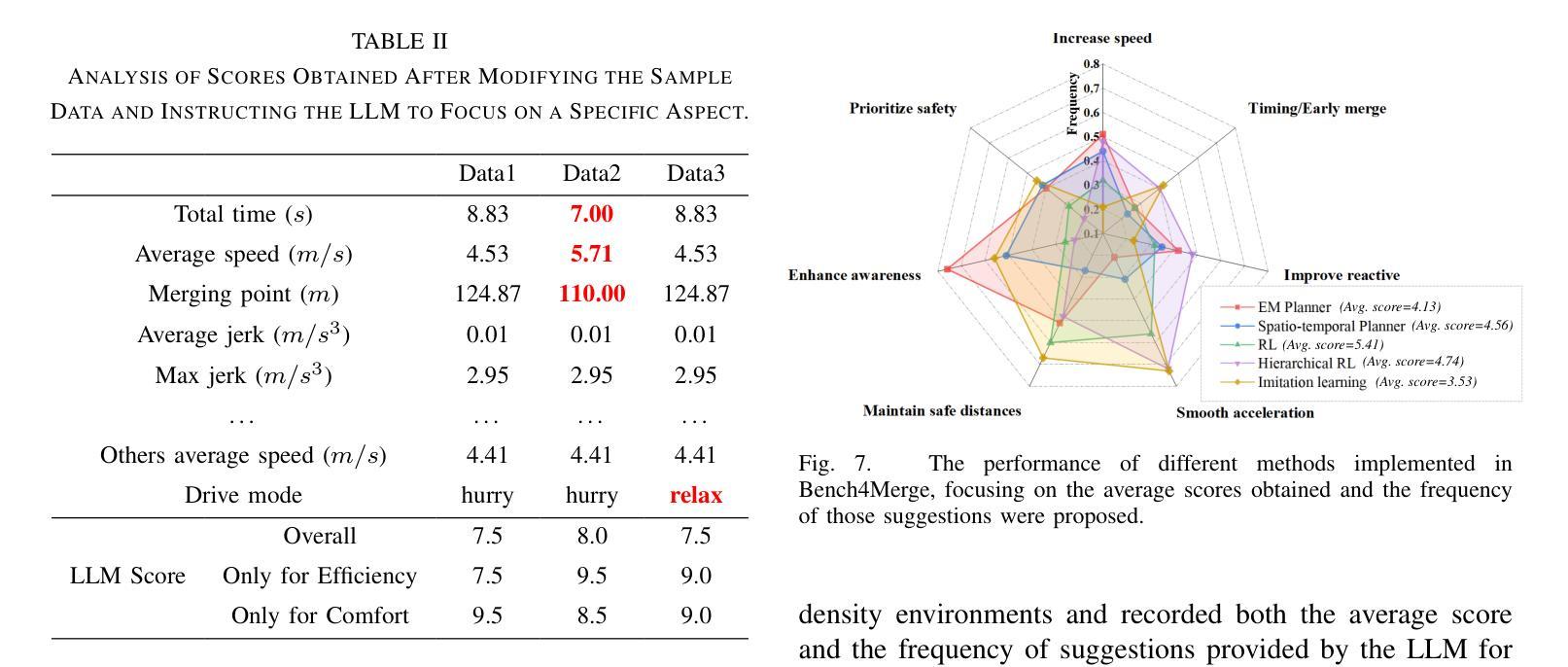
Authors:Zhengming Wang, Junli Wang, Pengfei Li, Zhaohan Li, Peng Li, Yilun Chen
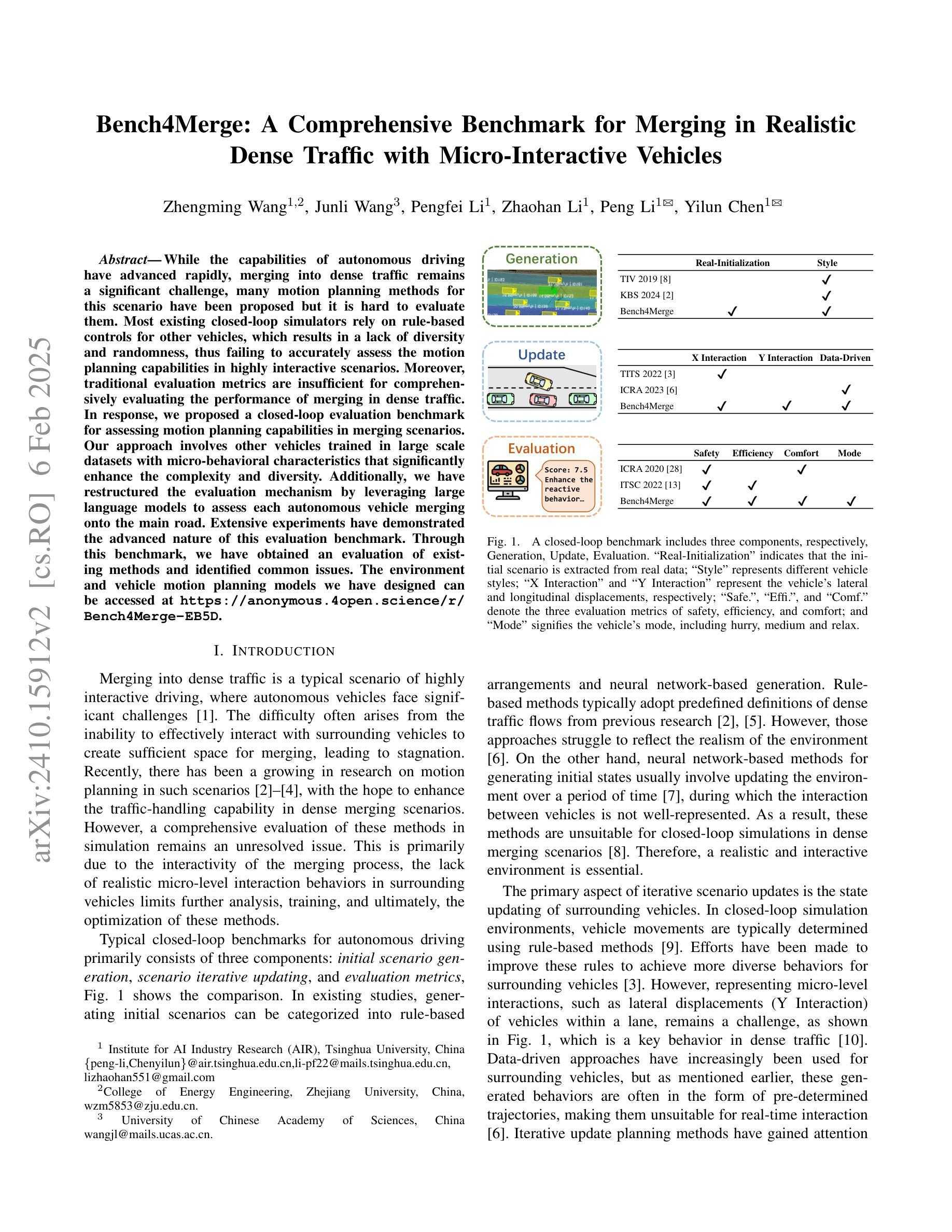
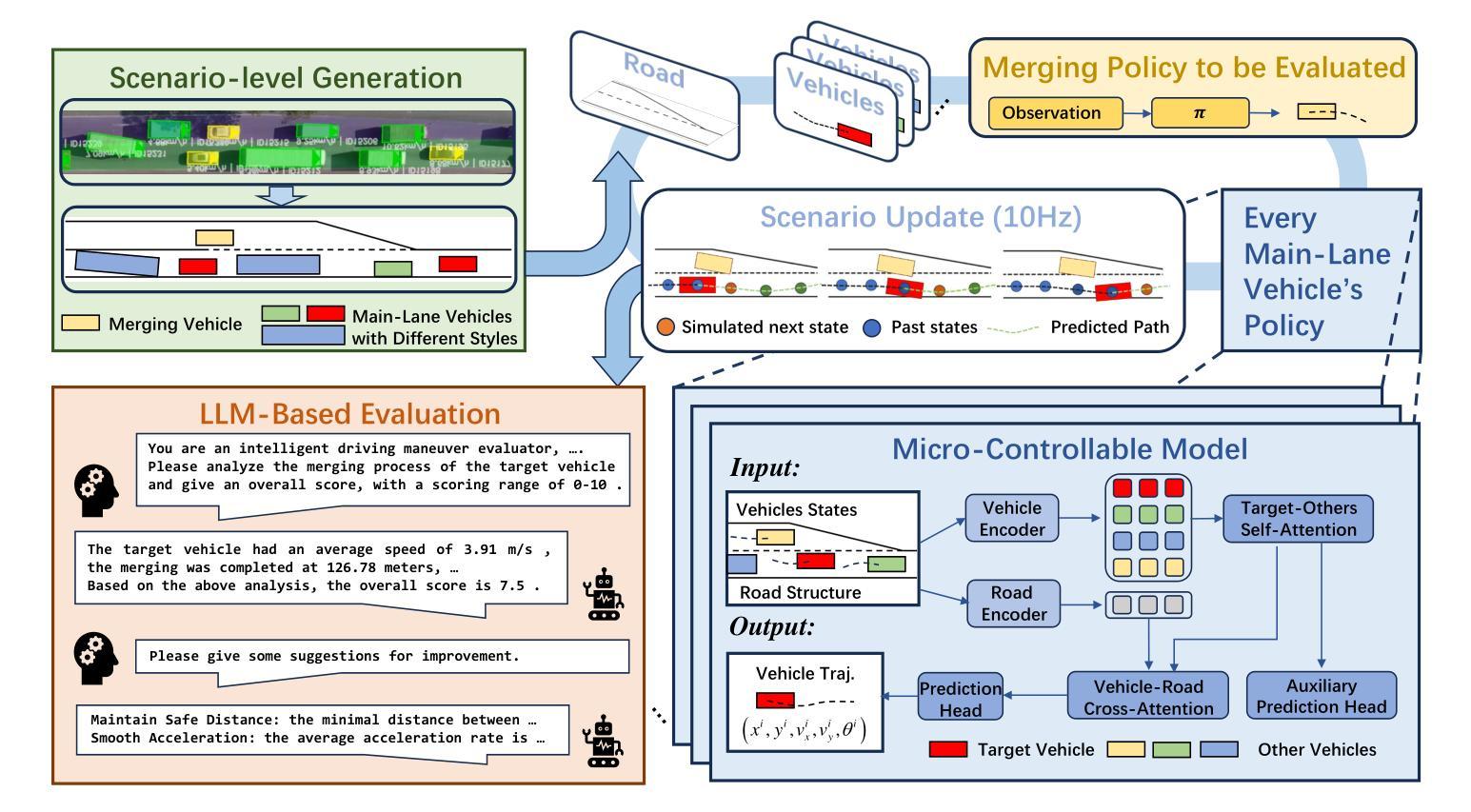
While the capabilities of autonomous driving have advanced rapidly, merging into dense traffic remains a significant challenge, many motion planning methods for this scenario have been proposed but it is hard to evaluate them. Most existing closed-loop simulators rely on rule-based controls for other vehicles, which results in a lack of diversity and randomness, thus failing to accurately assess the motion planning capabilities in highly interactive scenarios. Moreover, traditional evaluation metrics are insufficient for comprehensively evaluating the performance of merging in dense traffic. In response, we proposed a closed-loop evaluation benchmark for assessing motion planning capabilities in merging scenarios. Our approach involves other vehicles trained in large scale datasets with micro-behavioral characteristics that significantly enhance the complexity and diversity. Additionally, we have restructured the evaluation mechanism by leveraging large language models to assess each autonomous vehicle merging onto the main road. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the advanced nature of this evaluation benchmark. Through this benchmark, we have obtained an evaluation of existing methods and identified common issues. The environment and vehicle motion planning models we have designed can be accessed at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Bench4Merge-EB5D
虽然自动驾驶技术发展迅速,但在拥堵的交通环境中汇入仍是巨大的挑战。针对这一场景,已提出了许多运动规划方法,但难以进行评估。目前大多数封闭循环模拟器依赖于基于规则的车辆控制,导致缺乏多样性和随机性,因此无法准确评估在高度交互场景中运动规划的能力。此外,传统评估指标不足以全面评估拥堵交通环境中的合并性能。为此,我们提出了一个封闭循环评估基准,用于评估合并场景中的运动规划能力。我们的方法包括使用大规模数据集训练其他车辆,以具有微观行为特征的方式显著增强复杂性和多样性。此外,我们还通过利用大型语言模型对每辆汇入主干道的自主车辆进行评估来重建评估机制。大量实验证明此评估基准具有先进性。通过此基准,我们获得了对现有方法的评估并发现了常见问题。我们设计的环境和车辆运动规划模型可访问于:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Bench4Merge-EB5D。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 7 figures, on submitted
Summary
自动驾驶技术虽发展迅速,但在密集交通场景中并入主流仍面临挑战。评估其运动规划能力的方法多样但难以评估其效果。现有的闭环模拟器基于规则控制其他车辆,缺乏多样性和随机性,无法准确评估高度交互场景中的运动规划能力。为解决此问题,我们提出了一个闭环评估基准,采用大规模数据集训练其他车辆微行为特征,提高了复杂性和多样性。同时,我们利用大型语言模型重新构建评估机制,以评估每辆自主车辆并入主路的情况。实验证明了该评估基准的先进性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶在密集交通场景中并入主流仍存在挑战。
- 运动规划方法的评估困难,因为缺乏准确和全面的评估方法。
- 现有模拟器缺乏多样性和随机性,无法准确反映实际交通情况。
- 提出的闭环评估基准采用大规模数据集训练其他车辆的微行为特征。
- 利用大型语言模型重新构建评估机制,以更全面地评估自主车辆并入主路的情况。
- 实验证明了该评估基准的先进性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图

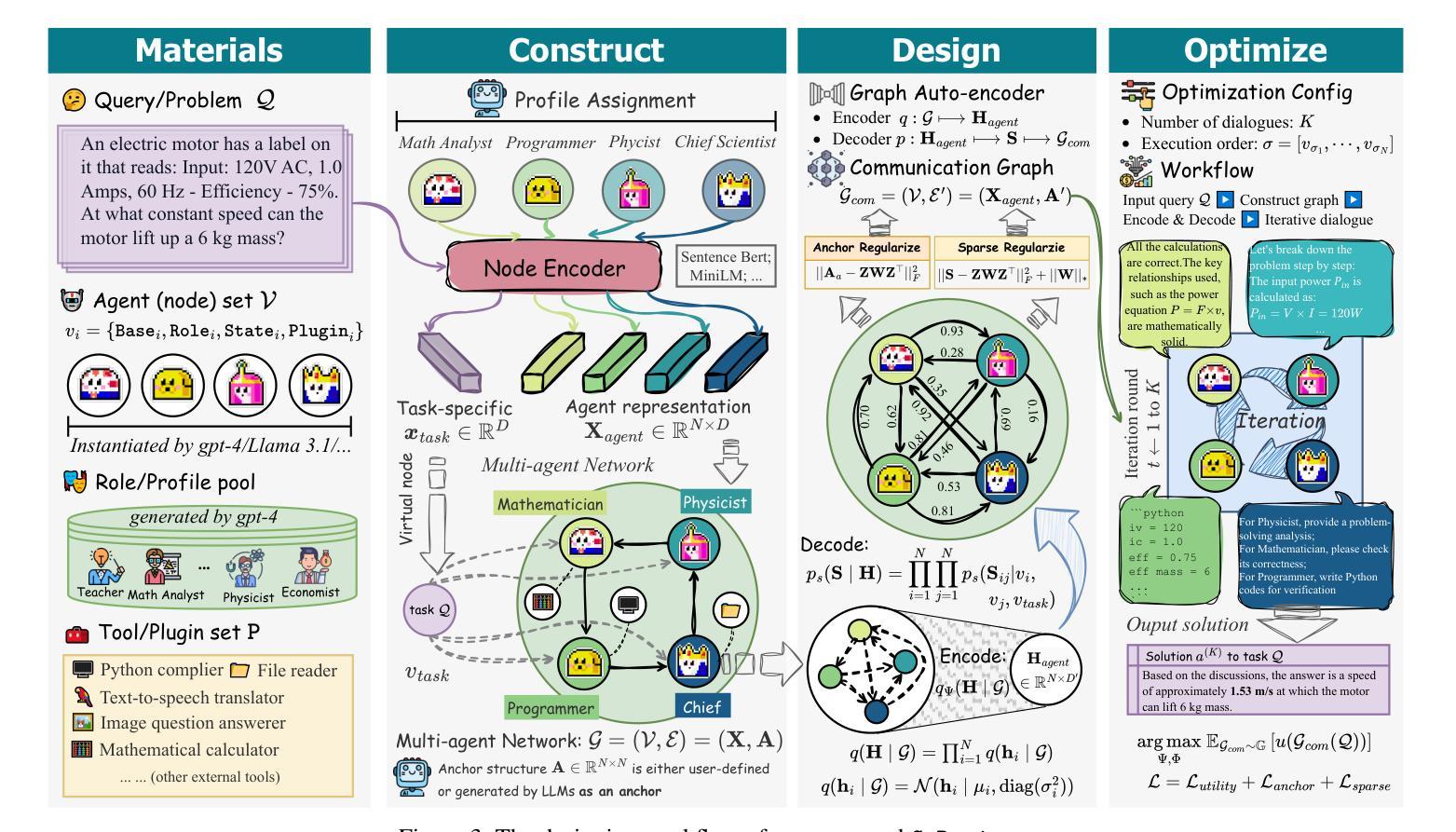
G-Designer: Architecting Multi-agent Communication Topologies via Graph Neural Networks
Authors:Guibin Zhang, Yanwei Yue, Xiangguo Sun, Guancheng Wan, Miao Yu, Junfeng Fang, Kun Wang, Tianlong Chen, Dawei Cheng
Recent advancements in large language model (LLM)-based agents have demonstrated that collective intelligence can significantly surpass the capabilities of individual agents, primarily due to well-crafted inter-agent communication topologies. Despite the diverse and high-performing designs available, practitioners often face confusion when selecting the most effective pipeline for their specific task: \textit{Which topology is the best choice for my task, avoiding unnecessary communication token overhead while ensuring high-quality solution?} In response to this dilemma, we introduce G-Designer, an adaptive, efficient, and robust solution for multi-agent deployment, which dynamically designs task-aware, customized communication topologies. Specifically, G-Designer models the multi-agent system as a multi-agent network, leveraging a variational graph auto-encoder to encode both the nodes (agents) and a task-specific virtual node, and decodes a task-adaptive and high-performing communication topology. Extensive experiments on six benchmarks showcase that G-Designer is: \textbf{(1) high-performing}, achieving superior results on MMLU with accuracy at $84.50%$ and on HumanEval with pass@1 at $89.90%$; \textbf{(2) task-adaptive}, architecting communication protocols tailored to task difficulty, reducing token consumption by up to $95.33%$ on HumanEval; and \textbf{(3) adversarially robust}, defending against agent adversarial attacks with merely $0.3%$ accuracy drop.
最近,基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人的进展表明,集体智能可以显著超越个体代理人的能力,这主要是因为精心设计的代理人之间的通信拓扑。尽管存在各种高性能的设计方案,但从业者在选择针对其特定任务的最有效管道时常常感到困惑:针对我的任务选择哪种拓扑是最好的选择,同时避免不必要的通信令牌开销并确保高质量的解决方案?针对这一难题,我们引入了G-Designer,这是一种自适应、高效且稳健的多代理部署解决方案,它可动态设计任务感知的自定义通信拓扑。具体而言,G-Designer将多代理系统建模为多代理网络,利用变分图自动编码器对节点(代理)和特定任务的虚拟节点进行编码,并解码出任务自适应且高性能的通信拓扑。在六个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,G-Designer具有以下特点:(1)高性能,在MMLU上的准确度达到84.50%,在HumanEval上的pass@1达到89.90%;(2)任务自适应,针对任务难度构建通信协议,在HumanEval上将令牌消耗减少高达95.33%;(3)对抗性稳健,抵御代理人对抗性攻击时准确率仅下降0.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期LLM模型的研究表明,集体智能通过巧妙的跨智能体通信拓扑设计可以大幅超越个体智能的表现。然而,在实践中选择合适的通信拓扑成为一大挑战。为解决此问题,提出一种自适应、高效且稳健的多智能体部署解决方案——G-Designer。它能根据任务动态生成定制化的通信拓扑,并通过实验验证其在性能、任务适应性和对抗稳健性方面的优势。
Key Takeaways
- LLM模型表明集体智能能够超越个体智能的表现,这得益于精心设计的智能体间通信拓扑。
- 实践者在选择通信拓扑时面临困惑,需要一种解决方案能根据任务需求动态调整。
- G-Designer是一种自适应、高效且稳健的解决方案,可以动态设计任务感知的定制通信拓扑。
- G-Designer将多智能体系统建模为多智能体网络,并利用变分图自编码器对节点(智能体)和任务特定虚拟节点进行编码。
- 实验表明,G-Designer在性能上表现优越,如在MMLU上的准确率达到了84.5%,在HumanEval上的pass@1达到了89.9%。
- G-Designer具有任务适应性,能够根据任务难度定制通信协议,并在HumanEval上减少了高达95.33%的令牌消耗。
点此查看论文截图


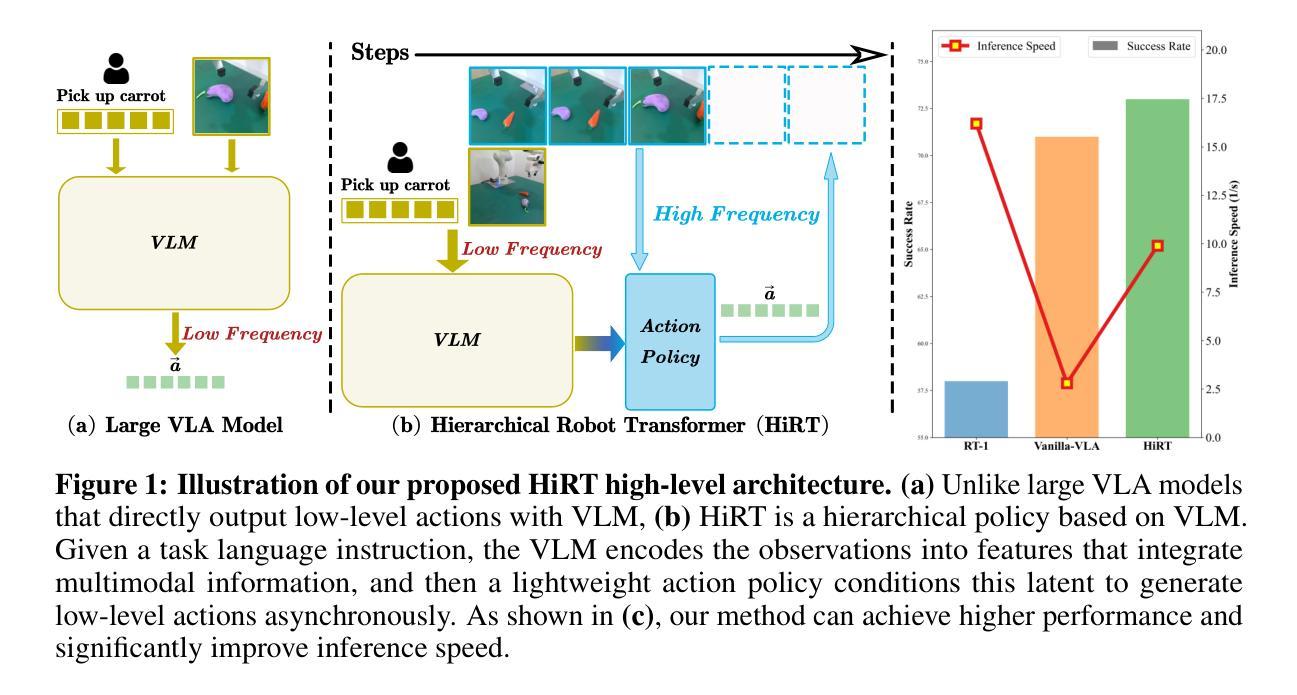
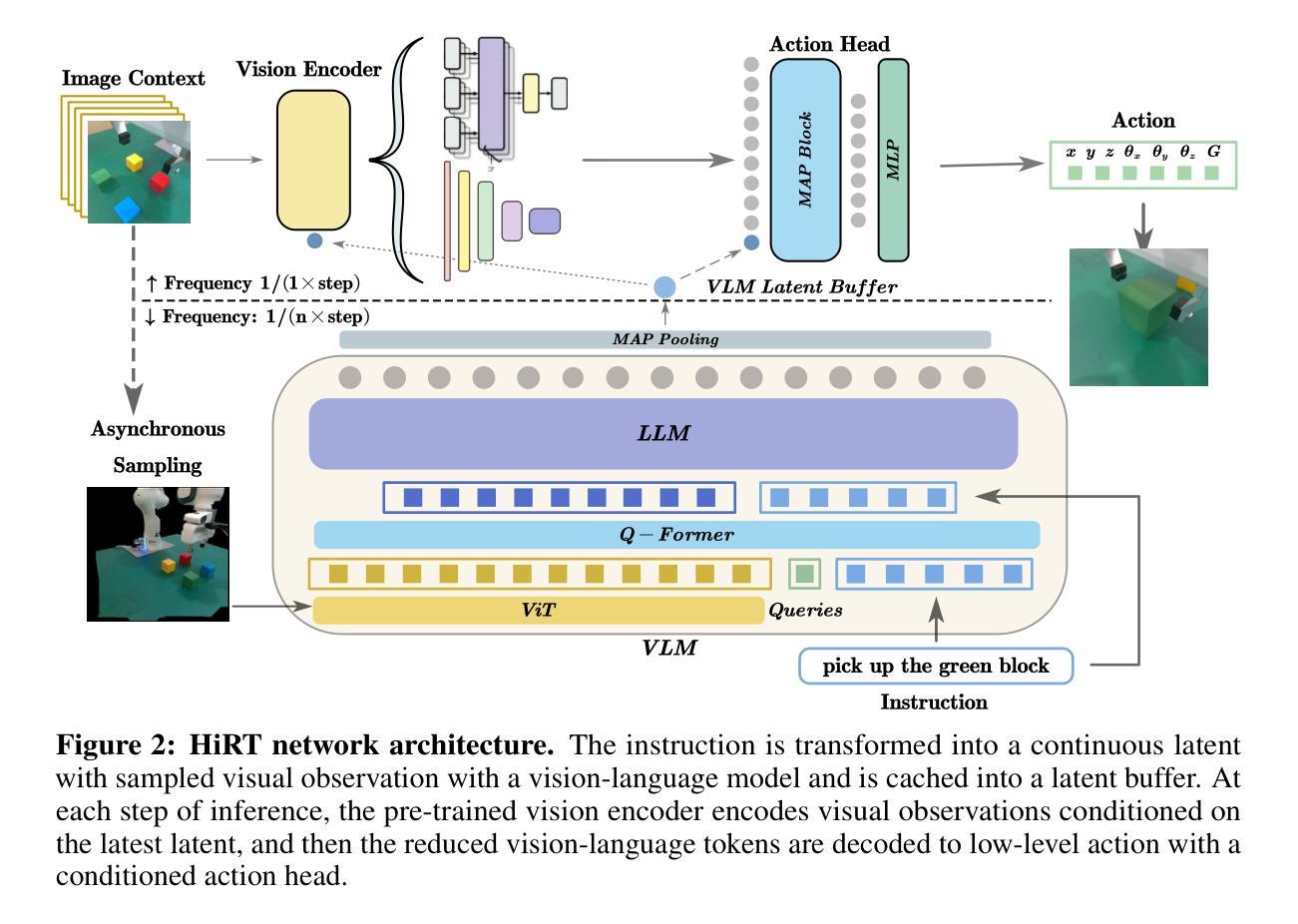
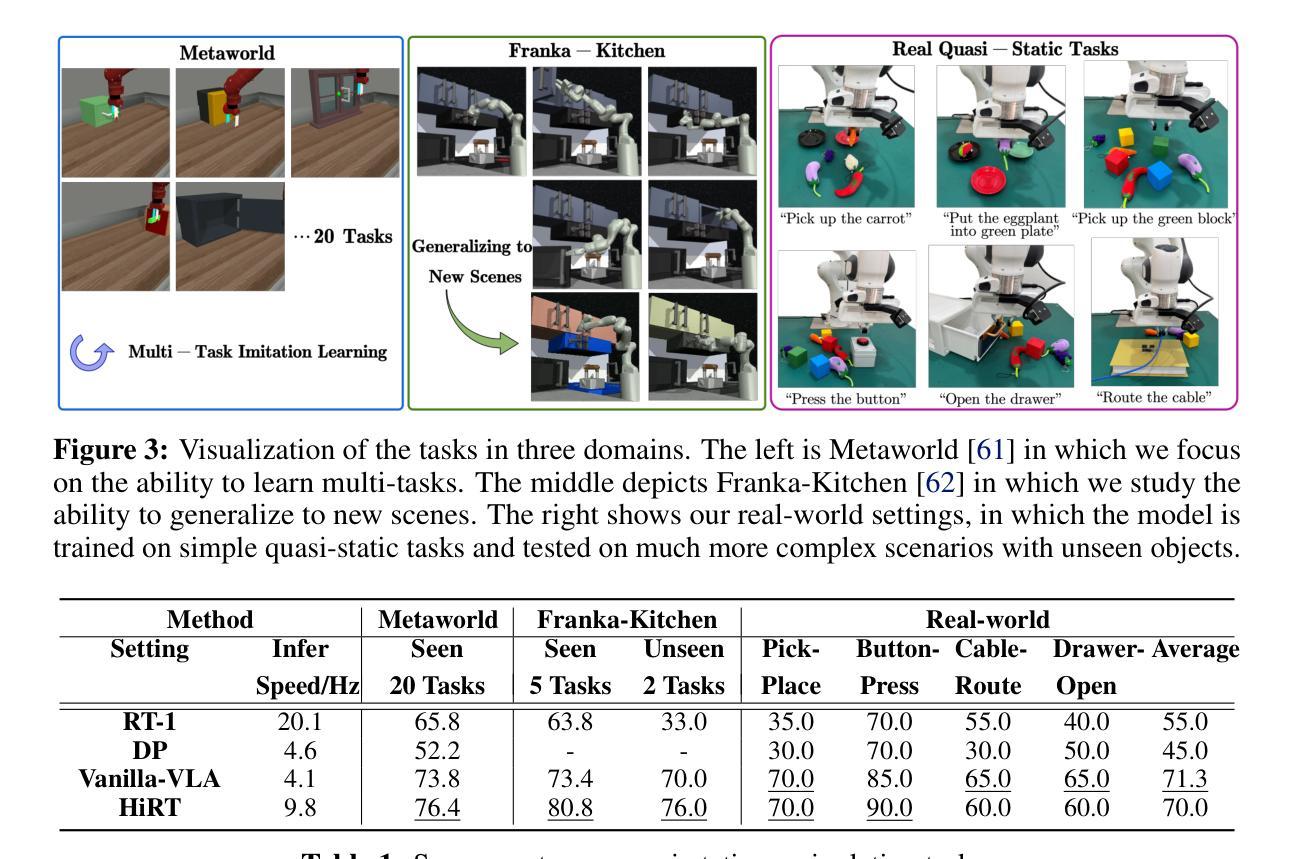
HiRT: Enhancing Robotic Control with Hierarchical Robot Transformers
Authors:Jianke Zhang, Yanjiang Guo, Xiaoyu Chen, Yen-Jen Wang, Yucheng Hu, Chengming Shi, Jianyu Chen
Large Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, leveraging powerful pre trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) backends, have shown promise in robotic control due to their impressive generalization ability. However, the success comes at a cost. Their reliance on VLM backends with billions of parameters leads to high computational costs and inference latency, limiting the testing scenarios to mainly quasi-static tasks and hindering performance in dynamic tasks requiring rapid interactions. To address these limitations, this paper proposes HiRT, a Hierarchical Robot Transformer framework that enables flexible frequency and performance trade-off. HiRT keeps VLMs running at low frequencies to capture temporarily invariant features while enabling real-time interaction through a high-frequency vision-based policy guided by the slowly updated features. Experiment results in both simulation and real-world settings demonstrate significant improvements over baseline methods. Empirically, in static tasks, we double the control frequency and achieve comparable success rates. Additionally, on novel real-world dynamic ma nipulation tasks which are challenging for previous VLA models, HiRT improves the success rate from 48% to 75%.
大型视觉语言动作(VLA)模型利用强大的预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)后端,由于其令人印象深刻的泛化能力,在机器人控制方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,成功是有代价的。它们对拥有数十亿参数的VLM后端的依赖导致了较高的计算成本和推理延迟,这限制了测试场景主要为准静态任务,并在需要快速交互的动态任务中影响了性能。为了应对这些局限性,本文提出了HiRT,一个分层机器人转换器框架,能够实现灵活频率和性能权衡。HiRT保持VLM以较低频率运行以捕获暂时不变的特征,同时通过由缓慢更新的特征引导的高频视觉策略实现实时交互。在模拟和真实环境中的实验结果表明,与基准方法相比,该方法有显著改善。在静态任务中,我们成功地将控制频率提高了一倍,并实现了相当的成功率。此外,对于以前对VLA模型具有挑战性的新型真实世界动态操作任务,HiRT将成功率从48%提高到75%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CORL 2024
Summary
大型视觉语言动作(VLA)模型利用预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)后端,在机器人控制领域展现出良好的通用性前景。然而,其成功背后存在计算成本高昂和推理延迟的问题,限制了测试场景主要为静态任务,难以应对需要快速交互的动态任务。为解决这些问题,本文提出HiRT,一种分层机器人转换器框架,可实现灵活频率和性能权衡。HiRT使VLM以较低频率运行以捕捉暂时不变的特征,同时通过由缓慢更新的特征引导的高频视觉策略实现实时交互。仿真和真实环境下的实验结果表明,与基准方法相比,HiRT在静态任务上实现了控制频率的翻倍,并获得了相当的成功率。此外,在之前对VLA模型具有挑战性的新现实动态操作任务上,HiRT将成功率从48%提高到75%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型VLA模型利用预训练的VLM后端展现出强大的通用性。
- VLA模型面临高计算成本和推理延迟的问题。
- HiRT框架被提出以解决这些问题,实现灵活频率和性能权衡。
- HiRT通过使VLM以低频率运行捕捉特征,并利用高频视觉策略实现实时交互。
- 在静态任务上,HiRT相比基准方法实现了控制频率翻倍。
- 在动态任务上,HiRT显著提高了之前的VLA模型的成功率。
点此查看论文截图

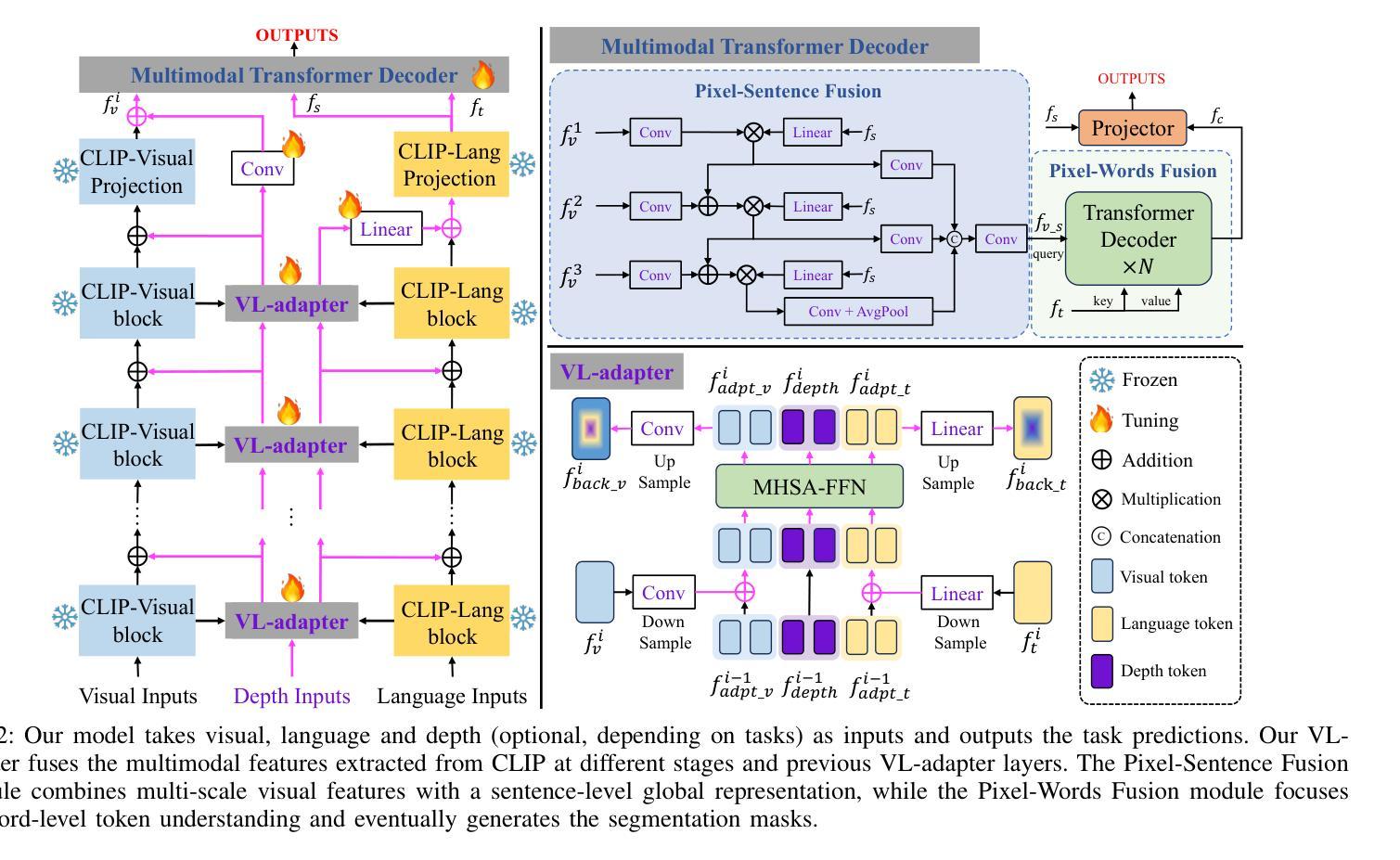
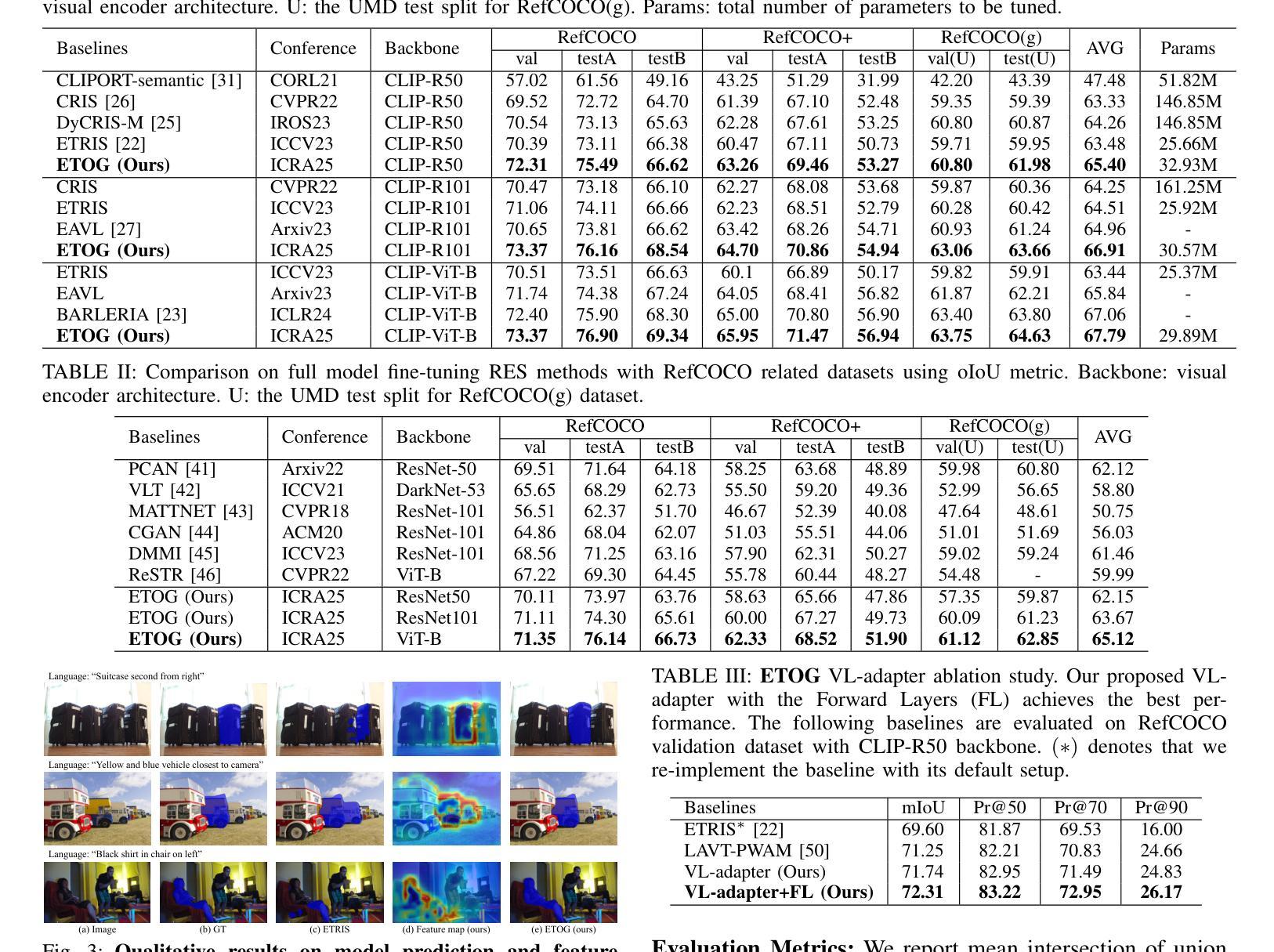
A Parameter-Efficient Tuning Framework for Language-guided Object Grounding and Robot Grasping
Authors:Houjian Yu, Mingen Li, Alireza Rezazadeh, Yang Yang, Changhyun Choi
The language-guided robot grasping task requires a robot agent to integrate multimodal information from both visual and linguistic inputs to predict actions for target-driven grasping. While recent approaches utilizing Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown promising results, their extensive computation and data demands limit the feasibility of local deployment and customization. To address this, we propose a novel CLIP-based multimodal parameter-efficient tuning (PET) framework designed for three language-guided object grounding and grasping tasks: (1) Referring Expression Segmentation (RES), (2) Referring Grasp Synthesis (RGS), and (3) Referring Grasp Affordance (RGA). Our approach introduces two key innovations: a bi-directional vision-language adapter that aligns multimodal inputs for pixel-level language understanding and a depth fusion branch that incorporates geometric cues to facilitate robot grasping predictions. Experiment results demonstrate superior performance in the RES object grounding task compared with existing CLIP-based full-model tuning or PET approaches. In the RGS and RGA tasks, our model not only effectively interprets object attributes based on simple language descriptions but also shows strong potential for comprehending complex spatial reasoning scenarios, such as multiple identical objects present in the workspace. Project page: https://z.umn.edu/etog-etrg
语言引导机器人抓取任务需要机器人代理整合视觉和语言输入的多模态信息,以预测目标驱动的抓取动作。虽然最近采用多模态大语言模型(MLLM)的方法已经取得了有希望的结果,但其庞大的计算和数据处理需求限制了其在本地部署和定制化的可行性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种基于CLIP的多模态参数高效调整(PET)框架,该框架旨在用于三项语言引导的对象定位和抓取任务:(1)指代表达式分割(RES),(2)指代抓取合成(RGS),(3)指代抓取属性(RGA)。我们的方法引入了两个关键创新点:一个双向视觉语言适配器,用于对齐多模态输入以实现像素级语言理解;一个深度融合分支,用于结合几何线索以促进机器人抓取预测。实验结果表明,在RES对象定位任务上,我们的性能优于现有的基于CLIP的全模型调整或PET方法。在RGS和RGA任务中,我们的模型不仅可以根据简单的语言描述有效地解释对象属性,而且还显示出在复杂的空间推理场景中表现出强大的潜力,如工作空间中存在多个相同对象的情况。项目页面:https://z.umn.edu/etog-etrg。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for ICRA 2025. Project page: https://sites.google.com/umn.edu/etog-etrg/home
Summary
本文介绍了语言引导机器人抓取任务,需要机器人代理融合视觉和语言输入的多模态信息来预测目标驱动抓取的动作。针对这一问题,提出一种基于CLIP的多模态参数高效调整(PET)框架,用于语言引导对象定位和抓取任务。该框架引入双向视觉语言适配器和深度融合分支,分别用于像素级语言理解和机器人抓取预测。实验结果表明,该框架在对象定位任务上表现出卓越性能,同时在抓取合成和抓取属性任务上具有强大的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 语言引导机器人抓取任务需要融合视觉和语言输入的多模态信息。
- 提出了一种基于CLIP的多模态参数高效调整(PET)框架。
- 框架包含双向视觉语言适配器和深度融合分支。
- 适配器用于像素级语言理解,而融合分支结合了几何线索以支持机器人抓取预测。
- 在对象定位任务上,该框架的性能超越了现有的CLIP全模型调优或PET方法。
- 在抓取合成和抓取属性任务上,该模型不仅能够基于简单语言描述解释对象属性,还展现出处理复杂空间推理场景的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

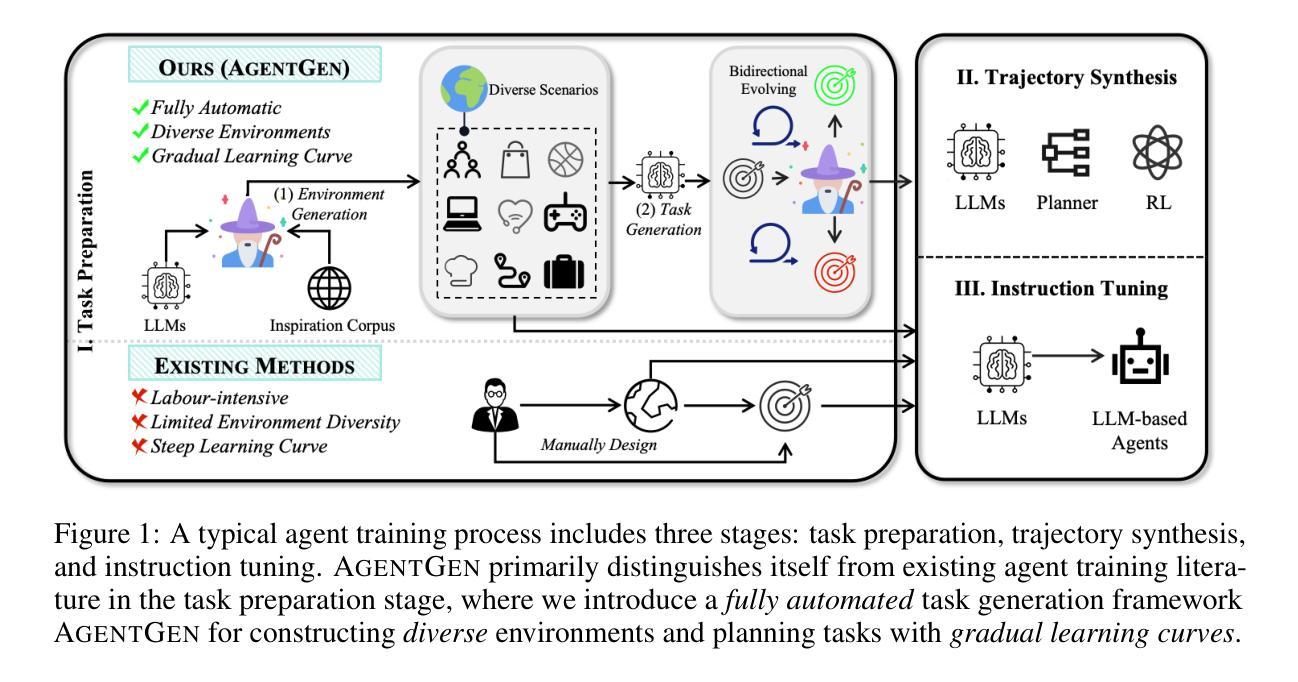
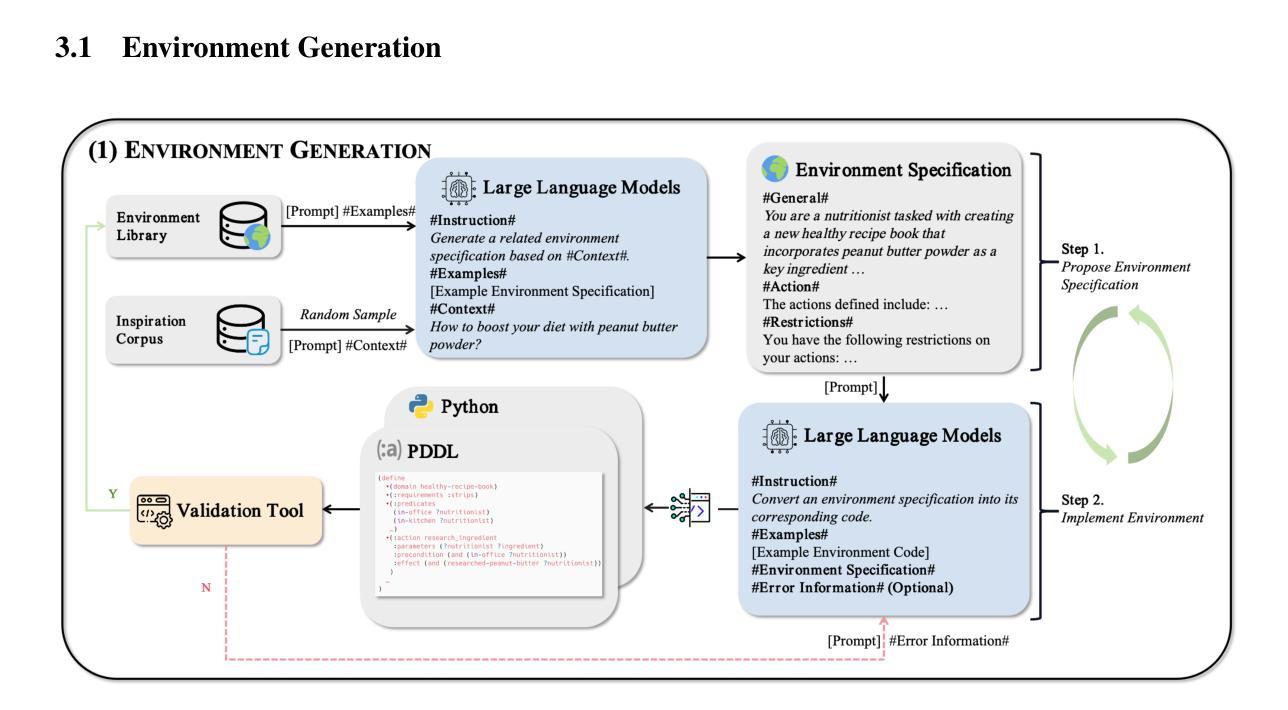
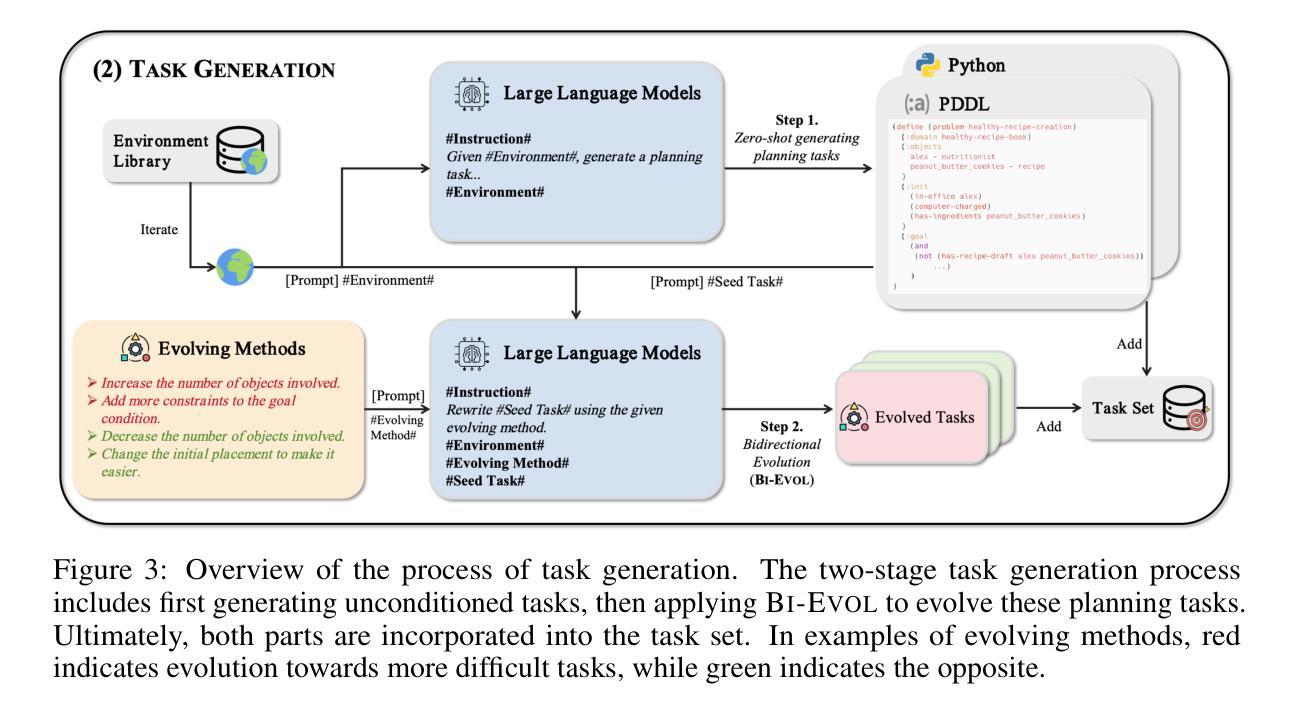
AgentGen: Enhancing Planning Abilities for Large Language Model based Agent via Environment and Task Generation
Authors:Mengkang Hu, Pu Zhao, Can Xu, Qingfeng Sun, Jianguang Lou, Qingwei Lin, Ping Luo, Saravan Rajmohan
Large Language Model-based agents have garnered significant attention and are becoming increasingly popular. Furthermore, planning ability is a crucial component of an LLM-based agent, which generally entails achieving a desired goal from an initial state. This paper investigates enhancing the planning abilities of LLMs through instruction tuning, referred to as agent training. Recent studies have demonstrated that utilizing expert-level trajectory for instruction-tuning LLMs effectively enhances their planning capabilities. However, existing work primarily focuses on synthesizing trajectories from manually designed planning tasks and environments. The labor-intensive nature of creating these environments and tasks impedes the generation of sufficiently varied and extensive trajectories. To address this limitation, this paper explores the automated synthesis of diverse environments and a gradual range of planning tasks, from easy to difficult. We introduce a framework, AgentGen, that leverages LLMs first to generate environments and subsequently generate planning tasks conditioned on these environments. Specifically, to improve environmental diversity, we propose using an inspiration corpus composed of various domain-specific text segments as the context for synthesizing environments. Moreover, to increase the difficulty diversity of generated planning tasks, we propose a bidirectional evolution method, Bi-Evol, that evolves planning tasks from easier and harder directions to synthesize a task set with a smoother difficulty curve. The evaluation results derived from AgentBoard show that AgentGen greatly improves LLMs’ planning ability, e.g., the AgentGen instruction-tuned Llama-3.1-8B surpasses GPT-3.5 in overall performance. Moreover, the AgentGen-tuned Llama-3.1-70B model achieves state-of-the-art results in planning tasks. Project page: https://agent-gen.github.io/.
基于大型语言模型的代理已经引起了广泛的关注,并越来越受欢迎。此外,规划能力是基于LLM的代理的重要组成,这通常涉及从初始状态实现预期目标。本文研究了通过指令调整增强LLM的规划能力,称为代理训练。最近的研究表明,利用专家级轨迹对LLM进行指令调整可以有效地增强它们的规划能力。然而,现有工作主要集中在从手动设计的规划任务和环境中合成轨迹。创建这些环境和任务的劳动密集型特性阻碍了足够多样和广泛的轨迹的生成。为了解决这一局限性,本文探讨了自动化合成多样环境和从简单到复杂的逐渐规划任务。我们引入了一个名为AgentGen的框架,它首先利用LLM生成环境,然后根据这些环境生成规划任务。为了提高环境多样性,我们建议使用由各种领域特定的文本片段组成的灵感语料库作为合成环境的上下文。而且,为了提高生成规划任务的难度多样性,我们提出了一种双向进化方法Bi-Evol,该方法从容易和困难的两个方向进化规划任务,以合成一个难度曲线更平滑的任务集。来自AgentBoard的评估结果表明,AgentGen极大地提高了LLM的规划能力,例如,经过AgentGen指令调整的Llama-3.1-8B在整体性能上超越了GPT-3.5。此外,使用AgentGen调整的Llama-3.1-70B模型在规划任务上达到了最新水平。项目页面:https://agent-gen.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by KDD 2025 (Research Track). Project page: https://agent-gen.github.io/
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)在近年来受到广泛关注并逐渐流行起来。计划能力是LLM中的一个关键部分,通常需要实现既定的目标状态。本研究通过指令微调来提升LLM的计划能力。最近的研究显示,使用专家级别的轨迹对LLM进行指令微调可以增强其规划能力。然而,现有的工作主要集中在从手动设计的规划和环境中合成轨迹,这种劳动密集型的特性限制了轨迹的多样性和广泛性。本研究探索了自动化合成多样化的环境和一系列规划任务,从简单到复杂。引入AgentGen框架,首先利用LLM生成环境,然后根据这些环境生成规划任务。为提高环境多样性,我们提出使用包含各种领域特定文本片段的灵感语料库作为合成环境的上下文。同时,为提高生成规划任务的难度多样性,我们提出了双向进化方法Bi-Evol,该方法从简单和困难两个方向进化规划任务,合成平滑的难度曲线任务集。来自AgentBoard的评估结果表明,AgentGen极大地提高了LLM的规划能力,例如,使用AgentGen指令调教的Llama-3.1-8B在整体性能上超越了GPT-3.5。此外,使用AgentGen调教的Llama-3.1-70B模型在规划任务上达到了最新水平。项目页面:https://agent-gen.github.io/。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)基于代理的训练正在受到关注,因为这种训练方式可以提升模型在规划任务方面的能力。
- 利用专家级别的轨迹进行指令微调被证实是增强LLM规划能力的一种有效方法。
- 当前的工作主要面临的问题是手动设计规划和环境,这一过程既费时又费力,限制了轨迹的多样性和广泛性。
- 提出了一种新的框架AgentGen,该框架可以自动生成环境和规划任务,从而解决了上述问题。
- AgentGen通过使用灵感语料库来提高环境多样性,该语料库包含各种领域特定的文本片段。
- 为了增加生成规划任务的难度多样性,AgentGen采用了双向进化方法Bi-Evol,使得生成的规划任务从简单到复杂。
- 评估结果显示,使用AgentGen调教的LLM模型在规划任务上的表现优于未使用该方法调教的模型。
点此查看论文截图