⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-08 更新
Llasa: Scaling Train-Time and Inference-Time Compute for Llama-based Speech Synthesis
Authors:Zhen Ye, Xinfa Zhu, Chi-Min Chan, Xinsheng Wang, Xu Tan, Jiahe Lei, Yi Peng, Haohe Liu, Yizhu Jin, Zheqi DAI, Hongzhan Lin, Jianyi Chen, Xingjian Du, Liumeng Xue, Yunlin Chen, Zhifei Li, Lei Xie, Qiuqiang Kong, Yike Guo, Wei Xue
Recent advances in text-based large language models (LLMs), particularly in the GPT series and the o1 model, have demonstrated the effectiveness of scaling both training-time and inference-time compute. However, current state-of-the-art TTS systems leveraging LLMs are often multi-stage, requiring separate models (e.g., diffusion models after LLM), complicating the decision of whether to scale a particular model during training or testing. This work makes the following contributions: First, we explore the scaling of train-time and inference-time compute for speech synthesis. Second, we propose a simple framework Llasa for speech synthesis that employs a single-layer vector quantizer (VQ) codec and a single Transformer architecture to fully align with standard LLMs such as Llama. Our experiments reveal that scaling train-time compute for Llasa consistently improves the naturalness of synthesized speech and enables the generation of more complex and accurate prosody patterns. Furthermore, from the perspective of scaling inference-time compute, we employ speech understanding models as verifiers during the search, finding that scaling inference-time compute shifts the sampling modes toward the preferences of specific verifiers, thereby improving emotional expressiveness, timbre consistency, and content accuracy. In addition, we released the checkpoint and training code for our TTS model (1B, 3B, 8B) and codec model publicly available.
基于文本的 大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展,特别是GPT系列和O1模型,展示了在训练时间和推理时间计算扩展方面的有效性。然而,当前利用LLM的最先进TTS系统通常是多阶段的,需要单独的模型(例如LLM之后的扩散模型),这使得在训练或测试期间扩展特定模型变得复杂。本文做出了以下贡献:首先,我们探索了语音合成的训练时间和推理时间计算的扩展。其次,我们提出了一个用于语音合成的简单框架Llasa,它采用单层向量量化(VQ)编码器和单个Transformer架构,与Llama等标准LLM完全对齐。我们的实验表明,扩展Llasa的训练时间计算始终提高了合成语音的自然度,并能够生成更复杂和准确的声音模式。此外,从扩展推理时间计算的角度来看,我们在搜索过程中使用了语音理解模型作为验证器,发现扩展推理时间计算使采样模式转向特定验证器的偏好,从而提高情感表现力、音色一致性和内容准确性。另外,我们公开发布了TTS模型(1B、3B、8B)和编码器模型的检查点和训练代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对语音合成的训练时间和推理时间计算的扩展研究的进展。作者提出了一个简单的用于语音合成的框架Llasa,该框架使用单层向量量化编解码器和单一的Transformer架构与标准的大型语言模型(LLM)如Llama完全对齐。实验表明,扩展训练时间的计算可以提高合成语音的自然度,并可以生成更复杂和准确的韵律模式。从扩展推理时间计算的角度来看,作者使用语音理解模型作为验证器进行搜索,发现扩展推理时间计算可以使采样模式转向特定验证器的偏好,从而提高情感表现力、音色一致性和内容准确性。该研究还公开发布了TTS模型(1B、3B、8B)和编解码器模型的检查点和训练代码。
Key Takeaways
- 文本基于大型语言模型(LLM)的近期进展,特别是在GPT系列和o1模型中的进展,表明了扩展训练时间和推理时间计算的有效性。
- 当前先进的TTS系统利用LLMs通常是多阶段的,需要单独模型(如扩散模型在LLM之后),这使得在训练或测试期间扩展特定模型变得复杂。
- 作者提出了一个简单的语音合成框架Llasa,使用单层向量量化编解码器和单一的Transformer架构,与标准LLMs对齐。
- 扩展训练时间计算可以提高合成语音的自然度,并生成更复杂和准确的韵律模式。
- 扩展推理时间计算可以使采样模式更符合特定语音理解模型的偏好,提高情感表现力、音色一致性和内容准确性。
- 研究公开了TTS模型和编解码器模型的检查点和训练代码,便于公众获取和使用。
点此查看论文截图

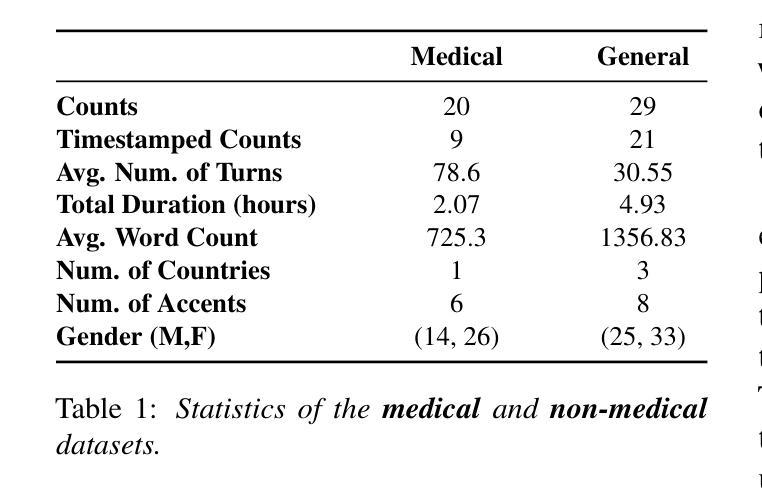
Afrispeech-Dialog: A Benchmark Dataset for Spontaneous English Conversations in Healthcare and Beyond
Authors:Mardhiyah Sanni, Tassallah Abdullahi, Devendra D. Kayande, Emmanuel Ayodele, Naome A. Etori, Michael S. Mollel, Moshood Yekini, Chibuzor Okocha, Lukman E. Ismaila, Folafunmi Omofoye, Boluwatife A. Adewale, Tobi Olatunji
Speech technologies are transforming interactions across various sectors, from healthcare to call centers and robots, yet their performance on African-accented conversations remains underexplored. We introduce Afrispeech-Dialog, a benchmark dataset of 50 simulated medical and non-medical African-accented English conversations, designed to evaluate automatic speech recognition (ASR) and related technologies. We assess state-of-the-art (SOTA) speaker diarization and ASR systems on long-form, accented speech, comparing their performance with native accents and discover a 10%+ performance degradation. Additionally, we explore medical conversation summarization capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to demonstrate the impact of ASR errors on downstream medical summaries, providing insights into the challenges and opportunities for speech technologies in the Global South. Our work highlights the need for more inclusive datasets to advance conversational AI in low-resource settings.
语音技术正在改变从医疗到呼叫中心和机器人等各个领域的交互方式,然而它们在非洲口音对话上的表现仍然被忽视。我们推出Afrispeech-Dialog数据集,其中包含模拟的50个非洲口音英语医疗和非医疗对话的基准数据集,旨在评估自动语音识别(ASR)和相关技术。我们评估了最新的发言人日记和ASR系统在长格式口音语音上的表现,与本地口音的表现进行比较,发现性能下降超过10%。此外,我们还探索大型语言模型(LLM)在医学对话摘要方面的能力,以展示ASR错误对下游医学摘要的影响,深入了解全球南方地区语音技术的挑战和机遇。我们的研究强调需要更多包容性的数据集,以推动低资源环境中的对话人工智能的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了语音技术正在改变各个领域的交互方式,但其对非裔口音对话的表现尚未得到充分了解。针对这一现状,提出了非洲英语口音的语音识别基准数据集Afrispeech-Dialog,该数据集包含模拟的非洲口音英语对话。通过对先进的说话人识别和语音识别系统在长语音中的表现进行评估,发现与原生口音相比性能有所下降。此外,探讨了语言模型对医疗总结的影响及应对的挑战与机遇。强调了更包容的数据集在推进全球非低资源设置环境下的语音技术是必须的。随着越来越多自动化技术的引入,人机交互领域面临诸多挑战和机遇。需要重视在非洲口音等全球背景下的数据收集和研究工作,以确保语音技术的准确性和公平性。这不仅关乎技术层面的进步,更关乎人文层面的平等与包容。
Key Takeaways
- 语音技术正在改变多个领域的交互方式,但在非裔口音对话方面的表现有待探索。
- 引入非洲英语口音的语音识别基准数据集Afrispeech-Dialog,包含模拟对话以评估语音识别系统性能。
- 与原生口音相比,先进语音识别系统在非洲口音方面的性能下降超过10%。
- 语言模型在医疗对话总结中的应用揭示了语音识别错误对下游任务的影响。
- 需要更多包容性的数据集来推进全球非低资源环境下的语音技术。
- 数据收集和研究工作应重视全球背景(如非洲口音),以确保语音技术的准确性和公平性。
点此查看论文截图


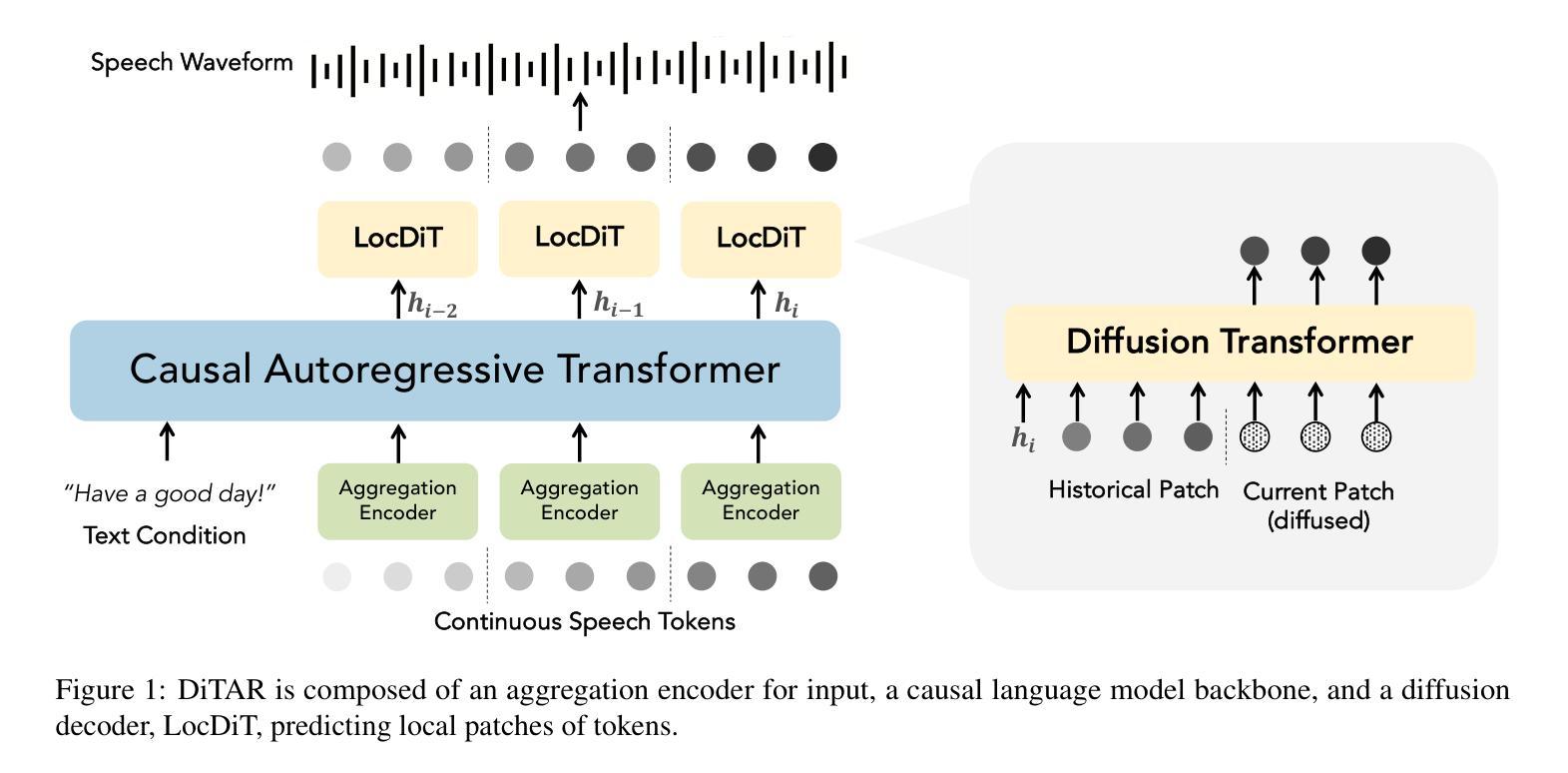
DiTAR: Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling for Speech Generation
Authors:Dongya Jia, Zhuo Chen, Jiawei Chen, Chenpeng Du, Jian Wu, Jian Cong, Xiaobin Zhuang, Chumin Li, Zhen Wei, Yuping Wang, Yuxuan Wang
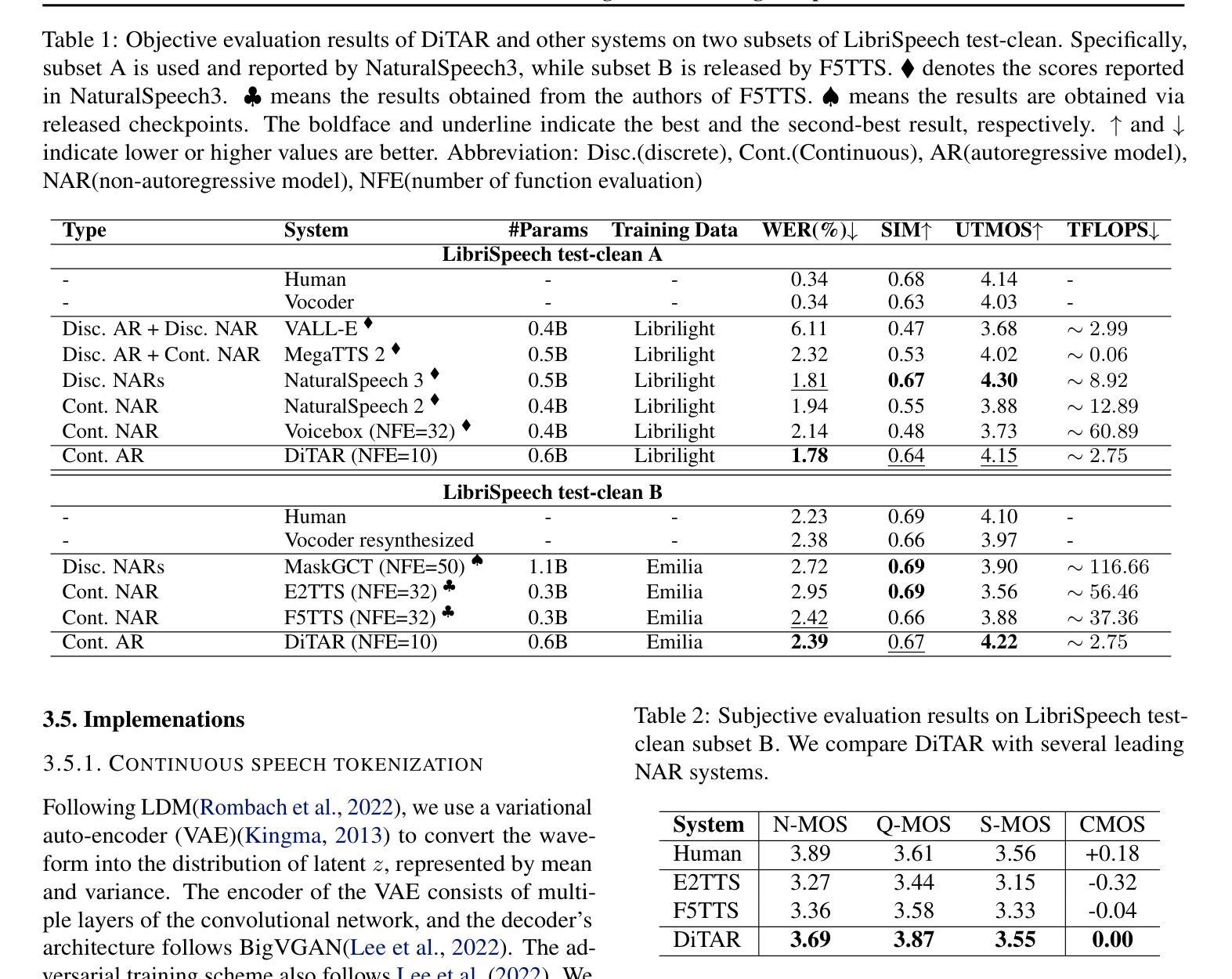
Several recent studies have attempted to autoregressively generate continuous speech representations without discrete speech tokens by combining diffusion and autoregressive models, yet they often face challenges with excessive computational loads or suboptimal outcomes. In this work, we propose Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling (DiTAR), a patch-based autoregressive framework combining a language model with a diffusion transformer. This approach significantly enhances the efficacy of autoregressive models for continuous tokens and reduces computational demands. DiTAR utilizes a divide-and-conquer strategy for patch generation, where the language model processes aggregated patch embeddings and the diffusion transformer subsequently generates the next patch based on the output of the language model. For inference, we propose defining temperature as the time point of introducing noise during the reverse diffusion ODE to balance diversity and determinism. We also show in the extensive scaling analysis that DiTAR has superb scalability. In zero-shot speech generation, DiTAR achieves state-of-the-art performance in robustness, speaker similarity, and naturalness.
近期有几项研究尝试结合扩散模型和自回归模型,无离散语音标记地自动生成连续语音表示。然而,这些方法常常面临计算负荷过大或结果不理想等挑战。在本研究中,我们提出了扩散变压器自回归建模(DiTAR),这是一个结合语言模型和扩散变压器的基于补丁块的自回归框架。此方法显著提高了自回归模型对连续标记的有效性,并降低了计算需求。DiTAR采用分而治之的策略进行补丁生成,其中语言模型处理聚合的补丁嵌入,随后扩散变压器根据语言模型的输出生成下一个补丁。对于推理,我们提议将温度定义为在反向扩散ODE过程中引入噪声的时间点,以平衡多样性和确定性。我们还通过广泛的规模分析表明,DiTAR具有出色的可扩展性。在零样本语音生成中,DiTAR在稳健性、说话人相似性和自然性方面达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling(DiTAR)的方法,它将语言模型与扩散变压器相结合,以基于补丁的自动回归框架生成连续语音表示。该方法提高了自动回归模型对连续标记的有效性,并降低了计算需求。DiTAR采用分而治之的策略进行补丁生成,并利用定义的温度来平衡多样性和确定性。在零样本语音生成中,DiTAR在稳健性、说话人相似性和自然性方面达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 结合扩散和自动回归模型生成连续语音表示,以提高模型性能。
- 提出Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling(DiTAR)方法,结合语言模型和扩散变压器。
- DiTAR采用分块处理的自动回归框架,提高计算效率。
- 通过定义温度来平衡生成语音的多样性和确定性。
- DiTAR在零样本语音生成方面表现出卓越的性能,特别是在稳健性、说话人相似性和自然性方面。
- DiTAR具有良好的可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

Dementia Classification Using Acoustic Speech and Feature Selection
Authors:Marko Niemelä, Mikaela von Bonsdorff, Sami Äyrämö, Tommi Kärkkäinen
Dementia is a general term for a group of syndromes that affect cognitive functions such as memory, thinking, reasoning, and the ability to perform daily tasks. The number of dementia patients is increasing as the population ages, and it is estimated that over 10 million people develop dementia each year. Dementia progresses gradually, and the sooner a patient receives help and support, the better their chances of maintaining their functional abilities. For this reason, early diagnosis of dementia is important. In recent years, machine learning models based on naturally spoken language have been developed for the early diagnosis of dementia. These methods have proven to be user-friendly, cost-effective, scalable, and capable of providing extremely fast diagnoses. This study utilizes the well-known ADReSS challenge dataset for classifying healthy controls and Alzheimer’s patients. The dataset contains speech recordings from a picture description task featuring a kitchen scene, collected from both healthy controls and dementia patients. Unlike most studies, this research does not segment the audio recordings into active speech segments; instead, acoustic features are extracted from entire recordings. The study employs Ridge linear regression, Extreme Minimal Learning Machine, and Linear Support Vector Machine machine learning models to compute feature importance scores based on model outputs. The Ridge model performed best in Leave-One-Subject-Out cross-validation, achieving a classification accuracy of 87.8%. The EMLM model, proved to be effective in both cross-validation and the classification of a separate test dataset, with accuracies of 85.3% and 79.2%, respectively. The study’s results rank among the top compared to other studies using the same dataset and acoustic feature extraction for dementia diagnosis.
痴呆症是一组影响认知功能的综合征的统称,如记忆、思维、推理和日常任务执行能力等。随着人口老龄化,痴呆症患者数量不断增加,据估计每年有逾1000万人患上痴呆症。痴呆症是一个逐渐发展的过程,患者越早得到帮助和支持,保持其功能能力的机会就越大。因此,对痴呆症的早期诊断非常重要。近年来,基于自然语言口语的机器学习方法已被开发出来用于痴呆症的早期诊断。这些方法的用户友好性、成本效益、可扩展性以及快速诊断能力都得到了证实。本研究使用著名的ADReSS挑战数据集,对健康对照者和阿尔茨海默病患者进行分类。该数据集包含来自厨房场景的图片描述任务的语音记录,记录对象包括健康对照者和痴呆症患者。不同于大多数研究,本研究并没有将音频记录分割成活跃语音片段,而是从整个记录中提取声音特征。该研究采用岭回归、极速学习机和线性支持向量机机器学习模型,基于模型输出计算特征重要性得分。岭回归在留一主体出交叉验证中的表现最佳,分类准确率为87.8%。极速学习机模型在交叉验证和对独立测试数据集进行分类时均表现出色,准确率分别为85.3%和79.2%。本研究的结果与其他使用同一数据集和声音特征提取进行痴呆症诊断的研究相比名列前茅。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了痴呆症的相关情况。随着人口老龄化,痴呆症患者数量不断增加。早期诊断对维持患者功能能力至关重要。近年来,基于自然语言的机器学习模型已被开发用于痴呆症的早期诊断。本文利用ADReSS挑战数据集,采用岭回归、极限学习机和线性支持向量机等机器学习模型,从整个录音中提取声学特征进行分类。研究结果表明,岭回归模型在留一法交叉验证中的分类准确率最高,达到87.8%。
Key Takeaways
- 痴呆症是一组影响认知功能的综合征,包括记忆、思维、推理和日常任务执行能力。
- 随着人口老龄化,痴呆症患者数量增加,每年估计有1000多万人患上痴呆症。
- 早期诊断对维持痴呆症患者功能能力至关重要。
- 基于自然语言的机器学习模型已被开发用于痴呆症的早期诊断,具有用户友好、成本低、可扩展和快速诊断能力。
- 本文使用ADReSS挑战数据集,不分割音频录音,从整个录音中提取声学特征进行分类。
- 岭回归模型在留一法交叉验证中表现最佳,分类准确率87.8%。
点此查看论文截图

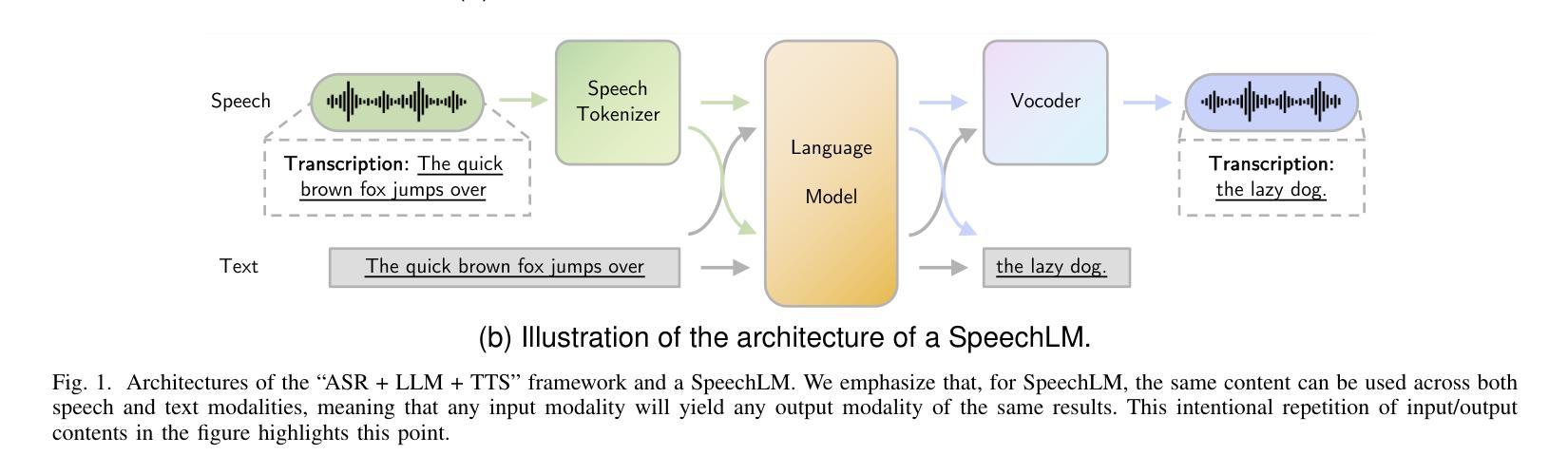
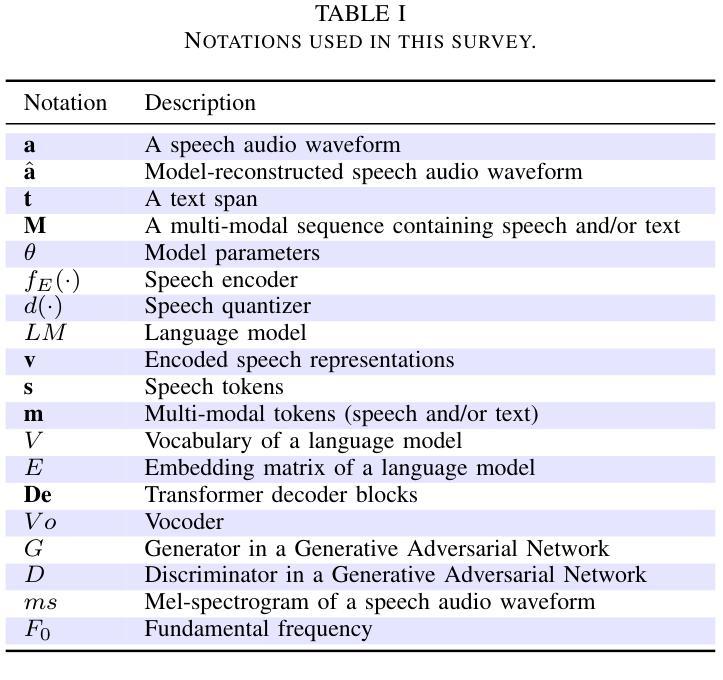
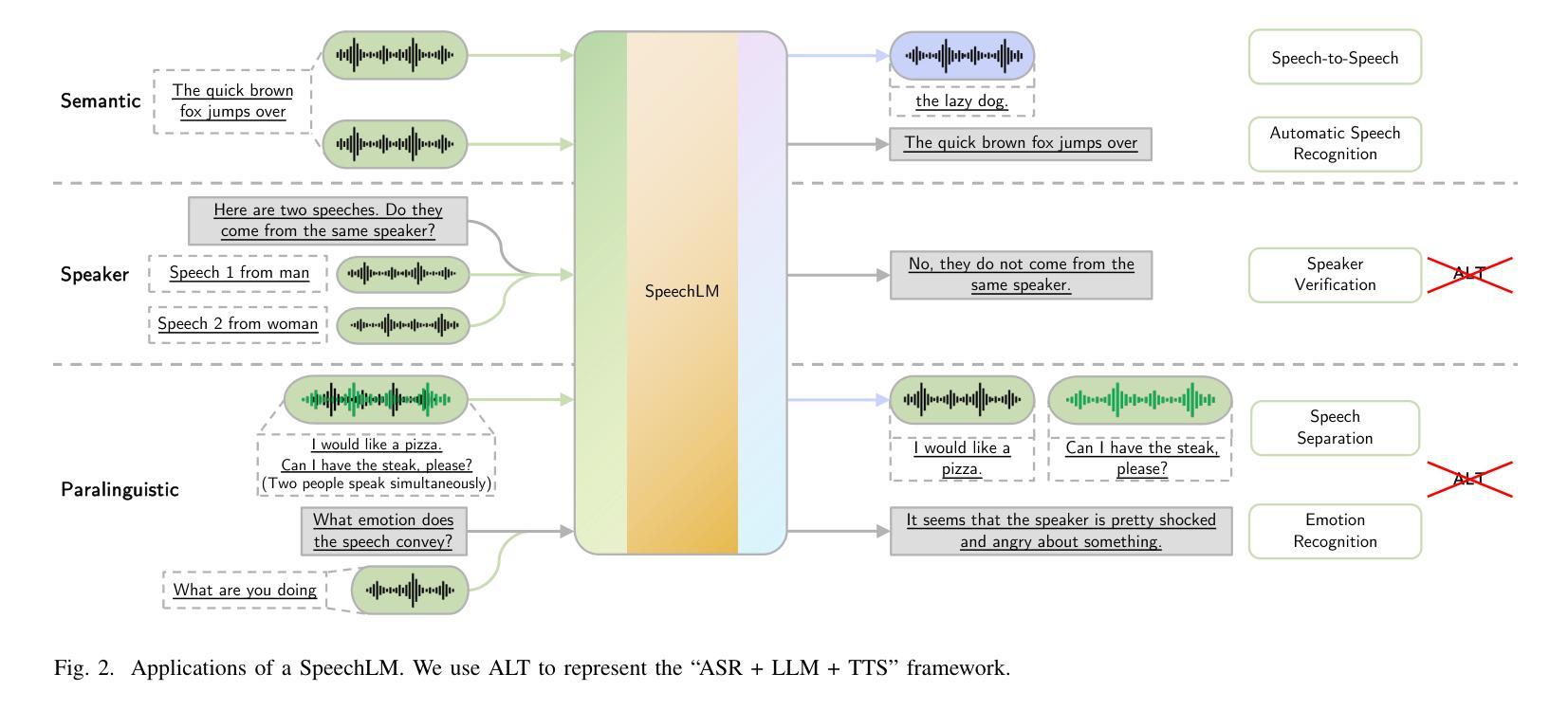
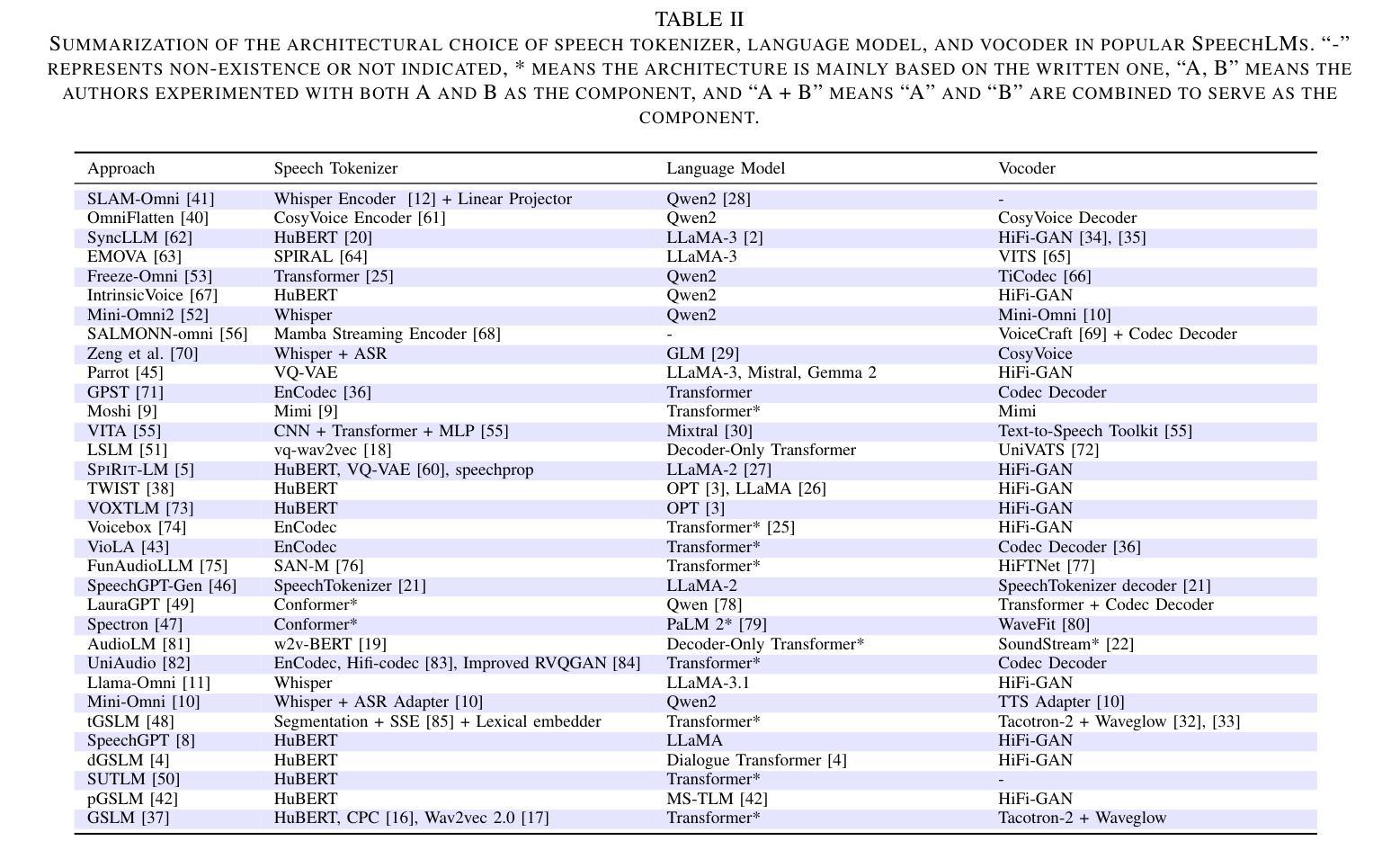
Recent Advances in Speech Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Wenqian Cui, Dianzhi Yu, Xiaoqi Jiao, Ziqiao Meng, Guangyan Zhang, Qichao Wang, Yiwen Guo, Irwin King
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently garnered significant attention, primarily for their capabilities in text-based interactions. However, natural human interaction often relies on speech, necessitating a shift towards voice-based models. A straightforward approach to achieve this involves a pipeline of ``Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) + LLM + Text-to-Speech (TTS)”, where input speech is transcribed to text, processed by an LLM, and then converted back to speech. Despite being straightforward, this method suffers from inherent limitations, such as information loss during modality conversion, significant latency due to the complex pipeline, and error accumulation across the three stages. To address these issues, Speech Language Models (SpeechLMs) – end-to-end models that generate speech without converting from text – have emerged as a promising alternative. This survey paper provides the first comprehensive overview of recent methodologies for constructing SpeechLMs, detailing the key components of their architecture and the various training recipes integral to their development. Additionally, we systematically survey the various capabilities of SpeechLMs, categorize their evaluation metrics, and discuss the challenges and future research directions in this rapidly evolving field. The GitHub repository is available at https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey
大型语言模型(LLM)近期引起了广泛关注,主要因其基于文本的交互能力。然而,自然人类互动通常依赖于语音,这要求向基于语音的模型转变。实现这一目标的一种直接方法是“自动语音识别(ASR)+ LLM + 文本到语音(TTS)”的管道,其中输入语音被转录为文本,由LLM处理,然后转回语音。尽管这种方法很直接,但它存在固有的局限性,例如在模态转换过程中的信息损失、由于复杂管道而产生的显著延迟以及三个阶段的错误累积。为了解决这些问题,语音语言模型(SpeechLM)——一种无需从文本转换即可生成语音的端到端模型——作为一种有前途的替代方案而出现。这篇综述论文首次全面概述了构建SpeechLM的最新方法,详细描述了其架构的关键组件以及对其发展至关重要的各种培训配方。此外,我们还系统地调查了SpeechLM的各种能力,对其评估指标进行了分类,并讨论了这一快速发展的领域所面临的挑战和未来研究方向。GitHub仓库可在https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary:
近期大型语言模型(LLMs)受到广泛关注,主要用于文本交互。然而,自然人类交互通常依赖于语音,因此需要向语音模型转变。一种实现这一转变的简洁方法是采用“自动语音识别(ASR)+大型语言模型(LLM)+文本到语音(TTS)”的管道,将输入语音转录为文本,由LLM处理后再转回语音。尽管这种方法看似简单,但却存在固有的局限性,如模态转换中的信息损失、复杂的管道导致的延迟以及三个阶段的误差累积。为解决这些问题,语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)——无需转换为文本即可生成语音的端到端模型——作为有前途的替代方案而出现。这篇综述论文首次全面概述了SpeechLMs的最新构建方法,详细介绍了其架构的关键组件以及促进其发展的各种培训食谱。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在文本交互领域受到关注,但自然人类交互更多依赖语音。
- 语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)作为端到端模型,可直接生成语音,无需转换为文本。
- 当前采用“ASR+LLM+TTS”的方法存在信息损失、延迟和误差累积的问题。
- SpeechLMs的出现解决了上述问题,并展示了其架构和训练方法的多样性。
- 综述论文提供了SpeechLMs的全面概述,包括构建方法、关键组件、培训食谱等。
- 论文还系统阐述了SpeechLMs的各种功能、评估指标、挑战和未来研究方向。
点此查看论文截图