⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-08 更新
A Self-supervised Multimodal Deep Learning Approach to Differentiate Post-radiotherapy Progression from Pseudoprogression in Glioblastoma
Authors:Ahmed Gomaa, Yixing Huang, Pluvio Stephan, Katharina Breininger, Benjamin Frey, Arnd Dörfler, Oliver Schnell, Daniel Delev, Roland Coras, Charlotte Schmitter, Jenny Stritzelberger, Sabine Semrau, Andreas Maier, Siming Bayer, Stephan Schönecker, Dieter H Heiland, Peter Hau, Udo S. Gaipl, Christoph Bert, Rainer Fietkau, Manuel A. Schmidt, Florian Putz
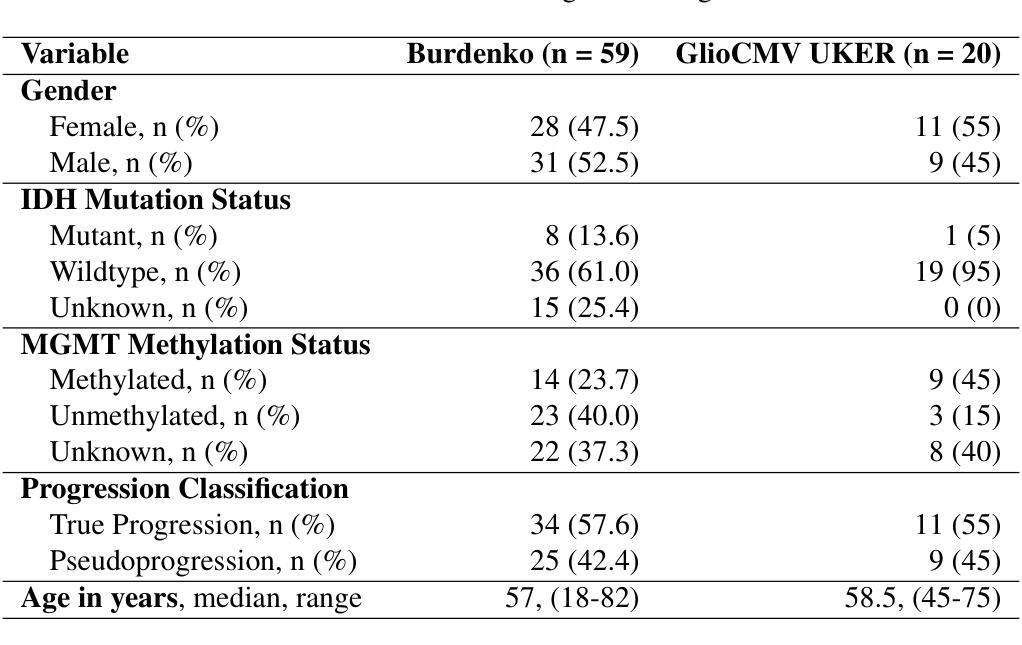
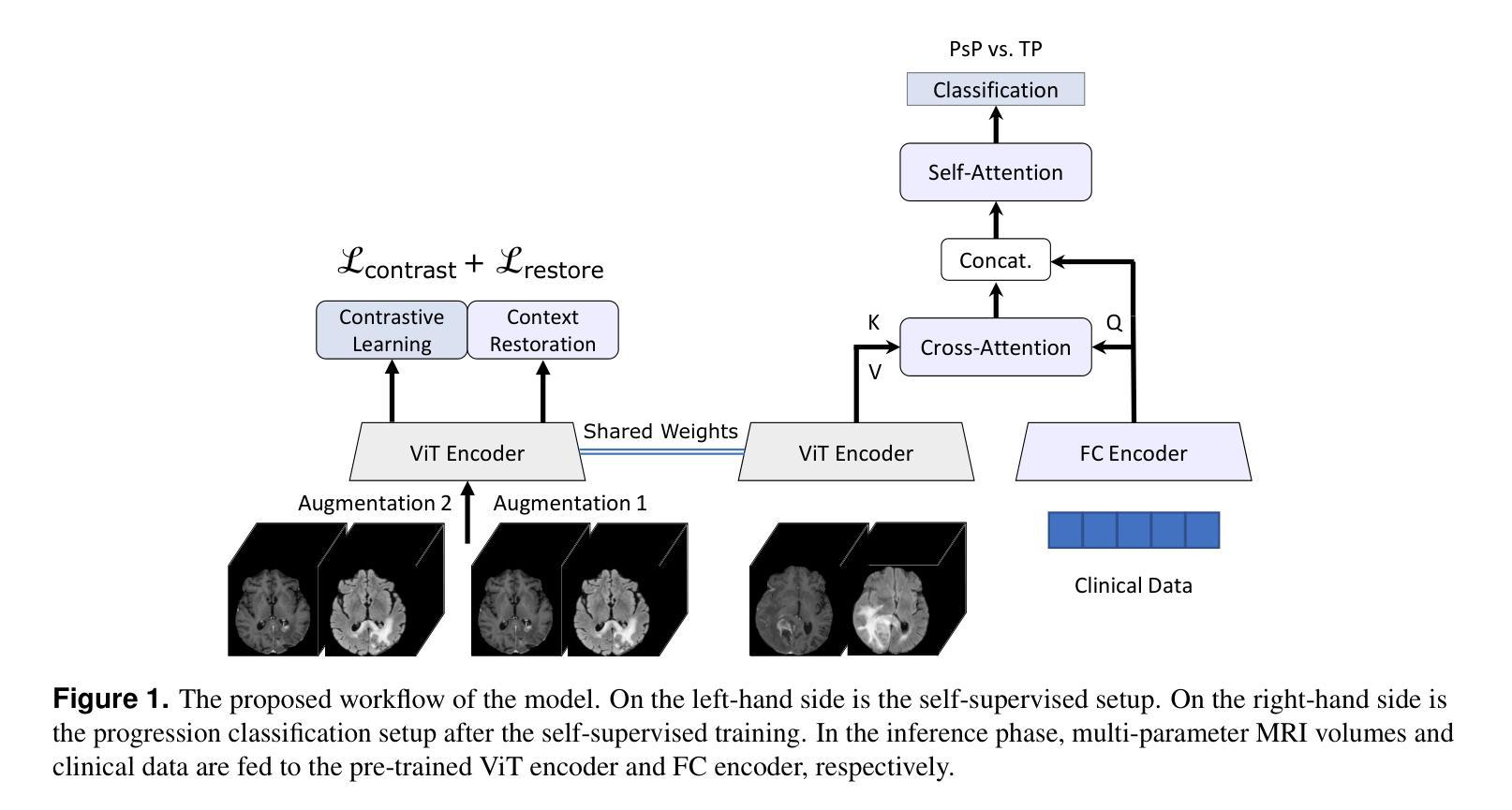
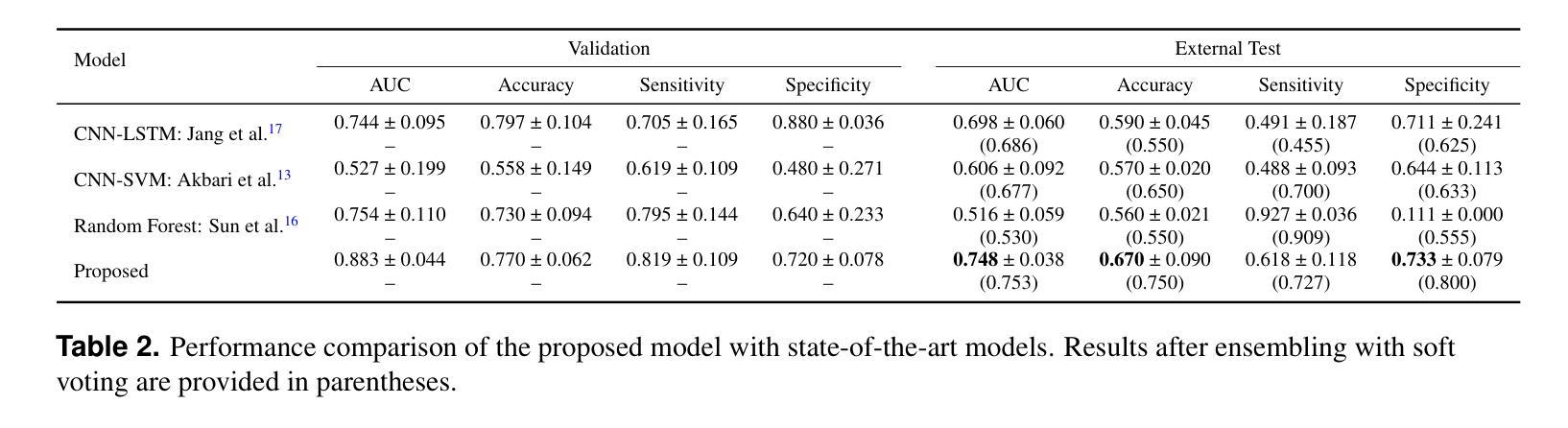
Accurate differentiation of pseudoprogression (PsP) from True Progression (TP) following radiotherapy (RT) in glioblastoma (GBM) patients is crucial for optimal treatment planning. However, this task remains challenging due to the overlapping imaging characteristics of PsP and TP. This study therefore proposes a multimodal deep-learning approach utilizing complementary information from routine anatomical MR images, clinical parameters, and RT treatment planning information for improved predictive accuracy. The approach utilizes a self-supervised Vision Transformer (ViT) to encode multi-sequence MR brain volumes to effectively capture both global and local context from the high dimensional input. The encoder is trained in a self-supervised upstream task on unlabeled glioma MRI datasets from the open BraTS2021, UPenn-GBM, and UCSF-PDGM datasets to generate compact, clinically relevant representations from FLAIR and T1 post-contrast sequences. These encoded MR inputs are then integrated with clinical data and RT treatment planning information through guided cross-modal attention, improving progression classification accuracy. This work was developed using two datasets from different centers: the Burdenko Glioblastoma Progression Dataset (n = 59) for training and validation, and the GlioCMV progression dataset from the University Hospital Erlangen (UKER) (n = 20) for testing. The proposed method achieved an AUC of 75.3%, outperforming the current state-of-the-art data-driven approaches. Importantly, the proposed approach relies on readily available anatomical MRI sequences, clinical data, and RT treatment planning information, enhancing its clinical feasibility. The proposed approach addresses the challenge of limited data availability for PsP and TP differentiation and could allow for improved clinical decision-making and optimized treatment plans for GBM patients.
对胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)患者在放疗(RT)后的假性进展(PsP)和真性进展(TP)的准确区分对于制定最佳治疗方案至关重要。然而,由于PsP和TP的成像特征重叠,这一任务仍然具有挑战性。因此,本研究提出了一种多模态深度学习的方法,该方法利用常规解剖MRI图像、临床参数和RT治疗计划信息的互补信息进行更准确的预测。该方法利用自监督的Vision Transformer(ViT)对多序列MR脑容积进行编码,以有效地从高维输入中捕获全局和局部上下文。编码器在无标签的胶质母细胞瘤MRI数据集(来自公开可用的BraTS2021、UPenn-GBM和UCSF-PDGM数据集)上进行自监督上游任务训练,从FLAIR和T1增强序列生成紧凑且临床相关的表示。这些编码后的MR输入然后与临床数据和RT治疗计划信息通过引导跨模态注意力进行整合,提高了进展分类的准确性。这项工作使用了来自不同中心的两个数据集进行开发和测试:使用Burdenko胶质母细胞瘤进展数据集(n=59)进行训练和验证,使用来自Erlangen大学医院(UKER)的GlioCMV进展数据集(n=20)进行测试。所提出的方法达到了75.3%的AUC,优于当前最先进的数据驱动方法。重要的是,所提出的方法依赖于可获得的解剖MRI序列、临床数据和RT治疗计划信息,增强了其临床可行性。所提出的方法解决了PsP和TP鉴别中数据有限性的挑战,并可能有助于改进胶质母细胞瘤患者的临床决策和优化的治疗方案。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在放射治疗后的胶质母细胞瘤患者中,对假性进展(PsP)与真实进展(TP)的准确鉴别对于制定最佳治疗方案至关重要。然而,由于PsP和TP的成像特征重叠,这一任务仍然具有挑战性。因此,本研究提出了一种多模态深度学习的方法,利用常规解剖MR图像、临床参数和放射治疗计划信息的互补信息,以提高预测准确性。该方法使用自监督的Vision Transformer(ViT)对多序列MR脑容积进行编码,以有效地捕捉高维输入的全局和局部上下文。编码器在未经标记的胶质母细胞瘤MRI数据集(来自开放的BraTS2021、UPenn-GBM和UCSF-PDGM数据集)上进行自监督上游任务训练,从FLAIR和T1增强序列生成紧凑且临床相关的表示。这些编码的MR输入然后与临床数据和放射治疗计划信息通过引导跨模态注意力进行整合,提高进展分类的准确性。该研究使用了来自不同中心的两个数据集:Burdenko胶质母细胞瘤进展数据集(n=59)用于训练和验证,以及Erlangen大学医院(UKER)的GlioCMV进展数据集(n=20)用于测试。所提出的方法达到了75.3%的AUC,优于当前数据驱动方法的最新水平。重要的是,该方法依赖于易于获得的解剖MRI序列、临床数据和放射治疗计划信息,增强了其临床可行性。所提出的方法解决了PsP和TP鉴别中数据有限性的挑战,并能改善临床决策和优化胶质母细胞瘤患者的治疗计划。
关键见解
- 区分假性进展(PsP)和真实进展(TP)对于胶质母细胞瘤患者的最优治疗计划至关重要。
- 研究提出了一种多模态深度学习的方法,结合常规解剖MR图像、临床参数和放射治疗计划信息,以提高预测准确性。
- 利用自监督的Vision Transformer(ViT)进行图像编码,捕捉全局和局部上下文信息。
- 所提出的方法在Burdenko和GlioCMV数据集上进行了验证,并取得了较高的AUC值。
- 该方法超越了当前的数据驱动方法,显示出其优越性。
- 所提出的方法依赖于易获得的解剖MRI序列、临床数据和放疗计划信息,具有临床可行性。
点此查看论文截图

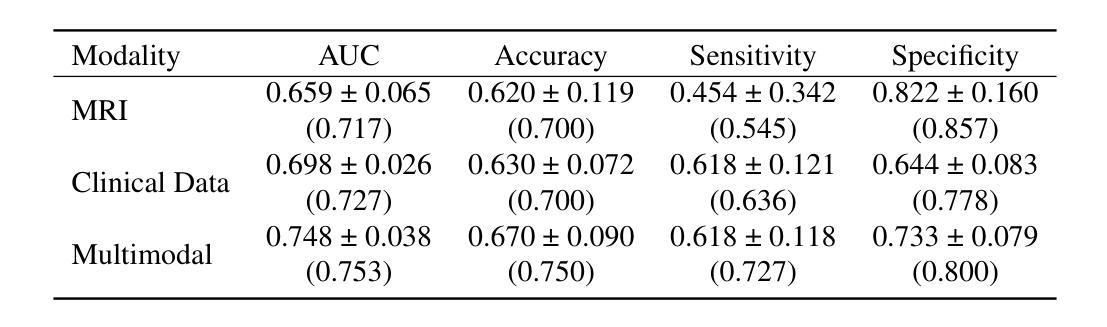
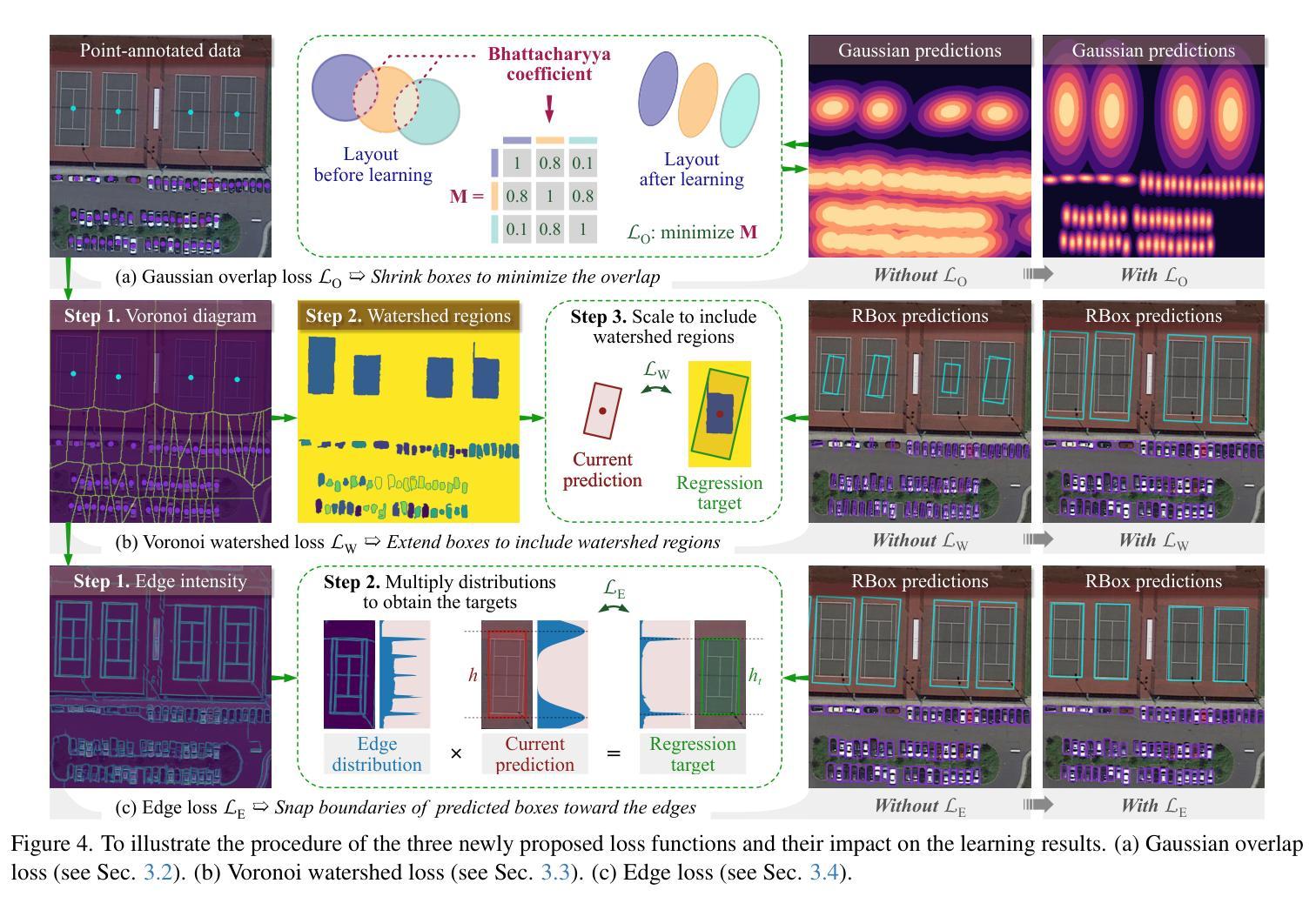
A Retrospective Systematic Study on Hierarchical Sparse Query Transformer-assisted Ultrasound Screening for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Authors:Chaoyin She, Ruifang Lu, Danni He, Jiayi Lv, Yadan Lin, Meiqing Cheng, Hui Huang, Lida Chen, Wei Wang, Qinghua Huang
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks as the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with early detection being crucial for improving patient survival rates. However, early screening for HCC using ultrasound suffers from insufficient sensitivity and is highly dependent on the expertise of radiologists for interpretation. Leveraging the latest advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging, this study proposes an innovative Hierarchical Sparse Query Transformer (HSQformer) model that combines the strengths of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) to enhance the accuracy of HCC diagnosis in ultrasound screening. The HSQformer leverages sparse latent space representations to capture hierarchical details at various granularities without the need for complex adjustments, and adopts a modular, plug-and-play design philosophy, ensuring the model’s versatility and ease of use. The HSQformer’s performance was rigorously tested across three distinct clinical scenarios: single-center, multi-center, and high-risk patient testing. In each of these settings, it consistently outperformed existing state-of-the-art models, such as ConvNext and SwinTransformer. Notably, the HSQformer even matched the diagnostic capabilities of senior radiologists and comprehensively surpassed those of junior radiologists. The experimental results from this study strongly demonstrate the effectiveness and clinical potential of AI-assisted tools in HCC screening. The full code is available at https://github.com/Asunatan/HSQformer.
肝细胞癌(HCC)是全球癌症死亡率的第三大原因,早期发现对于提高患者存活率至关重要。然而,使用超声进行HCC的早期筛查存在灵敏度不足的问题,并且高度依赖于放射科医生的解释。本研究利用医疗成像领域中人工智能(AI)的最新进展,提出了一种创新的分层稀疏查询转换器(HSQformer)模型。该模型结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)的优点,旨在提高超声筛查中HCC诊断的准确性。HSQformer利用稀疏潜在空间表示来捕获不同粒度的层次细节,无需进行复杂的调整,并采用了模块化、即插即用的设计思想,确保模型的通用性和易用性。HSQformer的性能在三种不同的临床情景中进行了严格测试:单中心、多中心和高危患者测试。在这三种环境中,它始终优于现有的最新模型,如ConvNext和SwinTransformer。值得注意的是,HSQformer甚至达到了资深放射科医生的诊断水平,并全面超越了初级放射科医生的水平。本研究的实验结果强烈证明了AI辅助工具在HCC筛查中的有效性和临床潜力。相关代码已发布在https://github.com/Asunatan/HSQformer。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
肝癌是世界上第三大癌症致死原因,早期检测对于提高患者生存率至关重要。本研究提出一种结合卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉变压器(ViT)优势的分层稀疏查询变压器(HSQformer)模型,利用人工智能增强肝癌超声筛查诊断的准确性。HSQformer采用稀疏潜在空间表示捕捉不同粒度的层次细节,无需复杂调整,采用模块化设计,确保模型的通用性和易用性。在单中心、多中心和高危患者测试等三种不同临床场景中,其性能均优于现有最先进的模型,如ConvNext和SwinTransformer。此外,HSQformer的诊断能力与资深放射学家相匹配,并超越了初级放射学家的水平。该研究实验结果强烈证明AI辅助工具在肝癌筛查中的有效性和临床潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 肝癌是世界上第三大癌症致死原因,早期检测对改善患者生存率至关重要。
- 当前超声筛查肝癌存在灵敏度不足和依赖放射学家解读的问题。
- 本研究提出了一种名为HSQformer的新型模型,结合CNN和ViT的优势来增强肝癌诊断的准确性。
- HSQformer利用稀疏潜在空间表示捕捉层次细节,设计模块化,易于使用。
- HSQformer在不同临床场景中性能优越,优于现有最先进的模型。
- HSQformer的诊断能力与资深放射学家相匹配,并超越了初级放射学家的水平。
点此查看论文截图

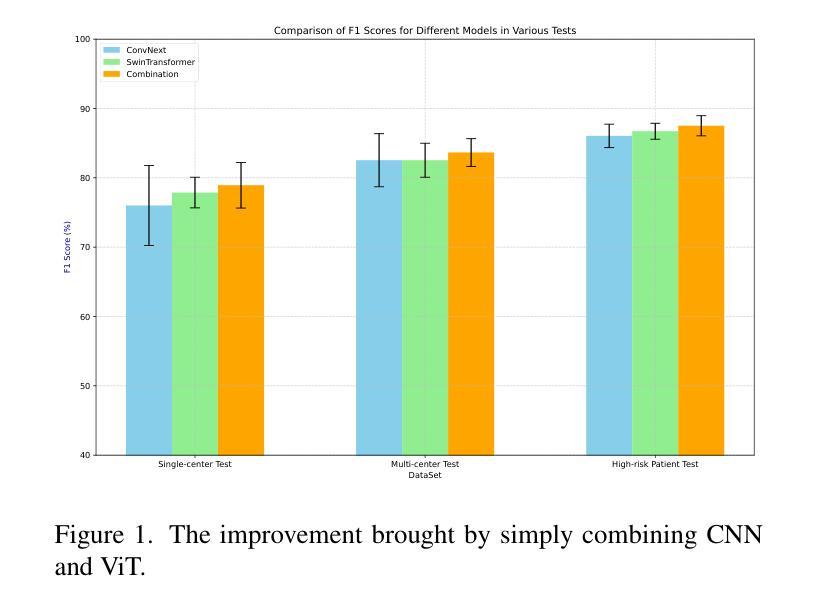
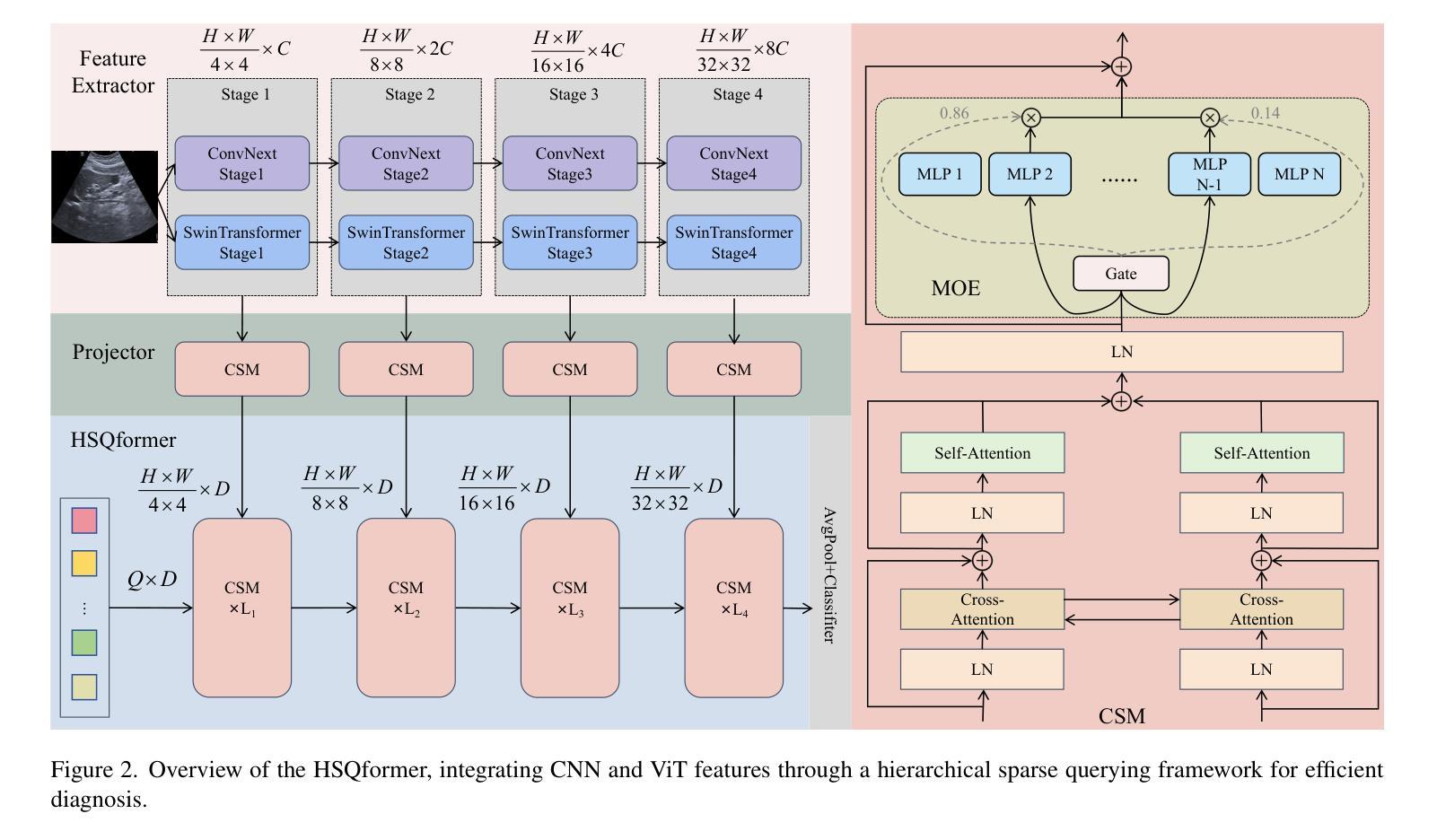
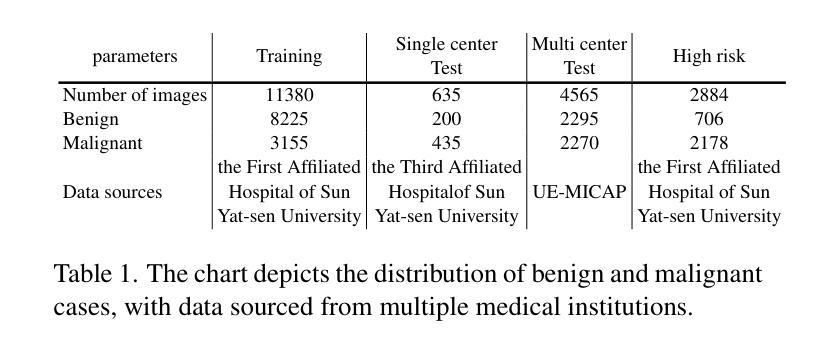
Scaling Laws in Patchification: An Image Is Worth 50,176 Tokens And More
Authors:Feng Wang, Yaodong Yu, Guoyizhe Wei, Wei Shao, Yuyin Zhou, Alan Yuille, Cihang Xie
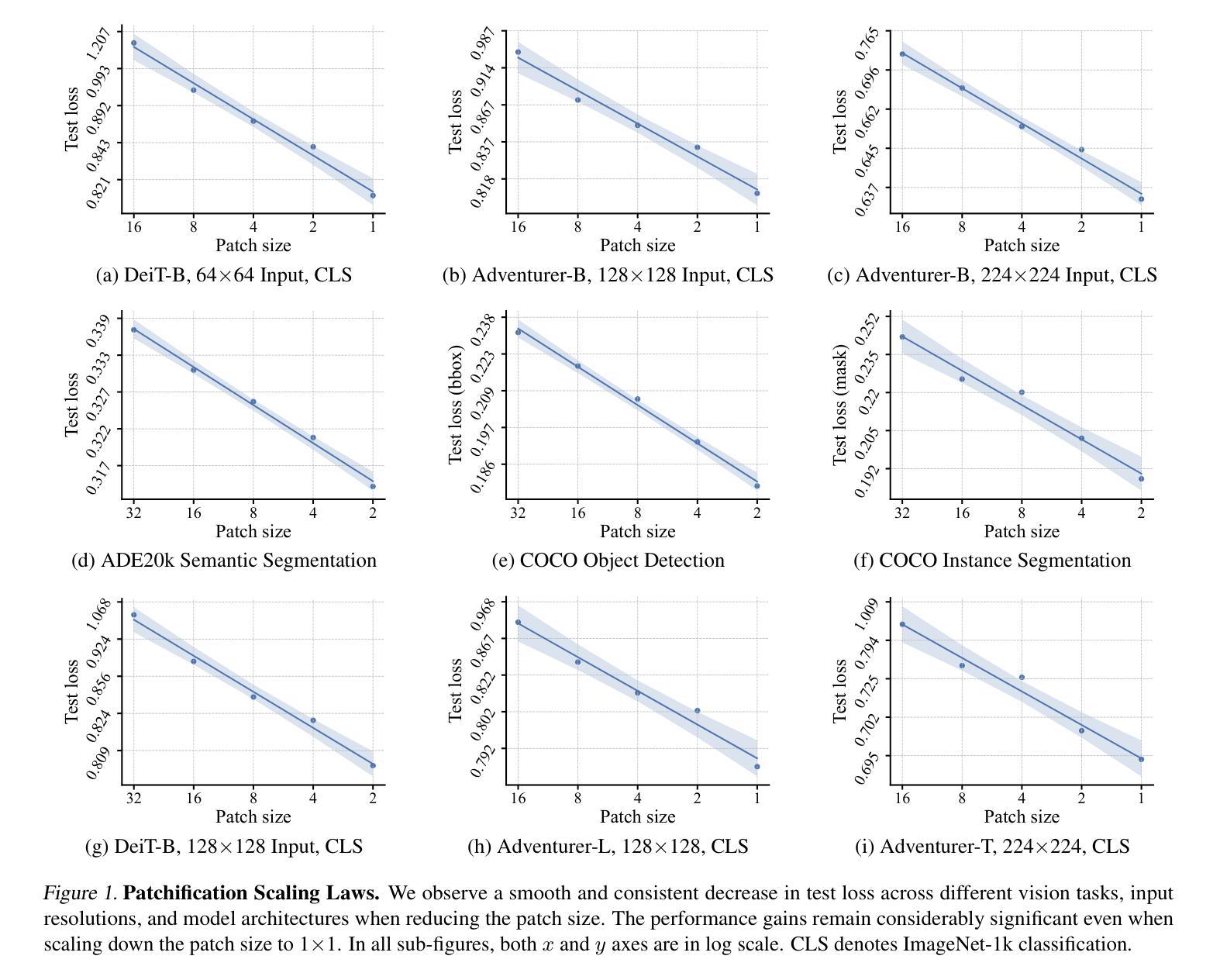
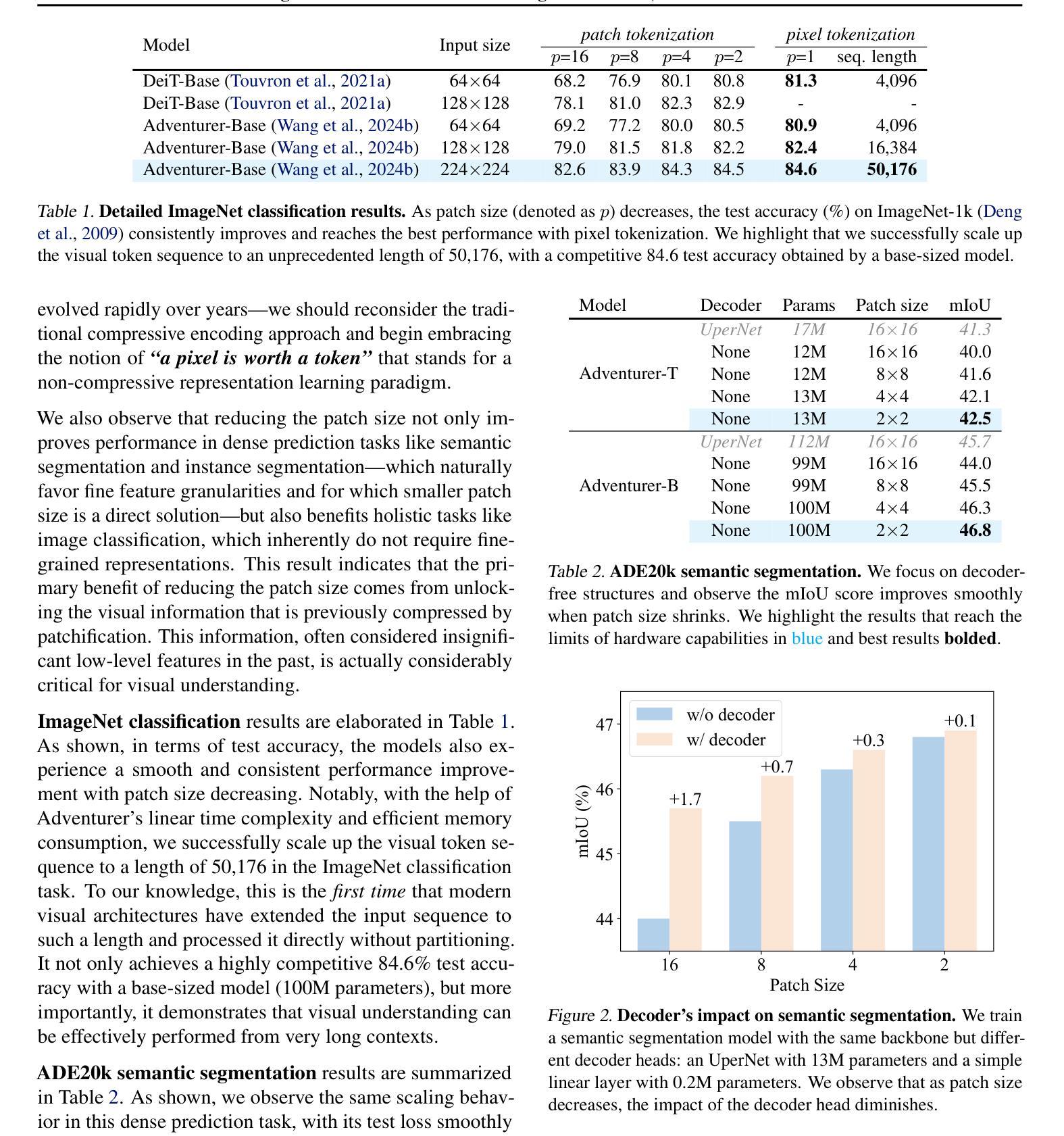
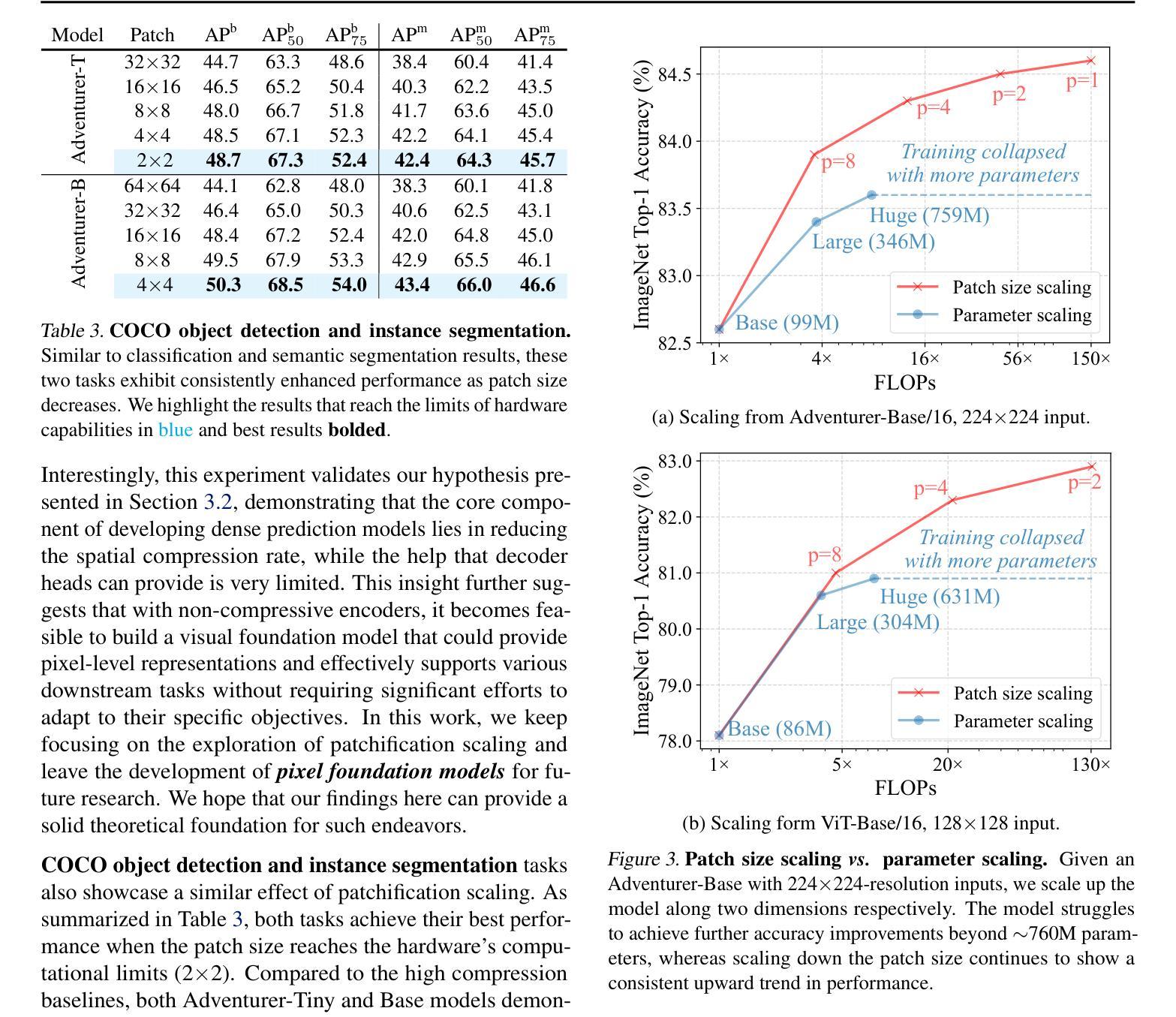
Since the introduction of Vision Transformer (ViT), patchification has long been regarded as a de facto image tokenization approach for plain visual architectures. By compressing the spatial size of images, this approach can effectively shorten the token sequence and reduce the computational cost of ViT-like plain architectures. In this work, we aim to thoroughly examine the information loss caused by this patchification-based compressive encoding paradigm and how it affects visual understanding. We conduct extensive patch size scaling experiments and excitedly observe an intriguing scaling law in patchification: the models can consistently benefit from decreased patch sizes and attain improved predictive performance, until it reaches the minimum patch size of 1x1, i.e., pixel tokenization. This conclusion is broadly applicable across different vision tasks, various input scales, and diverse architectures such as ViT and the recent Mamba models. Moreover, as a by-product, we discover that with smaller patches, task-specific decoder heads become less critical for dense prediction. In the experiments, we successfully scale up the visual sequence to an exceptional length of 50,176 tokens, achieving a competitive test accuracy of 84.6% with a base-sized model on the ImageNet-1k benchmark. We hope this study can provide insights and theoretical foundations for future works of building non-compressive vision models. Code is available at https://github.com/wangf3014/Patch_Scaling.
自从引入Vision Transformer(ViT)以来,切块化长期以来一直被视为普通视觉架构的图像令牌化方法的默认选择。通过压缩图像的空间尺寸,这种方法可以有效地缩短令牌序列并降低类似ViT的普通架构的计算成本。在这项工作中,我们旨在彻底检查基于切块化的压缩编码范式所引起的信息损失以及它对视觉理解的影响。我们进行了广泛的切块大小缩放实验,并观察到切块化中的有趣缩放定律:模型可以持续地从减小切块大小中受益,并获得改进的预测性能,直到达到最小的切块大小1x1,即像素令牌化。这一结论适用于不同的视觉任务、各种输入规模和多样化的架构,如ViT和最近的Mamba模型。此外,作为副产品,我们发现使用较小的切块时,特定任务的解码器头对于密集预测变得不那么关键。在实验中,我们成功地将视觉序列放大到50,176个令牌的异常长度,在ImageNet-1k基准测试上实现了具有竞争力的测试准确率84.6%。我们希望这项研究能为构建非压缩视觉模型提供见解和理论基础。代码可访问https://github.com/wangf3014/Patch_Scaling获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
研究了Vision Transformer中图像分片化的信息损失及其对视觉理解的影响。实验发现分片大小缩放规律:随着补丁尺寸的减小,模型性能持续改善,直至达到最小补丁尺寸,即像素标记化。该结论适用于不同的视觉任务、输入规模和架构。此外,研究发现较小的补丁使特定任务的解码头对于密集预测变得不那么关键。实验中将视觉序列扩展到异常长的标记序列长度,并在ImageNet-1k基准测试中实现了具有竞争力的准确率。本研究为构建非压缩视觉模型提供了见解和理论基础。
要点掌握
- Vision Transformer中普遍采用图像分片化作为图像标记化方法。
- 图像分片化通过压缩图像的空间尺寸来缩短令牌序列并降低计算成本。
- 研究深入探讨了分片化引起的信息损失及其对视觉理解的影响。
- 实验观察到分片大小的缩放规律:随着补丁尺寸的减小,模型性能持续提高。
- 这一结论适用于各种视觉任务、不同输入规模和架构。
- 在较小的补丁下,特定任务的解码头对密集预测的重要性降低。
点此查看论文截图

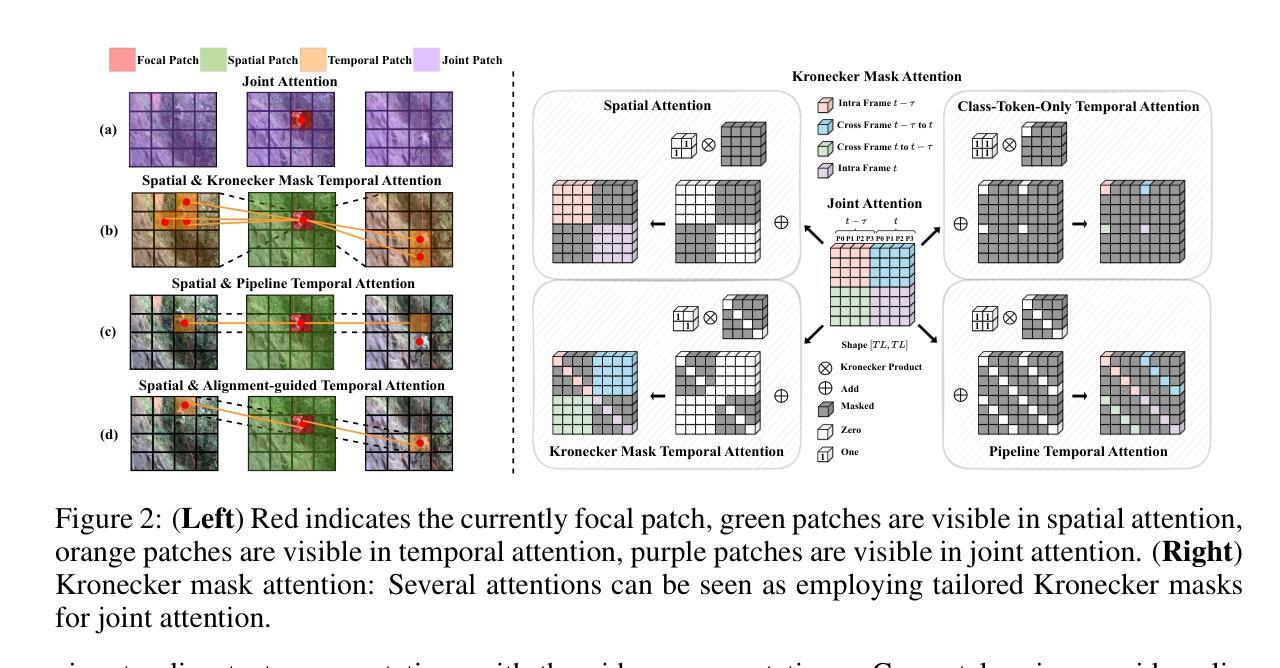
Kronecker Mask and Interpretive Prompts are Language-Action Video Learners
Authors:Jingyi Yang, Zitong Yu, Xiuming Ni, Jia He, Hui Li
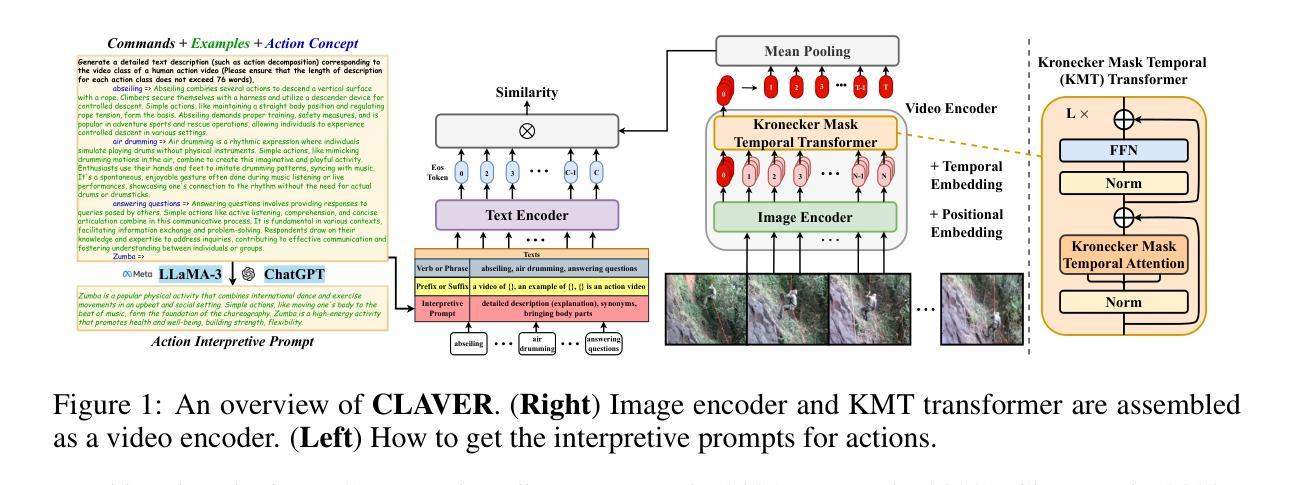
Contrastive language-image pretraining (CLIP) has significantly advanced image-based vision learning. A pressing topic subsequently arises: how can we effectively adapt CLIP to the video domain? Recent studies have focused on adjusting either the textual or visual branch of CLIP for action recognition. However, we argue that adaptations of both branches are crucial. In this paper, we propose \textbf{CLAVER}: a \textbf{C}ontrastive \textbf{L}anguage-\textbf{A}ction \textbf{V}ideo Learn\textbf{er}, designed to shift CLIP’s focus from the alignment of static visual objects and concrete nouns to the alignment of dynamic action behaviors and abstract verbs. Specifically, we introduce a novel Kronecker mask attention for temporal modeling. Our tailored Kronecker mask offers three benefits 1) it expands the temporal receptive field for each token, 2) it serves as an effective spatiotemporal heterogeneity inductive bias, mitigating the issue of spatiotemporal homogenization, and 3) it can be seamlessly plugged into transformer-based models. Regarding the textual branch, we leverage large language models to generate diverse, sentence-level and semantically rich interpretive prompts of actions, which shift the model’s focus towards the verb comprehension. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks and learning scenarios demonstrate the superiority and generality of our approach. The code will be available soon.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在基于图像的视觉学习方面取得了显著进展。随之而来出现了一个紧迫的问题:我们如何有效地将CLIP适应到视频领域?近期的研究主要集中在调整CLIP的文本或视觉分支进行动作识别。然而,我们认为两个分支的适应都是至关重要的。在本文中,我们提出了CLAVER,即对比语言-动作视频学习器(\textbf{C}ontrastive \textbf{L}anguage-\textbf{A}ction \textbf{V}ideo Learn\textbf{er}),旨在将CLIP的重点从静态物体和具体名词的对齐转向动态行为动作和抽象动词的对齐。具体来说,我们引入了一种新型克罗内克掩膜注意力来进行时序建模。我们的定制克罗内克掩膜提供了以下三个优点:1)扩大了每个令牌的临时感受野;2)作为有效的时空异构图归纳偏置,缓解了时空同质化的问题;3)可以无缝插入到基于Transformer的模型中。在文本分支方面,我们利用大型语言模型生成多样化、句子级别且语义丰富的动作解释性提示,使模型的重点转向动词理解。在各种基准测试和学习场景的大量实验证明了我们的方法的优越性和通用性。代码很快将可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
论文提出CLAVER模型,旨在将CLIP的重点从静态视觉对象和具体名词的对齐转移到动态行为动词的对齐上。采用新型的Kronecker Mask注意力机制进行时序建模,引入丰富的动作解释性提示,实现视频领域的有效适应。实验证明其优越性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- CLAVER模型旨在将CLIP的焦点从静态视觉对象和名词对齐转移到动态行为动词的对齐上。
- 引入Kronecker Mask注意力机制进行时序建模,扩大每个标记的临时接受范围,并作为有效的时空异质性归纳偏置。
- Kronecker Mask可以无缝插入基于transformer的模型。
- 利用大型语言模型生成多样、句子级别且语义丰富的动作解释性提示。
- 这些提示使模型更专注于动词理解。
- 在各种基准测试和学习场景下的实验证明了CLAVER模型的优越性和通用性。
点此查看论文截图

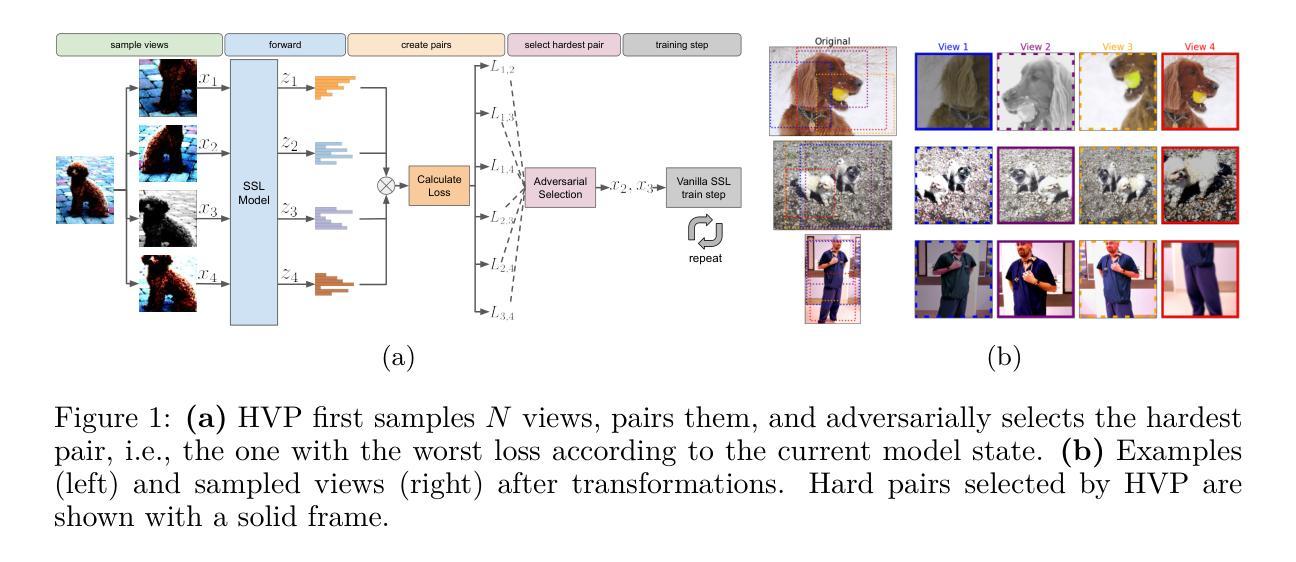
Beyond Random Augmentations: Pretraining with Hard Views
Authors:Fabio Ferreira, Ivo Rapant, Jörg K. H. Franke, Frank Hutter
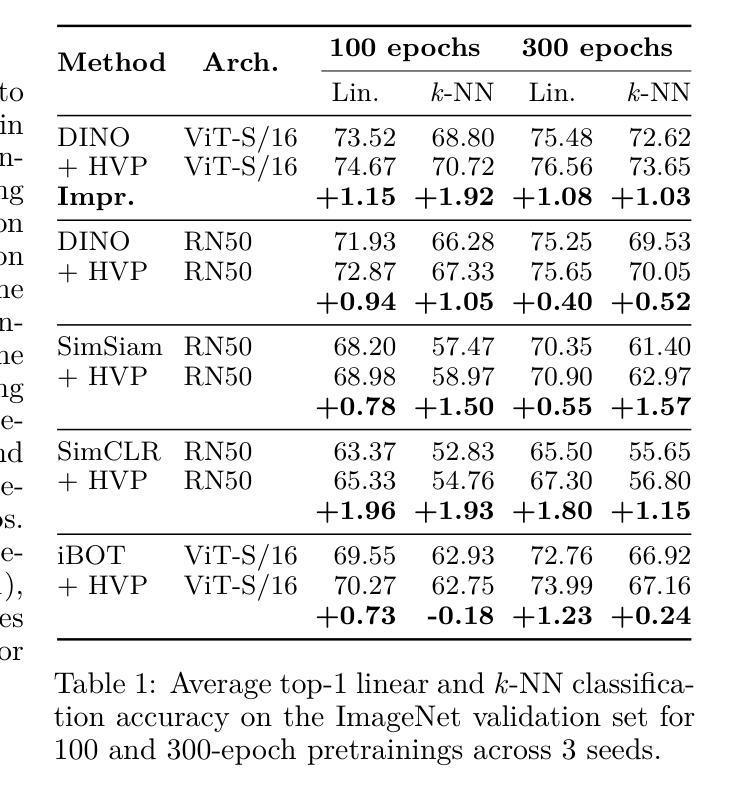
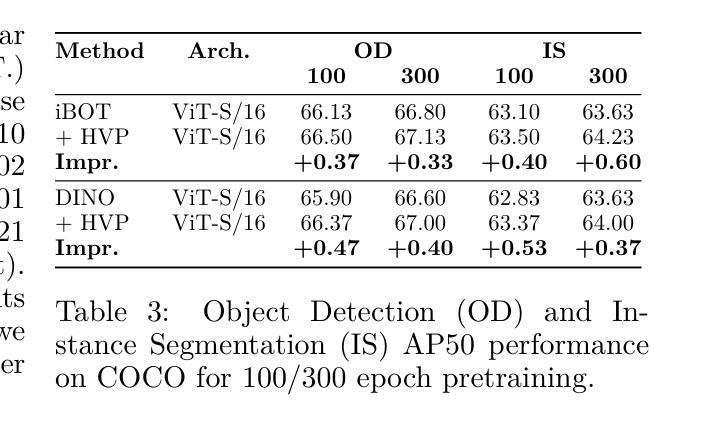
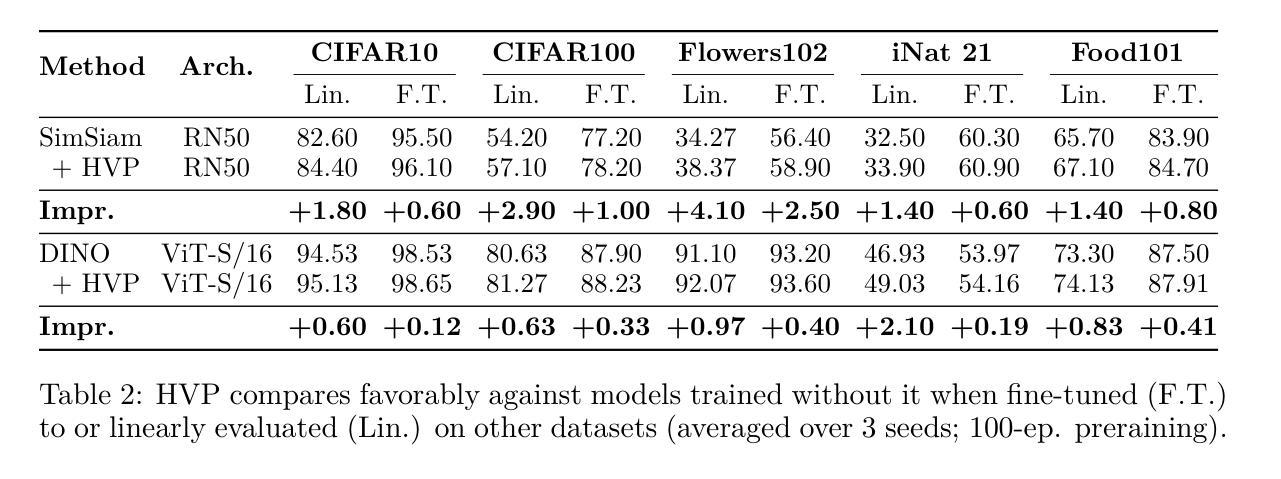
Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) methods typically rely on random image augmentations, or views, to make models invariant to different transformations. We hypothesize that the efficacy of pretraining pipelines based on conventional random view sampling can be enhanced by explicitly selecting views that benefit the learning progress. A simple yet effective approach is to select hard views that yield a higher loss. In this paper, we propose Hard View Pretraining (HVP), a learning-free strategy that extends random view generation by exposing models to more challenging samples during SSL pretraining. HVP encompasses the following iterative steps: 1) randomly sample multiple views and forward each view through the pretrained model, 2) create pairs of two views and compute their loss, 3) adversarially select the pair yielding the highest loss according to the current model state, and 4) perform a backward pass with the selected pair. In contrast to existing hard view literature, we are the first to demonstrate hard view pretraining’s effectiveness at scale, particularly training on the full ImageNet-1k dataset, and evaluating across multiple SSL methods, ConvNets, and ViTs. As a result, HVP sets a new state-of-the-art on DINO ViT-B/16, reaching 78.8% linear evaluation accuracy (a 0.6% improvement) and consistent gains of 1% for both 100 and 300 epoch pretraining, with similar improvements across transfer tasks in DINO, SimSiam, iBOT, and SimCLR.
自监督学习(SSL)方法通常依赖于随机图像增强或视图,以使模型对不同变换具有不变性。我们假设,通过明确选择有益于学习进度的视图,可以提高基于常规随机视图采样的预训练管道的有效性。一种简单而有效的方法是选择产生更高损失的硬视图。在本文中,我们提出了硬视图预训练(HVP),这是一种无学习策略,它通过暴露模型于更具挑战性的样本来扩展随机视图生成,在SSL预训练期间。HVP包括以下迭代步骤:1)随机采样多个视图,并通过预训练模型向前传递每个视图,2)创建两个视图的配对并计算其损失,3)根据当前模型状态对抗性地选择产生最高损失的配对,4)对所选配对执行反向传递。与现有的硬视图文献相比,我们首次证明了硬视图预训练在大规模上的有效性,特别是在完整的ImageNet-1k数据集上进行训练,并在多种SSL方法、ConvNets和ViTs中进行评估。因此,HVP在DINO ViT-B/16上创造了新的技术水平,达到78.8%的线性评估精度(提高了0.6%),在100和300个周期预训练中均取得了1%的持续增益,同时在DINO、SimSiam、iBOT和SimCLR中的迁移任务也都有类似的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了Hard View Pretraining(HVP)方法,这是一种无需学习的方法,扩展了随机视图生成,通过在SSL预训练过程中暴露模型于更具挑战性的样本。HVP通过以下步骤实现:1)随机采样多个视图并向前传播每个视图通过预训练模型;2)创建两个视图的配对并计算其损失;3)根据当前模型状态选择损失最高的配对;4)使用所选配对进行反向传播。本文首次证明了硬视图预训练在大规模数据上的有效性,特别是在ImageNet-1k数据集上进行训练,并在多个SSL方法、ConvNets和ViTs上进行了评估。HVP在DINO ViT-B/16上达到了线性评估准确率为78.8%,创下新的记录(提高了0.6%),在100和300轮预训练中均实现了一致的1%的提升,且在DINO、SimSiam、iBOT和SimCLR中的迁移任务也有类似的改进。
关键见解
- Hard View Pretraining(HVP)是一种无需学习的方法,能够增强模型对变换的鲁棒性,通过选择有利于学习进展的视图来提高预训练管道的效率。
- HVP通过选择产生更高损失的“硬”视图来扩展随机视图采样,从而创建更具挑战性的样本用于SSL预训练。
- HVP方法包括随机采样多个视图、创建视图对、计算损失、选择损失最高的视图对,并进行反向传播。
- 首次在大规模数据(如ImageNet-1k)上证明了硬视图预训练的有效性,并在多个SSL方法、ConvNets和ViTs上进行了评估。
- HVP在DINO ViT-B/16的线性评估中创下了新的记录,并在预训练的不同阶段以及不同的迁移任务中均实现了显著的改进。
- HVP方法具有广泛的应用潜力,可适用于不同的SSL方法和模型架构。
点此查看论文截图